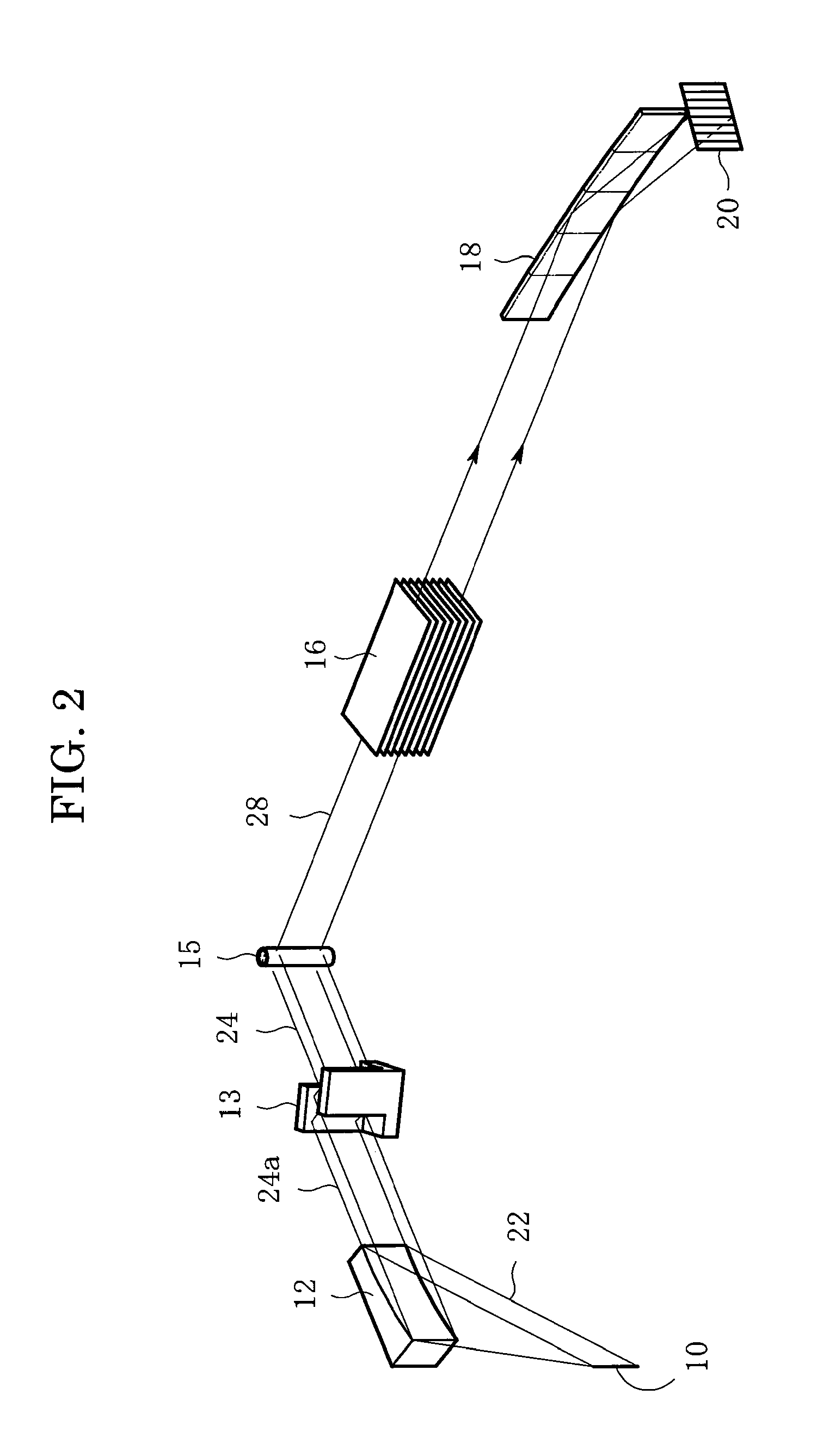
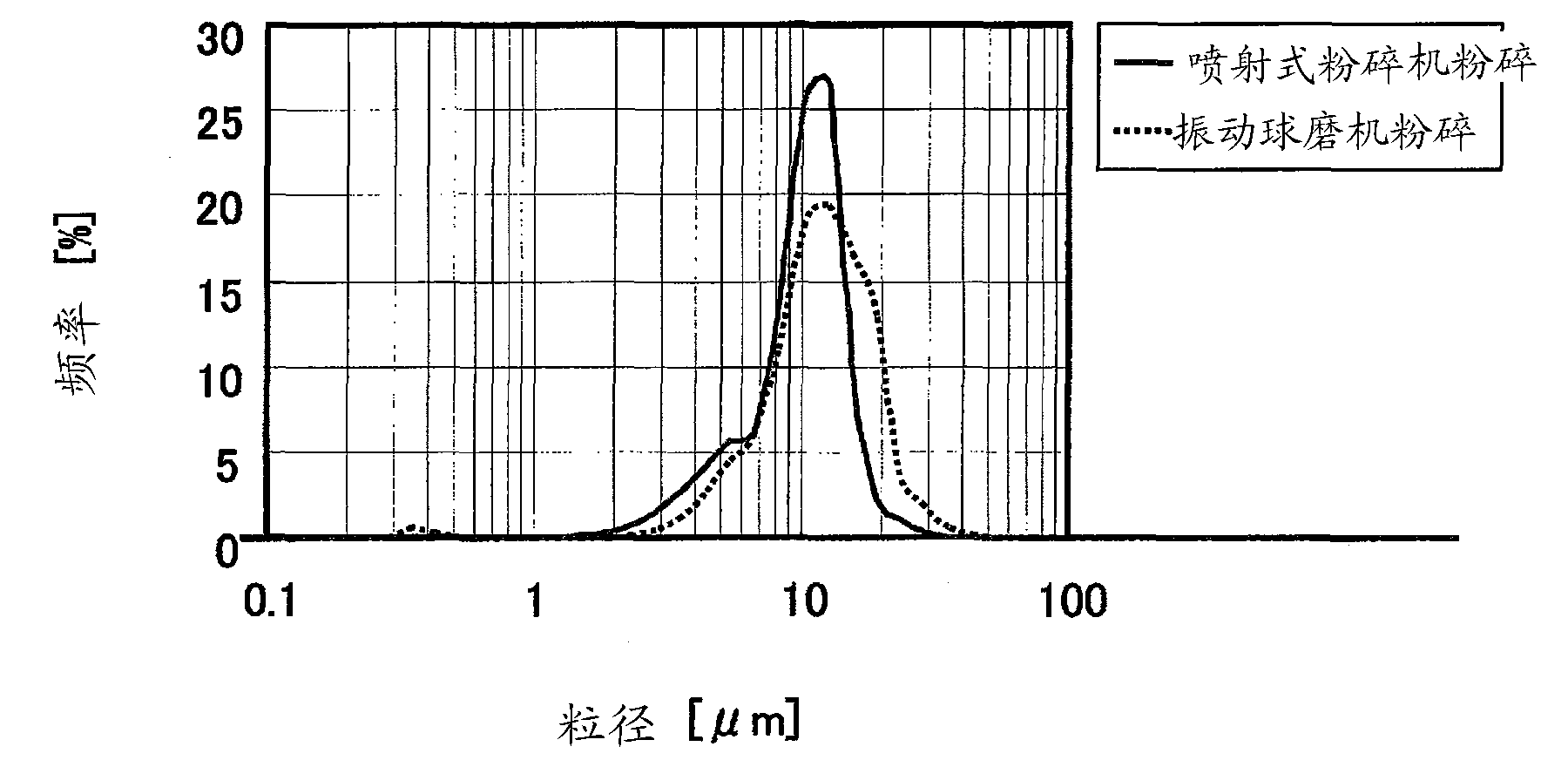
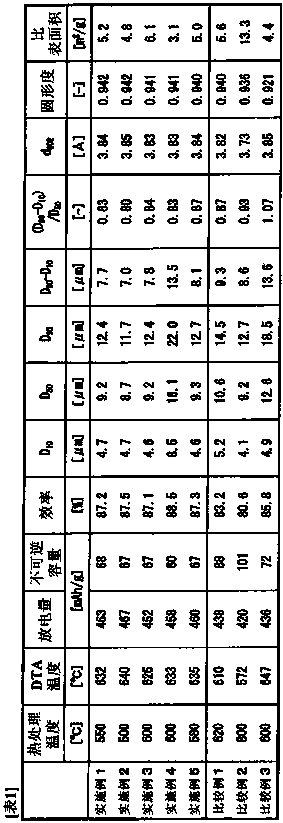
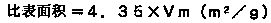Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
225 results about "X-ray scattering techniques" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
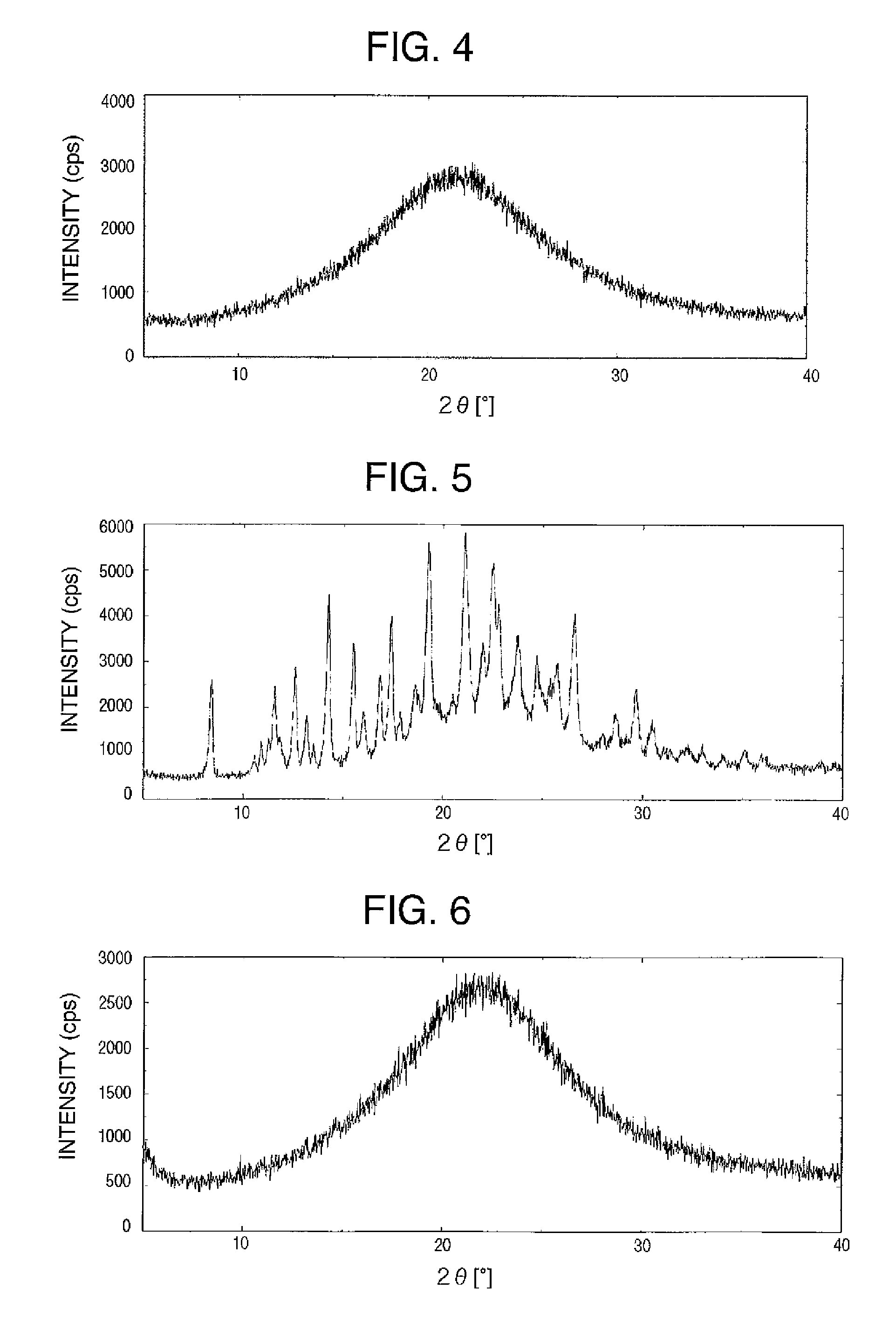
X-ray scattering techniques are a family of non-destructive analytical techniques which reveal information about the crystal structure, chemical composition, and physical properties of materials and thin films. These techniques are based on observing the scattered intensity of an X-ray beam hitting a sample as a function of incident and scattered angle, polarization, and wavelength or energy.
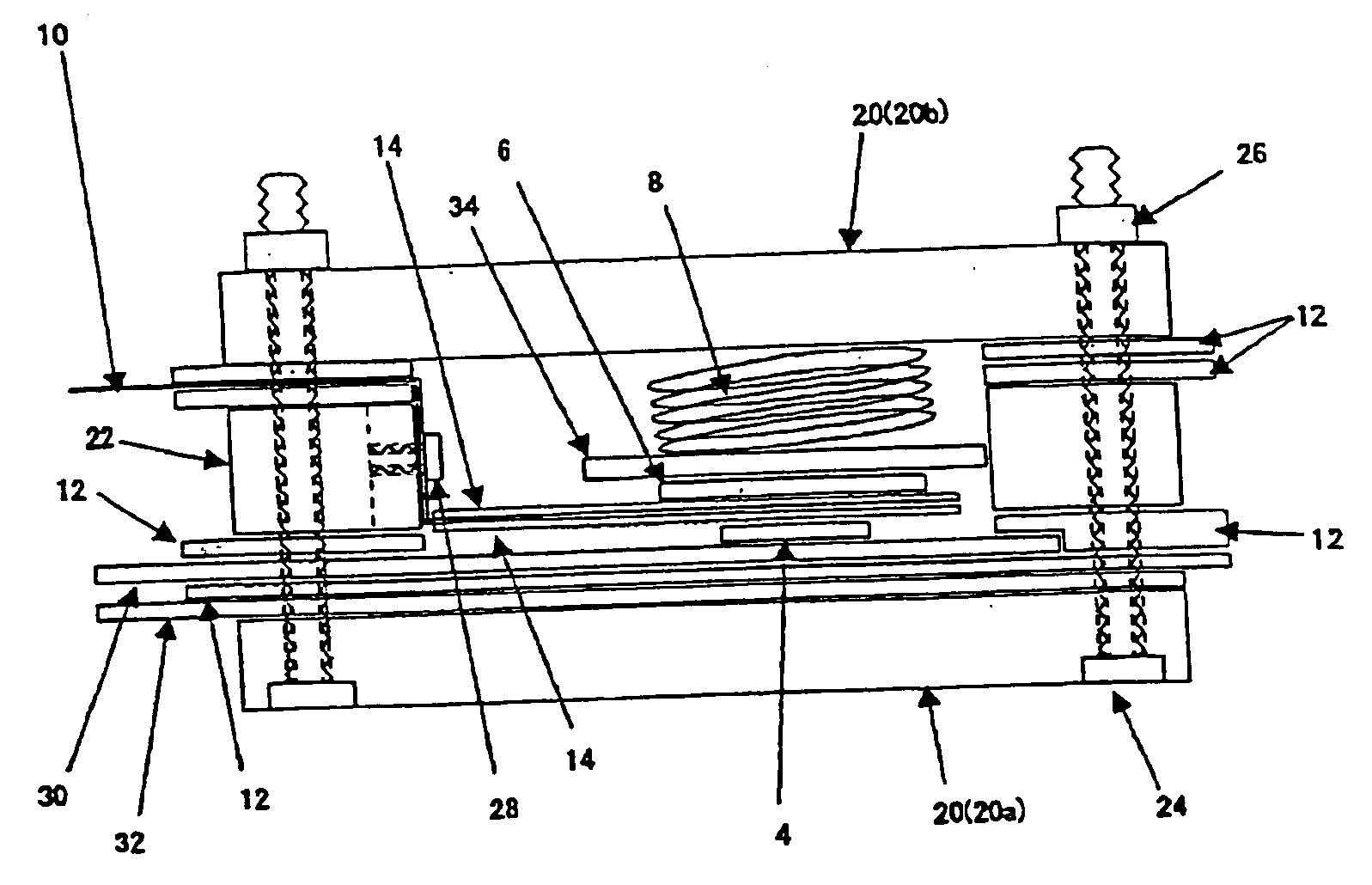
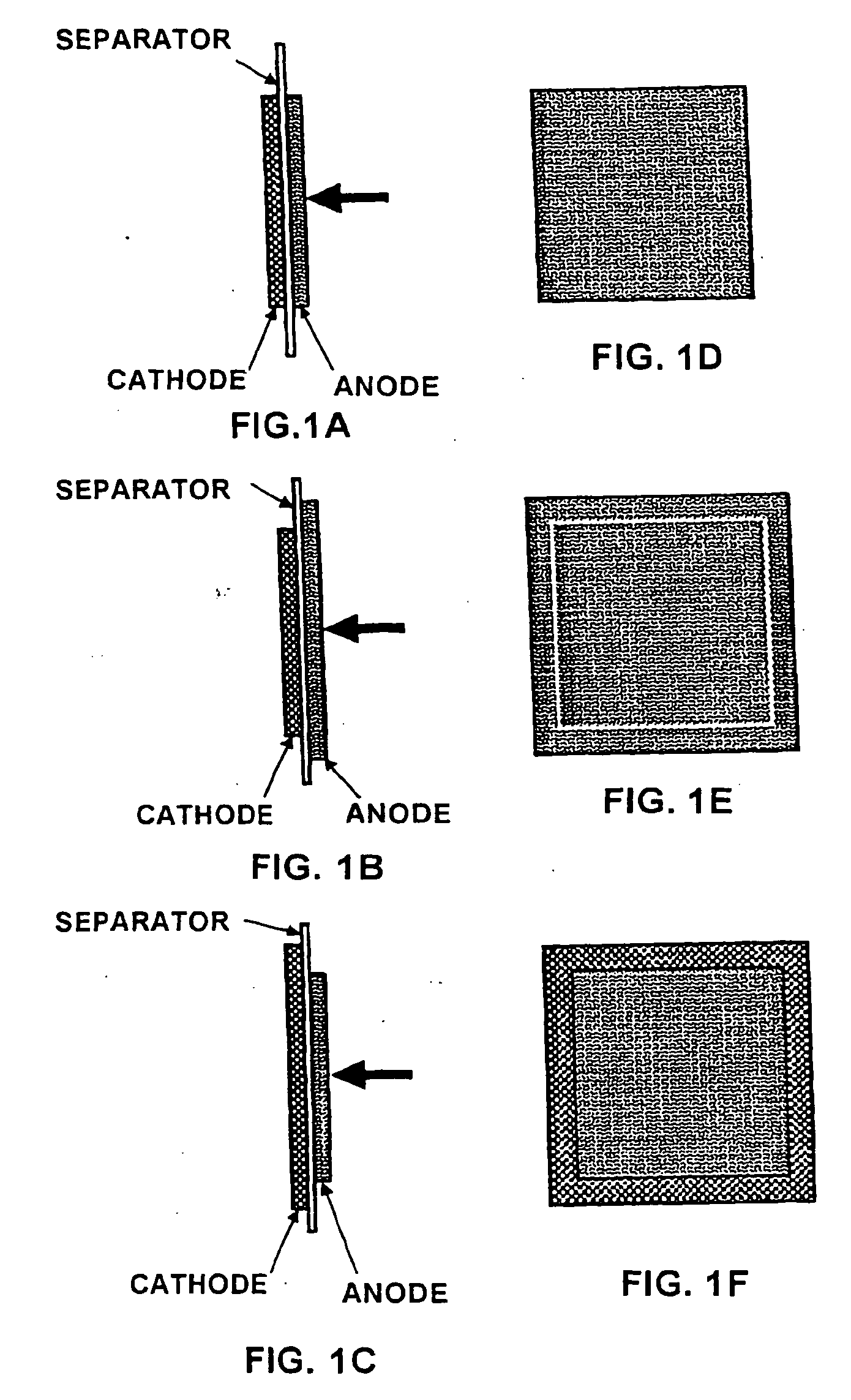
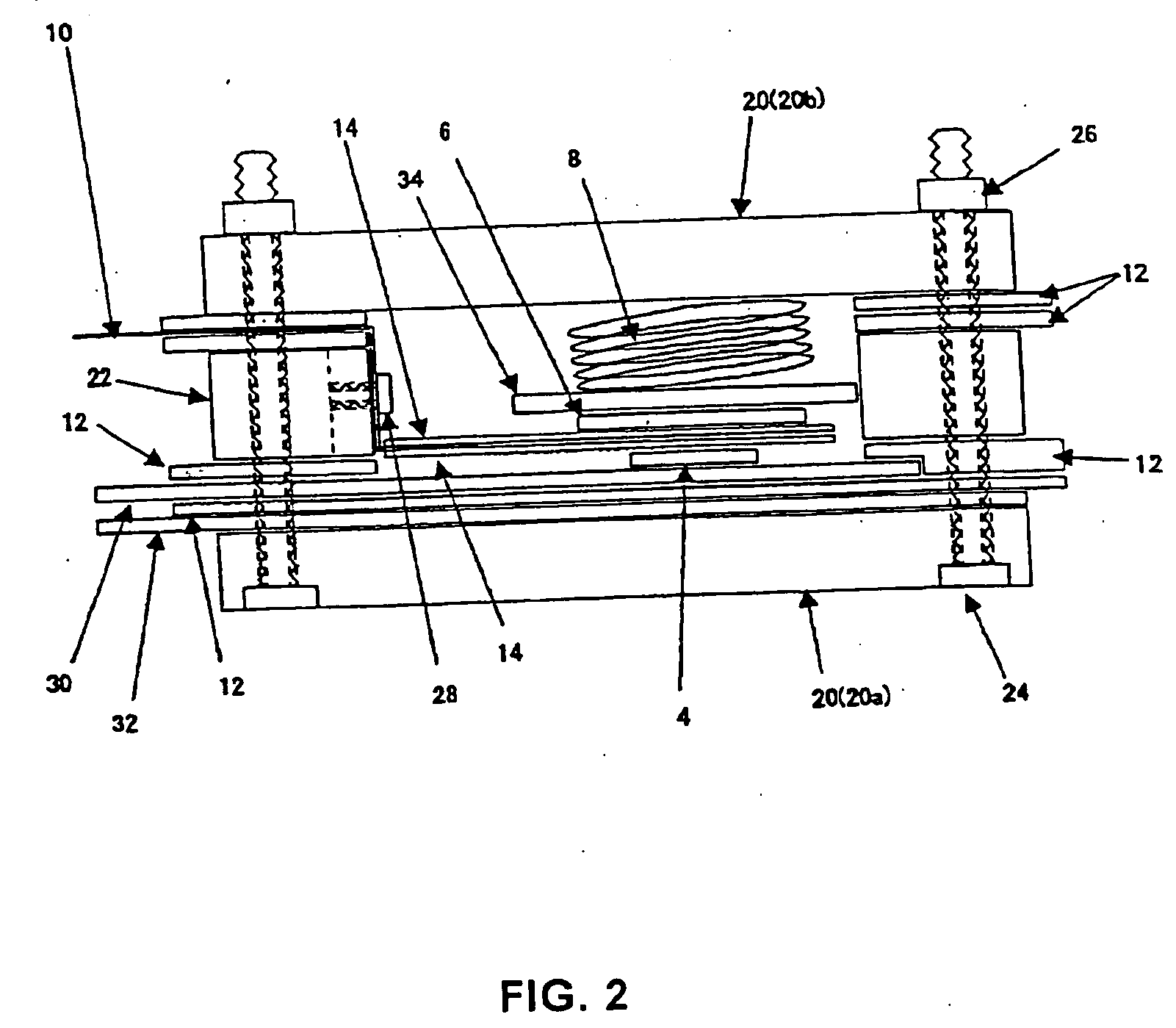
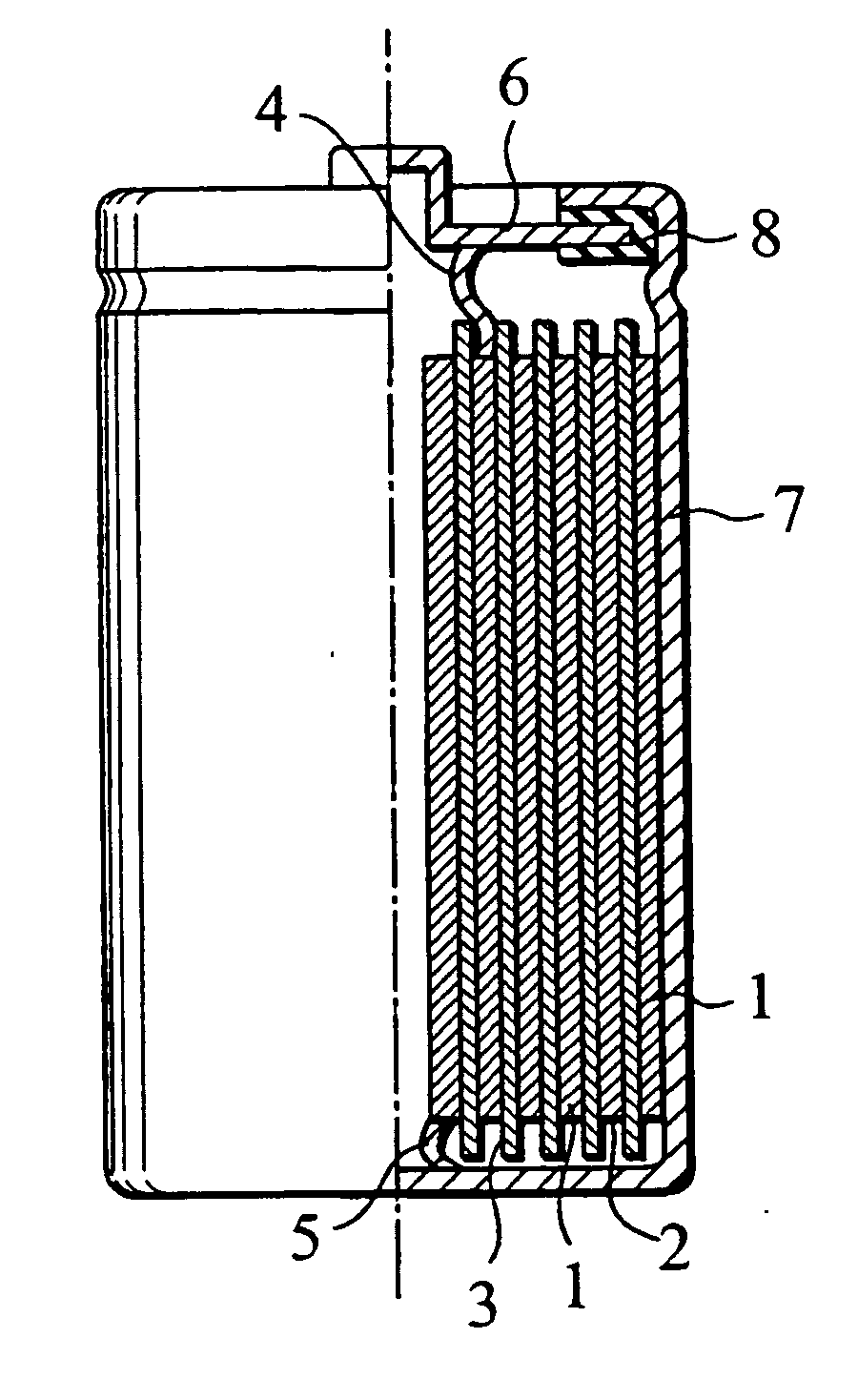
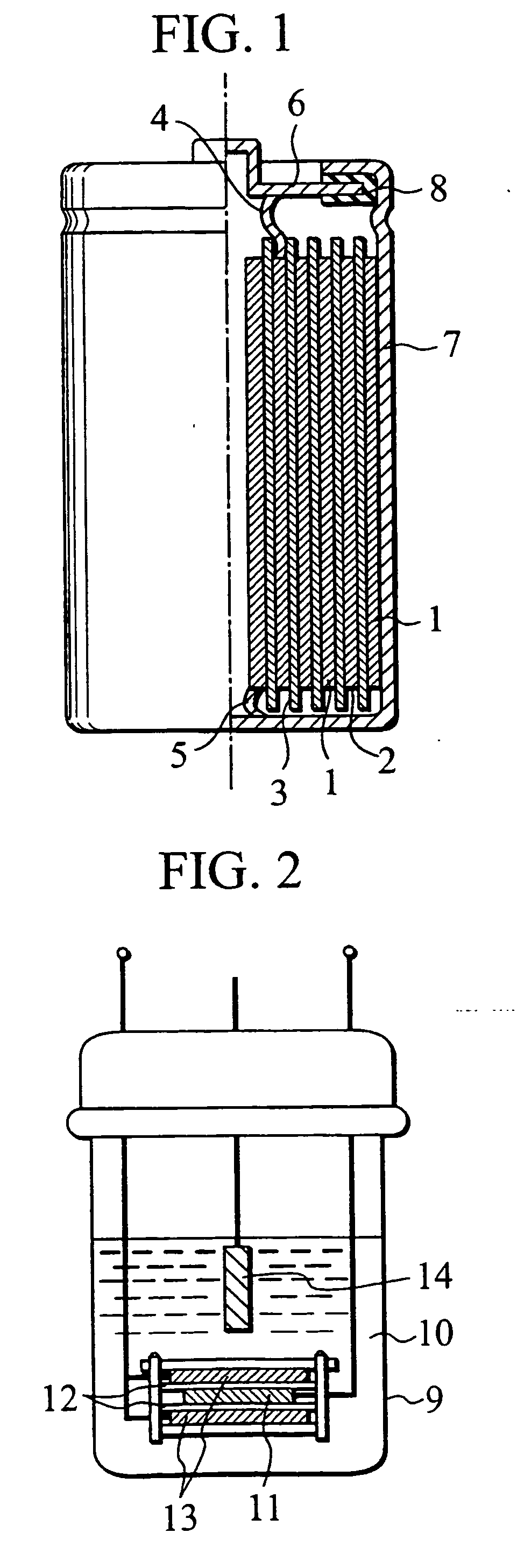
Non-aqueous secondary battery
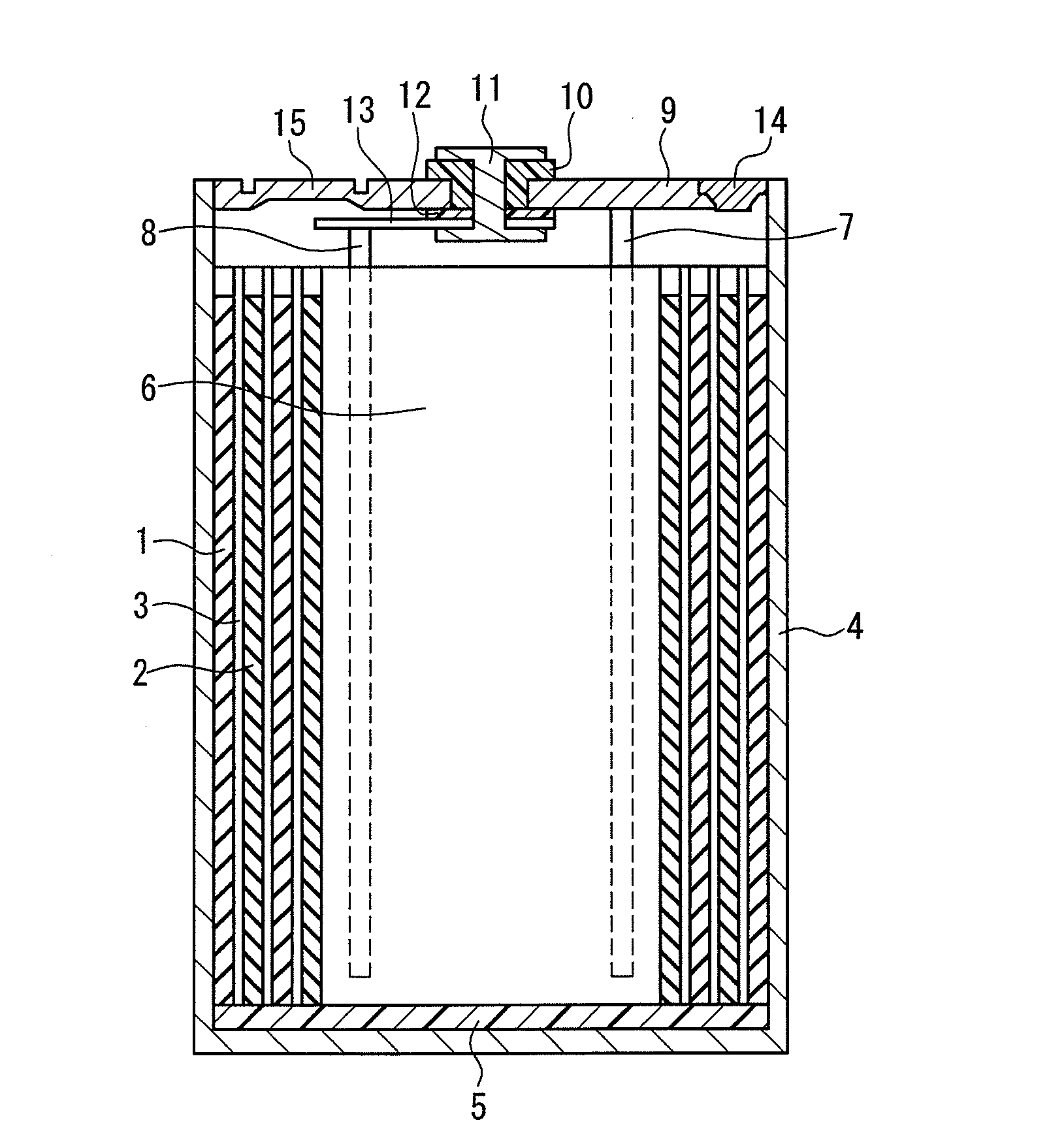
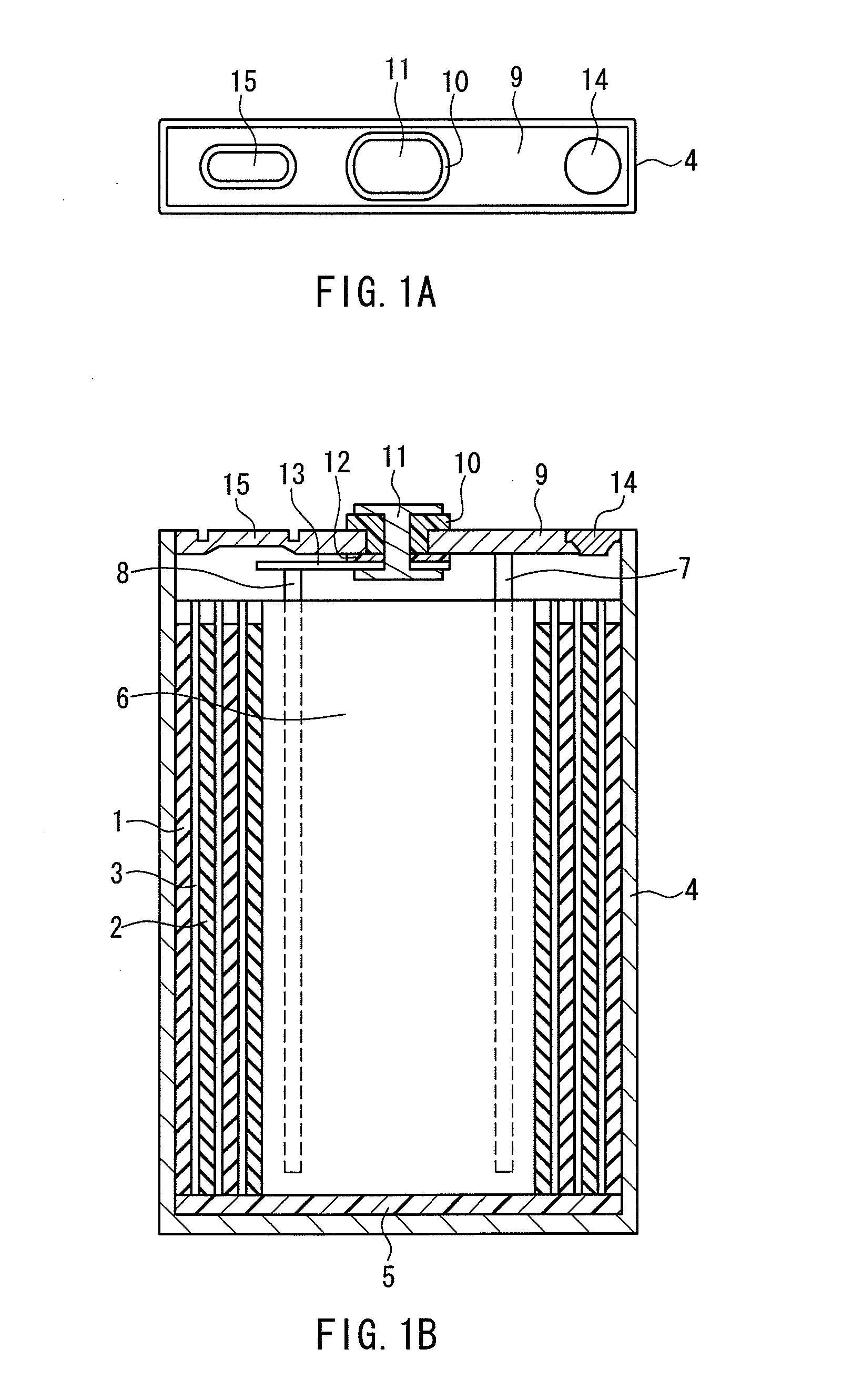
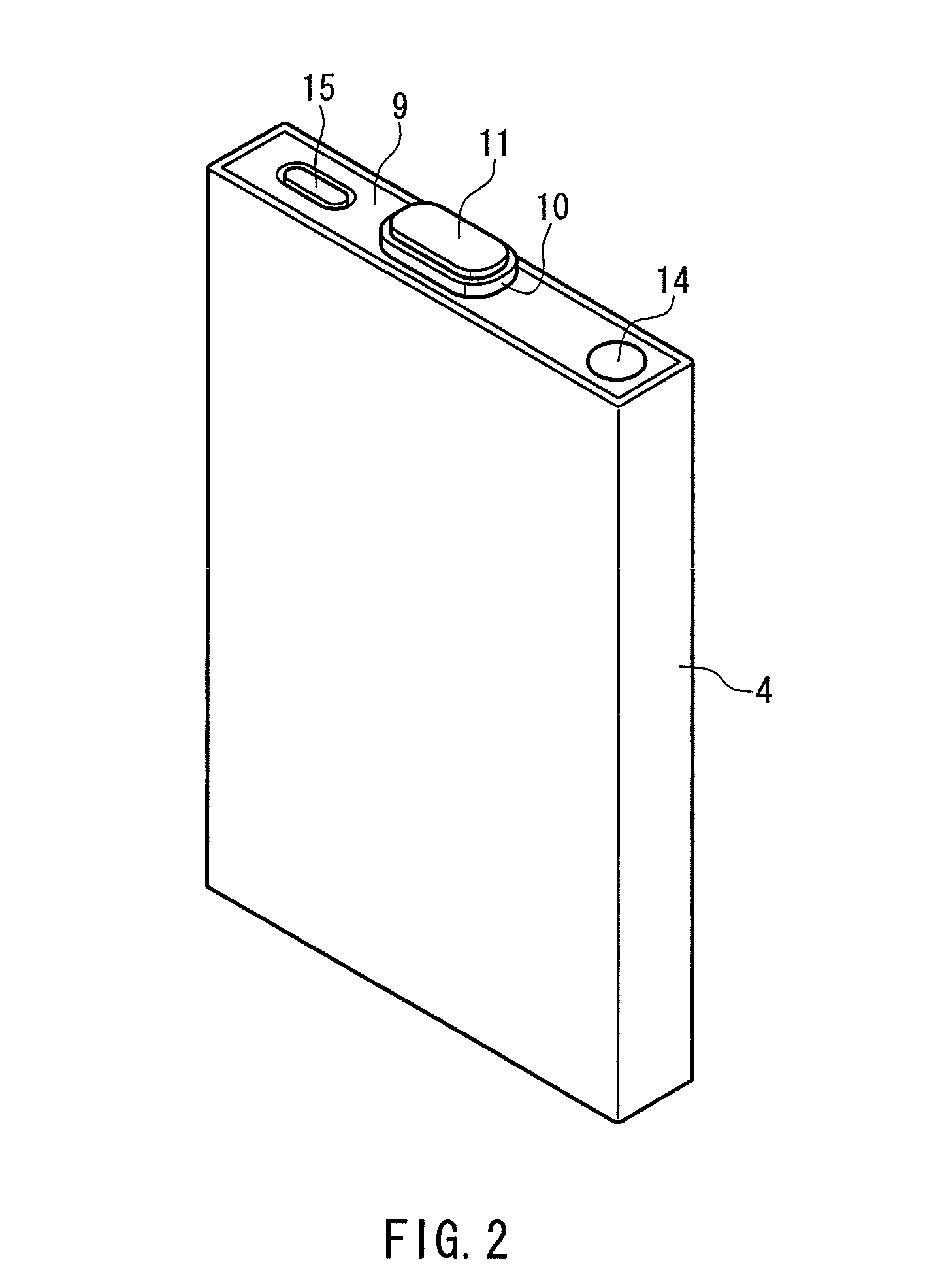
ActiveUS20120288742A1Large capacityImprove storage characteristicsFinal product manufactureOrganic electrolyte cellsCarbon coatingX-ray
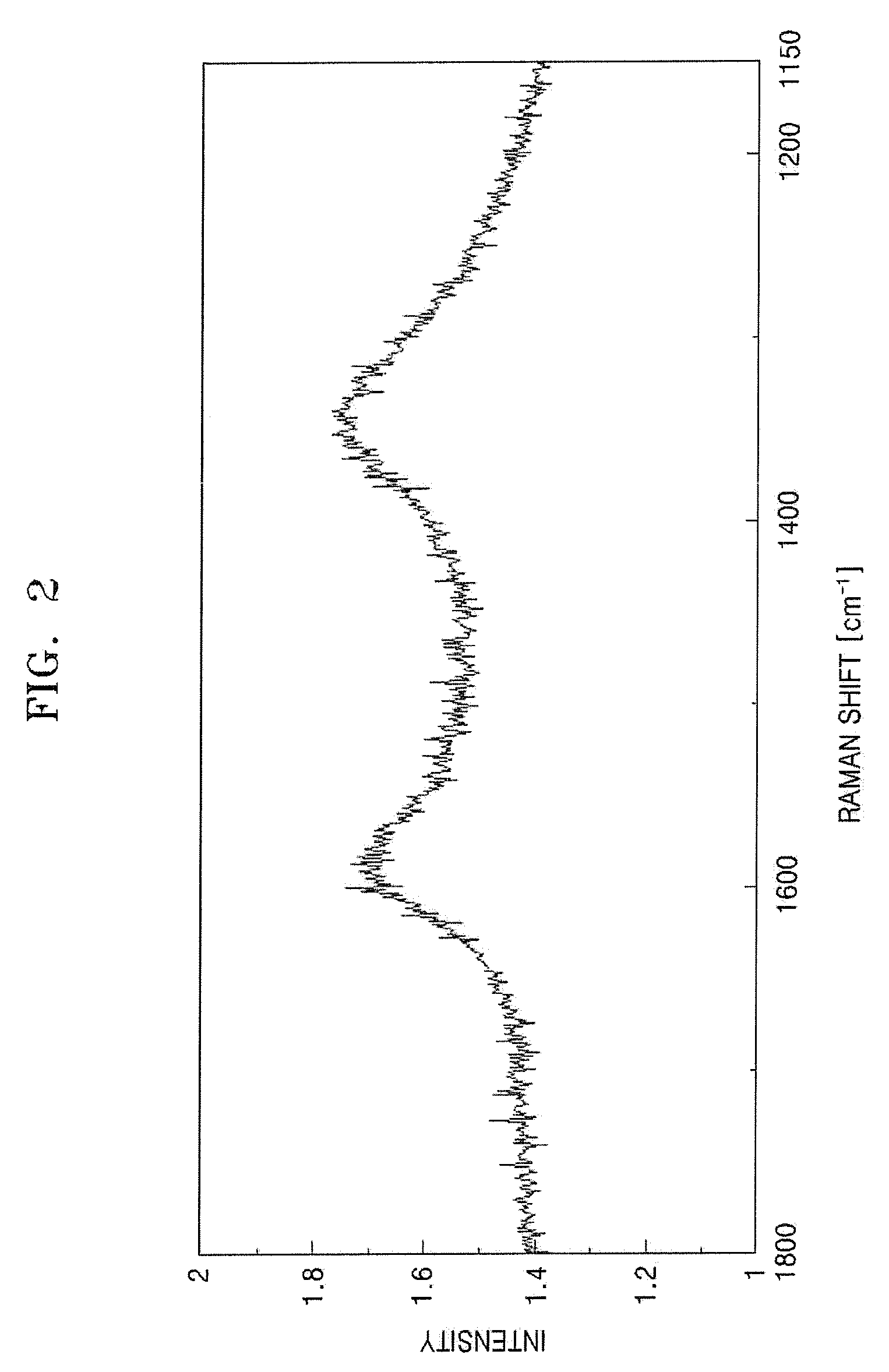
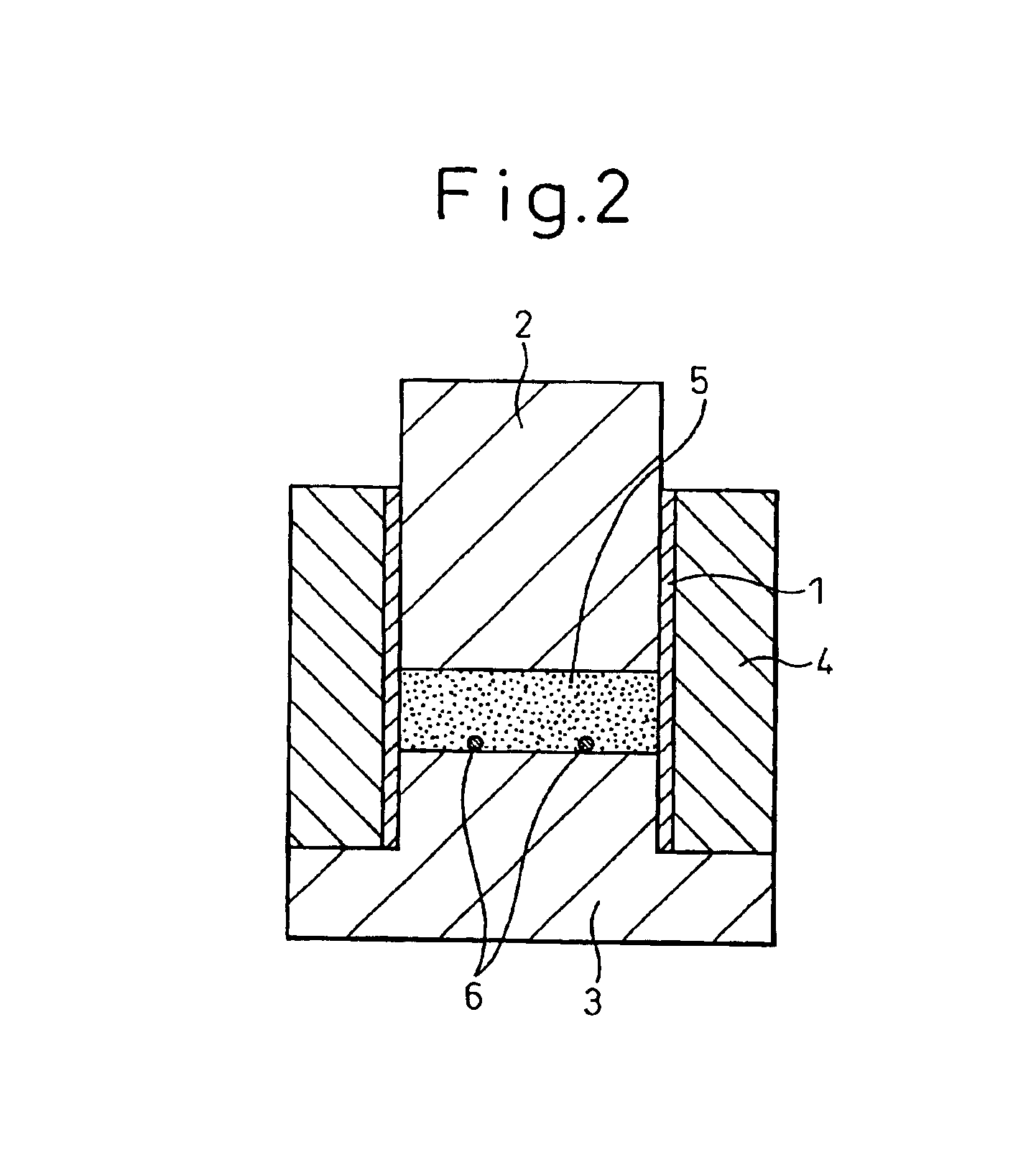
The non-aqueous secondary battery of the present invention includes a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a non-aqueous electrolyte, and a separator, the negative electrode contains a negative electrode active material containing a graphitic carbon material and a composite in which a carbon coating layer is formed on a surface of a core material containing Si and O as constituent elements, the composite has a carbon content of 10 to 30 mass %, the composite has an intensity ratio I510 / I1343 of a peak intensity I510 at 510 cm−1 derived from Si to a peak intensity I1343 at 1343 cm−1 derived from carbon of 0.25 or less when a Raman spectrum of the composite is measured at a laser wavelength of 532 nm, and the half-width of the (111) diffraction peak of Si is less than 3.0° when the crystallite size of an Si phase contained in the core material is measured by X-ray diffractometry using CuKα radiation.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
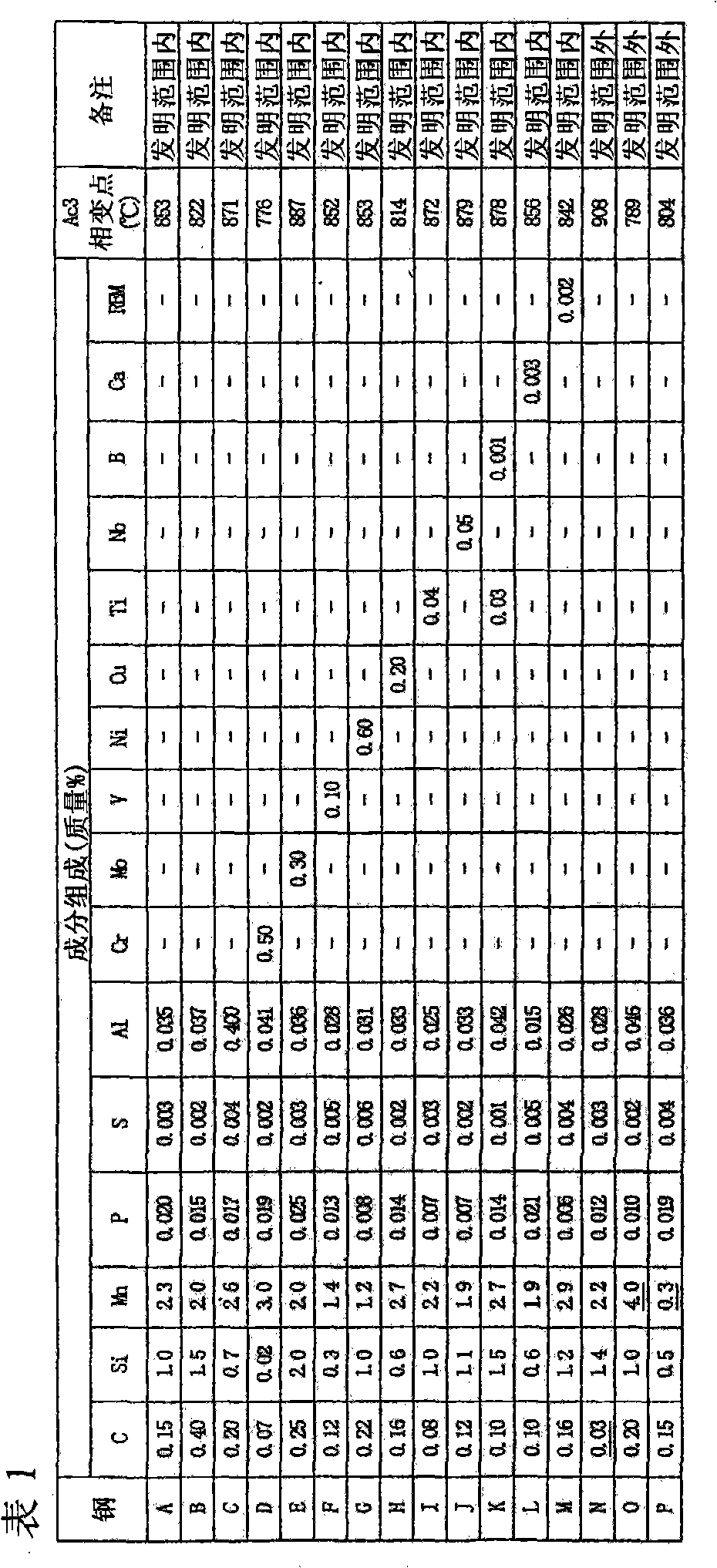
High strength galvanized steel sheet with excellent formability and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveCN101939456AEasy to processConducive to lightweightFurnace typesThin material handlingManganeseMartensite
A high-strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet with excellent processability is provided which has a TS of 1,200 MPa or higher, El of 13% or higher, and hole expansion ratio of 50% or higher. Also provided is a process for producing the steel sheet. The high-strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet with excellent processability has a composition comprising, in terms of mass%, 0.05-0.5% carbon, 0.01-2.5% silicon, 0.5-3.5% manganese, 0.003-0.100% phosphorus, up to 0.02% sulfur, and 0.010-0.5% aluminum, with the remainder being iron and incidental impurities, and has a microstructure comprising, in terms of areal proportion as determined through a structure examination, 0-10% ferrite, 0-10% martensite, and 60-95% tempered martensite and containing, in terms of proportion as determined by X-ray diffractometry, 5-20% retained austenite.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Raw material composite for carbon material used in electric double layer capacitor, manufacturing method of the same, electric double layer capacitor, and manufacturing method of the same
InactiveUS6882517B2Well formedIncrease capacitanceHybrid capacitor electrodesLiquid electrolytic capacitorsX-rayCrystal structure
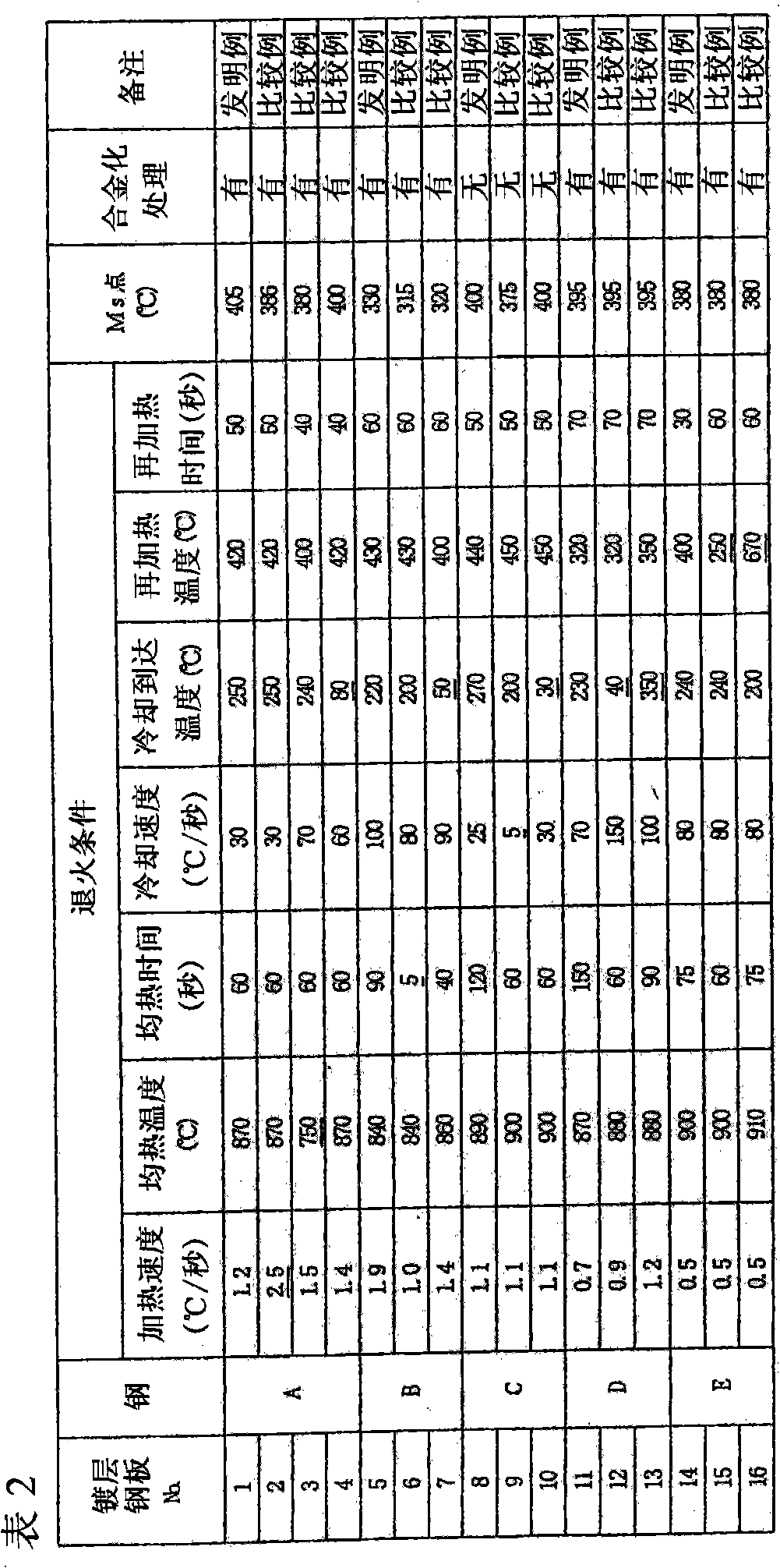
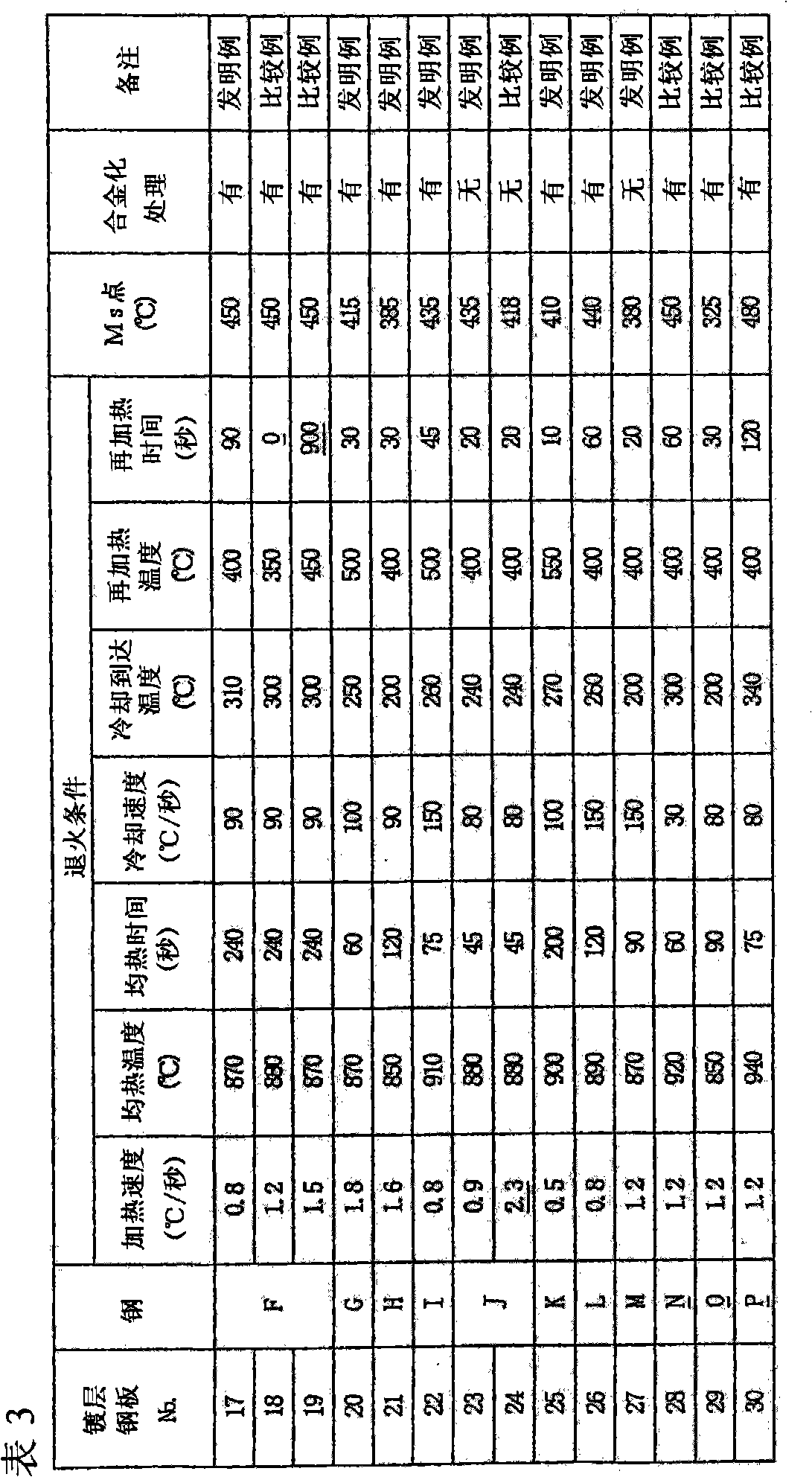
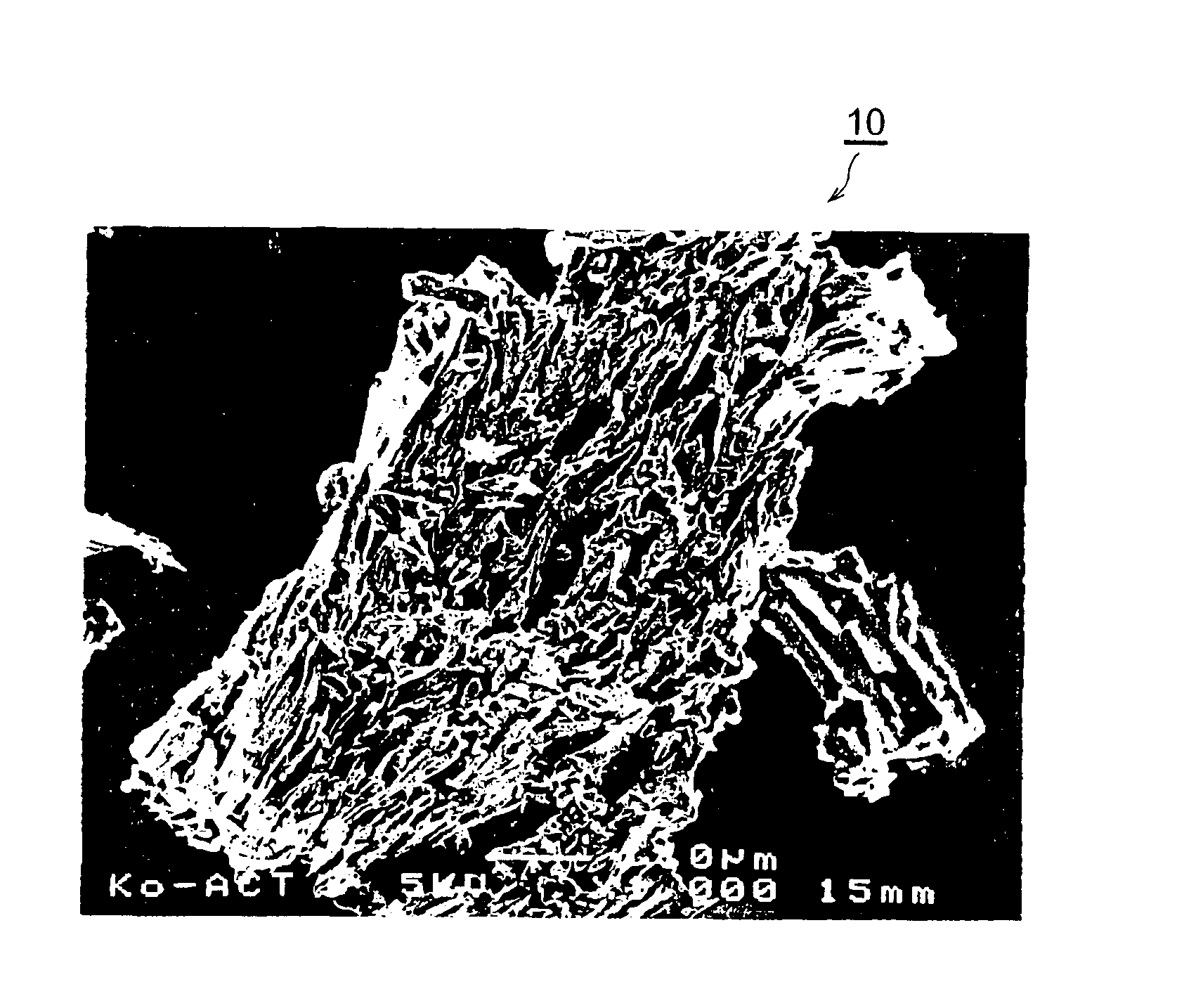
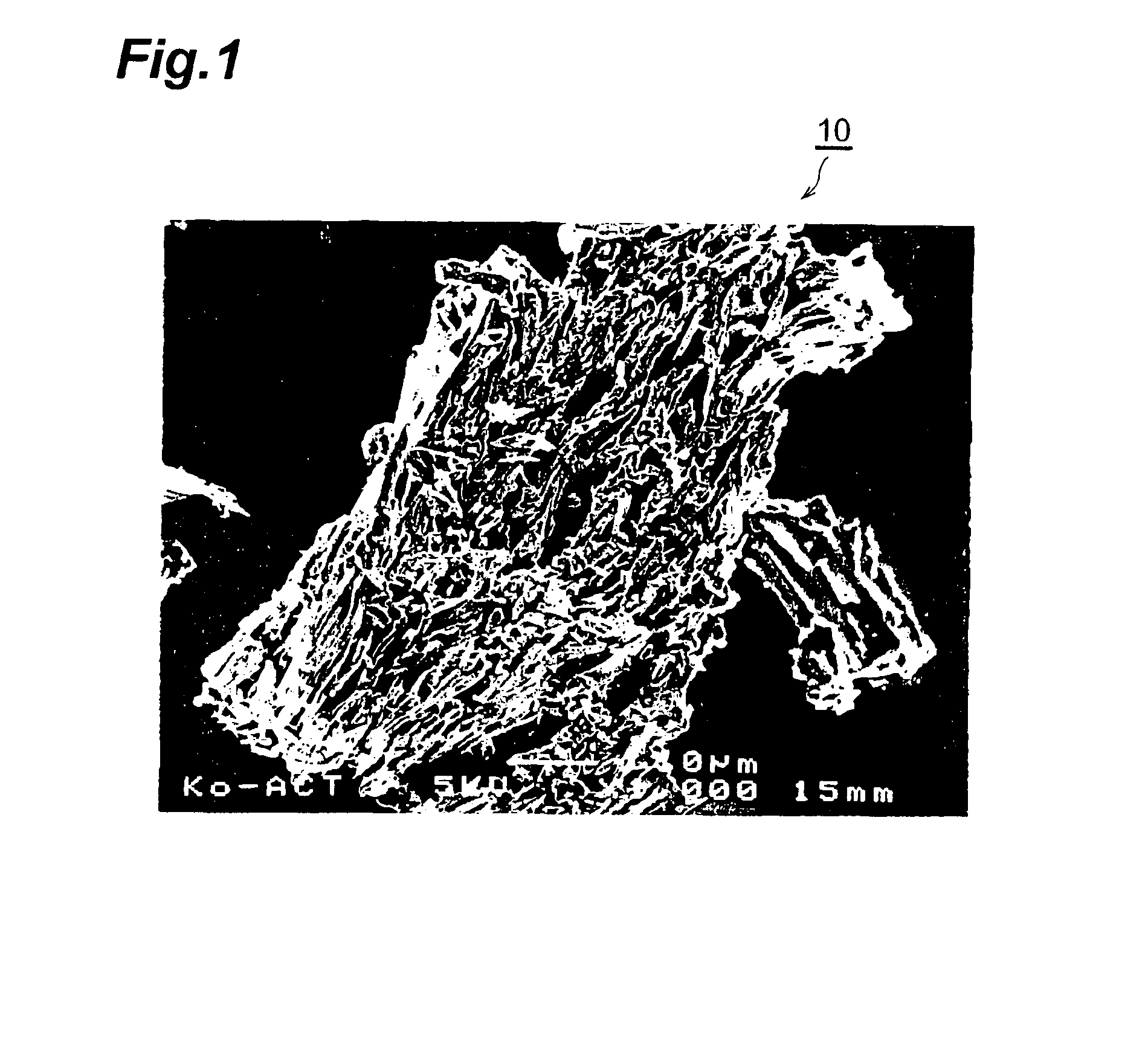
A raw material composite 10 for a carbon material used in an electric double layer capacitor contains microcrystalline carbon having a layered crystal structure similar to graphite, and is formed a carbon material for an electric double layer capacitor by undergoing an activation treatment. Here, the raw material composite is characterized in that a Hardgrove grindability index HGI defined by ASTMD-409-71 is 50 or above, an interlayer distance d002 of the microcrystalline carbon determined by an X-ray diffraction method is 0.343 NM or below, and a crystallite size Lc002 of the microcrystalline carbon determined by the X-ray diffraction method is 3.0 nm or below.
Owner:NIPPON OIL CORP +2
Polyimide film
This polyimide film is superior in heat resistance, rigidity and high frequency properties, is free of inconveniences due to curling even when various functional layers are laminated by heating, and is preferable as a substrate film superior in thermal degradation stability for electronic parts. This polyimide film has a planar orientation coefficient of 0.79-0.89 as measured by an X-ray diffraction method, a difference in the surface planar orientation degree between one surface thereof and the other surface thereof of not more than 2 and a curling degree of not more than 5%, which is obtained by imidation of a polyimide precursor film having a particular imidation rate.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Salts of cynnamide compound or solvates thereof
InactiveUS20090048448A1Avoid deformationMaintain good propertiesNervous disorderOrganic chemistryX-rayX-ray scattering techniques
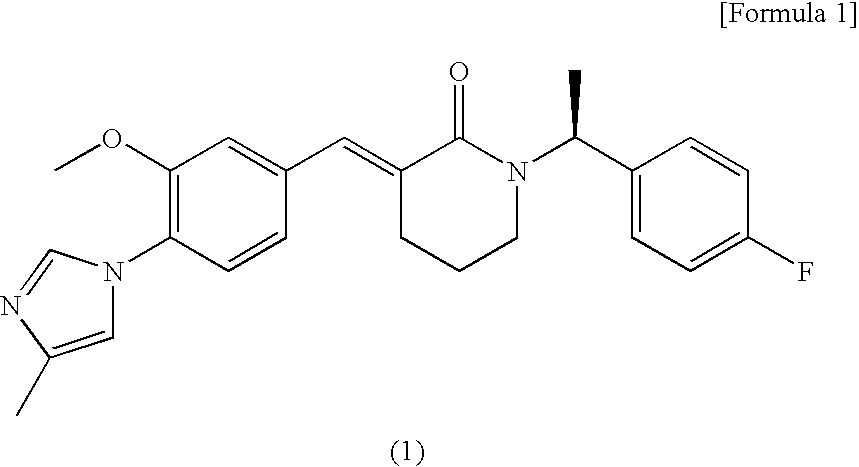
The invention provides crystals of dihydrochloride monohydrate of the compound of the following formula having an Aβ production inhibiting effect which crystals are characterized by exhibiting a diffraction peak at an angle of diffraction (2θ±0.2°) of 10.9° in powder X-ray diffractometry. Further, the invention also provides the compound in the form of various salts, crystal forms and amorphous forms which are suitable for the development of drugs.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
High-strength steel sheet excellent in workability and cold brittleness resistance, and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102828106AEasy to processImprove low temperature brittlenessFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesMartensiteAustenite
The invention relates to a steel sheet having a tensile strength of 1180 MPa or more, the steel sheet excels in workability and cold brittleness resistance. The high-strength steel sheet contains 0.10% to 0.30% of C, 1.40% to 3.0% of Si, 0.5% to 3.0% of Mn, 0.1% or less of P, 0.05% or less of S, 0.005% to 0.20% of Al, 0.01% or less of N, 0.01% or less of O, as well as Fe and inevitable impurities. The steel sheet has: (i) a ferrite volume fraction of 5% to 35% and a bainitic ferrite and / or tempered martensite volume fraction of 60% or more; (ii) a MA constituent volume fraction of 6% or less (excluding 0%); and (iii) a retained austenite volume fraction of 5% or more.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Electroacoustic transduction film and manufacturing method thereof, electroacoustic transducer, flexible display, vocal cord microphone, sensor for musical instrument
ActiveUS20180160248A1Sufficient volumeImprove conversion efficiencyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesElectrophonic musical instrumentsX-rayEngineering
Provided are an electroacoustic transduction film capable of reproducing a sound with a sufficient sound volume at a high conversion efficiency, a manufacturing method thereof, an electroacoustic transducer, a flexible display, a vocal cord microphone, and a sensor for a musical instrument. The electroacoustic transduction film includes: a polymer composite piezoelectric body in which piezoelectric body particles are dispersed in a viscoelastic matrix formed of a polymer material having viscoelasticity at a normal temperature; two thin film electrodes laminated on both surfaces of the polymer composite piezoelectric body; and two protective layers respectively laminated on the two thin film electrodes, in which an intensity ratio α1=(002) plane peak intensity / ((002) plane peak intensity+(200) plane peak intensity) between a (002) plane peak intensity and a (200) plane peak intensity derived from the piezoelectric body particles in a case where the polymer composite piezoelectric body is evaluated by an X-ray diffraction method is more than or equal to 0.6 and less than 1.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Ruthenium oxide powder, composition for thick film resistor elements using same, and thick film resistor element
ActiveCN103429537AInhibit growthHigh crystallinityRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum oxides/hydroxidesThick film resistorsX-rayEngineering
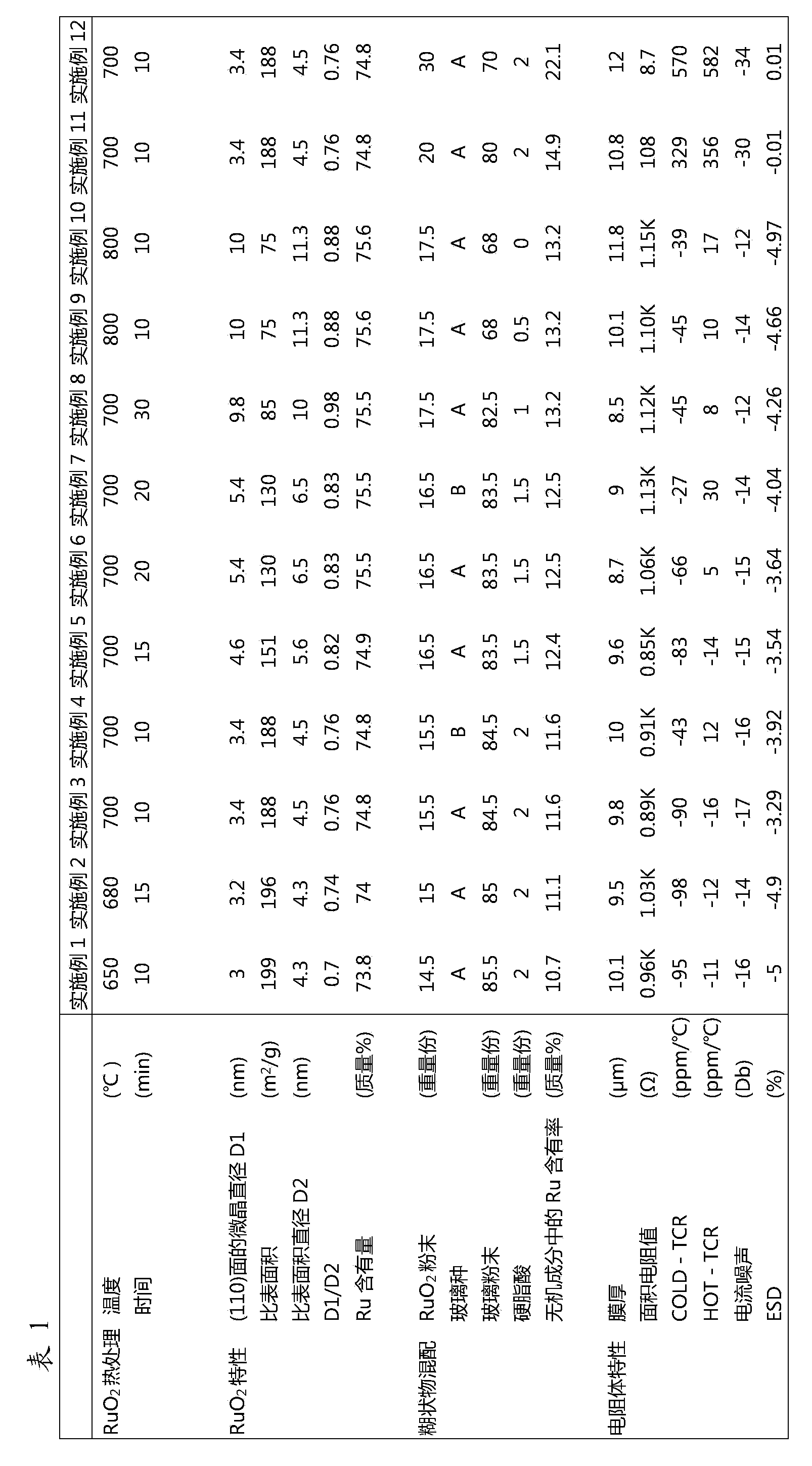
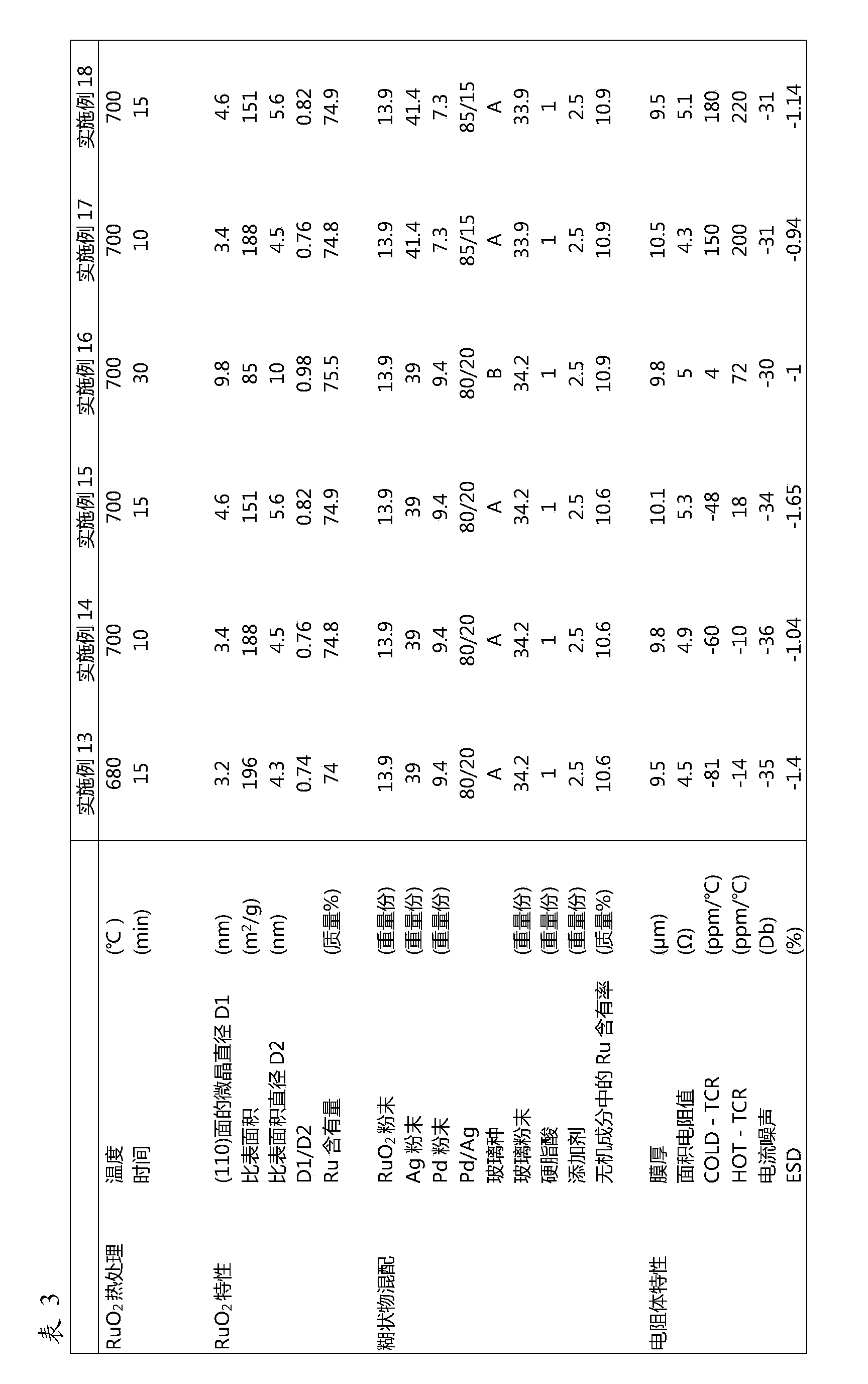
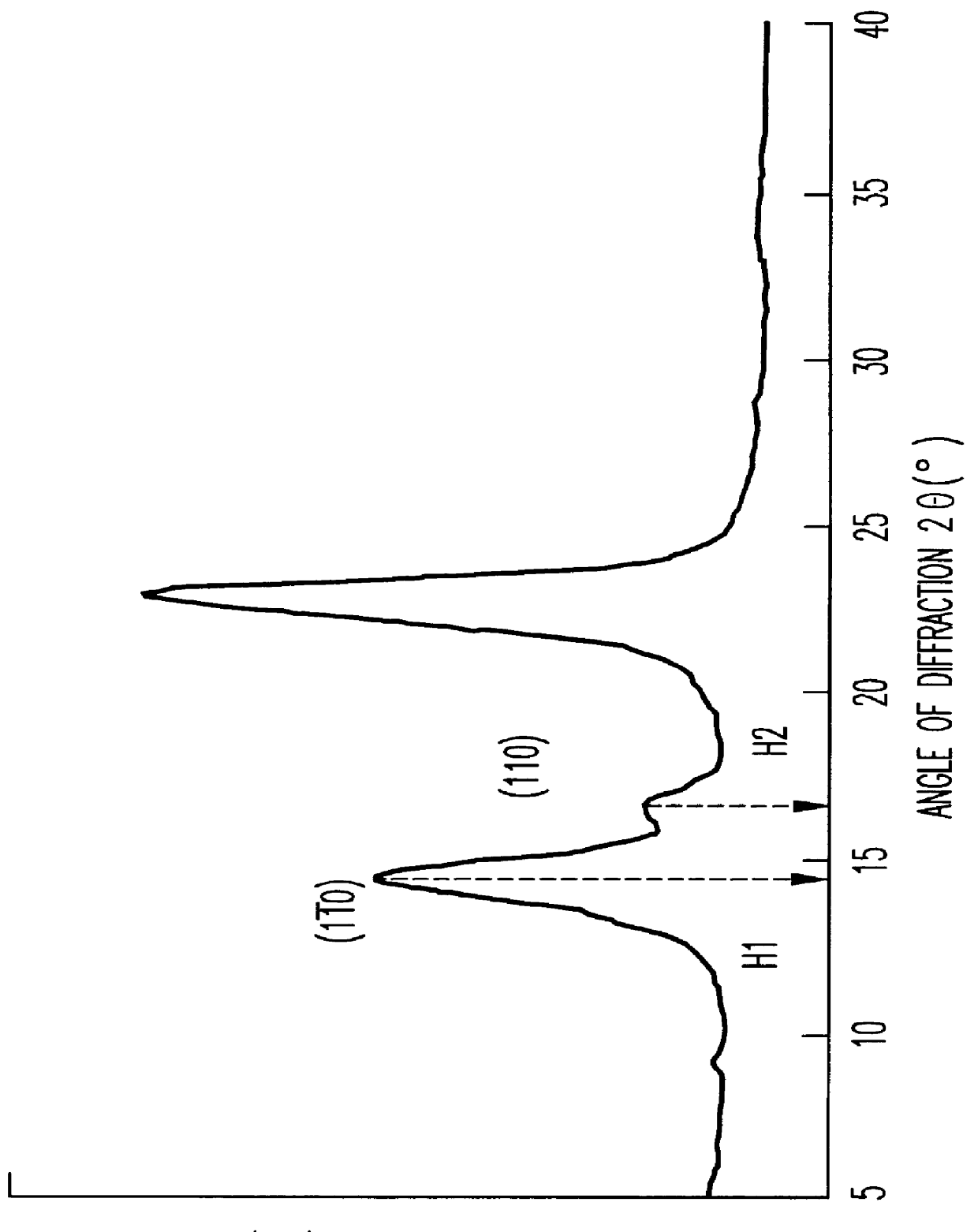
Provided are: a ruthenium oxide powder which is produced, at low cost, as a material for electronic components such as a chip resistor, a hybrid IC and a resistive network each having a sufficient performance, even if the ruthenium content thereof is low; a composition for thick film resistor elements, which uses the ruthenium oxide powder; and a thick film resistor element. Specifically provided are: a ruthenium oxide (RuO2) powder having a rutile crystal structure, which is characterized in that the crystallite diameter of the (110) plane as determined by an X-ray diffraction method is 3-10 nm and the Ru content is 73% by mass or more; a composition for thick film resistor elements, which is obtained by blending a glass powder and conductive particles that are formed of the ruthenium oxide powder as main constituent elements; and a thick resistor element paste, which is obtained by dispersing the composition for thick film resistor elements in an organic vehicle that contains a fatty acid, and which is characterized in that the content of the fatty acid is 0.1-10 parts by weight per 100 parts by weight of the ruthenium oxide.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Method for processing bacterial cellulose
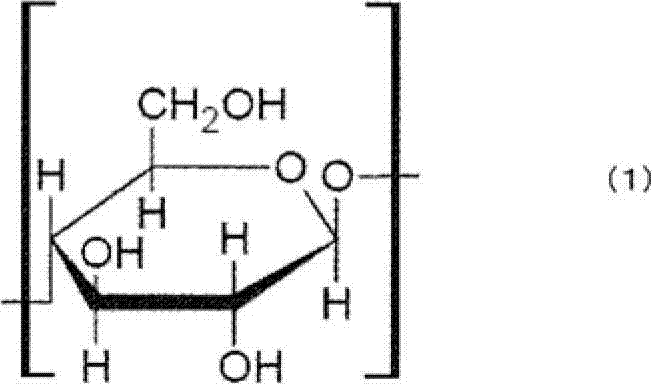
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 01949 Sec. 371 Date May 27, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date May 27, 1998 PCT Filed Jun. 9, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 48730 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 24, 1997The purpose of the present invention is to provide a convenient method for restoring the various properties of BC even after it is once dried. The present invention relates to a method for processing a bacterial cellulose comprising dehydrating and drying under tension the bacterial cellulose produced in an agitated culture followed by homogenization, and to a method for processing a bacterial cellulose comprising dehydrating and drying the bacterial cellulose produced in an agitated culture under such conditions that a degree of planar orientation (h1 / h2) (wherein h1 and h2 mean the height of a peak originating in the crystallographic plane (1+E,ovs 1+EE 0) and the crystallographic plane (110), respectively, in a diffraction curve obtained with X-ray diffractometry by a reflection method) will be 2 or more, followed by homogenization. An excellent retention aid for fillers and sheet with a high strength may be prepared by using the bacterial cellulose obtained by the above methods.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Target for cathode discharging arc ion plating and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7144547B2Prevent not uniform movementInhibition formationCellsVacuum evaporation coatingX-rayPeak intensity
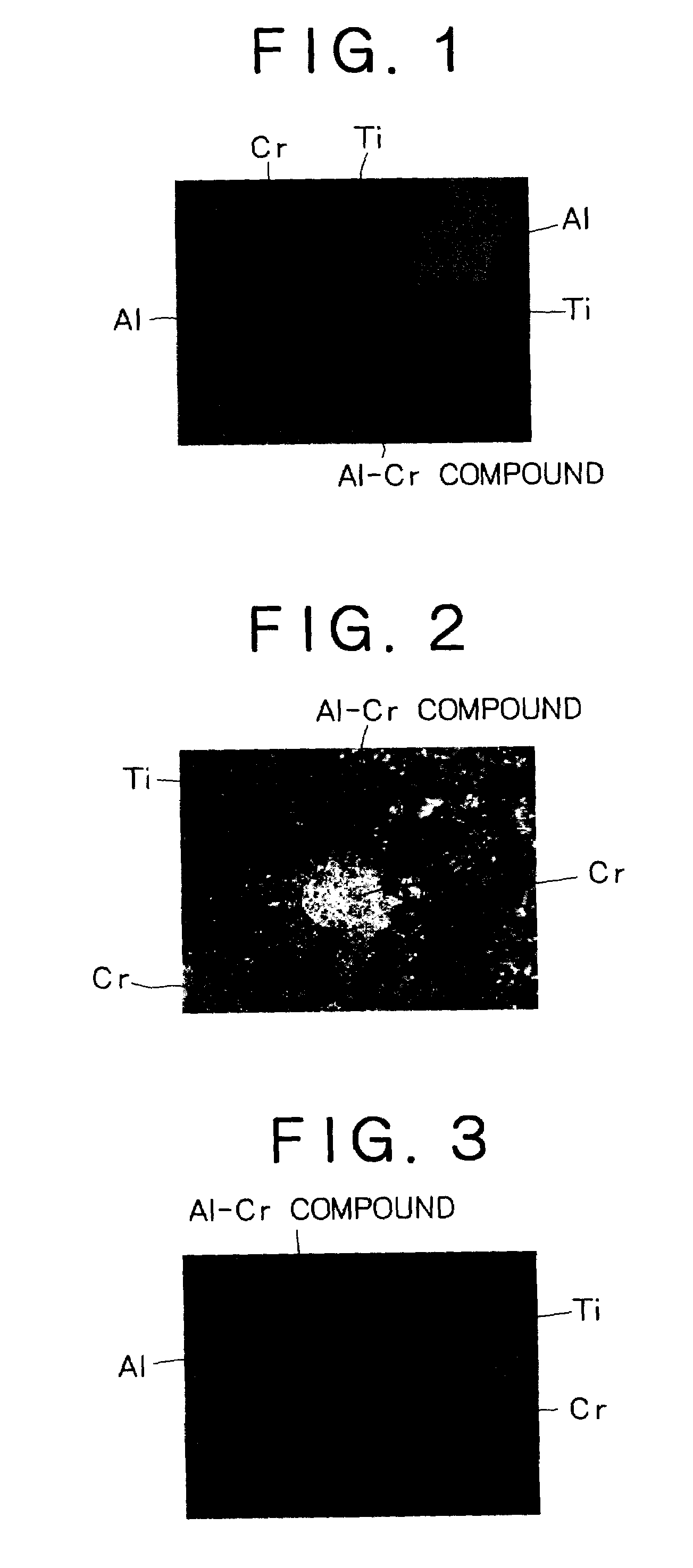
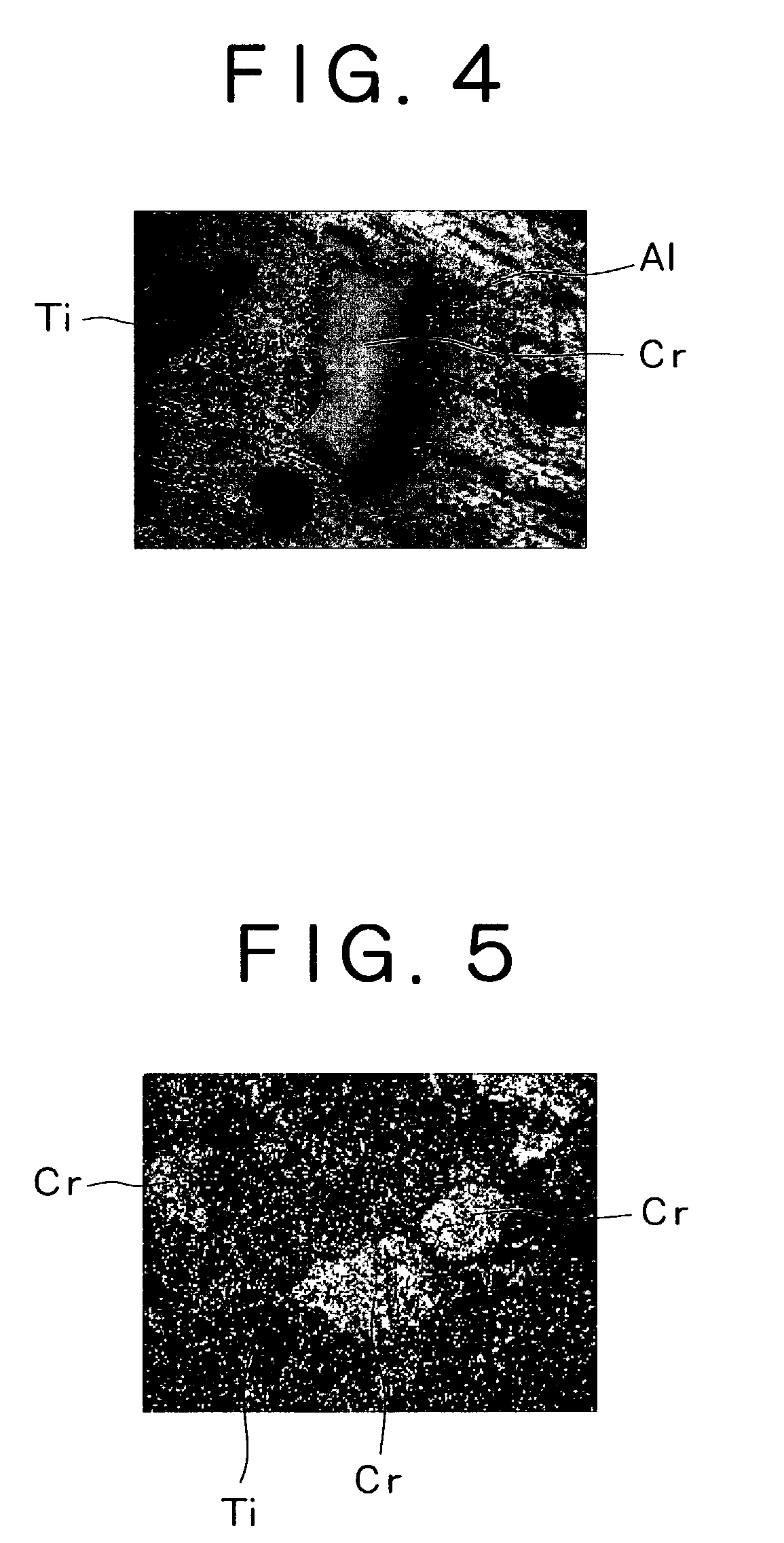
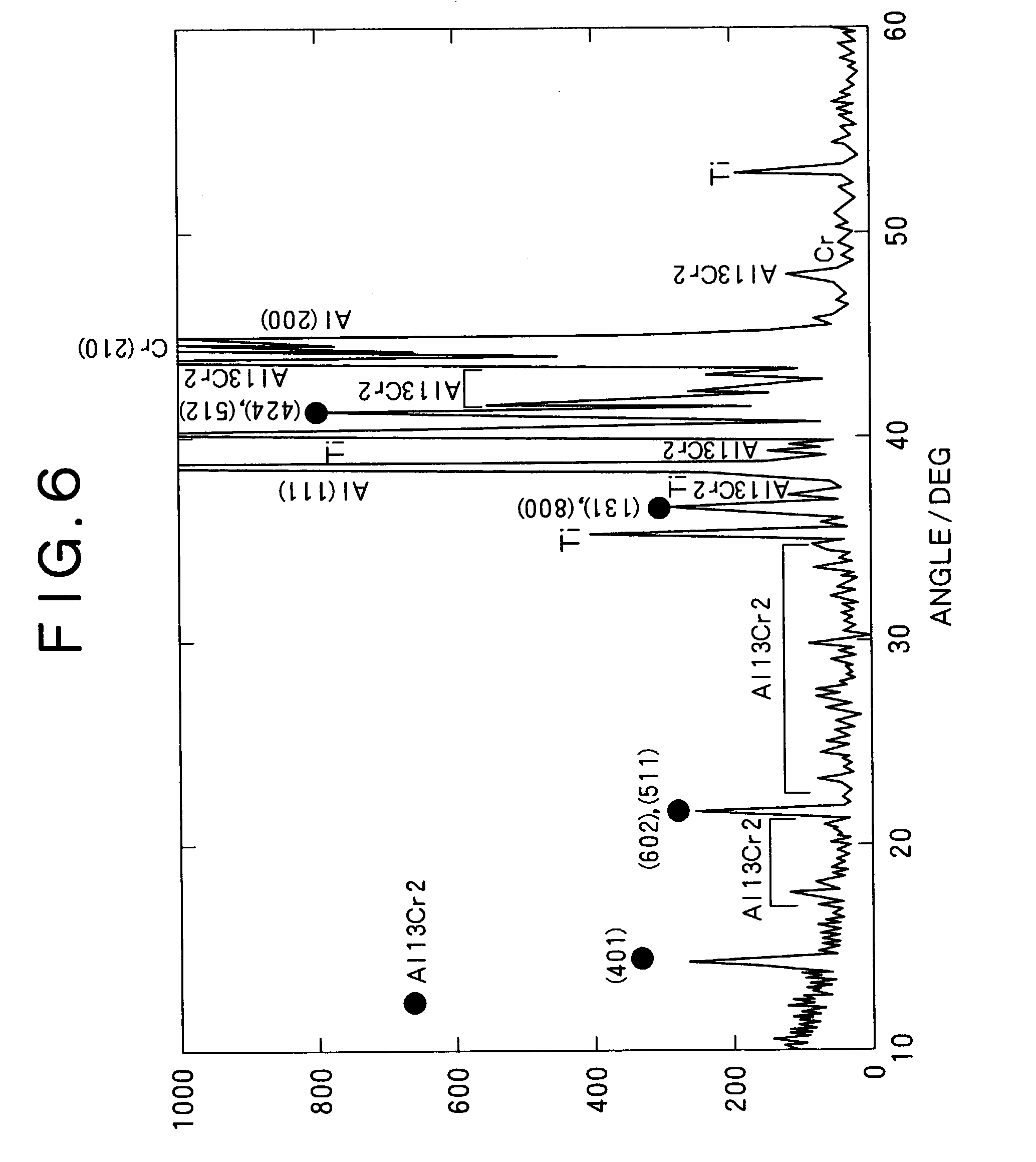
In a target for cathode discharging arc ion plating containing Al and Cr as an essential ingredient according to the invention, the thickness of the Al and Cr compound layer formed between Cr particles and Al contained in a target is 30 μm or less. Alternatively, the total for the peak intensities of Al—Cr compound observed between diffraction angles between 10 to 80° by X-ray diffractiometry according to θ=2θ method is 10% or less relative to the total for the peak intensities of Al, Cr and the Al—Cr compound. Further, the relative density of the target is 92% or more. The target is capable of forming hard films of high quality while preventing not uniform movement of arc spots and suppressing formation of macro particles.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
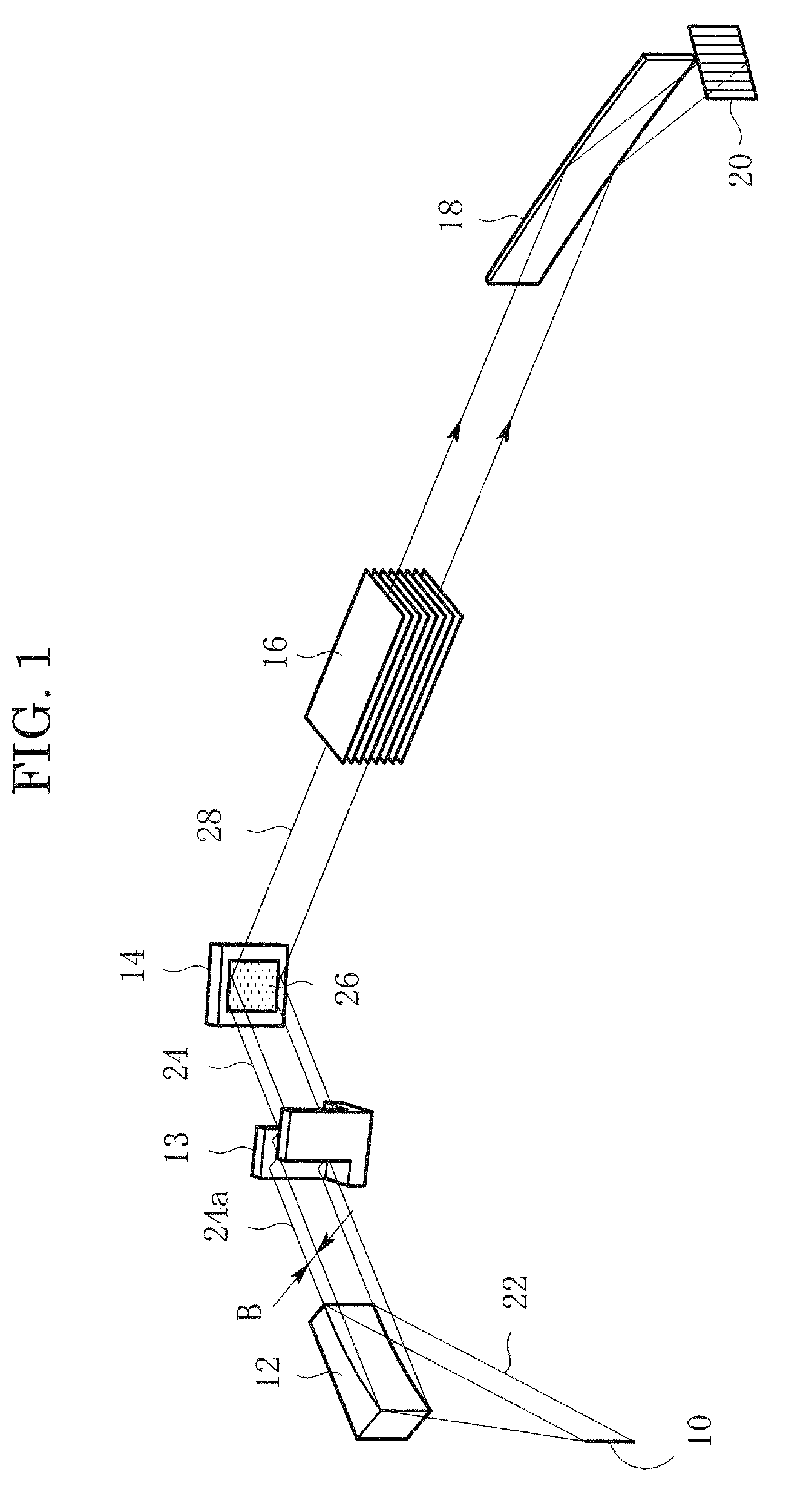
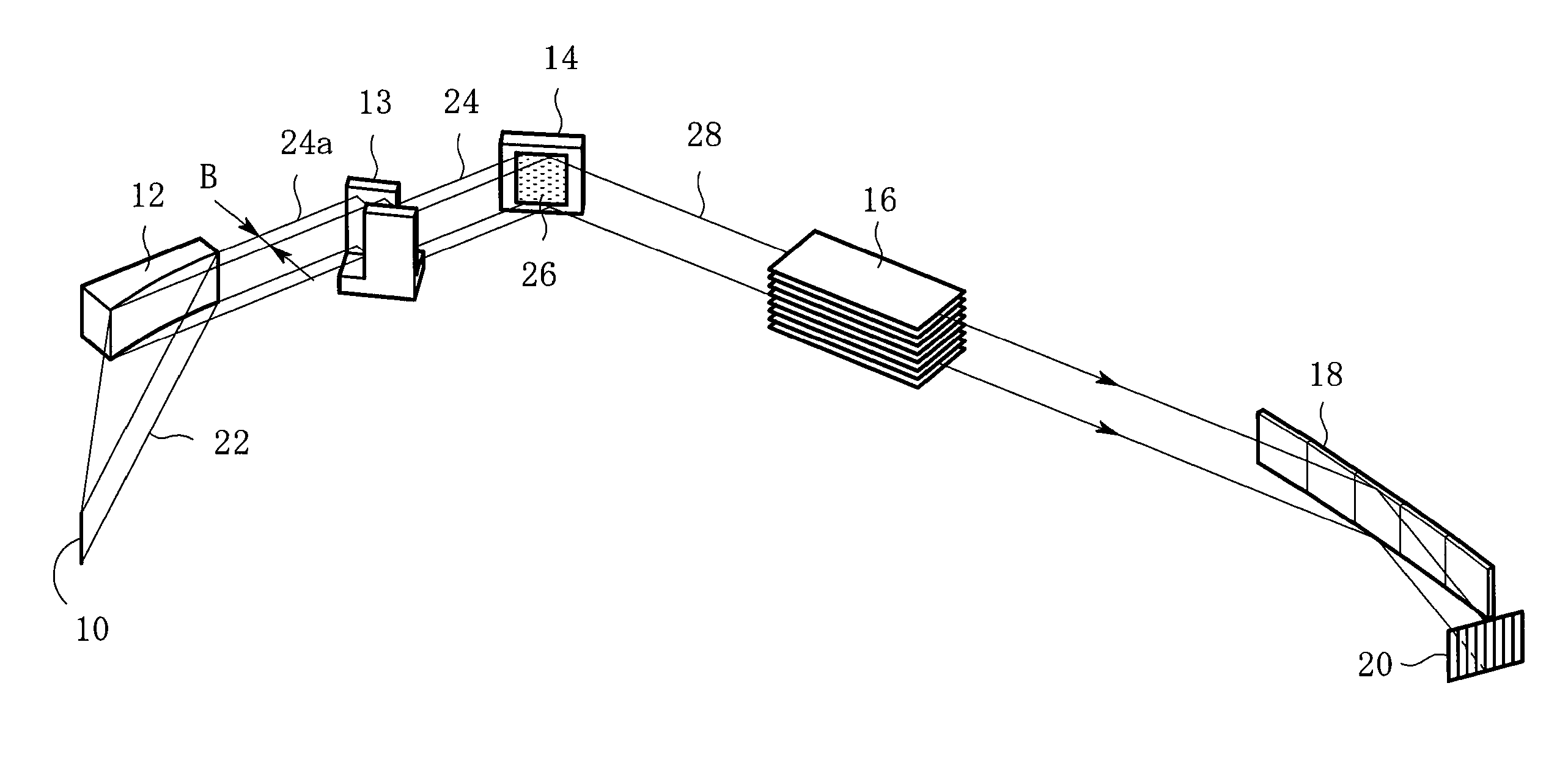
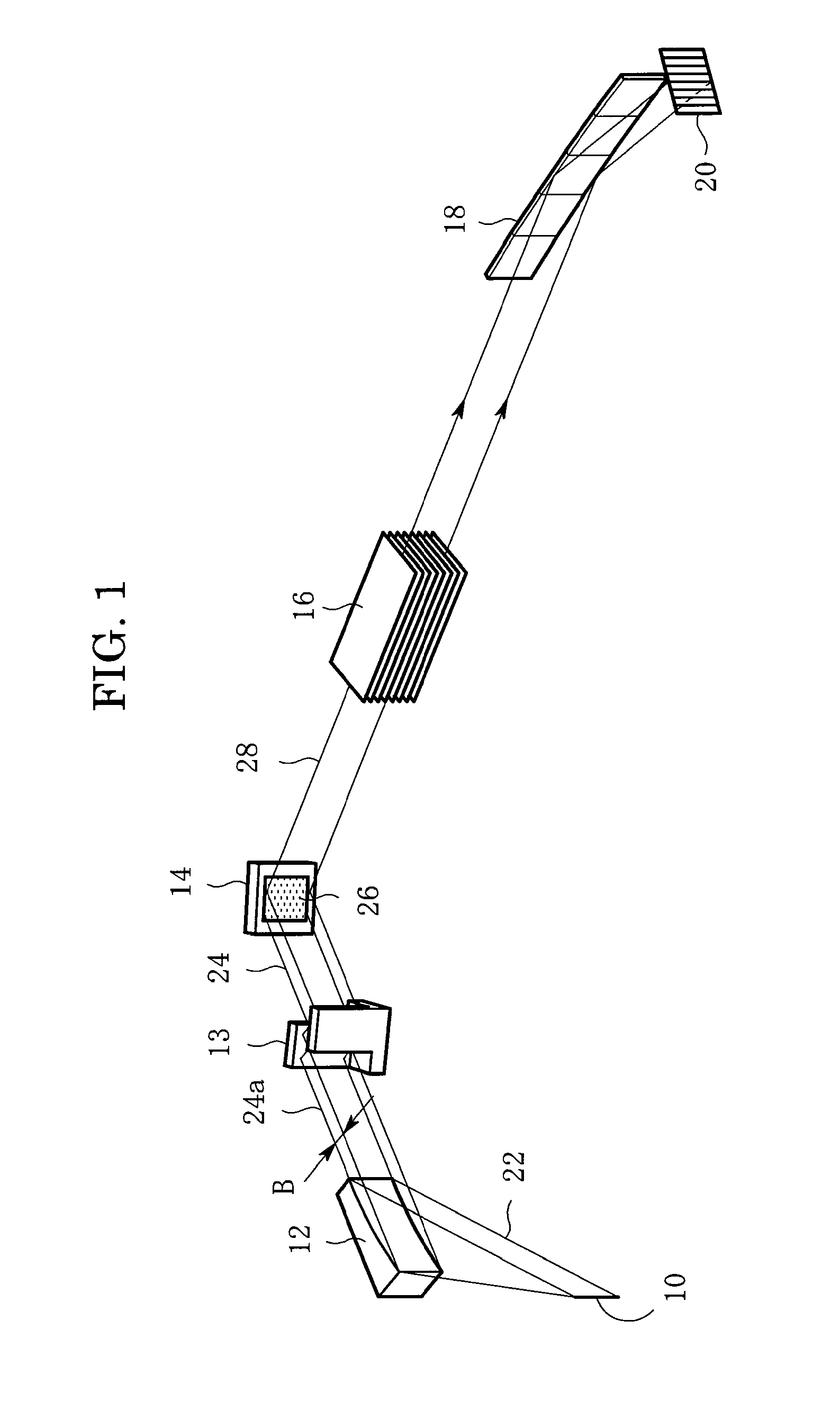
X-ray diffraction apparatus and X-ray diffraction method
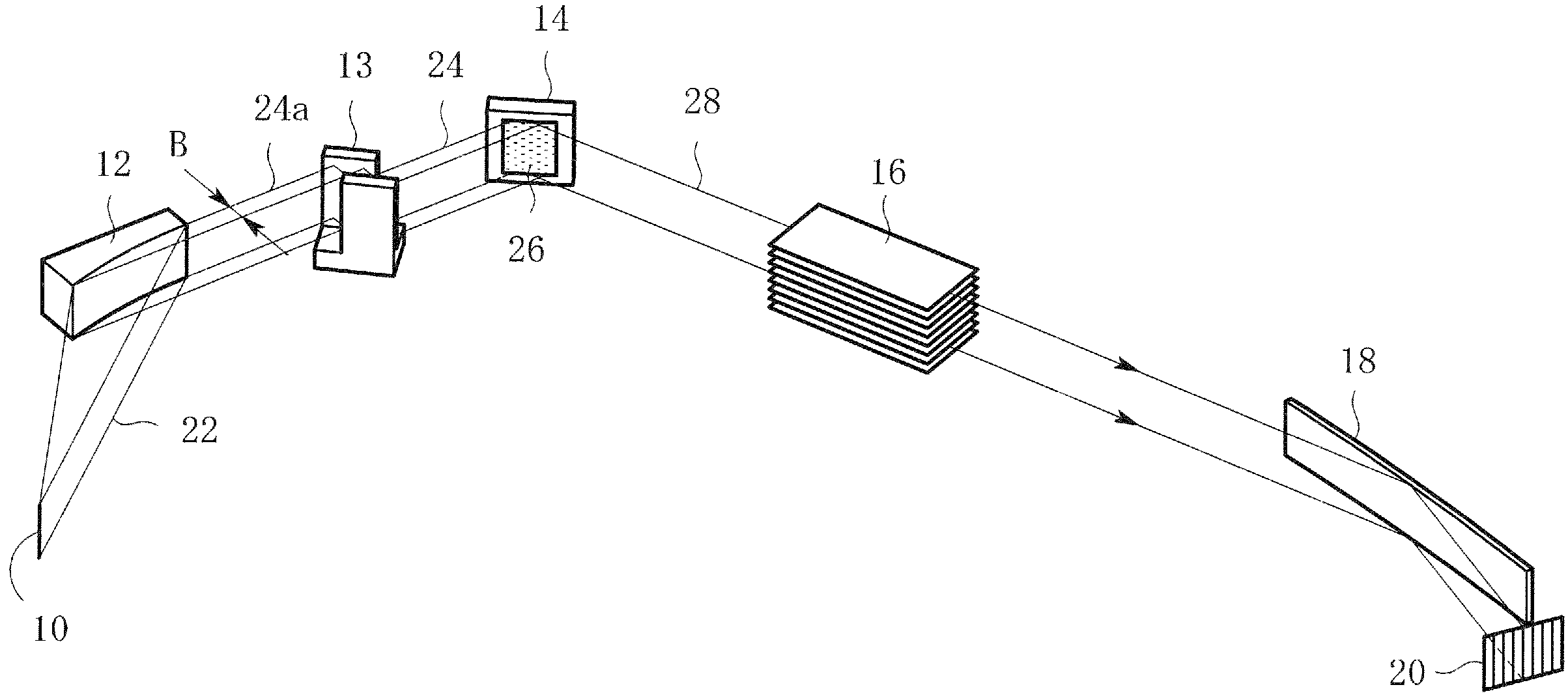
InactiveUS7801272B2Convenient angleSmall intensityHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionLattice planeX-ray
In an X-ray diffraction method using the parallel beam method, an X-ray parallel beam is incident on a sample, and diffracted X-rays from the sample are reflected at a mirror and thereafter detected by an X-ray detector. The reflective surface of the mirror has a shape of an equiangular spiral that has a center located on the surface of the sample. A crystal lattice plane that causes reflection is parallel to the reflective surface at any point on the reflective surface. The X-ray detector is one-dimensional position sensitive in a plane parallel to the diffraction plane. A relative positional relationship between the mirror and the X-ray detector is determined so that reflected X-rays from different points on the reflective surface of the mirror reach different points on the X-ray detector respectively. This X-ray diffraction method is superior in angular resolution, and is small in X-ray intensity reduction, and is simple in structure.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Carbonaceous material for electric double layer capacitor and process for production thereof
A carbonaceous electrode material for electric double layer capacitors having a large capacitor per volume, a low resistivity and a large bulk density, is provided as a carbonaceous material having a specific surface area of 800-2000 m2 / g as measured by the nitrogen adsorption BET method, and an average layer-plane spacing of at most 0.36 nm as measured by the X-ray diffraction method. The carbonaceous material is preferably produced by carbonizing and activating a carbon precursor of pitch origin in an oxidizing atmosphere.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Electrode active material having high capacitance, method for producing the same, and electrode and energy storage device comprising the same
ActiveUS20070195488A1Simple processIncrease the distance between layersHybrid capacitor electrolytesElectrode manufacturing processesCapacitanceX-ray
An active material of the present invention has fine pores formed in the interlayer of a carbon material capable of exhibiting electrochemical double layer capacitance. The fine pores are formed by forming an oxidized graphite structure combined with oxygen in the interlayer of a part or whole of the carbon material containing soft carbon and then removing a part or whole of oxygen in the interlayer. A method for producing an energy storage active material for use in an electrochemical double layer capacitor comprises pre-treating a carbon material through heat treatment and oxidizing the pre-treated carbon material using an oxidant. The method further comprises reducing the oxidized carbon material through heat treatment. The interlayer distances of an active material for respective steps, measured by a powder X-ray diffraction method, are 0.33˜0.36 nm in the pre-treatment step, 0.5˜2.1 nm in the oxidation step, and 0.34˜0.5 nm in the reduction step.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Seal ring
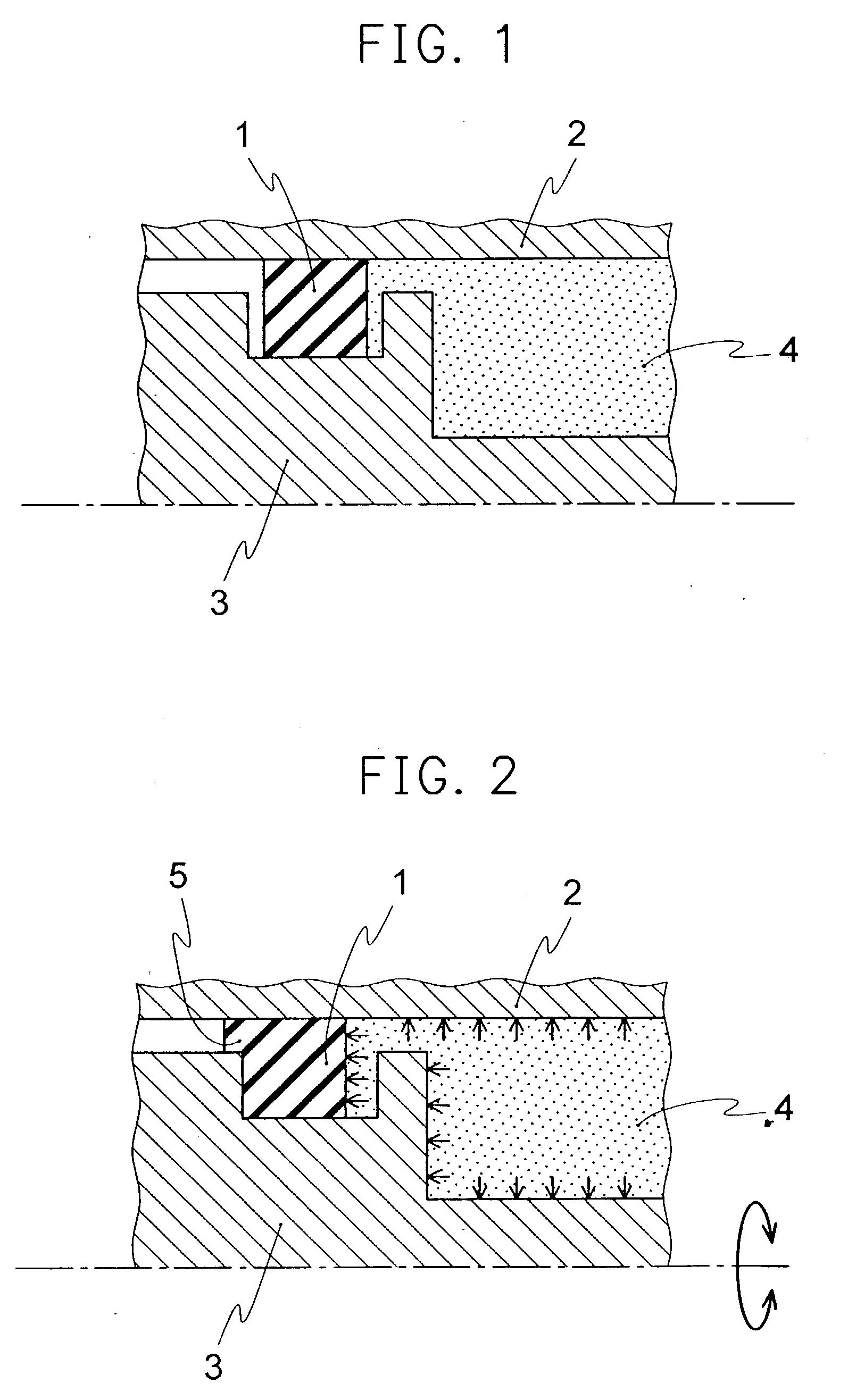
InactiveUS20030122318A1Improve adaptabilityEngine sealsOther chemical processesAutomatic transmissionX-ray
A seal ring which contains a scaly graphite powder essentially alone as a filler, and comprises 2 to 35% by weight of the graphite powder and 65 to 98% by weight of a polytetrafluoroethylene powder, wherein the graphite powder has an interplanar spacing of 0.335 to 0.340 nm, as measured by the powder X-ray diffraction method, and a size of a crystallite of (004) face of at least 70 nm is provided. Since deformation and extrusion of the seal ring are kept small even under a high pressure, and the abrasion of the opposite material can be prevented even if it is made of a soft metal, it is possible to maintain a stable sealing effect for a longer period of time. In addition, since the seal ring has small sliding resistance, handling property, response of the sealing device and suitability for fitting to the device can be largely improved. Thus, the seal ring is suitable for the valve device of power steering of automobiles, automatic transmission or shock absorber.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
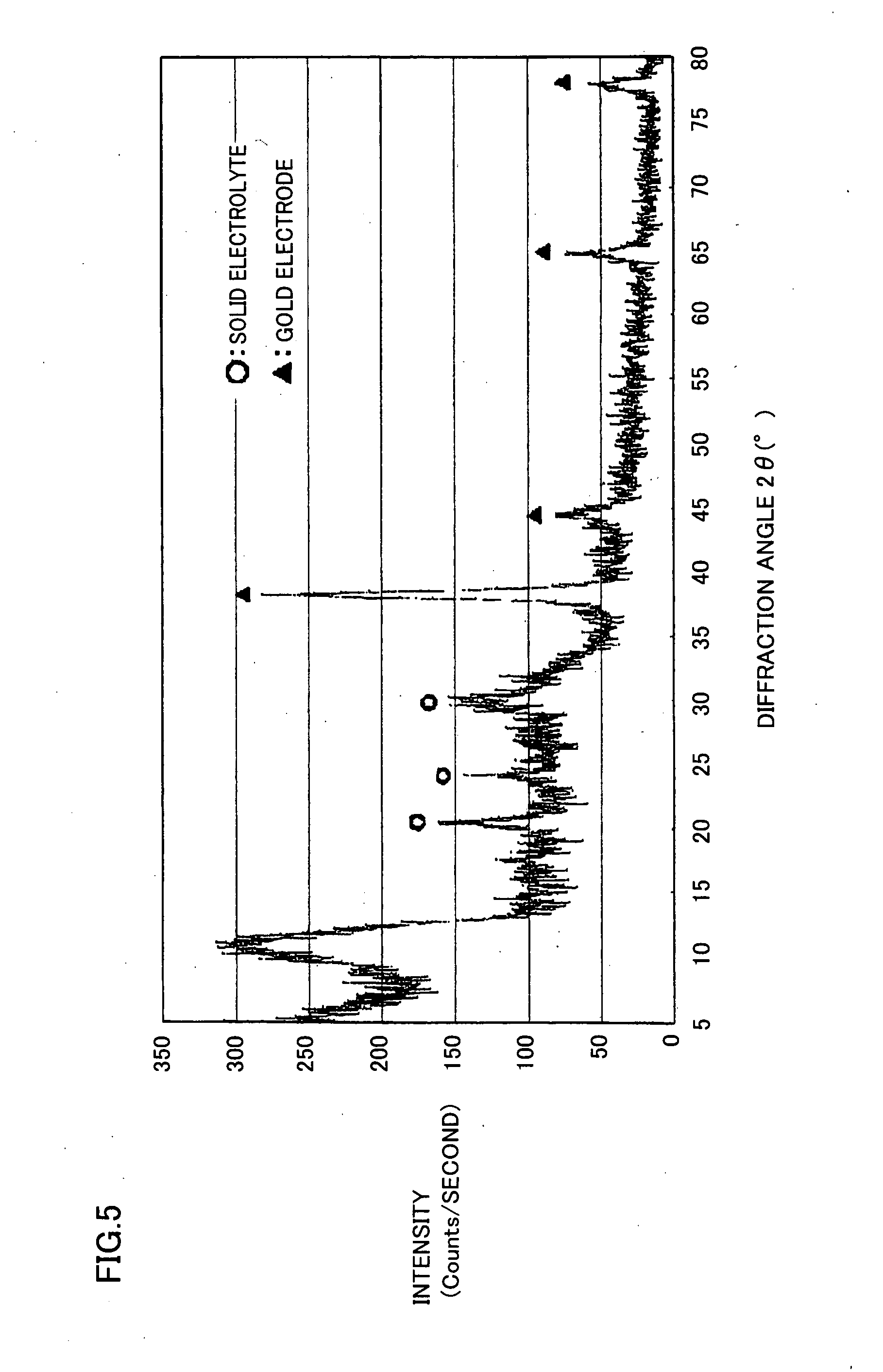
Solid electrolyte and method of producing the same
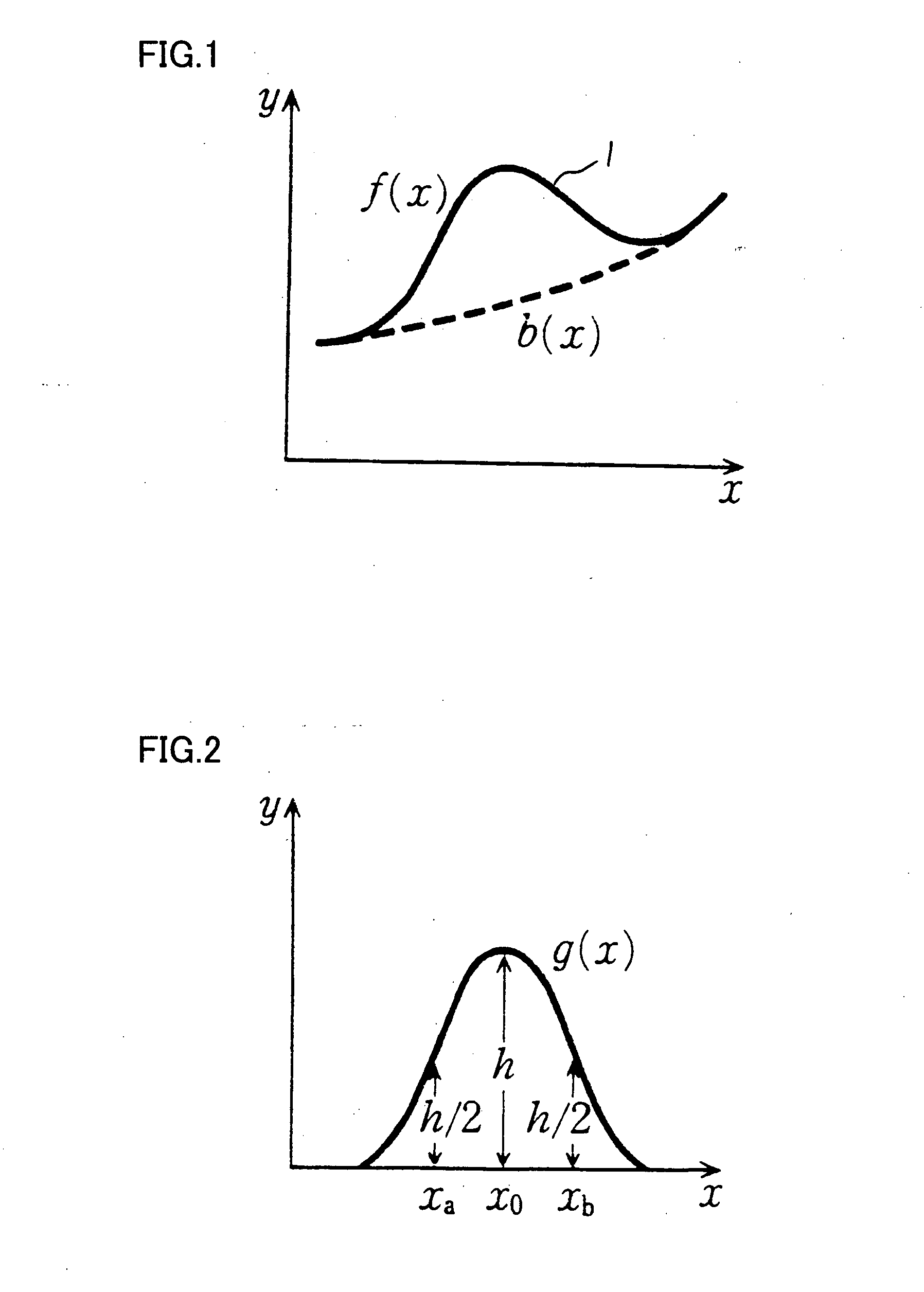
InactiveUS20070264579A1Improve pressure resistanceImprove ionic conductivityNon-metal conductorsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsLithiumCrystallography
A solid electrolyte and a method of manufacturing the same are provided. The solid electrolyte contains x atomic % of lithium, y atomic % of phosphorus, z atomic % of sulfur, and w atomic % of oxygen, in whichthe x, the y, the z, and the w satisfy the following expressions (1)-(5):20≦x≦45 (1)10≦y≦20 (2)35≦z≦60 (3)1≦w≦10 (4)x+y+z+w=100 , and (5)apexes of X-ray diffraction peaks in an X-ray diffraction pattern obtained by an X-ray diffraction method using a Kα-ray of Cu exist at diffraction angles 2θ of 16.7°±0.25°, 20.4°±0.25°, 23.8°±0.25°, 25.9°, 0.25°, 29.4°±0.25°, 30.4°±0.25°, 31.7°±0.25°, 33.5°±0.25°, 41.5°±0.25°, 43.7°±0.25°, and 51.2°±0.25°, respectively, in the X-ray diffraction pattern, and a half-width of each of the X-ray diffraction peaks is not larger than 0.5°.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
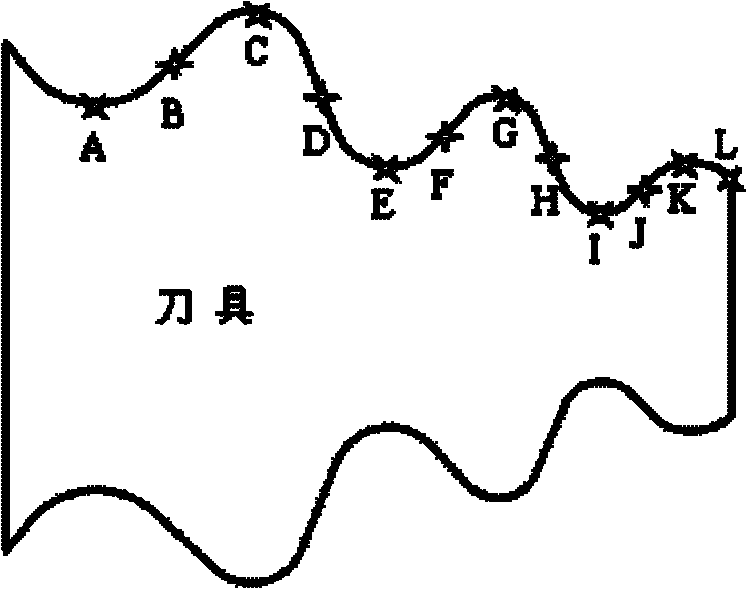
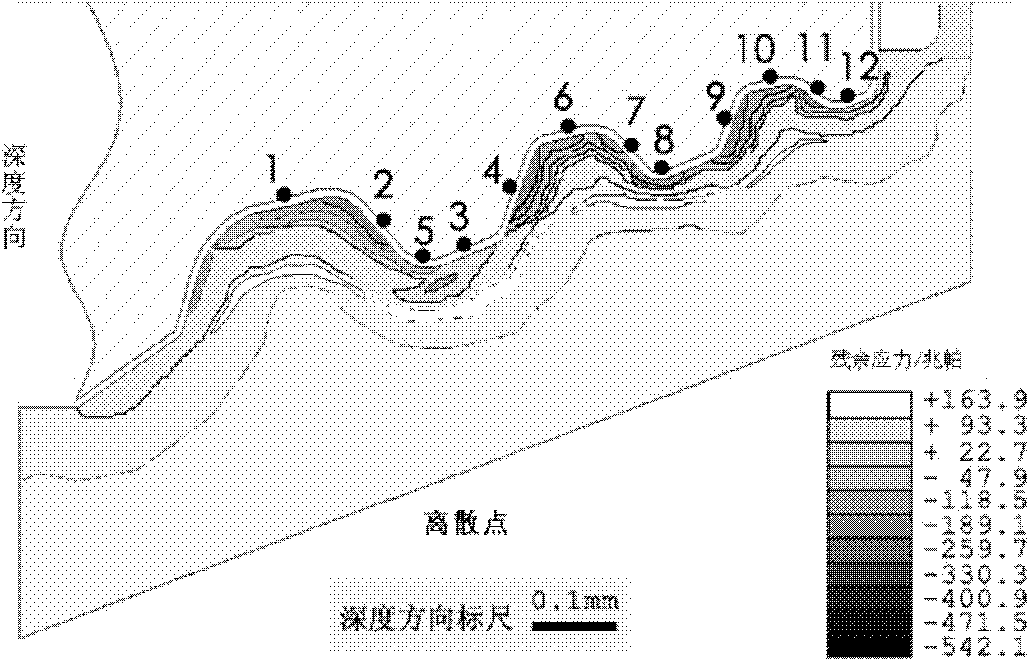
Method for reconstructing residual stress field of profile of large-dimension fir-type blade wheel groove
ActiveCN101840457AReduce consumption costReduce processingSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelMilling cutter
The invention relates to a method for reconstructing a residual stress field of a profile of a large-dimension fir-type blade wheel groove, comprising the following steps of: selecting a plurality of discrete points on the outline profile of a fir-type milling cutter as detection points to obtain the equivalent cutting speed, the equivalent cutting thickness and the equivalent feed speed of a standard cutting experiment carried out by using a standard integral cylindrical end milling cutter; obtaining the residual stress simulated by a finite element of each detection point by adopting an infinitesimal modeling method; carrying out the standard cutting experiment, measuring the residual stress by adopting an X-ray diffraction method and a corrosion method, and correcting an equivalent two-dimensional orthogonal cutting finite element model; simulating other discrete points by utilizing the corrected simulation model to obtain the residual stress of each discrete point, and thereby fitting to obtain the residual stress field distribution of the integral blade wheel groove profile. The method reduces subsequent rolling treatment times by aiming at the complex profile processing of the wheel groove, and thereby, the production efficiency is greatly improved, and the consumption cost of a rolling tool is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery
To improve battery characteristics by an optimum combination of an electrolytic solution and a negative electrode active material. An electrolytic solution of a nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery contains a metal salt, and an organic solvent having a heteroatom and satisfying, regarding an intensity of a peak derived from the organic solvent in a vibrational spectroscopy spectrum, Is>Io, when an intensity of an original peak of the organic solvent is represented as Io and an intensity of a peak resulting from shifting of the original peak is represented as Is. As a negative electrode, any of the following (1) to (5) is used: (1) a graphite whose G / D ratio, which is a ratio of G-band and D-band peaks in a Raman spectrum, is not lower than 3.5; (2) a carbon material whose crystallite size, calculated from a half width of a peak appearing at 2θ=20 degrees to 30 degrees in a X-ray diffraction profile measured by X-ray diffraction method, is not larger than 20 nm; (3) silicon element and / or tin element; (4) a metal oxide configured to occlude and release lithium ions; or (5) a graphite whose ratio (long axis / short axis) of long axis to short axis is 1 to 5.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
Carbide derived carbon, emitter for cold cathode including the same and electron emission device including the emitter
InactiveUS20080169749A1Improve uniformityLong life-timeDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectric discharge tubesChemical reactionX-ray
Provided are carbide derived carbon prepared by thermochemically reacting carbide compounds and a halogen element containing gas and extracting all atoms of the carbide compounds except carbon atoms, wherein the intensity ratios of the graphite G band at 1590 cm−1 to the disordered-induced D band at 1350 cm−1 are in the range of 0.3 through 5 when the carbide derived carbon is analyzed using Raman peak analysis, wherein the BET surface area of the carbide derived carbon is 1000 m2 / g or more, wherein a weak peak or wide single peak of the graphite (002) surface is seen at 2θ=25° when the carbide derived carbon is analyzed using X-ray diffractometry, and wherein the electron diffraction pattern of the carbide derived carbon is the halo pattern typical of amorphous carbon when the carbide derived carbon is analyzed using electron microscopy. The emitter has good uniformity and a long lifetime. An emitter can be prepared using a more inexpensive method than that used to manufacture conventional carbon nanotubes.
Owner:LOFFE PHYSICO TECHN INST OF RUSSIAN ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Lithium ion secondary battery negative electrode slurry composition, a lithium ion secondary battery negative electrode, and lithium ion secondary battery
InactiveCN102823029AImprove life characteristicsImprove life characteristics (charge-discharge cycle characteristicsCell electrodesSecondary cellsMonomer compositionPolymer science
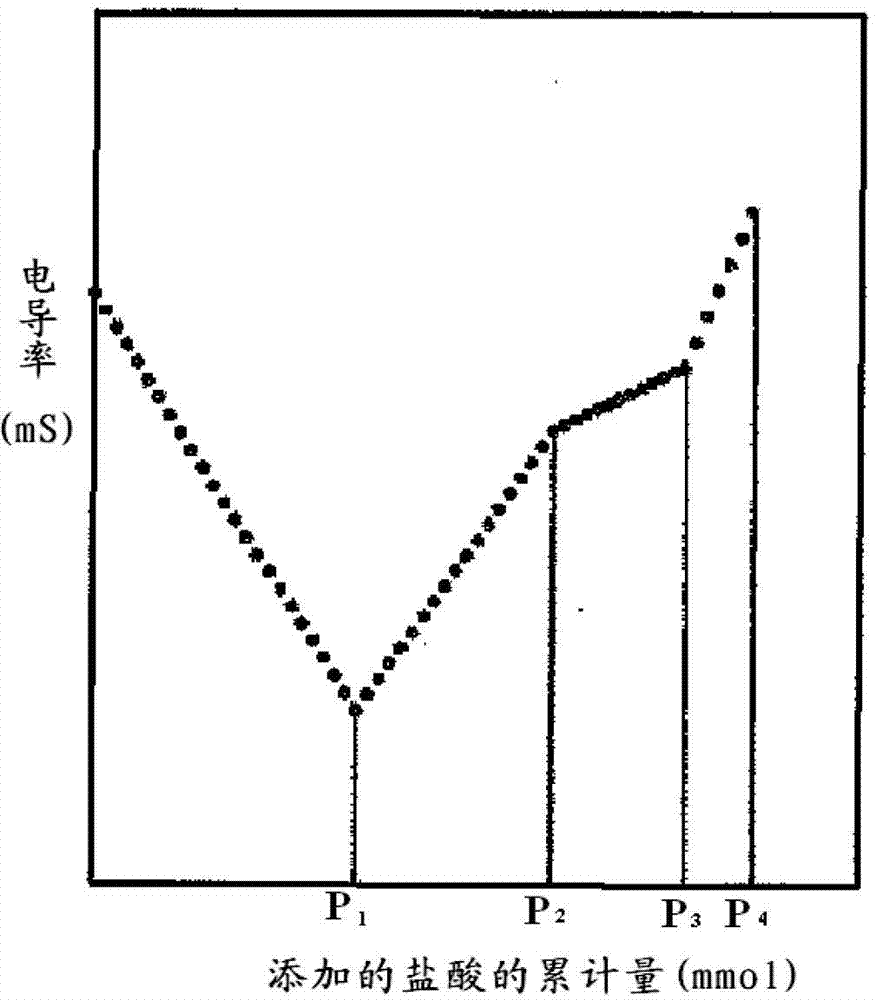
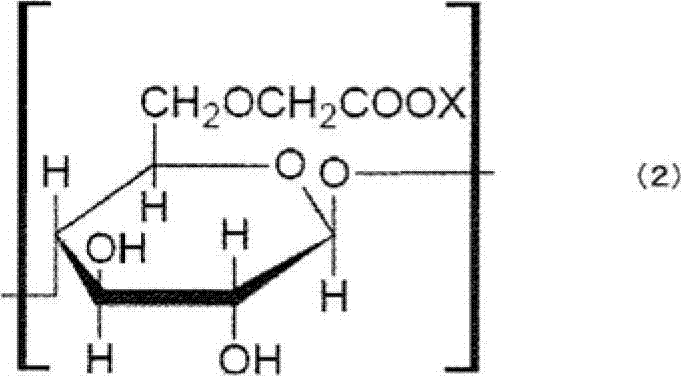
A lithium ion secondary battery negative electrode slurry composition comprising a negative electrode active material, a thickening agent, a binder of polymer particles and water, wherein the negative electrode active material includes a carbon material and the carbon material has a graphite interlayer distance (an interplanar spacing (d value) of the (002) plane as determined by an X-ray diffraction method) of 0.340 to 0.370 nm, the thickening agent is a polymer having a degree of polymerization of 1400 to 3000, the polymer particles are obtained by polymerizing a monomer composition including 1 to 10 wt % of a monocarboxylic acid monomer, and an amount of acid groups on the surface of the polymer particles as determined by a conductivity titration is 0.1 to 1.0 mmol per 1 g of the polymer particles.
Owner:ZEON CORP
Non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery and process for producing positive electrode for use in non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery
InactiveUS20060292447A1Large capacityExcellent cycle characteristicsOrganic electrolyte cellsSecondary cellsLithium metalDesorption
A non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery in which a positive electrode formed of a graphite powder and an negative electrode formed of a material capable of absorption / desorption of a lithium metal or lithium are placed to face each other in an electrolyte containing lithium salt. The positive electrode of this battery where a Lc (112) which is the size of crystallite in a c axis direction which is calculated from a (112) diffraction line of a graphite crystal and determined by a powder X-ray diffraction method which is from 4 nm to 30 nm, and a charge capacity at the first cycle which is calculated on the basis of a total weight of the graphite material of the positive electrode filled in the battery is 20 to 50 (mAh / g). Preferably, the graphite powder of the positive electrode has an ratio (A / B) which is the ratio of a specific surface area A determined by a nitrogen absorption (BET) method to a surface area B determined on the basis of an area average diameter of 20 or less.
Owner:FDK CORP
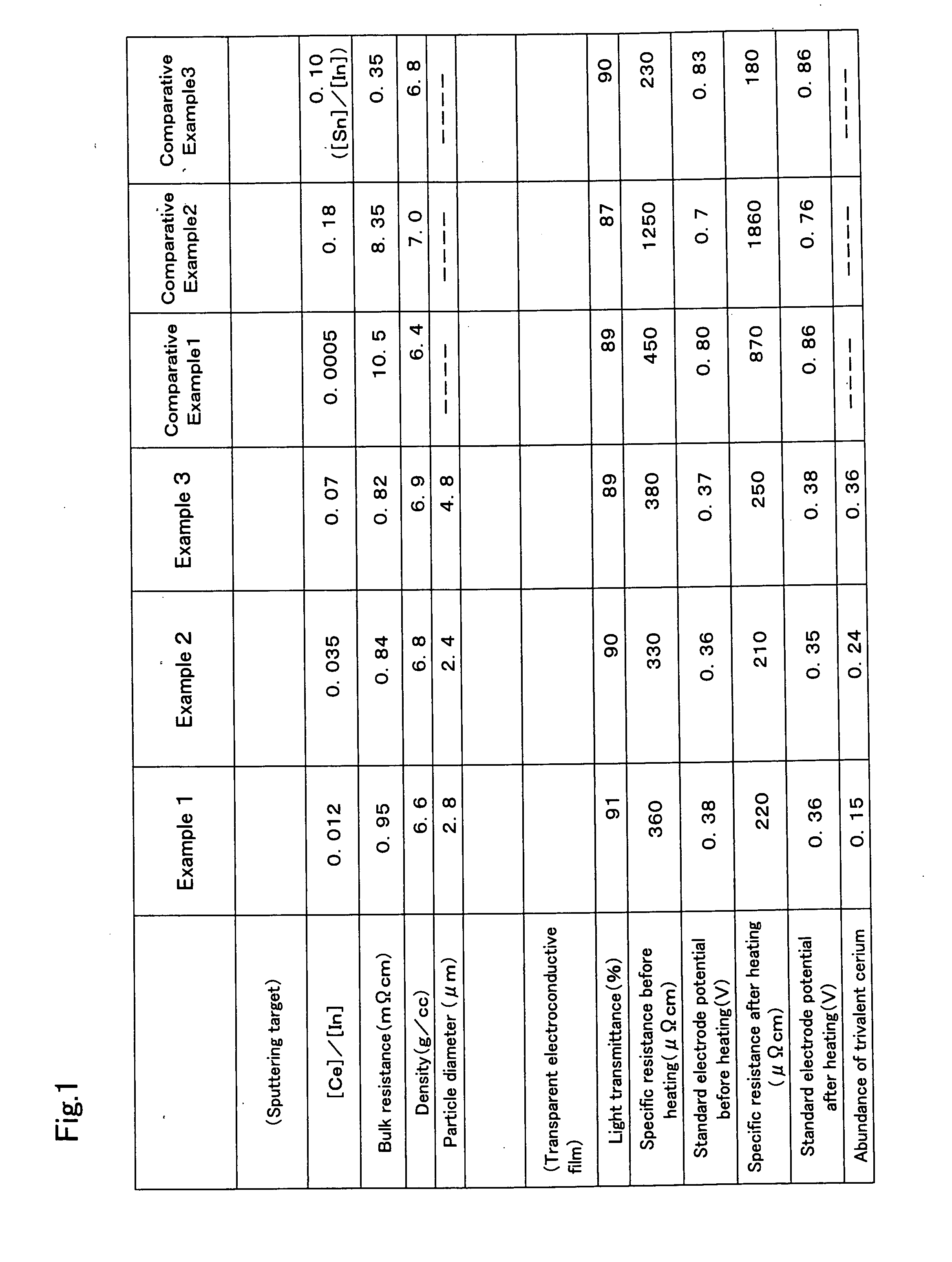
Indium Oxide-Cerium Oxide Based Sputtering Target, Transparent Electroconductive Film, and Process for Producing a Transparent Electroconductive Film
InactiveUS20070209928A1Restraining cell reactionConductive layers on insulating-supportsVacuum evaporation coatingOrganic acidIndium
A transparent conductive film for constructing a transparent electrode that is free from the generation of residue, etc. by etching with a weak acid (for example, organic acid). Further, there is provided a sputtering target for producing the transparent conductive film. In particular, there is provided a sputtering target composed of indium oxide and cerium oxide, characterized in that in the observation of crystal peaks by X-ray diffractometry, the presence of peaks ascribed to indium oxide and cerium oxide is observed, and that in the EPMA measurement, the diameter of cerium oxide particles dispersed in indium oxide is measured as being ≦5 μm. A transparent conductive film is formed by a sputtering technique with the use of this sputtering target. This transparent conductive film is substantially free from the generation of residue, etc. by etching with a weak acid (for example, organic acid).
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Negative electrode for non-aqueous secondary battery, and a non-aqueous secondary battery
ActiveUS20130136988A1Improve charge and discharge cycle characteristicsSuppress battery swellingLi-accumulatorsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesX-rayEngineering
[Objectives] The present invention provides a non-aqueous secondary battery in which a material containing Si and O as constituent elements is used in a negative electrode. The present invention provides a non-aqueous secondary battery having good charge discharge cycle characteristics, and suppressing the battery swelling associated with the charge and the discharge. Also, the present invention relates to a negative electrode that can provide the non-aqueous secondary battery. [Solution] The negative electrode includes a negative electrode active material, including a composite of a material containing Si and O as constitution elements (atom ratio x of O to Si is 0.5≦x≦1.5) in combination with a carbon material, and graphite. The graphite has an average particle diameter dg(μm) of 4 to 20 μm. The material containing Si and O as constitution elements has an average particle diameter ds(μm) of 1 μm or more. The ratio ds / dg (i.e., ds to dg) is 0.05 to 1. The material containing Si and O as constitution elements has a crystallite diameter of 50 nm or less, the crystallite diameter is calculated from a half width at a (220) plane of Si obtained by an X-ray diffraction method, using Scherrer Formula. In 100 mass % of the composite of the material containing Si and O as constitution elements, and the carbon material, a ratio of the material containing Si and O as constitution elements is 70 to 95 mass %.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Negative electrode for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery
A negative electrode for a lithium secondary battery, comprising a layer of a mixture containing graphite powder and an organic binder on a current collector, wherein a diffraction intensity ratio (002) / (110) measured by X-ray diffractometry of the layer of a mixture is 500 or less, and a lithium secondary battery, comprising the negative electrode f or a lithium secondary battery, and a positive electrode that includes a lithium compound. It results less deterioration in the rapid charge and discharge characteristics and the cycle characteristics when the density of the negative electrode is made higher. Thereby it provides a high capacity lithium secondary battery having the improved energy density per unit volume of the secondary battery.
Owner:RESONAC CORP
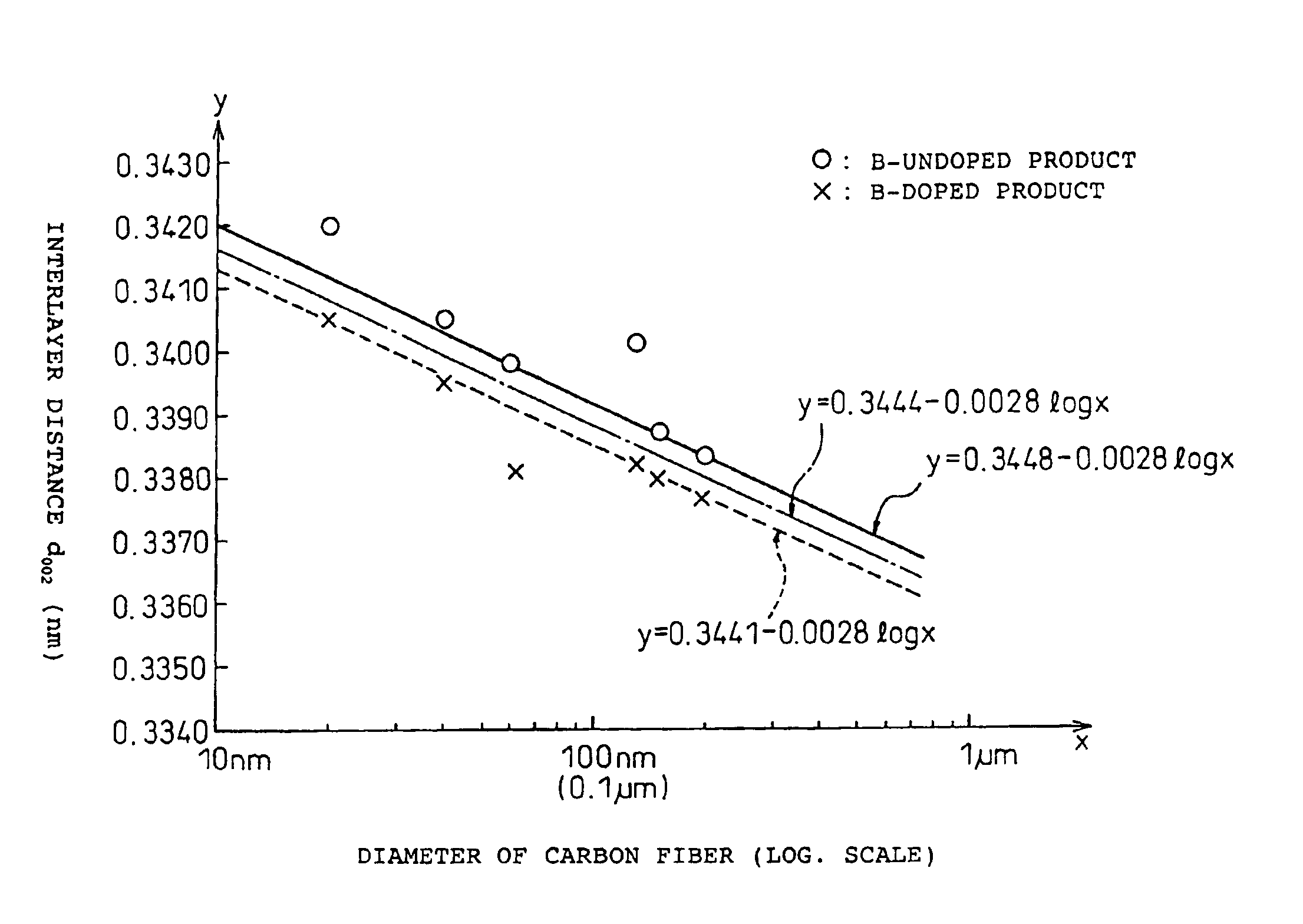
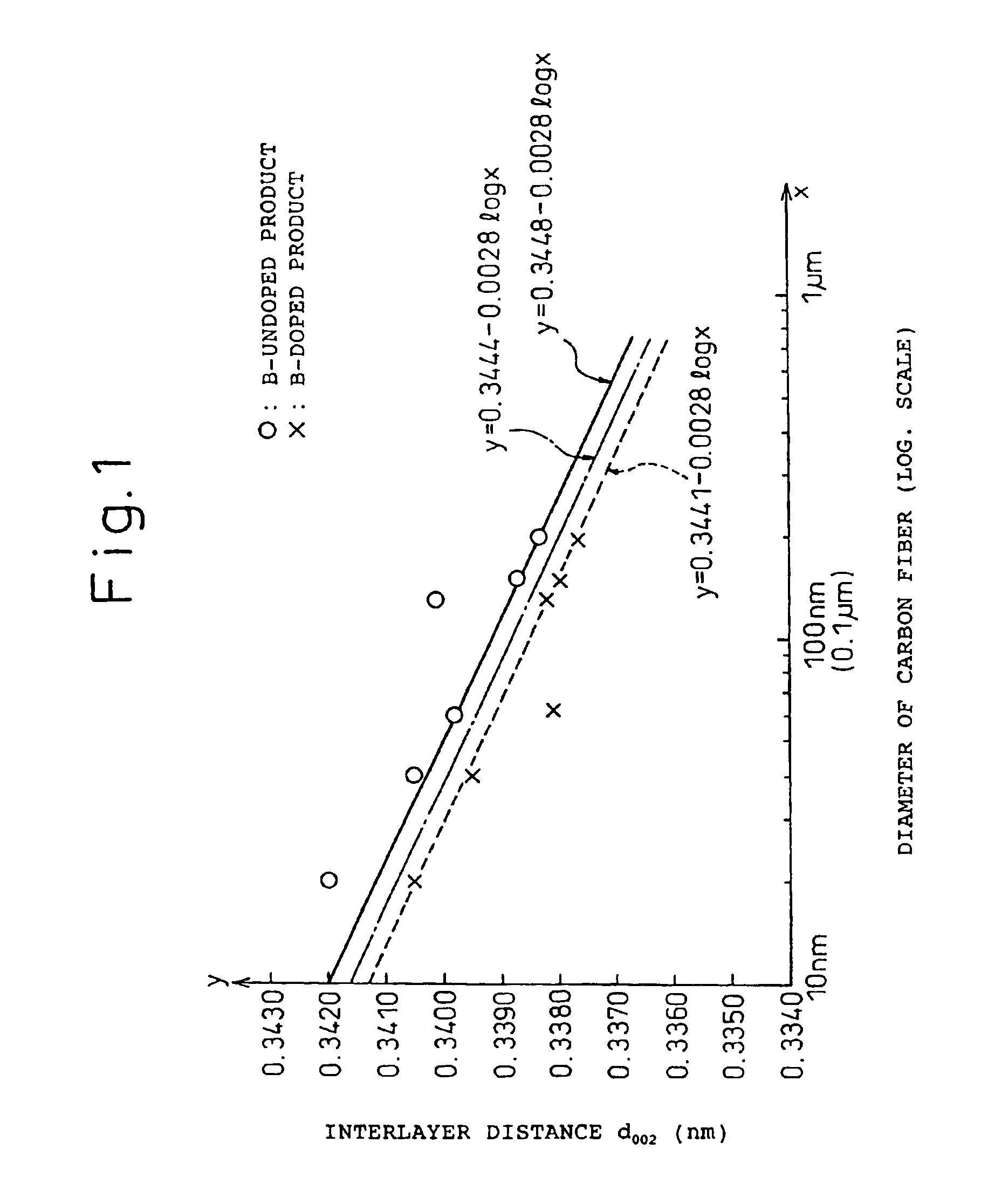
Carbon fibers, production process therefor and electrode for batteries
InactiveUS6946110B2High crystallinityImprove performanceMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentCarbon layerPolymer science
Fine carbon fibers having a fiber diameter of 1 μm or less, an interlayer distance d002 between carbon layers as determined by an X-ray diffraction method of 0.335 to 0.342 nm or less and satisfying d002<0.3448-0.0028 (log φ) where φ stands for the diameter of the carbon fibers, and a thickness Lc of the crystal in the C axis direction of 40 nm or less. Fine carbon fibers containing boron in crystals of the fiber. The fine carbon fibers can be produced by using vapor-grown fine carbon fibers as a raw material, adding a boron or a boron compound to the material; pressing the mixture to regulate the bulk density to preferably 0.05 g / cm3 or more; and heating at a temperature of 2000° C. or higher.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Nonreducing dielectric ceramic and ceramic electronic component using same
InactiveUS20020132127A1Low rate of changeHighly reliable with respectMultiple-port networksFixed capacitor dielectricAs elementRare-earth element
A nonreducing dielectric ceramic contains a tungsten-bronze-type crystal phase including at least Ba, RE and Ti as elements, and a pyrochlore-type crystal phase including at least RE and Ti as elements, where RE is at least one rare-earth element. The relationship 0.10<=b / (a+b)<=0.90 is satisfied, where a is the maximum peak intensity assigned to the tungsten-bronze-type crystal phase and b is the maximum peak intensity assigned to the pyrochlore-type crystal phase determined by X-ray diffractometry. A ceramic electronic component includes an electronic component body composed of the nonreducing dielectric ceramic and a conductor in contact with the nonreducing dielectric ceramic.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
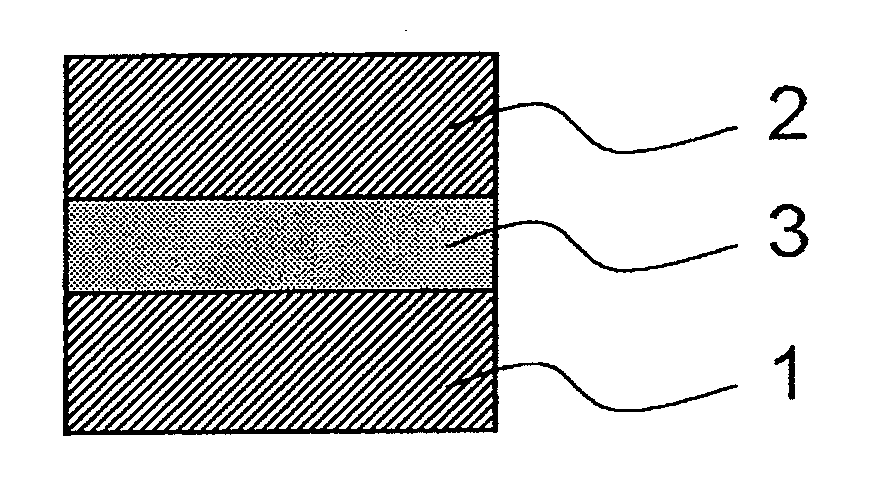
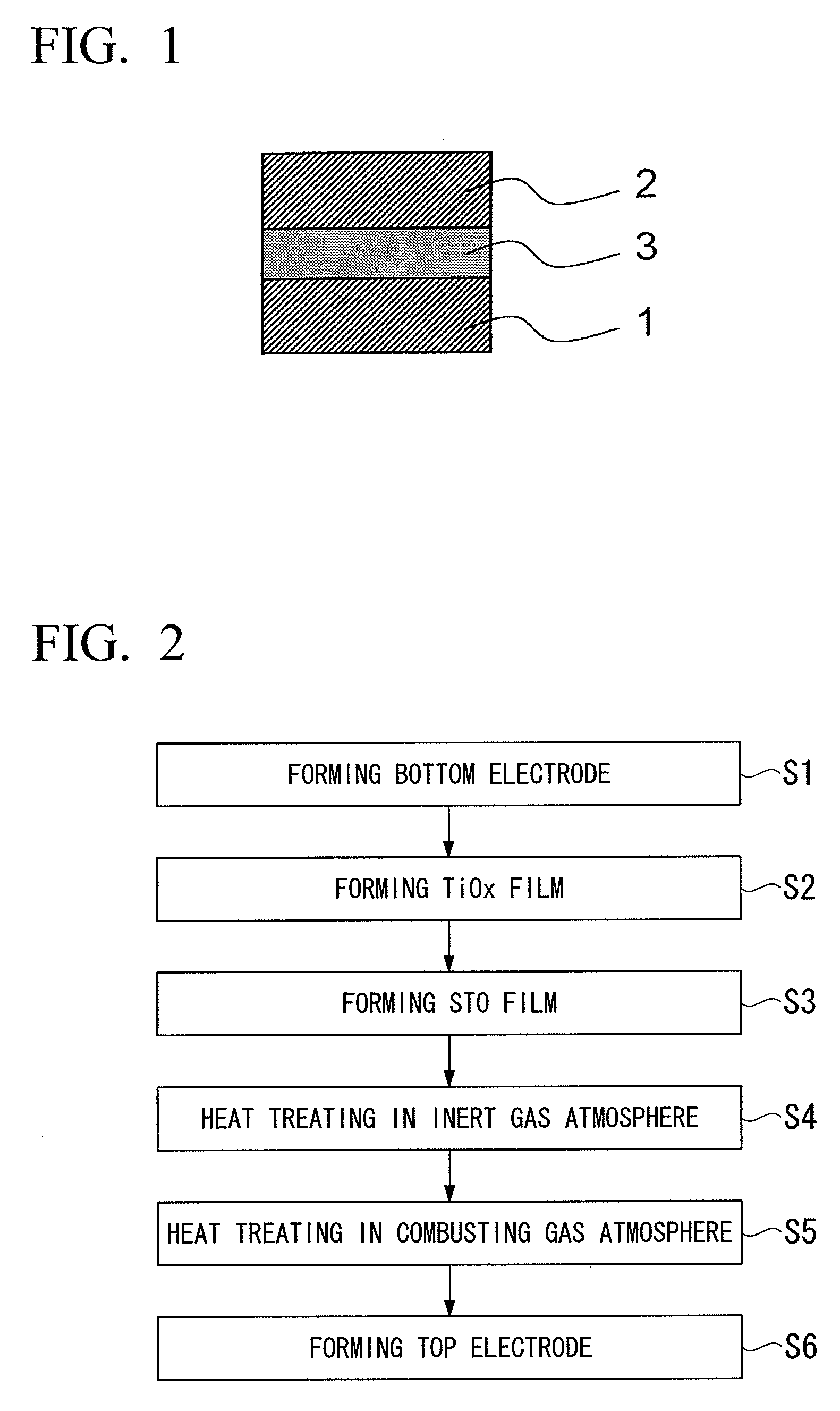
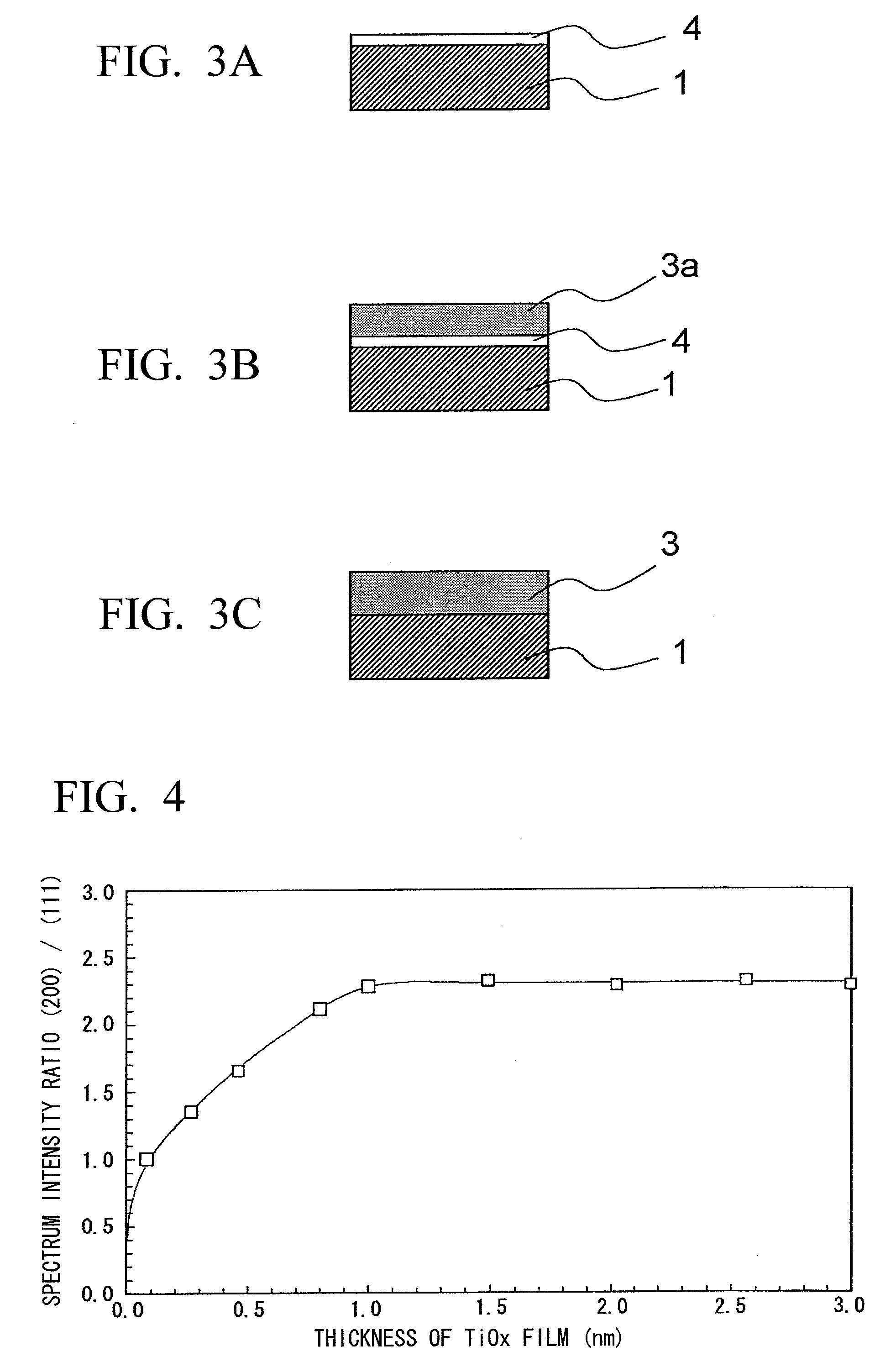
Capacitor insulating film, method of forming the same, capacitor and semiconductor device using the capacitor insulating film
A capacitor insulating film may include, but is not limited to, strontium, titanium, and oxygen. The capacitor insulating film has a ratio of a spectrum intensity of (200) crystal face of the capacitor insulating film to a spectrum intensity of (111) crystal face of the capacitor insulating film in the range of 1.0 to 2.3. Each of the spectrum intensities of (200) crystal face and (111) crystal face is measured by an X-ray diffraction method.
Owner:ELPIDA MEMORY INC
Carbonaceous material for negative electrodes of nonaqueous electrolyte secondary batteries, and method for producing same
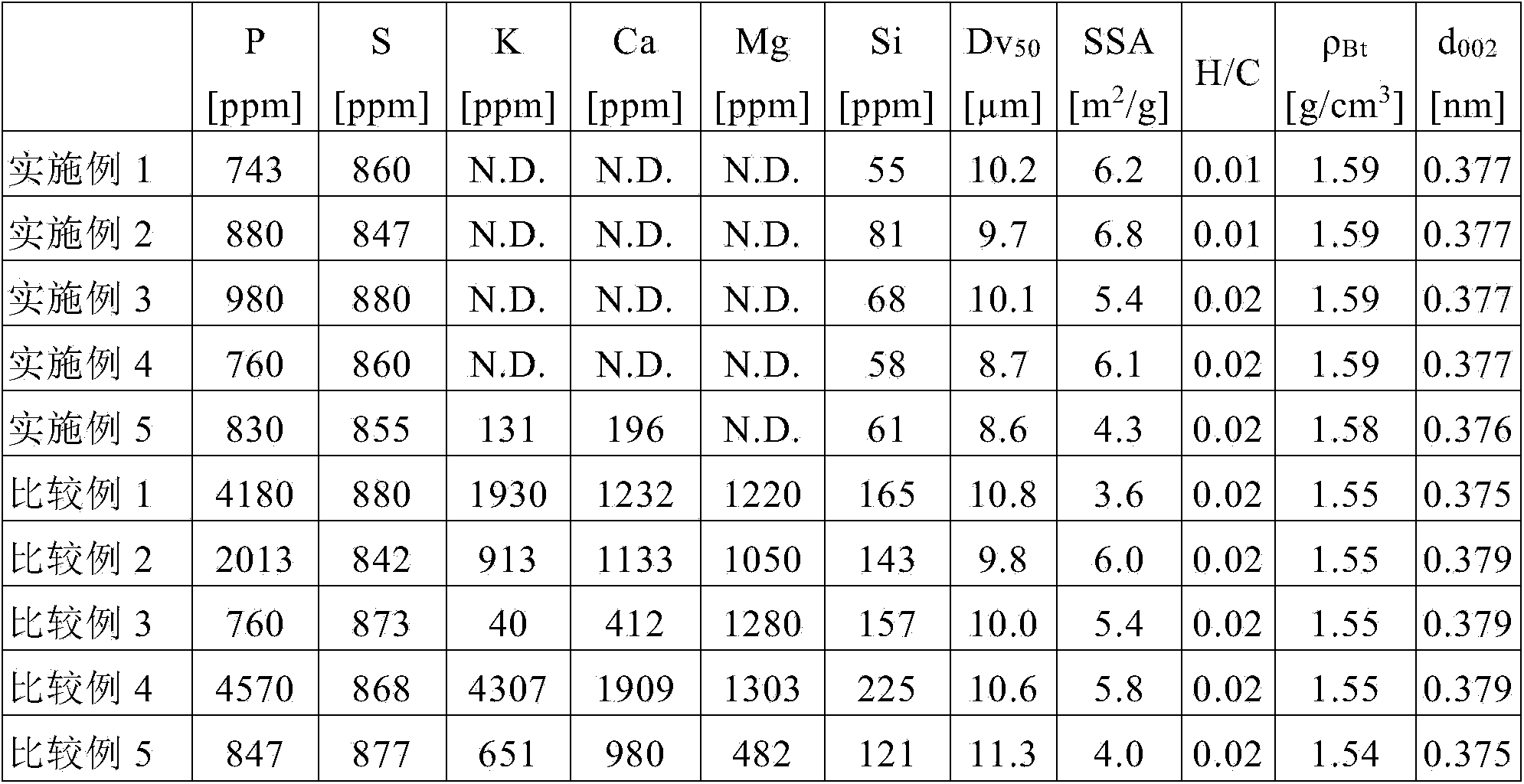
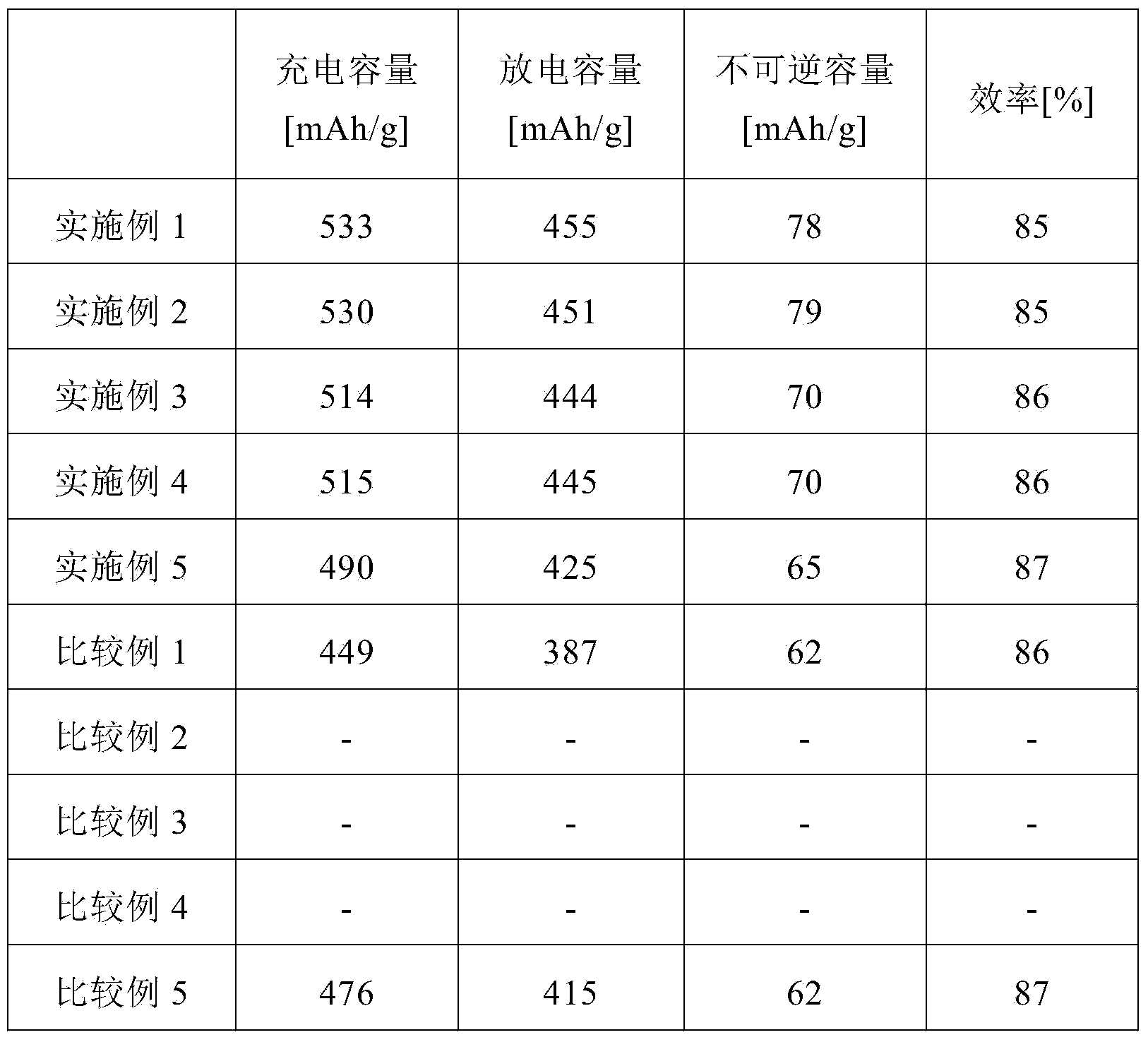
ActiveCN104412425AExcellent electrical propertiesImprove securityCell electrodesFinal product manufactureAlkaline earth metalElemental analysis
The purpose of the present invention is to provide: a carbonaceous material for negative electrodes of nonaqueous electrolyte secondary batteries, which uses a plant-derived organic material as a starting material, and from which alkali metals such as potassium element and alkaline earth metals such as calcium element are sufficiently removed by decalcification, so that the carbonaceous material has high purity and excellent discharge capacity and efficiency; a novel production method which is capable of efficiently mass-producing the carbonaceous material; and a lithium ion secondary battery which uses the carbonaceous material. The above-mentioned purpose can be achieved by a carbonaceous material for negative electrodes of nonaqueous electrolyte secondary batteries, which is obtained by carbonizing a plant-derived organic material, and which has an atomic ratio of hydrogen atoms to carbon atoms (H / C) as determined by elemental analysis of 0.1 or less, an average particle diameter (Dv50) of 2-50 mum, an average interplanar spacing of the (002) plane as determined by a powder X-ray diffraction method of 0.365-0.400 nm, a potassium element content of 0.5% by mass or less and a calcium element content of 0.02% by mass or less.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
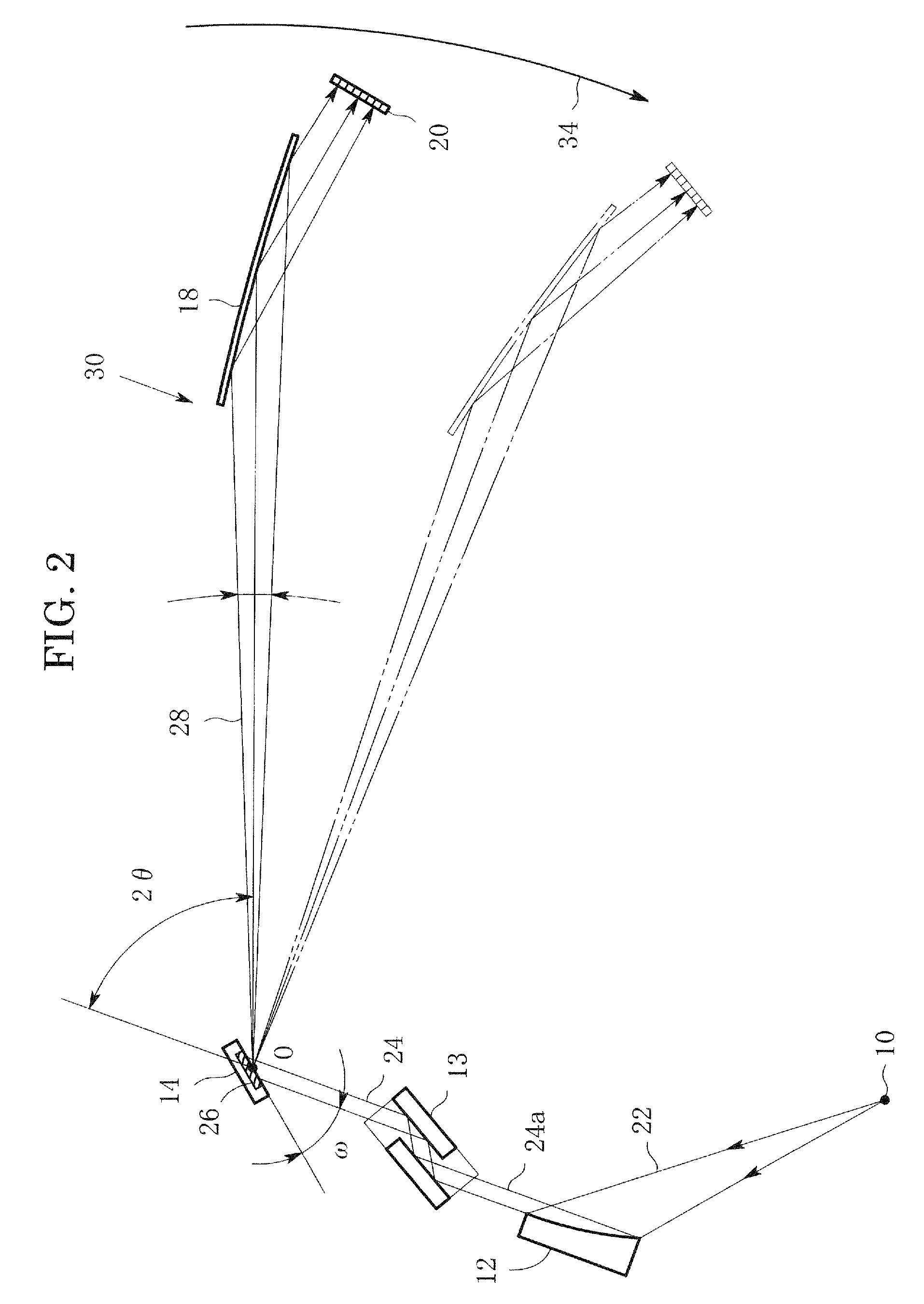
X-ray diffraction method and X-ray diffraction apparatus
InactiveUS8340248B2Convenient angleSmall intensityX-ray spectral distribution measurementNanoinformaticsSoft x rayLight beam
In an X-ray diffraction method, an X-ray parallel beam is incident on a sample, and diffracted X-rays from the sample are reflected at a mirror and thereafter detected by an X-ray detector. The reflective surface of the mirror is a combination of plural flat reflective surfaces, the respective centers of which are located on an equiangular spiral having a center that is located on a surface of the sample. The X-ray detector is one-dimensional position-sensitive in a plane parallel to the diffraction plane. X-rays that have been reflected at different flat reflective surfaces reach different points on the X-ray detector respectively. A correction is performed for separately recognizing different reflected X-rays that may have been reflected at the different flat reflective surfaces, and might be mixed with each other on the same detecting region of the X-ray detector.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Carbonaceous material for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery negative electrode
InactiveCN103415948AImprove charge and discharge efficiencyReduce thicknessCell electrodesCarbon preparation/purificationAir atmosphereMicrometer
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a carbonaceous material for a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery negative electrode, which has large charge-discharge capacity, high charge-discharge efficiency and excellent charge-discharge cycle properties. The purpose is achieved by a carbonaceous material for a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery negative electrode, characterized in that the average interlayer spacing on face (002) is 0.365-0.40 nm as measured by an X-ray diffraction method, no exothermic peak appears in a temperature region of 620 DEG C or lower as measured by a differential thermal analysis under an air atmosphere, the BET specific surface area is 1-7 m2 / g, the average particle diameter (D50) is 5-25 micrometer, and the (D90-D10) / D50 ratio is 1.05 or less.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Sintered body for use in battery, method for manufacturing sintered body for use in battery, and all-solid-state lithium battery
InactiveCN103119772AImprove output characteristicsDecreased charge and discharge characteristicsFinal product manufactureCell electrodesAll solid stateManganese
Provided are: a sintered body for use in a battery, wherein sintering-associated losses in charging / discharging characteristics are minimized; and a method for manufacturing said sintered body. Said sintered body is characterized by the provision of a solid electrolyte material, consisting of a NaSICON-type phosphoric acid compound, and an active material, consisting of LiCoO2, a transition metal oxide, or a spinel oxide containing nickel and / or manganese. The sintered body is also characterized in that X-ray diffraction analysis detects no components other than those of the abovementioned solid electrolyte material and active material at the interface between said solid electrolyte material and active material.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com