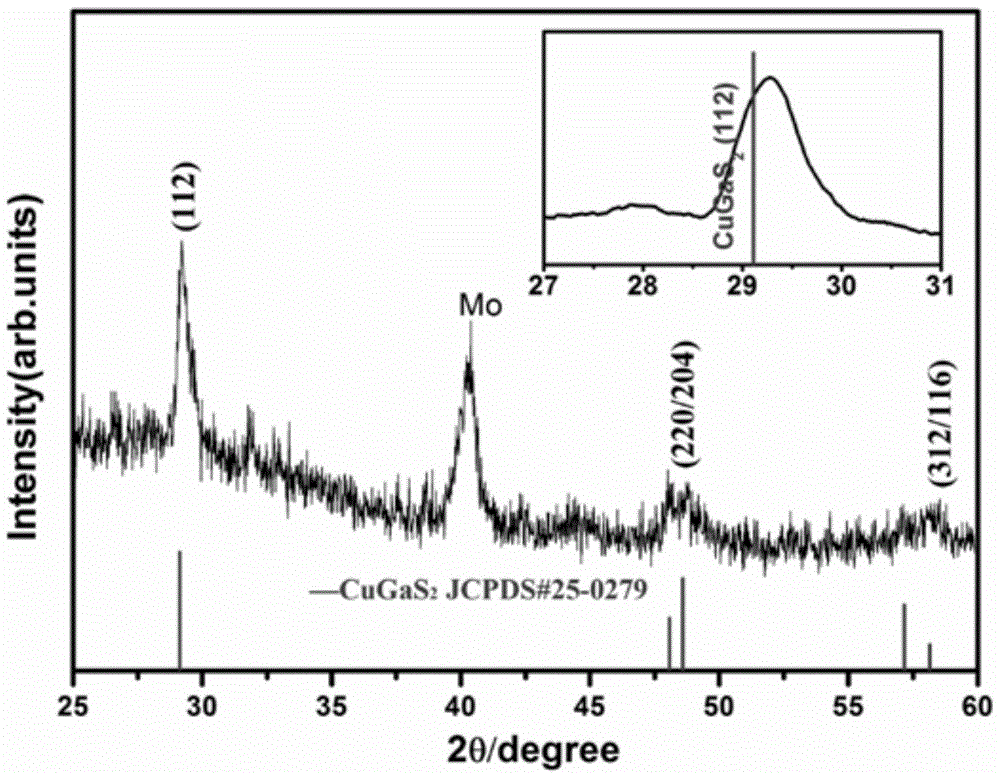
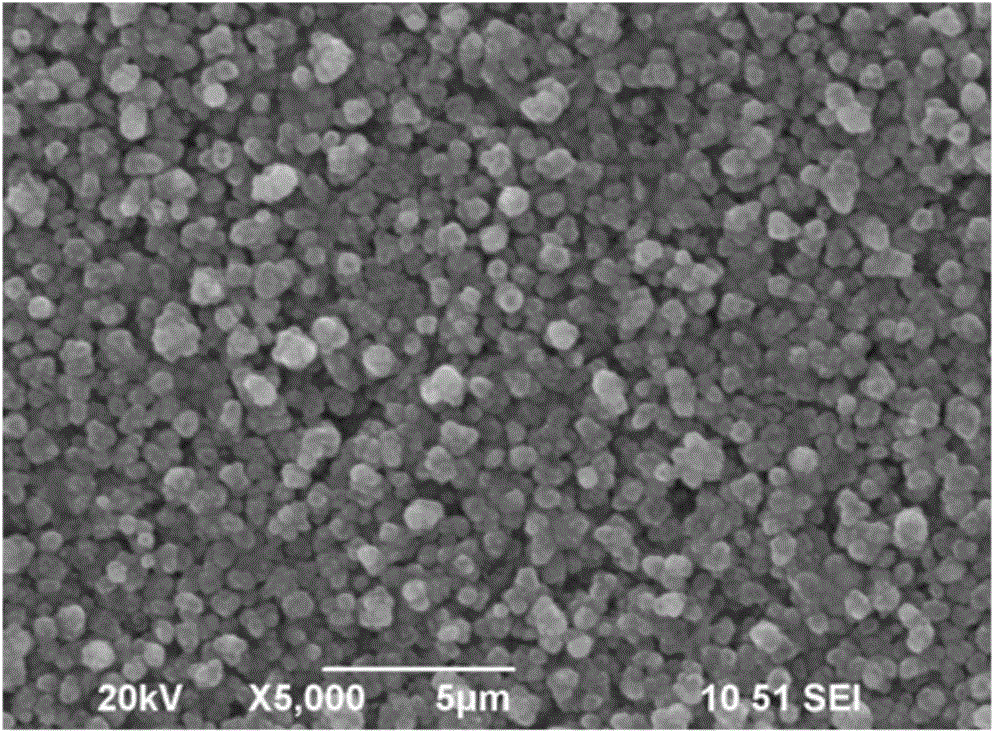
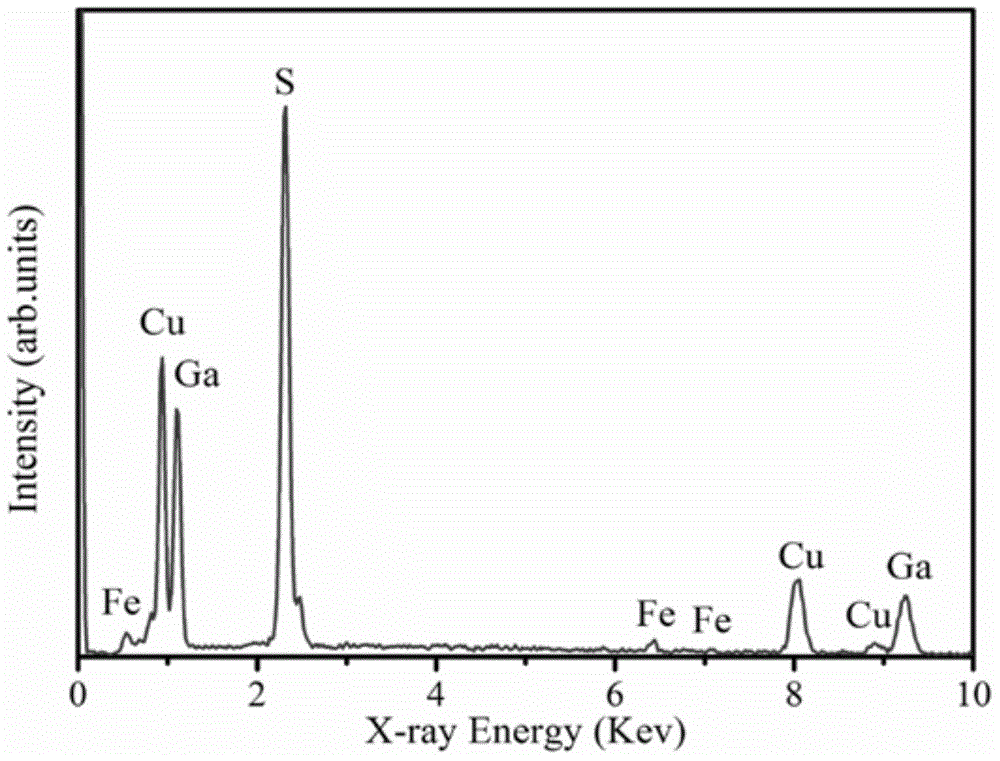
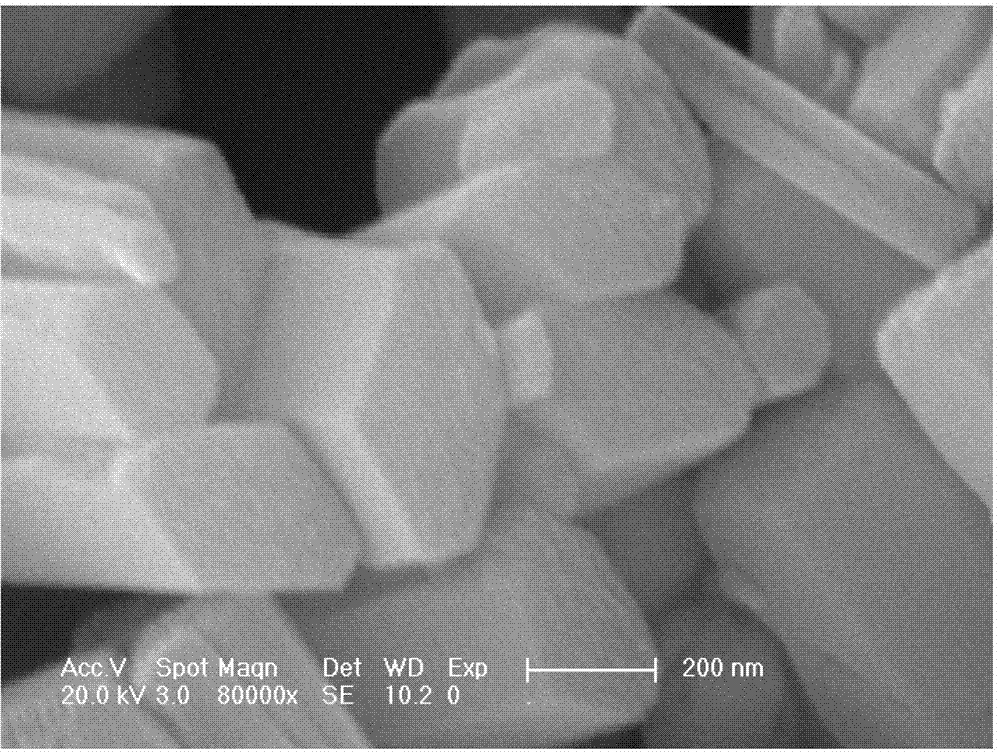
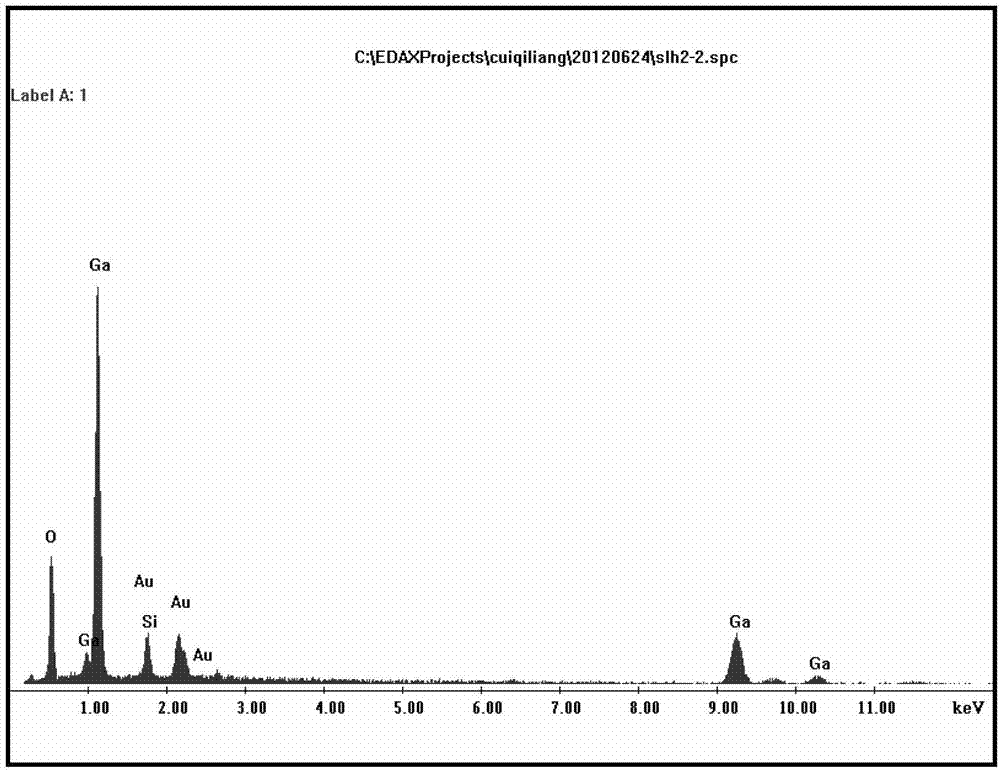
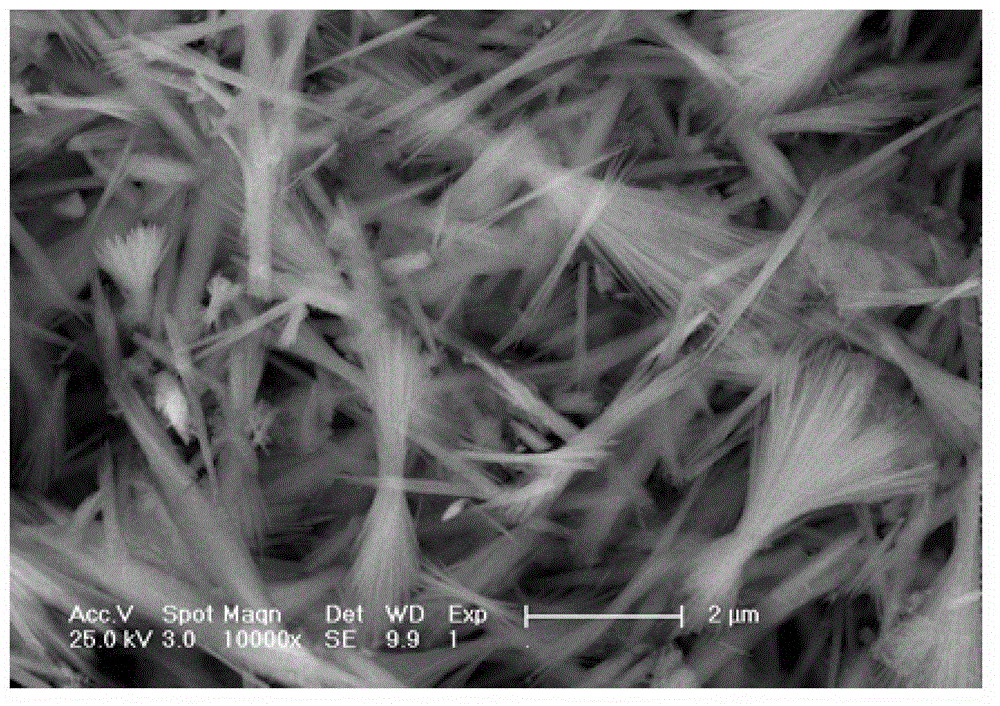
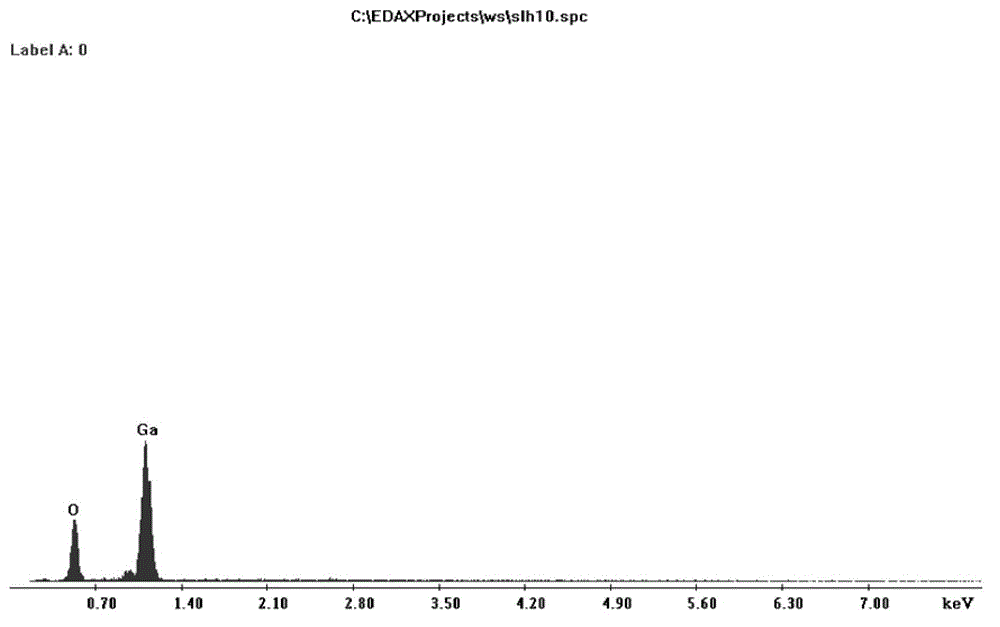
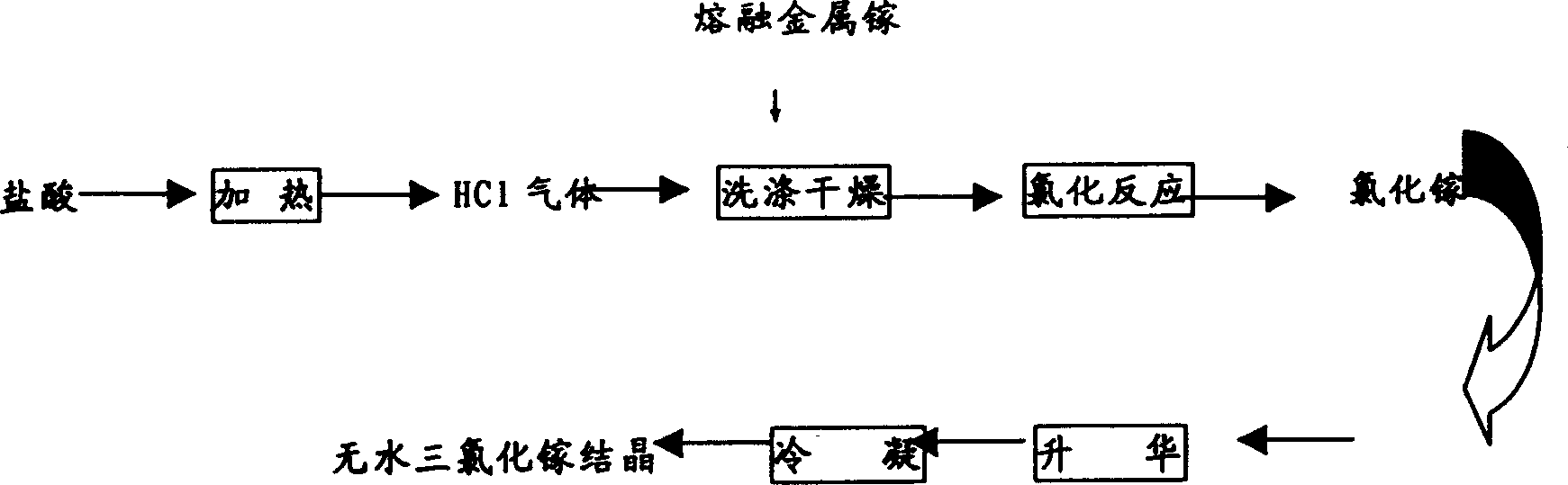
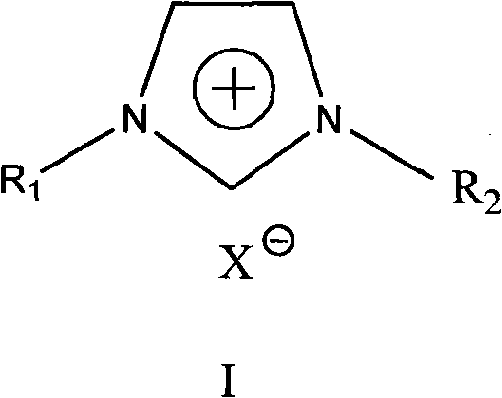
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
95 results about "Gallium chloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
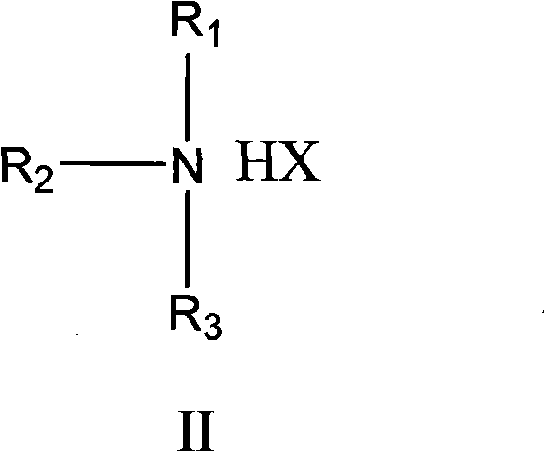
Gallium chloride may refer to: Gallium trichloride, GaCl₃ Gallium dichloride, GaCl₂
Production technique for extracting gallium from coal ash and coal gangue
ActiveCN101255504AEfficient use ofCreate pollutionProcess efficiency improvementLiquid wasteOn column
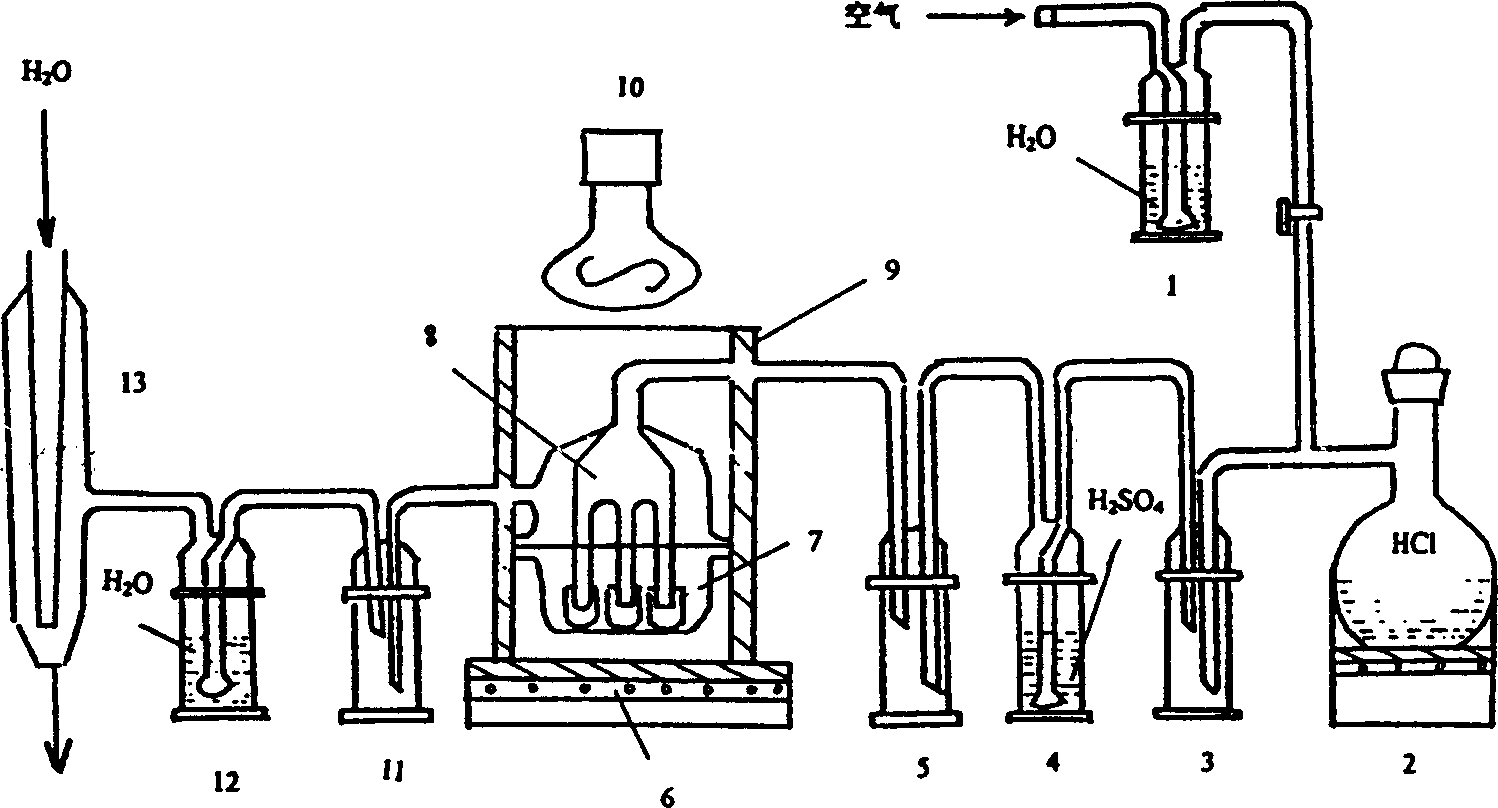
The invention discloses a production process for extracting gallium from flyash and coal refuse, which recycles gallium by further deep utilizing the produced waste liquid on the basis of extracting alumina, silica gel from coal series solid waste. According to the invention, gallium chloride is acquired after middle temperature calcinations, leaching, carbon dioxide decomposition, direct adsorption on column, eluting, etc., problems of large slag and low slag utilization added value in current technology are solved, the extraction rate of gallium form flyash and coal refuse can reaches over 80%; the whole process is performed under normal atmosphere, thus the equipment requirement is low, resources are effectively utilized during the whole process, and no new pollution is caused to surrounding environment.
Owner:潘爱芳
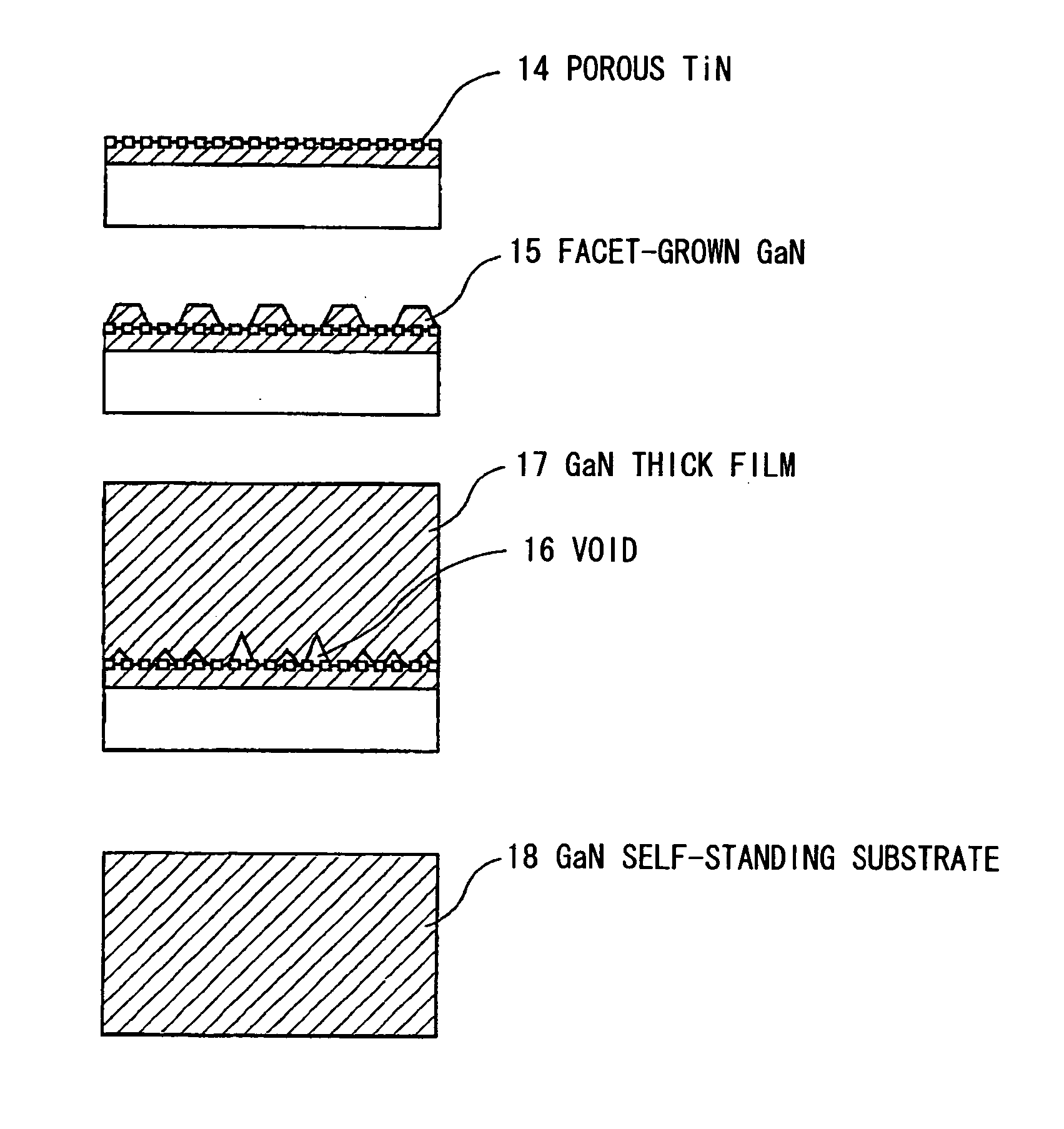
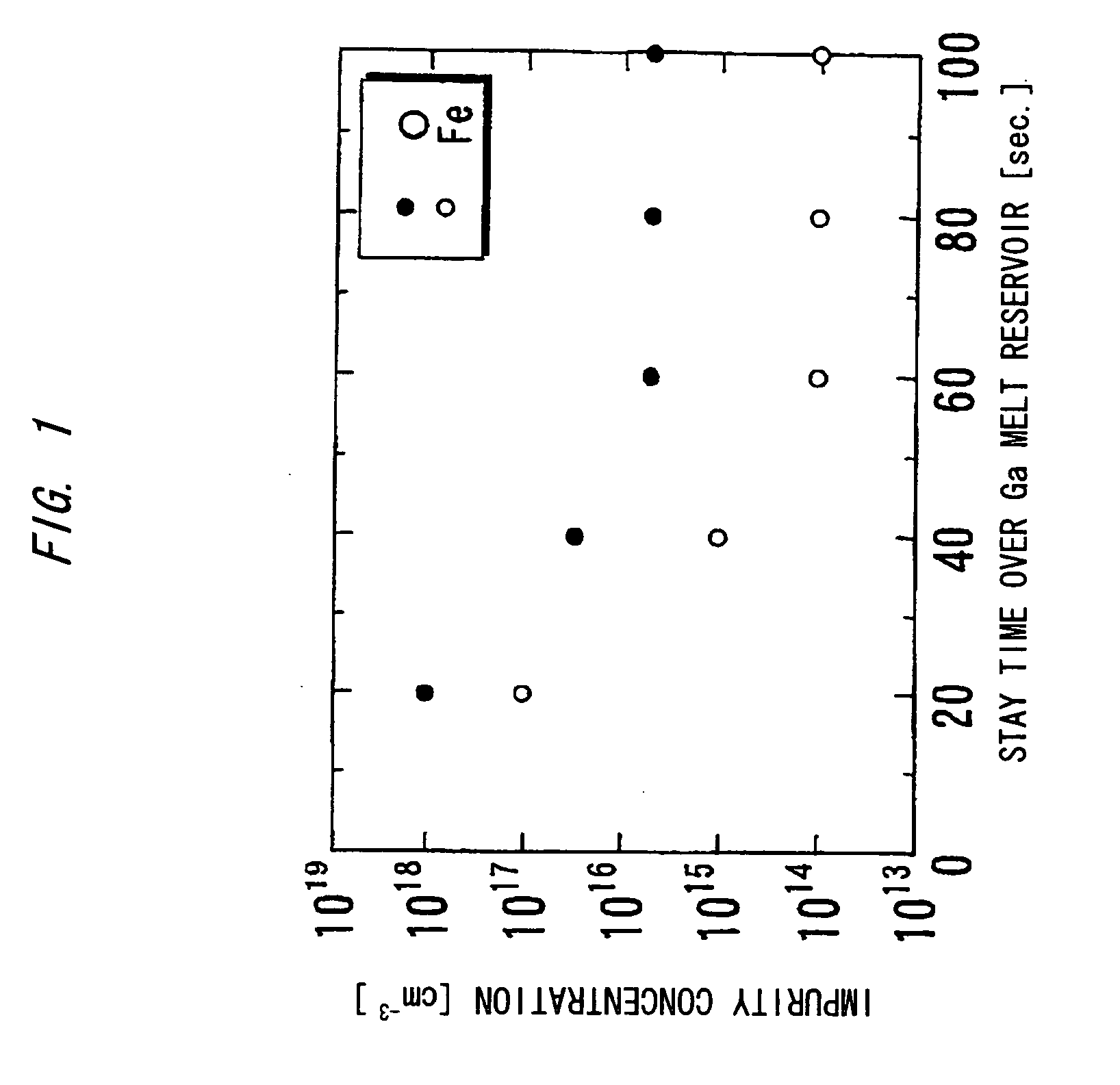
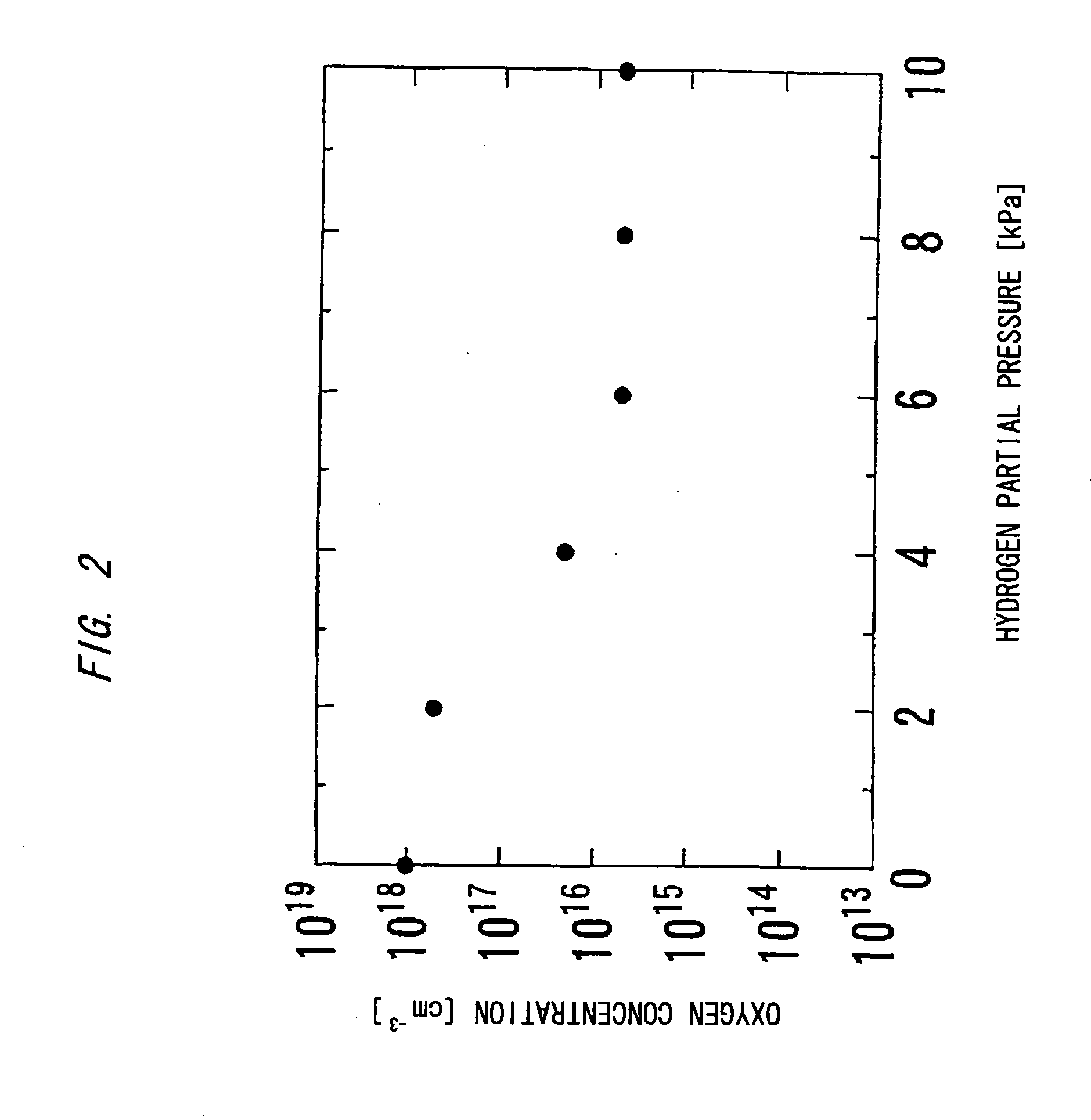
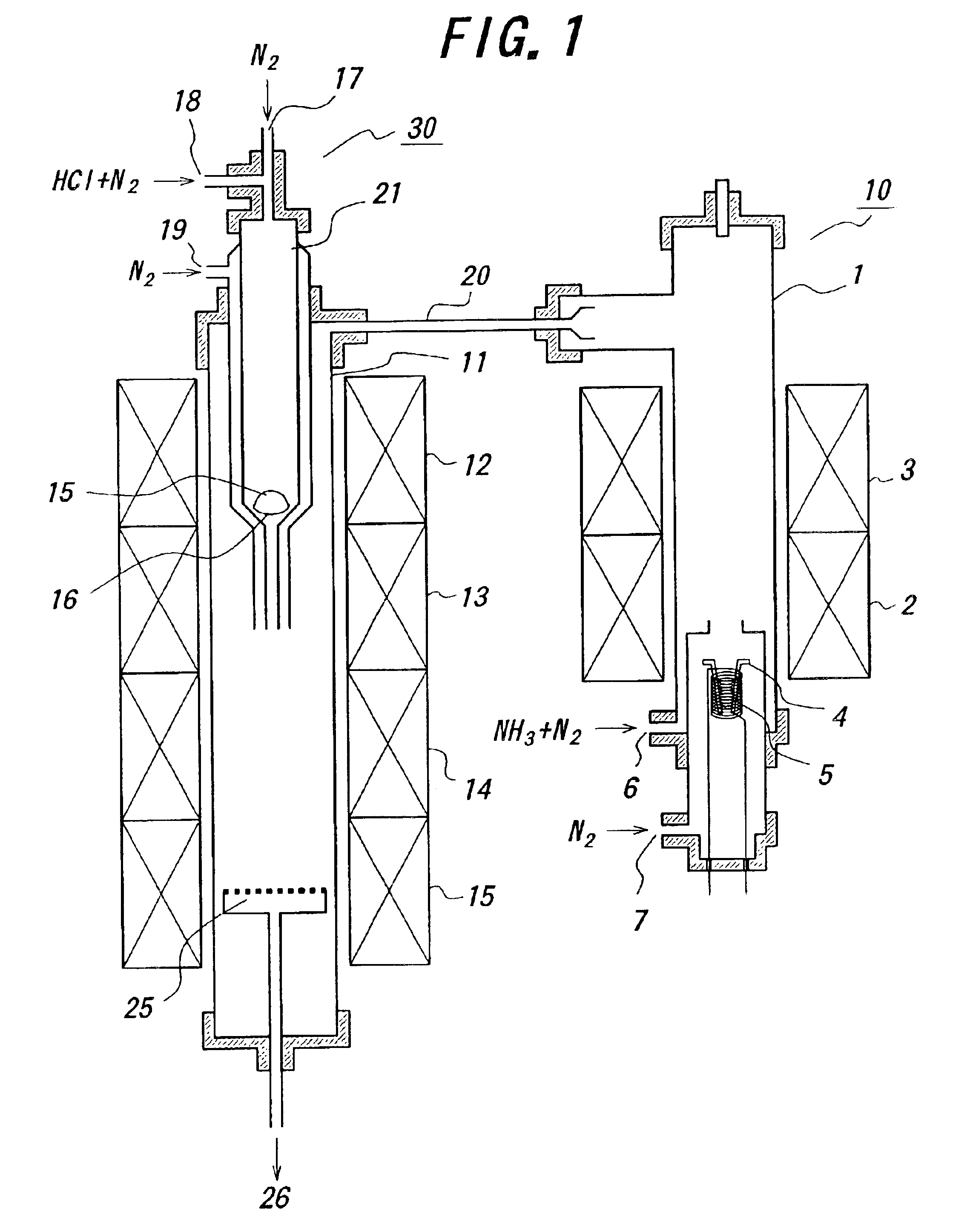
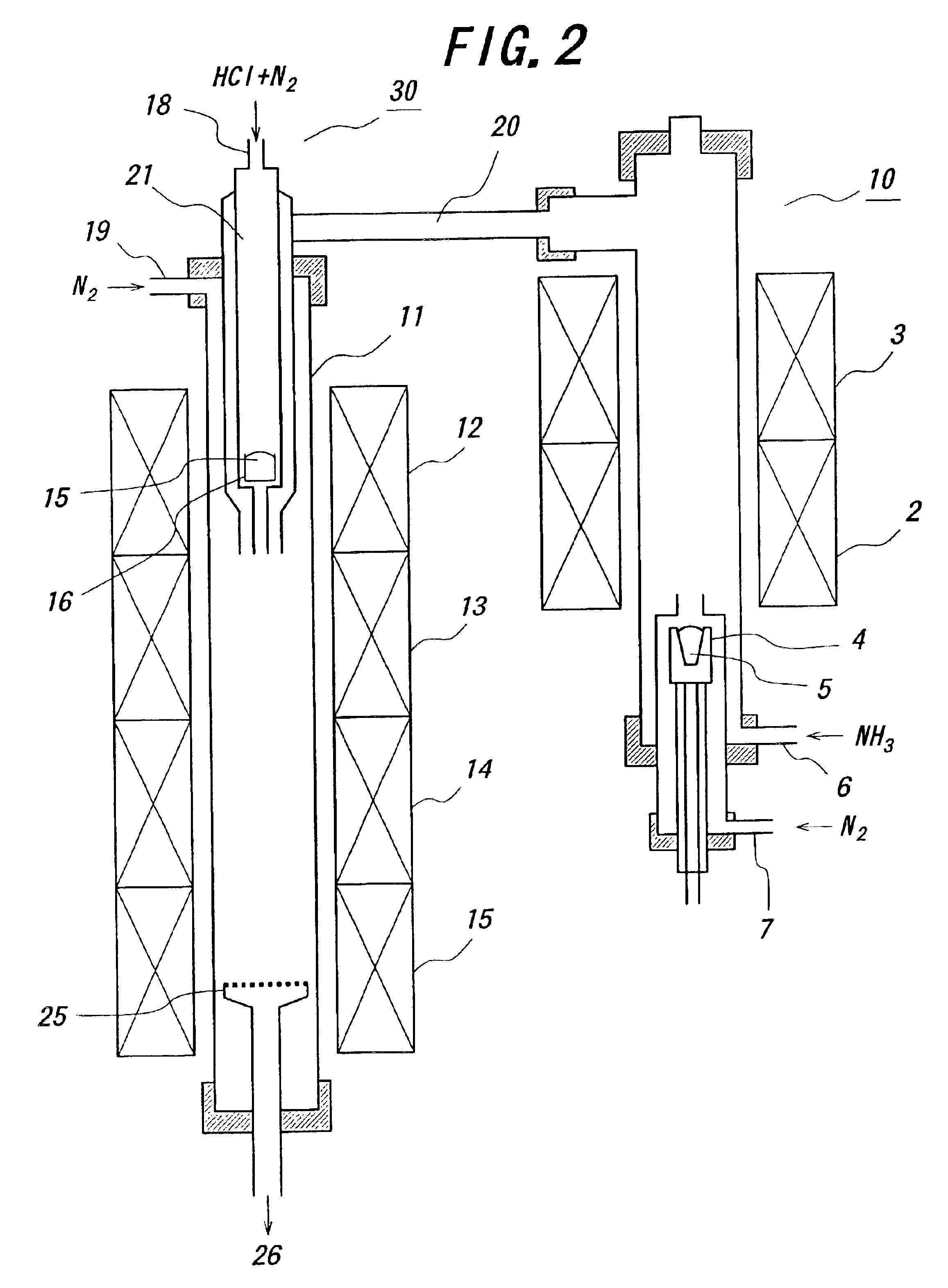
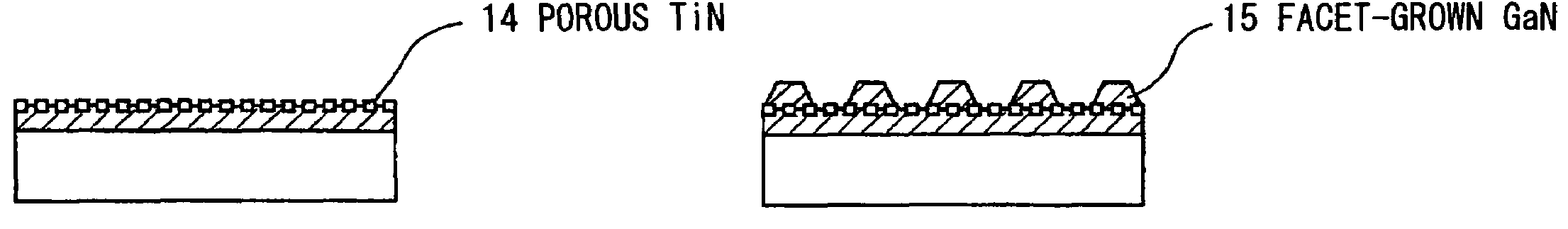
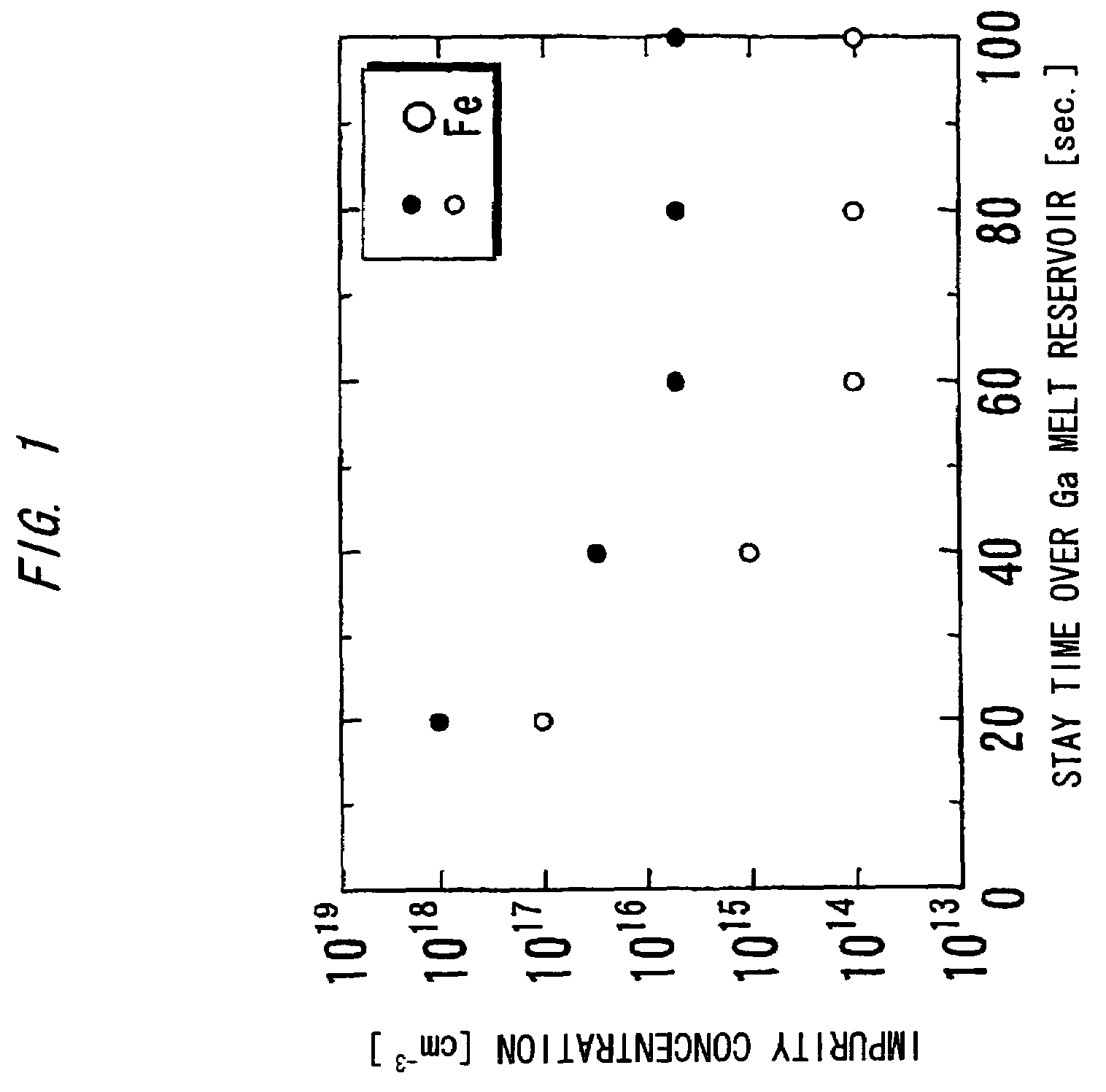
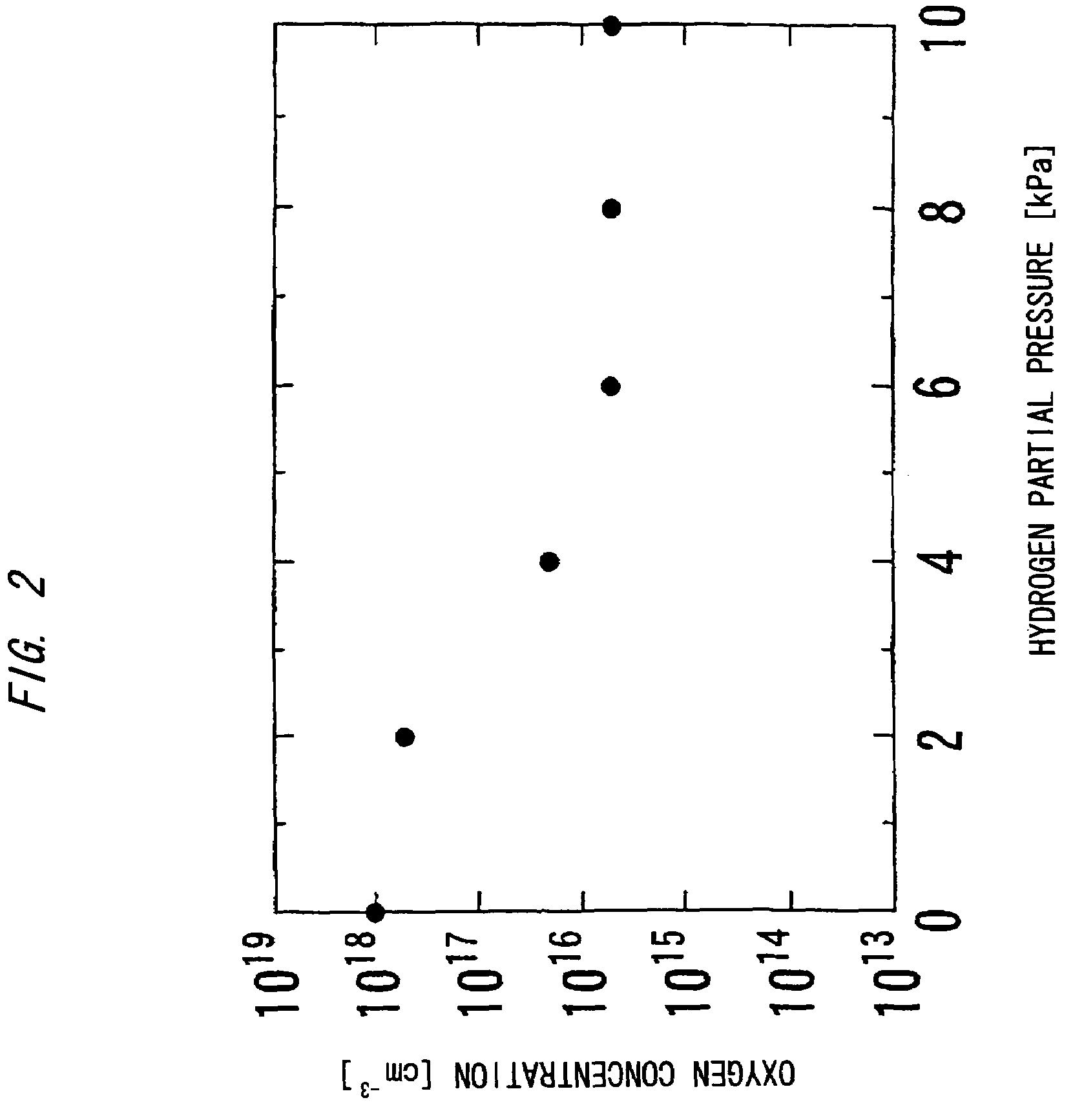
Nitride-based semiconductor substrate and method of making the same
ActiveUS20070096147A1High transparencyImprove conductivityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrometerLength wave
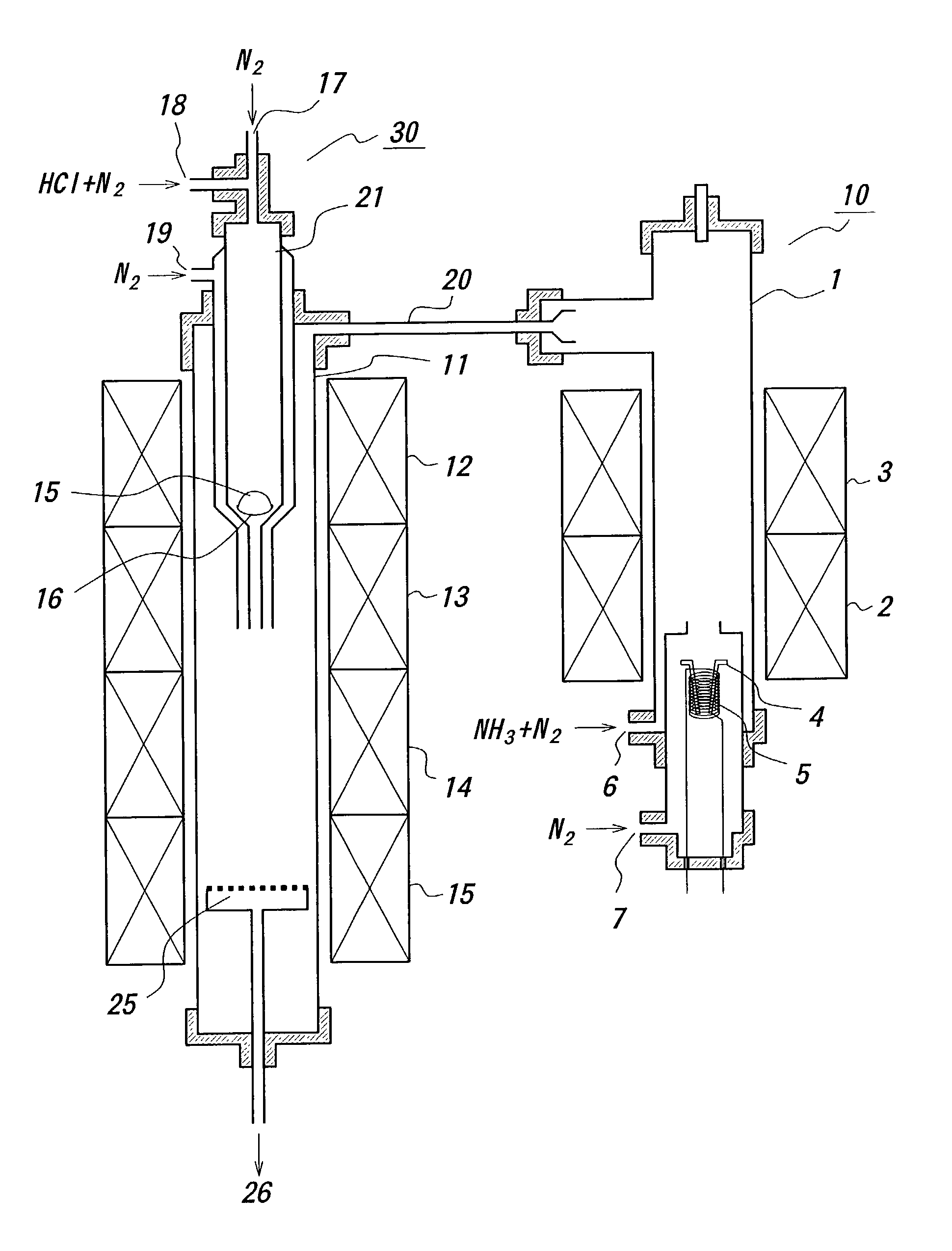
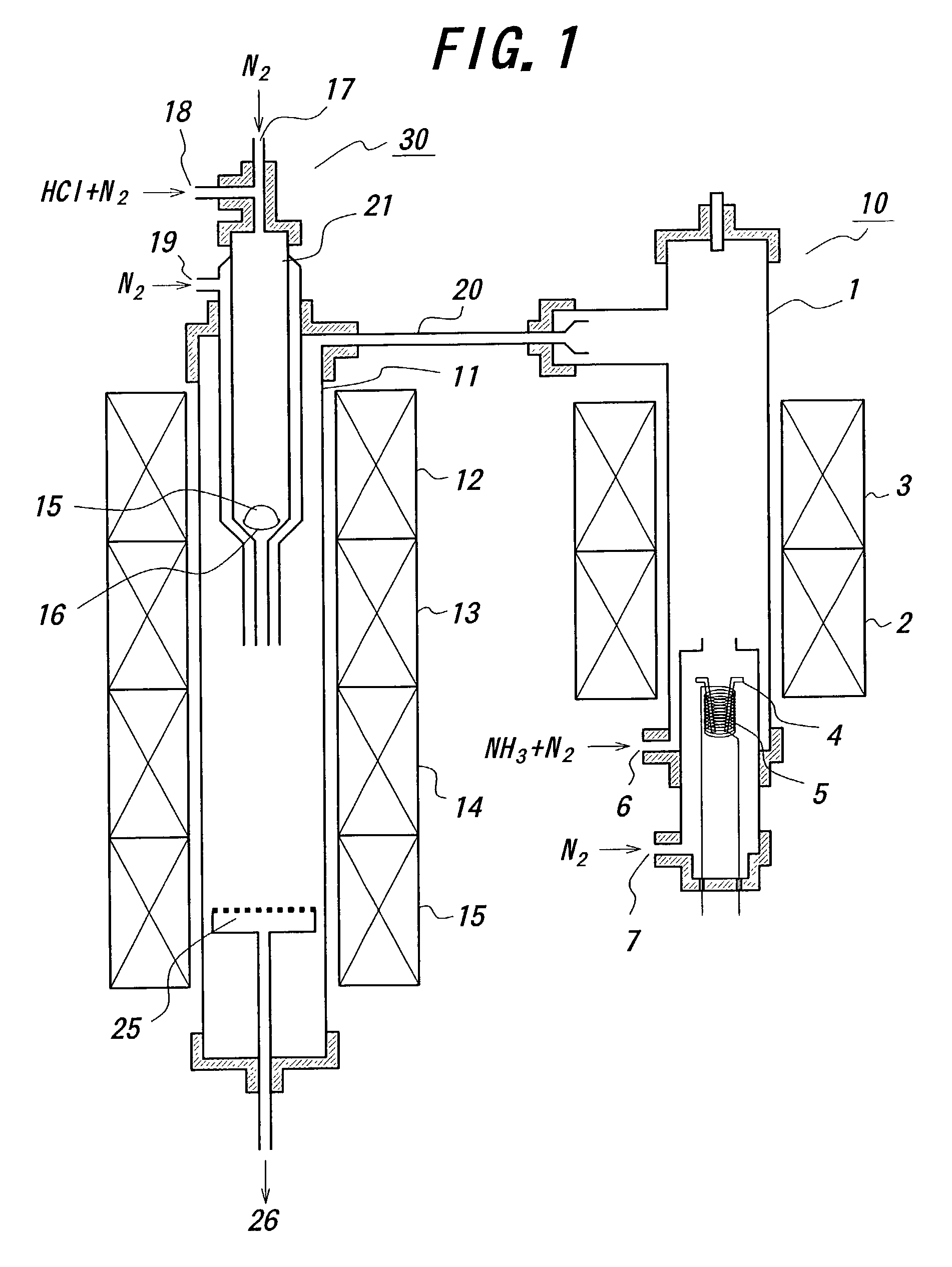
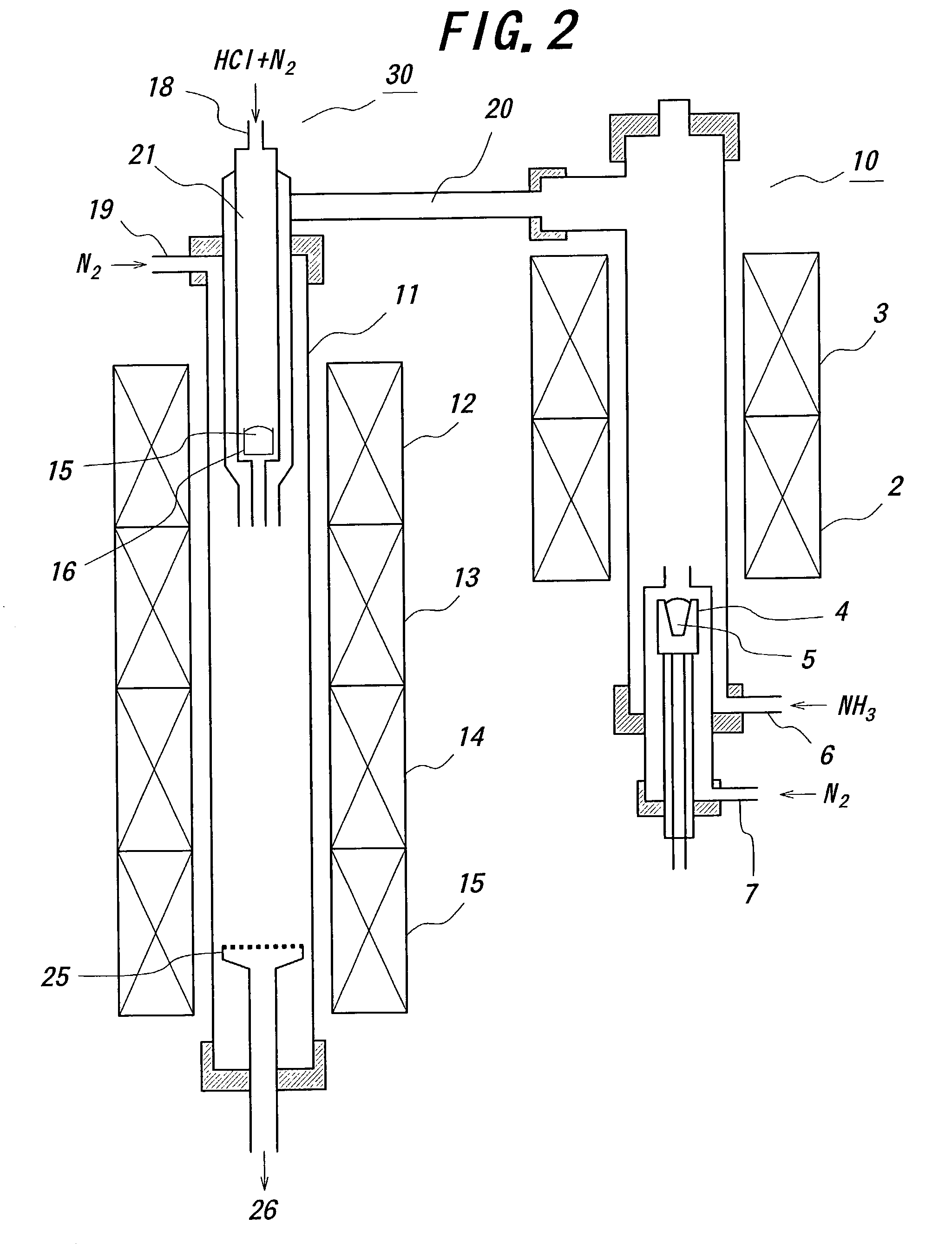
A nitride-based semiconductor substrate having a diameter of 25 mm or more, a thickness of 250 micrometers or more, and an optical absorption coefficient of less than 7 cm−1 to light with a wavelength of 380 nm or more. The nitride-based semiconductor substrate is made by the HVPE method that uses gallium chloride obtained by reacting a Ga melt with a hydrogen chloride gas. The Ga melt is contacted with the hydrogen chloride gas for one minute or more to produce the gallium chloride.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Method for producing powders made of gallium nitride and apparatus for producing the same
InactiveUS6911083B2Short timeProduce significantPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesNitrogenGallium nitride
Owner:TOKYO INST OF TECH
Preparation method of high-purity and low-loss chalcogenide glass
InactiveCN103332851AImprove uniformityHigh purityGlass furnace apparatusChalcogenide glassPhotochemistry
The invention provides a preparation method of high-purity and low-loss chalcogenide glass, belonging to a preparation method of the chalcogenide glass. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: removing hydrocarbon impurity in the glass by taking ultra-dry gallium chloride as a purifying agent, and distilling and purifying the glass in combination with the conventional deoxidant, aluminum, magnesium or zirconium metal; placing glass mixture into a quartz ampoule to be sealed in by means of vacuum supply, founding the glass mixture in a vacuum ampoule, dynamically distilling the glass, and remelting the mixture after distilling; and effectively removing the hydrocarbon impurity in the glass by taking the ultra-dry gallium chloride as the purifying agent, so that the Mie scattering imperfection is hardly formed in the finally-obtained high-purity chalcogenide glass, and the low-loss homogeneous glass can be obtained. According to the high-purity chalcogenide glass synthesized by the preparation method provided by the invention, the minimum loss under the infrared transmission waveband is less than 0.3dB / m, and the corresponding loss of the absorption peak of the residual impurity is less than 8dB / m, so that the preparation method can be used in the field of an infrared glass optical element and an infrared optical fiber. The ultra-dry gallium chloride purifying agent can be easily obtained, and is lower in price; the carbon, hydrogen and oxygen impurities can be removed from the chalcogenide glass at high efficiency; the prepared chalcogenide glass is better in uniformity and less in light scattering.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
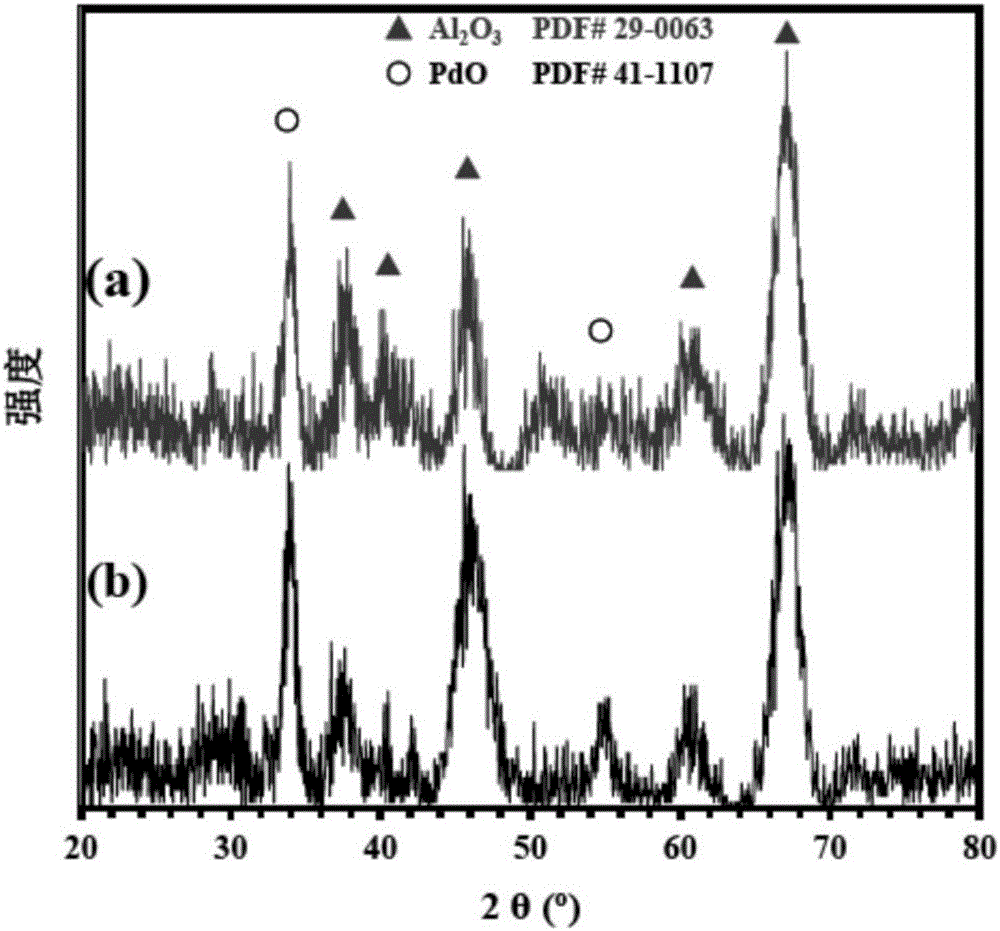
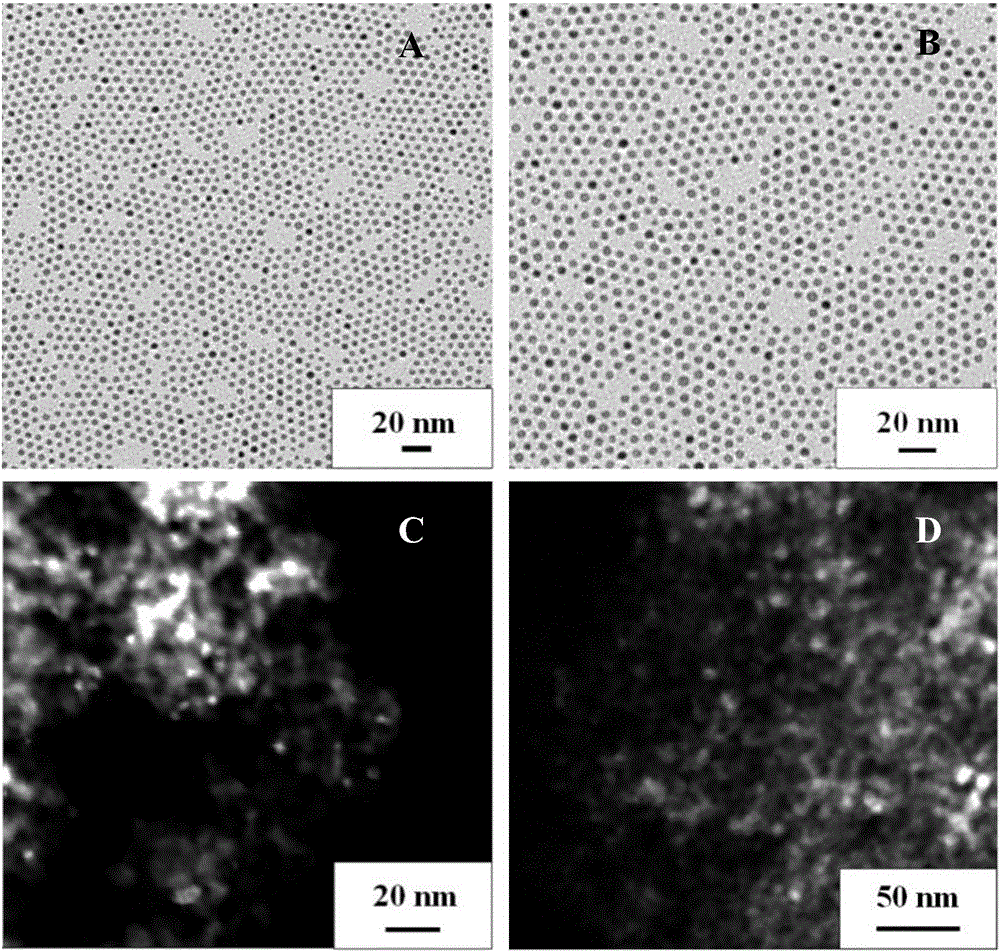
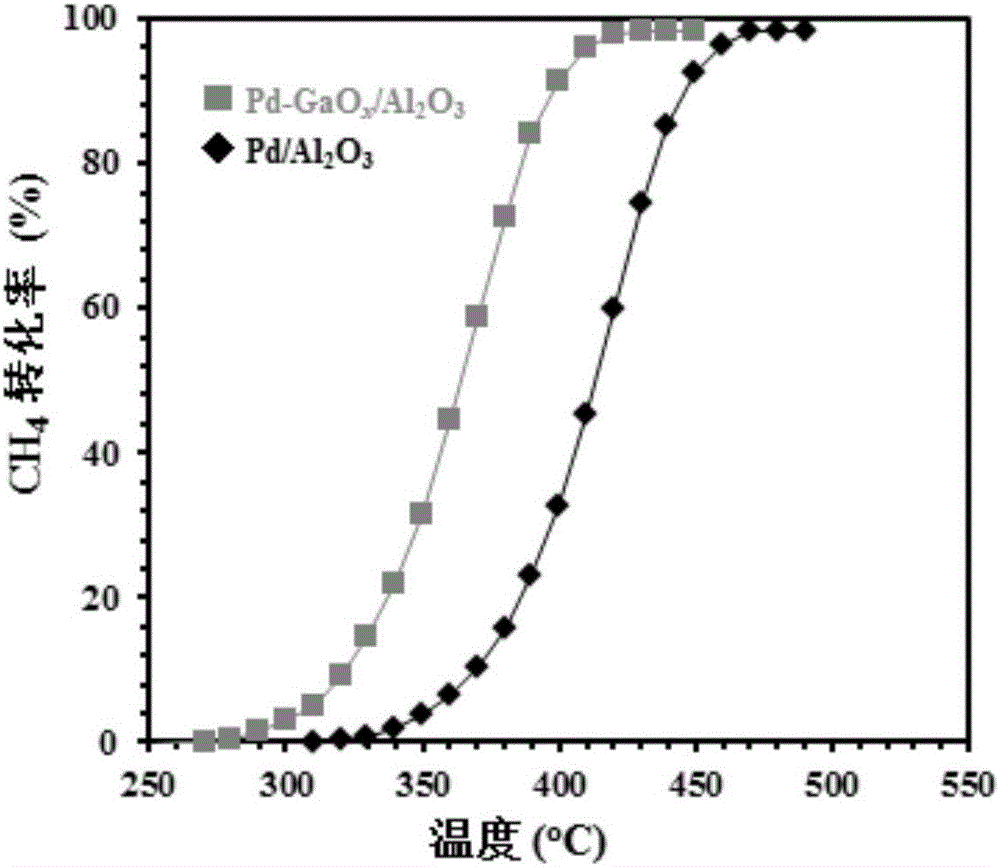
Palladium gallium oxide double-metal nano-catalyst capable of efficiently catalyzing methane to combust and preparation
InactiveCN106693987AUniform particle sizeGood size controlHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNano catalystMetal particle
The invention provides a palladium gallium oxide double-metal nano-catalyst capable of efficiently catalyzing methane to combust and preparation and belongs to the technical field of functional materials. PdGa double-metal nano-particles are loaded on a gamma-Al2O3 carrier, and then the carrier is fired to form a Pd-GaOx / Al2O3 catalyst. The loading amount of metal palladium is 1.0wt%. A preparation method comprises the following steps: simultaneously reducing palladium acetylacetonate and gallium chloride in an oleylamine system by adopting a liquid-phase co-reduction method, so as to form PdGa double-metal particles with a uniform size; loading the metal particles on an Al2O3 carrier by adopting an immersion method, wherein the Pd loading amount is 1.0wt%; and firing a load type catalyst at 450 DEG C to form the Pd-GaOx / Al2O3 nano-catalyst. The Pd-GaOx / Al2O3 nano-catalyst prepared by the invention has the advantages that a preparation process is simple, the size of the nano-particles is uniform, and the nano-catalyst has a good application prospect in the field of catalysis.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Electro-deposition method for preparing three band gap Fe-doped with copper gallium sulfur solar cell materials
ActiveCN104795456AIncrease photocurrentHigh crystallinityFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationVulcanizationCrystallinity
The invention discloses an electro-deposition method for preparing the three band gap Fe-doped with copper gallium sulfur solar cell materials. The method includes the following steps: dissolving the copper chloride, the gallium chloride and the ferric chloride in the ionic liquid, depositing the Cu, Ga and Fe prefabricated layers on the constant potential of the substrate, conducting the vulcanization annealing treatment on the prefabricated layers, and finally preparing the Fe-doped with copper gallium sulfur thin film materials. The electro-deposition method for preparing the three band gap Fe-doped with copper gallium sulfur solar cell materials can effectively reduce the adverse effect of the hydrogen evolution reaction on the quality of the thin film due to the fact that the ionic liquid is used as the solvent, simple in preparation technology, high in utilization rate of raw materials, low in production cost, strong in controllability, good in repeatability, capable of realizing the preparation of the large-area high-quality thin film and large-scale production, good in crystallinity, compact and flat in surface topography, and capable of broadening the absorption of the solar energy spectral by the materials through the generated sub-band gap and obviously increasing the photo-generated current of materials.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Preparation method of hydroxyl gallium oxide nanometer crystal
InactiveCN102786078AIncrease productionHigh purityMaterial nanotechnologyGallium/indium/thallium compoundsPrismGallium nitride
The invention relates to a preparation method of hydroxyl gallium oxide nanometer crystal, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of a nanometer material of oxyhydroxide. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: dripping a deionized water solution of CTAB (cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide) into a benzene solution of gallium chloride under an ultrasonic environment by the adoption of a principle of a liquid-liquid interface reaction, putting the mixed solution into a reaction kettle to carrying out heating reaction, and obtaining a sample of white powders. The hydroxyl gallium oxide is the raw material for compounding gallium nitride and gallium oxide, and the microcosmic morphological feature of the hydroxyl gallium oxide has very important influence on the performances of the prepared gallium nitride and gallium oxide. The hydroxyl gallium oxide nanometer crystal, prepared by the method provided by the invention, is prism-shaped, and has the characteristics of smooth surface, complete shape, uniform size, etc. The preparation method, provided by the invention, conquers the shortcomings that gallium chloride is very easy to absorb water and cause deliquescence, and abandons the complicated step that the pH value must be regulated in the past and does not need the vacuum environment; and has the advantages of simplicity in operation, high yield, little energy consumption, high repeatability and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Preparation method of gallium oxide hydroxide nano-crystals
InactiveCN102976393AOvercome the disadvantage of easy water absorption and deliquescenceResponse speed blockMaterial nanotechnologyGallium/indium/thallium compoundsMoistureMethanol
The invention provides a preparation method of gallium oxide hydroxide nano-crystals and belongs to the technical field of preparation of gallium oxide hydroxide nano-materials. According to the reaction kettle sealed heating alcoholysis method and the liquid-liquid interface reaction principle, through gradually dropwise adding methanol into a gallium oxide benzene solution disposed in an ultrasonic appliance and then enabling the mixed solution to be subjected to sealed low-temperature heating reaction, the prepared sample is white powders. The crystals in nano brush shape and which in smooth in surface, complete in shape and uniform in size are prepared under a preferable condition. According to the invention, the synthesis of gallium oxide hydroxide nano-crystals is carried out by using the alcoholysis reaction method for the first time, the disadvantage that the gallium oxide is very liable to absorb water and be decomposed by moisture is overcome, the operations are finished without adjusting pH (potential of hydrogen) and without using a vacuum condition, the reaction speed of the gallium oxide is significantly inhibited, so that the shape of the generated gallium oxide hydroxide is more easy to control. In addition, the product prepared by the method provided by the invention is high in yield and high in purity; and the preparation method is simple, excellent in repeatability and low in cost.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for electrodepositing gallium at low temperature by using ionic liquid
InactiveCN103031571AHigh operating temperatureHigh energy consumptionPhotography auxillary processesRecovering materialsDecompositionElectrochemical window
The invention relates to a method for electrodepositing gallium at low temperature by using an ionic liquid, which comprises the following steps: heating an ionic liquid used as an electrolyte to a colorless transparent state, dissolving gallium chloride in the ionic liquid, and electrodepositing the gallium chloride in the solution, wherein gallium is generated at the cathode of the electrolytic bath, and chlorine gas is emitted at the anode. In the electrodeposition process, the bath voltage of the electrolytic bath is higher than the decomposition voltage of gallium chloride, and lower than that of the electrochemical window of the ionic liquid. The invention has the advantages of low operating temperature, low energy consumption and low apparatus corrosiveness, can greatly lower the production cost, and is environment-friendly.
Owner:IRICO
Production of gallium chloride
InactiveCN1778683AHigh purityGuarantee product qualityGallium/indium/thallium compoundsHydrogen chloridePhotochemistry
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND
Method for producing powders made of gallium nitride and apparatus for producing the same
InactiveUS20030226497A1Achieve mass productionPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesNitrogenGallium nitride
In a creation section of GaN crystal nuclei, a gallium vapor and an ammonia gas are chemically reacted to create GaN crystal nuclei, which are transported into a growth section of GaN powders with a nitrogen carrier gas. In the growth section of GaN powders, a gallium chloride created in a pre-reactor is chemically reacted with the ammonia gas transported from the creation section of GaN crystal nuclei on the GaN crystal nuclei, to produce GaN powders through the crystal growth.
Owner:TOKYO INST OF TECH
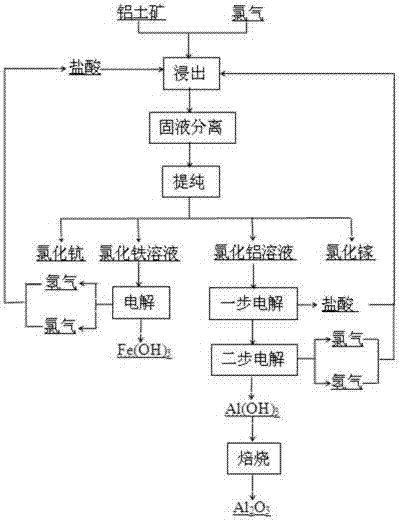
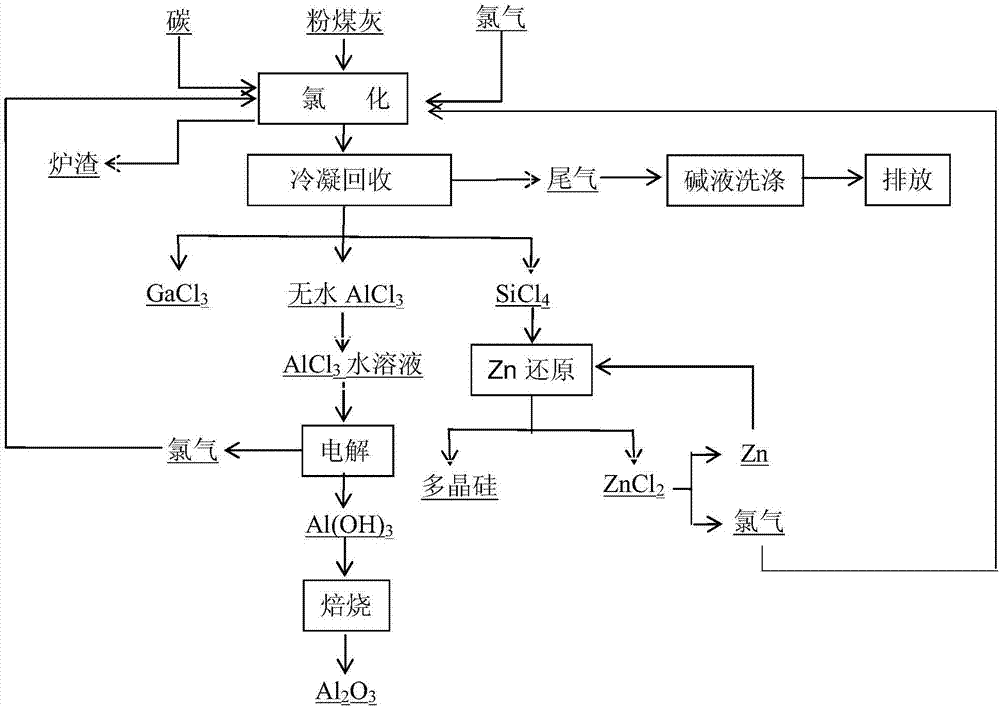
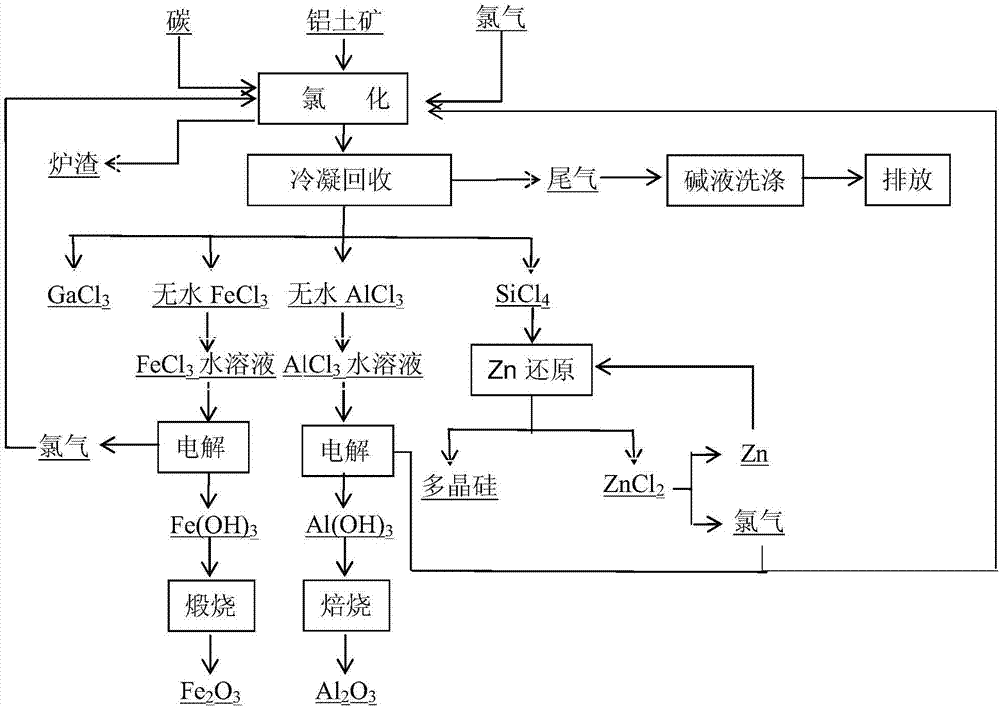
Method for preparing aluminum oxide through hydrochloric acid leaching and two-stage electrolysis of bauxite and comprehensively utilizing aluminum oxide
ActiveCN107128959AHigh degree of automationHigh purityAluminium compoundsRare earth metal chloridesAluminium chlorideElectrolysis
The invention relates to a method for preparing aluminum oxide through hydrochloric acid leaching and two-stage electrolysis of bauxite and comprehensively utilizing aluminum oxide. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out hydrochloric acid leaching, solid-liquid separation and purification on bauxite on bauxite, so as to obtain an iron chloride mixed solution and an aluminum chloride mixed solution; respectively separating and purifying the iron chloride mixed solution and the aluminum chloride mixed solution, so as to obtain scandium chloride, gallium chloride, an aluminum chloride water solution and an iron chloride water solution; setting electrolytic voltage and current density, and respectively carrying out two-stage electrolysis on the aluminum chloride water solution and the iron chloride water solution, so as to respectively obtain aluminum hydroxide, hydrogen and chlorine as well as iron hydroxide, hydrogen and chlorine; preparing a hydrochloric acid solution by using the generated hydrogen and chlorine, and returning the hydrochloric acid solution to a leaching stage for recycling; and roasting aluminum hydroxide, so as to obtain metallurgy level aluminum oxide or chemical aluminum oxide. Compared with a traditional acid method, the electrolysis method for recycling aluminum oxide in the bauxite and processing the bauxite has the advantages that the evaporation step and equipment, the concentration step and equipment are omitted, the operation is simplified, meanwhile, the cost is substantially lowered, and the product has relatively high purity.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
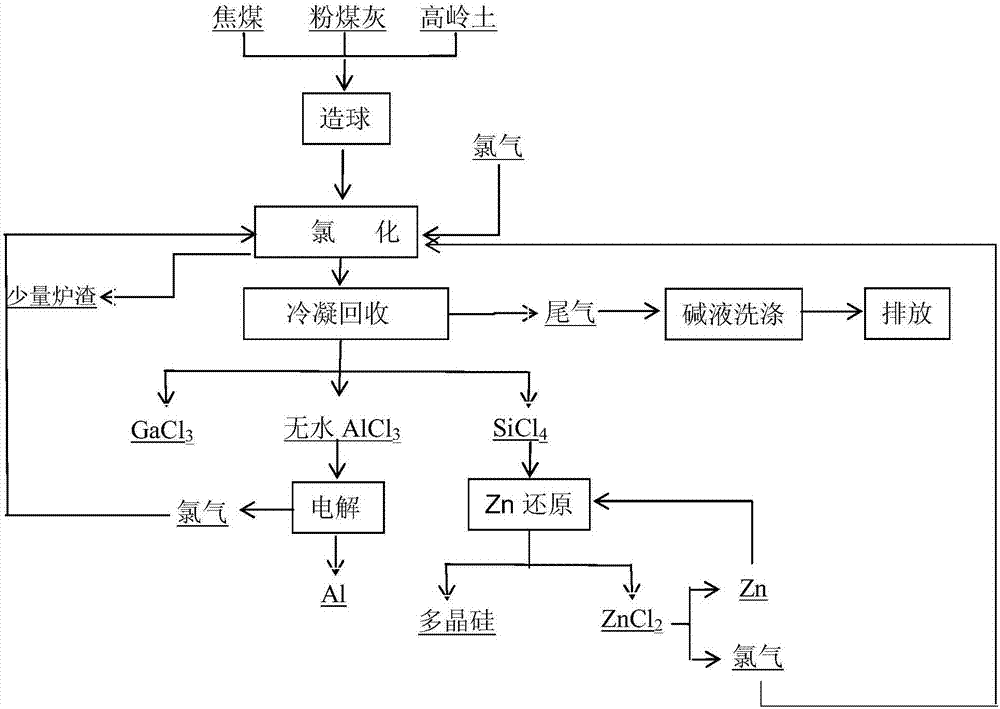
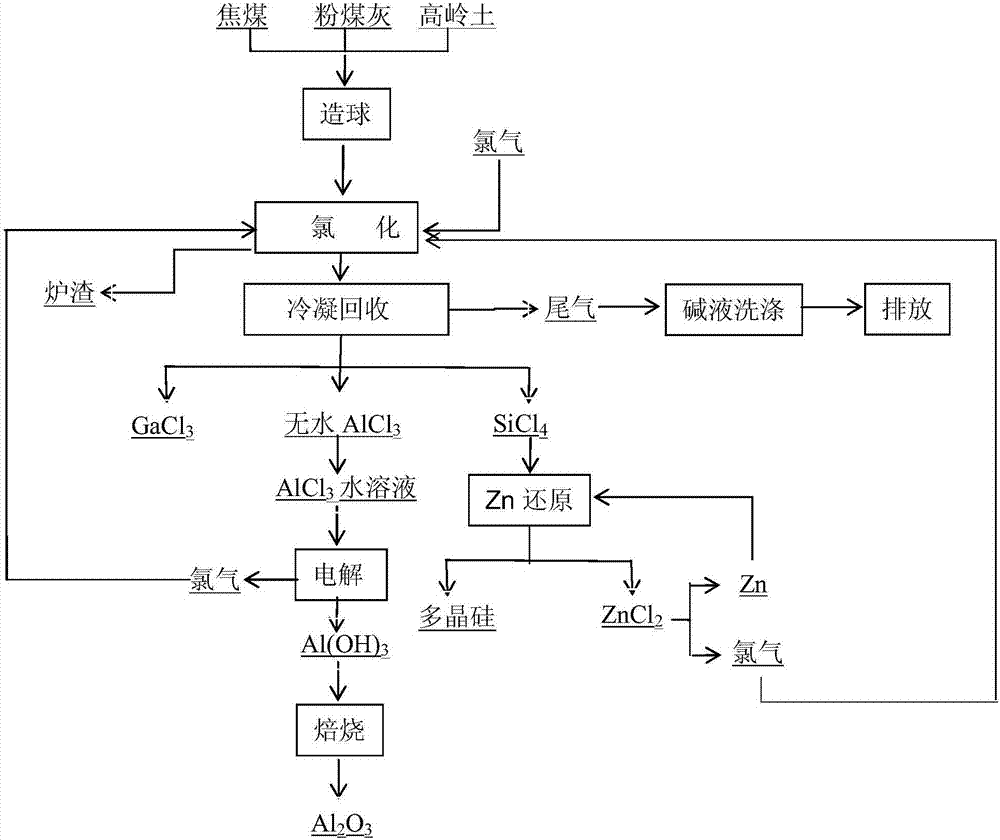
Method for preparing and comprehensively utilizing metal aluminum through coal ash pellet chlorination electrolysis
InactiveCN107128927AHigh degree of automationHigh purityGallium/indium/thallium compoundsSilicon compoundsElectrolysisMixed materials
The invention discloses a method for preparing and comprehensively utilizing metal aluminum through coal ash pellet chlorination electrolysis. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing coal ash, a carbon source and kaolin in a mass ratio of 1:(2-6):(0.05-0.3) so as to form a mixed material; adding a binding agent which accounts for 1.0-2.0% of the total mass of the mixed material and water which accounts for 2.0-5.0% of the total mass of the mixed material into the mixed material; uniformly mixing, pelletizing, and drying in air; performing chlorination and separation on pellets so as to respectively obtain anhydrous aluminum chloride, silicon tetrachloride and gallium chloride; directly electrolyzing the anhydrous aluminum chloride so as to obtain the metal aluminum and chlorine; feeding back the chlorine into a chlorination procedure; and further purifying the silicon tetrachloride, thereby obtaining polycrystalline silicon and zinc chloride. The method disclosed by the invention is low in cost, cheap and easy in raw material obtaining, complete in chlorination reaction through pelletization and chlorination, simple in operation process and high in electrolysis automation degree, the prepared metal aluminum is relatively high in purity, and raw materials such as chlorine and zinc can be recycled.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
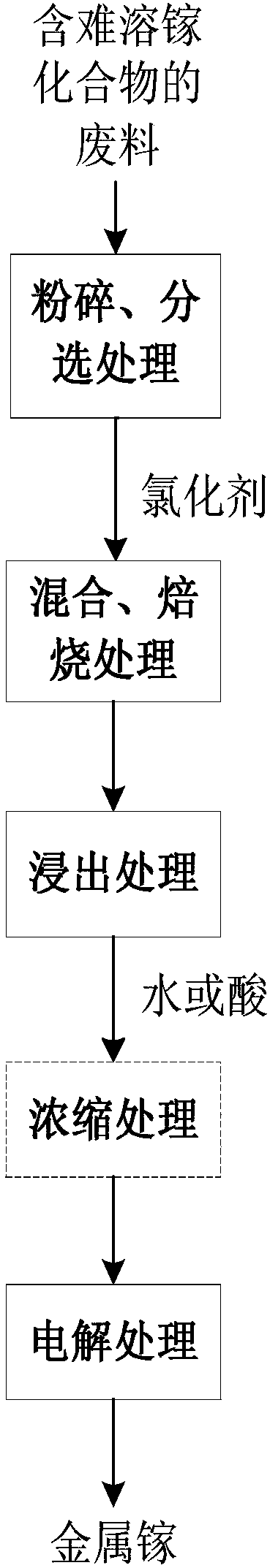
Method for recycling gallium from indissolvable gallium compounds and gallium recycled by virtue of method
ActiveCN108374091AImprove leaching rateEfficient leachingPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisLeaching rate
The invention provides a method for recycling gallium from indissolvable gallium compounds and gallium recycled by virtue of the method. The method comprises the steps of mixing waste containing the indissolvable gallium compounds with a chlorinating agent, sintering, leaching a sintered product, and carrying out electrolysis, so as to obtain metal gallium. According to the method, the waste containing the indissolvable gallium compounds is mixed with the chlorinating agent and is sintered, and the difficulty-leached gallium compounds are converted into easily-leached gallium chloride, so thatthe leaching rate of gallium is greatly increased, the recycling rate of gallium reaches 98% or above, and the purity of metal gallium can reach 99.9wt%. The process flow is simple, the consumed timeis relatively short, the waste gas and the dust which are harmful to the environment are not discharged, and the method has wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of high-purity and low-loss chalcogenide glass
InactiveCN103332851BImprove uniformityHigh purityGlass furnace apparatusChalcogenide glassPhotochemistry
The invention provides a preparation method of high-purity and low-loss chalcogenide glass, belonging to a preparation method of the chalcogenide glass. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: removing hydrocarbon impurity in the glass by taking ultra-dry gallium chloride as a purifying agent, and distilling and purifying the glass in combination with the conventional deoxidant, aluminum, magnesium or zirconium metal; placing glass mixture into a quartz ampoule to be sealed in by means of vacuum supply, founding the glass mixture in a vacuum ampoule, dynamically distilling the glass, and remelting the mixture after distilling; and effectively removing the hydrocarbon impurity in the glass by taking the ultra-dry gallium chloride as the purifying agent, so that the Mie scattering imperfection is hardly formed in the finally-obtained high-purity chalcogenide glass, and the low-loss homogeneous glass can be obtained. According to the high-purity chalcogenide glass synthesized by the preparation method provided by the invention, the minimum loss under the infrared transmission waveband is less than 0.3dB / m, and the corresponding loss of the absorption peak of the residual impurity is less than 8dB / m, so that the preparation method can be used in the field of an infrared glass optical element and an infrared optical fiber. The ultra-dry gallium chloride purifying agent can be easily obtained, and is lower in price; the carbon, hydrogen and oxygen impurities can be removed from the chalcogenide glass at high efficiency; the prepared chalcogenide glass is better in uniformity and less in light scattering.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing and comprehensively utilizing metal aluminum through coal ash pellet chlorination electrolysis
ActiveCN107128957AHigh degree of automationHigh purityZinc halidesElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisAluminium hydroxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing and comprehensively utilizing metal aluminum through coal ash pellet chlorination electrolysis. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing coal ash, a carbon source and kaolin in a mass ratio of 1:(2-5):(0.1-0.5) so as to form a mixed material; adding a binding agent and water; pelletizing, and drying in air; performing chlorination, separation and purification so as to respectively obtain anhydrous aluminum chloride, silicon tetrachloride and gallium chloride; converting the anhydrous aluminum chloride into an aluminum chloride solution, controlling voltage and current density, implementing electrolysis so as to obtain aluminum hydroxide, hydrogen and chlorine, and feeding back the chlorine to a chlorination procedure; roasting the aluminum hydroxide so as to obtain metallurgy-level / chemical aluminum oxide; and purifying the silicon tetrachloride. The method disclosed by the invention is low in cost, cheap and easy in raw material obtaining, complete in chlorination reaction through pelletization and chlorination, simple in operation process, high in automation degree and high in product purity, and raw materials such as chlorine and zinc can be recycled.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for preparing high viscosity lubricating oil
InactiveCN101565651AHigh catalytic activityIncrease conversion rate per passBase-materialsOil additiveReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for preparing high viscosity lubricating oil. A catalyst system consisting of acid ion liquid as a main catalyst and stannic chloride, iron chloride, gallium chloride or alkylaluminium halide as cocatalysts contacts 1-olefin under oligomerization condition to perform polyreaction. One or more straight-chain 1-olefins of C6-C18 are taken as raw materials to contact the ion liquid and metal halide at a reaction temperature of between 60 DEG C below zero and 180 DEG C and under a reaction pressure of between 0.1 and 10 MPa to obtain a product with the viscosity of between 10 and 1,000 mm.s. The high viscosity poly alpha-olefin can be used as lubricating oil base oil or lubricating oil additive. The catalysts related in the invention can be recycled; and the technological process does not generate pollutants such as waste solvent and the like, so the method is a green lubricating oil synthesizing process.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Electrothermal film, coating process and device
InactiveCN101610610AImprove adhesionUniform resistanceChemical vapor deposition coatingHeating element materialsUltrasound attenuationElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention provides an electrothermal film, which is prepared from tin tetrachloride, antimony chloride, chromium trichloride, gallium chloride and germanium chloride. The invention also provides a coating process and a vapor deposition device. The electrothermal film solves the technical problems that an electrothermal film layer has non-uniform resistance, uneven heat in the process of heating, lower electro-thermal conversion efficiency and short service life of the electrothermal film in the prior art, and simultaneously the technical problem that the unity of the resistance is difficult to control by the conventional electrothermal film production process. Compared with the electrothermal film in the prior art, the electrothermal film of the invention can ensure that the resistance is uniform, the resistance value can be controlled, and insusceptibility to burning and long service life can be achieved; and the adhesiveness of the electrothermal film is greatly improved, no shedding and attenuation, and long service life are ensured, so the electrical property is greatly improved and application range of the electrothermal film is greatly widen.
Owner:谭沉浮
Method for preparing copper-gallium-selenium photoelectric thin film from copper chloride and gallium chloride
InactiveCN106057930ALower requirementImprove continuityFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationCopper chlorideSolar cell
The invention discloses a method for preparing a copper-gallium-selenium photoelectric thin film from copper chloride and gallium chloride, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of photoelectric thin films for solar cells. The method comprises the following steps: cleaning a glass substrate first, then putting copper chloride, gallium chloride and selenium dioxide into a solvent, adjusting the pH value to 4.0-7.0, spinning the mixture onto the glass substrate to obtain a precursor thin film, drying, putting the precursor thin film into an airtight container containing diamide hydrate which is not in contact with the precursor thin film sample, charging the airtight container filled with the sample into an oven, heating and preserving the heat, finally taking out and drying the sample to obtain the copper-gallium-selenium photoelectric thin film. The method does not need high temperature or high vacuum, and is low in requirement for instruments, low in production cost, high in production efficiency and easy to operate. The copper-gallium-selenium photoelectric thin film has good continuity and uniformity; the main phase is a copper-gallium-selenium phase, and the new process easily controls the component and the structure of the target product, so that a production cost with low cost and capability of realizing industrialization is provided for preparing a high-performance copper-gallium-selenium photoelectric thin film.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
Preparation method for solar battery materials with three-zone gap tin doped with copper, gallium and sulphur
InactiveCN104692450APromote absorptionIncrease photocurrentMaterial nanotechnologyTin compoundsThioureaCrystallinity
The invention discloses a preparation method for solar battery materials with three-zone gap tin doped with copper, gallium and sulphur. According to the preparation method for the solar battery materials with the three-zone gap tin doped with the copper, the gallium and the sulphur, copper chloride, gallium chloride, thiourea and stannic chloride are dissolved into ethylene glycol and then are mixed uniformly, a solvothermal synthesis reaction is conducted in a sealed steel-bushing teflon reaction still, then a solvothermal product is washed, filtered and dried, and a product is obtained. It is inferred from the growth mechanism that the preparation method for solar battery materials with the three-zone gap tin doped with the copper, the gallium and the sulphur is suitable for the preparation for the solar battery materials with other transmission metal elements including VIII ( Co, Fe, Ir, Ni, Pd, Rh ) doped with the three-zone gap tin. The obtained product is good in crystallinity, high in purity and uniform in morphology and distribution; an obvious ligh-induced switching effect is possessed, when there is no light, the dark current is nearly zero, and when there is light, the current intensity rises quickly; The preparation method for the solar battery materials with the three-zone gap tin doped with the copper, the gallium and the sulphur has the advantages that the preparation technology is simple, the repeatability is good, the cost is low, the controllability is strong, and the material usage rate is high; sulfidizing is not needed, the resultant temperature is low, and green and environmental protection are possessed.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Method for preparing alkylate oil by catalysis of gallium chloride acid ion solution
InactiveCN102703112AEasy to separateHigh selectivityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsLiquid hydrocarbon mixtures productionPetrochemicalHigh activity
The invention relates to a method for preparing alkylate oil by catalyzing iso-butane and butylenes preparation by a modified gallium chloride acid ion solution in the field of petrochemical industries. The catalyst has higher activity, selectivity and stability in the alkylation process, so that the alkylate oil prepared by the catalyst is characterized in that the quality and the yield are good and high, the catalyst and the alkylation product are easy to separate, the operation is simple and convenient, the corrosion is small, few side product is generated, and little environment pollution is caused.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
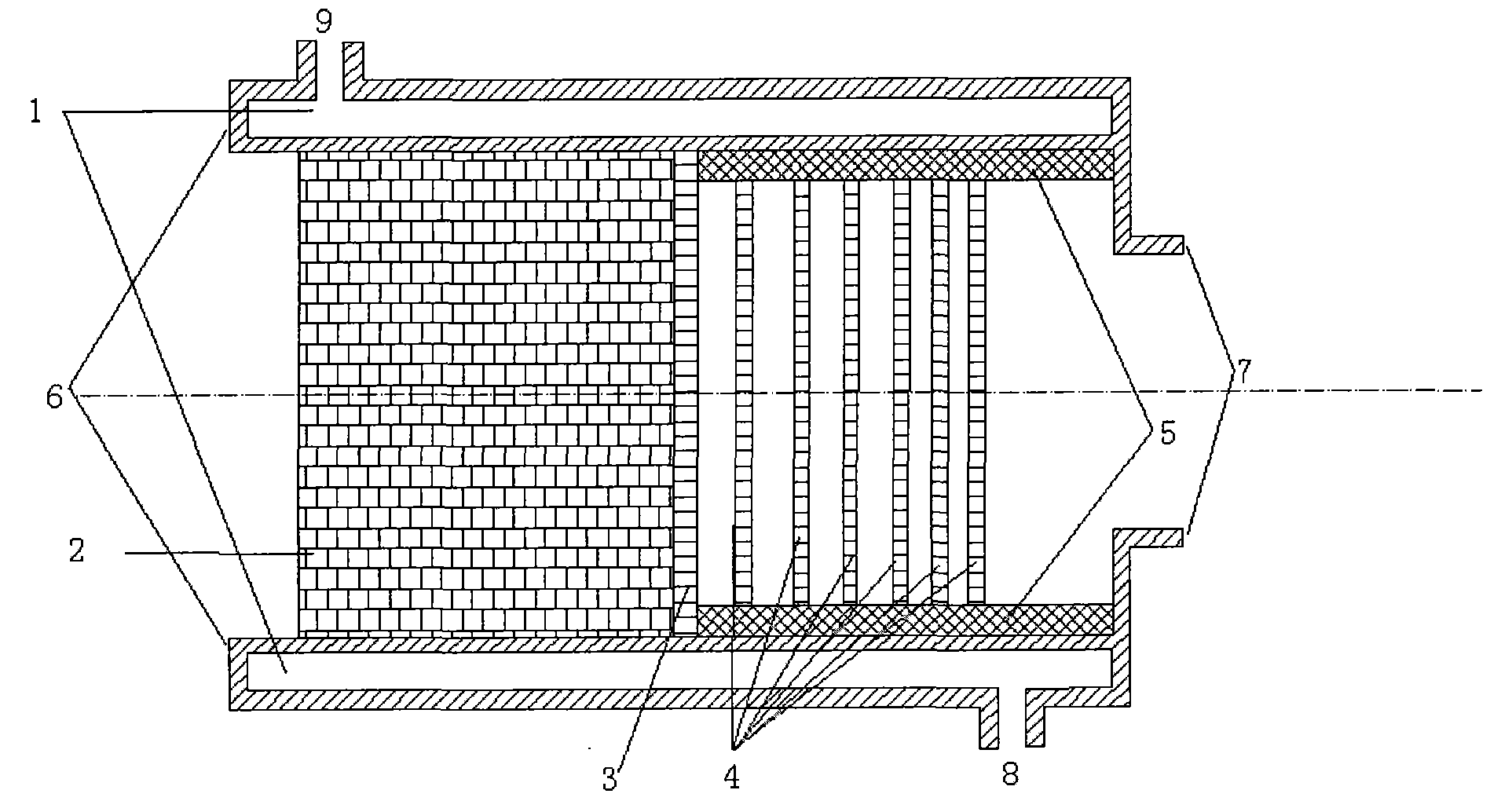
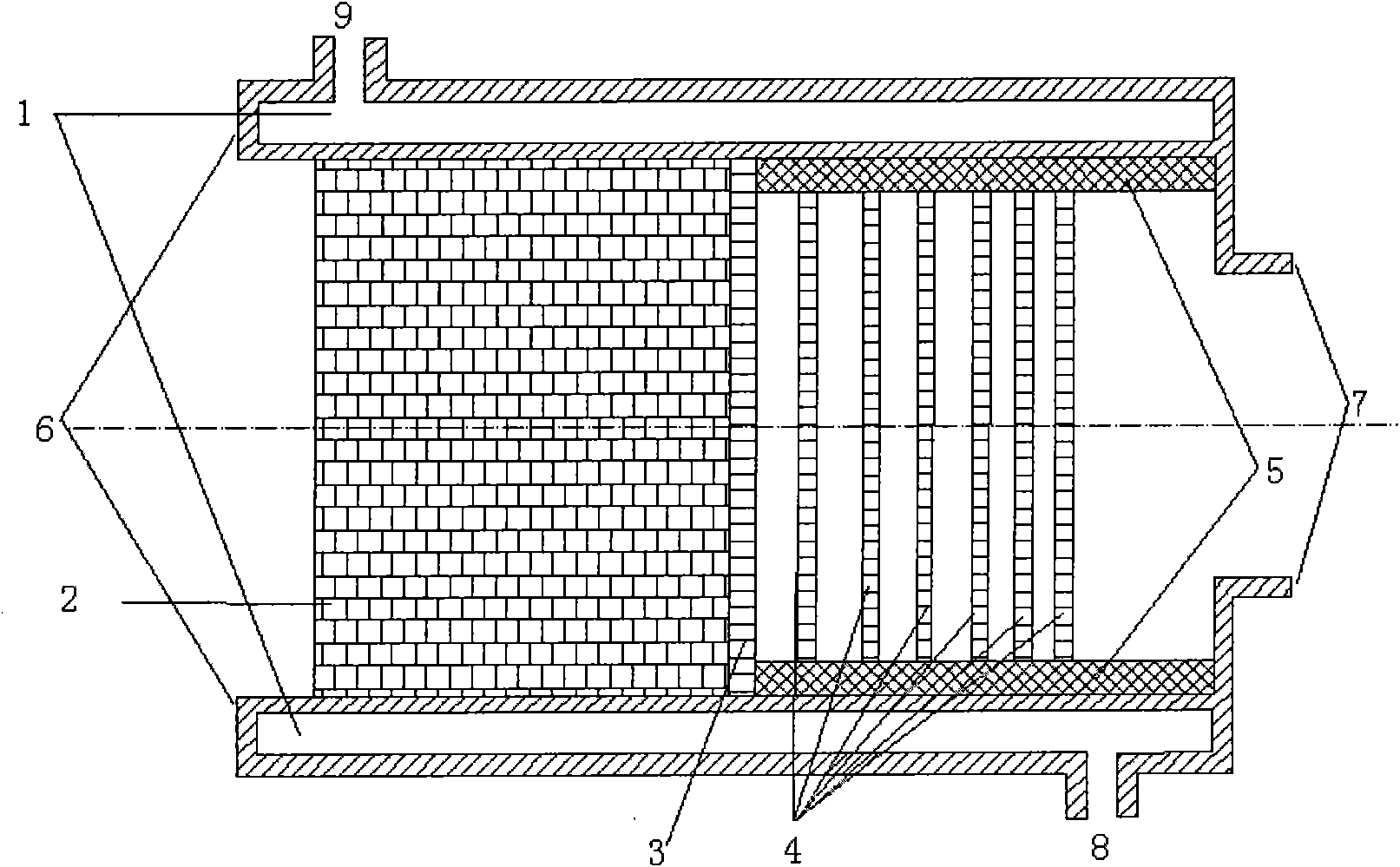
Tail gas filter for preparing gallium nitride by hydride or chloride vapor phase epitaxy
InactiveCN101810976AIncreased chance of collisionPromote generationDispersed particle filtrationWater jacketGallium nitride
The invention discloses a tail gas filter for preparing gallium nitride by hydride or chloride vapor phase epitaxy, which relates to a particle separator special for separating dispersed particles from air and adopting a rigid hollow filter body. The tail gas filter consists of a shell, a plug, a separation net, a screen and a clamp, wherein the shell is a columnar hollow water jacket; the plug is a sphere coiled into a columnar stainless steel net or a stainless steel wire; the separation net is made of stainless steel wires; the screen is a six to ten-layer anticorrosion metal silk screen; the plug is directly placed inside the shell at one end of an air inlet of the filter the separation net is directly placed at the position inside the shell between the plug and the clamp; and the screen is arranged at one end of an air outlet of the filter layer by layer and fixed inside the shell through the clamp. The tail gas filter reduces, even eliminates ammonium chloride dust, gallium vapor and gallium chloride vapor produced during preparing the gallium nitride by the hydride or chloride vapor phase epitaxy, promotes operators, environments and vacuum pumps, and optimizes the production process and the growth quality of the gallium nitride.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
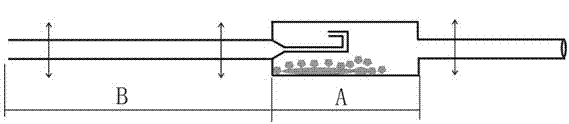
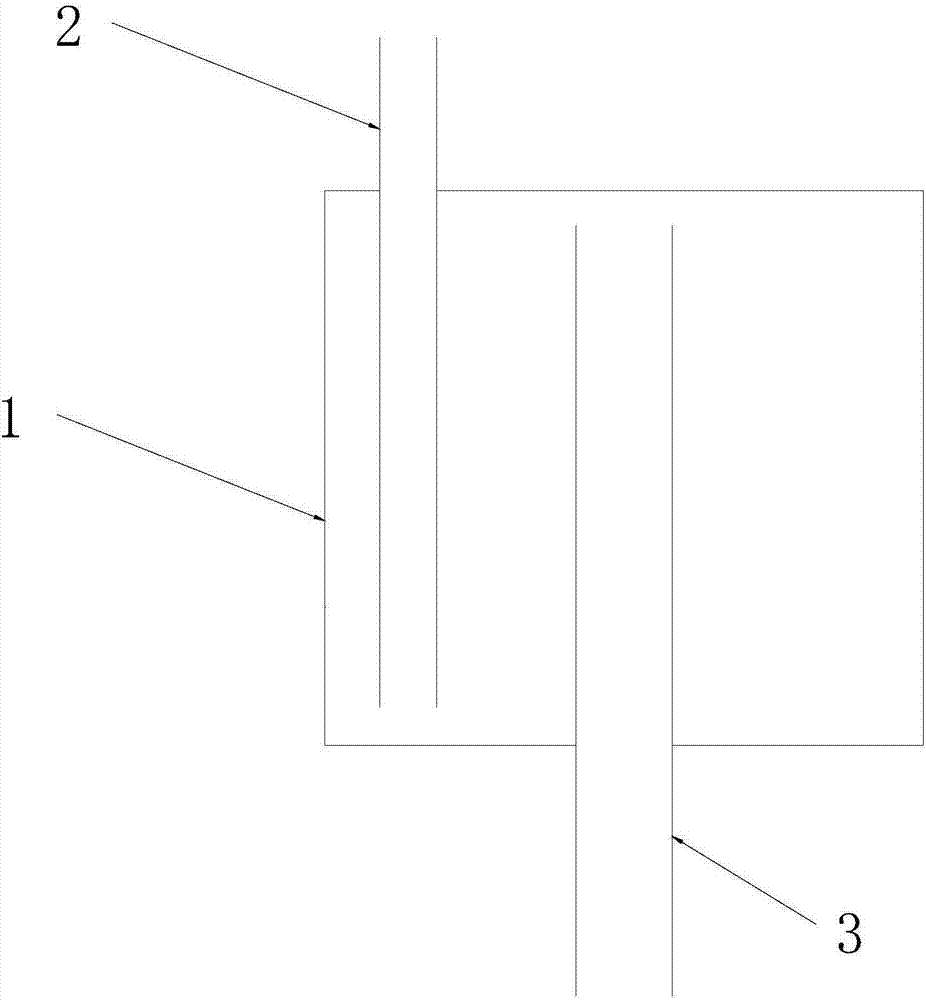
Gallium-source reactor
InactiveCN107012504AReduce the discharge rateAvoid depositionFrom chemically reactive gasesChemical vapor deposition coatingReaction layerBiochemical engineering
The invention provides a gallium-source reactor. The gallium-source reactor at least comprises a reaction layer, a first air inlet pipeline located on the top end of the reaction layer, and a first air outlet pipeline located on the bottom end of the reaction layer, wherein the bottom end of the first air inlet pipeline extends into the reaction layer and is arranged close to the bottom end of the reaction layer, and the top end of the first air outlet pipeline extends into the reaction layer and is arranged close to the top end of the reaction layer. According to the invention, since the bottom end, extending into the reaction layer, of the first air inlet pipeline is arranged close to the bottom end of the reaction layer and the top end, extending into the reaction layer, of the first air outlet pipeline is arranged close to the bottom end of the reaction layer, hydrogen chloride gas enters the reaction layer from the first air inlet pipeline; then since liquid metallic gallium totally soaks the bottom end of the first air inlet pipeline, the hydrogen chloride gas passes through the liquid metallic gallium and reacts with the liquid metallic gallium; eventually produced gallium chloride flows out from the first air outlet pipeline; and thus, the hydrogen chloride gas is allowed to fully react with metal gallium.
Owner:镓特半导体科技(上海)有限公司
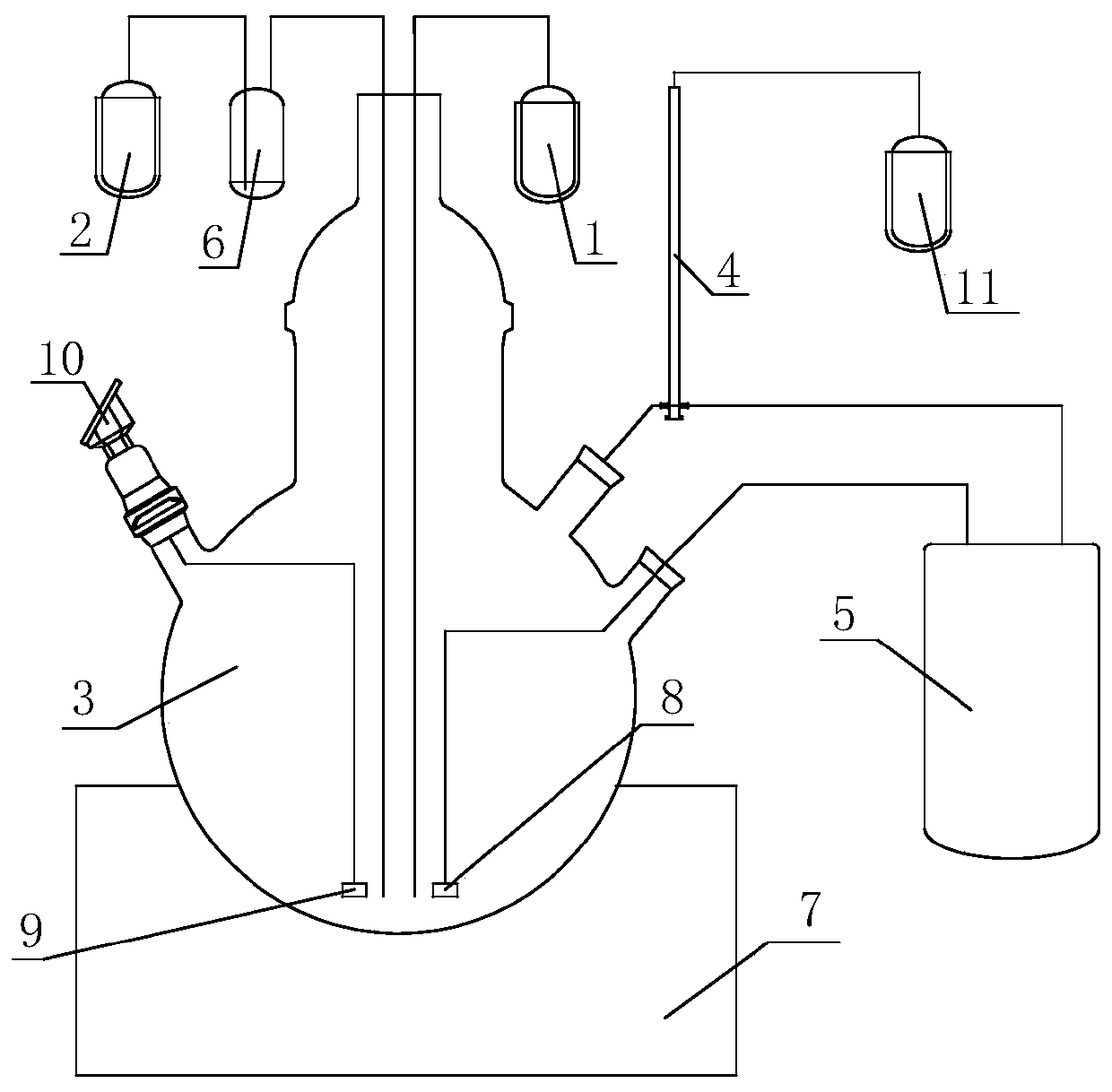
Method and equipment for preparing gallium trichloride
ActiveCN111072058ASolve technical problemsGallium/indium/thallium compoundsPressure vessel componentsReaction temperatureWater chlorination
The invention discloses a method for preparing gallium trichloride. The method comprises the following steps: adding liquid metal gallium into a reaction kettle, and introducing chlorine into the liquid metal gallium; controlling the temperature of the reaction kettle to be 200-400 DEG C, and obtaining a main product gallium monochloride and a byproduct gallium trichloride after a first preset time period; controlling the temperature of the reaction kettle to be 100-300 DEG C, and obtaining liquid gallium trichloride and gaseous gallium trichloride after a second preset time period; evaporating the obtained gaseous gallium trichloride into a fractionating tube, and performing cooling to enable the gaseous gallium trichloride to become liquid gallium trichloride to flow into a storage device. According to the method for preparing gallium trichloride provided by the invention, by setting reactions of two stages and setting different reaction temperatures of the two stages, the technicalproblem that a large amount of gallium monochloride and chlorine impurities are generated when chlorine is directly introduced into liquid metal gallium for reaction in the prior art can be effectively solved.
Owner:昆明先导新材料科技有限责任公司
Copper indium gallium selenium absorption layer prepared by non-vacuum method without selenizing process
ActiveCN109671787AStable structureFlat surfaceFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationIndiumAdhesive
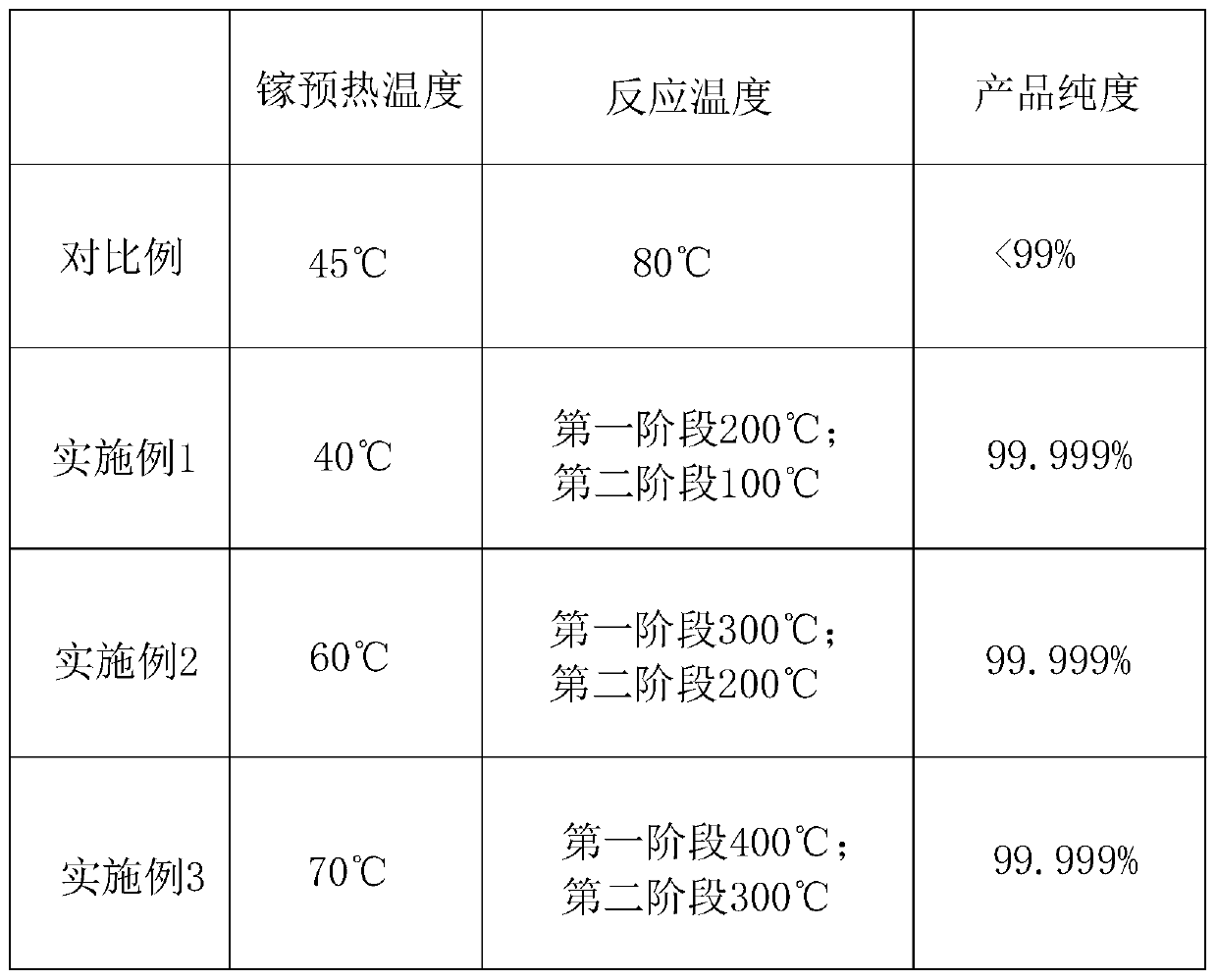
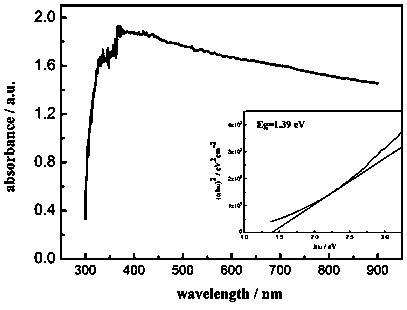
The invention relates to a copper indium gallium selenium absorption layer prepared by a non-vacuum method without a selenizing process. The non-vacuum method is characterized by comprising the threetechnological steps of: preparing copper indium gallium selenium colloid, preparing a copper indium gallium selenium precursor film and performing annealing heat treatment. Copper chloride, indium sulfate, gallium chloride and selenium dioxide are utilized as a Cu source, an In source, a Ga source and an Se source and are prepared according to the molar ratio (Cu to In to Ga to Se = 1 to 1.4 to 0.6 to 4); ethyl alcohol is utilized as a solvent; triethanolamine is simultaneously added into to serve as a complexing agent and an adhesive; the materials are stirred for dissolving under a certain temperature until white thick liquid is obtained; the white thick liquid is taken out, volatilized and aged; the white thick liquid is moderately dissolved into the ethyl alcohol and then scrape coatedor dispensed to a substrate; the copper indium gallium selenium absorption layer is obtained after certain-temperature heat treatment. The copper indium gallium selenium absorption layer disclosed bythe invention has the advantages of simple production technology and environmental protection; a flat copper indium gallium selenium film with a completed structure and a forbidden bandwidth of 1.39eV can be obtained without through any refeeding selenizing technology.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Aluminium oxide preparation and comprehensive utilization method through chlorination and electrolysis of fly ash
InactiveCN107200342AHigh degree of automationHigh purityElectrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesAluminium chlorideElectrolysis
An aluminium oxide preparation and comprehensive utilization method through chlorination and electrolysis of fly ash comprises the following steps: chloridizing and separating fly ash to obtain anhydrous aluminium chloride, silicon tetrachloride and gallium chloride; converting anhydrous aluminium chloride into an aluminium chloride water solution; controlling the voltage and the current density, and electrolyzing the aluminium chloride water solution to obtain aluminium hydroxide, hydrogen and chlorine; returning chlorine generated by electrolysis to a chlorination section; roasting aluminium hydroxide to obtain metallurgical-grade / chemical aluminium oxide; and performing distillation purification on silicon tetrachloride to generate polycrystalline silicon and zinc chloride. The aluminium oxide preparation and comprehensive utilization method is low in cost, cheap and easily accessible in raw material, simple in operation process, high in degree of automation and high in product purity, and the adopted raw materials, zinc, chlorine and the like, can be recycled.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Nitride-based semiconductor substrate and method of making the same
ActiveUS7662488B2High transparencyImprove conductivityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrometerLength wave
A nitride-based semiconductor substrate having a diameter of 25 mm or more, a thickness of 250 micrometers or more, and an optical absorption coefficient of less than 7 cm−1 to light with a wavelength of 380 nm or more. The nitride-based semiconductor substrate is made by the HVPE method that uses gallium chloride obtained by reacting a Ga melt with a hydrogen chloride gas. The Ga melt is contacted with the hydrogen chloride gas for one minute or more to produce the gallium chloride.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Method for chlorinating and electrolyzing bauxite to prepare alumina and comprehensively utilizing bauxite
InactiveCN107244682AReduce processing linksLow costZinc halidesPolycrystalline material growthFerric hydroxideAluminium chloride
A method for chlorinating and electrolyzing bauxite to prepare alumina and comprehensively utilizing bauxite comprises the following steps: chlorinating and separating chlorite to respectively obtain anhydrous aluminum chloride, anhydrous ferric chloride, silicon tetrachloride, titanium tetrachloride, scandium chloride and gallium chloride; converting the anhydrous aluminum chloride and the anhydrous ferric chloride into an aqueous aluminum chloride solution and an aqueous ferric chloride solution; electrolyzing the corresponding aqueous solutions at a controlled voltage and a controlled current density for a controlled electrolysis time to obtain aluminum hydroxide, ferric hydroxide, hydrogen and chlorine; returning the chlorine to the above chlorination section; calcining the aluminum hydroxide to obtain metallurgical grade / chemical grade alumina; calcining the ferric hydroxide to obtain iron red or other iron-containing products; rectifying and purifying the silicon tetrachloride to generate polysilicon and zinc chloride; refining the titanium tetrachloride to form a sponge titanium raw material; and enriching the scandium chloride in chloride residues to obtain a scandium extraction raw material. The method has the advantages of low cost, cheap and easily available raw materials, simple operating process, high automation degree, high product purity, and realization of recycling of zinc, chlorine and other raw materials.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
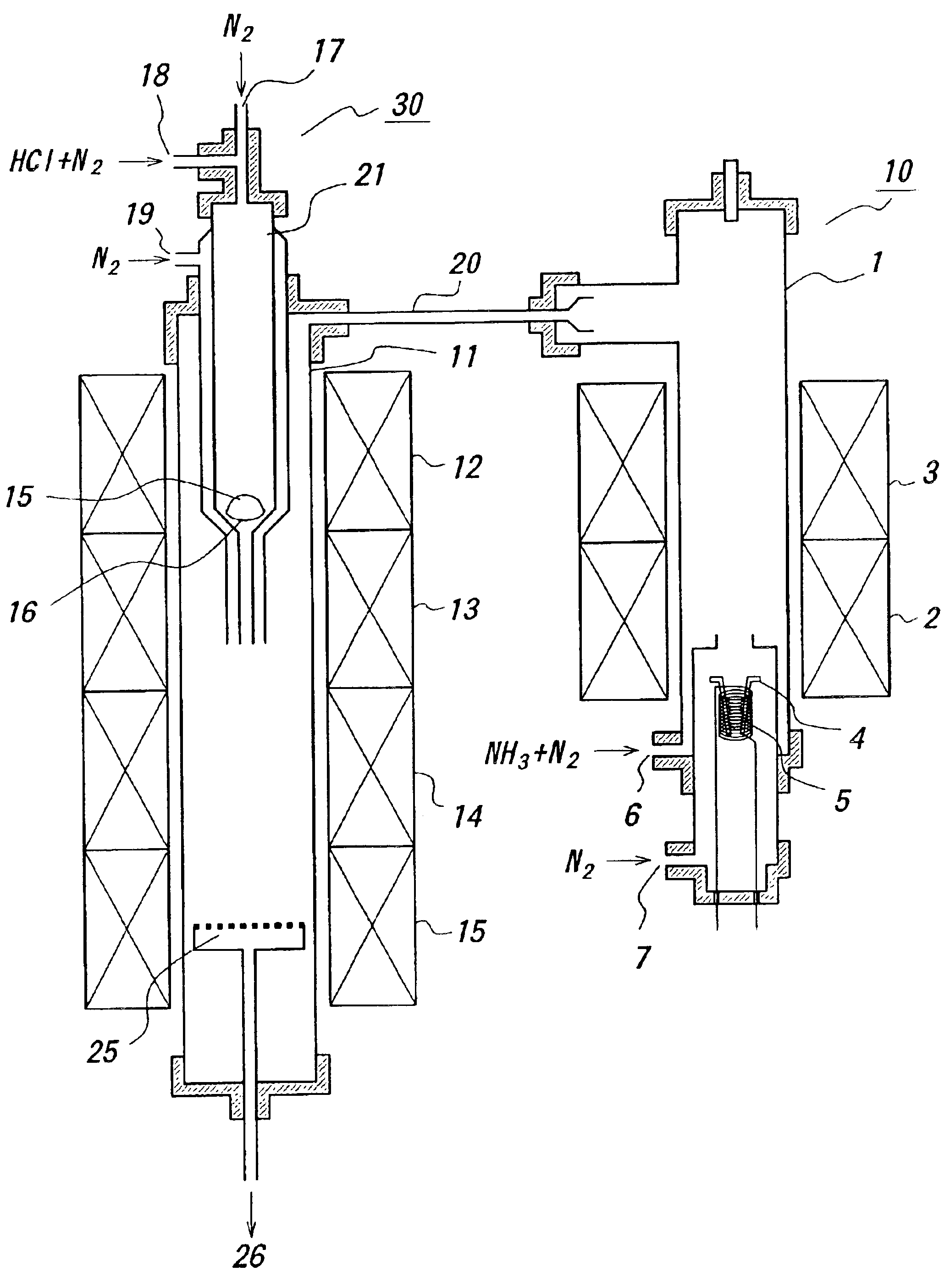
Process for producing gan single-crystal, gan thin-film template substrate and gan single-crystal growing apparatus
InactiveCN101517134AInhibit growthControl film thicknessPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsSingle crystal
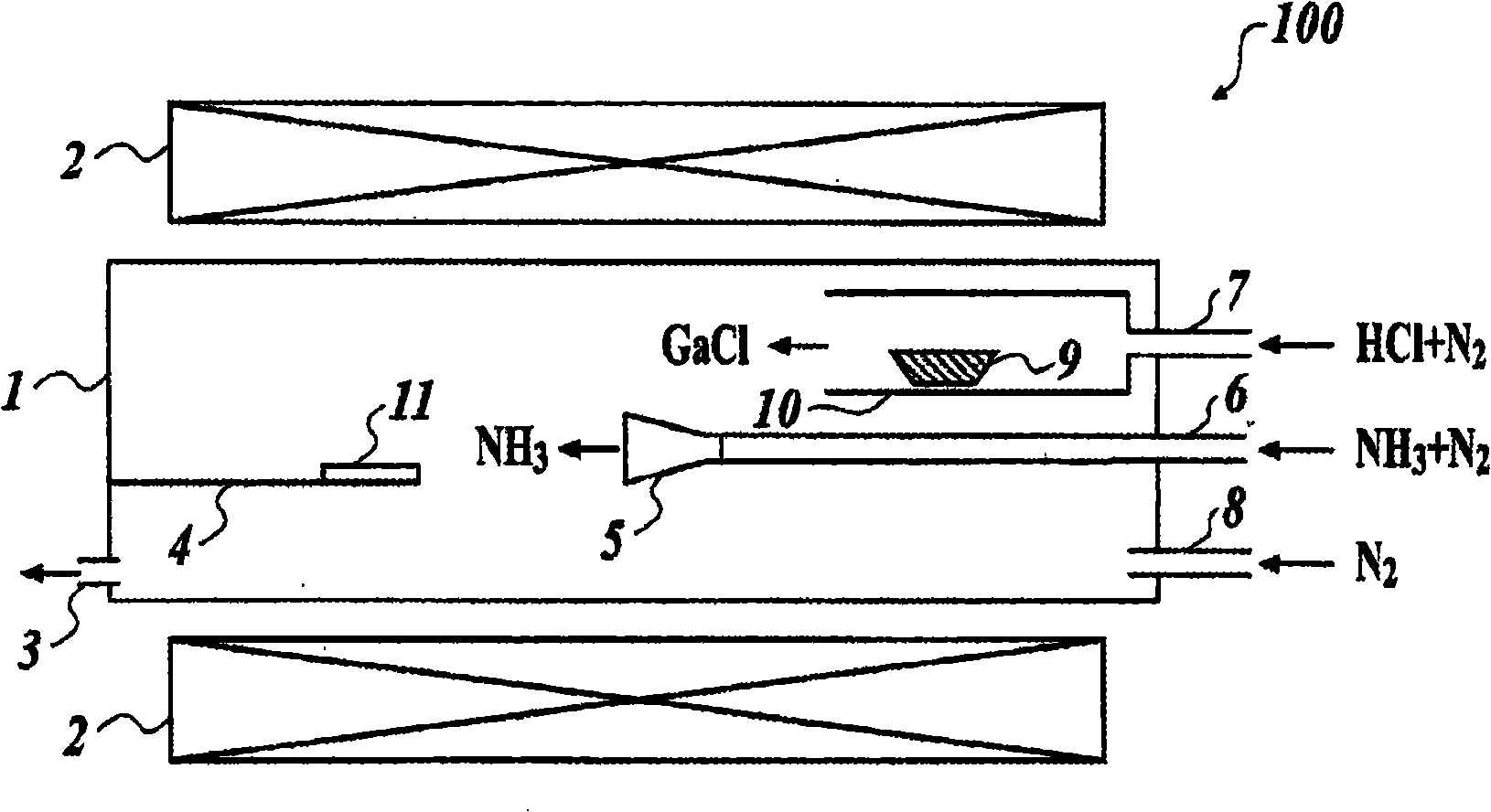
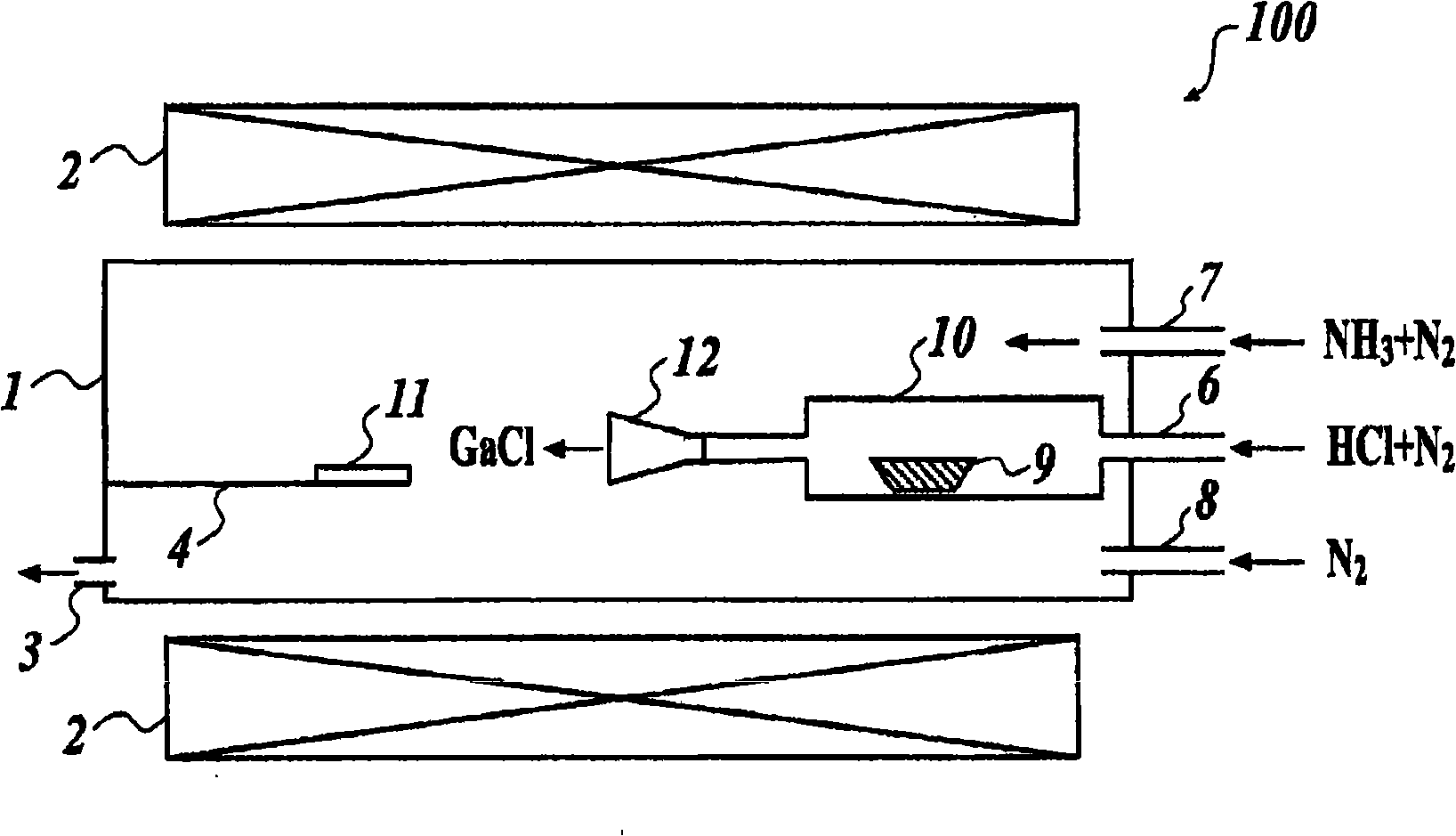
Provided are a manufacturing method of a GaN single crystal in which the film thickness of the GaN single crystal can be controlled accurately, even when a hydride vapor phase epitaxy is applied; a GaN thin film template substrate which is suitable for growing a GaN thick film with a fine property; and a GaN single crystal growing apparatus. Provided is a manufacturing method of a GaN single crystal by a hydride vapor phase epitaxy, wherein the hydride vapor phase epitaxy comprises: spraying HCl (hydrogen chloride) onto Ga (gallium) which is heated and fused in a predetermined temperature to generate GaCl (gallium chloride); and forming a GaN thin film by a reaction of the generated GaCl (gallium chloride) with NH 3 (ammonia) gas which is hydroxide gas on a substrate, the manufacturing method comprising supplying the NH 3 gas in a vicinity of the substrate (for example, at a position which is separated from the substrate by a distance of 0.7-4.0 times as longer than a diameter of the substrate) through a nozzle. Further, as the substrate, an NGO(011) substrate in which the lattice constant thereof is similar to that of GaN is used.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CO LTD
Preparation method of ionic liquid electrodeposition copper/indium/gallium/selenium CIGS thin-film materials
InactiveCN103343373AReproduce manufacturingLow costElectrolytic inorganic material coatingElectrolysisSe element
The invention discloses a preparation method of ionic liquid electrodeposition copper / indium / gallium / selenium CIGS thin-film materials, belonging to the technical field of materials. The method comprises the following steps: 1. measuring ionic liquid BMIm-OTF (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate), copper chloride, indium chloride, gallium chloride and selenium chloride, putting the ingredients into a sealed electrolytic bath, and uniformly stirring to obtain electroplate liquid; and 2. performing CIGS thin film electrodeposition on a base material of a working electrode by utilizing an electrodeposition method. The invention provides the method for manufacturing CIGS thin films with excellent appearance, and the method is low in cost, reproducible, and the CIGS thin-film materials are easy to prepare, excellent in comprehensive performance, stable in process, good in reproducibility and high in photoelectric conversion efficiency. The band gap width of the materials prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention can reach to 1.55 eV, and the charge carrier concentration and the hall coefficient are respectively 2.741*10<20>cm<-3> and 2.277*10<-2> cm<3> / C.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com