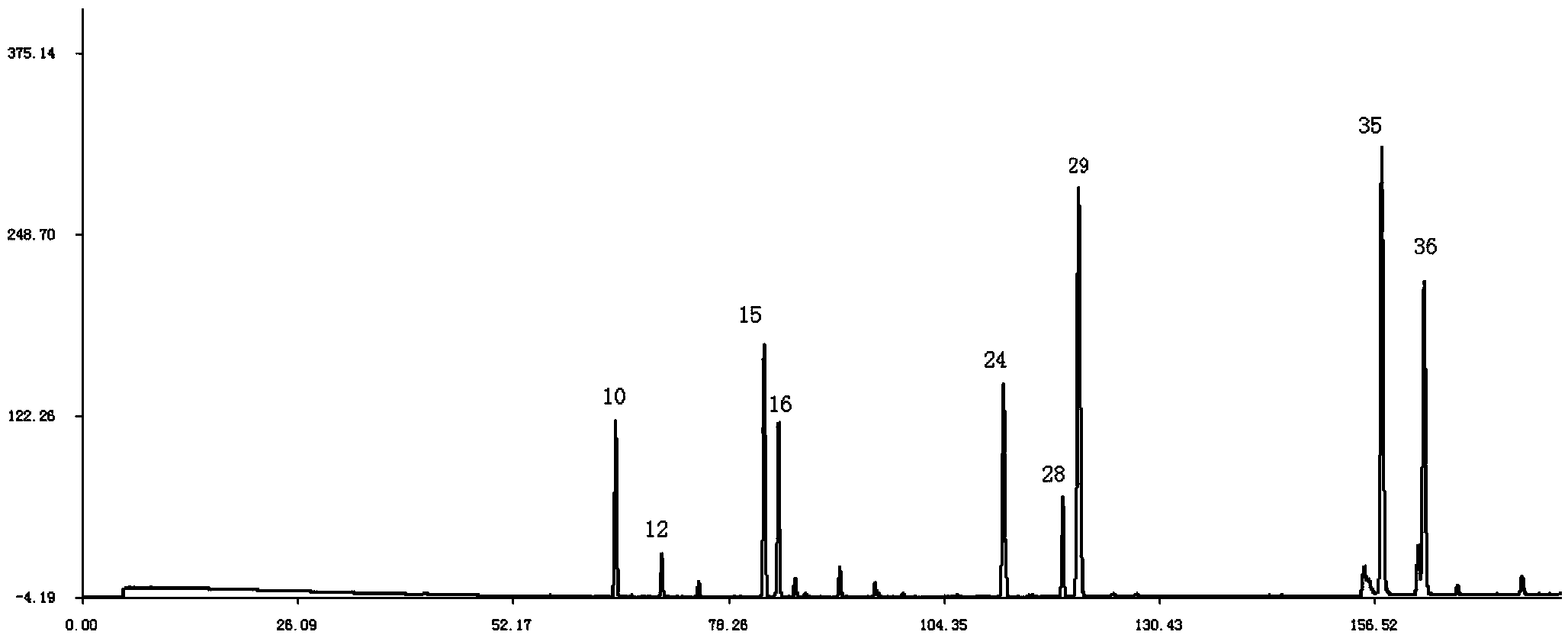
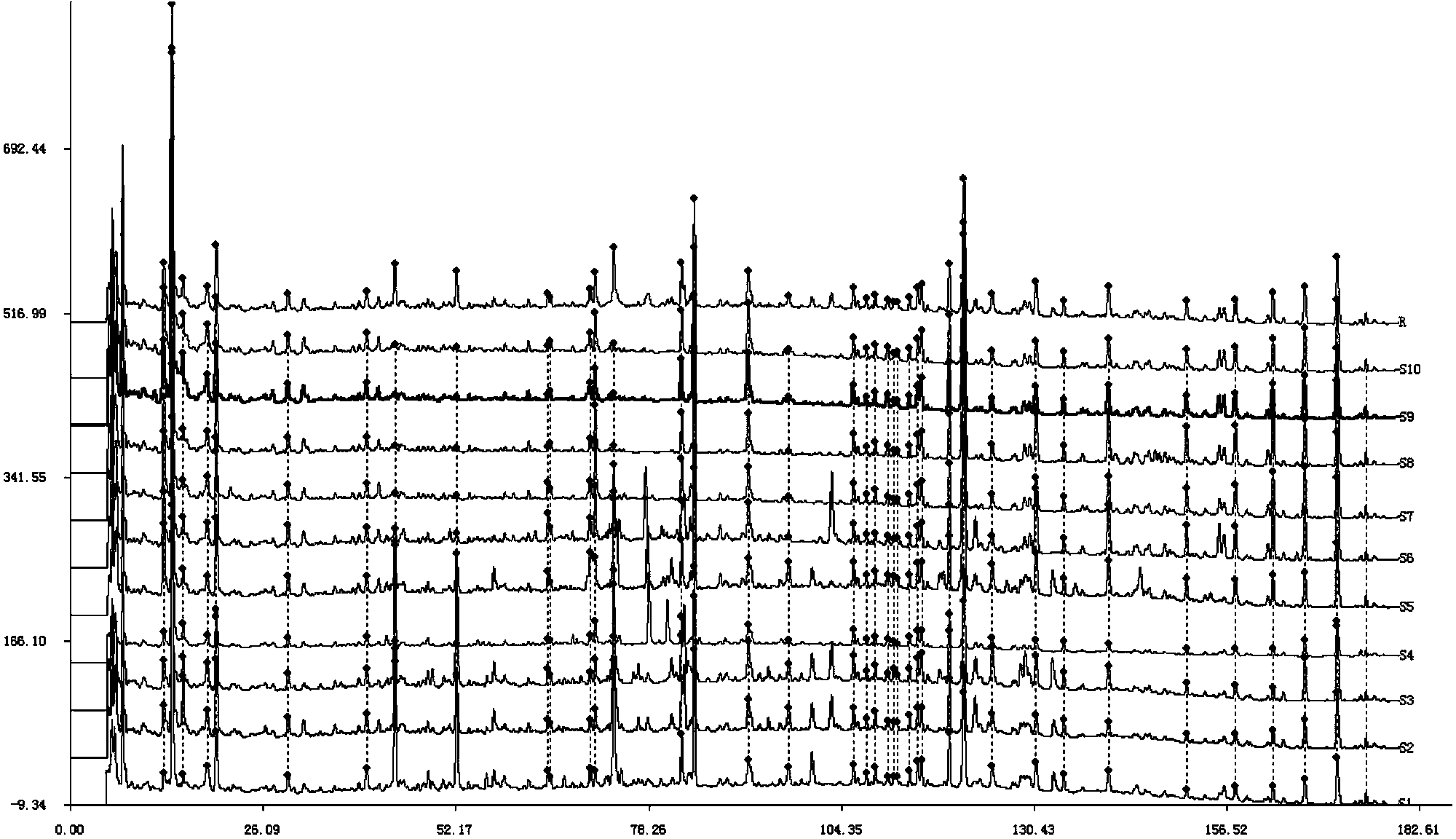
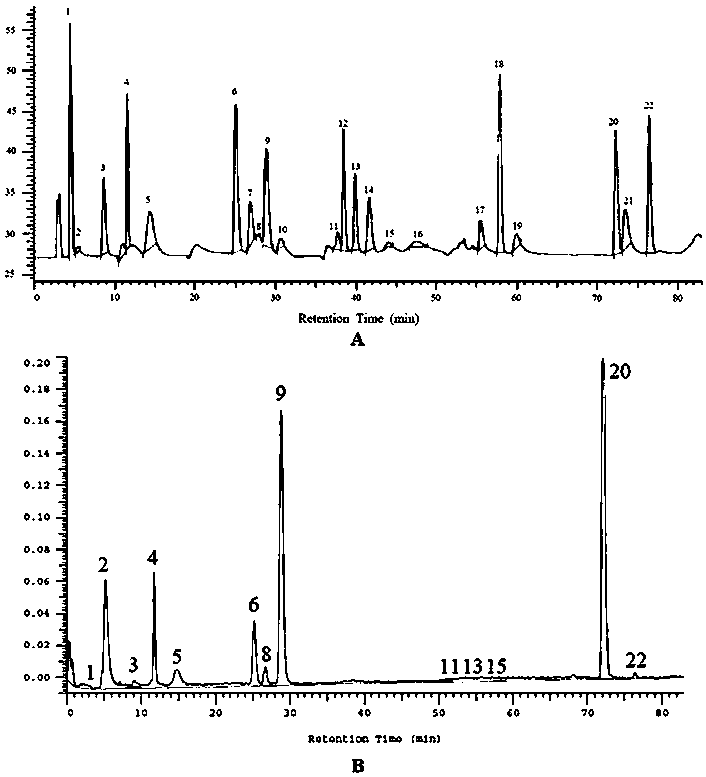
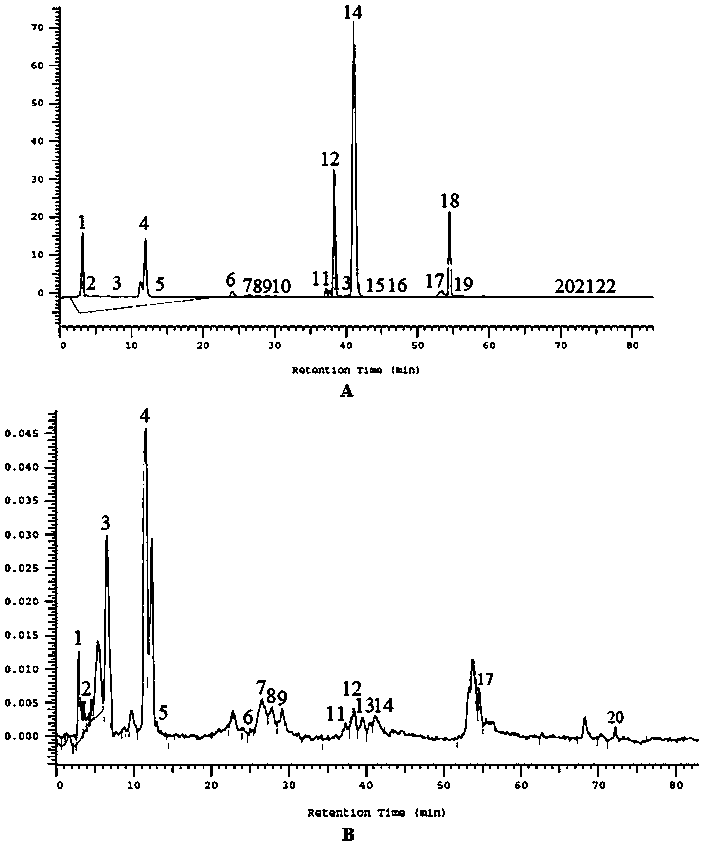
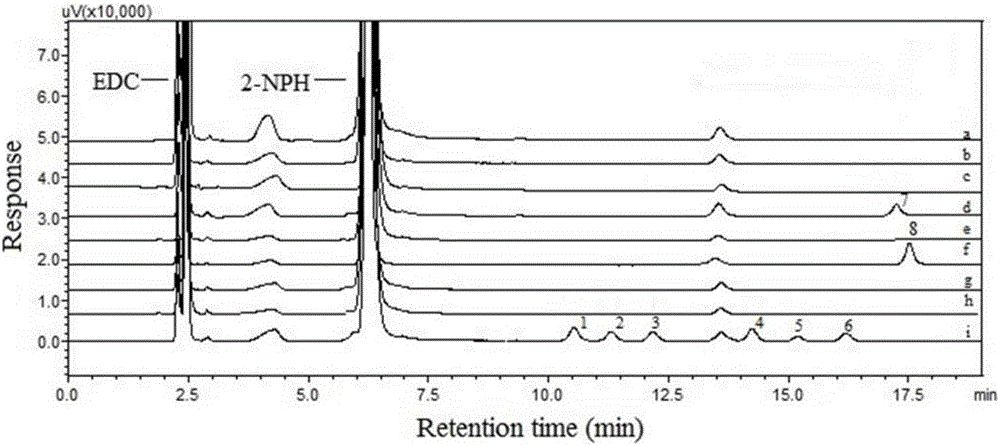
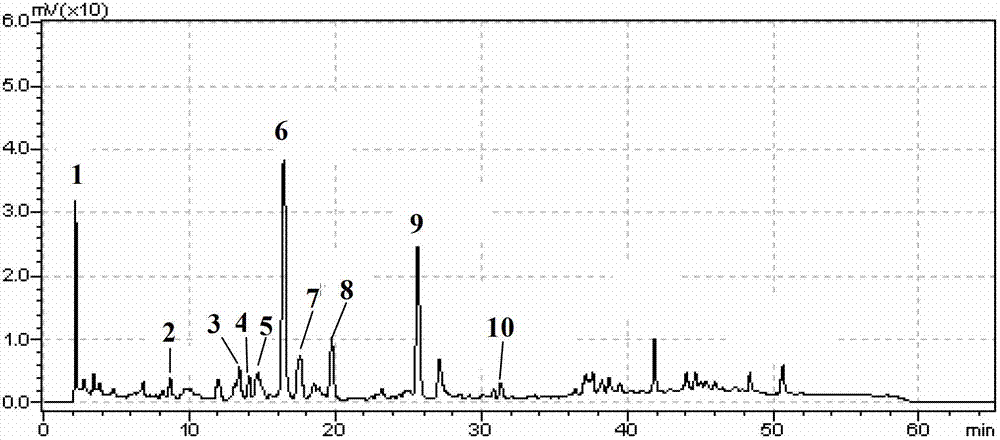
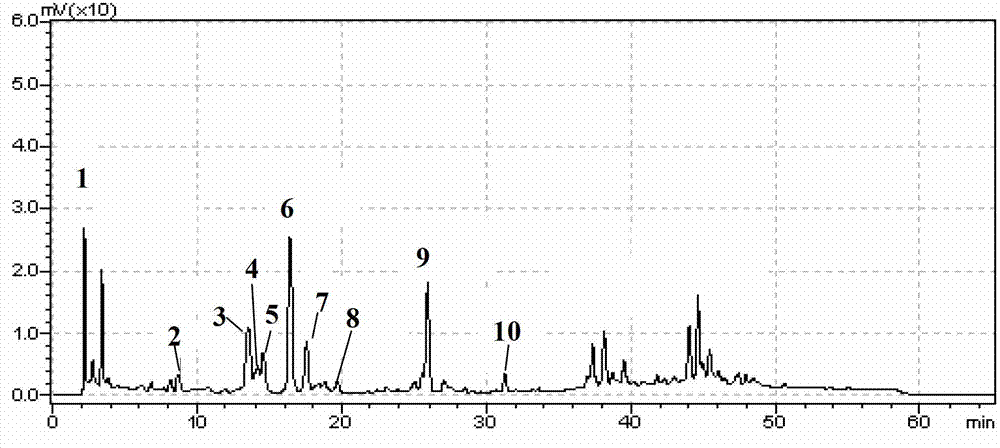
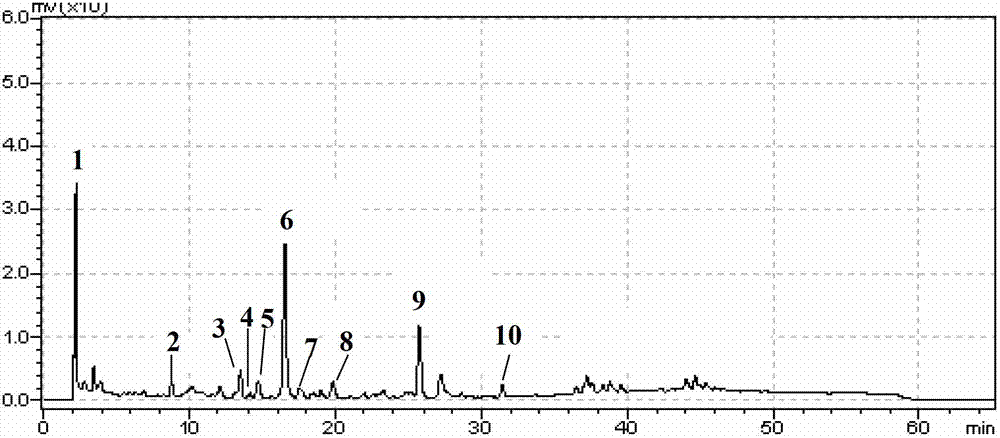
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
92 results about "Hplc dad" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
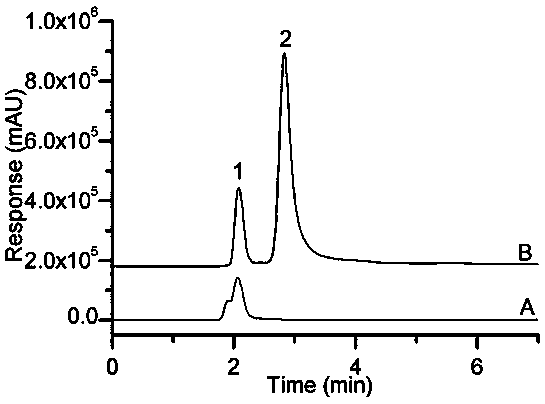
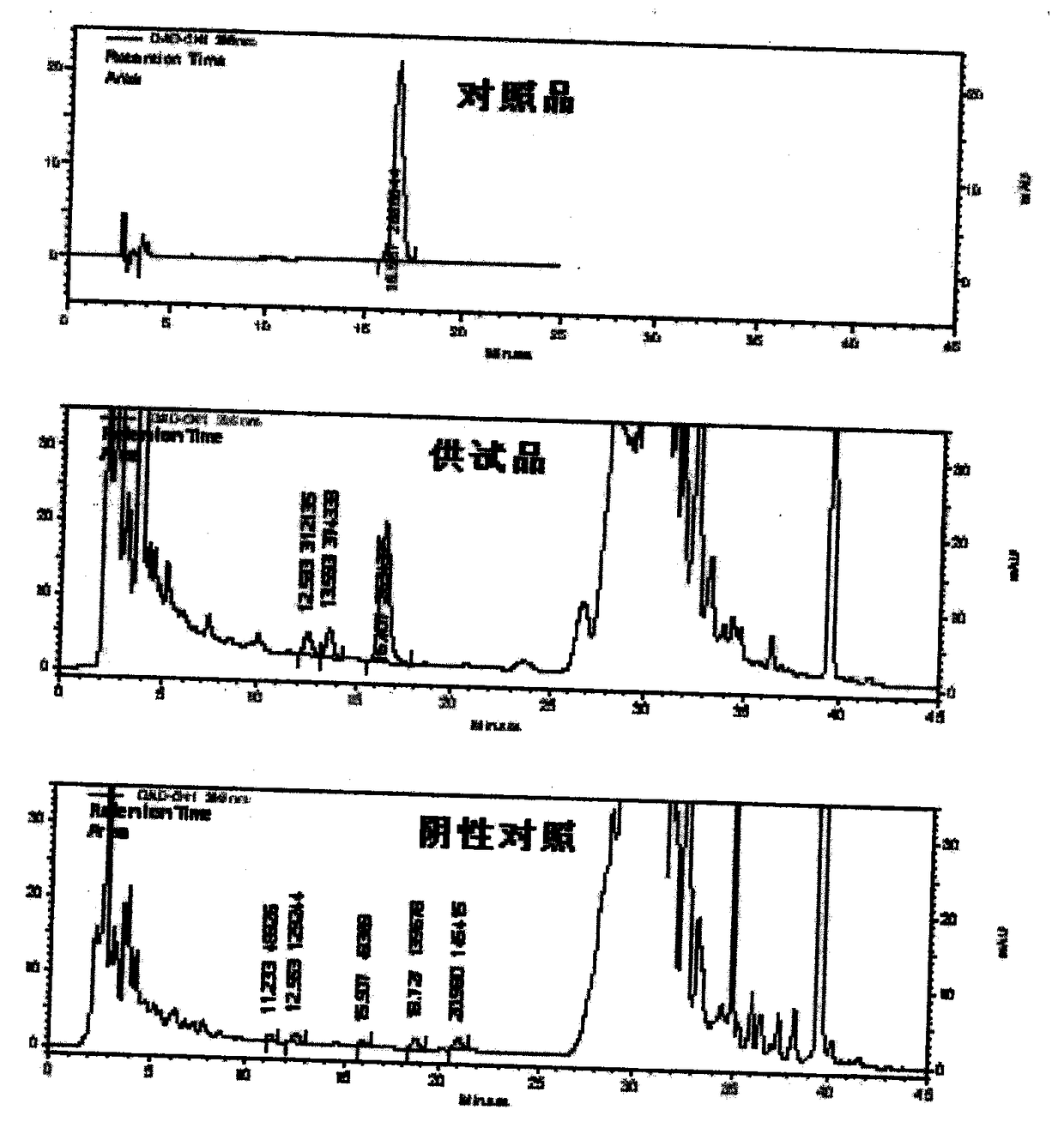
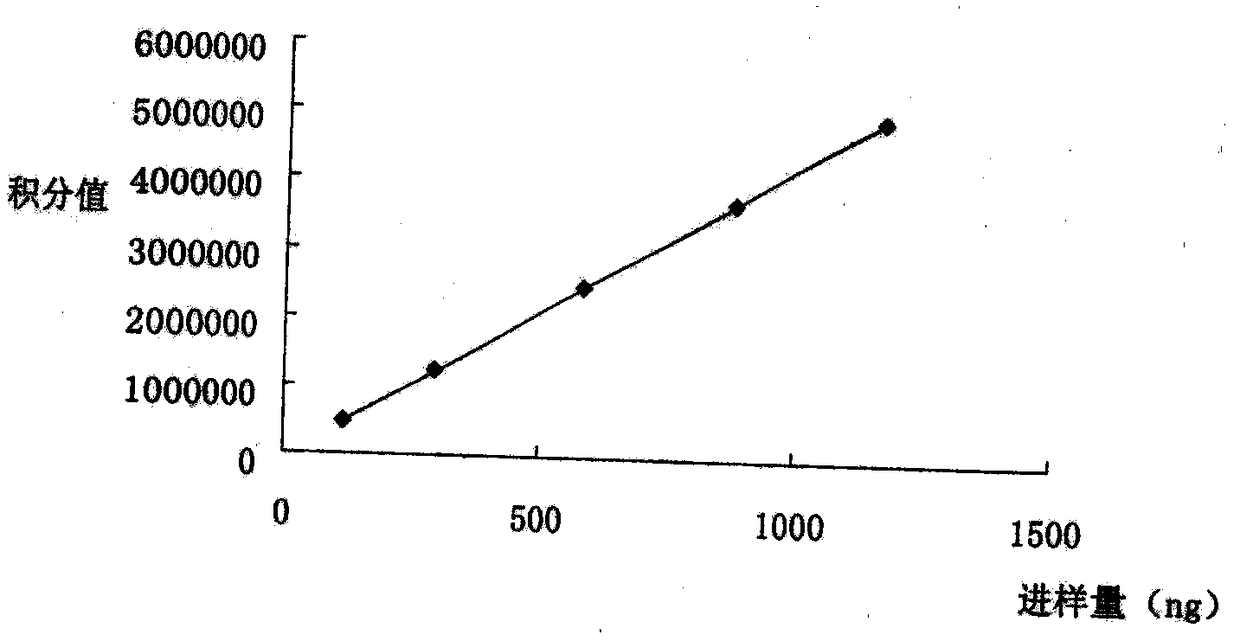
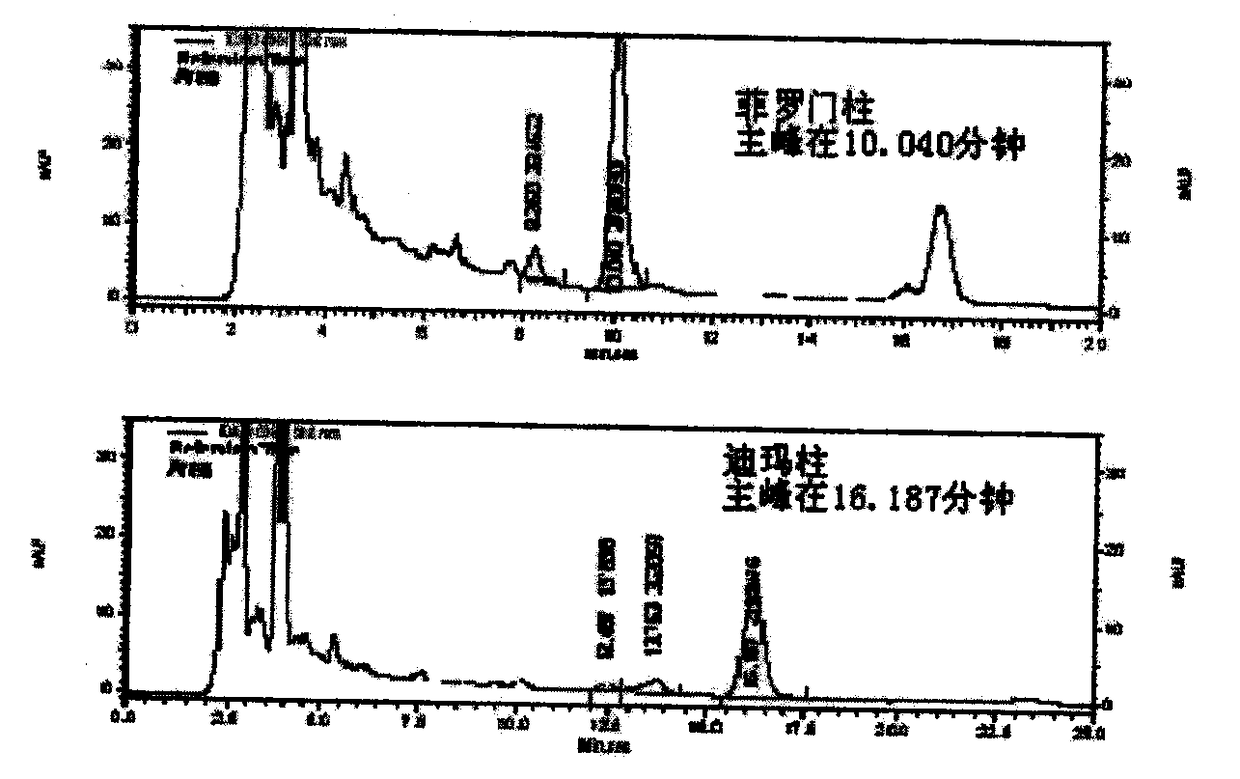
HPLC-DAD stands for High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode-Array Detection. This definition appears somewhat frequently and is found in the following Acronym Finder categories: Science, medicine, engineering, etc.
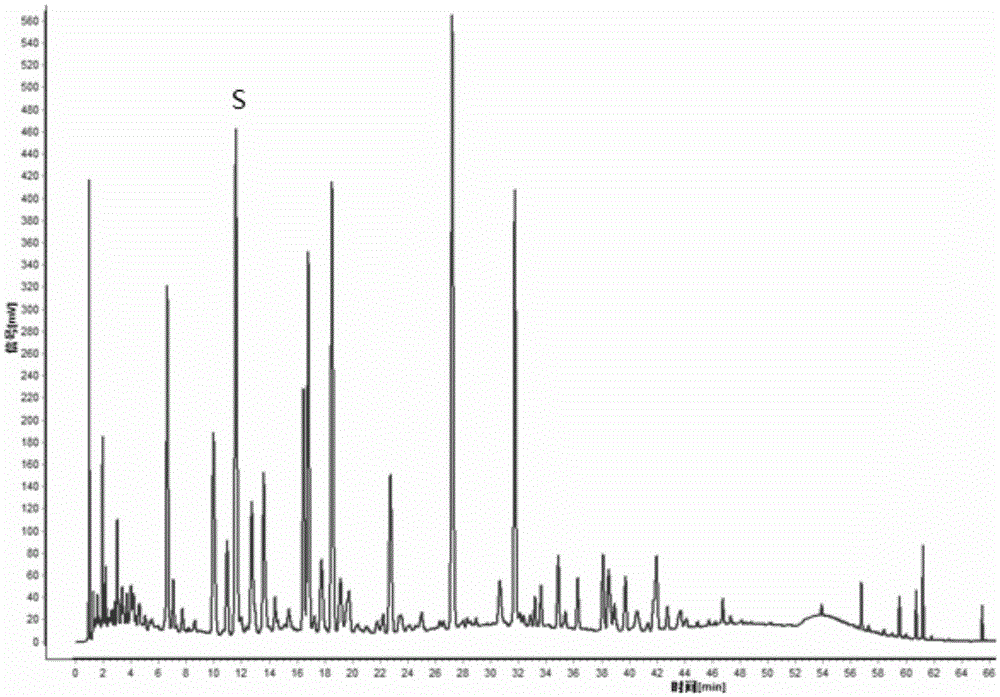
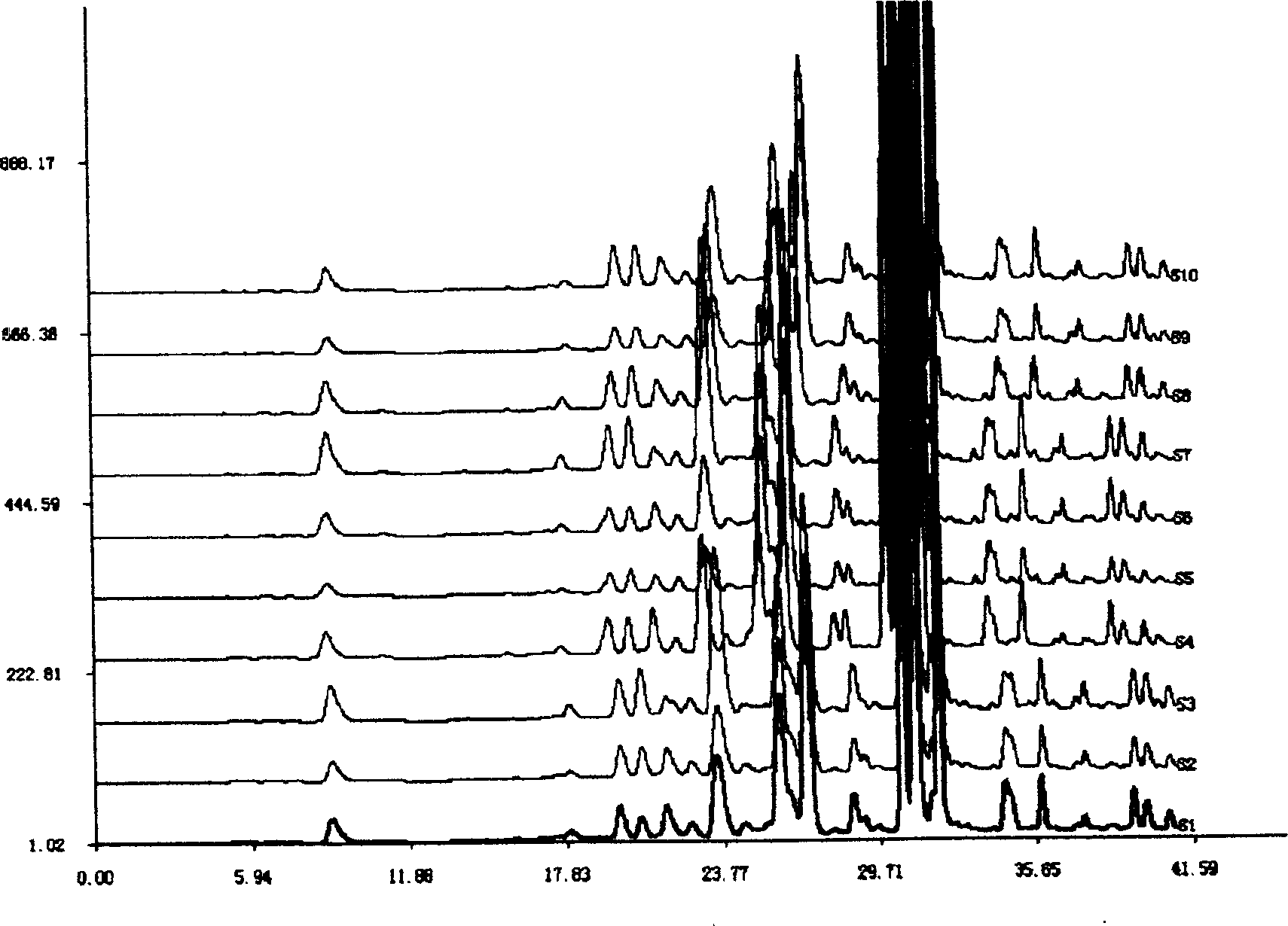
Detection method for fingerprint chromatogram of flavonoid and organic acid components in ginkgo biloba extract and application of detection method
The invention provides a detection method for a fingerprint chromatogram of flavonoid and organic acid components in a ginkgo biloba extract. The detection method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a test solution; (2) preparing a reference solution; (3) respectively determining the test solution and the reference solution by adopting high-performance liquid chromatography, and comparing the acquired fingerprint chromatogram with a standard fingerprint chromatogram to obtain the fingerprint chromatogram of the flavonoid and organic acid components in the test solution. The invention further provides the application of the detection method in the quality detection and the component test determination of the flavonoid and organic acid components in the ginkgo biloba extract. According to the detection method for the fingerprint chromatogram of flavonoid and organic acid components in the ginkgo biloba extract and the application of the detection method provided by the invention, the fingerprint chromatogram of flavonoid and organic acid medicinal components in the ginkgo biloba extract is established; the quality control level of the flavonoid and organic acid medicinal components in the ginkgo biloba extract is improved; effective quantitative analysis can be performed.
Owner:SPH XING LING SCI & TECH PHARM CO LTD
Quality detection method for compound prepn of red sage and notoginseng
InactiveCN1772041ASimple methodGood precisionComponent separationBlood disorderHplc dadSalvianolic acid B
The present invention relates to Chinese medicine quality detecting technology, and is especially the quality detection method for compound preparation of red sage and notoginseng. HPLC-DAD process is adopted to measure the contents of protocatechuic aldehyde, salvianolic acid B, cryptotanshinone, neotanshinone IIA, arasaponin R1, ginsenoside Rg1 and ginsenoside Rb1 in compound red sage preparation simultaneously. The process is simple, precise, repeatable and reliable, and may be used in the quality control of compound red sage preparation.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Quality control method for Kouyangqing granules and application thereof
ActiveCN101518616ASingle detection indexMonitor stabilityComponent separationDigestive systemQuality controlWork in process
The invention discloses a quality control method for Kouyanqing granules, which comprises the following steps: preparing and mixing a reference substance solution; preparing a methanol solution of the Kouyanqing granules as a test solution; analyzing the reference substance solution and the test solution by a high performance liquid chromatography to obtain a high efficiency liquid chromatography finger print of the Kouyanqing granules; and comparing and monitoring the quality of the Kouyanqing granules according to a chromatogram map of the reference substance solution and a finger print of the test solution. The invention also discloses application of the quality control method in identifying the Kouyanqing granules. The quality control method adopts the high efficiency liquid chromatography to establish the finger print of the Kouyanqing granules, and can monitor the stability of technical processes for producing semi-finished products and finished products through the established standard finger print. The method effectively avoids counterfeiting of products, ensures normal production and circulation order of the products, and has outstanding practicability.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAIYUSN HUTCHISON WHAMPOA CHINESE MEDICINE +1
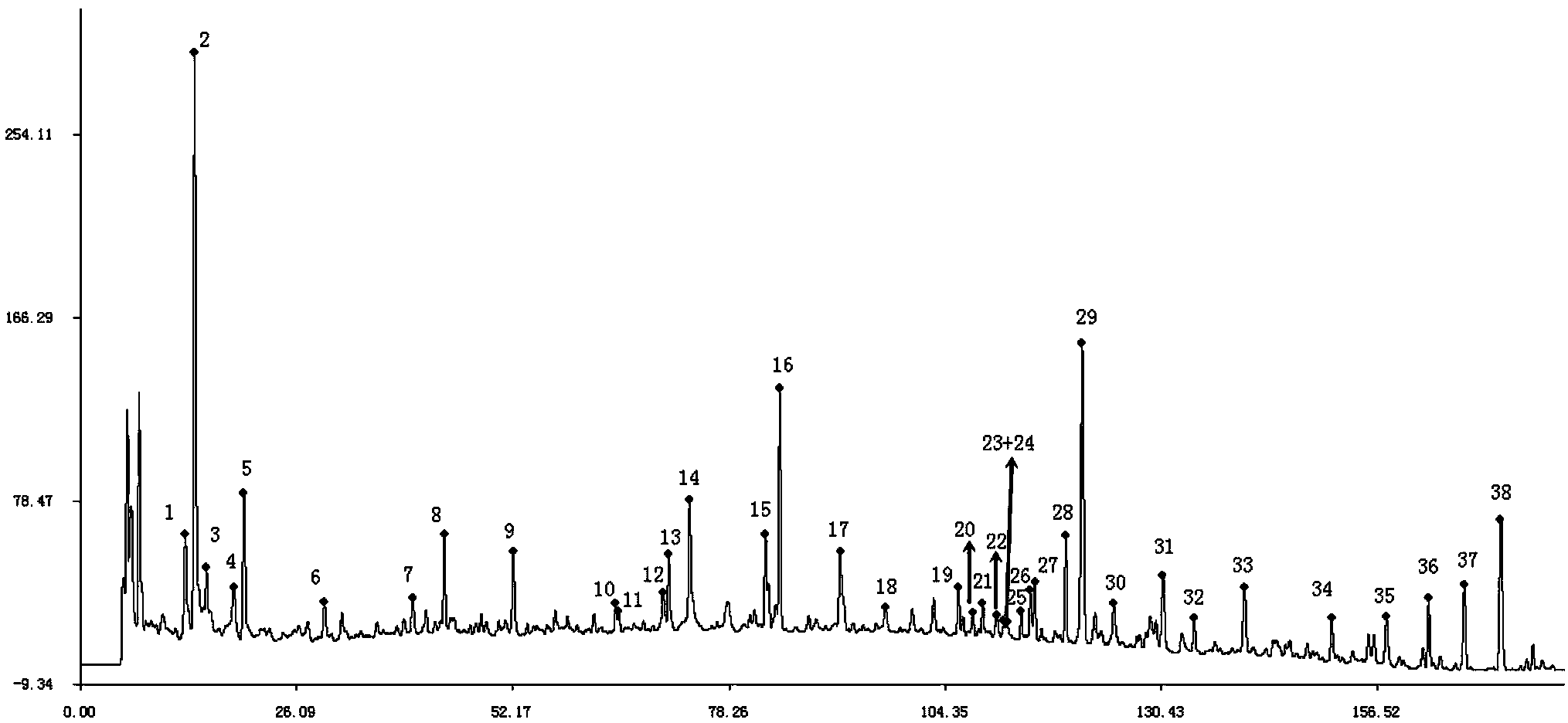
Shenqi hypoglycemic preparation HPLC standard finger print and construction method thereof
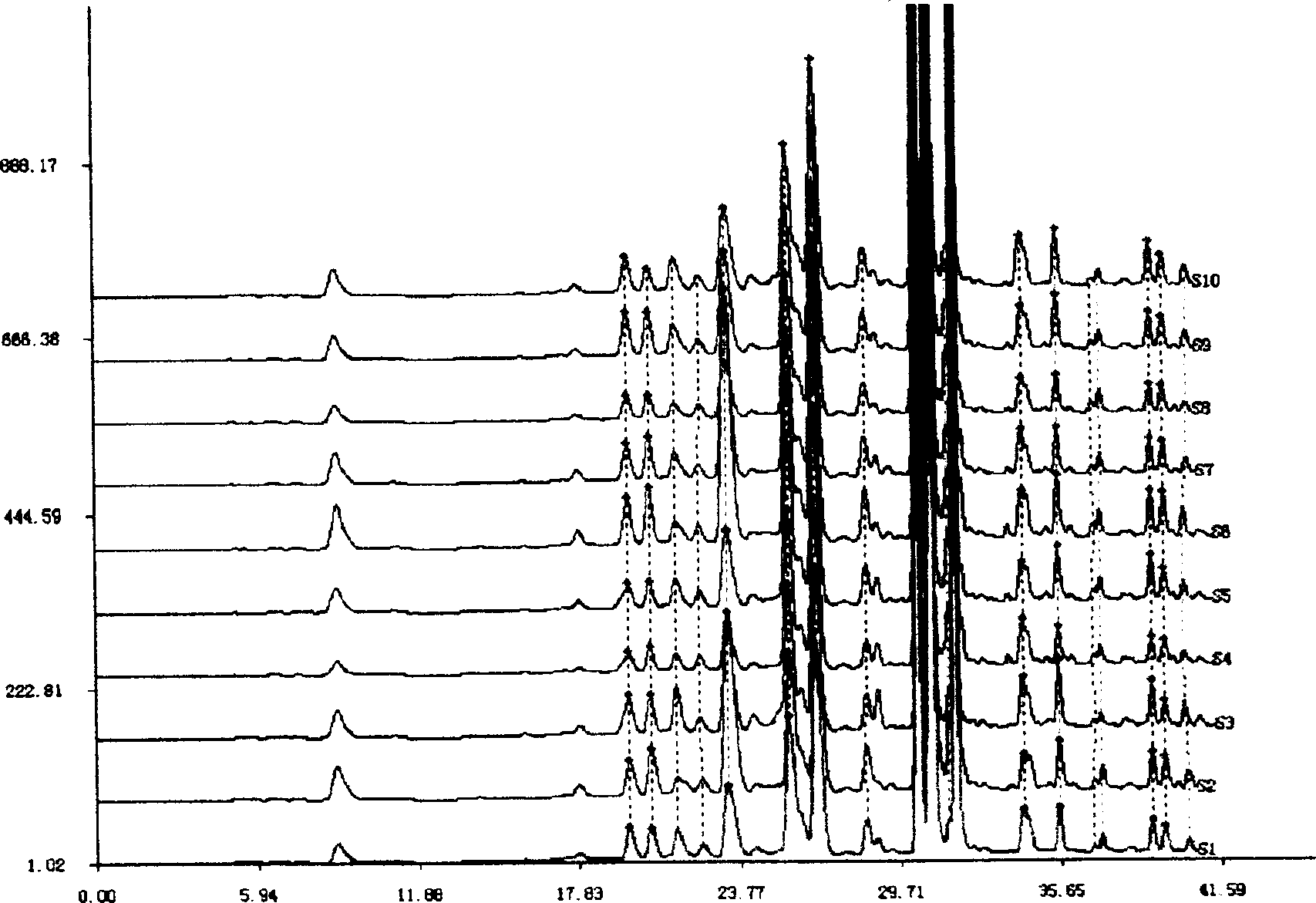
The present invention discloses a Shenqi hypoglycemic preparation HPLC standard finger print and a construction method thereof. The construction method comprises the following steps: preparing test sample solutions and a reference solution, measuring the test sample solutions and the reference solution by using the HPLC method and the linear gradient elution process, so as to obtain the Shenqi hypoglycemic preparation finger prints, wherein the chromatographic condition is that a mobile phase A is acetonitrile, a mobile phase B is 0.1% (v / v) phosphoric acid solution, the detection wavelength is 203nm, the column temperature is 25-35 DEG C and the flow rate is 0.8-1.2mL / min. The common characteristic peaks of at least ten finger prints are used as the characteristic peaks of the standard finger print; the standard finger print comprises 38 characteristic peaks, and the numbers of the characteristic peaks of saponin of ginseng stem and leaf, astragalus, Chinese magnoliaving, rehmannia root and raspberry are 13, 4, 7, 3 and 4 respectively. The Shenqi hypoglycemic preparation HPLC standard finger print and the construction method thereof can comprehensively and accurately evaluate the whole quality of the Shenqi hypoglycemic preparation, and facilitate to ensure the quality and the clinical curative effect of the Shenqi hypoglycemic preparation.
Owner:广东万年青制药股份有限公司
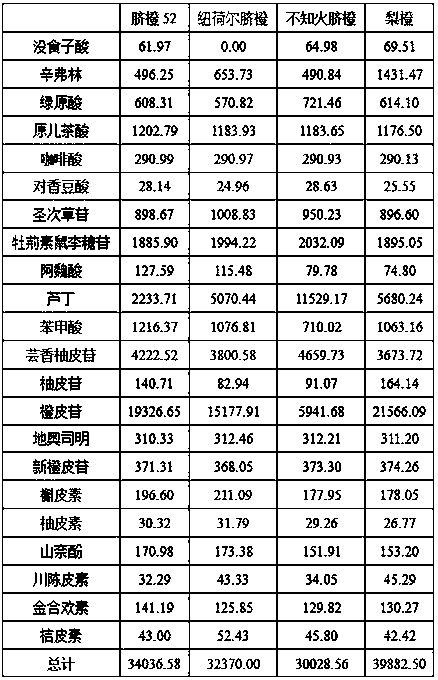
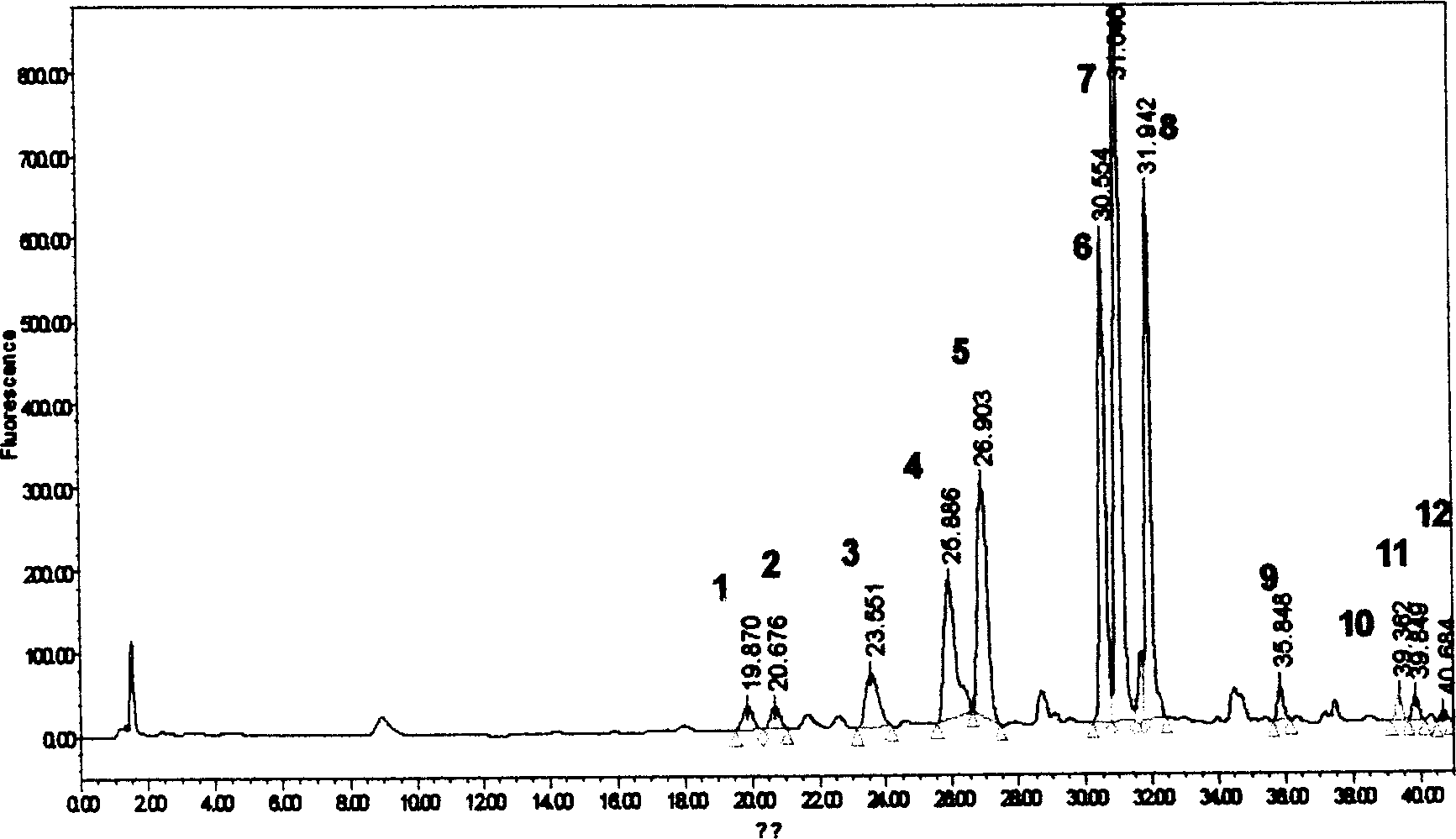
Method for simultaneously determining twenty-two flavones and phenolic acids in citrus fruits
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously determining twenty-two flavones and phenolic acids in citrus fruits by adopting high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector-fluorescence detector (HPLC-DAD-FLD). The method is capable of simultaneously determining twenty-two phenolic compounds in citrus fruits such as gallic acid, synephrine, chlorogenic acid, protocatechuic acid,caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, rhamnosylvitexin, eriocitrin, ferulic acid, rutin, benzoic acid, narirutin, naringin, hesperidin, diosmin, neohesperidin, quercetin, naringenin, kaempferol, nobiletin,hesperetin, acacetin and the like, derivatization is not needed, and the method is high in accuracy, high in sensitivity and excellent in repeatability.
Owner:INST OF AGRI ENG TECH FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method of simultaneously detecting various synthetic pigments in wheaten foods via HPLC-DAD
InactiveCN107748210AAvoid interferenceSimplify preprocessing stepsComponent separationHplc dadFood additive
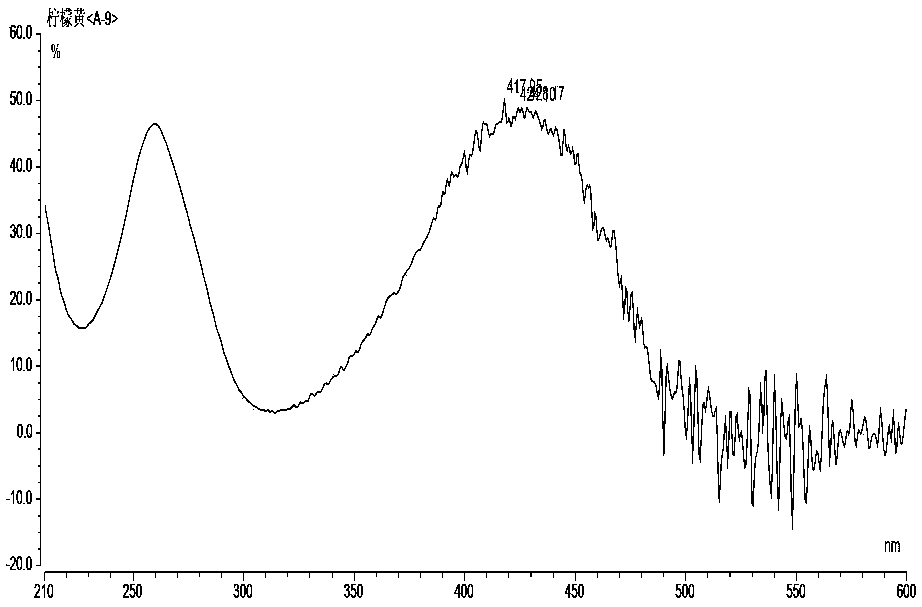
The invention relates to the technical field of detection of synthetic pigments and especially relates to a method of simultaneously detecting various synthetic pigments in wheaten foods via HPLC-DAD.The method includes the following steps: A) preparation of standard work solutions and samples; b) extraction of a sample solution; C) HPLC-DAD analysis to the solution prepared in the step B); D) calculation of content of to-be-detected substances with standard curve. In the HPLC-DAD detection method, pretreatment steps are simplified, wherein solid-phase extraction and concentration steps are avoided, thus reducing pretreatment time. Detection is carried under wavelength of 400-600 nm, so that interference due to majority of food additives and natural pigments is avoided. The method is accurate, quick and simple, has reliable quantitative results, can effectively detect ten artificially synthetic pigments in one time, and is very suitable for simultaneously treating samples in multi-batches.
Owner:昌邑市检验检测中心
Method for detecting amino acid component in Xiasangju preparation
ActiveCN1865988AEffectively Characterize QualityMonitor qualityComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationSodium acetrizoateFluorescence
The related detection method for amino acid content in Xiasangju preparation comprises: (a) preparing reference solution; (b) preparing sample solution; (c) chromatogram condition: using octadecylsilicane chemically bonded silica as filler, using the gradient elution liquid with 0.05~0.10mol / L NaAc solution buffer and 20-80% acetonitrile solution as mobile phase with pH value as 4.50-5.05, 30-50Deg temperature, activation wavelength 250nm, emission wavelength 395nm, flow rate as 0.5-1.5mL .min-1, and 30-80min; (d) obtaining the fingerprint spectrum with HPLC. This invention is simple and stable, and has well repeatability and precision.
Owner:GUANGZHOU XINGQUN PHARMA
Method for creating multi-index quantitative fingerprint spectrum for food retention-removing and cough-relieving oral solution for children
ActiveCN107315060ARaise quality standardsEnsure safe and rational drug useComponent separationHplc dadAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a method for creating a multi-index quantitative fingerprint spectrum for food retention-removing and cough-relieving oral solution for children, which includes the following steps: high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-diode array detector-electrospray ionization-quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry combination is adopted to detect chemical information characteristic peaks of a variety of common chemical substances in multiple batches of food retention-removing and cough-relieving oral solution for children, and according to the detected chromatographic peaks of a variety of the common chemical substances in the multiple batches of retention-removing and cough-relieving oral solution for children in combination with multi-index ingredient content determination, a fingerprint spectrum of the food retention-removing and cough-relieving oral solution for children is created. The method adopts the HPLC-DAD-ESI-Q-TOF / MS technique to analyze and identify chemical ingredients in the food retention-removing and cough-relieving oral solution for children, quality control indexes are chosen in reference to the principle of concerted application of Chinese herbal medicines and by referring to individual herb quality control indexes in one volume of 2015 edition of Chinese Pharmacopoeia and an identification result of each common peak, an HPLC multi-index quantitative fingerprint spectrum is created on the basis, and thereby a relatively comprehensive method and technical support are provided for the research on the evaluation of the overall quality of the food retention-removing and cough-relieving oral solution for children.
Owner:SHANDONG ANALYSIS & TEST CENT
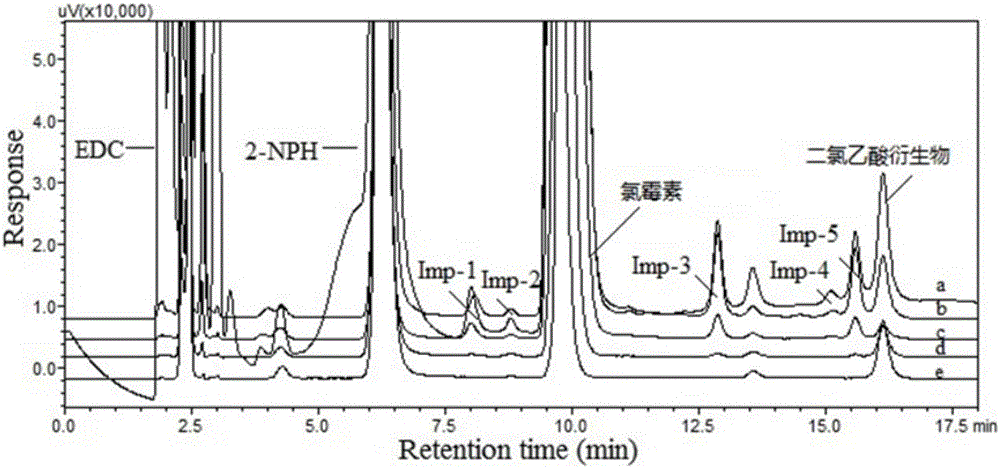
Method using derivatization HPLC-DAD method to determine small-molecule halogenated carboxylic acid in medicine
The invention discloses a method using a derivatization HPLC-DAD method to determine small-molecule halogenated carboxylic acid in medicine.The method includes: under normal temperature, using nitrobenzene hydrazine derivatization reagent to derivatize the small-molecule halogenated carboxylic acid so as to generate products with high absorption in the ultraviolet visible region; using the reaction liquid after the derivatization reaction as the feeding sample, and using the HPLC-DAD method to determine the derivatization products of halogenated carboxylic acid in the feeding sample in the ultraviolet visible region on the basis of the reversed phase partition chromatography principle so as to achieve the qualitative or quantitative detection of the small-molecule halogenated carboxylic acid.Due to the fact that the ultraviolet absorption band of the carboxylic acid derivatization products of the nitrobenzene hydrazine derivatization reagent has evident redshift effect due to the existence of nitro electron-withdrawing group on benzene ring and most medicine and impurities thereof are weak in absorption in the ultraviolet visible region (300-450 nanometers), the simple and universal method using pre-column derivatization HPLC-DAD to determine the small-molecule halogenated carboxylic acid is built.Methodology validation shows that the method is good in specificity.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Method for establishing Anoectochilus roxburghii fingerprint, and Anoectochilus roxburghii fingerprint and Anoectochilus formosanus Hay fingerprint
ActiveCN102768254AImprove quality controlQuality improvementComponent separationBiotechnologyHplc dad
The present invention discloses a method for establishing an Anoectochilus roxburghii fingerprint, and an Anoectochilus roxburghii fingerprint and an Anoectochilus formosanus Hay fingerprint. The method provided by the present invention comprises the following factors: (1) preparation of a test solution; (2) chromatographic condition: using an octadecylsilane bonded silica gel as a column filler; elution mode: using a gradient elution solution consisting of phosphoric acid and methanol as a mobile phase to conduct gradient elution; and ultraviolet detection with a detection wave length of 310-320nm; and (3) determination in accordance with a high performance liquid chromatography to obtain a fingerprint. The method provided by the invention employs high-performance liquid chromatography to establish the Anoectochilus roxburghii fingerprint and improve the level of quality control of Anoectochilus roxburghii; the invention provides an internal control peak fingerprint discrimination method to solve the problem of lack of reference substance for relevant components of Anoectochilus roxburghii; and the internal control peak is used as a reference to obtain stable relative retention time of each characteristic peak and relative peak area, and realize better precision of the method.
Owner:闽王(厦门)药业有限公司
Method for detecting acyl chloride in medicine or synthesized intermediate thereof by derivatization HPLC-DAD method
InactiveCN107014944AImprove stabilityObvious red shift effectComponent separationHplc dadRoom temperature
The invention discloses a method for detecting acyl chloride in a medicine or synthesized intermediate thereof by a derivatization HPLC-DAD method. The method comprises the following steps: derivatizing acyl chloride with a nitrophenylhydrazine derivatized reagent at room temperature to generate a product has relatively absorbability in an ultraviolet visible region; separating and detecting the derivatized product of acyl chloride in the ultraviolet visible region by using the derivatized reacting liquid as a feeding sample based on the principle of reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography so as to qualitatively or quantitatively detecting acyl chloride. Based on the quick reaction characteristic of acyl chloride and hydrazino and the ultraviolet visible absorption characteristic of the product generated after acyl chloride and nitrophenylhydrazine perform a biochemical reaction, interference of a medicine or the synthesized intermediate matrix thereof on acyl chloride detection can be effectively avoided, so that a simple and universal method for detecting acyl chloride in a medicine or synthesized intermediate thereof by a derivatization HPLC-DAD method can be established. Methodological verification results indicate that the method has excellent specificity and sensitivity.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Magnetic solid-phase extraction method of detecting ethoxyquine in fruits and vegetables
ActiveCN110133125AAchieve enrichmentAchieve extractionIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationHplc dadHydrogen
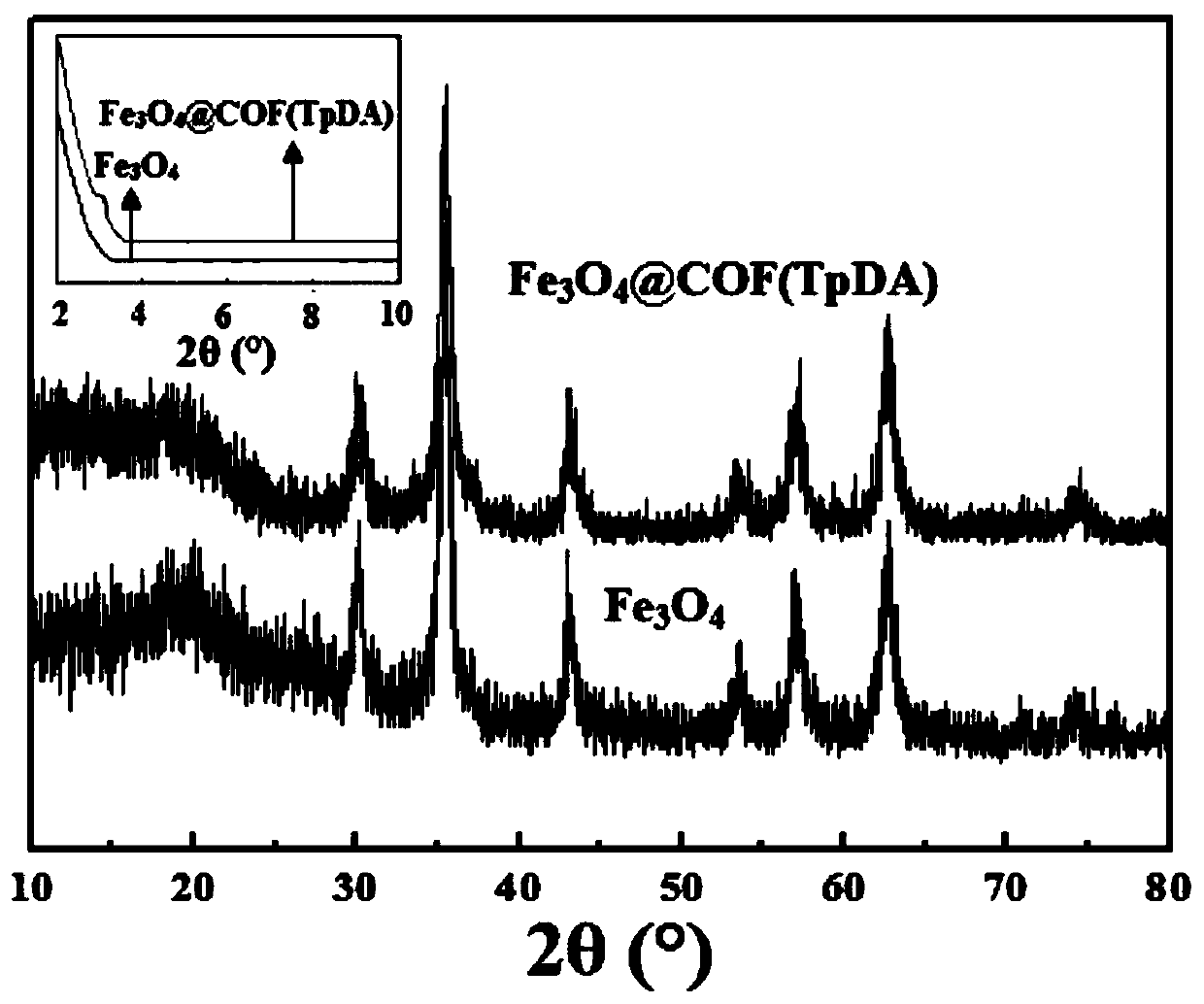
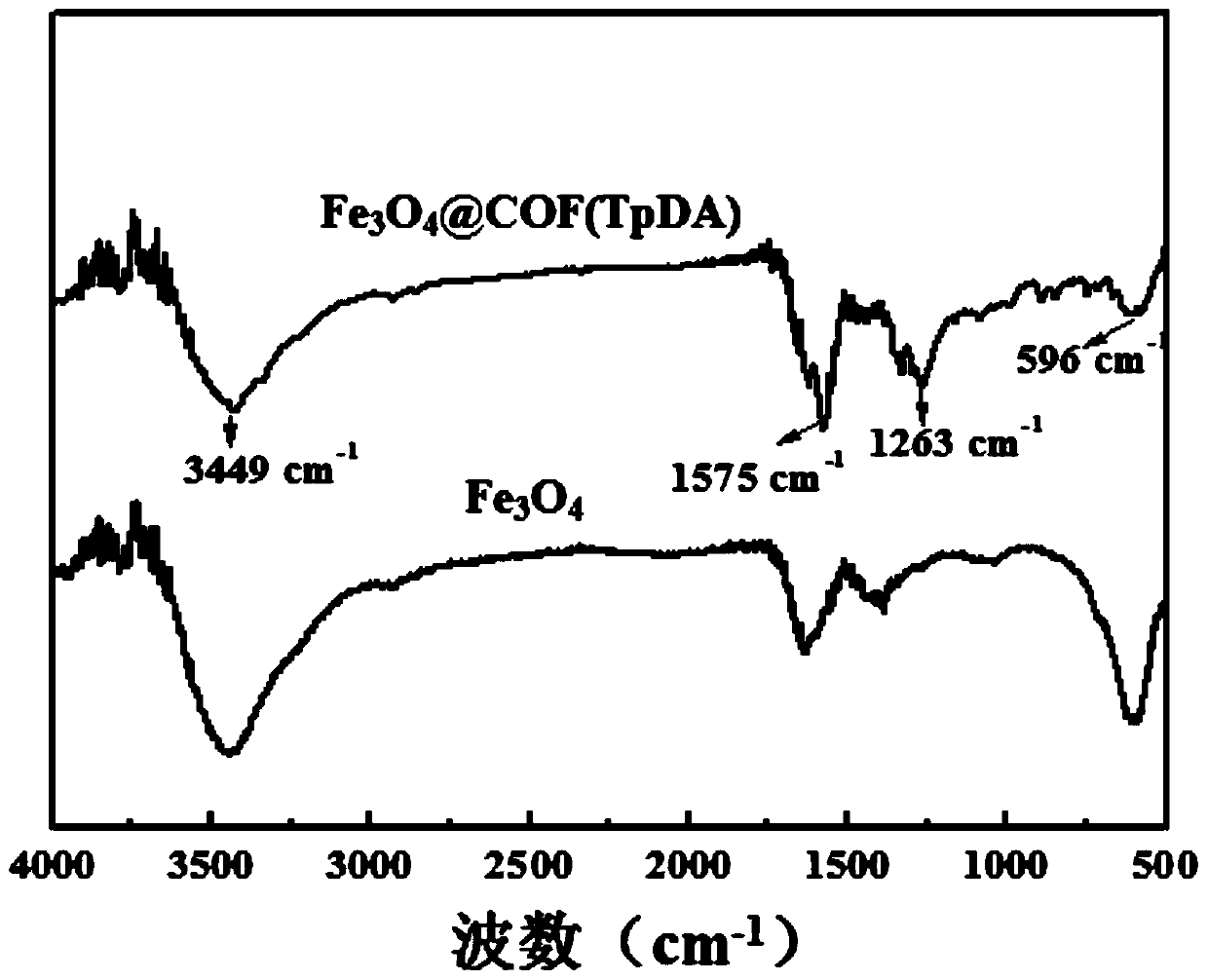
The invention discloses a magnetic solid-phase extraction method of detecting ethoxyquine in fruits and vegetables. The method uses a magnetic covalent organic skeleton material Fe3O4@COF(TpDA) as anadsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction, so as to extract ethoxyquine in fruits and vegetables. The method detects PGRs in fruits and vegetables by using an MSPE technology, and selects Fe3O4@COF(TpDA) as the adsorbent. The adsorbent is convenient to use, has multiple carbonyl and aromatic rings on the surface, can enrich and extract PGRs through hydrophobic interaction, pi-pi interaction and hydrogen bonds, has good extraction effect and high structure stability, can be reused, and can detect multiple trace PGRs in fruits and vegetables sensitively. In the method, MSPE of Fe3O4@COF(TpDA) and HPLC-DAD are combined for the first time for measuring PGRs, providing a new concept for detection of PGRs.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
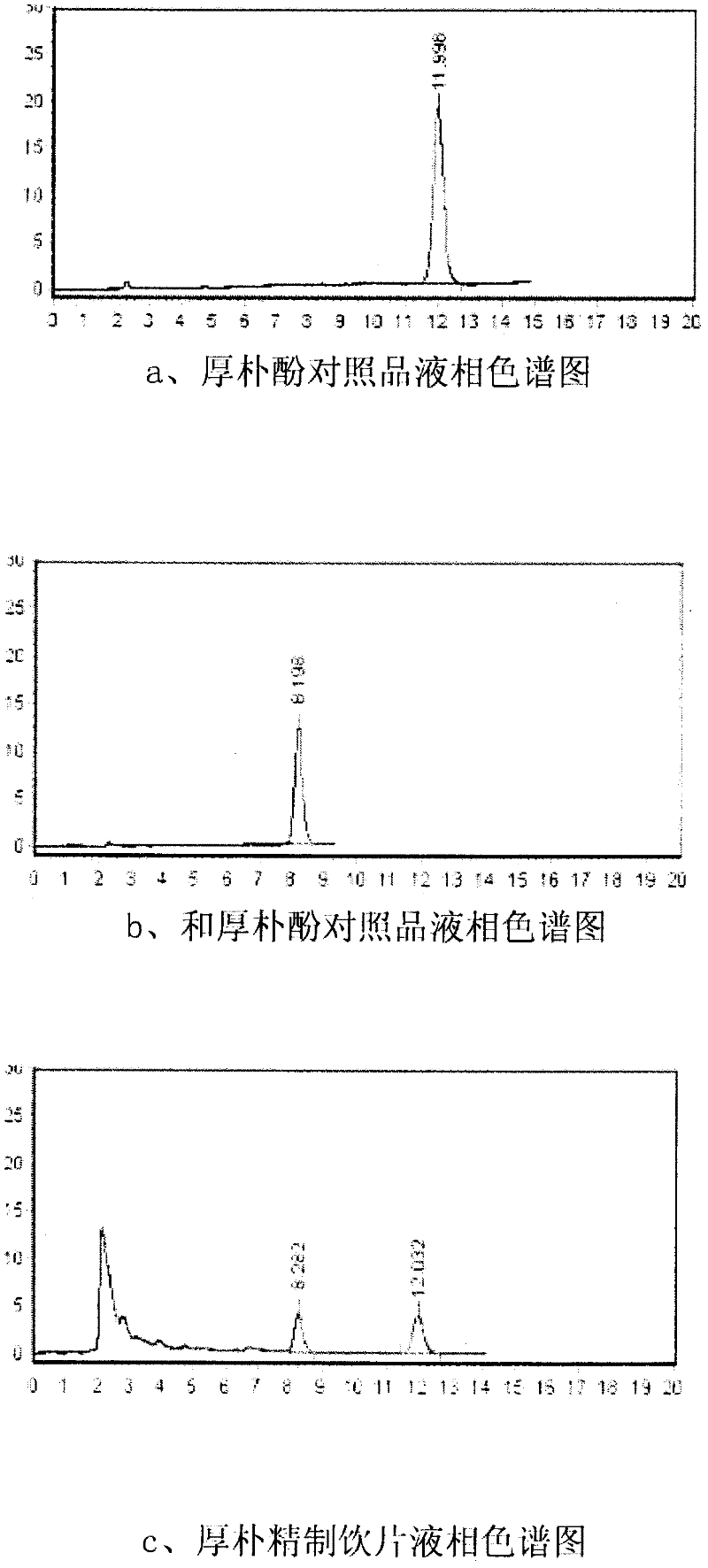
Quality control method of mangnolia officinalis refined medicinal slice
The invention relates to a quality control method of a mangnolia officinalis refined medicinal slice. The quality control method comprises the following steps that: the content of the mangnolia officinalis refined medicinal slice is determined by taking magnolol and a magnolol comparison product as comparisons through a high-performance liquid chromatography; the geoherbalism of contained mangnolia officinalis is determined by taking magnolol and magnolol as reference objects and taking relative retention time and relative retention peak area of a common peak of a high-performance liquid fingerprint through a high-performance liquid fingerprint method; the fact that whether the mangnolia officinalis exists and the content of the mangnolia officinalis can be detected; furthermore, the geoherbalism of the mangnolia officinalis is also further detected; and, due to specificity of traditional Chinese medicines, effects and performances of medicines are directly influenced by the geoherbalism of raw materials, which is recognized in the field; therefore, the quality control method disclosed by the invention is capable of ensuring that the quality of the mangnolia officinalis refined medicinal slice is steadier and more reliable.
Owner:重庆天生药业有限公司
Method for identifying regenerated polyester generated through chemical recycling method
ActiveCN105388241AStrongly nonlinear mappingAdaptableComponent separationBiological neural network modelsContent distributionPolyester
The content distribution difference of organic impurities entering a polyester macromolecular structure is an identification basis of protogenetic polyester and regenerated polyester generated through a chemical recycling method. A method for identifying the regenerated polyester generated through the chemical recycling method comprises the steps of depolymerizing the regenerated polyester generated through the chemical recycling method and the protogenetic polyester by adopting a methanolysis method, and extracting alcoholysate of trace organic impurities embedded into the polyester macromolecular structure; obtaining detection signal data by adopting HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography), and selecting detection signal data of a para orientation object of methyl benzoate; merging the detection signal data into a variable matrix, carrying out data preprocessing, then carrying out dimension reduction processing by adopting a PCA (Principle Component Analysis), extracting 2 to 6 principle components as characteristic variables, building a BP (Back-Propagation) artificial neural network to carry out a training and simulation verification by taking the obtained characteristic variables as input variables and protogenetic attributes and regenerated attributes of fiber as target variables, and identifying a to-be-identified sample to be the regenerated polyester generated through the chemical recycling method when a predicted value of the to-be-identified sample is matched with an attribute predicted value of the regenerated polyester generated through the chemical recycling method. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the accurate rate is high, and convenience and quickness are realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI TEXTILE GRP DETECTION STANDARD CO LTD +3
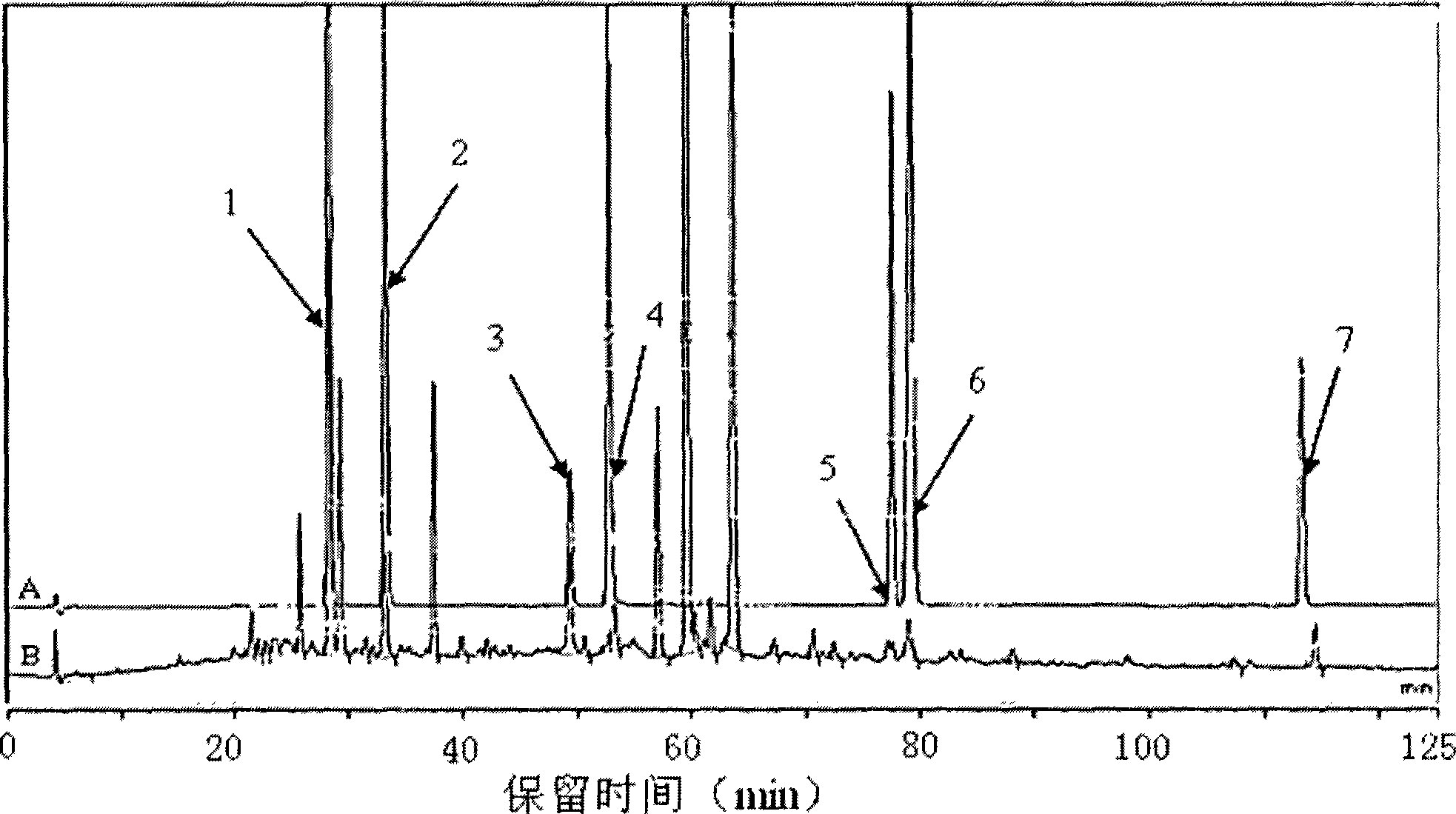
Fingerprint spectrum detection method and fingerprint spectrum of Yixinshu preparation
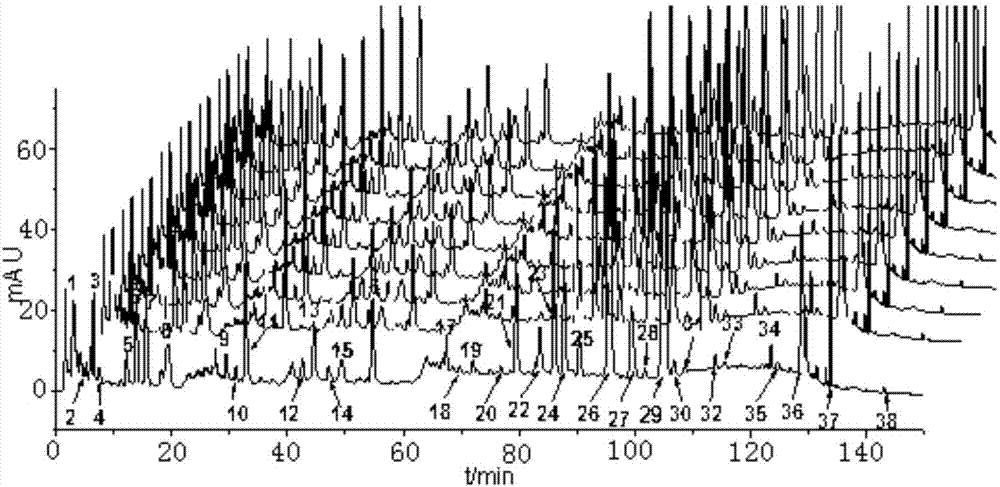
The invention discloses a fingerprint spectrum detection method and a fingerprint spectrum of a Yixinshu preparation. The fingerprint spectrum detection method comprises the following steps: by taking a schizandrin reference substance as reference, measuring the fingerprint spectrum by adopting high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The similarity of the HPLC fingerprint spectrum of the Yixinshu preparation established in the method and a reference spectrum is more than 0.9, the quality of the fingerprint spectrum can be effectively characterized, and the product quality is comprehensively monitored. Moreover, a common mode of the HPLC characteristic fingerprint spectrum of the Yixinshu preparation is established, 15 common peaks are calibrated, the established fingerprint spectrum is high in technical content, the simplicity and one-sidedness of the quality control of the Yixinshu preparation are avoided, and the possibility that the quality of the artificially handled product reaches the standard is reduced.
Owner:GUIZHOU XINBANG PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Method for evaluating color, flavor and taste multicomponent quantification combination fingerprint quality of saffron
ActiveCN106645529AImprove securityImprove effectivenessComponent separationHplc dadChemical composition
The invention discloses a method for evaluating color, flavor and taste multicomponent quantification combination fingerprint quality of saffron. According to the method, first an HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn technology is adopted to analyze and identify representative ingredients of color, flavor and taste in the saffron which are crocin, safranal and picrocrocin and the like, and 7 crocins, picrocrocin, aglycone (HTTC) of picrocrocin, safranal and 2 kaempferols are identified as flavonoids of aglycone. On the basis of color, flavor and taste multicomponent and mass spectrum identification in saffron, a wavelength switching HPLC-DAD technology is utilized to construct the method for multicomponent quality evaluation through the color, flavor and taste multicomponent quantification combination fingerprint, comprehensive quality analysis can be performed on saffron, and clinical application safety and effectiveness of saffron are improved.
Owner:HUZHOU CENT HOSPITAL
Method for chiral separation of various side chain protected amino acids
InactiveCN102824900ASolving Chiral Separation ProblemsLow costOther chemical processesOrganic compound preparationHplc dadFluid phase
The invention relates to a method for chiral separation of various side chain protected amino acids, and aims to solve the technical problems that a mobile phase system used in an HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) chiral separation system is complex and chiral HPLC columns are instable. According to the technical scheme, the method is characterized by including the steps of a, dissolving four racemates in methanol and water solution, performing ultrasonic treatment, filtering, and taking filtrate for standby; b, allowing well balanced chiral HPLC columns to respectively absorb the filtrate which is sent to the HPLC system, allowing a chromatographic work station to acquire chiral separation chromatograms, and checking separation parameters to acquire amino acid separation effects. Mobile phase used by the method is a common reagent in HPLC. A HPLC instrument needs no other instruments, cost is saved, and the various side chain protected amino acids can be chirally separated fast.
Owner:GL BIOCHEM SHANGHAI +2
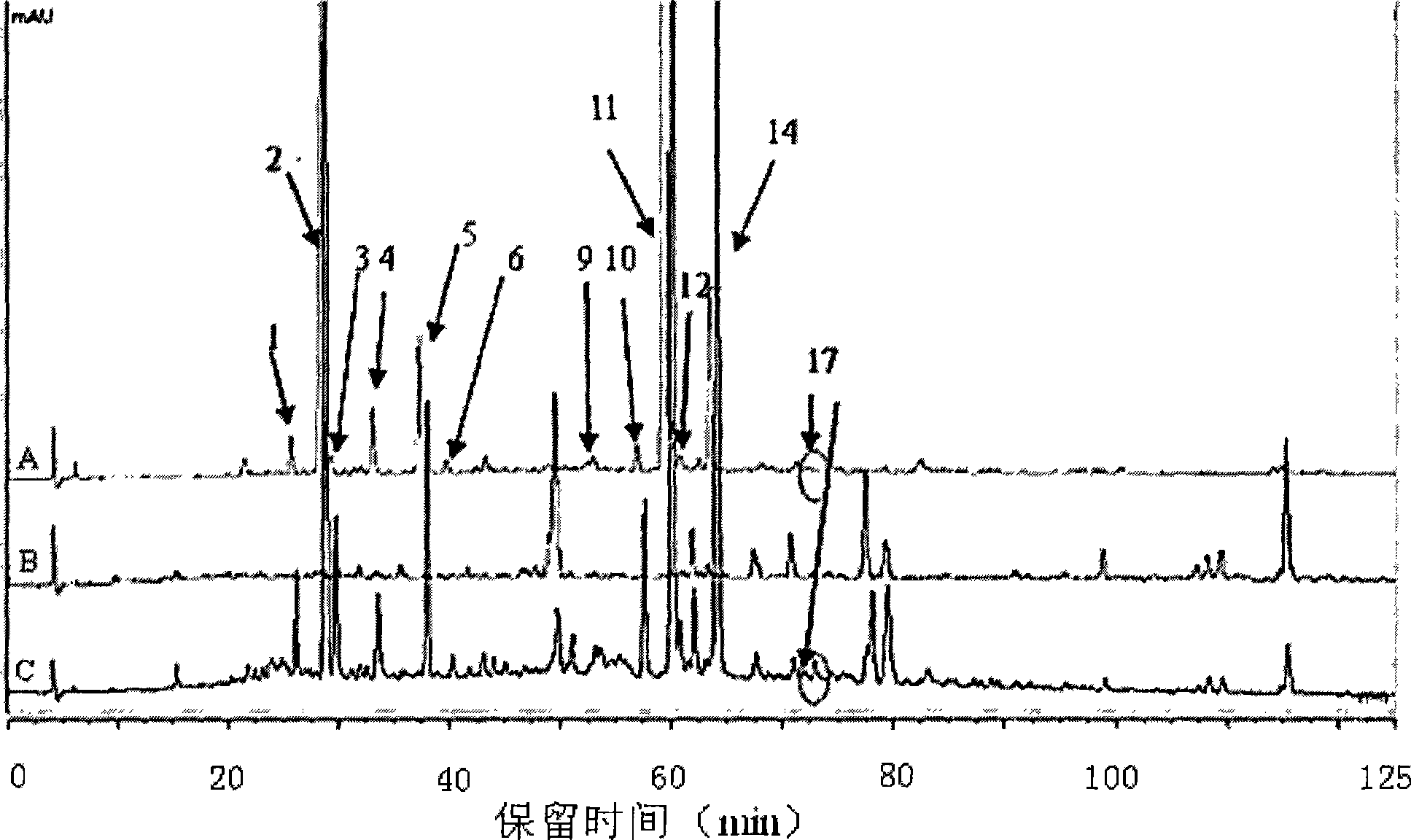
Detection method of fingerprint spectrum of astragalus membranaceus and poria cocos kidney invigoration tablet and obtained fingerprint spectrum of astragalus membranaceus and poria cocos kidney invigoration tablet
ActiveCN107782811ACharacterizing qualityImprove the quality evaluation systemComponent separationRepeatabilityComputer science
The invention discloses a detection method of a fingerprint spectrum of an astragalus membranaceus and poria cocos kidney invigoration tablet and the fingerprint spectrum of the astragalus membranaceus and poria cocos kidney invigoration tablet. According to the method, a standard fingerprint spectrum of the astragalus membranaceus and poria cocos kidney invigoration tablet is established; high performance liquid chromatography and gradient elution are adopted; the number of theoretical plates is calculated according to a sinomenine peak and is not less than 100000. The similarity between thefingerprint spectrum of the astragalus membranaceus and poria cocos kidney invigoration tablet obtained by the method and a control fingerprint spectrum is greater than 0.9; the fingerprint spectrum can comprehensively and effectively characterize quality of the astragalus membranaceus and poria cocos kidney invigoration tablet; a quality evaluation system of the astragalus membranaceus and poriacocos kidney invigoration tablet is perfected; the obtained fingerprint spectrum of the astragalus membranaceus and poria cocos kidney invigoration tablet has many characteristic peaks and is high insimilarity; the quality of the astragalus membranaceus and poria cocos kidney invigoration tablet can be monitored accurately and reliably; the detected fingerprint spectrum is recognized by a traditional Chinese medicine chromatographic fingerprint spectrum similarity evaluation system provided by Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission; the fingerprint spectrum of the astragalus membranaceus and poriacocos kidney invigoration tablet is evaluated according to an obtained similarity result; a conclusion is relatively objective and accurate; and the method has the advantages that the method is simpleand convenient, excellent in stability, high in precision, good in repeatability and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU KANION PHARMA CO LTD
Sensor for detecting phenolic substance in compost and detection method thereof
InactiveCN1837809AIncreased sensitivityImprove anti-interference abilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpecial data processing applicationsLinear regressionPhenol
This invention relates to a sensor for detecting phenolic substance in compost and detection method thereof. With the carbon paste electrode modified with laccase-Fe3O4 magnetic nano grain as the work electrode to detect the response current variation of compost leachate in tri-electrode electrolytic bath; with given regression equation that is linear for hydroquinone of 1*10-7~1.375*10-4M and pyrocatechin of 5*10-8~2.75*10-4M, and computing the phenol content in compost. This invention is faster than HPLC and overcomes the defects in spectrophotometry, and has wide application for domestic garbage compost control system.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for controlling quality of Jinji preparation
ActiveCN101721530AComponent separationSexual disorderControl qualityHigh-performance liquid chromatography
The invention discloses a method for controlling quality of a Jinji preparation. The method adopts the high performance liquid chromatography, has good precision, stability and reproductivity and can effectively control the quality of the Jinji preparation products.
Owner:广西葛洪堂药业有限公司
Quality detection method of desepidine
ActiveCN101042381AAvoid product qualityGuarantee product qualityComponent separationTesting medicinal preparationsTest samplePeak area
This invention discloses one Disheping quality test method, which can control its product quality effectively and tests the relative subject, mapping abnormal part content by use of effective liquid phase spectrum, wherein, the relative subject and abnormal structure provides test sample liquid spectrum peak area less than comparison main peak area and the content measuring is no less than 98.5 percent and the weight metal test is not more than ten of million and the dry loss is no more than 0.5 percent and the burst resides no more than 0.3 percent.
Owner:CHANGCHUN MAILING BIOLOGICAL ENG CO LTD
Method for identifying litchi honey
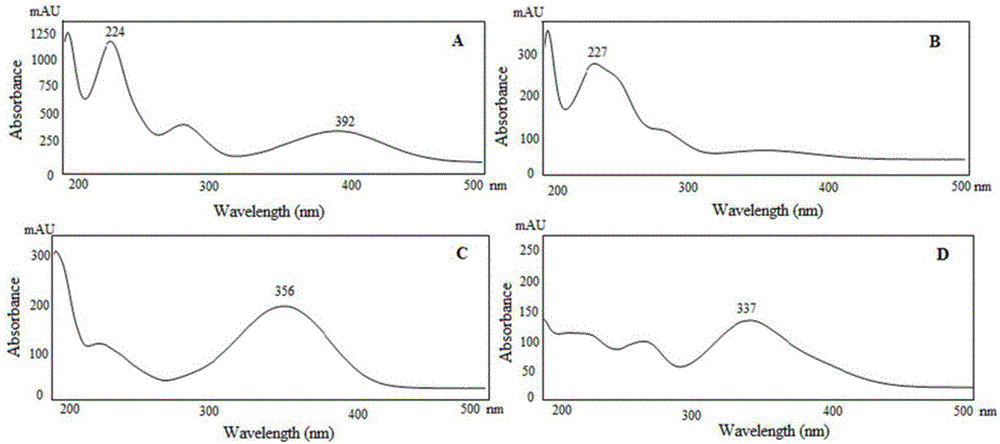
The invention discloses a method for identifying litchi honey. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing an HPLC-DAD (High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Diode Array Detection) fingerprint chromatogram of litchi honey, chaste honey and rape honey so as to determine characteristic markers of the litchi honey; then, separating and purifying the determined characteristic markers according to a preparative liquid chromatography so as to respectively obtain two kinds of characteristic markers with higher purity; and finally, analyzing the molecule information of the characteristic markers by using a quadrupole / time-of-flight mass spectrometer so as to finally determine that the molecular weight of the two kinds of characteristic markers is 264 and the molecular formulais C15H20O4, thereby conjecturing that the two kinds of characteristic markers are isomers. The method disclosed by the invention is reasonable in design, and the selected analytical instrument is high in sensitivity, high in analysis speed, high in separation efficiency and highstrong in feasibility and provides a basis for authenticity identification and quality control of the litchi honey.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN) +1
Simultaneous measuring method of various feeding condiments
The invention discloses a simultaneous measuring method of various feeding condiments. An efficient liquid-phase chromatography is adopted, octadecylsilane chemically bonded silica is used as a filling agent, column temperature is 30 DEG C, flow velocity is 1.0 mL / minute, and A (acetonitrile) and B (trifluoroacetic acid liquor with mass fraction of 0.1%, and pH of the trifluoroacetic acid liquor is regulated to 4.0 by triethylamine) are used as mobile phases to carry out gradient elution and 229nm-282nm variable-wavelength detection, so that content of 7 feeding condiments (I+G, acesulfame potassium, saccharin sodium, vanillin, maltol, ethyl maltol and NHDC (Dihydrochlcone) can be simultaneously measured, and therefore, the simultaneous measuring method is accurate and sensitive in detection, good in repeatability, economic and efficient, time-saving and labor-saving.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Quality control method for red sage root and notoginseng preparation
The invention relates to a HPLC-DAD fingerprint pattern identification method for the compound of salvia miltiorrhizae and pseudo-ginseng, which can be applied as one of the quality control indexes for compound preparations containing salvia miltiorrhizae and pseudo-ginseng medicinal materials such as Danqi tablet, compound salvia miltiorrhizae tablet and compound salvia miltiorrhizae drop pill.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Solid phase micro-extraction method of unsaturated compounds
ActiveCN109030677AReduce distractionsEasy to separateComponent separationHplc dadSolid-phase microextraction
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Detecting method of traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating coronary heart disease
InactiveCN108614066AGood peak symmetryExperimental results have no effectComponent separationSalvianolic acid BCoronary heart disease
The invention discloses a detecting method of a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating coronary heart disease. A formula is prepared from radix salviae miltiorrhizae, fructus piperis longi, lignum aquilariae resinatum, lignum dalbergiae odoriferae, semen myristicae, rhizoma kaempferiae, fructus choerospondiatis, lignum santali albi, fructus hippophae and lignum pterocarri accordingto a certain weight proportion and is prepared into capsules; the fructus piperis longi and the lignum aquilariae resinatum are distinguished by using TLC (Thin-Layer Chromatography); the content of salvianolic acid B by using HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography). The detecting method disclosed by the invention is capable of effectively ensuring the product quality during production and using of the traditional Chinese medicine composition, so that the curative effect of medicine products is ensured.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA TIANQI HAN&MONGOLIA PHARMA CO +1
HPLC-DAD method for determinating quetiapine drug concentration of human serum
The invention relates to the technical field of clinical blood concentration monitoring of psychotropic drugs, in particular to an HPLC-DAD method for determinating quetiapine drug concentration of human serum. The invention provides a method for determinating the quetiapine concentration of the serum after a quetiapine drug is taken. The method comprises the following steps: pretreating a human serum sample and performing high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC-DAD) analysis. The invention establishes the HPLC-DAD method with strong specificity, high sensitivity and high reproducibility.By the method for determinating the quetiapine blood concentration, established for the first time, verification results in aspects of accuracy, precision, specificity, stability and the like meet analytical requirements of the 2015 edition of relevant guiding principles of the Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China (9012) on a biological sample.
Owner:沈阳和合医学检验所有限公司
Method for establishing fusion-deduction fingerprint spectrum and application thereof in quality control of Yixuesheng capsule
ActiveCN110274970ASolve the problem of excessive proportion of the wholeHigh precisionComponent separationHplc dadQuality control
The invention relates to a method for establishing a fusion-deduction fingerprint spectrum and the application thereof in the quality control of Yixuesheng capsule. The method comprises the steps of selecting m detection wavelengths by high-performance liquid chromatography, detecting a sample to be tested at the detection wavelengths separately in order that a detection component in the sample to be tested has a large response value at at least one of the detection wavelengths; then selecting n deduction wavelengths, detecting the sample to be tested at the deduction wavelengths separately in order that the detection component in the sample to be tested has a low response value or no absorption at the deduction wavelengths and a non-detection component has a large response value at at least one of the deduction wavelengths; and then fusing the chromatographic peak information obtained by the detection wavelengths, and deducting the chromatographic peak information obtained from the deduction wavelengths to obtain a fusion-deduction fingerprint spectrum. The method obtains the most comprehensive and most accurate characteristic information of the Yixuesheng Capsule as much as possible, and solves the incomplete or inaccurate characteristic information or high noise of the traditional fingerprint spectrum technology.
Owner:JILIN JINFUKANG PHARMA
HPLC method based method for detecting kappa-casein typing
The invention provides a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method based method for detecting kappa-casein typing in milk. A provided HPLC method can be utilized to perform typing on two variants which are AE-kappa casein and B-kappa casein in milk, so that the B type kappa casein which can enhancing cheese output can be obtained.
Owner:北京市畜牧总站 +1
Method for simultaneously determining four components in herba cynomorii
InactiveCN107290442AGuaranteed separation effectAccurate methodComponent separationGallic acid esterGradient elution
The invention provides a method for simultaneously determining four components in a herba cynomorii-containing sample, in particular to a method for simultaneously determining gallic acid, protocatechuic acid, catechin and phlorizin in the herba cynomorii-containing sample by using a high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). According to the method, a standard product solution and a sample solution are determined by using the HPLC, and multi-gradient elution is carried out by using acetonitrile and 0.05% of a glacial acetic acid solution as mobile phases, so that the four components can be determined. Compared with the chemical composition determination method in the prior art, the method provided by the invention is simple in operation process, good in repeatability and high in accuracy, avoids the consumption of time and cost, can be used as an effective method for quantitatively controlling the quality of herba cynomorii, and is also used for detecting herba cynomorii-related effective components in Chinese patent medicines.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com