Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32results about How to "Reduce tissue stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Submicron grain Ti(C, N)-base cermet and its prepn process
The present invention relates to the preparation of cermet material, and the sintered alloy has submicron crystal grain structure, and high hardness, toughness and strength. The cermet is prepared through mixing IVB, VB, VIB, Ti, one or more metal carbide, nitride or complex solid solution carbide-nitride ceramic powder and iron family element Ni, Co, etc.; high-energy ball milling, drying, pressing to form, vacuum sintering, hot isostatic pressing and other steps. The cermet has hard crystal phase reaches submicron granularity of 0.6-1.0 micron. Under scanning electronic microscope, four kinds of metal structure may be observed including black core phase, white core phase, gray ring phase and white adhesion phase. Compared with available cermet, the present invention has obviously improved hardness and toughness, and may be used in cutter and other wear resistant parts.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cobalt less multi element high speed tool steel and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN1693527AReasonable range of performanceLow content of alloying elementsFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesElectrical resistance and conductanceChemical composition
A non-Co multi-element high-speed tool steel contains proportionally C, Si, Mn, S, P, Cr, V, Mo, W, Ni, Nb, Ti, Mg, RE and Fe. Its preparing process includes such steps as smelting by MF furnace, modifying with Y-based RE alloy, centrifugal casting, and heat treating.
Owner:JIUQUAN IRON & STEEL GRP
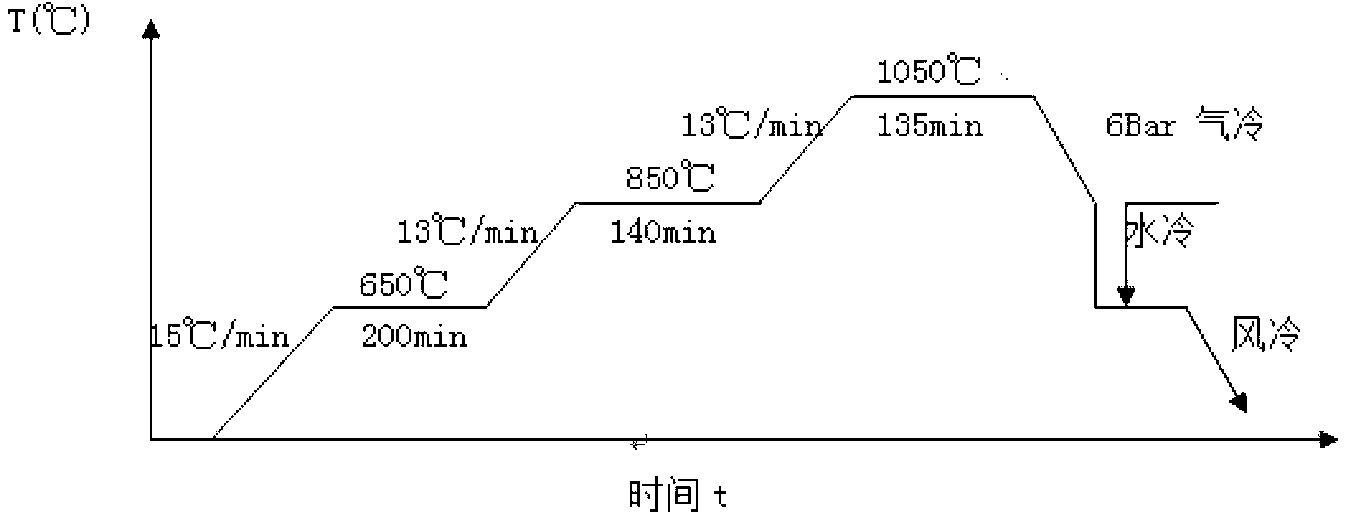
Spheroidizing annealing technology of H13 hot work die steel
The invention provides a spheroidizing annealing technology of H13 hot work die steel and belongs to the field of die steel heat treatment technologies. The spheroidizing annealing technology of the H13 hot work die steel comprises the steps that (1) a forged H13 steel blank is cooled to the temperature of 400-500 DEG C, the cooled H13 steel blank is fed into a furnace, the temperature is raised to 720-750 DEG C at the temperature raising speed of 25-80 DEG C per hour for preheating, the temperature is kept for 1-2 hours, the temperature is then raised to 980-1050 DEG C at the temperature raising speed of 25-80 DEG C per hour, after all the furnace charge reaches the temperature, the temperature is kept for 3-5 hours, then the temperature of the forged H13 steel blank is lowered to be not higher than 550 DEG C through furnace cooling, and air cooling and discharging are conducted; hot charging is conducted, the temperature is raised to 900-950 DEG C at the temperature raising speed of 25-80 DEG C per hour, after all the furnace charge reaches the temperature, the temperature is kept for 0.5-1 hour, air cooling and discharging are conducted, and then the pre-treatment process is completed; and charging is conducted at the temperature 300-400 DEG C, the temperature is raised to 880+ / -10 DEG C at the temperature raising speed of 25-80 DEG C per hour, the temperature is kept for 4-6 hours, the temperature is lowered to 760+ / -10 DEG C at the cooling speed of 15-20 DEG C per hour, after the temperature is kept for 8-12 hours, the H13 hot work die steel is cooled to be lower than or equal to 500 DEG C at the cooling speed of 15-20 DEG C per hour, and then air cooling and discharging are conducted. The spheroidizing annealing technology of the H13 hot work die steel has the advantages that carbides are evenly distributed in the structure, the structure is refined, the defects of network carbides and the like in an original structure are eliminated, and the annealing hardness is lowered.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
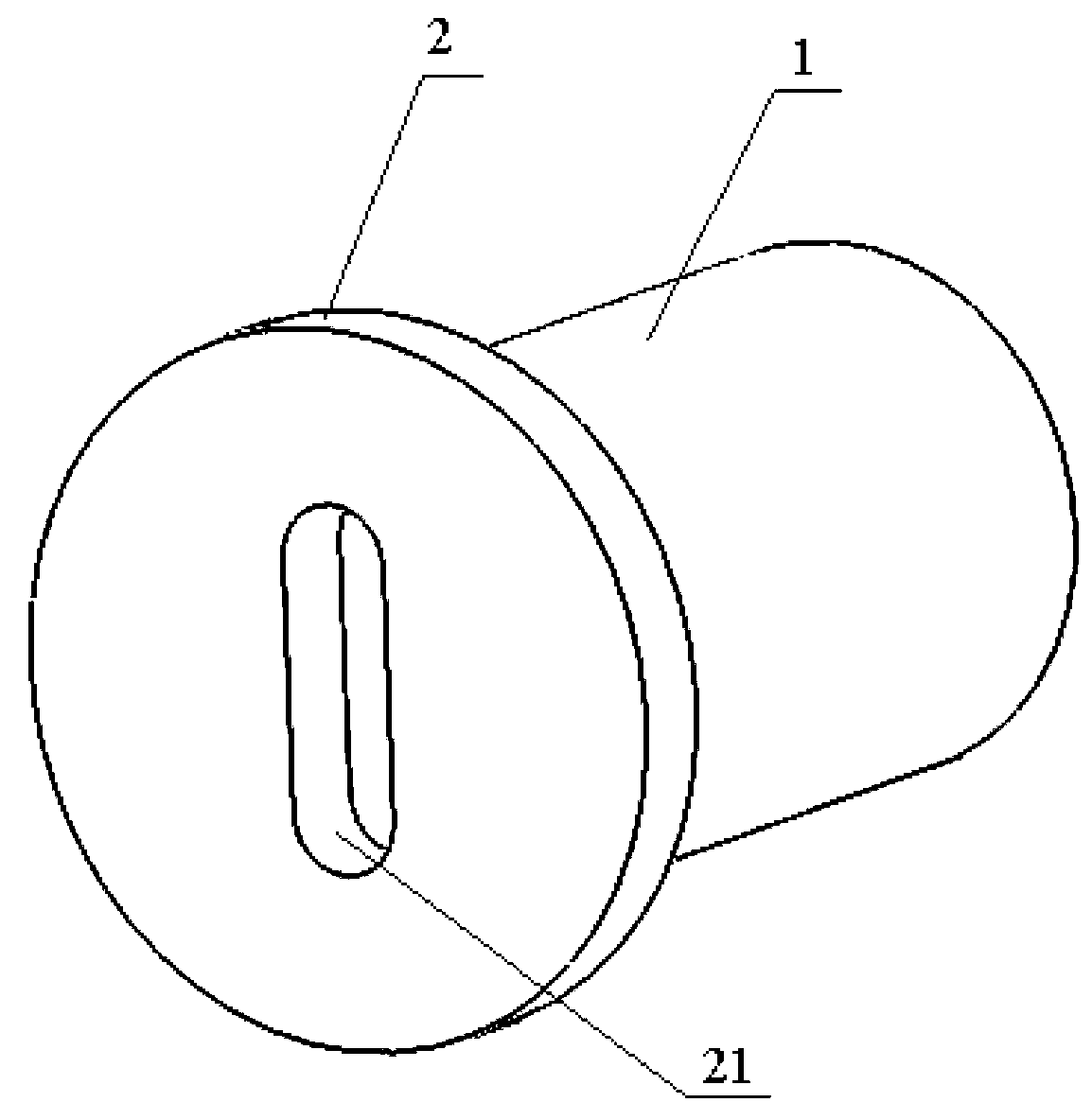
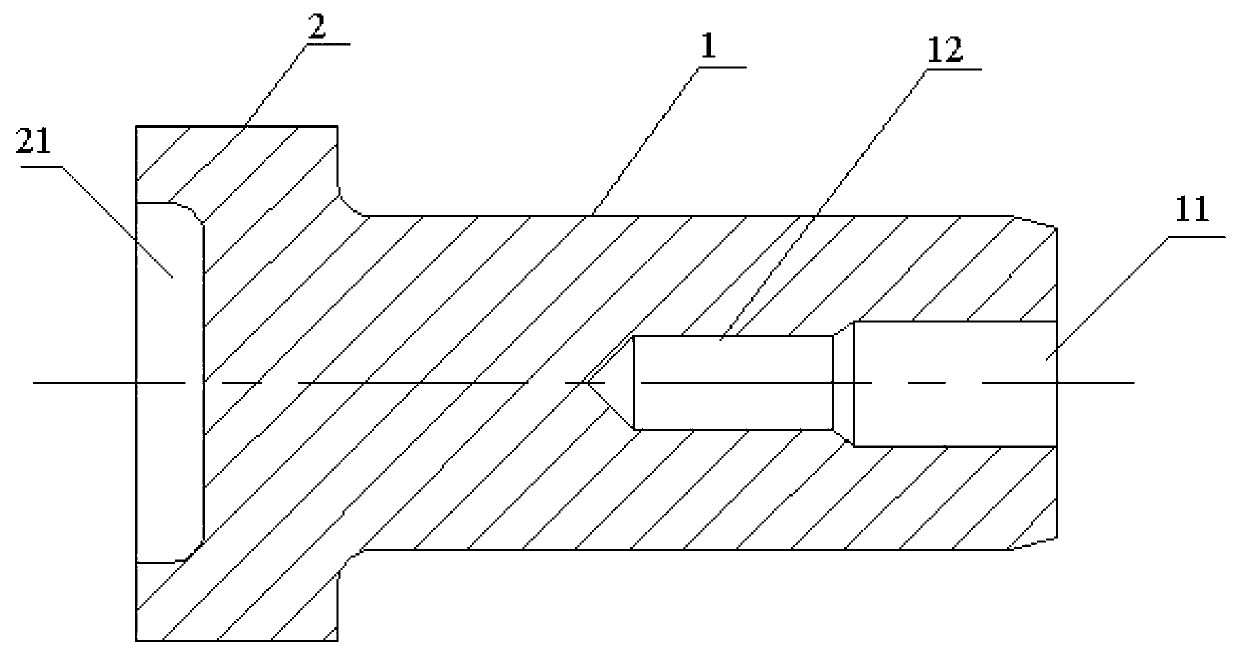
Anti-cracking machining method of small axial surface carburizing and hardening stepped shaft with end face provided with groove
The invention discloses an anti-cracking machining method of a small axial surface carburizing and hardening stepped shaft with an end face provided with a groove. The groove is arranged in an end face of a shaft section B of the stepped shaft, a shaft section A and a side face, close to the shaft section A, of the shaft section B have carburizing and hardening requirements, other parts have no hardness requirements, 20Cr steel serves as blanks of the stepped shaft, the procedures of blanking, rough machining, carburizing treatment, semi finish machining, hardening, fine machining, cutting and groove milling are sequentially carried out on the blanks, and then the stepped shaft with different shaft sections having different mechanical properties are machined. The anti-cracking machining method is simple in structure and convenient to achieve; a protective step is arranged before carburizing, the protective step before the hardening is machined to be a fillet, and cracking caused by oversize stress when the carburizing and hardening are carried out on the root portion of the step can be effectively avoided; a shaft section B carburized layer is milled off before the hardening, the hardness of the shaft section B after the hardening is reduced, and machining efficiency of following steps is improved.
Owner:HEBEI HUABEI DIESEL ENGINE
Method and device for progressive austempering heat treatment of bainite and martensite complex-phase steel/iron
ActiveCN104561462AReduce the temperature difference between inside and outsideReduce or prevent quenching cracking tendencyQuenching agentsQuenching devicesMartensite transformationMetallic materials
The invention relates to a method and device for progressive austempering heat treatment of bainite and martensite complex-phase steel / iron, and belongs to the technical field of metallic material heat treatment processes. The method comprises the following steps: performing water cooling on an austenitized workpiece for a certain period of time, taking out the workpiece for air cooling, and enabling the inner and outer temperatures of the workpiece to be close to each other by using waste heat temperature returning, thereby finishing a heat treatment cycle; putting the inner and outer parts of the workpiece into a lower bainite transformation temperature zone after finishing multiple heat treatment cycles; then performing isothermal transformation by using waste heat temperature returning or heat preservation by an insulation can; and finally performing air cooling to finish martensite transformation. By adopting the method, the defect that a workpiece with a relatively large wall thickness is easy to crack and generate early cracks during quenching can be overcome, and the obtained product is uniform in structure, good in comprehensive mechanical property, reliable in operation and low in cost and is green and environmentally-friendly.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Quench cooling process for H13 steel
The invention relates to a quench cooling process for H13 steel. The process sequentially comprises a grading heating step, a gas cooling step, a water cooling step and an air cooling step. During quench cooling in the invention, gas cooling, water cooling and air cooling occur in order. Water cooling speeds up the cooling rate of quenching, so that austenite is rapidly supercooled to a martensite region, thus ensuring a martensitic structure obtained during quenching. The air cooling after water cooling greatly slows down the cooling rate, therefore, the structural stress generated when the austenite structure transforms into the martensitic structure is reduced, thus guaranteeing that a workpiece does not crack and a deeper hardening layer can be obtained. The process provided in the invention is suitable for quench cooling of H13 steel.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DIE & MOLD MFG
1000MPa-grade high-toughness and high-magnetism hot-rolled magnetic yoke steel and production method thereof
ActiveCN111748732AReduce lattice distortionReduce residual internal stressUltimate tensile strengthMagnetism
The invention discloses 1000MPa-grade high-toughness and high-magnetism hot-rolled magnetic yoke steel and a production method thereof. The 1000MPa-grade high-toughness and high-magnetism hot-rolled magnetic yoke steel is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 0.20 to 0.50 percent of C, 0.2 to 1.0 percent of Si, 0.5 to 1.5 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.015 percentof P, less than or equal to 0.005 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.06 percent of Ti, less than or equal to 0.05 percent of Nb, 0.20 to 1.0 percent of Mo, 0.20 to 1.20 percent of Cr, 0.20 to 0.60percent of Ni, 0.03 to 0.15 percent of V, 0.0005 to 0.003 percent of B, 0.015 to 0.10 percent of Al, less than or equal to 0.010 percent of N, less than or equal to 0.0080 percent of O, and the balance of Fe and other unavoidable impurities; and meanwhile Cr+Mo+Ni is larger than or equal to 0.80 percent; Nb+V+Ti is larger than or equal to 0.06 percent; carbon equivalent CEV is larger than or equal to 0.50 percent. The yield strength of the hot-rolled magnetic yoke steel is larger than or equal to 1000MPa, the tensile strength is larger than or equal to 1050MPa; the impact power KV<2> is larger than or equal to 40J at the temperature of 20 DEG C below zero; the magnetic induction performance B<50> is larger than or equal to 1.58T; B<100> is larger than or equal to 1.73T; B<200> is larger than or equal to 1.90T; and B<300> is larger than or equal to 1.93T. The 1000MPa-grade high-toughness and high-magnetism hot-rolled magnetic yoke steel meets relevant requirements of the hydropower industry on rotor magnetic yoke steel.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Heat treatment process for high-hardenability Martensitic stainless steel for moving blades
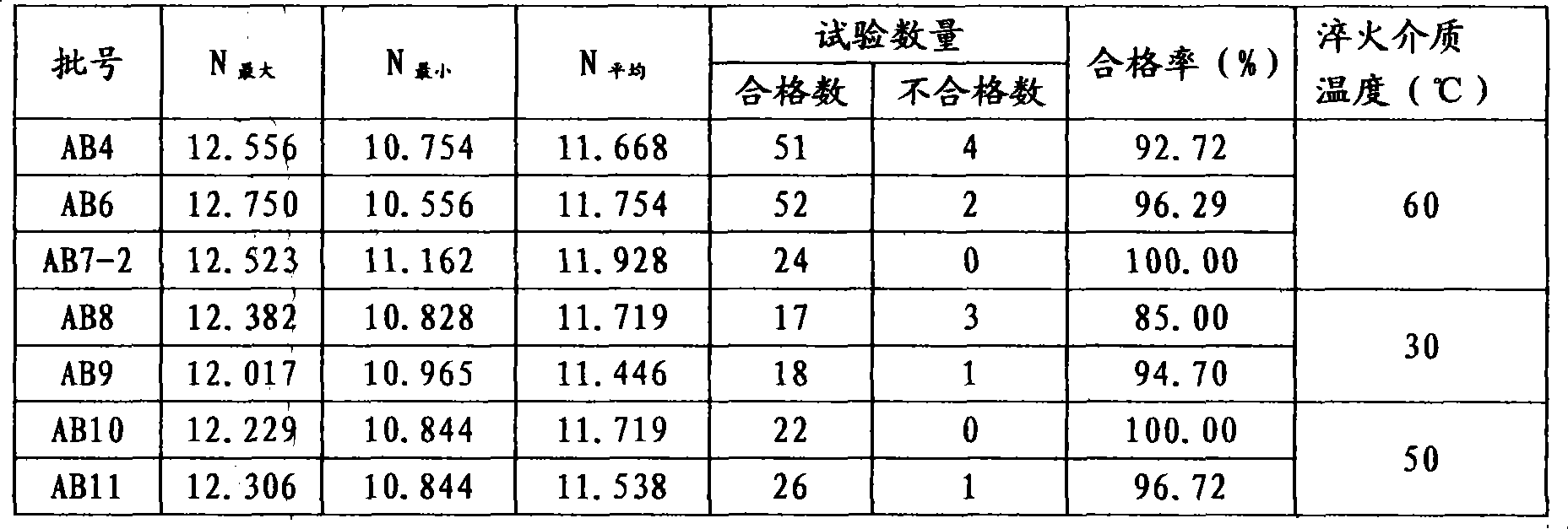
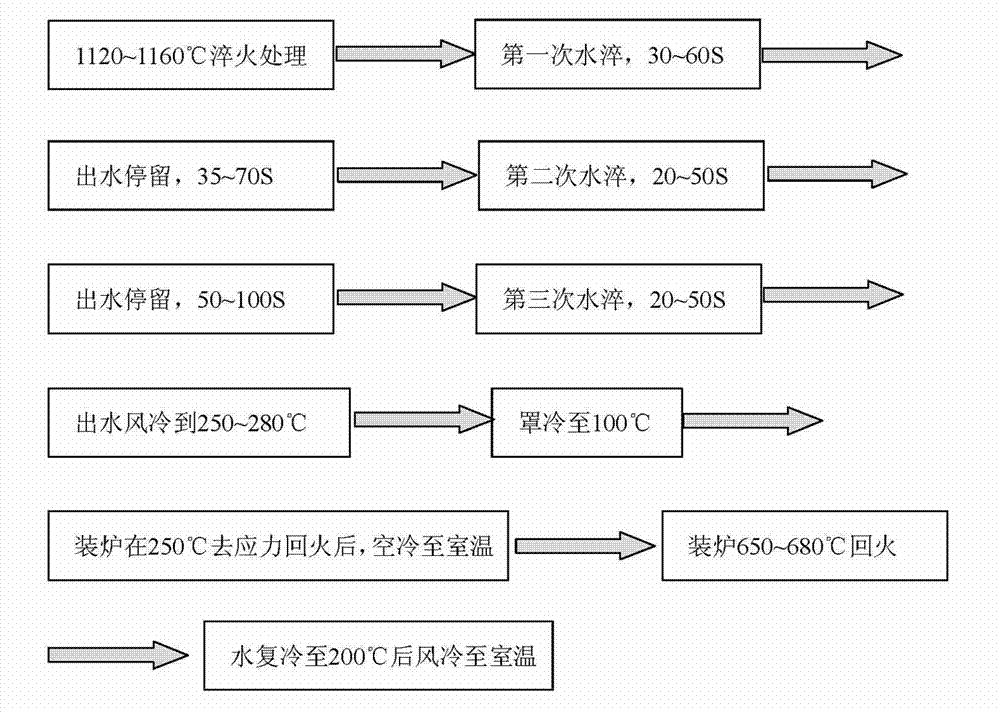
ActiveCN102417969AReduce distortionReduce tissue stressHeat treatment process controlProcess efficiency improvementTemperingMartensitic stainless steel
A heat treatment process for high-hardenability Martensitic stainless steel for moving blades includes the following steps: (1) a forged workpiece is cooled to 50 DEG C to 90 DEG C by the air and loaded into a furnace, and the temperature is increased to 1120 DEG C to 1160 DEG C after 1 to 2 hours of constant temperature; (2) after the temperature is preserved for 8 to 10 hours, three times of water quenching are carried out; (3) the workpiece is blown by a fan, rotated and cooled to 250 DEG C to 280 DEG C, and cooling under cover is started; (4) the workpiece is cooled under cover to 100 DEGC, loaded into a furnace and tempered to remove stress, and the tempering temperature is between 650 DEG C and 680 DEG C; (6) the workpiece is taken out of the furnace, recooled to 200 DEG C by waterand then cooled to the room temperature by the air. The heat treatment process effectively meets the technical requirements of moving blades, also effectively controls the content of residual austenite, and guarantees the dimension stability of the moving blade workpiece, and more importantly, the heat treatment process solves the problems of deformation and cracks in heat treatment.
Owner:沈阳科金特种材料有限公司
Microalloyed medium-thickness plate with high strength and toughness and good core metallurgical quality and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a microalloyed medium-thickness plate with high strength and toughness and good core metallurgical quality and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of hot-rolled steel plate manufacturing. The microalloyed medium-thickness plate with high strength and toughness and good core metallurgical quality comprises 0.07-0.17% of C, 0.05-0.3% of Si, 0.8-1.9% of Mn, 0.0005-0.018% of P, 0.0005-0.010% of S, 0.05-0.25% of Cr, 0.005-0.03% of Nb, 0.05-0.3% of Mo, 0.09-0.25% of V, 0.012-0.025% of N and the balance Fe and inevitable impurity elements. The metallographic structure of the core of the microalloyed medium-thickness plate is acicular ferrite, granular bainite and pearlite. The preparation method of the microalloyed medium-thickness plate comprises the steps of molten iron pretreatment, smelting, LF refining, continuous casting, rough rolling, finish rolling and cooling. By optimizing the chemical components, smelting, rolling and cooling processes, the allowable hydrogen content in molten steel is increased to 4.5ppm, the vacuum degassing process is not needed, and the steel plate has high strength and toughness and good core metallurgical quality.
Owner:LAIWU STEEL YINSHAN SECTION CO LTD +1
Method for manufacturing 105ksi steel grade sulfide stress corrosion resistant drill rod material
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a 105ksi steel grade sulfide stress corrosion resistant drill rod material. The method comprises the following steps of: smelting waste steel, sponge iron and (or) blast furnace molten iron serving as raw materials through an arc furnace, forming slag and removing phosphorus, performing ladle external refining, deoxidation, desulfuration and inclusion removal, adjusting and controlling chemical components, performing vacuum degassing, performing modification treatment on a calcium silk feeding inclusion, and performing continuous casting to form round billets; feeding the round billets into an annular furnace, and performing high-temperature heating, perforation and precise controlled continuous casting to prepare seamless steel tubes; andperforming tube end upsetting, tempering, thermal treatment and thermal straightening on the seamless steel tubes, cooling to room temperature, and performing flaw detection, mechanical property testand sulfide stress cracking (SSC) test. The manufacturing method has the advantages of low alloy content, low production cost, simple process and easiness in operation; based on the metallurgical clean steel, trace alloy components are added, so that the full hardening performance of the steel is improved; and the thermally treated tempered martensite tissues in which fine carbide granules are uniformly distributed have good SSC resistance.
Owner:TIANJIN STEEL PIPE MFG CO LTD
Tempering heat treatment method of mn series high-strength finish-rolled threaded steel bar
ActiveCN104212961BReduce intensityReduce hydrogen contentFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesSteel barMaterials science
The invention discloses a tempering heat treatment method of Mn-series high-strength finish rolling thread reinforcing steel bars. The method comprises a temperature rising process, a heat preservation process and a cooling process. According to the heat preservation process, the heat preservation temperature ranges from 200 DEG C to 600 DEG C, and the heat preservation time ranges from three hours to six hours. According to the method, a heat treatment heating furnace is utilized for performing heating, a martensitic structure obtained after rolled air cooling is decomposed, supersaturated carbon in martensite is precipitated, a reversed crystal lattice is basically restored to be normal, and therefore structural stress is eliminated, and a steel material structure is converted into bainite and a corresponding tempering structure; along with disappearance of the martensite, the strength of steel is reduced, the heat preservation time is increased, the steel hydrogen content is reduced, the hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of the steel is greatly reduced, obdurability of the high-strength finish rolling thread reinforcing steel bars is ensured, and the structural stress and the hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity are reduced. According to the method, the obdurability of the high-strength finish rolling thread reinforcing steel bars is ensured, the structural stress and the hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity are reduced, meanwhile, the production technology is simplified, the equipment requirement is reduced, and the method has the advantages of being simple in process and low in production cost.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Heat forming production line and production method of variable strength part
The invention discloses a heat forming production line and production method of a variable strength part. The production line comprises an unstacking device, a feeding device, a first heating furnace,a second heating furnace, a material outgoing device, a pressing machine and a discharging device which are sequentially arranged; a gas blowing cooling device is arranged on the discharging side ofthe first heating furnace; and a variable strength coating mold is arranged in the pressing machine, and comprises a soft area provided with a thermal barrier coating on the surface and a hard area internally provided with a cooling water way. Due to the heat forming production line and production method of the variable strength part, blank which is just discharged out of a furnace can be subjected to local transitory cooling, and the forming temperature of the blank is controlled within an ideal range. According to the prepared variable strength heat formed part, the soft area position can beany position of the part, meanwhile, a transition interval of the soft area and the hard area is narrow, the soft area is high in extending rate, and the production efficiency is high.
Owner:SUZHOU PRESSLER ADVANCED FORMING TECHNOLOGIES CO LTD
A spheroidizing annealing process of h13 hot work die steel
The invention provides a spheroidizing annealing technology of H13 hot work die steel and belongs to the field of die steel heat treatment technologies. The spheroidizing annealing technology of the H13 hot work die steel comprises the steps that (1) a forged H13 steel blank is cooled to the temperature of 400-500 DEG C, the cooled H13 steel blank is fed into a furnace, the temperature is raised to 720-750 DEG C at the temperature raising speed of 25-80 DEG C per hour for preheating, the temperature is kept for 1-2 hours, the temperature is then raised to 980-1050 DEG C at the temperature raising speed of 25-80 DEG C per hour, after all the furnace charge reaches the temperature, the temperature is kept for 3-5 hours, then the temperature of the forged H13 steel blank is lowered to be not higher than 550 DEG C through furnace cooling, and air cooling and discharging are conducted; hot charging is conducted, the temperature is raised to 900-950 DEG C at the temperature raising speed of 25-80 DEG C per hour, after all the furnace charge reaches the temperature, the temperature is kept for 0.5-1 hour, air cooling and discharging are conducted, and then the pre-treatment process is completed; and charging is conducted at the temperature 300-400 DEG C, the temperature is raised to 880+ / -10 DEG C at the temperature raising speed of 25-80 DEG C per hour, the temperature is kept for 4-6 hours, the temperature is lowered to 760+ / -10 DEG C at the cooling speed of 15-20 DEG C per hour, after the temperature is kept for 8-12 hours, the H13 hot work die steel is cooled to be lower than or equal to 500 DEG C at the cooling speed of 15-20 DEG C per hour, and then air cooling and discharging are conducted. The spheroidizing annealing technology of the H13 hot work die steel has the advantages that carbides are evenly distributed in the structure, the structure is refined, the defects of network carbides and the like in an original structure are eliminated, and the annealing hardness is lowered.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
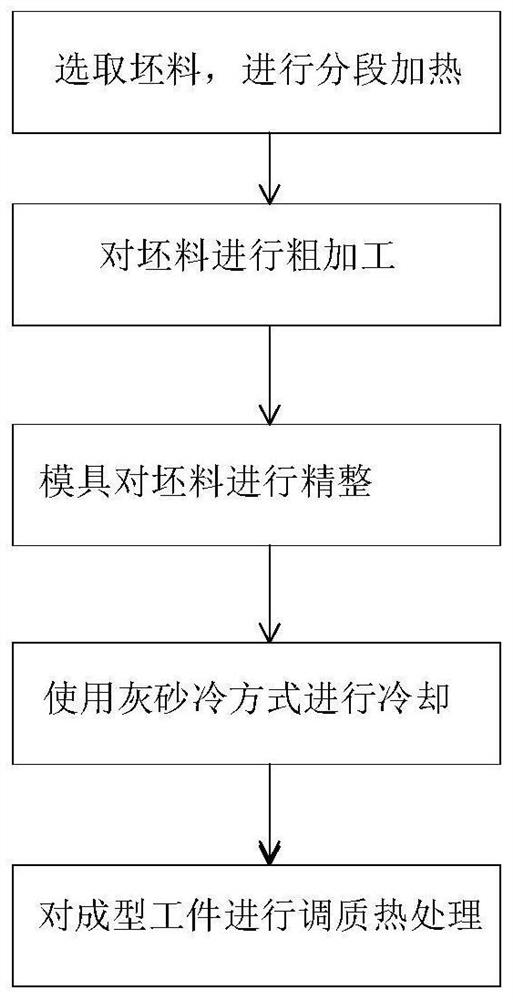
Method for overcoming explosion defect of 4140 steel tubing hanger body
The invention relates to a method for overcoming the explosion defect of a 4140 steel tubing hanger body. Firstly, a blank is heated section by section, then basic procedures are prepared, then die forging is carried out, then lime sand cooling is used for cooling, and finally a formed workpiece is subjected to quenched-tempered heat treatment. As the blank is slowly heated, the internal structureof the blank slowly changes, the effects of refining grain and homogenizing the structure are achieved, the actual grain size can reach a 7-10 level, and harmful structures such as a Widmannstatten structure generated by overburning and overheating are avoided. Due to the manner of die forging, too large surface stress triggered by hammer forging of free forging is avoided, sequential forging iscarried out in multiple directions, the fluidity of the blank is improved, and knife patterns and main cracks are avoided. During final quenching, the quenching cooling speed is reduced, the cooling speed of a martensite transformation region is reduced, thus, transgranular extension is avoided, structural stress of martensite transformation is reduced, and macroscopic cracks are avoided.
Owner:NANJING DEV ADVANCED MFG
A kind of bainite-martensite multiphase steel/iron graded austempering heat treatment method and device
ActiveCN104561462BReduce the temperature difference between inside and outsideReduce or prevent quenching cracking tendencyQuenching agentsQuenching devicesMartensite transformationMetallic materials
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Quench cooling process for H13 steel
The invention relates to a quench cooling process for H13 steel. The process sequentially comprises a grading heating step, a gas cooling step, a water cooling step and an air cooling step. During quench cooling in the invention, gas cooling, water cooling and air cooling occur in order. Water cooling speeds up the cooling rate of quenching, so that austenite is rapidly supercooled to a martensite region, thus ensuring a martensitic structure obtained during quenching. The air cooling after water cooling greatly slows down the cooling rate, therefore, the structural stress generated when the austenite structure transforms into the martensitic structure is reduced, thus guaranteeing that a workpiece does not crack and a deeper hardening layer can be obtained. The process provided in the invention is suitable for quench cooling of H13 steel.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DIE & MOLD MFG
Carburizing and quenching process for thin-wall gear
PendingCN114000094AReduced ellipse and warpageSmall quenching deformationSolid state diffusion coatingFurnace typesThin walledMetallic materials
The invention belongs to the technical field of metal material heat treatment, and particularly relates to a carburizing and quenching process of a thin-wall gear. The process comprises the following steps: low-temperature tempering and air cooling treatment is performed on the thin-wall gear after gear shaping; the thin-wall gear is subjected to pre-oxidation treatment, the temperature ranges from 400 DEG C to 500 DEG C, and the time ranges from 1 h to 2 h; carburizing treatment is conducted on the thin-wall gear; the thin-wall gear is heated to 900-930 DEG C in stages; strong carburizing treatment is conducted on the heated thin-wall gear for 3-5 h under the conditions that the temperature ranges from 900 DEG C to 930 DEG C and the carbon potential ranges from 1.0% to 1.2%; diffusion treatment is performed for 1 to 2 hours at the temperature of 900 to 930 DEG C and the carbon potential of 0.7 to 0.9 percent; the temperature is reduced to 800 DEG C to 850 DEG C under the condition that the carbon potential is 0.7% to 0.9%; temperature equalization treatment is performed under the conditions that the carbon potential is 0.7-0.9% and the temperature is 800-850 DEG C; the thin-wall gear is subjected to staged oil quenching cooling treatment; and after cooling of the thin-wall gear is finished, oil draining, cleaning, low-temperature tempering and air cooling are sequentially conducted, and carburizing and quenching are completed. The carburizing and quenching deformation of the thin-wall gear can be controlled, and it can be ensured that the heat treatment performance and the structure are not out of tolerance.
Owner:XUZHOU XCMG DRIVELINE TECH CO LTD
Thermoforming line and production method for variable strength parts
Owner:SUZHOU PRESSLER ADVANCED FORMING TECHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Ammunition belt heat treatment process
InactiveCN106801118AReduce tissue stressImprove toughnessFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesEngineeringHeat treating
The invention discloses an ammunition belt heat treatment process, which comprises: heating a work-piece to austenitize and homogenize, cooling to a temperature of 240-260 DEG C in a nitrate tank, carrying out isothermal maintaining, and carrying out water cooling. According to the present invention, with the ammunition belt heat treatment process, the requirements that the mechanical performance index of the ammunition belt are substantially improved and the qualification rate is increased to 100% are fundamentally met.
Owner:QINGDAO XINHEYI IND & TRADE CO LTD
A Vacuum Grading Gas Quenching Method for Thin-walled D6ac Ultra-High Strength Steel Shell
ActiveCN109055683BReduce distortionReduced tendency to crackFurnace typesQuenching agentsNitrogenNitrogen gas
Owner:西安长峰机电研究所
A method to overcome the cracking defects of 4140 steel tubing hanger body
The invention relates to a method for overcoming the cracking defects of the 4140 steel oil pipe hanger body. Firstly, the blank is heated in sections, then the basic process is prepared, and then the mold is forged, and then cooled with lime sand, and finally the formed workpiece is quenched and tempered. heat treatment. This application heats the billet slowly to make the internal structure change slowly, which plays the role of grain refinement and uniform structure. The actual grain size can reach 7 to 10 grades, avoiding the Widmanstatten caused by overheating and overheating. organizations and other harmful organizations. The die forging method is used to avoid excessive surface stress caused by free forging hammer forging. It is forged from multiple directions successively to increase the fluidity of the billet and avoid the generation of knife patterns and the formation of main cracks. In the final quenching, slow down the quenching cooling rate and reduce the cooling rate in the martensite transformation zone, thereby avoiding transgranular expansion, reducing the structural stress of martensite transformation, and avoiding macroscopic cracks.
Owner:NANJING DEV ADVANCED MFG
A microalloyed plate with high strength and toughness and good metallurgical quality in the core and its preparation method
ActiveCN113025895BQuality improvementImprove the qualified rate of flaw detectionRefining (metallurgy)Chemical composition
The invention discloses a micro-alloyed medium-thick plate with high strength and toughness and good metallurgical quality at the core and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of hot-rolled steel plate manufacturing. The microalloyed plate with high strength and toughness and good metallurgical quality in the core includes: 0.07‑0.17% of C, 0.05‑0.3% of Si, 0.8‑1.9% of Mn, 0.0005‑0.018% of P, and 0.0005‑05% of S 0.010%, Cr is 0.05‑0.25%, Nb is 0.005‑0.03%, Mo is 0.05‑0.3%, V is 0.09‑0.25%, N is 0.012‑0.025%, and the balance is Fe and unavoidable impurity elements; The metallographic structure of the core is acicular ferrite, granular bainite and pearlite. Its preparation method goes through molten iron pretreatment, smelting, LF refining, continuous casting, rough rolling, finish rolling, cooling, and through optimization of chemical composition, smelting, rolling, and cooling processes, the allowable hydrogen content in molten steel is increased to 4.5 ppm, no vacuum degassing process is required, which makes the steel plate have strong toughness and good core metallurgical quality.
Owner:LAIWU STEEL YINSHAN SECTION CO LTD +1
Inorganic polymer water-soluble quenching medium and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102061365BReduce transition speedReduced tendency to crackQuenching agentsPotassiumQuenching
The invention discloses an inorganic polymer water-soluble quenching medium which has reasonable cooling characteristic distribution and stable performance, is safe and environmentally friendly and has lower cost, and a preparation method thereof. The quenching medium is an aqueous solution formed by mixing polyaluminium chloride, sodium hydroxide, zinc chloride, potassium chloride and water, wherein the concentration of the aqueous solution is 8-35 Baume and the aqueous solution comprises the following raw materials by weight percent: 59-62% of the polyaluminium chloride, 19-21% of the 10% sodium hydroxide, 14-16% of zinc chloride, 11-13% of the potassium chloride and the balance water. The preparation method comprises the following steps in sequence: adding the polyaluminium chloride and water in a container, and stirring until the polyaluminium chloride is fully dissolved; adding the 10% sodium hydroxide solution in the container, and stirring evenly; dissolving the zinc chloride in water, then adding the zinc chloride solution in the container, and stirring evenly; dissolving the potassium chloride in water, then adding the potassium chloride solution in the container, and stirring evenly; and adding water to ensure that the concentration of the solution in the container is 8-35 Baume.
Owner:DALIAN SANJIN LUBRICANT
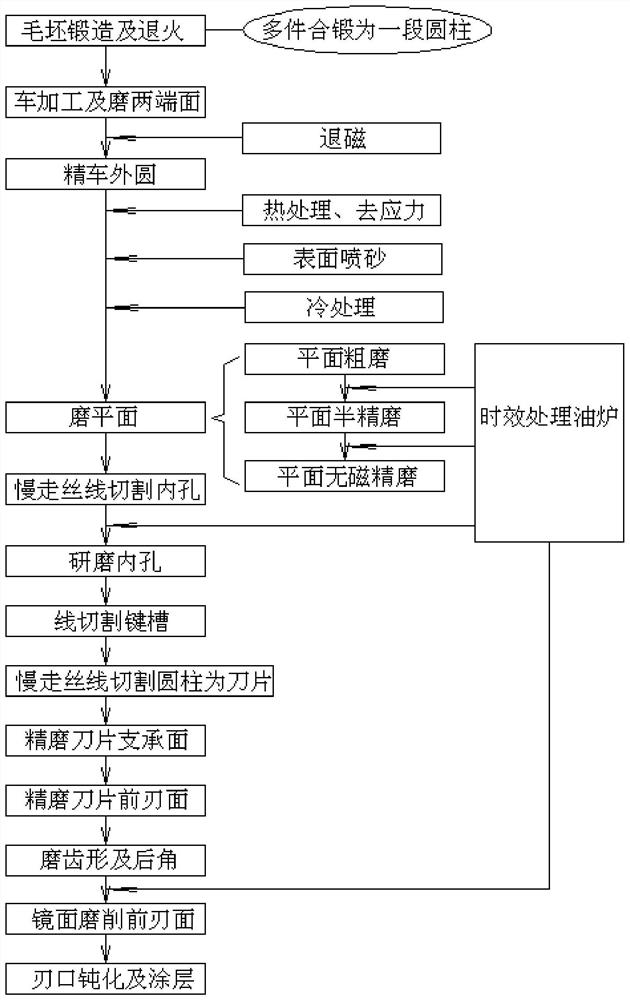
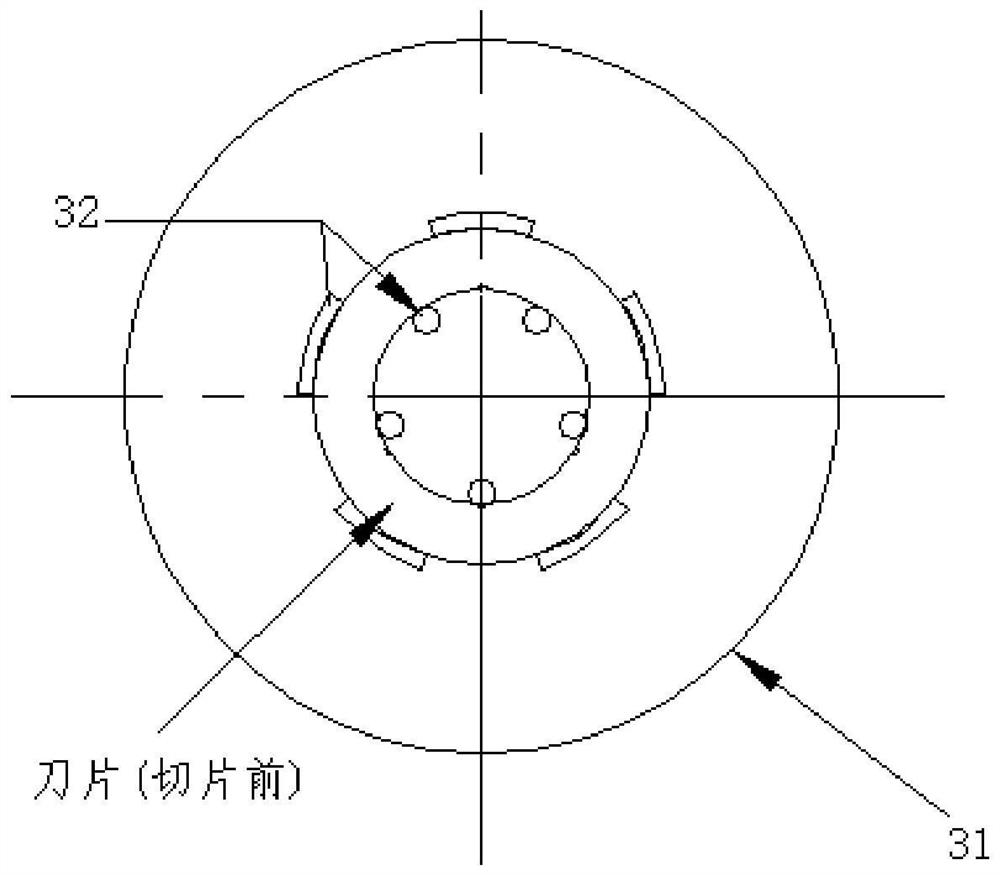
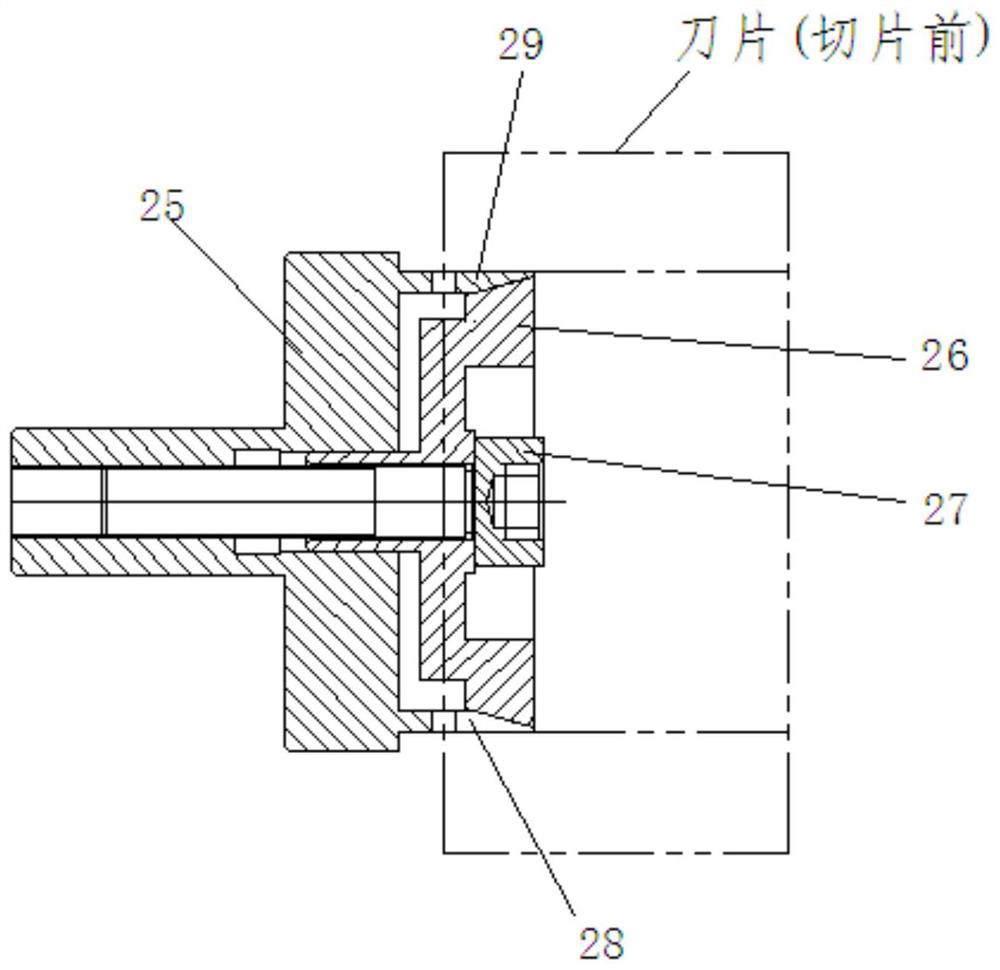
A manufacturing process of an ultra-thin shaper blade
The invention relates to the technical field of slotting cutter manufacturing, and discloses a manufacturing process of an ultra-thin slotting blade. According to the manufacturing procedure, the process sequentially includes the steps of forging and annealing a blank, lathing and grinding the two end faces, performing finish turning on an outer circle, grinding the flat face, cutting an inner hole through a slow-feeding wire, grinding the inner hole, cutting a key groove through the wire, cutting a cylinder into a blade through the slow-feeding wire, accurately grinding a blade supporting face, accurately grinding a blade front edge face, grinding a tooth profile and a relief angle, performing mirror grinding on a front blade face, passivating a cutting edge and conducting coating. In theblank forging and annealing step, multiple blades are combined and forged into the cylinder blank. The demagnetizing step is executed between the step of lathing and grinding the two end faces and the step of performing finish turning on the outer circle. The steps of heat treatment, destressing, surface sand blasting and cold treatment are sequentially executed between the step of performing finish turning on the outer circle and the step of grinding the flat face. By means of the manufacturing process, the manufacturing quality of the ultra-thin slotting blade is improved.
Owner:JIANGYIN SAITE PRECISION TOOL
Thermal treatment process of elastic chains
InactiveCN103805765AHigh strengthImprove toughnessFurnace typesQuenching agentsEngineeringThermal treatment
The invention discloses a thermal treatment process of elastic chains. The thermal treatment process comprises the following steps: heating workpieces to austenitize and homogenize; subsequently, cooling the workpieces to be 240-260 DEG C in a nitrate tank and transferring the workpieces into water to cool after the temperature is retained. Through the thermal treatment process of elastic chains, the requirements that the mechanical performance index of the elastic chains is greatly improved and the qualified rate is increased to 100% can be met fundamentally.
Owner:CHANGAN AUTOMOBILE (GRP) CO LTD
Treatment method for improving tensile property qualification rate of steel plate
ActiveCN111607690AImprove the pass rate of tensile propertiesAvoid wastingFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesEngineeringStructural engineering
The invention provides a treatment method for improving the tensile property qualification rate of a steel plate, and belongs to the technical field of steel and iron. The treatment method comprises the following steps that for a first stage, the steel plate is placed on a cooling bed and cooled to 300-550 DEG C; for a second stage, natural aging is carried out on the steel plate for 24 h or abovein a lower line stacking slow cooling manner, the steel plate is slit to obtain a plurality of sub-steel plates when the surface temperature of the steel plate is less than or equal to 150 DEG C, andsampling and initial inspection sample machining are carried out; and for a third stage, natural aging is carried out on an initial inspection sample and the plurality of sub-steel plates corresponding to the initial inspection sample for 24-72 h, and the tensile property of the initial inspection sample subjected to natural aging is detected. Compared with the mode of directly detecting the tensile property of the initial detection sample in the second stage, the method has the advantage that the qualification rate of the tensile property of the steel plate can be improved through the treatment in the third stage.
Owner:SGIS SONGSHAN CO LTD
Heat treatment process for high-hardenability Martensitic stainless steel for moving blades
ActiveCN102417969BReduce distortionReduce tissue stressHeat treatment process controlProcess efficiency improvementTemperingMartensitic stainless steel
A heat treatment process for high-hardenability Martensitic stainless steel for moving blades includes the following steps: (1) a forged workpiece is cooled to 50 DEG C to 90 DEG C by the air and loaded into a furnace, and the temperature is increased to 1120 DEG C to 1160 DEG C after 1 to 2 hours of constant temperature; (2) after the temperature is preserved for 8 to 10 hours, three times of water quenching are carried out; (3) the workpiece is blown by a fan, rotated and cooled to 250 DEG C to 280 DEG C, and cooling under cover is started; (4) the workpiece is cooled under cover to 100 DEGC, loaded into a furnace and tempered to remove stress, and the tempering temperature is between 650 DEG C and 680 DEG C; (6) the workpiece is taken out of the furnace, recooled to 200 DEG C by waterand then cooled to the room temperature by the air. The heat treatment process effectively meets the technical requirements of moving blades, also effectively controls the content of residual austenite, and guarantees the dimension stability of the moving blade workpiece, and more importantly, the heat treatment process solves the problems of deformation and cracks in heat treatment.
Owner:沈阳科金特种材料有限公司
Carburizing and quenching method for large and heavy-duty gears
ActiveCN104711401BSmall amount of deformationConsistent temperatureSolid state diffusion coatingFurnace typesCarbon potentialMechanical property
Owner:CRRC QISHUYAN INSTITUTE CO LTD
Cobalt-less multi-element high speed tool steel and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN100575528CReasonable range of performanceLow content of alloying elementsFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesChemical compositionAlloy
Owner:JIUQUAN IRON & STEEL GRP
Manufacturing process of ultra-thin slotting blade
The invention relates to the technical field of slotting cutter manufacturing, and discloses a manufacturing process of an ultra-thin slotting blade. According to the manufacturing procedure, the process sequentially includes the steps of forging and annealing a blank, lathing and grinding the two end faces, performing finish turning on an outer circle, grinding the flat face, cutting an inner hole through a slow-feeding wire, grinding the inner hole, cutting a key groove through the wire, cutting a cylinder into a blade through the slow-feeding wire, accurately grinding a blade supporting face, accurately grinding a blade front edge face, grinding a tooth profile and a relief angle, performing mirror grinding on a front blade face, passivating a cutting edge and conducting coating. In theblank forging and annealing step, multiple blades are combined and forged into the cylinder blank. The demagnetizing step is executed between the step of lathing and grinding the two end faces and the step of performing finish turning on the outer circle. The steps of heat treatment, destressing, surface sand blasting and cold treatment are sequentially executed between the step of performing finish turning on the outer circle and the step of grinding the flat face. By means of the manufacturing process, the manufacturing quality of the ultra-thin slotting blade is improved.
Owner:JIANGYIN SAITE PRECISION TOOL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com