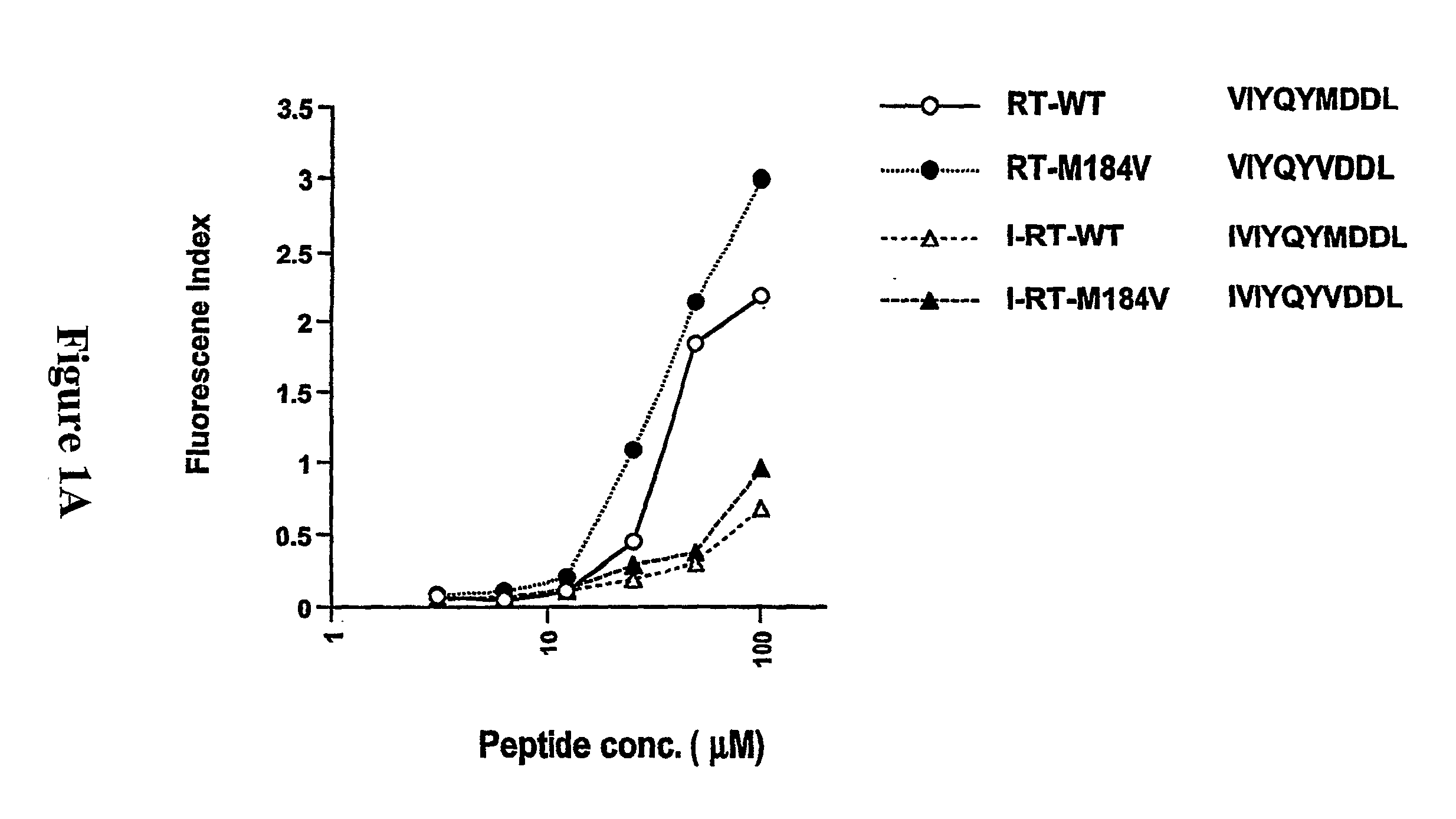
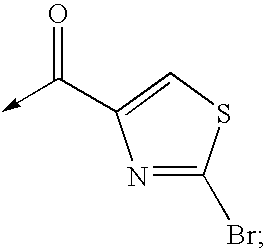
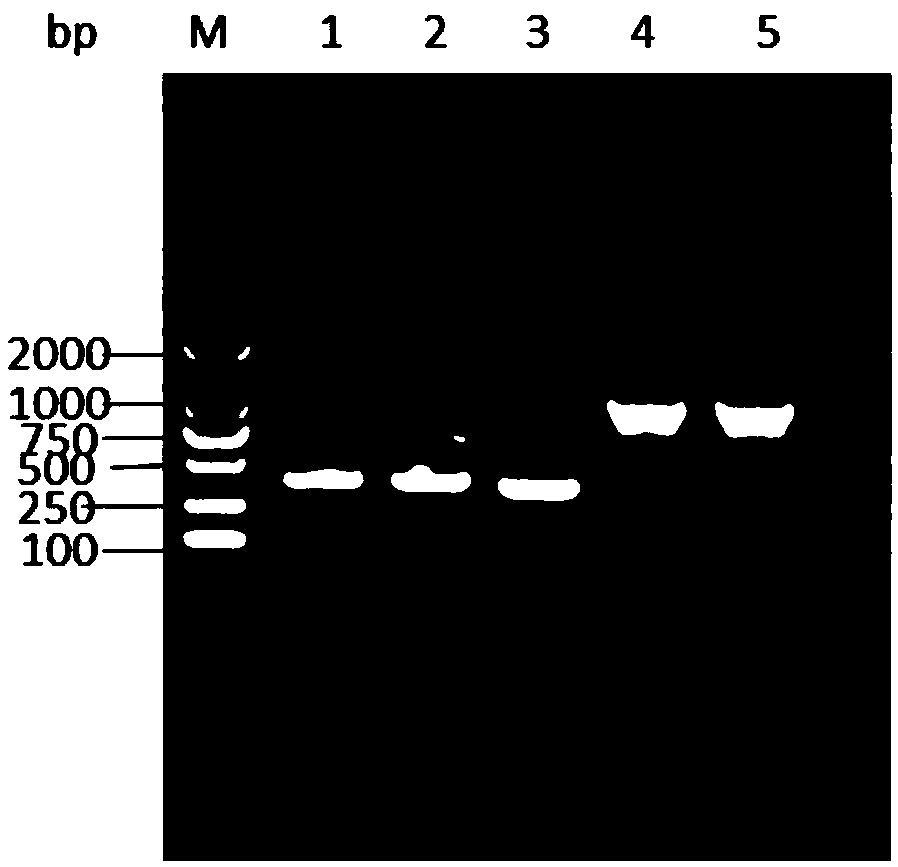
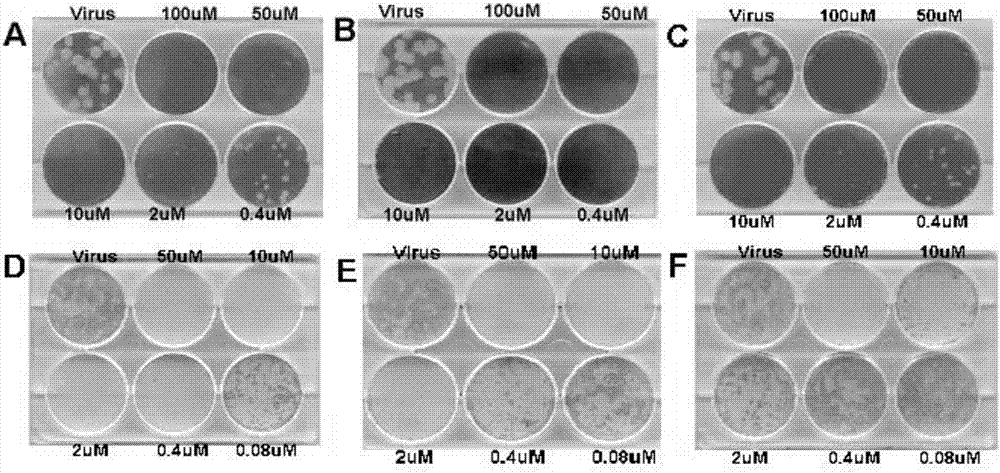
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Resistant virus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Oseltamivir is an antiviral drug that is used to treat flu illness. “Oseltamivir resistance” refers to a flu virus that is resistant to the drug oseltamivir. Similarly, influenza viruses can become resistant to other influenza antiviral drugs.
Anti-viral vectors
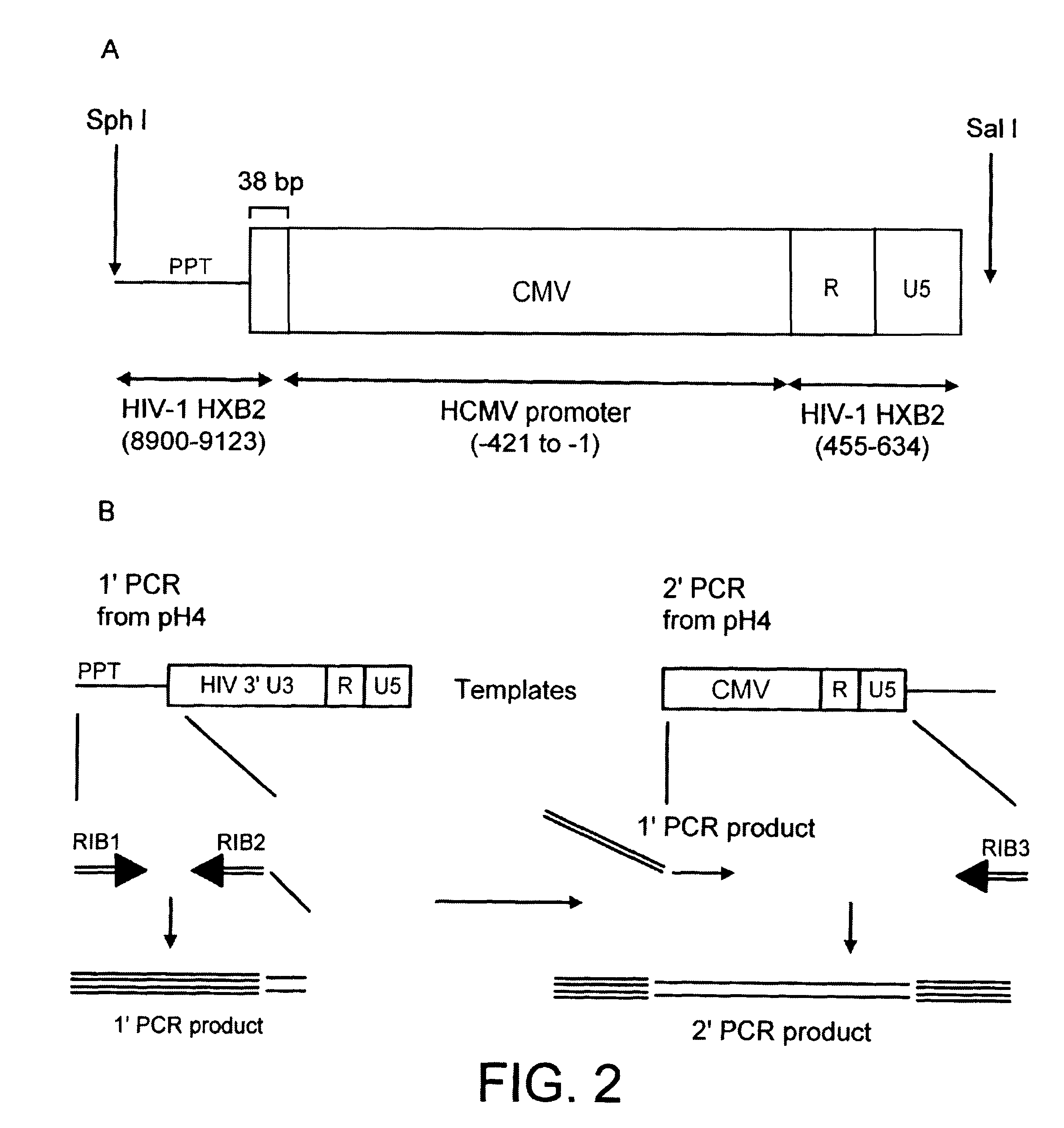
A viral vector production system is provided which system comprises:(i) a viral genome comprising at least one first nucleotide sequence encoding a gene product capable of binding to and effecting the cleavage, directly or indirectly, of a second nucleotide sequence, or transcription product thereof, encoding a viral polypeptide required for the assembly of viral particles;(ii) a third nucleotide sequence encoding said viral polypeptide required for the assembly of the viral genome into viral particles, which third nucleotide sequence has a different nucleotide sequence to the second nucleotide sequence such that said third nucleotide sequence, or transcription product thereof, is resistant to cleavage directed by said gene product. The viral vector production system may be used to produce viral particles for use in treating or preventing viral infection.
Owner:OXFORD BIOMEDICA (UK) LTD
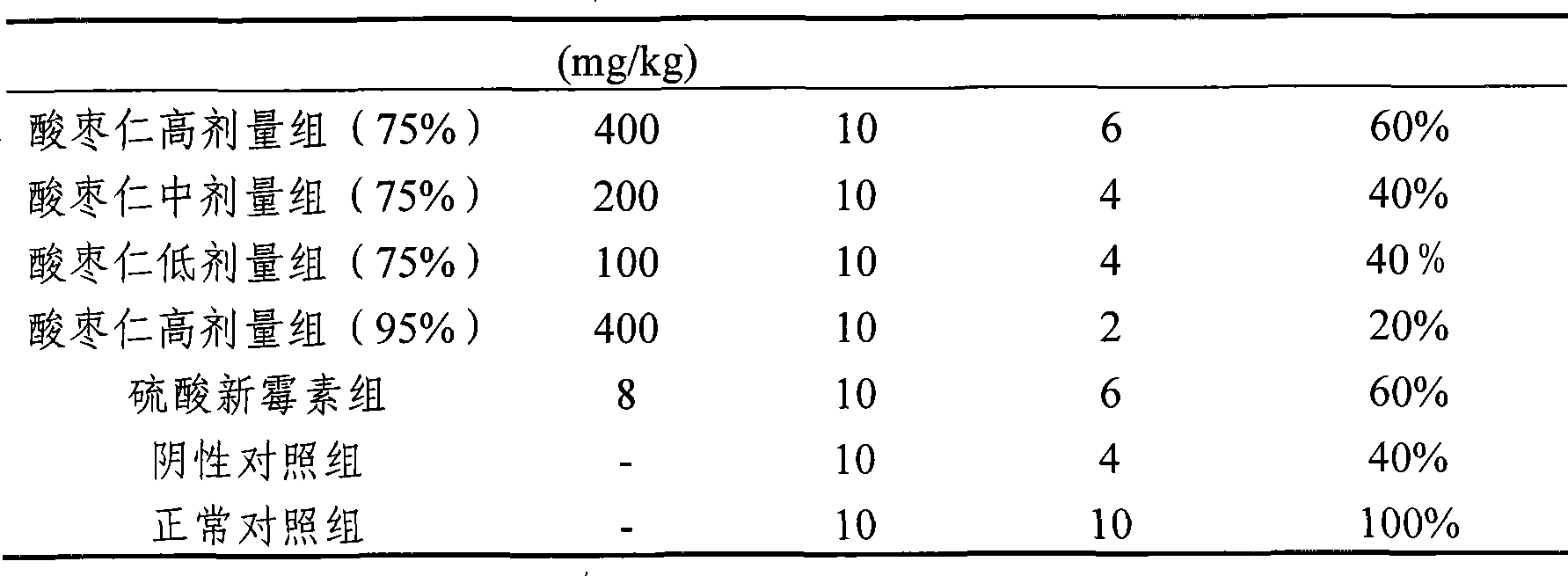
Wild jujube seeds extract and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN101455736AMake up for the loss caused by poor prevention effectMake up for the lossAntibacterial agentsAntiviralsDiseaseEscherichia coli
The invention relates to a wild jujube seed extract which is prepared by the following method: crushing wild jujube seeds, screening, soaking with ethanol to extract, after removing alcohol, adding water, uniformly stirring, leaching with aqueous n-butylalcohol, lastly concentrating and airing. The wild jujube seed extract of the invention can be prepared into oral liquid, granules, injection or freeze-drying powder injection through routine techniques. The wild jujube seed extract can be used prepare medicament compositions preventing poultry mycoplasma, Escherichia coli, brusal disease virus, avian H9 influenza virus disease, makes up for loss caused by poor preventing effect of existing bacterin in our country, substitutes bacteriophage to prevent and treat poultry resistant virus disease to control prevalence of infectious disease and solve a problem of bacteriophage residue in foods, thus guaranteeing food security and promoting export competitive ability of animal products.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Replication Stable and RNase Resistant Chimeras of Pestivirus with Insertion in 3' Nontranslated Region (3'NTR)
The invention relates to the field of nucleic acid amplification, particularly to quality control materials for use in viral RNA assays. It specifically relates to the construction of a recombinant Pestivirus by the identification of a region in the 3′NTR of the viral RNA genome where additional sequence elements can be stably inserted. Chimeric Pestivirus with sequence insertions in the 3′ nontranslated region (3′NTR) of the viral RNA genome were stable in replication and capable of forming infectious, RNase resistant virus particles. This chimeric Pestivirus with a 3′NTR insertion can be utilized as a quality control material in analytical assays for RNA targets, including external, internal controls, quantitative standards in PCR and NAT nucleic acid assays.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Vaccines and methods for prevention and treatment of drug-resistant hiv-1 and hepatitis b virus
ActiveUS20090317418A1Reduce viral loadLower viral loadSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviral drugResistant virus
The present invention provides methods for lowering a viral load of a virus resistant to an antiviral drug by inducing cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) to recognize a predetermined mutated epitope within a viral protein of the drug-resistant virus. CTLs are induced by immunizing a host with a peptide comprising the predetermined mutation. The immunostimulating peptide may be further improved by epitope-enhancement for inducing specific CTLs. The antiviral protection against drug-resistant virus shown by compositions of the present invention and mediated by human HLA-restricted CTL has not been previously achieved.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE DEPT OF
Bisheterocycle tandem compounds useful as antiviral agents, the uses thereof and the compositions comprising such compounds
InactiveUS7741348B2Inhibition of replicationEasy to prepareBiocideOrganic chemistryCytotoxicityResistant virus
The present invention provides small molecule compounds of bisheterocycle in tandem having the structural formula of P1-P2, and the use thereof as well as a composition containing the compounds, each of P1 and P2 is an unsaturated 5-member heterocyclic ring having one or two heteroatoms. This compound may effectively inhibit the replication of influenza virus, the DNA replication of hepatitis B virus (HBV), and the formation of HBsAg and HBeAg. These compounds can be used for the preparation of a medicament for viral diseases, and may overcome the limitations of the known nucleosides drugs, including cytotoxicity, the requirement of other drugs having different structures for against the drug-resistant virus variants induced by long-term therapy. The structure of the compounds according to the invention is relatively simple and easy to be prepared.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel HIV integrase inhibitors and HIV therapy based on drug combinations including integrase inhibitors
InactiveUS20050049242A1Strong synergyBiocideAnimal repellantsCombination drug therapyResistant virus
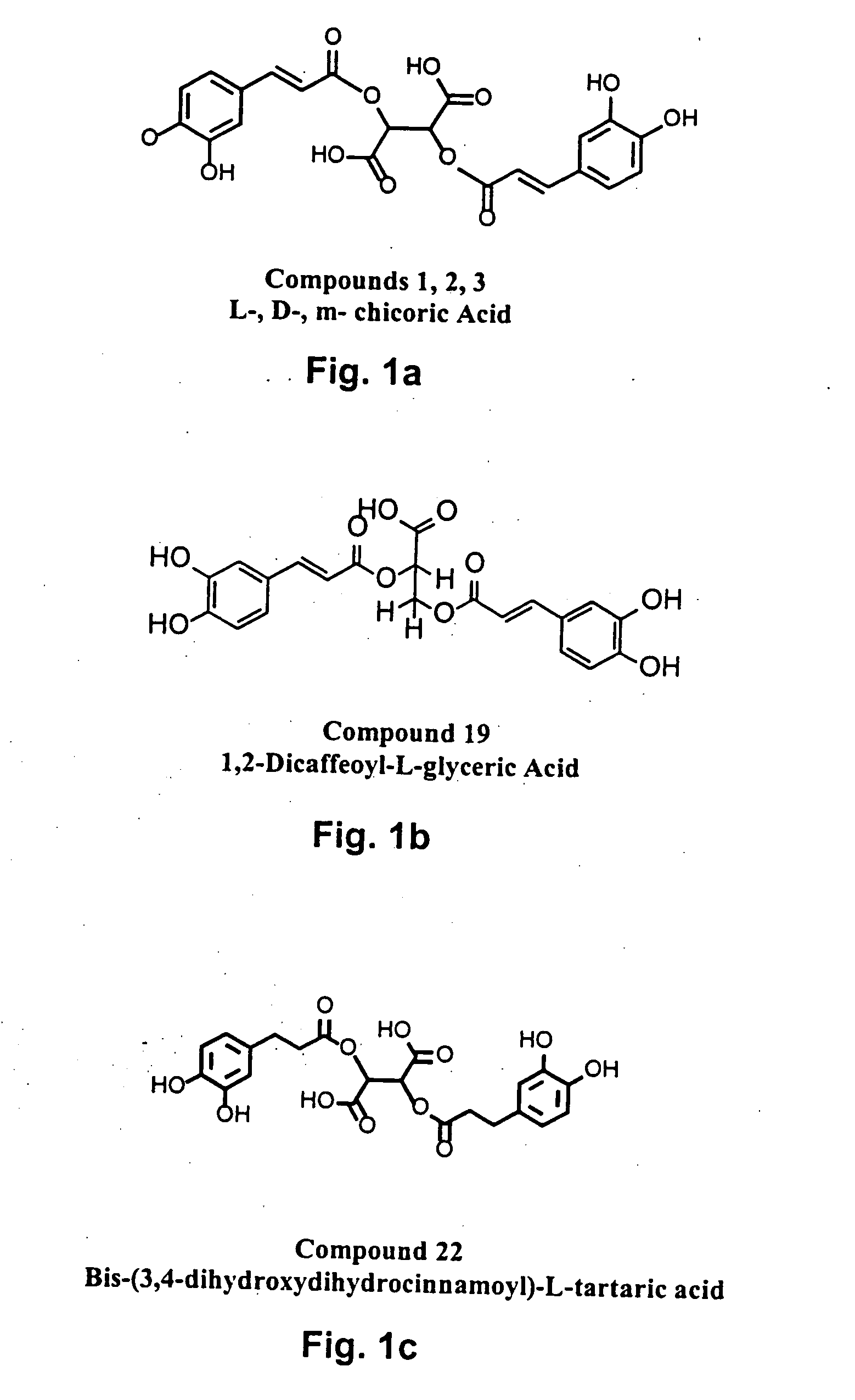
The present invention includes a group of novel compounds that are demonstrated to potently and selectively inhibit HIV integrase (IN) activity in vitro and to potently inhibit HIV replication in live, cultured cells at non-toxic concentrations. The novel compounds disclosed include 2,3-di(3,4-dihydroxy-dihydroxydihydrocinnamoyl)-L-tartaric acid, 2,3-di-(3,4-dihydroxybenzoyl)-L-tartaric acid, 2,3-di-(3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetyl)-L-tartaric acid, 2,3-di-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl-L-tartaric acid, 2,3-dicaffeoyldiamidopropionic acid, 1,2,-dicaffeoyl-L-glyceric acid, bis,-3,4-dicaffeoyldiamidobenzoic acid, di-3,4-dihydroxybenzylidene succinic acid, di-3,4-dihydrodihydroxybenzylidine succinic acid, 2,3-dicaffeoyl-L-serine, bis-dicaffeoyl-L-isoserine and 1,4-dicaffeoyl-L-lysine. Tests of integrase inhibitors with 2′,3′-dideoxycytidine, zidovudine and nelfinavir (protease inhibitor) indicated a potent synergy against reverse transcriptase inhibitor resistant virus. The potential benefit from the addition of integrase inhibitors to combination drug therapies is significant.
Owner:ROBINSON W EDWARD JR +2
Bisheterocycle Tandem Compounds Useful as Antiviral Agents, the Uses Thereof and the Compositions Comprising Such Compounds
InactiveUS20080306121A1Inhibition of replicationEasy to prepareBiocideOrganic chemistryCytotoxicityResistant virus
The present invention provides small molecule compounds of bisheterocycle in tandem having the structural formula of P1-P2, and the use thereof as well as a composition containing the compounds, each of P1 and P2 is an unsaturated 5-member heterocyclic ring having one or two heteroatoms. This compound may effectively inhibit the replication of influenza virus, the DNA replication of hepatitis B virus (HBV), and the formation of HBsAg and HBeAg. These compounds can be used for the preparation of a medicament for viral diseases, and may overcome the limitations of the known nucleosides drugs, including cytotoxicity, the requirement of other drugs having different structures for against the drug-resistant virus variants induced by long-term therapy. The structure of the compounds according to the invention is relatively simple and easy to be prepared.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
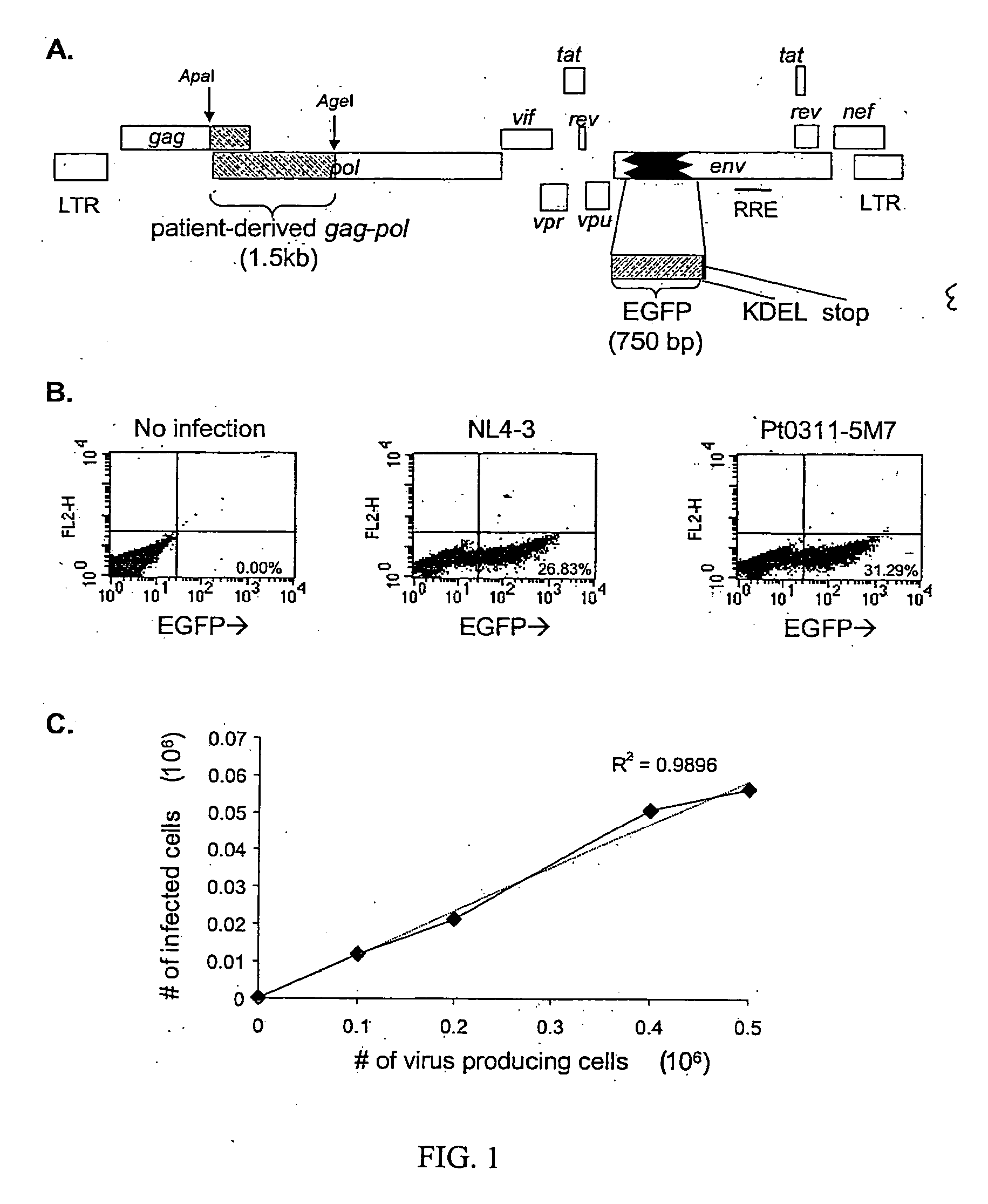
Single cell analysis of HIV replication capacity and drug resistance
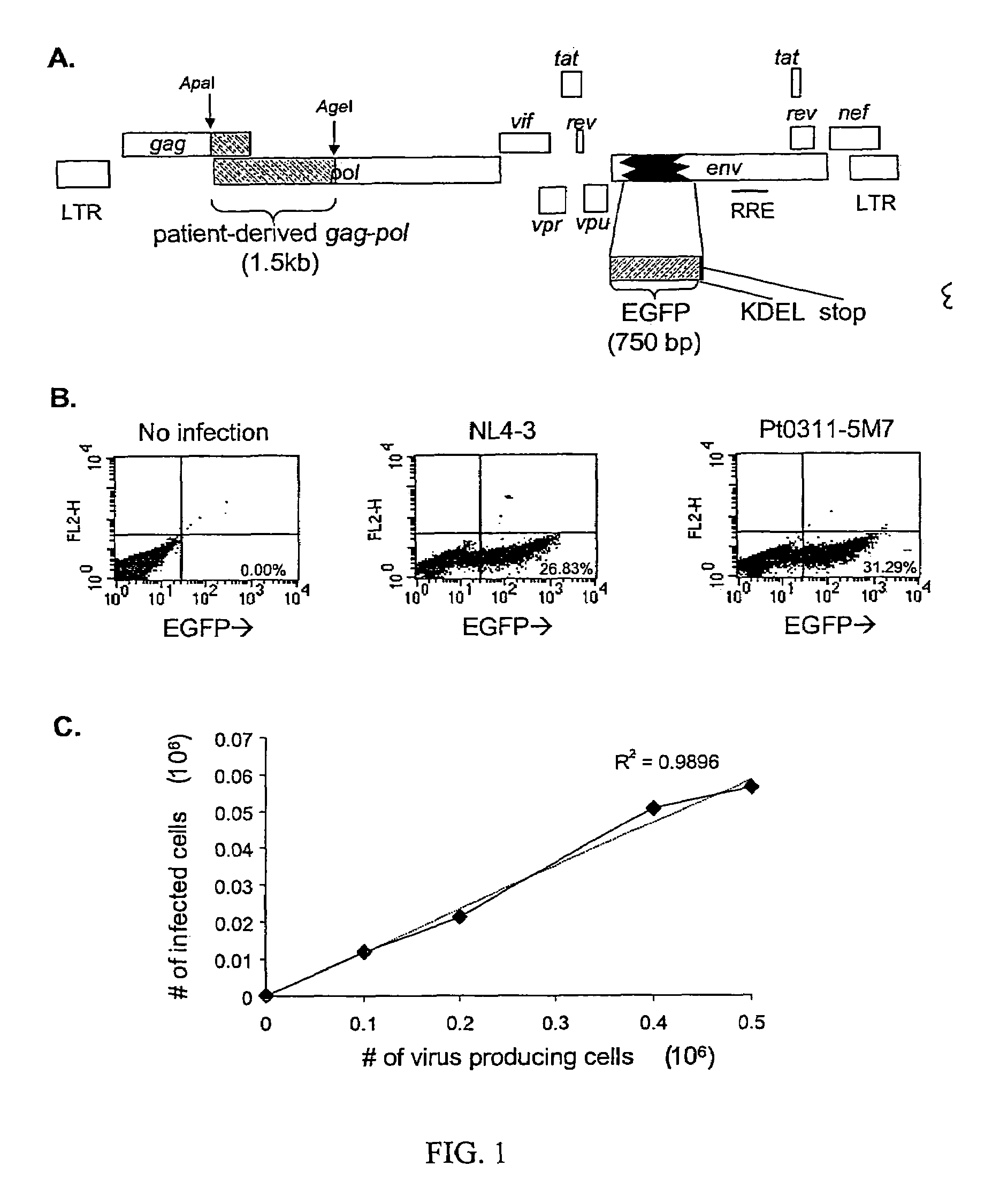
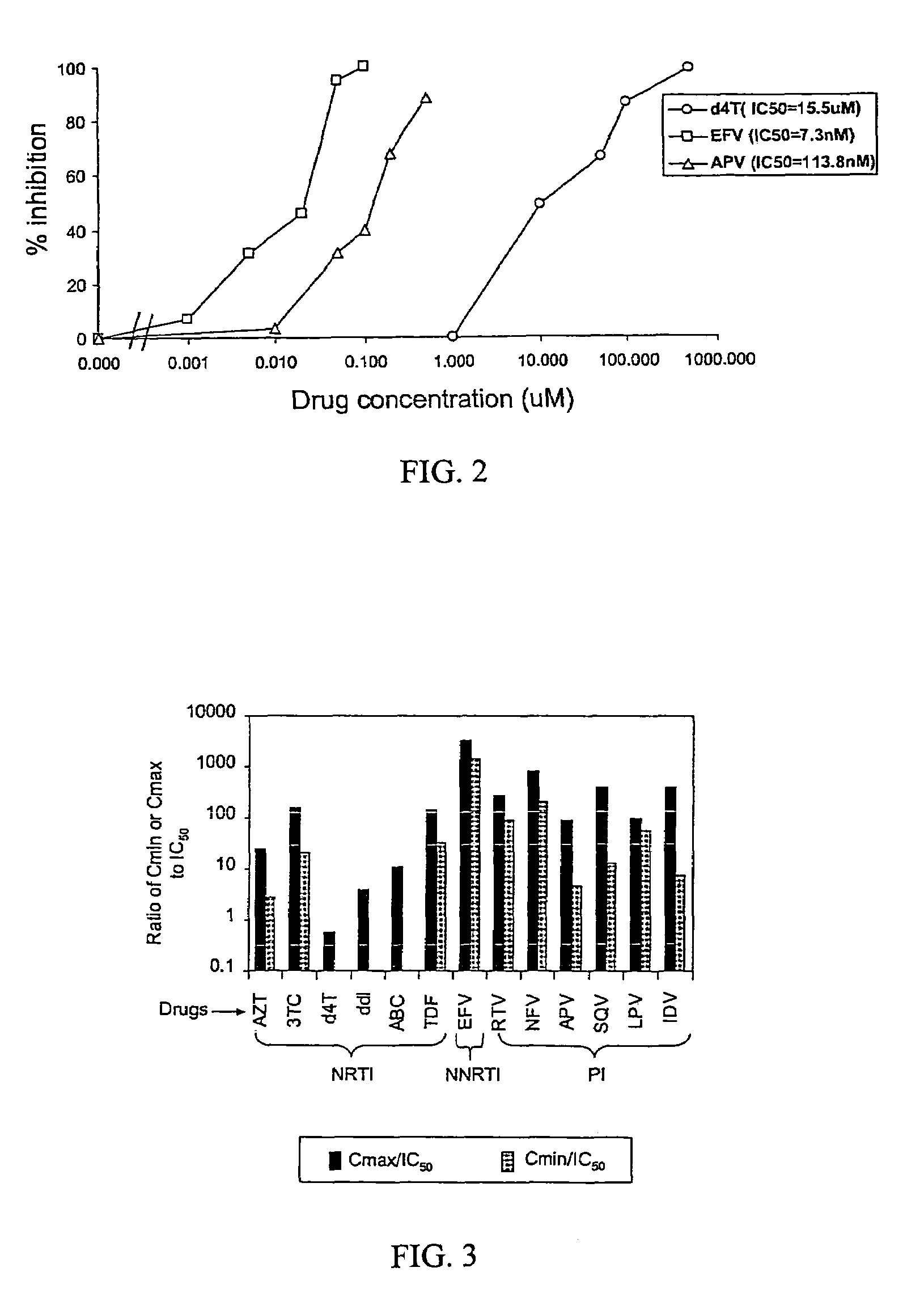
ActiveUS20050244818A1Less-effective in controllingAccurate countVectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementAssayResistant virus
A novel single-cell-level phenotypic assay is described, which can simultaneously analyze HIV-1 drug susceptibility and intrinsic replication capacity. This allows quantitative dissection of the functions of antiretroviral drugs into suppression of viral replication and selection of resistant viruses with diminished replication capacities. The disclosed assay provides a tool for the rational evaluation of treatment decisions for patients failing antiretroviral therapy and is expected to be an important part in clinical management of HIV.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Single cell analysis of HIV replication capacity and drug resistance
ActiveUS7468274B2Less-effective in controllingAccurate countVectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementResistant virusViral replication
A novel single-cell-level phenotypic assay is described, which can simultaneously analyze HIV-1 drug susceptibility and intrinsic replication capacity. This allows quantitative dissection of the functions of antiretroviral drugs into suppression of viral replication and selection of resistant viruses with diminished replication capacities. The disclosed assay provides a tool for the rational evaluation of treatment decisions for patients failing antiretroviral therapy and is expected to be an important part in clinical management of HIV.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Aniline derivative having Anti-rna viral activity
ActiveUS20110059950A1Excellent anti-RNA virus activityHigh activityBiocideOrganic chemistryProteinase activityReverse transcriptase
Viruses, and particularly RNA viruses, have high mutation rates. Hence, antiviral agents that have been developed to date targeting protease or reverse transcriptase of viruses have quickly lost their effectiveness and resistant viruses have emerged. Also, in recent years, viral diseases caused by various new viruses such as SARS, avian influenza, and the hepatitis C have become social menaces. Therefore, the development of a novel antiviral agent that can cope with a virus resistant to an existing drug or a new virus and has a wide range of applications has been demanded. The present invention provides a novel anti-RNA viral agent and a method for use thereof. The present invention further provides an anti-RNA viral agent that is also effective against a new virus or a drug-resistant virus, and a method for use thereof.
Owner:KINOPHARMA
Compositions and methods for determining the replication capacity of a pathogenic virus
InactiveUS20040063191A1Improve the quality of lifeEffective treatmentBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleoside Reverse Transcriptase InhibitorResistant virus
This invention relates to compositions and methods for determining the replication capacity of a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor resistant virus. The compositions and methods are useful for identifying effective drug regimens for the treatment of viral infections, and identifying and determining the biological effectiveness of potential therapeutic compounds.
Owner:VIROLOGIC INCORPORATED
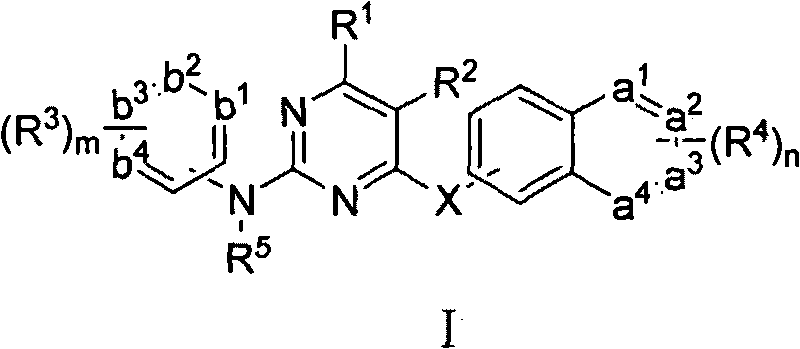
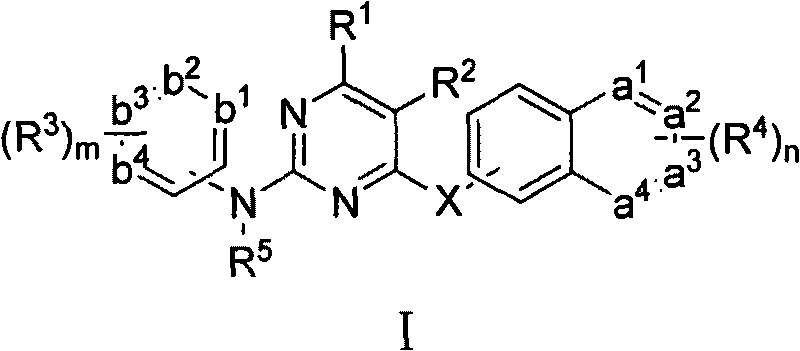
Diaryl pyrimidine derivative, preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101759684AEnhanced inhibitory effectGood anti-HIV-1 virus biological activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCytotoxicityResistant virus
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines and relates to a diaryl pyrimidine derivative of the general formula I, medicinal salts thereof, hydrates and solvolytes thereof, polycrystal and eutectic thereof, and precursors and derivatives thereof with the same biological functions, a preparation method thereof, application of combination containing one or more compounds in relative medicines for treating acquired immune deficiency syndrome and the like, a preparation method and use of the combination. Experimental results show that the compound of the invention not only has excellent biological activity of resisting HIV-1 virus and relatively small cytotoxicity, but also shows relatively good inhibitory action to a drug-resistant virus strain L103N+Y181C, can be used as medical candidate resisting the HIV and can be further developed as a medicine resisting AIDS.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Dry heat sterilizing method of cucurbitaceae stock seeds
The invention discloses a dry heat sterilizing method of cucurbitaceae stock seeds. The method comprises the steps of treating the harvested cucurbitaceae stock seeds by a dry heat sterilizer in three stages, wherein the temperature of the first stage is 35 DEG C, the temperature of the second stage is 50 DEG C, and the temperature of the third stage is 72 DEG C. The dry heat sterilizing method of cucurbitaceae stock seeds can effectively kill pathogenic bacteria, especially, high-temperature resistant viruses and the like without measures such as chemicals utilization or seed soaking for changing the seed status, the operation is simple, and therefore, the method is suitable for large-scale seed treatment.
Owner:NINGBO ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell line for secreting southern rice black-streaked dwarf resistant viruses and monoclonal antibody application thereof
ActiveCN102559602AAccurate detectionSensitive detectionImmunoglobulins against virusesTissue cultureAntibody typesBALB/c
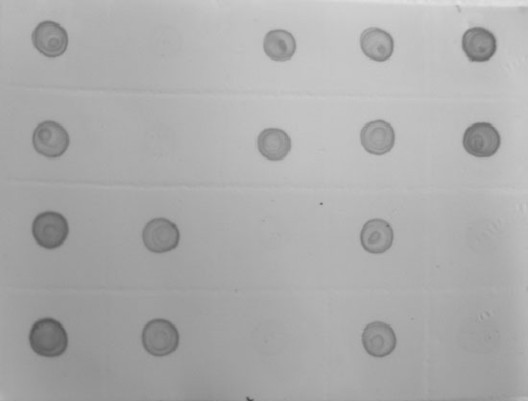
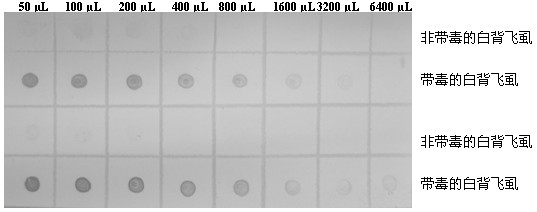
The invention discloses a monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell line for secreting southern rice black-streaked dwarf resistant viruses and monoclonal antibody application thereof. Polypeptide of 12 amino acids at the C end of a capsid protein of southern rice black-streaked dwarf viruses (SRBSDVs) coupled with bovine serum albumin is used as an antigen to immune a BALB / c mouse, one hybridoma cell line 3F1 capable of performing stable passage and secreting an SRBSDV monoclonal antibody is obtained through cell fusion, screening and cloning, and the preservation number of the hybridoma cell line 3F1 is China general microbiological culture collection center number (CGMCCNo.) 5535. Monoclonal antibody ascites indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) valence of the 3F1 reaches above 10-6, an antibody type and a subclass are immunoglobulin G (IgG1) and a kappa chain, the monoclonal antibody of the hybridoma cell line has specific reaction with a capsid protein subunit of SRBSDV56kD, and a method for detecting rice planthoppers and dot-ELISA of SRBSDV in rice is built by using the monoclonal antibody of the 3F1. When a single-head white backed rice planthopper is diluted to 6400mul, the viruses can still be detected when diseased leaves are diluted according to 1:320 times (w / v, g / mL). The preparation of the SRBSDV resistant monoclonal antibody and the building of the detection method provide technology and material supports for diagnosis, prediction and scientific prevention and control of the rice viruses.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Schisandrae fructus extracts for inhibition or prevention of h1n1 influenza virus infection and its application thereof
InactiveUS20120189719A1Inhibitory activityAvoid infectionBiocideKetone active ingredientsResistant virusInfluenza epidemics
Disclosed are an Schisandrae fructus extract for inhibition or prevention of influenza and its application, wherein the Schisandrae fructus extract is obtained by water, methanol, or ethanol extraction process and the extract comprises compounds such as schisandrone, benzoylgomisin P, wulignan A1, epigomisin O, epiwulignan A1, and tigloylgomisin P. The extracts and purified compounds of Schisandrae fructus has anti-influenza virus H1N1 and H1N1-TR (a Tamiflu drug resistant virus strain) activities, therefore the extracts and the purified compounds of Schisandrae fructus can be applied as an inhitibory agent of a pharmaceutical composition for treatment or prevention agent for influenza infection.
Owner:NAT DEFENSE MEDICAL CENT
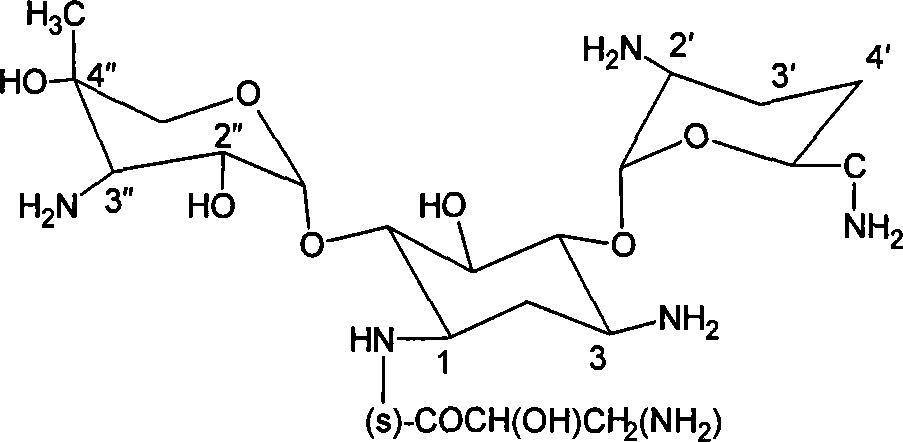
Aminoglycoside antibiotics
InactiveCN101139371ASame structural featuresSignificant anti-MRSA activityAminosugarsMedicineResistant virus
The present invention relate4s to an aminoglycoside antibiotic which belongs to the application technology filed of aminoglycoside antibiotic. The present invention provides the derivative of the structure of 2'-NH 2 -3 ', 4'-deoxy-3'-N demethylase 1-N acylation as well as the application of the derivative in the preparation of medicinal combination in the treatment of drug-resistant virus infections.
Owner:CHANGZHOU FANGYUAN PHARMA
Respiratory therapeutic electric heat source face mask
A therapeutic face mask apparatus for wearers with resistant respiratory viruses, is connected to a heat gun that provides adjustable heated and humidified air for inhalation. The heat gun heats ambient air that is breathed in through the face mask during normal breathing, which is worn over the nose and mouth of a person. A temperature gauge monitors temperature for future adjustment of the amount of heat generating current to raise the heat to a predetermined temperature to deactivate resistant viruses in compromised upper and / or lower respiratory systems of the wearer. The air in the chamber is heated for inhalation by a resistive element in the heat gun. The temperature of the resistive material (and by extension the warm air generated), is regulated / adjusted by increasing or decreasing the current output settings on the power source, so that heated and pressured air is produced.
Owner:SABIN ROBERT
Chimeric pestivirus with insertion in 3' nontranslated region (3' NTR) with stable replication and rnase resistance
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Single-chain antibody for porcine epidemic diarrhea resistant virus and application thereof
ActiveCN108659124ADigestive systemImmunoglobulins against virusesEpidemic diarrheaSingle-Chain Antibodies
The invention discloses a single-chain antibody for a porcine epidemic diarrhea resistant virus and application thereof. The single-chain antibody provided by the invention is a polypeptide composed of a light chain variable region, a connecting peptide, and a heavy chain variable region, wherein the connecting peptide is positioned between the light chain variable region and the heavy chain variable region; the light chain variable region is shown as amino acid residues at 1-107 sites from N terminal in a sequence 1 of a sequence table; the heavy chain variable region is shown as amino acid residues at 123-240 sites from N terminal in the sequence 1 of the sequence table. The single-chain antibody provided by the invention is capable of neutralizing the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, and has an important application value in prevention and / or treatment of porcine epidemic diarrhea.
Owner:青岛博隆基因工程有限公司
Lotion and use thereof
InactiveCN104013966ANon-irritatingHigh inhibitory killing effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsLower riskFull recovery
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine, and discloses a lotion and use thereof, and the lotion comprises a chitosan polymer, a hyaluronic acid, a pH regulator, a cosolvent and a transdermal enhancer; the lotion has good stability, and the study shows that the lotion is good in antibacterial effect, wide in antibacterial spectrum (propionibacterium acnes and the like resisting), wide in resistant virus (including high-risk HPV (human papilloma virus), low risk HPV, herpes virus), physical antimicrobial, free of drug resistance, biodegradable, safe, environmentally friendly, and long in drug efficacy duration time, and has the nourishing, lubricating, whitening, spot fading, repairing, scar formation inhibiting, and anti-adhesion effects on skin or mucosal tissues. The lotion is safe and non-toxic, and has the effects of resisting bacteria, repairing, moisturizing, and full recovery of vaginal or skin micro ecological balance.
Owner:符耿哲
Antimicrobial biopolymer compositions, methods of synthesis, and applications of use
ActiveUS20190224362A1Simplify and unify synthesisConnective tissue peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsAdhesiveBiopolymer
Biopolymer compositions comprising antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) for treating infections such as bacterial infections, viral infections, fungal infections, and parasitic infections. The compositions herein may also be used for treating infections associated with antibiotic-resistant bacteria, antifungal-resistant fungi, antiviral-resistant viruses, or for treating biological warfare agents (BWAs) such as Bacillus anthracis and Yersenia pestis. The present invention also provides methods of synthesis of said biopolymer compositions, wherein AMP biopolymers can be synthesized as an artificially engineered protein by genetically fusing an AMP; a protein that behaves similarly to polymer tethers; and a protein as a modifiable material platform that can transform to self-assembled nanoparticles, self-standing films, or adhesives to easily attach tethered AMPs onto any biomaterial surface for various clinical applications.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Antiviral-agent resistant virus detection system
ActiveUS20180346417A1Rapid and convenient mannerQuick buildOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsNanoparticleResistant virus
An oseltamivir analogue and nanoparticles having the analogue bound thereto, of the present invention, strongly bind to oseltamivir-resistant influenza virus, and thus, the use of the same can allow detection of oseltamivir-resistant influenza viruses quickly and conveniently with the naked eye. Therefore, the present invention can be favorably utilized in promptly establishing a therapeutic schedule for a patient infected with influenza viruses.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
Cyclohexene derivative or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and application of cyclohexene derivative and salt
ActiveCN107325040AHigh activityEnhanced inhibitory effectPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsCyclohexeneAnti influenza drug
The invention relates to a cyclohexene derivative or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and an application of the cyclohexene derivative and salt, and belongs to the technical field of a medicine. The cyclohexene derivative or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof shown in the formula I is a new broad-spectrum anti-influenza compound, has a better inhibition effect on influenza virus, particularly has high activity to oseltamivir-resistant virus strains, and can be used as a wide-spectrum anti-influenza neuraminidase inhibitor which is effective to tamiflu resistance and has broad spectrum. The cyclohexene derivative or pharmaceutically acceptable salt can be used for treating influenza caused by influenza virus and is a new broad-spectrum anti-influenza drug.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HENOVCOM BIOSCI CO LTD
Method for inhibiting reproduction of HIV-1 (human immunodeficiency virus-1) drug-resistant virus
The invention determines 1'-acetoxychavicol acetate and derivative thereof with a new function of inhibiting the reproduction of HIV-1 (human immunodeficiency virus-1) drug-resistant virus. The 1'-acetoxychavicol acetate and the derivative thereof can effectively inhibit the reproduction of the HIV-1 drug-resistant virus generated by an HIV-1 fusion inhibitor and a protease inhibitor under low consistency, and does not display cytotoxicity on host cells. Therefore, the 1'-acetoxychavicol acetate and the derivative thereof have potential application prospect in treating AIDS patients with drug resistance.
Owner:LP PHARM (XIAMEN) CO LTD
A kind of breeding method of high-quality pink fruit tomato with good taste and storage and transportation
ActiveCN110150136BUniform fruitingStrong growthPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyResistant virus
The invention relates to a breeding method of a good-taste and transport-and-storage-resistant pink tomato. The breeding method of the good-taste and transport-and-storage-resistant pink tomato comprises the following steps of taking Chunxuehong tomato as the female parent to perform 7 generations of individual selection and mixed seed reservation; taking Difenni tomato as the male parent to perform 4 generations of individual selection through a continuous selfing and molecular marker-assisted selection method to obtain 4th-generation strains, then combining tomato yellow leaf curl disease-resistant virus and performing 2 generations of individual selection to obtain 6th-generation strains, performing 2 generations of individual selection, removing abnormal plants and performing mixed seed reservation; crossing the female parent and the male parent to obtain seeds of the good-taste and transport-and-storage-resistant pink tomato. The bred good-taste and transport-and-storage-resistantpink tomato has the advantages of being good in taste, high in sugar degree, regular in fruit shape, good in color, resistant to transport and storage, robust in plant growth, high in comprehensive disease resistance and the like.
Owner:武汉楚为生物科技有限公司
Method for administrating preparations containing oseltamivir guanidyl carboxylate analogues and/or ethyl esters thereof
InactiveCN103446078AReduce dependenceLittle side effectsOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliverySide effectOral medication
The invention relates to a method for administrating preparations containing oseltamivir guanidyl carboxylate analogues and / or ethyl esters thereof. Administration is carried out through inhalation. The method can be used for treating cold caused by influenza viruses. By adopting the administration method provided by the invention, not only can dependence on the single variety of drugs such as oseltamivir, zanamivir and peramivir be reduced and new drug resistant virus strains generated by using the single variety in quantity be avoided but also the method which is favorable for greatly improving the bioavailability compared with oral administration or intravenous drip is provided for oseltamivir guanidyl carboxylate analogues or ethyl esters thereof; more importantly, the method which has the advantages of small drug dose, less side effects and high effect taking speed is provided.
Owner:陈永奇 +2
A kind of single-chain antibody against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and its application
ActiveCN108659124BDigestive systemImmunoglobulins against virusesEpidemic diarrheaSingle-Chain Antibodies
The invention discloses a single-chain antibody for a porcine epidemic diarrhea resistant virus and application thereof. The single-chain antibody provided by the invention is a polypeptide composed of a light chain variable region, a connecting peptide, and a heavy chain variable region, wherein the connecting peptide is positioned between the light chain variable region and the heavy chain variable region; the light chain variable region is shown as amino acid residues at 1-107 sites from N terminal in a sequence 1 of a sequence table; the heavy chain variable region is shown as amino acid residues at 123-240 sites from N terminal in the sequence 1 of the sequence table. The single-chain antibody provided by the invention is capable of neutralizing the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, and has an important application value in prevention and / or treatment of porcine epidemic diarrhea.
Owner:青岛博隆基因工程有限公司
Hiv-1 gp41 neutralization domain and use thereof
InactiveUS20110091491A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsResistant virusMonoclonal antibody
The invention relates to a region of the HIV-I gp41 protein that contains, at least in part, an epitope that allows potent neutralization of resistant virus particles. This site is present in the C-terminal heptad repeat region of gp41 (HR2), and adjacent to, but distinct from the MPER. Vaccines containing this region as well as monoclonal antibodies which specifically bind to this region and neutralize an HIV-I primary isolate are also provided as is a method for stimulating the formation of antibodies that neutralize infection by an HIV isolate.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Combination of ribavirin derivative and alpha-interferon in treating and/or preventing virus infection and related diseases induced by virus infection
ActiveCN109481669ANo side effectsOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSide effectResistant virus
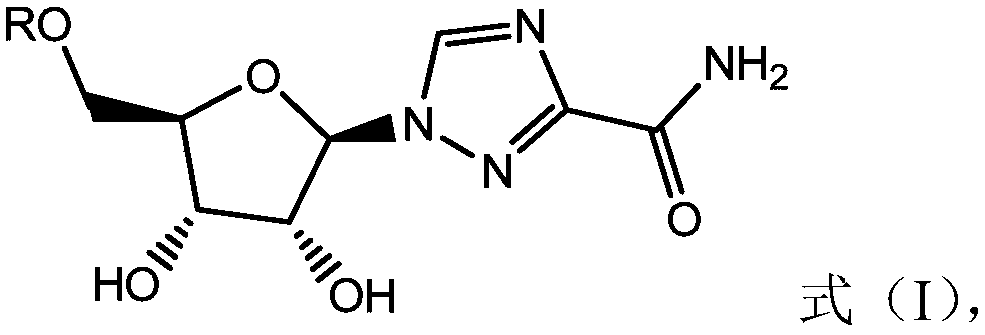
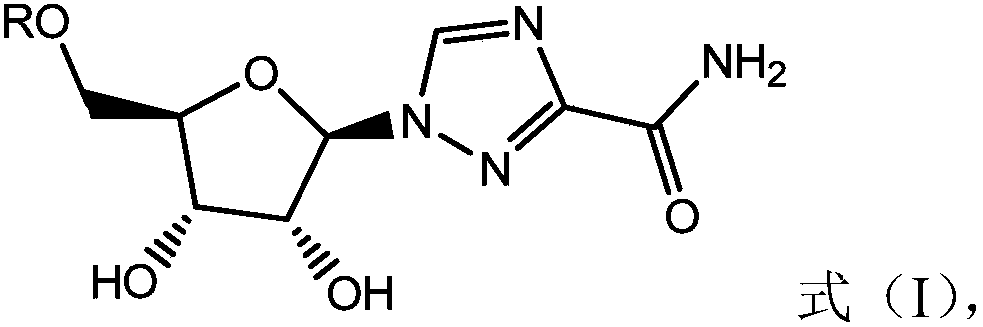
The invention relates to the field of ribavirin derivative resistant virus and discloses an application of combining a ribavirin derivative (shown in a formula (I)) and alpha-interferon in preparing adrug for treating and / or preventing virus infection and related diseases induced by virus infection, a pharmaceutical composition containing the ribavirin derivative and alpha-interferon and an application of the pharmaceutical composition in preventing virus infection and related diseases induced by virus infection. Combination of the ribavirin derivative (shown in a formula (I)) and alpha-interferon has an obvious better virus inhibiting effect and is free of side effects. The formula is as shown in the description.
Owner:江西诺立医药科技有限公司
Respiratory therapeutic electric heat source face mask
A therapeutic face mask apparatus for wearers with resistant respiratory viruses, is connected to a heat gun that provides adjustable heated and humidified air for inhalation. The heat gun heats ambient air that is breathed in through the face mask during normal breathing, which is worn over the nose and mouth of a person. A temperature gauge monitors temperature for future adjustment of the amount of heat generating current to raise the heat to a predetermined temperature to deactivate resistant viruses in compromised upper and / or lower respiratory systems of the wearer. The air in the chamber is heated for inhalation by a resistive element in the heat gun. The temperature of the resistive material (and by extension the warm air generated), is regulated / adjusted by increasing or decreasing the current output settings on the power source, so that heated and pressured air is produced.
Owner:SABIN ROBERT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com