Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
185 results about "L-tartaric acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
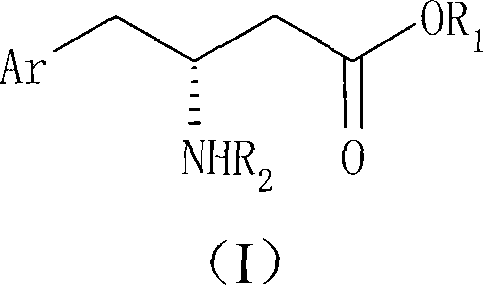
L-(+)-tartaric acid, can participate in several reactions. As shown the reaction scheme below, dihydroxymaleic acid is produced upon treatment of L-(+)-tartaric acid with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of a ferrous salt.
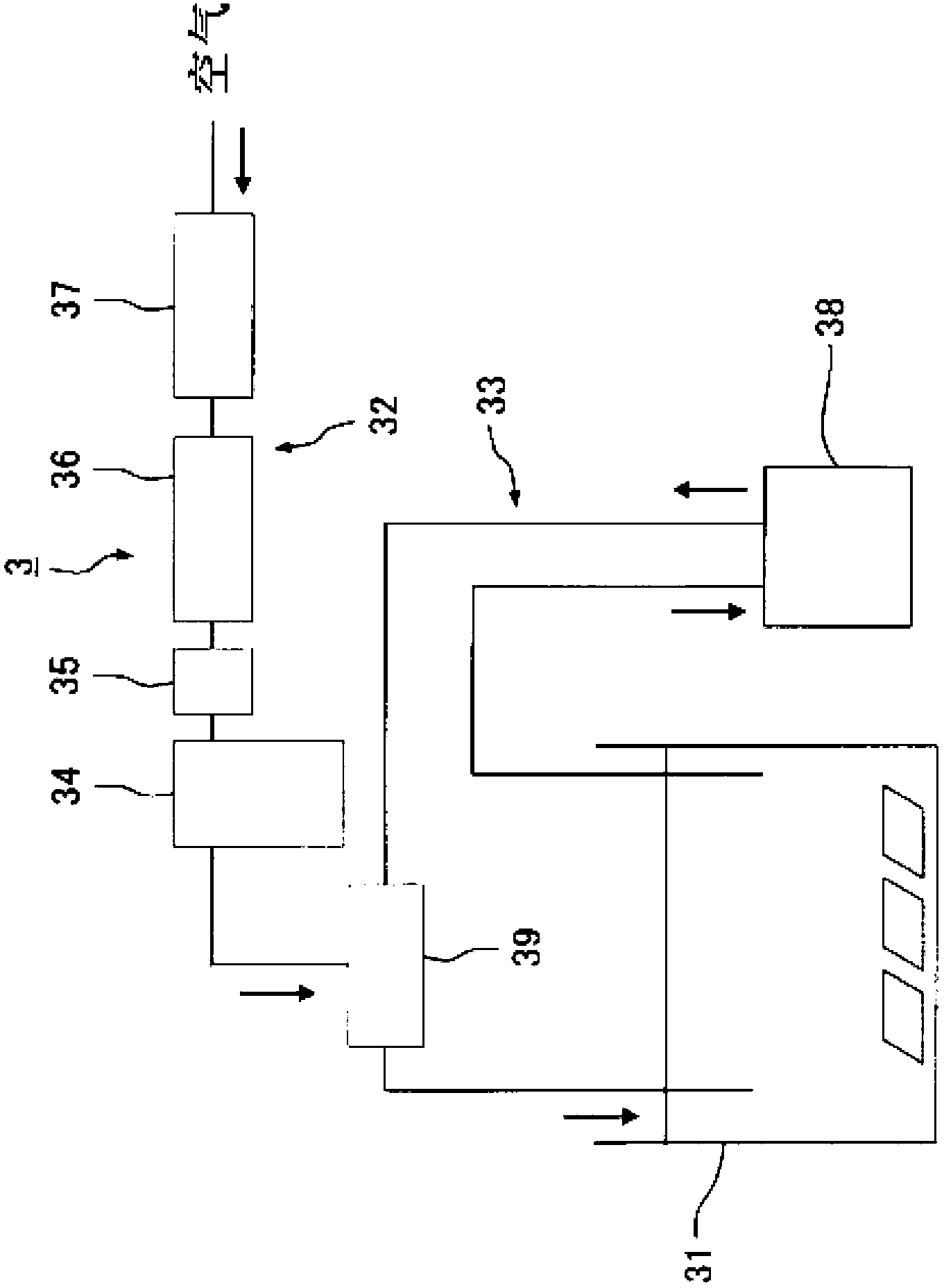
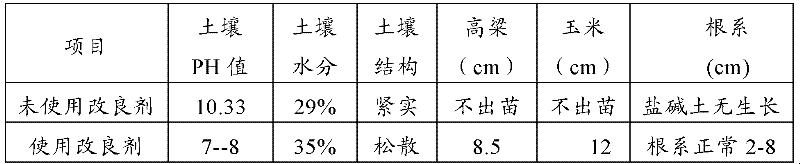
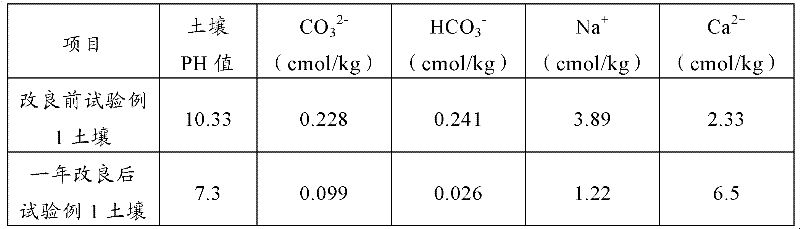
Saline-alkali soil improver
InactiveCN102517030ALower pHRaise the pHOther chemical processesOrganic fertilisersCis-Butenedioic AcidFatty alcohol
The invention relates to an improver for saline-alkali soil. The improver comprises a powder agent and a water agent, wherein the powder agent comprises the following components: organic matters, plant mycelium protein powder, active calcium, calcium superphosphate, aluminum sulfate, fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether ammonium sulfate, amino acid powder, bacillus subtilis and photosynthetic bacteria, and the water agent comprises the following components: citric acid, fulvic acid, humic acid, malic acid, maleic acid, fumaric acid, L-tartaric acid, pyrophosphoric acid, humic acid, lactic acid, oxalic acid, salicylic acid, sodium ion adsorbent, Tween-80 and water. The improver disclosed by the invention can improve the soil from multiple angles, namely soil structure, microorganism species, a chemical method and the like, obviously promote the release of iron and phosphorus in the soil, improve the soil structure, effectively reduce the content of sodium ions in the soil, reduce the pH value of the soil and restore land to a normal planting state after being used continuously for two years.
Owner:孙东军 +1
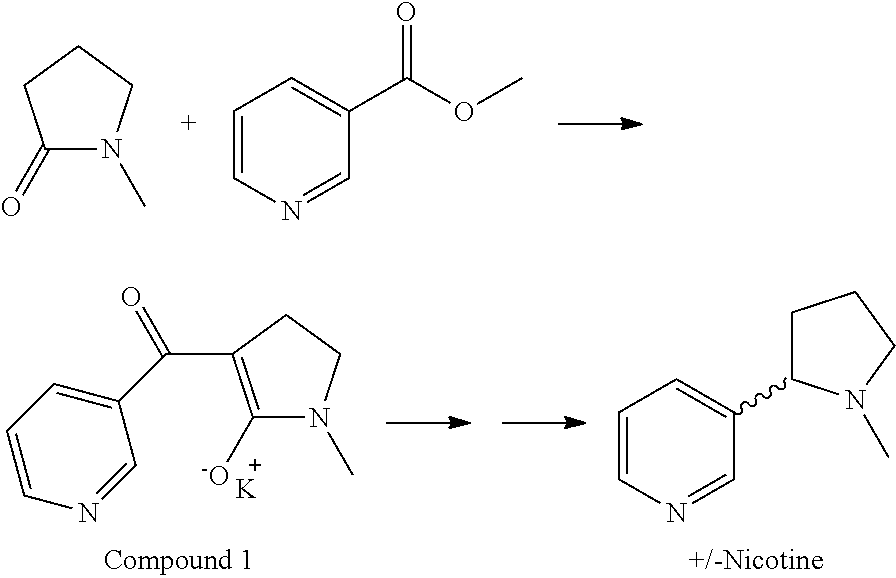
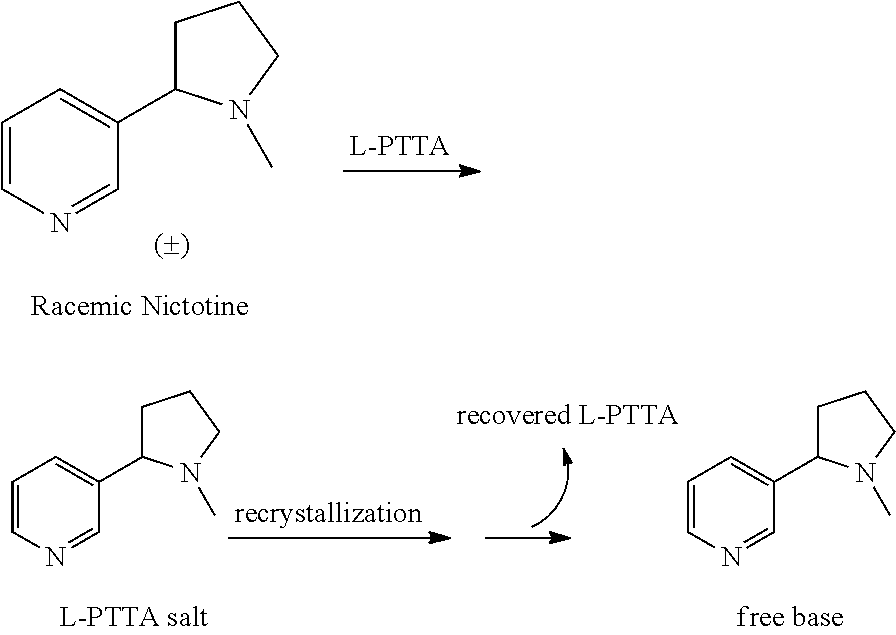
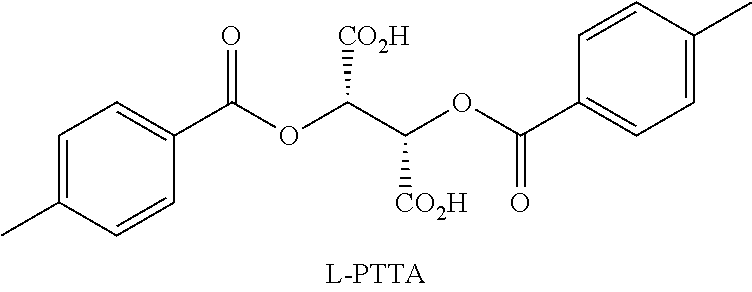
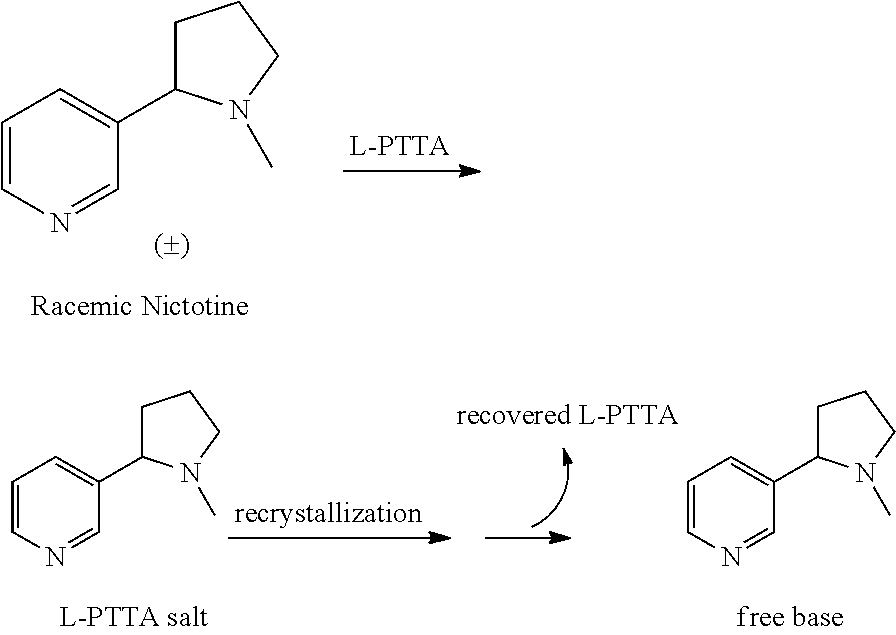
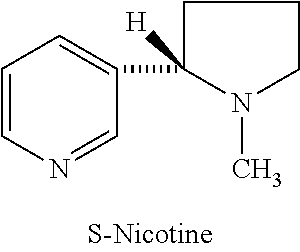
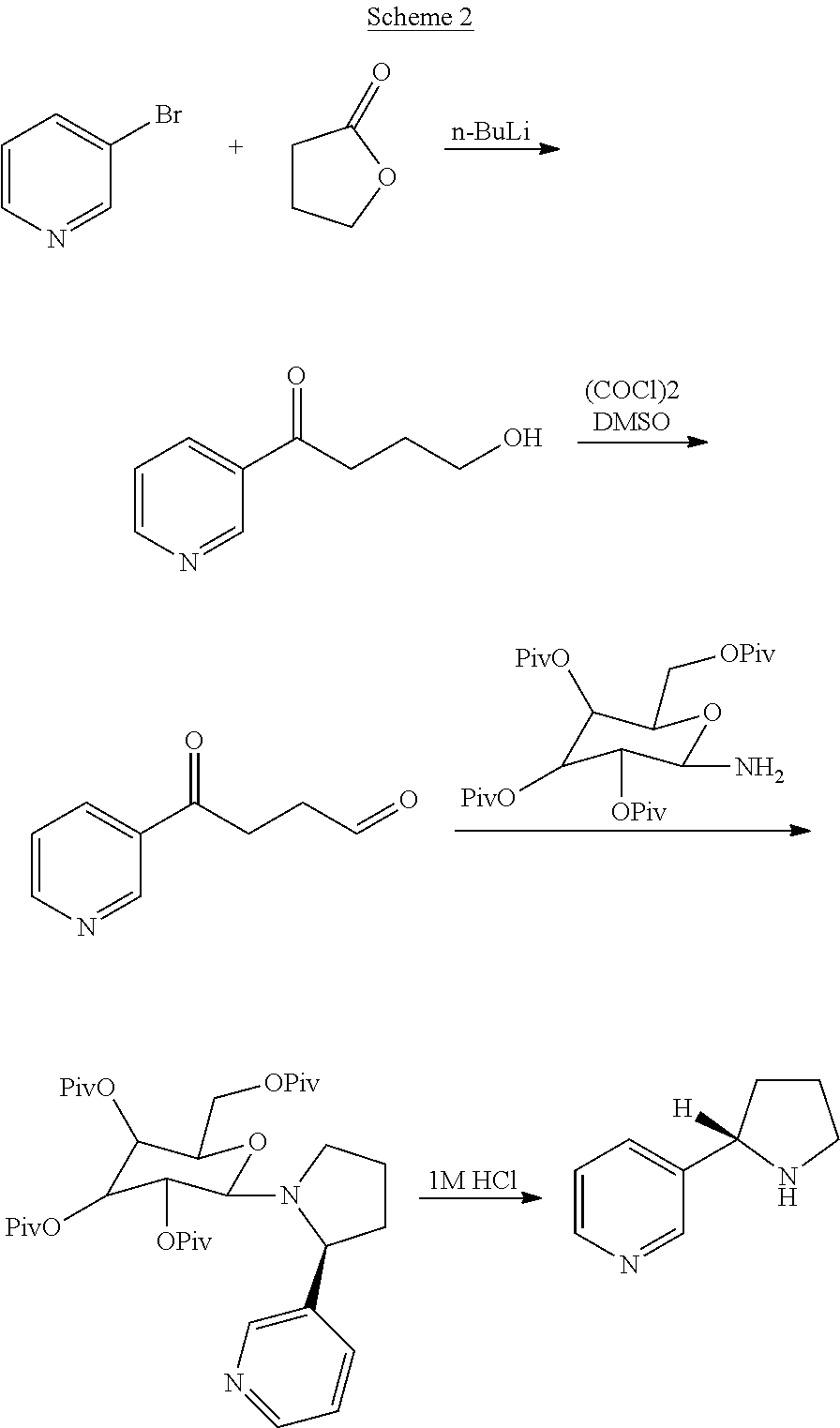
Synthesis and resolution of nicotine
The present disclosure generally relates to methods of preparing nicotine and resolving R,S nicotine to enrich the (S)(−) enantiomer. The method may comprise combining N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone or a salt thereof with a nicotinate compound in the presence of a solvent and a strong base to form 1-methyl-3-nicotinoyl-2-pyrrolidone or a salt thereof; and reducing the 1-methyl-3-nicotinoyl-2-pyrrolidone or salt thereof in solution with Na2S2O4 to produce racemic nicotine or salt thereof. Resolving the racemic nicotine (or other enantiomeric mixture) may comprise combining the nicotine with (−)-O,O′-di-p-toluoyl-L-tartaric acid (L-PTTA).
Owner:NJOY LLC
Apparatus and method for self-induced cough cardiopulmonary resuscitation
A apparatus and method for self-treatment of cardiac arrhythmia by a patient, comprising a container sized to be portable by the patient and having therein a chamber containing a medicament composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier mixed with a chemoirritant, preferably L-tartaric acid; a nebulizing valve connected to the chamber so as to provide an outlet therefor; a source of motivating force connected with the chamber so as to motivate the composition through the opening in the nebulizing valve to thereby cause nebulization of the composition; a wireless transmitter responsive to activation of the nebulizer for sending a wireless signal requesting medical assistance; and a power source operatively connected for providing power; wherein the chemoirritant is mixed in the composition in an amount sufficient for causing the patient to produce an involuntary cough effective to maintain at least partial blood circulation.
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
Synthesis and resolution of nicotine
The present disclosure generally relates to methods of preparing nicotine and resolving R,S nicotine to enrich the (S)(−) enantiomer. The method may comprise combining N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone or a salt thereof with a nicotinate compound in the presence of a solvent and a strong base to form 1-methyl-3-nicotinoyl-2-pyrrolidone or a salt thereof; and reducing the 1-methyl-3-nicotinoyl-2-pyrrolidone or salt thereof in solution with Na2S2O4 to produce racemic nicotine or salt thereof. Resolving the racemic nicotine (or other enantiomeric mixture) may comprise combining the nicotine with (−)-O,O′-di-p-toluoyl-L-tartaric acid (L-PTTA).
Owner:NJOY LLC
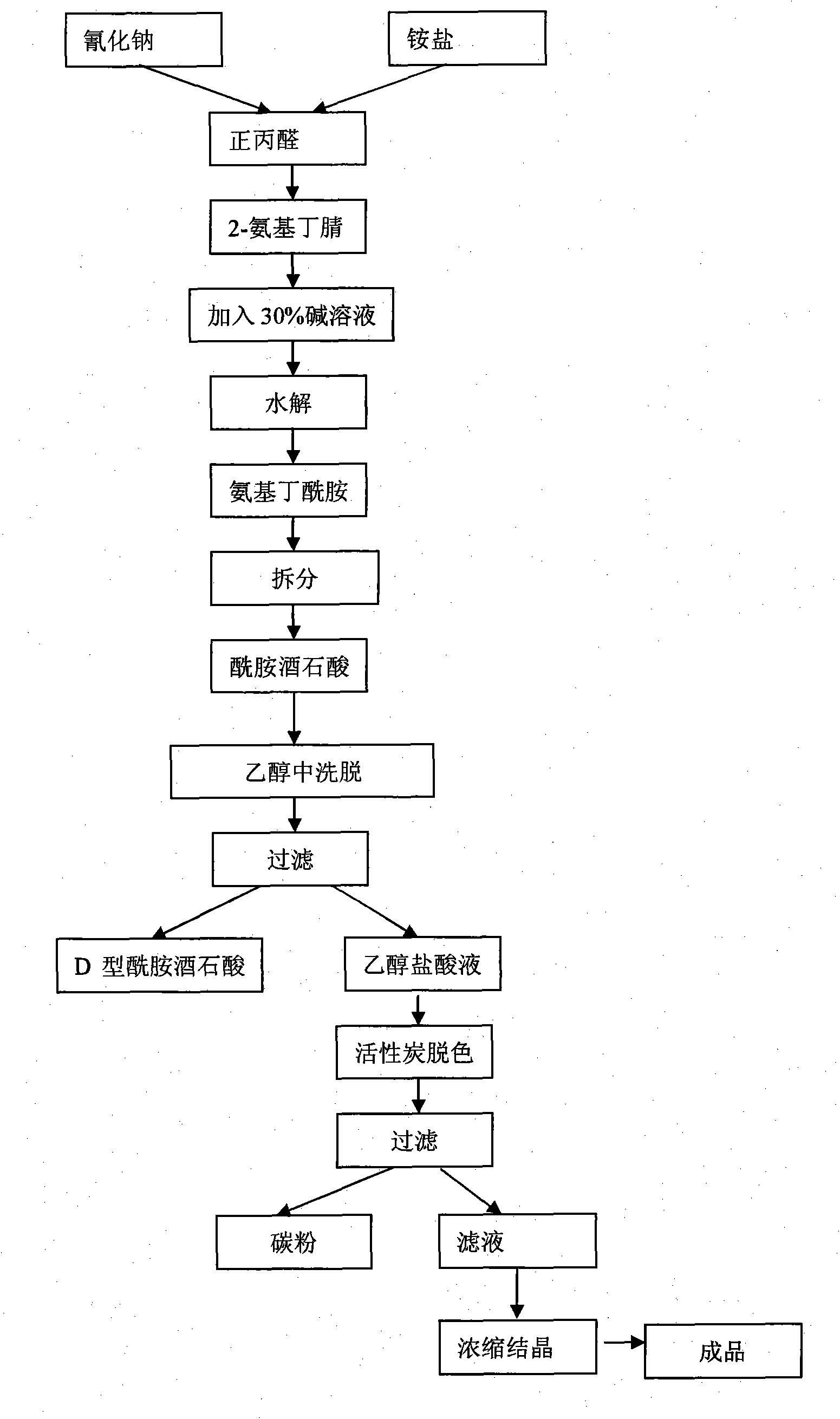
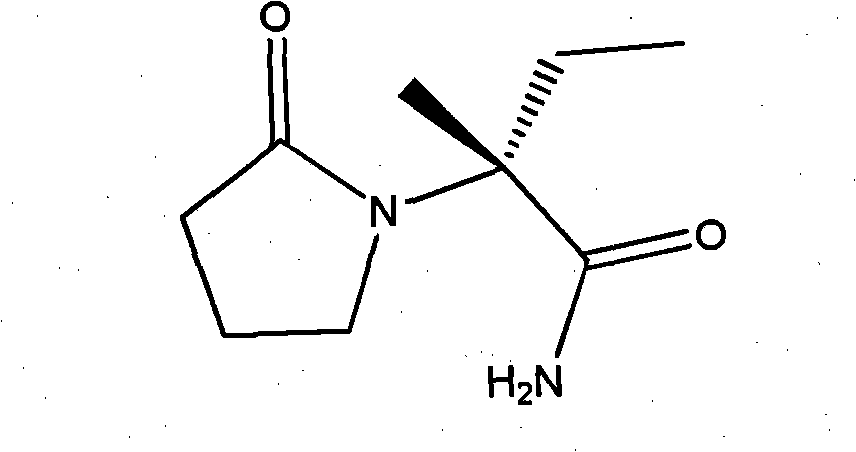
Process method for producing L-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride serving as intermediate of levetiracetam
InactiveCN101928229ALow costShort synthesis cycleOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationSodium cyanideHydrolysis
The invention discloses a process method for producing L-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride serving as an intermediate of levetiracetam, which solves the problem that the conventional produced product has excessively high impurity content or production cost is too high for an enterprise to bear and the like. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: reacting propionaldehyde with ammonia water, ammonium chloride and sodium cyanide to obtain 2-amino butyronitrile; hydrolyzing the 2-amino butyronitrile under an alkali condition to obtain 2-aminobutanamide; and splitting the 2-aminobutanamide with L-tartaric acid to obtain the L-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride. An L-2-amino amides product of which the content is over 99.5 percent is obtained by removing a byproduct, namely, sodium chloride by recrystallization so as to meet the use requirement of foreign customers. The process has the advantages of high yield, high safety and low cost and can be widely suitable for industrialized production of medium-sized and small enterprises.
Owner:HUANGGANG HUAYANG PHARMA
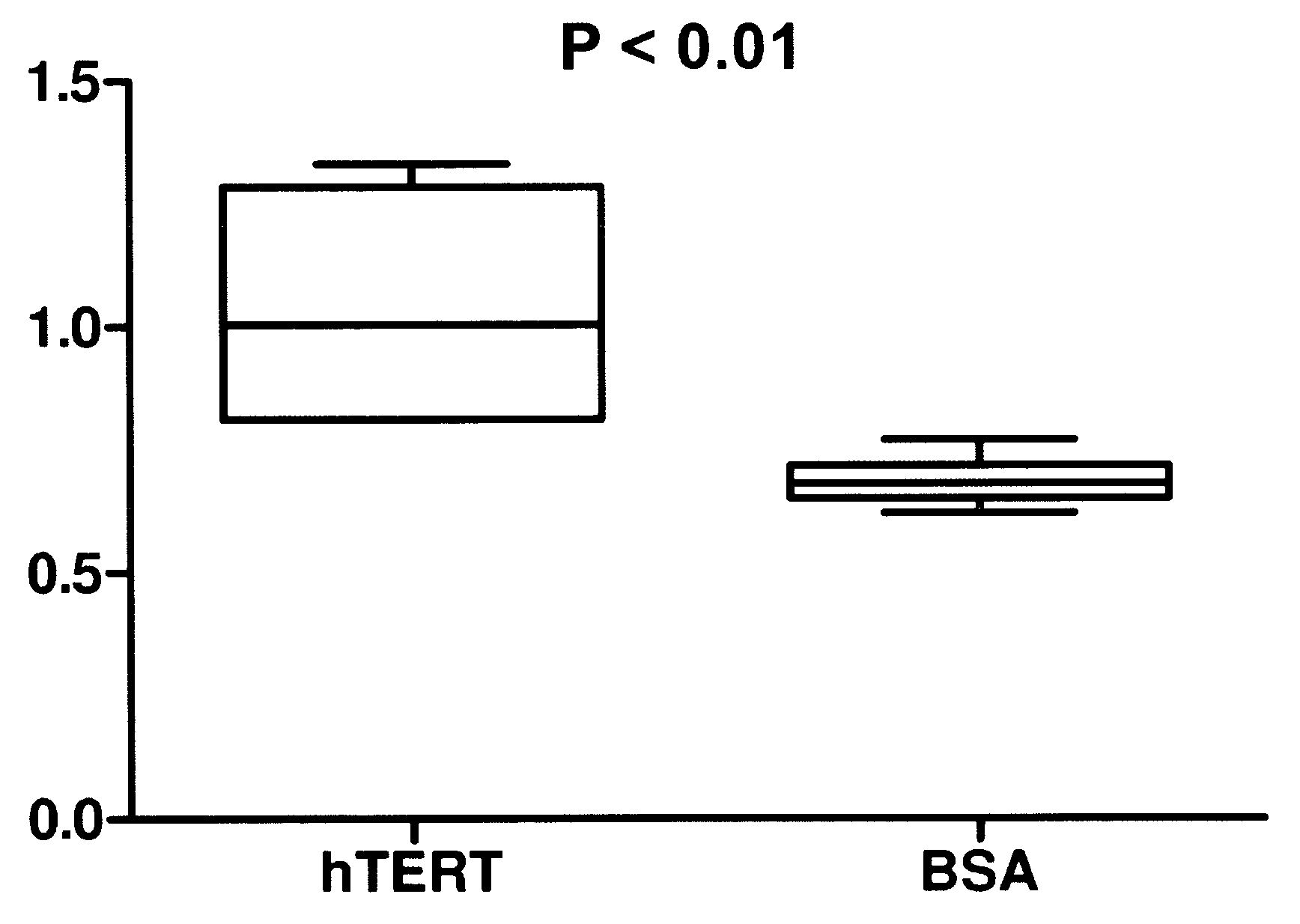
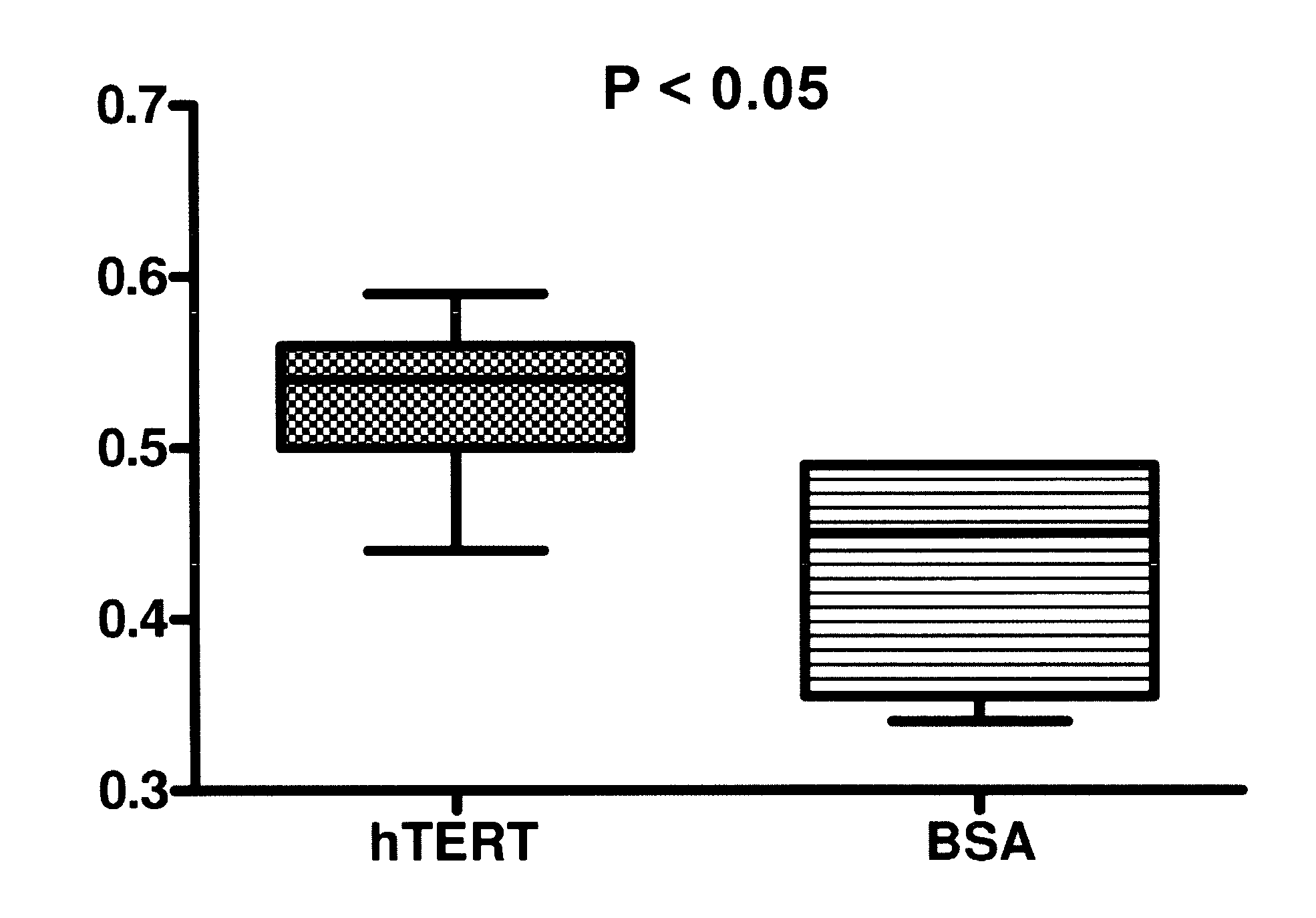
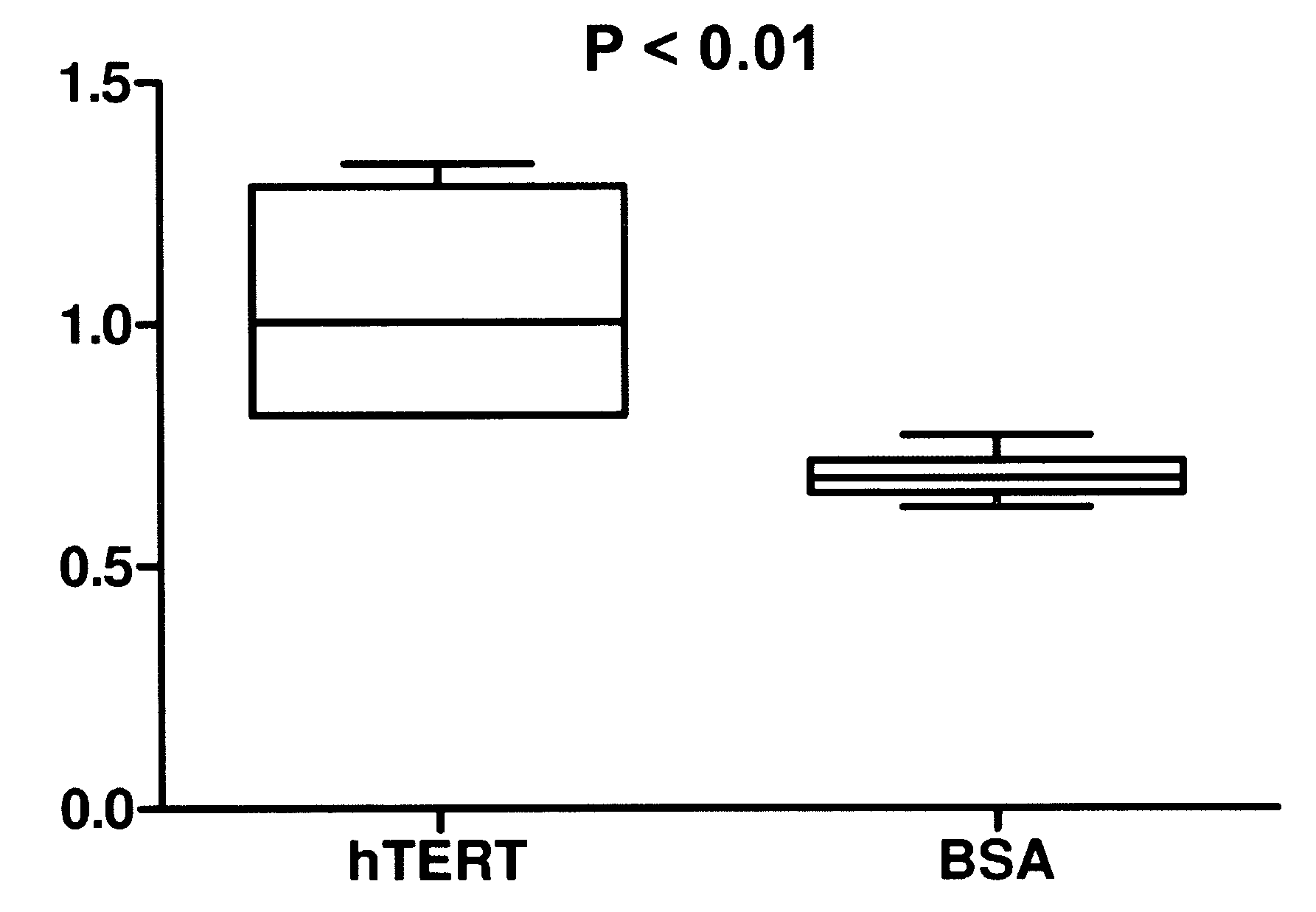
Telomerase delivery by biodegradable Nanoparticle
InactiveUS20090142408A1Effectively crossControl releasePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAge related diseaseHydrophilic polymers
A therapeutic compound consisting of human telomerase, its catalytic subunit hTert, or a known variant of either, and a biodegradable nanoparticle carrier, which can be administered to cells in a cell culture or in a living animal, is provided herein. The therapeutic compound is envisioned as a method for treating a wide variety of age-related diseases such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, aplastic anemia, dyskeratosis congenita, arteriosclerosis, macular degeneration, osteoporosis, Alzheimer's, diabetes type 2, and any disease that correlates with telomere shortening and may be corrected or ameliorated by lengthening telomeres. The therapeutic compound is also envisioned as method for potentially treating more generic problems of human aging. The nanoparticle carrier is comprised of certain biodegradable biocompatible polymers such as poly(lactide-co-glycolide), poly(lactic acid), poly(alkylene glycol), polybutylcyanoacrylate, poly(methylmethacrylate-co-methacrylic acid), poly-allylamine, polyanhydride, polyhydroxybutyric acid, polycaprolactone, lactide-caprolactone copolymers, polyhydroxybutyrate, polyalkylcyanoacrylates, polyanhydrides, polyorthoester or a combination thereof. The nanoparticle may incorporate a targeting moiety to direct the nanoparticle to a particular tissue type or a location within a cell. The nanoparticle may incorporate a plasticizer to facilitate sustained release of telomerase such as L-tartaric acid dimethyl ester, triethyl citrate, or glyceryl triacetate. A nanoparticle of the present invention can further contain a polymer that affects the charge or lipophilicity or hydrophilicity of the particle. Any biocompatible hydrophilic polymer can be used for this purpose, including but not limited to, poly(vinyl alcohol).
Owner:SARAD MATTHEW
Process for the resolution of (R,S)-nicotine
(R,S)-Nicotine was resolved through diastereomeric salt formation using dibenzoyl-d-tartaric acid and dibenzoyl-l-tartaric acid to obtain enantiomerically pure (S)-nicotine and (R)-nicotine.
Owner:DIVI S LAB LTD
R-amisulpride medicine salt, preparation method, crystal form and application thereof
ActiveCN106995397AGood curative effectLower blood sugarMetabolism disorderOrganic chemistry methodsPyrrolidineTriethylamine
The invention concretely relates to R-amisulpride medicine salt, a preparation method, a crystal form and application thereof in preparing a medicine for treating diabetes. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by adopting 2-aminomethyl-N-ethyl pyrrolidine as a raw material, and adopting L-tartaric acid, for splitting to obtain (R)-2-aminomethyl-N-ethyl pyrrolidine; directly condensing amisulpride acid and the (R)-2-aminomethyl-N-ethyl pyrrolidine under the catalysis of isopropyl chlorocarbonate and triethylamine, thus obtaining R-amisulpride; reacting the R-amisulpride obtained in the step (2) and acid to obtain the R-amisulpride medicine salt. The preparation method has the advantages of simplicity in operation, high safety, good product quality, low cost and the like, and is convenient for scale production.
Owner:SHENZHEN FONCOO PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Resolution method of optically active amlodipine
ActiveCN1927836AMoisture content no special requirementsShort reaction timeOrganic chemistrySolventAmlodipine
The present invention relates to chemical method of resolving despinner Amlodipine into (S)-(-)-Amlodipine and (R)-(+)-Amlodipine. The resolving agent is L-tartaric acid or D-tartaric acid; and the solvent is methyl ethyl sulfoxide or mixed solvent containing methyl ethyl sulfoxide. The present invention has greatly shortened reaction period and no special requirement on the water content in the solvent, and is especially suitable for large scale production.
Owner:CSPC ZHONGQI PHARM TECH (SHIJIAZHUANG) CO LTD +1
Method for preparing S-(-)-amlodipine and R-(+)-amlodipine by chirally resolving racemic amlodipine
ActiveCN101798280AWide variety of sourcesCheap sourceOptically-active compound separationOrganic racemisationSolventTartrate
The invention discloses a method for preparing S-(-)-amlodipine and R-(+)-amlodipine by chirally resolving racemic amlodipine. The resolving solvent is ethanol or a mixed solvent containing ethanol, chiral dibenzoyl-D-tartaric acid or dibenzoyl-L-tartaric acid is used as the resolving agent, the chiral resolving agent and the racemic amlodipine selectively form chiral amlodipine dibenzoyl tartrate, and the chiral amlodipine dibenzoyl tartrate is alkalified to obtain the chiral amlodipine. The invention adopts the ethanol as the resolving solvent; and when using industrial ethanol as the resolving solvent, the invention can also acquire good resolving effect and obtain the qualified medicinal amlodipine raw material, thereby obviously reducing the cost. The invention has the characteristics of simple reaction operation, easy control, low toxicity, environmental protection, high efficiency and the like, and is suitable for green large-scale production.
Owner:石家庄润柏医药科技有限公司
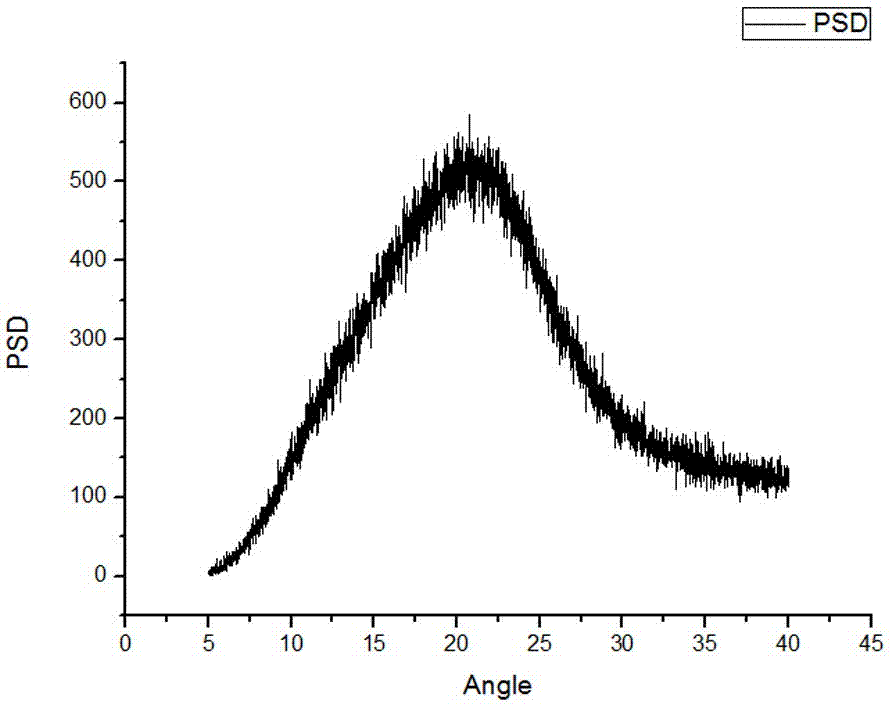
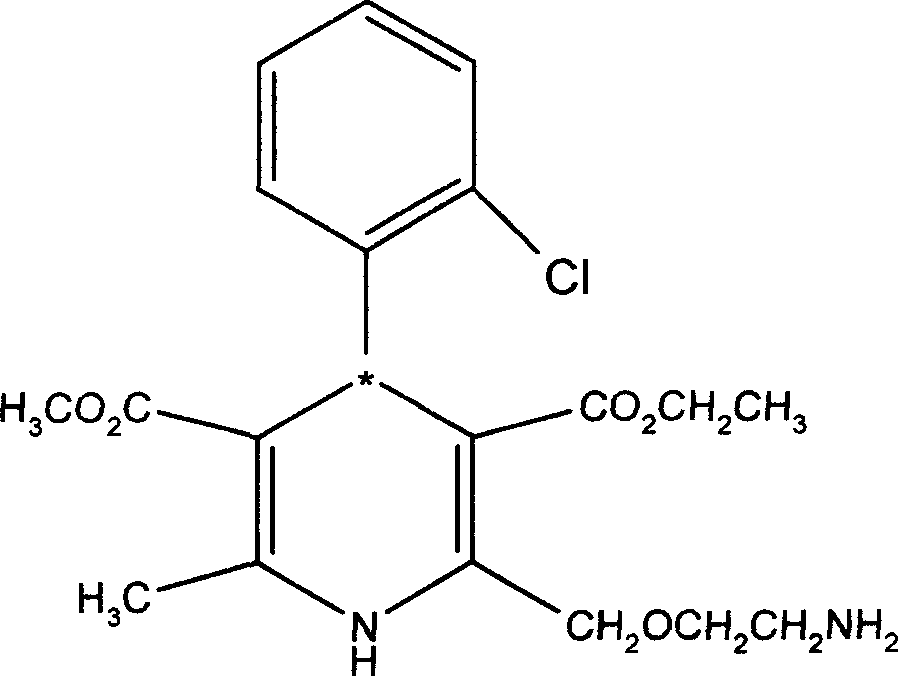
Process for the preparation of 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-hexane compounds and enantiomeric salts thereof
The present invention provides for a process for preparing racemic methyl 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3,1,0]hexane-2-carboxylate, its corresponding salt: (2S, 3R, 4S)-methyl 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3,1,0]hexane-2-carboxylate di-p-toluoyl-D-tartaric acid (“D-DTTA”) salt or a (2R, 3S, 4R)-methyl 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3,1,0]hexane-2-carboxylate di-p-toluoyl-L-tartaric acid salt (“L-DTTA”) in a high enantiomeric excess. This invention also provides for a process for preparing a (2S, 3R, 4S)-methyl 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3,1,0]hexane-2-carboxylate dibenzoyl-D-tartaric acid (“D-DBTA”) salt or a (2R, 3S, 4R)-methyl 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3,1,0]hexane-2-carboxylate L-tartaric acid (“L-DBTA”) salt in a high enantiomeric excess. Further, this invention provides a process for preparing intermediates II, IIB, III, IV, IV salt, V, VI, and VII.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Method for preparing R-beta-aminobenzene butyric acid derivative
ActiveCN101633625AHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationChemical synthesisSolvent
The invention relates to a method for preparing an R-beta-aminobenzene butyric acid derivative (I) serving as a chiral medicament midbody and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. In the method, chemical synthesis processes including the resolution of a DL body of a beta-aminobenzene butyric acid derivative by using a resolving agent are used to obtain a target matter of a special optical configuration. The preparation method comprises a step of using resolving agents which are di-p-toluoyl-L-tartaric acid and di-p-toluoyl-D-tartaric acid to salify and resolve in an alcohols solvent andan alcohols water solvent. The obtained R-beta-aminobenzene butyric acid derivative (I) has a high optical purity and an accumulated overall yield of the positive and negative resolution of up to over 70 percent. The R-beta-aminobenzene butyric acid derivative (I) prepared by the invention can better applied to synthesizing medicaments.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGRUI MEDICINE CO LTD
Phosphating liquid of high corrosion resistance black phosphating production process
ActiveCN101864563ACrystal fineFirmly attachedMetallic material coating processesO-Phosphoric AcidOptical instrumentation
The invention relates to phosphating liquid of a phosphating process, in particular to phosphating liquid of a high corrosion resistance black phosphating production process for steel piecec, which is characterized in that: the phosphating liquid comprises the following components: 25 to 35 g / L zinc oxide (ZnO), 120 to 135 g / L phosphoric acid H3PO4, 100 to 150 g / L zinc nitrate Zn(NO3)2.6H2O, 5 to 8 g / L nitric acid HNO3, 3 to 5 g / L citric acid, 0.5 to 1 g / L tartaric acid and 5 to 10 g / L nickel nitrate. The phosphating liquid ensures the fineness and smoothness of the phosphating film crystal of the steel piece, has firm attachment, good blackness and high abrasion resistance, and is particularly applicable to the steel components of the optical instrument.
Owner:西安北方光电有限公司
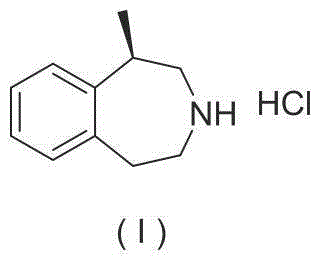
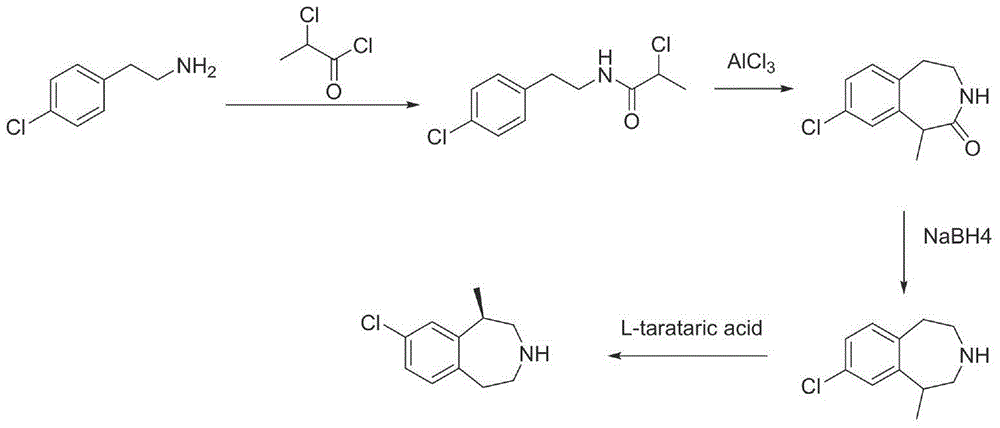
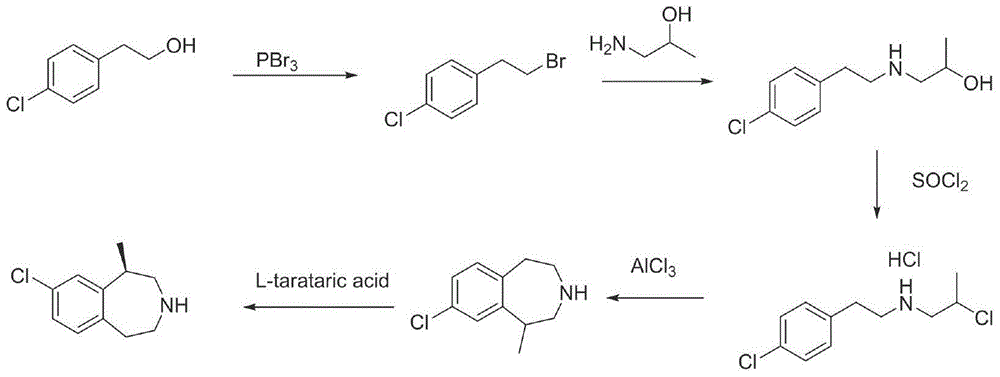
Preparation method of lorcaserin hydrochloride
The invention provides a preparation method of lorcaserin hydrochloride, namely (R)-8-chloro-1-methyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzazepine hydrochloride. The method comprises the following steps: taking p-chlorophenyl acetate as raw material, performing aminolysis with isopropanol amine, then performing chlorination, reduction and Friedel-Crafts alkylation, further splitting by L-tartaric acid, and performing salt formation to get the lorcaserin hydrochloride. The invention provides the preparation method of the lorcaserin hydrochloride. The method has the advantages of low cost, simplicity in operation and higher product purity; according to the process disclosed by the invention, the continuous operation can be performed, and the production cycle is greatly reduced; meanwhile a reagent is low in price and easy to obtain, the operation is simple, and the post-treatment is simple and convenient, so that the preparation method is a brand new and economic synthesis method which can realize industrial production.
Owner:SUZHOU HUIHE PHARMA
Kudzuvine root drink capable of relieving or neutralizing the effect of alcohol and production technique thereof
The invention discloses a Kudzuvine root drink capable of relieving or neutralizing the effect of alcohol and its preparation, wherein the drink comprises (by weight parts) root of kudzu vine extract 600-800, water 200-300, cane sugar 40-60, glucose 140-160, L-ascorbic acid 0.1-0.3, sodium succinate 0.3-0.5, sodium fumarate 0.3-0.5, L-malic acid0.3-0.5, L-tartaric acid 0.3-0.5, lactic acid 0.1-0.2, acetic acid 0.1-0.2, beta cyclodextrin 0.4-0.6, L-leucine 0.45-0.6, L-sulfo-aminolactic acid 0.45-0.6, sodium glutamate 0.4-0.6, L-alanine 0.4-0.6, glycine 0.5-0.6, catechin 0.1-0.3.
Owner:益阳市世纪塑业科技有限公司
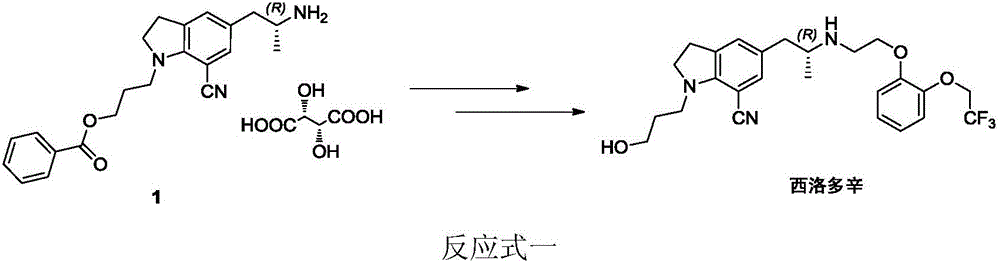
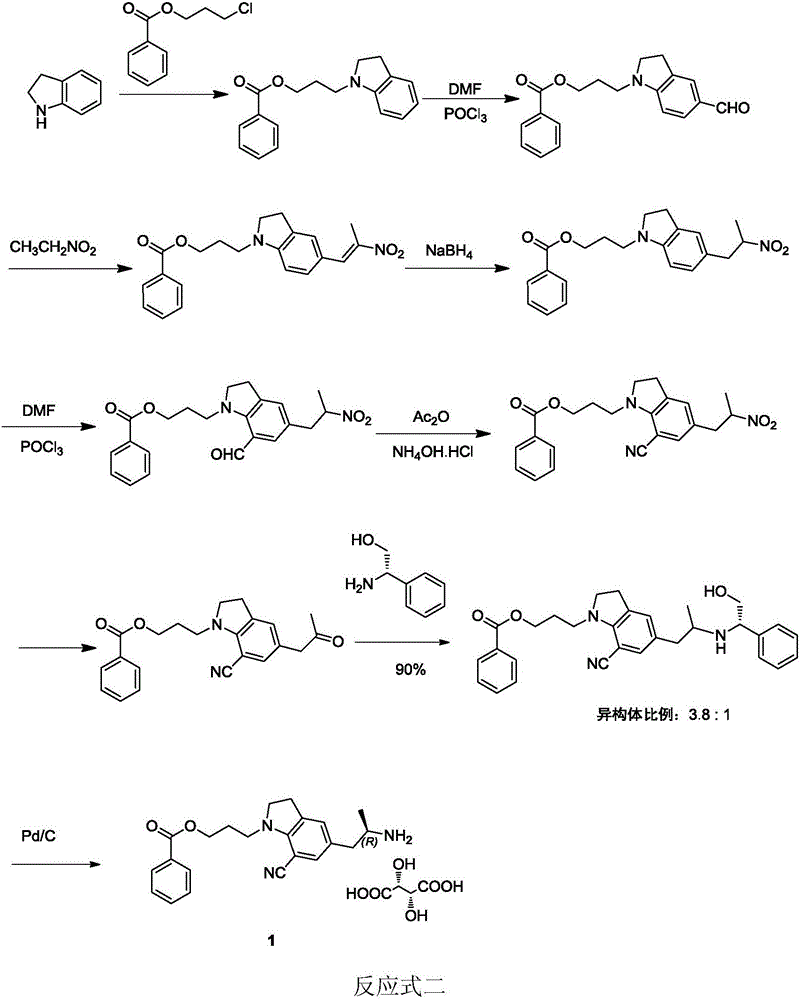
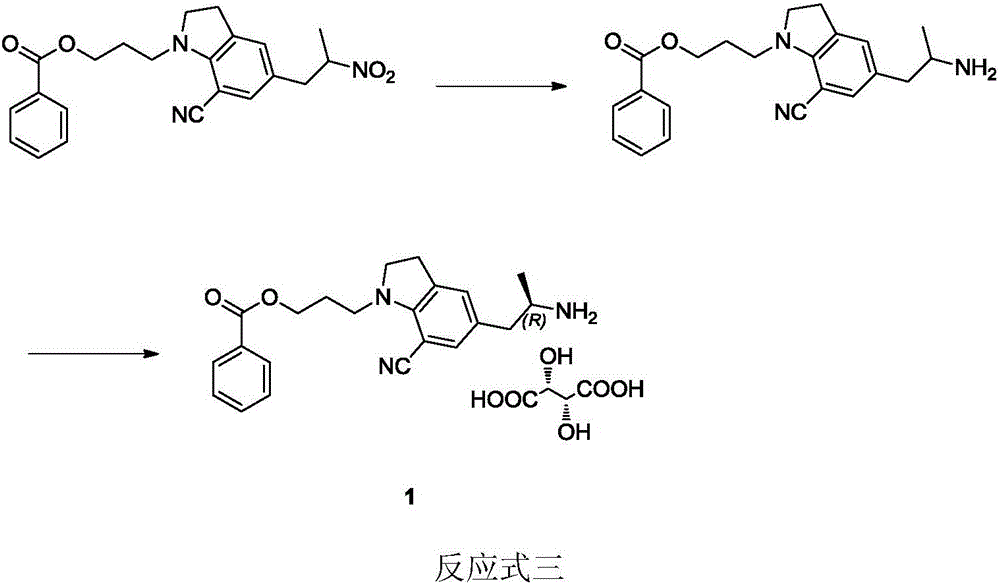
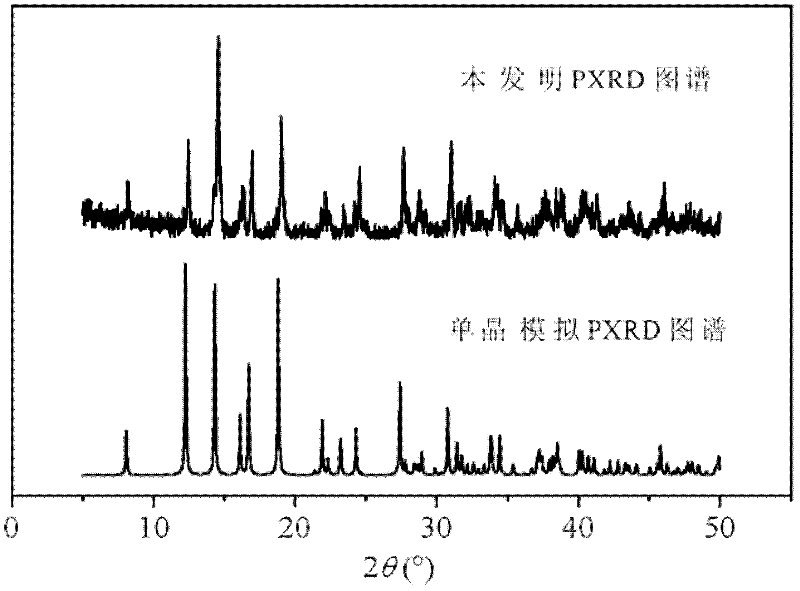
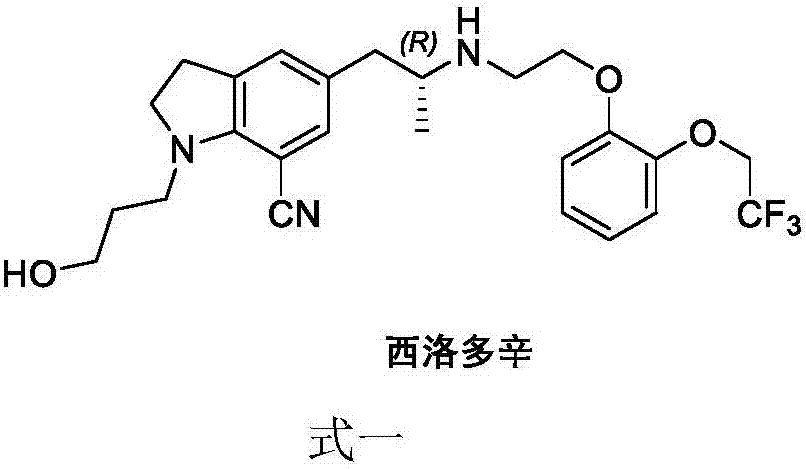
Preparation method of silodosin intermediate
The invention discloses a preparation method of a silodosin intermediate. The preparation method comprises the following steps that in an organic solvent, under the action of lewis acid, friedel-crafts acylation reaction occurs between a compound 2 and a compound 3, so as to obtain a compound 4, wherein the lewis acid is one of or more of zinc trifluoromethanesulfonate, bismuth trifluoromethanesulfonate, scandium trifluoromethanesulfonate and aluminum trichloride; under the action of organic acid or boron trifluoride ether complex, the compound 4 reacts with triethyl silicane, so as to obtain a compound 5; the compound 5 reacts with sodium azide, so as to obtain a compound 6; under the action of catalysts, the compound 6 reacts with di-tert-butyl dicarbonate ester and hydrogen, so as to obtain a compound 7; under an acidic condition, the deamination protective reaction of the compound 7 occurs, so as to obtain a compound 8; the compound 8 reacts with L-tartaric acid, so as to obtain a compound 1, namely the silodosin intermediate. The preparation method of the silodosin intermediate has the advantages of simplicity, economy and mild reaction conditions, and chiral resolution is not needed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TIANYU PHARMA
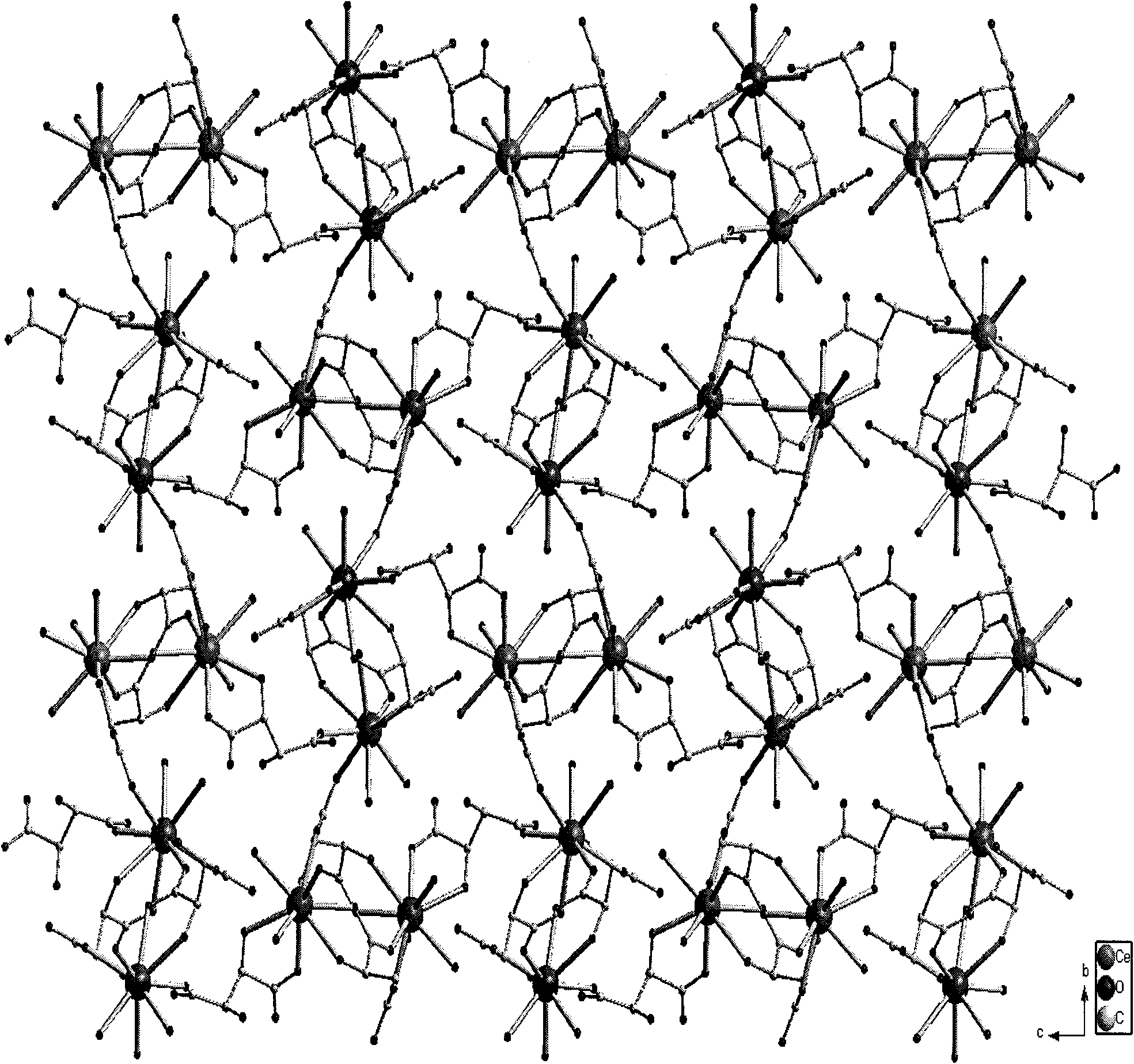
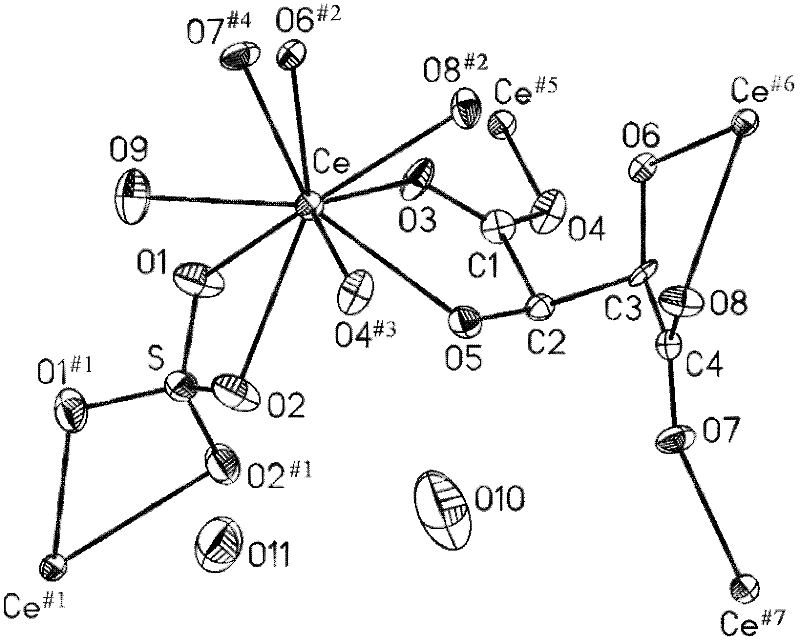
L-tartaric acid ceric sulfate ferroelectric functional material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102330153ASignificant features of ferroelectric functionLow costPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsSpace groupCeric sulfate
The invention discloses an L-tartaric acid ceric sulfate ferroelectric functional material. The molecular formula of the ferroelectric functional material is [[Ce2(H2O)2(L-(+)-tar)2(SO4)].4H2O]. The ferroelectric functional material can pass through a sieve with 100 meshes, is white monoclinic system powder and has a C2 space group structure. The 2Pr value of a ferroelectric hysteresis of the ferroelectric functional material is 0.316muC / cm<2>, the 2Ec value is 54.1kV / cm, the Ps value is 0.335muC / cm<2> and the saturated intensity of polarization of the ferroelectric functional material is 1.34 times of that of polarization of rochelle salt. The ferroelectric functional characteristics are remarkable. The preparation method of the ferroelectric functional material comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing cerium dioxide, L-(+)-tartaric acid and sulphuric acid; adding deionized water for a hydro-thermal reaction; after reaction, filtering to obtain an L-tartaric acid ceric sulfate tabular crystal; and grinding and sieving to obtain the colorless L-tartaric acid ceric sulfate monoclinic system powder ferroelectric functional material. The preparation method has the advantages of simple and feasible process, low requirement on equipment, low cost of raw material, high yield, no pollution and the like.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Synthesizing method of silodosin and intermediate thereof
ActiveCN107056675ASimplify conversion stepsHigh reaction yieldOrganic chemistry methodsProduction riskHydrolysis
The invention relates to the field of medicine chemistry, aims to solve the problems that the prior art is complex in reaction steps, high in production risk, low in yield, and the like, and provides a synthesizing method of silodosin and an intermediate thereof. The synthesizing method includes: using hydrochloric acid / acetic acid to perform deacetylation on chloride 2 to obtain indoline 3, performing SN2 substitution reaction to obtain imide 4, performing N alkylation reaction to obtain benzoate 5, reducing carbonyl to obtain indoline 6, performing Vilsmeier reaction to obtain aldehyde 7, performing oximation dewatering to obtain nitrile 8, performing hydrazine hydrate reaction to obtain amine 9, performing L-tartaric acid separation on the amine 9 to obtain the silodosin key intermediate 10, performing condensation under an alkaline condition to obtain a compound 11, allowing the compound 11 to have salt formation crystallization with L-malic acid to form salt 12, and performing alkaline hydrogen peroxide hydrolysis on the salt 12 to obtain the silodosin 1. The synthesizing method has the advantages that the L-malic acid is used to perform the salt formation crystallization, impurities such as bipolymer which are hard to remove are removed effectively, high reaction conversion rate is achieved, industrial production cost is lowered effectively, and synthesizing safety is increased by avoiding the use of dangerous reagents.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TIANYU PHARMA
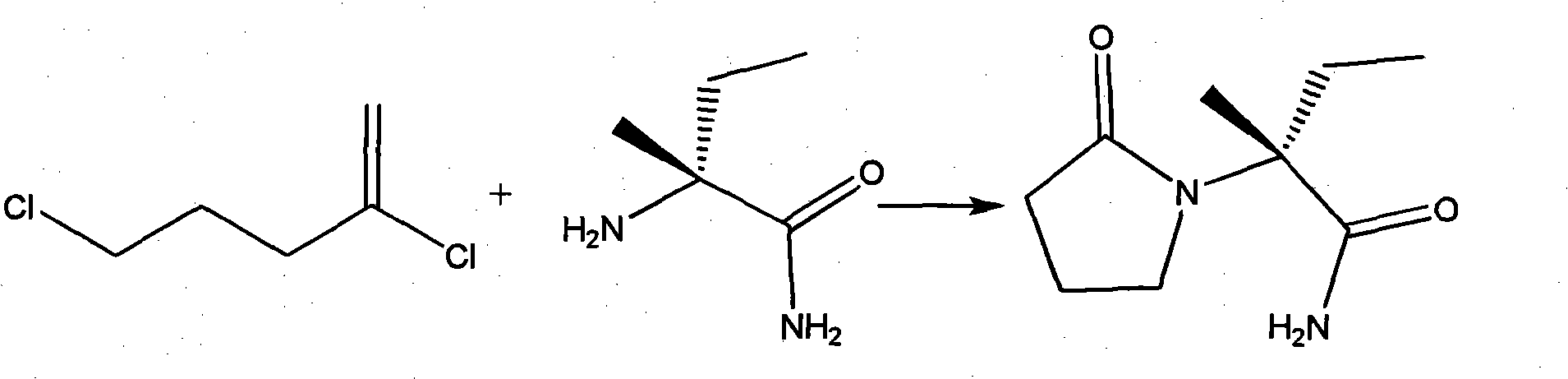
Synthesis method of S-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride
InactiveCN103012190ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationSynthesis methodsProcess safety
The invention discloses a synthesis method of S-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, which comprises the following steps of: 1) ammoniation: respectively carrying out ammoniation on methyl 2-bromobutyrate in a methanol-ammonia solution and anhydrous isopropyl alcohol so as to generate DL-2-aminobutanamide; 2) resolving: combining the DL-2-aminobutanamide with an L-tartaric acid to carry out salting-out, and carrying out resolution and purification on the obtained product; and 3) releasing and salifying: directly feeding hydrogen chloride into a crude product subjected to resolution and purification so as to carry out releasing and salifying, thereby obtaining S-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride with optical activity. The method disclosed by the invention is cheap and easily obtained in raw materials, simple in operation, mild in conditions, high in process safety, low in equipment requirement, and easy to realize industrialized large-scale production.
Owner:江苏拜克新材料有限公司
Process for the resolution of (r,s)-nicotine
Owner:DIVI S LAB LTD
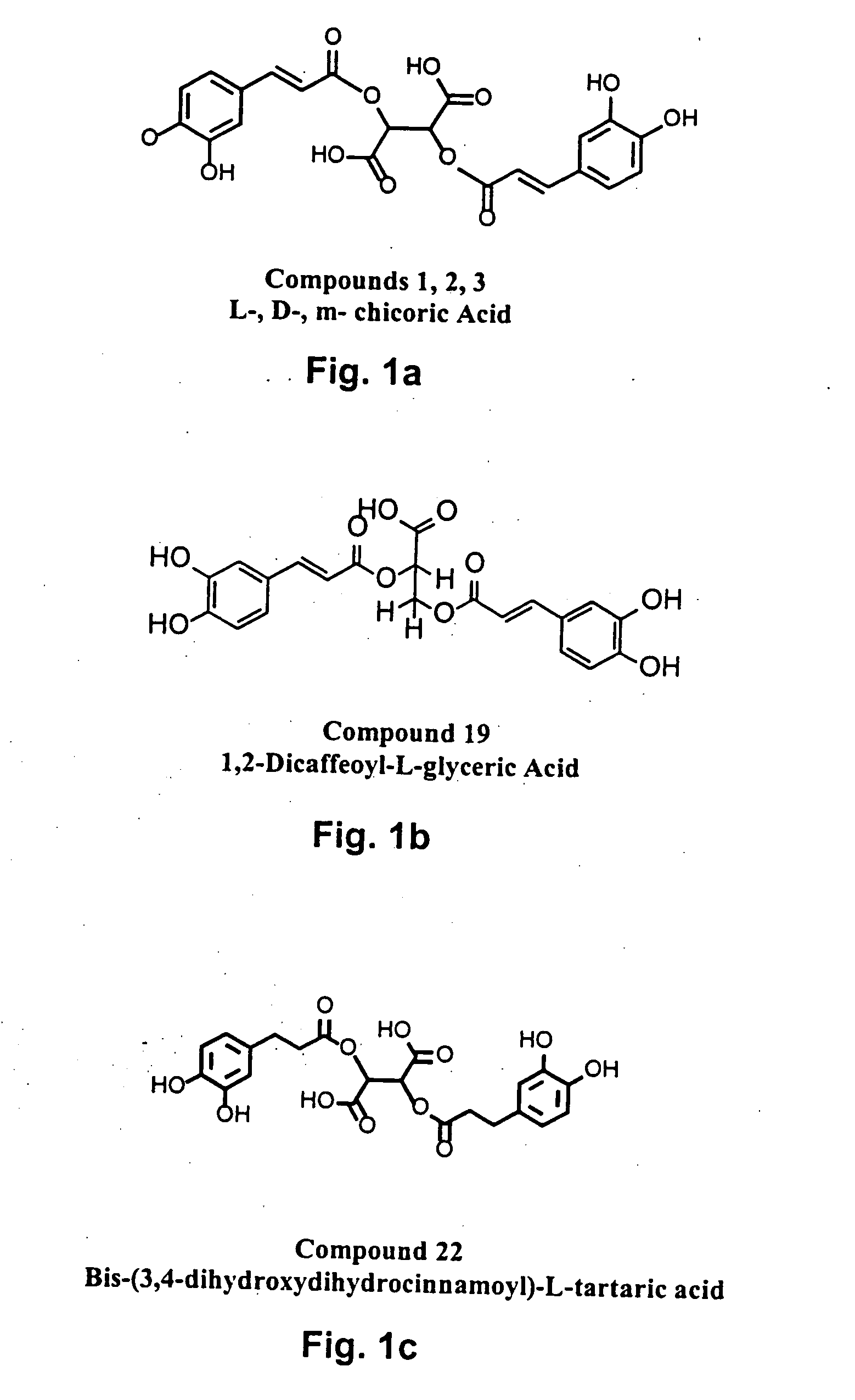
Novel HIV integrase inhibitors and HIV therapy based on drug combinations including integrase inhibitors
InactiveUS20050049242A1Strong synergyBiocideAnimal repellantsCombination drug therapyResistant virus
The present invention includes a group of novel compounds that are demonstrated to potently and selectively inhibit HIV integrase (IN) activity in vitro and to potently inhibit HIV replication in live, cultured cells at non-toxic concentrations. The novel compounds disclosed include 2,3-di(3,4-dihydroxy-dihydroxydihydrocinnamoyl)-L-tartaric acid, 2,3-di-(3,4-dihydroxybenzoyl)-L-tartaric acid, 2,3-di-(3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetyl)-L-tartaric acid, 2,3-di-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl-L-tartaric acid, 2,3-dicaffeoyldiamidopropionic acid, 1,2,-dicaffeoyl-L-glyceric acid, bis,-3,4-dicaffeoyldiamidobenzoic acid, di-3,4-dihydroxybenzylidene succinic acid, di-3,4-dihydrodihydroxybenzylidine succinic acid, 2,3-dicaffeoyl-L-serine, bis-dicaffeoyl-L-isoserine and 1,4-dicaffeoyl-L-lysine. Tests of integrase inhibitors with 2′,3′-dideoxycytidine, zidovudine and nelfinavir (protease inhibitor) indicated a potent synergy against reverse transcriptase inhibitor resistant virus. The potential benefit from the addition of integrase inhibitors to combination drug therapies is significant.
Owner:ROBINSON W EDWARD JR +2
Preparation method of L-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride
ActiveCN102584622ASimple and safe operationQuality improvementCarboxylic acid amides optical isomer preparationUnit operationHydrochloride
The invention provides a preparation method of L-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride. The method comprises the following steps: based on crude DL-2-aminobutanamide as a starting raw material, reacting with aromatic aldehyde to form DL-Schiff-base, separating, dissociating, and salifying to obtain L-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, wherein the Schiff base can be directly separated by using L-tartaric acid, the chiral purity ee value of the product is no less than 99%, the quality is stable, and the separation mother liquor can be recycled through racemization. According to the invention, the raw materials used in each step of the method are cheap and available, the unit operations are simple and safe, the post-treatment is convenient, the requirements on the equipment are low and the method issuitable for industrialized production.
Owner:ABA CHEM NANTONG
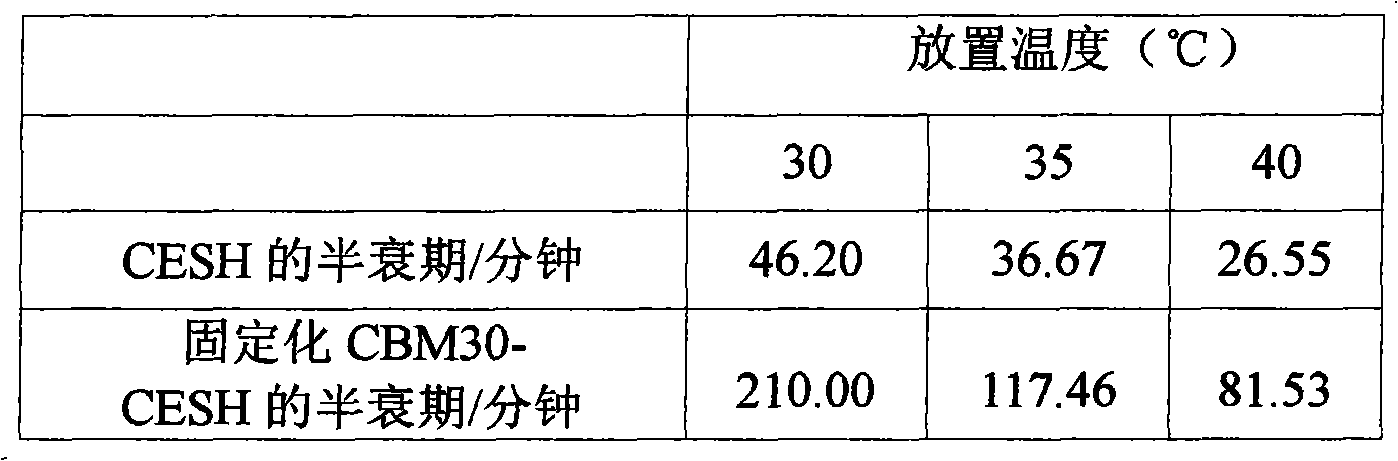
Cellulose immobilized cis epoxy succinic acid hydrolase and method for preparing tartaric acid
InactiveCN102703419ALow priceWide variety of sourcesOn/in organic carrierFermentationCelluloseEscherichia coli
The invention provides a method of cellulose immobilized cis epoxy succinic acid hydrolase. The method comprises the following steps: fusing gene coding cis epoxy succinic acid hydrolase and carbohydrate binding module CMB30, efficiently expressing the fused gene in Escherichia coli, and then carrying out purification and immobilization on fused enzyme in crude enzyme liquid by adopting the cellulose. The invention also provides a method for catalyzing and hydrolyzing epoxy succinic acid to convert into L-tartaric acid or D-tartaric acid by adopting the cellulose immobilized cis epoxy succinic acid hydrolase as biocatalyst. The method has the beneficial effects that: not only is the stability of enzyme obviously improved, but also the cellulose used as purified and fixed substrate is low in price and easy to get by adopting the cellulose immobilized cis epoxy succinic acid hydrolase, and has excellent economic prospect. The method for preparing tartaric acid by adopting the cellulose immobilized cis epoxy succinic acid hydrolase has the advantages of reaction specificity, high product purity, high reaction efficiency and the like.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for synthesizing D-valine
ActiveCN102070473AReduce dosageReduce pollutionOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationKetoneSolvent
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing D-valine, which comprises the following steps of: cyaniding isobutylaldehyde serving as an initiative raw material to prepare 2-amino-3-methyl-butanenitrile; performing catalytic hydrolysis by adopting inorganic base and a ketone catalyst to obtain mix spin freebase(+ / -)-2-amino-3-methylbutyrylamide; resolving by using a resolving agent of dibenzoyl-L-tartaric acid (L-DBTA) in a mixed solvent of acetone and water to obtain D-2-amino-3-methylbutyrylamideL-DBTA salt solid with optical activity; and acidifying and separating the resolving agent, and performing reflux hydrolysis and refining to obtain D-2-amino-3-methyl-butanoic acid, namely D-valine. The method has the advantages that: raw materials are low in cost and easily obtained, the method is easy and convenient to operate, the cost is low, the environmental pollution is light, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ABA CHEM SHANGHAI
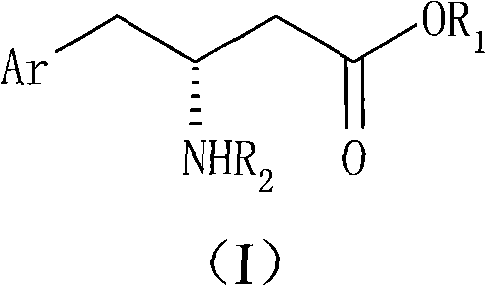
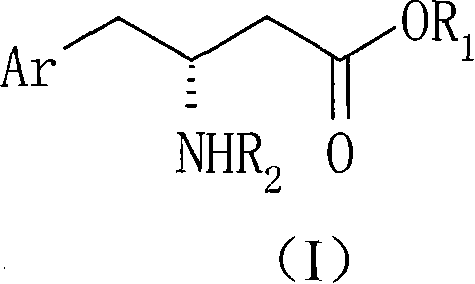
Process For The Preparation Of 6,6-Dimethyl-3-Azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-Hexane Compounds ...
The present invention provides for a process for preparing racemic methyl 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3,1,0]hexane-2-carboxylate, its corresponding salt: (2S, 3R, 4S)-methyl 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3,1,0]hexane-2-carboxylate di-p-toluoyl-D-tartaric acid (“D-DTTA”) salt or a (2R, 3S, 4R)-methyl 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3,1,0]hexane-2-carboxylate di-p-toluoyl-L-tartaric acid salt (“L-DTTA”) in a high enantiomeric excess. This invention also provides for a process for preparing a (2S, 3R, 4S)-methyl 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3,1,0]hexane-2-carboxylate dibenzoyl-D-tartaric acid (“D-DBTA”) salt or a (2R, 3S, 4R)-methyl 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3,1,0]hexane-2-carboxylate L-tartaric acid (“L-DBTA”) salt in a high enantiomeric excess. Further, this invention provides a process for preparing intermediates II, IIB, III, IV, IV salt, V, VI, and VII.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Split reagent and method for ofloxacin racemic mixture
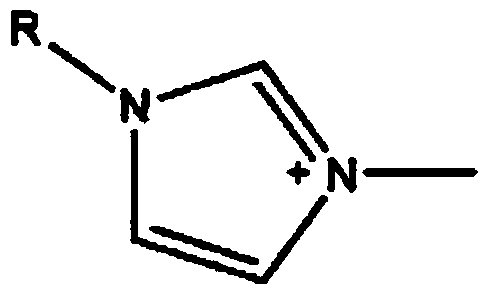
ActiveCN103664998AHigh selectivityImprove the efficiency of chiral resolutionOrganic chemistryL-ofloxacinTartrate
The invention discloses a split reagent and a split method for an ofloxacin racemic mixture. The method is as below: dissolving an ofloxacin racemic mixture and an alkyl imidazole L-tartaric acid salt ionic liquid in deionized water to form an aqueous phase, and at the same time dissolving D-dibenzoyl tartaric acid in n-decyl alcohol to form an organic phase; mixing the organic phase and the aqueous phase; oscillating the mixture in an oscillator and standing; detecting concentration of L-ofloxacin and D-ofloxacin in a clear aqueous phase; acquiring the concentration of L-ofloxacin and D-ofloxacin in organic phase respectively by the law of conservation of mass; respectively calculating the distribution coefficient of the L-ofloxacin and D-ofloxacin; and further calculating a separation factor. The reagent and the method have good separation effect, and is successfully in splitting. The invention uses alkyl imidazole L-tartaric acid salt ionic liquid and D-dibenzoyl tartaric acid for splitting of the ofloxacin racemic mixture, improves the splitting efficiency and reduces the reagents required by splitting; and the method has simple operation and high selectivity, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:CHINA CONSTR IND & ENERGY ENG GRP CO LTD +1
Solventhermal synthesis method for L-tartaric acid rare earth complexes
InactiveCN101921187ASimple processEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationReduction rateSynthesis methods
The invention provides a solventhermal synthesis method for L-tartaric acid rare earth complexes, which belongs to the field of synthesis of chiral compounds. The method has the advantages of controlling the particle sizes and shapes of products by changing the proportion of raw materials, crystallization temperature and temperature reduction rates, along with simple process flow and convenient operation. The synthesized L-tartaric acid rare earth complexes have high thermal stability, keep stable under alkaline condition and can be used for photoactivation materials or chiral resolving agents.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Sterilization auxiliary for ozone sterilization and ozone sterilization method
InactiveUS20130028787A1Efficient processLess ozoneBiocideWater treatment parameter controlAluminum IonPhosphoric acid
The present invention provides a sterilization auxiliary for ozone sterilization which is an aqueous solution including a Component (A) of an aluminum compound which produces aluminum ions in an aqueous solution, and a Component (B) of one or more of acids selected from phosphoric acid, citric acid, malic acid, succinic acid, gluconic acid, lactic acid, and L-tartaric acid, wherein the pH of the aqueous solution is greater than or equal to 1.0 and less than 5.0, and an ozone sterilization method for ozone-treating a substance to be treated using the sterilization auxiliary. According to the present invention, a sterilization auxiliary for ozone sterilization in which a high sterilizing effect may be obtained using less ozone without burdening sterilization apparatus and a substance to be treated, and a low-cost ozone sterilization method using the sterilization auxiliary can be provided.
Owner:LION CORP
Substrate of traditional Chinese medicine cataplasm
ActiveCN103040792ANon-allergicNo pollution in the processPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSheet deliveryAdditive ingredientDisodium Edetate
The invention discloses a substrate of a traditional Chinese medicine cataplasm, which is prepared by the following raw materials in parts by weight: 800-1000 parts of partially neutralized sodium polyacrylate, 600-800 parts of crosslinking povidone, 350-500 parts of polyvinylpyrrolidone, 25-50 parts of aluminum glycinate, 6-10 parts of edetate disodium, 4000-5000 parts of glycerol and 35-50 parts of L-tartaric acid. Experimental results indicate that the substrate of the traditional Chinese medicine cataplasm does not cause skin allergy, and is low in stimulation reaction and easy to peel; in a peeling process, a patient does not feel pain; no medicine is residual; the transdermal absorption of the medicine is high; a medicine effect is better; the patient can use the medicine conveniently; and an organic solvent is not used in a production process, so that the environment is not polluted. The substrate can be supported with a water-soluble effective ingredient and an oily effective ingredient clinically, and has a wider application range.
Owner:常熟雷允上制药有限公司
Disinfection aid for ozone disinfection and method for ozone disinfection
InactiveCN102834012AReduce ozoneImprove the bactericidal effectBiocideWater treatment parameter controlAluminum IonAcetic acid
A disinfection aid for ozone disinfection, which consists of an aqueous solution that contains (A) an aluminum compound capable of forming aluminum ions in an aqueous solution and (B) at least one acid selected from among phosphoric acid, acetic acid, citric acid, malic acid, succinic acid, gluconic acid, lactic acid, and L-tartaric acid and that has a pH of 1.0 to less than 5.0; and a method for ozone disinfection, which comprises subjecting an object to be disinfected to ozonization using the disinfection aid. Thus, a disinfection aid which, even when a smaller amount of ozone is used, can ensure high disinfection effect without a load on a disinfection apparatus or an object to be disinfected, and a low-cost method for ozone disinfection using the disinfection aid are provided.
Owner:LION CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com











![Process for the preparation of 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-hexane compounds and enantiomeric salts thereof Process for the preparation of 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-hexane compounds and enantiomeric salts thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/616865f1-32fc-4a7d-a092-5502ba2d7d9f/US07723531-20100525-C00001.png)
![Process for the preparation of 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-hexane compounds and enantiomeric salts thereof Process for the preparation of 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-hexane compounds and enantiomeric salts thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/616865f1-32fc-4a7d-a092-5502ba2d7d9f/US07723531-20100525-C00002.png)
![Process for the preparation of 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-hexane compounds and enantiomeric salts thereof Process for the preparation of 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-hexane compounds and enantiomeric salts thereof](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/616865f1-32fc-4a7d-a092-5502ba2d7d9f/US07723531-20100525-C00003.png)










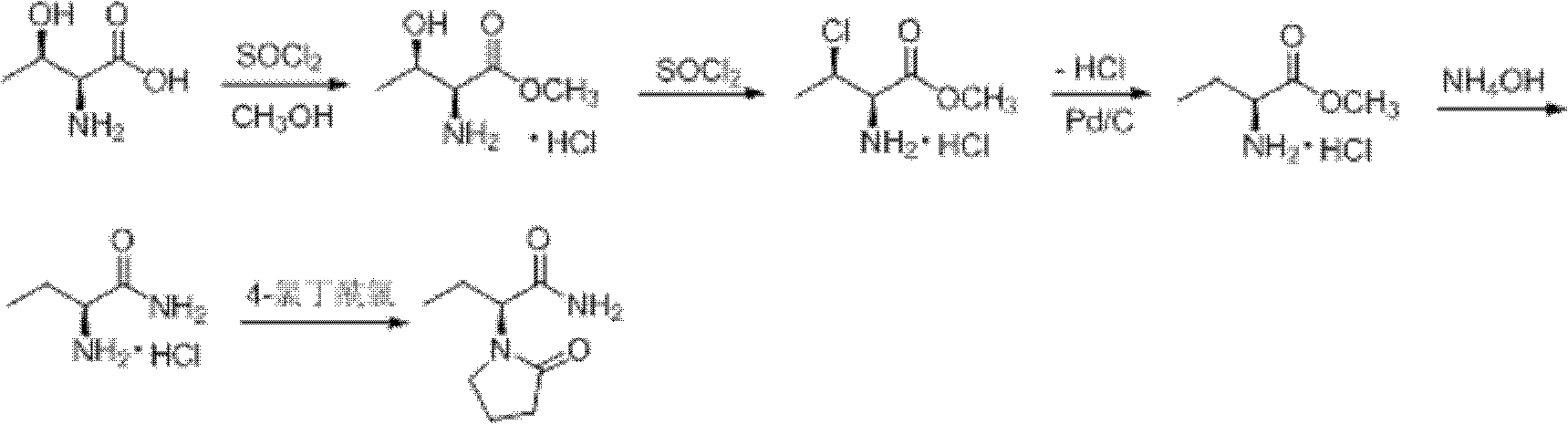


![Process For The Preparation Of 6,6-Dimethyl-3-Azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-Hexane Compounds ... Process For The Preparation Of 6,6-Dimethyl-3-Azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-Hexane Compounds ...](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/7e6ad494-c2a9-401b-b49b-4c10730f2e3f/US20090240063A1-20090924-C00001.png)
![Process For The Preparation Of 6,6-Dimethyl-3-Azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-Hexane Compounds ... Process For The Preparation Of 6,6-Dimethyl-3-Azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-Hexane Compounds ...](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/7e6ad494-c2a9-401b-b49b-4c10730f2e3f/US20090240063A1-20090924-C00002.png)
![Process For The Preparation Of 6,6-Dimethyl-3-Azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-Hexane Compounds ... Process For The Preparation Of 6,6-Dimethyl-3-Azabicyclo-[3.1.0]-Hexane Compounds ...](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/7e6ad494-c2a9-401b-b49b-4c10730f2e3f/US20090240063A1-20090924-C00003.png)