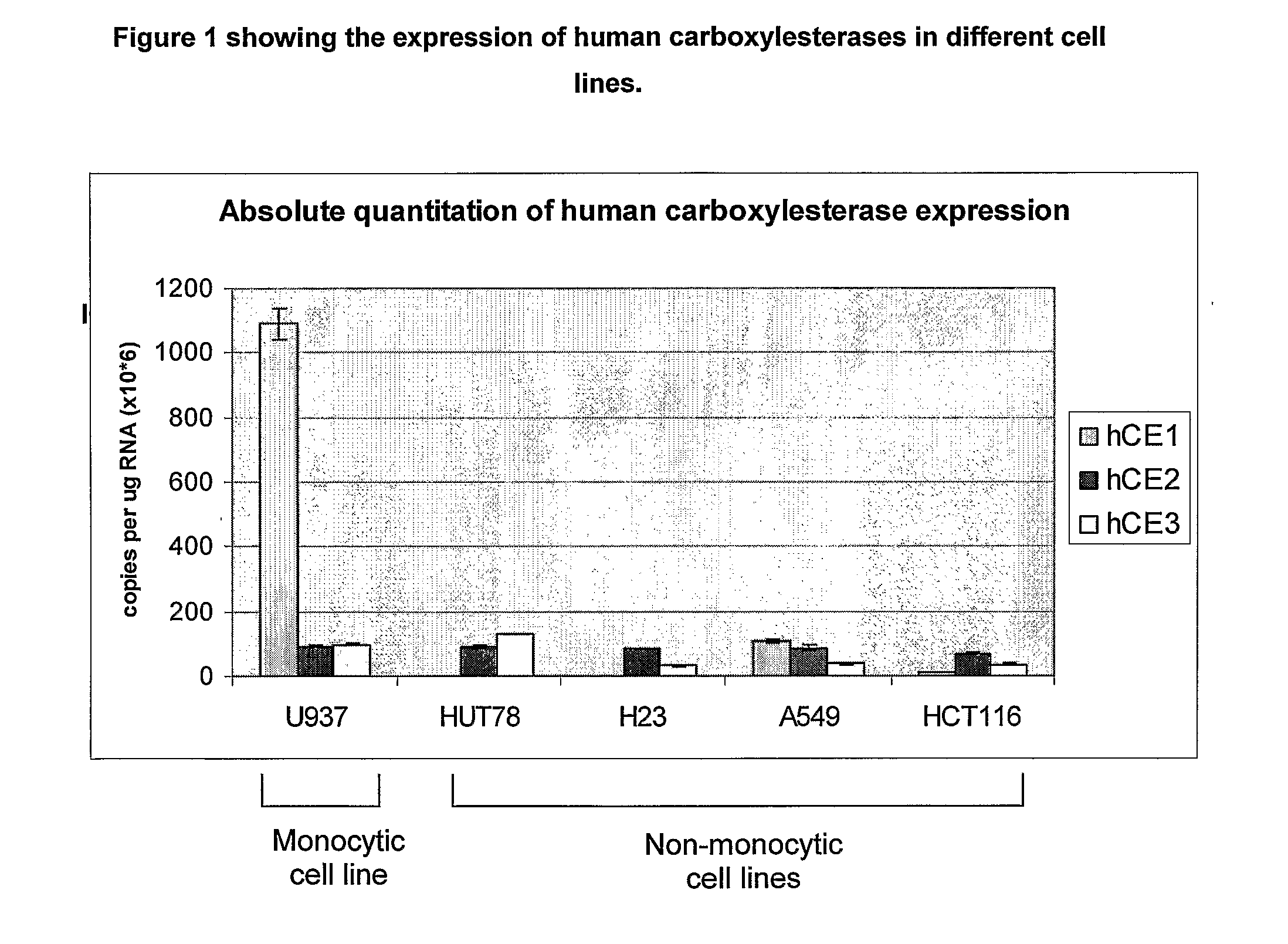
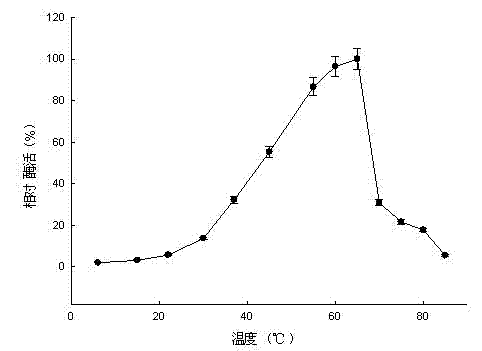
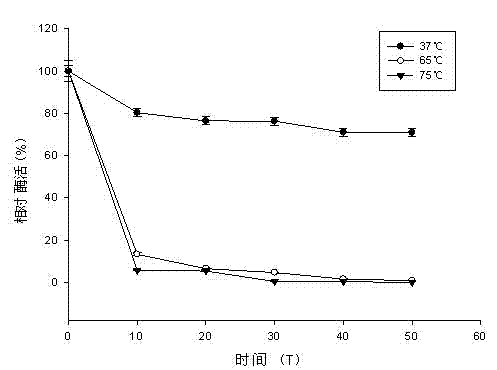
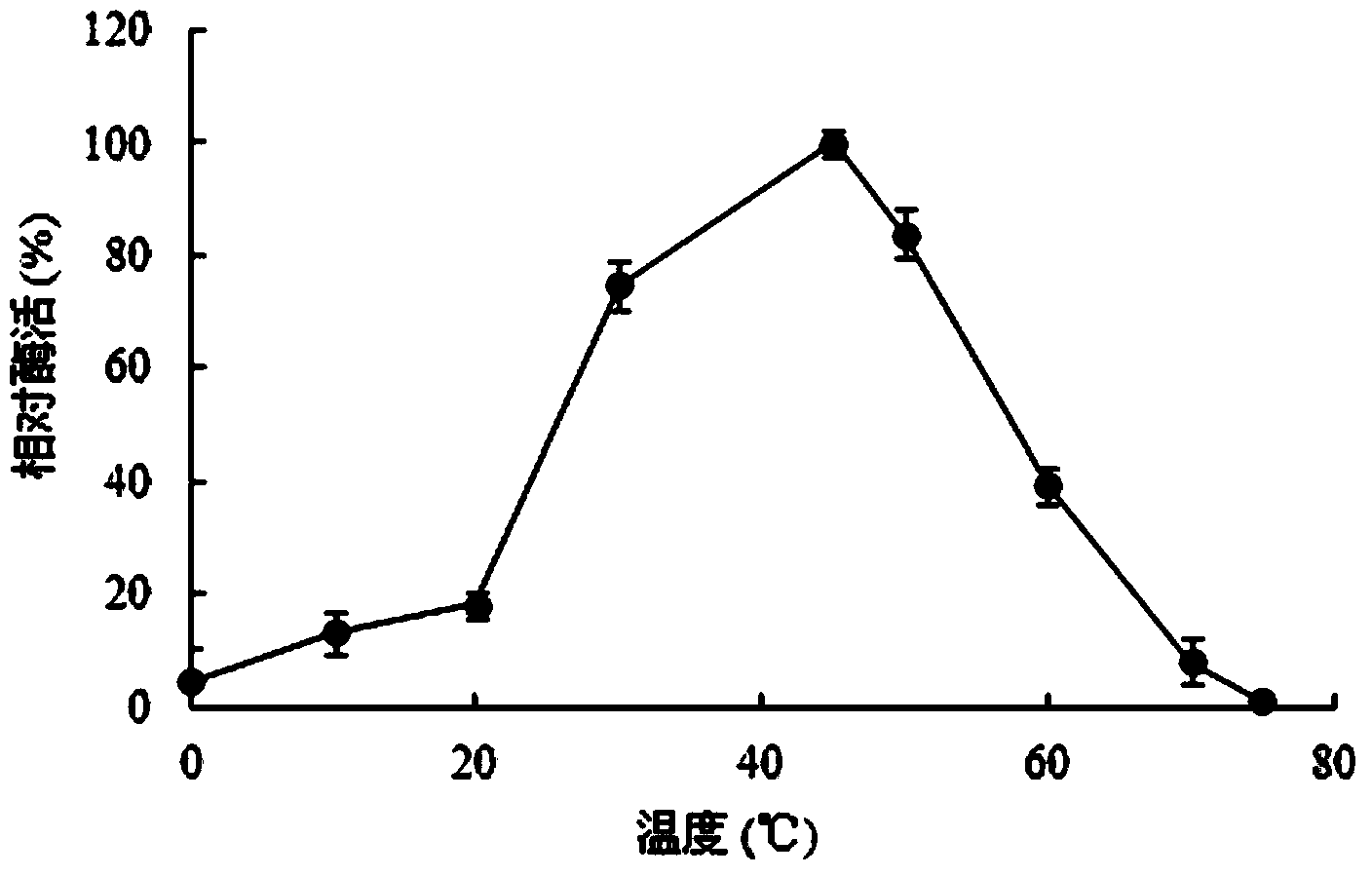
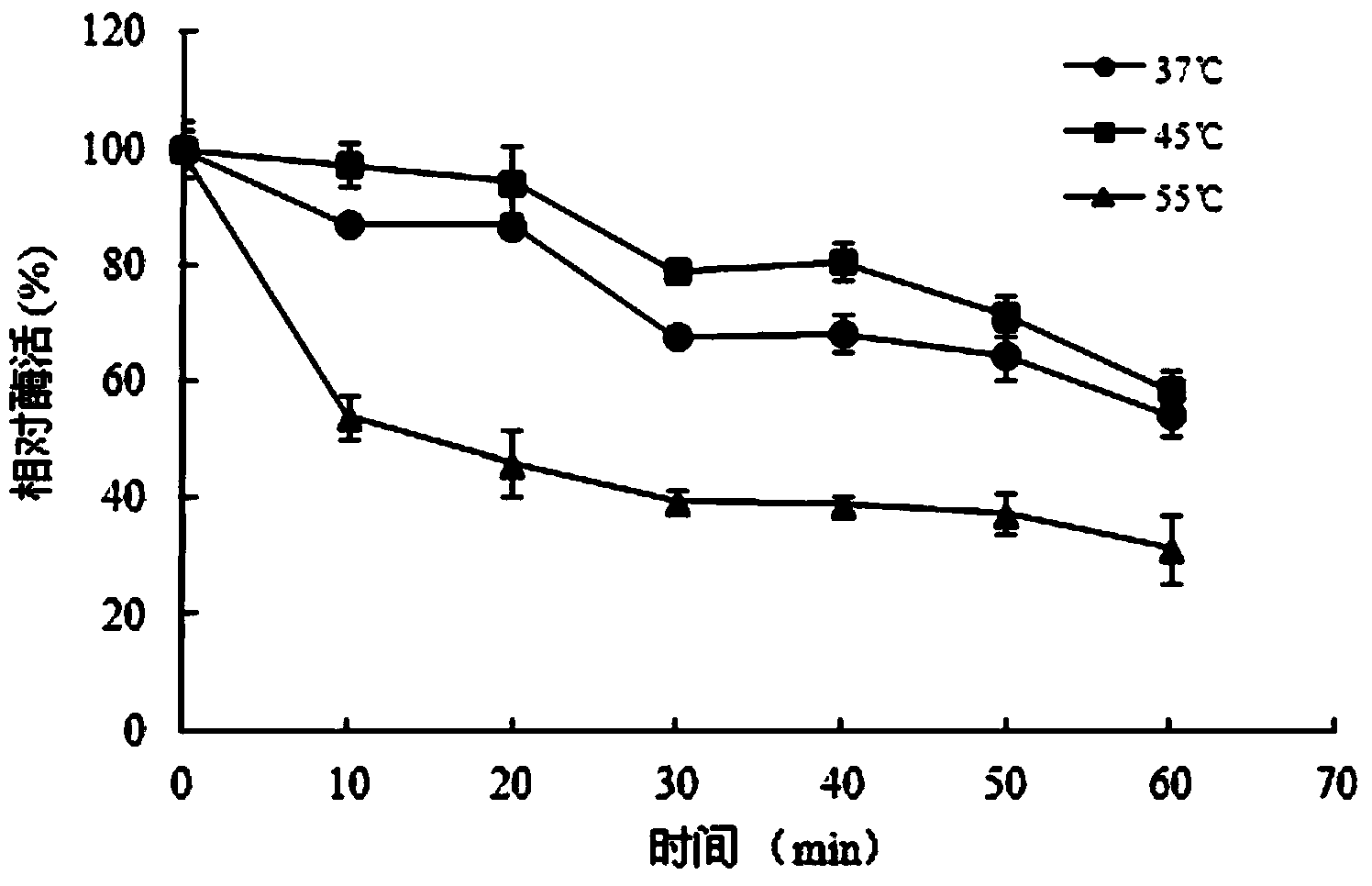
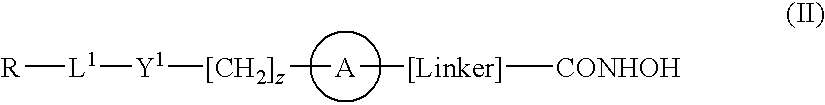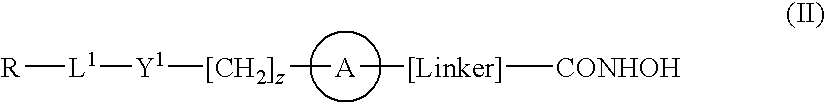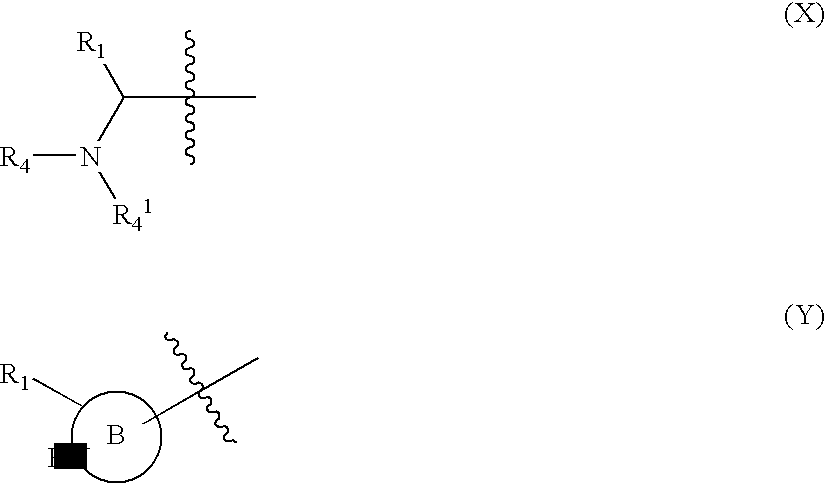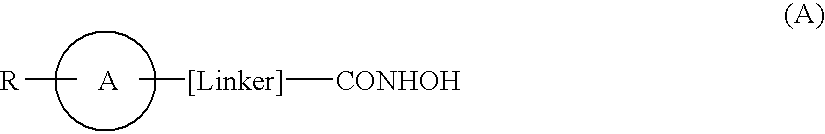Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
148 results about "Carboxylesterase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In enzymology, a carboxylesterase or carboxylic-ester hydrolase (EC 3.1.1.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes a chemical reaction of the form a carboxylic ester + H₂O ⇌ an alcohol + a carboxylate Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are carboxylic ester and H₂O, whereas its two products are alcohol and carboxylate. Most enzymes from this group are serine hydrolases belonging to the superfamily of proteins with alpha/beta hydrolase fold.
Thermostable carboxylesterase gene, coding protein and application thereof
The invention discloses a thermostable carboxylesterase gene, coding protein and application thereof, the esterase has amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1. Compared with the prior art, the esterase containing EstW is thermostable esterase obtained from streptomycete in known mesophilic bacteria, can be widely applied to production of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or ferulic acid.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
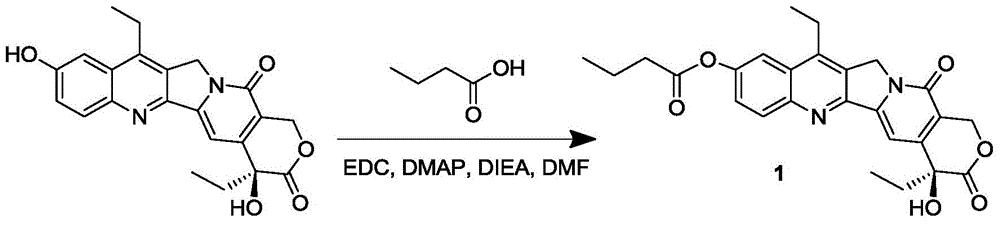
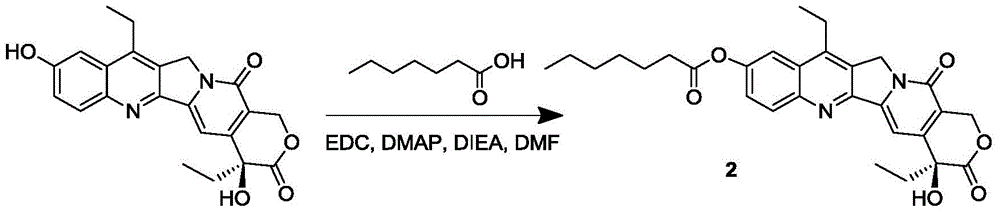
7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecine drug precursor, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105315294AGood antitumor activityImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistrySolubility7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin
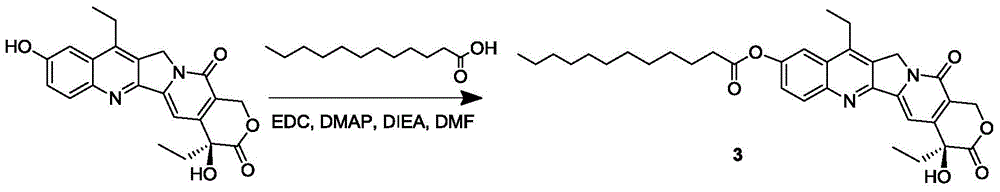
The invention discloses a 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecine drug precursor, a preparation method and an application thereof. A structure formula of the drug precursor is represented as the formula I or II. The drug precursor is prepared through an esterification reaction between a C-10 hydroxyl group or a C-20 hydroxyl group of 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecine and a hydrophobic molecule. The drug precursor has excellent anti-tumor activity and can directly release active components in vivo in a hydrolysis manner without catalytic hydrolysis of carboxylesterase, thereby achieving a high bioavailability. The drug precursor not only has excellent solubility in water but also has great solubility in amphipathic surfactants, such as tween-80 and the like, wherein the solubility can reach more than 30 mg / ml, and a high stability is achieved even that the drug precursor is diluted in water. The drug precursor can be prepared just through a one-step esterification method, is high in yield and low in preparation cost, is high in stability and good in safety, satisfies requirements in clinical medication and in large-scale industrial production, and has excellent market prospect and clinical application value.
Owner:王杭祥
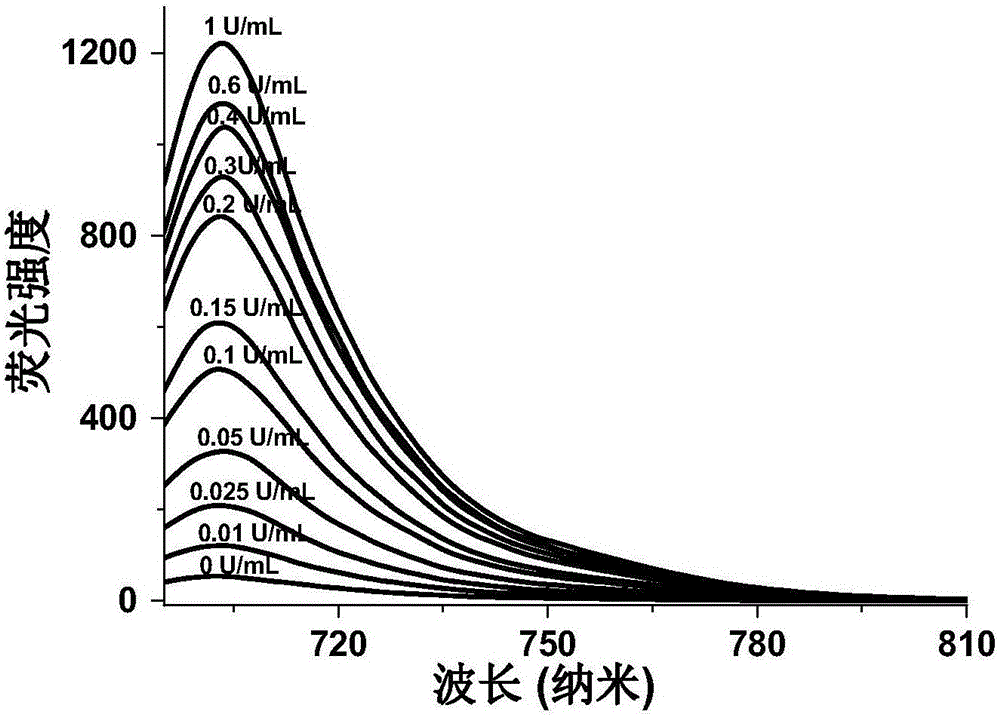
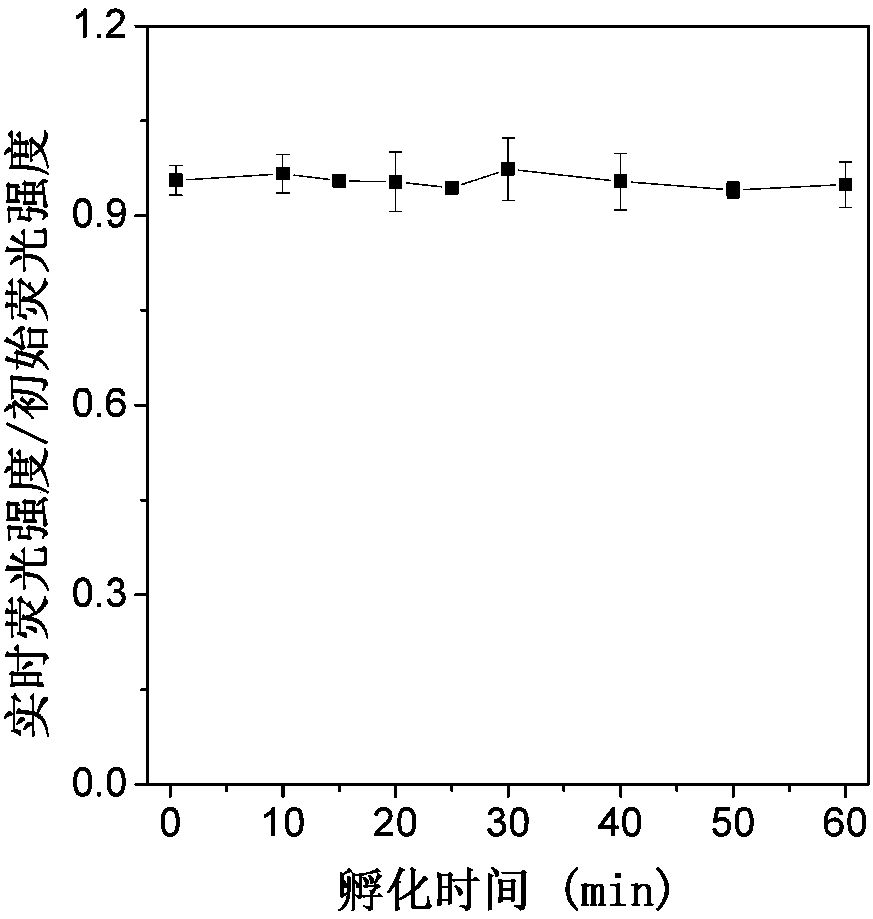
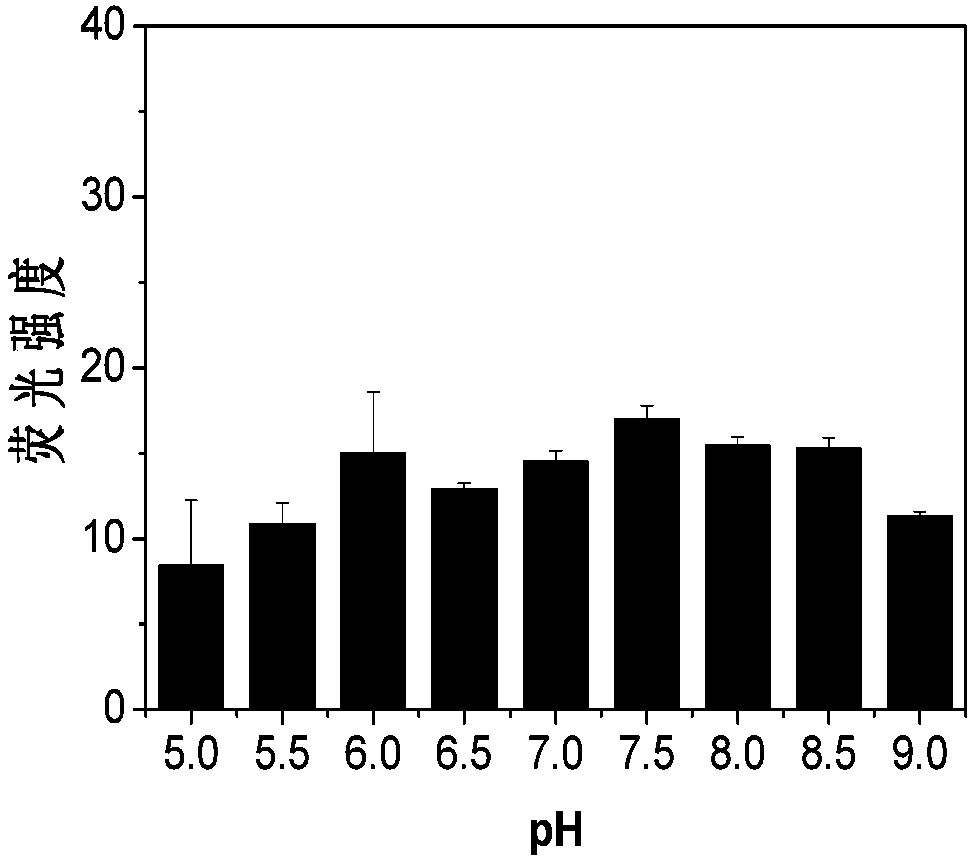
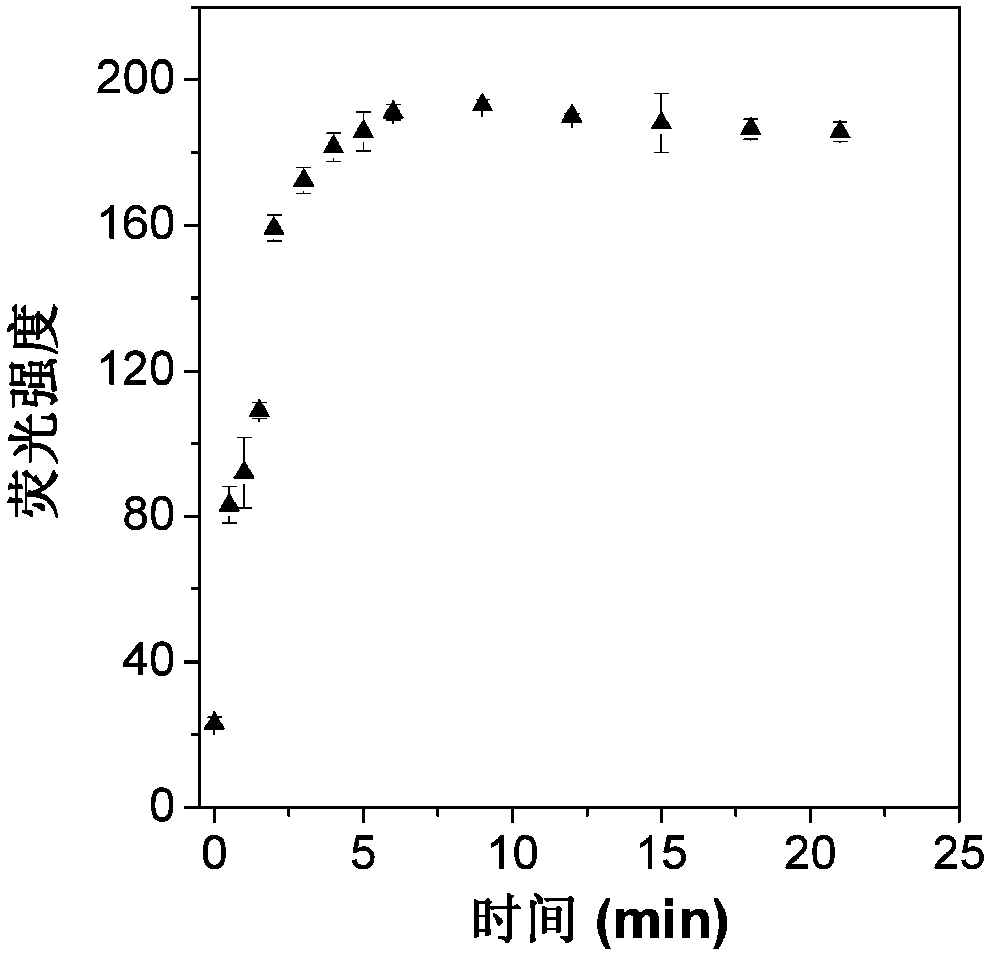
Detection method for activity of carboxylesterase and activity of carboxylesterase inhibitor
ActiveCN102788776AAvoid generatingHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceHydrolysis
The invention discloses a detection method for the activity of carboxylesterase and the activity of a carboxylesterase inhibitor, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The detection method solves the problems of lower sensitivity, frequent occurrence of false positive signals, complex method, expensive price and long consumed time in the existing enzyme activity detection method. The detection method comprises the following steps of: reacting substrate molecules and carboxylesterases with different concentrations so as to obtain a hydrolysis product; and mixing the obtained hydrolysis product, silver nitrate solution, polyanion solution and a micromolecule probe with positive charges, and carrying out fluorescence detection on the activity of the carboxylesterase. The invention also provides a detection method for the activity of the carboxylesterase inhibitor. The method has higher sensitivity, and the detection limit is 0.05mU / mL, and is lower than that of the existing certain detection method by 1 or 2 order of magnitudes; and simultaneously, experiments prove that the method has good selectivity, simpleness and convenience and low cost.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Specific fluorescence probe substrates of human carboxylesterase 2 and application thereof
InactiveCN104120164AEasy to detectThe synthesis process is simpleOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteHydrolysis
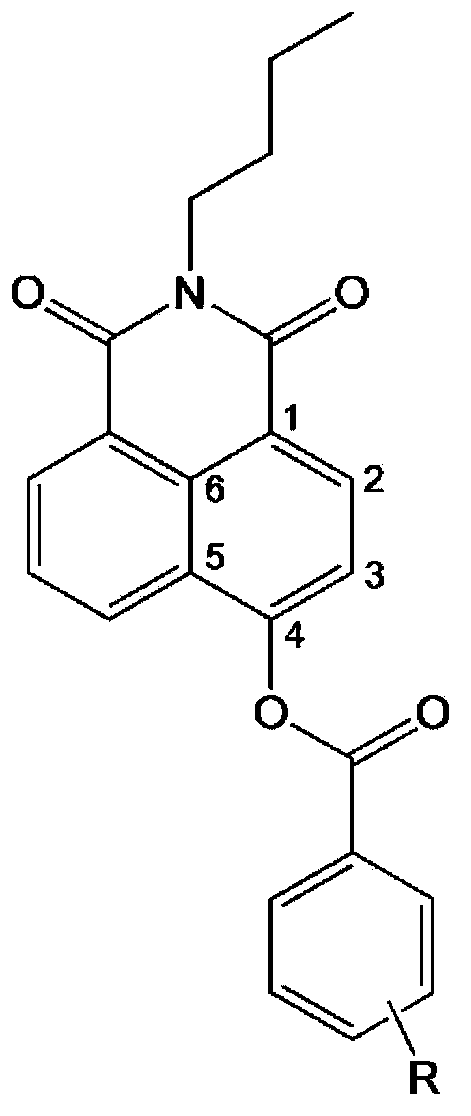
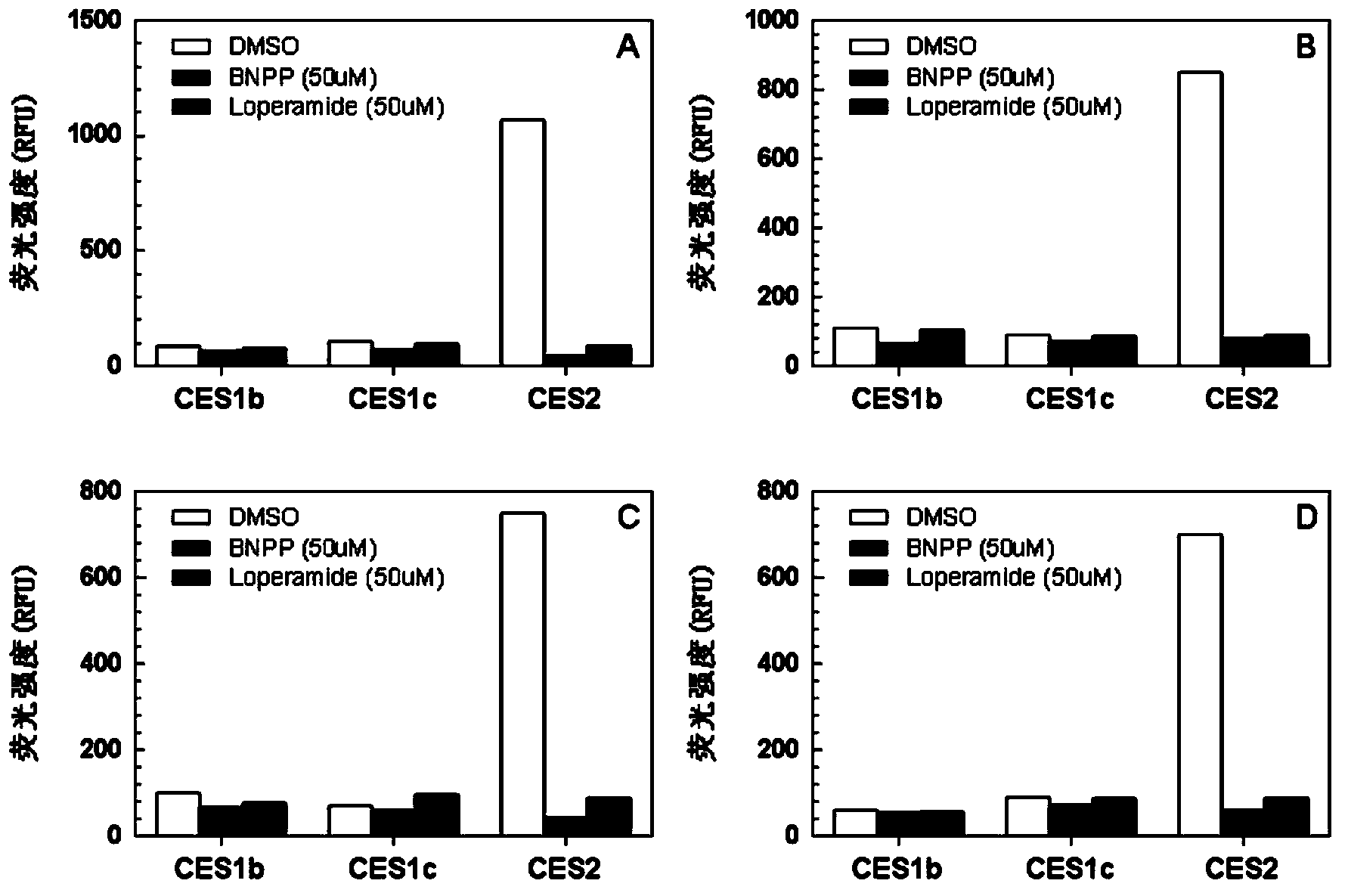
The invention provides a specific fluorescence probe substrates of human carboxylesterase 2 (CES2) and application thereof. The specific probe substrate is a benzoateb compound of a C4 hydroxyl naphthalimide, and is applicable to determine the enzyme activity of CES2 in a biological system. The CES2 enzyme activity determination flow comprises: selecting a hydrolysis benzoyl-removal reaction of the benzoate compound of the C4 hydroxyl naphthalimide as a probe reaction, and quantitatively determining the generation amount of a hydrolysis metabolite of the compound in a unit time, so as to determine the enzyme activity of CES2 in all biological samples, cells, bodies and integral organs. The probe is applicable to quantitative assessment of CES2 enzyme activity in biological samples of different species and different individual sources, and quantitative determination on CES2 enzyme activity in different sources of animal tissue cell culture fluids and cell preparation substances, so that the probe is expected to help to realize assessment on medicine disposal capability of important drug metablic enzyme CES2. Additionally, the probe also is applicable as an inhibitor for rapidly screening CES2 in vitro by means of the probe reaction.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
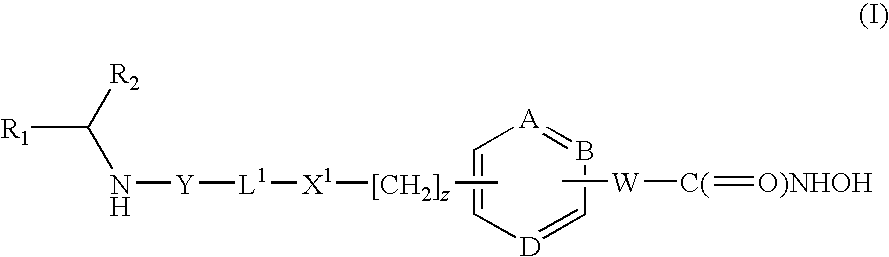
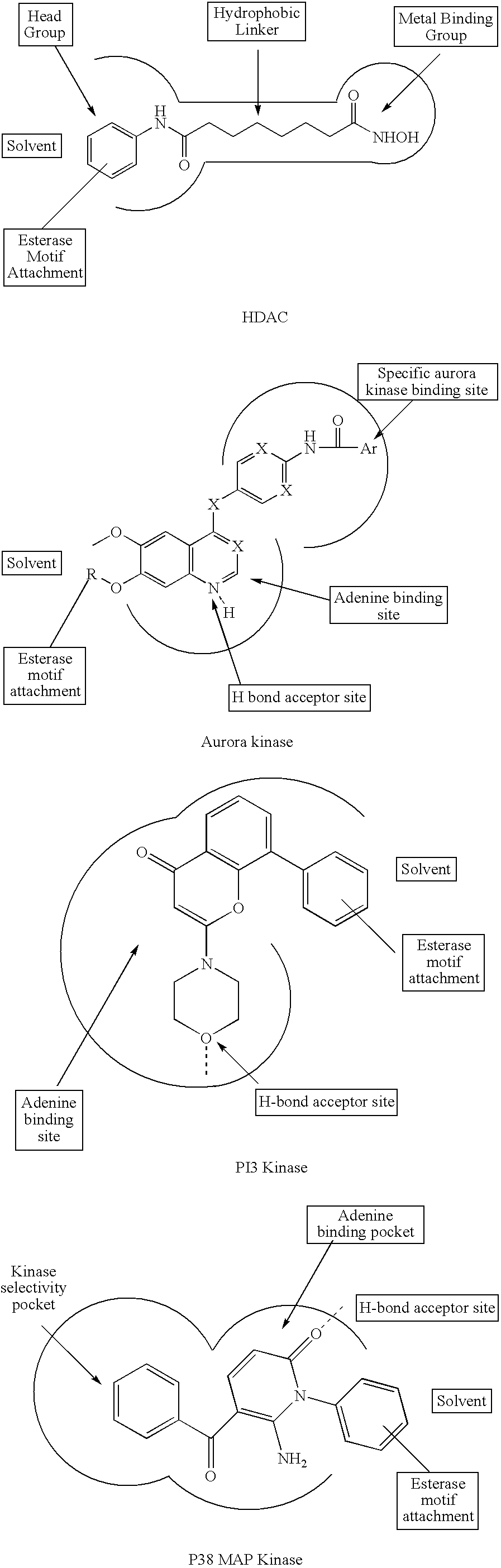
Hydroxamic acid derivatives as inhibitors of HDAC enzymatic activity
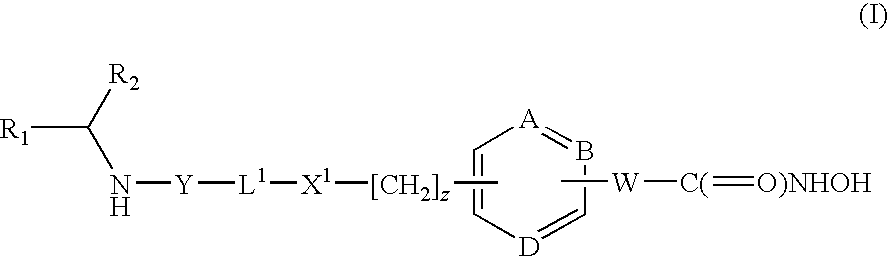
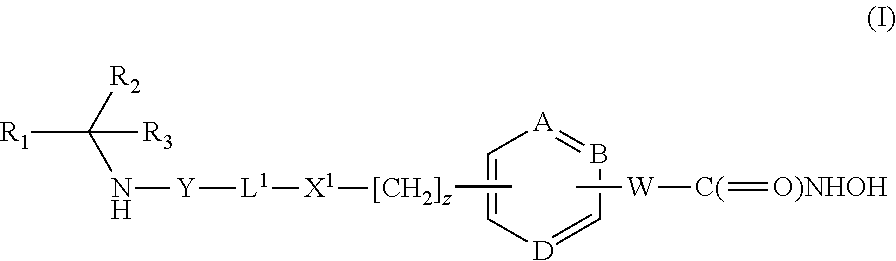
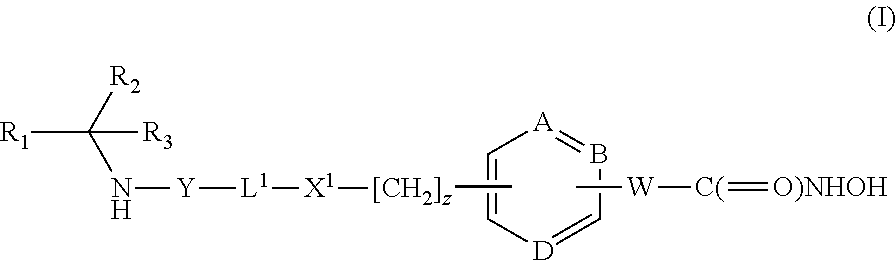
Compounds of formula (I) are inhibitors of histone deacetylase activity, and are useful in the treatment of, for example, cancers:wherein Y1 is a bond, —(C═O)—, —S(O2)—, —C(═O)O—, —OC(═O)—, —(C═O)NR3—, —NR3(C═O)—, —S(O2)NR3—, —NR3S(O2)—, or —NR3(C═O)NR5—, wherein R3 and R5 are independently hydrogen or optionally substituted (C1-C6)alkyl, L1 is a divalent radical of formula -(Alk1)m(O)n(Alk2)p— wherein m, n, p, Alk1, Alk2 and Q are as defined in the claims; z is 0 or 1; A represents an optionally substituted mono-, bi- or tri-cyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring system; -[Linker]- represents a divalent linker radical; R is a radical of formula (X) or (Y):wherein R1 is a carboxylic acid group (—COOH), or an ester group which is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular carboxylesterase enzymes to a carboxylic acid group; R4 is hydrogen; or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl, C3-C7cycloalkyl, aryl, aryl(C1-C6 alkyl)-, heteroaryl, heteroaryl(C1-C6 alkyl)-, —(C═O)R3, —(C═O)OR3, or —(C═O)NR3 wherein R3 is hydrogen or optionally substituted (C1-C6)alkyl, C3-C7 cycloalkyl, aryl, aryl(C1-C6 alkyl)-, heteroaryl, or heteroaryl(C1-C6 alkyl)-; R41 is hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl; and B is a monocyclic heterocyclic ring of 5 or 6 ring atoms wherein R1 is linked to a ring carbon adjacent the ring nitrogen shown, and ring B is optionally fused to a second carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring of 5 or 6 ring atoms in which case the bond shown intersected by a wavy line may be from a ring atom in said second ring;
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE INTPROP DEV LTD
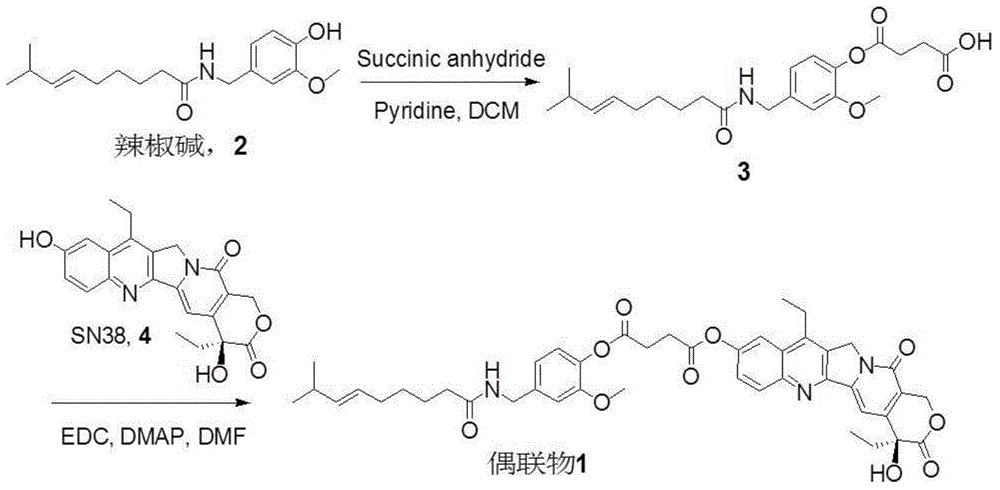
Capsicine-camptothecin anti-cancer drug conjugate and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104447777AImprove solubilityGood antitumor activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistrySN-38Solvent
The invention discloses a capsicine-camptothecin anti-cancer drug conjugate and a preparation method and application thereof. In the preparation method disclosed by the invention, chemical modification is performed on capsicine, the modified capsicine is coupled to camptothecin anti-cancer drug through ester bonds, and the obtained capsicine-camptothecin anti-cancer drug conjugate can be dissolved in pharmacy solvents which can be accepted in clinic, for example, Tween, so that the conjugate can be directly used for oral medication in clinic; coupling occurs on C20 hydroxy of the camptothecin or on C10 or C20 hydroxy of SN-38. Through the coupling of the ester bonds, the conjugate can directly release two kinds of activated components in a body in a hydrolytic manner. On one hand, the camptothecin or the SN-38 can be released without the catalytic hydrolysis of carboxylesterase, so that the bioavailability of the SN-38 can be effectively improved; on the other hand, the capsicine has a certain anti-cancer activity and can take synergistic action with the SN-38 after being released in the body, so that the anti-cancer effect of the SN-38 is intensified.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
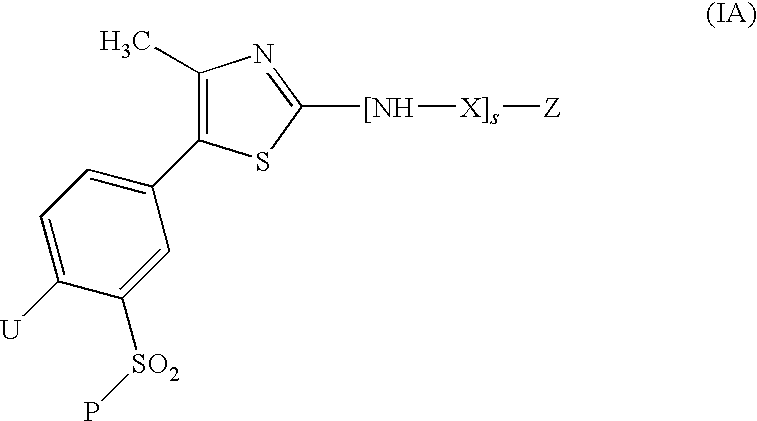
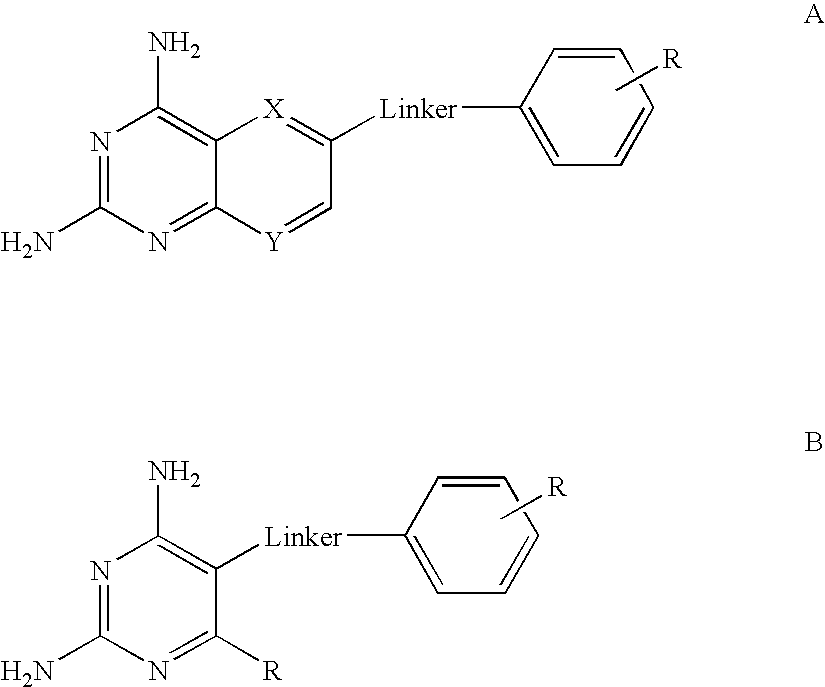
Thiazole derivatives as inhibitors of p13 kinase
Compounds of formula (I) are inhibitors of P13 kinase activity, and useful in treatment of, inter alia, autoimmune, inflammatory and proliferative diseases: wherein: s is 0 or 1; U is hydrogen or halogen; X is —(C═O), an optionally substituted divalent phenylene, pyridinylene, pyrimidinylene, or pyrazinylene radical, or a bond; P is optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl and Z is —(CH2)Z—X1-L1-NHCHR1R2; or Z is optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl and P is —(CH2)Z—X1-L1-NHCHR1R2; R1 is a carboxylic acid group (—COOH), or an ester group which is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular carboxylesterase enzymes to a carboxylic acid group; R2 is the side chain of a natural or non-natural alpha amino acid; X1 is (i) a bond; —NR4C(═O)NR5— or —NR4S(═O)2—; or except when X is —(C═O)— (ii) —C(═O)—, —S(═O)2—, or —S(═O)2NR4— wherein R4 and R5 are independently hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl; and z and L1 are as defined in the specification.
Owner:CHROMA THERAPEUTICS
Preparation method and application of double-rate-type multifunctional high-sensitivity florescent probe for carboxylesterase detection
InactiveCN106588846ASensitive detectionAccurate detectionOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceOsmium tetroxideDisease
The invention relates to a preparation method and an application of a double-rate-type (ultraviolet / fluorescence) multifunctional (calorimetric / fluorescence / ultraviolet) high-sensitivity florescent probe for carboxylesterase detection. Firstly, 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde, diethyl glutaconate and anhydrous piperidine react in ethyl alcohol to produce a product 1, the product 1 and acetic anhydride react in anhydrous pyridine to produce a product 2, the product 2 reacts with osmium tetroxide and sodium periodate in tetrahydrofuran to produce a product 3, and the product 3 reacts with anhydrous potassium carbonate in methyl alcohol to produce a product 4; then methylpyridine and methyl iodide react in absolute ether to produce a product 5; next, the product 4 and the product 5 are dissolved in absolute ethanol, piperidine is added for a reaction, and a product 6 is obtained; finally, the product 6 is dissolved in acetic anhydride, anhydrous sodium acetate is added, and the double-rate-type multifunctional florescent probe for carboxylesterase detection is obtained. The probe is applicable to qualitative and quantitative analysis of carboxylesterase in biological samples, is sensitive, accurate and quick in detection, and can be applied to related fields of analytical chemistry, life organic analytical chemistry, disease pre-diagnosis, clinical medical examination and the like.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
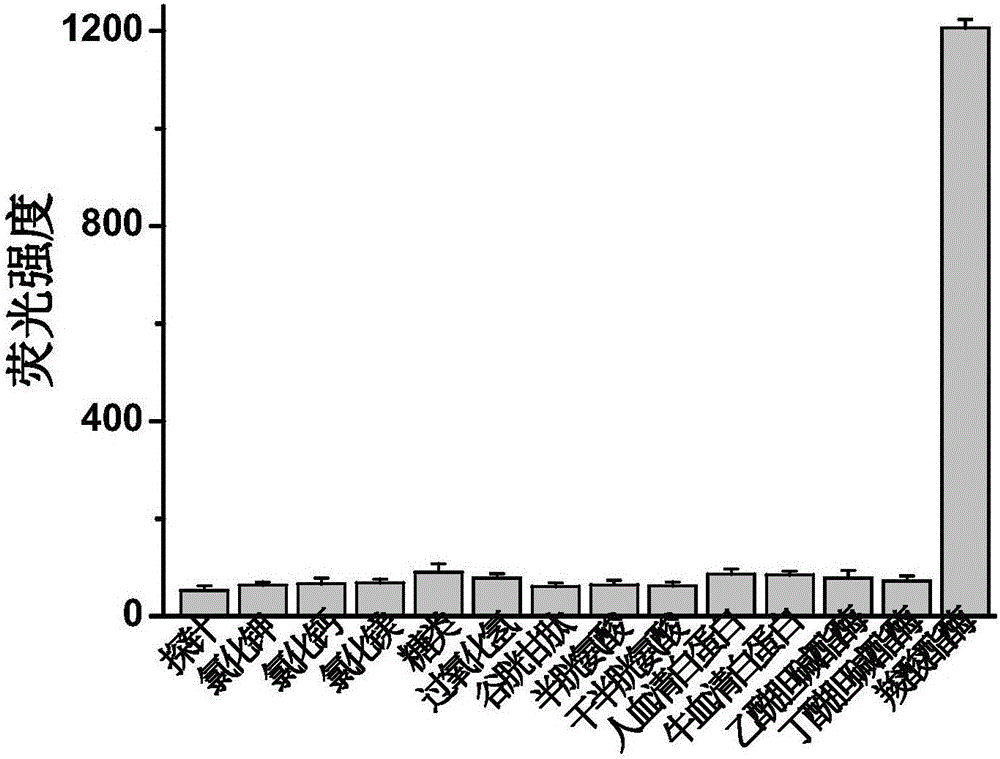
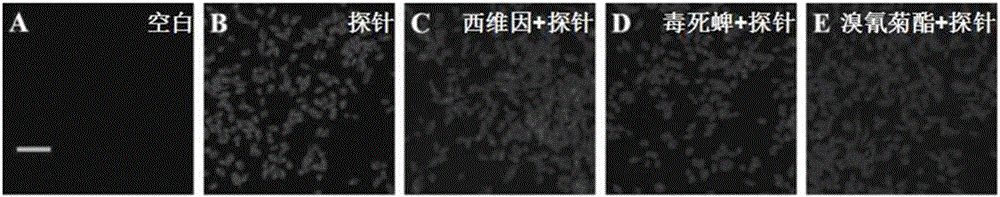
Fluorescent probe and pesticides residue detection kit based on carboxylesterase inhibition method
ActiveCN106496204ADecreased fluorescence intensityQuick responseOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescencePhosphatePesticide residue
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe and a pesticide residue detection kit based on a carboxylesterase inhibition method. The pesticide residue detection kit comprises a reagent stock solution a and a reagent stock solution b, wherein the reagent stock solution a is a buffer solution containing phosphate, and the reagent stock solution b is a solution of the fluorescent probe. Experiments find that the strength of the self fluorescence of the probe is very weak, and after carboxylesterase is added, the probe react and release an IR-780 hemicyanine skeleton fluorescent parent body, the fluorescence of the solution is remarkably strengthened, showing that the method can be used for detection of the activity of the carboxylesterase; after adding a tiny amount of pesticides in the carboxylesterase, the fluorescence of the solution is remarkably weakened, showing that a tiny amount of the pesticides can inhibit the activity of the carboxylesterase, and thus the fluorescent probe can be used for detection of pesticide residues. The fluorescent probe has the advantages of being easy to operate, low in cost, fast, efficient and sensitive, and the fluorescent probe is convenient for application and popularization, and has a huge application prospect in the fields of agriculture, food and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
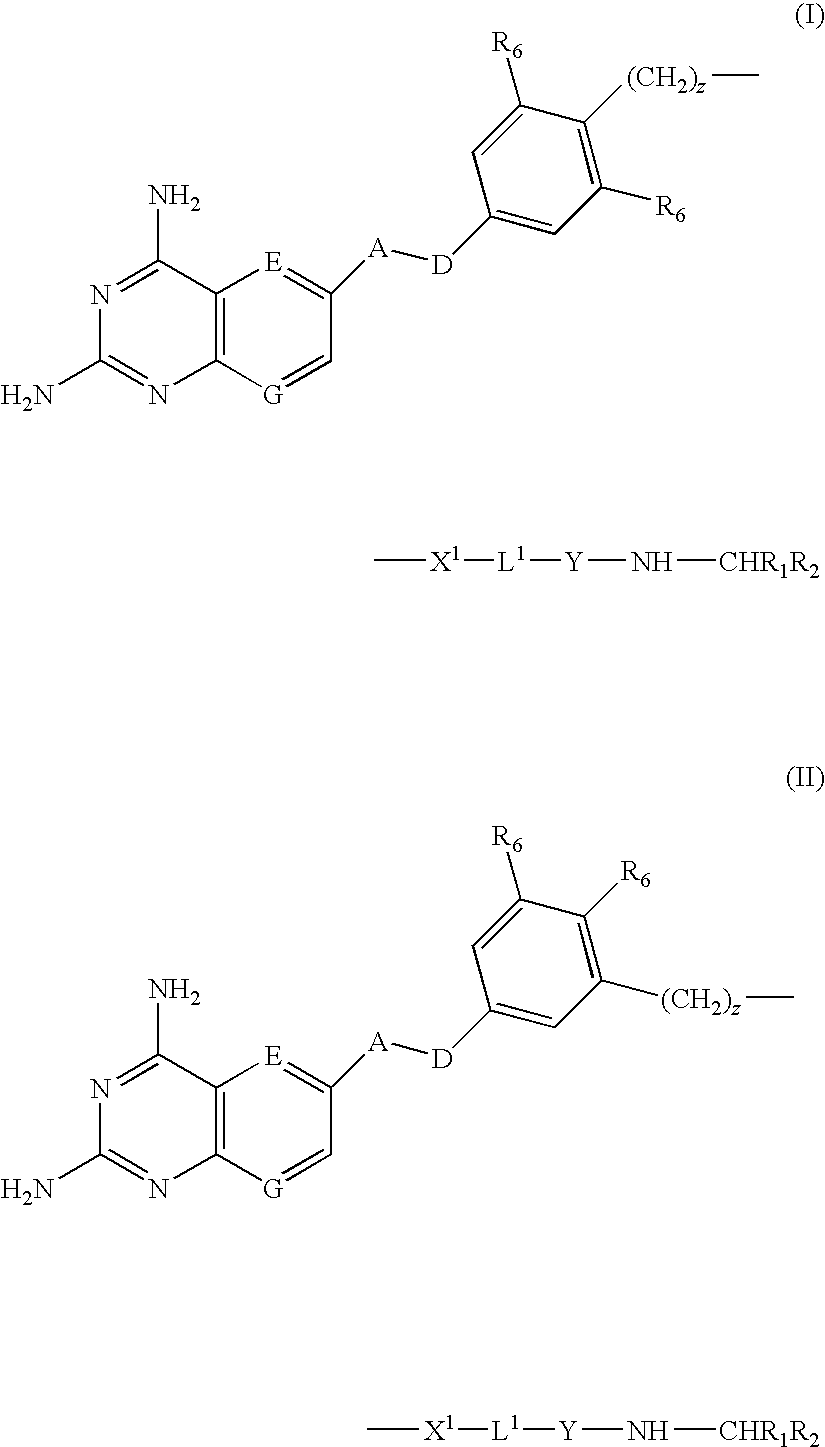
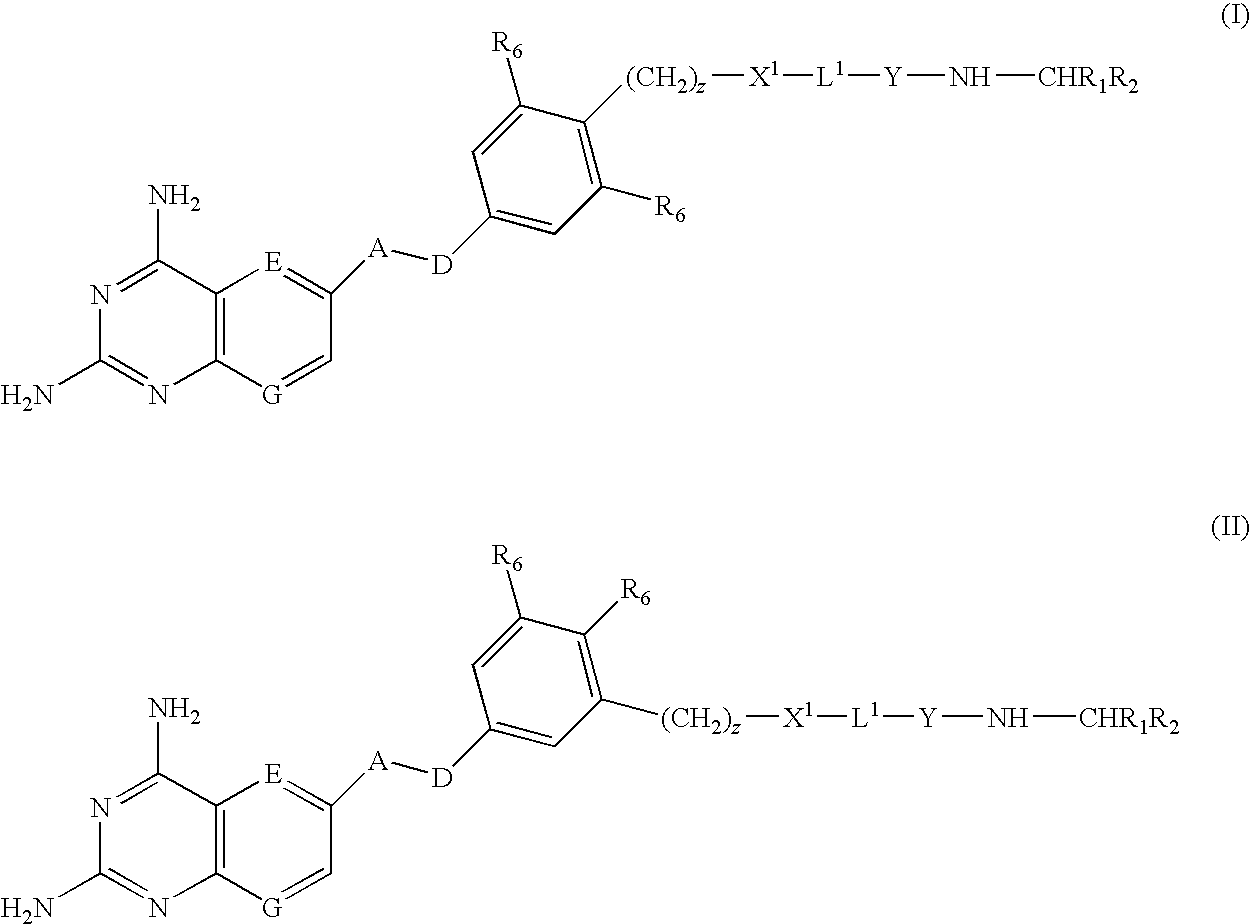
DHFR enzyme inhibitors
Compounds of formula (I) or (II) are dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors, useful for the treatment of, for example, cell proliferative diseases:wherein A and D are independently —CHR7— or —NR7—; E and G are independently ═CR7— or ═N—; each R6 independently represents hydrogen or —OR7; R7 is hydrogen or C1-C6 alkyl; R1 is a carboxylic acid group (—COOH), or an ester group which is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular carboxylesterase enzymes to a carboxylic acid group; R2 is the side chain of a natural or non-natural alpha amino acid which does not contain a carboxyl, or carboxyl ester group; Y is a bond, —C(═O)—, —S(═O)2—, —C(═O)NR3—, —C(═S)—NR3, —C(═NH)NR3 or —S(═O)2NR3— wherein R3 is hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl; L1 is a divalent radical of formula -(Alk1)m(Q)n(Alk2)p- wherein m, n and p are independently 0 or 1, and Q, Alk1 and Alk2 are as defined in the claims; X1 represents a bond; —C(═O); or —S(═O)2—; —NR4C(═O)—, —C(═O)NR4—, —NR4C(═O)NR5—, —NR4S(═O)2—, or —S(═O)2NR4— wherein R4 and R5 are independently hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl; and z is 0 or 1.
Owner:CHROMA THERAPEUTICS
Enzyme and Receptor Modulation
InactiveUS20090215800A1Prolonged and increased activityEasy accessBiocideOrganic chemistryCarboxylic acidHydrolysis
Covalent conjugation of an alpha amino acid ester to a modulator of the activity of a target intracellular enzyme or receptor, wherein the ester group of the conjugate is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular carboxylesterase enzymes to the corresponding acid, leads to accumulation of the carboxylic acid hydrolysis product in the cell and enables improved or more prolonged enzyme or receptor modulation relative to the unconjugated modulator.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE INTPROP DEV LTD
Hydroxamic acid derivatives as inhibitors of HDAC enzymatic activity
Compounds of formula (I) are inhibitors of histone deacetylase activity, and are useful in the treatment of, for example, cancers:wherein Y1 is a bond, —(C═O)—, —S(O2)—, —C(═O)O—, —OC(═O)—, —(C═O)NR3—, —NR3(C═O)—, —S(O2)NR3—, —NR3S(O2)—, or —NR3(C═O)NR5—, wherein R3 and R5 are independently hydrogen or optionally substituted (C1-C6)alkyl, L1 is a divalent radical of formula -(Alk1)m(Q)n(Alk2)p wherein m, n, p, Alk1, Alk2 and Q are as defined in the claims; z is 0 or 1; A represents an optionally substituted mono-, bi— or tri-cyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring system; -[Linker]- represents a divalent linker radical; R is a radical of formula (X) or (Y):wherein R1 is a carboxylic acid group (—COOH), or an ester group which is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular carboxylesterase enzymes to a carboxylic acid group; R4 is hydrogen; or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl, C3-C7cycloalkyl, aryl, aryl(C1-C6 alkyl)-, heteroaryl, heteroaryl(C1-C6 alkyl)-, —(C═O)R3, —(C═O)OR3, or —(C═O)NR3 wherein R3 is hydrogen or optionally substituted (C1-C6)alkyl, C3-C7 cycloalkyl, aryl, aryl(C1-C6 alkyl)-, heteroaryl, or heteroaryl(C1-C6 alkyl)-; R41 is hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl; and B is a monocyclic heterocyclic ring of 5 or 6 ring atoms wherein R1 is linked to a ring carbon adjacent the ring nitrogen shown, and ring B is optionally fused to a second carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring of 5 or 6 ring atoms in which case the bond shown intersected by a wavy line may be from a ring atom in said second ring.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE INTPROP DEV LTD
High-specificity fluorescent probe of human carboxylesterase CES2 and application thereof
ActiveCN104650854AHas fluorescent propertiesSensitive detectionOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementMetabolite3-Hydroxyflavone
A high-specificity fluorescent probe of human carboxylesterase CES2 and an application thereof. A substrate of the high-specificity fluorescent probe is an ester derivative of a 3-hydroxyl flavonoid compound, which can be used for detecting the existence of the CES2 in different bio-samples and quantitatively measuring the activity of the CES2. A particular measurement process of the enzyme activity includes following steps: selecting a hydrolysis reaction of the derivative of the 3-hydroxyl flavonoid compound as a probe reaction; selecting generation amount of a hydrolytic metabolite, 3-hydroxyl flavonoid, in unit time through quantitative detection with selection of a proper substrate concentration in a linear reaction section so that the actual activity of the CES2 enzyme in various bio-samples, cells, in-vivo organs and overall organs can be measured. The high-specificity fluorescent probe not only can be used for quantitative evaluation of the enzyme activity of the CES2 in the bio-samples from different sources, but also can be used for in-vitro quickly screening an inhibitor of the CES2 by means of the probe reaction.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG IND TECH RES INST CO LTD DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
HDAC inhibitors
InactiveUS20100010010A1Improve permeabilityProlong the action timeBiocideNervous disorderSide chainCarboxylic acid
Compounds of formula (I) inhibit HDAC activity, wherein A, B and D independently represent ═C— or ═N—; W is a divalent radical —CH═CH— or CH2CH2—; R1 is a carboxylic acid group (—COOH), or an ester group which is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular carboxyesterase enzymes to a carboxylic acid group; R2 is the side chain of a natural or non-natural alpha amino acid; z is 0 or 1; and Y, L1, and X1 are as defined in the claims.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE INTPROP DEV LTD
Niraparib granules with high utilization efficiency and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110314094AStrong reductionPromote absorptionPharmaceutical product form changeSolid materialVitamin CD-Glucose
The invention discloses niraparib granules with a high utilization efficiency and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of medicine production. The components of the niraparib granules include niraparib, glucose, vitamin C and a carboxylesterase inhibitor. A granule packaging machine adopted in the preparation method comprises a storage bin and a transparent upper discharge pipe, wherein the transparent upper discharge pipe penetrates through the storage bin, the two sides of the upper discharge pipe are provided with an infrared emitter and an infrared receiver respectively, the infrared emitter and the infrared receiver are capable of lifting and lowering, a turntable is arranged below the upper discharge pipe, a curved through hole is formed in the turntable,a retractable stop block with a proximity switch is arranged on one side of the turntable, and a curved groove is formed in the turntable. By adopting the niraparib granules, the amount of niraparib discharged along with excretion can be reduced, and the pharmacodynamic effect of the niraparib can be maintained; valve-related components of the granule packaging machine adopted in the preparation process of the niraparib granules have longer service life, it can be ensured that the amount of the material discharged each time is sufficient, the remaining granules with a remaining amount less than a set value are remained in the upper discharge pipe, and the application is convenient.
Owner:ANHUI HAIKANG PHARMA
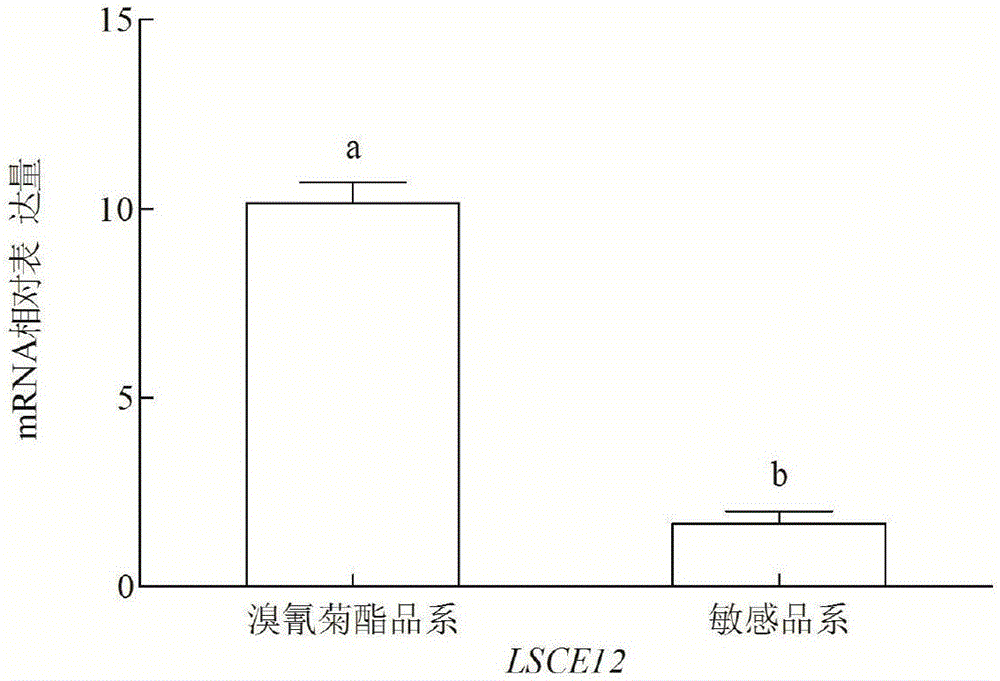
Small brown rice planthopper drug-resistant carboxylesterase gene LSCE12, gene segment for lowering drug resistance of small brown rice planthoppers and application thereof
ActiveCN106191003ADelay drug resistanceAchieving Antimicrobial Resistance GovernanceHydrolasesFermentationPlanthopperDrug resistance
The invention relates to a small brown rice planthopper drug-resistant carboxylesterase gene LSCE12, a gene segment for lowering drug resistance of small brown rice planthoppers and application thereof. The sequence of the small brown rice planthopper drug-resistant carboxylesterase gene LSCE12 is disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1. The sequence of the gene segment for lowering drug resistance of small brown rice planthoppers is disclosed as SEQ ID NO.3. The gene segment is used for lowering drug resistance of small brown rice planthoppers. The gene segment can be used for detecting drug resistance of small brown rice planthoppers and implementing drug resistance treatment of small brown rice planthoppers.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
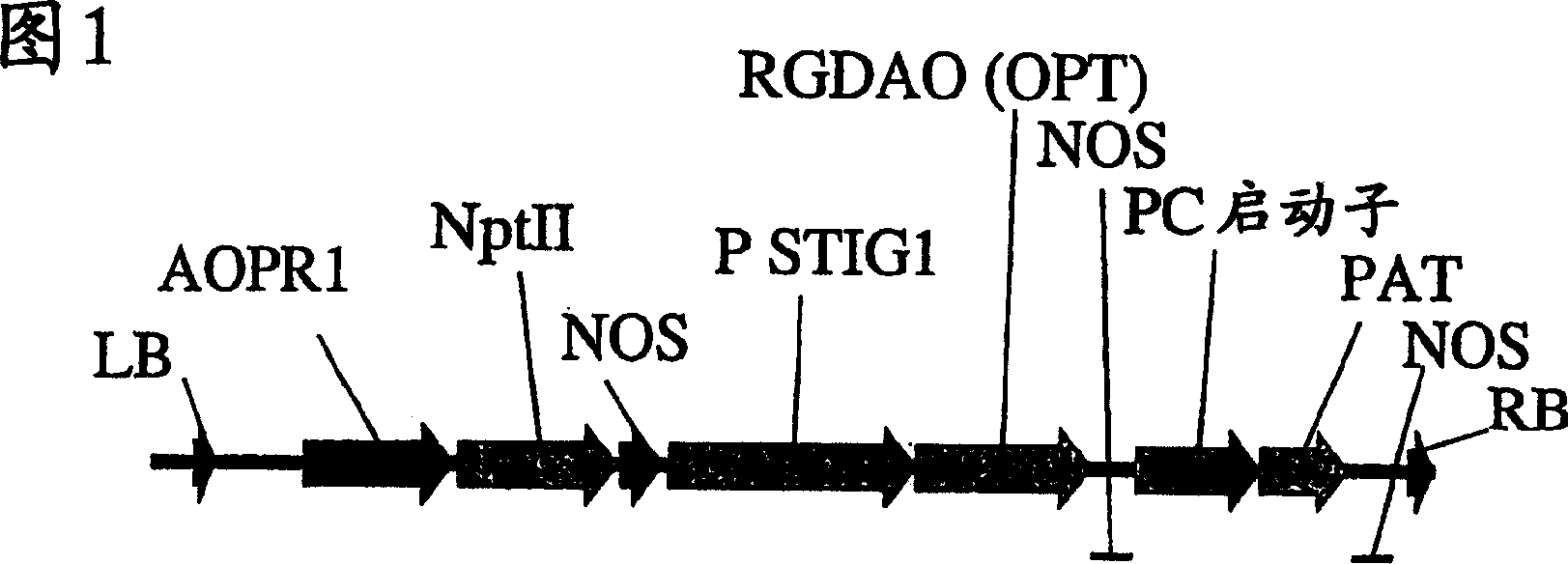
A method of selectively producing male or female sterile plants
A method of producing male or female sterile plants comprising the steps of transforming plant material with a polynucleotide which encodes at least one enzyme which reacts with a non-phytotoxic substance to produce a phytotoxic one, and regenerating the thus transformed material into a plant, wherein the said non-phytotoxic substance is applied to the plant up to the time of male or female gamete formation and / or maturation, so that the non-phytotoxic substance provides for the production of a phytotoxic one which selectively prevents the formation of or otherwise renders the said gametes non-functional, wherein the enzyme is expressed preferentially in either male or female reproductive structures, characterised in that (i) the non-phytotoxic substance is selected from the group consisting of ester derivatives of non-phosphonate herbicides which herbicides are directly phytotoxic to non-green tissue, D-alpha amino acids, peptide derivatives of non-protein D-alpha amino acids, S-enantiomers of aryloxyphenoxypropionates and S-enantiomers of ester derivatives of aryloxyphcnoxypropionatcs and (ii) the enzyme is selected from the group consisting of carboxylesterases, D-amino acid oxidases, D-amino acid dehydrogenases, D-amino acid racemases, 2-arylpropionyl-CoA epimerases, alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemases, thioesterases and acyl-CoA synthetases.
Owner:SYNGENTA BIO TECH CHINA
Carboxylesterase fluorescent probe as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108164450AImprove stabilityLong excitation wavelengthOrganic chemistryDisease diagnosisTwo-photon absorptionCarboxylic acid
The invention provides a carboxylesterase fluorescent probe of a structure of formula I. The carboxylesterase fluorescent probe provided by the invention is a hemicyanine compound with a naphthalene nuclear two-photon absorption unit and a D-pi-A structure, has the two-photon absorption and emission properties, and can be applied to detection on intracellular carboxylesterase. Experiment results of the embodiment show that the carboxylesterase fluorescent probe provided by the invention is capable of prolonging excitation wavelengths (800nm) of carboxylesterase in cells and tissue, reducing optical damage to cells and tissue and increasing tissue penetration depths and imaging depths; meanwhile, when being adopted to detect carboxylesterase, the carboxylesterase fluorescent probe providedby the invention is good in stability, short in response time (7 minutes), no sensitive to pH values, good in specificity for intracellular carboxylesterase imaging, and capable of detecting carboxylesterase in living cells under a two-photon excitation condition.
Owner:GANNAN NORMAL UNIV
Carboxylesterase and application thereof in degradation of pesticides malathion and carbaryl
The invention relates to the application of carboxylesterase D-1CarE3, gene D-1CarE3 and carboxylesterase D-1CarE3 in the degradation of pesticides malathion and carbaryl. The amino acid sequence of carboxylesterase D-1CarE3 is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, the amino acid sequence of the encoding gene D-1CarE3 of the carboxylesterase is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2, and the carboxylesterase comprises recombinant vector of carboxylesterase D-1CarE3 and the recombination strain of the carboxylesterase D-1CarE3. The invention further provides the application of the carboxylesterase D-1CarE3 in the degradation of pesticides malathion and carbaryl. The carboxylesterase has the advantages that the cultivation period is short, the pure protein is easy to obtain, and the malathion can be degraded at high efficiency, and compared with the reported carboxylesterase from insects, the carboxylesterase is higher in efficiency for depredating the pesticide malathion and carbaryl. The invention has an important significance in the aspect of the treatment of pesticide pollution.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Low odor compositions and methods to attain low odor compositions
ActiveUS20110166257A1Surgical adhesivesPaper coatingGas chromatography–mass spectrometryMass chromatography
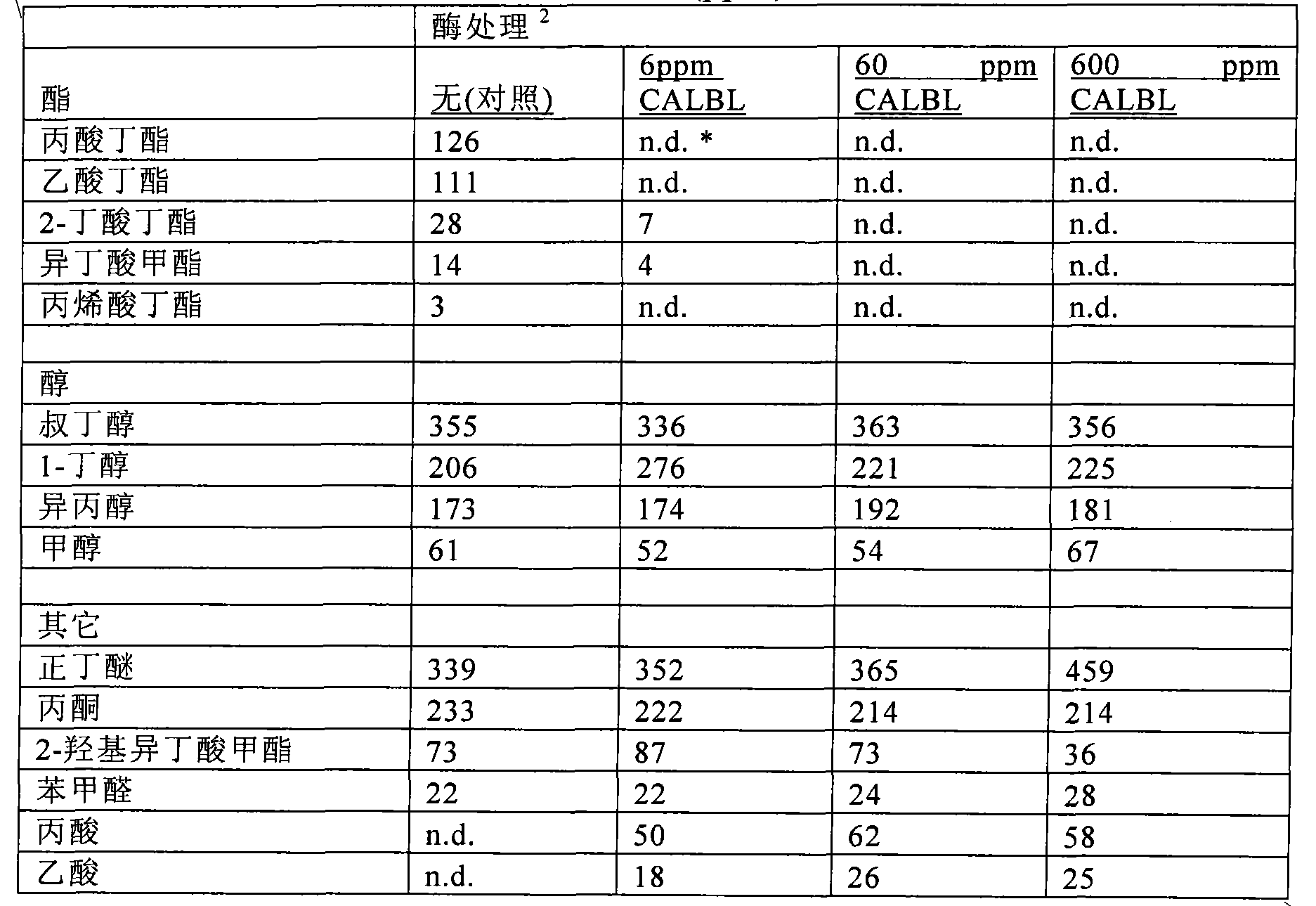
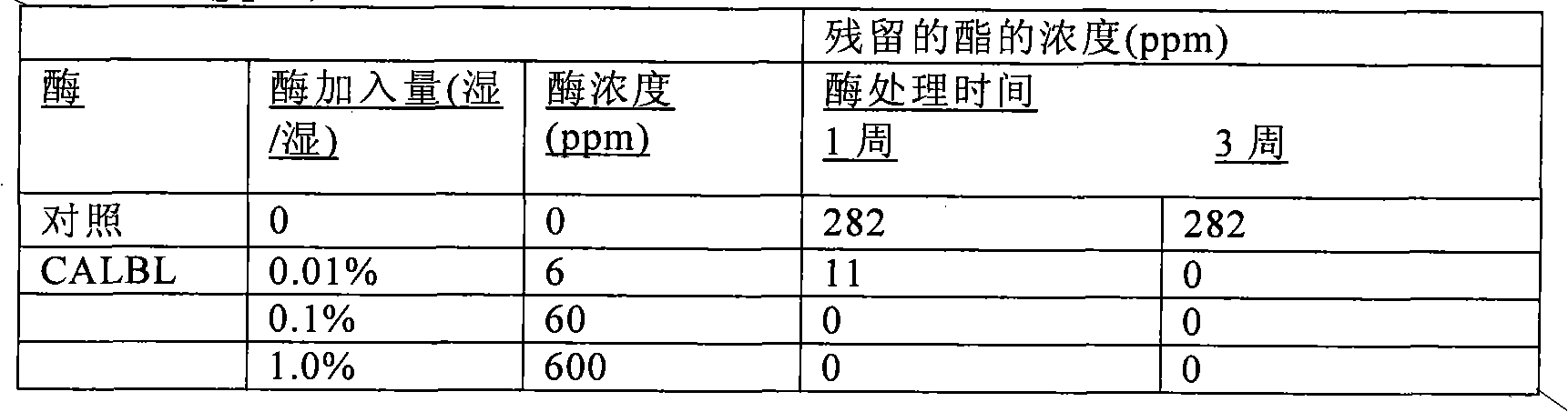
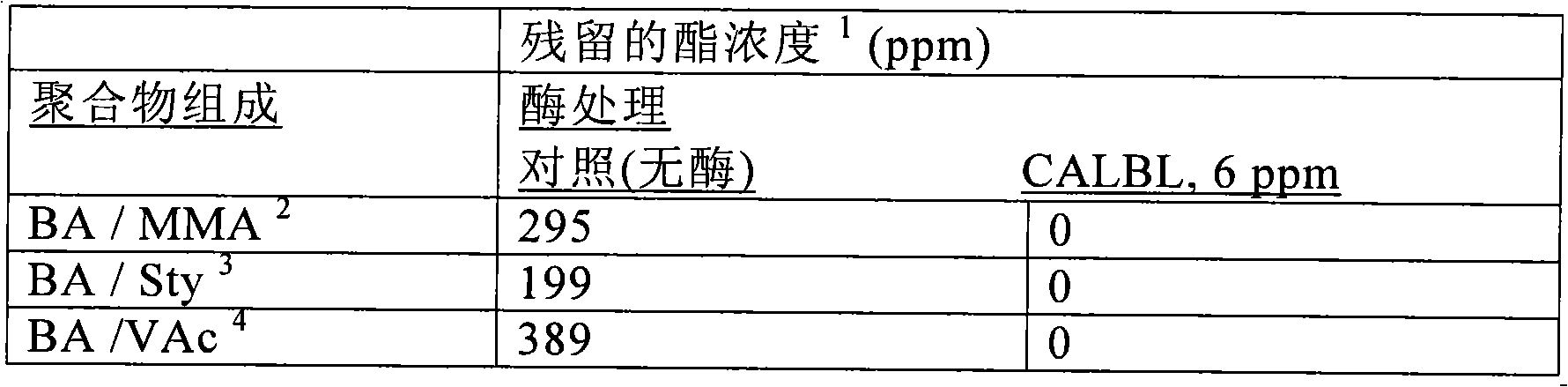
This invention provides stable aqueous compositions including stable coating compositions, and methods of their production. The stable aqueous compositions and stable aqueous coating compositions comprise i) an aqueous dispersion of one or more emulsion-polymerized addition polymer comprising polymerized units of one or more carboxylester monomer, wherein at least one carboxylester monomer is a vinyl ester monomer; ii) one or more carboxylesterase enzyme; iii) one or more mono-alcohol with a formula molecular weight of less than 76; iv) optionally, acetaldehyde; and v) optionally, one or more organic carboxylester with a normal boiling point of less than 150° C.; and wherein the aqueous composition has a headspace volatile organic compound(VOC) content, as measured by headspace gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) at 33° C., characterized by a content of less than 10 ppm of acetaldehyde, and less than 10 ppm of the one or more organic carboxylester, and more than 50 ppm of the one or more mono-alcohol. Preferably, the ester hydrolysis activity in the composition is less than 0.010 micromole / minute.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Carboxylesterase as well as coding gene and application thereof
The invention provides a carboxylesterase, a gene encoding the carboxylestearase, a recombination carrier comprising the gene, a recombination strain comprising the gene, and application of the carboxylesterase in degrading diisobutyl phthalate, wherein the amino acid sequence of the carboxylesterase is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The carboxylesterase gene CarEW comes from a hot spring environment, is proven to have good activity and stability under the condition of 45DEG C, and can be used for degrading phthalate ester compounds (phthalate) such as diisobutyl phthalate in the environment, thus having important significance on the aspect of environment pollution treatment.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Low odor coating compositions and paints
This invention provides low odor stable coating compositions, and methods of their production. The stable aqueous coating compositions and paints comprise one or more emulsion-polymerized addition polymer and one or more carboxylesterase enzyme having an ester hydrolysis activity in the composition of less than 0.03 micromole / minute, wherein the aqueous coating composition has a headspace volatile organic compound (VOC) content, as measured by headspace gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) at 33° C., of less than 10 ppm of the one or more organic carboxylester with a normal boiling point of less than 150° C. and more than 50 ppm of the one or more mono-alcohol with a formula molecular weight of less than 76.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Fluorescent probe used for detecting carboxylesterase and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106478576AImprove anti-interference abilityFluorescent signal does not increaseOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceBenzopyranFluorescence
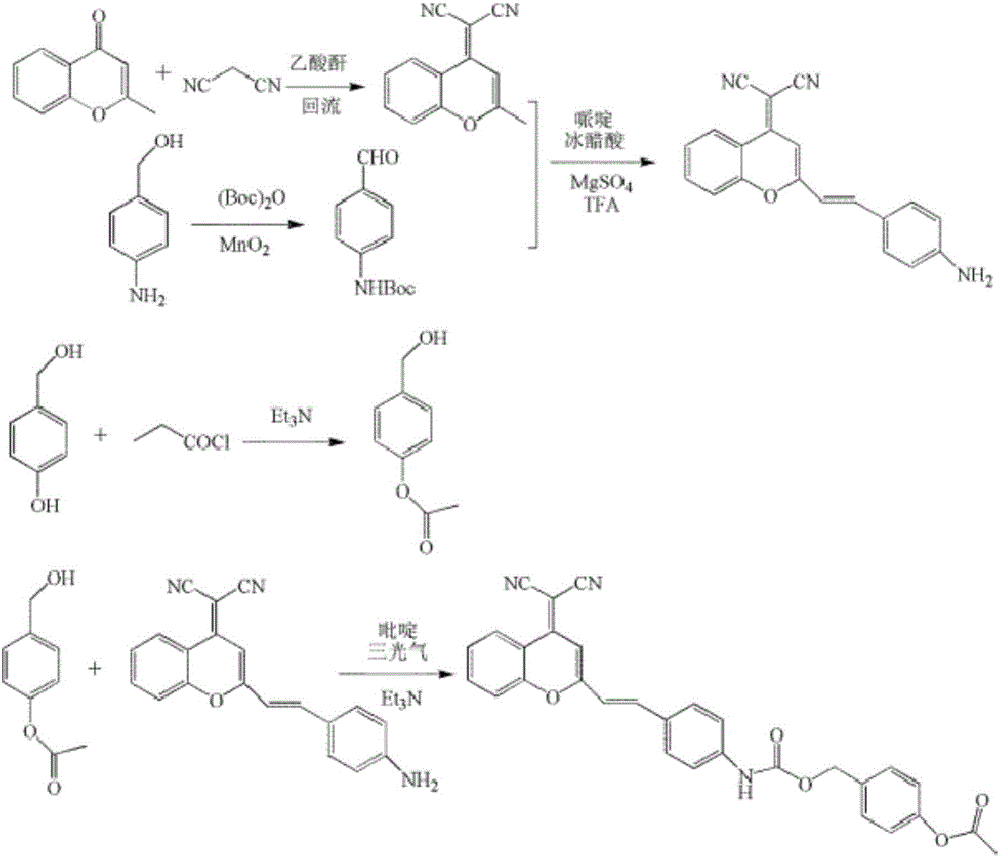
The invention belongs to the technical field of analysis and detection, and discloses a fluorescent probe used for detecting carboxylesterase and a preparation method and an application thereof. The fluorescent probe is 2-{2-[4-(4'-benzyl acetate benzyloxy-formamido)-styryl]-4H-benzopyran-4-yl}-malononitrile, and has a structural formula in a formula (I). and the fluorescent probe is used for detecting carboxylesterase. Compared with the current detection technique of fluorescence, the fluorescent probe has high selective response for carboxylesterase, strong anti-interference performance, and effective and visual detection mode, low investment cost, and simple synthesis route and method, and is suitable for enlarge production and practical application.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Carboxyesterase and application thereof to production of cyclohexene formic acid by kinetic resolution of cyclohexene formate
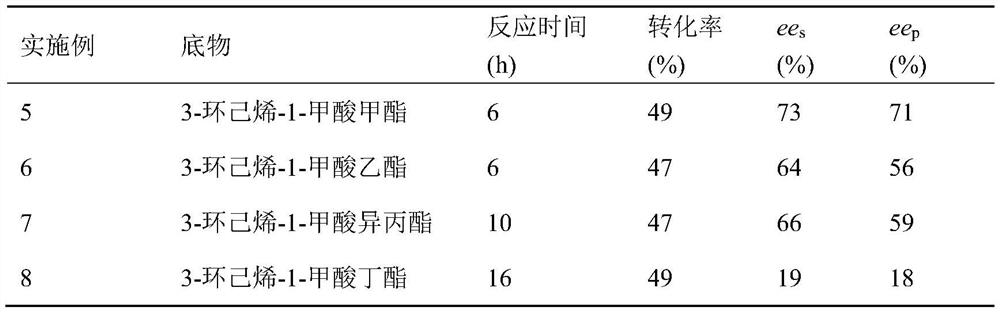
ActiveCN112813131AGood prospects for industrial application developmentHigh optical purityBacteriaHydrolasesPtru catalystFormate
The invention discloses carboxylesterase and an application thereof to production of cyclohexene formic acid by kinetic resolution of cyclohexene formate. In the application of the carboxylesterase as a catalyst to preparation of chiral cyclohexene formic acid by asymmetric resolution of chiral cyclohexene formate, the carboxylesterase is good in substrate tolerance, high in optical purity (the ees value reaches 99% or above), mild in reaction condition, environment-friendly, simple and convenient to operate and easy to industrially amplify. Therefore, the carboxylesterase and a gene thereof have good industrial application and development prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Carboxylesterase-1 Polymorphisms and Methods of Use Therefor
InactiveUS20110020801A1Improve throughputEfficient CatalysisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisCaucasian populationNucleotide
Methods and kits are provided for detecting polymorphisms in carboxylesterase-1 (CES1). Several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in CES1 in humans, and methods for detecting the same, are provided (e.g., Gly143Glu, 12754T>del). Results indicate that the Gly143Glu (9486G>A) polymorphism has an allelic frequency of 1.5% in the Caucasian population. Polymorphisms of the present invention may alter the function of the carboxylesterase-1 enzyme (hCES1). Thus, the methods and kits of the present invention may be used to personalize a therapy and / or avoid adverse consequences of altered metabolism of a therapeutic or compound (e.g., enalapril, methylphenidate, etc.) which may result due to a CES1 polymorphism. In addition, recombinant cells lines overexpressing wild-type CES1 or expressing CES1 mutants are provided. Such cell lines may be used to assess the effects of candidate compounds on CES1, and the action of CES1 on these candidate compounds.
Owner:MARKOWITZ JOHN S +1
Enzyme inhibitors
Compounds of formula (I), inhibit HDAC activity: wherein A, B and D independently represent ═CH— or ═N—; W is —CH═CH—Or —CH2CH2—; R1 is a carboxylic acid group (—COOH), or an ester group which is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular carboxylesterase enzymes to a carboxylic acid group; R2 and R3 are selected from the side chains of a natural or non-natural alpha amino acid, provided that neither R2 nor R3 is hydrogen, or R2 and R3, taken together with the carbon to which they are attached, form a 3-6 membered saturated cycloalkyl or heterocyclyl ring; Y is a bond, —C(═O)—, —S(═O)2—, —C(═O)O—, —C(═O)NR′—, —C(═S)—NR′, —C(═NH)NR′ or —S(═O)2NR— wherein R′ is hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl; L1 is a divalent radical of formula -(Alk1)m(Q)n(Alk2)p- wherein m, n, p, Q. Alk1 and Alk2 are as defined in the claims; X1 represents a bond; —C(═O); or —S(═O)2—; —NR4C(═O)—, —C(═O)NR4—, —NR4C(═O)NR5—, —NR4S(═O)2—, or —S(═O)2NR4— wherein R4 and R5 are independently hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl; and z is 0 or 1.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE INTPROP DEV LTD
Enzyme and receptor modulation
InactiveUS20100317865A1Prolonged and increased activityEasy accessBiocideOrganic chemistryGlycineAcid hydrolysis
Covalent conjugates of an α,α-disubstituted glycine ester and a modulator of the activity of a target intracellular enzyme or receptor, wherein the ester group of the conjugate is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular carboxylesterase enzymes to the corresponding acid and the α,α-disubstituted glycine ester is conjugated to the modulator at a position remote from the binding interface between the inhibitor and the target enzyme or receptor pass into cells and the active acid hydrolysis product accumulates within the cells.
Owner:CHROMA THERAPEUTICS
Delaying controlled-release acid for acidizing unblocking, preparation method of acid and acidizing unblocking method
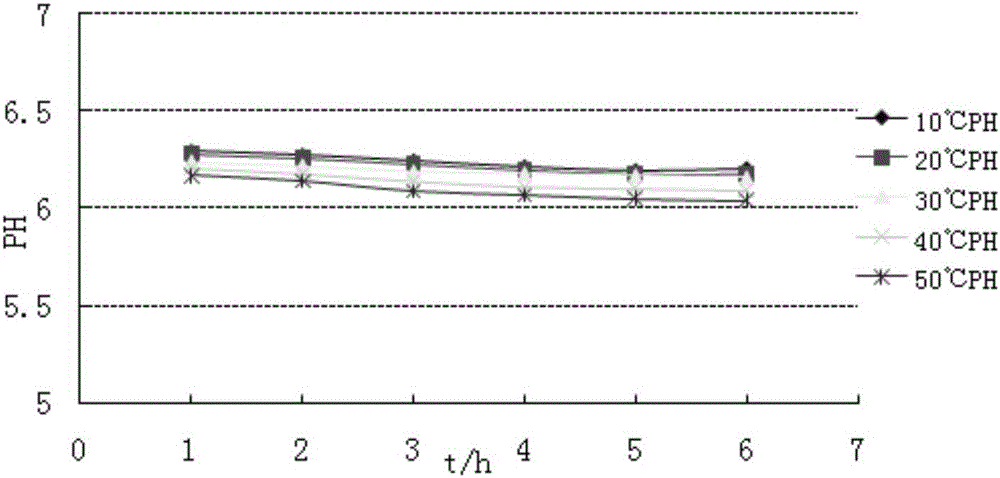
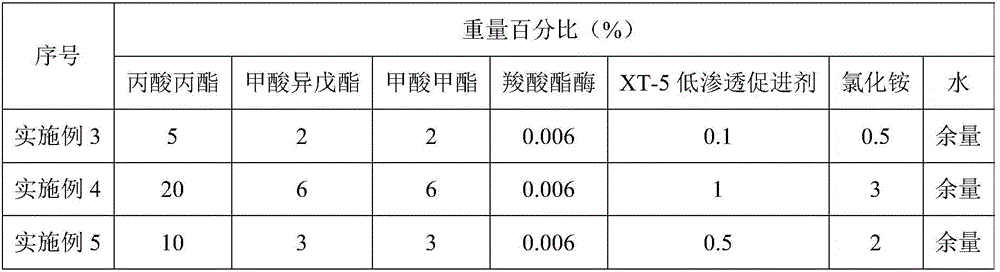
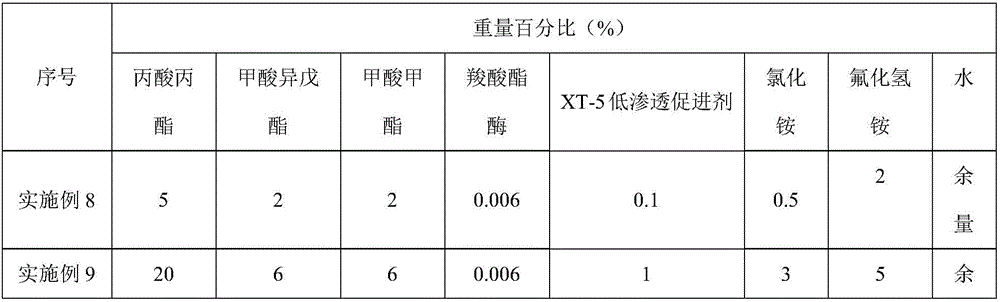
InactiveCN105950126ALess corrosiveImprove the blocking effectDrilling compositionHydrogen fluorideControlled release
The invention discloses delaying controlled-release acid for acidizing unblocking, a preparation method of the acid and an acidizing unblocking method. The delaying controlled-release acid is prepared from components in percentage by weight as follows: 5%-20% of propyl propanoate, 2%-8% of isoamyl formate, 2%-8% of methyl formate, 0.006% of carboxylesterase, 0.1%-1% of a discharge aiding agent, 0.5%-3% of ammonium chloride, 0-8% of ammonium hydrogen fluoride and the balance of water. According to the delaying controlled-release acid, an acid producing precursor is formed by propyl propanoate, isoamyl formate and methyl formate and catalyzed under the action of carboxylesterase to generate H<+>, and the reaction time is controllable; H<+> is combined with F<-> in ammonium hydrogen fluoride to generate HF acid, the stratum structure can be effectively improved, and the purpose of unblocking and reconstructing the stratum is achieved on the basis that oil well equipment is free of corrosion.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Low odor compositions and low odor coating compositions
This invention provides stable aqueous compositions including stable coating compositions, and methods of their production. The stable aqueous compositions and stable aqueous coating compositions comprise one or more emulsion-polymerized addition polymer, one or more carboxylesterase enzyme, and one or more carboxylesterase deactivating agent, such that the ester hydrolysis activity in the composition is less than 0.010 micromole / minute, and wherein the aqueous composition has a headspace volatile organic compound (VOC) content, as measured by headspace gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) at 33 DEG C, of less than 10 ppm of organic carboxylester with a normal boiling point of less than 150 DEG C and more than 50 ppm of mono-alcohol with a formula molecular weight of less than 76.The carboxylesterase enzyme is employed to minimize the free carboxylester content in the composition, thereby providing a low odor composition, and the carboxylesterase is deactivated in situ in order to minimize the residual carboxylesterase enzyme activity.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
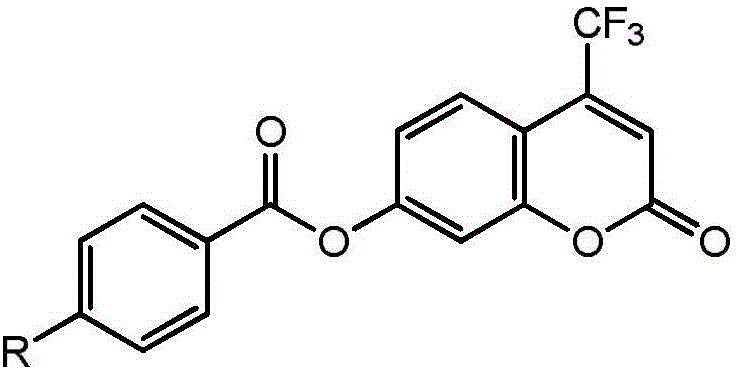
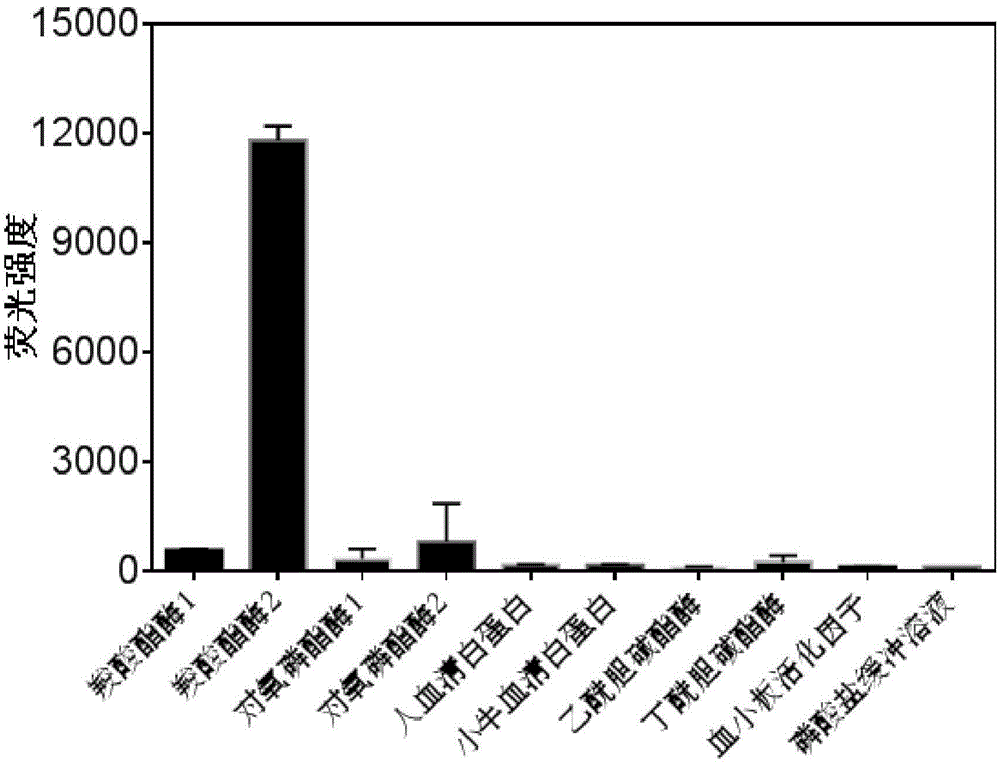
High-specificity fluorescent probe for human carboxylesterase hCE2 and application thereof
ActiveCN104592985AHas fluorescent propertiesSensitive detectionOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteFluorescence
The invention discloses a high-specificity fluorescent probe for human carboxylesterase hCE2 and an application thereof. The substrate of the specific probe is an ester derivative of a 4-trifluoromethyl-7-umbelliferone compound and can be used for detection for the existence of hCE2 in different biological samples and quantitative determination for the vitality of hCE2. A specific flow for determining the enzymatic activity is as follows: selecting a hydrolysis reaction of the 4-trifluoromethyl-7-umbelliferone ester derivative as a probe reaction, selecting a proper substrate concentration, and determining the actual activity of the hCE2 enzyme in various biological samples, cells, carriers and overall organs by quantitatively detecting the generation amount of a hydrolysis metabolite 4-trifluoromethyl-7-umbelliferone in a unit time within a linear reaction interval. The high-specificity fluorescent probe disclosed by the invention can be used for quantitative evaluation for the activity of the hCE2 enzyme in biological samples from different sources; in addition, the probe reaction can also be used for rapidly screening an hCE2 inhibitor in vitro.
Owner:CHANGSHU RES INST OF DALIAN UNIV OF TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com