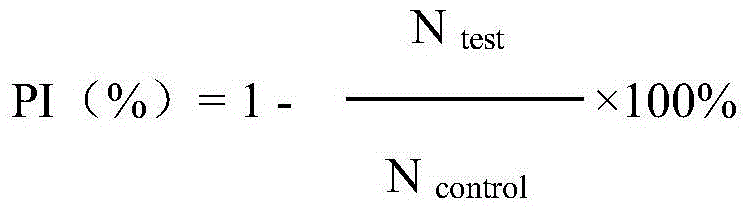Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
170 results about "Glutathione S-transferase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
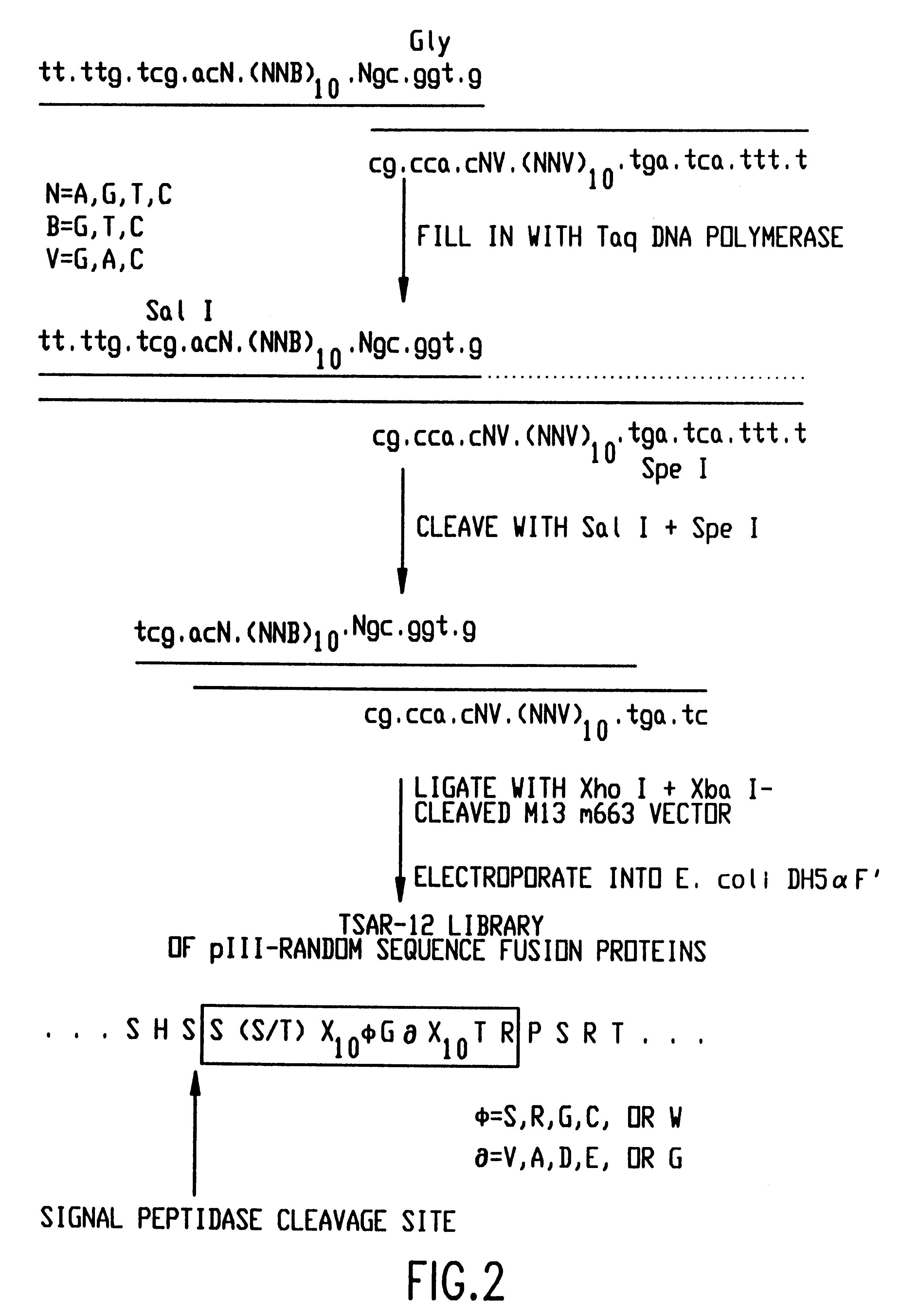
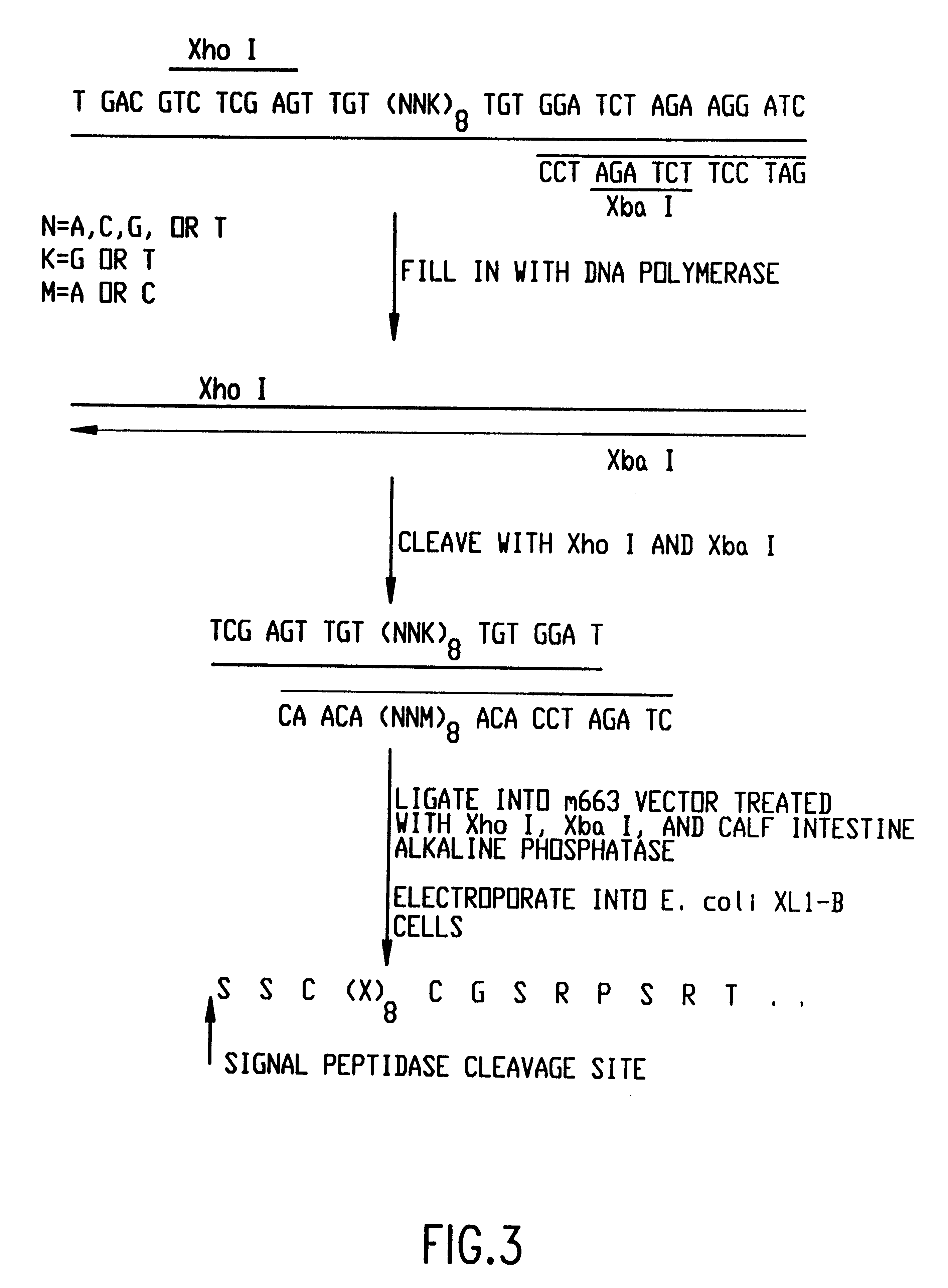
Glutathione S-transferases (GSTs), previously known as ligandins, comprise a family of eukaryotic and prokaryotic phase II metabolic isozymes best known for their ability to catalyze the conjugation of the reduced form of glutathione (GSH) to xenobiotic substrates for the purpose of detoxification. The GST family consists of three superfamilies: the cytosolic, mitochondrial, and microsomal—also known as MAPEG—proteins. Members of the GST superfamily are extremely diverse in amino acid sequence, and a large fraction of the sequences deposited in public databases are of unknown function. The Enzyme Function Initiative (EFI) is using GSTs as a model superfamily to identify new GST functions.
Vivo use of glutathione s-transferase activated nitric oxide donors
ActiveUS20050171066A1Increase delayReduce tumor volumeBiocideOrganic active ingredientsApoptosisNitric oxide
The present invention provides for a method of simultaneously treating both cancer and the Multidrug Resistance Phenotype via inhibition of cellular thiols, such as Glutathione S-Transferase (GST). This enzyme is overproduced in leukemia and solid tumor cells and is one of the main pathways involved in the Multidrug Resistance phenotype. The treatment provides for the administration of a chemically inert pro-drug, designed to be a specific substrate for the GST enzyme that, once cleaved, liberates the bioactive toxin Nitric Oxide (NO) intracellularly at the site of a malignant growth. NO then acts to inhibit the growth of the malignant cells and to induce cellular differentiation and apoptosis therein, effectively treating an existing cancerous condition. Additionally, once NO is liberated from the pro-drug, the remaining structure acts to inhibit further GST activity, providing a treatment for the Multidrug Resistant phenotype.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
GRB2 SH3 binding peptides and methods of isolating and using same
InactiveUS6184205B1Increase ratingsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRandom Peptide LibraryADAMTS Proteins
Peptides having general and specific binding affinities for the Src homology region 3 (SH3) domains of proteins are disclosed in the present invention. In particular, SH3 binding peptides have been isolated from phage-displayed random peptide libraries which had been screened for isolates that bind to bacterial fusion proteins having an SH3 domain and glutathione S-transferase (GST). Preferred peptides are disclosed which comprise a core 7-mer sequence (preferably, a consensus motif) and two or more, preferably at least six, additional amino acid residues flanking the core sequence, for a total length of 9, preferably at least 13, amino acid residues and no more than about 45 amino acid residues. Such peptides manifest preferential binding affinities for certain SH3 domains. The preferred peptides exhibit specific binding affinities for the Src-family of proteins. In vitro and in vivo results are presented which demonstrate the biochemical activity of such peptides.
Owner:CYTOGEN CORP +1
Methods for detecting major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events
InactiveUS20110045514A1Raise the possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisTissue factorAnalyte
The present teachings relate to a method of assessing the probability of a major adverse cardiovascular or cerebrovascular event in a human. The method can include measuring a concentration, in a blood-based sample of a human, of a set of analytes, for example, alpha-fetoprotein, cancer antigen 125, glutathione S-transferase, and tissue factor. The method also can include determining a MACCE index for the set of analytes and identifying the human as having an increased likelihood of a major adverse cardiovascular or cerebrovascular event if the MACCE index is greater than zero, or a decreased likelihood of a major adverse cardiovascular or cerebrovascular event if the MACCE index is less than or equal to zero.
Owner:BG MEDICINE
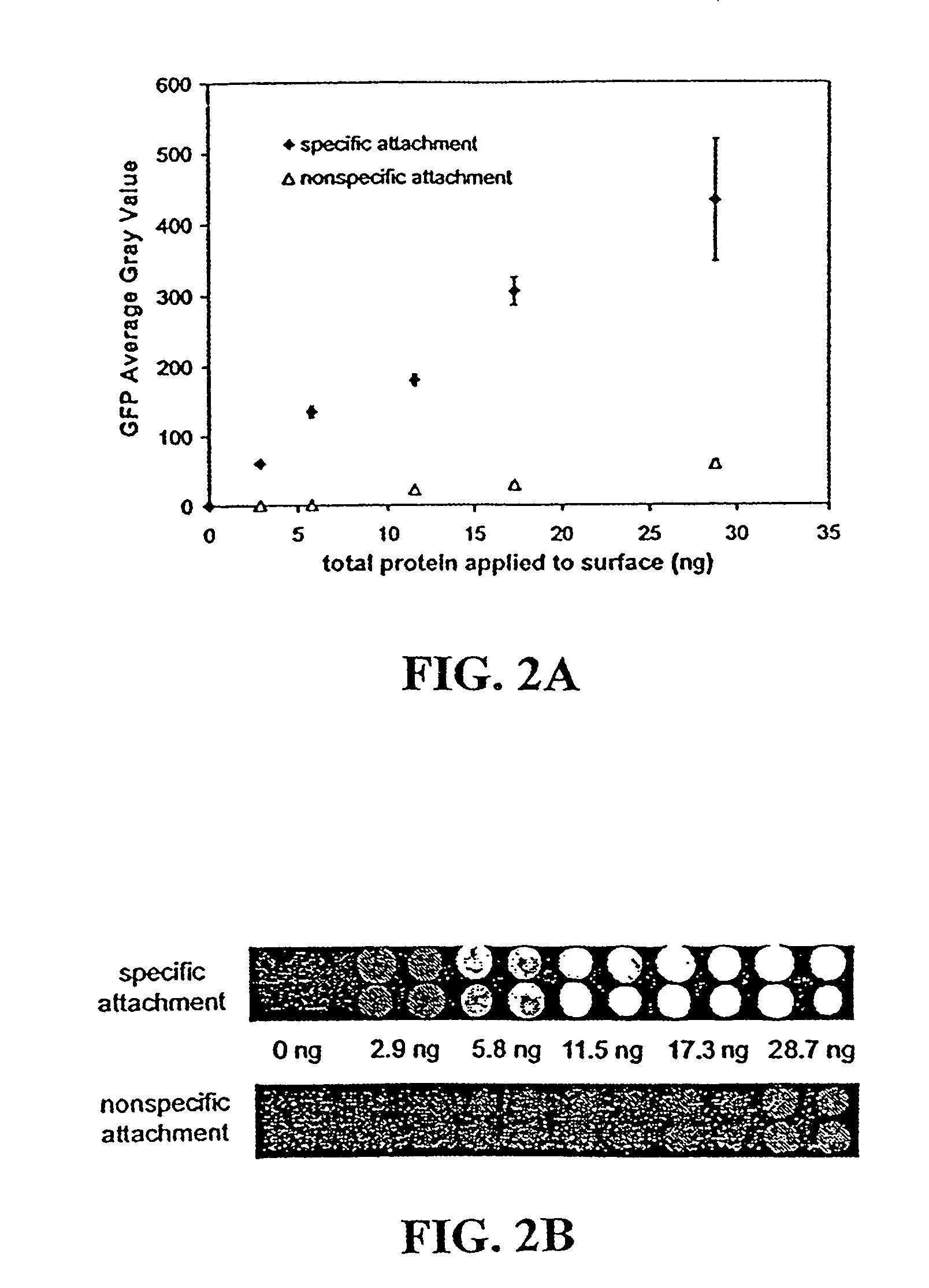
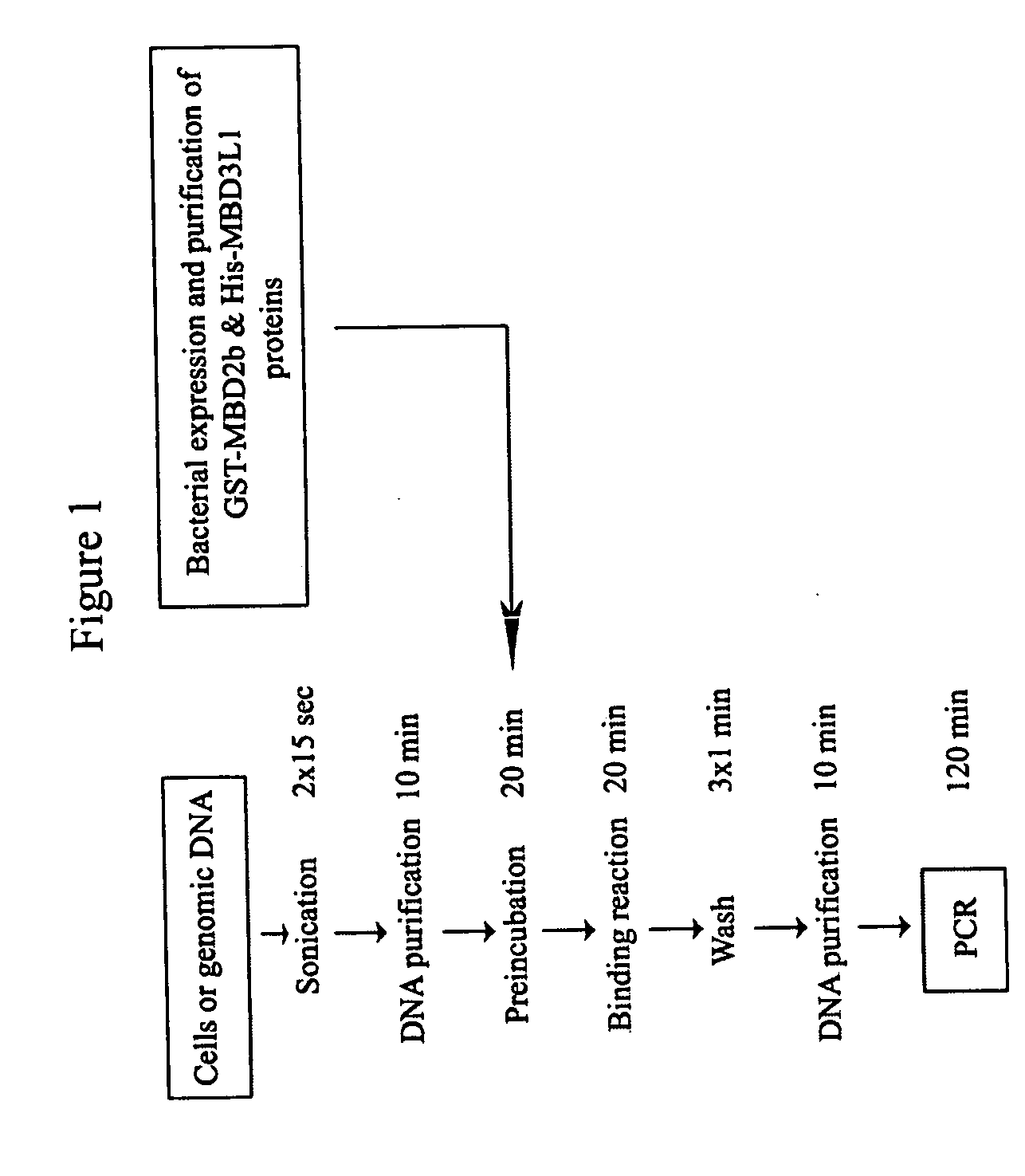
Method for detecting methylated CpG islands
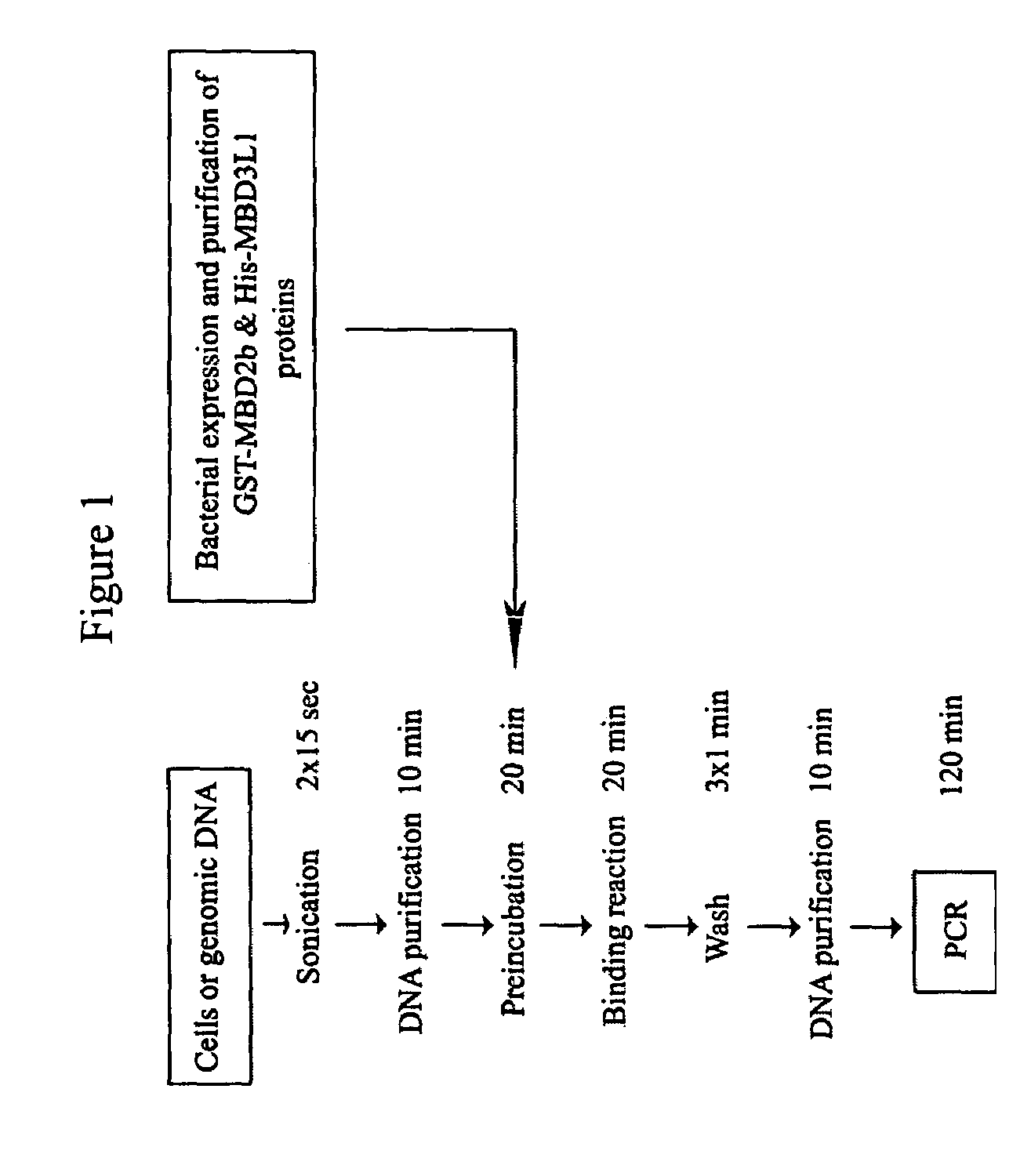
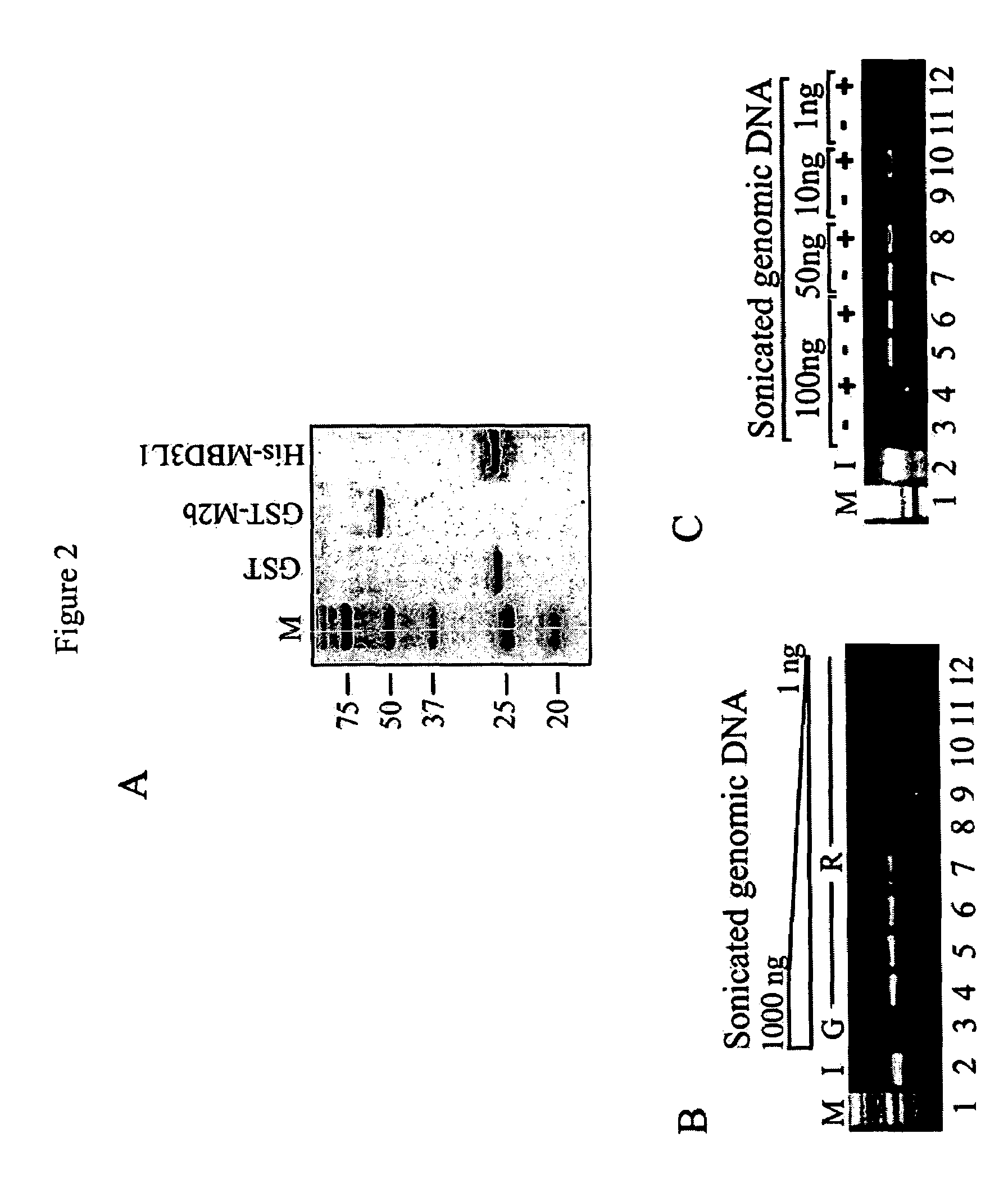
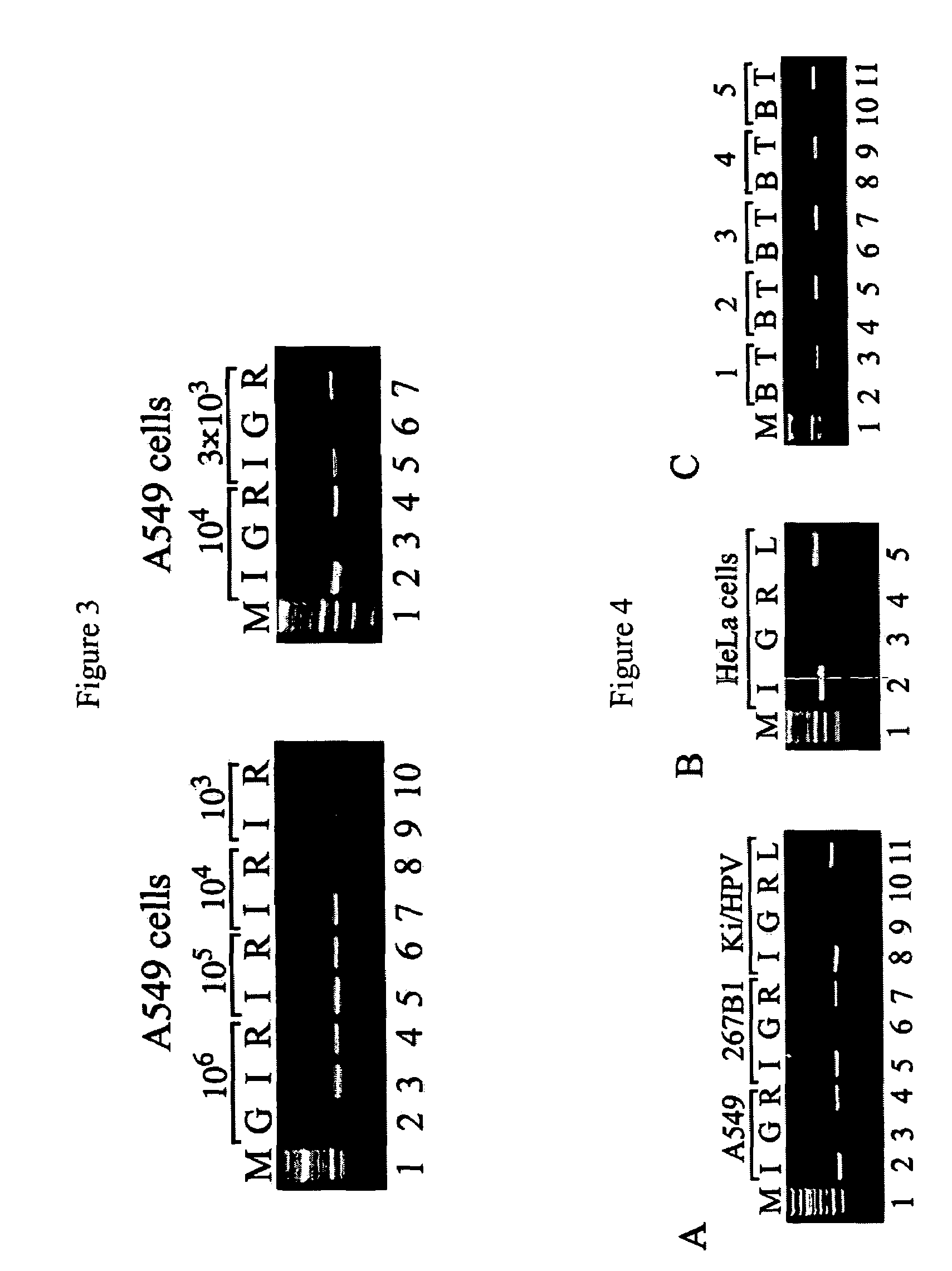
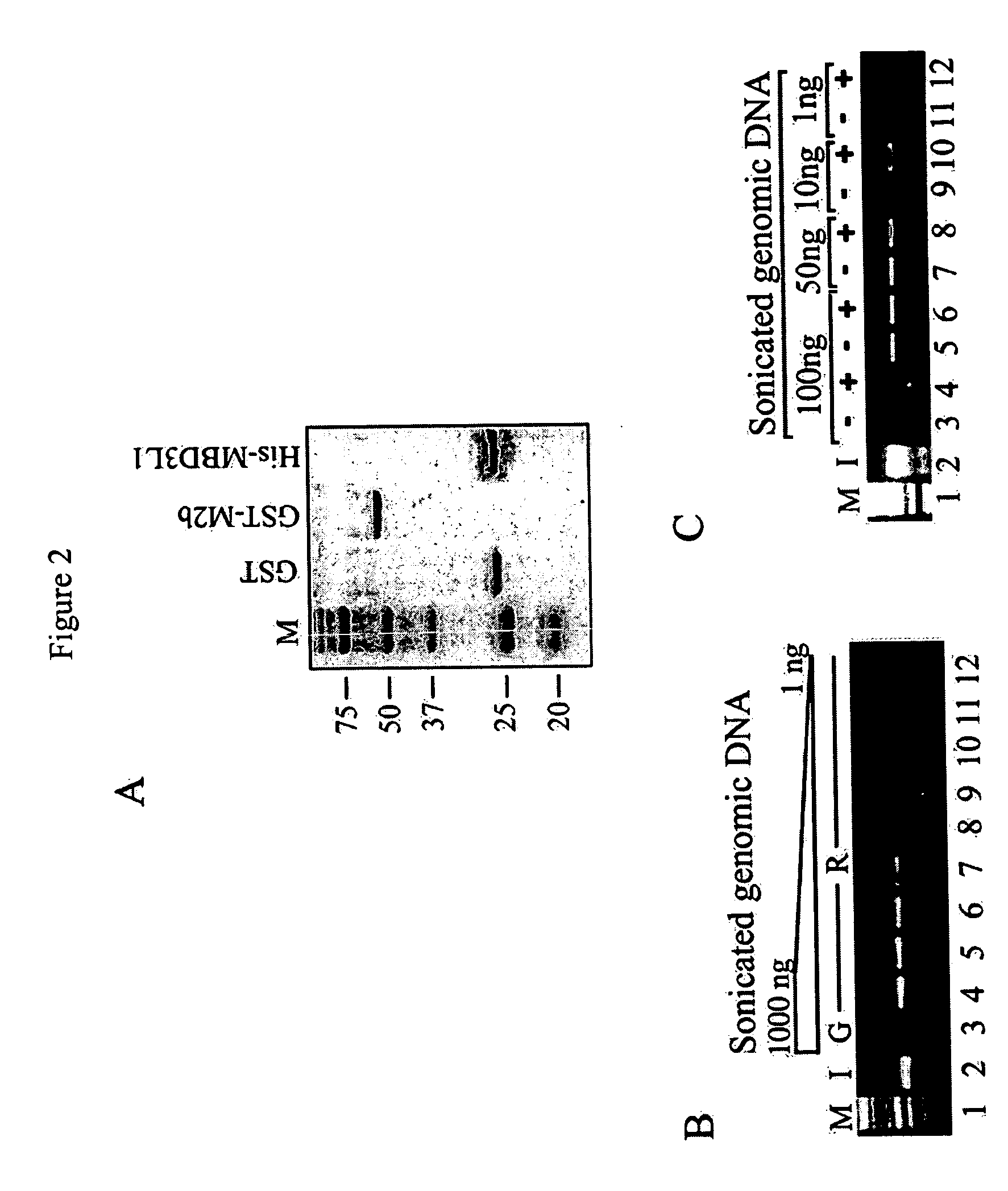
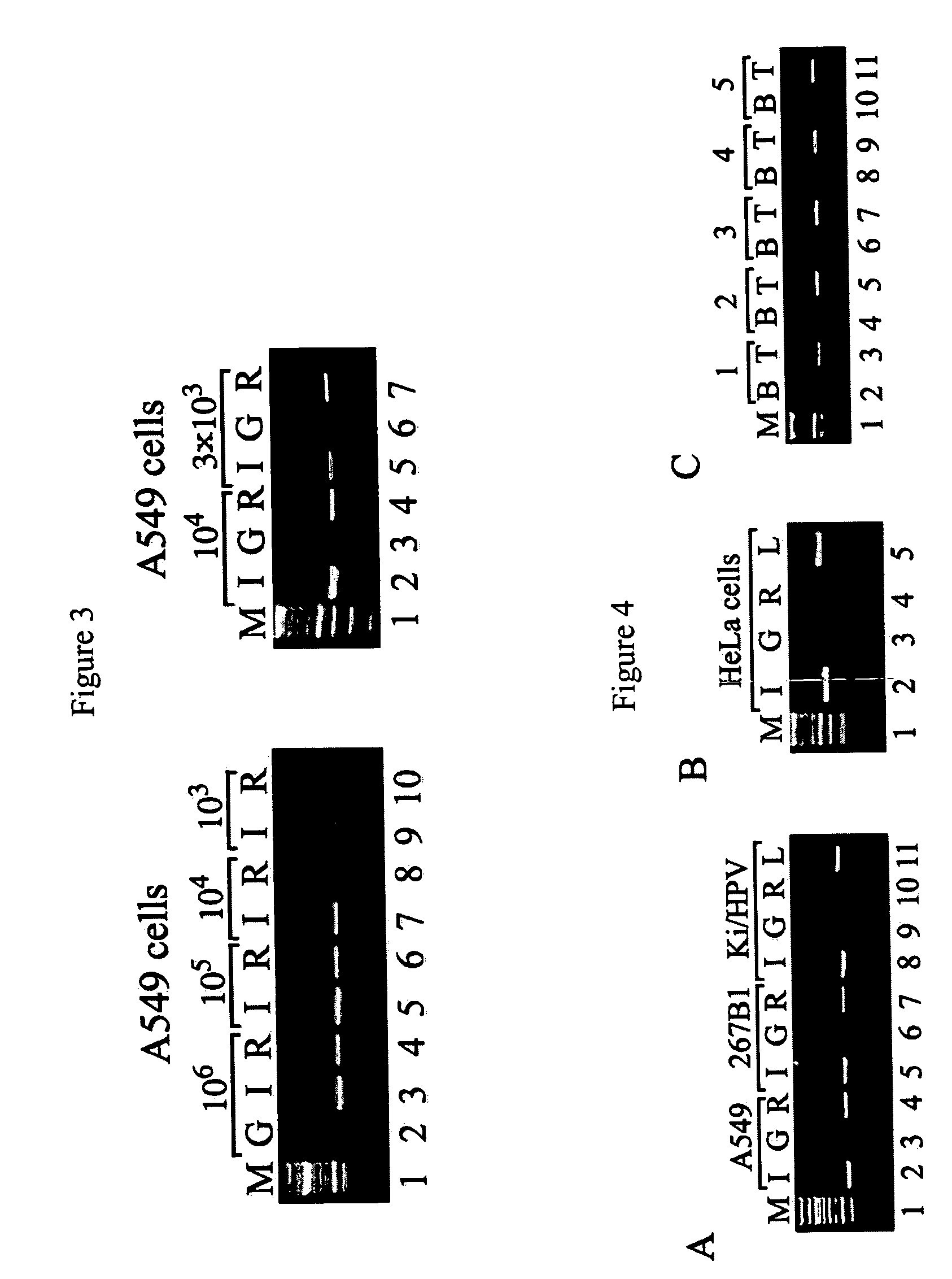
The present invention provides new and improved assay for detection of genomic methylated CpG islands. This new method is termed the methylated-CpG island recovery assay (MIRA). In accordance with one embodiment, MIRA comprises the steps of: (a) incubating genomic DNA fragments with a methylated CpG island binding protein in the presence of a binding partner for the binding protein to produce bound DNA containing methylated CpG islands, (b) isolating the bound DNA, and (c) detecting CpG island methylation by gene-specific amplification reactions. In accordance with a preferred embodiment, MIRA comprises the steps of: (a) incubating sonicated genomic DNA with a matrix containing a fusion protein of glutathione S-transferase (GST) and MBD2b (GST-MBD2b) in the presence of MBD3L1 to produce bound DNA containing methylated CpG islands, (b) eluting bound DNA from the matrix, and (c) detecting CpG island methylation by gene-specific amplification reactions.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Plants with Increased Yield
InactiveUS20120227134A1MicroorganismsVector-based foreign material introductionUbiquitin-Protein LigasesSerine hydroxymethyltransferase
A method for producing a plant with increased yield as compared to a corresponding wild type plant whereby the method comprises at least the following step: increasing or generating in a plant or a part thereof one or more activities of a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase, 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphate phosphatase, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase, 5OS chloroplast ribosomal protein L21, 57972199. R01.1-protein, 60952769. R01.1-protein, 60S ribosomal protein, ABC transporter family protein, AP2 domain-containing transcription factor, argonaute protein, AT1 G29250.1-protein, AT1 G53885-protein, AT2G35300-protein, AT3G04620-protein, AT4G01870-protein, AT5G42380-protein, AT5G47440-protein, CDS5394-protein, CDS5401_TRUNCATED-protein, cold response protein, cullin, Cytochrome P450, delta-8 sphingolipid desaturase, galactinol synthase, glutathione-S-transferase, GTPase, haspin-related protein, heat shock protein, heat shock transcription factor, histone H2B, jasmonate-zim-domain protein, mitochondrial asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase, Oligosaccharyltransferase, OS02G44730-protein, Oxygen-evolving enhancer protein, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase family protein, plastid lipid-associated protein, Polypyrimidine tract binding protein, PRLI-interacting factor, protein kinase, protein kinase family protein, rubisco subunit binding-protein beta subunit, serine acetyltransferase, serine hydroxymethyltransferase, small heat shock protein, S-ribosylhomocysteinase, sugar transporter, Thioredoxin H-type, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, ubiquitin-protein ligase, universal stress protein family protein, and Vacuolar protein.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Bivalent inhibitors of Glutathione-S-Transferases
InactiveUS20050004038A1High affinityHigh selectivityBiocideTetrapeptide ingredientsCrystallographyIsozyme
Bivalent inhibitors having affinity for one or more dimeric GST isozymes are provided. The bivalent inhibitors comprise two ligand domains connected by a molecular linker, wherein the ligand domains have affinity for one or more monomers in the one or more dimeric GST isozymes. The ligand domains are separated by a distance ranging from about 5 to about 100 Å. The bivalent inhibitors of the invention demonstrate greatly improved affinity for GST isozymes. In a specific embodiment, the bivalent inhibitors of the invention further provide affinity for substantially one GST isozyme and for substantially one GST class. The bivalent inhibitors of the invention have numerous uses that include the treatment of drug-resistant cancer, malaria, and stimulation of hematopoiesis.
Owner:LYON ROBERT P +3
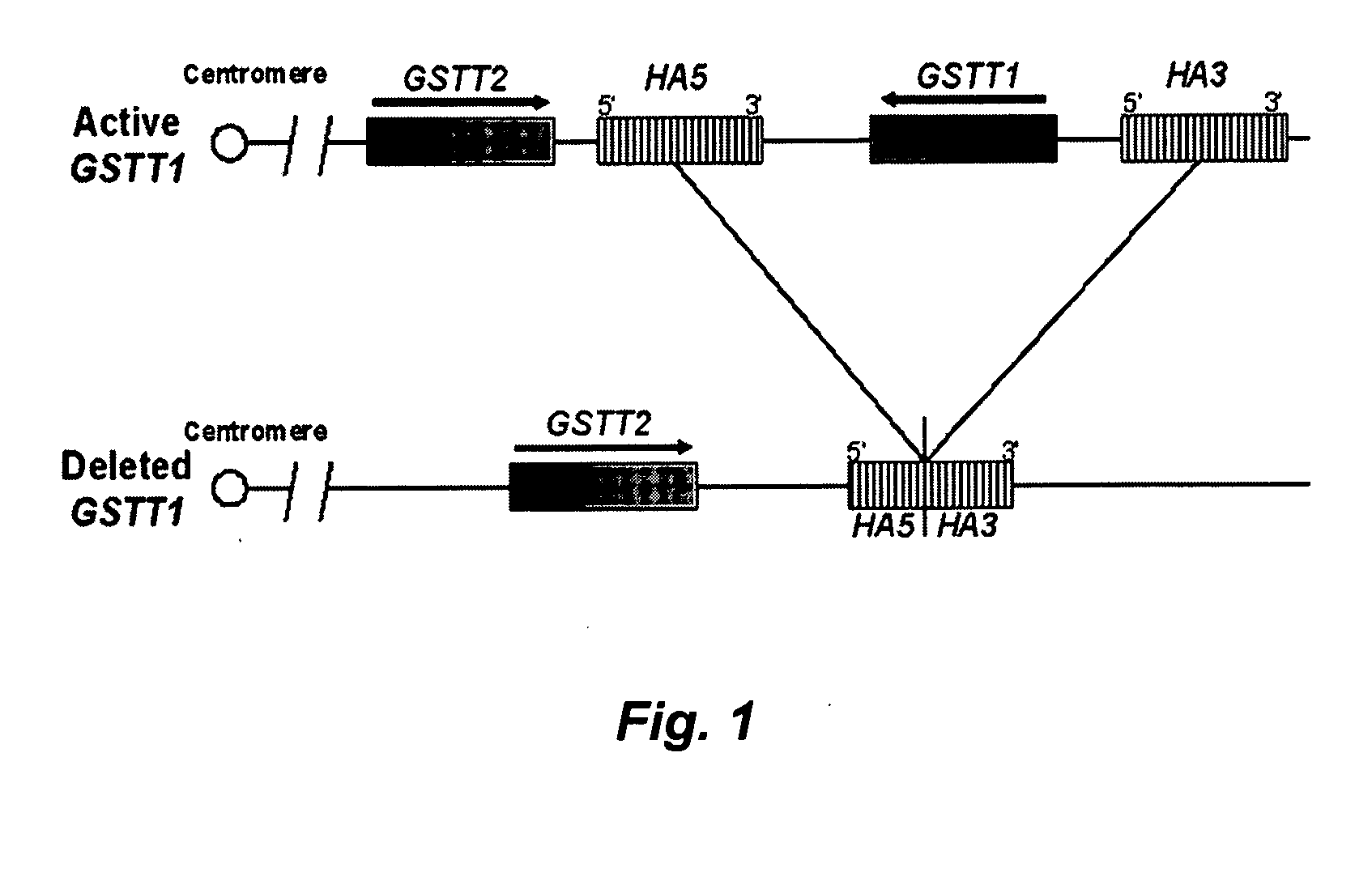
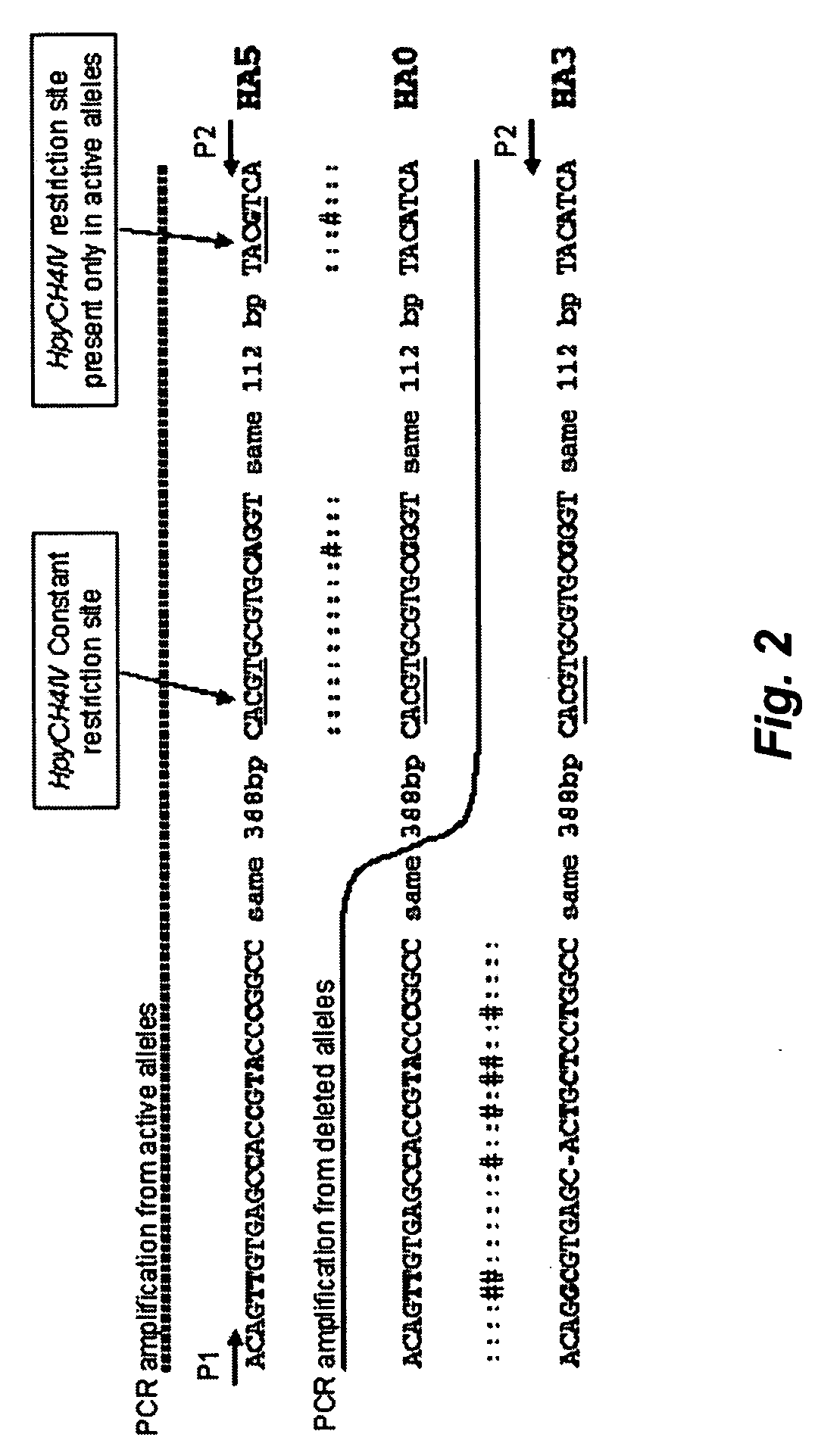
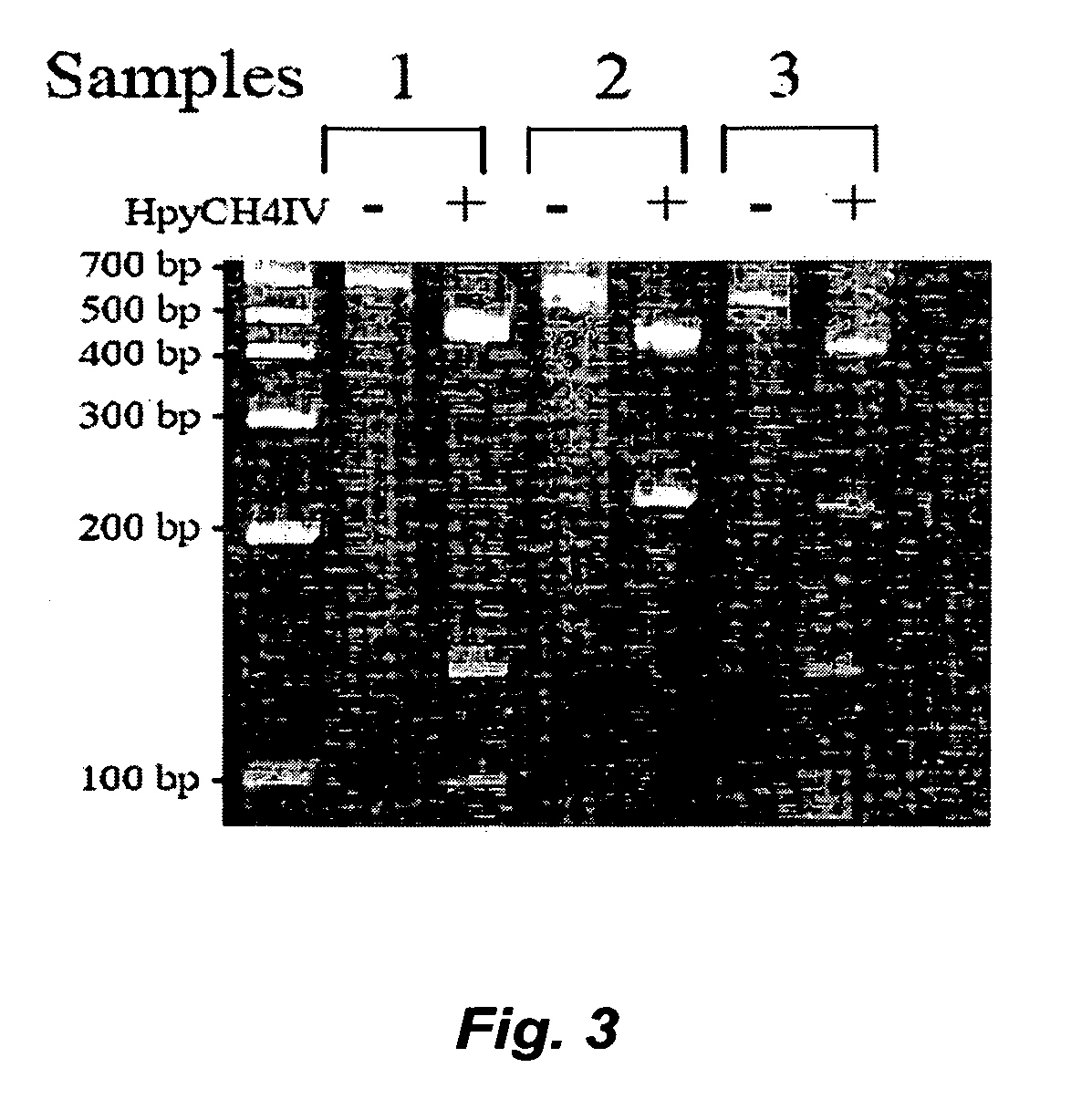
Methods for determining glutathione S-transferase theta-1 genotype
InactiveUS20060269925A1Avoids the lack of certaintyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenotypeGlutathione S-transferase
The invention relates to methods for determining GSTT1genotype, and the diagnostic and prognostic uses of these methods.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
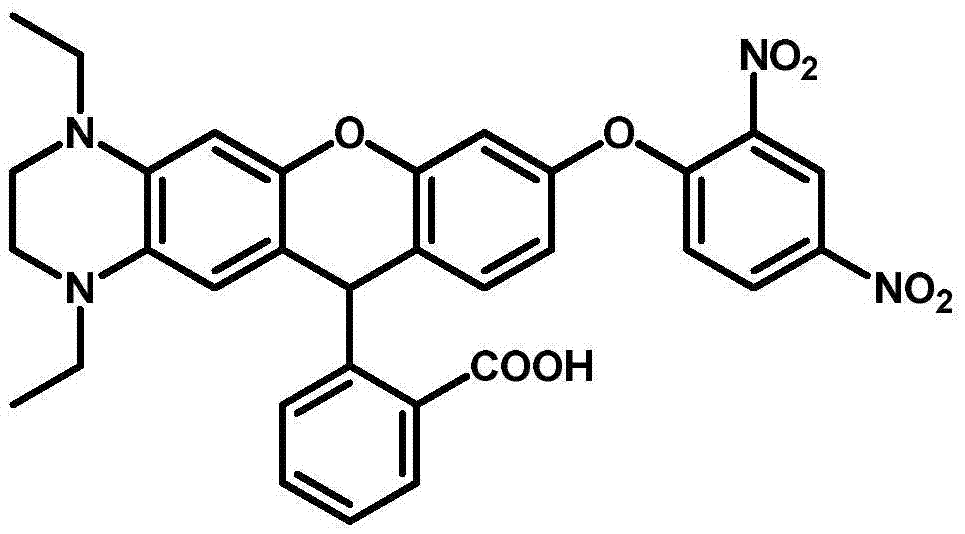
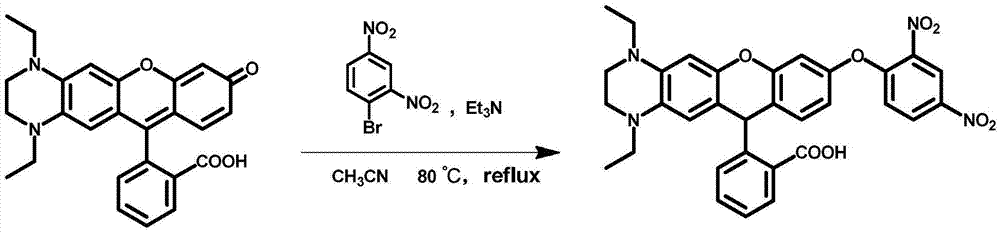
Fluorescent probe for detecting glutathione in blood, and synthesis method and application thereof
ActiveCN106866689AHigh selectivitySpecific recognition abilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe for detecting the content of glutathione (GSH) in blood, and a synthesis method and an application thereof. The synthesis steps of the probe are simple, and the light stability is good. In the detection process, the fluorescent probe firstly as a substrate is combined with glutathione S-transferase (GST), and undergoes a reaction with another specific substrate GSH of the GST to produce fluorescence, the fluorescence is enhanced by about 35 times, and the maximum emission wavelength is at the near infrared region (beyond 700 nm). Compared with conventional GSH fluorescent probes, the probe can specifically detect the content of the GSH in a complex system, and has the advantages of wide dynamic response window, high efficiency and the like. The probe realizes the specific and high-efficiency identification on the GSH in the complex environment, and has extremely important application value in the biological and medical fields.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
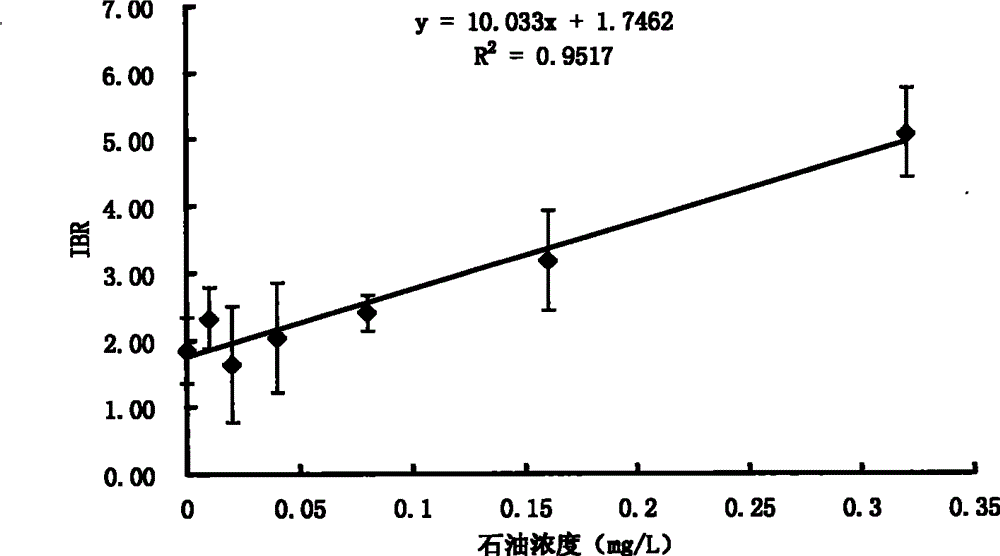
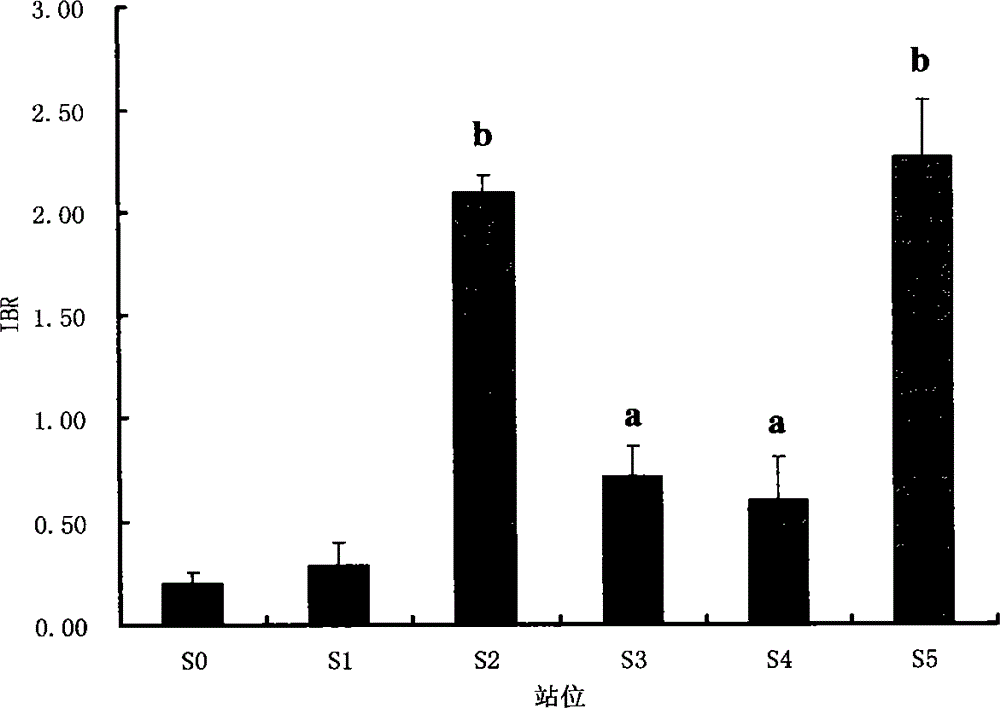
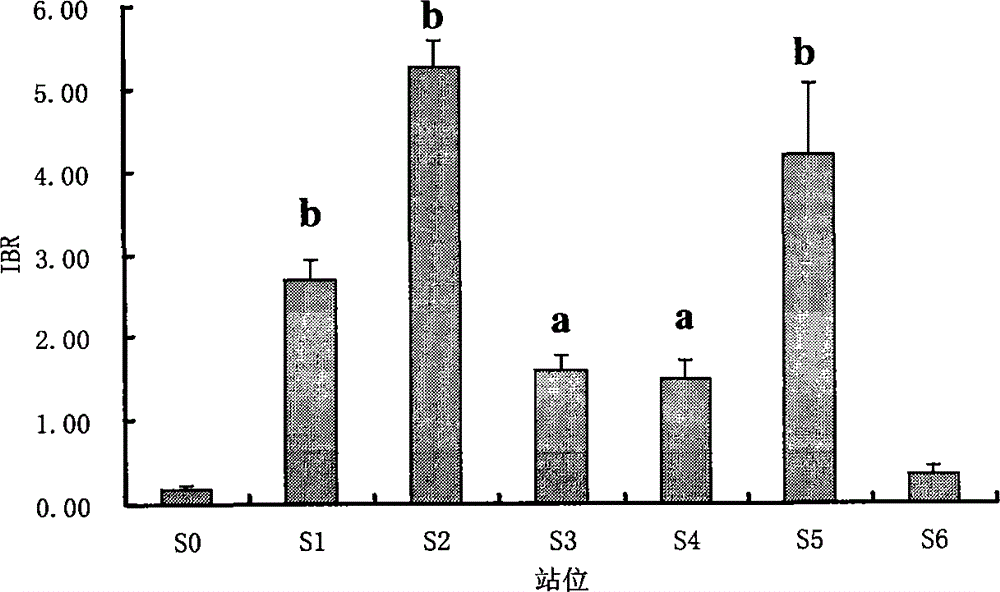
Shellfish monitoring method for ocean oil spill pollution base on integration biomarker method
InactiveCN103146805AReduced stabilityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementShort-necked clamPeroxidase
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological monitoring environment, and specifically relates to a shellfish monitoring method for ocean oil spill pollution. The shellfish monitoring method comprises the steps of utilizing typical bivalve mollusk such as short-necked clam and chlamys farreri in China to determine the shellfish visceral mass autioxidant enzyme activities including superoxide dismutase, glutathione glutathione S-transferase, peroxidase, glutathione peroxidase and catalase activity, integrating the enzyme activities so as to form an integration biomarker responding index (IBR), establishing a dose-effect relationship between the IBNNR and petroleum concentration, adopting a one-dimensional variance components method (ANOVA) to carry out notable difference analysis, determining the forcing degree of petroleum pollution on organisms, and finally judging pollution level of the ocean oil spill.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Genetic markers for predicting disease and treatment outcome
InactiveUS20070218487A1Microbiological testing/measurementThymidine Phosphorylase DeficiencyPlatinum
The present invention provides for a method for identifying patients that are suitably treated by a therapy, such as a therapy involving administration of a fluoropyrimidine drug and / or a platinum drug. The method includes determining the expression level of at least one gene selected from a phospholipase 2 (PLA2) gene, a thymidine phosphorylase (TP) gene, and a glutathione S-transferase P1 (GSTP-1) gene in suitable sample isolated from the patient. Overexpression of the gene or genes identifies the patient as not being suitable for the therapy.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Methods and kits for the diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome
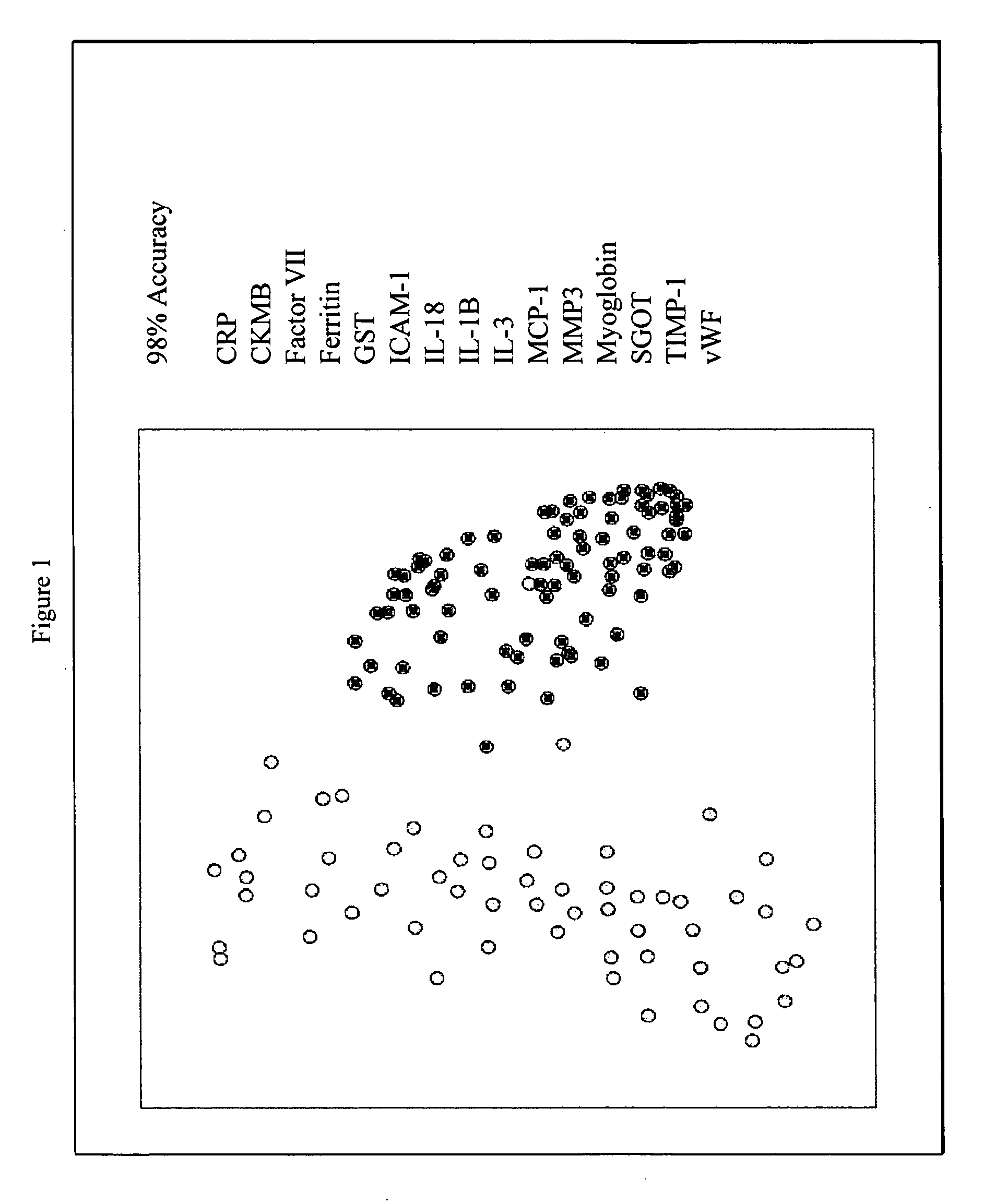
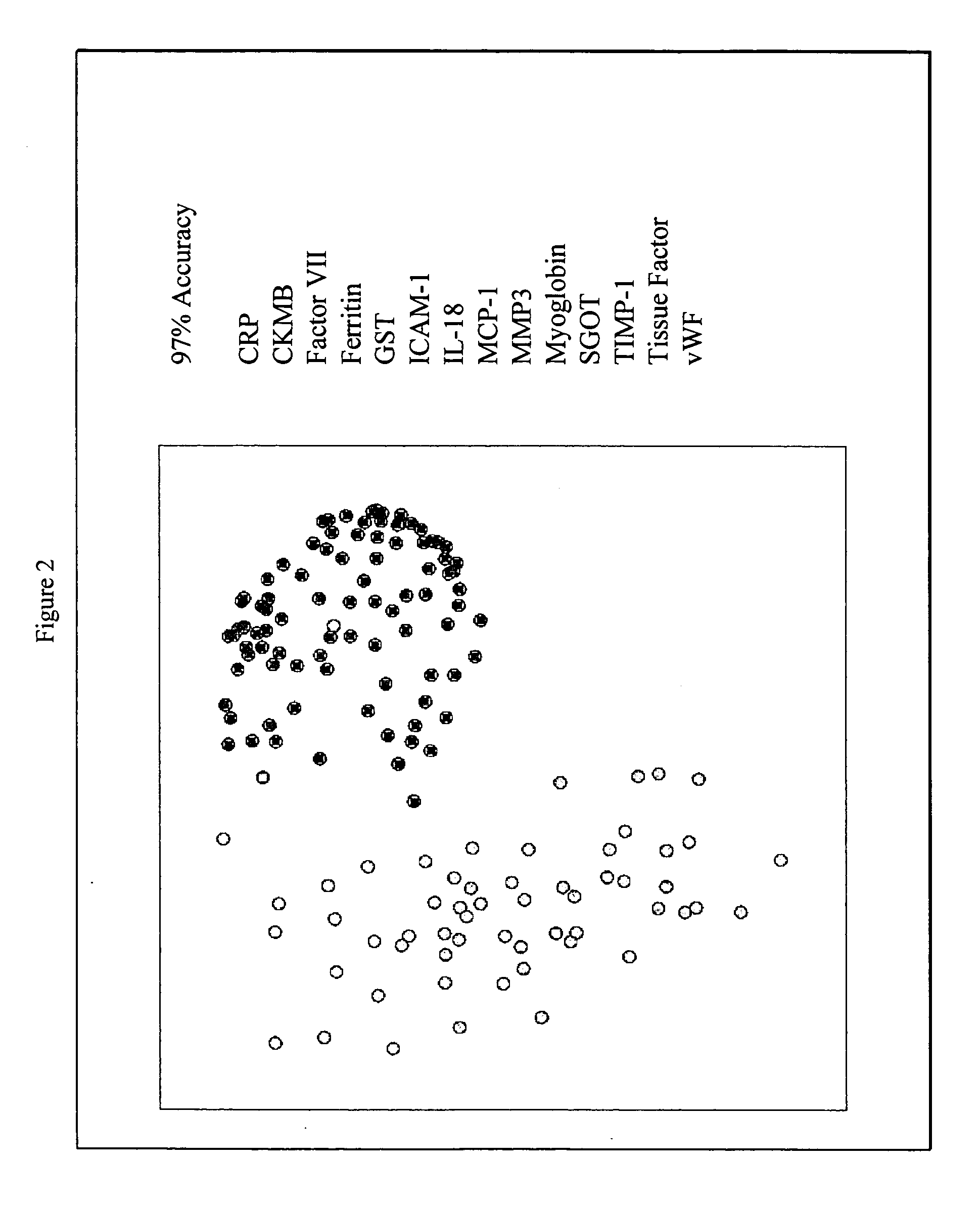
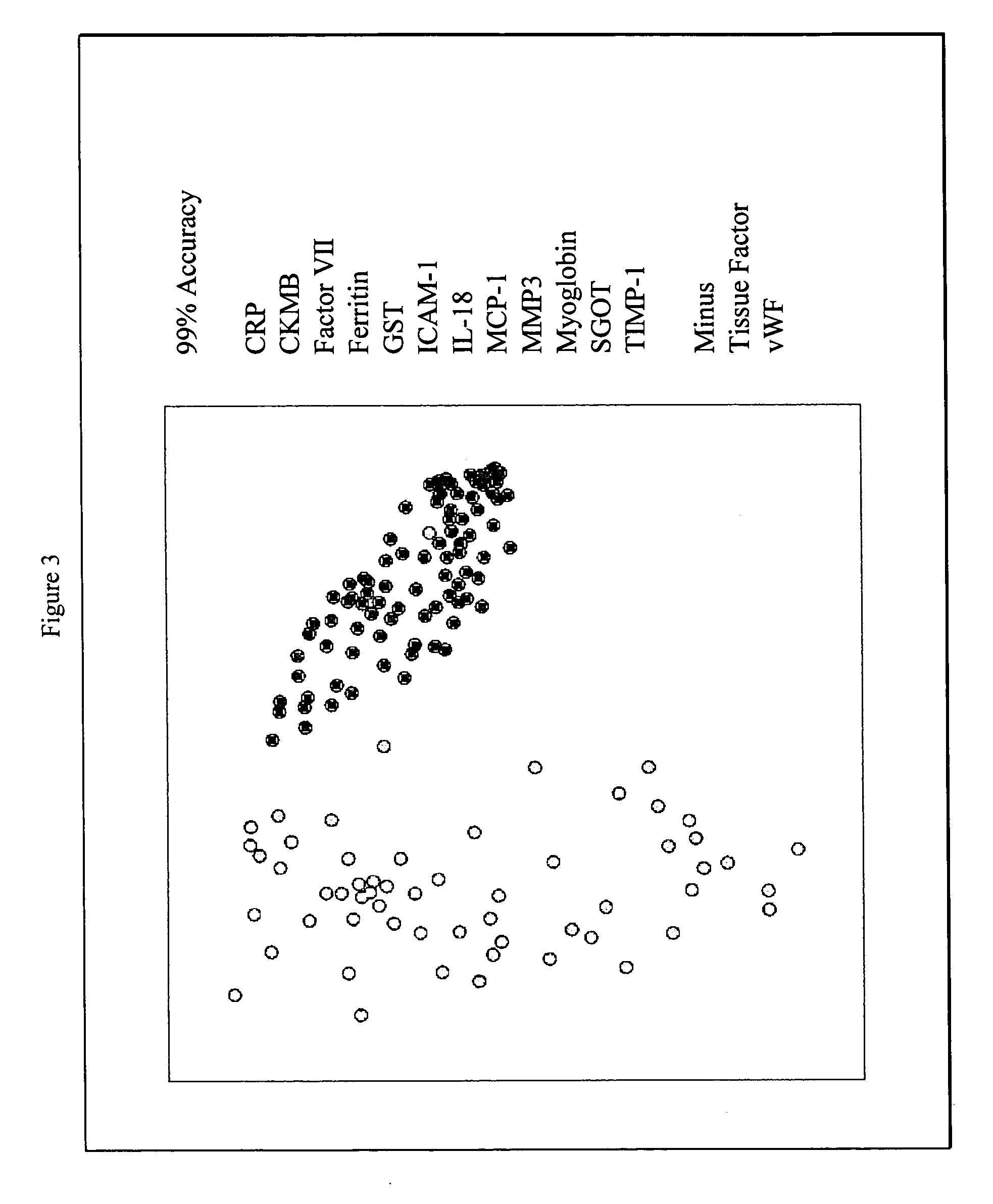
InactiveUS20070003981A1Quick checkAccurate diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisComplement 3Factor VII
Provided are methods for the detection and diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome or ACS. The methods are based on the discovery that abnormal levels of selected analytes in sample fluid, typically blood samples, of patients who are at risk are supportive of a diagnosis of ACS. At least two new biomarkers for ACS are thus disclosed, MMP-3 and SGOT. Altogether the concentrations of twelve analytes provide a sensitive and selective picture of the patient's condition, namely, whether the patient is suffering a heart attack. Other important biomarkers for ACS are described, including but not limited to IL-18, Factor VII, ICAM-1, Creatine Kinase-MB, MCP-1, Myoglobin, C Reactive Protein, von Willebrand Factor, TIMP-1, Ferritin, Glutathione S-Transferase, Prostate Specific Antigen (free), IL-3, Tissue Factor, alpha-Fetoprotein, Prostatic Acid Phosphatase, Stem Cell Factor, MIP-1-beta, Carcinoembryonic Antigen, IL-13, TNF-alpha, IgE, Fatty Acid Binding Protein, ENA-78, IL-1-beta, Brain-Derived Nerotrophic Factor, Apolipoprotein A1, Serum Amyloid P, Growth Hormone, Beta-2 microglobulin, Lipoprotein (a), MMP-9, Thyroid Stimulating hormone, alpha-2 Macroglobulin, Complement 3, IL-7, Leptin, and IL-6. Kits containing reagents to assist in the analysis of fluid samples are also described.
Owner:RULES BASED MEDICINE
Codon-optimized 7 beta-hydroxy steroid dehydrogenase gene
InactiveCN102827847AComplete structureSimple purification methodBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliProkaryotic expression
The invention discloses a codon-optimized 7 beta-hydroxy steroid dehydrogenase gene, a recombination expression vector Pgex-6P-1-7 beta-HSDH containing an optimized gene and escherichia coli containing the recombination expression vector. Glutathione S-transferase (GST) fusion expression of the codon-optimized 7 beta-hydroxy steroid dehydrogenase gene and a prokaryotic expression vector Pgex-6P-1 in the escherichia coli is adopted, so that a large quantity of active target proteins with an integral structure can be generated in a short time; and a method for purifying the GST fusion expression protein is simple and quick, so that the active target proteins can be quickly obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI KAIBAO PHARMA
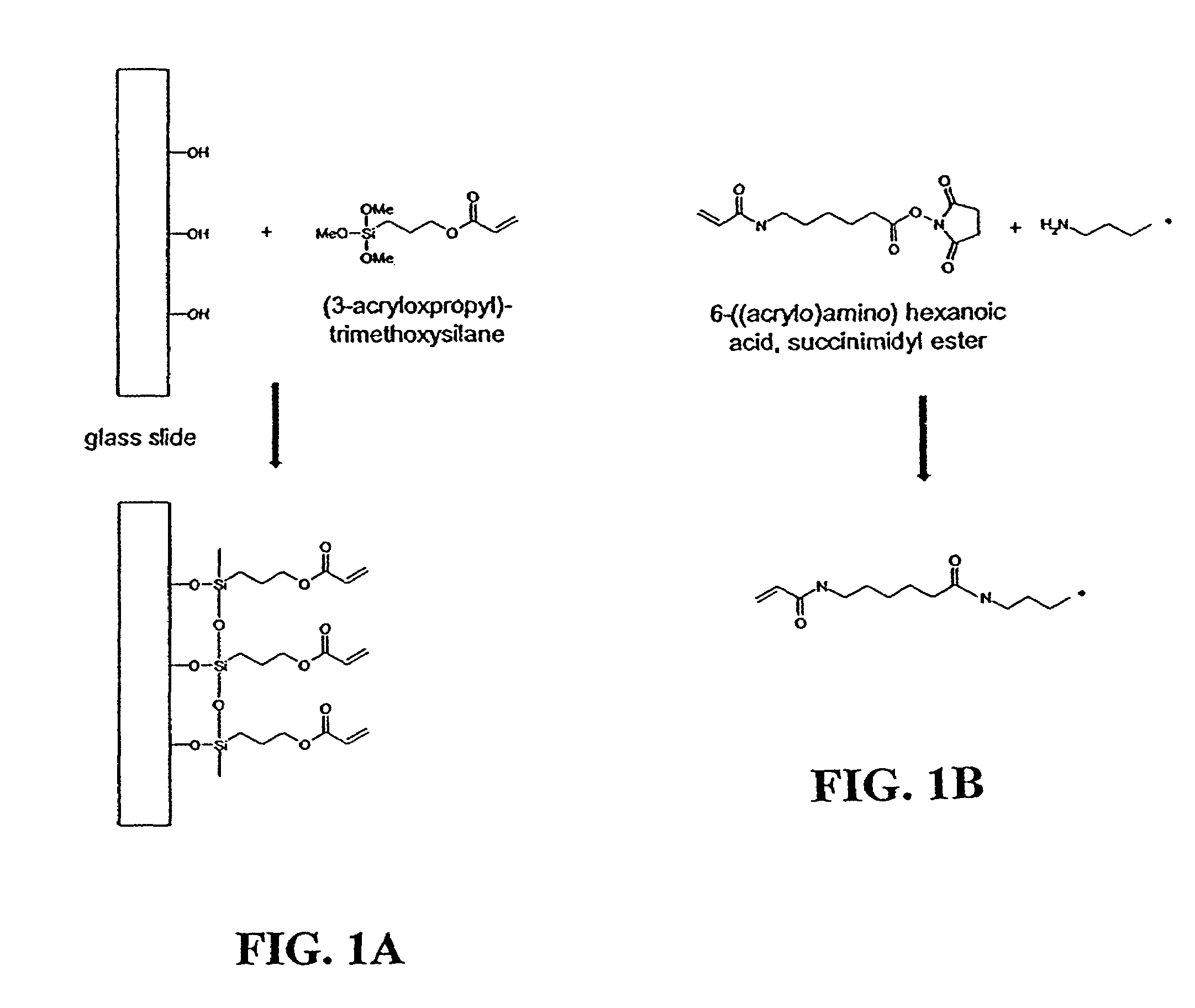
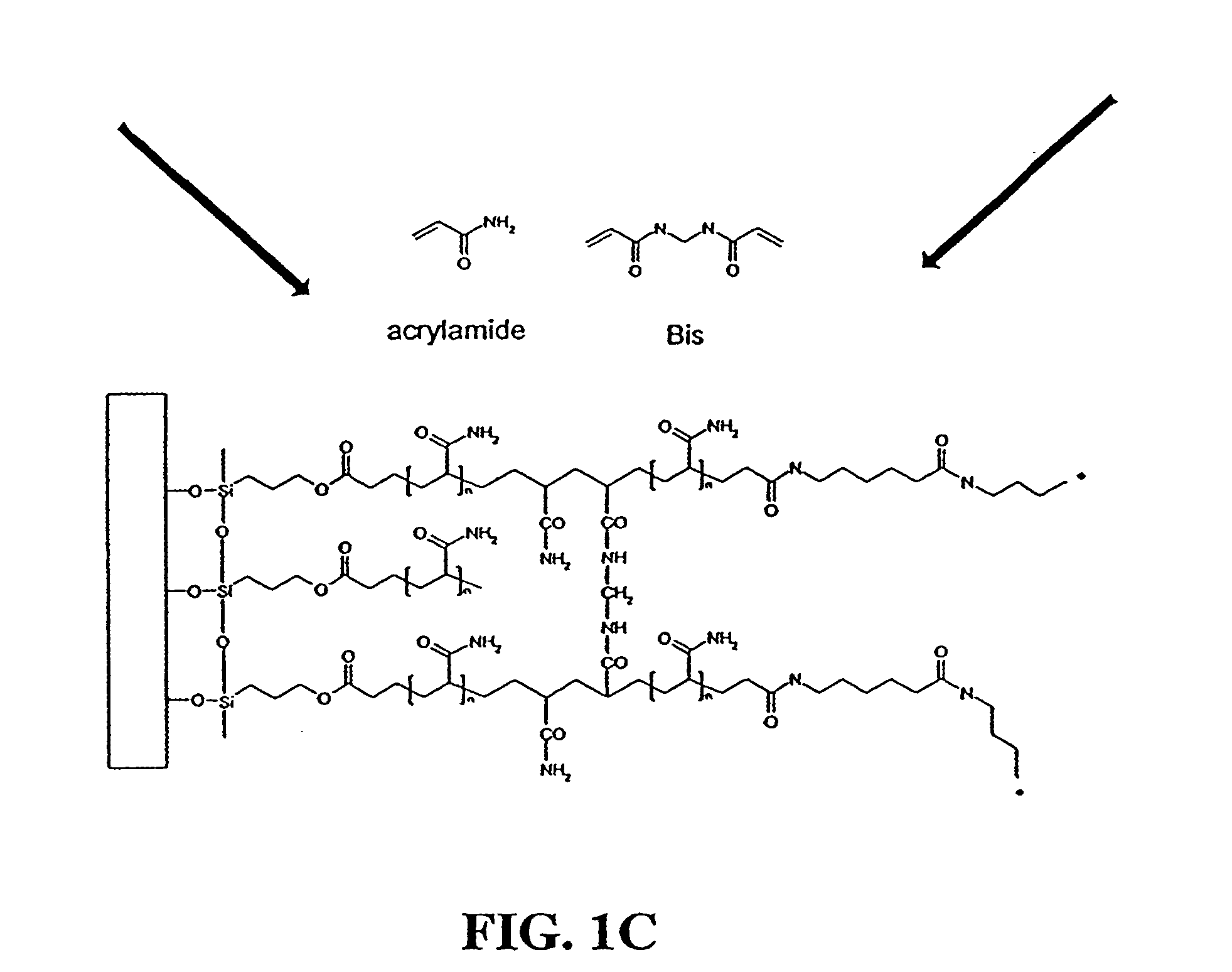
Hydrogels for biomolecule analysis and corresponding method to analyze biomolecules
InactiveUS7588906B2Eliminate needSamples introduction/extractionMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphorylationFluorescence
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for detecting methylated CpG islands
The present invention provides new and improved assay for detection of genomic methylated CpG islands. This new method is termed the methylated-CpG island recovery assay (MIRA). In accordance with one embodiment, MIRA comprises the steps of: (a) incubating genomic DNA fragments with a methylated CpG island binding protein in the presence of a binding partner for the binding protein to produce bound DNA containing methylated CpG islands, (b) isolating the bound DNA, and (c) detecting CpG island methylation by gene-specific amplification reactions. In accordance with a preferred embodiment, MIRA comprises the steps of: (a) incubating sonicated genomic DNA with a matrix containing a fusion protein of glutathione S-transferase (GST) and MBD2b (GST-MBD2b) in the presence of MBD3L1 to produce bound DNA containing methylated CpG islands, (b) eluting bound DNA from the matrix, and (c) detecting CpG island methylation by gene-specific amplification reactions.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Edyuillia FS110 glutathione S-transferase gene GliG promoter and application thereof
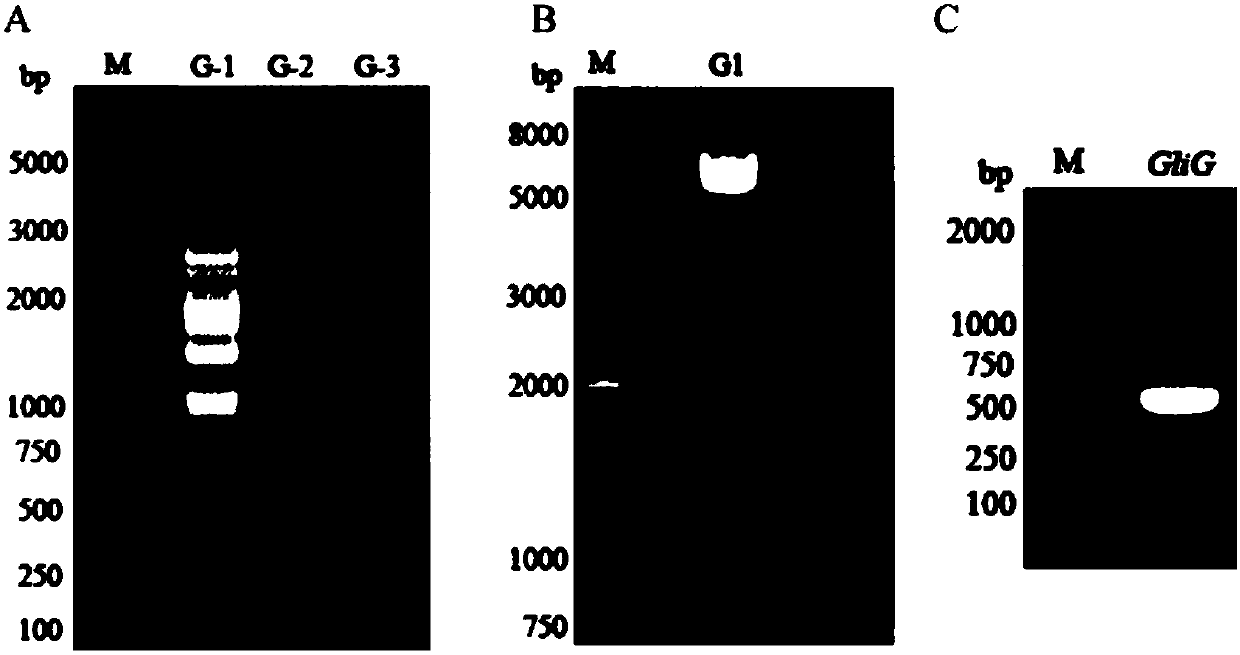
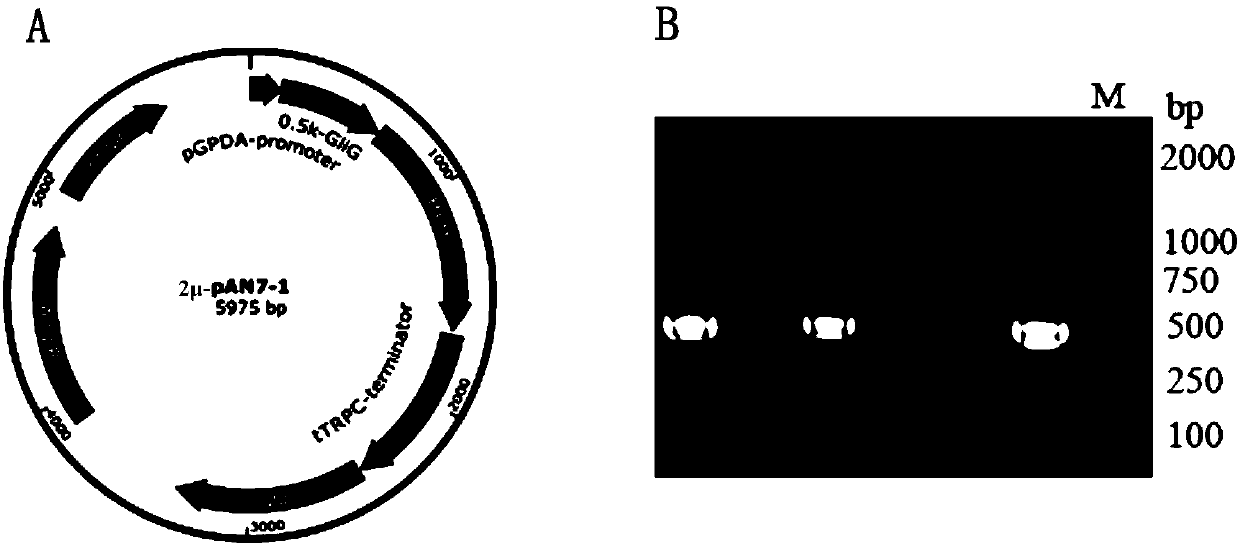
The invention discloses an edyuillia FS110 glutathione S-transferase gene GliG promoter and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the promoter is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The upstream promoter sequence of the gene GliG is obtained by a chromosome walking technology, the core area of the promoter is predicted, and the edyuillia FS110 glutathione S-transferase gene GliG promoter is obtained. The promoter provided by the invention can efficiently start the expression of a hygromycin resistance gene hph, and the starting efficiency is obviously higher than that of a pgpdA promoter, so that a molecular biology base is laid for increasing the yield of gliotoxin through transcriptional control and heterogeneous expression in later period.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
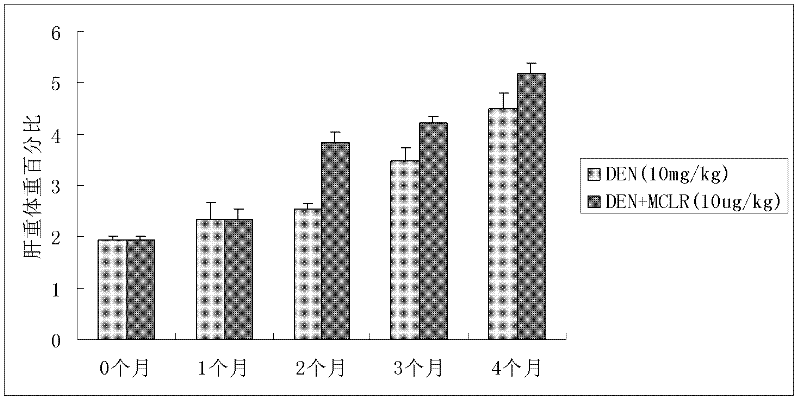
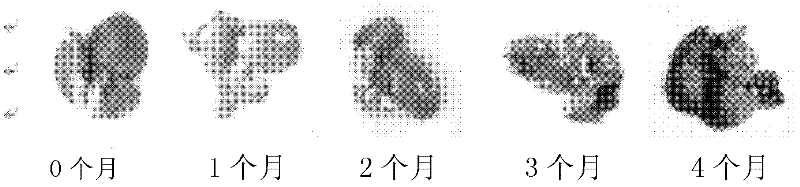
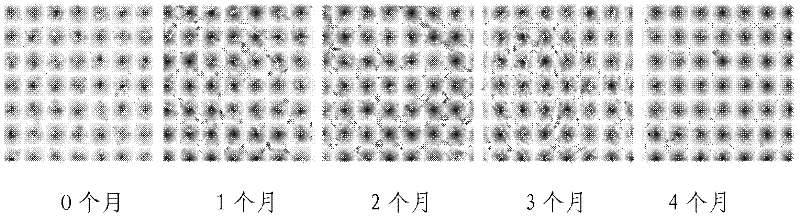
Method for establishing microcystin MC-LR promoted diethyl nitrosamine DEN induced rat liver cancer model
InactiveCN102524180ACyclic peptide ingredientsVeterinary instrumentsIntraperitoneal routeProcess mechanism
The invention discloses a method for inducing a rat liver cancer model by injecting diethyl nitrosamine DEN in coordination with microcystin MC-LR into a rat body through intraperitoneal injection. Indexes such as liver weight to body weight ratio, liver appearance, liver histopathological slicing and GST-Pi (Glutathione S-transferase) protein expression level clearly show liver cell injury phase, liver cell hyperplasia-hepatocirrhosis phase and liver cell carcinomatous change process in a rat liver cancer occurring process, and find that the liver cancer model induced by the DEN in coordination with the microcystin MC-LR has a more obvious effect at the same time than that induced by DEN independently; the tumor formation time is shorter; and the model is an ideal model for researching occurrence of the liver cancer of a human body. The model has the characteristic of clearly showing each stage for occurrence of the liver cancer and contributing to research of a liver cancer occurrence process mechanism, detection of precancerous lesion and development of treatment medicaments.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
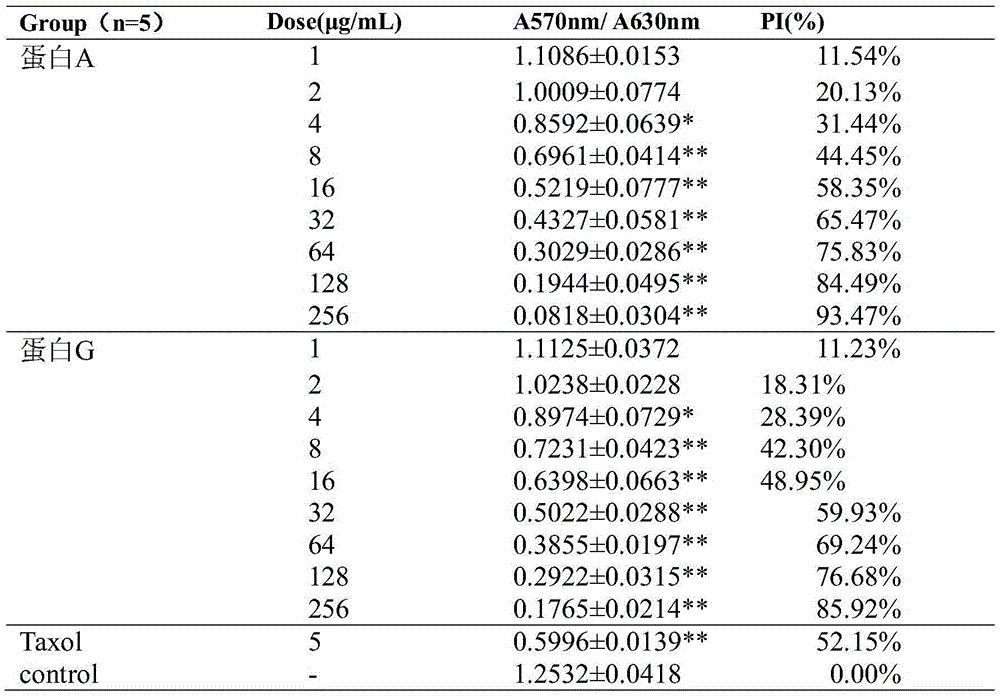
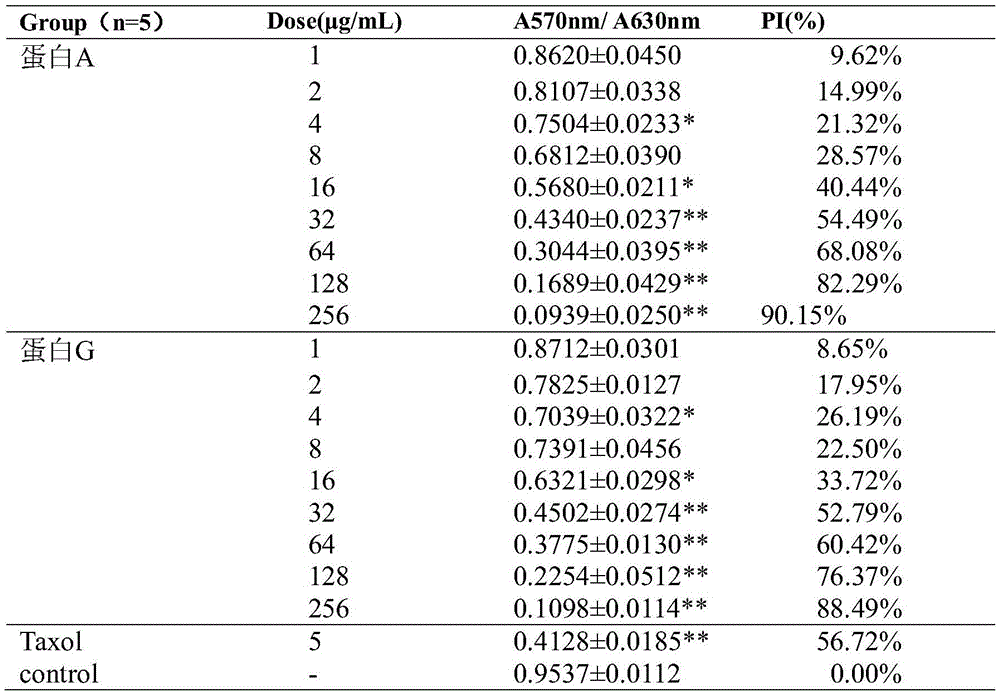
Fusion protein with anti-tumor, anti-inflammation and oculopathy-treatment functions and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105418769AInhibition of newbornsImprove ductilitySenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsTumor angiogenesisHalf-life
The invention discloses fusion protein with anti-tumor, anti-inflammation and oculopathy-treatment functions and a preparation method and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of biological pharmacy. Specifically, the invention relates to the fusion protein of an integrin blocking agent, which has the function of inhibiting tumor angiogenesis and has the integrin affinity and the combining capacity. A rigid (R) or flexible (F) linker is adopted to fuse two polypeptides, so as to respectively obtain protein A and protein G, the medicine effect can be increased, the half-life period can be extended, the stability can be enhanced, and the fusion protein has the characteristics of strong action effect, low toxicity and the like and can be used for preventing and treating solid tumors, all kinds of inflammation and angiogenesis oculopathy. The fusion protein structurally comprises two angiogenesis inhibiting polypeptides and the amino acid linker between the two angiogenesis inhibiting polypeptides, and the fusion protein is expressed in colibacillus or eukaryocyte by using a genetic engineering method and is obtained through separation and purification of a GST (Glutathione S Transferase) affinity column.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 and application thereof
The invention discloses a rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 and application thereof.Sequences of the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 are shown as SEQ ID NO:1 in sequence tables, and amino acid sequences of glutathione S-transferase (GSTs) of an encoding protein of the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 are shown as SEQ ID NO:2 in the sequence tables.As proved by ectopic expression of yeast, the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 has cadmium toxicity tolerant characteristics.The rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 and the application have the advantages that knockout lines and over-expression lines of the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 are constructed, as discovered in seed germination comparative experiments on the knockout lines, the over-expression lines and wild type rice, the knockout lines of the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 are poor under cadmium stress, but the over-expression lines of the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 and the wild type rice can germinate, and germination and growth of the over-expression lines of the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37are superior to germination and growth of the wild type rice; important effects of the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 in cadmium-tolerant mechanisms can be equivalently described; over-expression vectors of the rice cadmium-tolerant gene OsGSTU37 are constructed, and plants are transformed by the aid of the over-expression vectors, so that cadmium-tolerant plant varieties can be obtained, the cadmium stress resistance of the plants can be improved, and theoretical bases can be provided for breeding novel cadmium-tolerant crop varieties.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Porcine circovirus disease detection method based on ORF2 (Open Reading Frame 2) antigen domain
InactiveCN101936993AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresVirus peptidesFermentationOpen reading frameFluorescence
The invention relates to a PCV (Porcine Circovirus) disease detection method based on an ORF2 (Open Reading Frame 2) antigen domain. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining GST-ORF2-E infusion protein through the fusion expression of a special amino acid segment (113-147aa) on PCV2 ORF2 as a target with GST (Glutathione S-Transferase); and purifying the fusion protein by utilizing affinity chromatography and using the purified fusion protein as the antigen to coat an ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) 96 pore plate and establishing an ELISA method. The special amino acid segment selected by the method is a segment with higher antigenicity on the PCV2 ORF2 and used as the coated antigen in ELISA to improve the sensitivity and the specificity of a traditional PCV2 ELISA method. Compared with a commonly applied immunofluorescence detection method, the specificity and the sensitivity of the method are respectively 87.7 percent and 93.57 percent. The ORF2 without antigen cross between the PCV1 and the PCV 2 can be used for differentiating and judging the infection of the PCV1 and the PCV 2. The method can be used for differentiating animals infected by the PCV1 and the PCV 2.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Nck SH3 binding peptides
InactiveUS6432920B1Increase ratingsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRandom Peptide LibraryBinding peptide
Peptides having general and specific binding affinities for the Src homology region 3 (SH3) domains of proteins are disclosed in the present invention. In particular, SH3 binding peptides have been isolated from phage-displayed random peptide libraries which had been screened for isolates that bind to bacterial fusion proteins having an SH3 domain and glutathione S-transferase (GST). Preferred peptides are disclosed which comprise a core 7-mer sequence (preferably, a consensus motif) and two or more, preferably at least six, additional amino acid residues flanking the core sequence, for a total length of 9, preferably at least 13, amino acid residues and no more than about 45 amino acid residues. Such peptides manifest preferential binding affinities for certain SH3 domains. The preferred peptides exhibit specific binding affinities for the Src-family of proteins. In vitro and in vivo results are presented which demonstrate the biochemical activity of such peptides.
Owner:CYTOGEN CORP +1
High throughput screening of important schistosoma japonicum antigens and application of antigens in schistosomiasis diagnosis
The invention discloses high throughput screening of important schistosoma japonicum antigens and application of the antigens in schistosomiasis diagnosis. Specifically, the invention provides important schistosoma antigens and application thereof in schistosomiasis diagnosis and vaccine preparation. Based on a high throughput functional protein screening technology of glutathione S transferase (GST) fusion expression, 24 positive antigens capable of being identified by the serum of a schistosomiasis patient are acquired, wherein 8 antigens represent strong positive reaction. Schistosomiasis serologic detection shows that the positive antigens for detecting schistosoma have high sensitivity and specificity. The invention also provides a corresponding method and a kit for diagnosing and monitoring the schistosomiasis.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
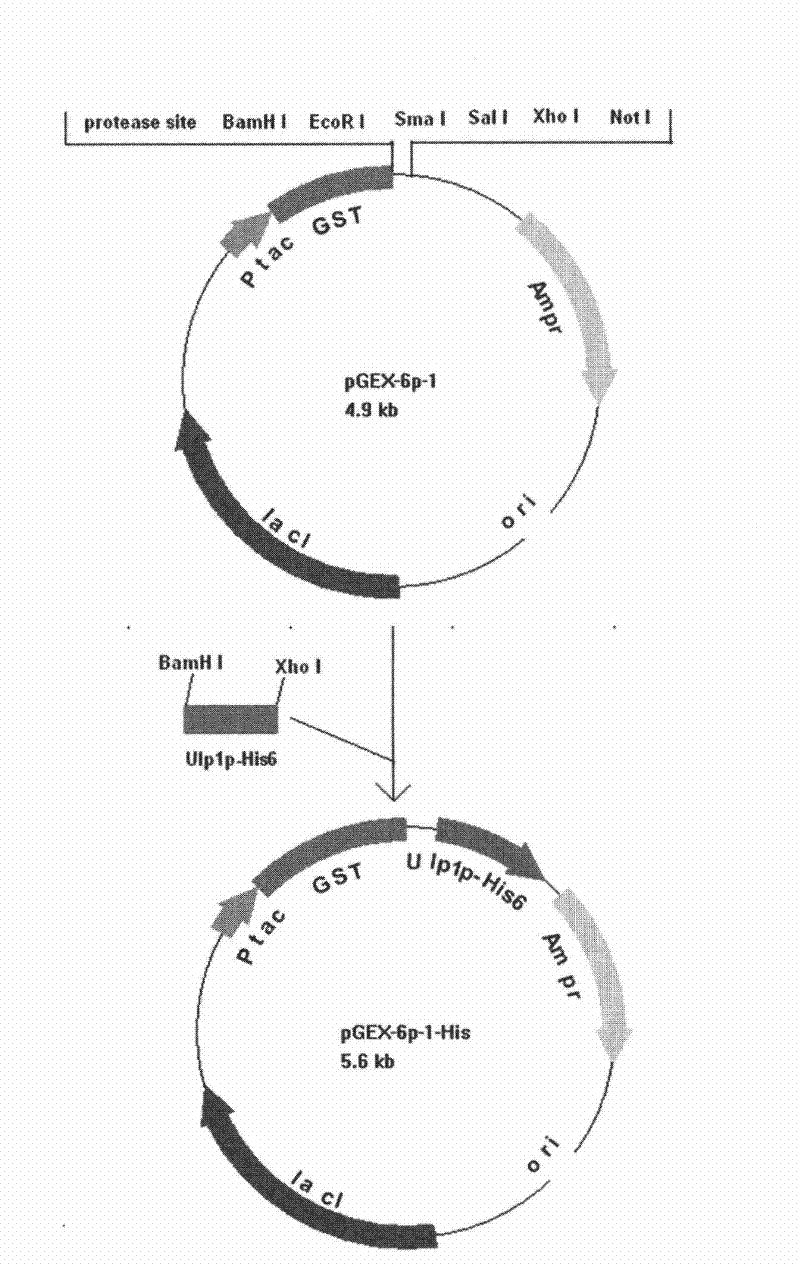
Recombinant small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) protease and preparation method as well as application thereof
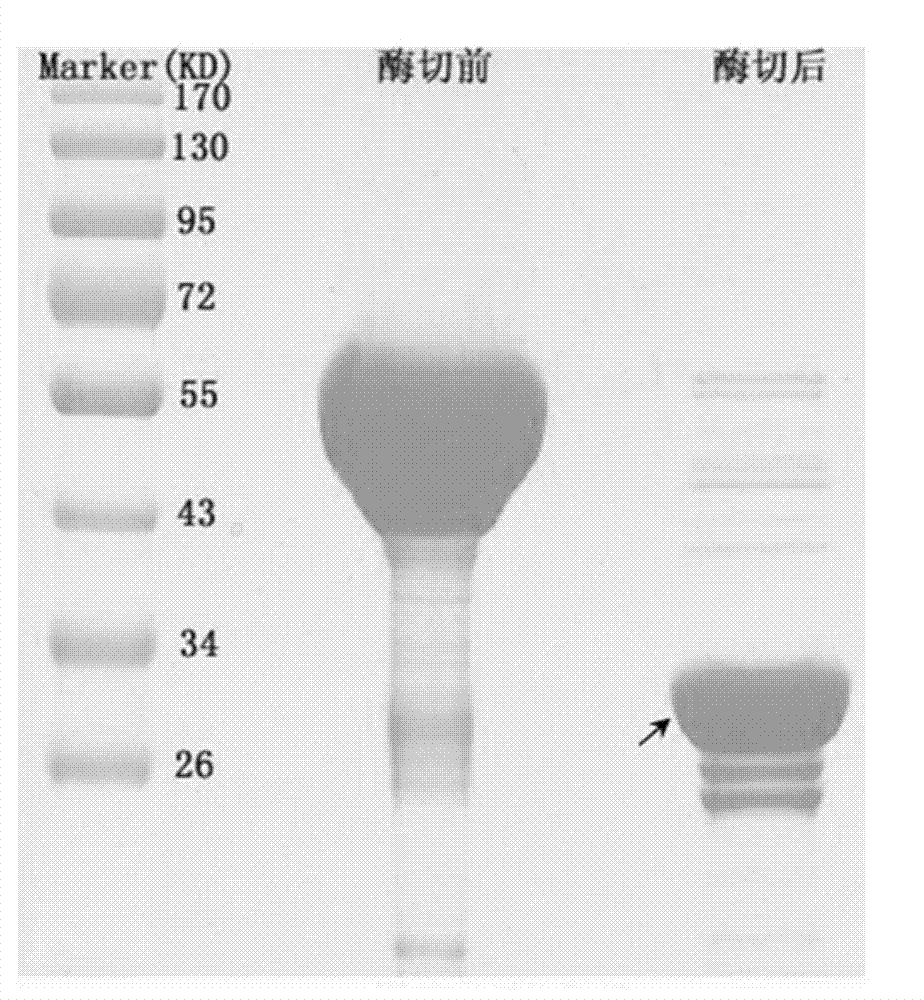
ActiveCN102234640AEasy to purifyImprove stabilityFungiBacteriaHigh activityGlutathione S-transferase
The invention discloses a recombinant small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) protease and a preparation method as well as application thereof. The recombinant protease is composed of a GST (glutathione-s-transferase) tag, a ULP1P (ubiquitin-like-specific protease 1) sequence and a poly-His (histidine) tag, wherein the amino acid sequence of the recombinant protease is shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The recombinant SUMO protease disclosed by the invention recognizes a complete SUMO tag protein sequence and can efficiently cut off the SUMO from fusion protein. Compared with recognition sites of proteases such as EK, TEV and the like, the restriction reaction has very high specificity and keeps higher activity in reaction environment systems in a wider range. The recombinant SUMO protease disclosed by the invention is not only provided with the poly-His tag to be convenient for affinitive layer purification after cutting of the fusion protein, but also provided with the GST tag to be convenient for purifying the protease and enhancing the stability of the protease.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Combination detection reagent for detecting schistosomiasis and detecting method thereof
InactiveCN1700007AImprove standardizationEasy specificityTransferasesImmunoglobulinsAntigenGlutathione S-transferase
The invention relates to a combined medium and method for testing snail fever. It has the following characters: the medium contains recombination antigen mixture and recombination snail signal protein (rSj14-3-3) monoclonal antibody, and recombination antigen is mixed as recombination snail signal protein (rSj14-3-3) and recombination snail glutathione-s-transferase (rSjGST). The test operation is separately according to indirect enzyme immunosorbent test and double antibody bedded texture method. The invention adopts the two advantage diagnosis antigen molecule and its corresponding monoclonal antigen to form combined testing medium box.
Owner:ANHUI MEDICAL UNIV
Method for improving degradation ability of transgenic plants to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
InactiveCN103468738AImprove tolerancePromote degradationFermentationGenetic engineeringPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonOxygenase
The invention discloses a method for improving degradation ability of transgenic plants to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. The method comprises the following specific steps of constructing a divalent gene plant expression vector by using a transformed P450 mono-oxygenase gene and a synthesized grape glutathione s-transferase (GST) gene, and then converting the divalent gene expression vector to plants through agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation. The tolerance and the degradation ability of the transgenic plants obtained by using the method to the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are increased; and the planting of the transgenic plants is beneficial to the remediation of soil environments polluted by the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Owner:上海瑞丰农业科技有限公司 +1
Rapid assays for the assessment of organ status based on the detection of one or more isoenzymes of glutathione S-transferase
InactiveUS6080551ARapid assessmentLittle trainingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisCapture antibodyOrgan damage
PCT No. PCT / IE96 / 00019 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 3, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 3, 1997 PCT Filed Apr. 2, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 31779 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 10, 1996The present invention is drawn to a method for the rapid assessment of organ status, including organ damage following immunological or toxicological insult, in a subject based on the detection of one or more isoenzymes of glutathione S-transferase (GST) in diverse biological fluids comprising contacting a particle-labelled anti-GST antibody specific for said isoenzyme with a sample of a biological fluid suspected of containing said isoenzyme, said antibody having a sensitivity sufficient to detect at least a picomolar amount of said isoenzyme, and capturing the particle-labelled antibody-isoenzyme complex on an immobolised capture antibody to generate a visually detectable signal.
Owner:ARGUTUS INTPROP
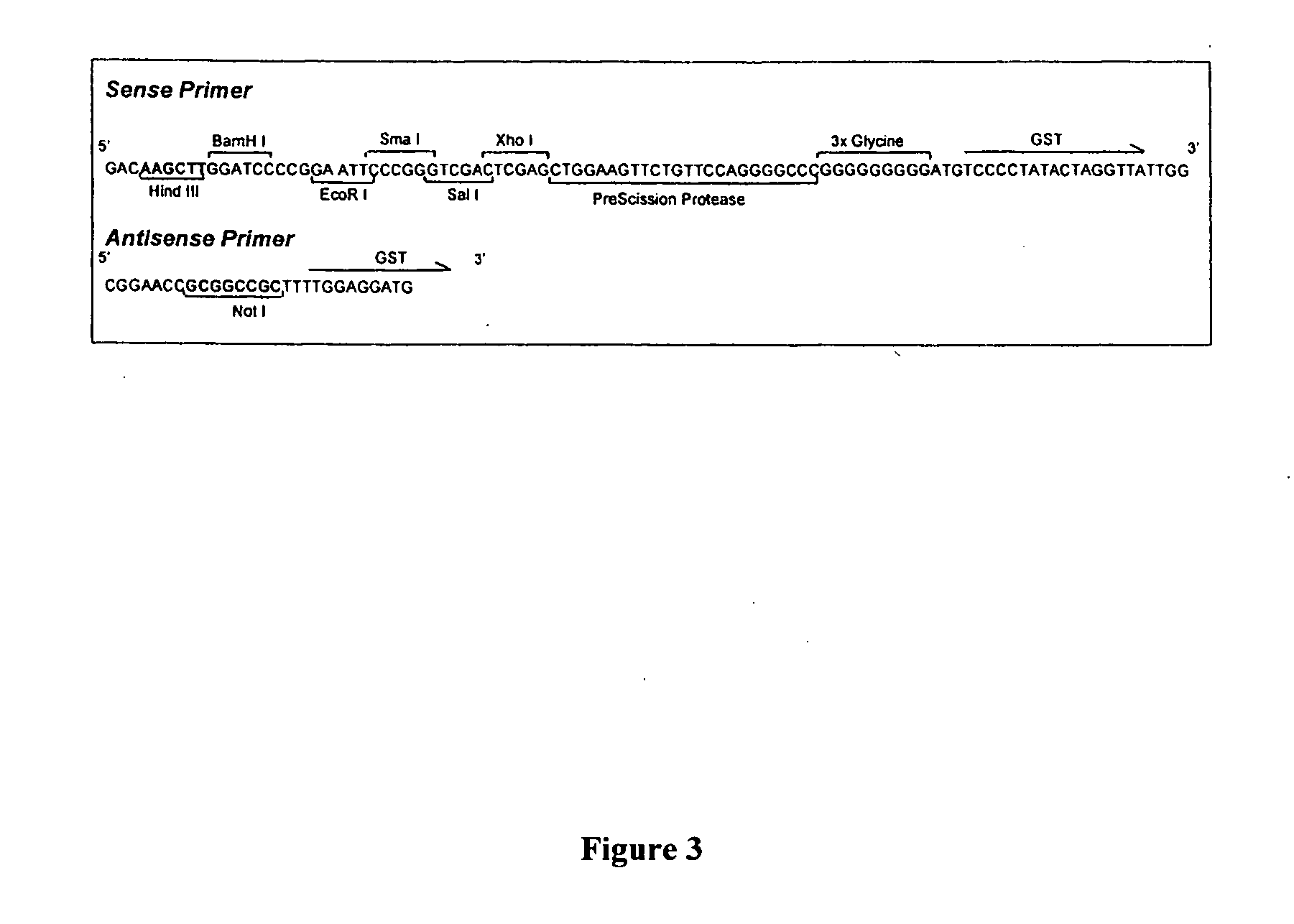
Expression vector, host cell and method for producing fusion proteins
InactiveUS20050106671A1Avoid interferenceHigh expressionSugar derivativesTransferasesNucleotideSecretory protein
The present invention relates to an expression vector comprising, in 5′ to 3′ direction, a promoter, a multiple cloning site and a nucleotide sequence encoding glutathione-S-transferase (GST), for production of a fusion protein comprising a membrane protein, secretory protein or toxic protein or peptide, fused directly or indirectly with the N-terminal of GST. Preferably, the fusion protein comprises GST and a membrane protein or membrane localised peptide. The invention is especially suitable for membrane proteins having their C-terminals in the cytoplasm. The invention also relates to methods for producing such fusion proteins using host cells transformed with the expression vector in which a desired gene has been cloned.
Owner:BIRSE DARCY +1
Kit for genetic detection of breast cancer
InactiveCN101608225AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceEstrogen receptor
The invention discloses a kit for genetic detection of breast cancer. The kit comprises a specific primer pair and a specific probe pair which are used for detecting the mononucleotide polymorphism loci genotype of an estrogen receptor alpha gene (ER-alpha), a catechol-o-methyltransferas gene (COMT), a glutathione-s-transferase P1 gene (GSTP1), a human breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 (BRCA1), and a human breast cancer susceptibility gene 2(BRCA2), a fluorescent quantitative PCR general component and the like. The kit can evaluate the genetic risk of individuals suffered from the breast cancer by detecting the polymorphism loci genotype of the genes closely related to the genetic risk of the breast cancer at the same time.
Owner:XINBAXIANG SHANGHAI MOLECULAR MEDICAL TECH SHANGHAI
cDNA of glutathione-s-transferase (GST) gene in ostrinia furnacalis and method for constructing RNAi interference engineering bacteria of GST gene in ostrinia furnacalis
InactiveCN102181460AInhibition of growth and developmentReduced toleranceBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention relates to cDNA of a glutathione-S-transferase (GST) gene and a method for constructing RNAi interference engineering bacteria of the GST gene, in particular to cDNA of a glutathione-S-transferase (GST) gene in ostrinia furnacalis and a method for constructing RNAi interference engineering bacteria of the GST gene in the ostrinia furnacalis. The nucleotide sequence and amino acid sequence of the GST gene in the ostrinia furnacalis respectively refer to SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. The method comprises the following steps: 1. extracting the total DNA of the ostrinia furnacalis, synthesizing the first cDNA chain, designing primers and carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification to obtain Of-GST-RNAi320; 2. carrying out double digestion on Of-GST-RNAi320 and L4440, recovering the needed target fragments and connecting the target fragments and constructing L4440-Of-GST; and 3. transforming L4440-Of-GST to escherichia coli HT115 (DE3), thus completing the construction. The method is simple to operate, is low in cost and has obvious effect on inhibiting growth and development of the ostrinia furnacalis.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Fugu rubripes nervous necrosis virus capsid protein egg yolk antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN104725503AExpression continues to be stableHigh potencyEgg immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against virusesEscherichia coliInclusion bodies
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnologies, and particularly relates to a fugu rubripes nervous necrosis virus capsid protein egg yolk antibody and an application of the egg yolk antibody. The egg yolk antibody is prepared by a method comprising the following steps that: a fugu rubripes nervous necrosis virus capsid protein gene is recombined to a GST (Glutathione S-Transferase) fusion gene expression vector pGEX-5x-1; a pGEX-5x-1-CP recombinant plasmid is constructed and transformed into escherichia coli, and induces a fusion gene to express; a GST-CP recombinant protein is obtained by extraction and purification with an inclusion body purification technology; a hen is immunized by the GST-CP recombinant protein; a hen egg is collected; and the egg yolk antibody is extracted from the hen egg. The prepared egg yolk antibody can effectively inhibit a fugu rubripes nervous necrosis virus, is high in titer, has good immune protection efficacy, and can serve as a nervous necrosis virus vaccine to be added to fish feed in a juvenile fish period of fish.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV +1
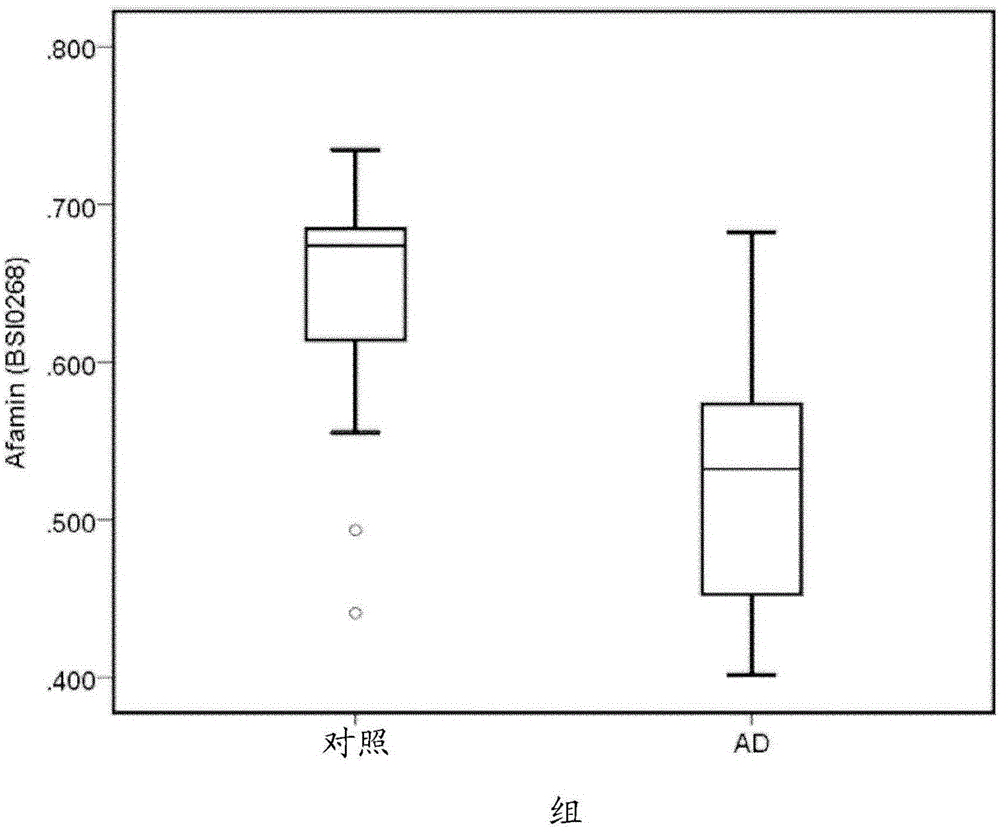
Methods and compositions for the diagnosis of alzheimer's disease
ActiveCN105164536AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsSerine/Threonine-Protein Kinase TBK1Apolipoprotein E
The present invention relates to methods for the diagnosis of subjects that have or are at risk of having Alzheimer's disease (AD). In particular the present invention identifies individuals who have or are at risk of having AD through measurement of the levels of Afamin in combination with at least one other biomarker such as Alpha-1-antichymotrypsin, Alpha-2- macroglobulin, ApoB 100, Complement C5, Serine threonine protein kinase TBK1 or Complement C3 in a fluid sample taken from a subject. Furthermore, genotype (ApoIipoprotein E or glutathione S-transferase Omega) may also be taken into consideration and used within classification algorithms to determine the probability of a subject having or being at risk of having AD.
Owner:兰道克斯有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com