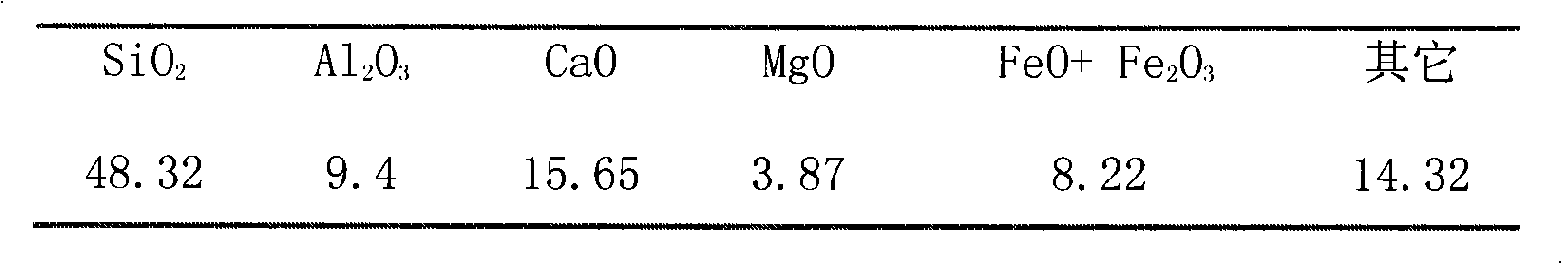Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1002 results about "Forming pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pressure forming is an advanced plastic manufacturing process whereby a plastic sheet is molded to a complex and detailed shape. Pressure forming is an enhancement to the vacuum forming process. With traditional vacuum forming, the parts are being formed by creating a vacuum on the mold side of the sheet.
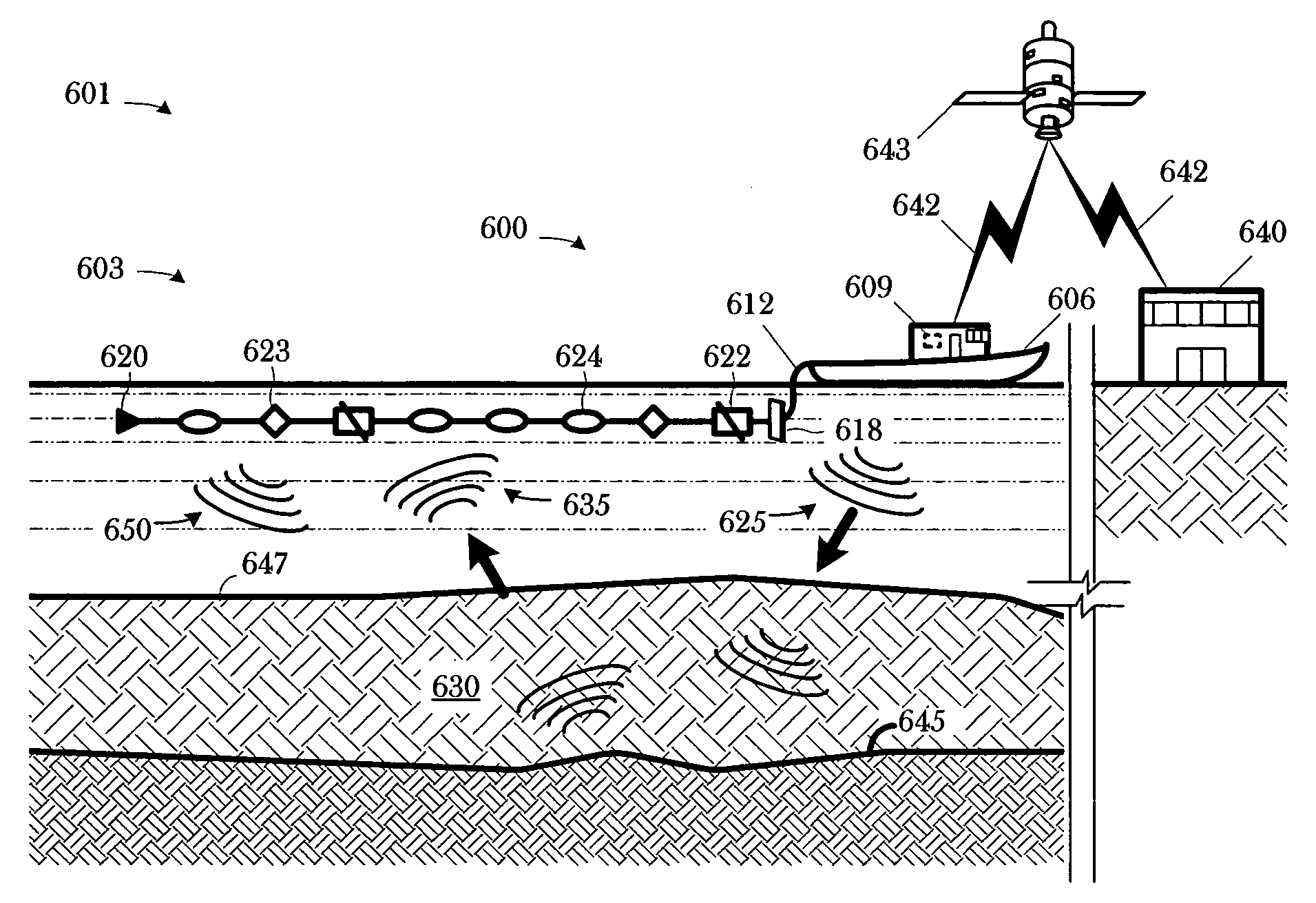
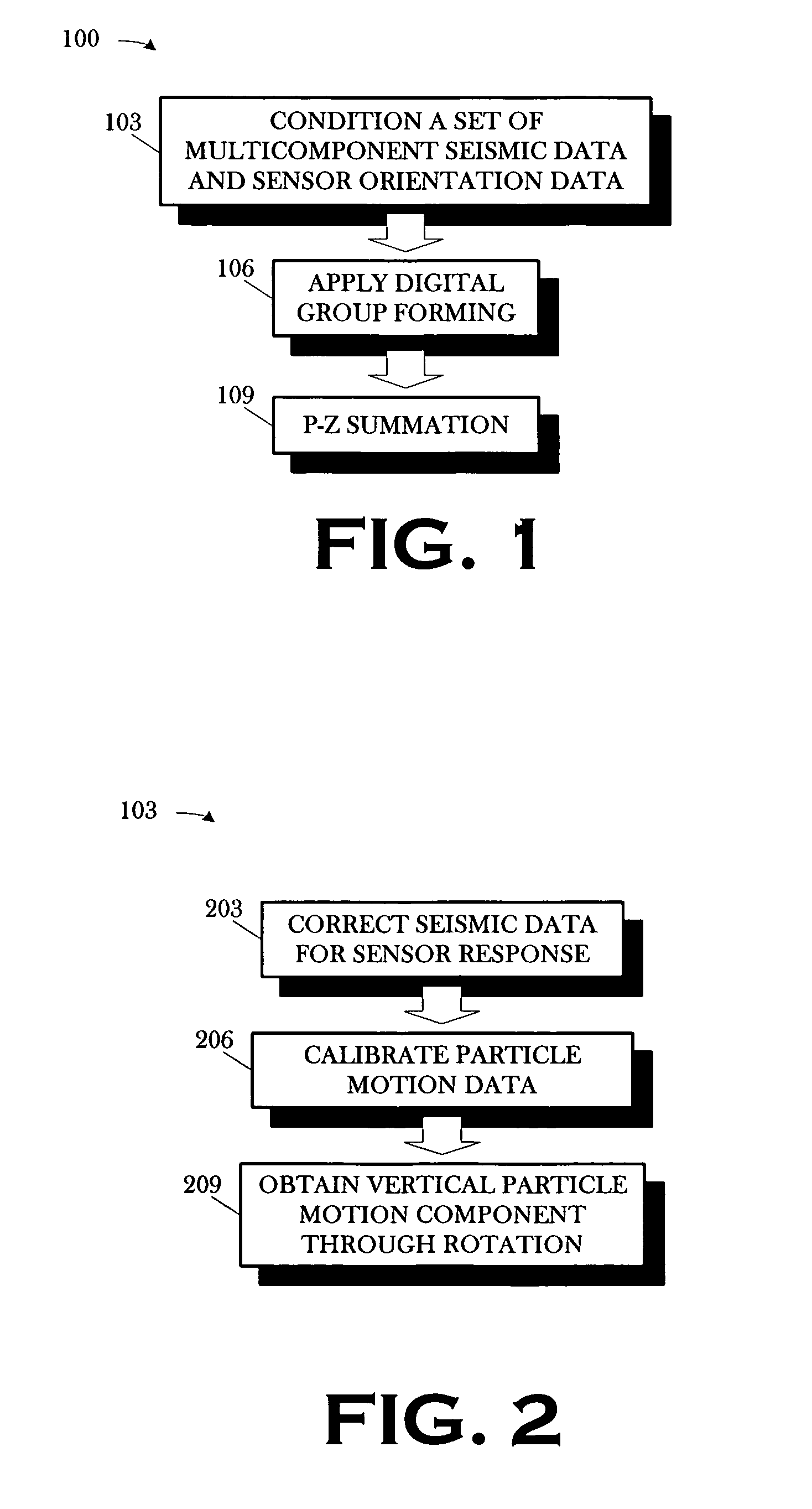
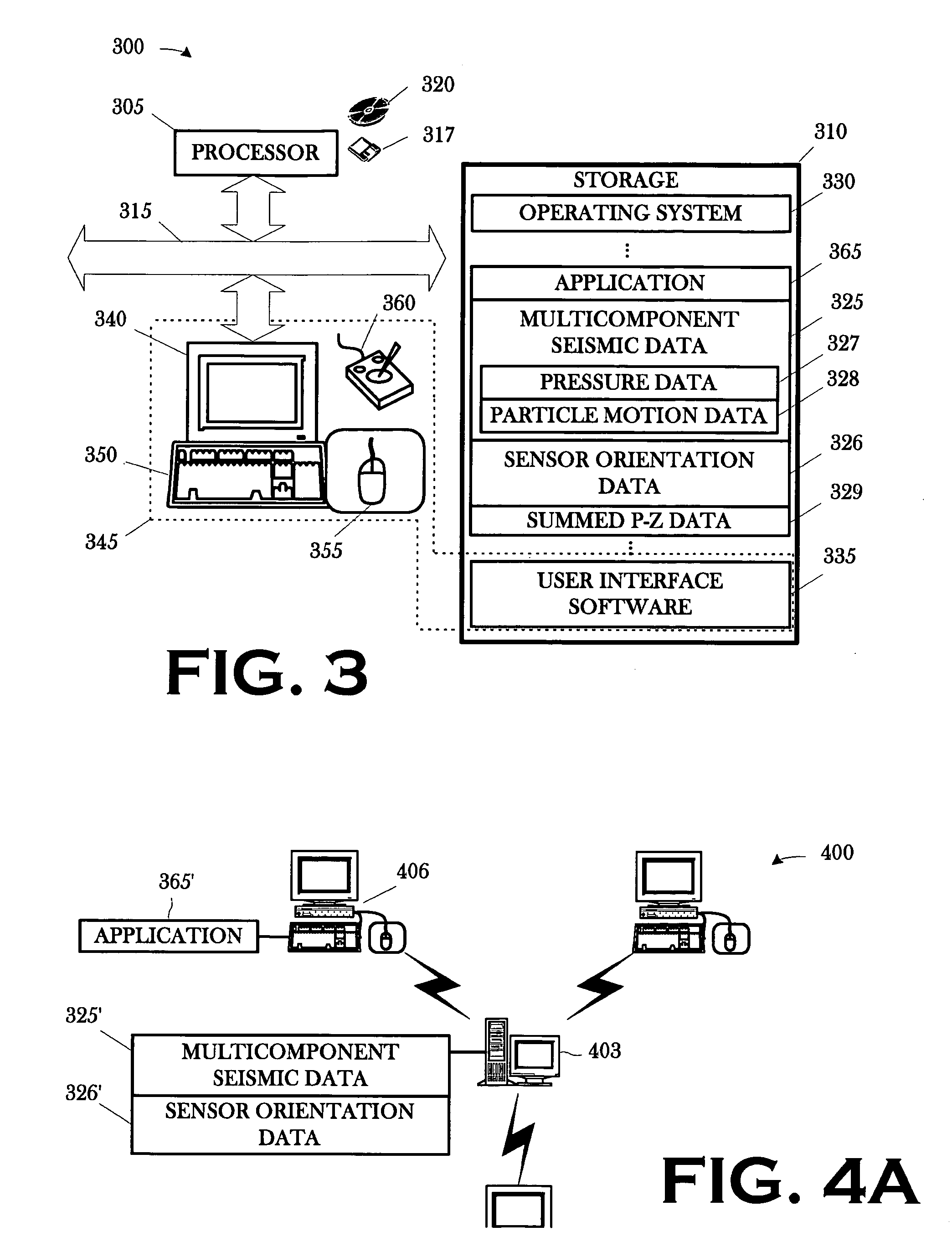
Workflow for processing streamer seismic data
ActiveUS20080049551A1Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyWork flow
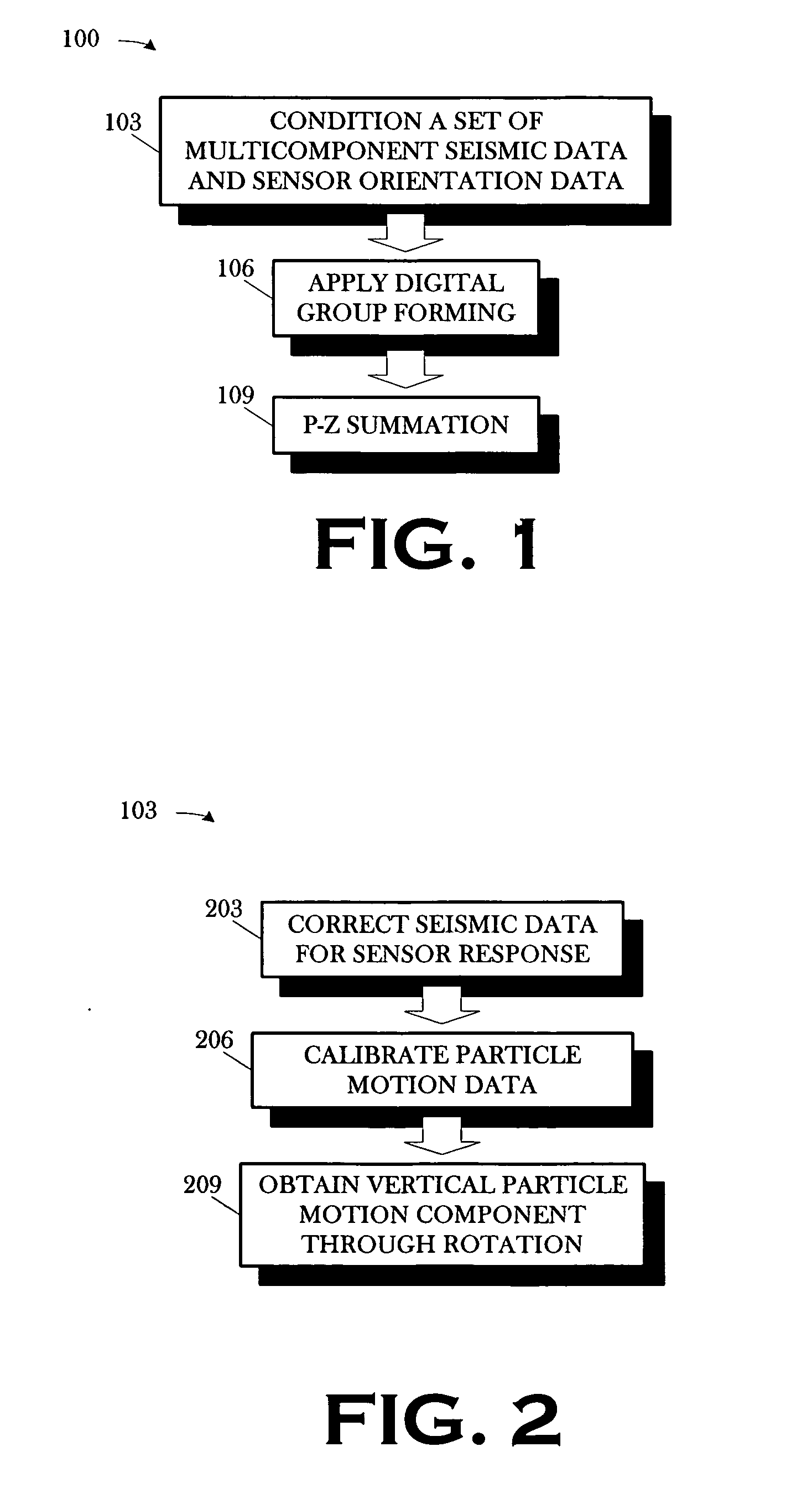
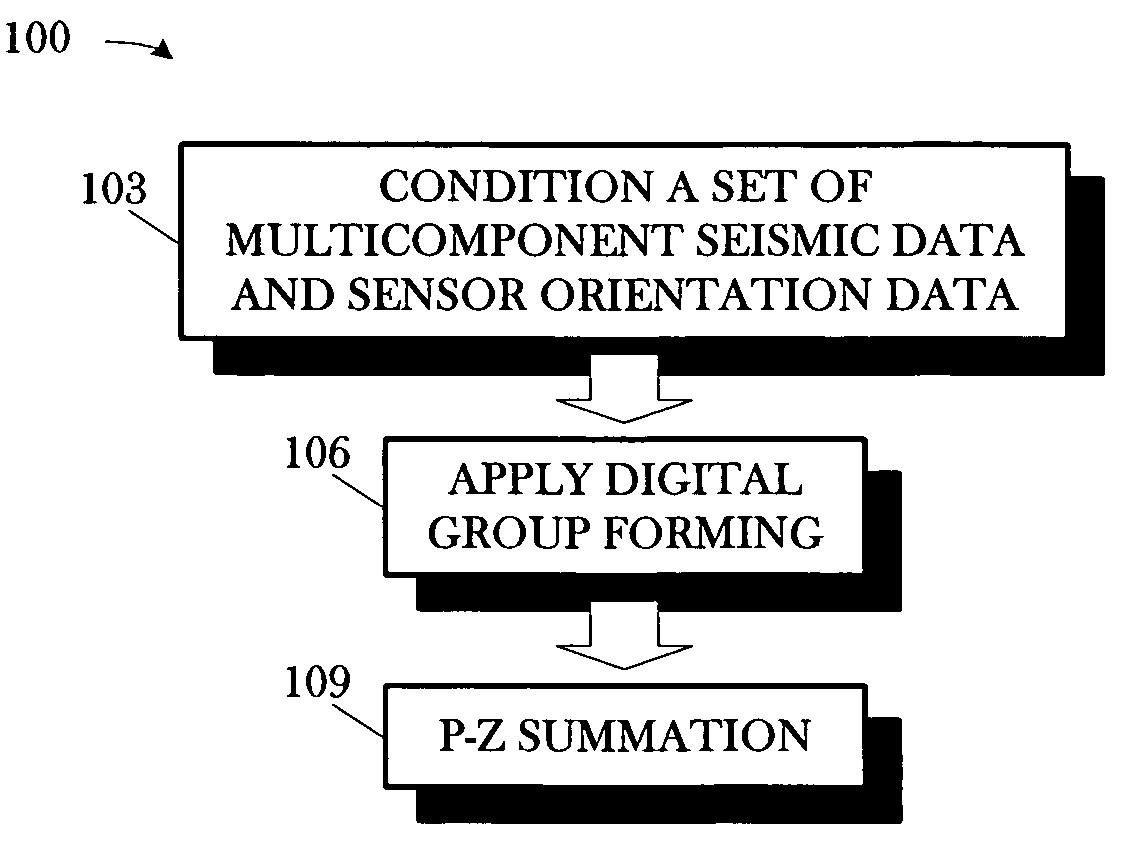
A method includes conditioning a set of multicomponent seismic data and sensor orientation data, the multicomponent seismic data including pressure data and particle motion data, acquired in a towed array, marine seismic survey; digital group forming the conditioned pressure data, a vertical particle motion component of the conditioned particle motion data, and the conditioned sensor orientation data; and summing the digitally group formed pressure data and the digitally group formed vertical particle motion component.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Workflow for processing streamer seismic data
A method includes conditioning a set of multicomponent seismic data and sensor orientation data, the multicomponent seismic data including pressure data and particle motion data, acquired in a towed array, marine seismic survey; digital group forming the conditioned pressure data, a vertical particle motion component of the conditioned particle motion data, and the conditioned sensor orientation data; and summing the digitally group formed pressure data and the digitally group formed vertical particle motion component.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
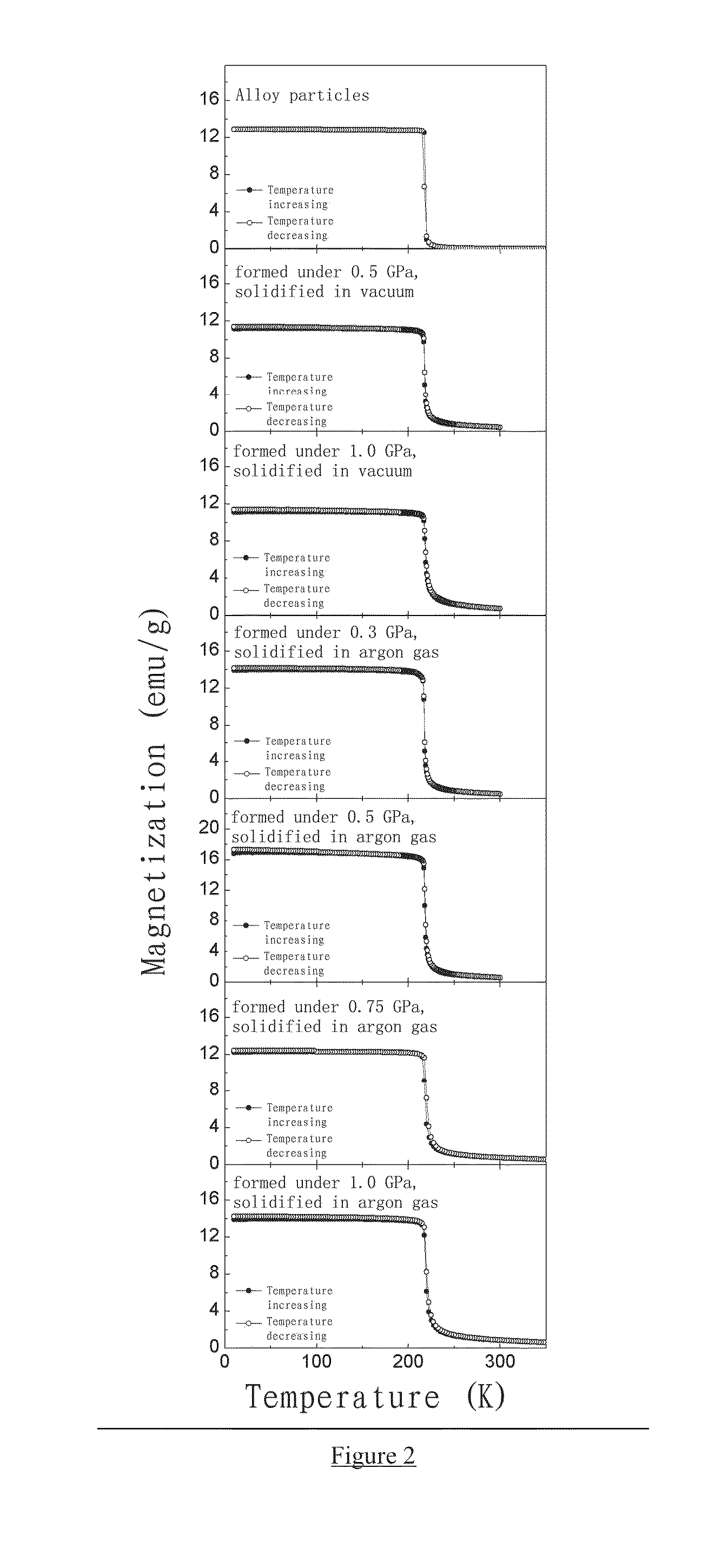
BONDED La(Fe,Si)13-BASED MAGNETOCALORIC MATERIAL AND PREPARATION AND USE THEREOF
InactiveUS20150047371A1Low priceEasy to operateInorganic material magnetismMachines using electric/magnetic effectsCeriumCobalt
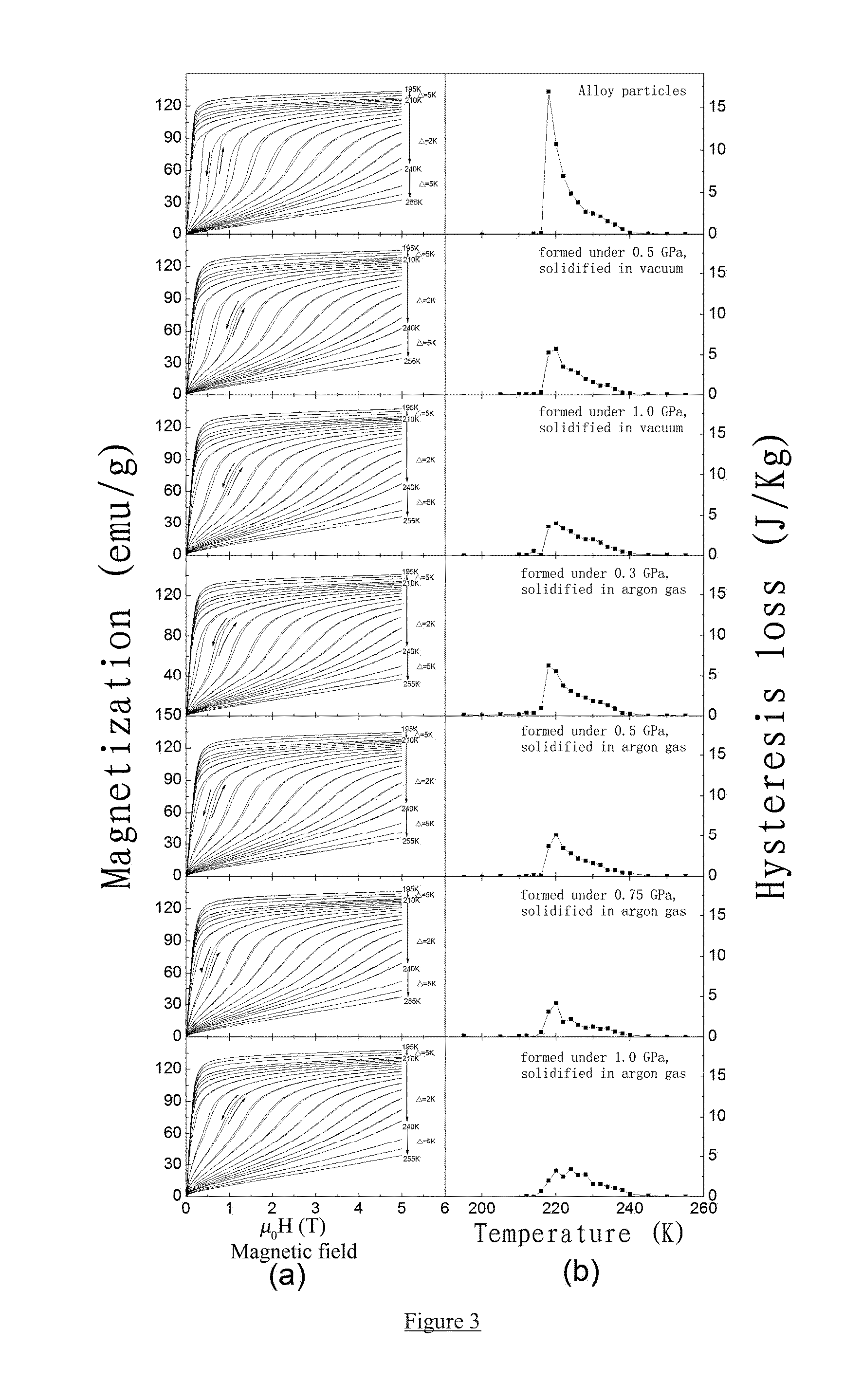
Provided is a high-strength, bonded La(Fe, Si)13-based magnetocaloric material, as well as a preparation method and use thereof. The magnetocaloric material comprises magnetocaloric alloy particles and an adhesive agent, wherein the particle size of the magnetocaloric alloy particles is less than or equal to 800 μm and are bonded into a massive material by the adhesive agent; the magnetocaloric alloy particle has a NaZn13-type structure and is represented by a chemical formula of La1-xRx(Fe1-p-qCopMnq)13-ySiyAα, wherein R is one or more selected from elements cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr) and neodymium (Nd), A is one or more selected from elements C, H and B, x is in the range of 0≦x≦0.5, y is in the range of 0.8≦y≦2, p is in the range of 0≦p≦0.2, q is in the range of 0≦q≦0.2, α is in the range of 0≦α≦3.0. Using a bonding and thermosetting method, and by means of adjusting the forming pressure, thermosetting temperature, and thermosetting atmosphere, etc., a high-strength, bonded La(Fe, Si)13-based magnetocaloric material can be obtained, which overcomes the frangibility, the intrinsic property, of the magnetocaloric material. At the same time, the magnetic entropy change remains substantially the same, as compared with that before the bonding. The magnetic hysteresis loss declines as the forming pressure increases. And the effective refrigerating capacity, after the maximum loss being deducted, remains unchanged or increases.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
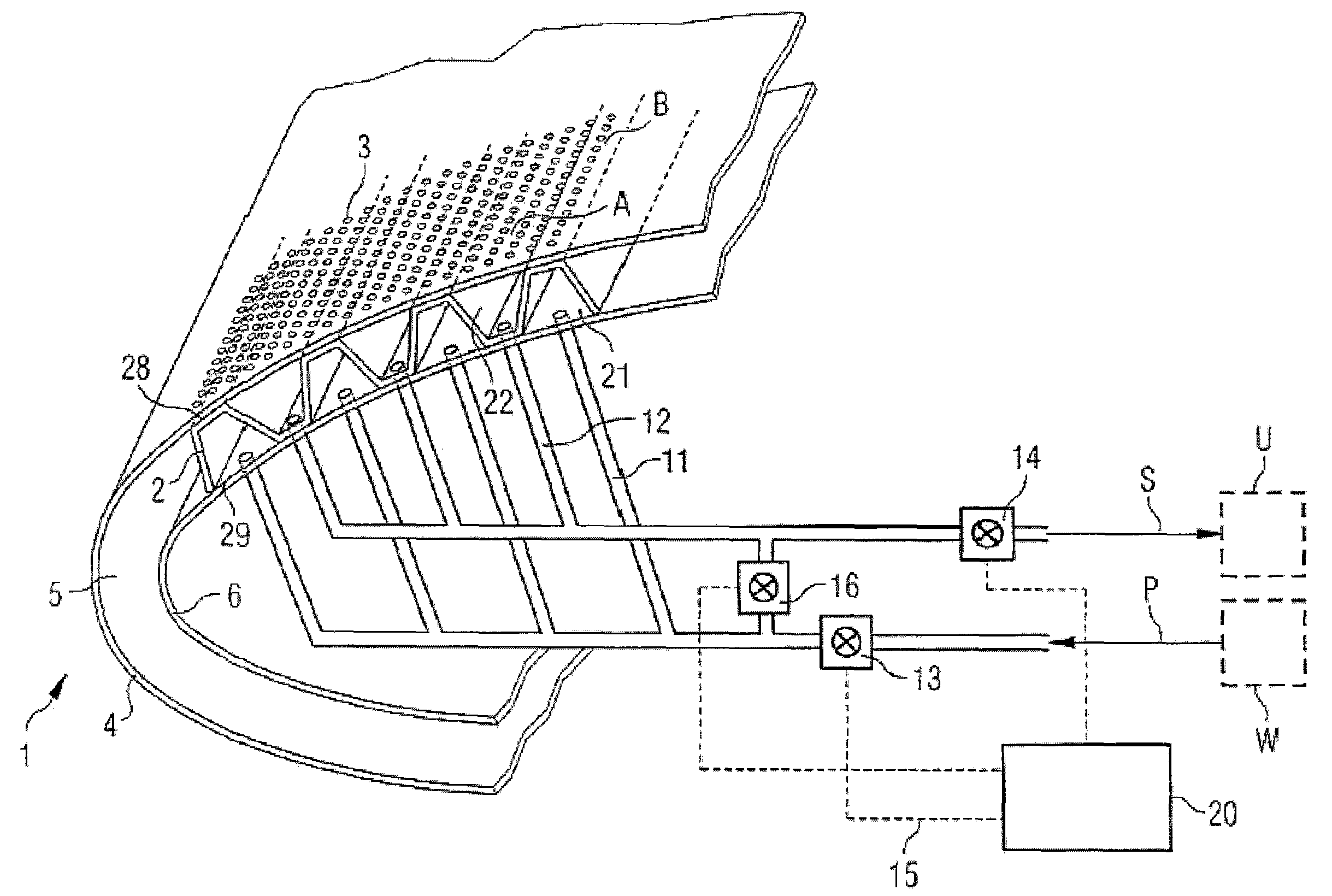
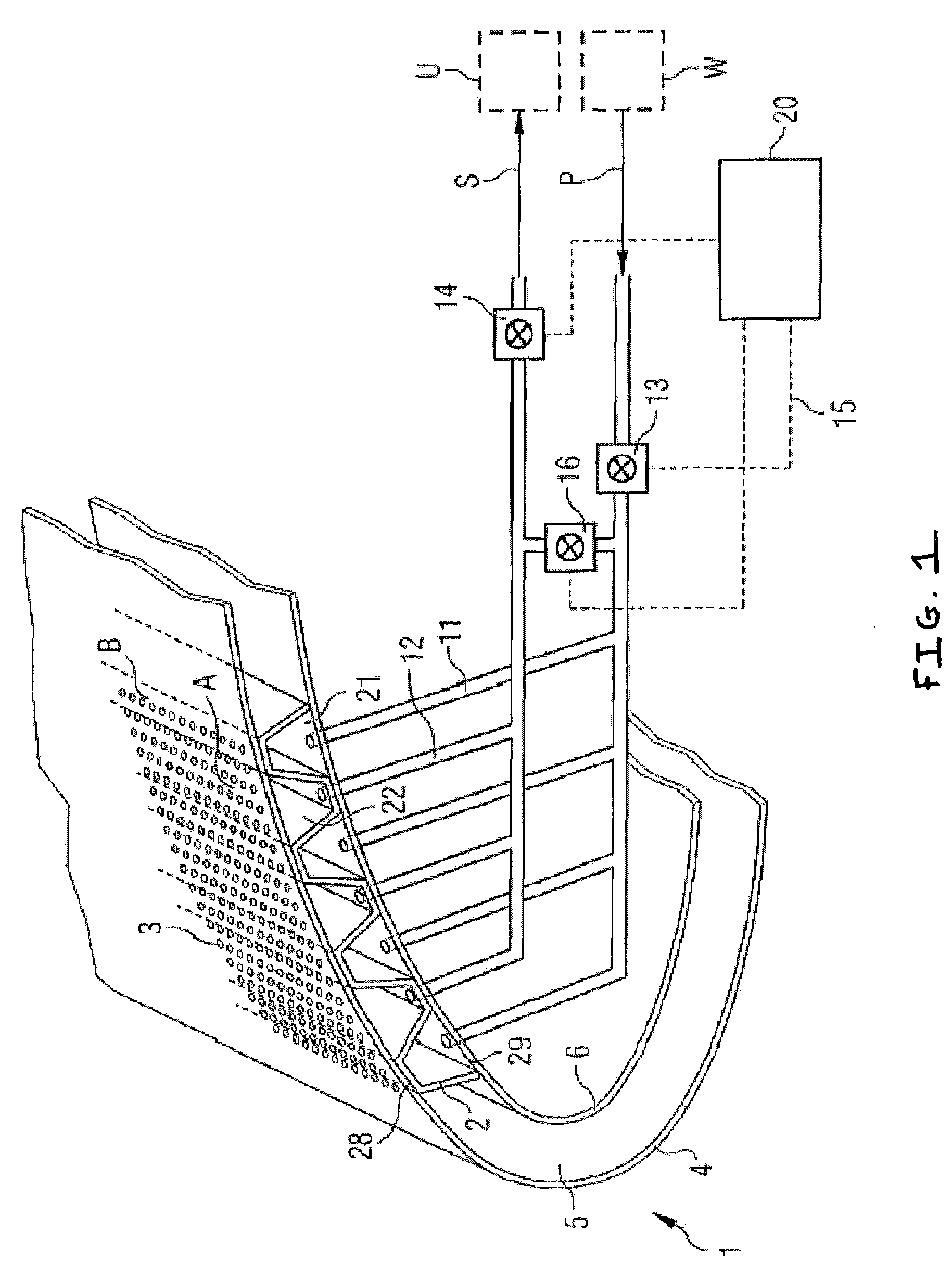
Aircraft component exposed to streaming surrounding air
ActiveUS7673832B2Avoid insufficient heatingAircraft stabilisationDe-icing equipmentsCross connectionEngineering
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Pressure-sensitive adhesive composition
InactiveUS20050277729A1Improve responseNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesLayered productsInfraredHindered amine light stabilizers
A pressure-sensitive adhesive composition which comprises a pressure-sensitive adhesive polymer (A), a near-infrared absorbing dye (B), an ultraviolet absorber (C) and / or a hindered amine light stabilizer (D) is provided. The pressure-sensitive adhesive composition makes it possible to lessen deterioration of the near-infrared absorbing dye used by ultraviolet rays. Also, the composition is suited for use in forming pressure-sensitive adhesive layers and the like for sticking together laminar materials forming plasma displays and the like, can combine the functions of the respective layers in the plasma display front face plate in the pressure-sensitive adhesive layer formed, is capable of absorbing near-infrared rays as well as ultraviolet rays and, further, exhibits a color tone-adjusting function.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Wall-attachment fluidic sprinkler
InactiveCN101224444AEasy to openEasy to closeMovable spraying apparatusSpray nozzlesWater flowEngineering
The invention pertains to a key equipment for water-saving irrigation, which is a wall-attached fluidic sprinkler, comprising a sprinkler body, a thrust jet, a rotary sealing mechanism, a spacing ring, a reversing mechanism and a fluidic element body. The sprinkler is characterized in that the fluidic element consists of a reverse gulp nozzle, a signal water joint nozzle, an outlet cover, a signal water entry nozzle and a draft tube; on the outer wall of the fluidic element body, the signal water joint nozzle and the reverse gulp nozzle positioned below signal water joint nozzle are arranged at one side; the signal water entry nozzle is arranged at the other side. The signal water joint nozzle and signal water entry nozzle are connected by the draft tube; the outlet cover is arranged at the upper end of the fluidic element body. The signal water inside the signal water joint nozzle causes one side of the main fluid to form a low pressure vortex region discontinuously. The opening and closing of the gulp nozzle causes another side of the main fluid to switch between high pressure and low pressure, thus forming pressure difference between two ends of the main fluid to realize water attaching and complete direct jetting of the nozzle, stepping and reverse running of the sprinkler.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Electrical heating numerical control incremental forming processing method and device for plate
The invention relates to a device and a method of the electrical heating numerical control incremental forming processing of a sheet metal and belongs to the technical field of the sheet metal incremental forming processing. The key points of the device and the method lie in that a large current-carrying wire is used for forming an auxiliary power supply, a forming pressure head, a forming clamp and the sheet metal into a current loop; the power supply provides a low-voltage large current to cause the materials in a processing area to generate joule heat and to be softened in the sheet metal processing and forming so as to ensure the smooth implementation of the incremental forming processing. The heating method is fast in temperature rising, convenient in control and low in price, thus solving the problem that other heating methods are complex to control, improving the processing precision and being favorable for forming complex parts. At the same time, the method is suitable for the incremental processing of sheet metals such as the titanium magnesium sheet metal, and the like, which are hard to be plastically formed at normal temperature.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +1
High-pressure gas injection hole-drilling pressure-releasing outburst prevention method
ActiveCN102080525AIncrease the exposed areaImprove breathabilityLiquid/gas jet drillingFluid removalEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention discloses a high-pressure gas injection hole-drilling pressure-releasing outburst prevention method which comprises the steps of: firstly, carrying out common drilling operation in a bottom plate stone drift (2) of a coal bed (1) in front of a coal mining or driving face; after a drill hole (3) enters a design depth of the coal bed, drawing back a drill, sending a jet nozzle (4) anda high-pressure drill rod (5) connected with the jet nozzle into the drill hole, and connecting a high-pressure gas-storing device (6) connected with the tail of the high-pressure drill rod (5) with a high-pressure gas compressing device (7) through a high-pressure tube; starting the high-pressure gas compressing device (7), carrying out near cylinder rotary impacting, cutting and holing on the hole wall of the drill hole in the coal bed (1) by using high-pressure impact wave as a power source through the jet nozzle (4) capable of jetting high-pressure airflow and automatically rotating to ensure that the coal body around the drill hole (3) is gradually crushed and separated from the hole wall to form pressure releasing space and subjected to the pressure balanced permeability increase through ground pressure and gas pressure action. According to the invention, the drainage efficiency of the gas in the coal bed is greatly improved and the outburst damage of the coal bed is reduced.
Owner:河南省迪卡尔机电设备制造有限公司
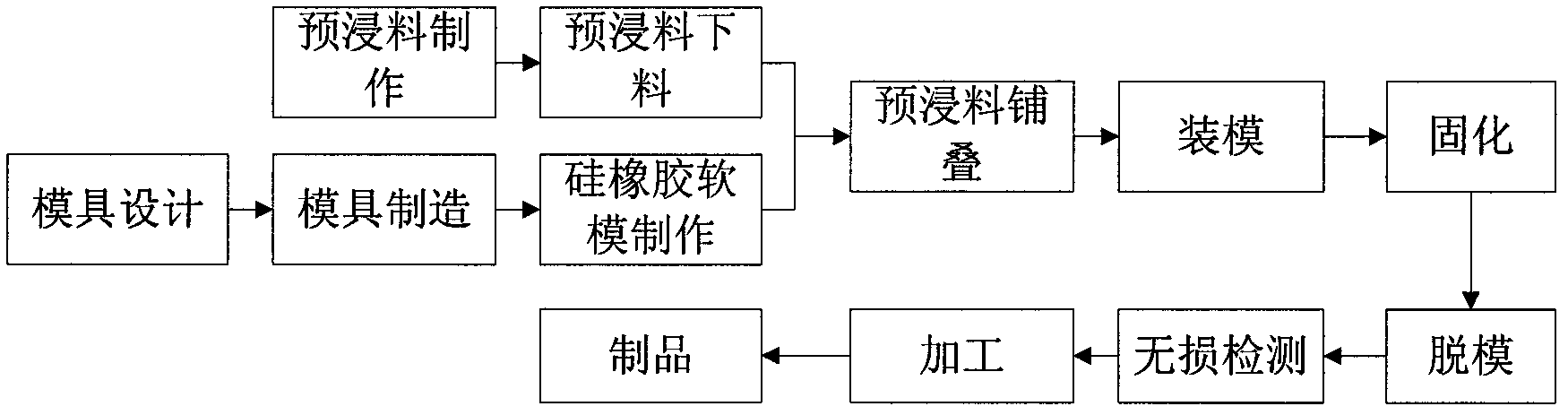
Forming process of curved composite tube
ActiveCN102320139ASolve the difficulty of demouldingSolve sizeTubular articlesCavity sizeHigh dimensional
The invention provides a forming process of a curved composite tube. The forming process comprises the following steps of: manufacturing a forming die; preparing prepregs; laying up the prepregs; assembling the die; curing; and de-molding. The forming process has the beneficial effects that a closed and combined hard die is utilized as the forming die, a silicon rubber flexible die is utilized asthe inner cavity of the curved composite tube, and the size of the silicon rubber flexible die is determined by means of the forming pressure and the swelling property of silicon rubber, which solvesthe difficulties of the curved composite tube such as difficult de-molding process and difficult control of the cavity size of the product and ensures that the size of the inner cavity meets the requirements after the formed product is smoothly de-molded; the integral informing technology is adopted so as to solve the difficulties of extension positions at two sides of the curved composite tube such as difficult pressurization, difficult control of overall quality and the like, thus achieving the purpose of one-time forming of the product and meeting the requirements for dimensional precision; and by means of layering design and forming process control of a composite material, the problem of easiness in deformation of the formed curved composite tube is solved so as to meet the requirements for accuracy control of the product. The curved composite tube formed by the forming process has the advantages of better structural quality, higher performance, higher dimensional precision and higher curvature forming precision.
Owner:AEROSPACE RES INST OF MATERIAL & PROCESSING TECH
Photocurable composition for the formation of pressure-sensitive adhesive layer and dicing tape produced using the same
InactiveCN101376797ALow maximum peel strengthGood pickupNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesFilm/foil adhesivesPolymer resinDicing tape
The present invention discloses a photocurable composition used for forming pressure sensitive adhesive layer. The photocurable composition comprises pressure sensitive adhesive binder, reactive acrylate, thermal curing agent and phtoinitiator. The pressure sensitive adhesive binder is composed of pressure sensitive adhesive polymer resin and low molecular weight acrylate which comprises carbon-carbon double bond and is led into side chain of pressure sensitive adhesive resin. The reactive acrylate comprises dimethyl cyclosiloxane unit in molecular chain. The invention also discloses a cutting rubber belt which comprises a pressure sensitive adhesive layer formed by the photocurable composition. When a thin wafer is installed on cutting rubber belt, cut and radiated by UV, no connection occurs. Therefore the maximum peeling strength between the pressure sensitive adhesive layer and thin wafer is quite low, and the collecting capability of thin wafer is excellent.
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
Process for preparing coal-based agglomerated activated carbon
The invention discloses a process for preparing coal-based agglomerated activated carbon. The process has the following beneficial effects: the non-caking coal produced in the wide ditches is taken as a main raw material; the special caking coal type, namely gas-fat coal, is blended in the coal blending procedure; furthermore, the oxidation procedure is added in the process; the process parameters such as pulverized coal particle distribution, forming pressure, coal activation temperature and time and the like in the general production process are adjusted; at the same time, the slow carbonization technology is used instead of the traditional rapid carbonization procedure; and oxygen-enriched air is fed into activation equipment. The coal-based activated carbon prepared by the process can ensure the product strength and bulk density on the basis of satisfying the iodine adsorption of the activated carbon and is better in industrial application value.
Owner:SHENHUA XINJIANG ENERGY
Multi-deformed bending forming method and device for pipe fitting
The invention discloses a multi-deformed bending forming method for a pipe fitting. The method comprises the following steps: 1) placing a tube blank into an inner cavity of a hydraulic bulging die, 2) filling up a cylinder at an external part of the hydraulic bulging die with liquid, and mounting a punch with a through hole and an overflow valve on the cylinder, 3) driving movement of a piston of the cylinder to extrude the liquid in the cylinder so as to obtain high-pressure liquid, and injecting the high-pressure liquid into the tube blank through the punch, so that the tube blank obtains a hydraulic pressure required for bulging, 4) starting applying an axial force to the end part of the tube blank by the punch when the piston contacts the punch arranged inside the cylinder, and 5) controlling the axial force by controlling a travel of the piston, and controlling the size of the hydraulic pressure for forming the tube blank by adjusting an overflow value of the overflow valve so as to gradually increase a forming pressure of a forming apparatus, so that a transition fillet of the tube blank gradually gets close to the hydraulic bulging die, and achieves the required shape. The invention also discloses a multi-deformed bending forming device of the pipe fitting. The procedure and the die are simplified and the cost is reduced.
Owner:吉林省元隆达工装设备有限公司
Method of forming metal
InactiveUS8015849B2Electromagnets without armaturesMetal-working apparatusEngineeringElectromagnetic forming
Electromagnetic forming can lead to better formability along with additional benefits. The spatial distribution of forming pressure in electromagnetic forming can be controlled by the configuration of the actuator. A type of actuator is discussed which gives a uniform pressure distribution in forming. It also provides a mechanically robust design and has a high efficiency for flat sheet forming.
Owner:AMERICAN TRIM
Method for manufacturing large silicon oxide ceramic sheet
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a large silicon oxide ceramic sheet. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing blank soil particles serving as raw materials, preparing the green body of the large silicon oxide ceramic sheet, preparing the base body layer plain panel of the large silicon oxide ceramic sheet and preparing the large silicon oxide ceramic sheet finished product. The large silicon oxide ceramic sheet is prepared from the following raw materials in part by weight: 30 to 60 parts of needle-like wollastonite, 25 to 30 parts of clay, 15 to 20 parts of mullite, 15 to 20 parts of china clay, 10 to 20 parts of feldspar and 10 to 30 parts of bentonite; the needle-like wollastonite accounts for 28.57 to 36.36 percent based on the total weight of the raw materials; and the draw ratio of the needle-like wollastonite is (16.5-20):1. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: pressing blank soil particles serving as the raw materials to form the green body under the forming pressure of 6,000 to 7,000tons / m<2>; drying at the temperature of between 80 and 250 DEG C for 40 to 100 minutes; biscuitfiring the base body layer plain panel at the temperature of between 800 and 1,300 DEG C for 50 to 120 minutes; and glazing, printing, firing at the temperature of between 900 and 1,300 DEG C for 30 to 120 minutes to obtain the large silicon oxide ceramic sheet finished product. A rubber pad and redundant green body materials are completely recycled. The specification of the large silicon oxide ceramic sheet finished product is that: the ratio of length to width to thickness is 1,500-2,200mm to 800-1,500mm to 3-6mm.
Owner:山东德惠来装饰瓷板有限公司
Al-C fireproof material for continuous casting and its production method
A fireproof material containing aluminum and carbon for continuous casting. Taking aluminum oxide and carbon as the main components, it includes 0.5í½5.0úÑ boron nitride and 1.0í½5.0úÑ carborumdum by weight. The preparation method thereof comprises mixing white alundum, graphite, zirconium mullite, carborundum, industrial silicon ,2.0úÑ??.0úÑ solid phenol resin and 5úÑí½15úÑ liquid phenol resinby weight, and moulding at equal static pressure of 120í½150Mpa for 10-20 min, the moulded semi-product is dried and burned at 1280í½1350degree C for 60-70 hours. The product is suitable for columns of sagger, downspouts, with good heat-shock stability and resistibility of erosion.
Owner:山东淄川特种耐火材料有限公司
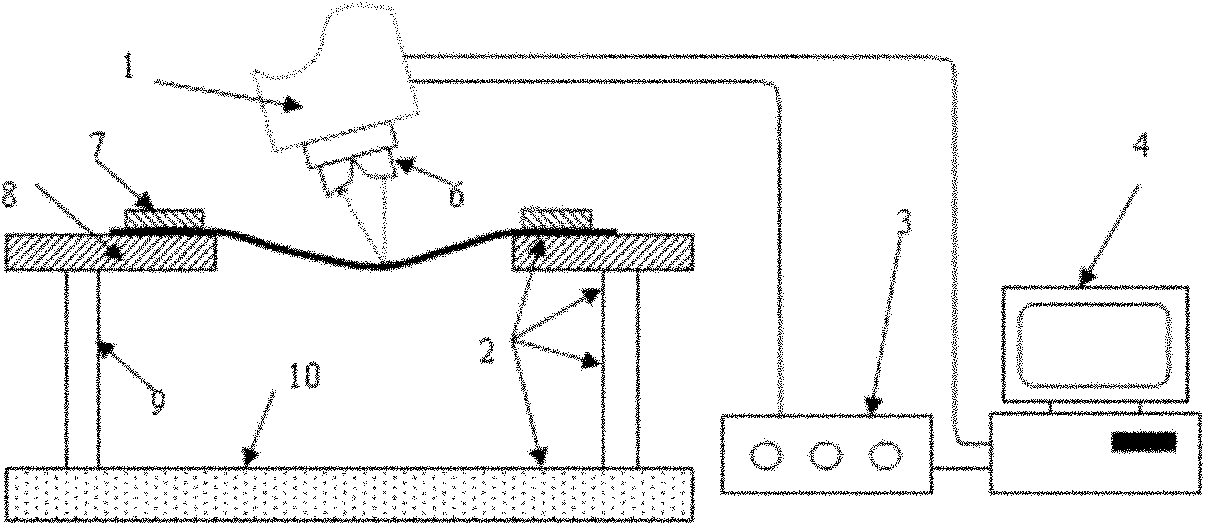
Numerical control precision progressive forming device and precision progressive forming method for plates
ActiveCN102211121AReduce development costsAvoid occupyingMetal-working feeding devicesMetal working apparatusNumerical controlGeometric error
The invention discloses a numerical control precision progressive forming device and a precision progressive forming method for plates, and belongs to the technical field of plate processing. The device comprises a five-axis numerical control forming machine, a plate fixture, a data acquisition system and an optimal control module, wherein the plate fixture is arranged on a worktable of the machine; the data acquisition system is connected with the five-axis numerical control forming machine and the optimal control module respectively, and transmits processing parameters and control instructions; the tail end of a spindle of the five-axis numerical control forming machine is provided with a forming pressure head or a laser ranging system; and the laser ranging system is connected with thedata acquisition system and transmits a laser ranging signal. By alternately using the forming pressure head and the laser ranging system, cyclic operation including plate progressive forming, error measurement and formed path modified forming is completed. The device can save development cost of a die, avoid occupying a press, ensure the dimensional accuracy of sheet metal parts, and reduce material loss due to geometric errors in actual production.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for preparing sintered Nd-Fe-B alloy magnetic material
InactiveCN101071668AGood orientationIncrease the degree of orientation, fromInorganic material magnetismAntioxidantAlloy
This invention discloses a sintered NdFeB alloy magnetic materials preparation methods, the method is the weight of the shares in the 100 Nd-Fe-B alloy powder to add 0.01 to 0.2 in antioxidants, mixed after ground into a uniform particle size 2.8 - 4.5 mu m powder; good Nd-Fe-B powder in the mill to add 0.01 to 0.5 in the lubricant, argon or nitrogen, under the protection of uniform mixing obtained magnetic; will magnetic suppression after forming and sintering heat treatment, access to the final product . This invention in the Nd-Fe-B magnets milling through the process of adding antioxidants, in the process of accession lubricant mixture, in the suppression of the Nd-Fe-B magnetic particle forming process, the magnetic field intensity in the same circumstances raise powder orientation, thereby improving Magnetic products if the production is the same as the magnetic properties of magnets, we can reduce the forming pressure and time, so that get more capacity and reduce costs.
Owner:ZHAOQING SANHUAN JINGYUE MAGNETIC MATERIAL +1
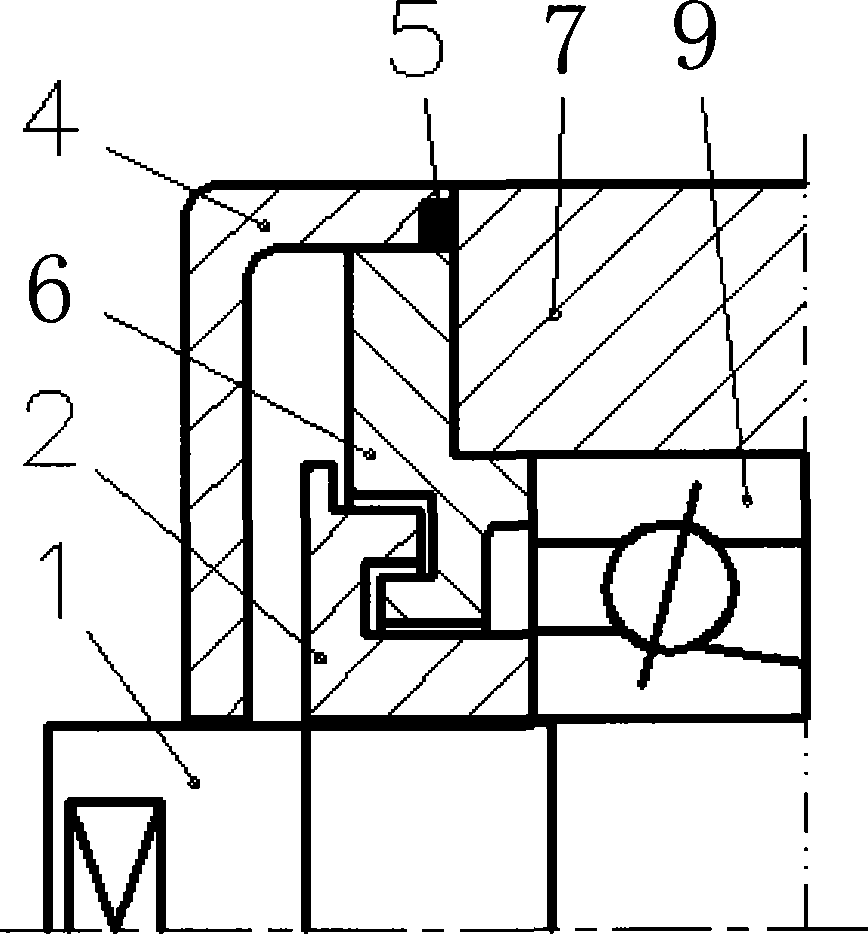
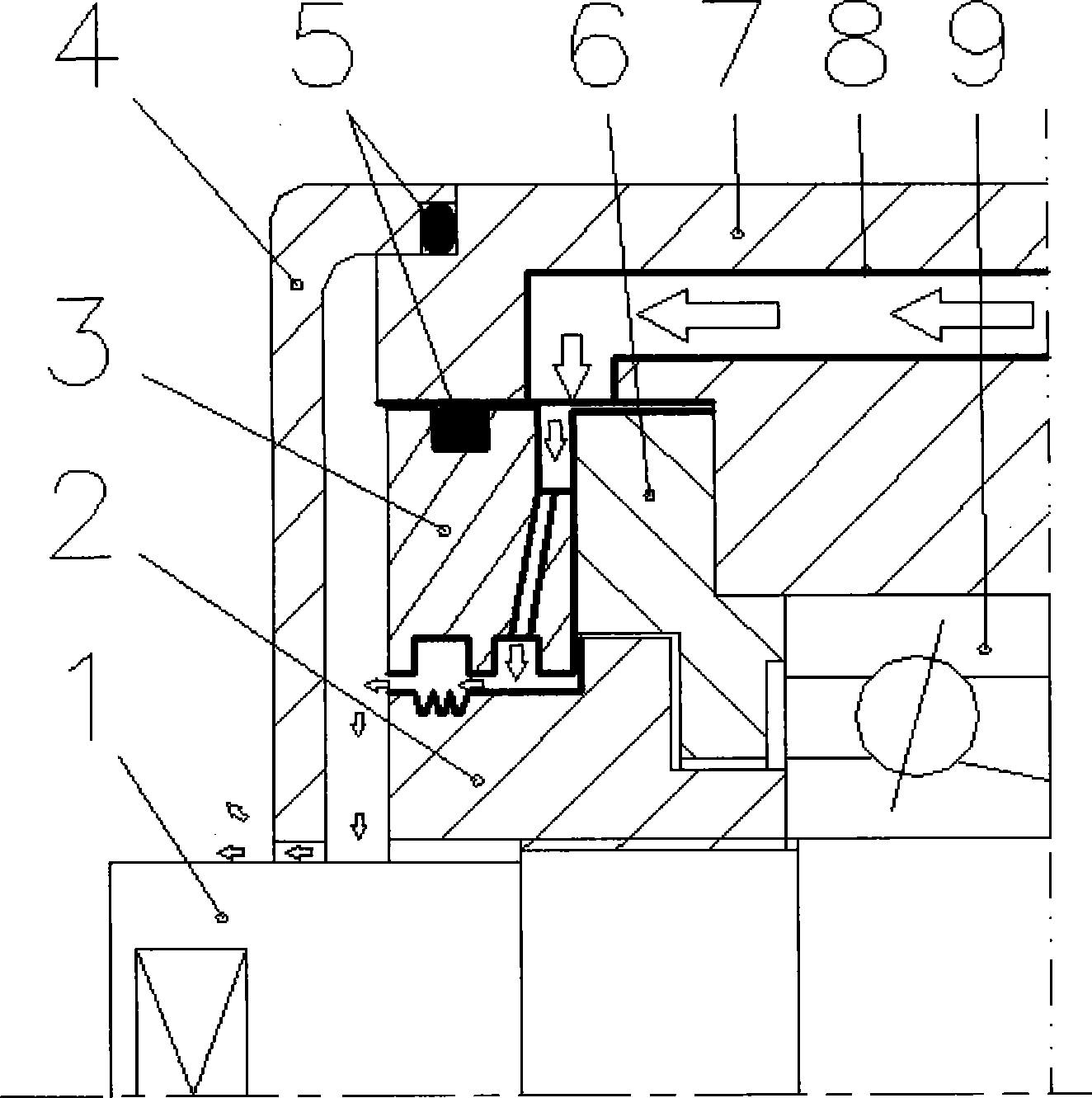
Air sealing construct design for electric main shaft of oil grease mill
ActiveCN101478190AExtended seal lifeGuaranteed uptimeEngine sealsSupports/enclosures/casingsEngineeringAir tightness
The invention relates to a design of an air seal structure of an electric spindle used for a grease film. The air with a certain pressure enters in an annular cavity between a baffle plate 3 and a front small cover 6 through an air passage 8 arranged on a front bearing seat 7 and then reaches an annular groove through a radial slant hole, a clearance is formed between the inner circle of the baffle plate and the outer circle of a front screw cap 2, a sawtooth-shaped groove is designed on the front screw cap and corresponds to the other annular groove of the baffle plate, the pressure air forms pressure air sealing rings in the clearance and the two grooves along with the rotation of the rotating axle at high speed, and the pressure air sealing rings are used for preventing the cooling fluid and the foreign impurities from entering in the rotating axle; an O-shaped sealing ring is sealed at the sealing point among the baffle plate, a dust cap and the front bearing seat for ensuring the air tightness of running of the pressure air in the air passage; and the sawtooth shape of the front screw cap can prevent a small amount of cutting solution from infiltrating, the small amount of the cutting solution can be thrown into the other annular groove of the baffle plate along with the rotation of the front screw cap, and then is discharged outside the electric spindle through the baffle plate and a guide groove or guide hole for the dust cap, so that the reliable air tightness is provided for the high-precision running of a bearing 9.
Owner:LUOYANG BEARING RES INST CO LTD
Gradient-pore silicon nitride and silicon carbide combined film tube and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN105727755AGuaranteed corrosion resistanceExtended service lifeSemi-permeable membranesCeramicwareChemical industryPorous ceramics
The invention belongs to the field of porous ceramic materials and particularly relates to a gradient-pore silicon nitride and silicon carbide combined film tube and a preparation method therefor. The film tube material is prepared from silicon nitride and silicon carbide, and a gradient filtering structure is formed by a supporting body layer and a surface film layer; a supporting body is formed through combining silicon nitride produced from a reaction with coarse silicon carbide grains and has the average pore size of 10 to 80 microns, the surface film layer is formed through combining the silicon nitride produced from the reaction with fine silicon carbide grains and has the average pore size of 0.1 to 20 microns, and the overall porosity of the film tube is 35% to 50%. The preparation method sequentially comprises the steps of carrying out batching, forming the supporting body, preparing the film layer and carrying out firing, wherein the forming is carried out by adopting isostatic pressing, the forming pressure is controlled to 40MPa to 150MPa, the firing temperature is controlled to 1,400 DEG C to 1,650 DEG C, and the heat preserving time is 3 to 5 hours. The film tube can be used in an oxidative atmosphere, can also be used in a reducing atmosphere, is high in acid-alkali corrosion resistance and can be applied to the filtering and purifying of various high- and low-temperature fluids of coal gasification chemical industry, IGCC and PFBC coal-gasified power generation, high-temperature flue gas, automobile exhaust gas, water purification and the like.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-purity pressure-maintaining deep sea hot liquid sampler
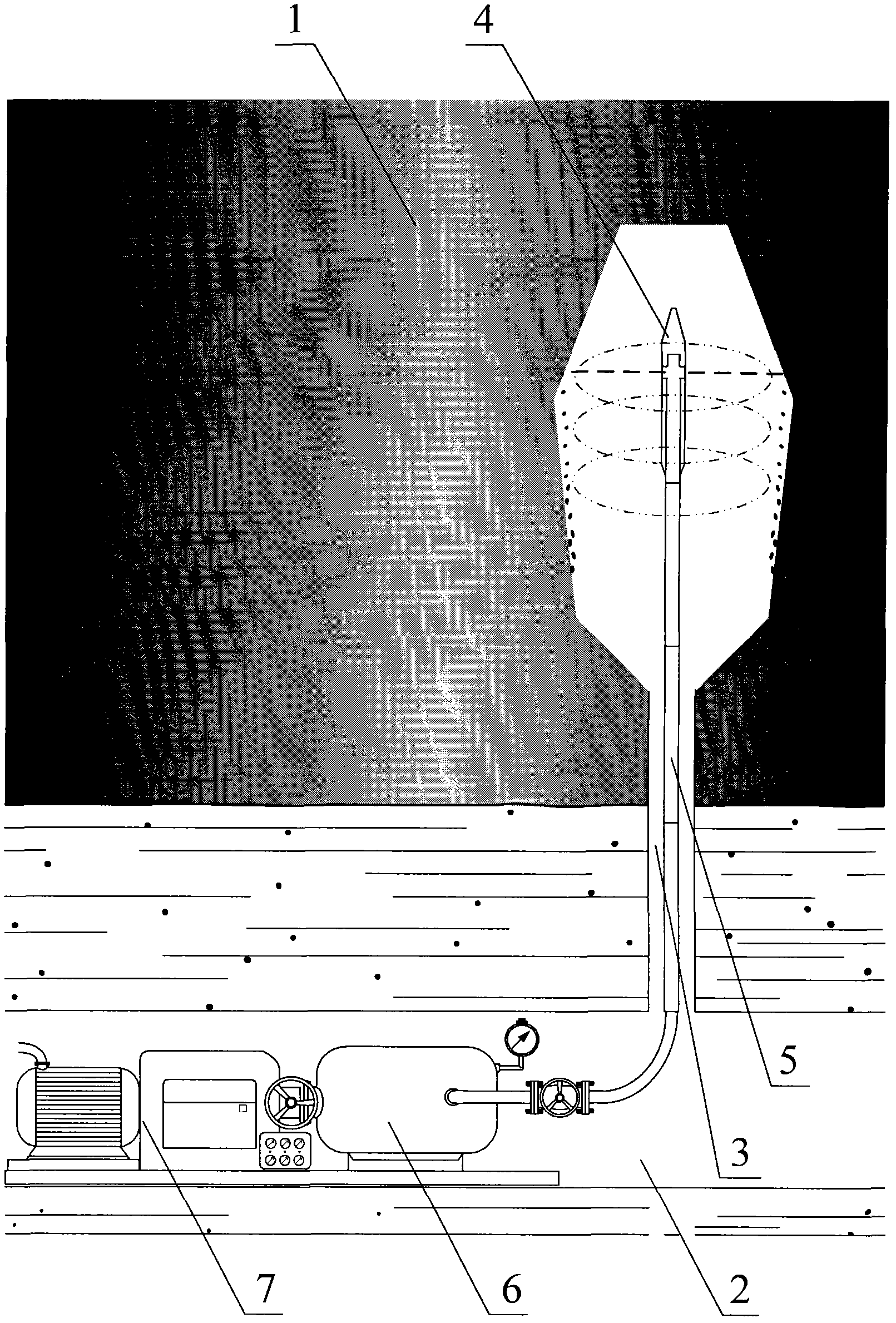
InactiveCN1453567ASolve water absorptionSolve the problem of non-sample seawater in the dead volume of the sampling valveWithdrawing sample devicesAutomatic controlEngineering
The present invention belongs to the field of marine technological instrument and equipment. One sample barrel with I-shaped sample cavity piston and one pressure accumulating barrel with pressure accumulating cavity piston are fixed to two ends of one containing body with axial small hole separately, to form pressure accumulating cavity, isolated water cavity, pre-sucking cavity and sample cavity. There are one one-way valve mechanism set in front of the sample cavity piston; varying-damp throttle mechanism comprising the throttle rod on pressure accumulating cavity piston and the small hole in the connecting body; valve plate, sampling valve and water sucking pipe in front end of the sample barrel; and inflating valve behind the pressure accumulating barrel. The present invention hashigh sample purity and automatically controlled sample speed, and is suitable for collecting deep sea hot liquid flow sample.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
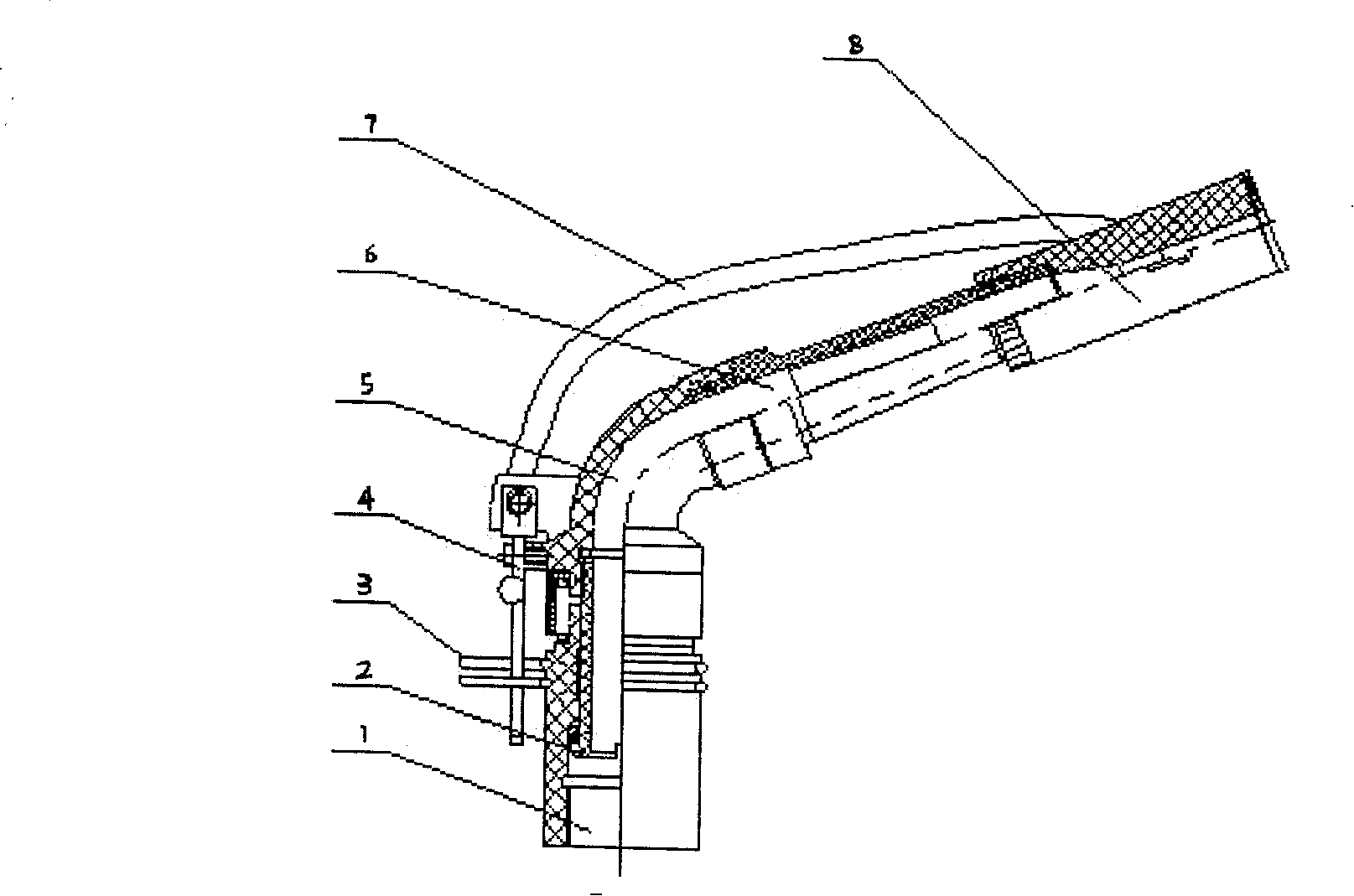
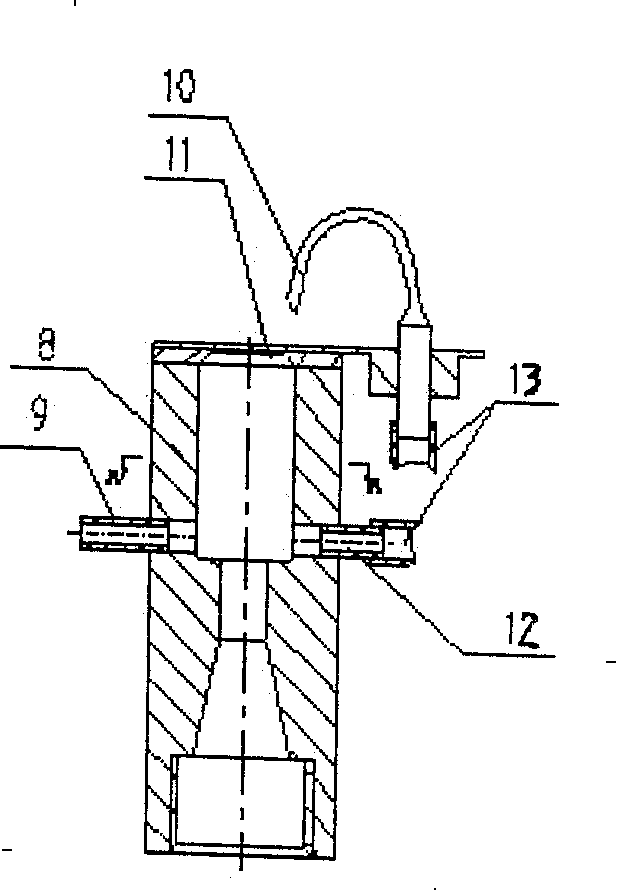
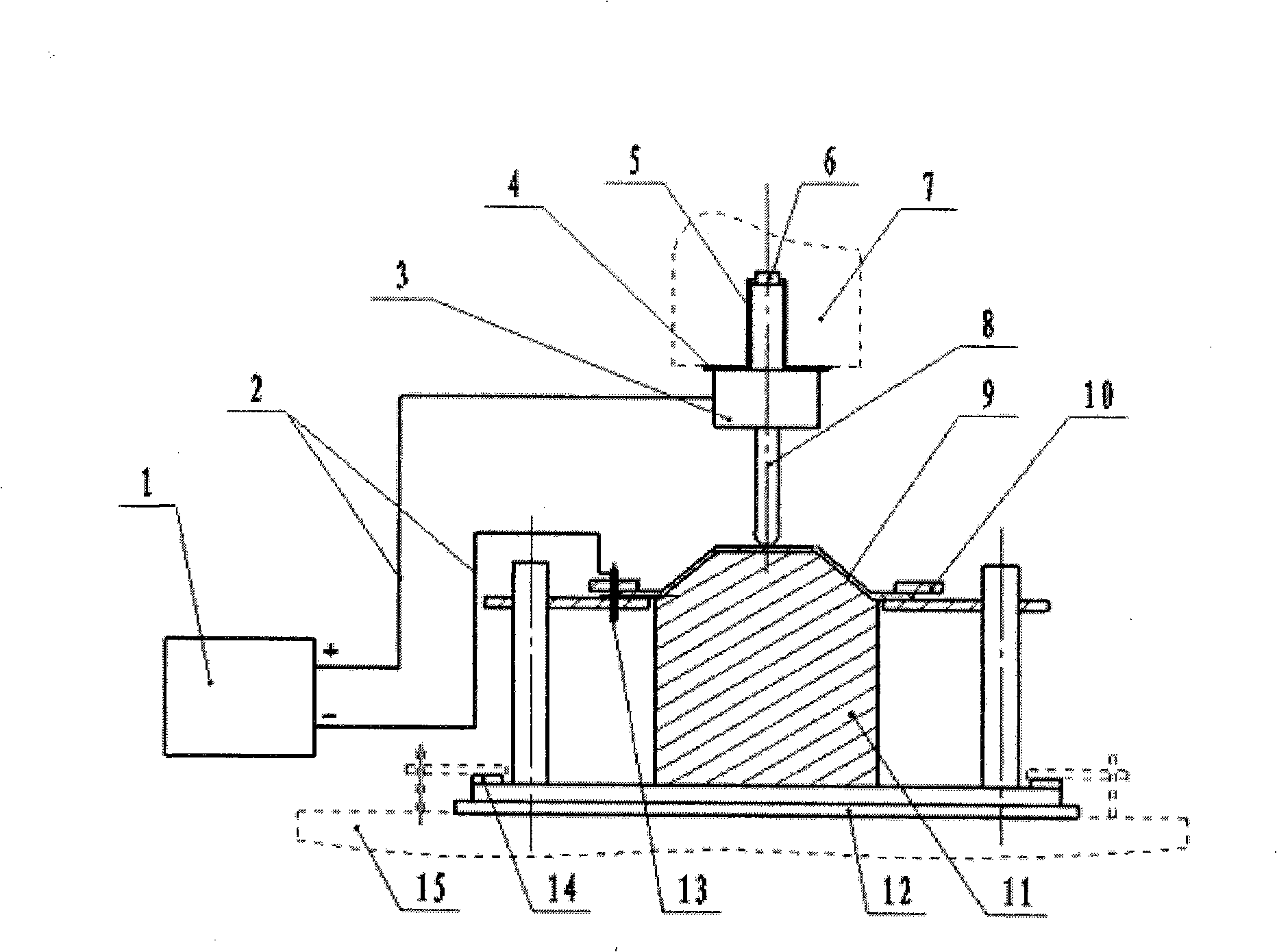
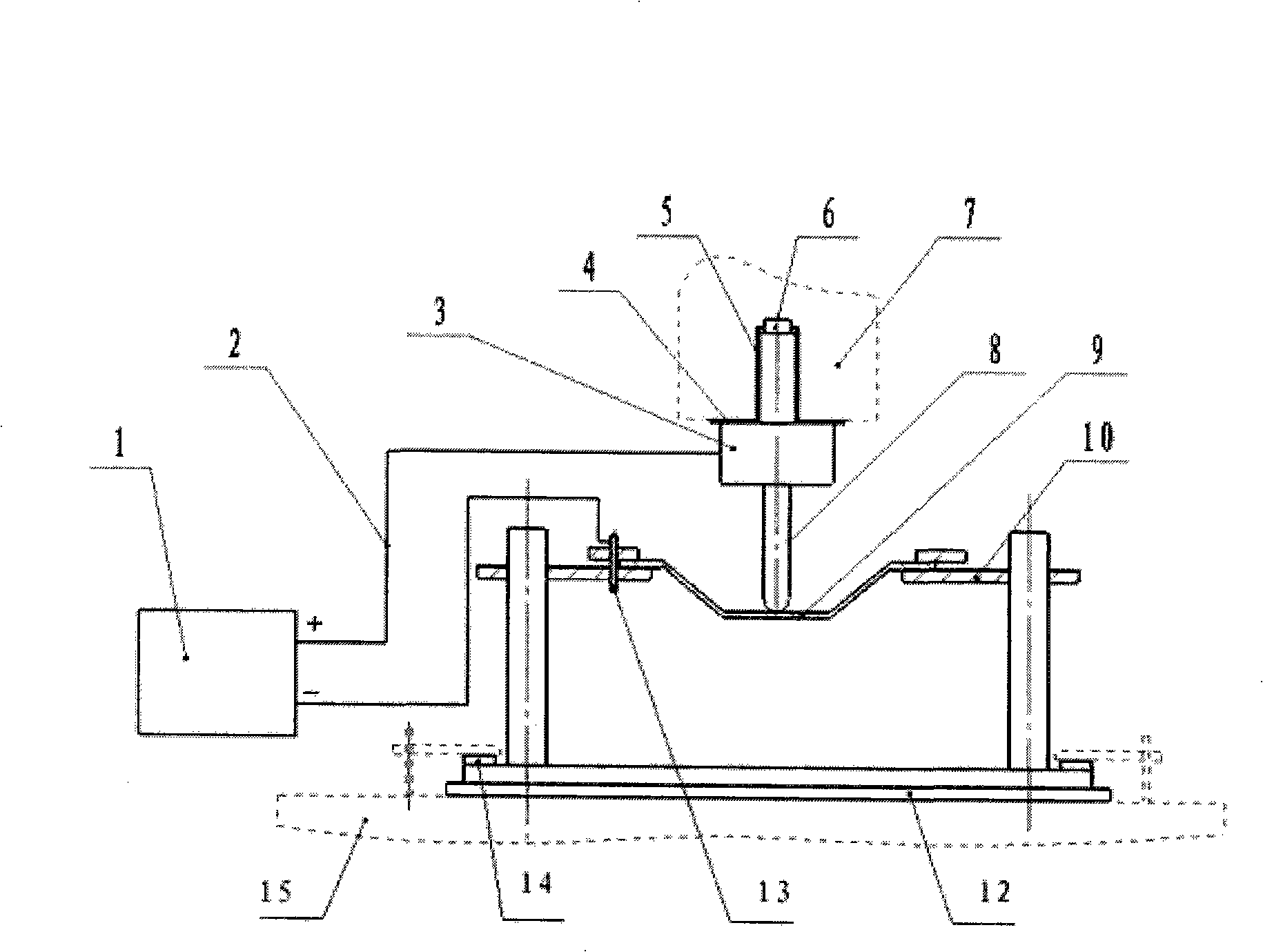
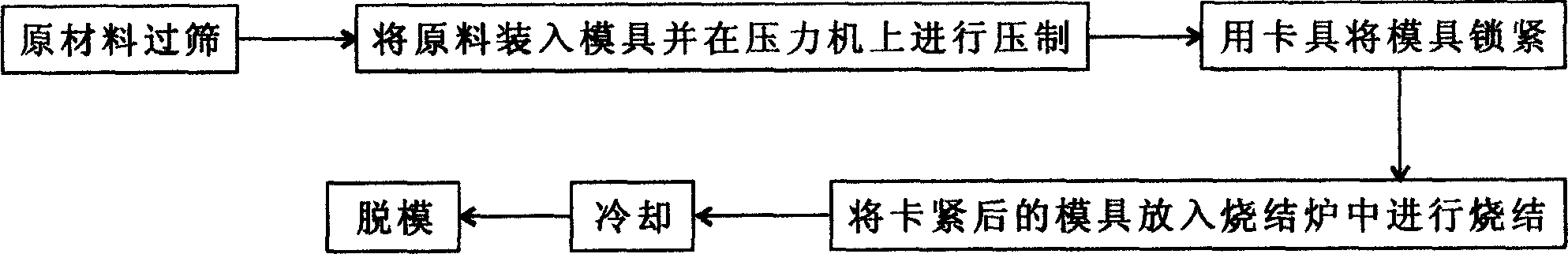
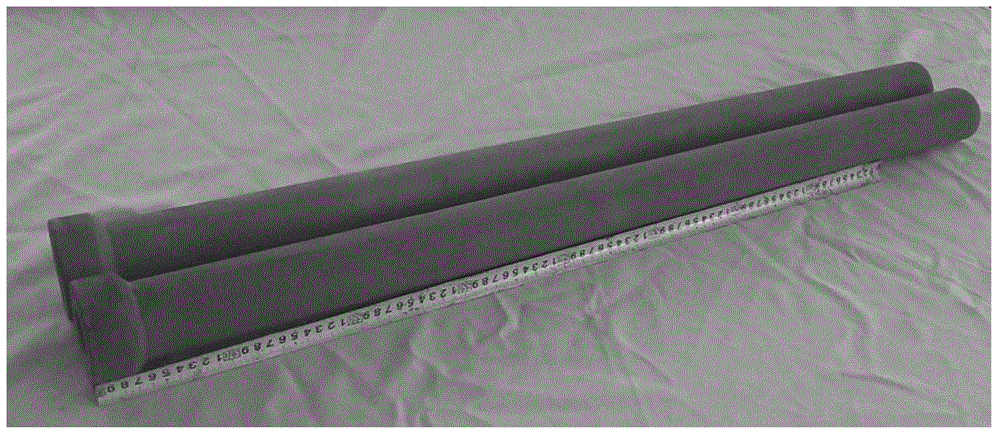
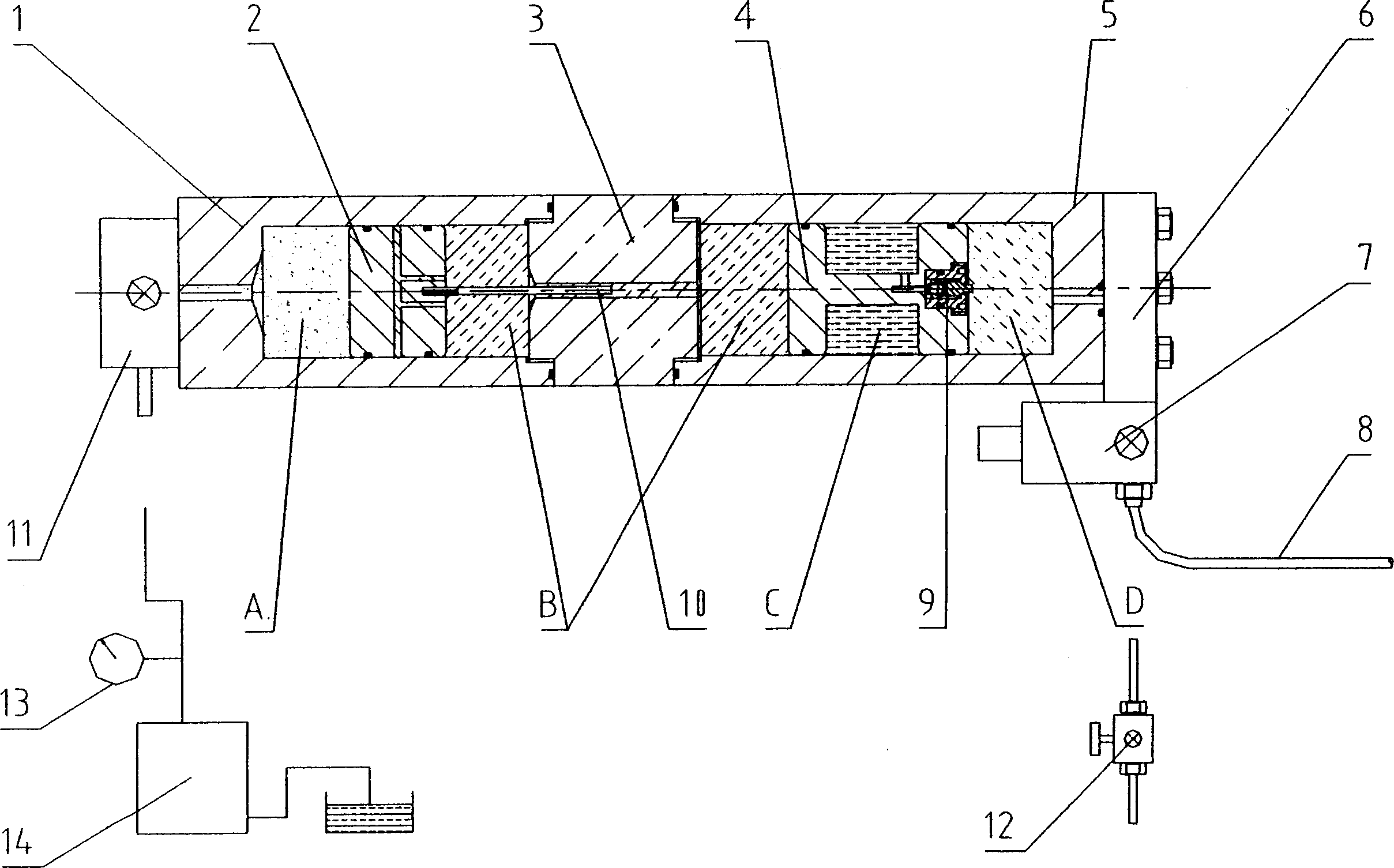
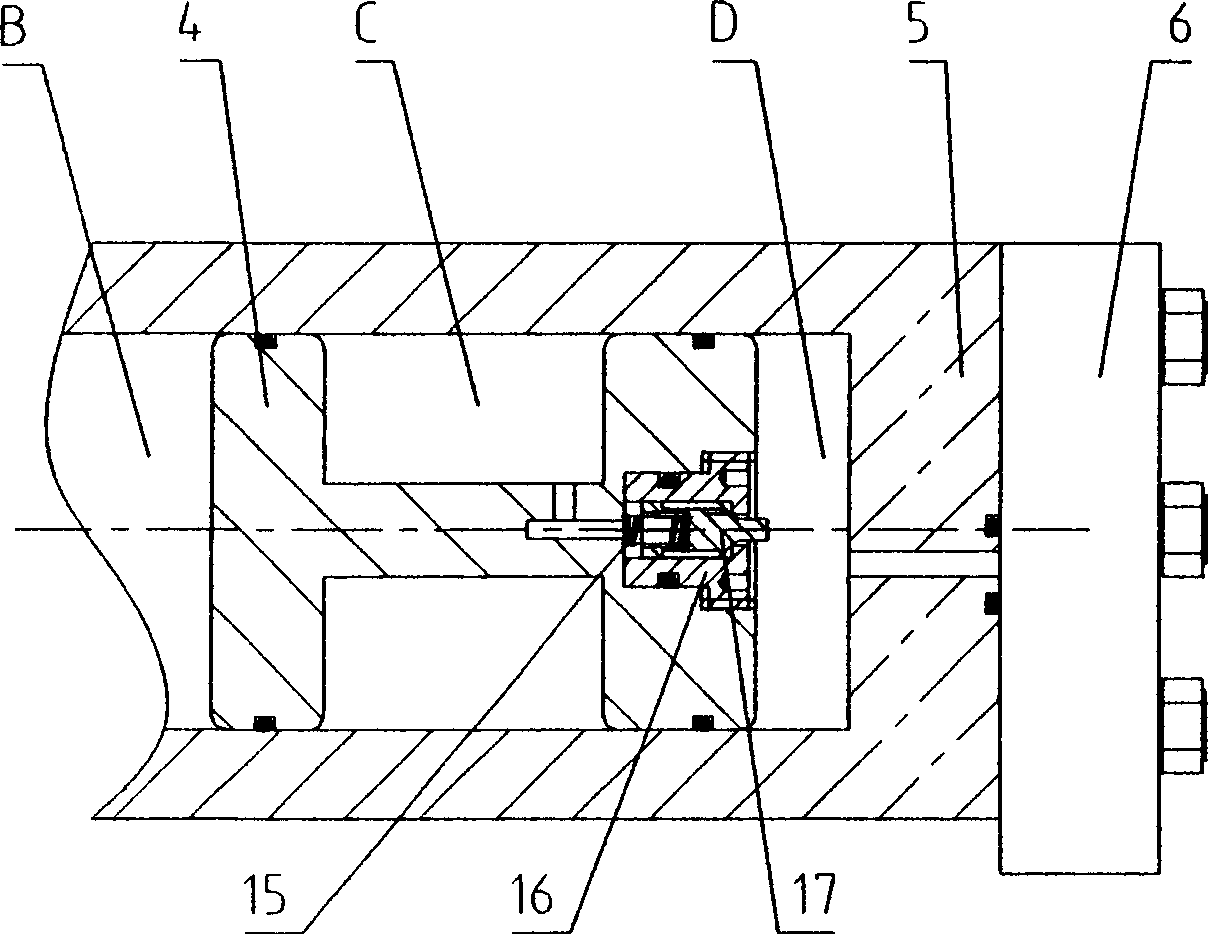
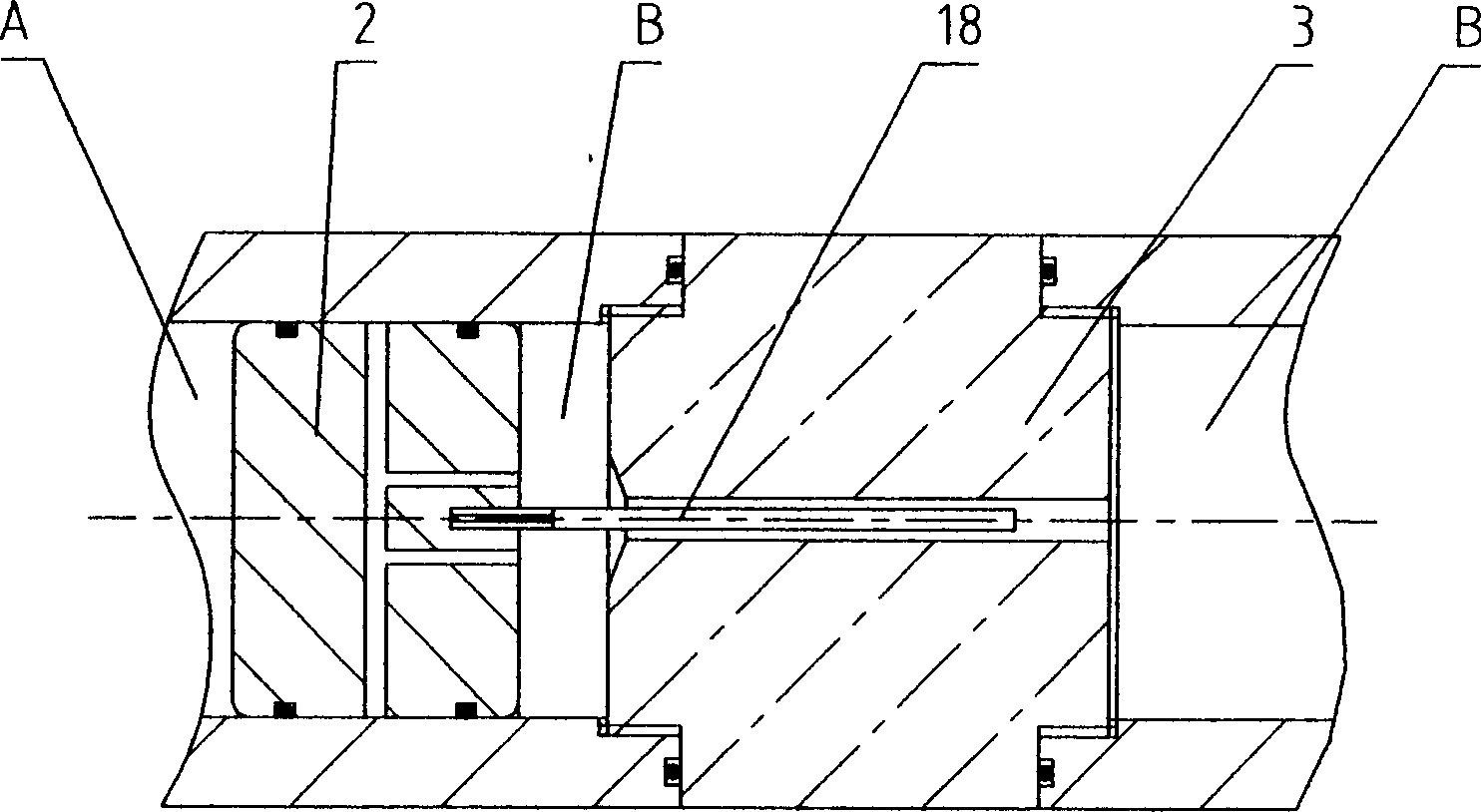
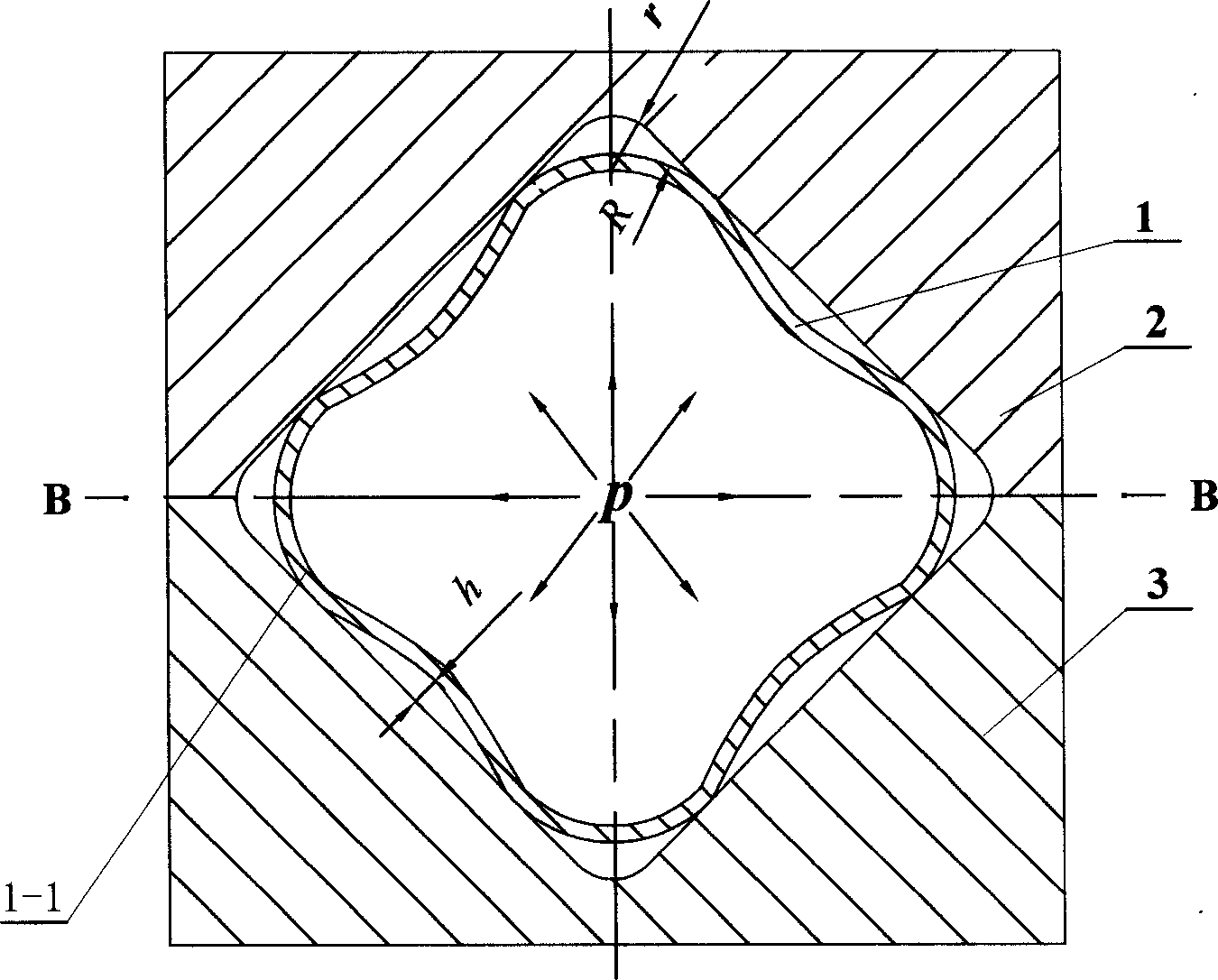
High-pressure forming method in tubular member for lowering forming pressure
An internal high pressure method for forming tubular part with decreased forming pressure includes such steps as preshaping the tubular part to make its cross-section like a multi-petal flower shape, putting it in the cavity of lower die, closing upper and lower dies, and introducing high-pressure liquid to the tubular part to expand it for plastic deformation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Thermally-conductive and insulating polymer composite material with three-dimensional isolation structure and preparation method of thermally-conductive and insulating polymer composite material
The invention relates to thermally-conductive and insulating polymer composite material with a three-dimensional isolation structure and a preparation method of the thermally-conductive and insulating polymer composite material. The thermally-conductive and insulating polymer composite material comprises, by weight, 70-99 parts of polymer powder and 1-30 parts of thermally-conductive and insulating filler. The preparation method includes the steps of firstly, mixing the 1-30 parts of thermally-conductive and insulating filler with the 70-99 parts of polymer powder, and mechanically grinding to prepare a thermally-conductive and insulating filler@polymer powder core-shell structure, wherein the grinding pressure is 3-30MPa, and the grinding time is 5-60 minutes; secondly, placing the thermally-conductive and insulating filler@polymer powder core-shell structure into a die to prepare the thermally-conductive and insulating polymer composite material with the three-dimensional isolation structure through thermo-compression formation, wherein the formation pressure is 5-50MPa, the formation temperature is 80-350 DEG C, and the formation time is 10-60 minutes.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Porous devitrified glass and manufacturing method thereof
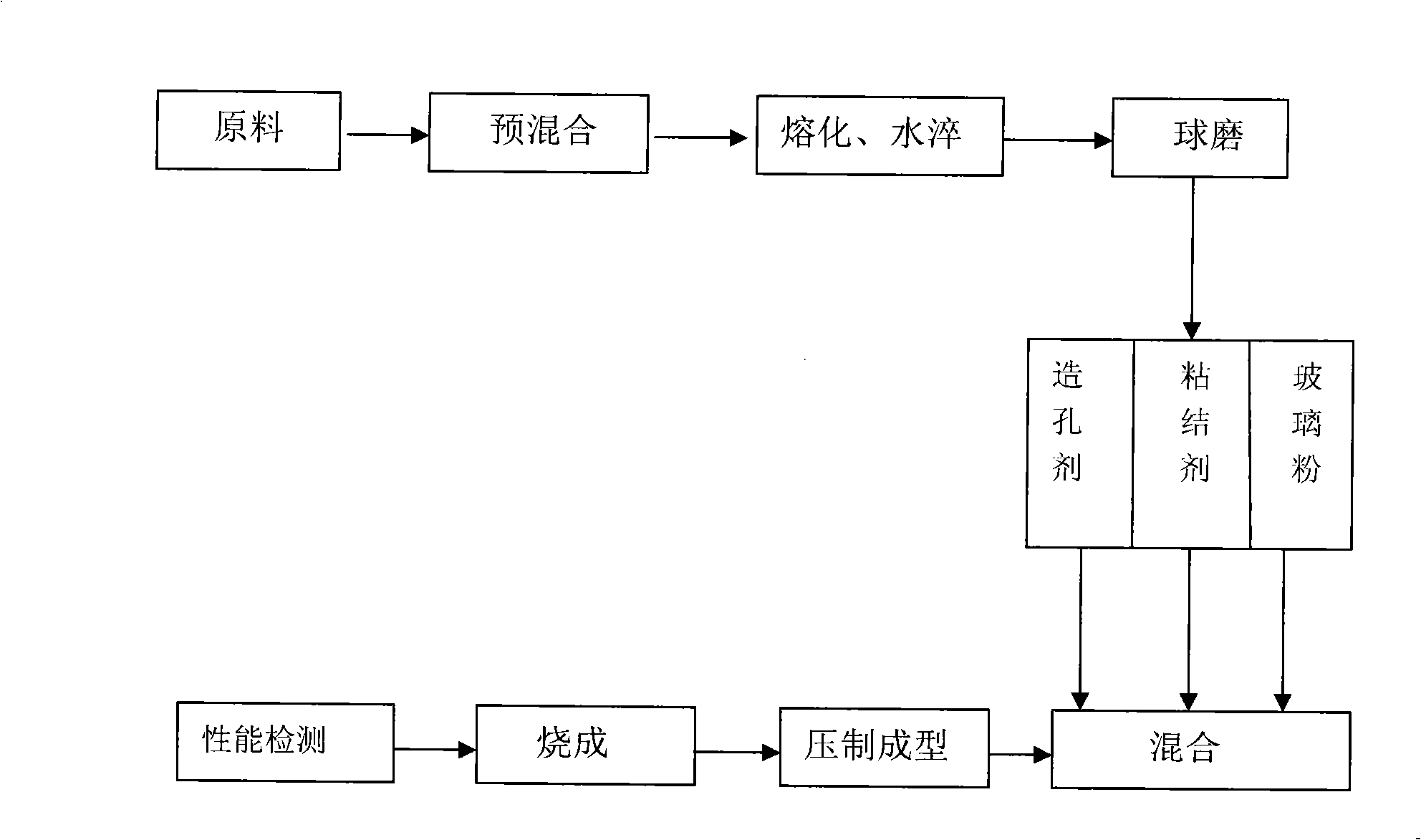
The invention relates to a porous glass-ceramics and a method for preparing the same belonging to the glass-ceramics filter material field, which is characterized by preparing a glass powder of CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2 system by means of water quenching using fly ash and rare earth tailings as raw materials; preparing the porous glass-ceramics mainly open pores by adding pore formers. The rare earth tailings of the invention not only contains the main chemical compositions for preparing the glass-ceramics, but also contains rare earth, niobium and fluorite as composite nucleating agents which can reduce the nucleation activation energy, improve the nucleation and crystallization of the glass to make the microcrystalline finer, thereby improving the mechanical property of the glass-ceramics. Meanwhile the cost for preparing the porous glass-ceramics is greatly reduced and the high intensity communicating pore porous glass-ceramics which satisfies different filtration objects with an adjustable porosity and pore size distribution are obtained by adjusting the species, granularity, dosage and forming pressure of the pore formers.
Owner:内蒙古科韵环保材料股份公司
Supersonic vibrating auxiliary plastic forming device
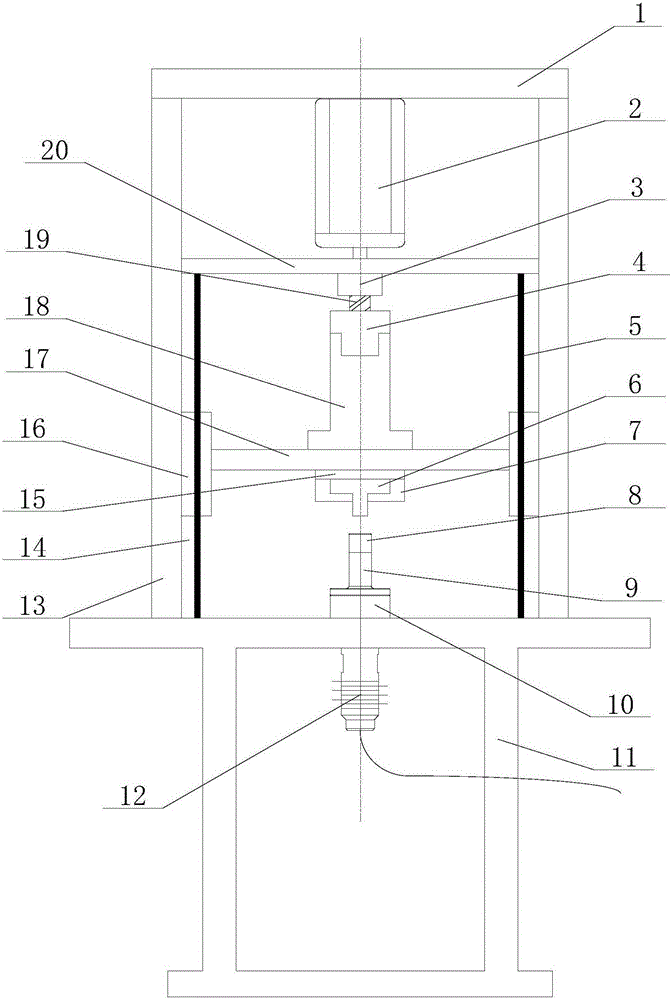
InactiveCN105195584ACompact structureEasy to operateShaping toolsMetal working apparatusGratingMetallic materials
The invention belongs to the technical field of plastic forming, and particularly relates to a supersonic vibrating auxiliary plastic forming device. The supersonic vibrating auxiliary plastic forming device is characterized in that a servomotor is arranged in the middle of an upper crossbeam of a rack; a middle fixed crossbeam is provided with a coupler; a ball screw is connected with a spindle of the servomotor and penetrates through the coupler to be meshed with a ball nut; the ball nut is fixed on a movable crossbeam by a cylindrical sleeve; two ends of the movable crossbeam move up and down along guide rails by sliding blocks to drive an upper die to move, a pressure sensor is arranged between the upper die and the movable crossbeam and used for detecting the forming pressure between the upper die and a lower die; a vertical guide rail is provided with a precise grating ruler for detecting and controlling the position of the upper die. The supersonic vibrating assistant plastic forming device is simple and reliable in structure and capable of being used for supersonic auxiliary forming machining of metal materials of copper and nickel and non-metallic materials such as resin and rubber and can realize higher machining precision.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for preparing biomass molded coal
The invention relates to a method for preparing biomass molded coal, which comprises: (a) crushing and sieving raw coal and biomass, and mixing and heating in a first mode of mixing raw coal and biomass and heating to a preset temperature or a second mode of heating the raw coal and biomass to a first temperature and a second temperature respectively, mixing and heating to the preset temperature; (b) performing pressing molding of the mixture of the raw coal and the biomass, which is obtained in the first mode or second mode, by using a mold under a forming pressure; and (c) cooling the molded coal and demolding to obtain the biomass molded coal. In the method, the biomass contains lignin, the preset temperature is a temperature at which the lignin in the biomass softens or liquefies, and the first temperature is lower than or equal to the second temperature. When the method is used for forming fuel, the high-strength biomass composite molded coal can be produced without using adhesive.
Owner:CHNA ENERGY INVESTMENT CORP LTD +2
Low temperature and low pressure BMC (Bulk Molding Compound) material, preparation method thereof and purpose thereof
The invention relates to a low temperature and low pressure BMC (Bulk Molding Compound) material. The low temperature and low pressure BMC material comprises unsaturation resin, a low shrinkage additive, a filler, a curing agent, a mold release agent, a polymerization inhibitor, an auxiliary and glass fiber, wherein the mold release agent is a mixture of zinc stearate and calcium stearate. The molding temperature of the low temperature and low pressure BMC material provided by the invention is only 110-130 DEG C and is reduced by about 30% when compared with the molding temperature of the traditional BMC molding material; and the molding pressure of the low temperature and low pressure BMC material provided by the invention is only 70-100 kg / cm2 and is reduced by about 50% when compared with the molding pressure of the traditional BMC molding material.
Owner:WUXI XINHONGTAI ELECTRIC TECH CO LTD
Aircraft component exposed to streaming surrounding air
InactiveUS7922126B2Avoid insufficient heatingAircraft stabilisationDe-icing equipmentsCross connectionMechanical engineering
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Filled 0-degree carbon fiber prepreg preforming tooling and preforming process
The invention discloses a filled 0-degree carbon fiber prepreg preforming tooling and a preforming process. The tooling comprises a forming pressure plate, forming mandrels, a base plate and limit stops, wherein multiple forming mandrels are closely and parallelly arranged on the base plate, the chamfers of the forming mandrels are consistent with an R angle of a long joist, filled 0-degree carbon fiber prepregs are located at the chamfers of the forming mandrels, the pressure plate is arranged above the mandrels, and the outer sides of the mandrels at the two ends are respectively provided with a limit stop. The preforming process comprises the following steps: (1) manufacturing a preforming tooling; (2) calculating the theoretic application amount of filled 0-degree carbon fiber prepregs; and (3) filling the 0-degree carbon fiber prepregs: weighting the 0-degree carbon fiber prepregs, cutting the 0-degree carbon fiber prepregs into fiber bundles with a size of 3-4mm, feeding the cut 0-degree carbon fiber prepregs into the preforming tooling, slightly compacting the prepregs by using a scraping plate, and after the prepregs are subjected to vacuum compaction on a heating platform at temperature of 70-80 DEG C for 15 min, transferring the prepregs to a normal-temperature workbench for cooling, and then taking out the obtained products. According to the invention, the forming quality of long joists is improved, and a situation that the shape of long joists after being manufactured is irregular is greatly improved.
Owner:SHENYANG AIRCRAFT CORP
Preparation method for high-density fine grain tungsten copper alloy
The invention relates to a preparation process for high-density fine grain tungsten copper alloy. The alloy consists of 50 to 90 percent of W and 10 to 50 percent of Cu. The preparation process synthesizes the mechanical alloying advantage of ball milling and dry milling and the quick grain refining advantage of wet milling in the aspect of preparation of powder, and also synthesizes the liquid phase rearrangement advantage of liquid phase sintering and the forming pressure-reducing and sintering time-shortening advantages of solid phase hot-pressed sintering in the aspects of sintering process, so the high-density fine grain tungsten copper alloy with the relative density of 99.2 to 99.5 percent and tungsten crystal grain of 0.3 to 0.8 micron is prepared at the relatively low sintering temperature. The tungsten copper alloy prepared by the preparation process is uniform in structure, low in oxygen content, small in crystal grain and high in density; and the process is simple and the used equipment is industrial common powder manufacturing equipment and sintering equipment, so industrialized production is facilitated.
Owner:兰溪市金铎金属材料科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com