Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47results about How to "Good structural consistency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
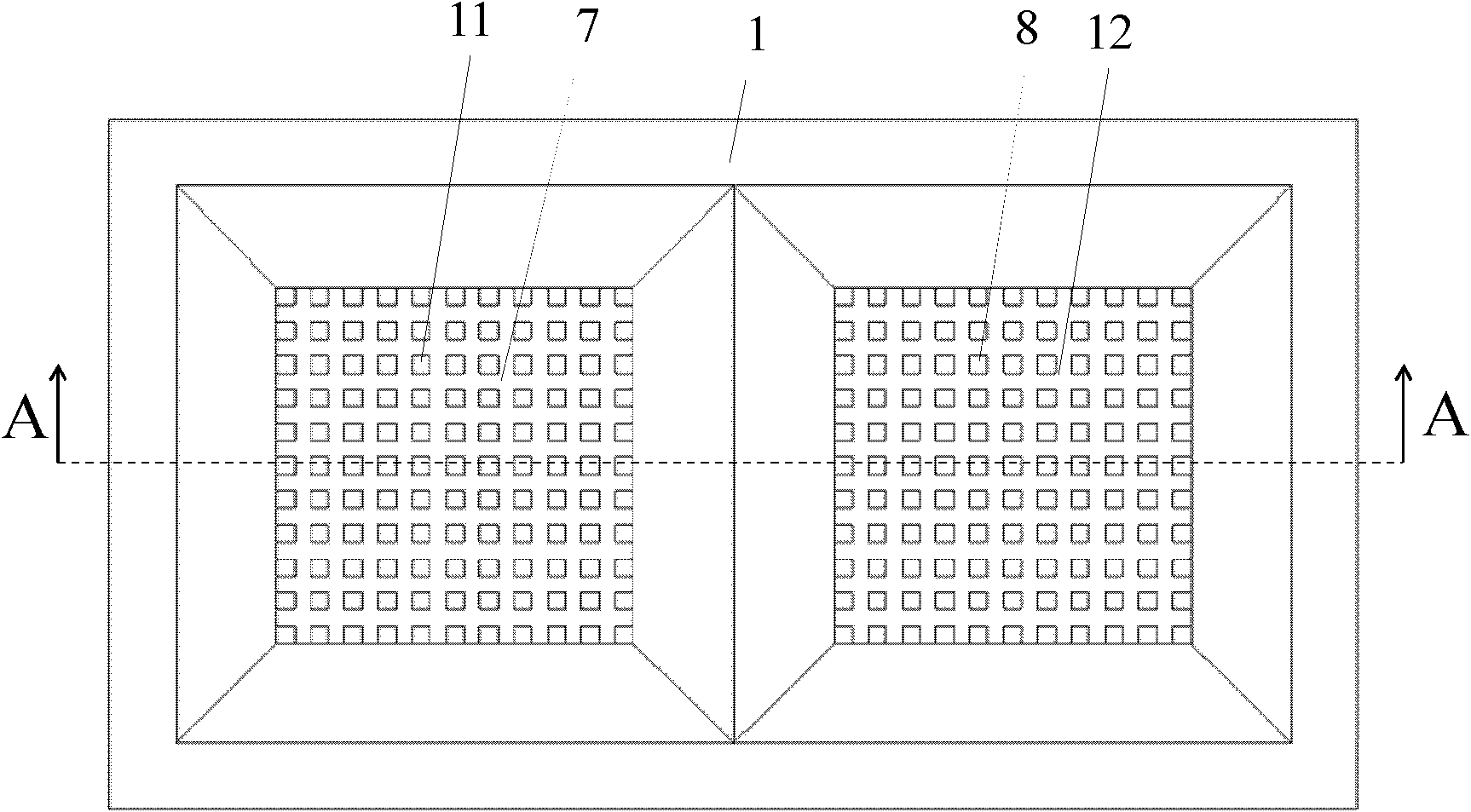
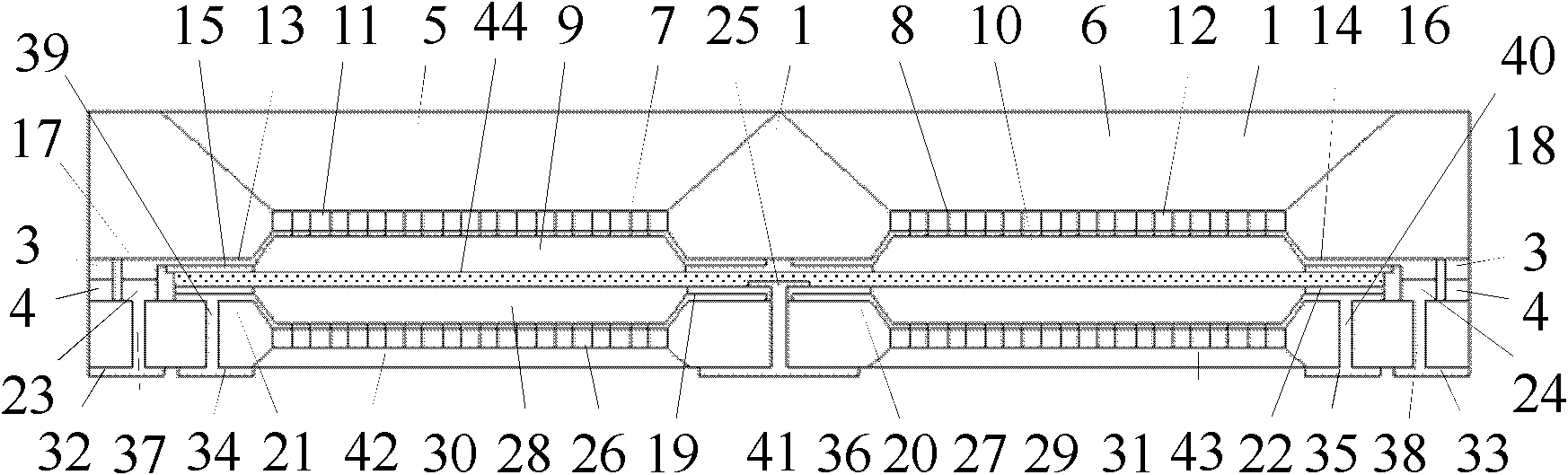
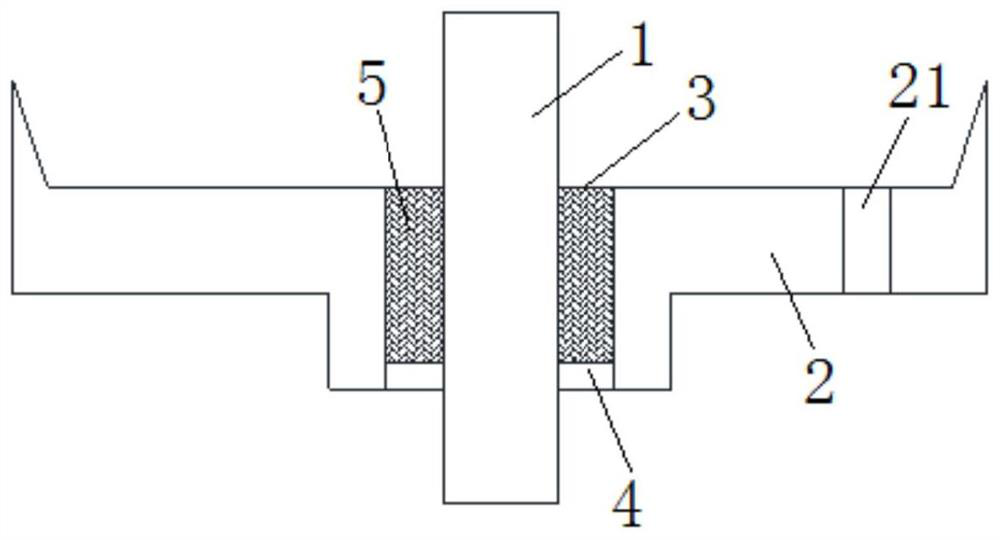
Partition-optimized ultrathin VC with thickness of 0.1-0.4 mm and preparation method
PendingCN111879158AEmission reductionSpeed up distributionIndirect heat exchangersMicro nanoNano structuring
The invention discloses a partition-optimized ultrathin VC with the thickness of 0.1-0.4 mm and a preparation method. The ultrathin VC comprises an upper cover plate and a lower cover plate, and the upper cover plate and the lower cover plate are welded. Each of the upper cover plate and the lower cover plate comprises an evaporation section, a heat insulation section and a condensation section; the surface of the evaporation section of the upper cover plate is of a super-hydrophilic cavity-shaped micro-nano structure, the surface of the heat insulation section of the upper cover plate is of asuper-hydrophilic equal-width groove micro-nano structure, and the surface of the condensation section of the upper cover plate is of a super-hydrophobic conical micro-nano structure; and a super-hydrophilic conical micro-nano structure is arranged on the surface of the area of the evaporation section of the lower cover plate, a super-hydrophilic cactus-like wedge-shaped groove micro-nano structure is arranged on the surface of the area of the heat insulation section, and a super-hydrophilic conical micro-nano structure is arranged on the surface of the area of the condensation section. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the ultrathin VC. A steam cavity structure, a liquid cavity structure and volume distribution in a heat pipe can be optimized, and good capillary water absorption performance and low water resistance and heat resistance of the heat pipe can be guaranteed.
Owner:绍兴镭纳激光科技有限公司
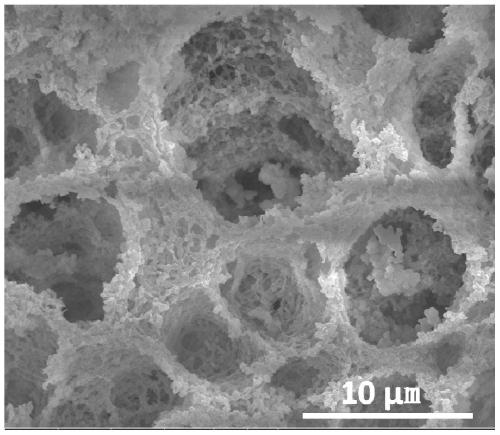
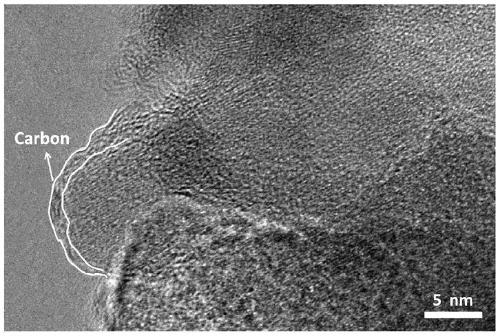
Exotic atom-doped porous carbon material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110148733ALarge specific surface areaImprove sodium storage performanceCell electrodesCross-linkN dimethylformamide
The invention discloses an exotic atom-doped carbon material and a preparation method and an application thereof. The doped carbon material prepared according to the method is a honeycomb three-dimensional multi-level porous structure material, wherein macropores are constructed by mutually cross-linked flakes, the flakes are stacked by nanoparticles, and random mesopores and micropores are distributed between the nanoparticles. The preparation method comprises the steps of firstly dissolving polyacrylonitrile into an N, N-dimethylformamide solution, then adding one or more reagents containingtarget doping atoms into the solution, conducting a solvothermal reaction to obtain a precursor, placing the precursor in a protective atmosphere for calcination so as to obtain a single or multi-atom doped carbon material with uniform nanometer size and excellent electrochemical performance. Sodium-ion batteries show high specific capacity, excellent rate performance and ultra-long cycle stability when the exotic atom-doped carbon material is used as a negative electrode material of the sodium-ion batteries.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
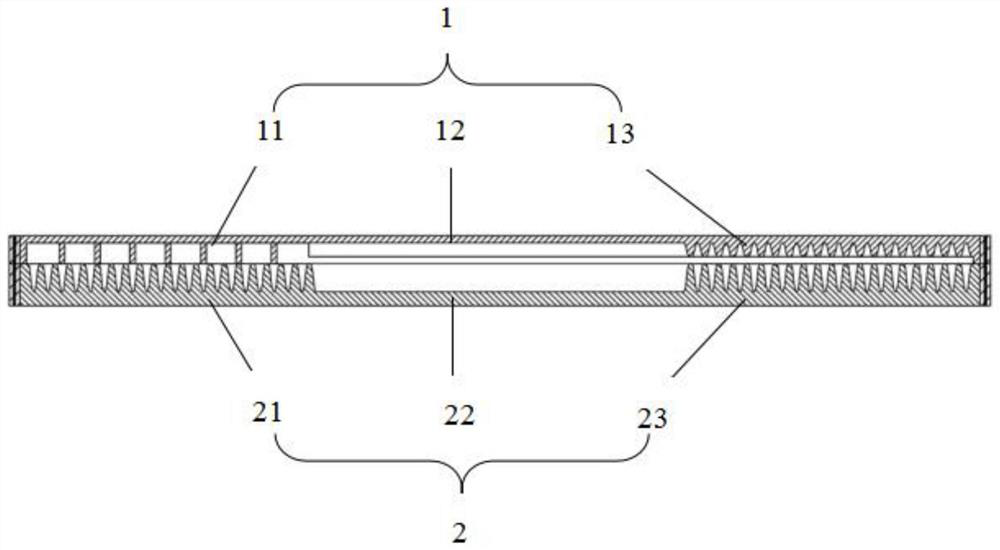
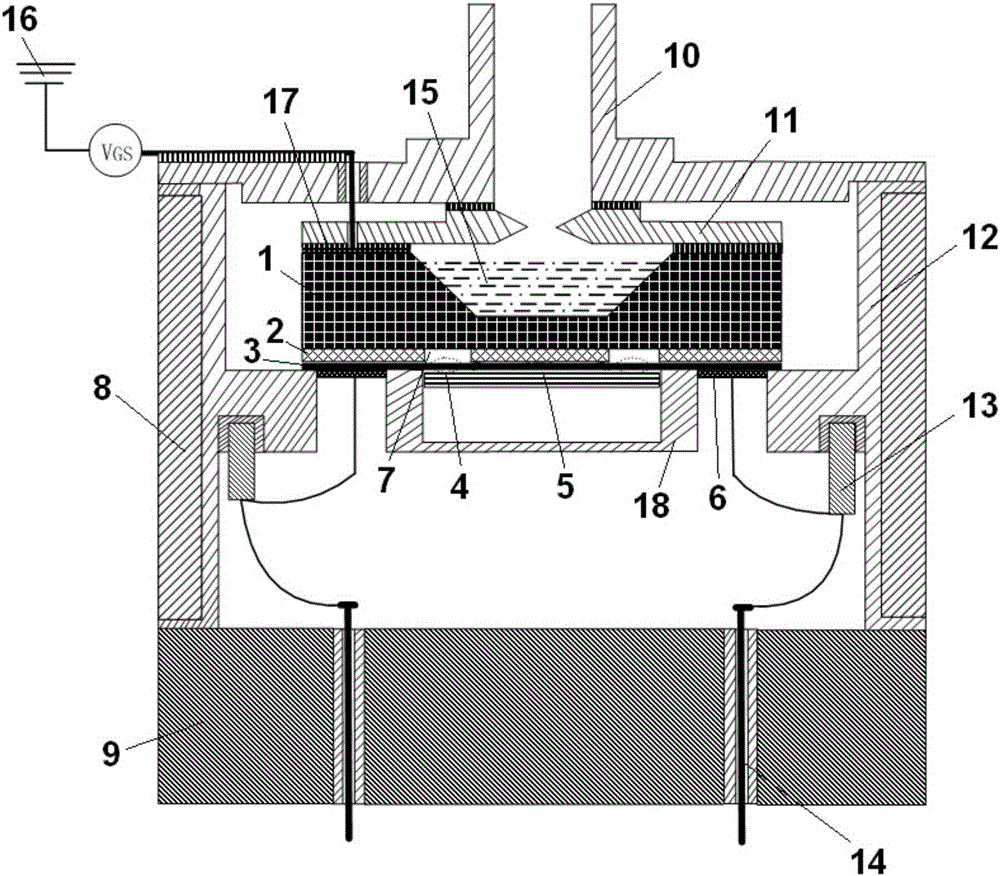
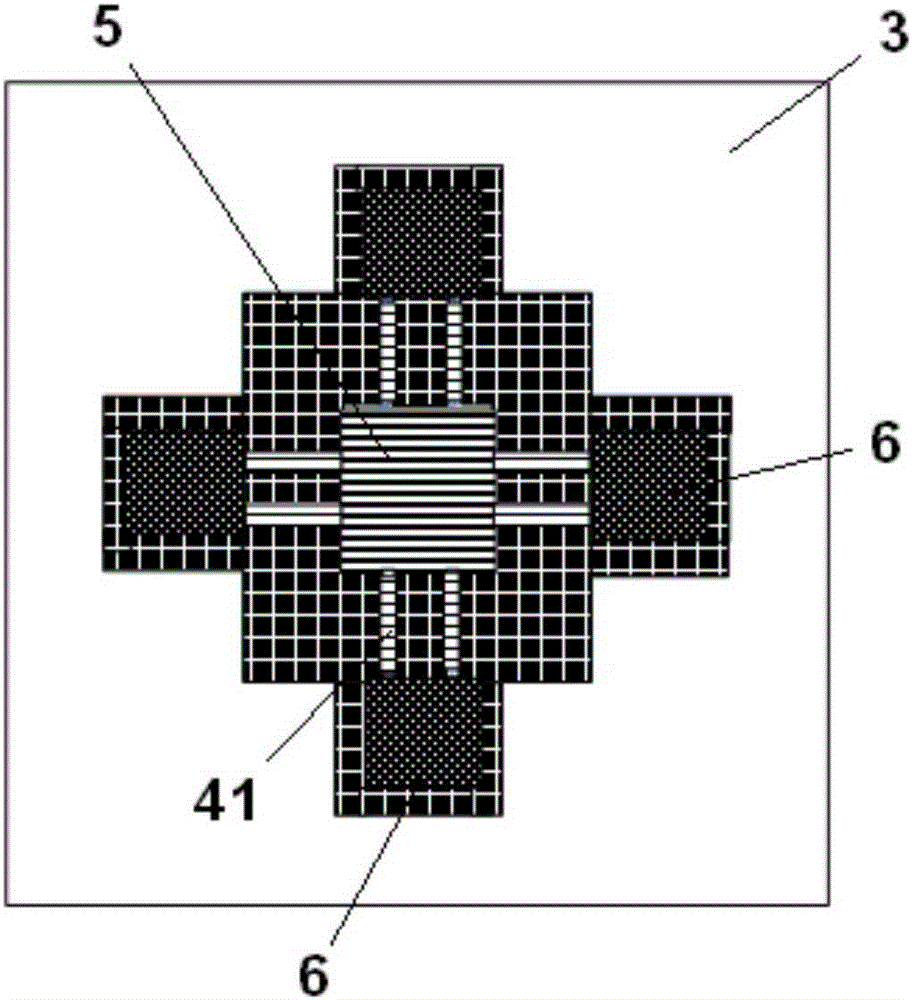
Huge piezoresistive property-based silicon nanowire pressure sensor and packaging structure thereof
ActiveCN105181189AThe concentration of holes is greatly reducedPinch-off effect achievedNanosensorsForce measurement using piezo-resistive materialsSilicon nanowiresAtmospheric pressure
The invention discloses a huge piezoresistive property-based silicon nanowire pressure sensor and a packaging structure thereof. The huge piezoresistive property-based silicon nanowire pressure sensor comprises a shell and a sensor chip, wherein the sensor chip comprises a silicon nanowire huge piezoresistive sensitive structure, a silicon bottom layer, an insulated silicon dioxide layer and a silicon top layer; the silicon nanowire huge piezoresistive sensitive structure comprises a plurality of silicon nanowires, a stress strain film layer and a plurality of electrodes; the plurality of silicon nanowires comprise four pairs of silicon nanowires which are arranged in parallel; the four pairs of silicon nanowires arranged in parallel are connected between four electrodes and the stress strain film layer respectively; straight grooves are formed in the positions, corresponding to the insulated silicon dioxide layer, on the silicon nanowires. According to the huge piezoresistive property-based silicon nanowire pressure sensor and the packaging structure thereof disclosed by the invention, mechanical stress is formed by the sensor chip through external environment pressure to change great reduction of hole concentration or even pinch-off of conducting channels of the silicon nanowires, so that the huge piezoresistive effect is achieved.
Owner:南京瑞菲科机电科技有限公司
Ceramic slurry and ceramic shell, and preparation methods thereof
The invention discloses a ceramic slurry and ceramic shell, and preparation methods thereof. The preparation method for the ceramic shell comprises the following steps: S1, mixing ceramic powder with deionized water according to a solid content of 55 to 60% so as to form a solution; S2, adding organic monomer and a cross-linking agent into the solution; S3, adjusting the pH value of the solution to 9 to 9.5 and then adding a dispersing agent accounting for 0.55 to 0.6% of the mass of the ceramic powder; S4, carrying out sufficient ball milling so as to form slurry and carrying out vacuum stirring to remove bubbles in the slurry; S5, adding a catalyst accounting for 1 to 1.5% of the sum of the mass of the organic monomer and the cross-linking agent into the slurry; S6, adding an initiator into the slurry; S7, injecting the slurry into the mold cavity of an injection machine, carrying out heating at 50 to 80 DEG C for curing and molding and taking a molded green body from the mold cavity; and S8, processing the molded green body so as to obtain the ceramic shell. The ceramic green body prepared in the invention is not prone to deformation and has high strength and small sintering contraction.
Owner:DONGGUAN HUAJING POWDER METALLURGY +1
Repairing and plugging material and preparation method thereof
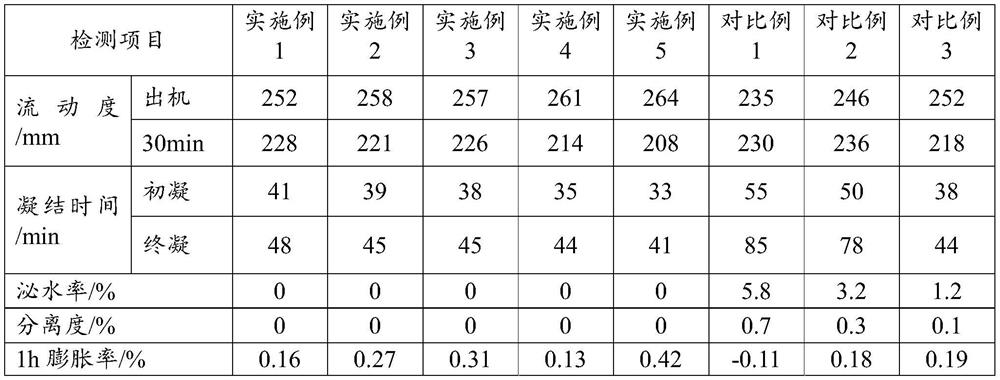
The invention provides a repairing and plugging material and a preparation method thereof. The repairing and plugging material is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 65 to 80 percent of a composite cementing material, 10 to 25 percent of an enhanced composite mineral admixture, 5 to 12 percent of a composite expansion component, 0.2 to 1.0 percent of a rheological agent, 0.5 to 1.2 percent of a water reducing agent, 0.05 to 0.1 percent of a defoaming agent, 0.08 to 0.12 percent of an anti-seepage water repellent, 0.4 to 1.0 percent of a coagulation accelerator and 2 to 6 percent of an activity enhancing component. The prepared repairing and leaking stoppage material is specially used for repairing and leaking stoppage of leakage and the like caused by structural concrete cracks and infiltration line lifting of water conservancy projects, has the characteristics of high filling degree, micro expansion, high seepage prevention, early strength, high strength, high durability and the like, can realize rapid repairing and leaking stoppage, and is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Method for making high-square-degree sintered NdFeB permanent magnets with cerium, titanium, cobalt and zirconium compound additive
InactiveCN104821226AImprove squarenessHigh densityInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsHydrogenCerium
The invention discloses a method for making high-square-degree sintered NdFeB permanent magnets with a cerium, titanium, cobalt and zirconium compound additive. The method comprises the steps that raw materials are prepared with 27.0% to 29.0% of Nd, 2.5% to 4.0% of Ce, 63.5% to 67.5% of Fe, 1.0% to 1.2% of B, 0.5% to 1.0% of Nb, 1.0% to 3.0% of Co, 0.1% to 0.3% of Zr, 10.5% to 1.0% of A, 0.1% to 0.3% of Cu, and 0.1% to 0.3% of Ti, the raw materials are smelted under the temperature of 1380 DEG with a vacuum induction rapid-hardening casting strip furnace, smelted alloy liquid is processed through electromagnetic stirring to be uniform, and is poured to a rotating water-cooling copper stick, and the alloy liquid is rapidly cooled to form alloy slices with the thickness ranging from 0.2 mm to 0.5 mm; NdFeB alloy slices are broken into NdFeB alloy particles with the length ranging from 120 microns to 200 microns with a hydrogen breaking furnace; the particles are further broken into NdFeB alloy powder with the length ranging from 3.0 microns to 4.5 microns by an air-current mill; the powder is formed in a forming press, and is further densified through isostatic cool pressing; formed initial blanks are sintered, and sintered permanent magnets are finally obtained. With the method for making high-square-degree sintered NdFeB permanent magnets with the cerium, titanium, cobalt and zirconium compound additive, the squre degree of the permanent magnets can be improved, and the production cost can be greatly reduced.
Owner:安徽万磁电子股份有限公司
Microwave device surface processing device capable of restraining secondary electron emission and microwave device surface processing method capable of restraining secondary electron emission
ActiveCN104646832AImprove launch performanceReduce processLaser beam welding apparatusLaser etchingMicrowave
The invention provides a microwave device surface processing device capable of restraining secondary electron emission and a microwave device surface processing method capable of restraining secondary electron emission. The device consists of a laser output module, a micro lens, a movable table and a control module, wherein the control module outputs control signals to the laser output module and the movable table, so as to control the laser output power, the laser output interval time, the movement distance of the movable table and the movement time of the movable table; by virtue of a small-area deep hole array continuous moving and filling method, laser etching of a centimeter-scale large-area deep hole array structure on the surface of a microwave device is finished. The microwave device surface structure processed by the device and the method is of a rectangular uniformly-spaced or triangular uniformly-spaced micronano deep hole array, so that the secondary electron emission coefficient of the surface of the microwave device can be effectively reduced. The device and the method are automatic in processing, simple in process and high in efficiency, and can be used for performing processing treatment on the surfaces of parts such as gold or plated gold; the surface performance of the processed microwave device has long-term stability, and the processed microwave device is applicable to ground and aerospace environments.
Owner:CHINA AEROSPACE TIMES ELECTRONICS CORP
Injection molding process
InactiveCN101579909AImprove surface brightnessGood internal structure consistencyCoatingsSurface finishingInjection molding process
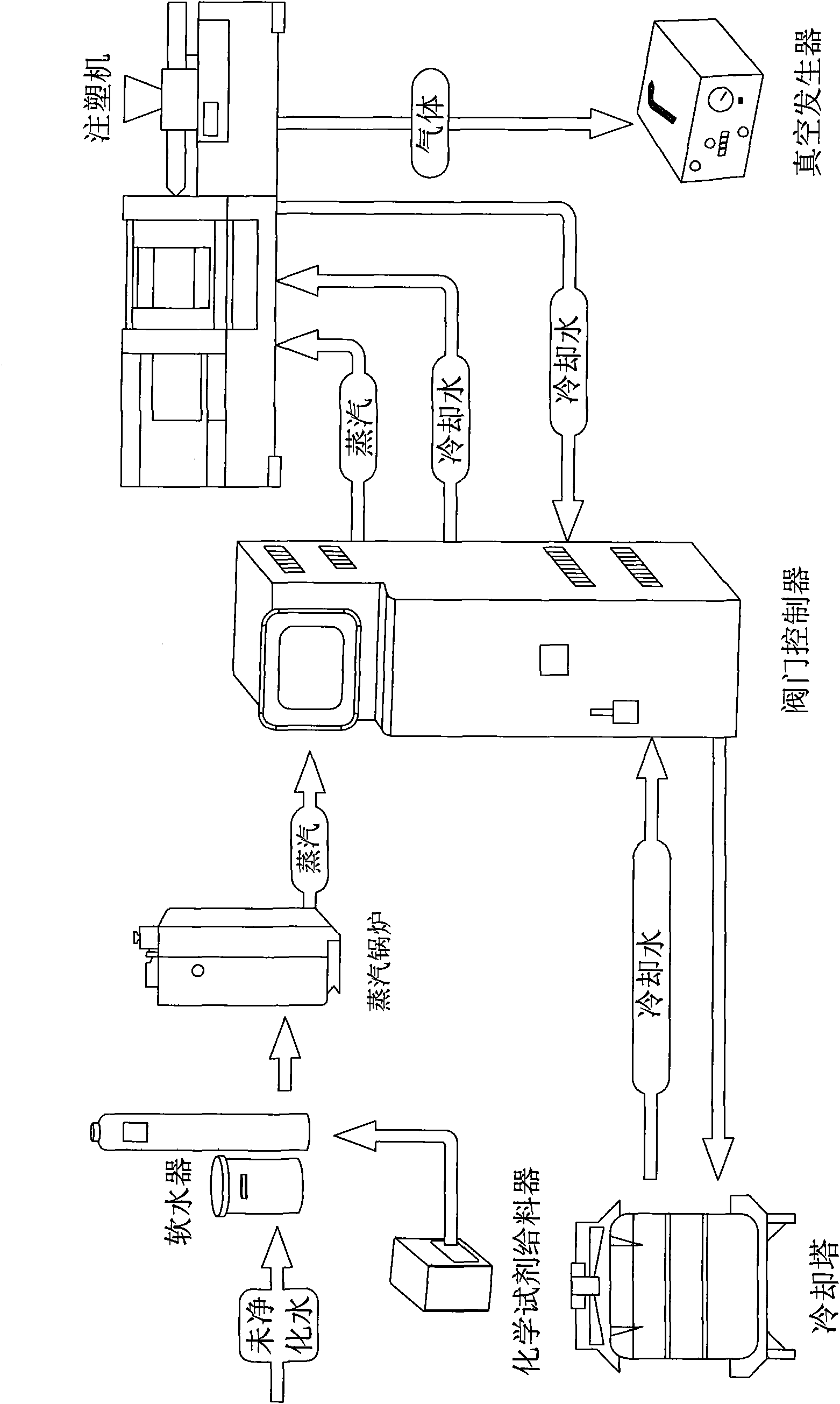
The invention relates to an injection molding process, which comprises the following processing steps: 1) conveying water vapor into a water passage in a mould to make the mould raise temperature and maintaining the temperature; 2) injecting high-temperature molten plastics into the mould; 3) conveying cooling water into the water passage; and 4) opening the mould to obtain a finished product. The water vapor is firstly softened by a water softener before entering the water passage. The process has the advantages that: after the product is formed, the product has high surface gloss, does not need surface treatment anymore, has good internal structural integrity of a wall body material, does not have the problem of a welding line, and has excellent mechanical property and consistent shrinkage factor.
Owner:李永能
MEMS (micro-electro-mechanical system) acoustic sensor based on graphene
ActiveCN102638753BExcellent mechanical propertiesExcellent electrical propertiesElectrets selectrostatic transducerElectrostatic transducer microphonesGrapheneMaterials science
An MEMS (micro-electro-mechanical system) acoustic sensor based on graphene mainly structurally comprises an upper structure, an understructure and graphene. Sound collecting cavities, gap cavities, through hole plates, pickup holes, upper metal layers, upper insulating layers, upper metal connecting positions and an upper bonding metal layer are produced on an upper structure layer; through hole plates, gas cavities, damping holes, damping cavities, under metal layers, under insulating layers, under metal connecting positions, a graphene connecting position, an under metal bonding layer, upper metal pads, under metal pads, upper metal connecting holes, under connecting holes and a graphene connecting hole are produced on an understructure layer; and a graphene layer is clamped between the upper insulating layers and the under insulating layers. Graphene materials with thickness of a single carbon atom layer have remarkable mechanical characteristics and electrical characteristics, so that sensitivity and resolution of the acoustic sensor with graphene serving as a vibrating diaphragm are higher and acoustic detection data of the acoustic sensor are detailed, accurate and reliable.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
High-performance primary large-particle ternary positive electrode composite material, manufacturing method and application thereof
ActiveCN110718679AImprove conductivityImprove thermal stabilityCell electrodesSecondary cellsConductive polymerActive agent
The invention discloses a high-performance primary large-particle ternary positive electrode composite material, a manufacturing method and an application thereof. The composite material comprises a ternary positive electrode material with a primary particle size of 5-8 microns, a sulfur coating layer and a composite modified layer, wherein the sulfur coating layer and the composite modified layersuccessively wrap the surface of the ternary positive electrode material from inside to outside. The composite modified layer is formed by compounding a high-molecular conductive polymer and a surfactant. The method comprises the following steps of 1) carrying out one time sintering on a ternary positive electrode material precursor matched with lithium to obtain a ternary positive electrode material in which primary particles are agglomerated into secondary particles; 2) mixing with a fluxing agent, carrying out wet ball milling to change a particle size to a nano-scale, and carrying out secondary sintering; and 3) coating sulfur and a composite modifier formed by compounding a high-molecular conductive polymer and a surfactant to obtain the ternary positive electrode composite material.The manufacturing of the primary large-particle high-nickel ternary positive electrode material with a high specific discharge capacity, high conductivity and high thermal stability can be effectively realized, a process is simple, and large-scale production is easy to realize.
Owner:SHENZHEN CITY BATTERY NANOMETER TECH
Refrigerating instrument
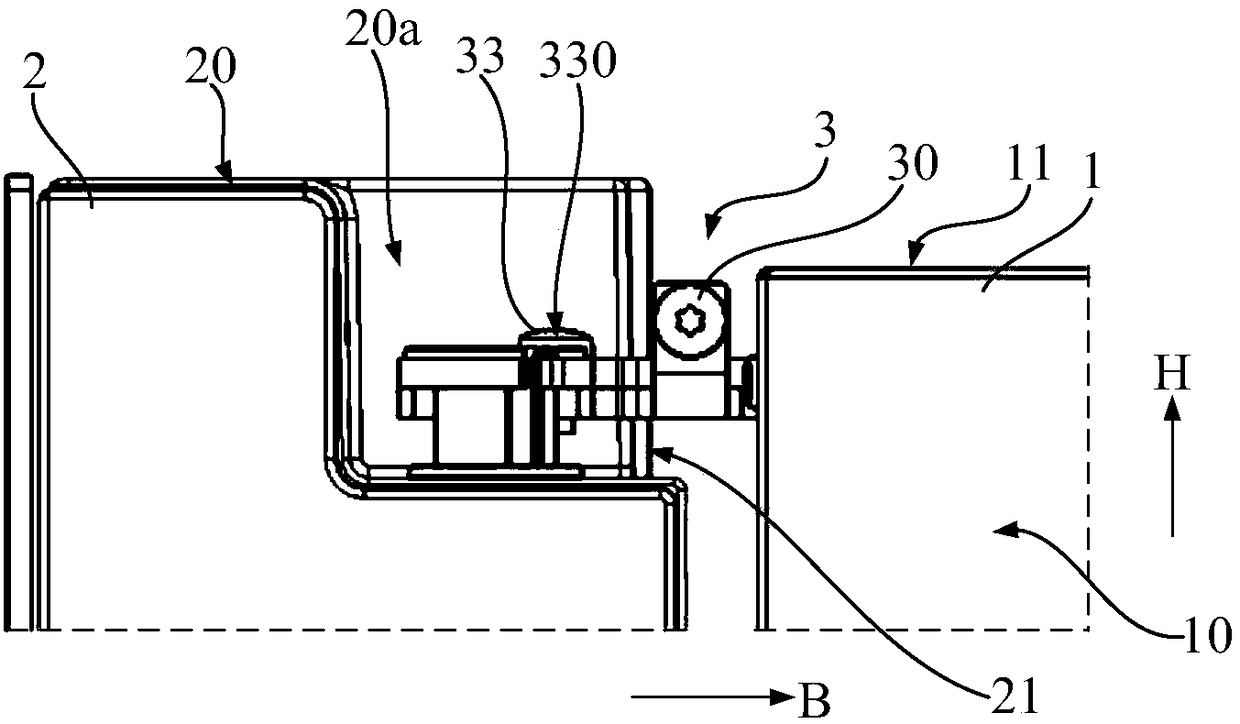
ActiveCN108661468ASolve fit problemsSolve the coordination problemDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusMechanical engineeringEngineering
The invention discloses a refrigerating instrument. The refrigerating instrument comprises a box body (1), doors (2) and a hinge assembly (3), wherein the hinge assembly (3) is connected with the boxbody (1) and the doors (2); the hinge assembly comprises a mounting part (31), a hinge part (32) and an adjusting unit, wherein the installing part (31) is fixed on the box body (1), the hinge part (32) is connected to a hinge chain shaft (320) provided with the doors (2) of the mounting part (31); and the adjusting unit comprises an adjusting part (30) which is connected to the hinge chain part (32), the adjusting part (30) is used for adjusting the hinge chain part (32) in the adjusting direction relative to the position of the mounting part (31), and the adjusting direction is the width direction of the doors (2) or the front-back direction of the box body (1). According to the technical scheme, the problems that the appearance or sealing caused by irregular distance between two doors (2) or the doors (2) and the box body (1) is solved.
Owner:BSH ELECTRICAL APPLIANCES JIANGSU +1
Steel concrete assembled beam by asymmetric section steel beam
Owner:DAEWOO ENG & CONSTR CO LTD +3
Pipeline transmission continuous vacuum coating production line structure and production method
PendingCN113637951AStrong expandabilityEasy to operateVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingProduction lineIsolation valve
The invention discloses a pipeline transmission continuous vacuum coating production line structure, and particularly relates to the technical field of vacuum coating equipment. The production line structure comprises a workpiece frame and machining assemblies. At least one of the machining assemblies is provided with machining pipes provided with internal machining spaces and used for coating a to-be-machined workpiece, and at least one isolating valve used for isolating or communicating the different spaces; and the multiple machining pipes are arranged in sequence, the isolating valves are arranged between the adjacent machining pipes, and after the adjacent machining pipes are connected through the isolating valves, the internal machining spaces of the adjacent machining pipes are communicated to form a channel allowing the workpiece frame to be conveyed. The invention further provides a pipeline transmission continuous vacuum coating production method, compared with the prior art, the production line structure has the advantages of being flexible in structure, good in consistency, high in automation degree, high in controllability and the like, and the production method has the beneficial effects of being good in expansibility, convenient to operate, high in coating efficiency, high in device utilization rate and the like.
Owner:TRITREE METAL SHENZHEN +1
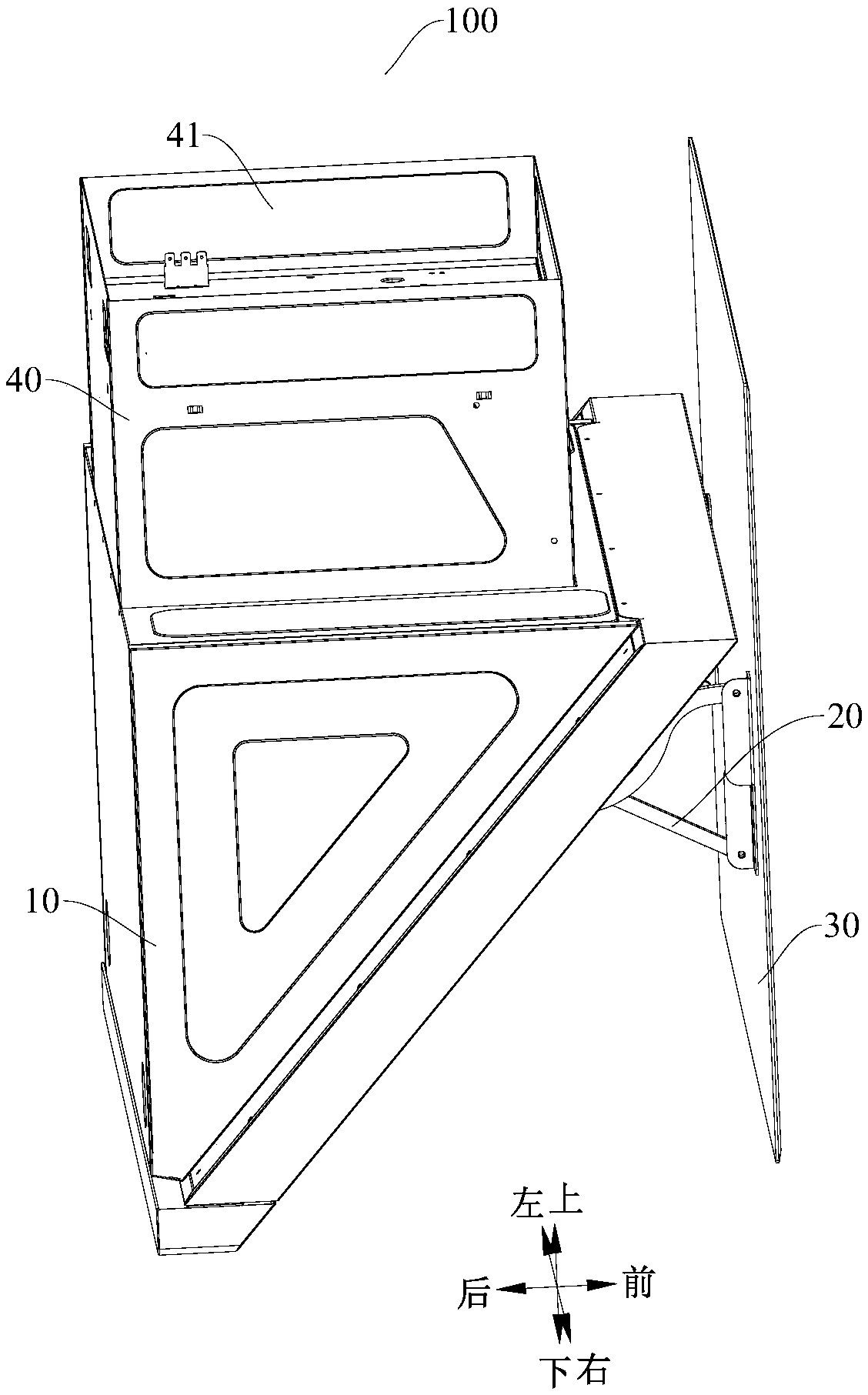
Range hood
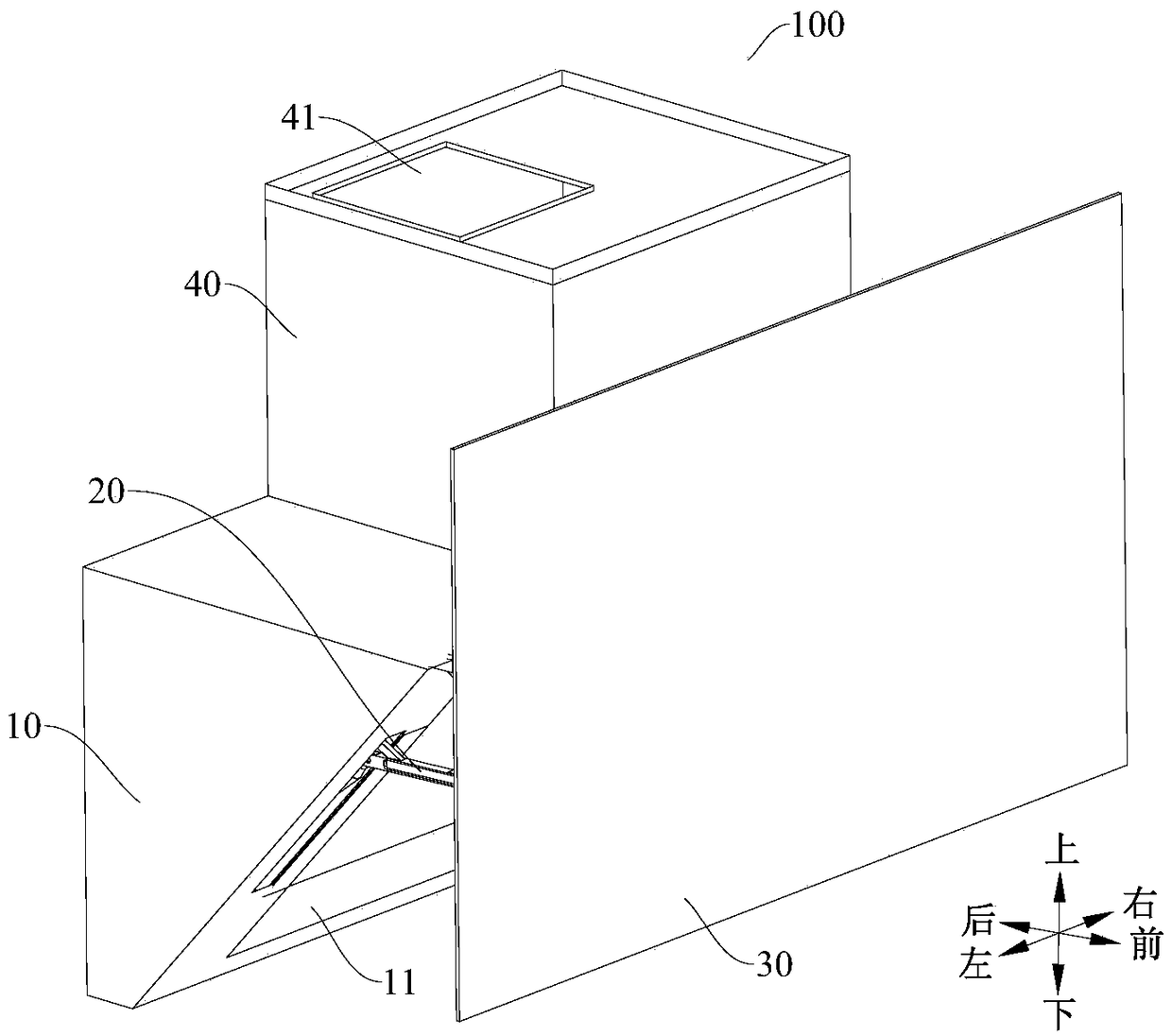
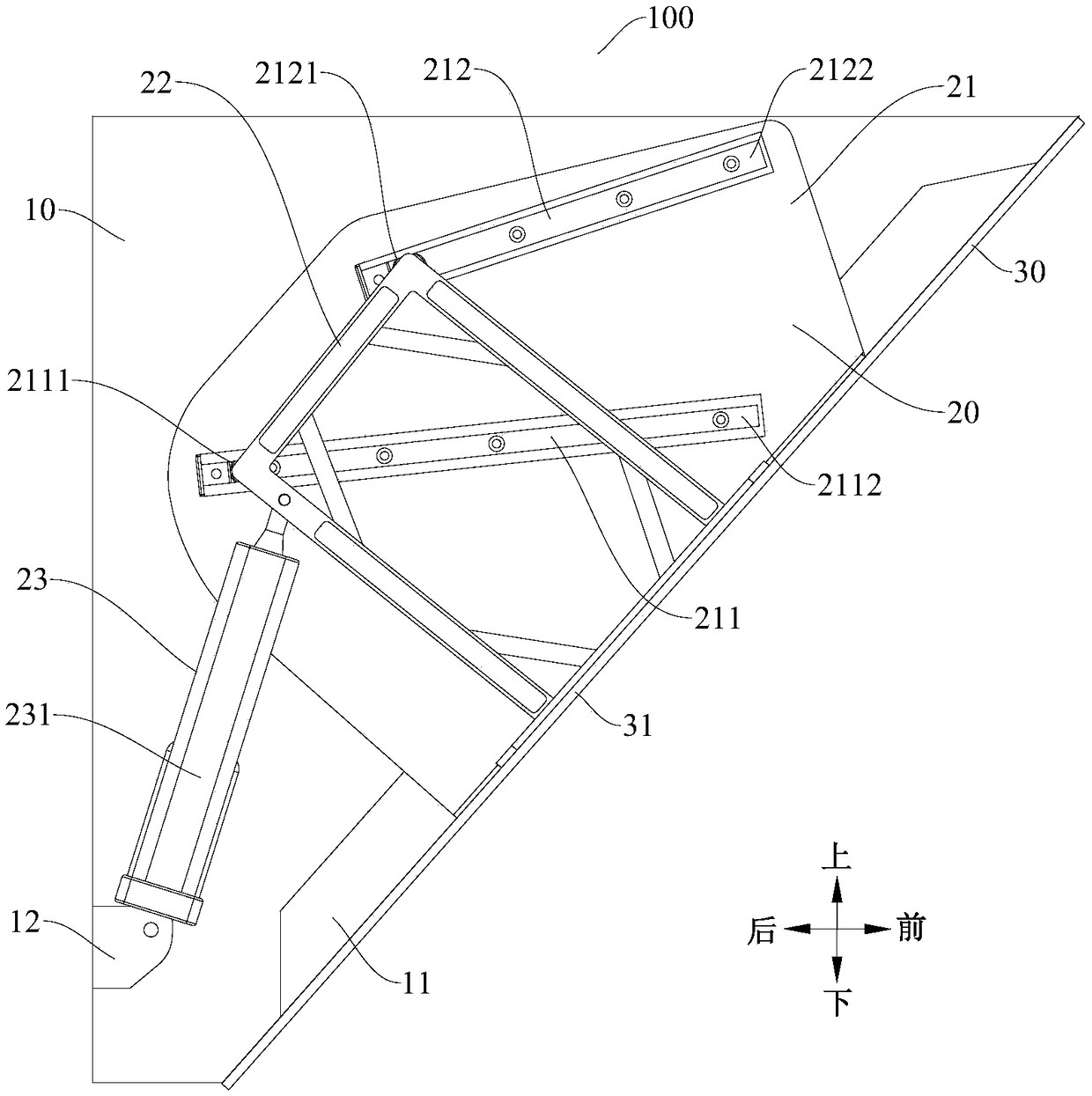
ActiveCN108980939AGood structural consistencyNice appearanceDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringSight line
The invention discloses a range hood which comprises a tank body component, a full screen and a drive mechanism; the tank body component is provided with an oil fume inlet; the full screen is used foropening and closing the oil fume inlet; the drive mechanism is installed on the tank body component; the full screen is installed on the drive mechanism; the drive mechanism drives the full screen tolife and overturn relative to the tank body component and comprises a driving rod and a drive device; one end of the driving rod is pivotably installed on the tank body component, and the other end of the driving rod is pivotably installed on the full screen; and the drive device is hinged to the driving rod and drives the driving rod to rotate to drive the full screen to lift and overturn. The range hood according to the embodiment of the invention has the advantages that the range hood is good in consistency of the whole structure, beautiful in appearance and convenient to clean, cannot block a sight line of a user in the use process, cannot hinder the user in space and is good in user experience and the like.
Owner:FOSHAN SHUNDE MIDEA WASHING APPLIANCES MFG CO LTD
Electrode with excellent rate capability and current cycling performance
InactiveCN106099117AHigh tap densityGood structural consistencyMaterial nanotechnologyElectrode carriers/collectorsFiberSpinning
The invention provides an electrode with excellent rate capability and current cycling performance. The electrode is made of a specific nano material. A uniform sol precursor solution is prepared mainly from polymers with different molecular weights and metal salt, nano fiber is obtained through electrospinning, gradient heat treatment is conducted, and then the high-quality contractile nano material with an adjustable internal structure is obtained; decomposition of composition fiber is controlled by skillfully utilizing different heating rates of two stages, and a morphology with a nested structure where both layers face inwards is formed under accurate and convenient control.
Owner:耿云花
Production method of gel polymer electrolyte porous membrane
InactiveCN110760225AHigh porosityHigh liquid absorptionFinal product manufactureElectrolyte accumulators manufactureElectrical batteryPorous polymer membrane
The invention discloses a production method of a gel polymer electrolyte porous membrane and relates to the technical field of batteries. The method comprises the steps that S1, a polymer is added into a mixed solution of a solvent and a non-solvent, the mixed solution is sealed after being uniformly dispersed, the temperature is increased to 50-120 DEG C, stirring is performed for 1-4 hours, vacuum pumping is performed after cooling to remove bubbles, and a polymer solution is obtained; S2, the polymer solution obtained in the step S1 is uniformly spread on the surface of a base material, andthe base material after coating is baked under the temperature of 30-140 DEGC for 6-20min through a stage baking mode; and S3, the residual solvent and non-solvent on the base material obtained in the step S2 are removed thoroughly, and the gel polymer electrolyte porous membrane is obtained. Through the method, the porous polymer membrane can be produced continuously and quickly, production efficiency is high, and operation is easy; the prepared gel polymer electrolyte membrane is uniform in pore structure and high in porosity, has less solvent residues and is beneficial for improving the energy density of the batteries; lithium battery generation equipment can be directly used, the requirement on the equipment is low, cost is saved, and the membrane is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:REAL POWER IND LTD
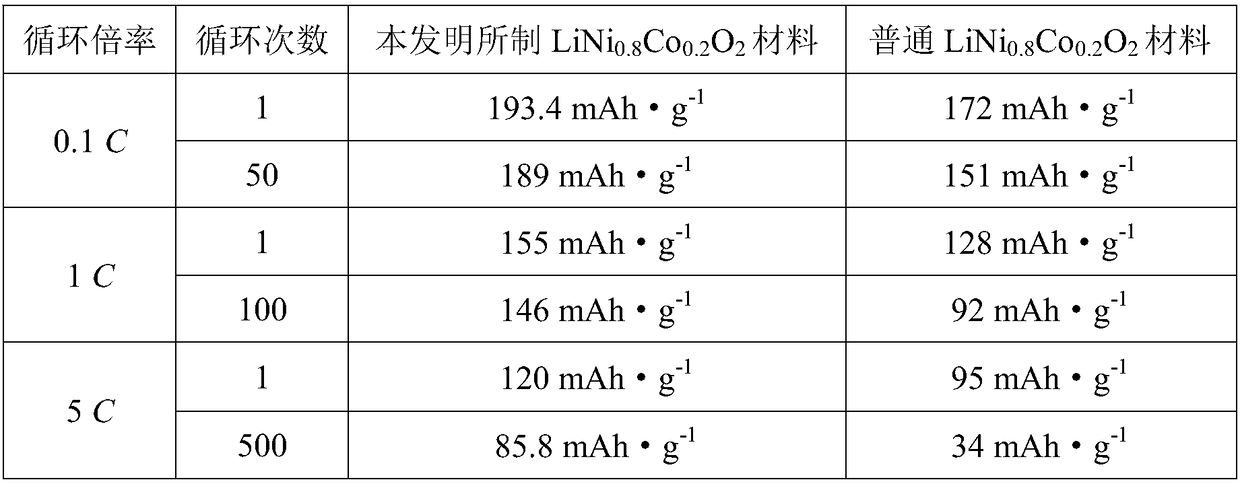
Preparation method and application of LiNi<0.8>Co<0.2>O<2> material
InactiveCN108199040AGood structural consistencyEvenly distributedCell electrodesSecondary cellsCyclic processLithium
The invention relates to a preparation method of a LiNi<0.8>Co<0.2>O<2> material. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) dissolving a lithium salt, a nickel salt, a cobalt salt and urea in water, and performing hydrothermal reaction under 160 DEG C to obtain a precursor solution, wherein the mole ratio of the lithium salt, the nickel salt and the cobalt salt is 1:0.8:0.2: and(2) drying the precursor solution to remove water, and performing calcination under 750-850 DEG C in an oxygen atmosphere to obtain the LiNi<0.8>Co<0.2>O<2> material. According to the method, a positive ion mixing phenomenon of the material during the synthesis process is effectively reduced by controlling structural morphology of a precursor product, the structural orderliness of the material isimproved, the structure collapse of the material during the circulation process can be reduced, and the cycle stability and the rate property of the battery are effectively improved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
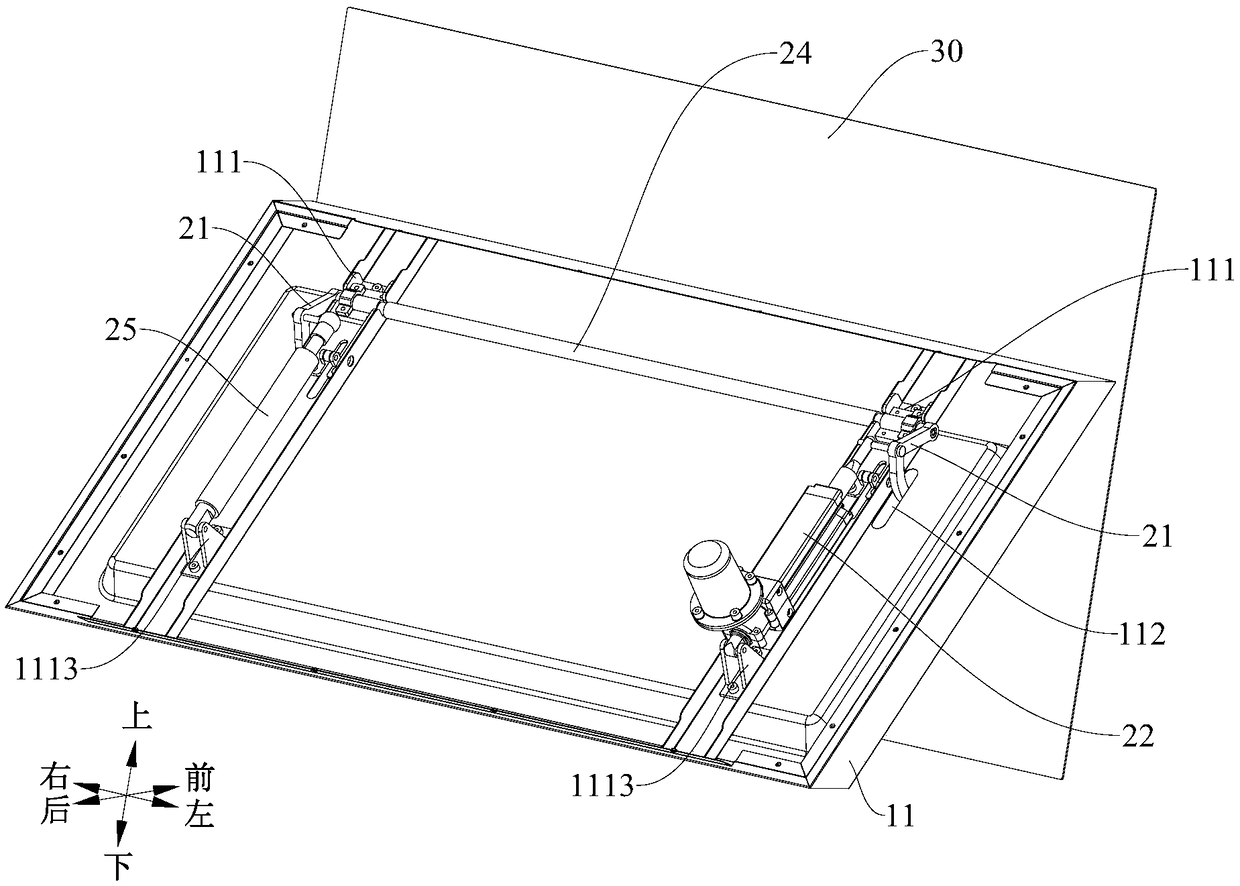
Range hood
ActiveCN108800264AThe overall structure is consistentNice appearanceDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusEngineering
The invention discloses a range hood. The range hood comprises a box assembly, a full screen, a driving mechanism and a driving assembly, wherein the box assembly is provided with an air inlet; the full screen is used for opening and closing the air inlet; the driving mechanism is mounted on the box assembly, and the full screen is mounted on the driving mechanism; the driving mechanism comprisesa sliding groove assembly and a connecting rod assembly, the sliding groove assembly is arranged on the box assembly and is provided with a first sliding groove and a second sliding groove; the connecting rod assembly is fixed to the full screen and is provided with a first sliding part matched with the first sliding groove and a second sliding part matched with the second sliding grove; the driving device is connected with the connecting rod assembly and is used for driving the connecting rod assembly to enable the first sliding part and the second sliding part to slide in the first sliding groove and the second sliding groove to ascend, descend and turn over the full screen. The range hood provided by the embodiment of the invention has the advantages that the overall structure consistency is good, the appearance is attractive, the sight of a user cannot be blocked in the using process, the user cannot be hindered in space, and user experience is good.
Owner:GUANGDONG MIDEA KITCHEN APPLIANCES MFG CO LTD +1
Device for preparing metal ingot through rapid solidification and lamination compounding
The invention relates to the technical field of metal ingots, in particular to a device for preparing a metal ingot through rapid solidification and lamination compounding. The device comprises a rapid quenching belt forming system which is used for melting metal to prepare a solid rapid quenching belt which is kept at a set temperature and feeding the rapid quenching belt into an accelerating system; the accelerating system can accelerate the rapid quenching belt and separate the rapid quenching belt from a liquid beam carried by the rapid quenching belt to form an independent rapid quenchingbelt; a heating system is used for heating the independent rapid quenching belt from the accelerating system to keep the independent rapid quenching belt at a set temperature; a deflection system isused for applying deflection force to the rapid quenching belt from the heating system to enable the rapid quenching belt to deviate from the original movement direction; and a lamination compoundingsystem is used for depositing the rapid quenching belt from the deflection system onto a receiver, and a lamination compounding cast ingot is formed through a compactor. According to the device, rapidsolidification and lamination compositing are carried out at the same time, the defects which cannot be avoided by a conventional casting method can be effectively avoided, casting defects and sintering holes are well eliminated, and high-quality metal ingots can be manufactured in a short process.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
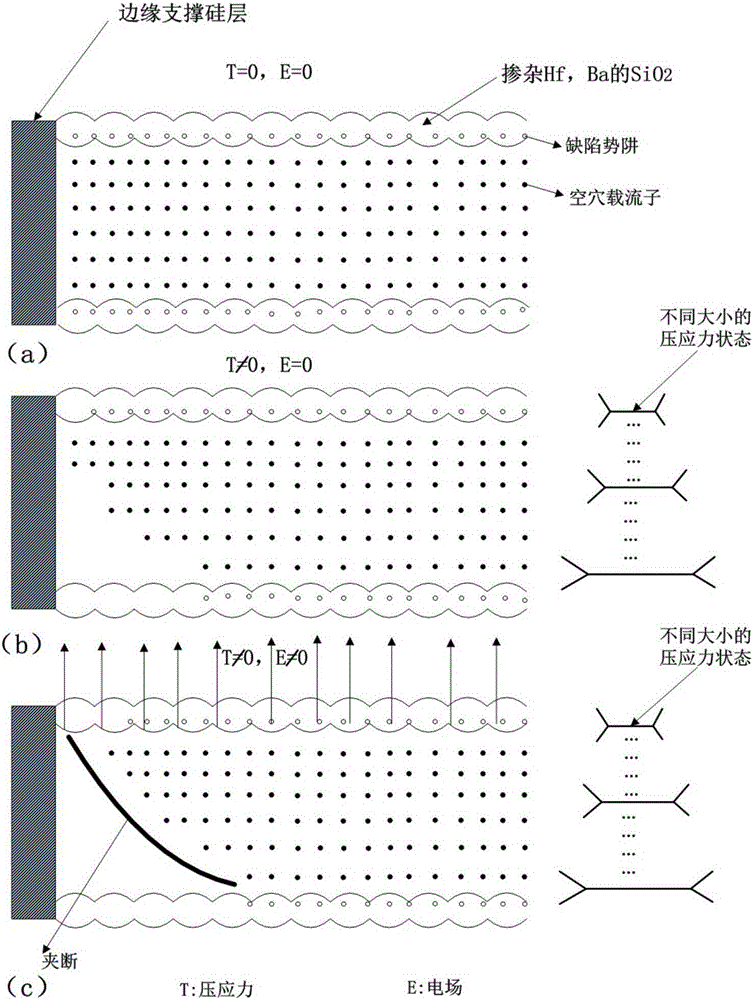
High-sensitivity micro-nano giant piezoresistive rainfall sensor and preparation method and measurement structure thereof
ActiveCN106125163ARealization of giant piezoresistive effectEliminate the effects ofRainfall/precipitation gaugesHeterojunctionMicro nano
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity micro-nano giant piezoresistive rainfall sensor and a preparation method and a measurement structure thereof. The sensor comprises a sensor array which includes multiple silicon aluminum heterojunction sensing units, power supply electrode pairs, signal detection lead-out electrode pairs and reference lead-out electrode pairs. Each sensing unit includes two silicon aluminum heterojunction pressure sensitive structures, a bottom silicon layer, an insulating silicon dioxide layer and a top silicon layer. The two silicon aluminum heterojunctions which are consistent in structure and property are arranged at the two ends of the sensor in parallel. The side parts of the silicon aluminum heterojunctions are provided with an excitation electrode and a detection electrode. When the sensor is used, mechanical stress of the sensor chip is formed through rainfall pressure and the size of the contact potential barriers of the silicon aluminum heterojunctions is changed so that the giant piezoresistive effect is realized; and the change of the volt-ampere properties of the silicon aluminum heterojunctions acting as a reference part is not caused by stress and the silicon aluminum heterojunctions can act as a differential reference circuit to eliminate the influence of temperature. The sensor is high in measurement sensitivity and accurate and suitable for the occasion of high-precision rainfall measurement.
Owner:南京瑞菲科机电科技有限公司
Battery cover sealing structure, manufacturing method thereof and battery
PendingCN112909393AImprove temperature resistanceExtend your lifeFinal product manufactureElectric connector introductionStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a battery cover sealing structure and a manufacturing method thereof and a battery. The battery cover sealing structure comprises a central pole, the central pole is sleeved in a battery cover plate, and an annular gap is arranged between the central pole and the battery cover plate; the glass fixing body and the glass fixing ring are sequentially and tightly inserted into the annular gap in a penetrating manner, and the glass fixing body and the glass fixing ring are arranged on the central pole in a sleeving manner; the glass fixing ring is arranged below the glass fixing body, and the upper surface of the glass fixing ring is tightly connected with the lower surface of the glass fixing body; the glass fixing body is arranged between the central pole and the battery cover plate, so that the sealing property and the sealing strength between the central pole and the battery cover plate are effectively improved, and the glass fixing ring is arranged between the central pole and the battery cover plate, so that the corrosion of battery electrolyte to the glass fixing body is avoided, and the sealing performance of the battery cover sealing structure is improved, so the service life of the battery is prolonged; the manufacturing method is simple, and the sealing performance of the battery cover is ensured.
Owner:杜欢阳
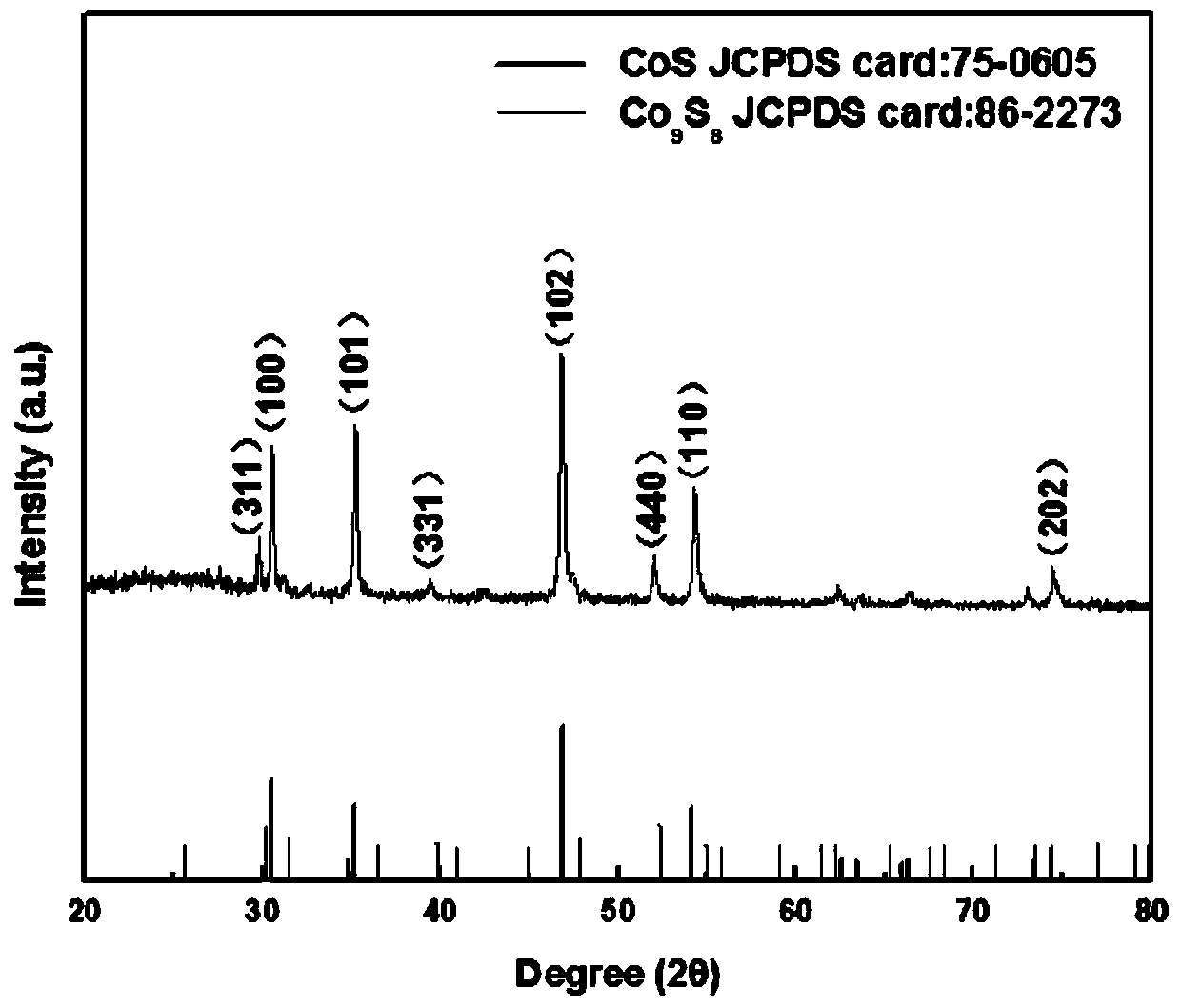
A preparation method and application of carbon-coated cobalt sulfide/cobalt octasulfide nine-cobalt nanoparticles with multi-level hole structure
ActiveCN108336338BIncrease profitShape is easy to controlMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesElectrolytic agentElectrical battery
The invention discloses a preparation method of carbon-coated cobaltous sulfide / cobaltous octosulfide nano particles having a multistage porous structure and an application thereof. Based on a solvothermal method, PAN is employed as a carbon source and is taken as a carrier of an active substance, the carbon-coated CoS / Co9S8 nano particles having a specific structure is obtained by adding a certain mass of sulfur powder through calcining and sulfuration under protection atmosphere, and the carbon-coated CoS / Co9S8 nano particles have the multistage porous structure. The multistage porous structure constructed by the carbon-coated active substance particles is in favor of full contacting of an electrolyte and an active substance, provides more reaction active sites, shortens diffusion distance of lithium ions, increases the multiplying power performance of a battery, alleviates volume expansion during a lithium insertion process, prevents powdering and shedding of the active substance, and greatly increases the cycle life of the battery. The preparation method has the advantages of easy operation, and controllable reaction condition, and is easy for an amplification experiment.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
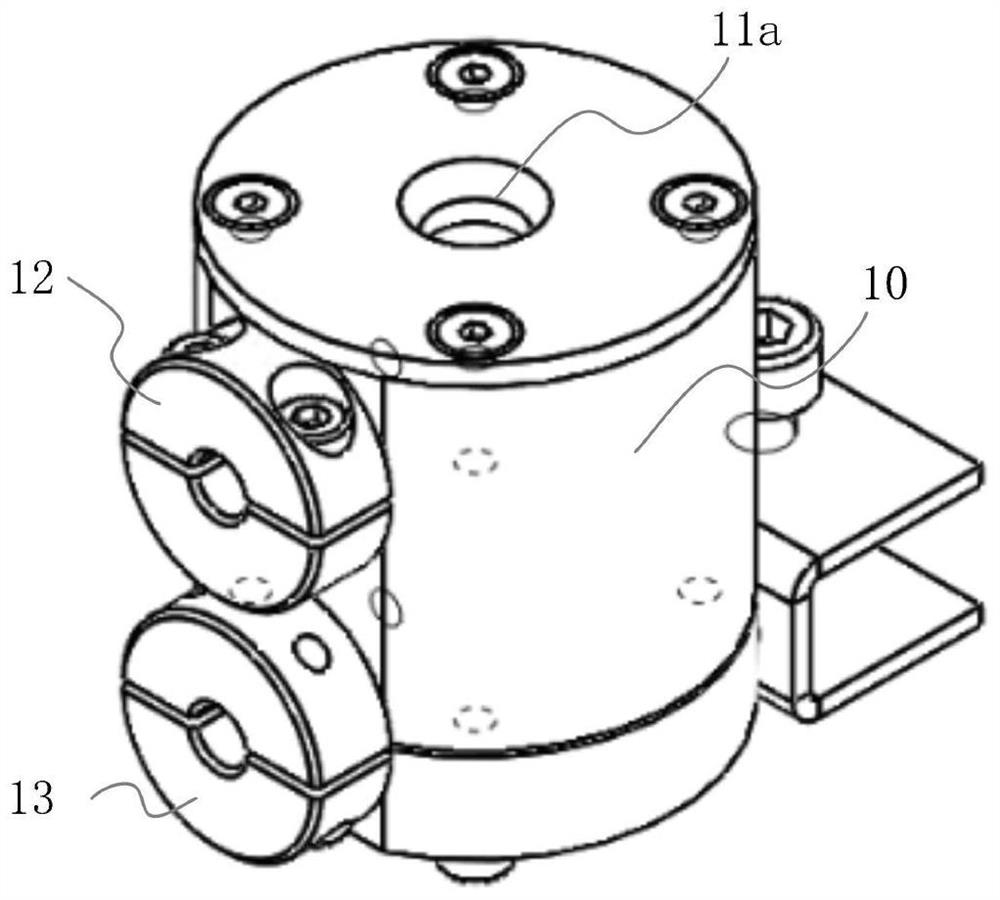
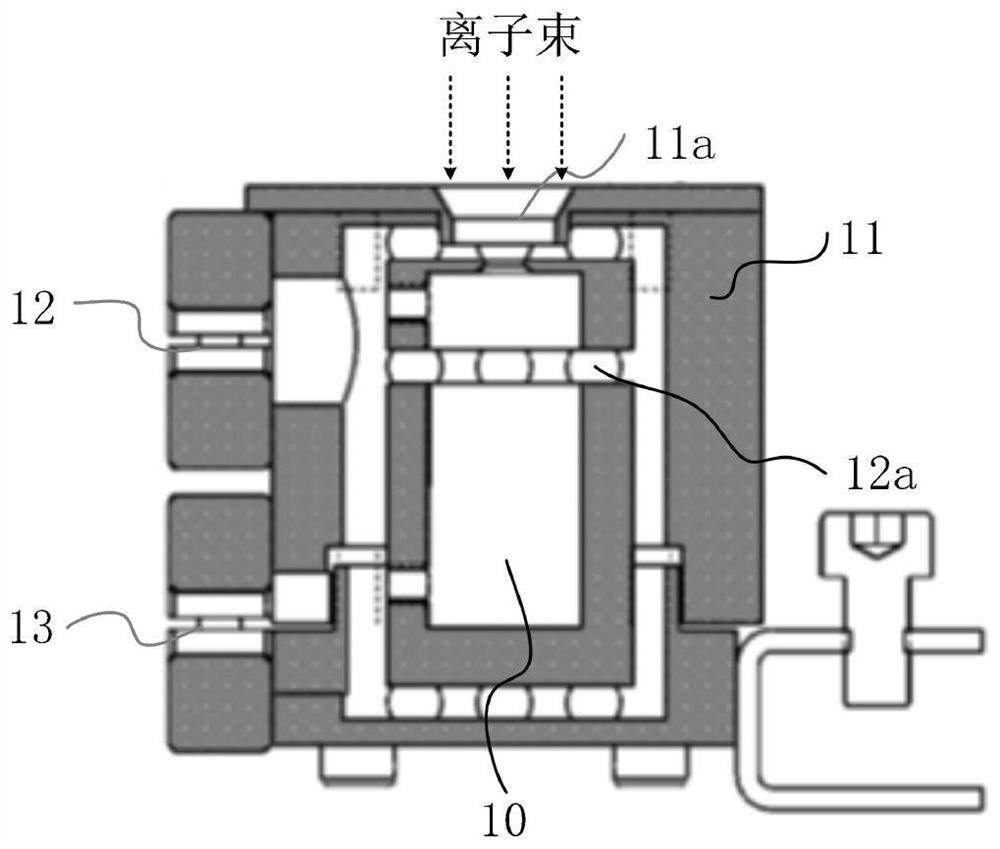
Faraday cup and ion beam measurement system
PendingCN114296121ASimple structureEasy to installElectrical measurementsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a Faraday cup and an ion beam measurement system. The Faraday cup comprises a front end part, a suppression assembly, an isolation assembly and a collector assembly which are stacked in sequence. An ion beam collecting opening is formed in the front end part; wherein the front end part is provided with a measuring port; the collector assembly comprises a first PCB substrate, the middle part of the first PCB substrate is provided with a first metal layer, and the edge of the first metal layer is provided with a first PCB insulating layer; a measured ion beam enters from an ion beam collection port of the front end part, is collected by the first metal layer after electrons are shielded by the suppression assembly, and is used for detecting beam data of the ion beam; according to the technical scheme, the collector assembly is made of the PCB, the PCB insulating layer on the PCB substrate and the metal layer in the middle of the PCB insulating layer are used for collecting ion beams, the Faraday cup structure is simplified by adopting the PCB technology, equipment installation is facilitated, the structural consistency is good, the production and manufacturing cost is low, and later maintenance is simple.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN IBD TECH CO LTD +1
Method for gluing hair elastic ring
InactiveCN101716026BAvoid breakingGood structural consistencyCurling devicesAlcoholEthyl-2-cyanoacrylate
Owner:ZHANGZHOU BEITE COSTUME
A microwave device surface processing device and method for suppressing secondary electron emission
ActiveCN104646832BImprove launch performanceReduce processLaser beam welding apparatusLaser etchingMicrowave
The invention provides a microwave device surface processing device capable of restraining secondary electron emission and a microwave device surface processing method capable of restraining secondary electron emission. The device consists of a laser output module, a micro lens, a movable table and a control module, wherein the control module outputs control signals to the laser output module and the movable table, so as to control the laser output power, the laser output interval time, the movement distance of the movable table and the movement time of the movable table; by virtue of a small-area deep hole array continuous moving and filling method, laser etching of a centimeter-scale large-area deep hole array structure on the surface of a microwave device is finished. The microwave device surface structure processed by the device and the method is of a rectangular uniformly-spaced or triangular uniformly-spaced micronano deep hole array, so that the secondary electron emission coefficient of the surface of the microwave device can be effectively reduced. The device and the method are automatic in processing, simple in process and high in efficiency, and can be used for performing processing treatment on the surfaces of parts such as gold or plated gold; the surface performance of the processed microwave device has long-term stability, and the processed microwave device is applicable to ground and aerospace environments.
Owner:CHINA AEROSPACE TIMES ELECTRONICS CORP
High-temperature-resistant polyurethane elastic fiber spinning control method
ActiveCN112725929AOvercoming the problem of poor elastic propertiesGood orientationSpinnerette packsMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentFiberPolymer science
The invention provides a high-temperature-resistant polyurethane elastic fiber spinning control method. According to the method, the temperature of the upper portion of a channel is set to be slightly higher than the boiling point temperature of a spinning solution solvent; meanwhile, the relatively low air speed and the low air pressure are set, so that the solvent volatilization speed difference between the interiors of filaments and the surfaces of the filaments is relatively small, and the temperature of the middle of the spinning channel is set to be 250-270 DEG C; and meanwhile, the corresponding air speed and air pressure are set in a matched mode, the solvent diffused to the surfaces of the filaments from the interiors of the filaments is further volatilized, the temperature of the lower portion of the channel is set to be 20-30 DEG C lower than the temperature of the middle of the channel, the concentration of the solvent in the filaments is volatilized to the minimum, and finally the drafting speed of a drafting roller is set. The high-temperature-resistant polyurethane elastic fiber which is good in orientation, high in crystallinity and uniform in structural consistency can be obtained from the polyurethane elastic fiber filaments through spinning control conditions.
Owner:宁夏宁东泰和新材有限公司
High-sensitivity micro-nano giant piezoresistive rain sensor and its preparation method and measurement structure
ActiveCN106125163BRealization of giant piezoresistive effectEliminate the effects ofRainfall/precipitation gaugesMicro nanoHeterojunction
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity micro-nano giant piezoresistive rainfall sensor and a preparation method and a measurement structure thereof. The sensor comprises a sensor array which includes multiple silicon aluminum heterojunction sensing units, power supply electrode pairs, signal detection lead-out electrode pairs and reference lead-out electrode pairs. Each sensing unit includes two silicon aluminum heterojunction pressure sensitive structures, a bottom silicon layer, an insulating silicon dioxide layer and a top silicon layer. The two silicon aluminum heterojunctions which are consistent in structure and property are arranged at the two ends of the sensor in parallel. The side parts of the silicon aluminum heterojunctions are provided with an excitation electrode and a detection electrode. When the sensor is used, mechanical stress of the sensor chip is formed through rainfall pressure and the size of the contact potential barriers of the silicon aluminum heterojunctions is changed so that the giant piezoresistive effect is realized; and the change of the volt-ampere properties of the silicon aluminum heterojunctions acting as a reference part is not caused by stress and the silicon aluminum heterojunctions can act as a differential reference circuit to eliminate the influence of temperature. The sensor is high in measurement sensitivity and accurate and suitable for the occasion of high-precision rainfall measurement.
Owner:南京瑞菲科机电科技有限公司
Clutch structure of electric operating mechanism for circuit breaker
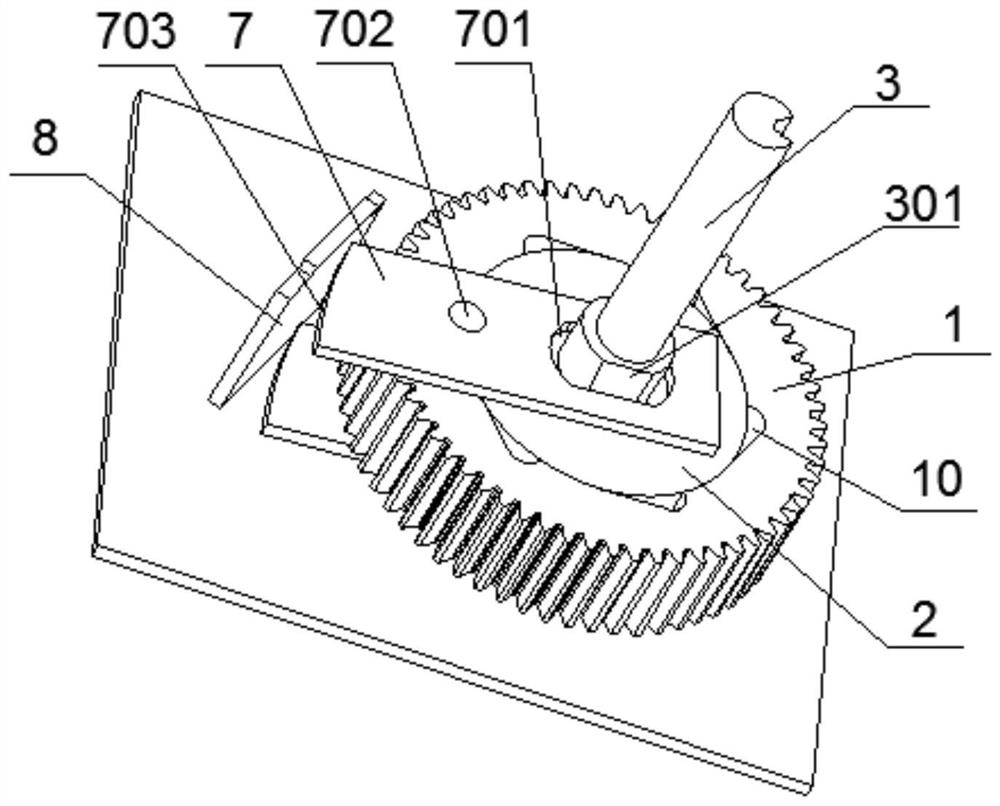
PendingCN112863961AAchieve clutch effectDoes not change external dimensionsProtective switch operating/release mechanismsReciprocating motionGear wheel
The invention provides a clutch structure of an electric operating mechanism for a circuit breaker, which comprises a gear, a star wheel, push rods and a top plate, wherein the star wheel is coaxially arranged in a center hole of the gear, and the push rods capable of reciprocating in the radial direction of the star wheel are arranged on the two sides of the star wheel in a sleeving mode; a spring is arranged in the star wheel, a stop pin is arranged at the other end of the spring in a telescopic mode, and the two ends of the stop pin and the push rod are fixedly arranged; a plurality of spigots matched with the stop pin are annularly arranged on the outer edge of the center hole, and the stop pin can be switched in the center hole and the spigot; and the top plate is arranged on the outer side of the gear and is fixed in position. The clutch structure is simple, does not occupy external space, is good in action consistency, is more suitable for batch production, realizes clutch on the premise of not increasing axial and radial sizes, and is low in manufacturing cost.
Owner:WUXI KAIXUAN MOTOR
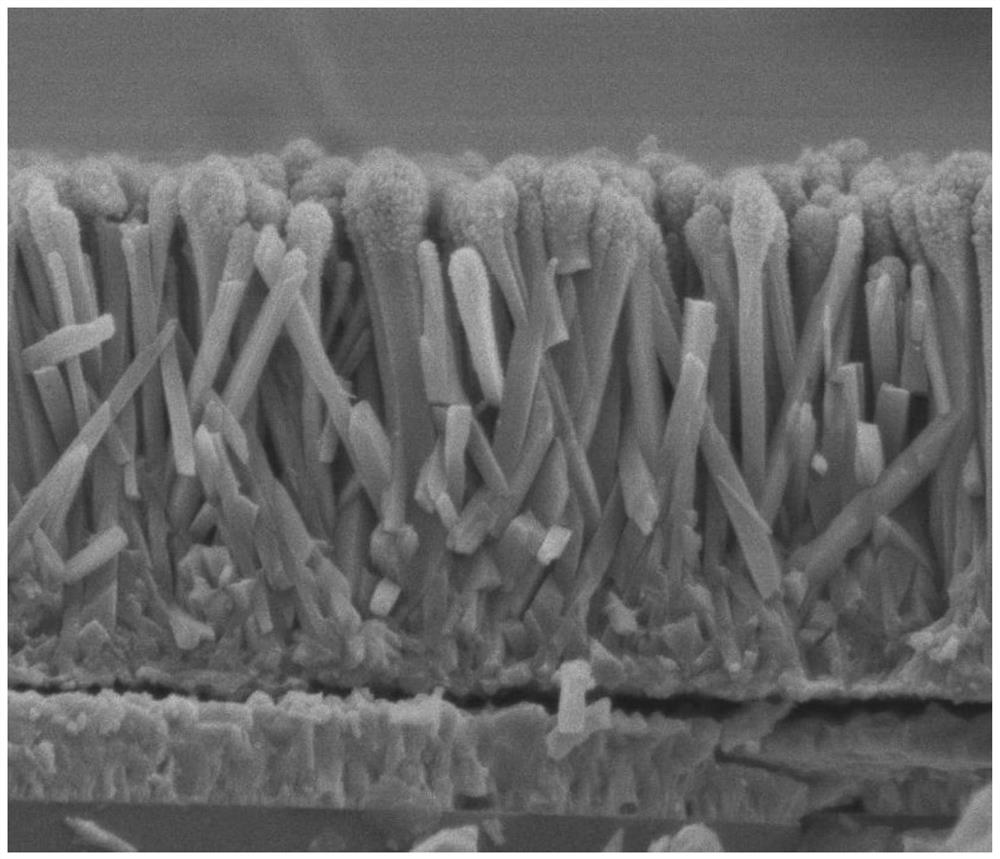
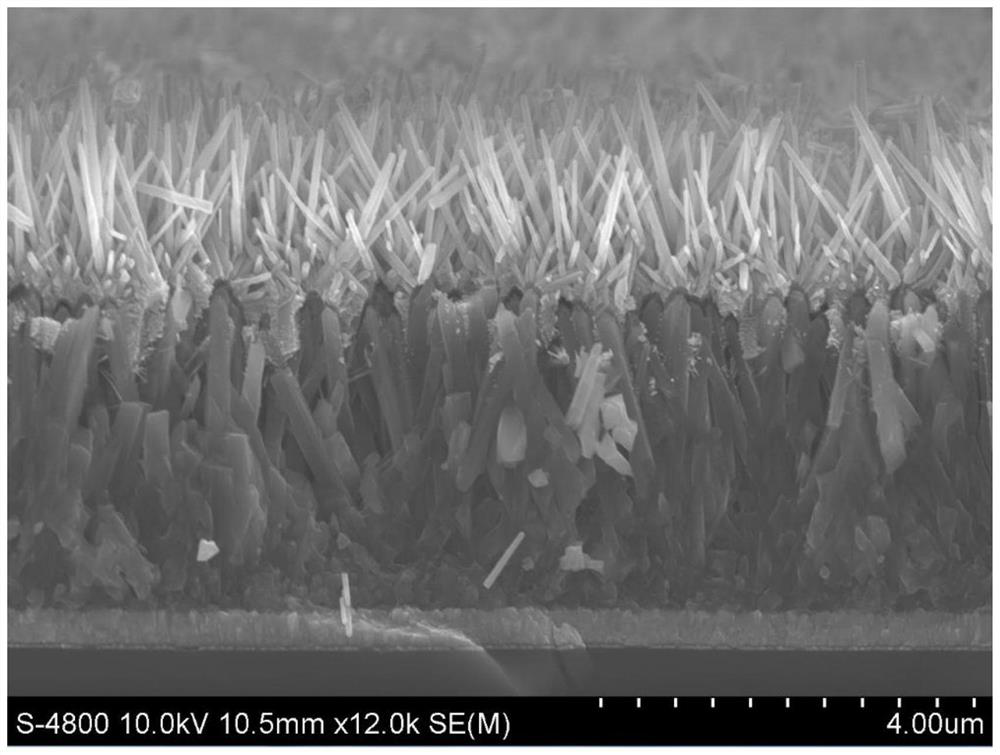
Zinc oxide/titanium oxide double-layer nanorod array heterojunction structure and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112509911AGood structural consistencyHighly ordered orientationMaterial nanotechnologyVacuum evaporation coatingHeterojunctionNanoparticle
The invention relates to a zinc oxide / titanium oxide double-layer nanorod array heterojunction structure and a preparation method thereof. According to the preparation method, sputtering parameters are optimized, ZnO nano-particles are obtained through deposition on the top of each nano-rod in a TiO2 nano-rod array, the ZnO nano-particles are used as seed crystals to grow on the tops of the TiO2 nano-rods again through a hydrothermal method to obtain ZnO nano-rods, and finally the ZnO nano-rods are cleaned and annealed. Therefore, a double-layer nanorod array heterojunction composite structurewith the one-dimensional zinc oxide nanorod array and the one-dimensional titanium dioxide nanorod array can be obtained. According to the preparation method, due to the existence of the ZnO seed crystal particles, the subsequent ZnO nanorods can continuously grow along the growth direction of the TiO2 nanorods, so that the finally grown two-layer nanorod array has the advantages of good structural consistency and highly ordered orientation due to the fact that the two-layer nanorod array grows perpendicular to the substrate.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
Medium-frequency induction sintering method for neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser ceramic
InactiveCN105198400AGood structural consistencyEliminate adverse effects of optical propertiesYttrium Aluminum Garnet LasersCrucible
The invention relates to a medium-frequency induction sintering method for neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser ceramic and belongs to the technical field of laser ceramic preparation. In the prior art, a temperature field formed in a furnace chamber is not uniform, and the sintering is carried out according to a predetermined process curve without utilizing a real-time fine adjustment sintering process, so that the rate of finished products is decreased, the sintering process is complex, and the sintering time is long. According to the medium-frequency induction sintering method for the neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser ceramic, a laser ceramic blank is sintered into a laser ceramic finished product at a high temperature. The medium-frequency induction sintering method is characterized by comprising the following steps: putting the laser ceramic blank into a metal crucible into a furnace chamber of a medium-frequency induction furnace; vacuumizing the furnace chamber; carrying out medium-frequency induction heating to increase the temperature to be 1350 DEG C at a temperature increase rate of 5DEG C / min-10DEG C / min, carrying out constant-temperature processing for 1-5 hours, then heating to 1750 DEG C at the temperature increase rate of 5DEG C / min-10DEG C / min, constant-temperature processing for 8-16 hours, then stopping heating, and naturally cooling to the room temperature, so as to obtain the finished neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser ceramic.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com