Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Quantum dot lasers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
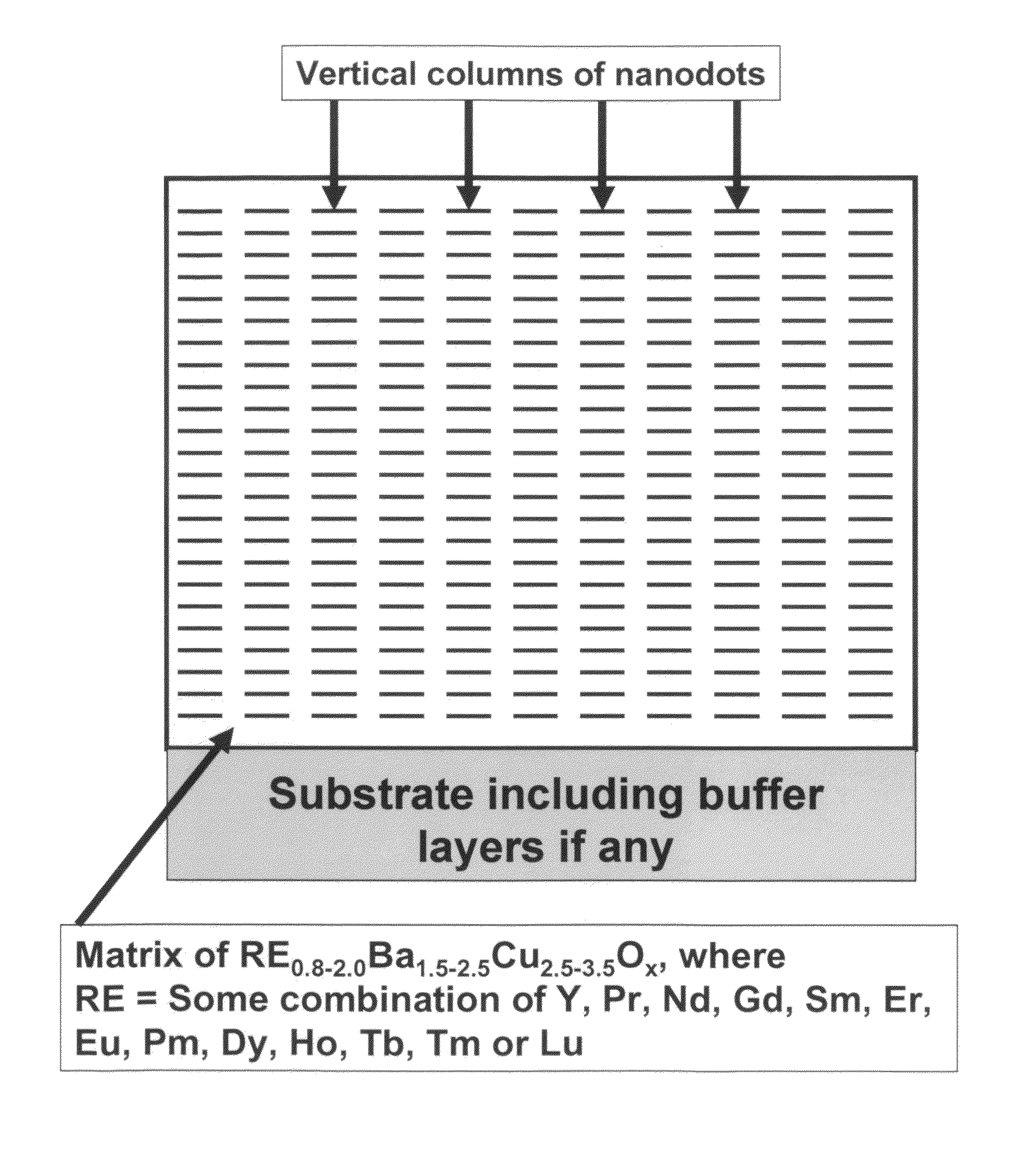
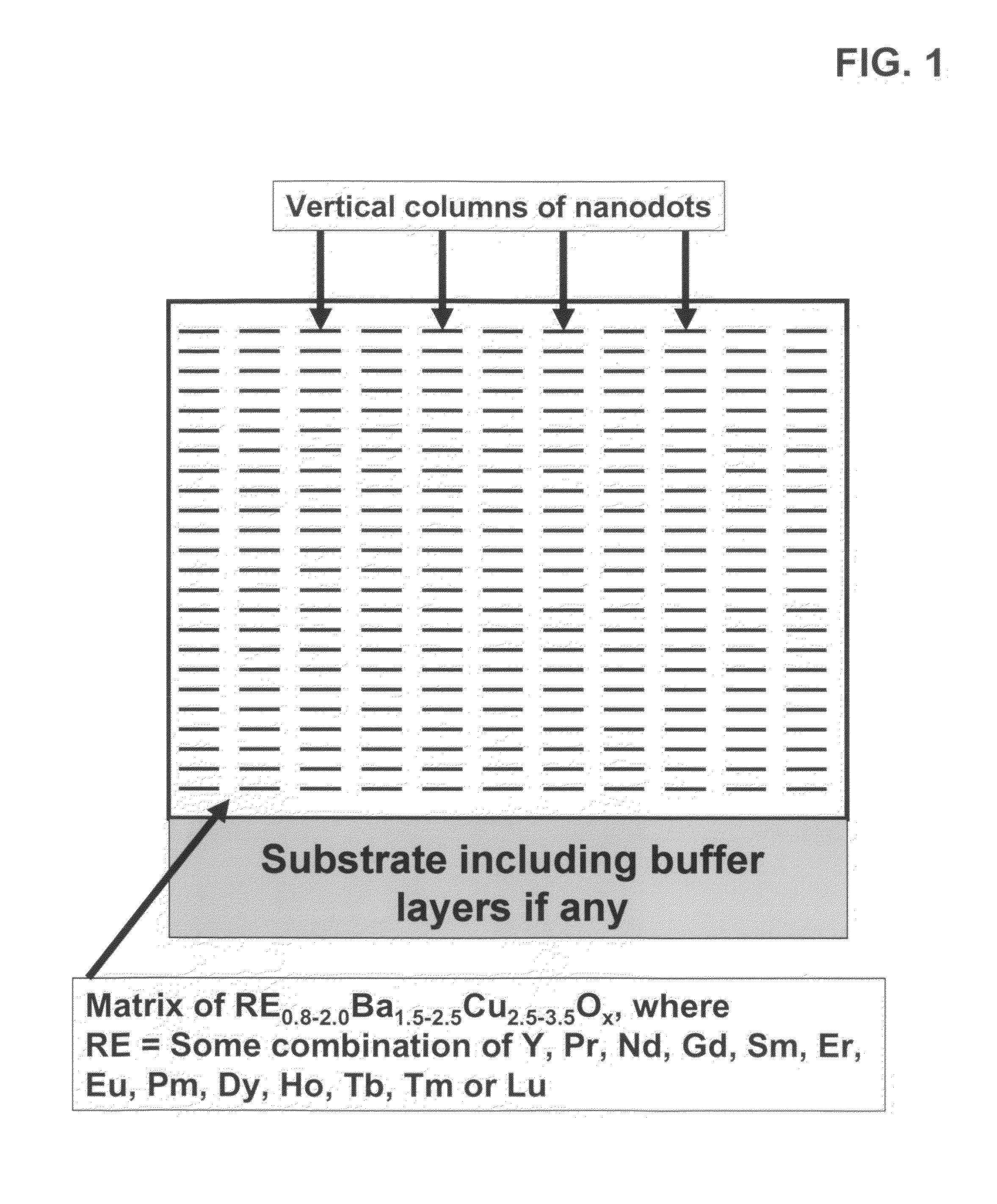
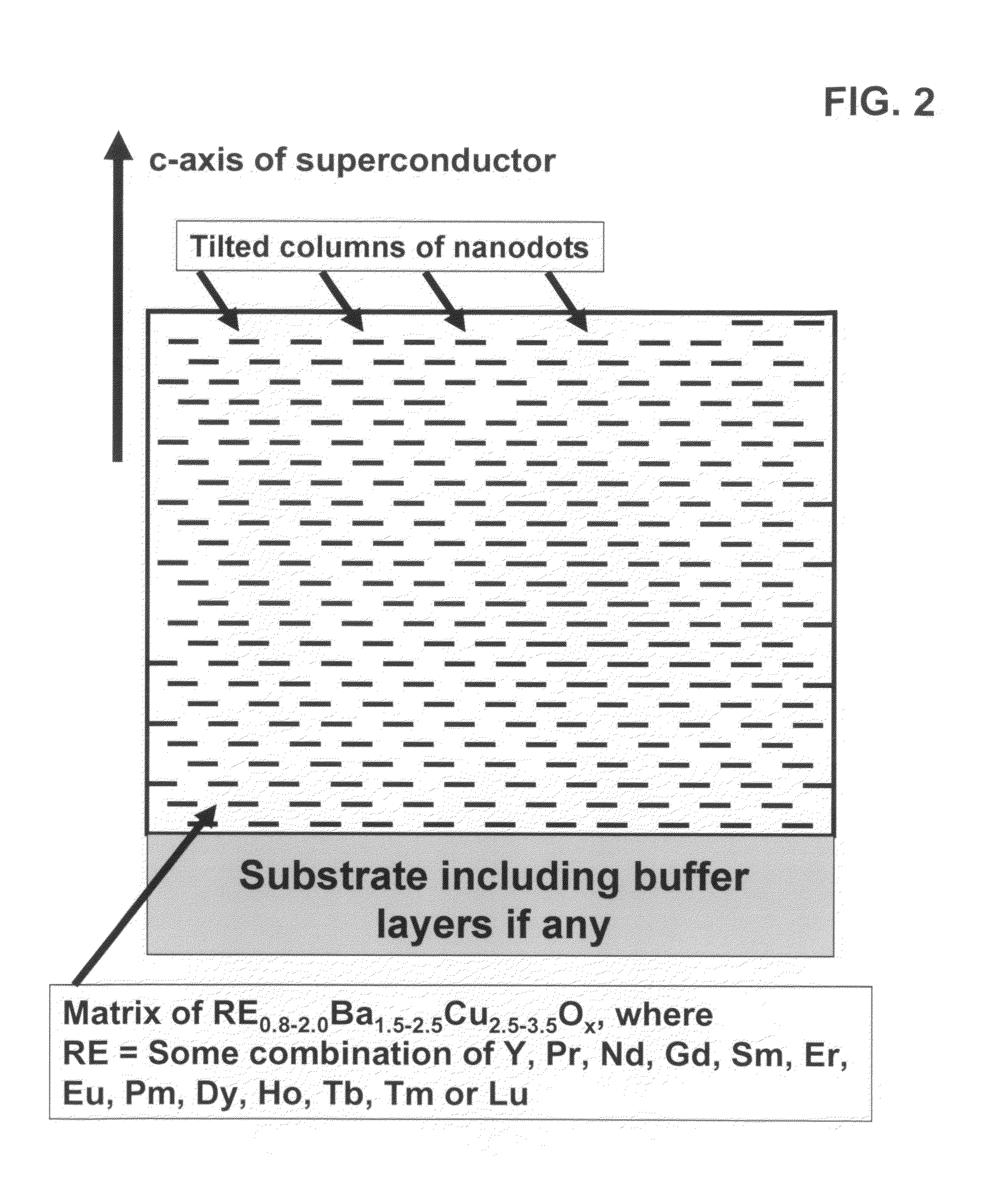
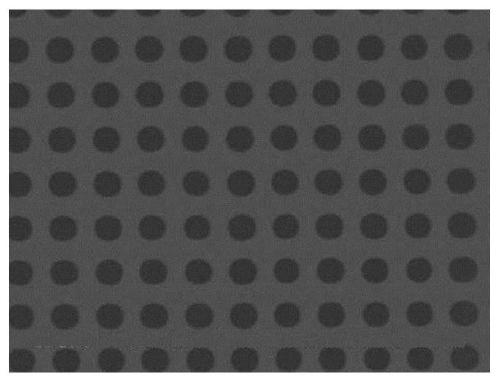
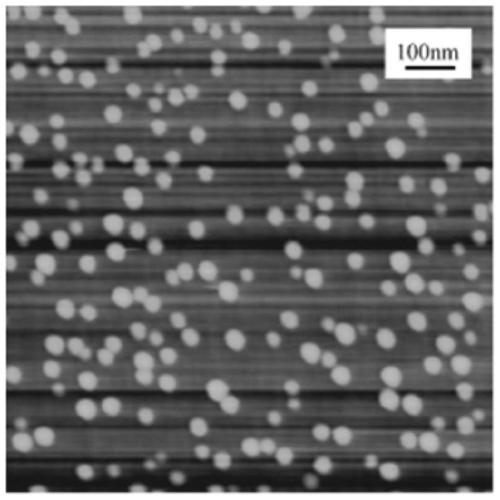
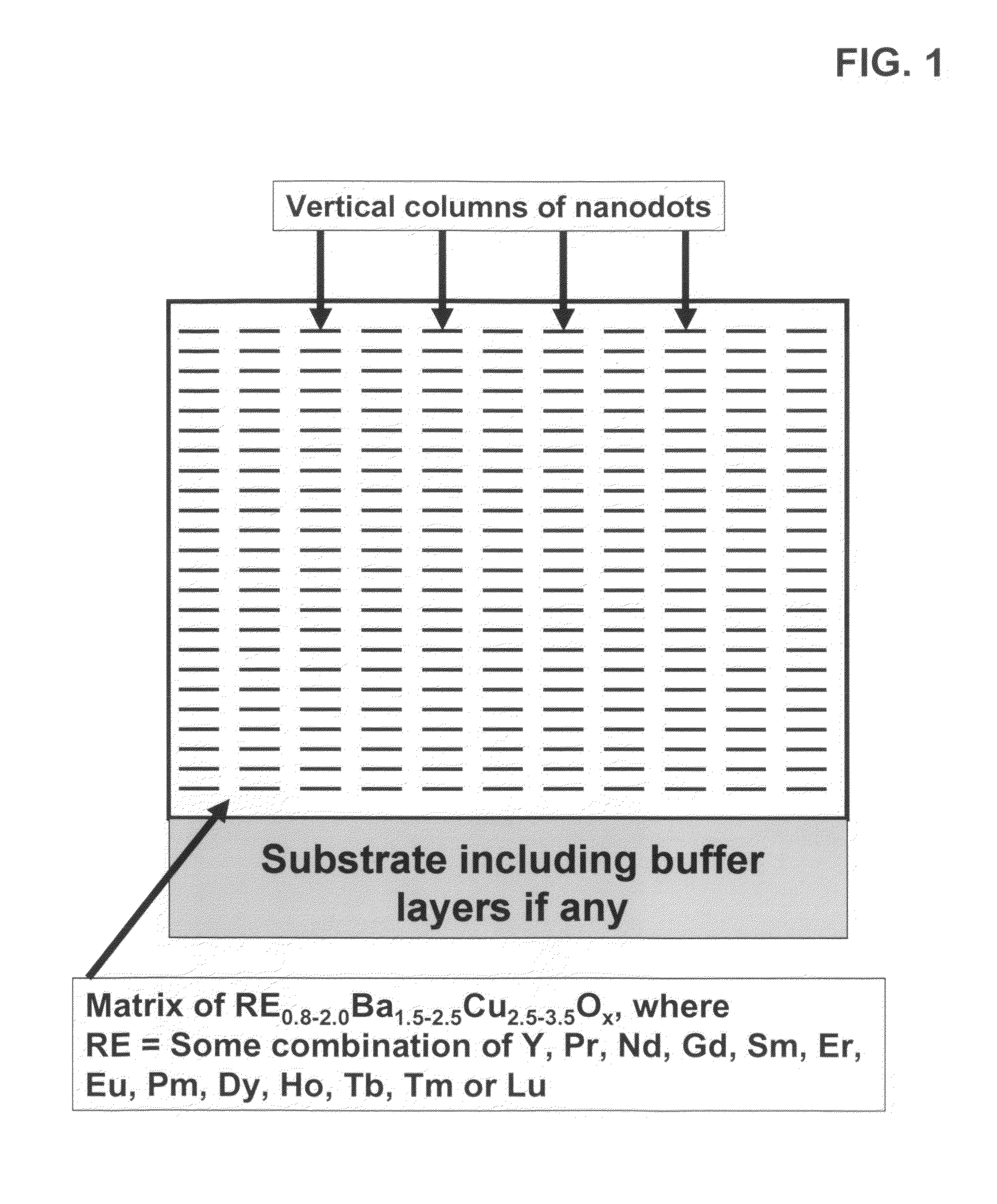
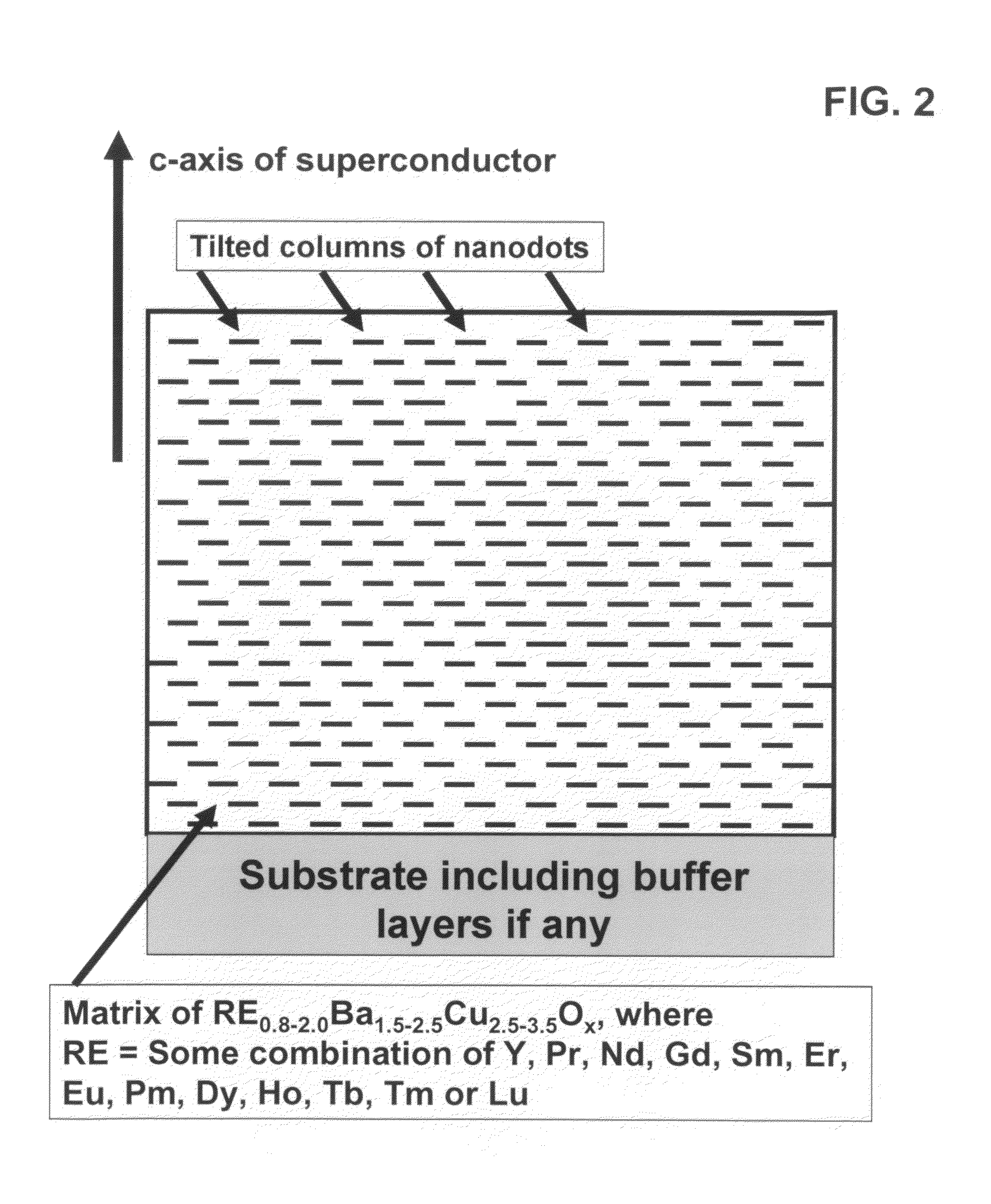
High performance devices enabled by epitaxial, preferentially oriented, nanodots and/or nanorods
ActiveUS20080176749A1Improve performanceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionNanodotPhotoluminescence
Novel articles and methods to fabricate same with self-assembled nanodots and / or nanorods of a single or multicomponent material within another single or multicomponent material for use in electrical, electronic, magnetic, electromagnetic, superconducting and electrooptical devices is disclosed. Self-assembled nanodots and / or nanorods are ordered arrays wherein ordering occurs due to strain minimization during growth of the materials. A simple method to accomplish this when depositing in-situ films is also disclosed. Device applications of resulting materials are in areas of superconductivity, photovoltaics, ferroelectrics, magnetoresistance, high density storage, solid state lighting, non-volatile memory, photoluminescence, thermoelectrics and in quantum dot lasers.
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
<100> or 45 degrees-rotated <100>, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices
InactiveUS20110062446A1Good lattice matchingSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHard disc drivePhotoluminescence
Novel articles and methods to fabricate the same resulting in flexible, {100}<100> or 45°-rotated {100}<100> oriented, semiconductor-based, electronic devices are disclosed. Potential applications of resulting articles are in areas of photovoltaic devices, flat-panel displays, thermophotovoltaic devices, ferroelectric devices, light emitting diode devices, computer hard disc drive devices, magnetoresistance based devices, photoluminescence based devices, non-volatile memory devices, dielectric devices, thermoelectric devices and quantum dot laser devices.
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
Semiconductor-based large-area flexible electronic devices
InactiveCN101981699AFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHard disc drivePhotoluminescence
Novel articles and methods to fabricate the same resulting in flexible, {100}<100> or 45 DEG -rotated {100}<100> oriented, semiconductor-based, electronic devices are disclosed. Potential applications of resulting articles are in areas of photovoltaic devices, flat-panel displays, thermophotovoltaic devices, ferroelectric devices, light emitting diode devices,, computer hard disc drive devices, magnetoresistance based devices, photoluminescence based devices, non-volatile memory devices, dielectric devices, thermoelectric devices and quantum dot laser devices.
Owner:阿米特·戈亚尔
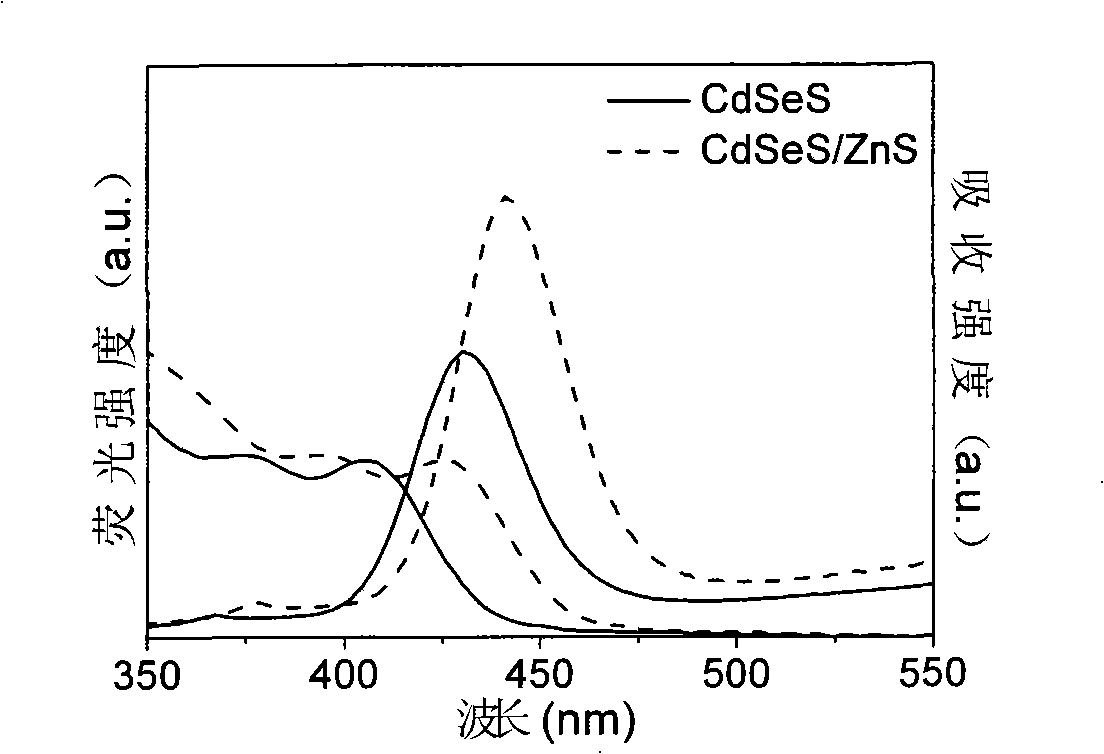
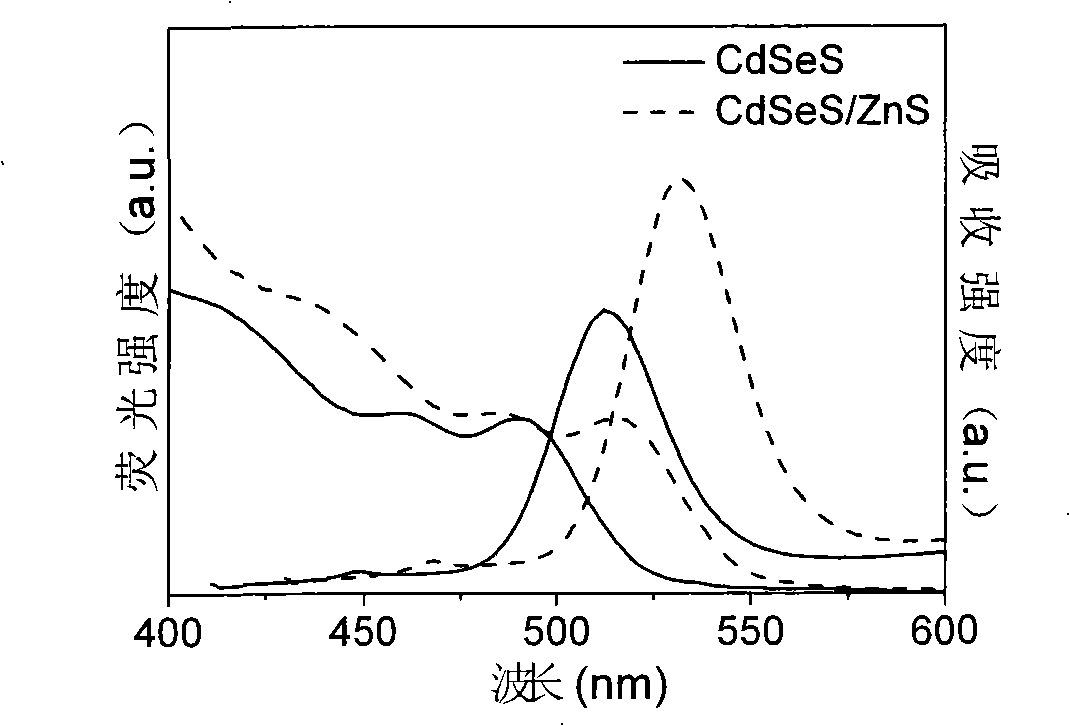
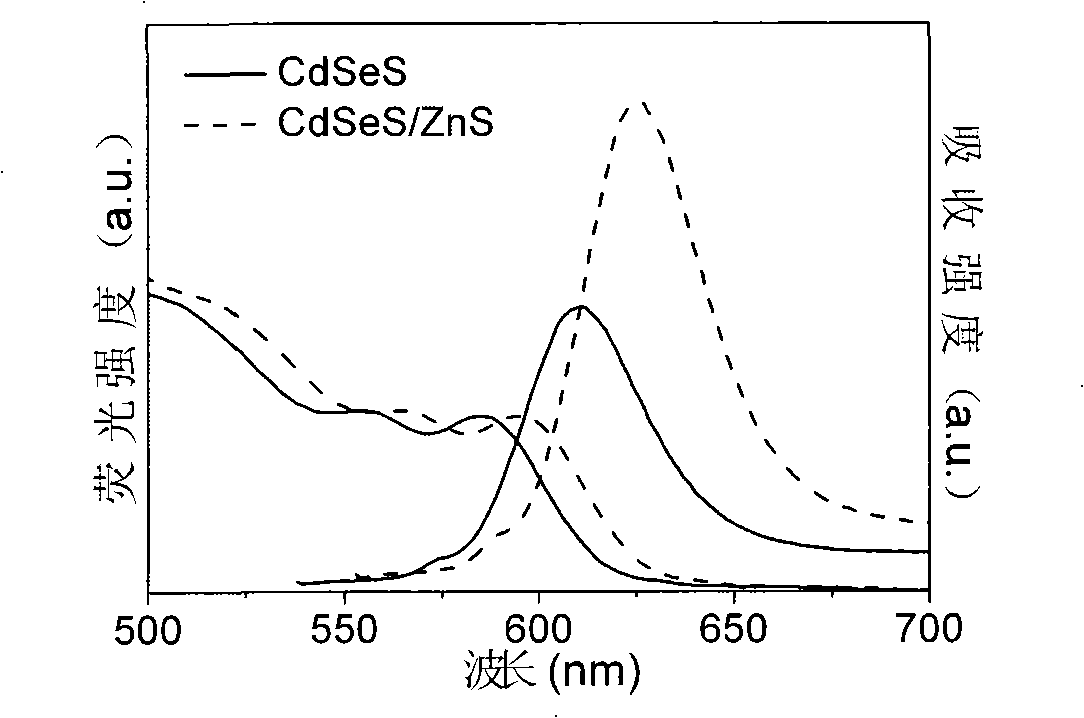
Production method for CdSeS and CdSeS/ZnS core-shell type quantum point
InactiveCN101319139AStrong fluorescenceImprove stabilityLuminescent compositionsLong chain fatty acidFluorescence
The present invention discloses a method for preparing CdSeS and CdSeS / ZnS core-shell quantum dots, belonging to the semiconductor nanometer luminescent material technical field. The method is to dissolves Cd0 or Cd salt with a long chain fatty acid to obtain a precursor solution of Cd; a Se powder and a S powder are respectively dissolved in liquid paraffin to form a precursor mixed solution of Se and S after mixing; the precursor solution of Cd is reacted with the precursor mixed solution of Se and S to give a CdSeS quantum dot solution; Zn salt is used as a precursor of Zn for incrustation, (TMS)2S is selected as a precursor of S for incrustation, and thus a ZnS shell precursor solution is obtained, which is reacted with the CdSeS quantum dot solution to give a CdSeS / ZnS quantum dot solution; the quantum dot solution is purified to obtain the CdSeS and CdSeS / ZnS core-shell quantum dots. The fluorescence quanta is high in yield, uniform in size distribution, and good in stability, and can be applied to creature tags, illuminator members and quantum dot lasers.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
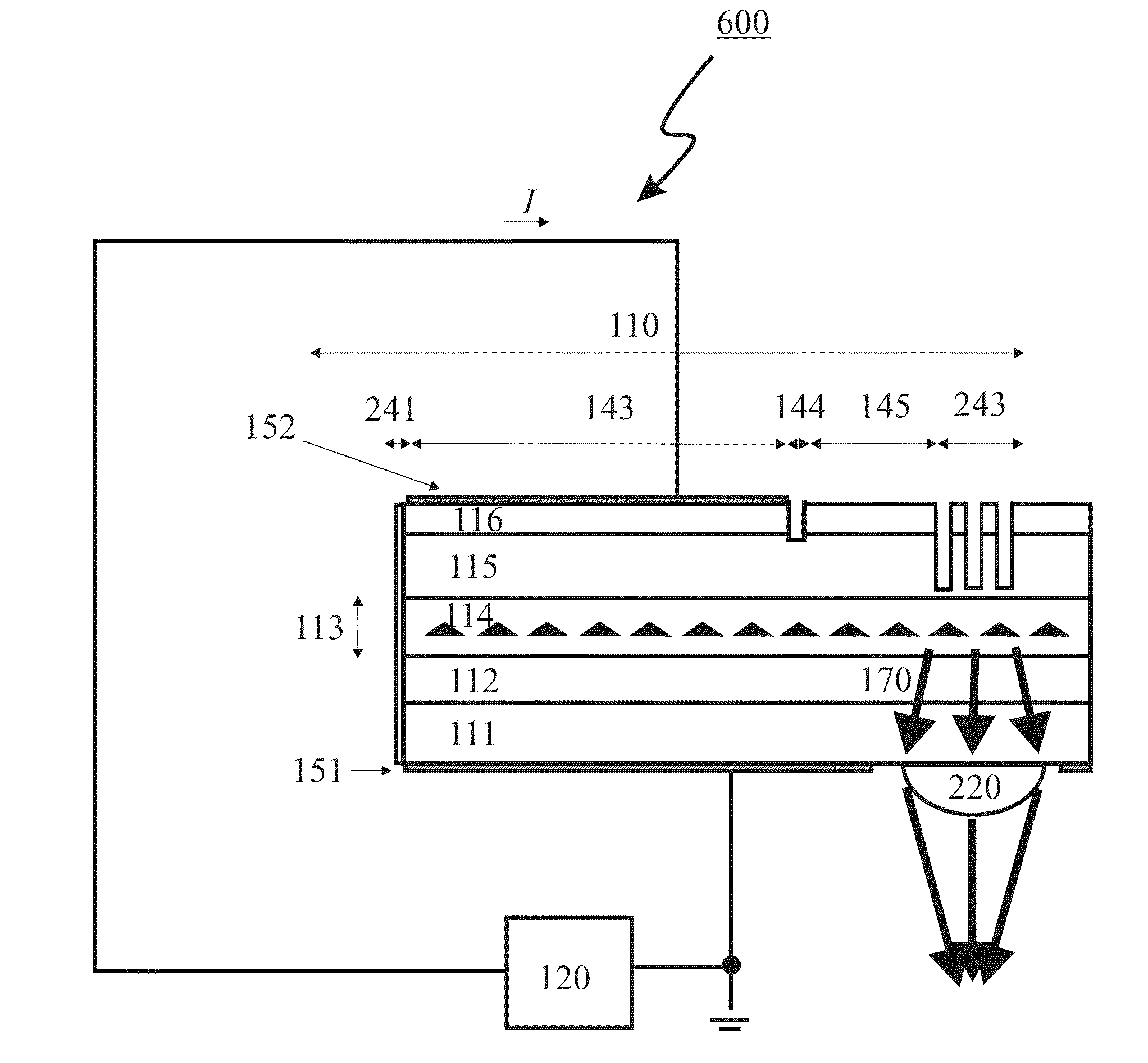
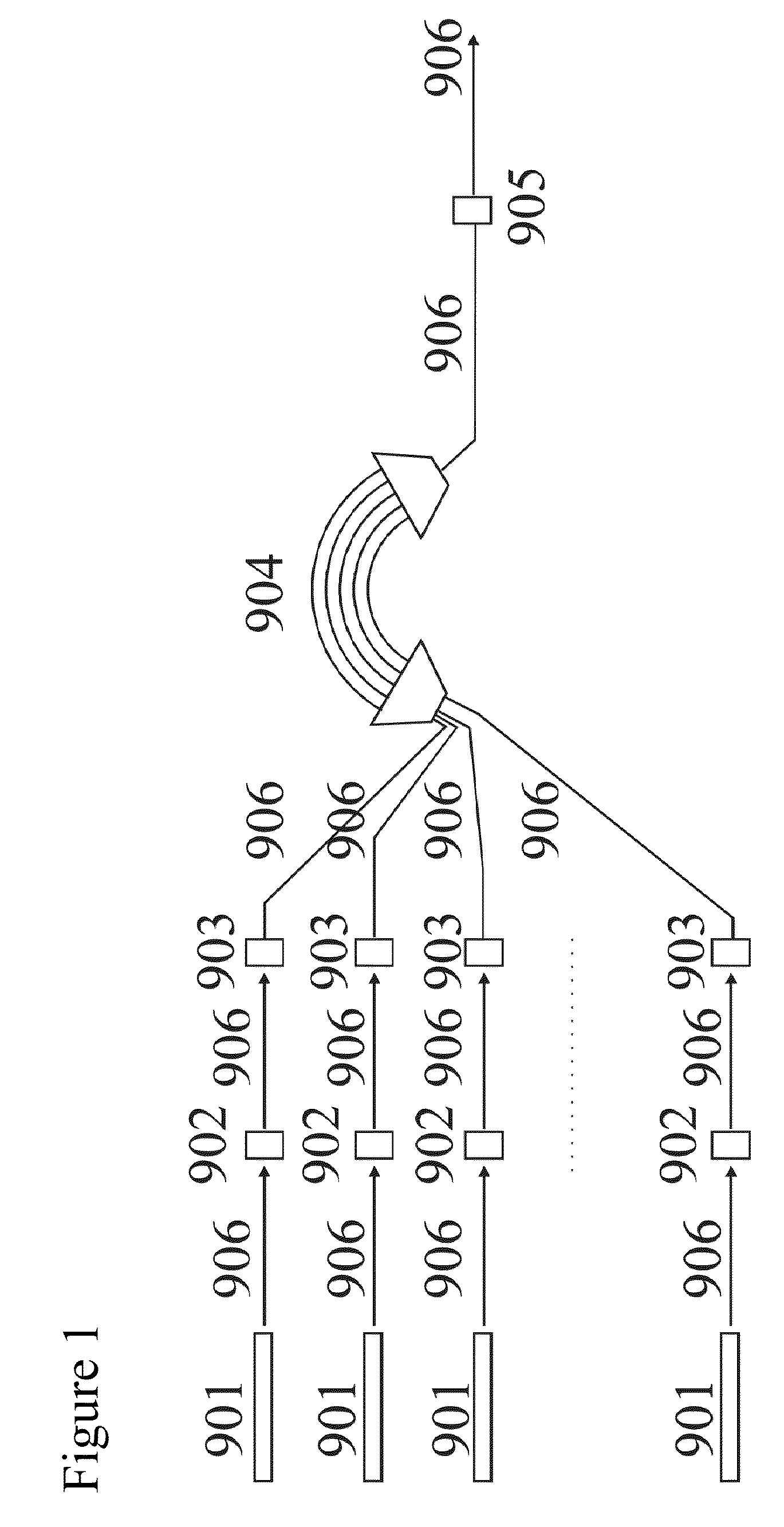
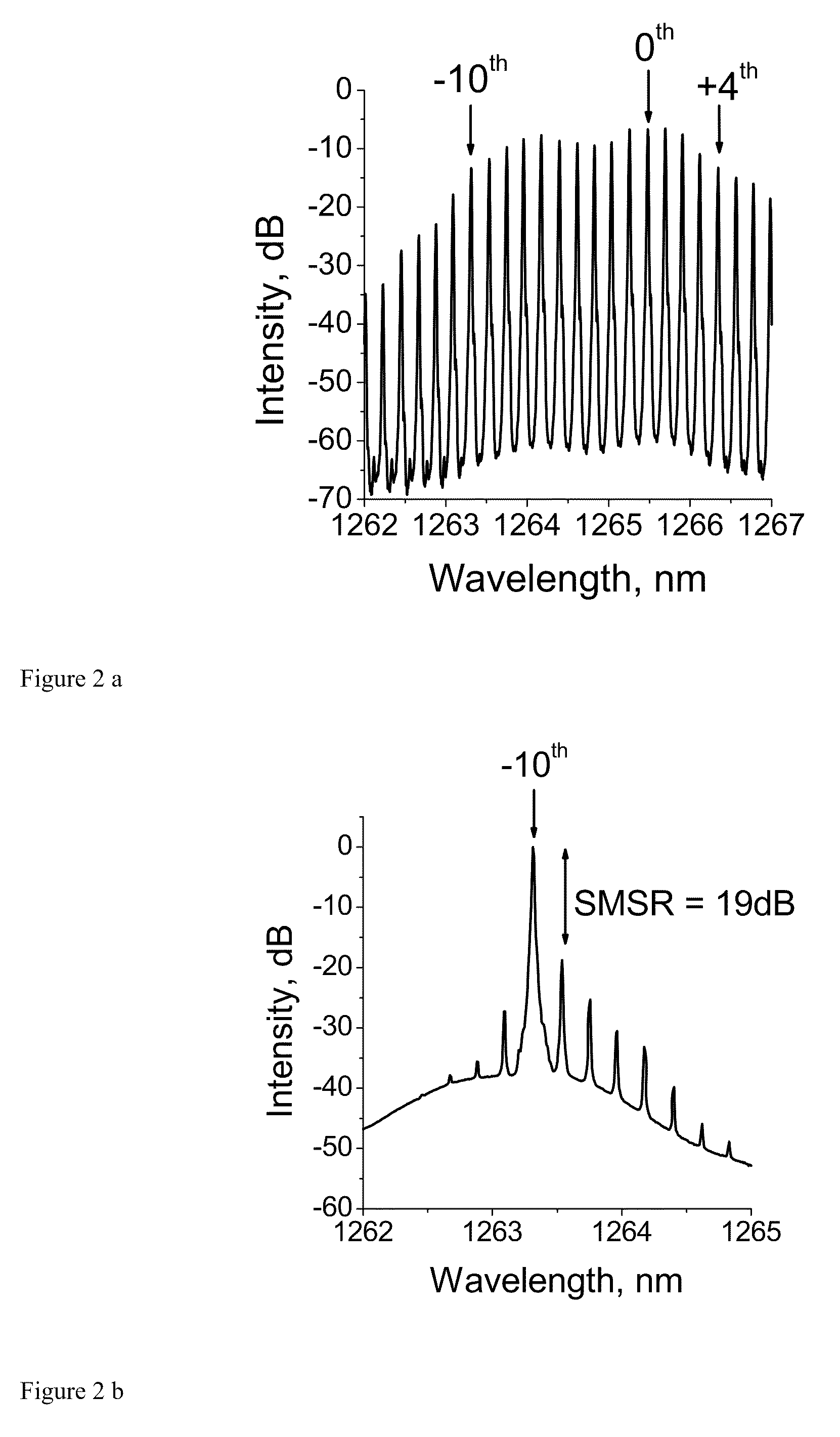
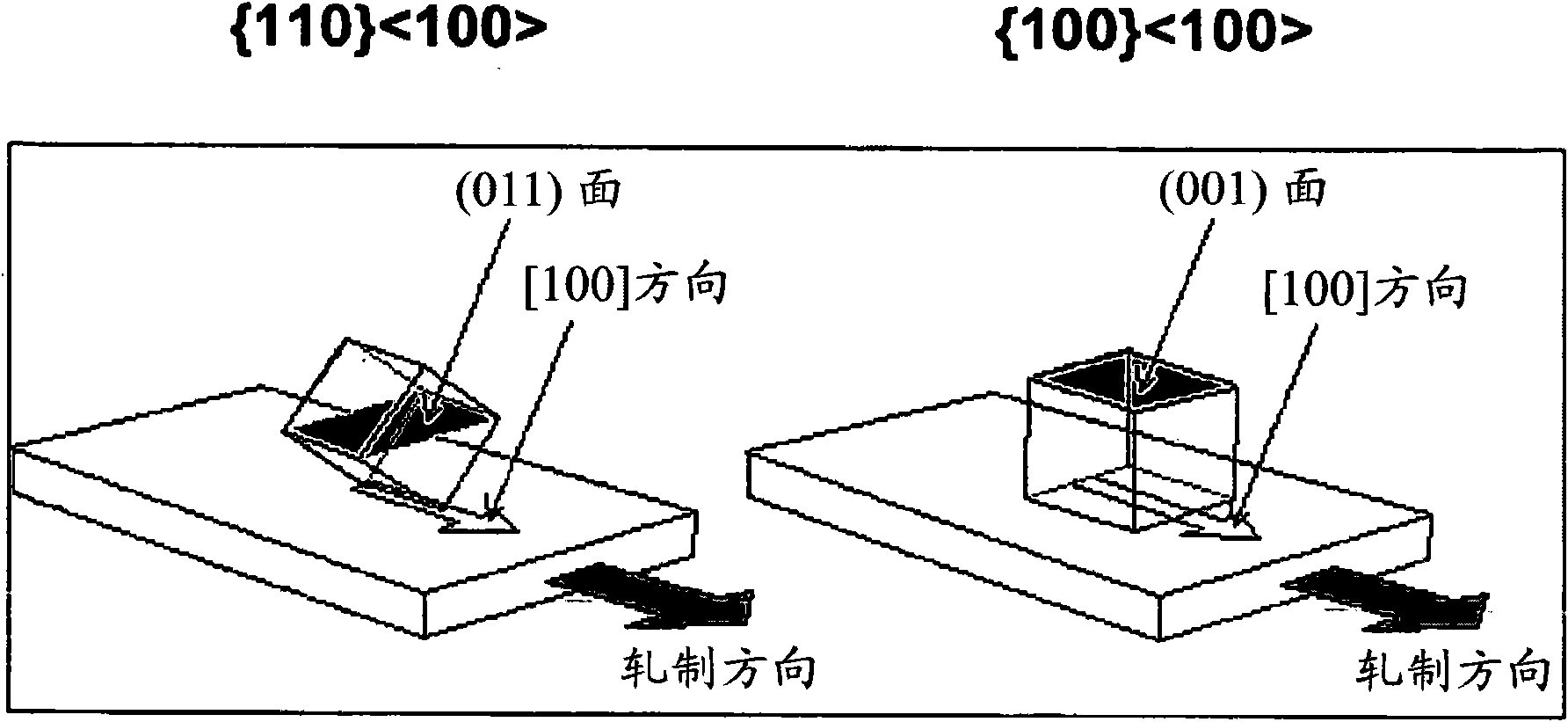
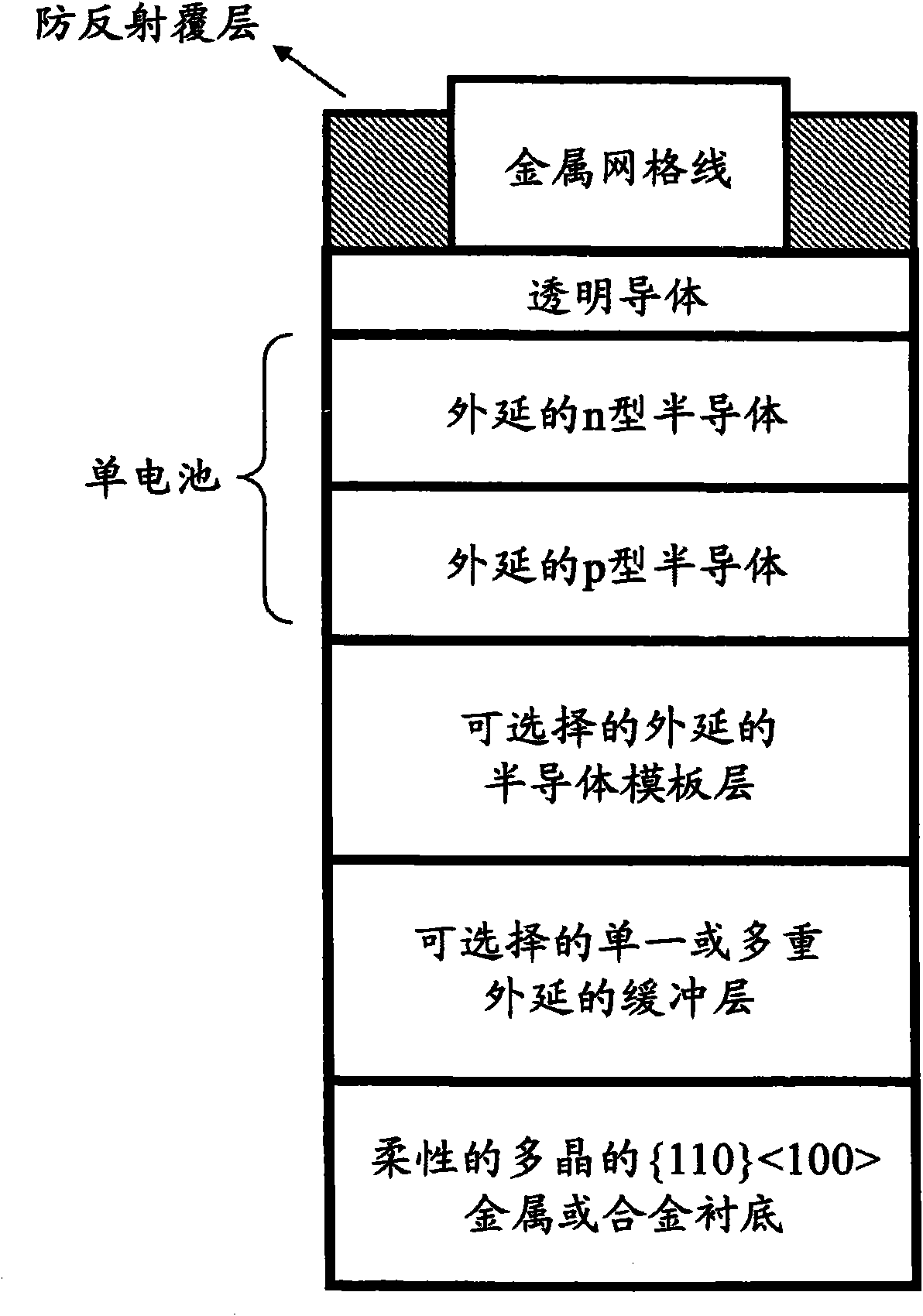
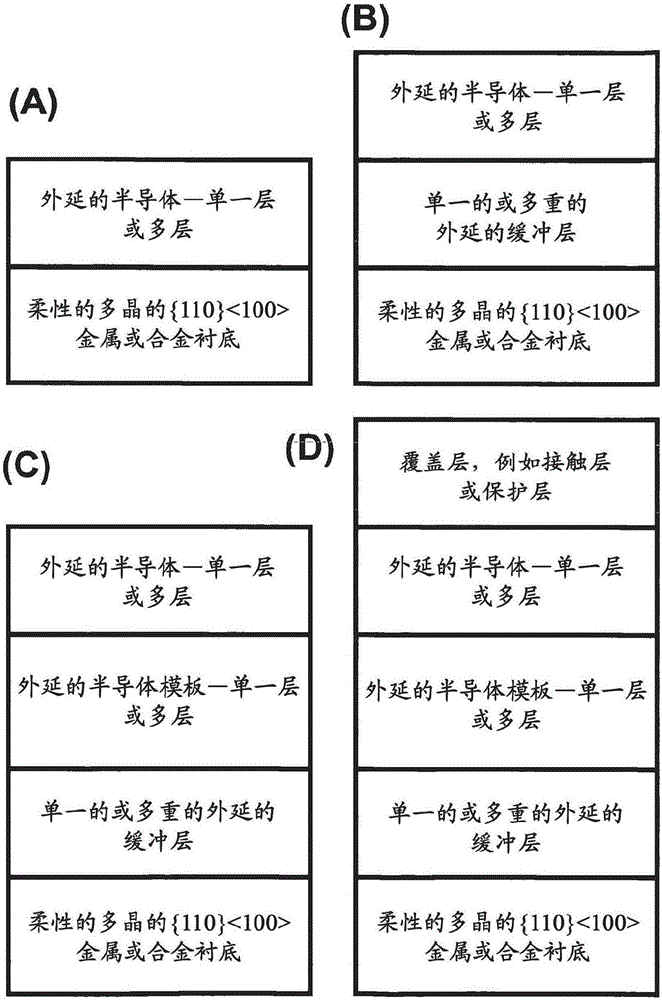
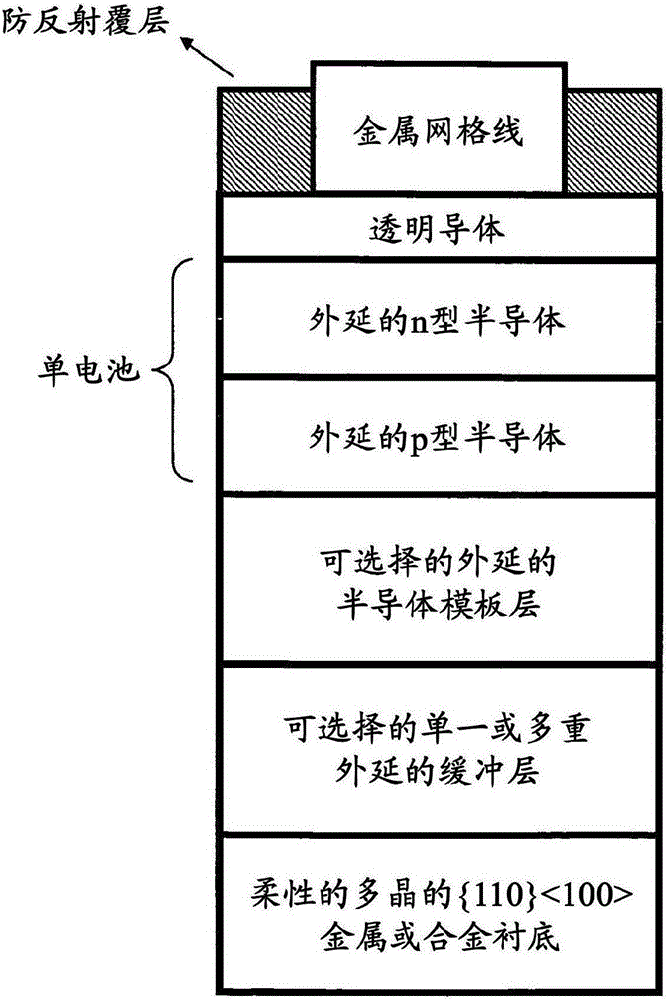
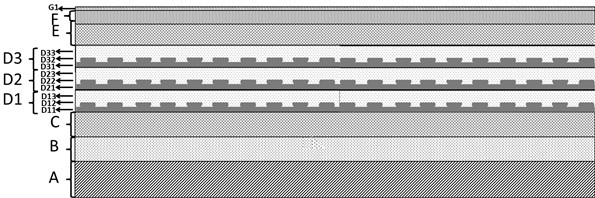
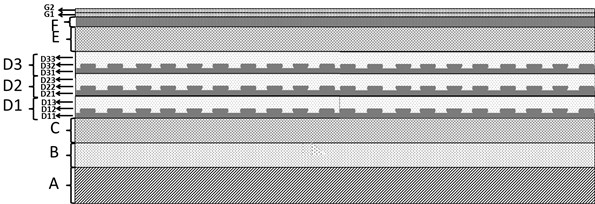
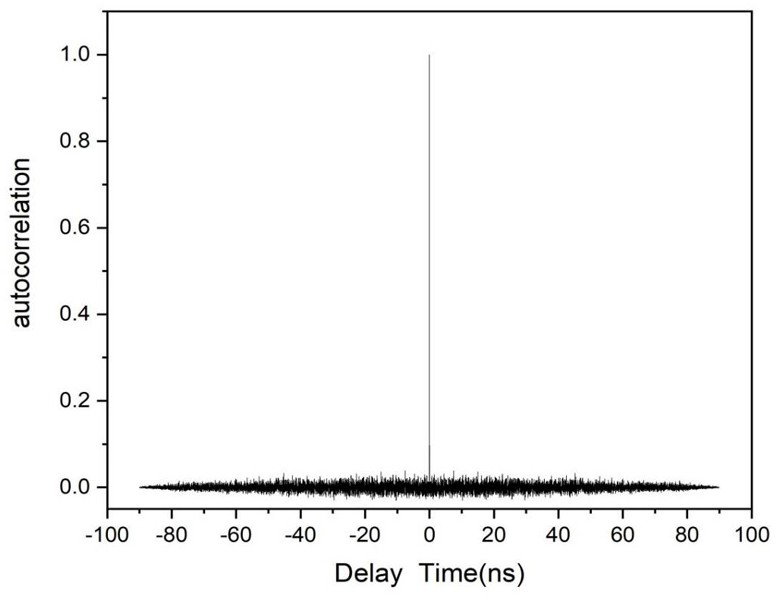
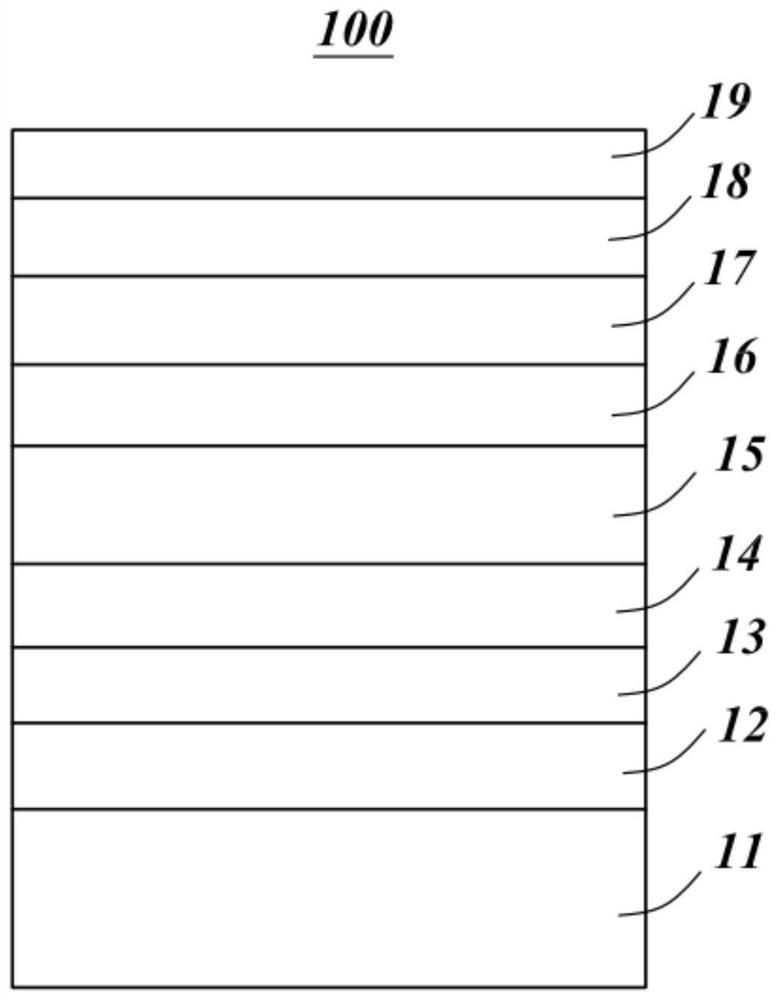
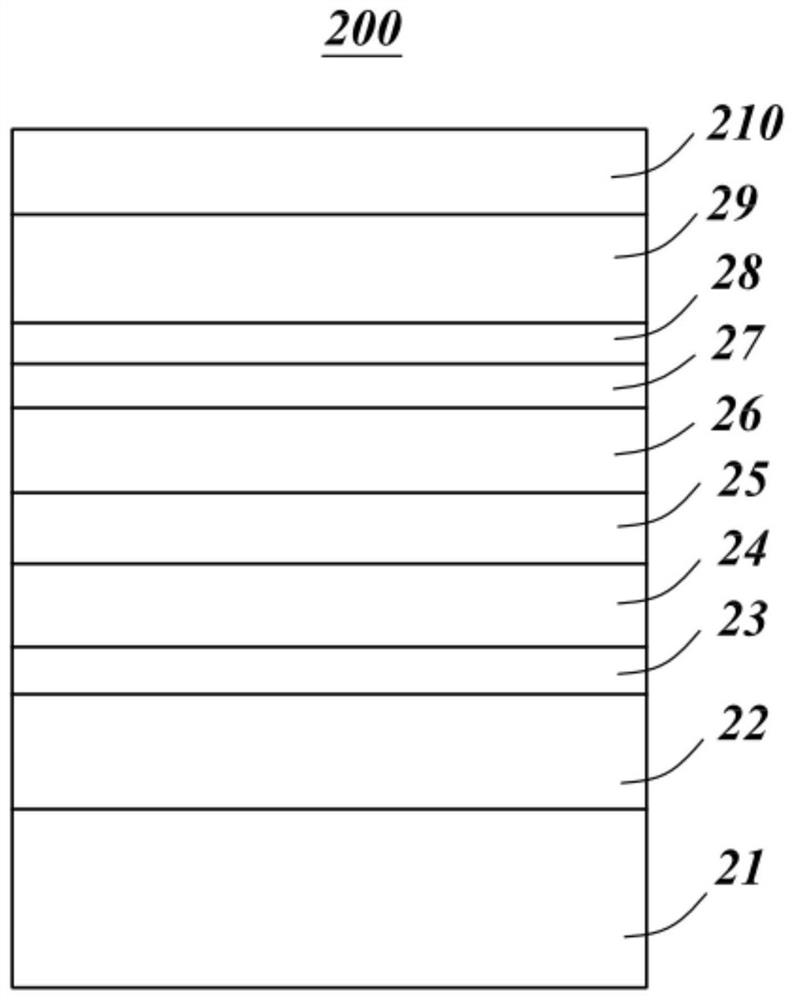
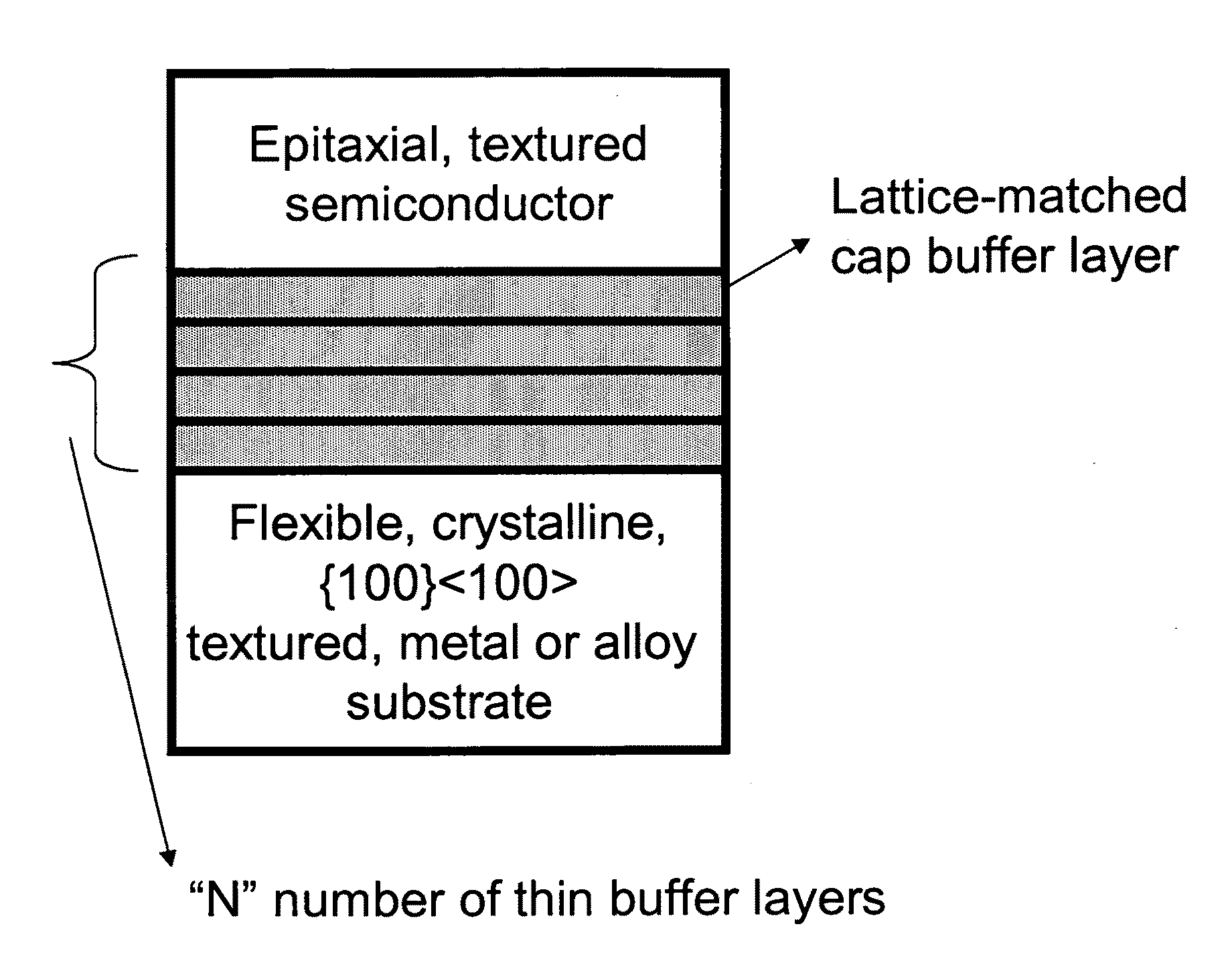
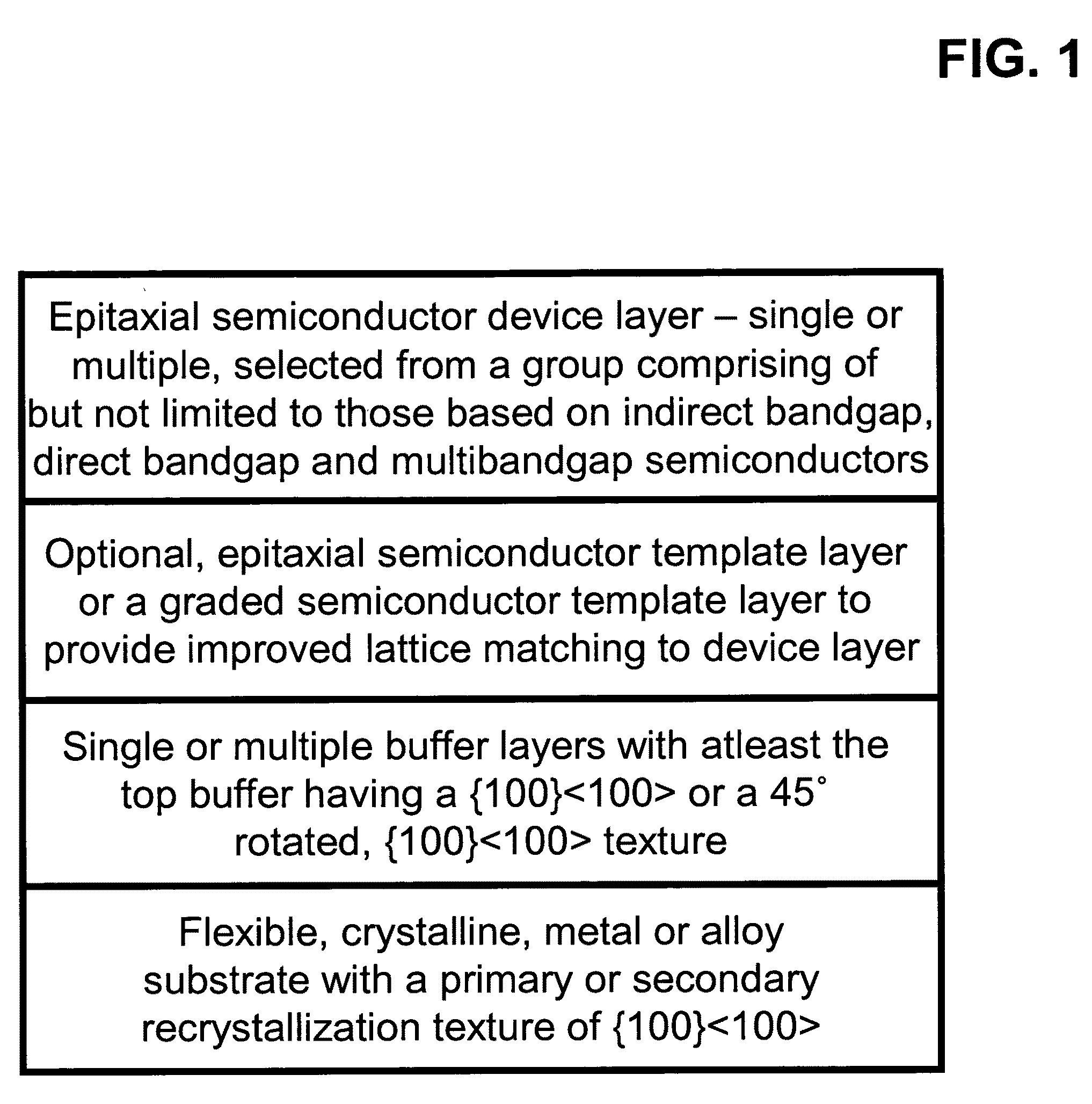
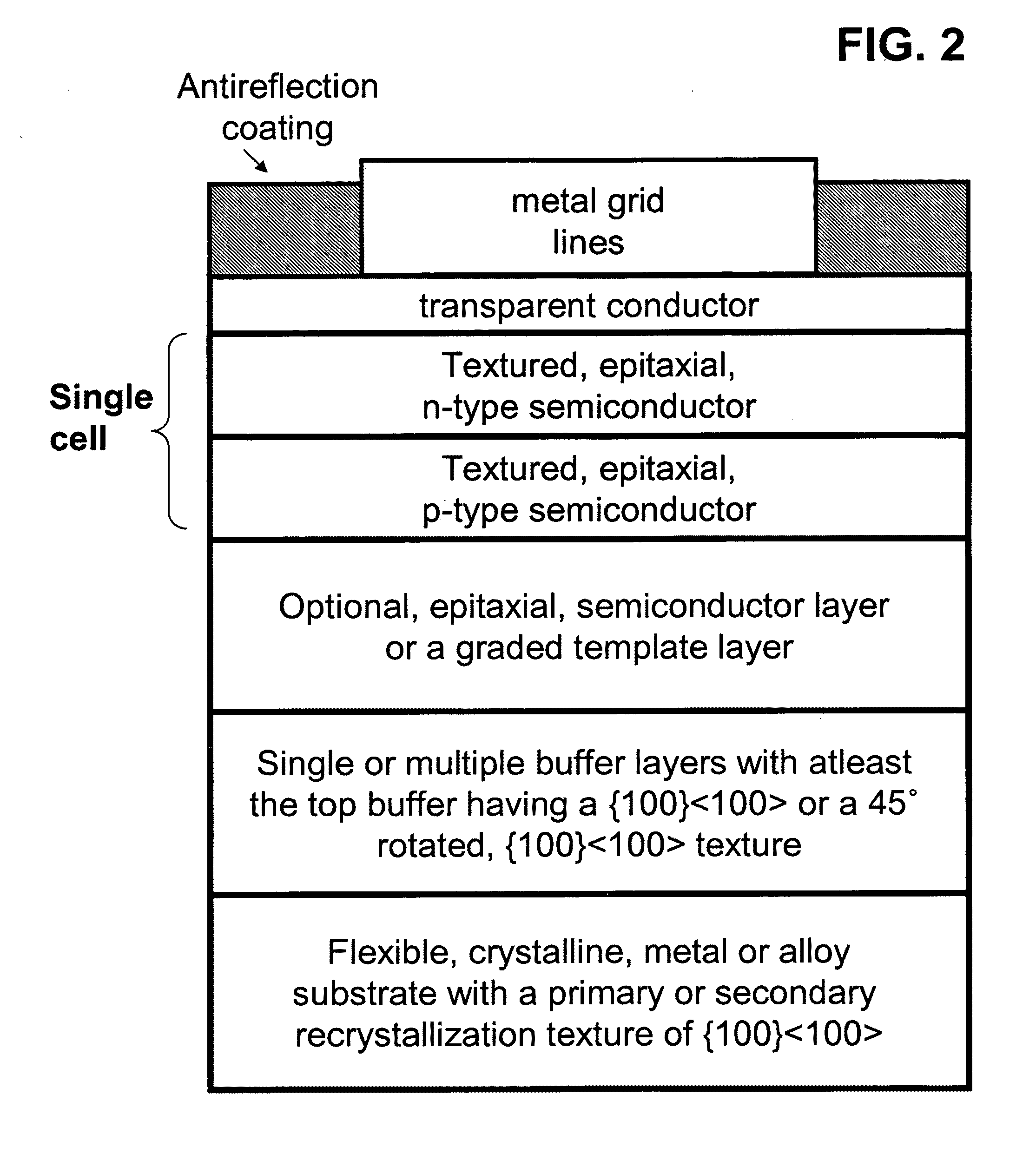
[100] or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices
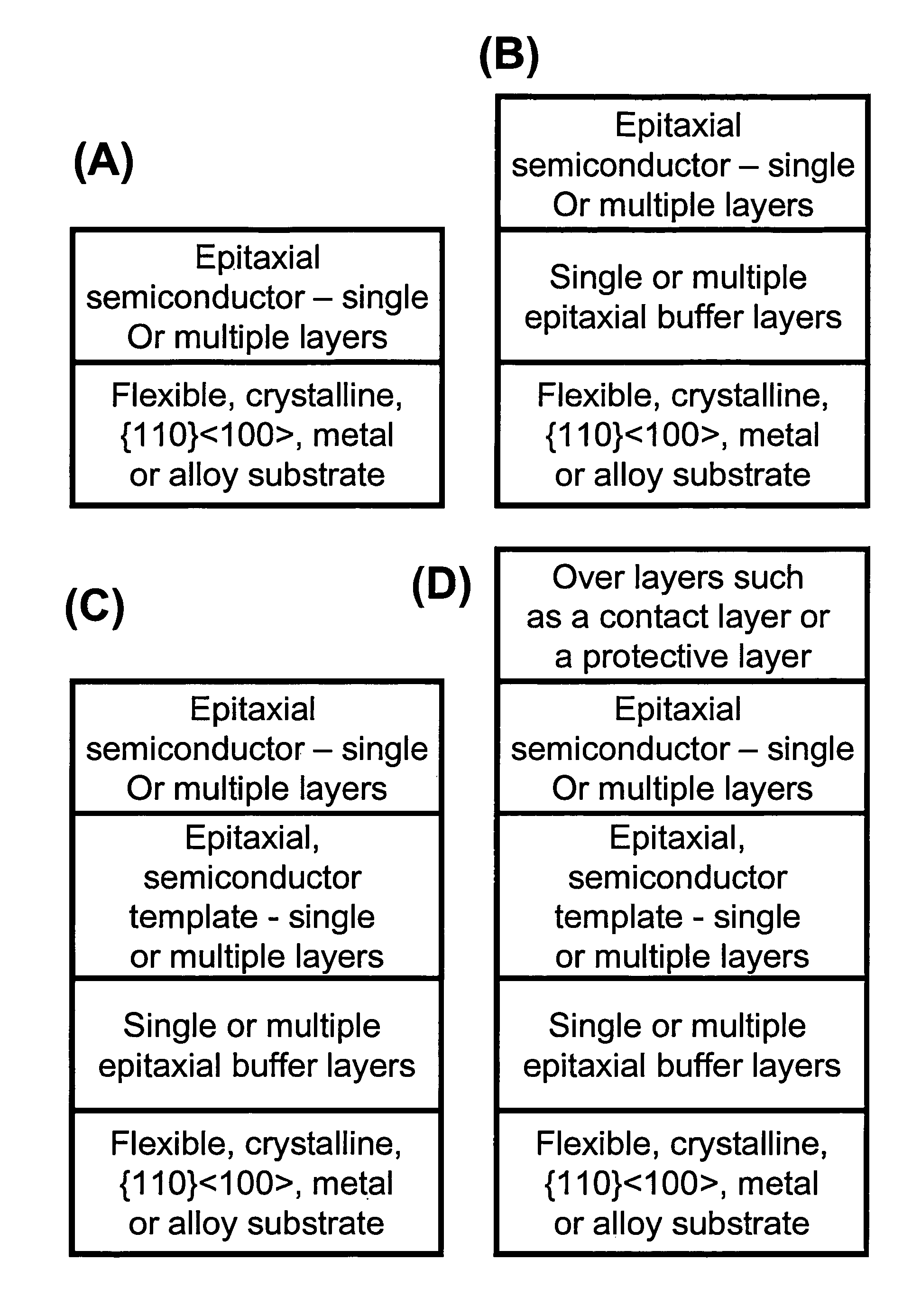
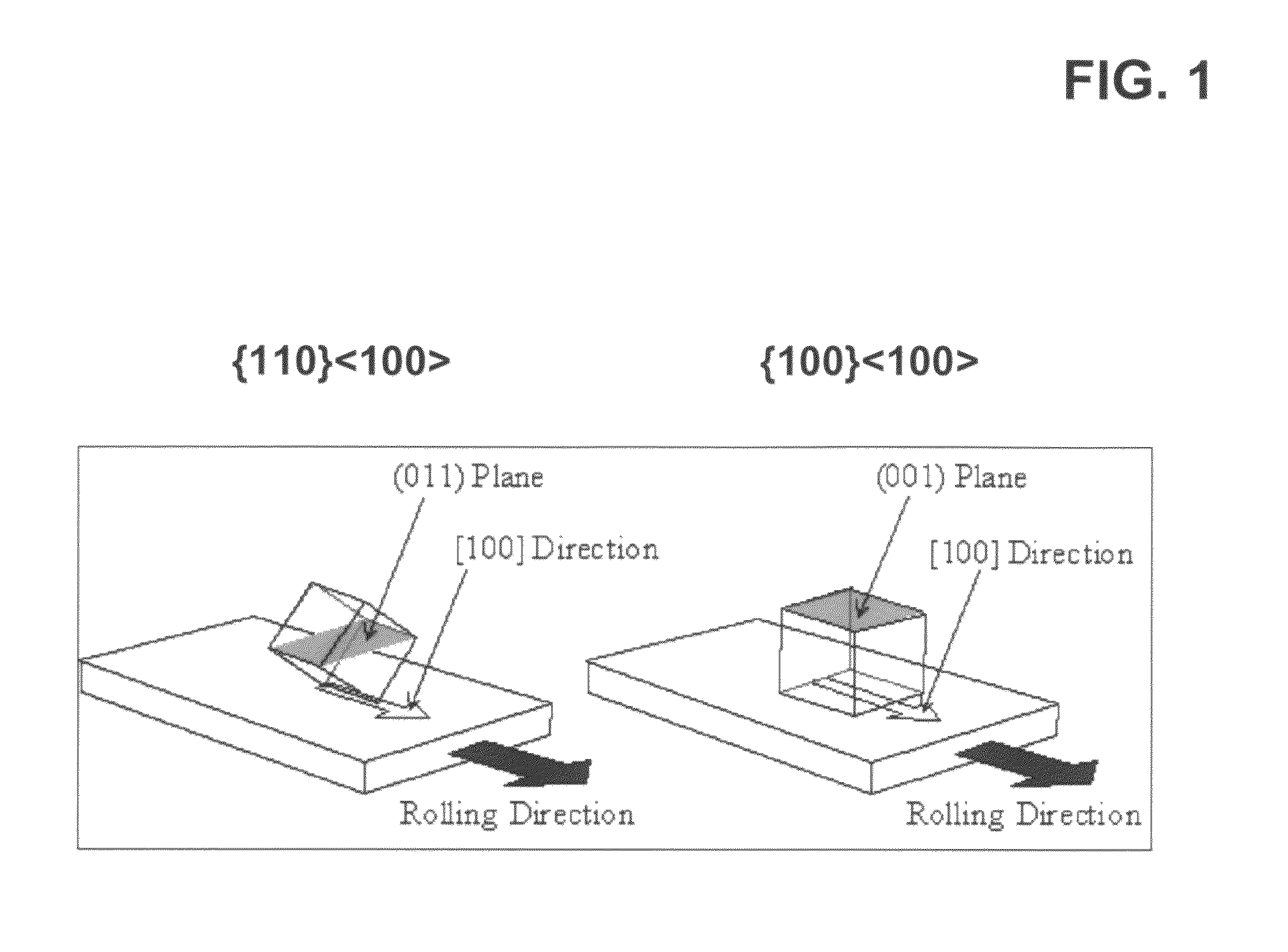
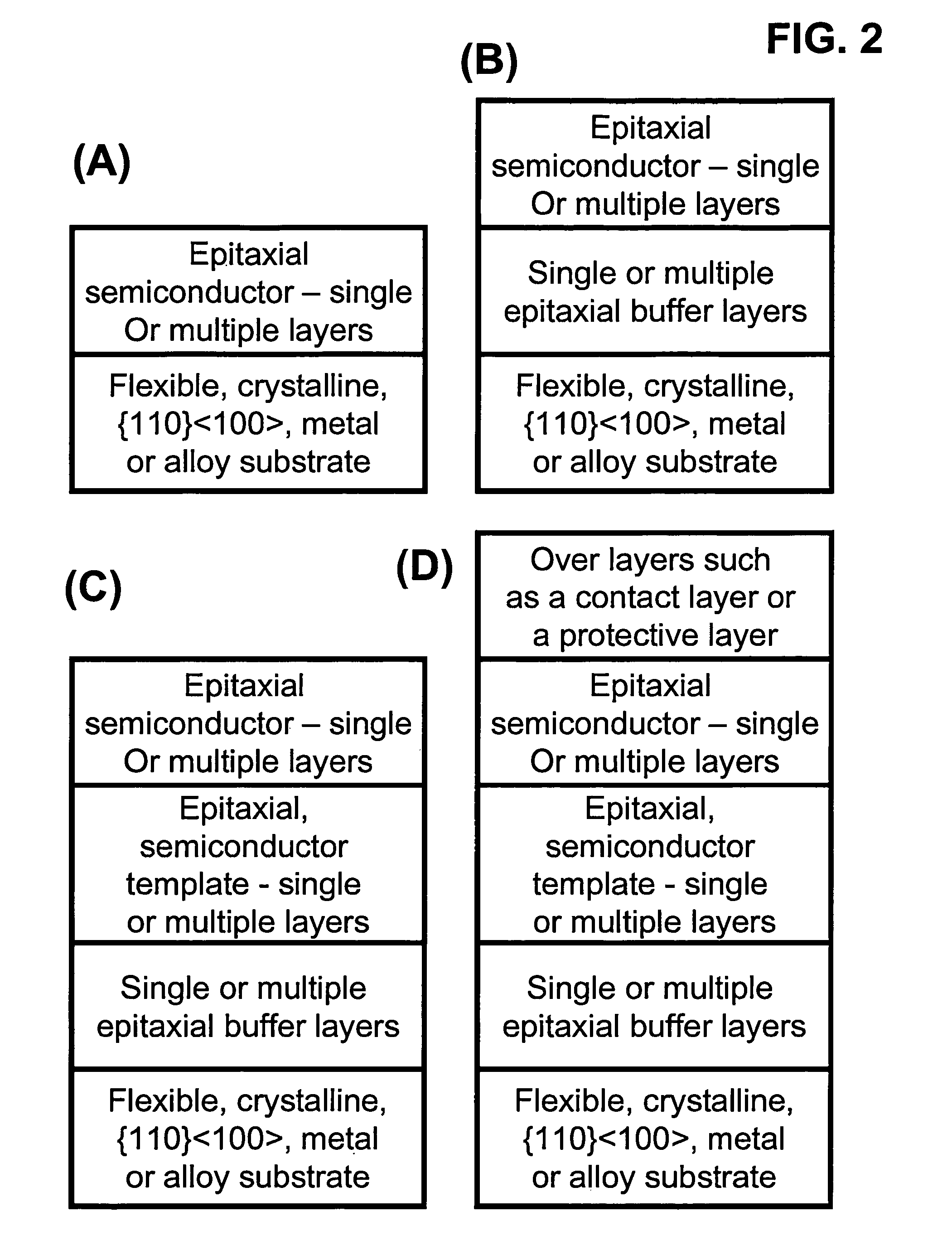
Novel articles and methods to fabricate the same resulting in flexible, large-area, [100] or [110] textured, semiconductor-based, electronic devices are disclosed. Potential applications of resulting articles are in areas of photovoltaic devices, flat-panel displays, thermophotovoltaic devices, ferroelectric devices, light emitting diode devices,, computer hard disc drive devices, magnetoresistance based devices, photoluminescence based devices, non-volatile memory devices, dielectric devices, thermoelectric devices and quantum dot laser devices.
Owner:阿米特·戈亚尔
Epitaxial growth design and method for realizing high-efficiency 1.5mu m communication band laser structure by adopting cylindrical InGaSb quantum dots
InactiveCN101626143AImprove performanceThreshold current and maximum optical power output improvementsLaser active region structureVacuum evaporation coatingElectronic band structureQuantum dot
With specific lattice parameters and energy band structure properties, III-V antimonides show more and more important research value and application value in the aspect of near and medium infrared semiconductor devices. The research and development of GaAs-based 1.5mu m Sb-based quantum dot lasers can provide the probability for replacing InP-based material devices, overcome the disadvantages of difficult superintegration among the InP-based materials and poor temperature stability, and provide a novel optical source with low cost, low power consumption and good performance for optical communication. The invention relates to epitaxial growth design and a method for realizing high-efficiency 1.5mu m communication band laser structure by adopting cylindrical InGaSb quantum dots, which can realize the research and development of the low-dimension epitaxial growth of antimonide systems.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
1.55-micron-wavelength silicon-based quantum dot laser epitaxial material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111628410AImprove heat dissipation characteristicsDoes not affect growth qualityLaser detailsLaser active region structureWaveguideMaterials science
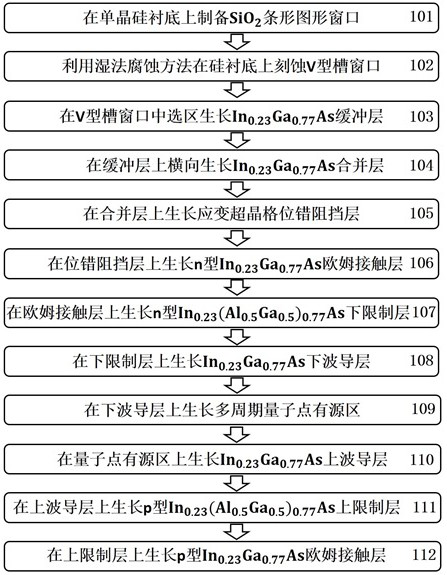
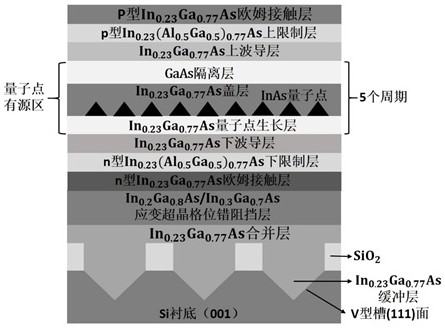
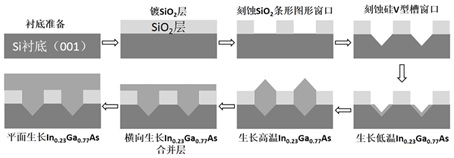
The invention relates to the technical field of semiconductor lasers, in particular to a 1.55-micron-wavelength silicon-based quantum dot laser epitaxial material and a preparation method thereof. Themethod is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 101, preparing a strip-shaped pattern mask on a monocrystalline silicon substrate; 102, etching a window of the V-shaped groove; 103, selectively growing a buffer layer in the V-shaped groove window region; 104, transversely growing a merging layer; 105, growing a strain superlattice dislocation barrier layer; 106, growing an n-type ohmic contact layer; 107, growing an n-type lower limiting layer; 108, growing a lower waveguide layer; 109, growing a multi-layer quantum dot active region; 110, growing an upper waveguide layer; 111,growing a p-type upper limiting layer; and 112, growing a p-type ohmic contact layer to complete preparation. The growth quality of the laser epitaxial material is effectively improved, and the performance of the laser is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU HUAXING LASER TECH CO LTD
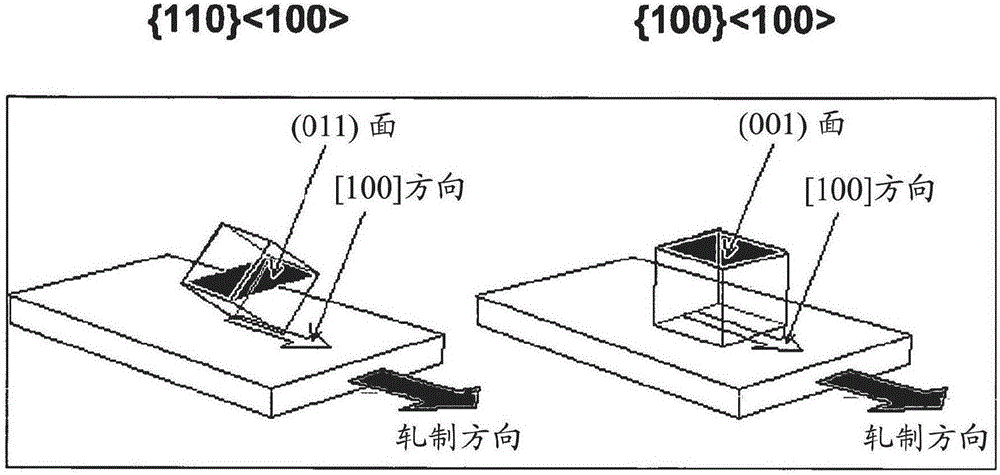
Semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices on {110}<100> oriented substrates
InactiveUS8795854B2Good lattice matchingTransistorSuperconductors/hyperconductorsHard disc drivePhotoluminescence
Novel articles and methods to fabricate the same resulting in flexible, oriented, semiconductor-based, electronic devices on {110}<100> textured substrates are disclosed. Potential applications of resulting articles are in areas of photovoltaic devices, flat-panel displays, thermophotovoltaic devices, ferroelectric devices, light emitting diode devices, computer hard disc drive devices, magnetoresistance based devices, photoluminescence based devices, non-volatile memory devices, dielectric devices, thermoelectric devices and quantum dot laser devices.
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
High performance devices enabled by epitaxial, preferentially oriented, nanodots and/or nanorods
InactiveUS8034745B2Improve performanceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionNanodotPhotoluminescence
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
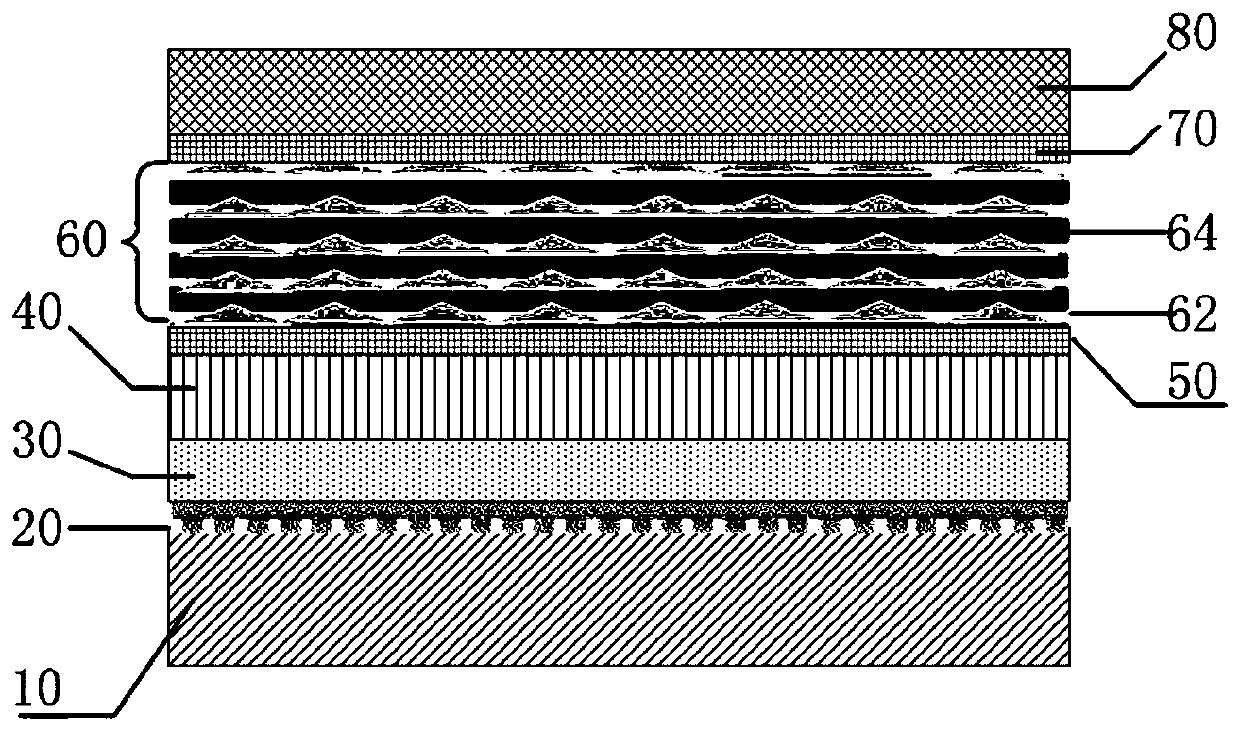
Quantum dot laser and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111276869ASimple methodEasy to operateLaser active region structureLattice mismatchErbium lasers
The invention belongs to the technical field of lasers, and particularly relates to a quantum dot laser and a preparation method thereof. The quantum dot laser sequentially comprises a porous monocrystalline silicon substrate, a filling layer, a lower electrode, a first superlattice waveguide layer, an active region, a second superlattice waveguide layer and an upper electrode from bottom to top.Due to the fact that lattice mismatch exists between the monocrystalline silicon substrate and the active region, adverse effects are brought to manufacturing and performance of the device. Accordingto the quantum dot laser, the porous monocrystalline silicon substrate is adopted, and a large number of dislocation defects caused by lattice mismatch of the monocrystalline silicon substrate and theactive region are released by using a porous structure, so that the performance of the obtained quantum dot laser is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Semiconductor laser with low relative intensity noise of individual longitudinal modes and optical transmission system incorporating the laser
A semiconductor laser comprises an electrically isolated active section and at least one noise reducing section and operates on a ground state transition of a quantum dot array having inhomogeneous broadening greater than 10 nm. The laser preferably emits more than 10 optical modes such that a total relative intensity noise of each optical mode is less than 0.2% in the 0.001 GHz to 10 GHz range. The spectral power density is preferably higher than 2 mW / nm. An optical transmission system and a method of operating a quantum dot laser with low relative intensity noise of each optical mode are also disclosed.
Owner:INNOLUME
Semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices on {110}<100> oriented substrates
Novel articles and methods to fabricate the same resulting in flexible, {110}<100> or 45 DEG -rotated {110}<100> oriented, semiconductor-based, electronic devices are disclosed. Potential applications of resulting articles are in areas of photovoltaic devices, flat-panel displays, thermophotovoltaic devices, ferroelectric devices, light emitting diode devices,, computer hard disc drive devices, magnetoresistance based devices, photoluminescence based devices, non-volatile memory devices, dielectric devices, thermoelectric devices and quantum dot laser devices.
Owner:阿米特·戈亚尔
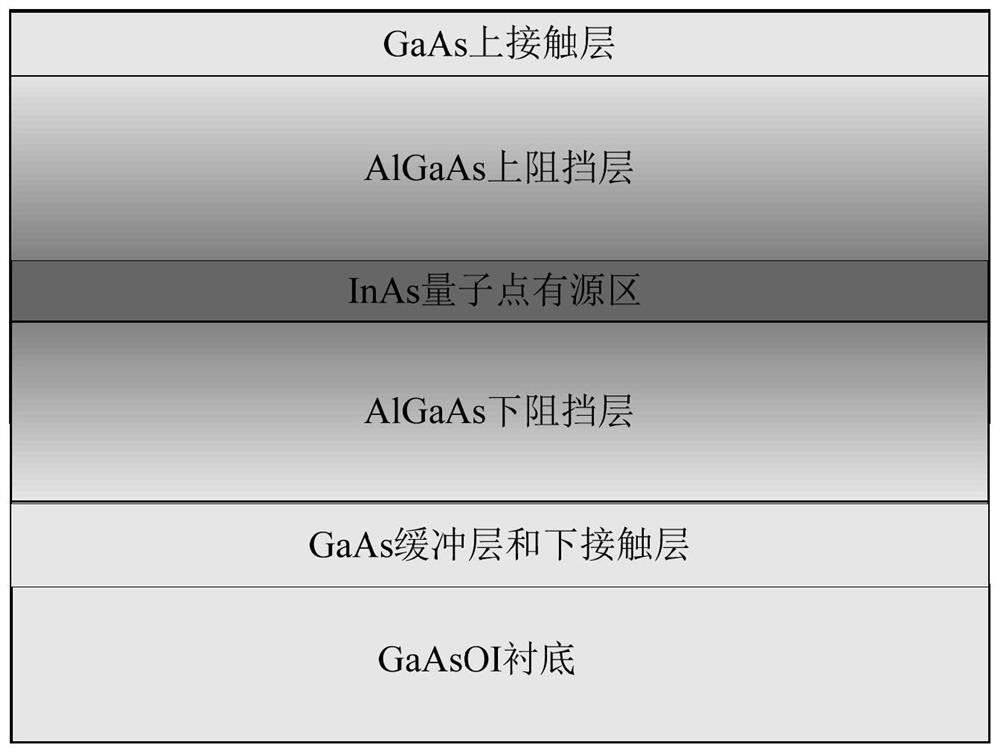
InAs quantum dot laser structure based on GaAsOI substrate and preparation method
PendingCN113178771AMature technologyReduce manufacturing costLaser detailsSemiconductor laser structural detailsSingle crystalContact layer
The invention provides an InAs quantum dot laser structure based on a GaAsOI substrate and a preparation method of the InAs quantum dot laser structure. The InAs quantum dot laser structure based on the GaAsOI substrate comprises the GaAsOI substrate, a GaAs buffer layer, a lower contact layer, an AlGaAs lower barrier layer, an InAs quantum dot active region, an AlGaAs upper barrier layer and a GaAs upper contact layer which are sequentially arranged in a stacked manner. The GaAsOI substrate is a GaAs single crystal film which is obtained by being stripped from the GaAs substrate, transferred to an SOI substrate compatible with a CMOS and processed. According to the invention, the InAs quantum dot laser can be prepared on the SOI substrate compatible with a CMOS process, and the InAs quantum dot laser structure and the method are suitable for the development of silicon-based photoelectric integration without a core light source, and have wide application prospect.
Owner:湖南汇思光电科技有限公司
Method for assembling quantum dot laser on planar superlattice nanowire
ActiveCN112366521AExpand new ideasControl the degree of etchingOptical wave guidanceMaterial nanotechnologyPhoto irradiationUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses a method for assembling a quantum dot laser on a planar superlattice nanowire, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the spin coating of a quantum dot solution on the etched superlattice nanowire, and obtaining a superlattice nanowire embedded with quantum dots after drying; employing ultraviolet light or infrared light for irradiating quantum dots embedded intosuperlattice nanowires so that the quantum dots emit light, taking the silicon nanowires at the two ends of the superlattice structure as optical waveguides, locating quantum dot optical signals and transmitting the signals through the nanowire guided wave effect, and testing the light collection and transmission effects of the nanowires of the superlattice structure.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible electronic devices on {110}<100> oriented substrates
InactiveCN106653822ANanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHard disc drivePhotoluminescence
The invention relates to semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible electronic devices on {110}<100> oriented substrates. Novel articles and methods to fabricate the same resulting in flexible, {110}<100> or 45-degree-rotated {110}<100> oriented, semiconductor-based electronic devices are disclosed. Potential applications of resulting articles are in areas of photovoltaic devices, flat-panel displays, thermophotovoltaic devices, ferroelectric devices, light emitting diode devices,, computer hard disc drive devices, magnetoresistance based devices, photoluminescence based devices, non-volatile memory devices, dielectric devices, thermoelectric devices and quantum dot laser devices.
Owner:阿米特·戈亚尔
Preparation method of refrigeration-free anti-reflection InP-based quantum dot/quantum well coupled EML epitaxial wafer
PendingCN114188823AStable jobGood effectLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionDistributed feedback laserOptical isolator
According to the preparation method of the refrigeration-free anti-reflection InP-based quantum dot / quantum well coupling EML epitaxial wafer, a quantum well electric absorption modulation region which is covered by an ohmic contact layer and is horizontally coupled with a quantum dot stacking region is additionally arranged in the quantum dot stacking region in a quantum dot laser based on an InP substrate. The electro-absorption modulated laser is prepared through molecular beam epitaxy or metal organic chemical vapor deposition and is formed by integrally growing a quantum dot distributed feedback laser and a quantum well electro-absorption modulator in a butt-joint growth mode; the electro-absorption modulated laser combines the characteristics of excellent reflection resistance and high temperature stability of a quantum dot laser and the characteristic of high modulation rate of a quantum well electro-absorption modulator, and realizes stable work at 5-75 DEG C under the conditions of no optical isolator and no refrigeration. The preparation method is clear and simple in steps and easy to operate, and the prepared electro-absorption modulated laser is good in effect, stable in performance, capable of working continuously, high in practicability and wide in applicability.
Owner:JIANGSU HUAXING LASER TECH CO LTD
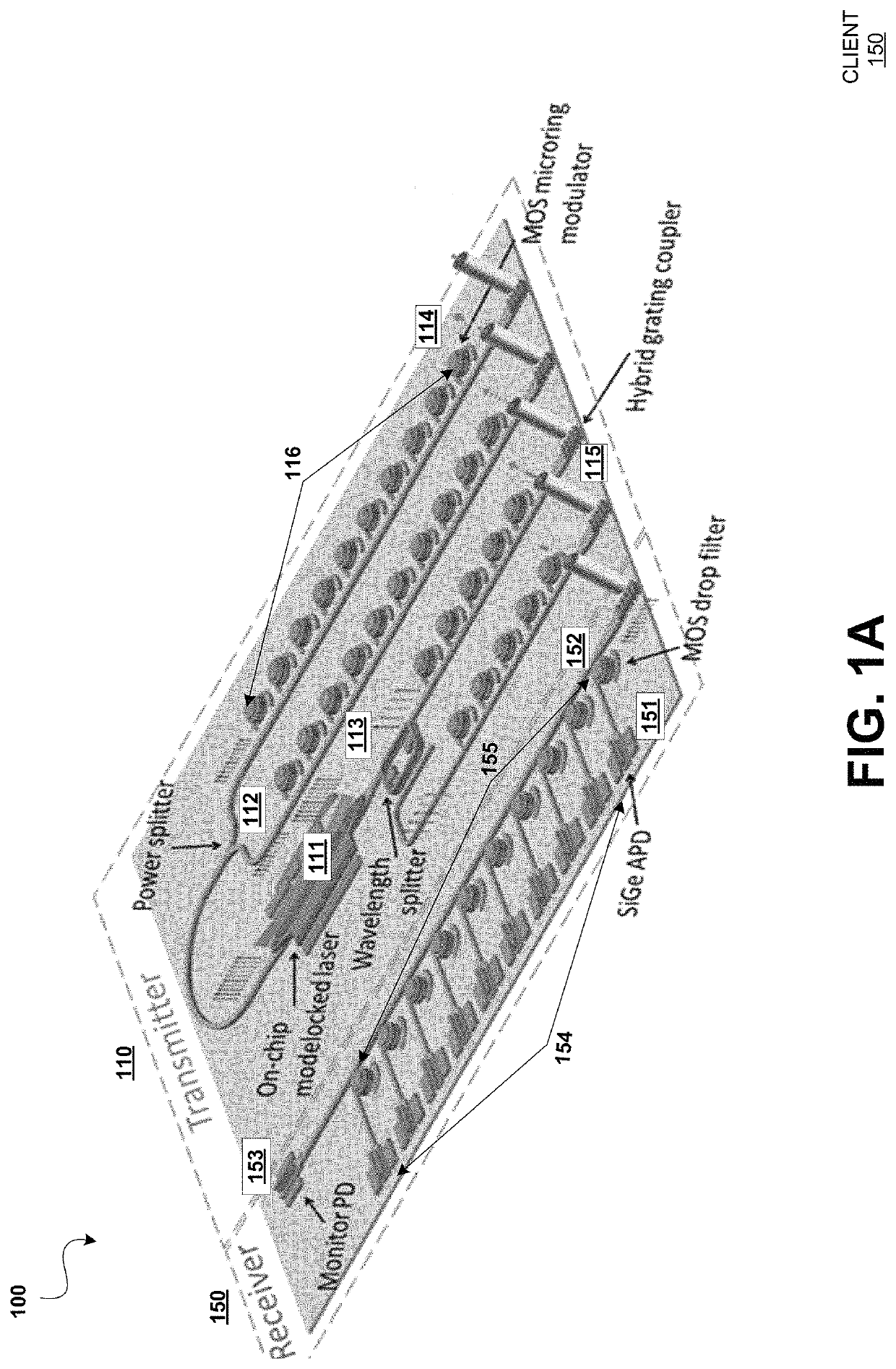
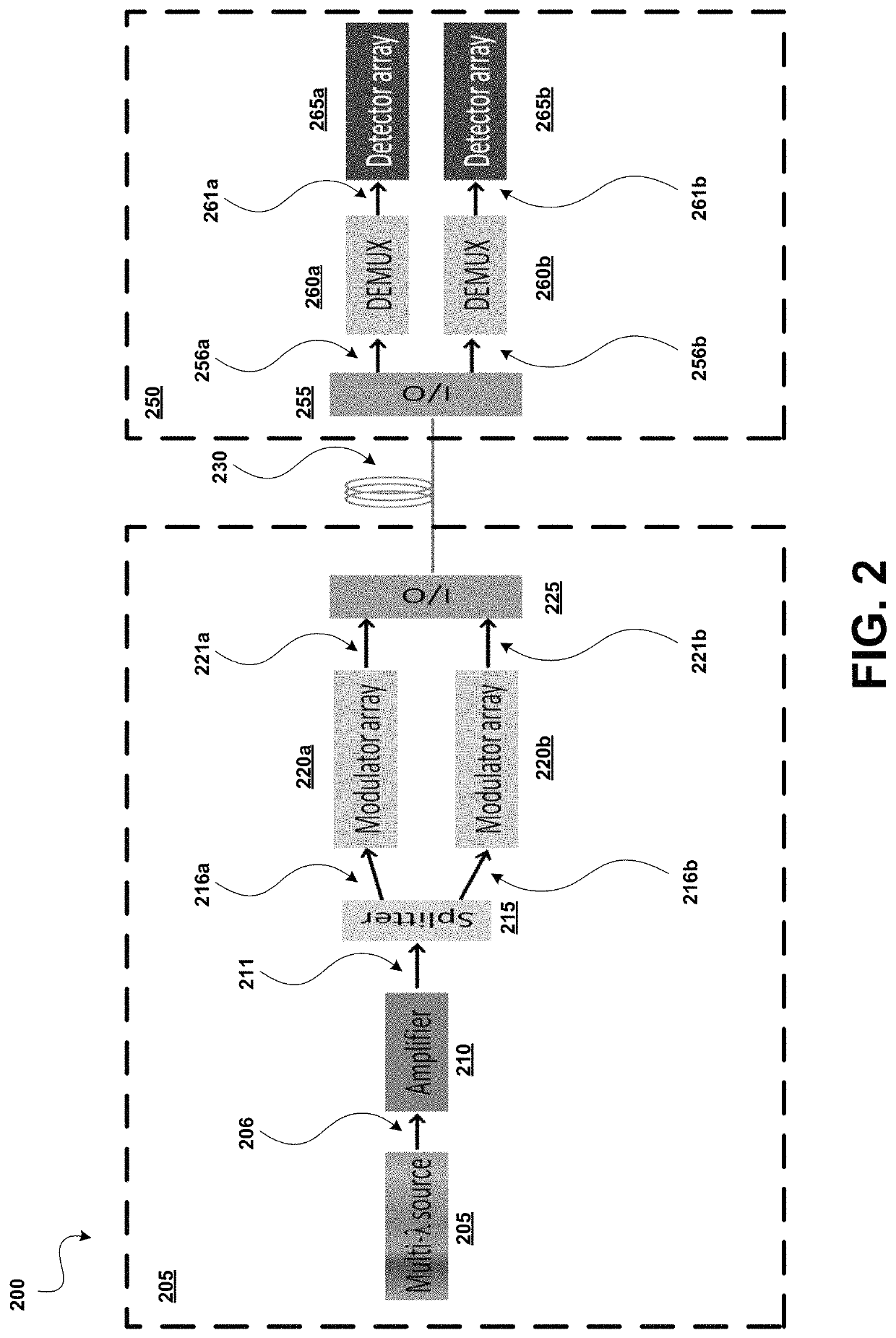
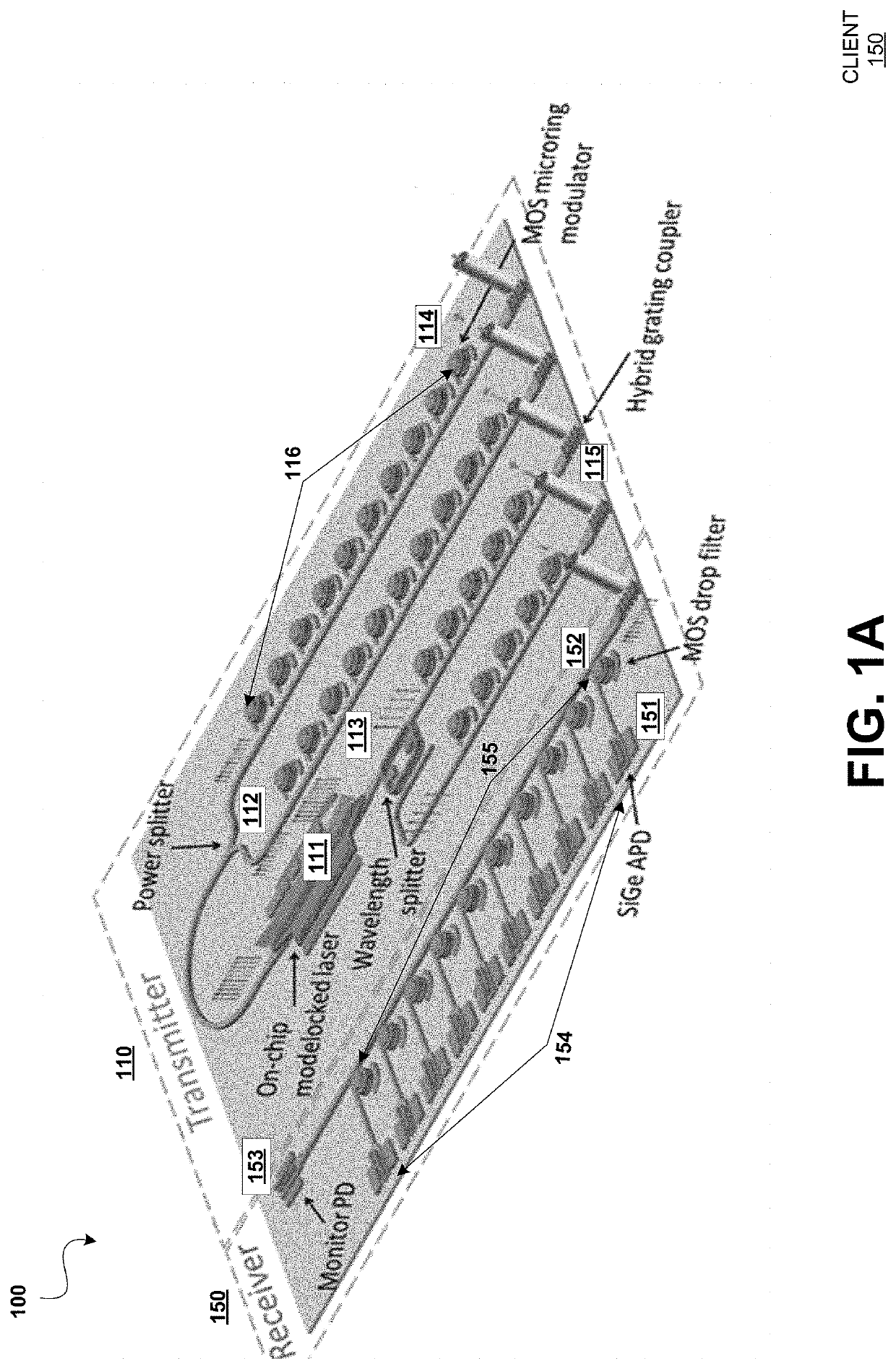
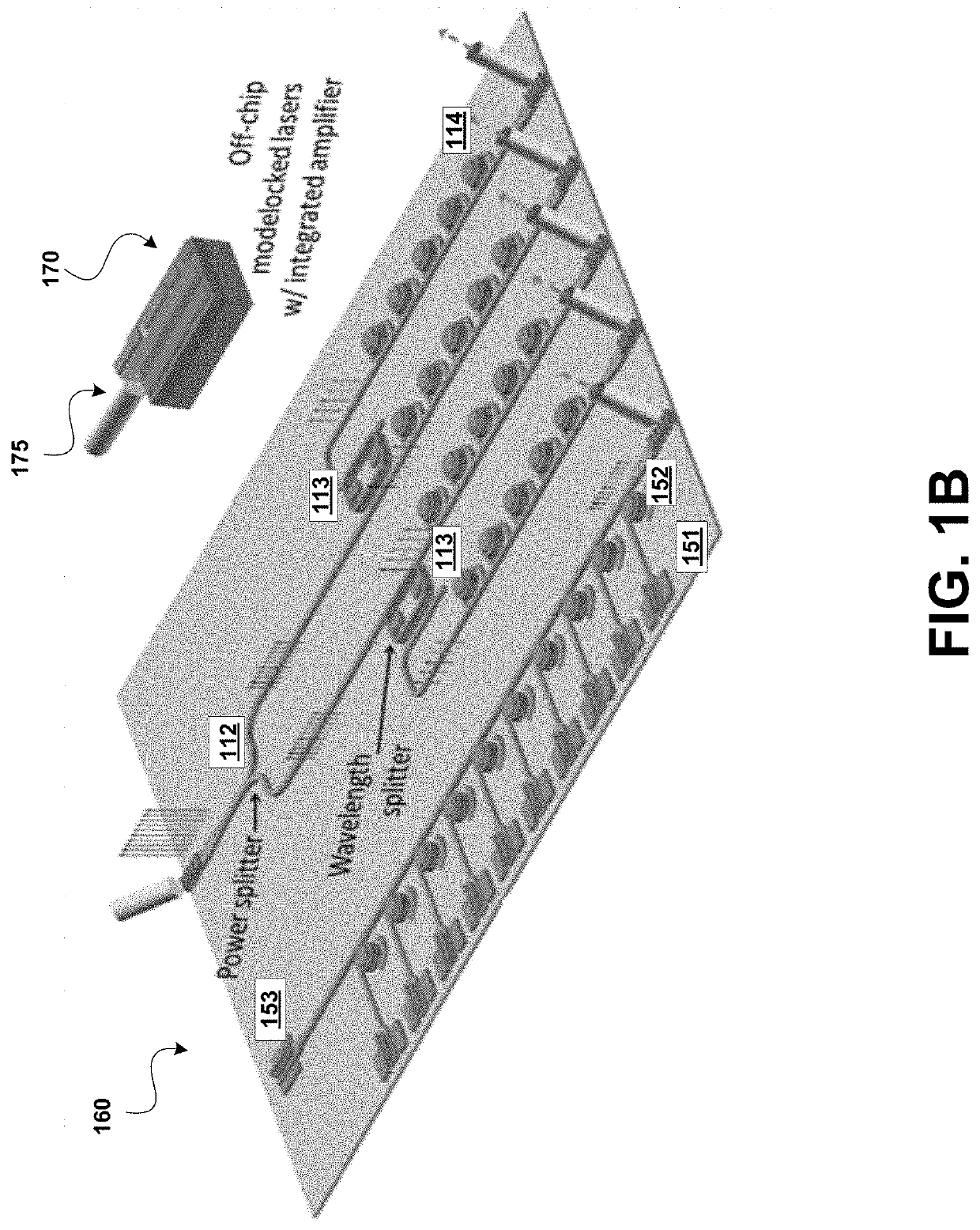
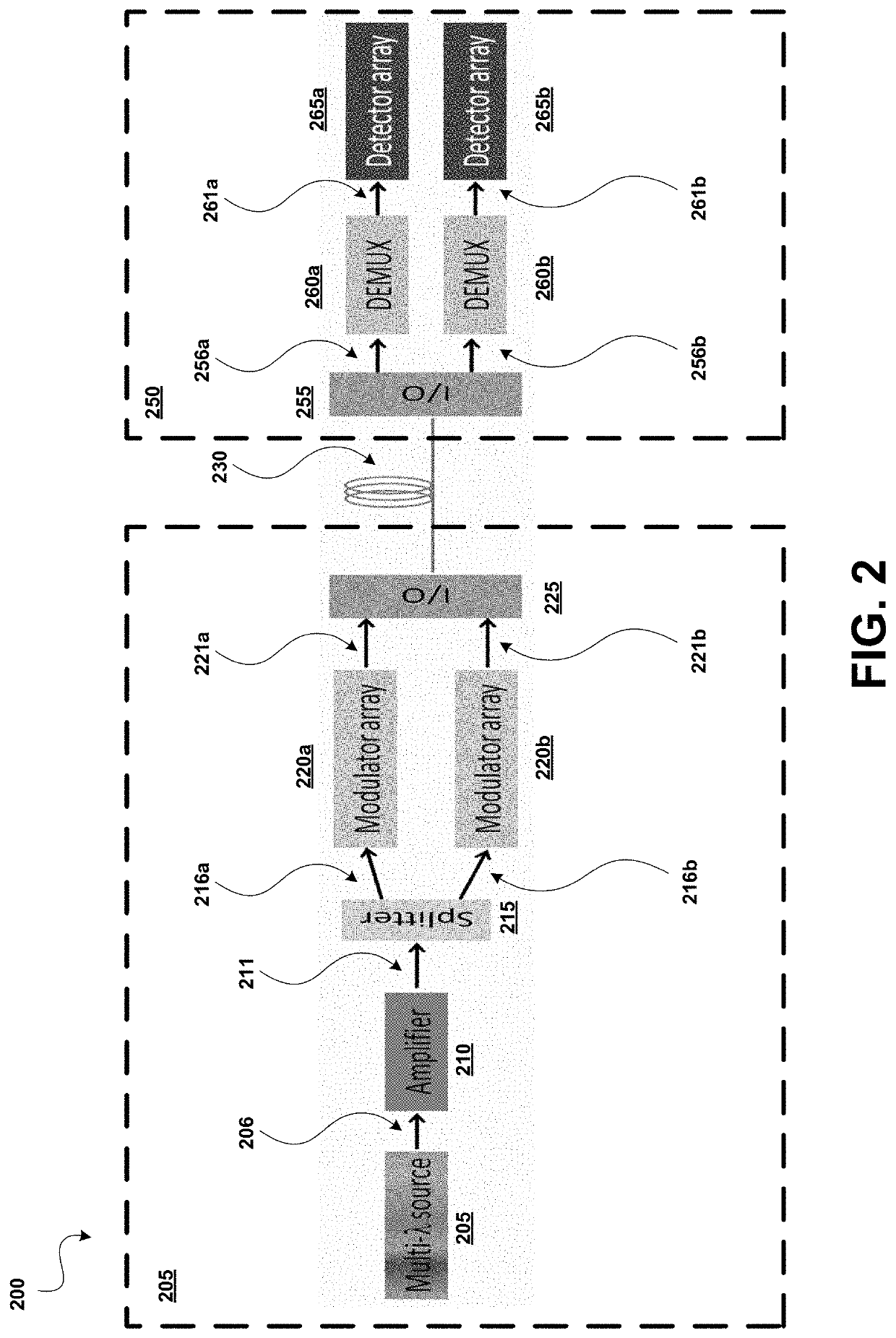
Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) photonic integration platform
A Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) photonic integration circuit (PIC) that implements a DWDM system, such as a transceiver, is described. The DWDM PIC architecture includes photonic devices fully integrating on a single manufacturing platform. The DWDM PIC has a multi-wavelength optical laser, a quantum dot (QD) laser with integrated heterogeneous metal oxide semiconductor (H-MOS) capacitor, integrated on-chip. The multi-wavelength optical laser can be a symmetric comb laser that generates two equal outputs of multi-wavelength light. Alternatively, the DWDM PIC can be designed to interface with a stand-alone multi-wavelength optical laser that is off-chip. In some implementations, the DWDM PIC integrates multiple optimally designed photonic devices, such as a silicon geranium (SiGe) avalanche photodetector (APD), an athermal H-MOS wavelength splitter, a QD photodetector, and a heterogenous grating coupler. Accordingly, fabricating the DWDM PIC includes a unique III-V to silicon bonding process, which is adapted for its use of SiGe APDs.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) photonic integration platform
A Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) photonic integration circuit (PIC) that implements a DWDM system, such as a transceiver, is described. The DWDM PIC architecture includes photonic devices fully integrating on a single manufacturing platform. The DWDM PIC has a multi-wavelength optical laser, a quantum dot (QD) laser with integrated heterogeneous metal oxide semiconductor (H-MOS) capacitor, integrated on-chip. The multi-wavelength optical laser can be a symmetric comb laser that generates two equal outputs of multi-wavelength light. Alternatively, the DWDM PIC can be designed to interface with a stand-alone multi-wavelength optical laser that is off-chip. In some implementations, the DWDM PIC integrates multiple optimally designed photonic devices, such as a silicon geranium (SiGe) avalanche photodetector (APD), an athermal H-MOS wavelength splitter, a QD photodetector, and a heterogenous grating coupler. Accordingly, fabricating the DWDM PIC includes a unique III-V to silicon bonding process, which is adapted for its use of SiGe APDs.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Flight object detection method based on double-channel alert quantum-dot compound eye system
ActiveCN106546994ATroubleshoot fine-grained trackingSolve the problem of fine tracking accuracyElectromagnetic wave reradiationContinuous scanningWavelength
The invention discloses a flight object detection method based on double-channel alert quantum-dot compound eye system, and the method is realized in the double-channel alert quantum-dot laser system on the system of component eye bionic optics. The system is mainly composed of a main controller, a connecting rod, a left-eye three-axis revolver, a right-eye three-axis revolver and left and right compound eyes. The method comprises the steps of laser emission, rough tracking, initial positioning, fine tracking and spatial track description. The method has the advantages that active quantum dot laser emission sources and echo detection unit matching small eye channels are constructed in the compound eyes simultaneously, and the wavelength and the intensity are selected so that the compound eyes are adapted to different environments; a double-compound-eye three-axis continuous scanning detection manner is used to solve the problem in the fine tracking precision of a spatial object; and compared with that of a traditional system, the method is more suitable for 3D track detection of the flight object.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device and method for generating broadband noise source based on quantum dot micro-column laser
ActiveCN112490843AHigh bandwidthLaser detailsSemiconductor laser optical deviceBroadband noiseMacroscopic scale
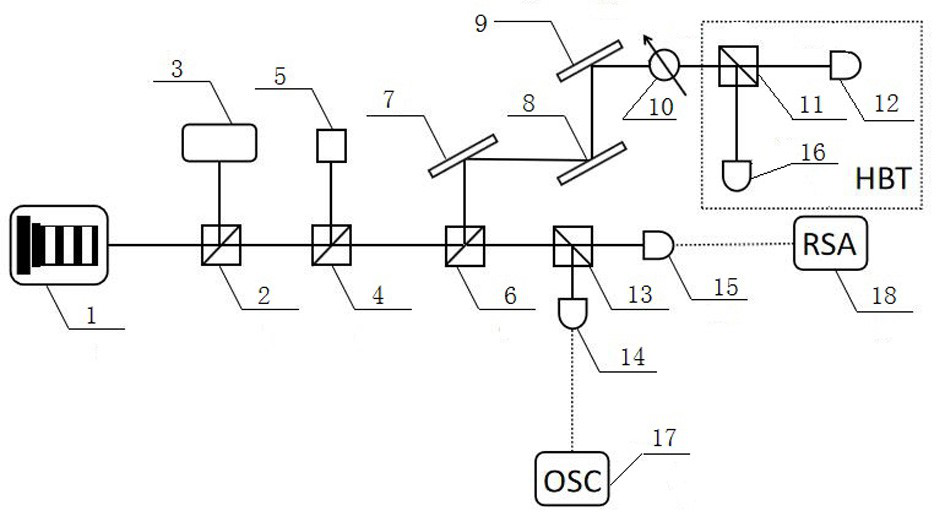
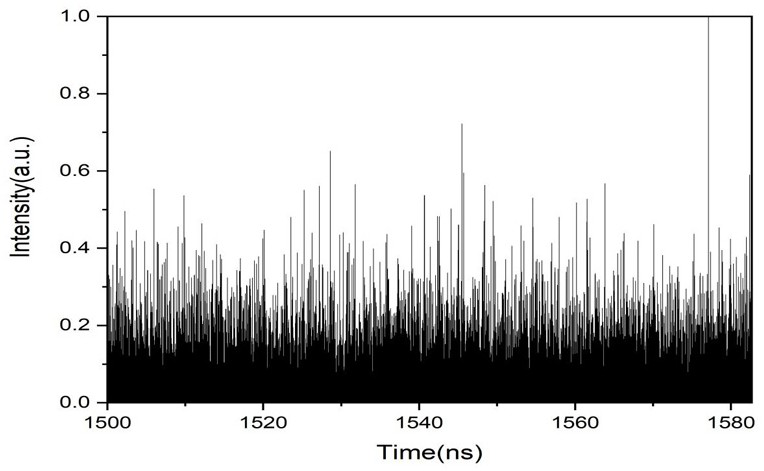
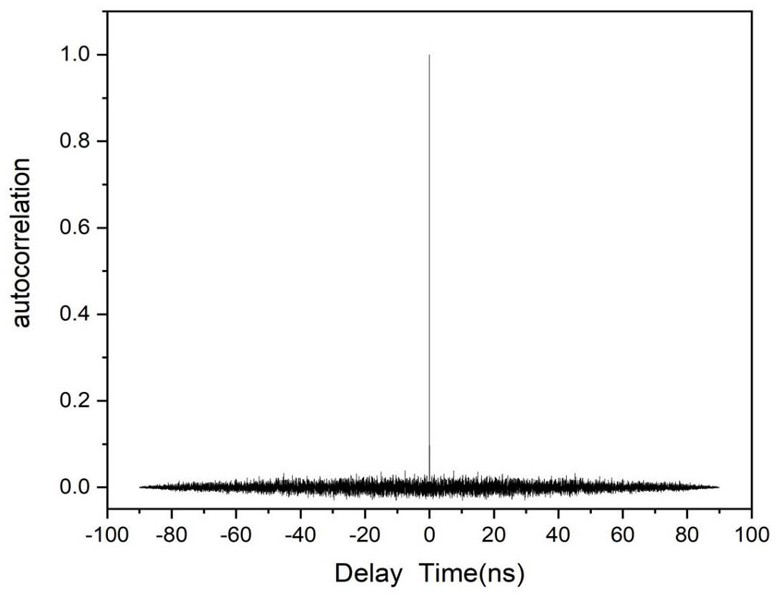
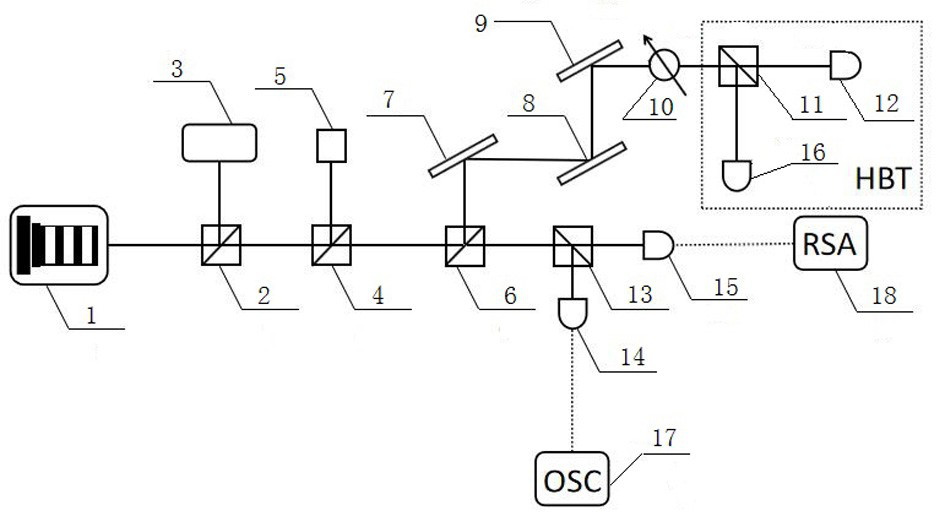
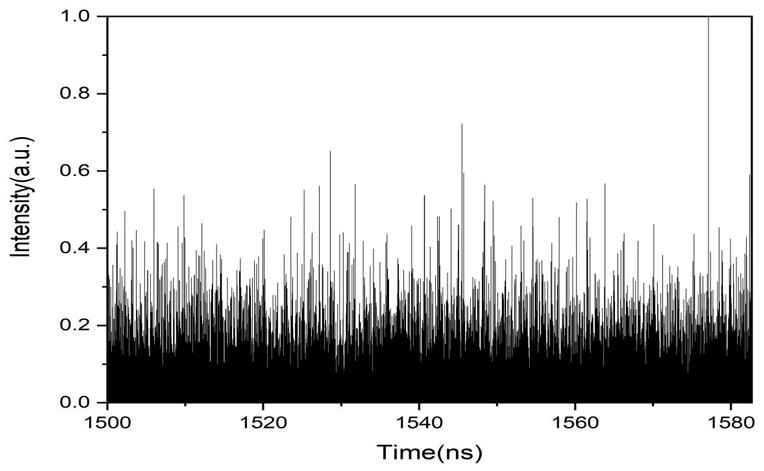
The invention discloses a device of a method for generating a broadband noise source based on a quantum dot micro-column laser, and belongs to the technical field of broadband noise source generationmethods. The technical problem to be solved is to provide an improvement of a method for generating a broadband noise source based on a quantum dot micro-column laser. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the steps: preparing a quantum dot micro-column laser serving as a first light source; injecting external narrow-band optical noise into the quantum dot laser prepared in the first step to generate a broadband noise signal, splitting an optical signal output by the quantum dot laser through a beam splitter, converting one path of optical signal into an electric signal through a photoelectric detector, and outputting the electric signal to an oscilloscope and a frequency spectrograph for macroscopic observation; and outputting the other path of the optical signal to a Hanbury-Brown and Twiss interference measurement device to carry out microscopic photon statistical measurement. The method is applied to signal generation, the broadband noise signal generated by the method has the characteristics of high bandwidth and no external cavity period, and the communication safety is improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
A preparation method of controllable quantum dot array based on photothermal effect
ActiveCN107993923BIncrease the areaLow costMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical synthesisSolar cell
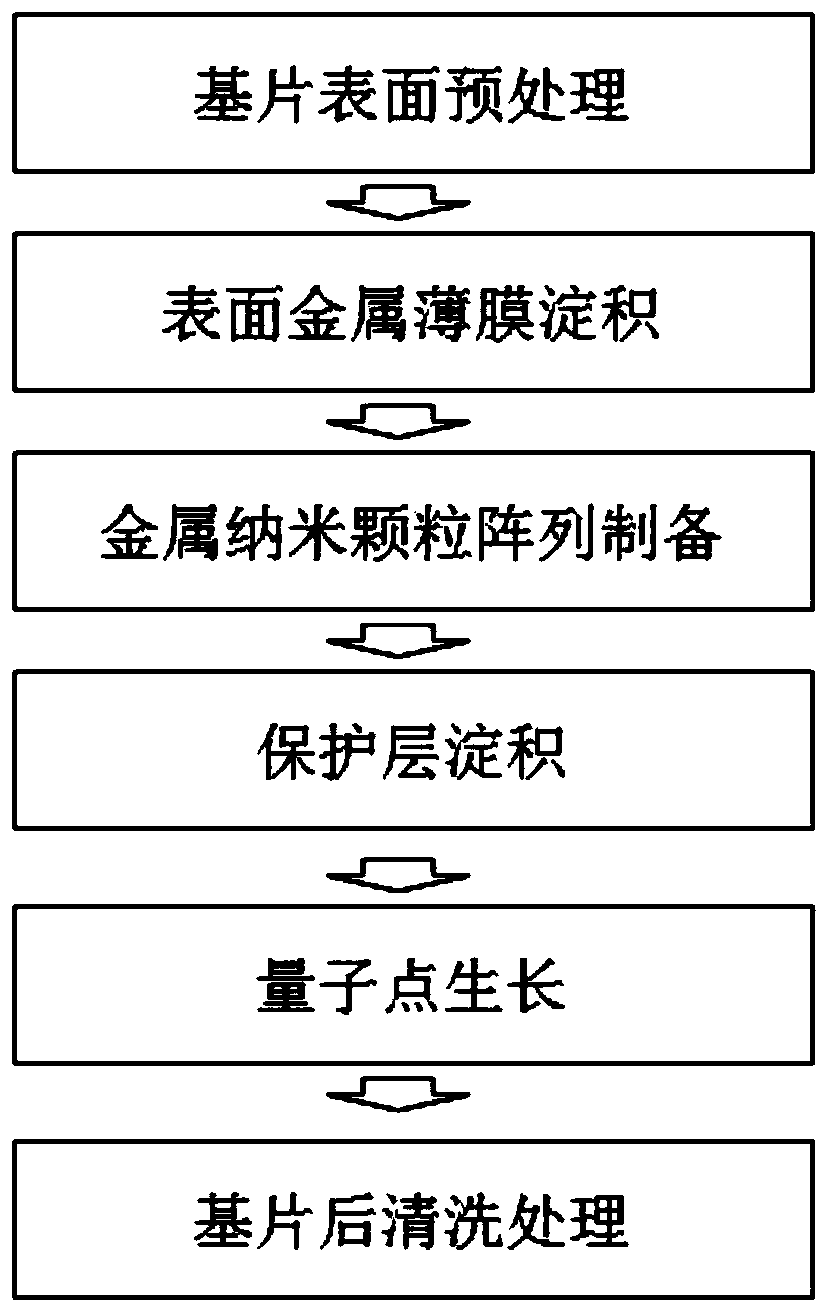
The invention discloses a controllable quantum dot array preparing method based on the photo-thermal effect. According to the method, a metal or alloy nanoparticle array serves as a template, the reaction conditions of a quantum dot precursor are controlled through the local surface plasmon thermal effect irritated by a light source, and therefore the preparing site, size and nucleation density ofthe precursor is controlled. The method mainly includes the steps of preprocessing the surface of the substrate, conducting thin-film deposition on surface metal, preparing the metal nanoparticle array, depositing a protecting layer, growing the quantum dot and conducting post-washing on the substrate. The large-area low-cost quantum dot array is prepared through a chemical synthesis method. Themethod can be combined with a semiconductor processing technology, the prepared quantum dot array can be applied for machining and preparing a quantum dot laser device, a single photon light source, asolar cell, a high-efficiency light-emitting diode, a storage and other devices.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
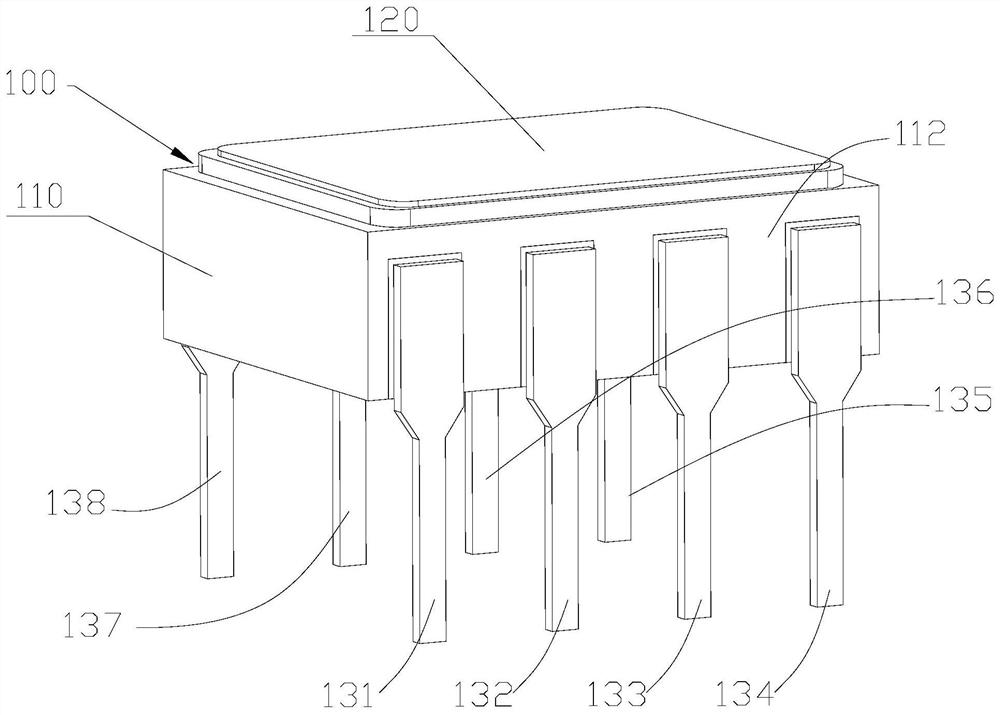
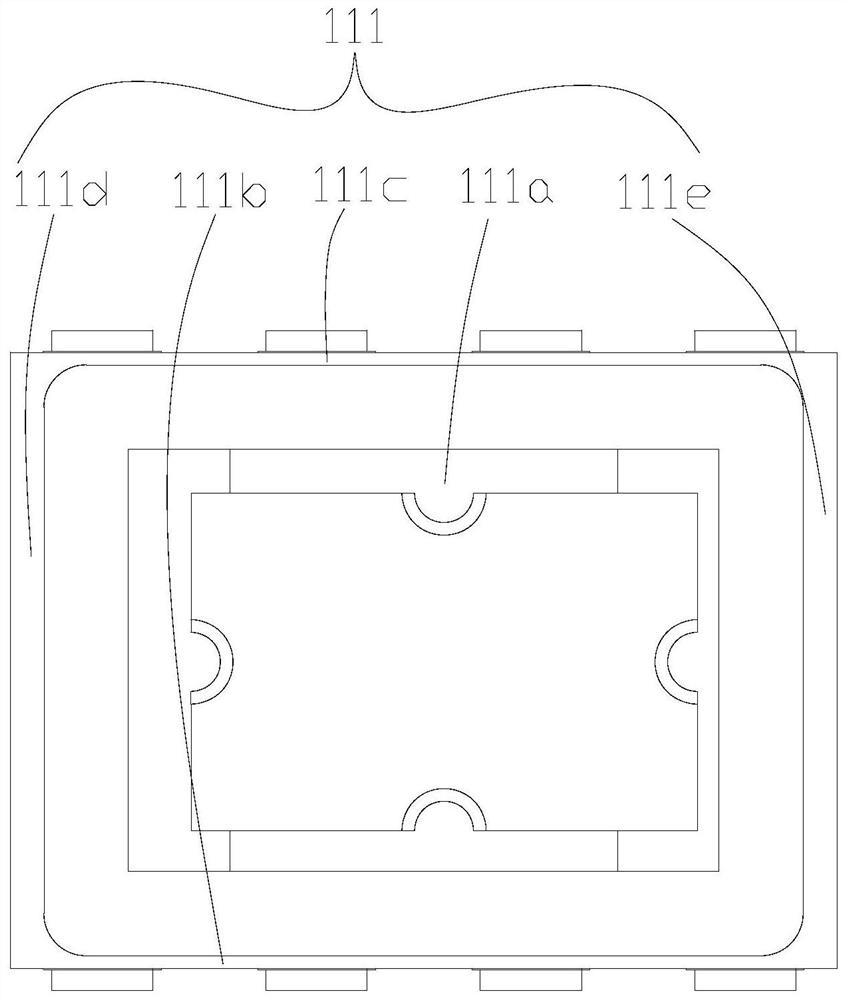
High-speed high-precision linear optocoupler based on quantum dot laser and InGaAs detector
ActiveCN113922207ASolving Coupled Process IssuesHigh transmission accuracyLaser detailsLaser active region structureBeam splitterPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses a high-speed and high-precision linear optocoupler based on a quantum dot laser and an InGaAs detector. The optocoupler comprises an insulating packaging shell with a plurality of pins, two groups of InGaAs photoelectric detectors formed in the insulating packaging shell, a variable-ratio light beam splitter which is formed in the insulating packaging shell and is positioned above the InGaAs photoelectric detector, and a quantum dot laser which is formed in the insulating packaging shell and is positioned above the variable-ratio beam splitter. The InGaAs photoelectric detector and the quantum dot laser are electrically connected with the corresponding pins; the variable-ratio beam splitter is provided with a light inlet used for receiving laser light generated by the quantum dot laser, two light outlets used for emitting the laser light to the two groups of InGaAs photoelectric detectors respectively, and two laser transmission channels formed between the two light outlets and the light inlet.
Owner:THE 44TH INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
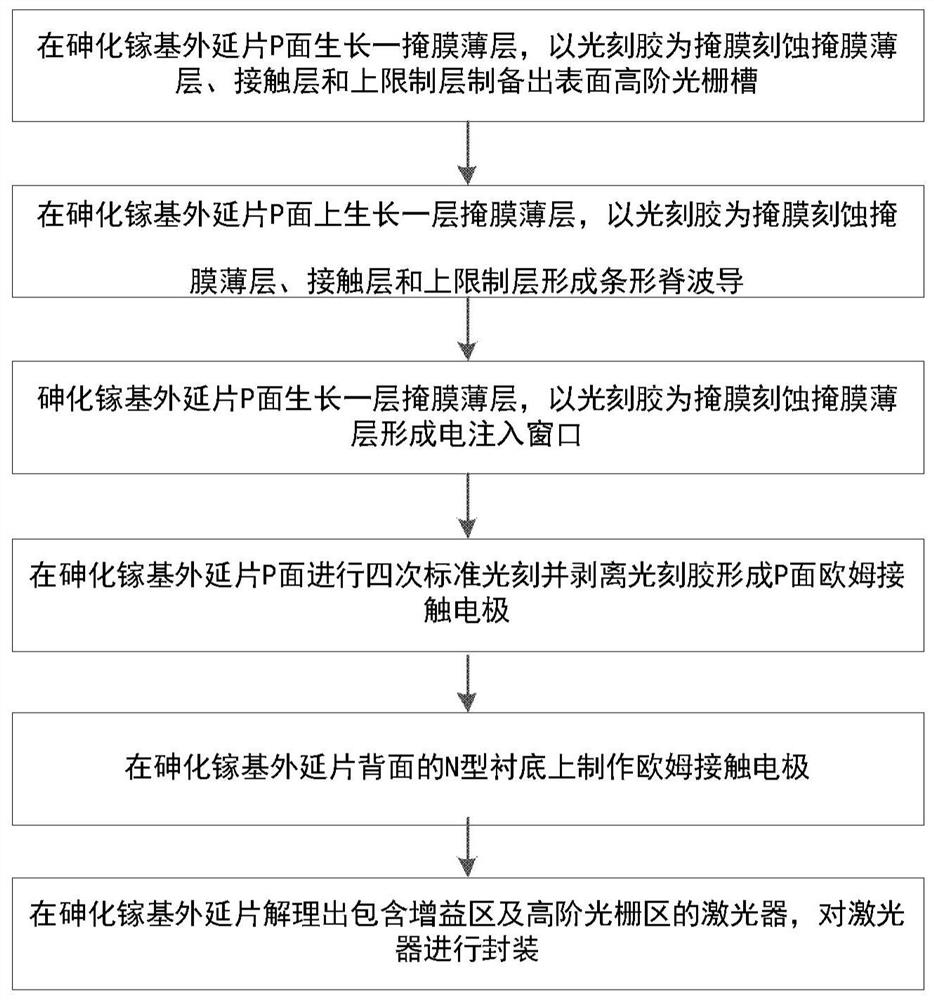
Preparation method of single-mode gallium arsenide-based quantum dot laser
ActiveCN110611244BGuaranteed single mode lasingReduce complexityLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGratingGain
A method for preparing a single-mode gallium arsenide-based quantum dot laser, the method comprising: growing a mask thin layer on the P-side of a gallium arsenide-based epitaxial wafer, and performing a standard photolithography on the mask thin layer to produce surface high-order Grating groove; then grow a thin mask layer on the P surface of the epitaxial wafer, and perform standard photolithography twice on the thin mask layer to produce a strip-shaped ridge waveguide; then grow a thin mask layer, and perform standard photolithography three times Form an electrical injection window; perform standard photolithography four times on the P side of the epitaxial wafer and peel off the photoresist to form an ohmic contact electrode on the P side; finally make an ohmic contact electrode on the N-type substrate on the back of the GaAs-based epitaxial wafer, and resist the arsenic Gain-based epitaxial wafers are cleaved into lasers including gain regions and high-order grating regions, and the lasers are packaged. The invention can generate stable single-mode lasing without making small-period gratings and secondary epitaxy through the standard photolithography process, reduces the complexity and cost of the process, and facilitates device preparation and large-scale production.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing indium arsenide/indium phosphide quantum dot laser epitaxial wafer with ultra-wide light emission spectrum
PendingCN113745971AAchieve stack growthRealize controllable adjustmentPolycrystalline material growthLaser detailsIndiumIndium arsenide
The invention discloses a method for preparing an indium arsenide / indium phosphide quantum dot laser epitaxial wafer with an ultra-wide light emission spectrum. The method comprises the following steps of: epitaxially growing a buffer layer and a lower respective limiting layer on an indium phosphide substrate; stacking and growing a plurality of quantum dot active layers; and depositing an upper respective limiting layer and an ohmic contact layer to finish the preparation. The size of the grown quantum dots is adjusted by controlling the deposition thickness of the quantum dots, and meanwhile, the height of the grown quantum dots is adjusted by adjusting the thickness of a first cover layer in two-step growth of quantum dot cover layers, so that stacked growth of the quantum dots with different sizes and heights is realized, and further the size and the height are adjusted to enable the prepared indium arsenide / indium phosphide quantum dot epitaxial wafer to have an ultra-wide light emission spectrum, the preparation method is simple in step, convenient to operate, controllable and adjustable, and the prepared epitaxial wafer is an ideal material for preparing a tunable laser and has very high practicability and wide applicability.
Owner:JIANGSU HUAXING LASER TECH CO LTD
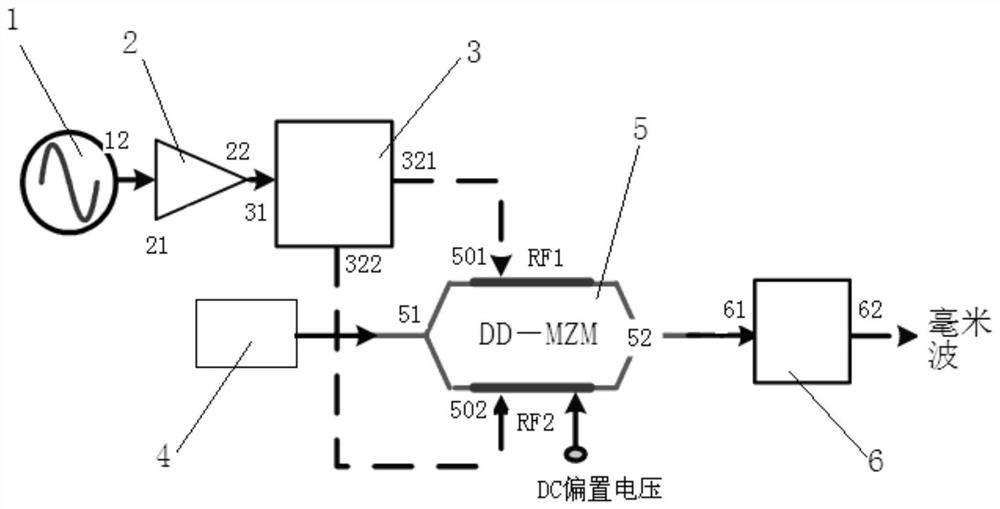
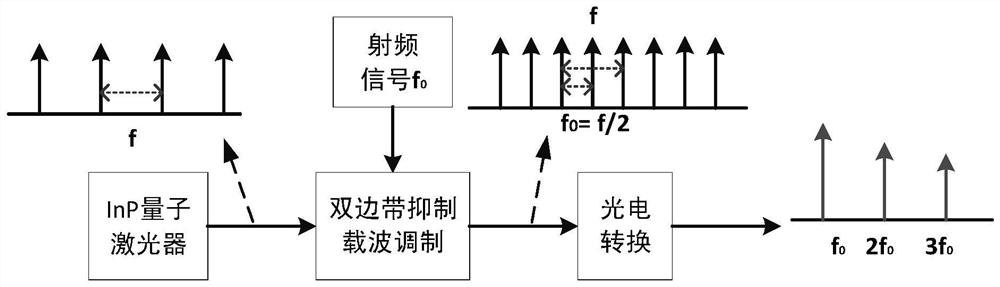
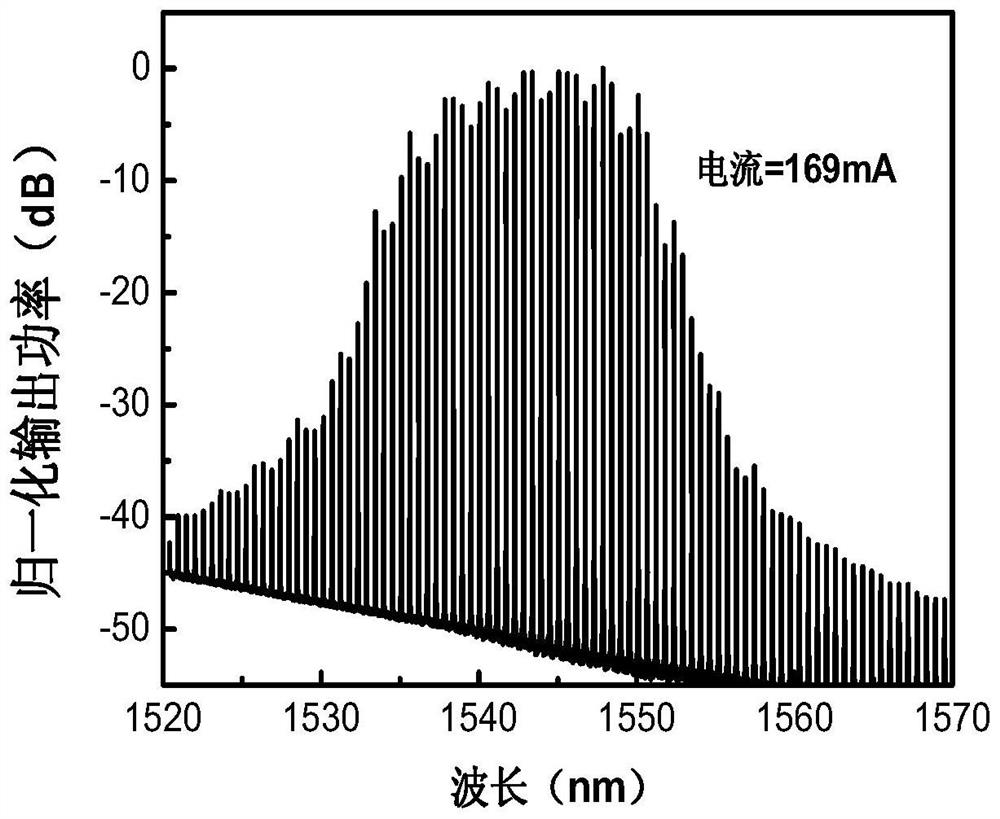
Millimeter wave generation system and method based on quantum dot laser
ActiveCN109361469BSimple structureReduce noisePhotonic quantum communicationElectromagnetic transmittersPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
The invention discloses a millimeter wave generation system and method based on quantum dot lasers. The generation system includes: a radio frequency signal generator for outputting radio frequency signals, a radio frequency power amplifier, and a 180-degree phase-shifting hybrid power splitter for generating InP monolithic integrated quantum dot laser for comb spectral signals, dual-arm Mach-Zehnder modulator, the input end is connected to InP monolithic integrated quantum dot laser for receiving comb spectral signals, the upper electrode and the lower electrode are respectively shifted by 180 degrees The first output terminal and the second output terminal of the phase hybrid power divider are connected to receive two radio frequency signals, and the output terminal is used to output the comb spectrum signal generated by modulation; after photoelectric conversion by the single row carrier photodetector, the output millimeter wave signal.
Owner:NINGBO DAHONGYING UNIV
A method of preparation of a GaaS base laser laser
ActiveCN111342345BIncrease powerQuality improvementLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersQuantum dotErbium lasers
A preparation method of a GaAs-based quantum dot laser, by growing the N waveguide layer three times, the Ga input of the first N waveguide layer is increased when the second N waveguide layer is grown, and the third N waveguide layer is grown compared to the second N waveguide layer. When the N waveguide layer is reduced, by growing the P waveguide layer three times, the Ga flux of the second P waveguide layer is increased relative to the growth of the first P waveguide layer, and the growth of the third P waveguide layer is relatively lower than that of the second P waveguide layer. , realize the growth of three layers of GaInP stress buffer layers with different flow rates under the quantum dot active area, and grow three layers of GaInP stress buffer layers with different flow rates above the quantum dot active area to reduce the stress caused by restrictive growth , to provide the best growth conditions for the formation of quantum dots, which is conducive to the formation and aggregation density of quantum dots, and through stress release, the laser power can be increased, the threshold current can be reduced, and the quality of quantum dots can be improved.
Owner:Shandong Huaguang Optoelectronics Co. Ltd.
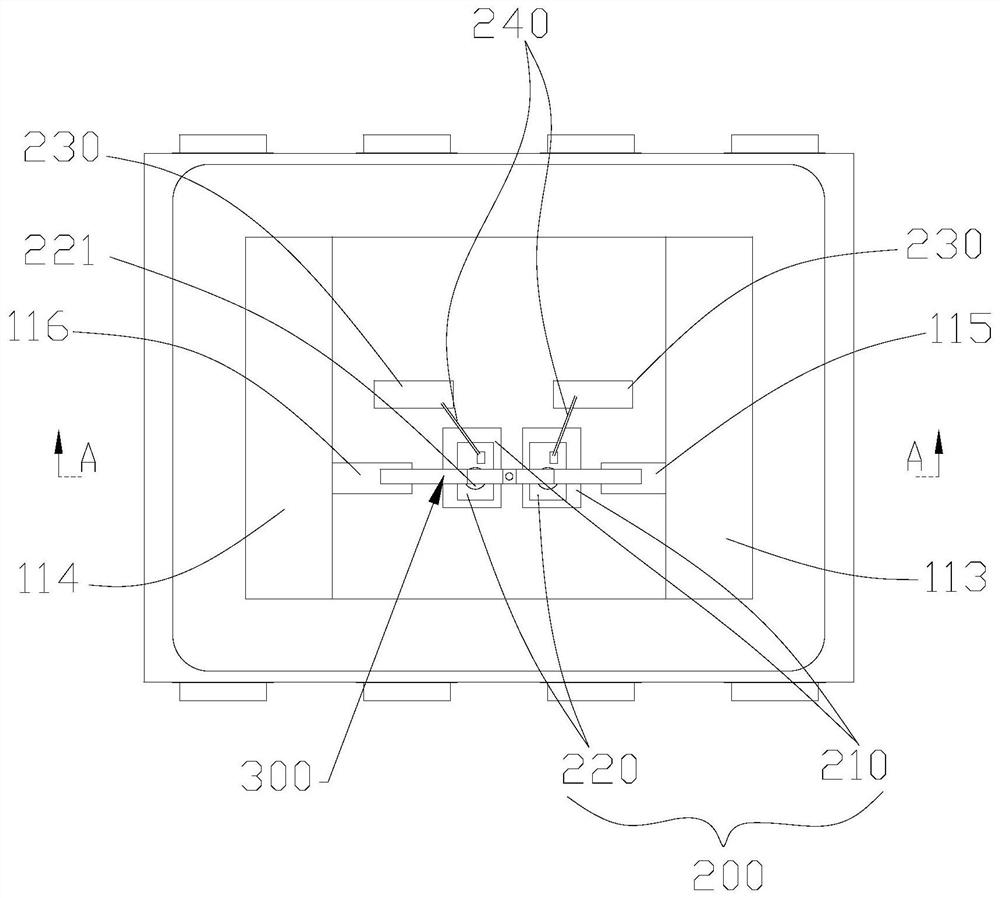
Electrically pumped perovskite composite cavity laser
ActiveCN109687290BSimple structureEasy to implementOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsElectron holeGrating
The invention provides an electric pumping perovskite composite cavity laser, and belongs to the field of quantum dot lasers. The electric pumping perovskite composite cavity laser comprises light-emitting units and insulating micro discs; each light-emitting unit sequentially comprises an N-shaped electrode, an electronic transmission layer, a perovskite quantum dot layer, an electron hole transmission layer and a P-shaped electrode from top to bottom; each insulating micro disc comprises a disc and a lateral grating; the insulating micro discs are embedded between the light-emitting units; and the equivalent refractive index of the insulating micro discs are different from the equivalent refractive index of the light-emitting units. According to the electric pumping perovskite compositecavity laser, by additionally arranging the insulating micro discs with the lateral gratings, echo wall mode resonance is formed between the light-emitting units and the insulating micro discs, and the efficiency of the perovskite laser outer quantum is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of all-inorganic semiconductor quantum dot laser
PendingCN113572014AGood optical performanceAvoid instabilityMaterial nanotechnologyLaser active region structureGainErbium lasers
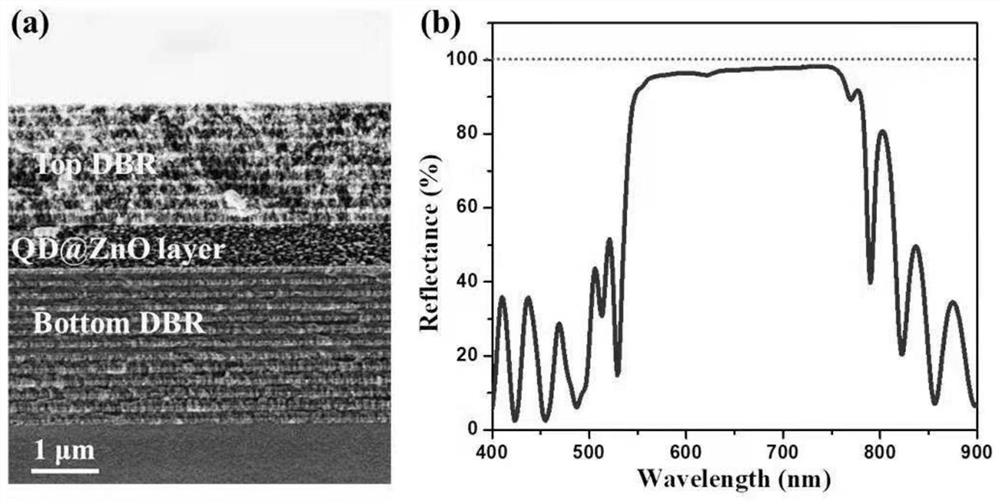
The invention discloses a preparation method of an all-inorganic semiconductor quantum dot laser, all-inorganic quantum dots are CdSe / CdS@ZnO quantum dots modified by taking inorganic ZnO sol as a surface ligand, and a quantum dot film is subjected to high-temperature annealing treatment and then is used as an optical gain dielectric layer of a quantum dot micro laser. Afterwards, high-quality upper high-reflectivity mirror is deposited in room temperature environment through electron beam thermal evaporation method; and finally, the all-inorganic semiconductor quantum dot micro laser is manufactured. The all-inorganic quantum dot laser can effectively solve the problem that the optical performance and the device performance of a traditional quantum dot are unstable due to organic ligands on the surface of the traditional quantum dot, and then the emission performance and the stability of the quantum dot laser are enhanced. According to the preparation method of the full-inorganic quantum dot laser, the quantum dot micro laser device can be promoted to be practically applied.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
A device and method for generating a broadband noise source based on a quantum dot microcolumn laser
ActiveCN112490843BHigh bandwidthLaser detailsSemiconductor laser optical deviceBroadband noiseMacroscopic scale
The present invention is a device based on a method for generating a broadband noise source based on a quantum dot microcolumn laser, which belongs to the technical field of broadband noise source generation methods; the technical problem to be solved is: to provide a device for generating a broadband noise source based on a quantum dot microcolumn laser Improvement of the method; the technical solution adopted to solve the above technical problems is: prepare a quantum dot microcolumn laser as the first light source; inject the external narrowband optical noise into the prepared quantum dot laser in step 1 to generate a broadband noise signal, and the quantum dot laser After the output optical signal is split by the beam splitter, one optical signal is converted into an electrical signal by the photodetector and then output to the oscilloscope and spectrum analyzer for macroscopic observation, and the other is output to Hanbury-Brown and Tevez interferometry The device performs statistical measurement of microphotons; the invention is applied to signal generation, and the broadband noise signal generated by the invention has the characteristics of high bandwidth and no external cavity period, which improves the security of communication.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Manufacturing method of quantum dot laser
ActiveCN114725778AReduce processing costsFast growth ratePolycrystalline material growthLaser detailsMaterial growthPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a quantum dot laser, which comprises the following steps: in MOCVD (Metal Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition) equipment, sequentially growing an n-type limiting layer and an n-type waveguide layer on a substrate to obtain a preliminary sample; and transferring the preliminary sample to MBE equipment, and then sequentially growing a quantum dot active region, a p-type waveguide layer, an electron limiting layer, a p-type limiting layer and a p-type contact layer on the n-type waveguide layer. The GaN-based quantum dot laser has the advantages that the MOCVD process is low in cost and high in growth rate, and the MBE process is good in low-dimensional material growth and is prepared on p-GaN, so that the prepared GaN-based quantum dot laser has the characteristics of high-temperature stability, low threshold current density and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com




![[100] or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices [100] or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d60eaec6-5dc6-46e1-9416-bd73b03fea27/HPA00001232175600011.PNG)
![[100] or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices [100] or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d60eaec6-5dc6-46e1-9416-bd73b03fea27/HPA00001232175600021.PNG)
![[100] or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices [100] or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/d60eaec6-5dc6-46e1-9416-bd73b03fea27/HPA00001232175600031.PNG)