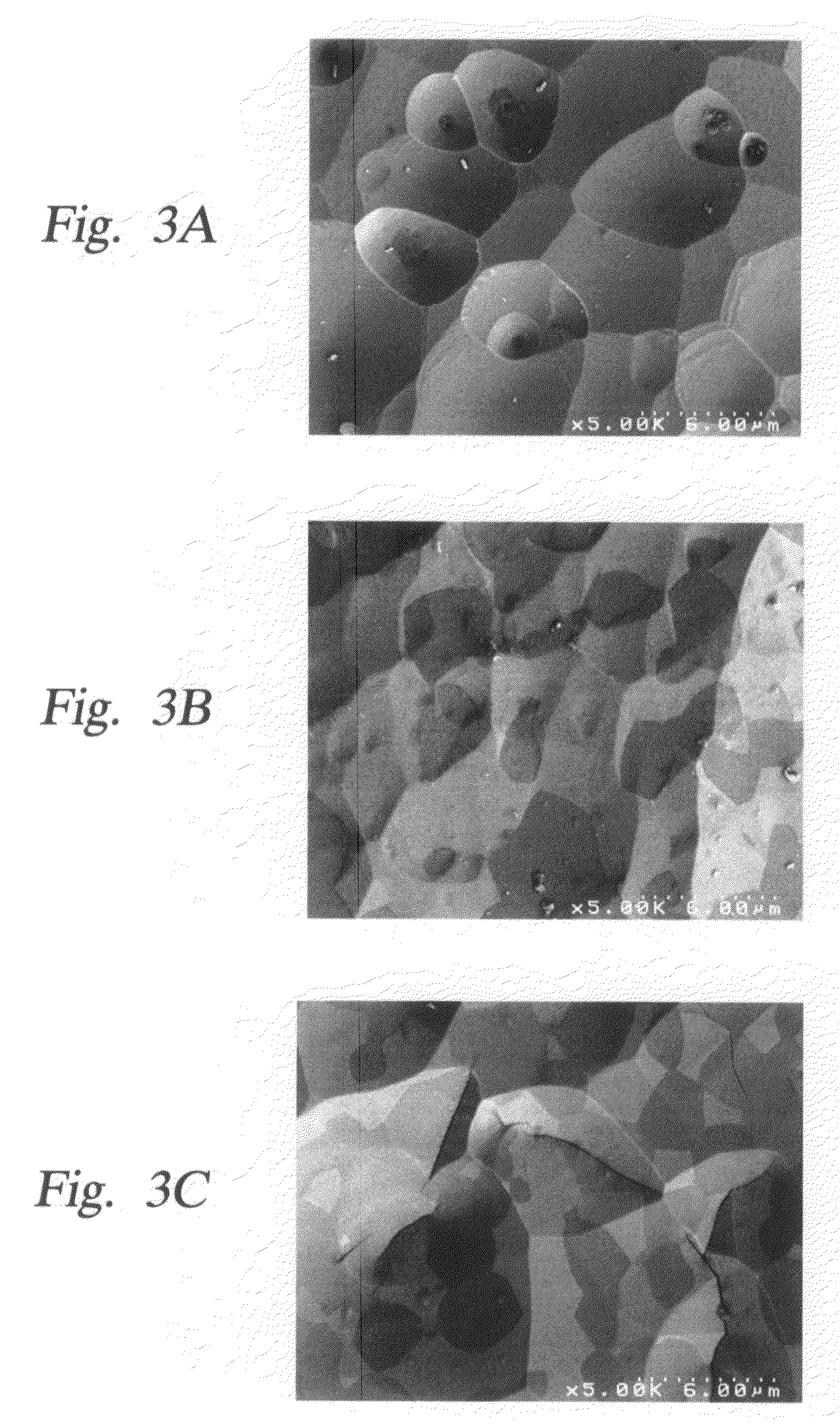
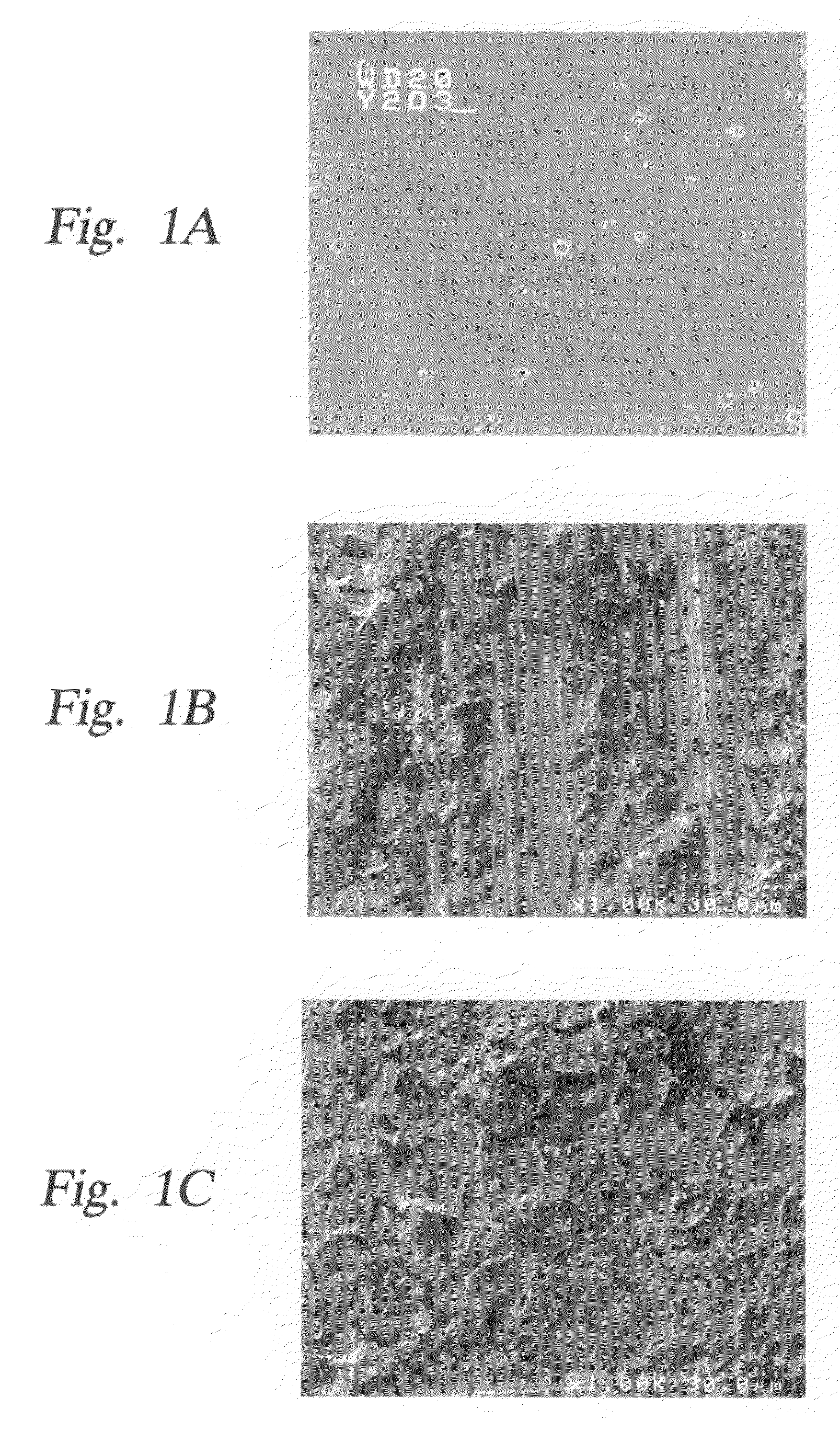
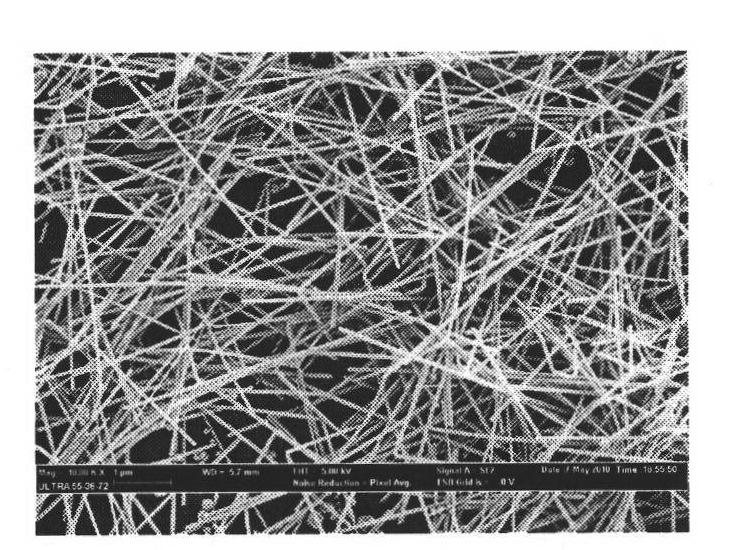
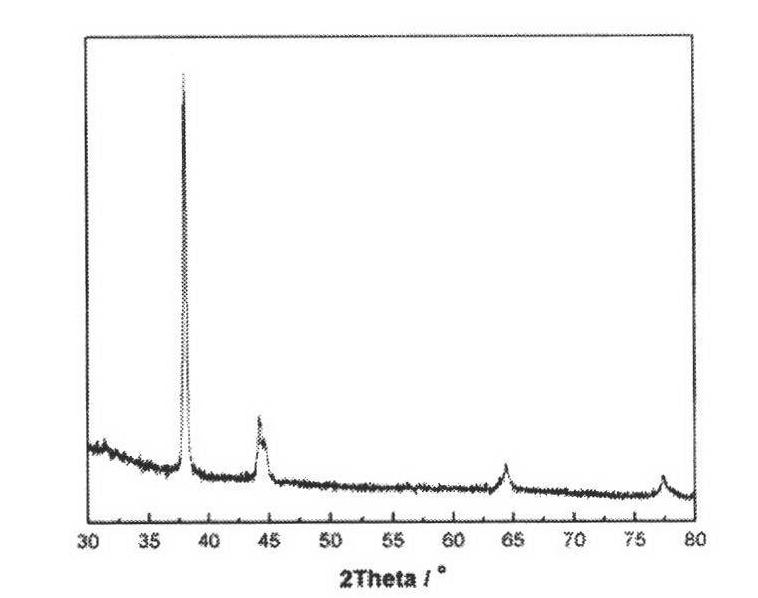
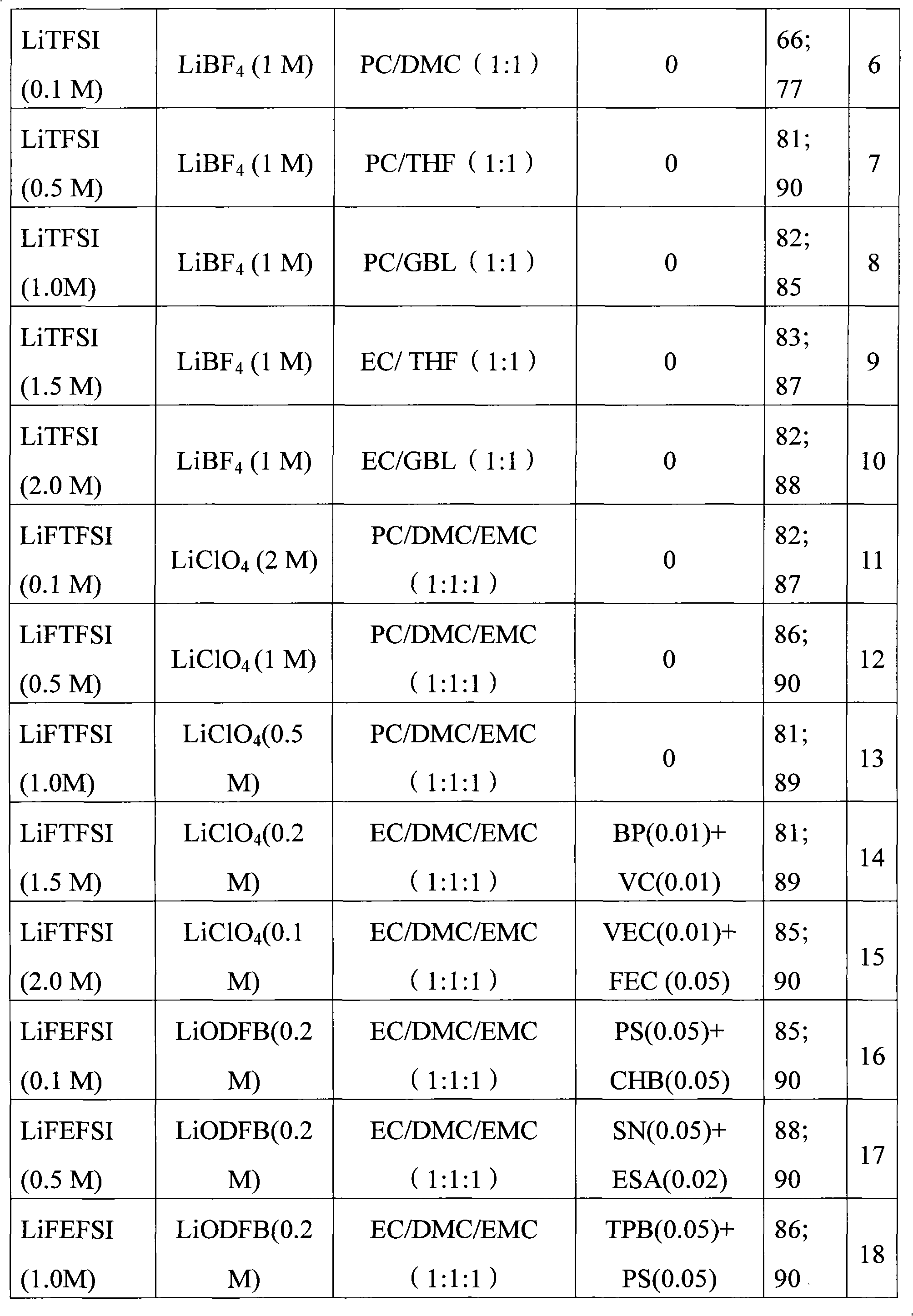
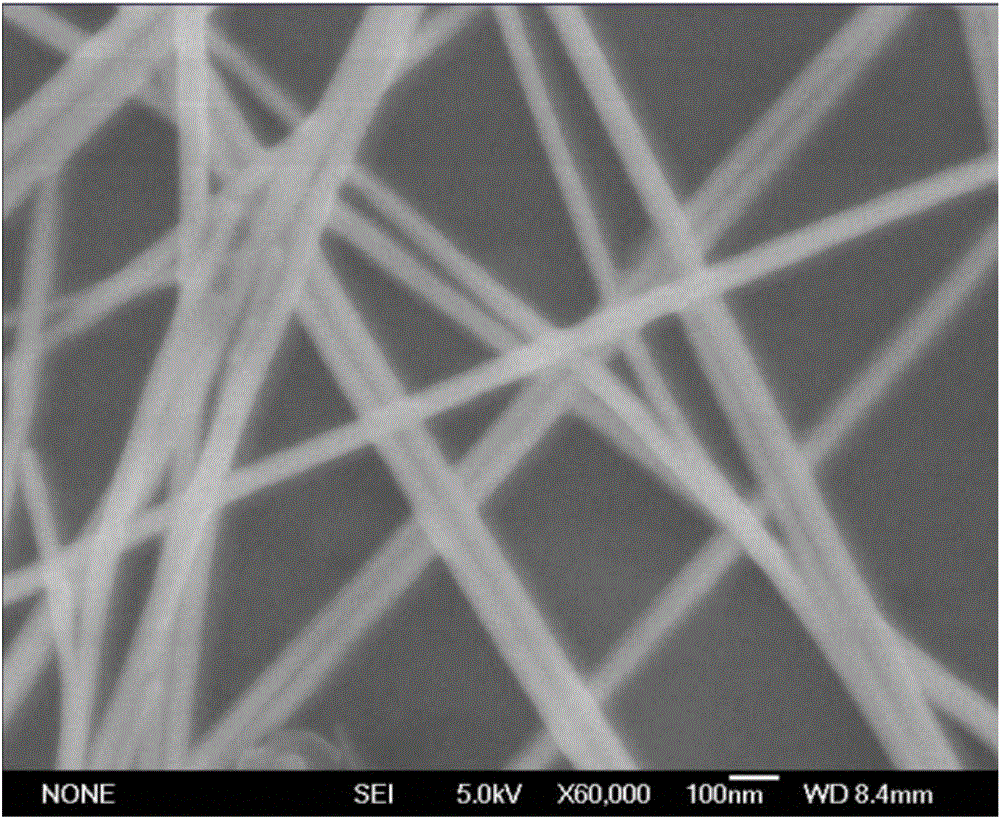
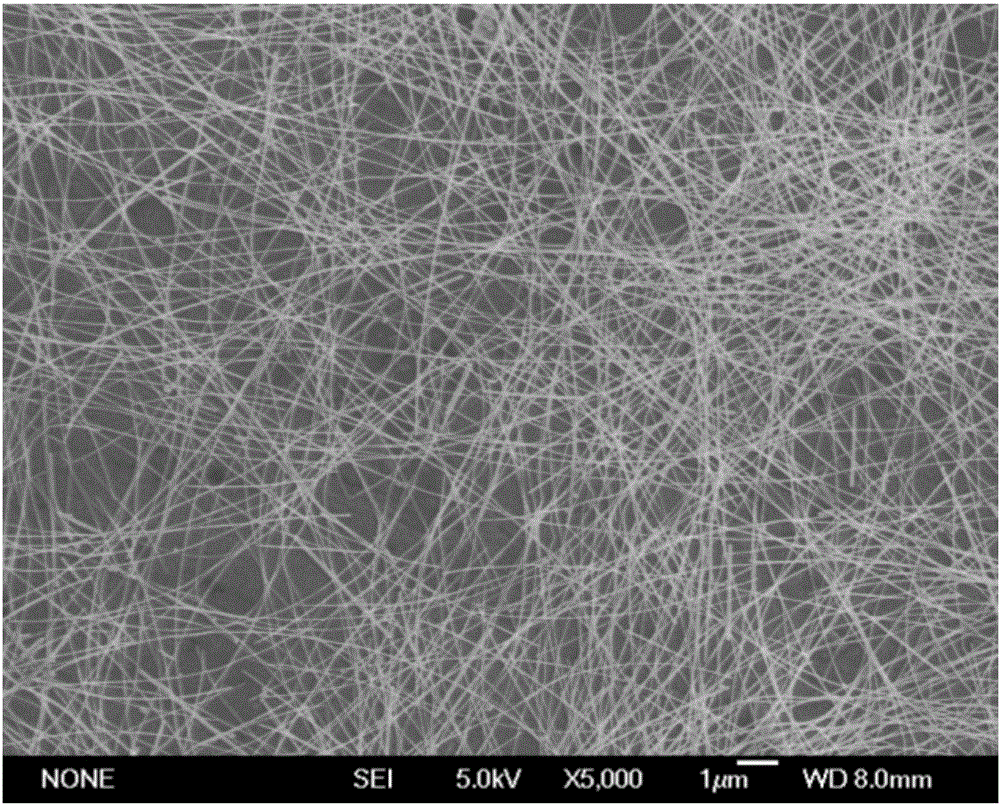
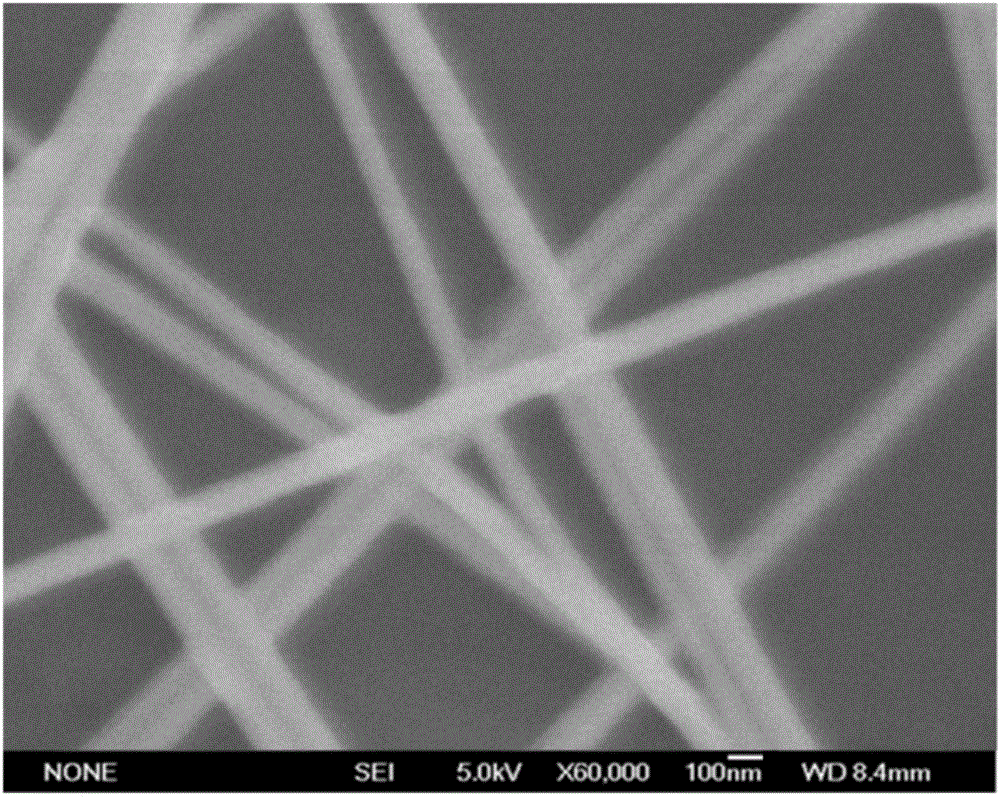
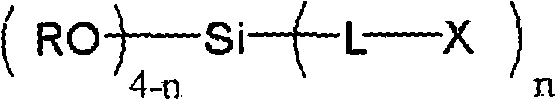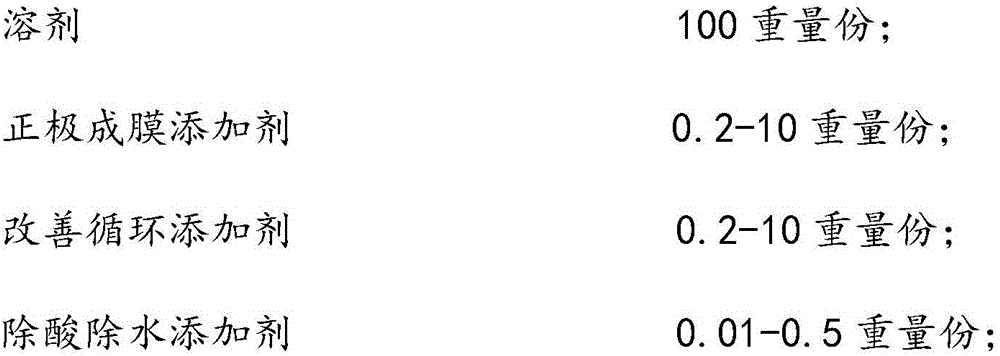Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1512 results about "Molar concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molar concentration (also called molarity, amount concentration or substance concentration) is a measure of the concentration of a chemical species, in particular of a solute in a solution, in terms of amount of substance per unit volume of solution. In chemistry, the most commonly used unit for molarity is the number of moles per litre, having the unit symbol mol/L. A solution with a concentration of 1 mol/L is said to be 1 molar, commonly designated as 1 M.
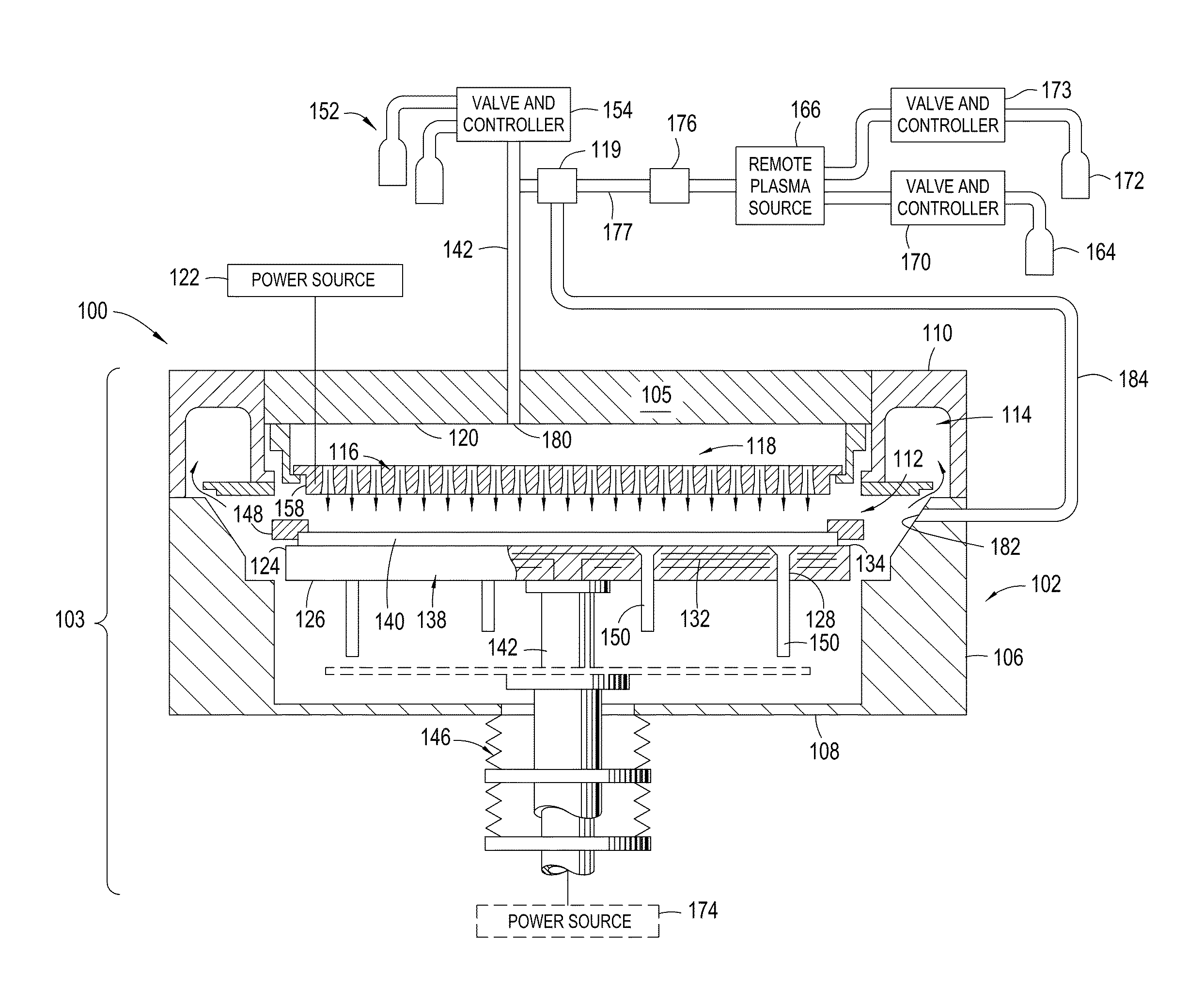
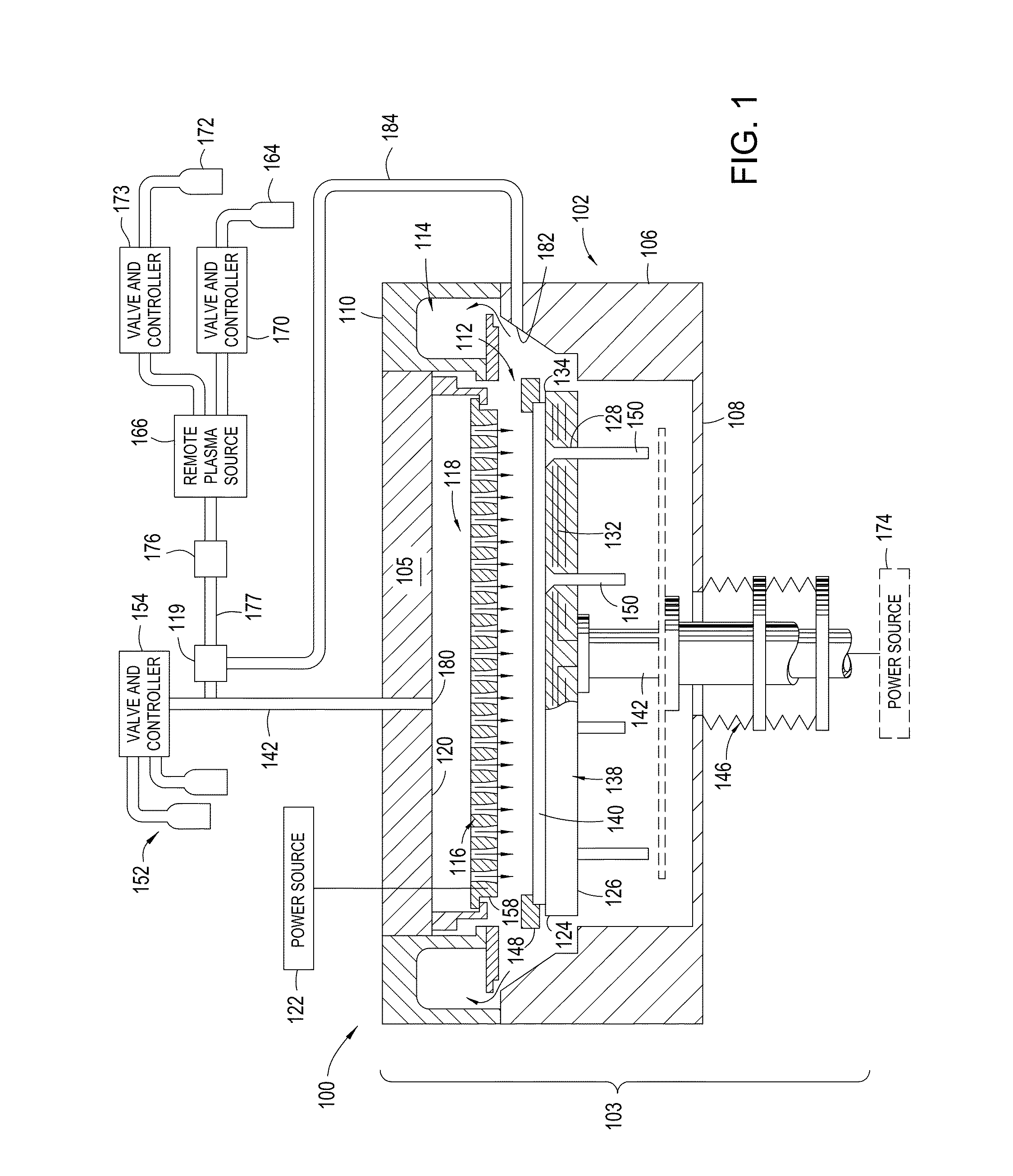
Yttria-based material coated chemical vapor deposition chamber heater
ActiveUS20140263272A1Improve wear resistanceImprove flexural strengthLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingYTTERBIUM OXIDEFlexural strength
Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to heated substrate supports having a protective coating thereon. The protective coating is formed from yttrium oxide at a molar concentration ranging from about 50 mole percent to about 75 mole percent; zirconium oxide at a molar concentration ranging from about 10 mole percent to about 30 mole percent; and at least one other component, selected from the group consisting of aluminum oxide, hafnium oxide, scandium oxide, neodymium oxide, niobium oxide, samarium oxide, ytterbium oxide, erbium oxide, cerium oxide, and combinations thereof, at a molar concentration ranging from about 10 mole percent to about 30 mole percent. The alloying of yttrium oxide with a compatible oxide improves wear resistance, flexural strength, and fracture toughness of the protective coating, relative to pure yttrium oxide.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and apparatus which reduce the erosion rate of surfaces exposed to halogen-containing plasmas
ActiveUS20080264565A1Improve plasma resistanceImprove corrosion resistanceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingYTTERBIUM OXIDEErosion rate
A ceramic article which is resistant to erosion by halogen-containing plasmas used in semiconductor processing. The ceramic article includes ceramic which is multi-phased, typically including two phase to three phases. The ceramic is formed from yttrium oxide at a molar concentration ranging from about 50 mole % to about 75 mole %; zirconium oxide at a molar concentration ranging from about 10 mole % to about 30 mole %; and at least one other component, selected from the group consisting of aluminum oxide, hafnium oxide, scandium oxide, neodymium oxide, niobium oxide, samarium oxide, ytterbium oxide, erbium oxide, cerium oxide, and combinations thereof, at a molar concentration ranging from about 10 mole % to about 30 mole %.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and apparatus which reduce the erosion rate of surfaces exposed to halogen-containing plasmas
ActiveUS7696117B2Reduce erosion rateImprove mechanical propertiesElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingErosion rateYttrium
A ceramic article which is resistant to erosion by halogen-containing plasmas used in semiconductor processing. The ceramic article includes ceramic which is multi-phased, typically including two phase to three phases. The ceramic is formed from yttrium oxide at a molar concentration ranging from about 50 mole % to about 75 mole %; zirconium oxide at a molar concentration ranging from about 10 mole % to about 30 mole %; and at least one other component, selected from the group consisting of aluminum oxide, hafnium oxide, scandium oxide, neodymium oxide, niobium oxide, samarium oxide, ytterbium oxide, erbium oxide, cerium oxide, and combinations thereof, at a molar concentration ranging from about 10 mole % to about 30 mole %.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of reducing the erosion rate of semiconductor processing apparatus exposed to halogen-containing plasmas
InactiveUS20080264564A1Improve plasma resistanceImprove corrosion resistanceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingErosion rateYttrium
A ceramic article useful in semiconductor processing, which is resistant to erosion by halogen-containing plasmas. The ceramic article is formed from a combination of yttrium oxide and zirconium oxide. In a first embodiment, the ceramic article includes ceramic which is formed from yttrium oxide at a molar concentration ranging from about 90 mole % to about 70 mole %, and zirconium oxide at a molar concentration ranging from about 10 mole % to about 30 mole %. In a second embodiment, the ceramic article includes ceramic which is formed from zirconium oxide at a molar concentration ranging from about 96 mole % to about 94 mole %, and yttrium oxide at a molar concentration ranging from about 4 mole % to about 6 mole %.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
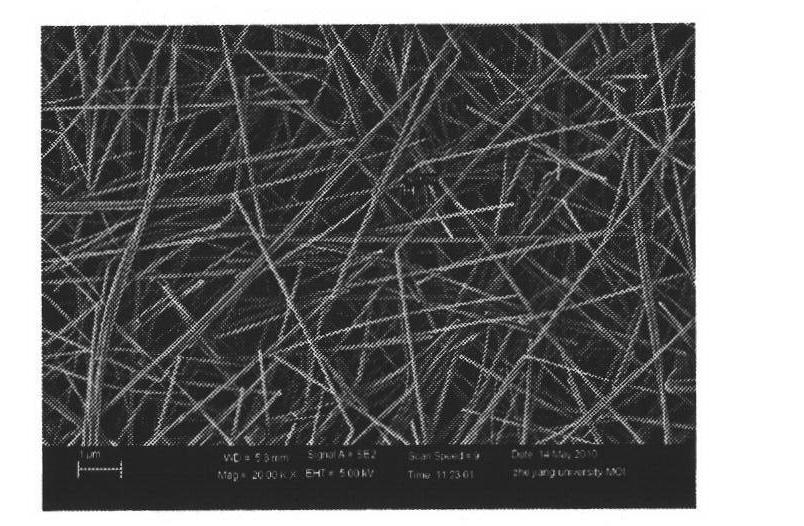
Quick and efficient synthesis method for silver nanowires
InactiveCN101934377AImprove production efficiencyReduce reaction preparation timeHigh concentrationSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a quick and efficient synthesis method for silver nanowires. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) introducing inert gas into a reactor, adding 2 volume parts of glycol into the reactor, and stirring, heating, condensing and refluxing the glycol; quickly adding 1 volume part of glycol solution of silver nitrate at molar concentration of between 0.1 and 0.5m into the reactor; slowly dropwise adding 1 to 2 volume parts of PVP at molar concentration of between 0.15 and 0.75m and 4 to 32 mu m of glycol solution of MnCl2 at the same time; and reacting and cooling the mixture to the room temperature to obtain reaction mother liquor of the silver nanowires; and 2) transferring the reaction mother liquor of the silver nanowires into a centrifugal tube; adding acetone into the centrifugal tube and performing centrifugal separation to remove supernatant and retain precipitate; adding de-ionized water or ethanol into the centrifugal tube and performing centrifugal separation to remove the supernatant and retain precipitate, and repeating the operation for 1 to 3 times; and extracting and dispersing the precipitate with ethanol to obtain the silver nanowires. The method shortens the reaction time and also has high selectivity for the synthesis of the silver nanowires under conditions of high concentration.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Novel vanadium halide redox flow battery
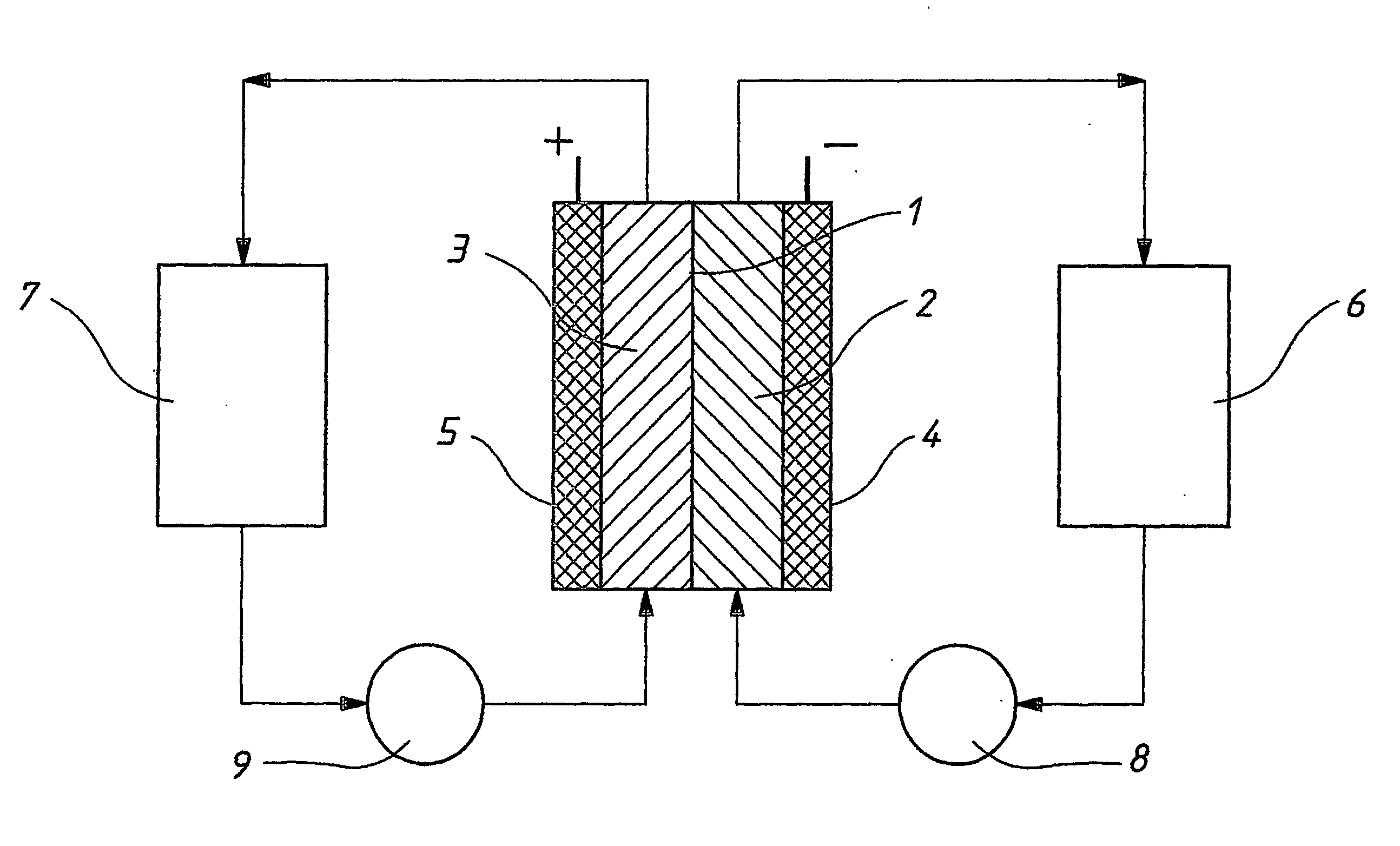
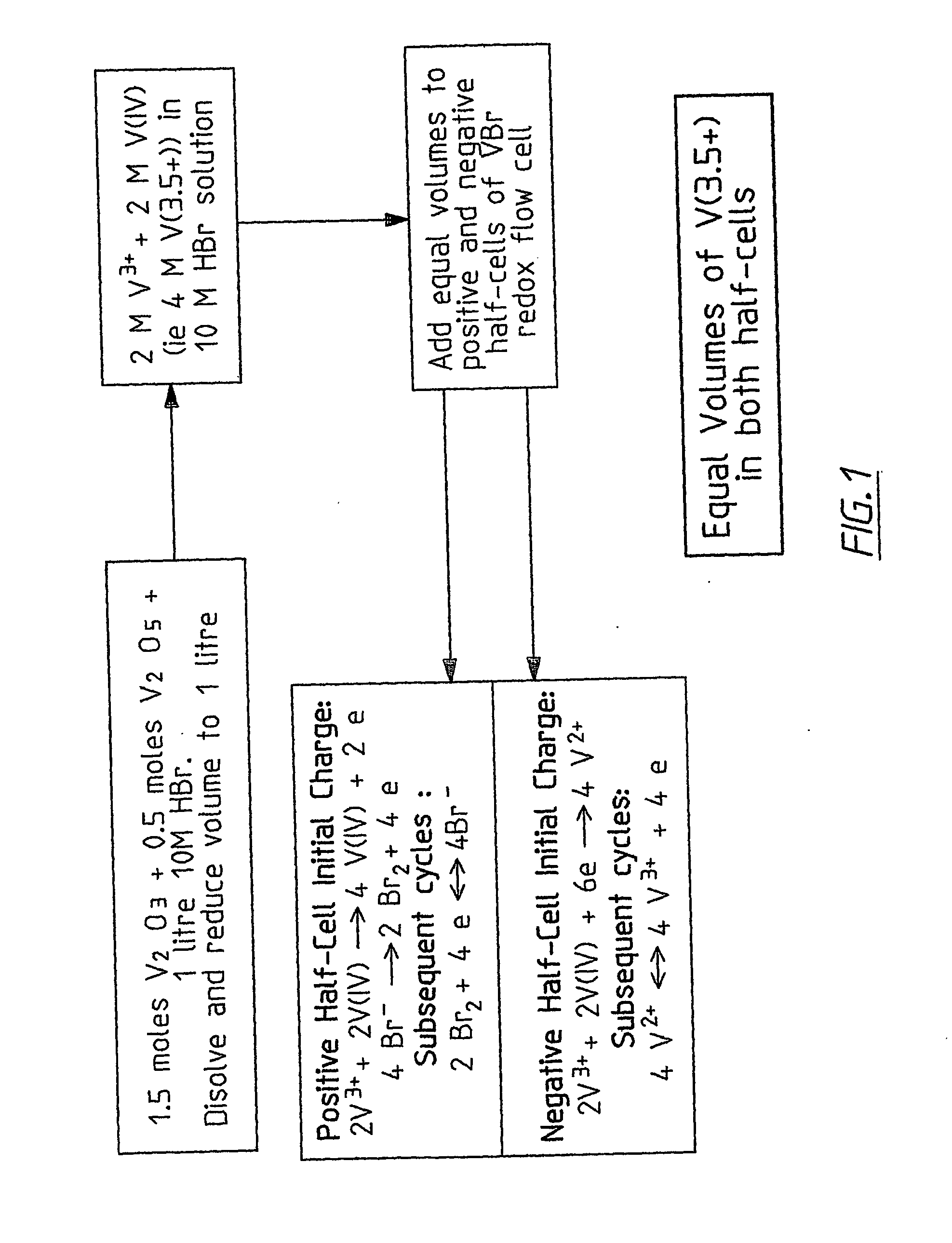
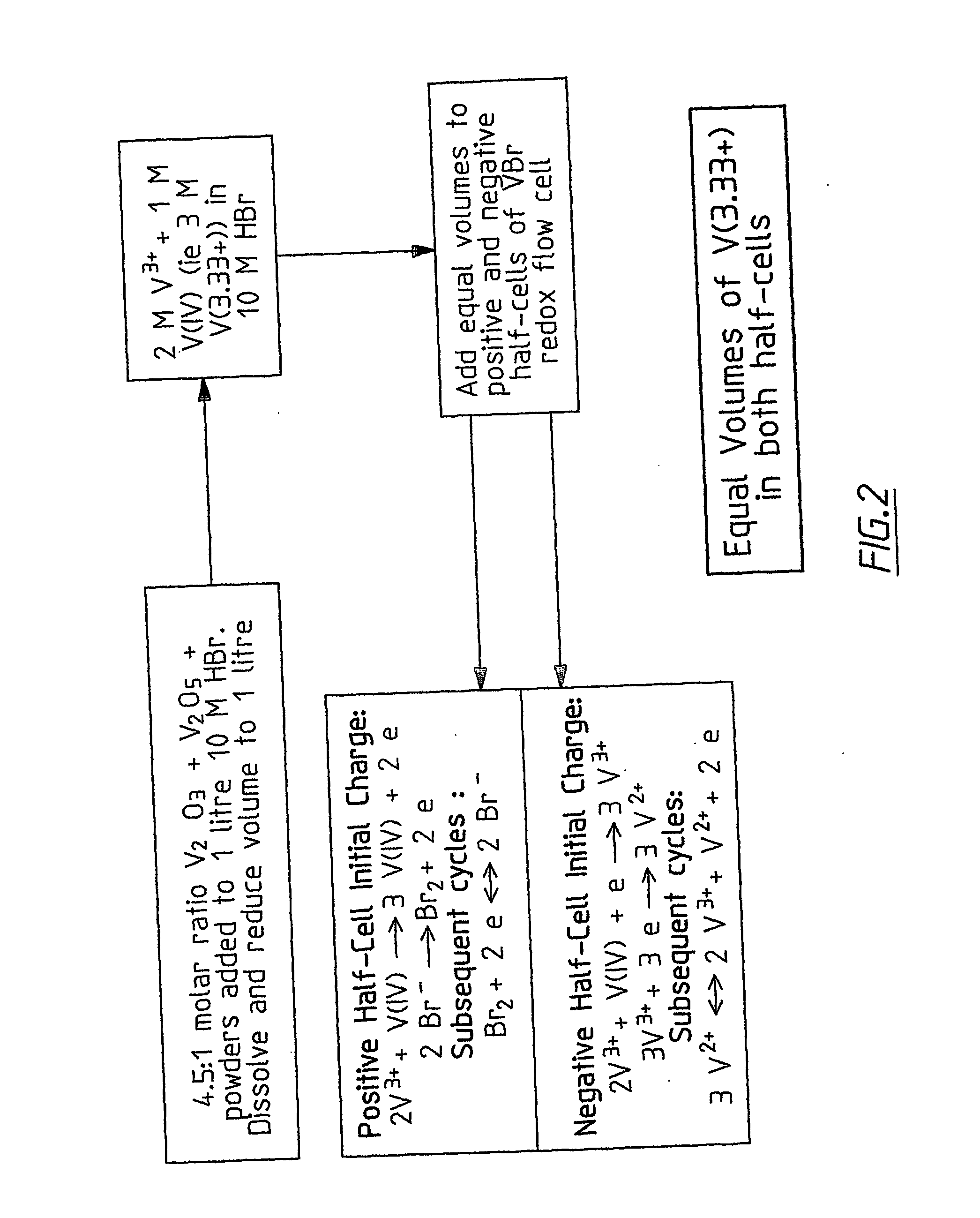
InactiveUS20060183016A1Avoid excessive bromine generationStabilise the bromine producedCharging stationsCell electrodesRedoxPhysical chemistry
A prior to charge vanadium halide redox cell, a vanadium halide redox cell which is at a state of charge selected from the group consisting of a zero state of charge and a near zero state of charge and vanadium halide redox cell which are fully charged and partially charged are described. The prior to charge vanadium halide redox cell comprises a positive half cell containing a positive half cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte, vanadium (III) halide and vanadium (IV) halide, a negative half cell containing a negative half cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte, vanadium (III) halide and vanadium (N) halide wherein the amounts of vanadium (III) halide, vanadium (IV) halide and halide ions in the positive and negative half cell solutions are such that in a first charging step comprising charging the prior to charge vanadium halide redox cell, a vanadium halide redox cell having a state of charge selected from the group consisting of a zero state of charge and a near zero state of charge comprising predominantly vanadium (N) halide in the positive half cell solution and predominantly V(III) halide in the negative half cell solution can be prepared. The vanadium halide redox cell which is at a state of charge selected from the group consisting of a zero state of charge and a near zero state of charge comprises a positive half cell containing a positive half cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte and a vanadium halide which is predominantly vanadium (N) halide, a negative half cell containing a negative half cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte and a vanadium halide which is predominantly vanadium (III) halide wherein the amount of vanadium (N) halide in the positive half cell solution and the amount of vanadium (III) halide in the negative half cell solution are such that the vanadium halide redox cell is at a state of charge selected from the group consisting of a zero state of charge and a near zero state of charge. The vanadium halide redox cell which is fully charged comprises a positive half cell containing a positive half cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte, a polyhalide complex, vanadium (IV) halide and vanadium (V) halide, a negative half cell containing a negative half cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte and vanadium (II) halide wherein the molar concentration of vanadium (V) and polyhalide complex:molar concentration of vanadium (II) halide is about stoichiometrically balanced. The vanadium halide redox cell which is partially charged comprises a positive half cell containing a positive half cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte, a polyhalide complex, vanadium (IV) halide and vanadium (V) halide, a negative half cell containing a negative half cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte, vanadium (II) halide and vanadium (III) halide wherein the number of moles of moles of polyhalide complex and vanadium (V): number of moles of vanadium (II) halide is about stoichiometrically balanced.
Owner:NEWSOUTH INNOVATIONS PTY LTD
Semiconductor processing apparatus comprising a solid solution ceramic of yttrium oxide and zirconium oxide
ActiveUS20100160143A1Reduce erosion rateImprove mechanical propertiesElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHalogenSolid solution
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for the rapid detection of whole microorganisms on retaining membranes by use of chaotropic agents
InactiveUS6846648B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntigenThiourea
Owner:ANDA BIOLOGICALS
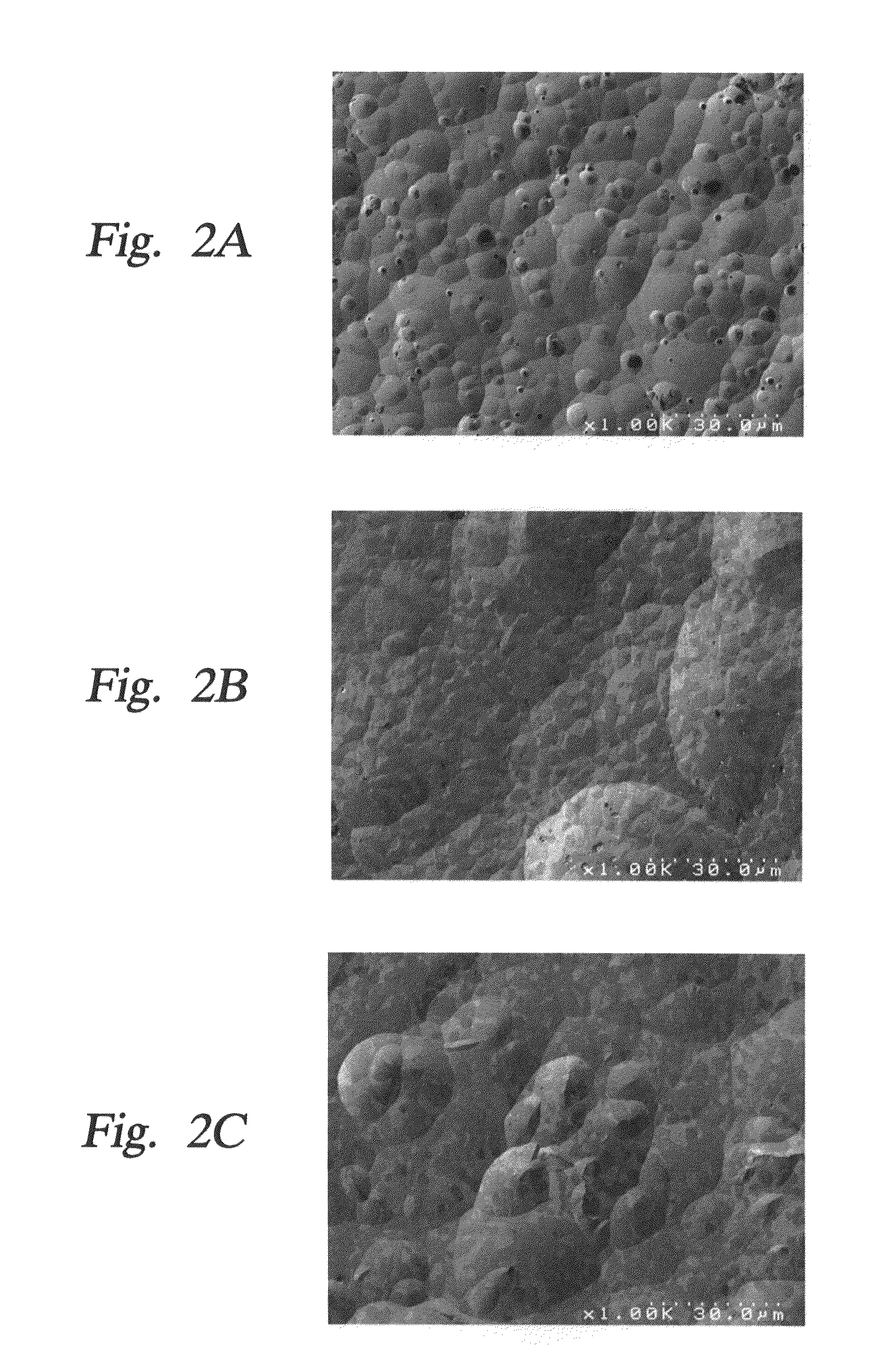
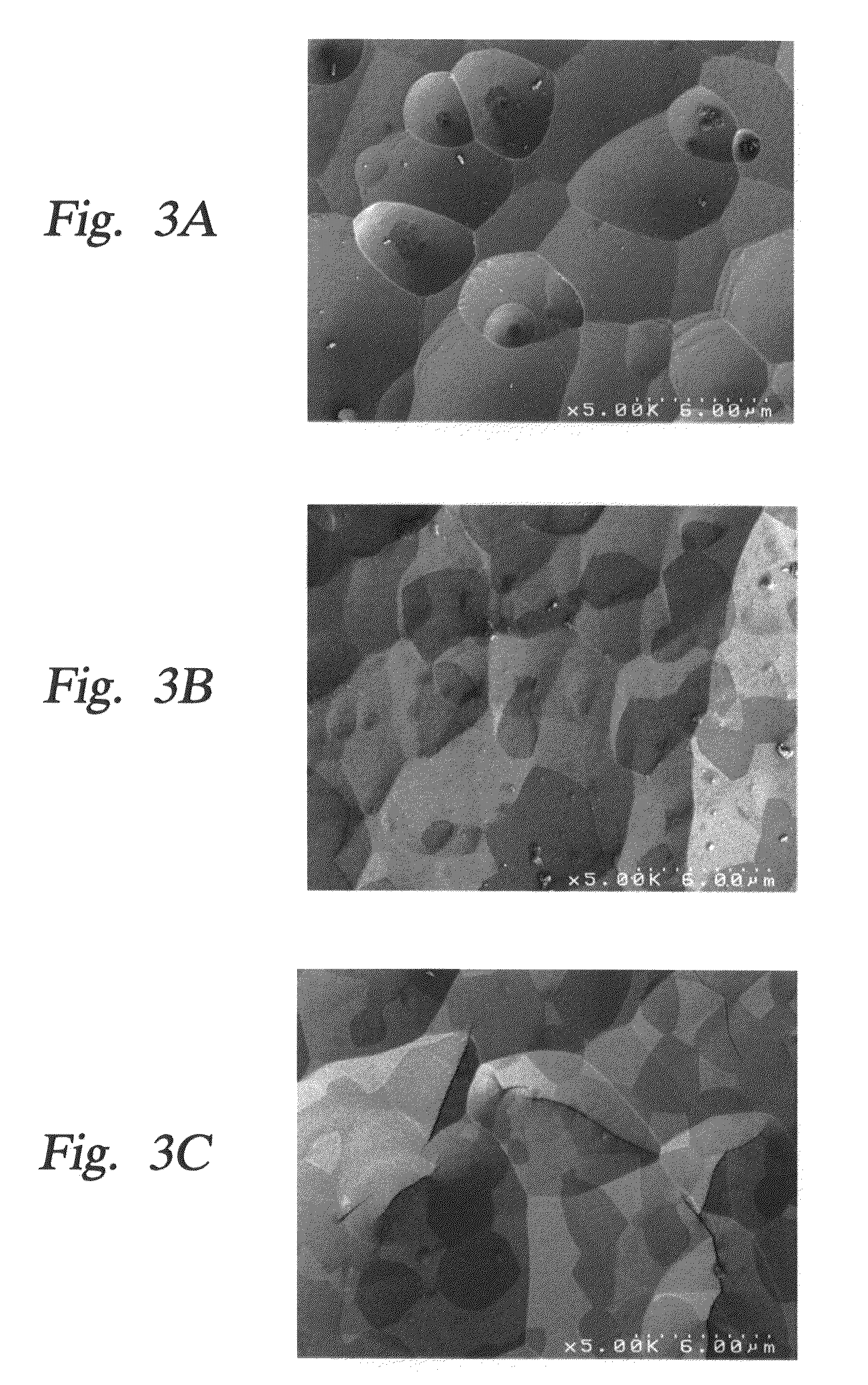
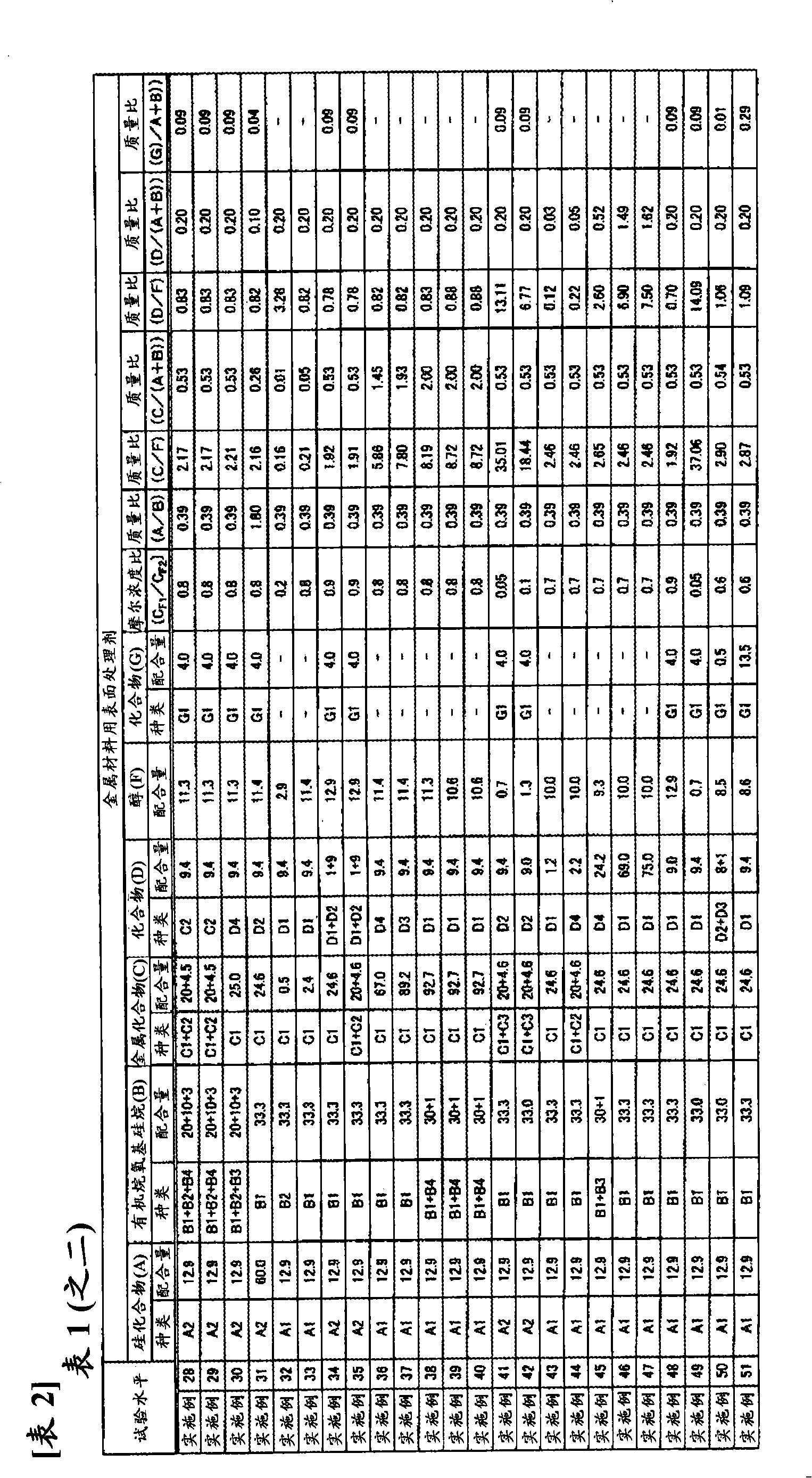
Surface treating agent for metallic materials
ActiveCN102257178AImprove adhesionImprove corrosion resistanceAnti-corrosive paintsMetallic material coating processesAlcoholSilicic acid
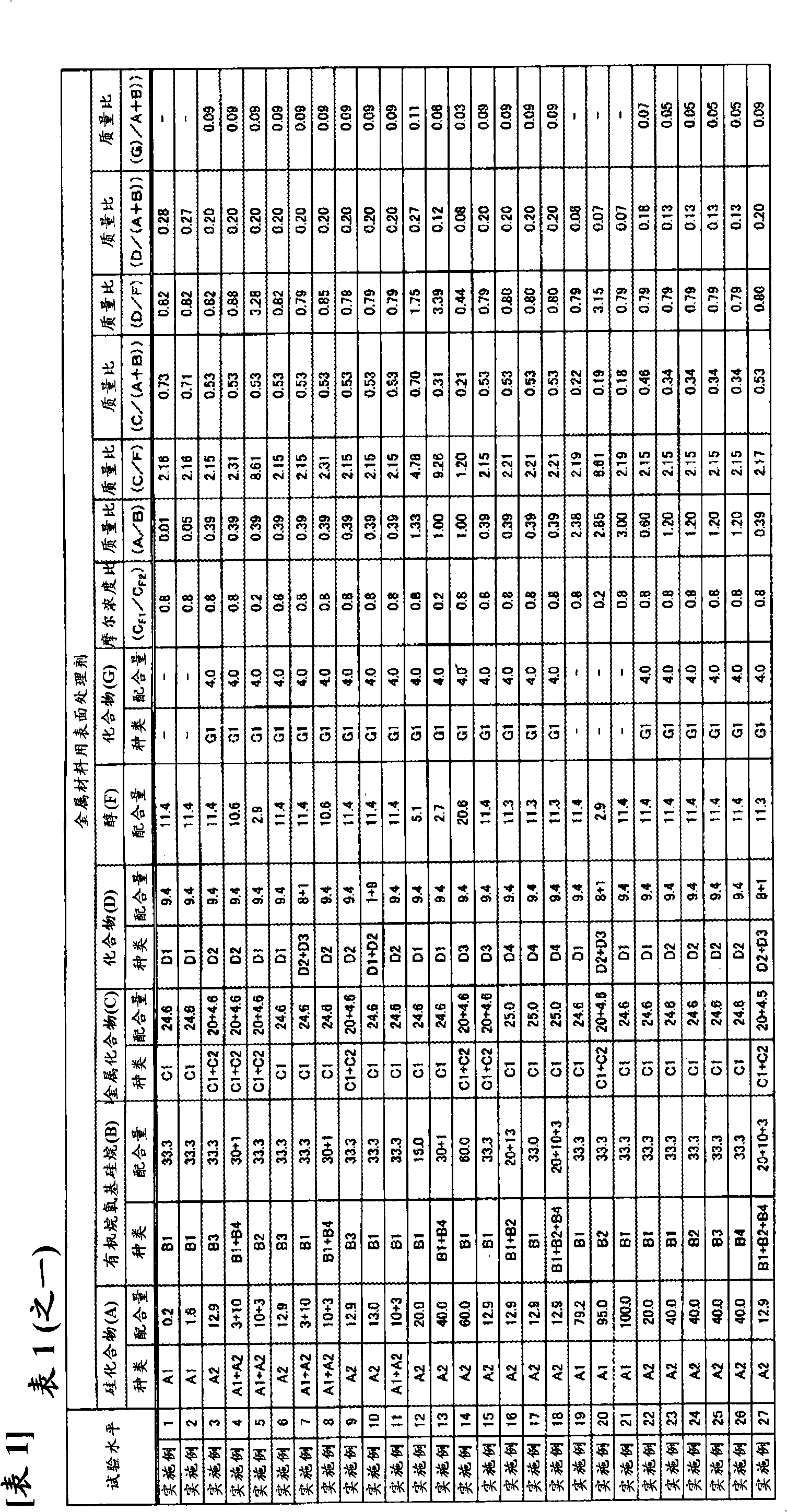
Disclosed is a surface treating agent for metallic materials that has various properties such as corrosion resistance and overcoating properties and, when used in coating-type surface treatment, particularly can form a film , which has excellent adhesion to the surface of metallic materials, and can fix, within the film, a component capable of functioning as a corrosion inhibitor for metallic materials. The surface treating agent for metallic materials comprises a silicic acid compound (A), an organoalkoxysilane (B), a metallic compound (C) containing at least one metal element selected from the group consisting of Zr, Ti, Co, Fe, V, Ce, Mo, Mn, Mg, Al, Ni, Ca, W, Nb, Cr, and Zn, at least one compound (D) selected from the group consisting of phosphoric acid compounds and fluoro compounds, water (E), and an alcohol (F) produced upon hydrolysis of the organoalkoxysilan (B). The molar concentration (mol / L) of the alcohol (F) in the treating agent has been regulated in a predetermined range.
Owner:NIHON PARKERIZING
Lithium ion power battery non-water electrolyte
InactiveCN106025359AImprove normal temperature cycle performanceEasy to useSecondary cellsHigh temperature storageLithium
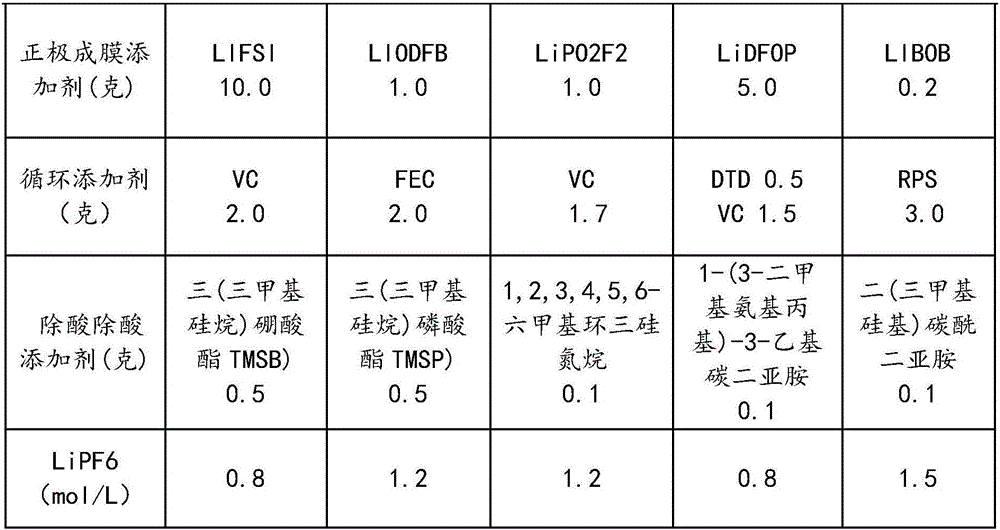
The invention discloses a lithium ion power battery non-water electrolyte. The lithium ion power battery non-water electrolyte is prepared from, by weight, 100 parts of solvents, common lithium salts, 0.2-10 parts of anode film formation additives, 0.2-10 parts of circulation improvement additives and 0.01-0.5 part of acid and water removal additives. The solvents are cyclic carbonic ester and / or chain carbonic ester, and the molar concentration of the common salts in the solvents is 0.8-1.5 mol / L. Due to the combination use of the anode film formation additives, the circulation improvement additives and the acid and water removal additives, during first formation, a CEI film can be formed on the surface of an anode, the stability of a cathode SEI film can be improved, and the normal temperature circulation performance, the high-temperature 45 DEG C circulation performance and the high-temperature storage performance of a power battery can be remarkably improved.
Owner:ZHUHAI SMOOTHWAY ELECTRONICS MATERIALS
Preparation method of zinc oxide nano-rod film on fibre product
InactiveCN101012621ASmall granularityHigh purityFibre treatmentLiquid/gas/vapor textile treatmentFiberChemical solution
The invention relates to a manufacturing method for nanometer rod film of zinc oxide on fiber product, comprising (1) by sol-gel method ZnO nano-crystal grain is prepared and a great deal of ZnO seed crystal is deposited on the surface of fiber product, molar concentrations of zinc salt and alkaline agent are all 0.001M-0.75M; (2) by hydrothermal method or precipitation of chemical solution pool, nanometer rod film of zinc oxide grows on fiber product, molar concentrations of zinc salt solution and complexing agent solution are all 0.001M-0.05M; ZnO nanometer rod film with equal surface and good directivity is obtained. The manufacturing method is provided with simple method and low cost. It is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Semiconductor nanocrystals and preparation methods thereof
A nanocrystal includes a core including a Group III-V semiconductor and a transition metal alloyed with the Group III-V semiconductor, wherein the transition metal is present at a higher molar concentration in an outermost surface layer of the core than in a central portion of the core.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Preparation method and application of porous nano metal organic framework material
ActiveCN104892518AIncrease surface areaLarge hole volumeMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesSulfurMetal-organic framework
The invention aims to provide a preparation method and application of a porous nano metal organic framework material, and is characterized in that the preparation method comprises the steps: adding a metal ion, an organic ligand, a surfactant and a nanocrystalline guide agent or a reagent forming the nanocrystalline guide agent into a growth medium, forming a framework structure through chemical complexation, crystallizing, filtering, washing, drying, and finally obtaining the porous nano metal organic framework material. The addition amount of the surfactant is 0-30% of the molar concentration of the metal ion; the metal ion is one or more of Cu<II>, Al<III>, Mg<II>, Fe<III>, Ni<II>, Co<II> and Zn<II>; the organic ligand has at least one atom independently selected from oxygen, sulfur and nitrogen and can be subjected to coordinated complexation to the metal ion through the atom. The method not only can effectively suppress the size of MOFs materials, but also easily improves size homogeneity and synthetic efficiency of the product.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pasting Preparation
InactiveUS20080038328A1Superior drug percutaneous absorptionBiocideNervous disorderOrganic acidMolar concentration
The patch preparation of the present invention is a patch preparation comprising a backing and an adhesive layer provided on the backing; wherein, the adhesive layer contains (A) a volatile organic acid and (B) a basic drug; the molar concentration ratio [(MA) / (MB)] between the molar concentration (MA) of the component (A) and the molar concentration (MB) of the component (B) in the adhesive layer is 0.5 or more; and the component (B) contains a basic drug formed as an ion pair with an anion component.
Owner:HISAMITSU PHARM CO INC
Modified zirconium oxide ceramic material and application thereof
InactiveCN104446457ARich Appearance StyleHigh dielectric constantBarium titanateUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a modified zirconium oxide ceramic material. The modified zirconium oxide ceramic material comprises the following components in percentage by molar concentration: 0-6mol% of yttrium oxide, 0-15mol% of cerium oxide, 0.02-1mol% of titanium oxide, 0-20mol% of aluminum oxide, 0-5mol% of barium titanate and the balance of zirconium oxide. The invention also discloses zirconium oxide ceramic and a dielectric cover plate prepared from the modified zirconium oxide ceramic material. The dielectric cover plate prepared from the modified zirconium oxide ceramic material has the advantages of high hardness, good toughness, high strength and high dielectric constant.
Owner:CHAOZHOU THREE CIRCLE GRP
Strengthened toughened regenerated silk fibers and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103572395ASimple preparation processMonocomponent protein artificial filamentAnimal fibresMolar concentrationGraphite oxide
The invention relates to strengthened toughened regenerated silk fibers and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of 1, degumming silkworm cocoons, and dissolving the degummed silkworm cocoons to obtain a regenerated silk fibroin aqueous solution, 2, blending a graphene oxide aqueous solution subjected to ultrasonic treatment and the regenerated silk fibroin aqueous solution according to a certain ratio, 3, adding metal-oxide hydrosol into the mixture according to a certain ratio, 4, adding a CaCl2 solution into the mixture obtained by the step 3 to adjust a calcium ion molar concentration to 0.15-0.3mol / L, and sequentially carrying out concentration, 5, carrying out dry spinning on the concentrated solution as a spinning liquid at a room temperature, and 6, after-treating the composite fibers by an ethanol-water solution. The preparation method has simple processes and utilizes the raw materials having wide sources. The treated composite fibers have good strength and good toughness and have breaking strength of 70-380MPa, breaking elongation of 20-150% and breaking energy of 30-100J / g.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Incombustible mixed refrigerant suitable for copious cooling temperature of 90-140DEG C below zero
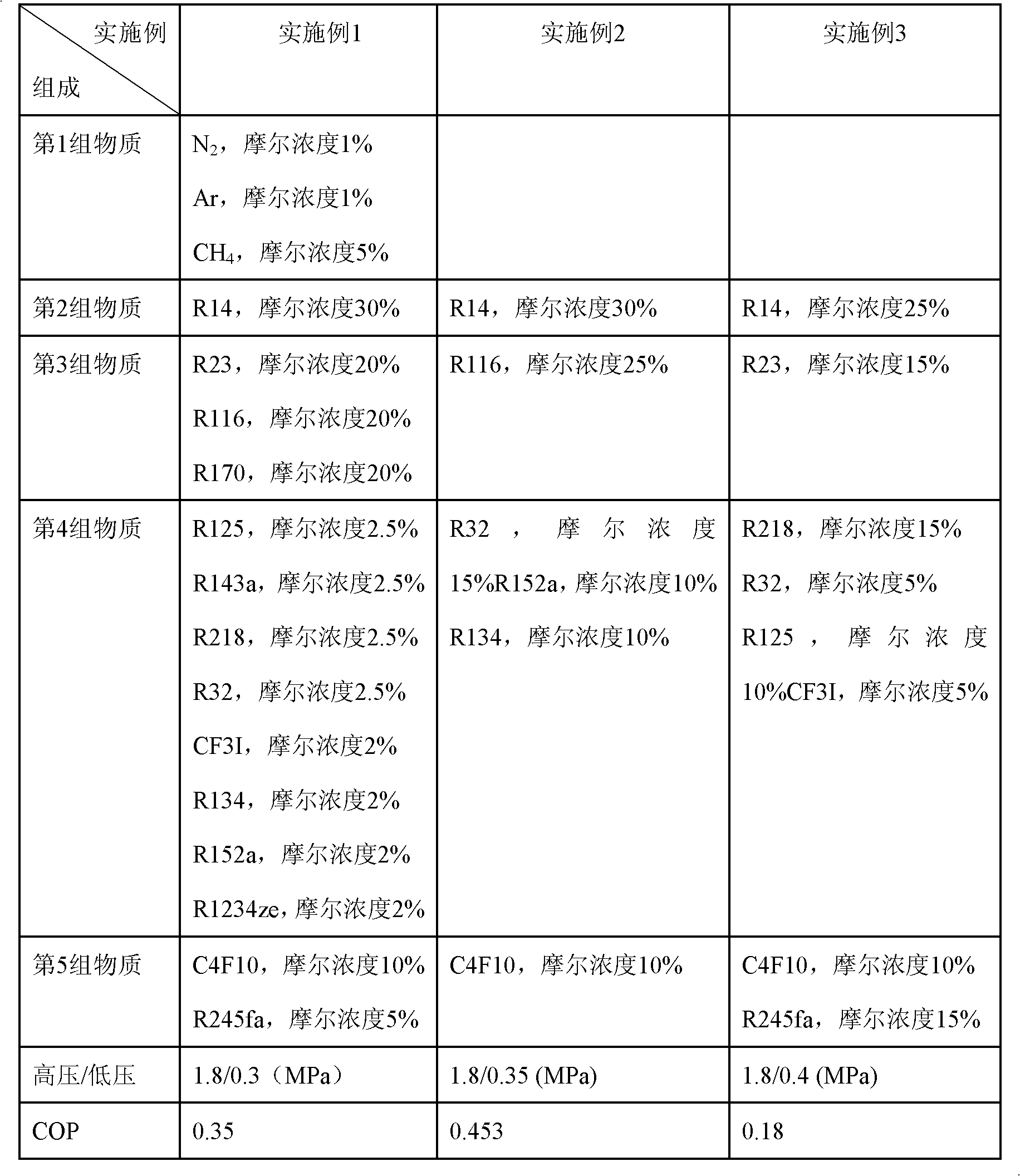
ActiveCN102660229AIncrease concentrationReduce concentrationHeat-exchange elementsNitrogenRefrigeration
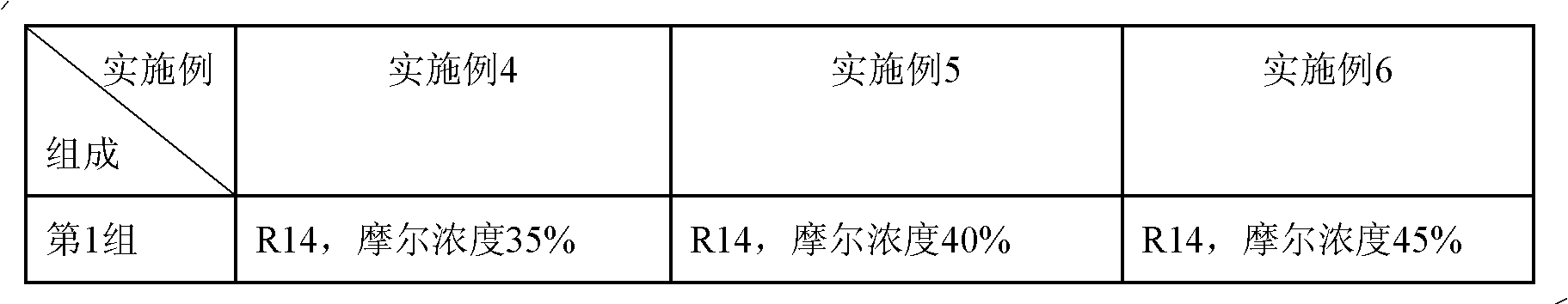
The invention relates to an incombustible mixed refrigerant suitable for the copious cooling temperature of 90-140DEG C below zero, which comprises the following five groups of substances: the first group is nitrogen, argon, methane or mixture; the second group is R14; the third group is R23, R116, R170, R1150, R41 or mixture; the fourth group is R218, R125, R32, R143a, R290, R1270, R13I1, R134, R134a, R152a, R1216 or mixture; the fifth group is R1234ze, R245cb, R227ea, R3110, R236fa, R254cb, R143, R236ea, R245fa, R329mcc, R347mcc, R338mcf, R245eb, R245ca, R338mee, R338mcc or mixture; the molar concentrations of the five groups are respectively 5-35%, 10-40%, 5-20%, 5-20% and 5-25%. The incombustible mixed refrigerant suitable for the copious cooling temperature of 90-140DEG C below zero has the advantages of low integral greenhouse effect, no ozone damage and the like, is safe in a regeneration type throttling and refrigerating system, and refrigeration in the temperature zone of 90-140DEG C below zero can be realized.
Owner:中科赛凌(北京)科技有限公司
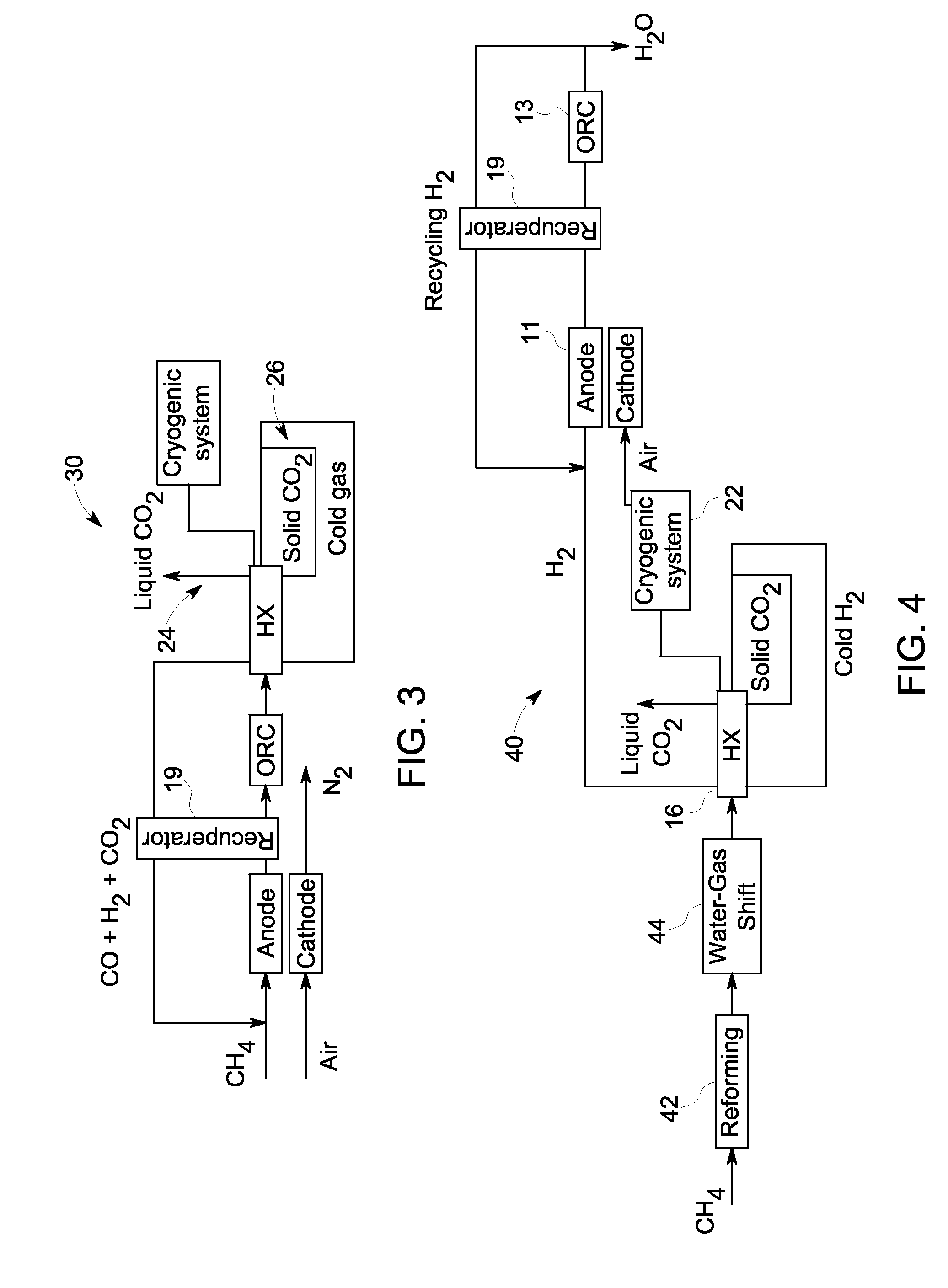
Recirculation complex for increasing yield from fuel cell with co2 capture
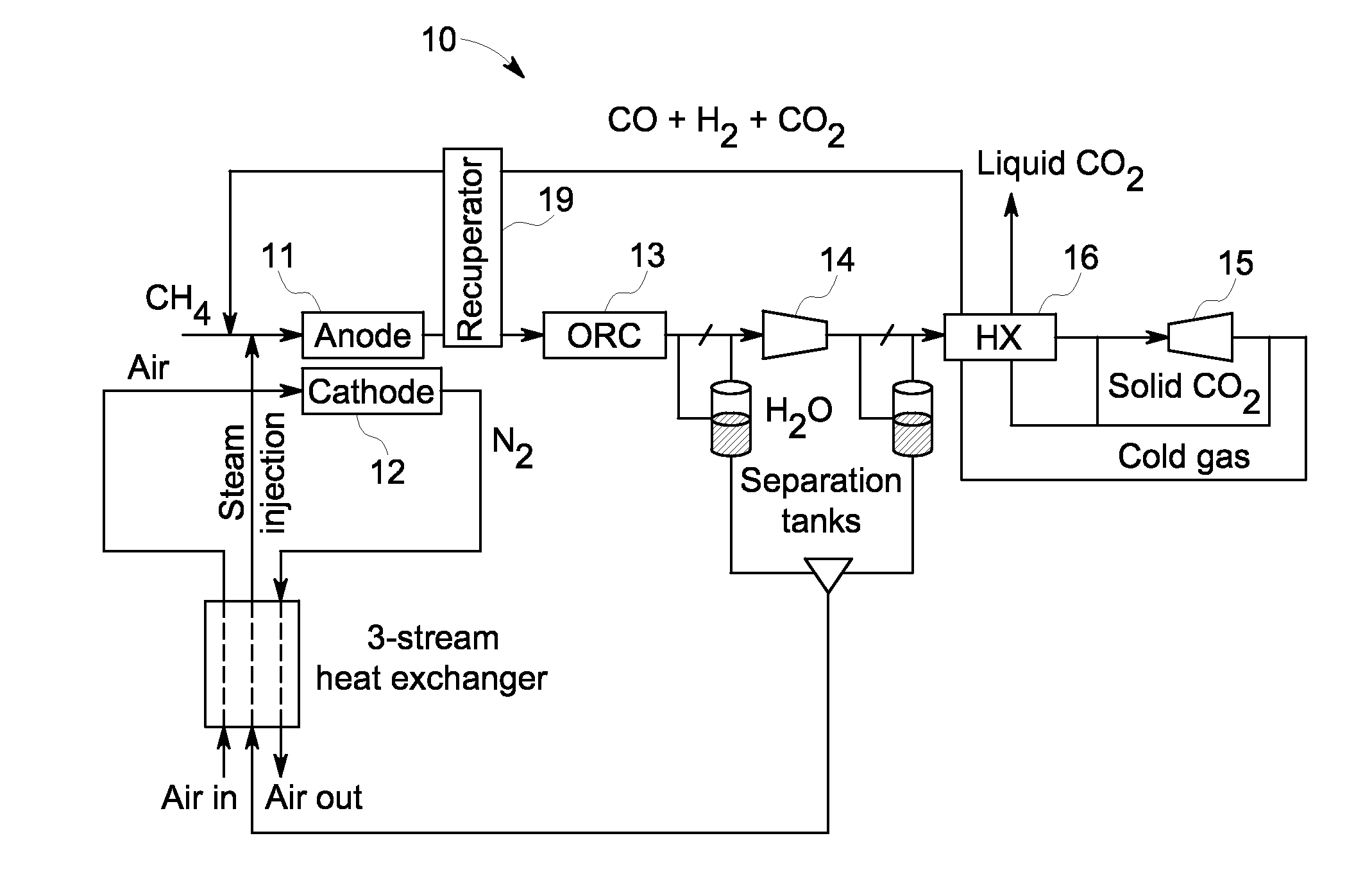
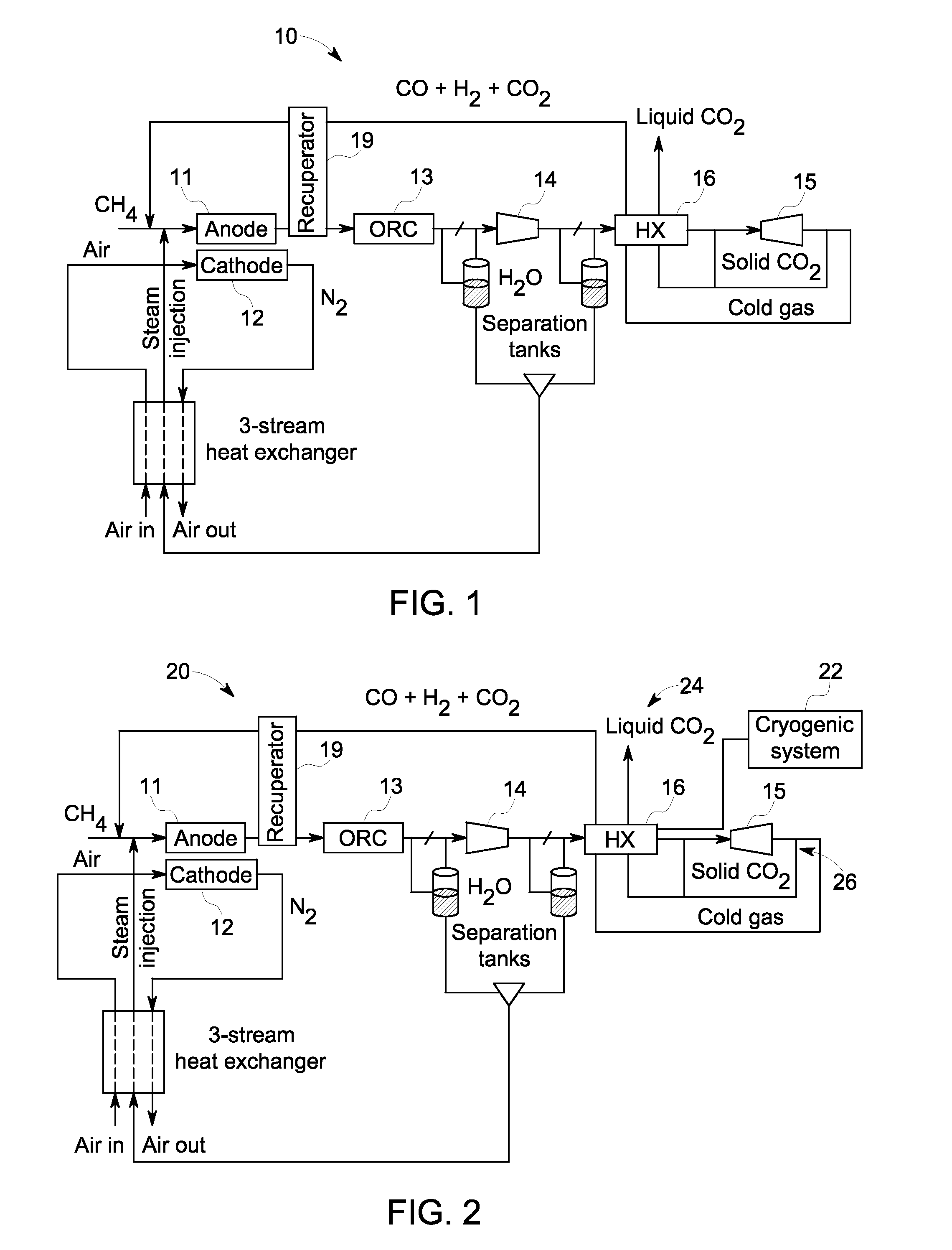
A system and method are provided for boosting overall performance of a fuel cell while simultaneously separating a nearly pure stream of CO2 for sequestration or for use in generating electrical power to further increase overall efficiency of the process. The system and method employ a heat exchanger system configured to generate a stream of fuel that is returned to the inlet of the fuel cell anode with a higher molar concentration of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2) fuel than was initially present in the fuel cell anode outlet.
Owner:CUMMINS ENTERPRISE LLC
Multifunctional nuclear shell structure drug carrier material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101670107AIncrease temperatureHigh purityInorganic non-active ingredientsGranular deliveryMagnetite NanoparticlesRare earth
Owner:如皋市生产力促进中心
Process for the gas-phase polymerization of olefins
Process for the gas-phase polymerization of olefins of the formula CH2=CHR where R is hydrogen or an alkyl or aryl radical with 1 to 8 carbon atoms carried out in one or more reactors having a fluidized or mechanically agitated bed, using a catalyst obtained by reaction of a titanium halide or haloalcoholate and optionally an electron-donor compound supported on an active Mg-dihalide with an Al-trialkyl compound and optionally an electron-donor compound, comprising the steps of:a) contacting the catalyst components in the absence of polymerizable olefin or optionally in the presence of said olefin in an amount to from up to 3 g per g of solid catalyst component;b) prepolymerizing propylene or mixtures of propylene with ethylene or an alpha-olefin to form a propylene polymer having an insolubility in xylene of at least 60% by weight, in an amount of from 5 g of polymer per g of solid catalyst component to 10% by weight of the final catalyst yield; andc) polymerizing one or more CH2=CHR olefins in the gas phase in the presence of the prepolymer-catalyst system obtained in b), while maintaining in the gas phase an alkane in a molar concentration with respect to the total gases of from 20 to 90%.
Owner:MONTELL TECH CO BV
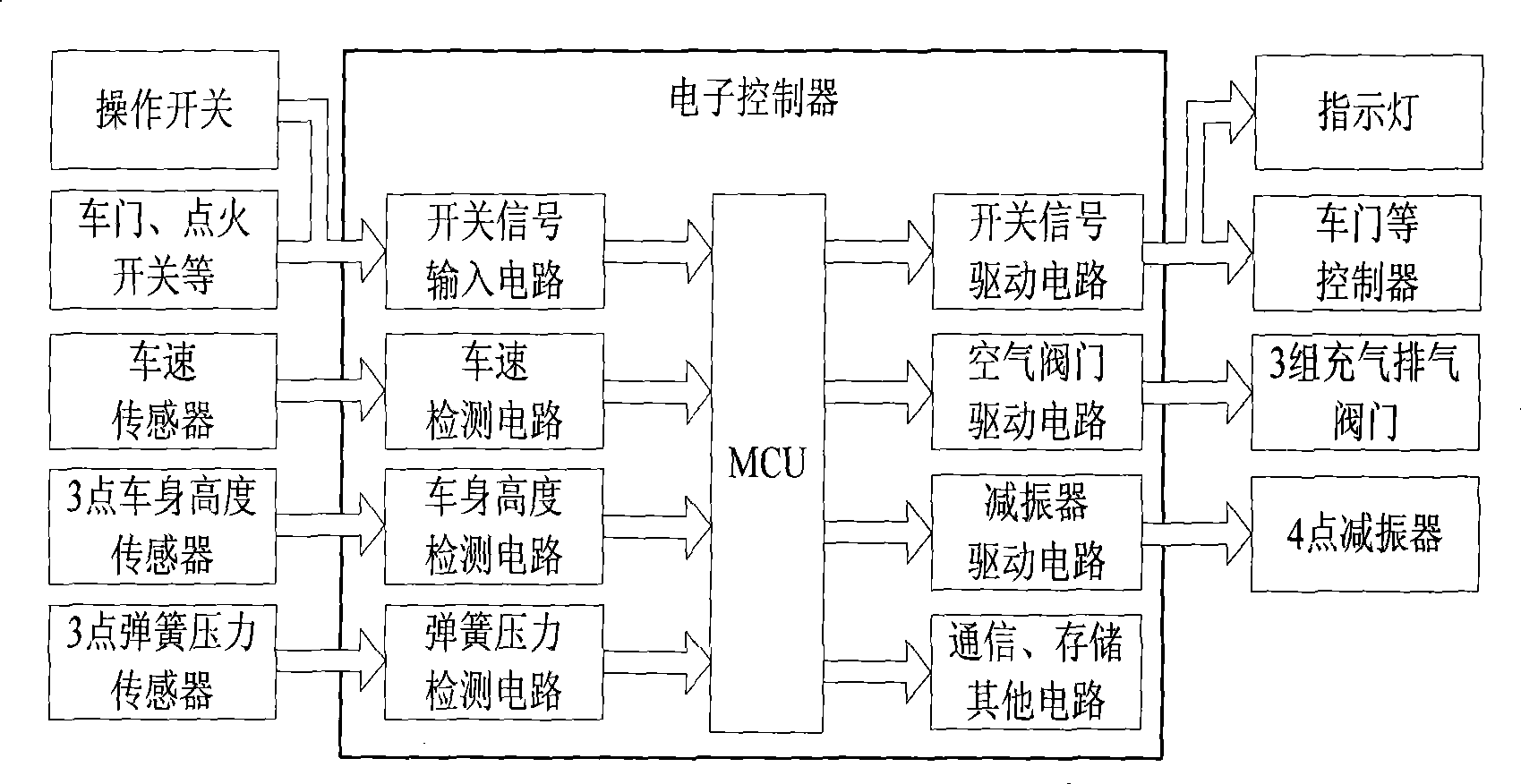
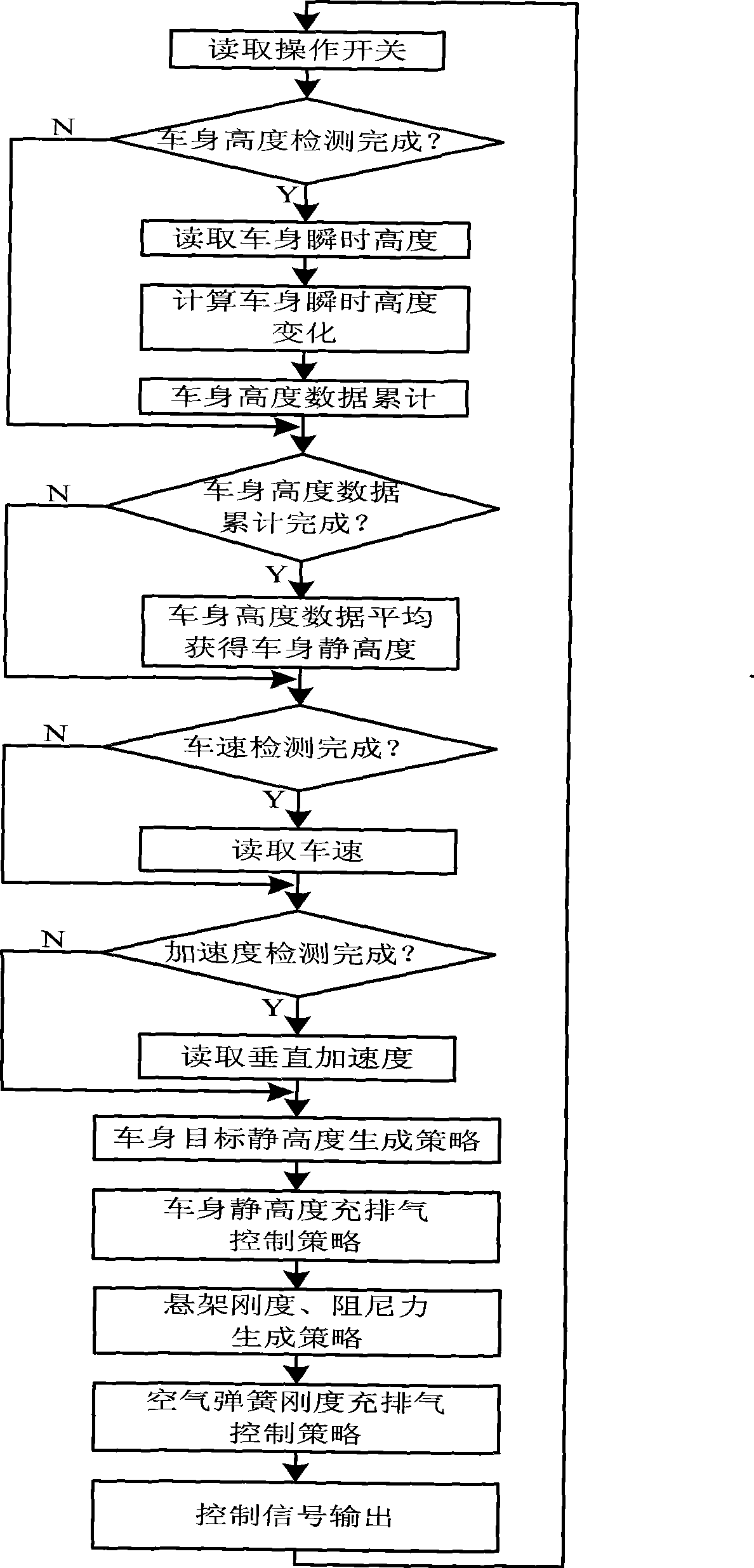
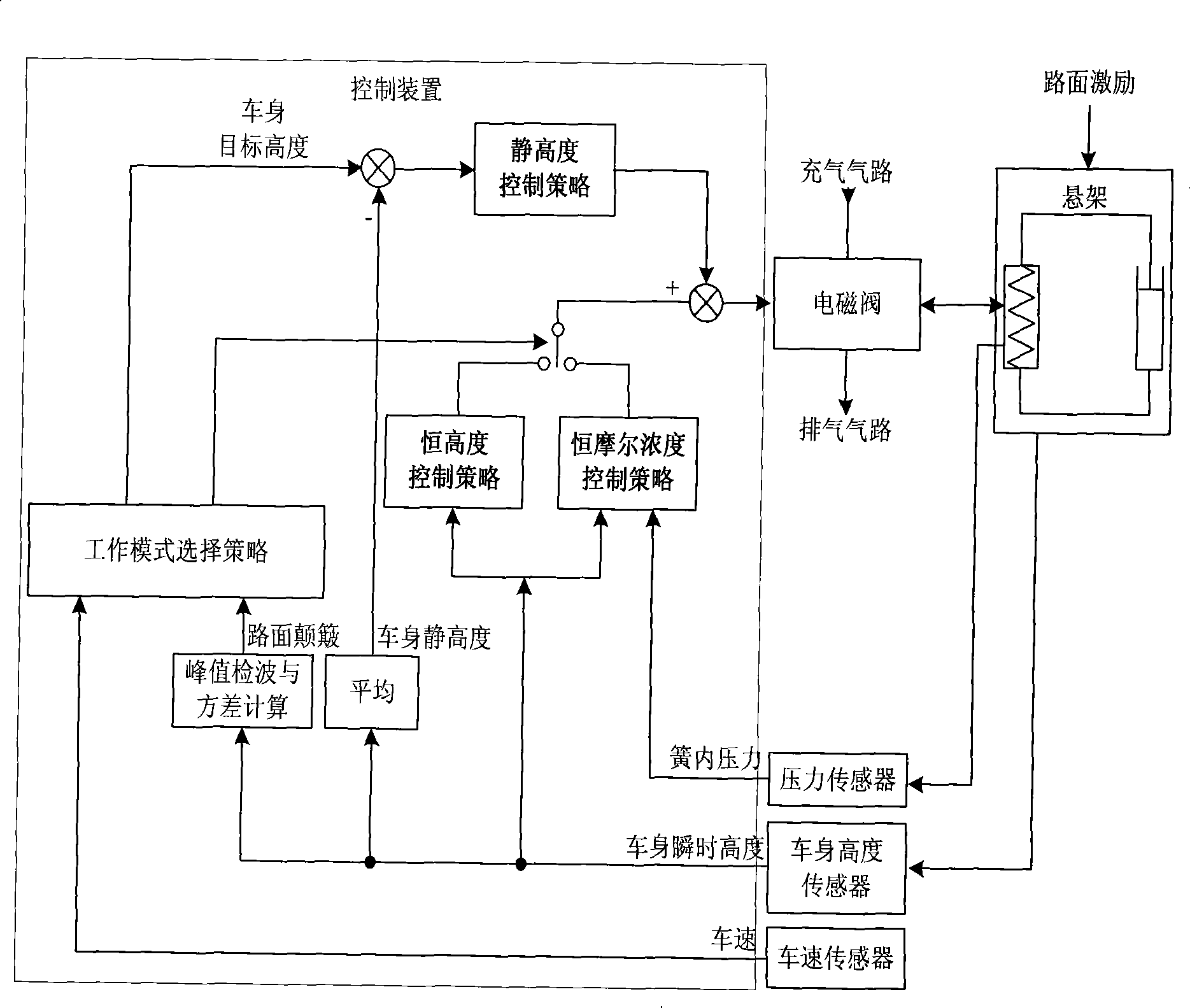
Control method of automobile air suspension
The invention discloses a control method for a vehicle air suspension; the invention takes the electric control device of a hardware part as the core and is configured with components such as various external sensors, an air spring, an air valve, and an adjustable shock absorber, and the like; the software part comprises signal detection, data processing and secondary calculation, a control method and control output; and firstly different working models are judged by calculating the variance of the input vehicle body height and the vehicle speed; open-loop control and a neural network are used for realizing online self-correction function; the electric control device controls the implementation of the air valve according to the air charge and discharge time which is obtained by the neural network, and then the air molar concentration and the deviation quantity in the spring are obtained by calculation; and finally a detail control signal is obtained. The control method causes the vehicles to be controlled flexibly under different pavement conditions, has appropriate flexibility and damping performance under various road conditions, effectively solves the conflicts when parameters are matched to be suitable for various road conditions, and improves the handling performance, the safety, the comfort and the off-road performance of the vehicles.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV +1
Oriented ZnO nanorod or nanowire film and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN1763263AHigh crystallinityGood orientationPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsHydrothermal depositionZinc
The present invention relates to directional nanometer zinc oxide stick or linear film and its preparation process, and belongs to the field of low-dimensional nanometer film material technology. The present invention adopts hydrothermal deposition process, in which zinc salt solution in molar concentration 1-25 mM and amine surfactant solution are mixed homogeneously and set inside stainless steel reactor with PTFE lining, substrate of glass, polymer, inorganic metal, non-metal or other material and with directional texture ZnO crystal seed is set inside the lining, so as to react at 50-150 deg.c for 1-6 hr. After cooling naturally, directionally grown and high crystallized ZnO nanometer stick array film or nanometer stick of diameter 10-500 nm may be form. The process has low synthesis temperature and easy control, and the grown ZnO film is well directional. The present invention is suitable for industrial production of directional nanometer ZnO stick or film.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Nonaqueous electrolyte for high-voltage lithium ion battery
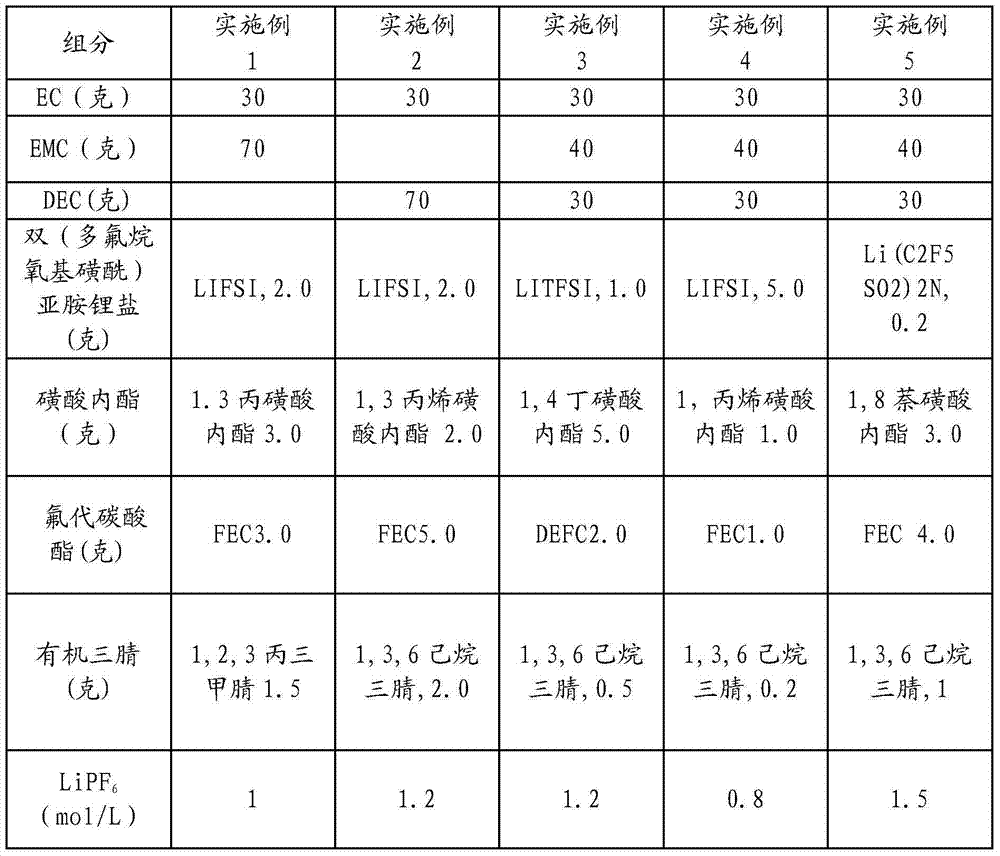
ActiveCN104505535AImprove wettabilityImprove oxidation resistanceSecondary cellsCarbonate esterCombined use
The invention discloses nonaqueous electrolyte for a high-voltage lithium ion battery. The nonaqueous electrolyte consists of a solvent, an inorganic lithium salt, a fluoro-ester additive, a sultone additive, an organic tri-nitrile additive, a bi(polyfluoroalkoxy sulfonyl) imine lithium salt and a lithium battery electrolyte additive, wherein the addition amount of the solvent is 100 weight parts; the addition amount of the fluoro-carbonate additive is 0.2-10 weight parts; the addition amount of the nitrile additive is 0.2-10 weight parts; the addition amount of the bi(polyfluoroalkoxy sulfonyl) imine lithium salt is 0.2-10 weight parts; the addition amount of the common lithium battery electrolyte additive is 0-10 weight parts; the solvent refers to cyclic carbonate and / or chain carbonate; and the molar concentration of the inorganic lithium salt in the solvent is 0.8-1.5mol / L. According to combined use of the sultone additive, the fluoro-ester carbonate additive, the bi(polyfluoroalkoxy sulfonyl) imine lithium salt and the organic tri-nitrile additive, the oxidation resistance of the SEI film during primary formation of the electrolyte can be improved, and the normal-temperature and high-temperature cycle performance of the high-voltage electrolyte is obviously improved.
Owner:ZHUHAI SMOOTHWAY ELECTRONICS MATERIALS
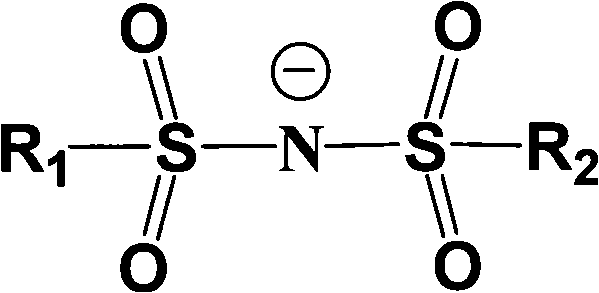
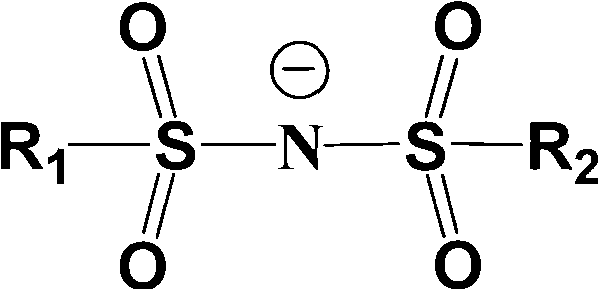
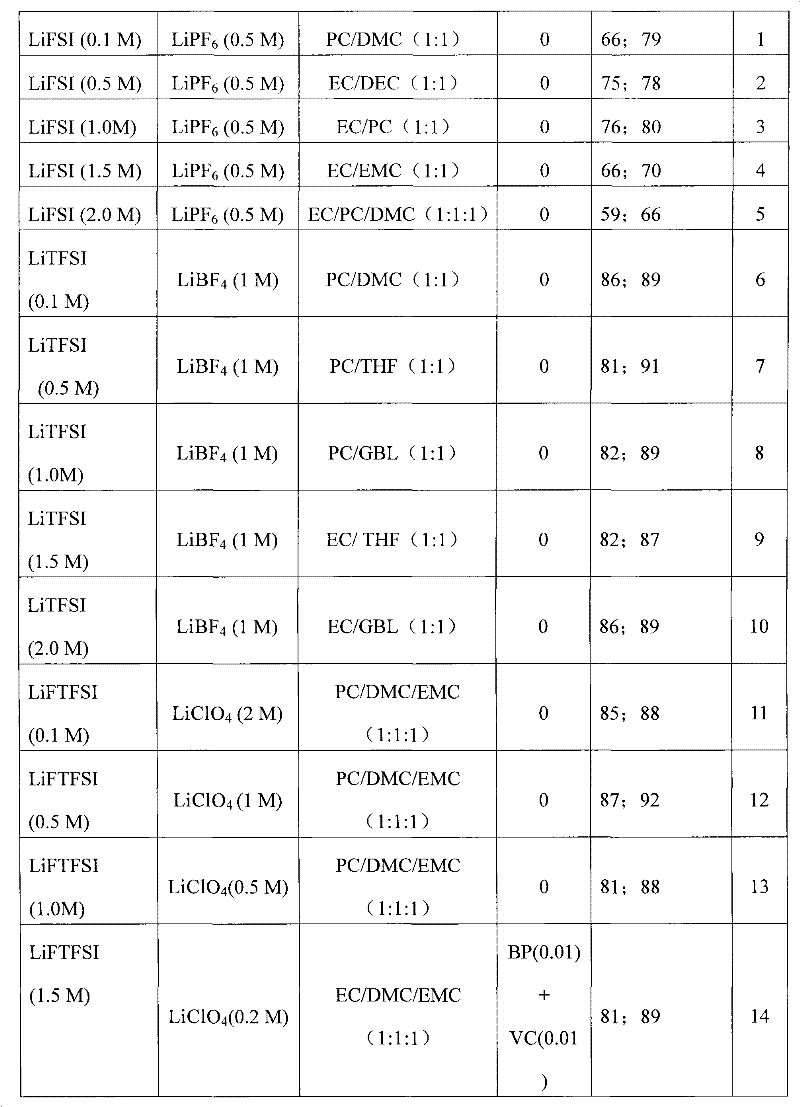
Electrolyte solution of fluorine-containing lithium sulfonimide salt and application thereof
InactiveCN102074734ARaise the temperatureImprove low temperature performanceLi-accumulatorsOrganic solventEther
The invention provides an electrolyte solution of fluorine-containing lithium sulfonimide salt and application of the electrolyte solution. The electrolyte solution consists of the following four components: fluorine-containing lithium sulfonimide, other lithium salts, carbonate and / or ether organic solvent and other functional addictives, wherein the molar concentration of fluorine-containing lithium sulfonimide salt is 0.001-2 mole / L in the electrolyte solution, the molar concentration of other lithium salts is 0-2 mole / L in the electrolyte solution, and the molar concentration of other functional addictives is 0-0.5 mole / L; and the fluorine-containing lithium sulfonimide is an ion-type compound, wherein the cation is lithium ion. The fluorine-containing lithium sulfonimide is contained in the electrolyte solution provided by the invention, thus the low temperature property of the electrolyte solution is improved greatly; and after the electrolyte solution is applied to a lithium battery, the capacity percentage of the lithium battery is improved at the high temperature more than 50 DEG C or at the low temperature below minus 20 DEG C, which is beneficial to improving the cycle life and the storage life of the lithium battery.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG GUOTAI HUARONG NEW CHEM MATERIALS CO LTD
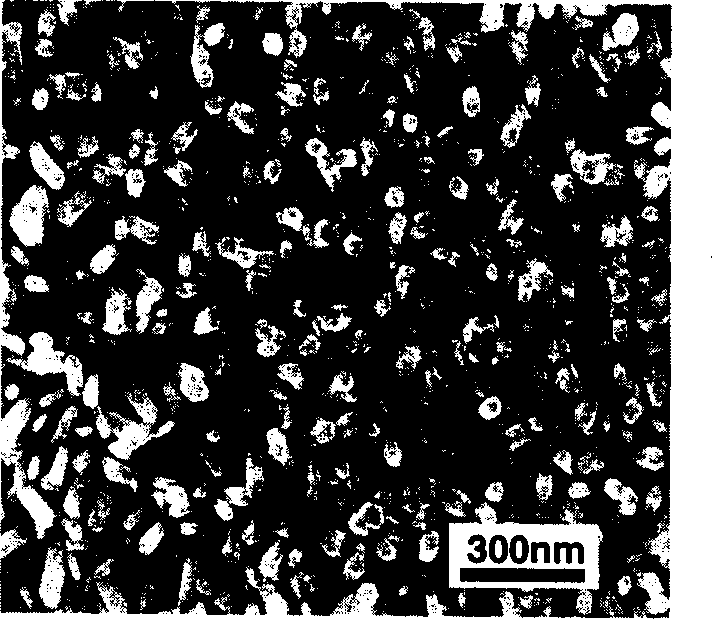
Preparation method of nanometer sliver colloid solution
The invention discloses a safe, environment-friendly and stable preparation method of a nanometer sliver colloid solution, comprising the following steps: mixing the alkylated cyclodextrin aqueous solution and the silver ammonia solution according to the volume ratio of 1:100-1:10, wherein the mass percent of the alkylated cyclodextrin aqueous solution is 0.1-10%, and the mass molar concentration of the silver ammonia solution is 0.01-1.0mol / L; and stirring for 1-120min at 10-100 DEG C to obtain the nanometer sliver colloid solution of which the average grain diameter is 1-100nm. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple preparation process and can ensure the application safety of the nanometer sliver colloid solution, and the prepared nanometer sliver colloid solution has the characteristics of good stability, small grain diameter of nanometer sliver, less dosage and high antibiosis efficiency in the function materials of the nanometer sliver.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG NELLNANO TECH
Method for deeply purifying minim phosphor in water with composite resin
ActiveCN101343093APhosphate content decreasedLarge amount of processingSpecific water treatment objectivesWater contaminantsFiltrationDesorption
The invention discloses a method for deeply purifying micro-phosphorus in water by composite resin. The pH value of water is firstly adjusted to between 5.0 and 9.0 for filtration, then the filtrate passes through an absorption tower filled with composite resin materials to make the micro-phosphorus in water be adsorbed on the composite resin; and the adsorption stops when the adsorption reaches the leakage point, a mixed solution of NaOH and NaCl serves as a desorption agent for desorption and regeneration, then a CO2 saturated solution is used to leach the absorption tower filled with composite resin materials for regenerating resin. The method takes composite resin of surface supported nano-hydrous ferric oxide or hydrous manganese oxide particles as an adsorbent to deeply purify micro-phosphorus in water. After the treatment by the method, the phosphate content (as P) in effluent can still be reduced to below 20ppb from 0.05-20ppm when the molar concentration of coexistent competing ions of Cl<->, HCO3<-> and SO4<2-> is far higher than that of phosphate ions. The method has large treatment capacity, and the materials are renewable and recyclable.
Owner:JIANGSU NJU ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Resource recycling method of waste battery cathode materials
InactiveCN106328927ALow costIncrease capacityCell electrodesWaste accumulators reclaimingRecovery methodElectric capacity
The invention relates to a resource recycling method of waste battery cathode materials. The resource recycling method comprises the following steps: performing high-temperature calcinating to the waste battery cathode materials so as to separate active powder in the cathode materials from aluminum foil; dissolving the obtained active powder into acid solution, and then filtering to obtain filtrate; determining the concentration of metal ions in the filtrate, and correspondingly supplementing nickel and / or cobalt and / or manganese ions into the solution, so that the molar concentration ratio of nickel, cobalt and manganese ions is 1:1:1; adding sodium hydroxide into the prepared nickel, cobalt and manganese mixture solution, and heating to lead the nickel, cobalt and manganese ions to be co-precipitated, then filtering the precipitate and washing and drying to obtain a nickel-cobalt-manganese precursor; adding sodium carbonate into the filtrate obtained in the step IV, and reacting to obtain lithium carbonate precipitate, filtering, washing and drying the lithium carbonate precipitate, to obtain lithium carbonate powder; and mixing the nickel-cobalt-manganese precursor with the lithium carbonate powder, and calcinating to obtain the lithium nickel cobalt manganese cathode materials. A ternary cathode material is prepared by resource recycling ofvarious battery materials, and batteries produced from the ternary cathode material are lower in cost, higher in electric capacity and better in performance compared with single cobalt-lithium batteries, manganese-lithium batteries and nickel-lithium batteries.
Owner:王剑
Method for preparing nano sliver wire dispersion liquid controllable in wire diameter and high in length-diameter ratio in batches
InactiveCN105665742AQuality improvementSimple preparation processNanotechnologyDiameter ratioMolar concentration
The invention discloses a method for preparing nano sliver wire dispersion liquid controllable in wire diameter and high in length-diameter ratio in batches. The method comprises the preparation steps that (1), a silver salt alcoholic solution with the molar concentration of 0.005-0.5 mol / L is prepared; (2), a template agent alcoholic solution with the molar concentration of 0.005-0.5 mol / L is prepared; (3), a halide alcoholic solution with the concentration of 10-100 mmol / L is prepared; (4), mixed liquid with the molar ratio of PVP to silver being 0.8-10 or 1-4 is prepared; and (5), complex mixed liquid with the molar concentration of halide being 0.1-200 mmol / L is prepared and heated to 90-200 DEG C to react for 0.5-14 hours, and the nano sliver wire dispersion liquid high in length-diameter ratio is obtained. The method has the characteristics that the cost is low, the process is simple and easy to implement, the wire diameter is controllable, the length-diameter ratio is high, the nano sliver wire dispersion liquid can be prepared in batches, and the method is suitable for preparation of the nano sliver wire dispersion liquid high in length-diameter ratio.
Owner:HUNAN HAOZHI TECH
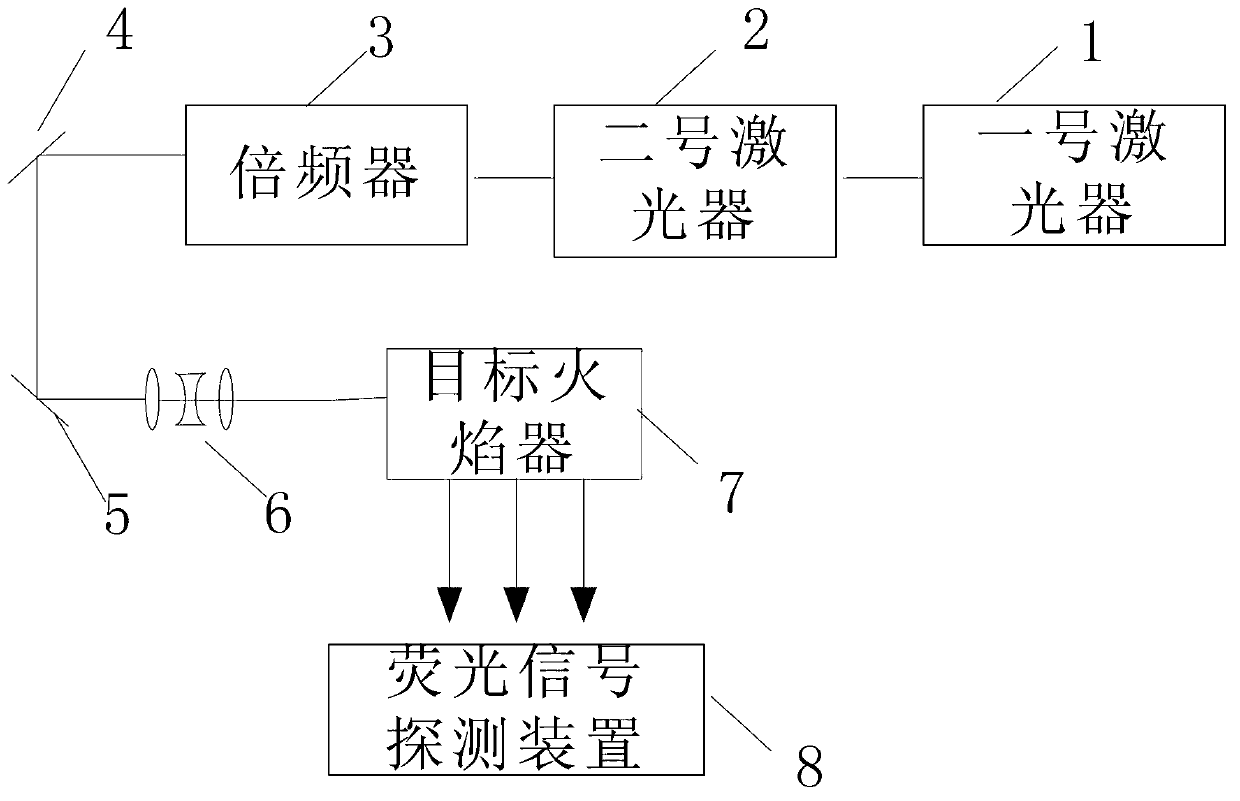
Planar laser induced fluorescence (PLIF) imaging device and method for acquiring hydroxyl (OH) concentration spatial distribution through device
InactiveCN103344619ASimple processHigh precisionFluorescence/phosphorescencePlanar laser-induced fluorescenceFluorescence
The invention discloses a planar laser induced fluorescence (PLIF) imaging device and a method for acquiring hydroxyl (OH) concentration spatial distribution through the device, and relates to a method for determining the OH-radical concentration spatial distribution. According to the device and the method, the problem that the average concentration of components on a certain line can be only determined and the spatial distribution of the concentration cannot be determined through a PLIF imaging technology is solved. A laser generates a laser signal, the laser signal is subjected to frequency multiplication through a frequency multiplier, and a sheet pulse signal is obtained through a sheet beam reshaping system; a target flame device excites an OH-radical fluorescence signal; a fluorescence signal detection device detects the OH-radical fluorescence signal to obtain an OH-radical fluorescence image; n to-be-measured points and n auxiliary points are selected from the OH-radical fluorescence image, the gray value and light intensity of the OH-radical fluorescence image of each to-be-measured point and each auxiliary point are calculated; the average molar concentration of each to-be-measured point is obtained according to a Lambert-Bill absorption law so as to obtain the OH-radical concentration spatial distribution. The invention is applied to the method for determining the OH-radical concentration spatial distribution.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Energy storage battery with non-aqueous electrolyte solution of lithium perfluoro-alkoxy (-phenoxy) sulfonylimide
InactiveCN102544584AImprove cycle lifeExtended shelf lifeCell electrodesSecondary cellsOrganic solventManganate
The invention provides an energy storage battery with a non-aqueous electrolyte solution of lithium perfluoro-alkoxy (-phenoxy) sulfonylimide. A negative pole material based on a lithium titanate parent structure and a positive pole material based on a lithium manganate parent structure are adopted in the lithium perfluoro-alkoxy (-phenoxy) sulfonylimide of the battery, the electrolyte solution comprises the lithium perfluoro-alkoxy (-phenoxy) sulfonylimide, other lithium salts, a carbonic ester type and / or ether type organic solvent and other functional additives, the molar concentration of the lithium perfluoro-alkoxy (-phenoxy) sulfonylimide in the electrolyte solution is 0.001-2 mol / L, the molar concentration of the other lithium salts in the electrolyte solution is 0-2 mol / L, and the molar concentration of the other functional additives in the electrolyte solution is 0-0.5 mol / L. The lithium perfluoro-alkoxy (-phenoxy) sulfonylimide in the battery can greatly improve the high / low-temperature performance and the film forming performance of the electrolyte solution, after the lithium perfluoro-alkoxy (-phenoxy) sulfonylimide is applied to the lithium titanate / manganese lithium energy storage battery, the percentage by volume of the battery is improved under high-temperature and low-temperature situations, and the lithium perfluoro-alkoxy (-phenoxy) sulfonylimide is further conductive to circulating a lithium cell and prolonging storage life.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG GUOTAI HUARONG NEW CHEM MATERIALS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com