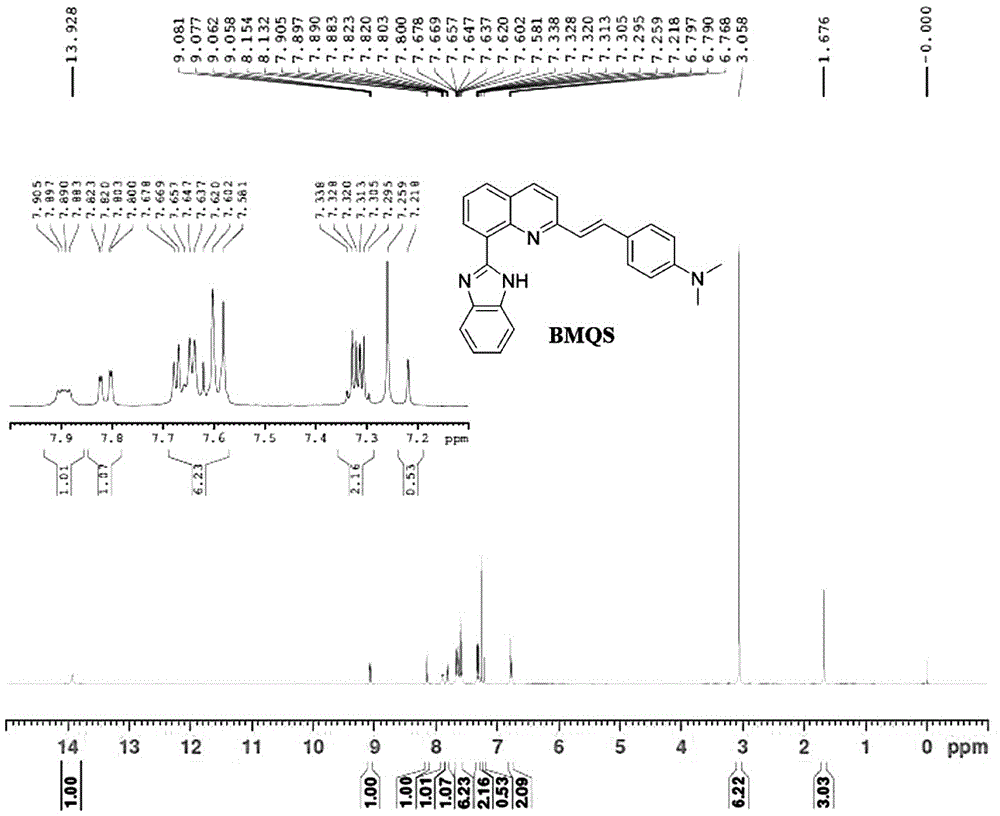
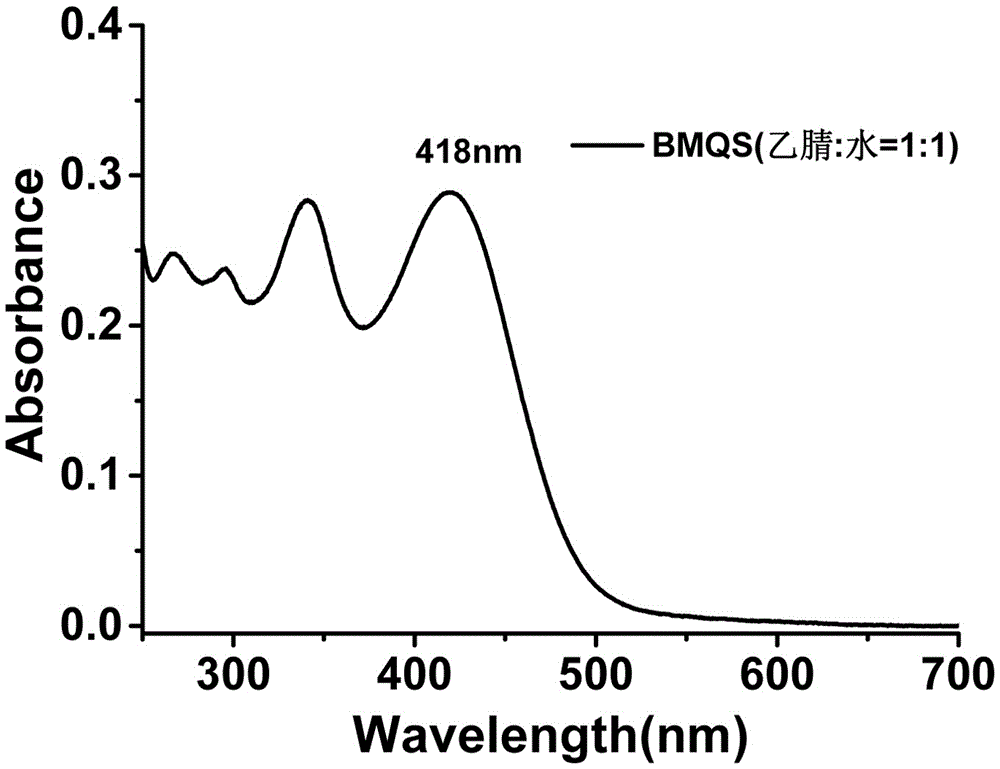
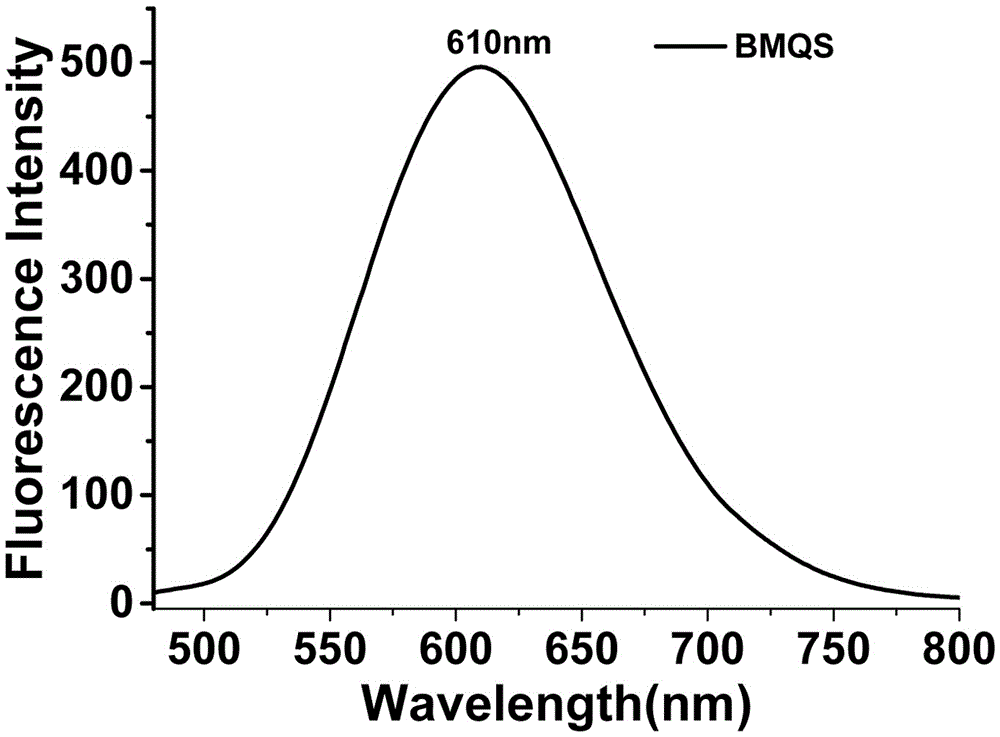
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
346results about How to "Decreased fluorescence intensity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
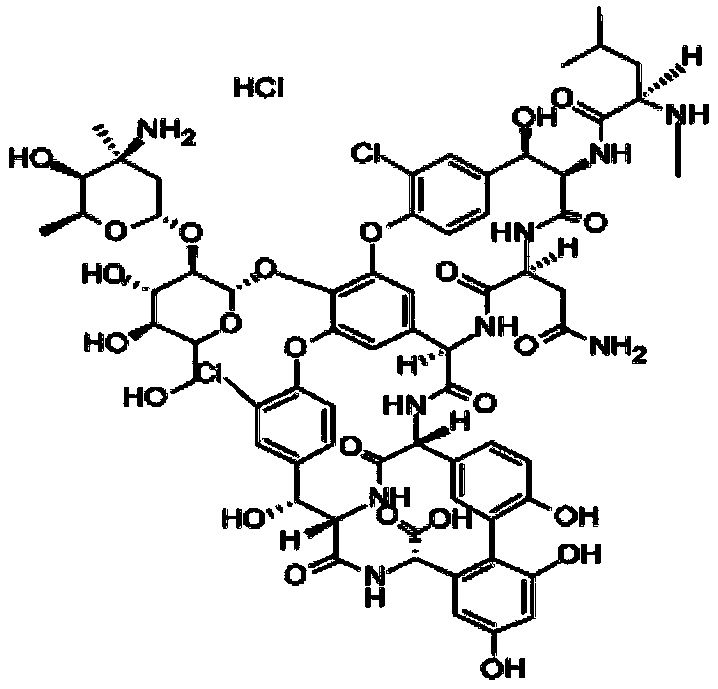
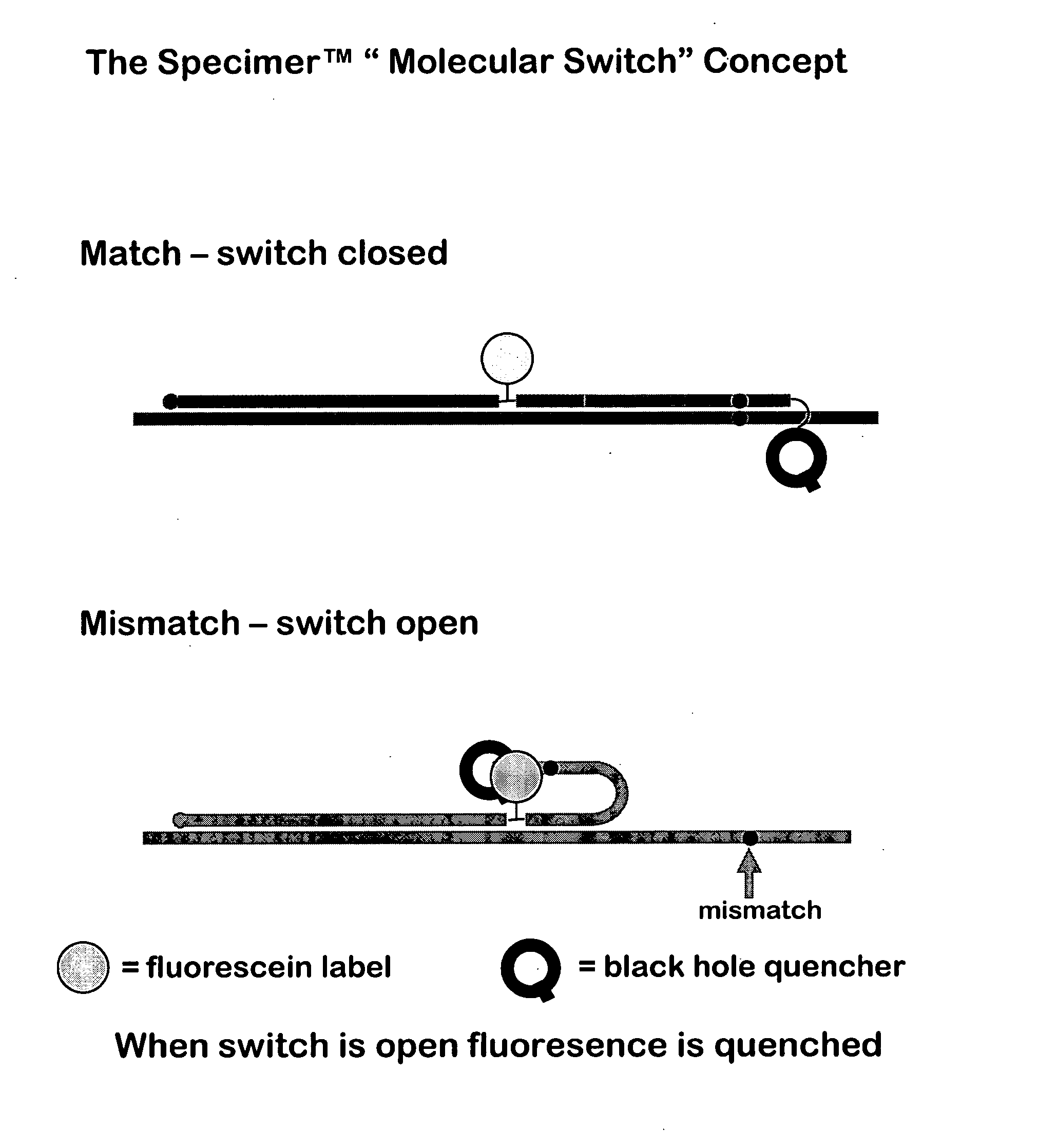
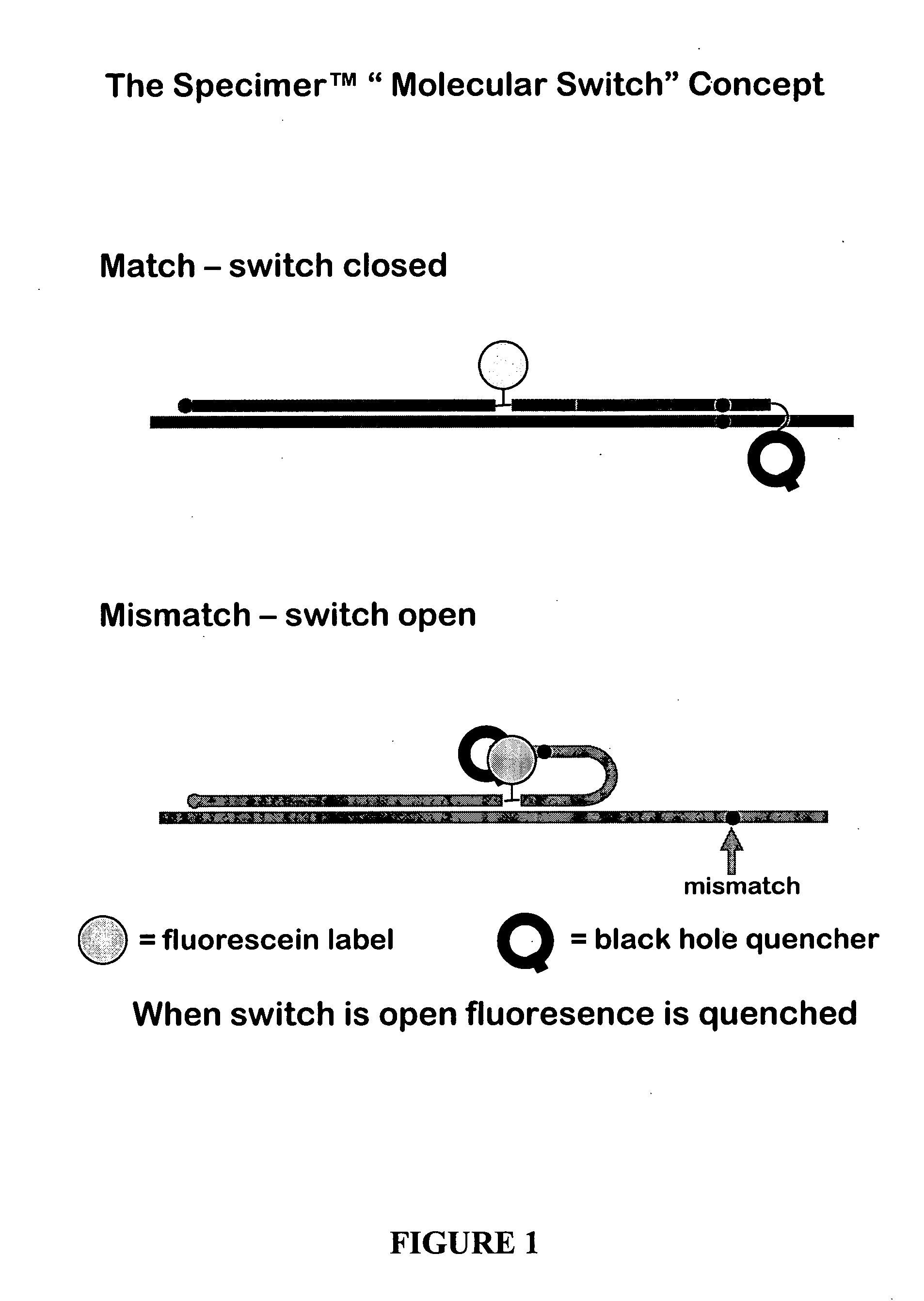
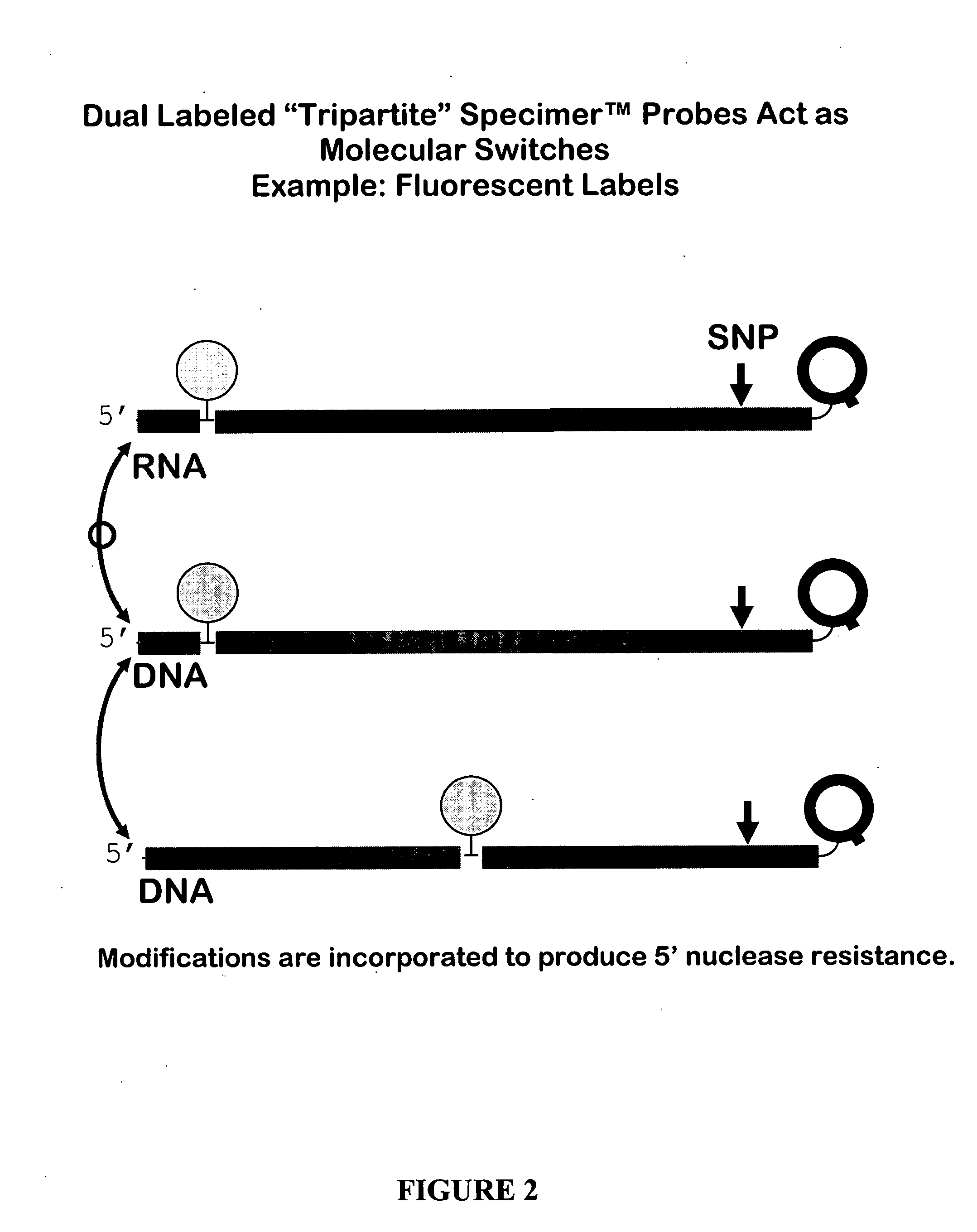
Oligonucleotides comprising a molecular switch
ActiveUS20050042638A1Strong specificityGuaranteed positioningSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding domainMolecular switch
This invention relates to oligonucleotides comprising a molecular switch which may exist in an “open” or “closed” position. The molecular switch portion of the probe is particularly sensitive to the identity of sequences complementary to the molecular switch. Oligonucleotides containing a molecular switch are applicable to all kinds of hybridization processes. Due to the sensitivity of the switch domain of the oligonucleotide, probes containing a molecular switch are particularly useful in the identification of single point mismatches. More specifically, a portion, but not all, of the oligonucleotide becomes unbound from a mismatched target. The invention further relates to methods of using said oligonucleotides for research reagents, and clinical diagnostics. An exemplary oligonucleotide comprises a first hybridizable domain, a second bridging block domain, and a third binding domain.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Nanometer level three-dimension magnetic resonance molecule imaging device based on diamond NV-color center
InactiveCN105738845ADecreased fluorescence intensityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMicrowaveColour centre
The invention discloses a diamond-based NV ‑ A nanoscale three-dimensional magnetic resonance molecular imaging device for color centers, comprising: a glass base; a laser, arranged inside the glass base, for emitting laser light to the outside; containing NV ‑ The diamond with the color center is arranged on the upper surface of the glass base, and the laser emitted by the laser is directly irradiated to the diamond; the microwave pulser is used to input microwave pulses to the diamond; the microscope objective lens is used to make the NV of the diamond ‑ Fluorescence from the color center is emitted outward through the microscope objective; a monochromatic filter for filtering the NV of the diamond ‑ Fluorescence from color centers; nanoconvex lenses that filter the NV of the diamond ‑ The fluorescence emitted by the color center is further concentrated; the distributed optical imaging lens is used to realize the imaging function; the packaging device is used to realize the functions of stable temperature, electromagnetic shielding and isolation protection.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
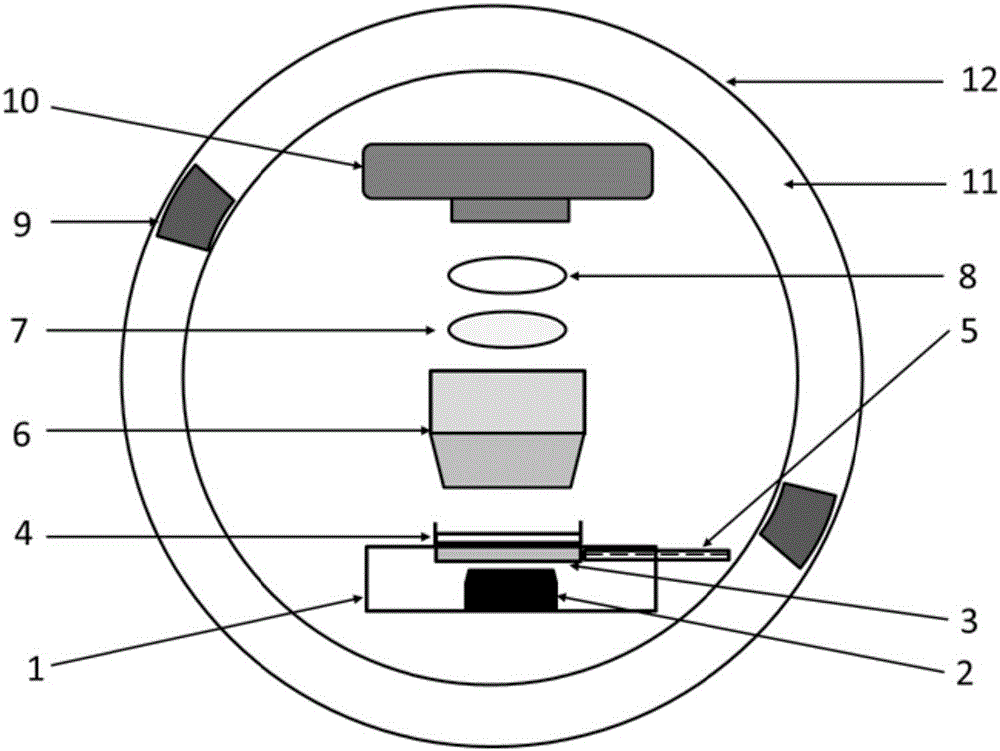
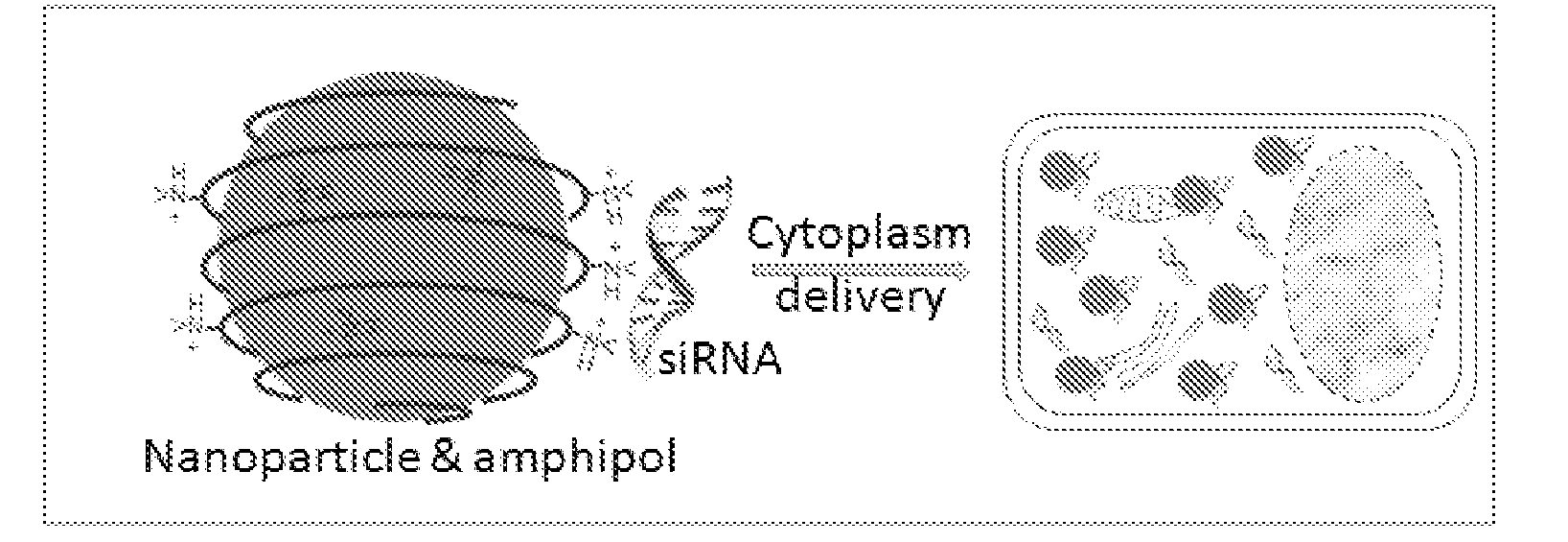
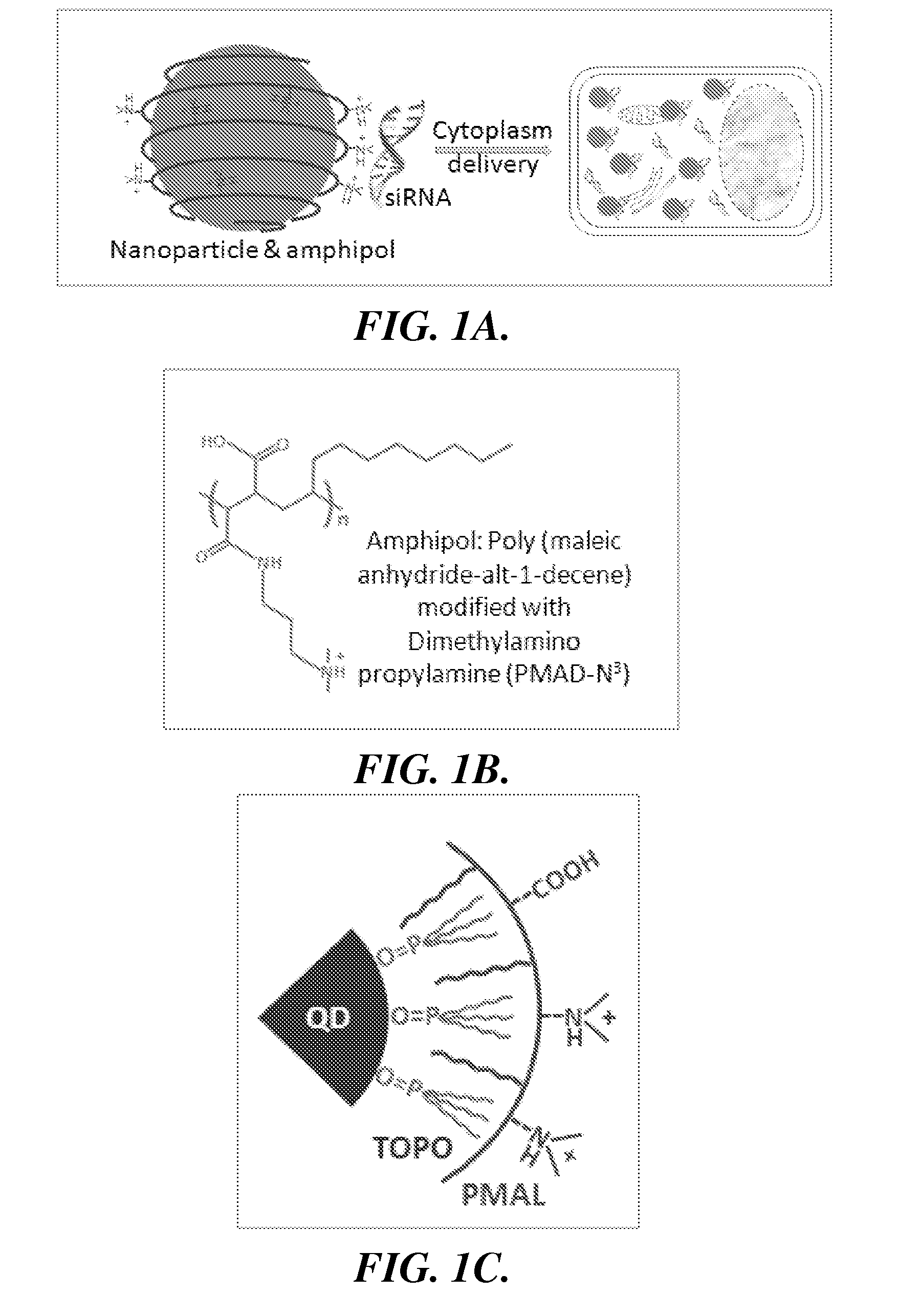
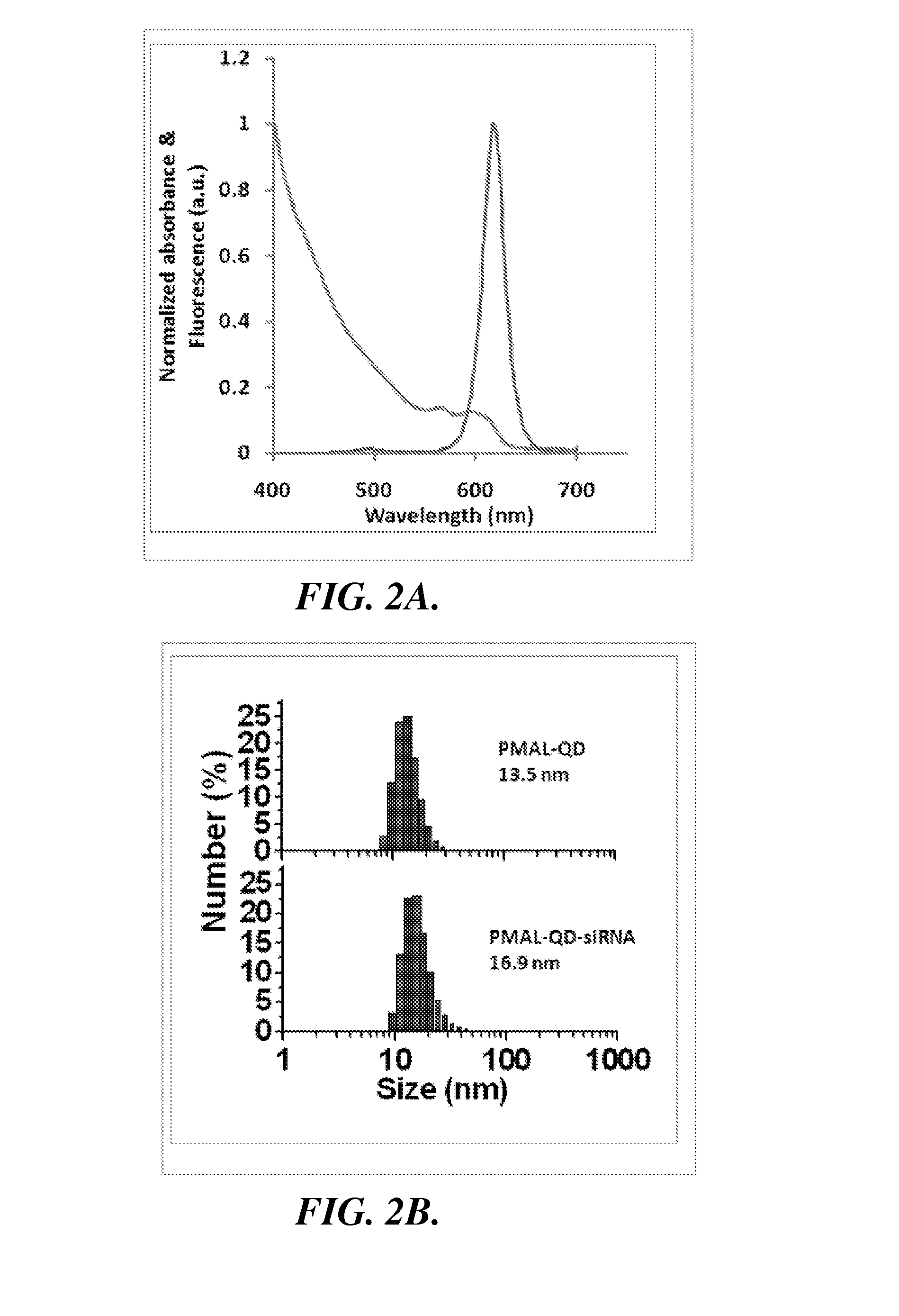
Nanoparticle-amphipol complexes for nucleic acid intracellular delivery and imaging
InactiveUS20090322327A1Strong absorption capabilityFacilitated releaseRadiation measurementNanomedicineNanoparticlePolymer
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Method for synthesizing carbon quantum dots by using amino acid as precursor and application of carbon quantum dots in detection of metal ion concentration
InactiveCN104787744ALow fluorescence quantum yieldStrong fluorescence quantum yieldNanoopticsFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuantum yieldSolubility
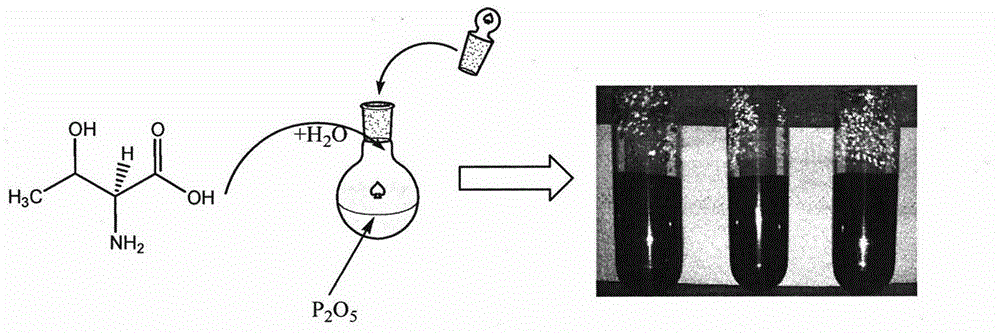
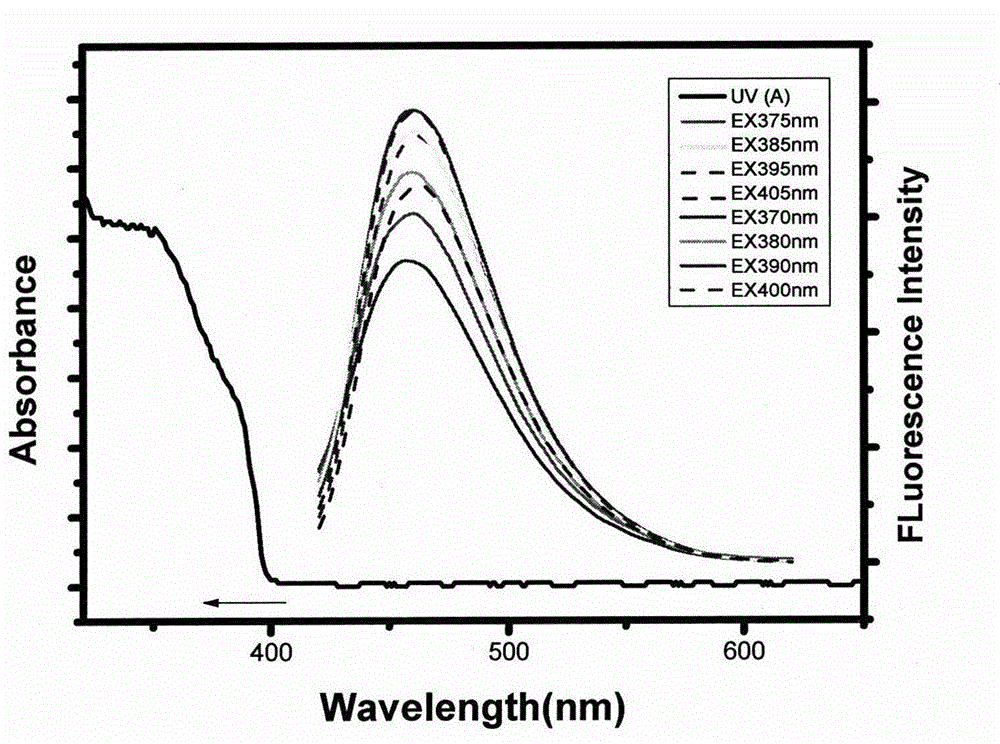
The invention relates to a preparation method of carbon quantum dots based on amino acid and an application of carbon quantum dots in direct detection of metal ion concentration. The method comprises the following specific steps: uniformly mixing amino acid and distilled water, rapidly adding the uniformly-mixed solution (amino acid is dissolved in distilled water) into a round-bottom flask filled with phosphoric pentoxide, rapidly plugging the bottleneck so as to obtain water-soluble carbon quantum dots, and applying the prepared carbon quantum dots in detection of metal ion concentration by a fluorescence quenching method. The synthetic method provided by the invention has a simple process, and reagents and raw materials are green and nontoxic. The prepared carbon quantum dots have characteristics of high quantum yield, strong light stability, good water-solubility and the like. Based on the quantum dots, a simple, rapid and sensitive method for metal ion quantitative detection can be established.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Rare earth organic framework material for iron ion fluorescence detection and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107556486AEnables ratiometric fluorescence detectionNovel structureFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceRare earth
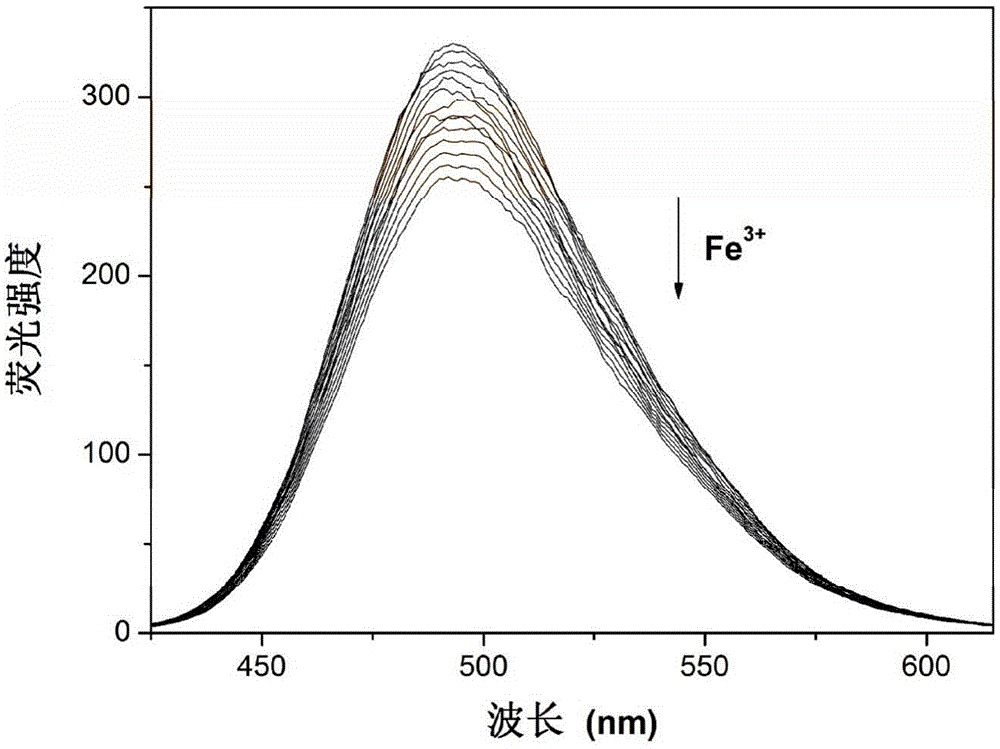
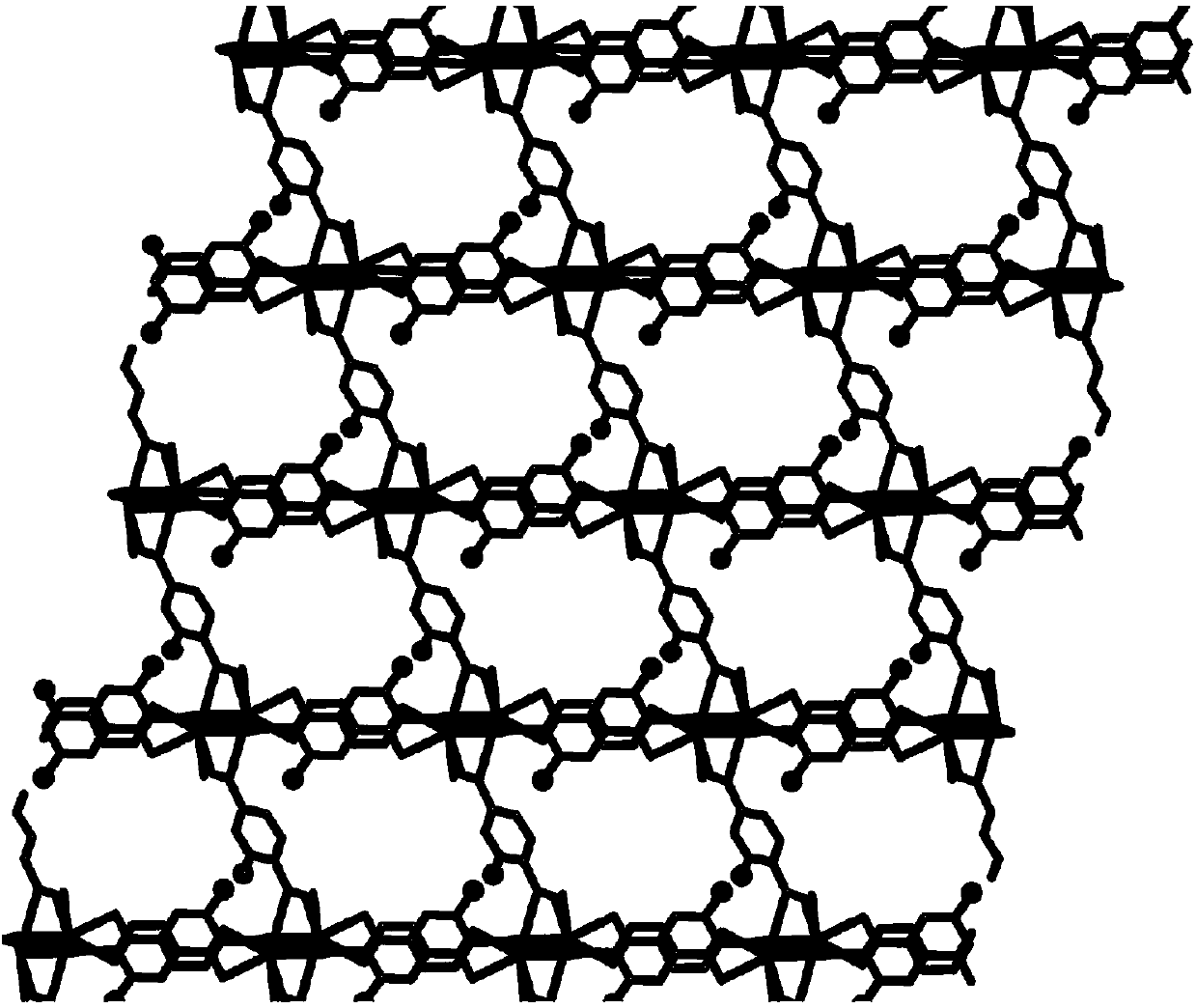
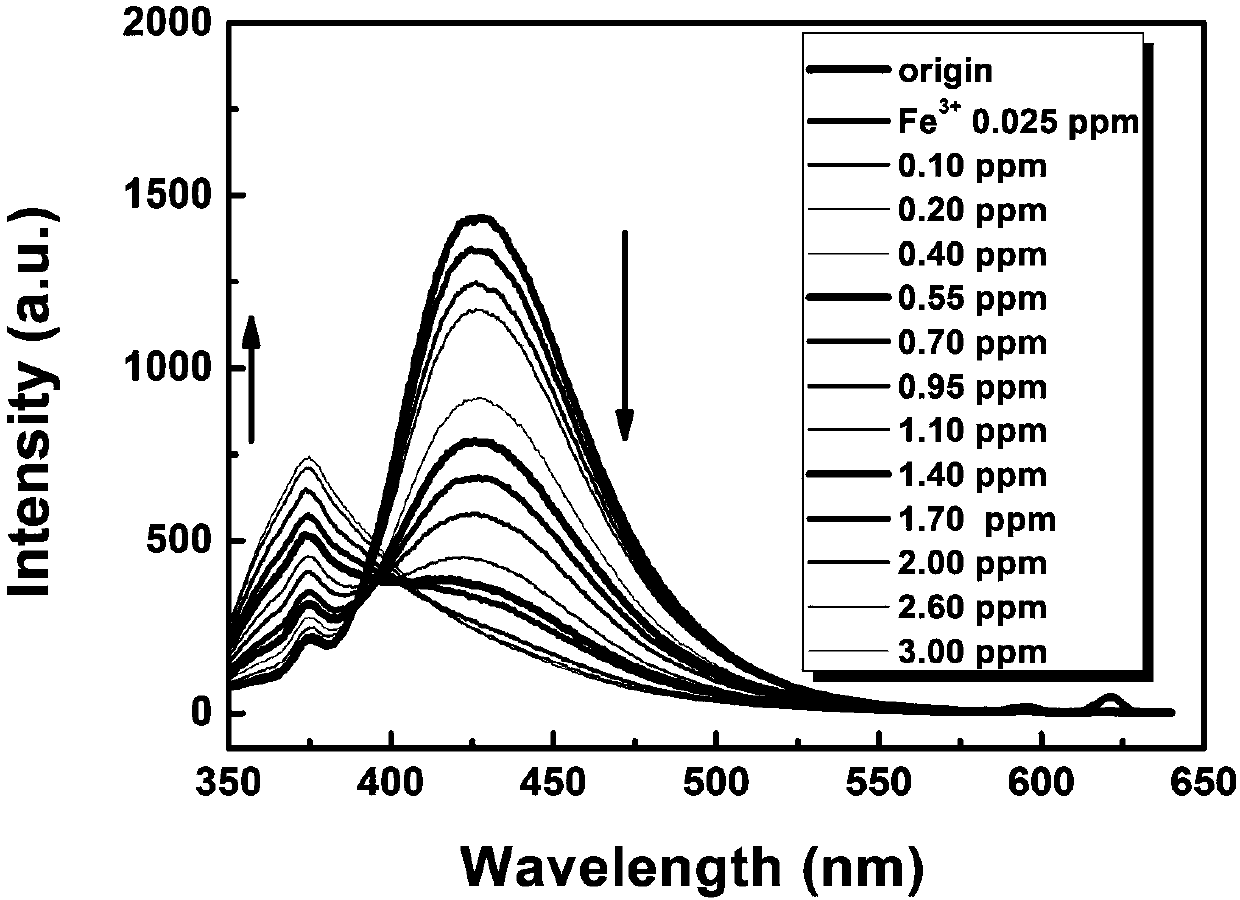
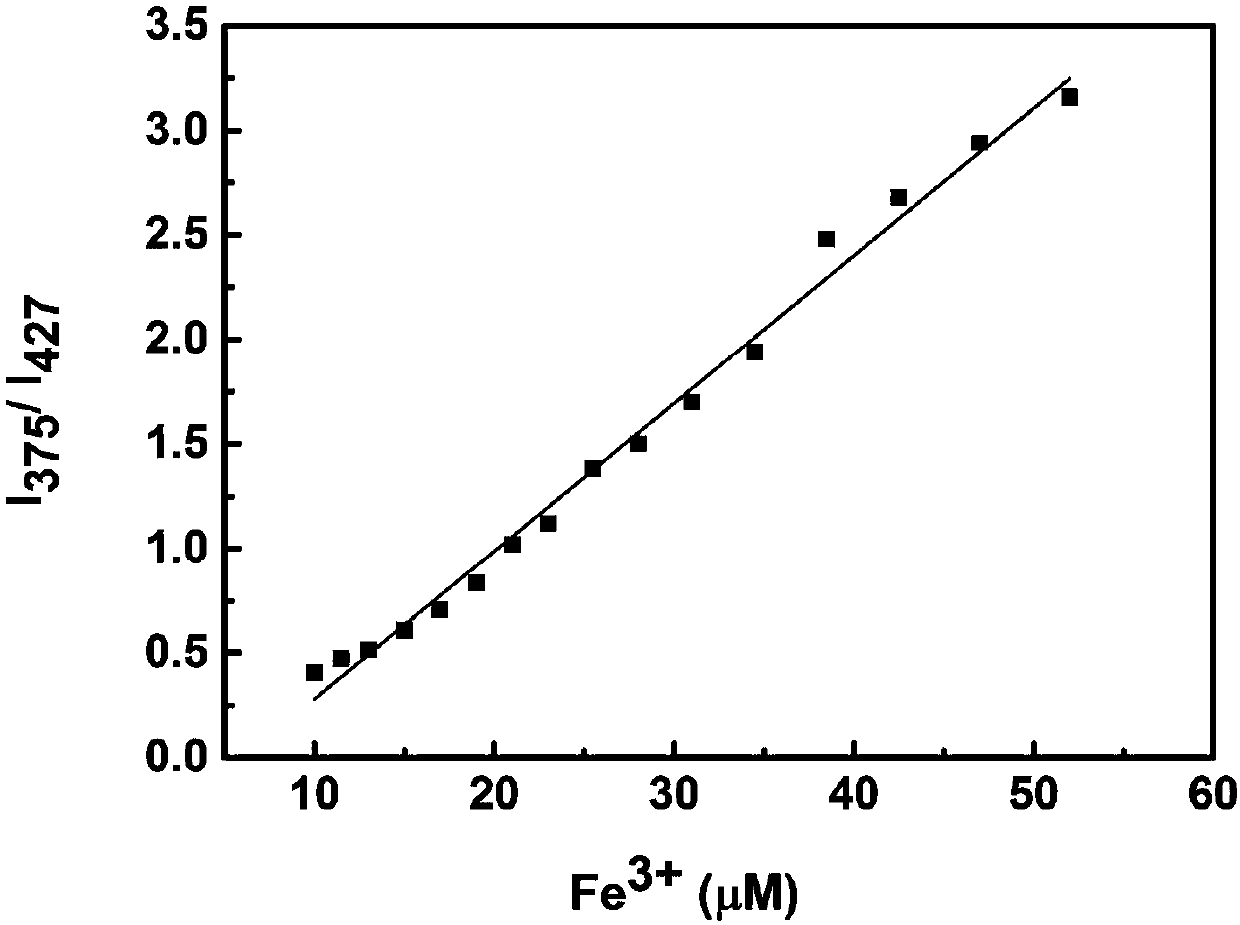
The invention discloses a rare earth organic framework material for iron ion fluorescence detection and a preparation method thereof. Methoxyl functional group-containing linear dicarboxylic acid (L-OCH3) is used as an organic raw material, a hydrothermal reaction is performed on the organic raw material and metal rare earth salt, and in the reaction process, an in-situ reaction is performed on methoxyl functional groups of an organic ligand to produce hydroxyl functional groups and the rare earth organic framework material is obtained. After adoption of the hydrothermal preparation method, the method is simple and the yield is high; the prepared rare earth organic framework material can be used as a fluorescent probe and interacts with iron ions, so that fluorescence of the organic ligandis quenched and new fluorescence generating a Ln2 (L-OH) 3-Fe<3+> compound is enhanced, and the intensity ratio between two peaks has a relatively good linear relationship with the concentration of the iron ions; the rare earth organic framework material can be applied to ratio detection of the iron ions.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane as well as preparation method and application thereof
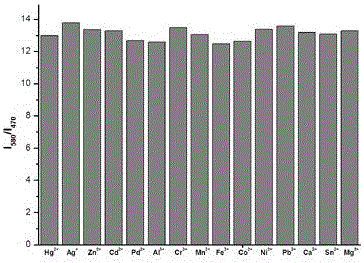
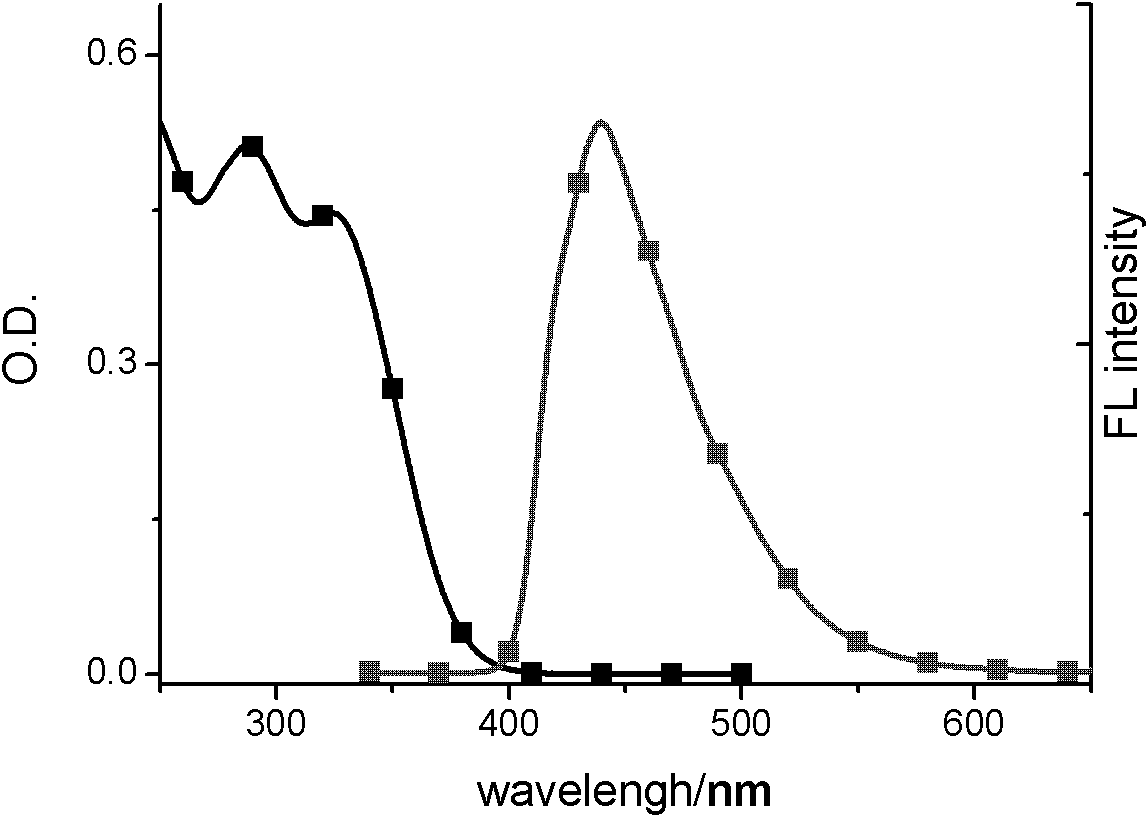
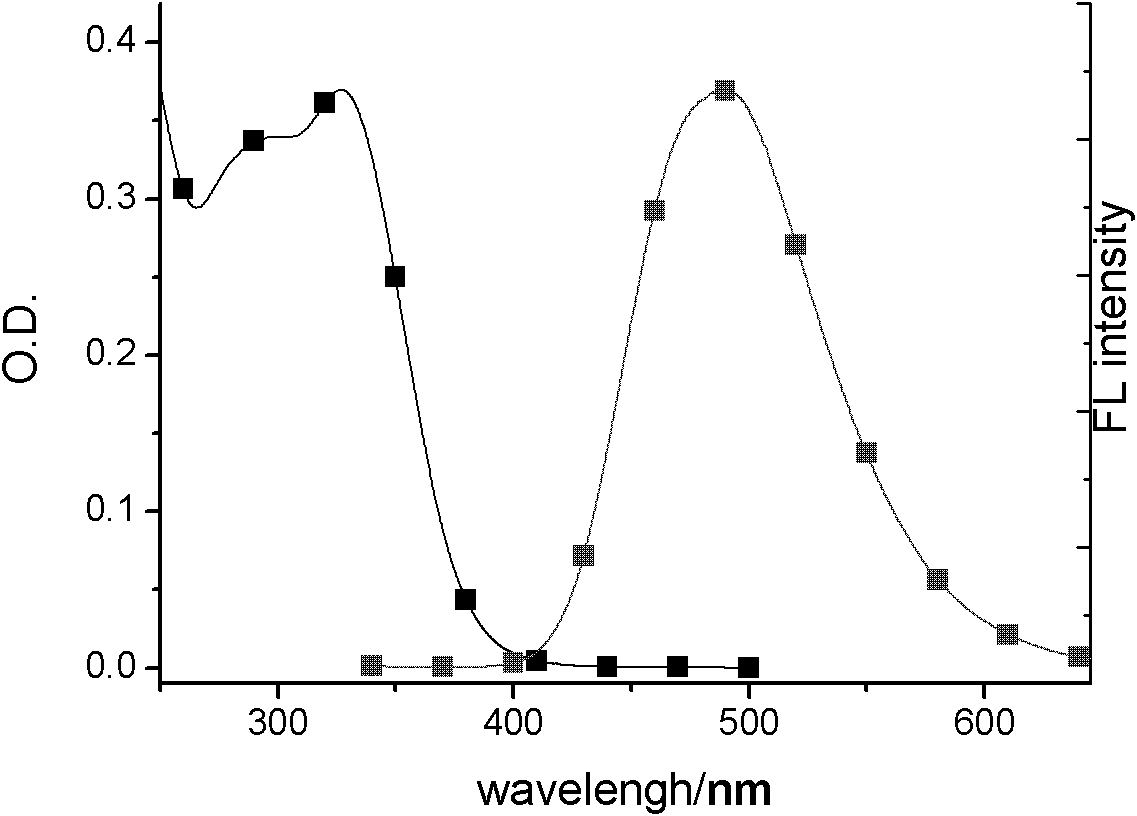
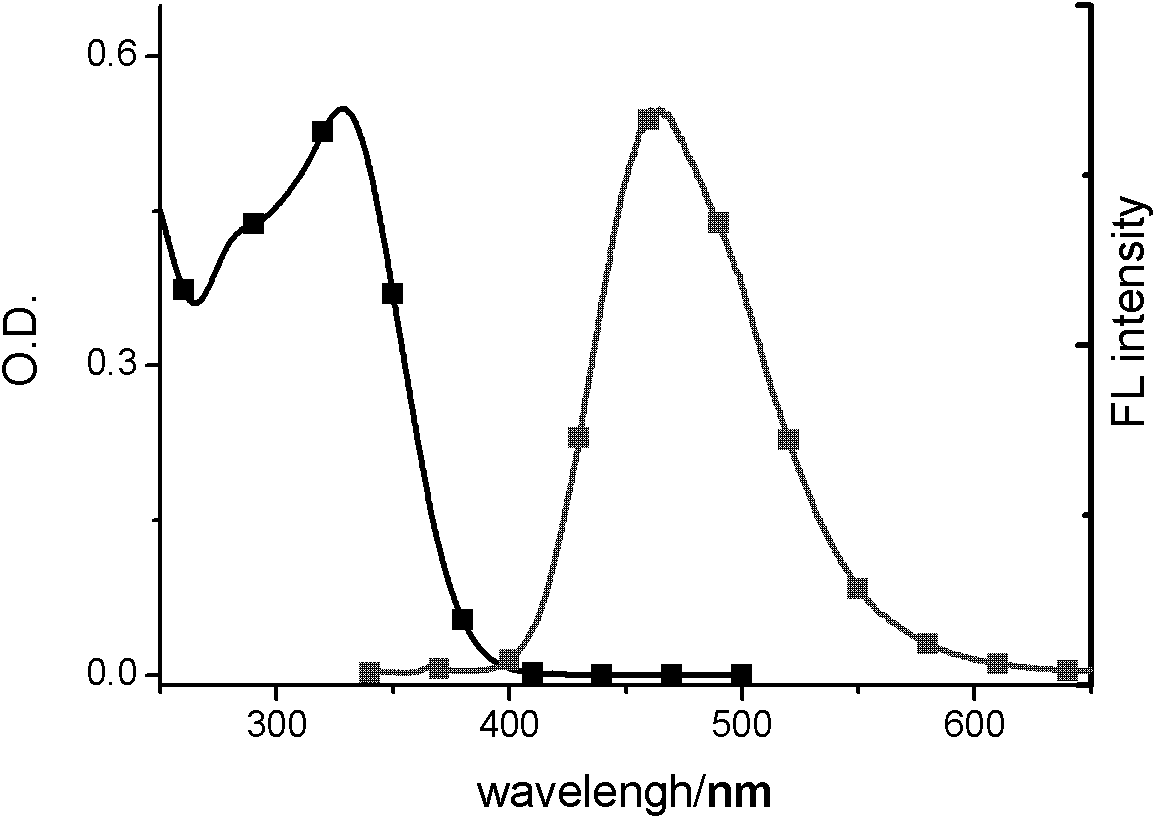
InactiveCN104447768ADecreased fluorescence intensityLow detection limitOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceArginineOrganic synthesis
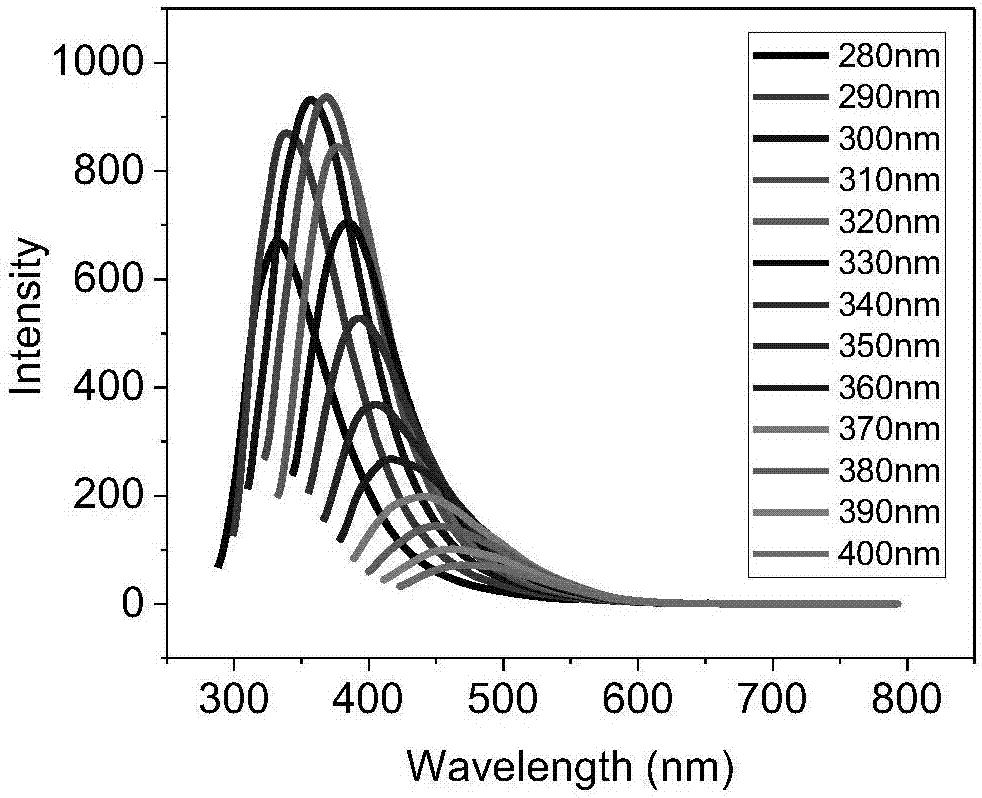
The invention discloses a cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of organic synthesis and analytical chemistry. A fluorescence probe cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane prepared by the method can be applied to high-selectivity and high-sensitivity detection of lysine or arginine or a mixture of the lysine and the arginine. Under the medium condition of an aqueous solution, a trace amount of lysine or arginine or the mixture of the lysine and the arginine can be detected by taking cucurbit urils supramolecular self-assembly as a probe system by adopting a fluorescence emission spectrophotometry at high sensitivity and high selectivity. The invention also discloses a preparation method and a technological condition of the cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane. The reacting fluorescence excitation wavelength of the cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane and the lysine or the arginine or the mixture of the lysine and the arginine is 317nm; and the maximal emission wavelength is 375nm.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Chemical preparation method for CdTe quantum dot fluorescent probe for detecting trace amount of paraquat
ActiveCN104359880ALarge specific surface areaMultiple recognition sitesFluorescence/phosphorescencePhotochemistrySurface modification
A chemical preparation method for a CdTe quantum dot fluorescent probe for detecting a trace amount of paraquat comprises the step of modifying thioglycollic acid on the surface of the CdTe quantum dot fluorescent probe emitting a red emission spectrum band so as to enable the CdTe quantum dot fluorescent probe is provided with carboxyl functional groups on the surface. The preparation process comprises the following two specific steps: firstly, preparing a NaHTe solution; then, synthesizing CdTe quantum dots of which the surfaces are modified with thioglycollic acid, and adjusting the pH value to be 10-12 with KOH, so as to obtain the CdTe quantum dot fluorescent probe. According to the invention, carboxyl with negative charge on the surfaces of the CdTe quantum dots and target paraquat molecules with positive charge have the electrostatic interaction through the positive charge and negative charge, when the CdTe quantum dots and the paraquat approach to each other in space, the red spectrum band emitted by the CdTe quantum dot fluorescent probe can be absorbed by green target analyte paraquat modules through the fluorescence resonance energy transfer principle, and the detection of a trace amount of paraquat can be implemented through the utilization of the variation of the CdTe quantum dot fluorescence intensity.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV
AHF associated dispersion system and method for preparation
InactiveUS20020132982A1Reduce peak intensityIncrease temperaturePeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesStabilizing AgentsProtein formation
A method for complexing AHF in a dispersed medium, includes: a) providing an AHF protein, b) altering the conformational state of the AHF protein to expose hydrophobic domains therein, c) binding a stabilizer to the exposed hydrophobic domains, and d) at least partially reversing the alteration to associate at least a portion of the protein with the stabilizer. A pharmaceutically effective stabilized AHF dosage wherein above about 0.5%, preferably above about 3%, and more preferably above about 25%, of the AHF molecule is associated with a stabilizer is also disclosed.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
Base fluorescence image capturing system device and method for high-flux genome sequencing
InactiveCN105039147AHigh speedHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceLaser light
The invention discloses a base fluorescence image capturing system device for high-flux genome sequencing. During the genome sequencing process, a to-be-tested DNA fragment sample is placed into a gene chip of a genome sequencer. The base fluorescence image capturing system device comprises a laser control unit and an image capturing unit, wherein the laser control unit is used for controlling parallel linetype laser beams in the Y direction and output by a laser light source to scan the gene chip in X direction and Y direction, and exciting a fluorochrome group carried by nucleotide in the to-be-tested DNA fragment sample to give out light; the image capturing unit is used for separating light emitted by the fluorochrome group so as to obtain a plurality of kinds of light with different wave lengths, and imaging the light by utilizing a TDI camera module. The invention further provides a method utilizing the base fluorescence image capturing system device to capture images, which comprises the following steps: controlling a scanning galvanometer to carry out linear array scanning, converting the optical information into electric signals by utilizing a photovoltaic conversion method as to generate image information finally, and processing through an image processing algorithm to obtain the sequence of the bases of the DNA fragment. With the adoption of the device and the method provided by the invention, high-flux sequencing of the DNA fragment is satisfied, and meanwhile, the device and the method have the advantages of safety and stability, and high degree of automation.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Visible-light response hybrid aerogel and preparation method and application thereof in waste gas processing
ActiveUS20200016585A1Low costEasily recombinedMaterial nanotechnologyGas treatmentPollutionMaterials science
Visible-light response hybrid aerogel and a preparation method and application thereof in waste gas processing are disclosed. Dicyandiamide is taken as a precursor and is calcined in two times to prepare a carbon nitride nanosheet; the carbon nitride nanosheet is dispersed in water, silver metavanadate quantum dots are subjected to in-situ growth to prepare a silver metavanadate quantum dot / carbon nitride nanosheet composite material; the silver metavanadate quantum dot / carbon nitride nanosheet composite material and graphene oxide carry out hydrothermal reaction, and are then frozen and dried to prepare silver metavanadate quantum dot / carbon nitride nanosheet / graphene hybrid aerogel which is the visible-light response hybrid aerogel. The problems of large reduction dosage, serious secondary pollution, complexity in operation and the like generated when waste gas is processed by a traditional flue gas denitration technology are overcome.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
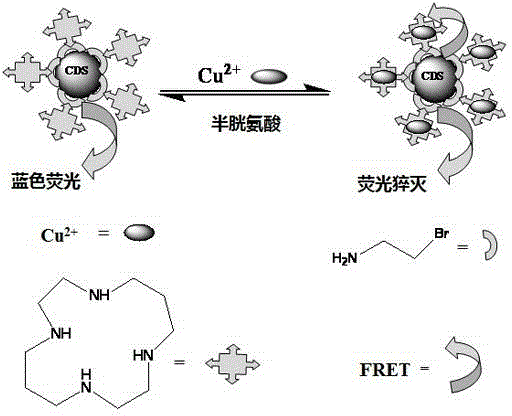
Carbon quantum dot sensor with copper ion and cysteine recognition functions, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104357048AHighly selective detection and identificationThe synthetic route is simpleFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsBromineIon
The invention discloses a carbon quantum dot sensor with copper ion and cysteine recognition functions, a preparation method and application thereof. The carbon quantum dot sensor is prepared by the following steps: taking citric acid and ethylene diamine as raw materials, adopting a microwave method to synthesize a carbon quantum dot containing carboxyl on the surface, then taking 2-bromoethylamine and 1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane as surface functionalizing reagents, and utilizing a surface grafting technology. The carbon quantum dot sensor is good in dispersity in water, and can be used for double-selectivity fluorescence detection to the copper ion and cysteine. Compared with the existing detection technology, the carbon quantum dot sensor disclosed by the invention can detect trace of copper ion and cysteine in a pure water medium with high sensitivity and high selectivity, is simple in synthetic route, convenient to use, and suitable for large-scale synthesis and actual application in production, and has the enormous application prospect in the fields such as biology and environment detection.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
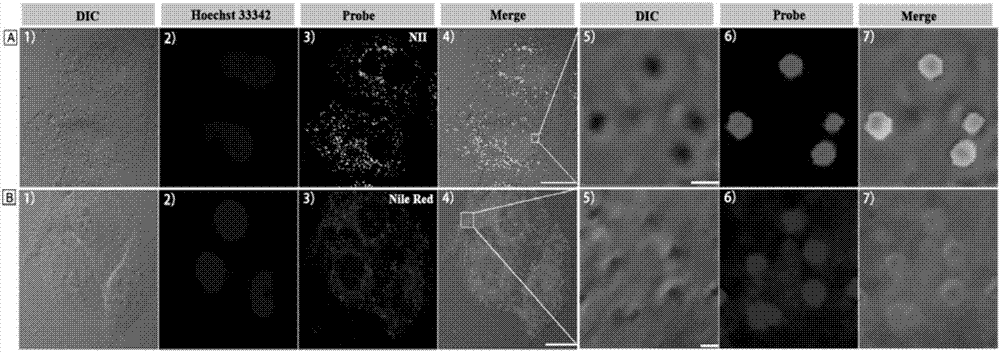
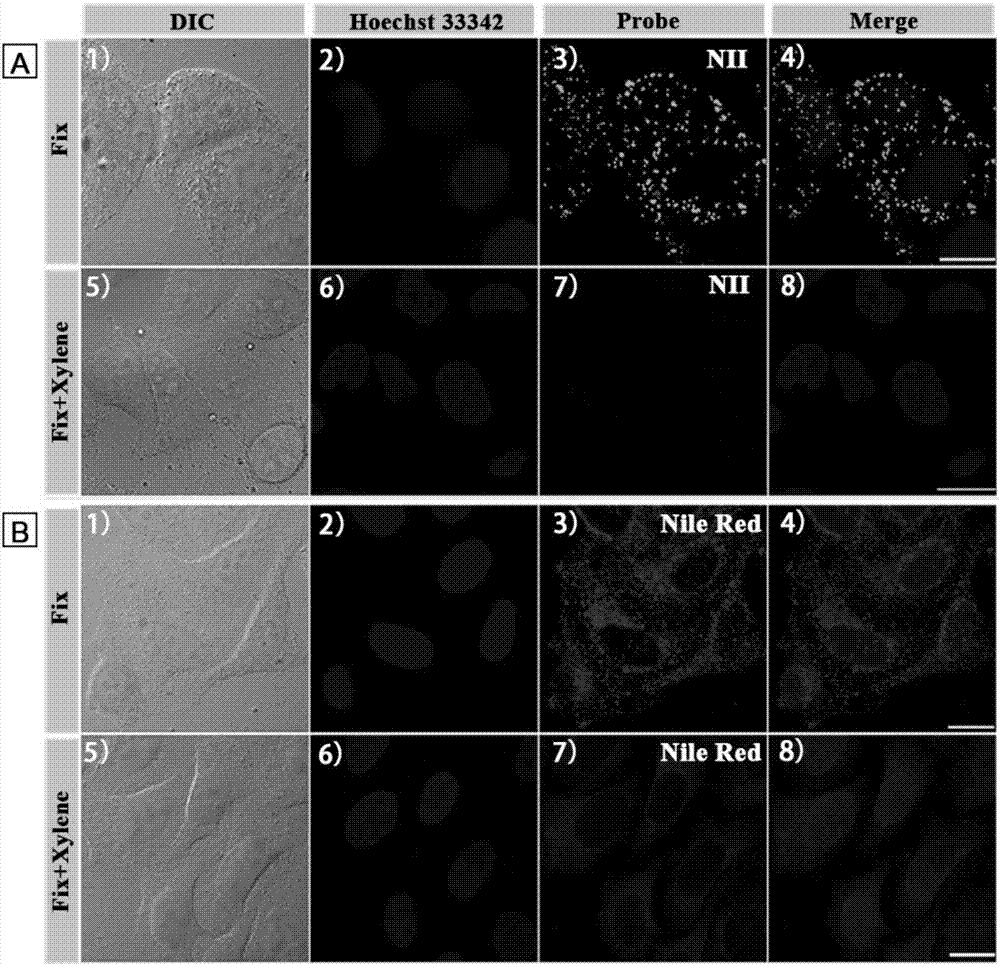
Amphiphilic lipid-droplet fluorescent probe with super-high selectivity and application thereof
ActiveCN106905309ACapable of two-photon imagingHigh selectivityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceStainingFluorescence
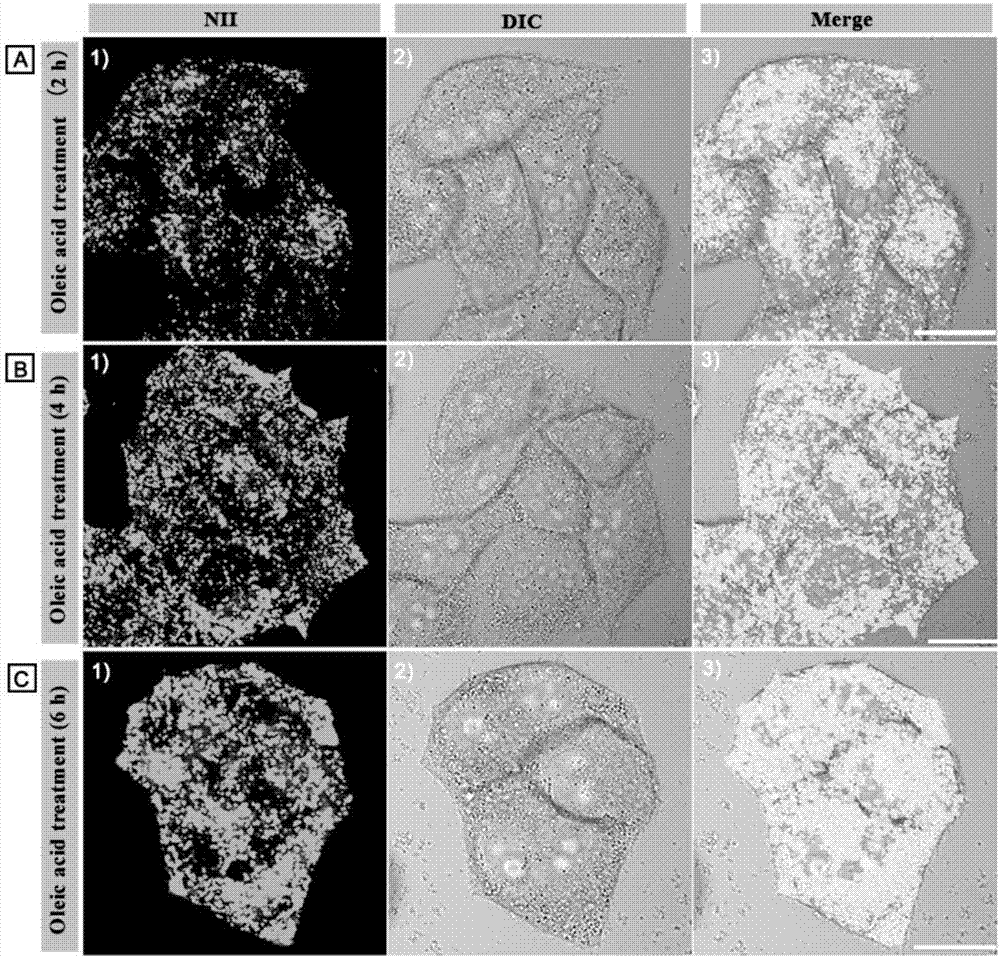
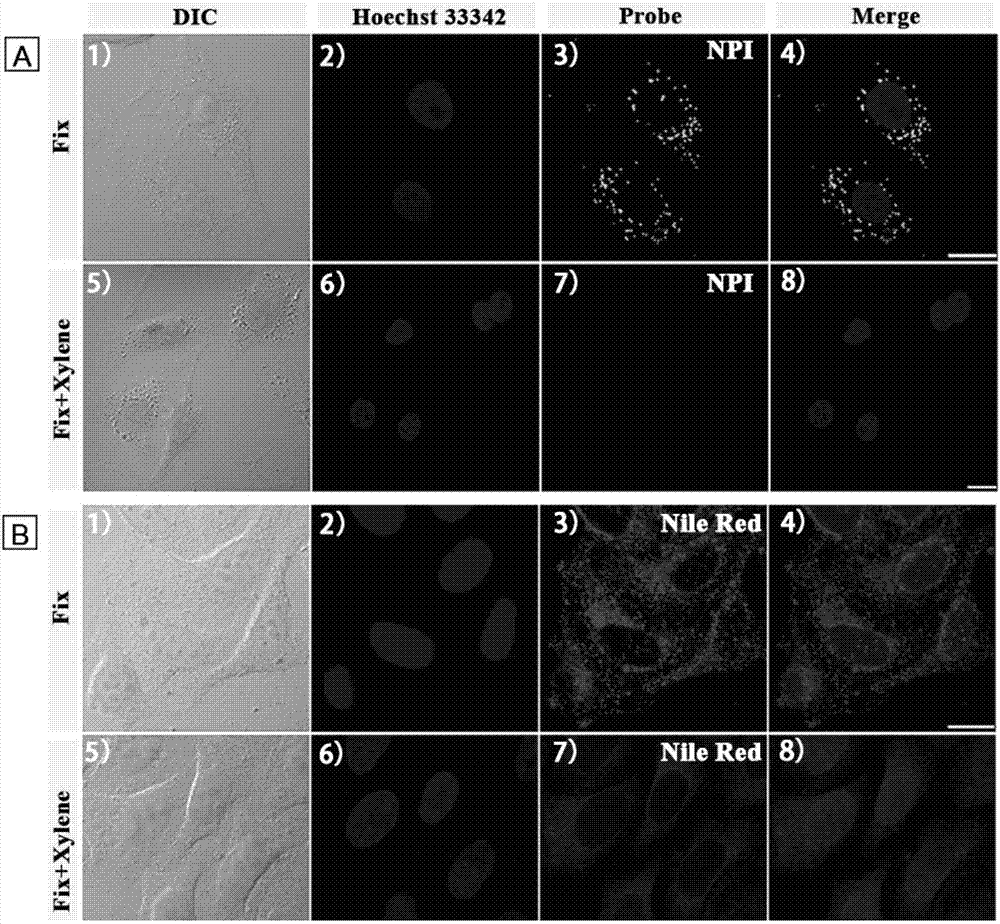
The invention discloses an amphiphilic lipid-droplet fluorescent probe with super-high selectivity. The amphiphilic lipid-droplet fluorescent probe with super-high selectivity is characterized in that chemical name of the probe is 1-(3'-(7'-nitrobenzofurazan-4'-)aminopropyl)-2,3,3-trimethylindole bromine, NII for short; and the general chemical formula is as shown in the formula (I). The invention also discloses application of the probe in specifically marking or displaying the form and distribution of lipid droplets in living cells or tissues. Experiments confirm that the probe of the invention is a brand-new probe, has a wide range of application, has good single- and two-photon photostability, fast staining speed and low cytotoxicity, can specifically image lipid droplets in living cells and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Cell lipid droplet specific-labeling fluorescent probe
InactiveCN106946869AHigh selectivityCapable of two-photon imagingOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceCytotoxicity
The invention discloses a cell lipid droplet specific-labeling fluorescent probe. The fluorescent probe has a chemical name of 1-(3'-(7'-nitrobenzofuran-4'-)aminopropyl)-4-methylpyridine bromide and has a general chemical formula shown in the formula (I). The invention also discloses a use of the fluorescent probe in specific labeling or display of a lipid droplet form and distribution in living cells. An experiment result shows that the cell lipid droplet specific-labeling fluorescent probe has the characteristics of very high selectivity, background noise-free imaging, two-photon performances, very good light stability, fast dyeing ability, no use of washing and low cytotoxicity and has a great application prospect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
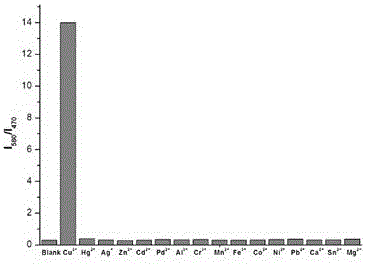
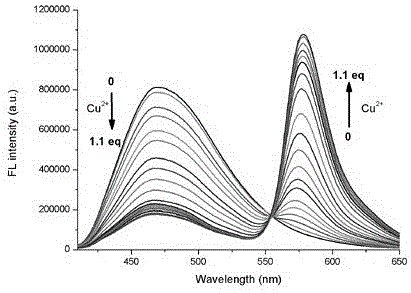
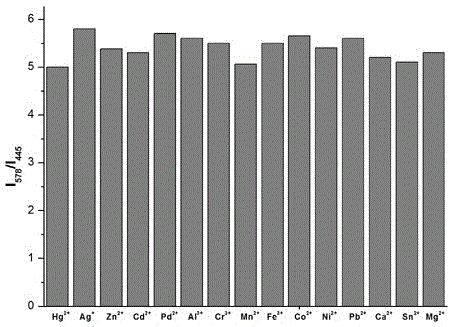
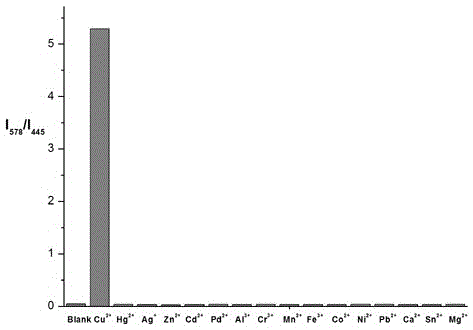
Imidazo pyridine rhodamine hydrazide type cupric ion ratio fluorescence probe and application thereof
InactiveCN105754587ADecreased fluorescence intensityHigh fluorescence intensityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceCupric IonPyridine
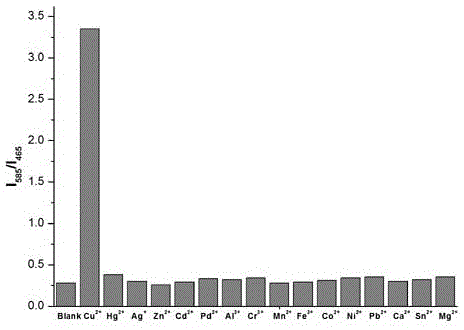
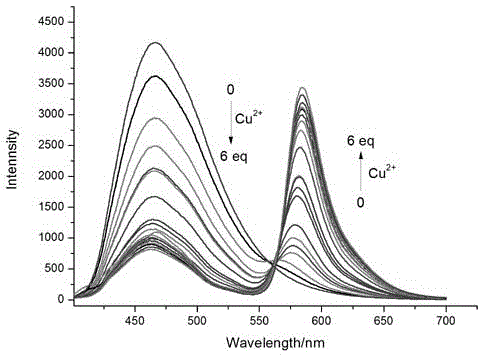
The invention discloses an imidazole [1,5-a] pyridine-rhodamine hydrazide derivative Cu<2+> ratio fluorescence probe.The probe is imidazole [1,5-a] pyridine substituted rhodamine hydrazide, a chemical structural formula of the probe is shown as a formula (1).The fluorescence probe has the unique fluorescence selectivity to Cu<2+> in an ethanol solution, higher sensitivity and stronger other ion interference capability and has a great application prospect.
Owner:TAISHAN MEDICAL UNIV
Star-shaped tetraarylethene compound and its preparation method and use
ActiveCN102276414AFree spin suppressionDecreased fluorescence intensityOrganic compound preparationHydrocarbonsCADA compoundDecomposition
The invention discloses star-shaped tetraaryl ethylene compounds. In the invention, the star-shaped tetraaryl ethylene compounds with rigid frameworks are synthesized through molecular design, each compound molecule contains one or more tetraaryl ethylene groups, and the compounds have special luminescent properties, namely the properties that the compounds almost have no fluorescence in dilute solution and fluorescence is greatly enhanced in an aggregation state or solid state. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the star-shaped tetraaryl ethylene compounds. The compounds have higher decomposition temperature and high thermal stability, and can be used as organic fluorescent materials which are applied to devices. The structural general formula of the compounds is shownin the specification, wherein X and Y are positive integers and the sum of X and Y is equal to 6.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rhodamine B targeted lysosome pH fluorescent probe with cysteine ethyl ester structure and application of rhodamine B targeted lysosome pH fluorescent probe
InactiveCN103320120AQuick responseHigh sensitivityOrganic chemistryBiological testingLysosomePh regulation
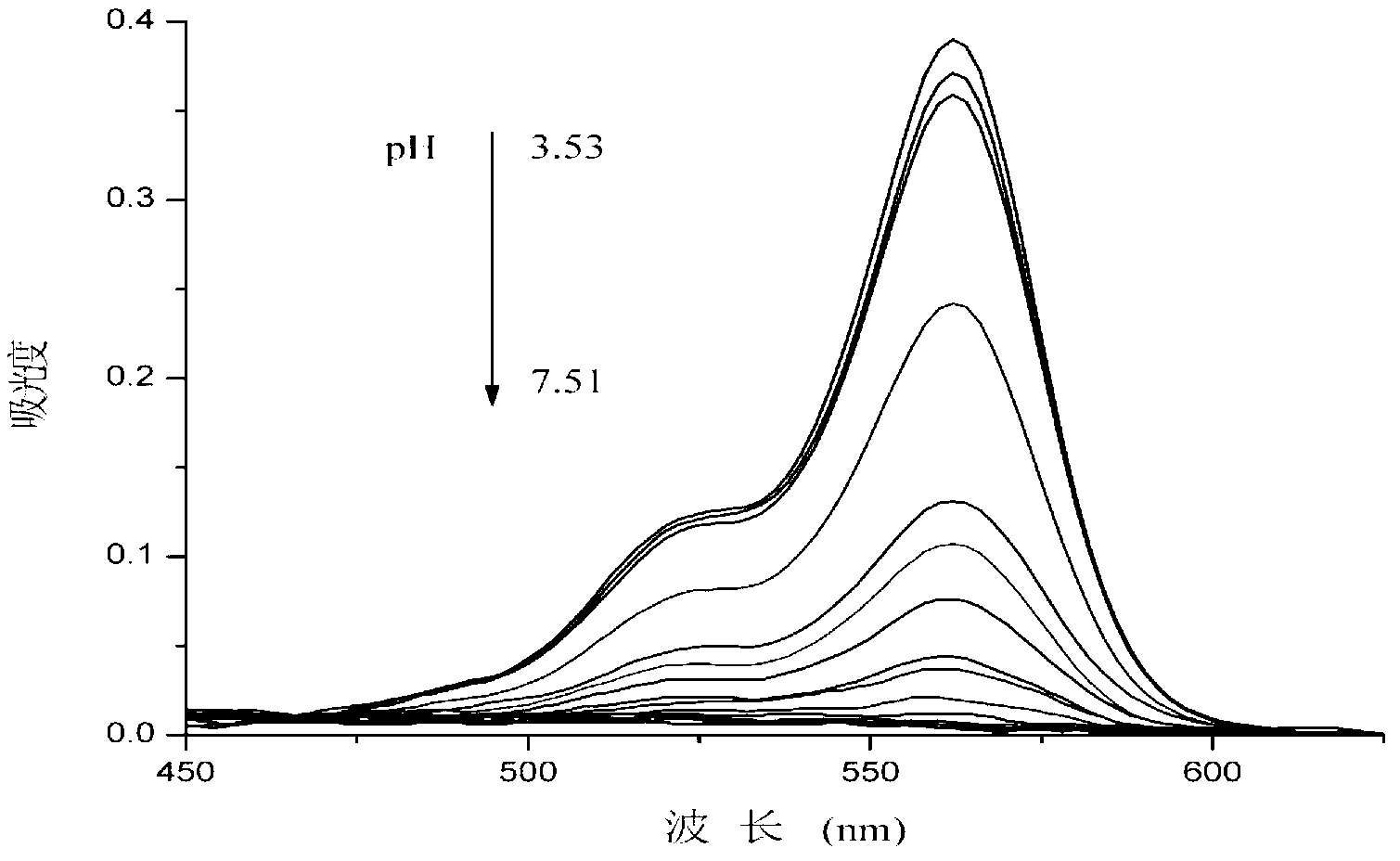
The invention discloses a rhodamine B targeted lysosome pH fluorescent probe with a cysteine ethyl ester structure, wherein the rhodamine B targeted lysosome pH fluorescent probe has the structure as shown in a formula (I). Meanwhile, the invention discloses an application of the probe as a living cell lysosome pH fluorescent probe. Experiments show that the probe provided by the invention does not generate fluorescence under the neutral and alkaline conditions, the fluorescence intensity is rapidly enhanced along with the reduction of the pH value of the solution, is up to the maximum value when the pH value is about 4.0 and is enhanced by about 150 times when the pH value ranges from 7.51 to 3.53, and the probe has favorable antijamming capability and reversibility in the presence of various metal ions. An intracellular colocalization experiment and an interlysosome pH regulation experiment prove that the probe can specially mark a lysosome and sensitively monitor the small change of the interlysosome pH value. A cell survival rate experiment shows that the probe is nontoxic to cells, which indicates that the probe disclosed by the invention has an important application value in the aspects of imaging the cells and monitoring the change of the interlysosome pH value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Fluorescent quantum dot/nano-metal particle conjugate and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN102590160ADecreased fluorescence intensityFluorescence intensity recoveryNanoopticsBiological testingFluorescenceQuantum dot
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
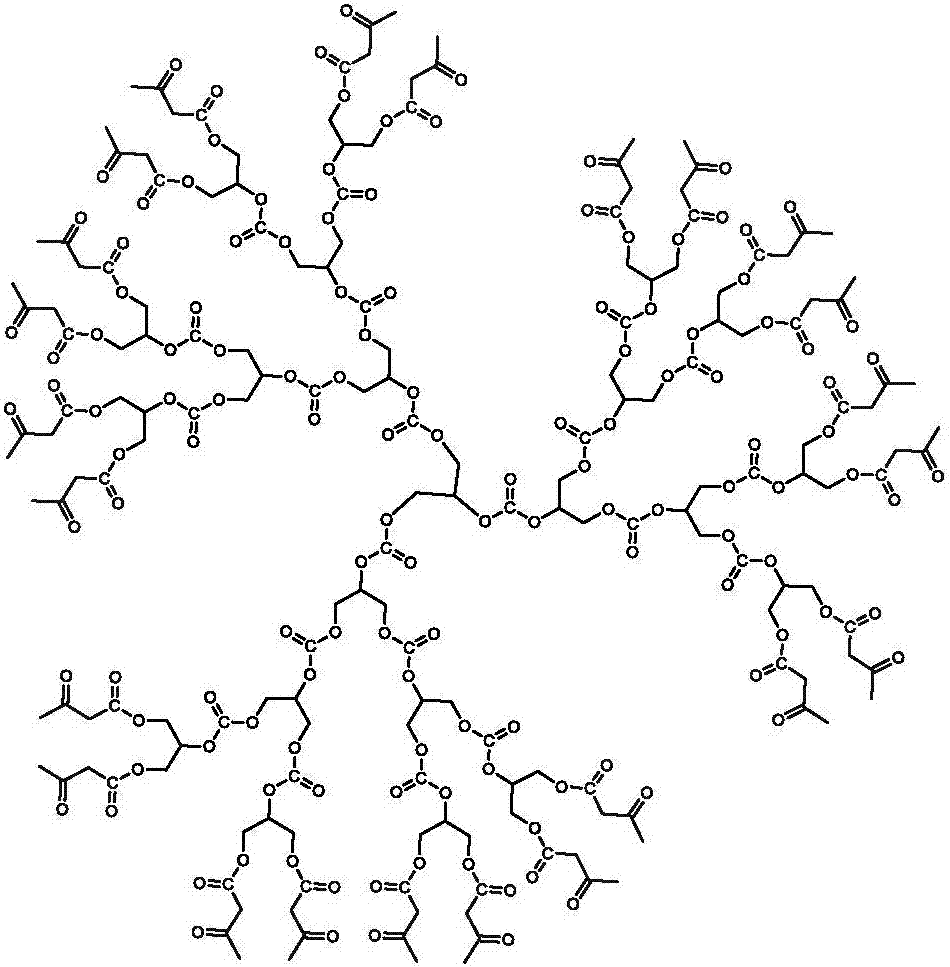
Carbonyl terminated hyperbranched polycarbonate capable of emitting bright fluorescence and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to carbonyl terminated hyperbranched polycarbonate capable of emitting bright fluorescence. Glycerol and diethyl carbonate are used as raw materials; a simple and controllable ester exchange condensation method is used for synthesizing the terminated hyperbranched polycarbonate; then, tert-Butyl acetoacetate is used for termination to obtain the hyperbranched polycarbonate. The synthesized hyperbranched polycarbonate does not contain pi keys such as benzene rings; the addition of fluorescent powder is not needed; the bright blue fluorescence can be given out; the characteristics of simple process, controllable process and low three-waste pollution are realized; in addition, the product stability is high; the toxicity is high; the biodegradability is high; the light intensity is high; the application range is wide.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Indolizine-rhodamine hydrazide type cupric ion ratiometric fluorescent probe and application thereof
InactiveCN106632406ADecreased fluorescence intensityHigh fluorescence intensityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceCupric IonHydrazide
The invention discloses an indolizine-rhodamine hydrazide derivative type Cu<2+> ratiometric fluorescent probe. The probe is indolizine substituted rhodamine hydrazide, and the chemical formula of the probe is as shown in formula (1). The fluorescent probe has unique fluorescent selectivity to Cu<2+> in an ethanol solution and is high in sensitivity, high in resistance to interference of other ions and promising in application prospect.
Owner:TAISHAN MEDICAL UNIV
Method for detecting ferric ions through fluorescence
InactiveCN103983765ADecreased fluorescence intensityBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescencePaper documentQuenching
The invention provides a fluorescent detection method for quantitatively detecting ferric ions on the basis of a coumarin derivative (molecular formula: C14H5NO3), and the coumarin derivative 7-lignocaine coumarin-4-formaldehyde is synthesized according to documents. The method comprises the steps: coordinating Fe<3+> and two carbonyls in the 7-lignocaine coumarin-4-formaldehyde structure in a HEPES buffer solution in a pH value of 7.0, and detecting the ferric ions through the fluorescence quenching. The detection method is high in sensitivity and selectivity for the display of the ferric ions, the detection reagent is cheap, the detection process is simple, sensitive and rapid, and the detection result is accurate. In addition, a confocal fluorescence image further proves that a probe can be used for recognizing the Fe<3+> in a living cell.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Fluorescent probe and pesticides residue detection kit based on carboxylesterase inhibition method
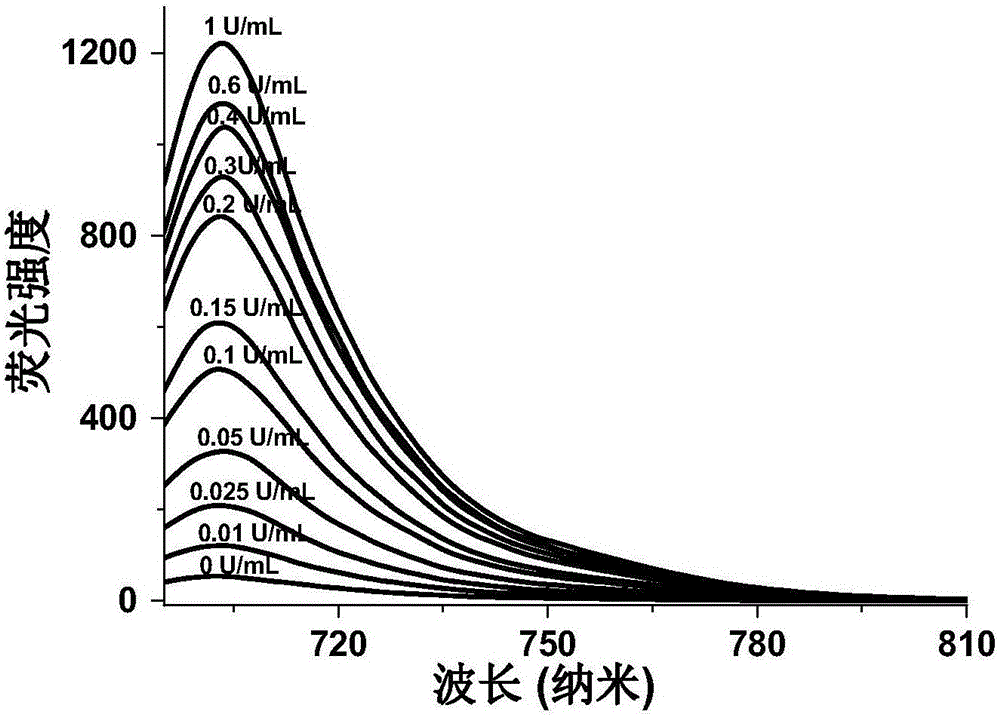
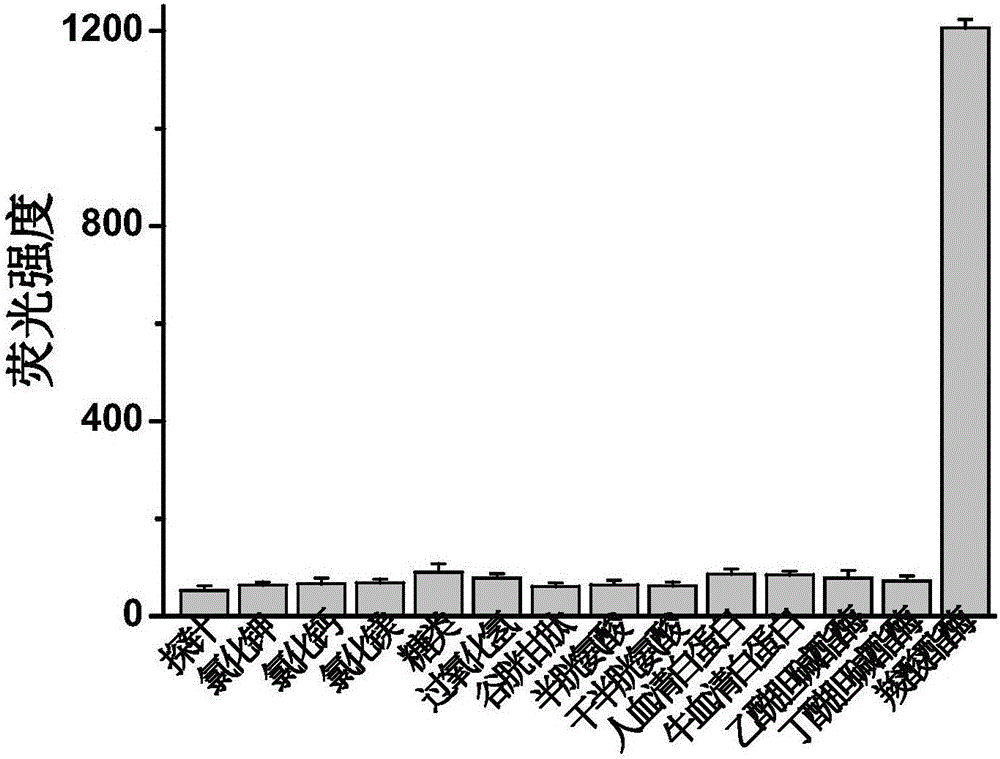
ActiveCN106496204ADecreased fluorescence intensityQuick responseOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescencePhosphatePesticide residue
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe and a pesticide residue detection kit based on a carboxylesterase inhibition method. The pesticide residue detection kit comprises a reagent stock solution a and a reagent stock solution b, wherein the reagent stock solution a is a buffer solution containing phosphate, and the reagent stock solution b is a solution of the fluorescent probe. Experiments find that the strength of the self fluorescence of the probe is very weak, and after carboxylesterase is added, the probe react and release an IR-780 hemicyanine skeleton fluorescent parent body, the fluorescence of the solution is remarkably strengthened, showing that the method can be used for detection of the activity of the carboxylesterase; after adding a tiny amount of pesticides in the carboxylesterase, the fluorescence of the solution is remarkably weakened, showing that a tiny amount of the pesticides can inhibit the activity of the carboxylesterase, and thus the fluorescent probe can be used for detection of pesticide residues. The fluorescent probe has the advantages of being easy to operate, low in cost, fast, efficient and sensitive, and the fluorescent probe is convenient for application and popularization, and has a huge application prospect in the fields of agriculture, food and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Fluorescent substance-containing silica nanoparticles and biosubstance labeling agent
ActiveUS20120252140A1Excellent long-term storage stabilityHigh sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologySilicaSilica nanoparticlesFluorescence
Disclosed are fluorescent substance-containing silica nanoparticles containing a fluorescent substance therein featured in that the surface of the silica nanoparticles is coated with a material having a bulk refractive index of from 1.60 to 4.00. The invention can provide fluorescent substance-containing silica nanoparticles excellent in long term storage stability and a biosubstance labeling agent employing the same.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA MEDICAL & GRAPHICS INC
Up-conversion fluorescent aptamer-based side stream test paper detection method
ActiveCN108196044ARealize quantitative measurementStrong specificityMaterial analysisGold particlesRare earth
The invention discloses an up-conversion fluorescent aptamer-based side stream test paper detection method, and belongs to the technical fields of environment detection and food safety detection. A nucleic acid aptamer capable of specifically identifying target bacteria is modified on the surface of each nano-gold particle; cDNA which is in complementary pairing with the aptamer is modified on thesurface of each rare earth up-conversion fluorescent particle; and after the two kinds of nanoparticles are mixed, the basic groups of the two segments of nucleic acid sequences are in complementarypairing and the distance of the two kinds of particles are pulled closely, so that fluorescence of the upper-conversion fluorescent particles is quenched. After a target object is added, the target object can be bound with the aptamer with cDNA competitiveness, so that fluorescence recovery of the up-conversion nanoparticles is caused. According to different fluorescence recovery intensity, quantitative measurement of the target bacteria can be realized. The method provided by the invention is high in sensitivity, high in specificity and simple and convenient in operation, various target objects can be measured through change of the aptamer sequence, and very import significance in the aspects of environment monitoring, food analysis and the like is achieved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Imidazopyridine rhodamine salicylaldehyde copper ion ratio fluorescence probe and application thereof
InactiveCN106083897ADecreased fluorescence intensityHigh fluorescence intensityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescencePyridine
The invention discloses an in imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine-rhodamine salicylaldehyde copper ion ratio fluorescence probe and an application thereof. The probe is imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine substituted rhodamine salicylaldehyde, and the chemical structural formula of the probe is represented by formula (1). The fluorescence probe has unique fluorescence selectivity and high sensitivity on Cu<2+> in an ethanol solution, has strong resistance to interference of other ions, and has great application prospect.
Owner:TAISHAN MEDICAL UNIV
Method for improving photocatalytic activity of bismuth tungstate through excessive Bi source
InactiveCN102989445AEfficient transferInhibitory complexWater/sewage treatment by irradiationCatalyst activation/preparationTungstateCatalytic oxidation
The invention discloses a method for improving the photocatalytic activity of bismuth tungstate through an excessive Bi source. Through adjusting the raw material mole ratio of Bi (NO3) 3.5 H2O and Na2WO4.2 H2O, a series of photocatalysts with different mole ratios of Bi / W are prepared by using a simple hydrothermal method implemented without any organic molecule additives, and the performances of the photocatalysts on playing a catalytic oxidation role on dye rhodamine B under simulated sunlight irradiation are studied. Results show that when the Bi source is excessive, the performances of the photocatalysts are improved at different levels; and X-ray diffraction results show that when the Bi source is excessive, besides a Bi2WO6 matrix, trace bismuth subnitrate Bi6O6 (OH) 3 (NO3) 3.1.5 H2O also can be obtained, and the appearance of a sample is integrally of a sheet hypersphere structure, but the rigidity and the assembling density of a sheet layer are higher than those of pure Bi2WO6, and the thickness of the sheet layer is obviously thinner than that of the Bi2WO6 by 15-30nm. Fluorescence tests show that the recombination probability of a photon-generated carrier of a sample with the excessive Bi source is really and effectively inhibited.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Benzimidazole quinoline derivative and preparation method and application
ActiveCN105669644AImprove complexation effectQuick responseOrganic chemistryColor/spectral properties measurementsBenzaldehydeQuinoline
The invention provides a benzimidazole quinoline derivative, a preparation method and application in copper ion detection, and particularly relates to a 2-(4-N,N-bis-substituted styryl)-8-1H-benzimidazole) quinoline derivative. Particularly, 2-aminobenzoic acid is used for preparing 2-methylquinoline-8-carboxylic acid, then the 2-methylquinoline-8-carboxylic acid and o-phenylenediamine are subjected to condensation to obtain 2-methyl-8-(2-benzimidazolyl) quinoline, the 2-methyl-8-(2-benzimidazolyl) quinoline and N,N-bis-substituted benzaldehyde are subjected to condensation to obtain the benzimidazole quinoline derivative. A probe has the good complexation with copper ions, when the copper ions exist, derivation of the solution is observed with naked eyes, and the solution is changed from yellow to purple, absorption at the 418 nm position on an ultraviolet visible absorption spectrum is weakened, and a novel absorption peak appears at the 550 nm and gradually increases when the concentration of the copper ions is increased; the benzimidazole quinoline derivative can be used for real-time and rapid measurement of complex samples and can also be used for semiquantitative detection of micro / trace Cu2+ of environment samples from different sources.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
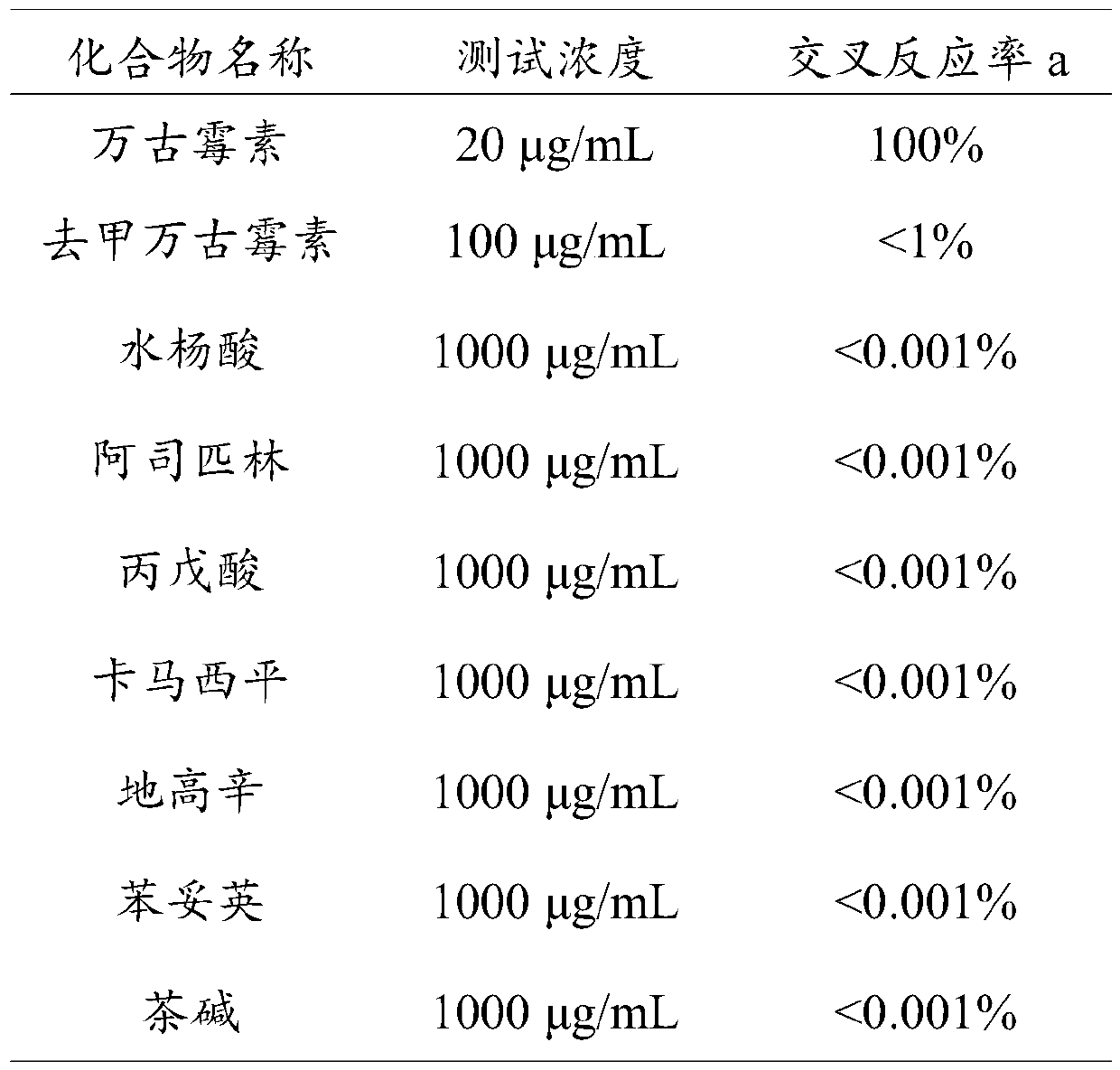
Time-resolved fluorescence immunochromatographic test strip for detecting vancomycin and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109813693AStrong specificityHigh potencySerum albuminBiological testingLap jointBovine serum albumin
The invention provides a time-resolved fluorescence immunochromatographic test strip for detecting vancomycin and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of detection of drug concentration in in-vitro diagnostic reagents. The test strip comprises a bottom plate, a sample absorption pad, a fluorescent microsphere pad, a nitrocellulose membrane and a water absorption pad, wherein the sample absorption pad, the fluorescent microsphere pad, the nitrocellulose membrane and the water absorption pad are in sequential lap joint and adhere to the bottom plate; the nitrocellulose membrane is coated with vancomycin-carrier protein conjugate; a vancomycin monoclonal antibody with a fluorescent microsphere marker is sprayed on the fluorescent microsphere pad; the vancomycin monoclonal antibody is prepared with vancomycin-bovine serum albumin conjugate as an immunogen. The test strip is free of a cross reaction with various vancomycin analogues, and has the advantages of being high in detection accuracy and high in specificity.
Owner:BEIJING DIAGREAT BIOTECH CO LTD
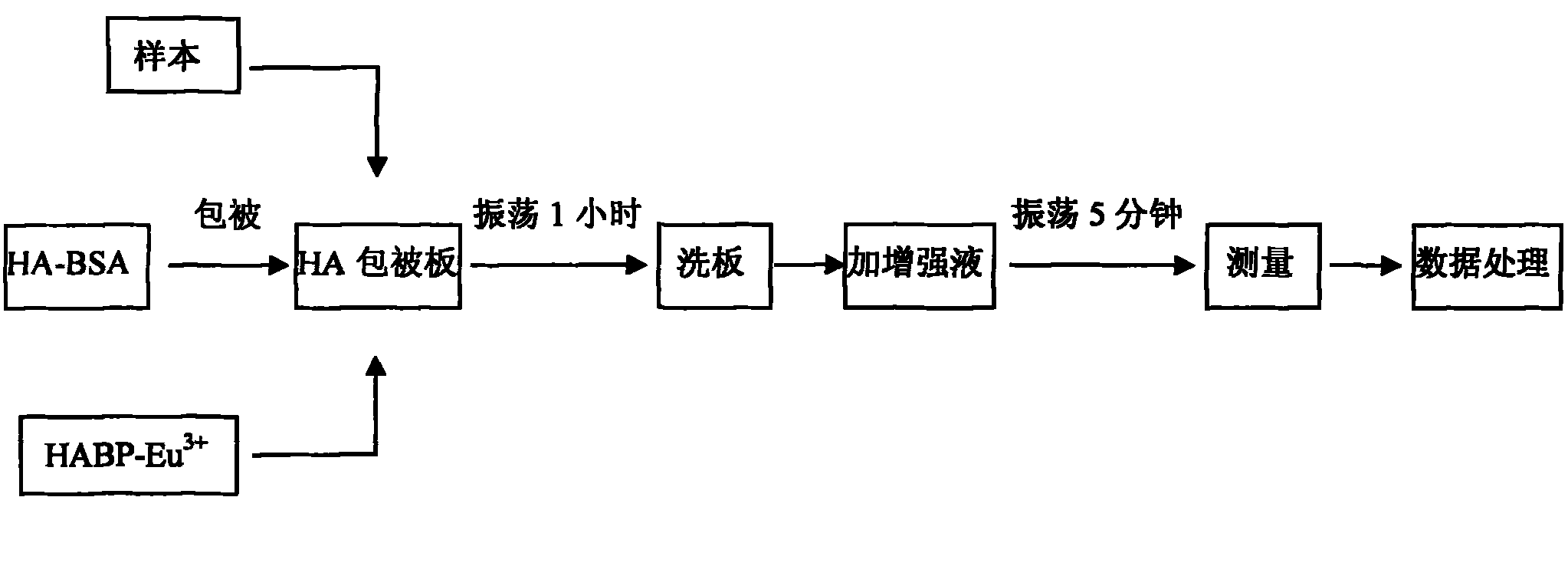
Method for detecting content of hyaluronic acid in human serum
InactiveCN102095847ADecreased fluorescence intensityImprove bindingMaterial analysisEuropiumPollution
The invention relates to a method for detecting hyaluronic acid in human serum, body fluid or tissue homogenate by a radioimmunoassay method. By a method of using solid phase-coated and europium-marked hyaluronic acid binding protein (HABP-Eu<3+>), reagents such as a first antibody, a second antibody and the like are not needed, a sample is easy to add, reaction is quick, the reagents have long shelf life and are environmental-friendly, europium is stably combined with HABP, storage time can be more than 12 months, and radioactive pollution is avoided.
Owner:BEIJING NORTH INST OF BIOLOGICAL TECH
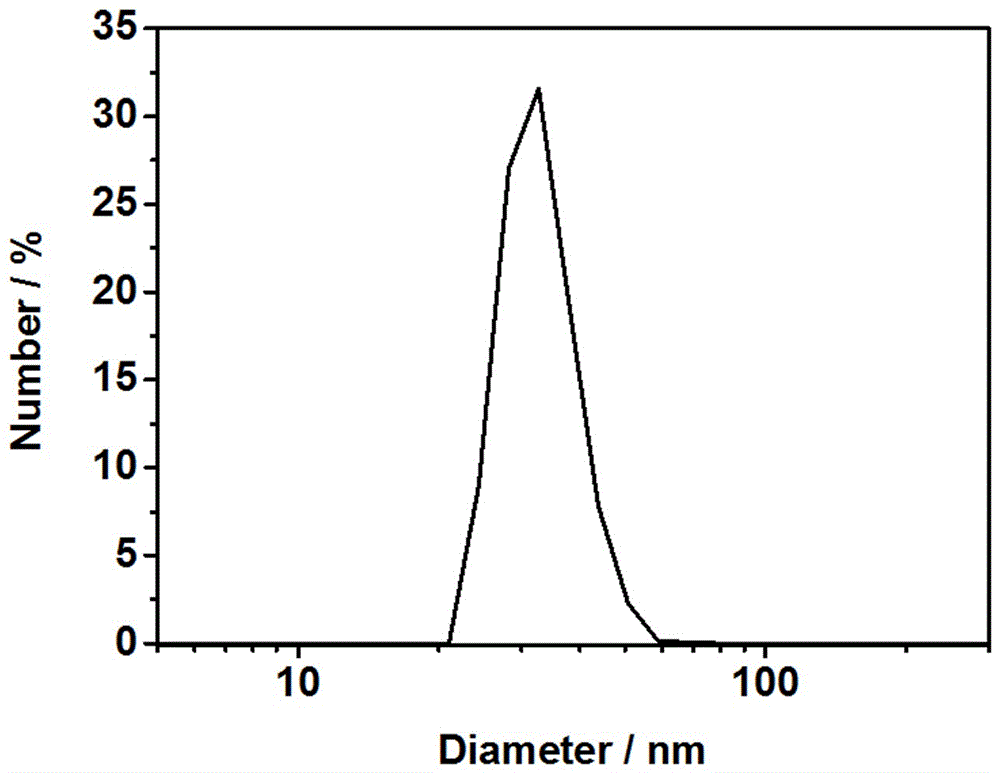
Polymer nanoparticles capable of detecting hypochlorous acid and copper ions as well as preparation method and application of polymer nanoparticles
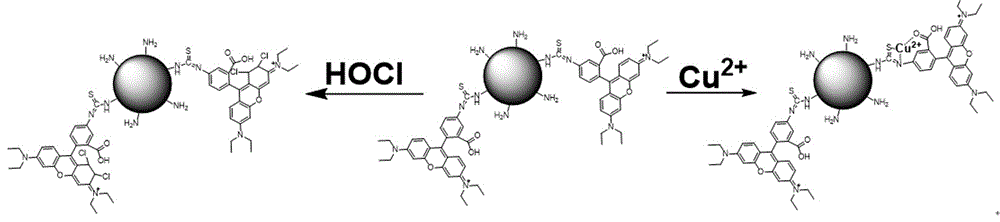
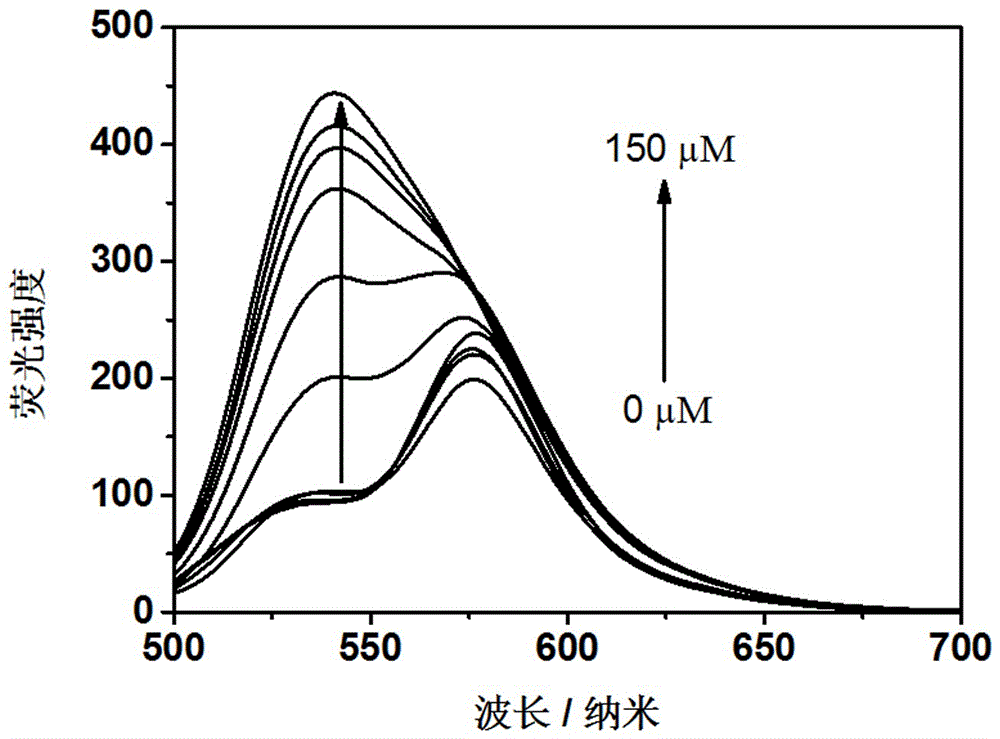
ActiveCN106221107AExcellent ratio detectionDecreased fluorescence intensityFluorescence/phosphorescenceMethacrylateIsothiocyanic acid
The invention discloses polymer nanoparticles capable of detecting hypochlorous acid and copper ions. The polymer nanoparticles are novel polymer nanoparticles prepared by taking a polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether chain transfer agent, styrene, 2-aminoethylmethacrylate hydrochloride, rhodamine B isothiocyanate and a 9,9-dioctyl polyfluorene-benzothiadiazole alternate copolymer as raw materials. The polymer nanoparticles can realize high-sensitivity ratio fluorescence detection on the hypochlorous acid and the copper ions in a pure water solution. Compared with an existing fluorescence detection technology, the prepared polymer nanoparticles have a double-ratio detection function and good biocompatibility; a synthetic route is simple and a detection method is simple and convenient; the polymer nanoparticles are applicable to amplified synthesis and actual production application, and have a great application prospect in the technical fields including analytical chemistry, life science, environmental science and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation and application of ATP fluorescent probe for positioning mitochondria
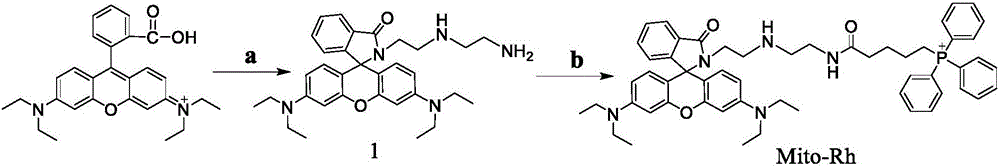
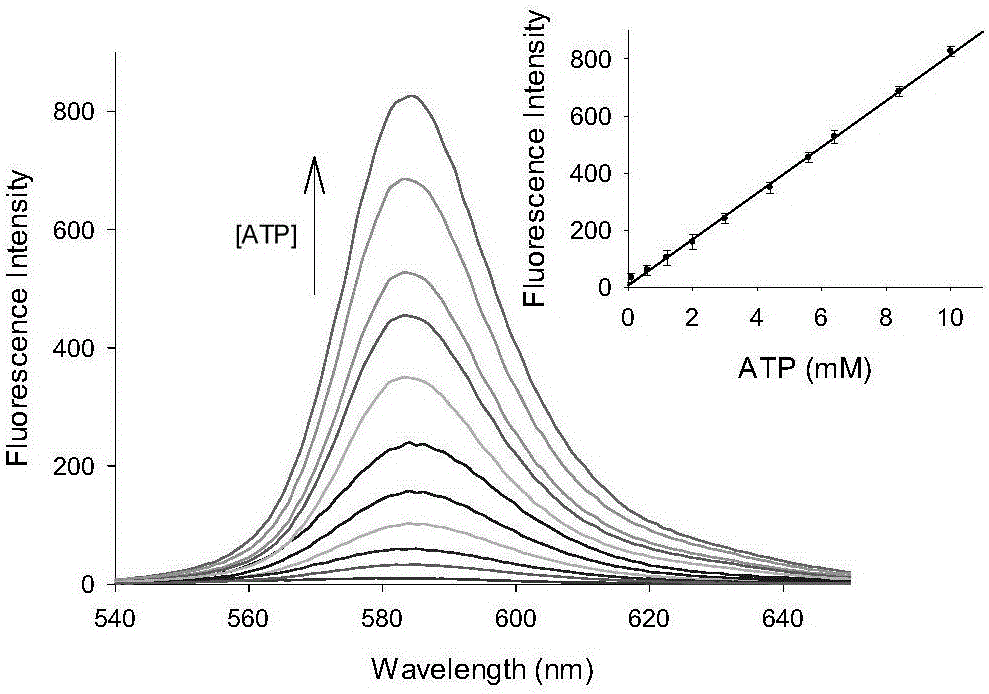
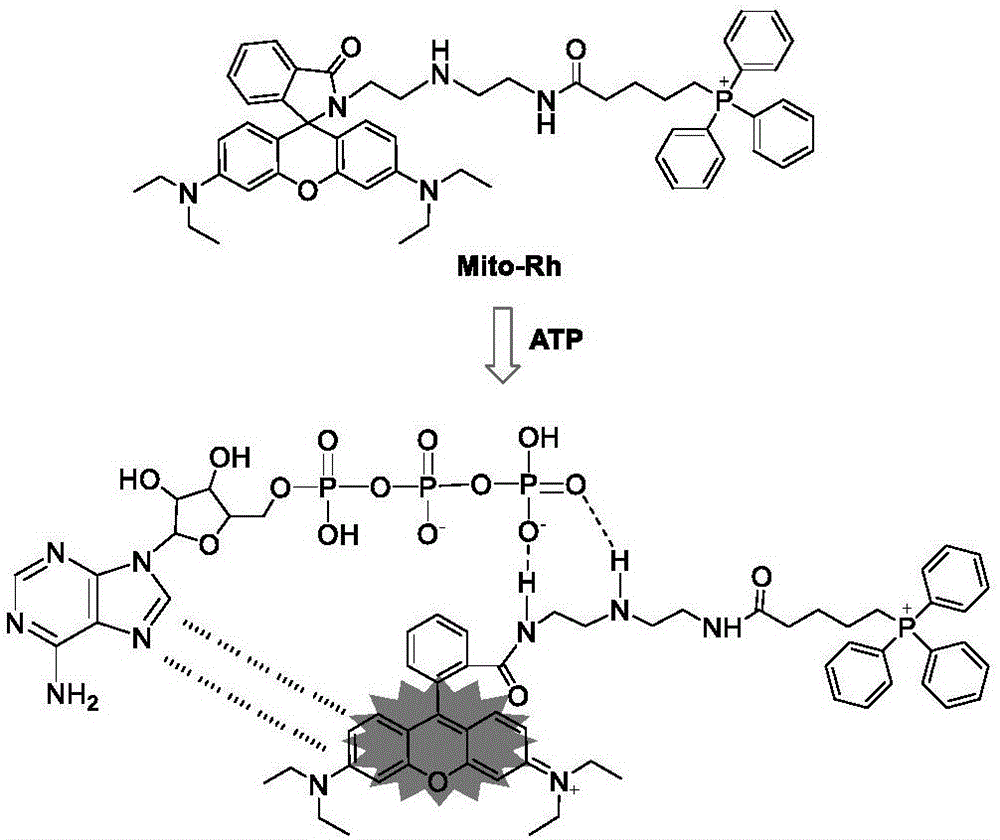
InactiveCN106543226AReal-time monitoring of content changesDecreased fluorescence intensityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiethylenetriamineStructural formula
The invention discloses preparation and application of an ATP fluorescent probe for positioning mitochondria, wherein the probe has the structural formula defined in the specification and is synthesized by rhodamine B, diethylenetriamine, 5-bromo-valeric acid and triphenylphosphine as raw materials. In the system, ATP induces ring opening of a rhodamine lactam structure, strong fluorescence is produced, and high sensitivity is showed on ATP detection. At the same time, the probe shows good selectivity on the ATP, and is hardly interfered by other biological anions or inorganic anions. When the pH value is 6.0-8.0, ATP determination of the probe is not affected. In addition, the probe can be positioned in the mitochondria, and changes of the content of the ATP in the mitochondria are real-timely monitored.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

![Cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane as well as preparation method and application thereof Cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane as well as preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/f5cfb341-3563-4d21-97d3-1224b9056f79/130923152944.PNG)
![Cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane as well as preparation method and application thereof Cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane as well as preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/f5cfb341-3563-4d21-97d3-1224b9056f79/130923152948.PNG)
![Cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane as well as preparation method and application thereof Cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane as well as preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/f5cfb341-3563-4d21-97d3-1224b9056f79/130923152951.PNG)