Preparation and application of ATP fluorescent probe for positioning mitochondria
A fluorescent probe and mitochondrial technology, applied in the field of fluorescent probes, can solve the problems of lack of mitochondrial positioning groups, poor selectivity of biological anions, inconsistency, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
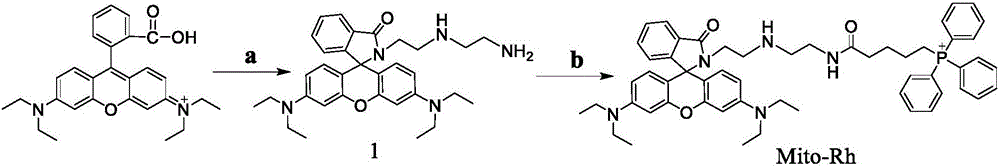
[0025] Synthetic route such as figure 1 shown.
[0026] The synthesis of compound 1: add Rhodamine B (2.0g, 4.18mmol) in the 100mL round-bottomed flask that contains 50mL ethanol, after dissolving completely, solution presents purple, and diethylenetriamine (10.0mL, 92.00mmol) is added dropwise under stirring ) into the above reaction system, refluxed for 24h. The solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. The crude product was separated by column chromatography with an eluent of dichloromethane / ethanol 10:1 (volume ratio) to obtain a yellow solid (compound 1) (0.15 g, yield: 6.40%). 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ):δ7.88(d,J=8.0Hz,1H),7.42(m,2H),7.08(m,1H),6.42(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),6.36(s,2H),6.26 (d, J=8.0Hz, 2H), 3.35-3.18(m, 10H), 2.71(d, J=8.0Hz, 2H), 2.55(t, J=8.0Hz, 2H), 2.20(t, J= 8.0Hz, 2H), 1.16(t, J=8.0Hz, 12H). 13 C NMR (100MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ167.9, 153.6, 153.3, 148.7, 132.2, 131.3, 129.0, 128.9, 128.0, 127.9, 123.7, 122.7, 108.1, 105.7, 97.9, 64.9, 51.7, 51.3, 50.5,...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Solution preparation of fluorescent probe Mito-Rh interacting with ATP
[0030] A certain amount of fluorescent probe was dissolved in water to obtain a probe stock solution with a concentration of 100 μM. Dissolve a certain amount of ATP in water, pour it into a 500mL volumetric flask, add water to dilute to the mark, and obtain ATP with a concentration of 1000mM. The 1000mM ATP aqueous solution was gradually diluted with twice distilled water to obtain a 0.1-100mM ATP aqueous solution. Add 1.0mL probe stock solution and 1.0mL ATP aqueous solution into a 10mL volumetric flask, and dilute to the volume with buffer solution PBS to obtain a fluorescent probe with a concentration of 10μM and an ATP test solution with a concentration of 0.01-100mM.
Embodiment 3
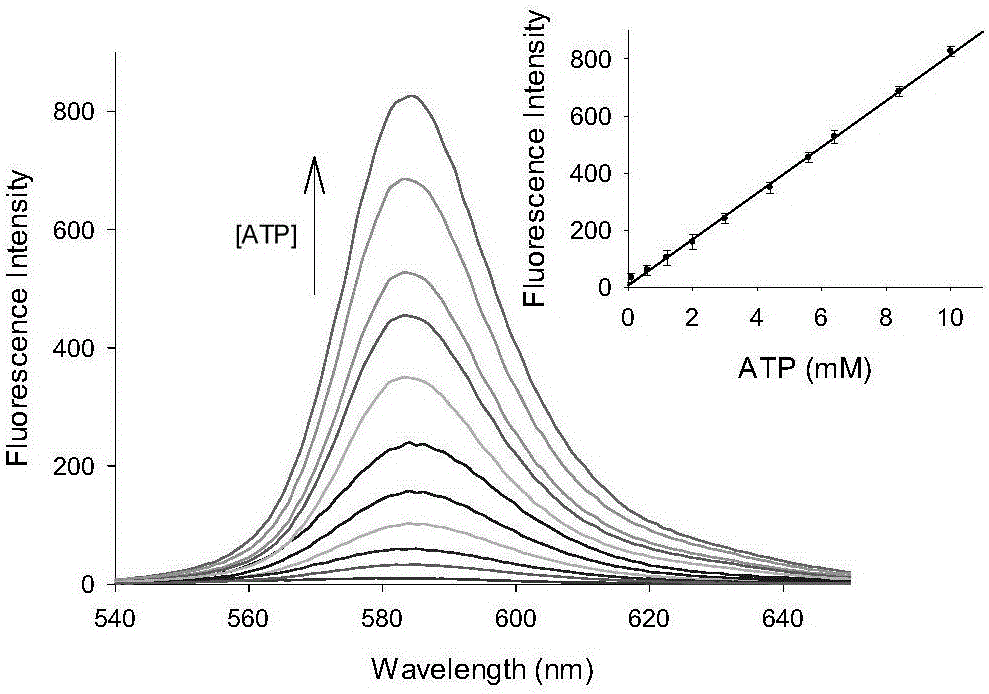
[0032] Determination of Fluorescent Spectrum Properties of Fluorescent Probe Mito-Rh Interaction with ATP
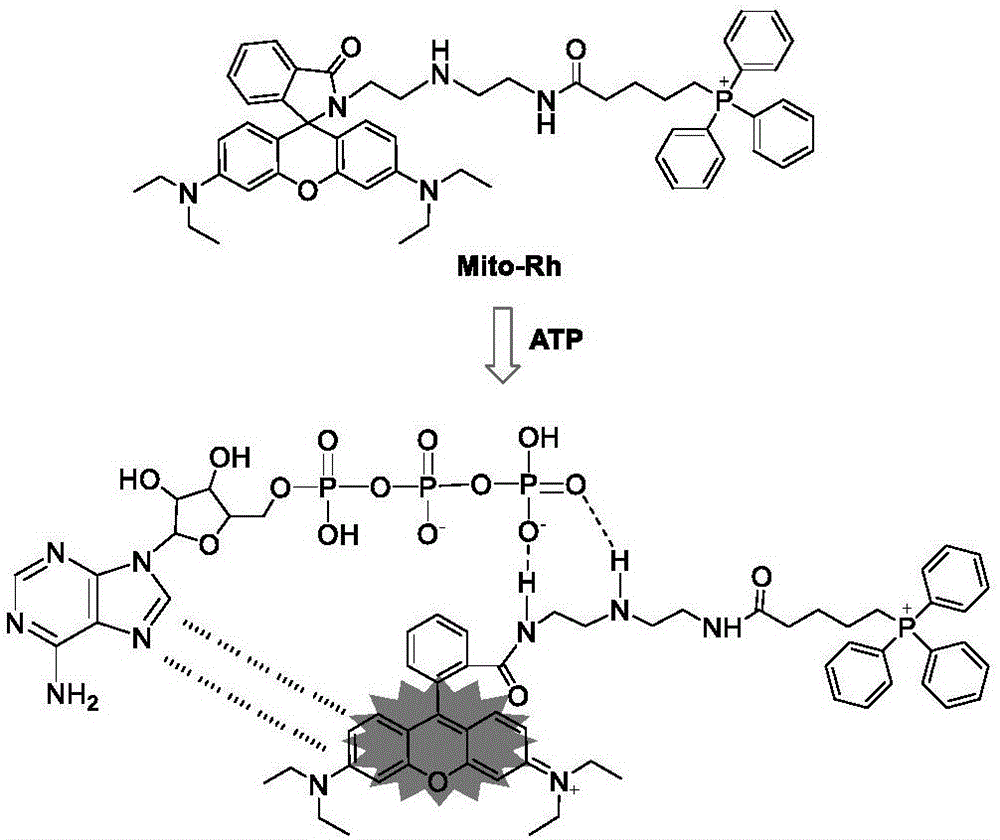
[0033] The PBS buffer solution with a pH value of 7.0 was used as a solvent to measure the fluorescence spectrum of the fluorescent probe interacting with ATP with a Perkin Elmer LS 55 fluorescence spectrophotometer. The results are as follows: figure 2. The concentration of the fluorescent probe is 10μM, the concentration of ATP is 0, 0.1, 0.6, 1.2, 2.0, 3.0, 4.4, 5.6, 6.4, 8.4, 10.0mM, the excitation wavelength is fixed at 520nm, and the emission wavelength range is 530-650nm. The slit width is 5nm / 5nm. Before adding ATP, the fluorescent probe has almost no fluorescence. After adding ATP, the emission peak of rhodamine appears at 583nm. This is because the structure of the probe molecule changes, and the structure changes from the closed ring form of rhodamine to the open ring form. . And with the increase of ATP concentration, the fluorescence intensity of the pro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com