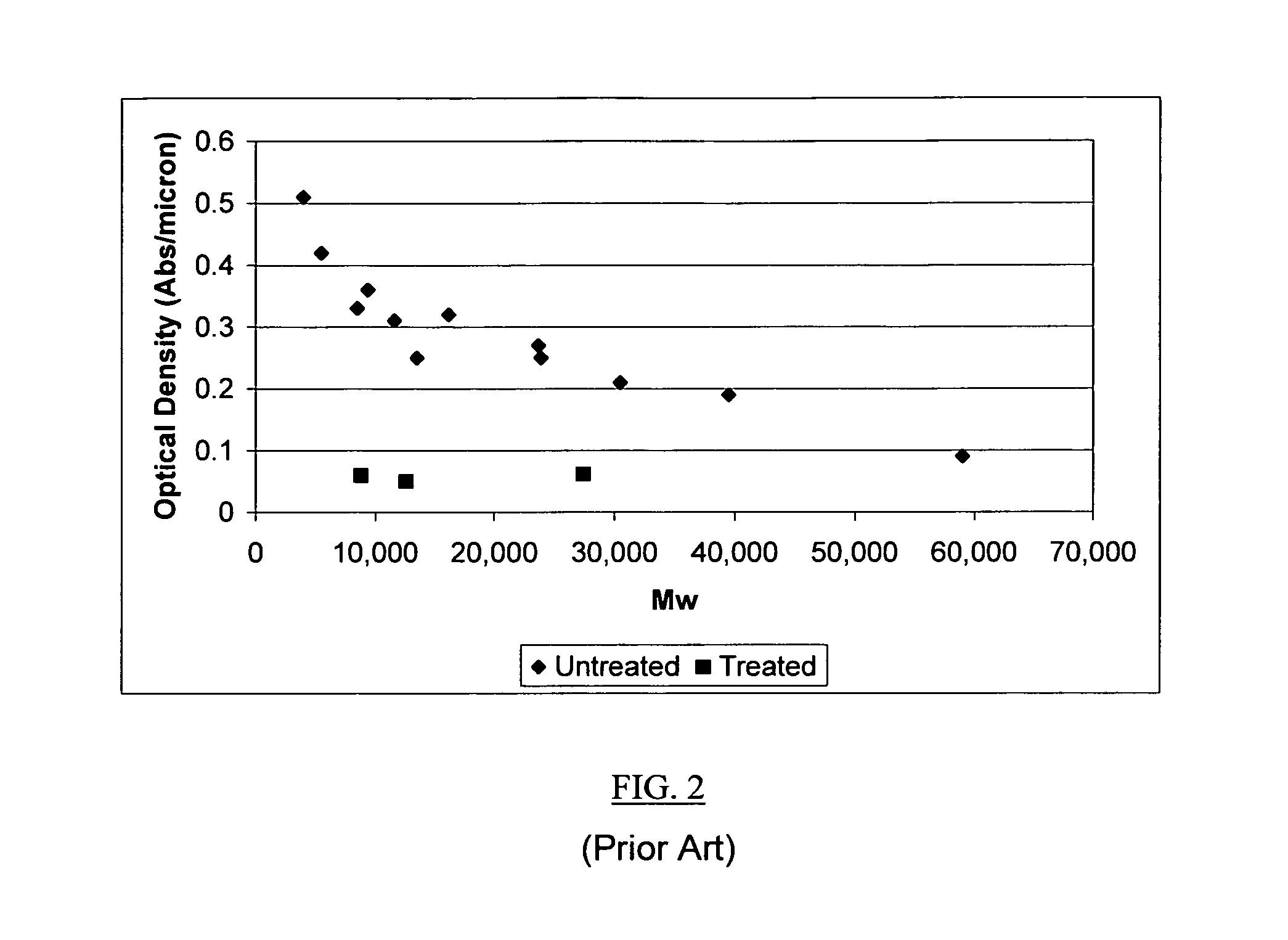
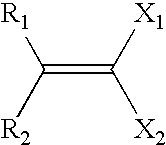
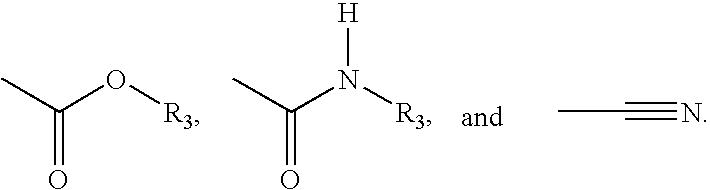
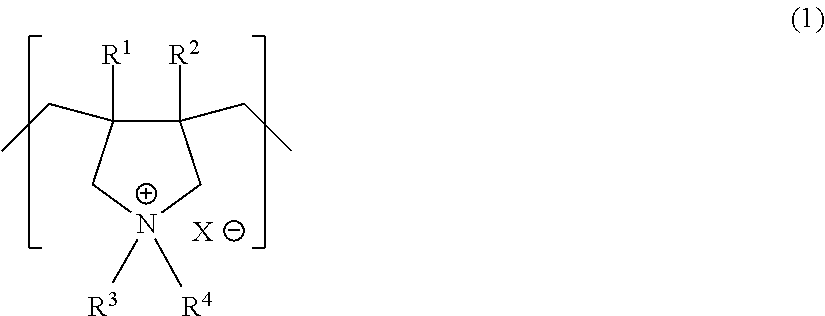
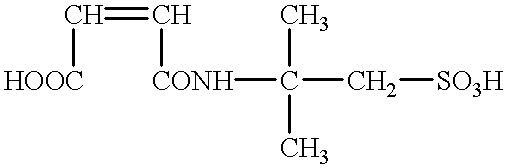
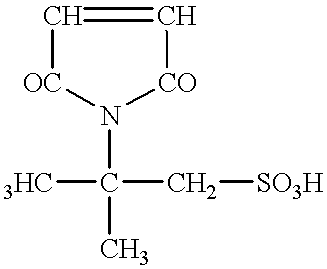
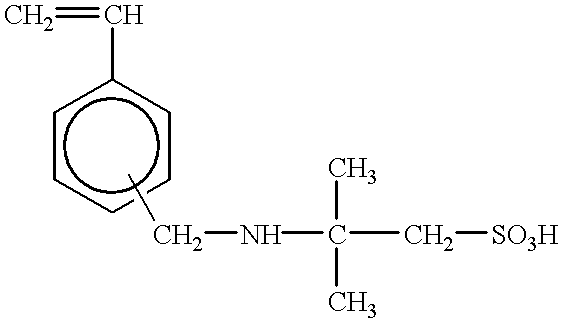
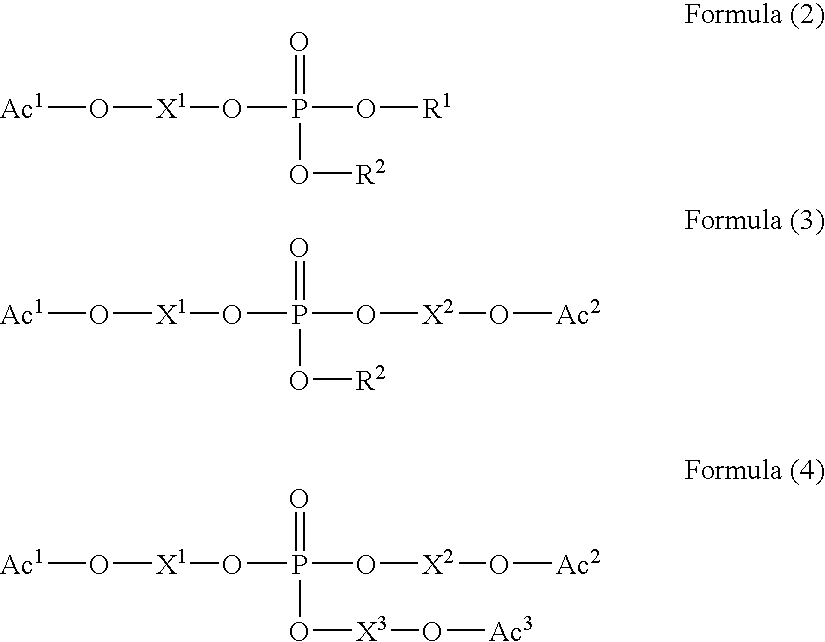
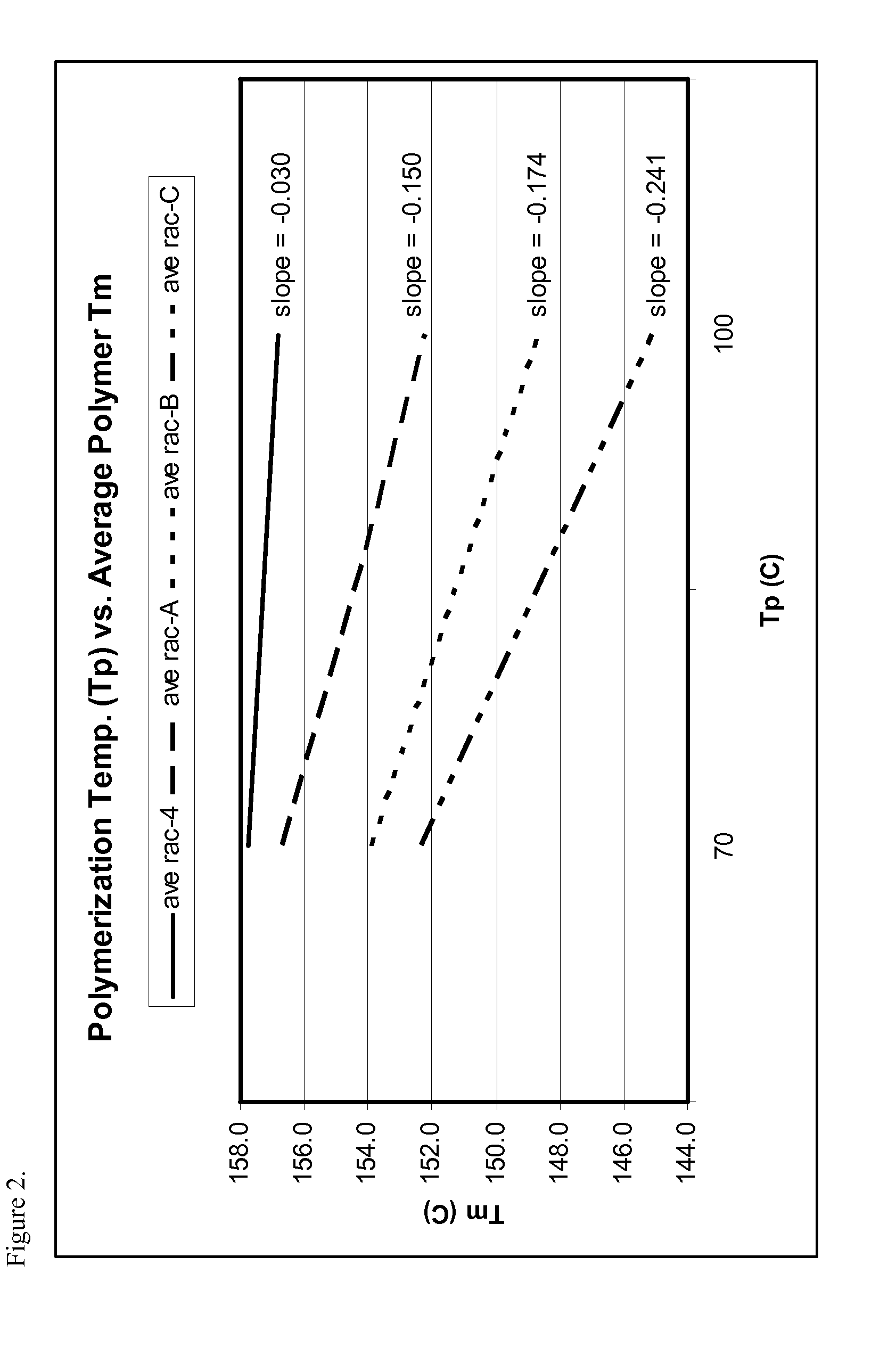
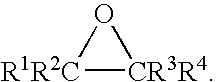
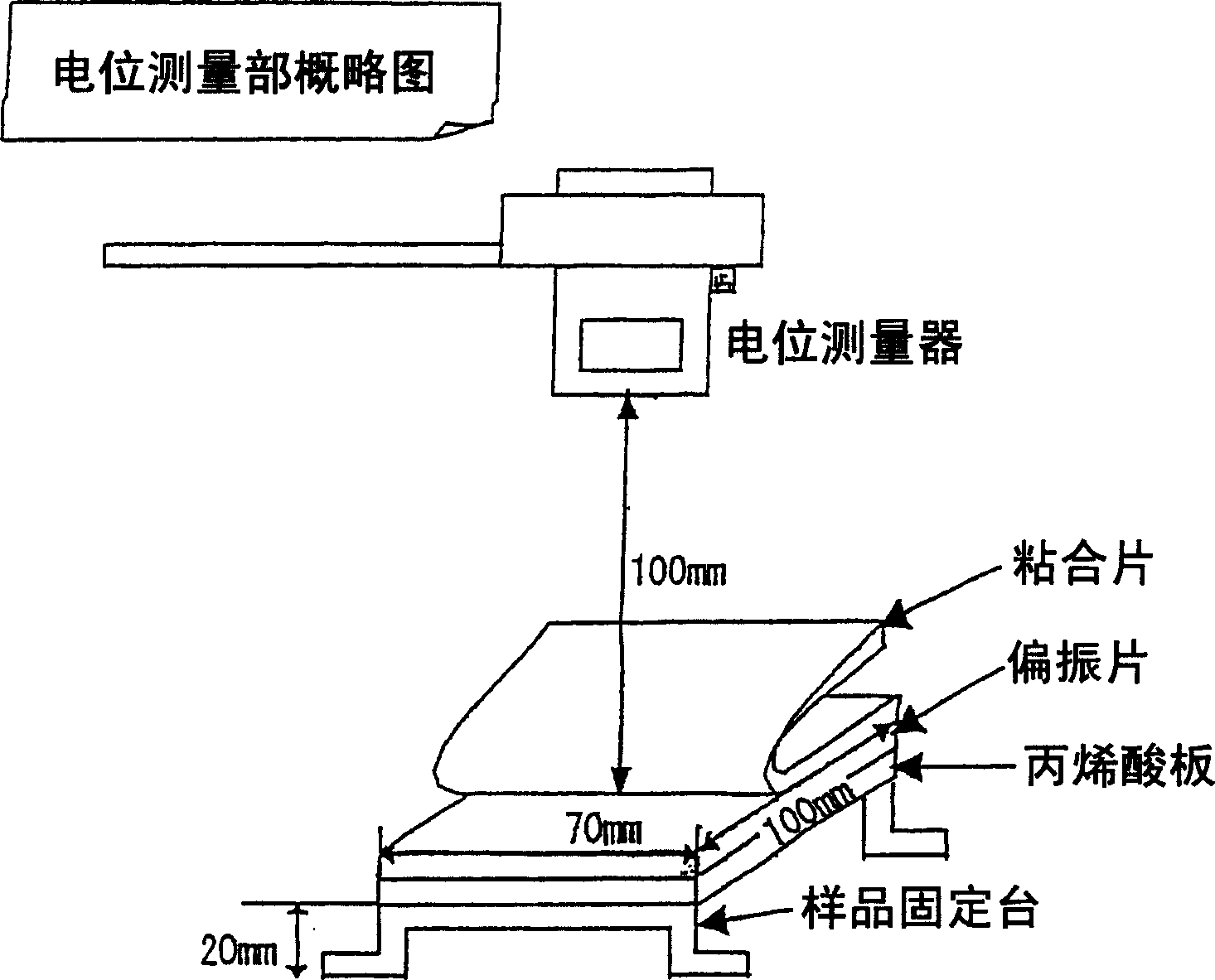
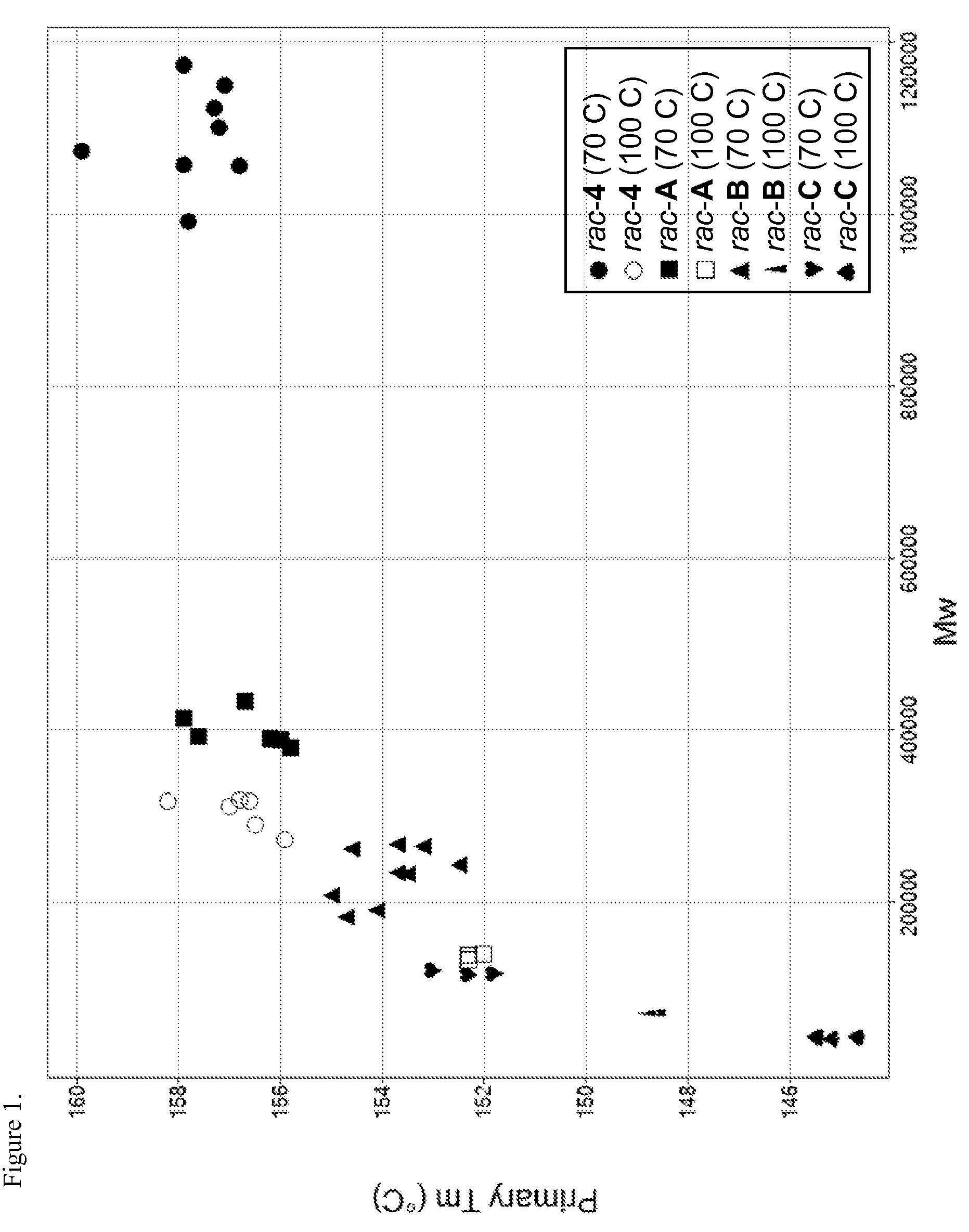
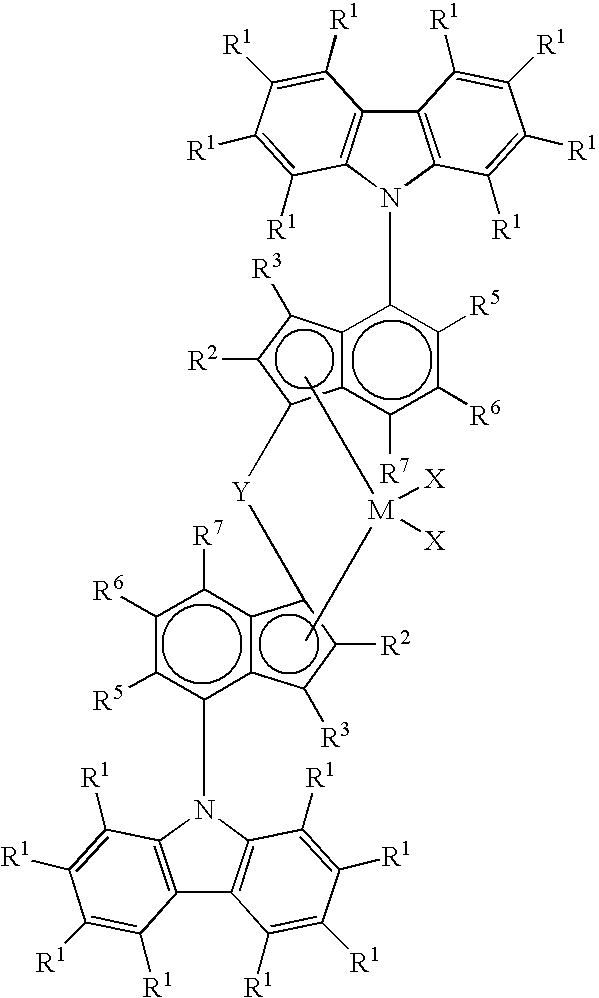
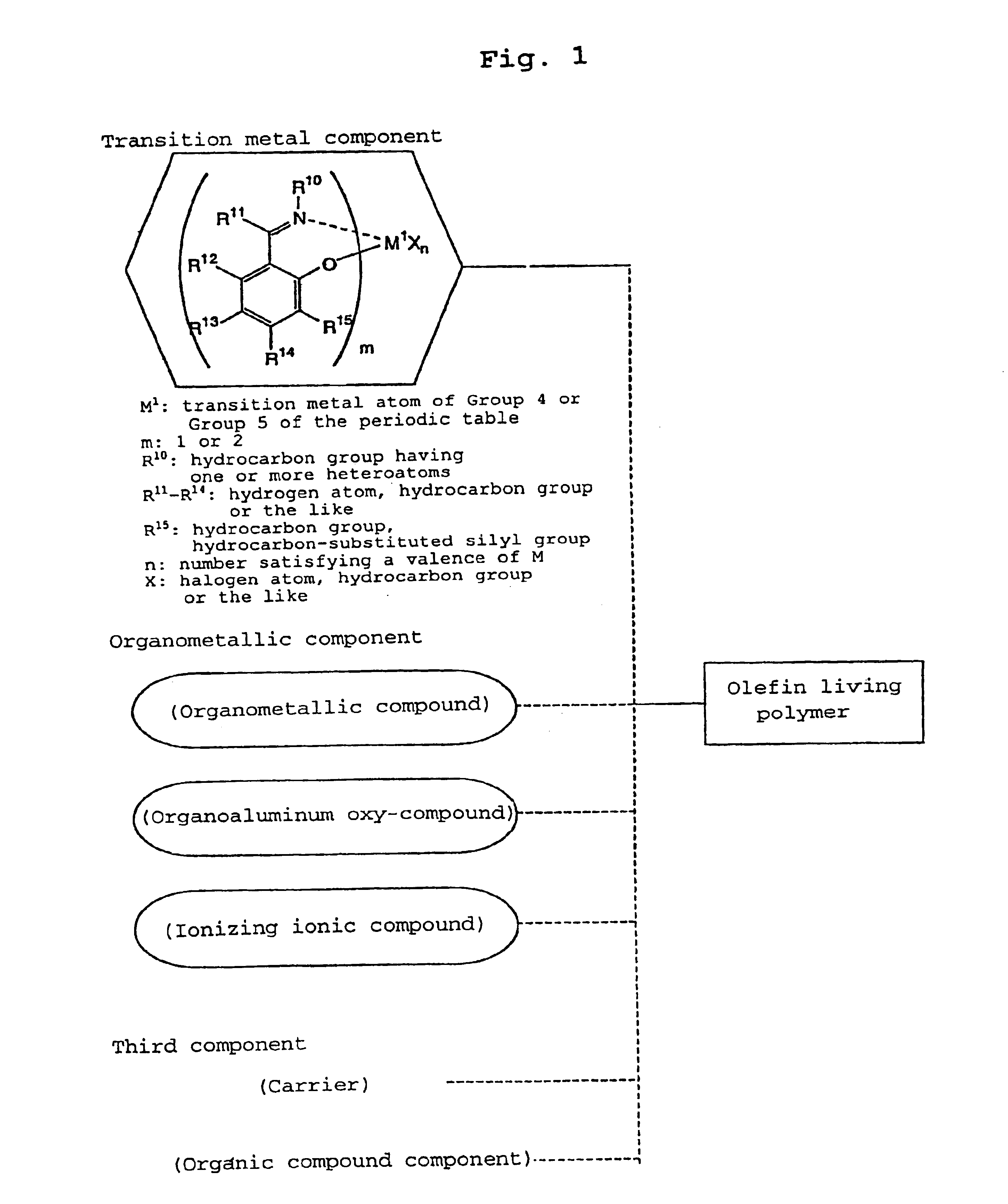
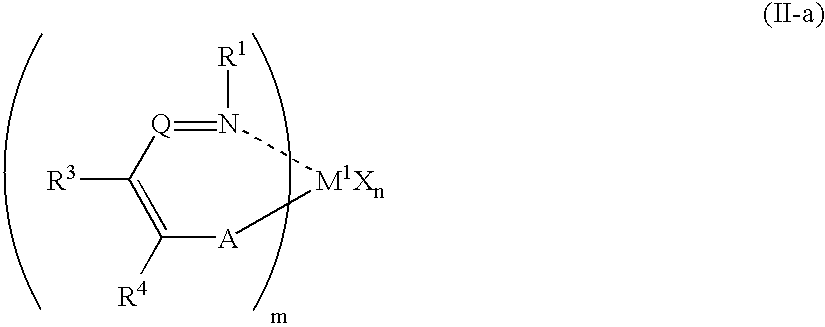
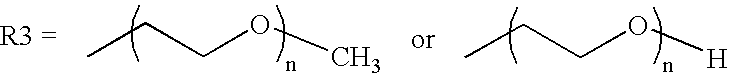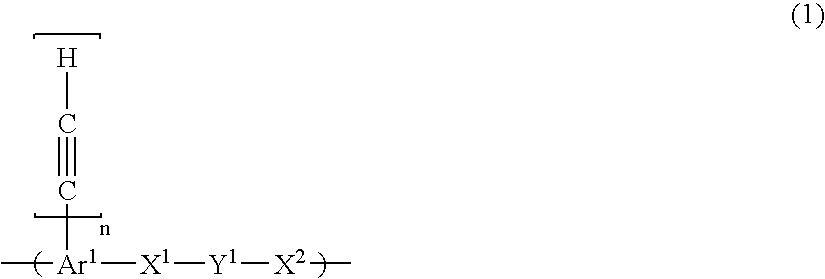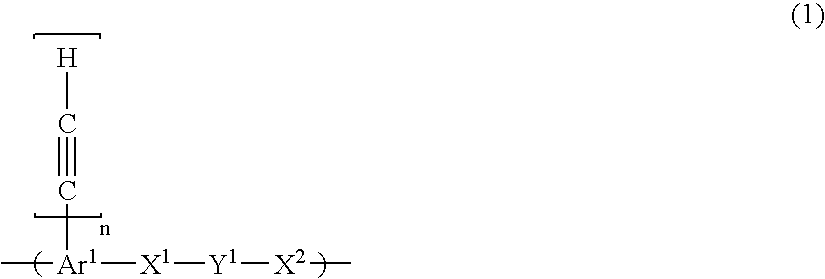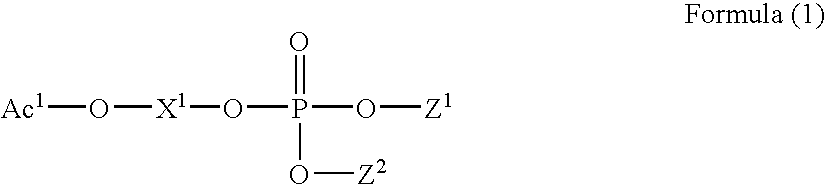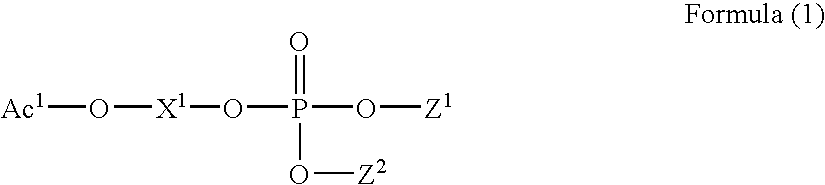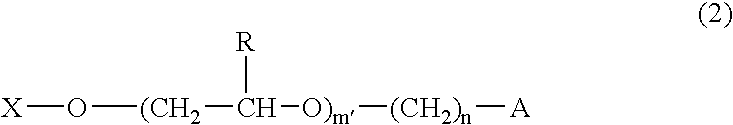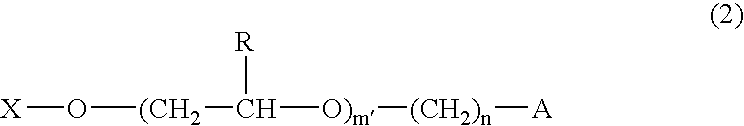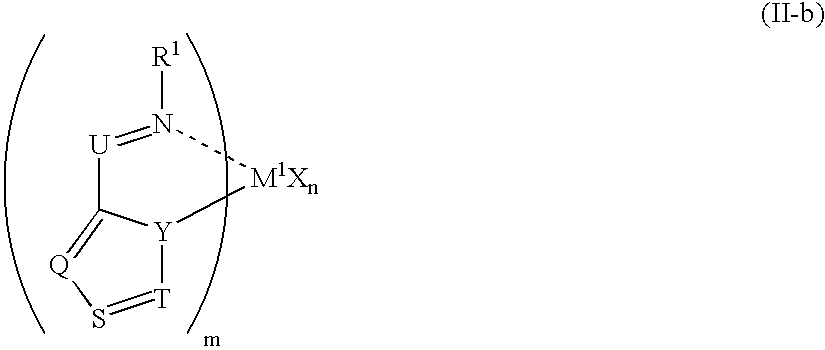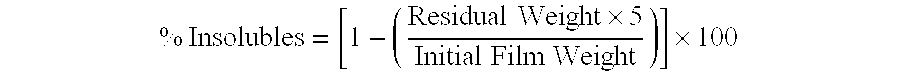Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
873 results about "Monomer composition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polymeric composites including dicyclopentadiene and related monomers
InactiveUS6310121B1Group 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsFiberMonomer composition
Compositions including fibers, fillers, reinforcing agents or other property-enhancing agents added to a polymeric matrix formed from DCPD monomer or related compounds such as norbornene and norbornadiene are disclosed. The composition has a mechanically forgiving matrix due to the polymer with the inherent strength and other physical properties of the enhancement agent according to the invention. Enhancement agents according to the invention generally include inorganic, organic and metallic substances in a variety of forms.
Owner:CYMETECH
Electrochromic polymeric solid films, manufacturing electrochromic devices using such solid films, and processes for making such solid films and devices
InactiveUS20050079326A1Low viscosityMinimal shrinkageSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsMonomer compositionPolymer science
An electrochromic mirror device suitable for use in a vehicle comprises a first transparent substrate having a transparent conductive layer on a surface thereof and a second substrate having a conductive layer on a surface thereof. The conductive layer of the first substrate opposes the second conductive layer of the second substrate in a spaced-apart relationship thereby forming an interpane distance between the substrates. A boundary seal is interposed between the first and second substrates spacing apart the substrates and forming a cavity wherein the interpane distance is at least about 10 microns. An electrochromic cross-linked polymeric solid film is disposed within the cavity. The electrochromic cross-linked solid polymeric film is formed from an electrochromic monomer composition that includes at least one cathodic electrochromic compound. The second conductive layer comprises a metallic reflective layer.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
High water reduction high collapse protection type polycarboxylate high-performance water reducer and pyrogen-free preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of concrete additives in building materials. The high water reduction high collapse protection type polycarboxylate high-performance water reducer mainly comprises the following monomer components: unsaturated methyl vinyl polyoxyethylene ether (A), a chain transfer agent (B), a mixture (C) of one or more of unsaturated acid and unsaturated acid derivatives, an oxidant (D) and a reducing agent (E), wherein the molar ratio A: B: C: D: E of the monomers is 1:0.01-0.5:2-8:0.08-0.5:0.02-0.3. The high water reduction high collapse protection type polycarboxylate high-performance water reducer is prepared by regulating the polymer mass concentration to between 20 and 40 percent by using water, and polymerizing a redox initiator system at normal temperature. The water reducer has the advantages of low doping amount, high water reducing ratio, excellent slump retaining capacity, and high cement adaptability, and the technology has the advantages of no need of extra heat source, implementation at normal temperature, low equipment investment, low cost and suitability for large area popularization and application.
Owner:大连华建科技有限公司
Fluorochemical composition comprising a fluorinated polymer and treatment of a fibrous substrate therewith
InactiveUS7094829B2Easy to oilGood water repellency propertyStain/soil resistant fibresLiquid repellent fibresFiberOrganic solvent
A fluorochemical composition for rendering fibrous substrates oil repellent, water repellent, and / or stain repellent and comprising a fluorinated polymer dispersed in water or dissolved or dispersed in an organic solvent, the fluorinated polymer comprising units derived from (i) a mixture of two or more fluorinated polyether monomers that differ in at least their molecular weight, the fluorinated polyether monomers having an ethylenically unsaturated group and a perfluorinated polyether group and wherein at least 90% by weight of the mixture consists of fluorinated polyether monomers that have a perfluorinated polyether group having a molecular weight of at least 750 g / mol and (ii) one or more units derived from one or more co-monomers other than a fluorinated polyether monomer and wherein the co-monomers comprise at least one non-fluorinated monomer. Also, method for treating fibrous substrate with such composition, fluorinated polyether monomers, and fluorinated polymers derived from such monomers.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Electrochromic polymeric solid films, manufacturing electrochromic devices using such solid films, and processes for making such solid films and devices
InactiveUS6855431B2Minimal shrinkageImprove adhesionOptical signallingGlass/slag layered productsMonomer compositionInherent safety
The present invention relates to electrochromic polymeric solid films, manufacturing electrochromic devices using such solid films and processes for making such solid films and devices. The electrochromic polymeric solid films of the present invention exhibit beneficial properties and characteristics, especially when compared to known electrochromic media. The electrochromic polymeric solid films are transformed in situ from a low viscosity electrochromic monomer composition by exposure to electromagnetic radiation, and in so doing minimum shrinkage occurs. The electrochromic polymeric solid films of the present invention also perform well under prolonged coloration, outdoor weathering and all-climate exposure, and provide an inherent safety aspect not known to electrochromic media heretofore.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
Systems and methods for producing contact lenses from a polymerizable composition
ActiveUS20070035050A1Minimizing lens distortionImproving edge shapeConfectioneryOptical articlesMonomer compositionLight energy
Systems and methods of manufacturing ophthalmic lenses, for example, soft, extended wear silicone hydrogel contact lenses, are provided. The systems generally include a housing having an illuminated chamber, a carrier, for example a tray, movable in the illuminated chamber from an inlet portion to an outlet portion of the housing, and the tray configured to carry a plurality of contact lens molds. Polymerizing light energy is provided, for example, by multiple fluorescent lamps, to the molds at an intensity effective to at least initiate polymerization of a monomer composition located in each of the molds. The light may be illuminated onto two opposing sides of each mold. In some cases, the intensity of the light provided to one side of the mold may be different to the light intensity provided to the opposing side of the mold. In addition, the system may include features that are effective to provide for an instantaneous start and an instantaneous end to the light induced cure of the monomer in the molds. The system may include DALI protocol based technology for controlling the fluorescent lamps.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD +1
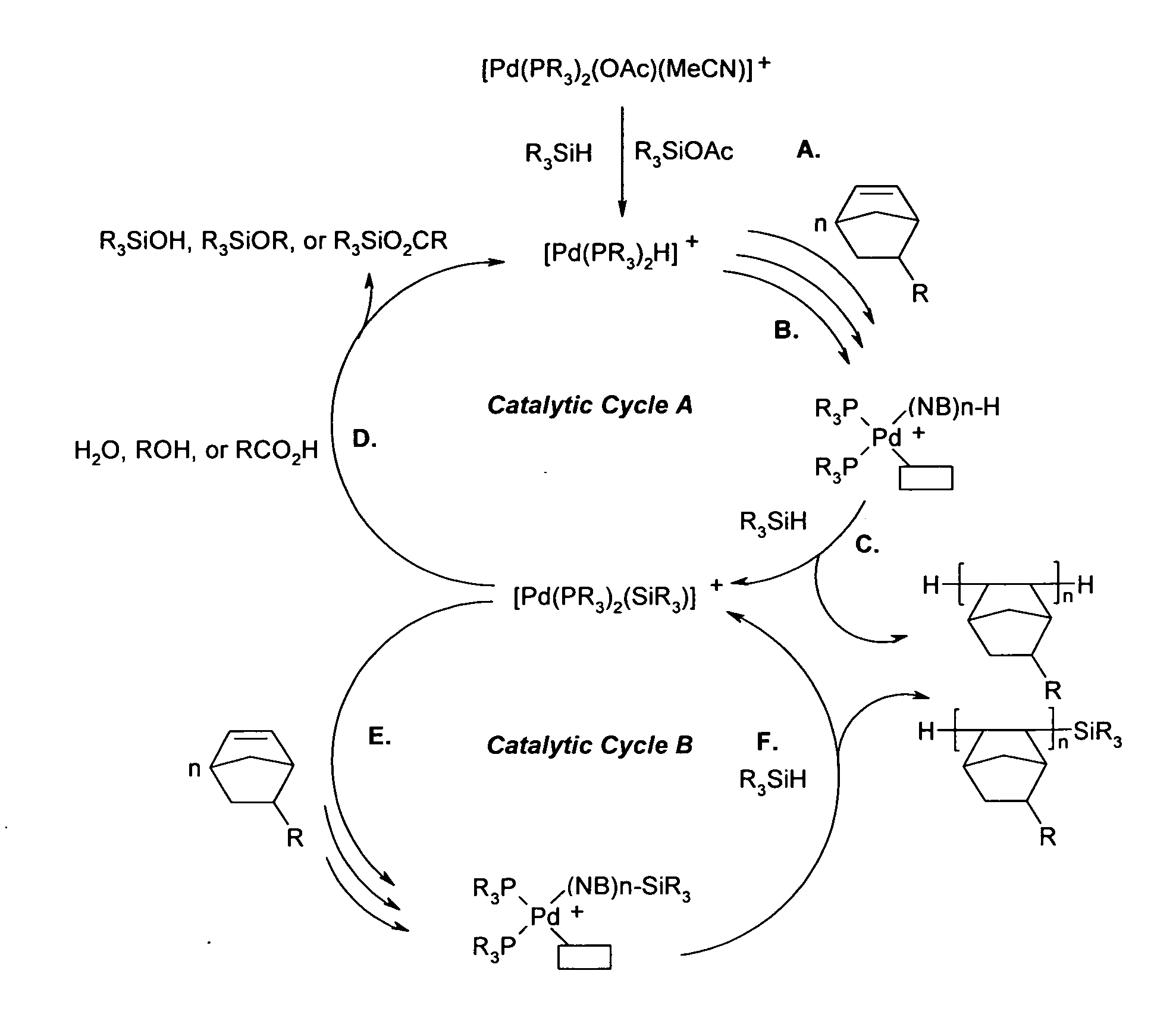
Vinyl addition polycylic olefin polymers prepared using non-olefinic chain transfer agents and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070066775A1Photosensitive material auxillary/base layersPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusMonomer compositionHydrogen
A method of polymerizing poly(cyclic)olefin monomers encompassing (a) combining a monomer composition containing the poly(cyclic)olefin monomers, a non-olefinic chain transfer agent and an activator compound to form a mixture; (b) heating the mixture; and (c) adding a polymerization catalyst containing Ni and / or Pd. The non-olefinic chain transfer agent includes one or more compounds selected from H2, alkylsilanes, alkylalkoxysilanes, alkylgermanes, alkylalkoxygermanes, alkylstannanes, and alkylalkoxystannanes. The activator is characterized as having an active hydrogen with a pKa of at least 5. The resulting poly(cyclic)olefin polymers can be used in photoresist compositions.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Surgical adhesive compostion and process for enhanced tissue closure and healing
InactiveUS20070092483A1Promotes cellPromotes tissue in-growthPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSynthetic polymeric active ingredientsPorositySide chain
A surgical tissue adhesive composition contains at least one 1,1-disubstituted electron-deficient olefin macromer. The adhesive composition of the invention has improved biocompatibility as well as controlled biodegradation characteristics and bioactivity. Adhesive co-monomer compositions contain at least one macromer with a pendant oligomer, polymer, or peptide chain as an acrylic ester of the reactive olefin. The polymers formed therefrom have a grafted brush-like nature. The composition is particularly useful for creating an adhesive bond at the junction of living tissue in surgical applications. The adhesive composition may further comprise co-monomer, co-macromer, cross-linker, or inter-penetrating polymer compounds containing peptide sequences that are bioactive or enzyme responsive. The peptide sequences are selected to promote tissue infiltration and healing in a particular biological tissue. The sequences may contain specific cell-adhesion, cell-signaling, and enzyme-cleavable domains. Furthermore, a degradable filler material may be included in the composition to create a reinforced composite. The filler preferably has a higher degradation rate than the polymer matrix, generating porosity upon degradation. The adhesive may further contain entrapped or incorporated drugs or biologics, including antibiotics or growth factors. The adhesive can be used to bind together the edges of living tissues during surgical procedures. The cured composition provides interfacial bonding and mechanical fixation while promoting tissue infiltration and replacement of the adhesive polymer.
Owner:POLLOCK POLYMER GROUP
Composition for porous organic film
InactiveUS20050025892A1Pretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic filmMonomer composition
The present invention provides a composition comprising the following (A) and (B): (A) at least one selected form the group consisting of an aromatic polymer having a repeating unit of the following formula (1) and a monomer having in the molecule at least two —C≡CH groups, (B) at least one selected form the group consisting of a heat transpirable compound and a heat decomposable compound:
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Electrolyte membrane for lithium battery, lithium battery using the electrolyte membrane, and method of preparing the electrolyte membrane
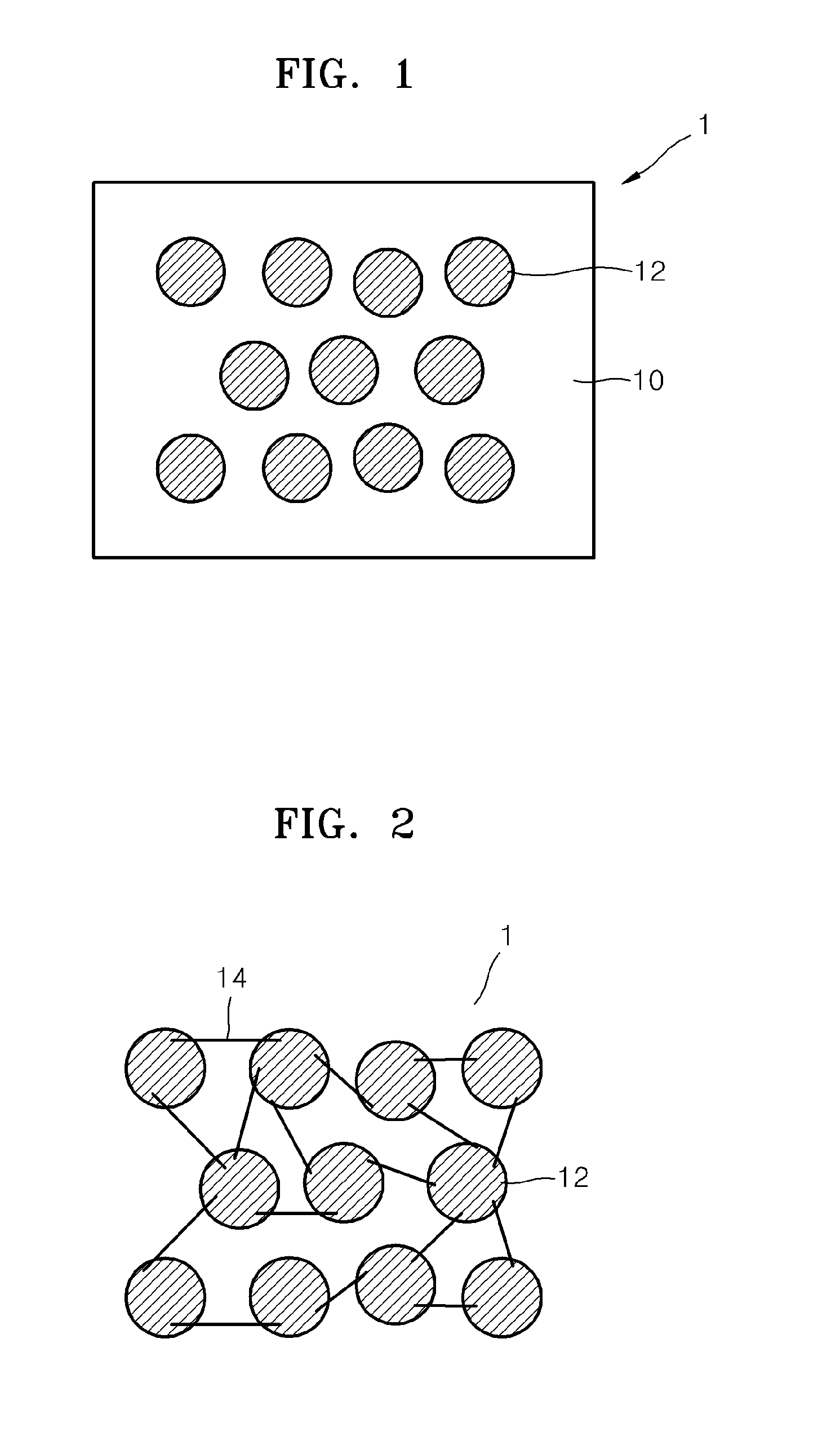
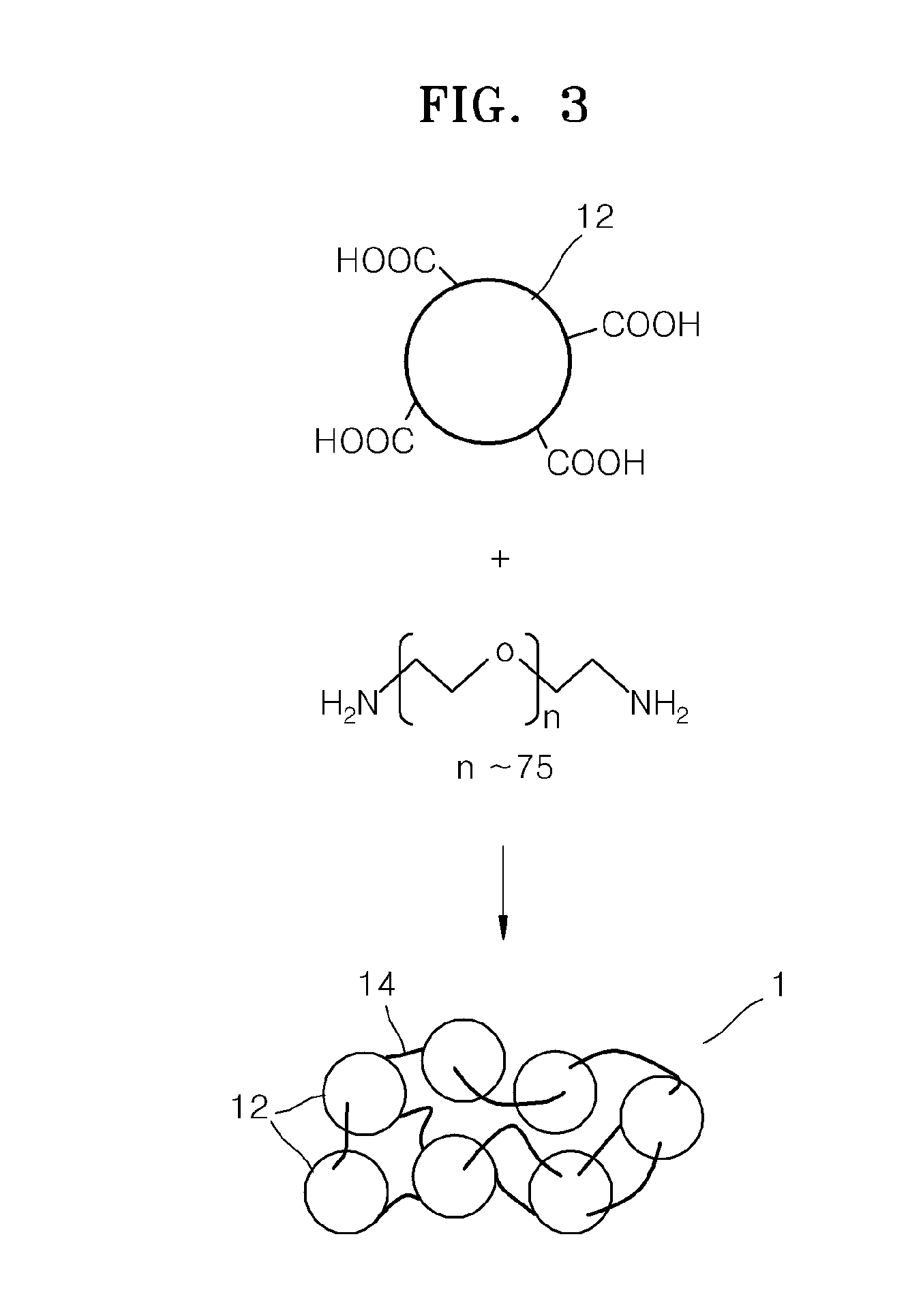
An electrolyte membrane for a lithium battery, the electrolyte membrane including: a matrix including a polymerization product of a (meth)acrylate monomer composition; and a porous metal-organic framework dispersed in the matrix, wherein the metal-organic framework includes a crystalline compound including a metal ion or metal ion cluster which is chemically bound to an organic ligand, and a liquid electrolyte including a lithium salt and a nonaqueous organic solvent.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Solid catalyst for olefin polymerization and process for producing olefin polymer with the same
InactiveUS6455647B1High activityNarrow molecular weight distributionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationSolid componentMonomer composition
The present invention relates to a solid catalyst (D) for olefin polymerization comprising a magnesium-containing solid component (A) carrying thereon an organoaluminum-oxy compound (B) and a metallocene compound (C), the magnesium-containing compound (A) being obtained by heat treating a magnesium compound represented by the general formula: MgX2.nH2O where X represents a halogen atom and n is an integer of 1 to 12, and to a method of producing an olefinic polymer using the catalyst. In the case where the above solid catalyst for olefin polymerization is used, catalyst activity, particularly activity per solid catalyst, is high. Therefore, a deashing treatment step such as catalyst removal can be omitted. Further, the olefinic polymer produced has a narrow molecular weight distribution, and in the case of a copolymer, its monomer composition is uniform.
Owner:MARUZEN PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Anion-exchange membrane and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20110281197A1Good alkali resistanceHigh ion exchange capacityIon-exchanger regenerationFinal product manufactureMonomer compositionQuaternary ammonium cation
Disclosed is an anion-exchange membrane which does not easily deteriorate even when used at high temperatures in a strong alkaline atmosphere. Also disclosed is a method for producing the anion-exchange membrane. The anion-exchange membrane is a microporous membrane which is composed of a water-insoluble resin and an anion-exchange resin filling the pores of the microporous membrane. The anion-exchange resin is composed of an anion-exchange resin wherein a quaternary ammonium salt group serving as an anion-exchange group is directly bonded to an aliphatic hydrocarbon chain, said anion-exchange resin being obtained by polymerizing and crosslinking a monomer composition which contains a crosslinking agent and a monomer component including a diallyl ammonium salt.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
Toner, toner production process and image forming method
InactiveUS6569589B2Improve charging effectSlightly affectedDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusMonomer compositionEngineering
Owner:CANON KK
Fluoropolymer aqueous hybrid compositions with improved film formation
The invention relates to aqueous fluoropolymer hybrid compositions made by a seeded emulsion polymerization process, having improved film formation properties. The seed is a fluoropolymer dispersion. At least two different monomer compositions are added sequentially to the seeded dispersion. These monomer compositions preferably include acrylic monomers. The first monomer composition is selected for miscibility with the fluoropolymer dispersion. The second monomer composition is selected to have a glass transition temperature (Tg) of less than 30° C. The final composition can be formulated to make coatings with a minimum film forming temperature (MFFT) of less than 5° C., and a maximum VOC of 50 g / liter. The composition is especially useful for coatings and films.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Gas-barrier laminate film and method for producing same, and image display device
InactiveUS20070231592A1Improve abilitiesImprove folding resistanceElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesMonomer compositionPhosphate
A method for producing a gas-barrier laminate film comprising at least one inorganic layer and at least one organic layer on a substrate film, which comprises forming the organic layer by polymerizing a monomer composition comprising an acrylate monomer having a phosphate ester group, a monomer having a phosphate ester group or their mixture. The produced gas-barrier laminate film maintains its excellent gas-barrier property even when folded.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Production of Propylene-Based Polymers
ActiveUS20090186995A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationMonomer compositionPolymer science
In a process for producing a propylene-based olefin homopolymer or copolymer, a monomer composition comprising propylene is contacted with a polymerization catalyst system under homogeneous polymerization conditions (such as solution, supersolution or supercritical conditions), wherein the polymerization catalyst system includes an activator and a bridged bis-indenyl transition metal (group 4) compound substituted with a carbazole (unsubstituted or substituted) at the 4 position.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Methods for forming coated high index optical elements
InactiveUS20090189303A1High indexMinimize occurrenceOptical articlesCoatingsMonomer compositionRefractive index
Disclosed is a method of forming a coated optical element. The method includes providing a mould assembly having opposed mould sections and applying a UV-curable hard coat monomer composition to the casting face of at least one of the mould sections to form a hard coat monomer layer. The hard coat layer is irradiated with UV radiation under conditions to form a partially cured hard coat layer. The assembled mould is filled with a high index optical element precursor material the optical element precursor material and the partially cured hard coat layer are cured to form a high index optical element having a hard coat.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION AUSTRALIA HO
Polyolefin-based adhesive resins and method of making adhesive resins
InactiveUS7064163B2Speed up the processReduce the amount requiredAdhesive processesMacromolecular adhesive additivesMonomer compositionPolyolefin
A method for producing polyolefin-based adhesive resins having improved physical and optical properties and the improved adhesive resins thereby produced, eliminates at least one reheating and melting of polyolefin polymer, comprises polymerizing a monomer composition of at least one olefin, mixing the polymerization product without pelletizing the polyolefin polymer with at least one graft polymer or copolymer in a heated mixing device at a temperature above the melting point of the components, and recovering the resulting polyolefin-based adhesive resin.
Owner:MSI TECH LLC
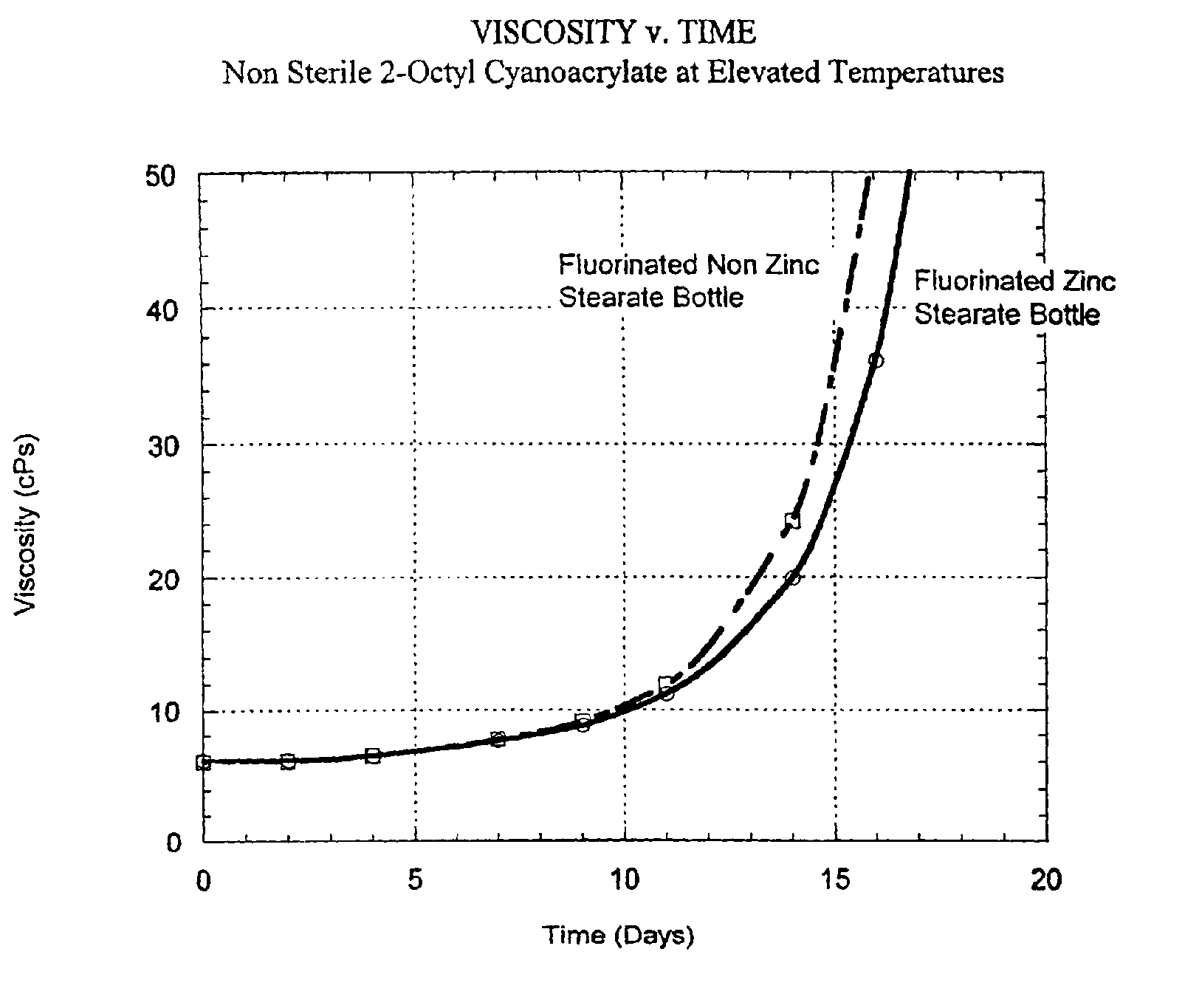
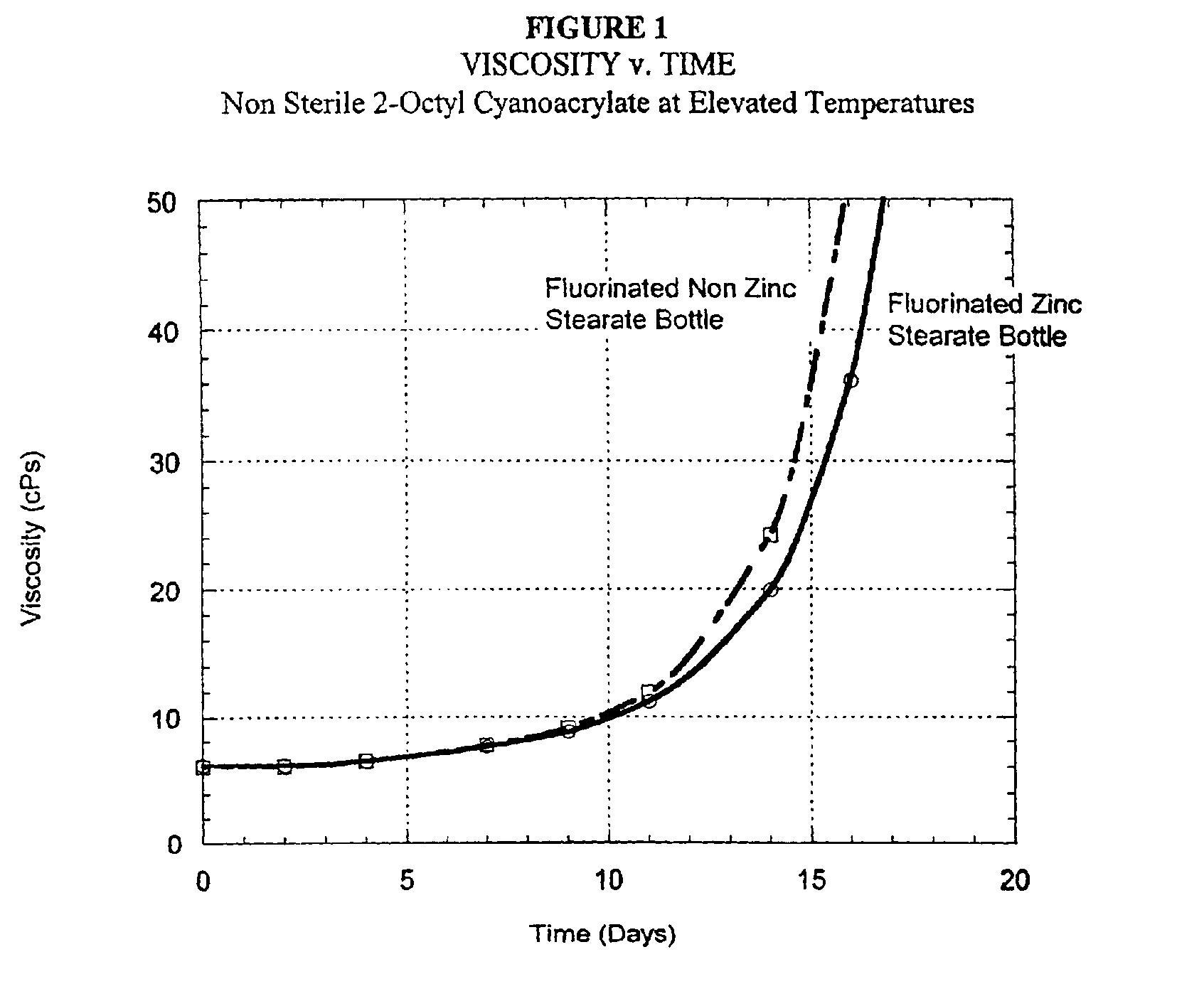
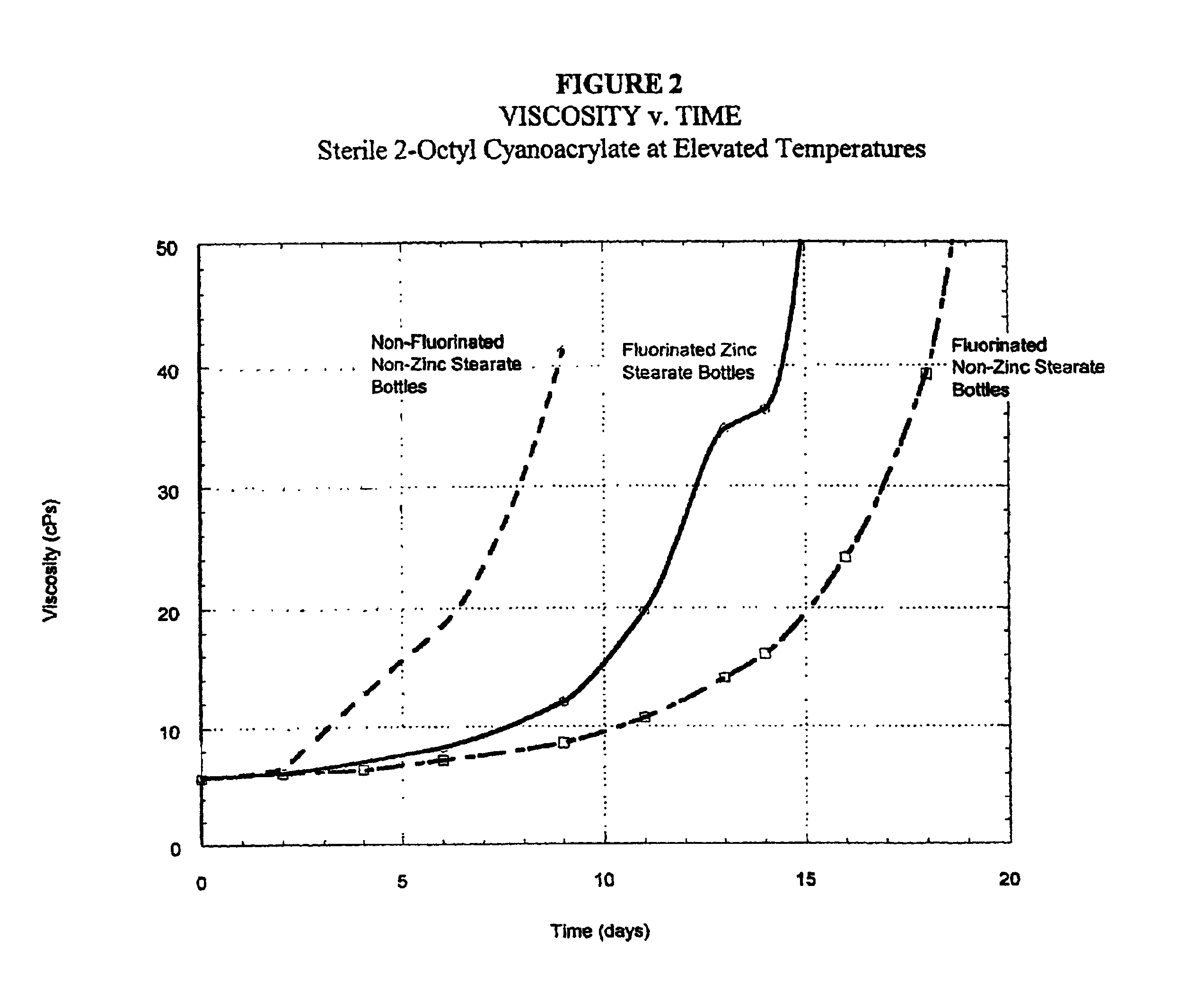
Halogenated polymeric containers for 1, 1-disubstituted monomer compositions
InactiveUS6896838B2Facilitated releaseEasy to moveWood working apparatusContainer/bottle contructionMonomer compositionAdhesive
A container made without employing a mold release agent, comprised of halogenated polymeric material provides an extended shelf-life for 1,1-disubstituted ethylene adhesive monomer compositions.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Curable encapsulant composition, device including same, and associated method
InactiveUS20060135705A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMonomer compositionElectronic component
An encapsulant for encapsulating electronic components and a method of making and / or using the encapsulant may be provided. An electronic device that includes the encapsulant may be provided. The curable encapsulant composition may include a mixture of a functionalized polymer and at least one reactive monomer composition. The reactive monomer composition may include a reactive monomer component that may be a low temperature solid and may be present in an amount in the reactive monomer composition a range of greater than about 20 weight percent based on the total weight of reactive monomer composition. The mixture, at about low temperature, may be solid or tack-free, or both solid and tack-free.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Pressure-sensitive adhesive compositions, pressure-sensitive adhesive sheets and surface protecting films
ActiveCN1749344AReduce pollutionPrevent static electricityFilm/foil adhesivesEster polymer adhesivesMonomer compositionAcid value
An adhesive combination comprises (methyl) acrylic acid series polymer and alkali metal salt, wherein the (methyl) acrylic acid series polymer takes the following compositions as monomer composition: 5 to 100 weight percent (methyl) acrylic acid alkylene oxide addition compound, 0 to 95 weight percent (methyl) acrylic acid series monomer of alkyl with one to fourteen carbon atoms except the addition compound and 0 to 95 weight percent other polymerizing monomer; moreover, the acid value of the (methyl) acrylic acid series polymer is less than ten. Therefore, the invention can provide an anti-static adhesive combination which can prevent an adherend receiving no destaticization from carrying static electricity during stripping, thereby reducing the pollution on the adherend and having high adhesion reliability; moreover, the invention also provides an anti-static adhesion slice class and surface protective film formed by the combination.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
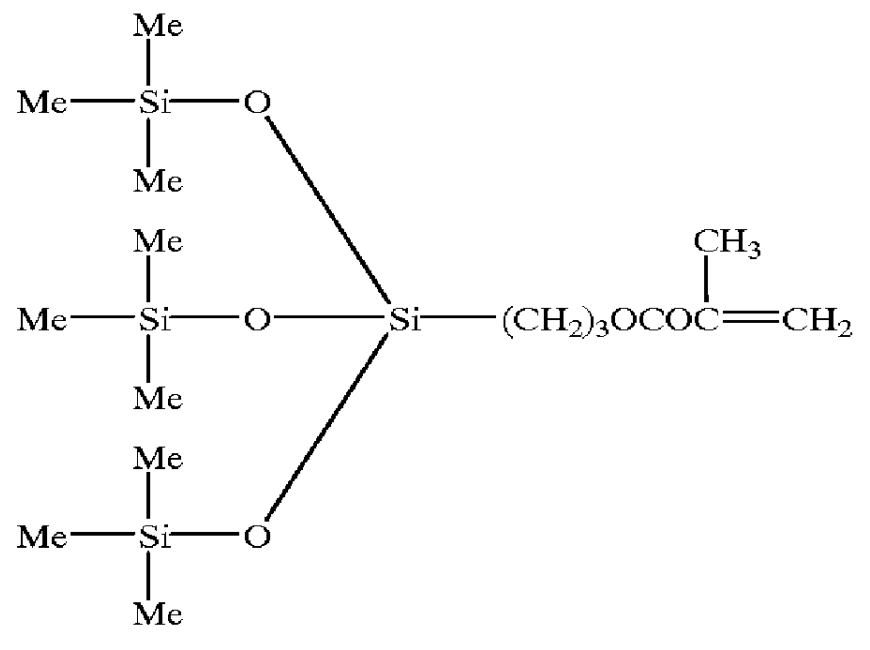
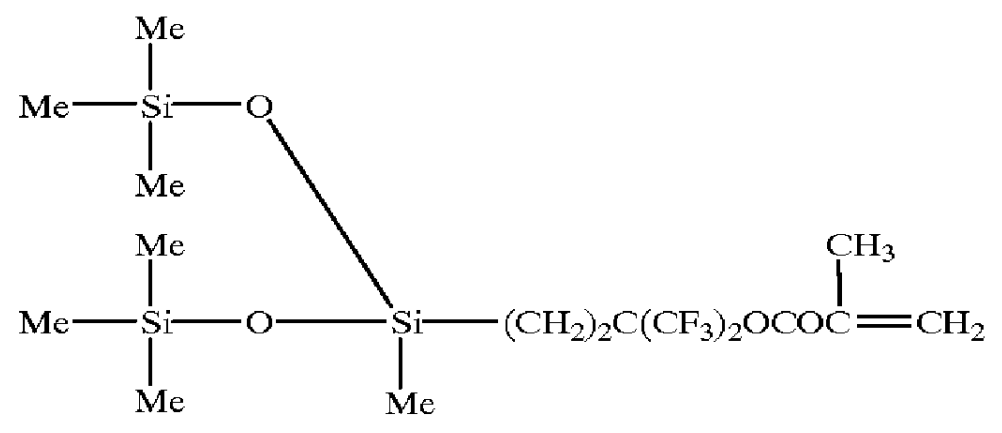
Siloxanyl-containing monomers
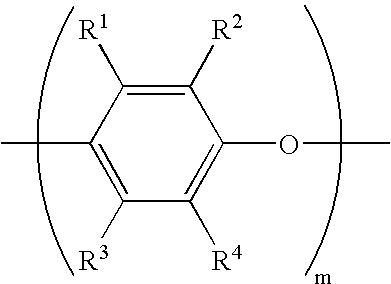
Monomers for polymers having high oxygen permeability, high water content and a low modulus of elasticity are provided, and polymers and ophthalmic lenses comprised of said monomers are provided. They are monomers represented by formula (1) or (2) below:X—O—(CH2CH2CH2O)m—(CH2)n—A (1)wherein, X is a polymerizable group having carbon-carbon unsaturated bonds; A is a siloxanyl group; R is H or a methyl group; m is an integer of 1 to 10; m′ is an integer of 2 to 10; and n is an integer of 2 to 10.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Production of propylene-based polymers
ActiveUS7812104B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationMonomer compositionPolymer science
In a process for producing a propylene-based olefin homopolymer or copolymer, a monomer composition comprising propylene is contacted with a polymerization catalyst system under homogeneous polymerization conditions (such as solution, supersolution or supercritical conditions), wherein the polymerization catalyst system includes an activator and a bridged bis-indenyl transition metal (group 4) compound substituted with a carbazole (unsubstituted or substituted) at the 4 position.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Golf balls with cores or intermediate layers prepared from highly-neutralized ethylene copolymers and organic acids
Disclosed are golf balls comprising cores or intermediate layers prepared from thermoplastic compositions having coefficients of restitution equal to or greater than 0.83 and PGA compressions greater than 100. Also disclosed is a composition comprising or prepared from (a) at least one aliphatic, mono-functional organic acid having from 16 to 20 carbon atoms, wherein the organic acid is unsaturated and linear; (b) an ethylene acid copolymer consisting essentially of copolymerized comonomers of ethylene and from 18 to 24 weight % of copolymerized comonomers of at least one C3 to C8 α,β ethylenically unsaturated carboxylic acid, based on the total weight of the ethylene acid copolymer, having a melt index from about 200 to about 600 g / 10 minutes; wherein the combined acid moieties of (a) and (b) are nominally neutralized to a level from about 120% to about 200%; and optionally (c) filler.
Owner:PERFORMANCE MATERIALS NA INC
Olefin polymer and production processes thereof
InactiveUS6838540B2Narrow molecular weight distributionHigh polymerization activityMonomer compositionPolymer science
The present invention provides an olefin polymer having a narrow molecular weight distribution and a specific molecular weight, an olefin polymer having a functional group introduced at the terminal, a tapered polymer containing a segment wherein monomer composition continuously changes in the polymer chain, an olefin polymer having different segments which are bonded to each other, and a process for preparing these polymers. The olefin polymers of the invention are polymers of olefins of 2 to 20 carbon atoms and have a number-average molecular weight of not less than 500 and Mw / Mn of not more than 1.5. In the process for preparing an olefin polymer, an olefin of 2 to 20 carbon atoms is polymerized in the presence of an olefin polymerization catalyst comprising a transition metal compound represented by, for example, the following formula (I):LmMXn (I)wherein M is a transition metal atom of Group 3 to Group 11 of the periodic table, m is 1 to 5, n is a number satisfying a valence of M, L is a ligand coordinated to the central metal M and is a ligand containing a heteroatom having no direct bond to the central metal, and X is a halogen atom, a hydrocarbon group or the like.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Golf balls with cores or intermediate layers prepared from highly-neutralized ethylene copolymers and organic acids
InactiveUS8044136B2Synthetic resin layered productsAbsorbent padsOrganic acidCoefficient of restitution
Owner:PERFORMANCE MATERIALS NA INC
Golf balls with cores or intermediate layers prepared from highly-neutralized ethylene terpolymers and organic acids
Described are golf balls comprising cores or intermediate layers prepared from thermoplastic compositions having coefficients of restitution equal to or greater than 0.83 and PGA compression greater than 100. Also described is a composition comprising or prepared from (a) at least one aliphatic, mono-functional organic acid having from 16 to 20 carbon atoms, wherein the organic acid is unsaturated and linear; (b) an ethylene acid copolymer consisting essentially of copolymerized comonomers of ethylene and from 18 to 24 weight % of copolymerized comonomers of at least one C3 to C8 α,β ethylenically unsaturated carboxylic acid, based on the total weight of the ethylene acid copolymer, having a melt index from about 200 to about 600 g / 10 minutes; wherein the combined acid moieties of (a) and (b) are nominally neutralized to a level from about 120% to about 200%; and optionally (c) filler.
Owner:PERFORMANCE MATERIALS NA INC
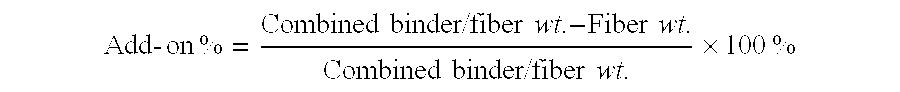
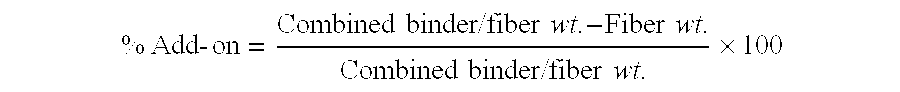
High strength polyvinyl acetate binders
InactiveUS20070184732A1Excellent tensile strength performanceEasy curingFibre treatmentSynthetic resin layered productsMonomer compositionEmulsion
A binder composition for fibrous substrates that includes a low-pressure polymerized emulsion resin comprising vinyl acetate monomer units and post-crosslinking monomer composition. The inventive compositions enable fibrous substrates with high tensile strengths and excellent curability, and are particularly useful as binders in synthetic fiberfill applications.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Method for Chemically Modifying the Internal Region of a Hair Shaft
InactiveUS20120180807A1Low variabilitySimplification of processCosmetic preparationsHair removalMonomer compositionMedicine
A method for chemically modifying the internal region of a hair shaft. The method comprises applying an oxidising formulation to the hair; de-wetting the hair; applying a monomer composition to the hair, wherein the monomer composition comprises an ethylenic monomer having a molecular weight of 500 g / mole or less and a cosmetically acceptable carrier. Also a kit which comprises: application instructions comprising the method; and the monomer composition.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Surface active agent containing fluorine and coating compositions using the same
InactiveUS6156860AImprove the level ofTransportation and packagingMixingMonomer compositionPolymer science
The invention provides a surface active agent containing fluorine, which is a copolymer composed of several ethylenic unsaturated monomers containing a fluorinated alkyl group, a silicone chain, and a polyoxyalkylene group, and the surface loss energy of which is less than 110x10-5 mJ in an organic solvent. The copolymer of the surface active agent is soluble to water and in various organic solvents, and has a good compatibility with other ingredients used to form the coating compositions. The present surface active agent reduces the dynamic surface tension of the coating composition, and thereby, have a good foam-preventing property, coating compositions containing the present surface active agent yield coated films with uniform and smooth level surfaces without forming irregularity and striation even by coating operations at high speed and high shearing force.
Owner:DAINIPPON INK & CHEM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com