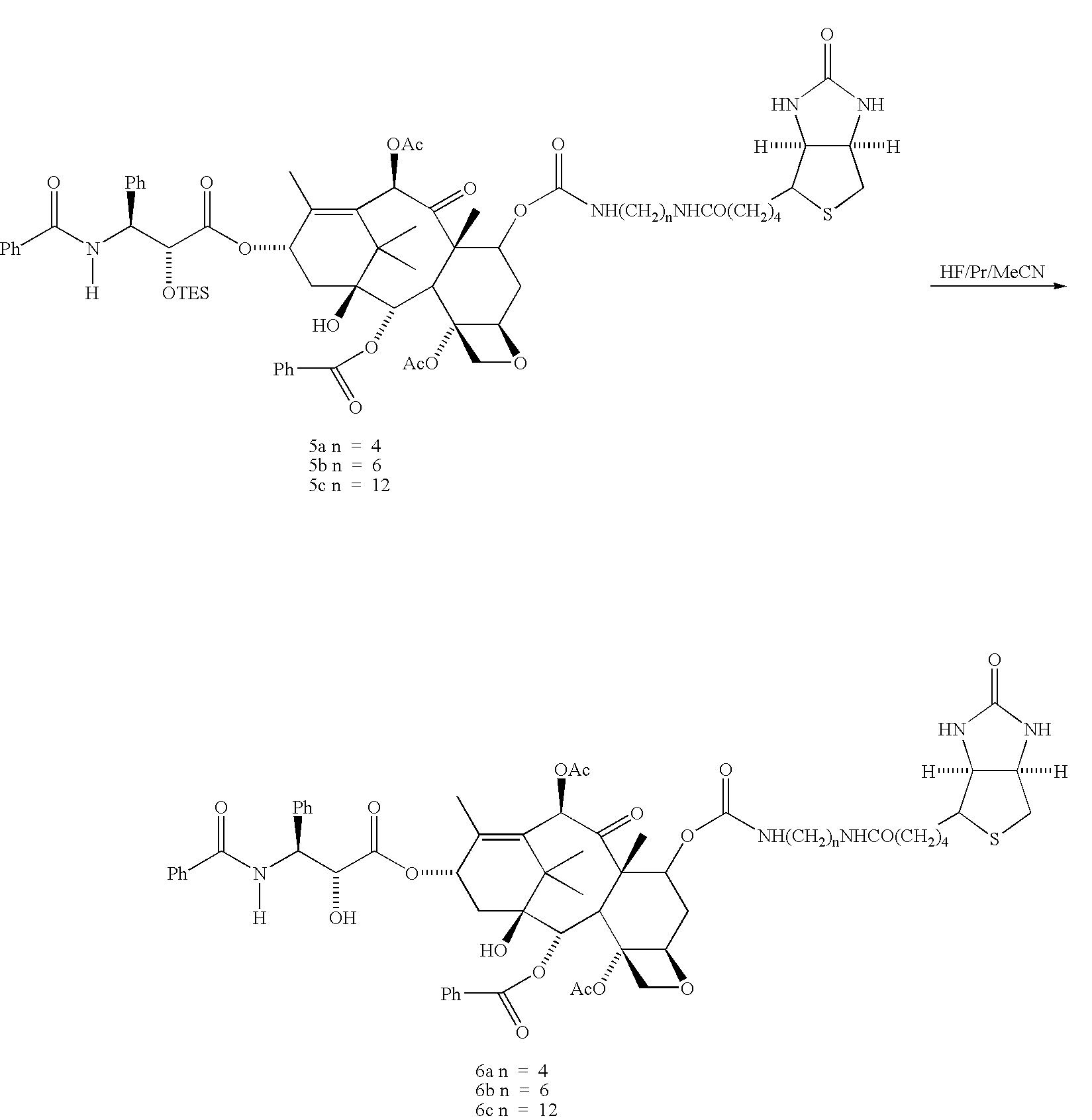
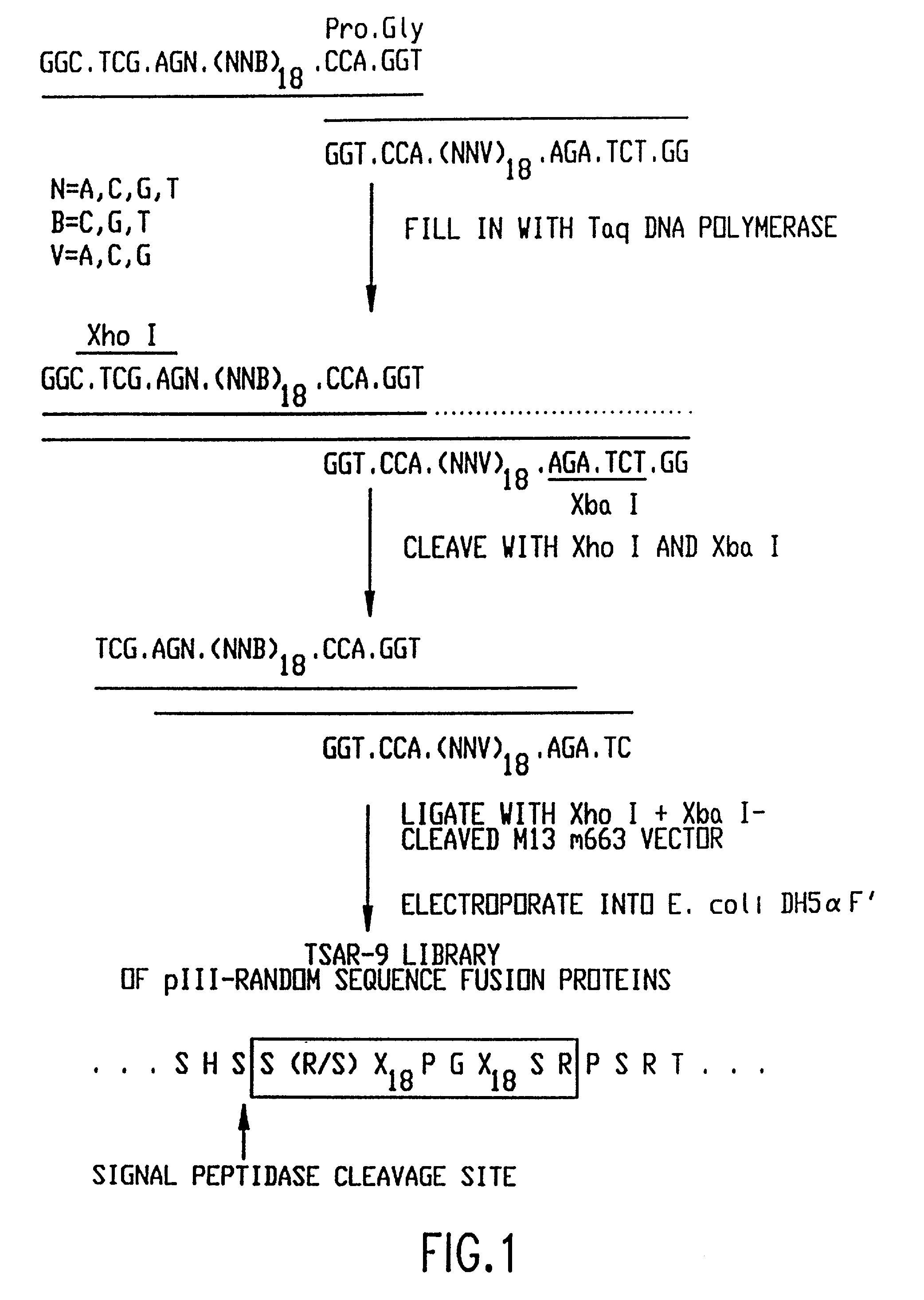
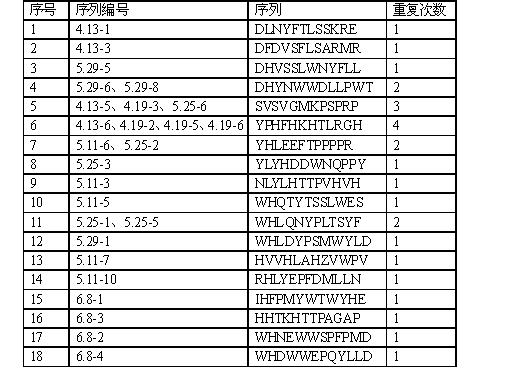
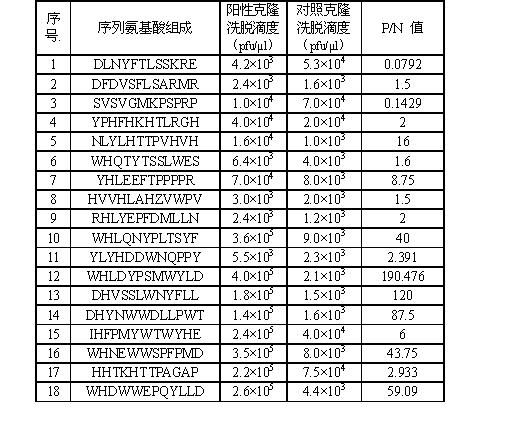
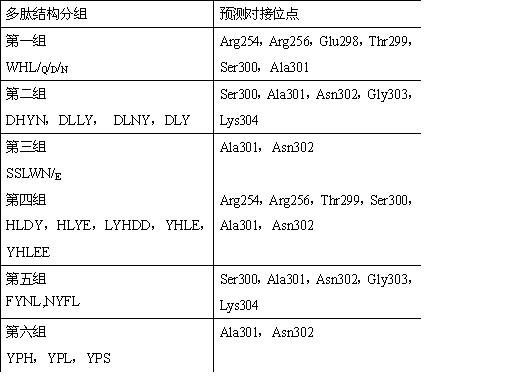
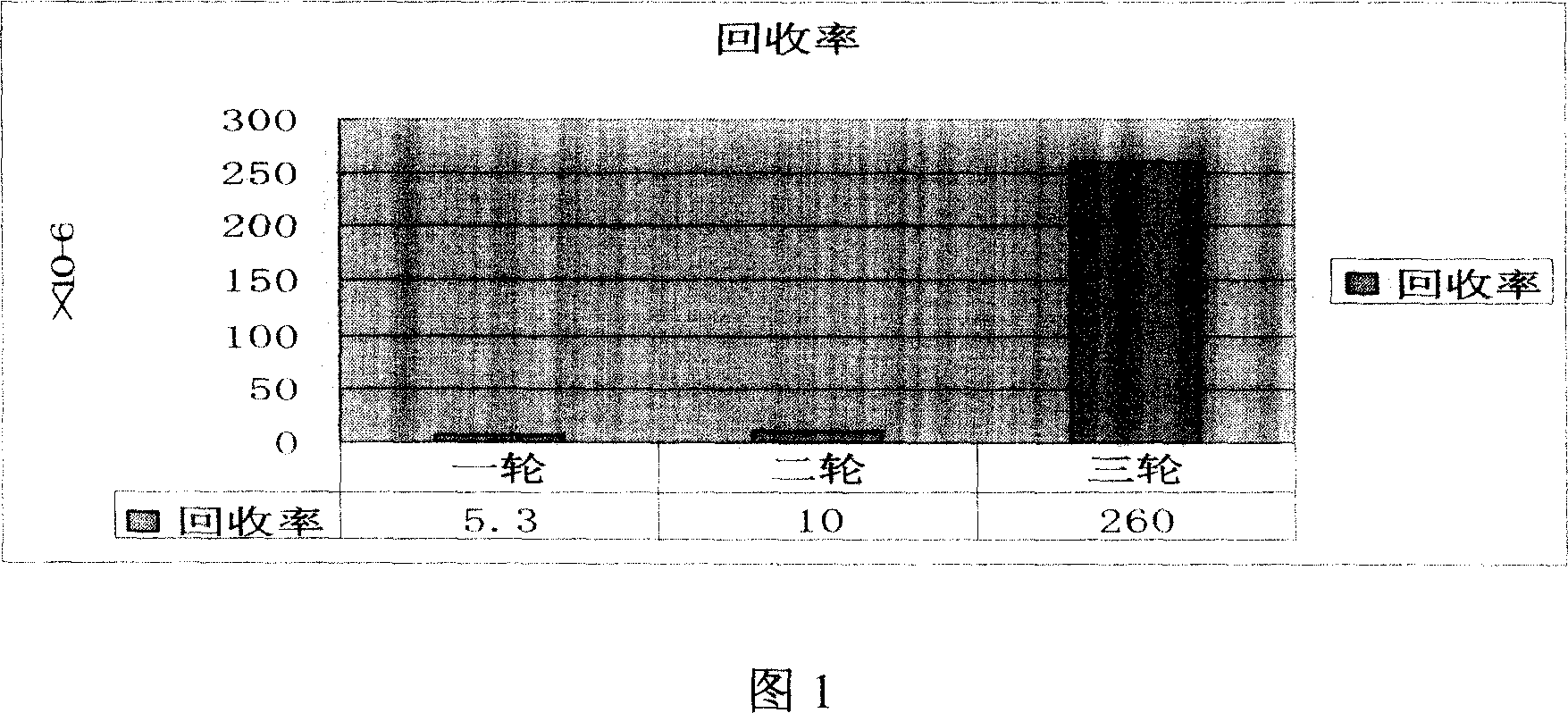
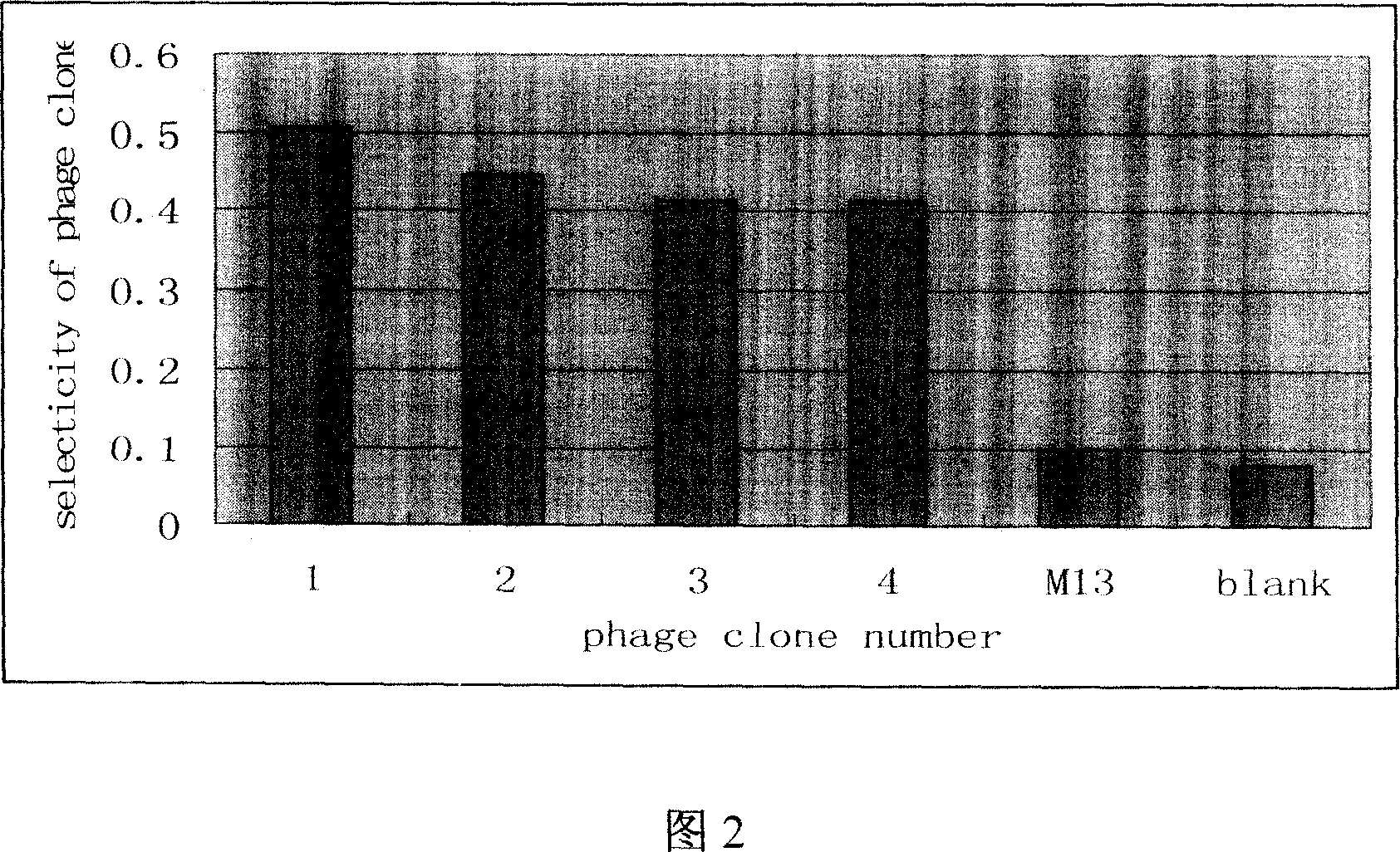
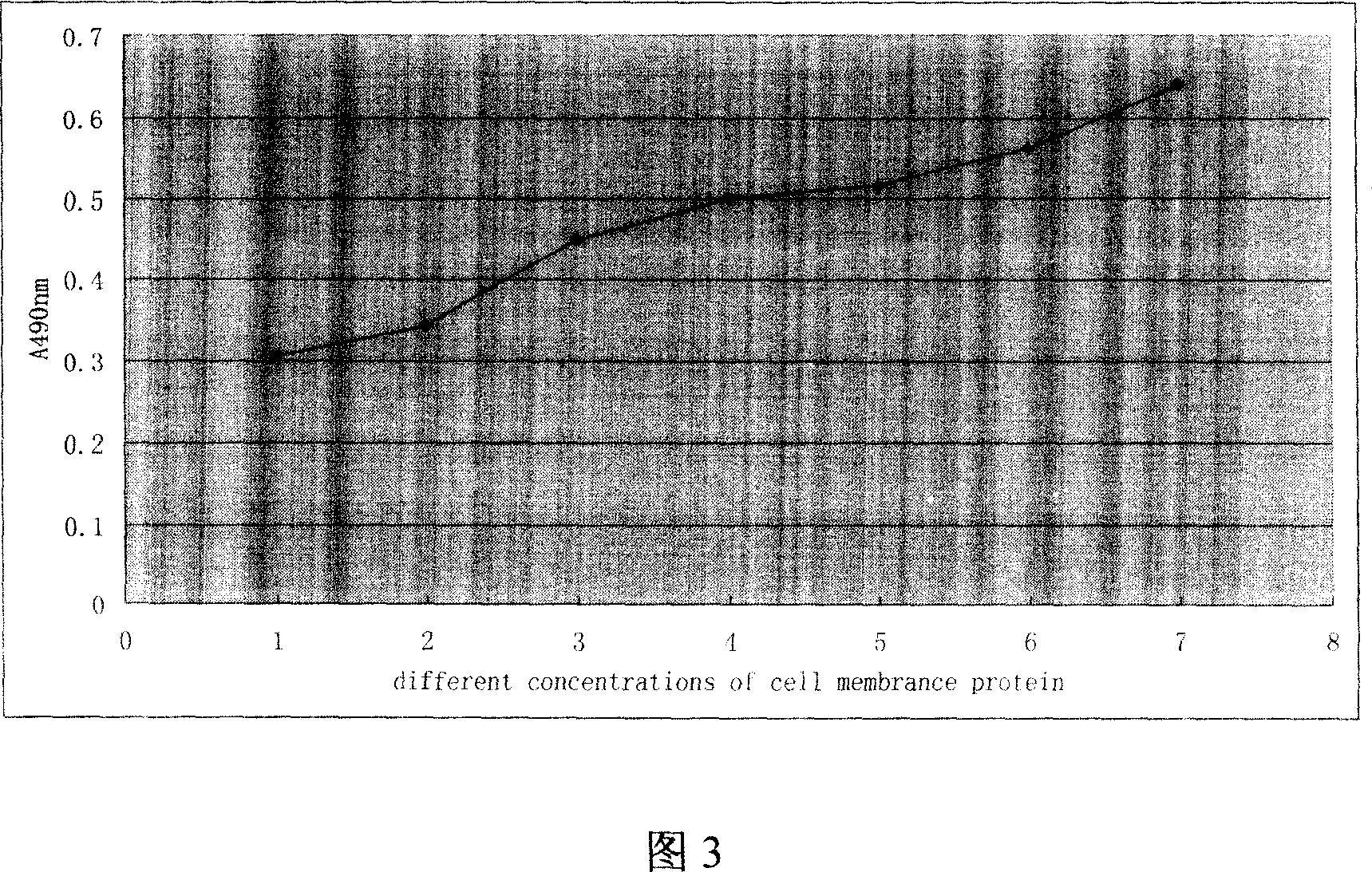
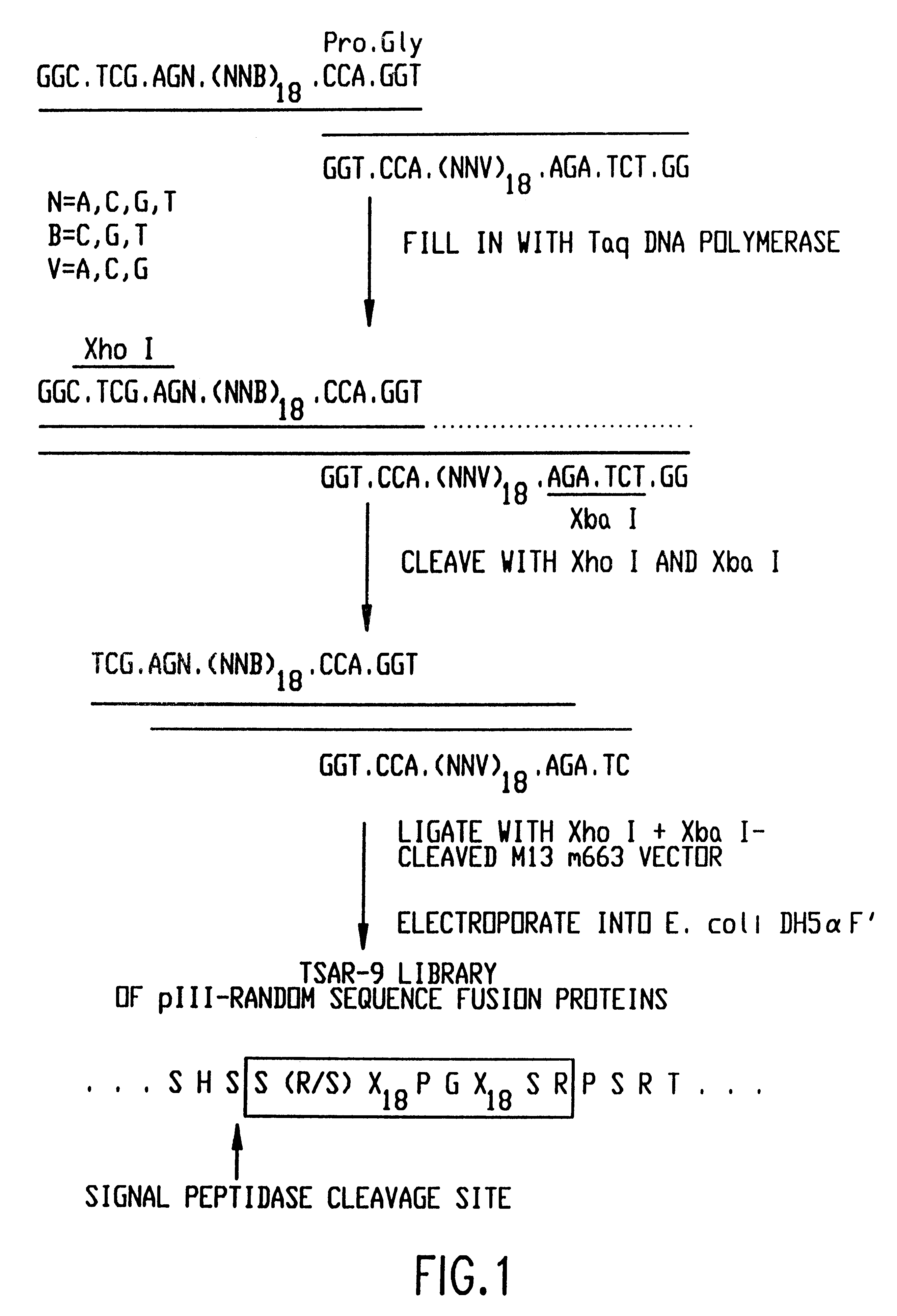
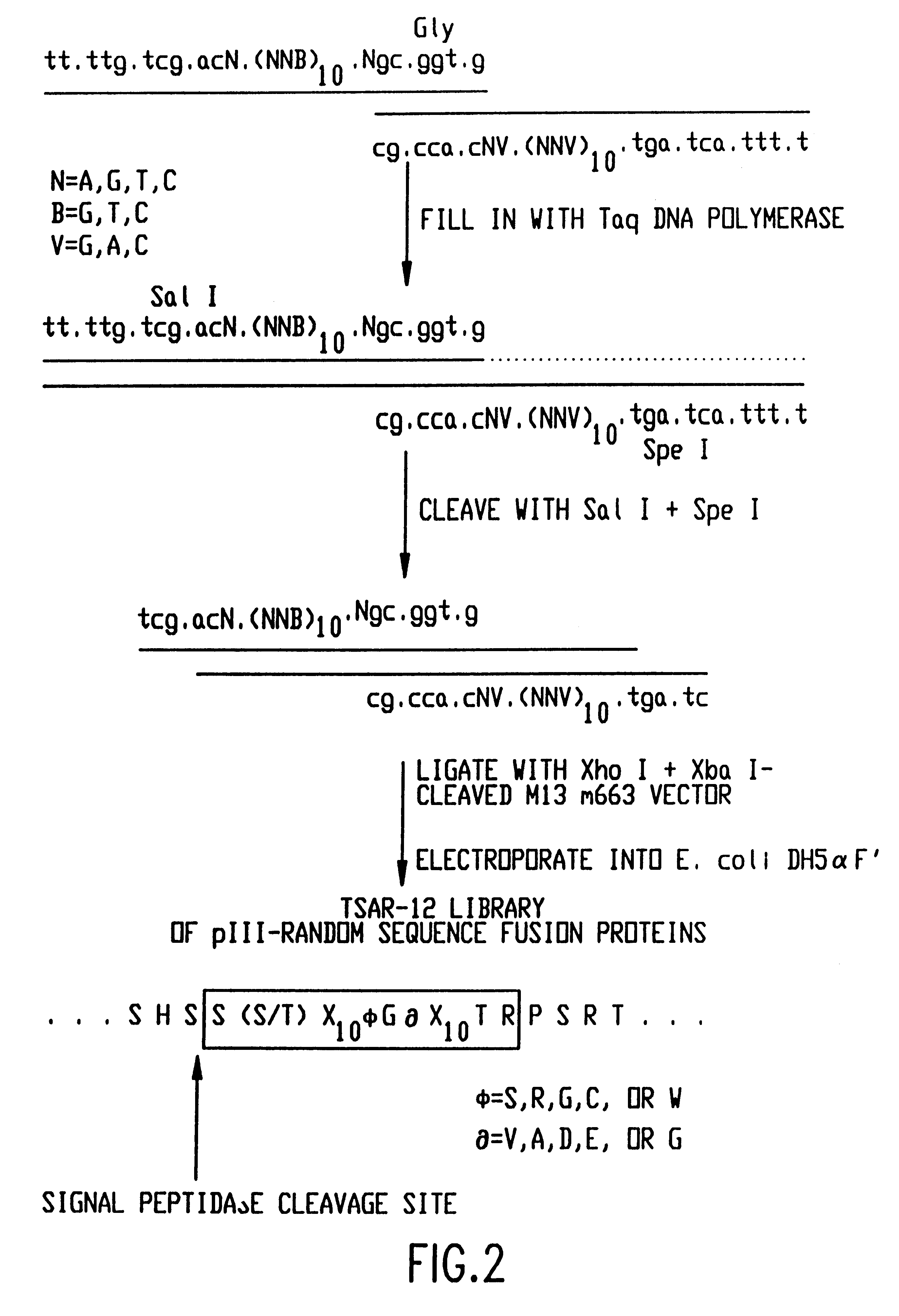
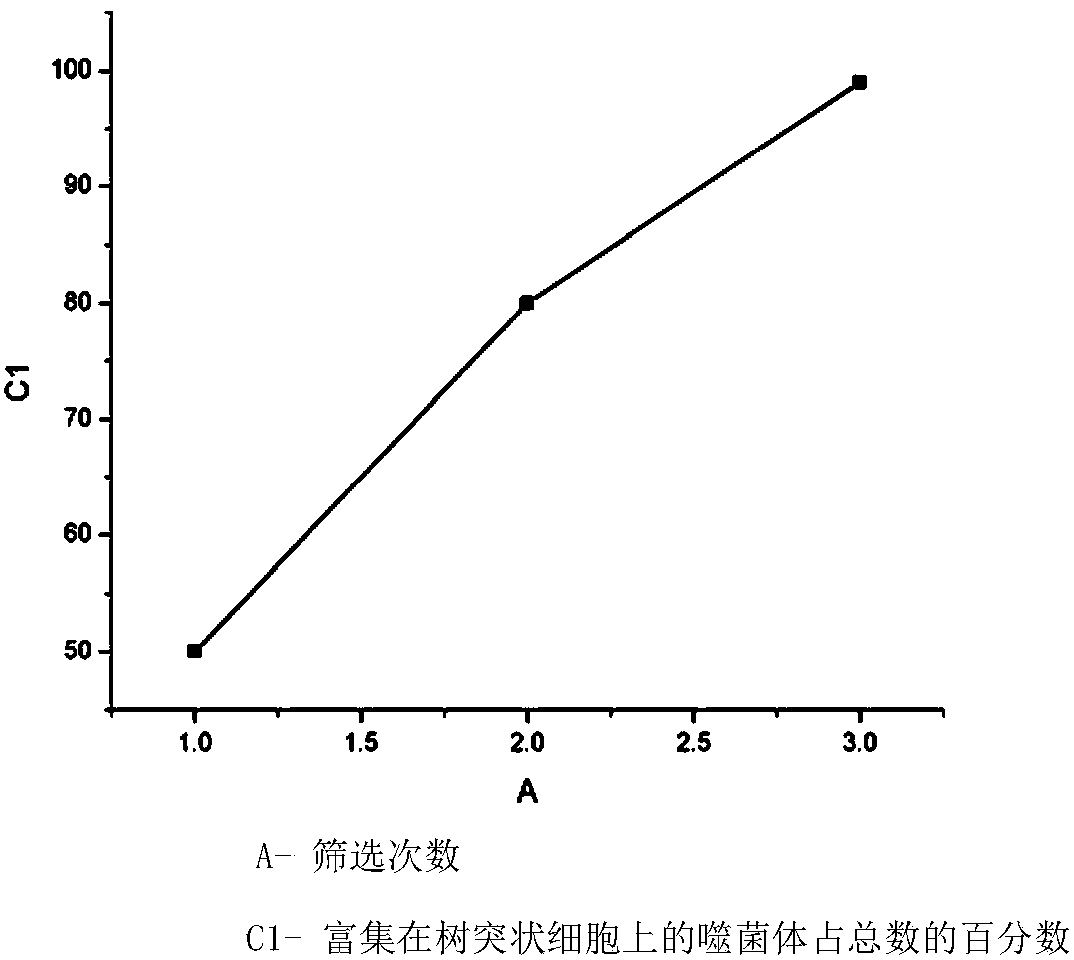
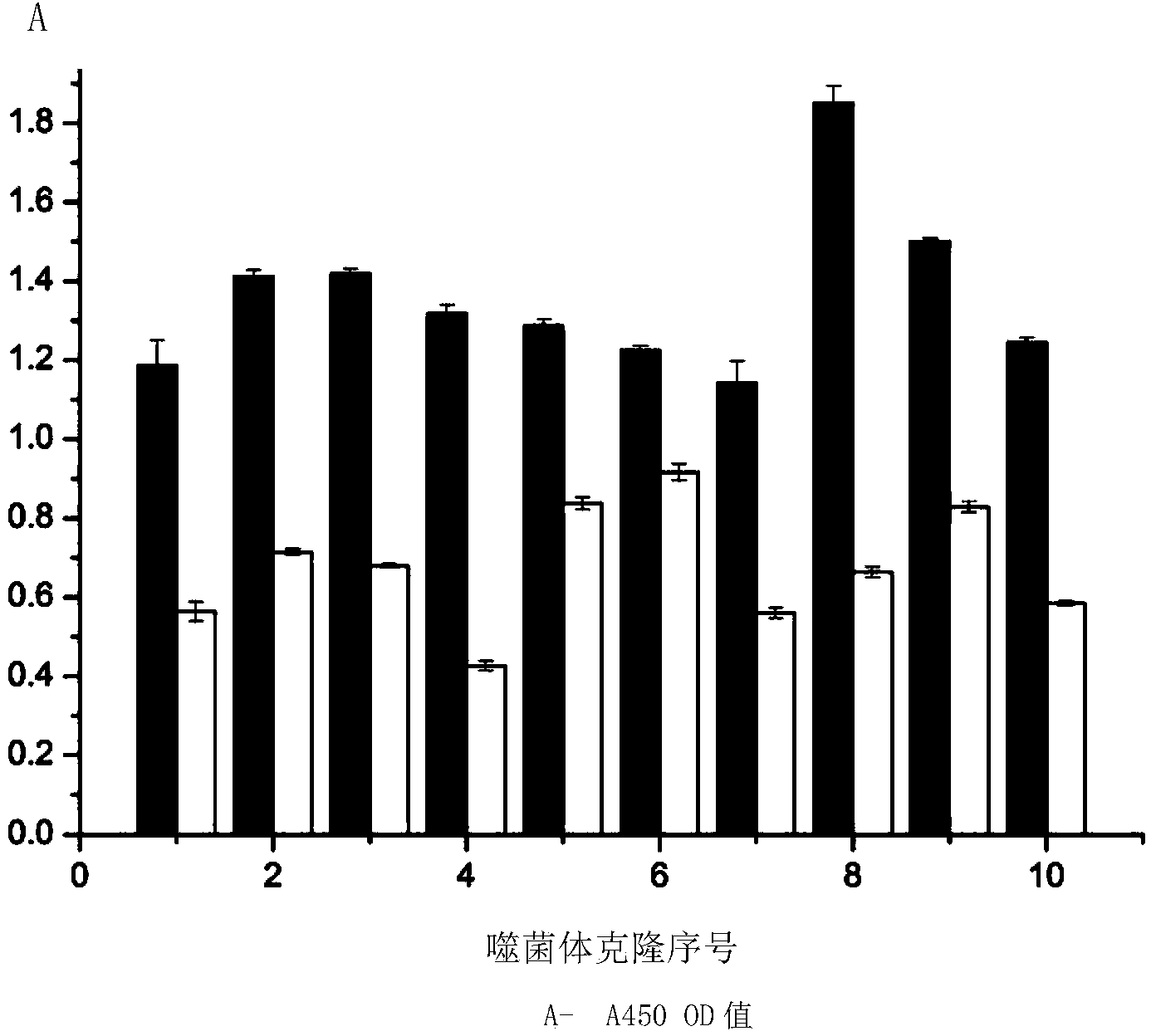
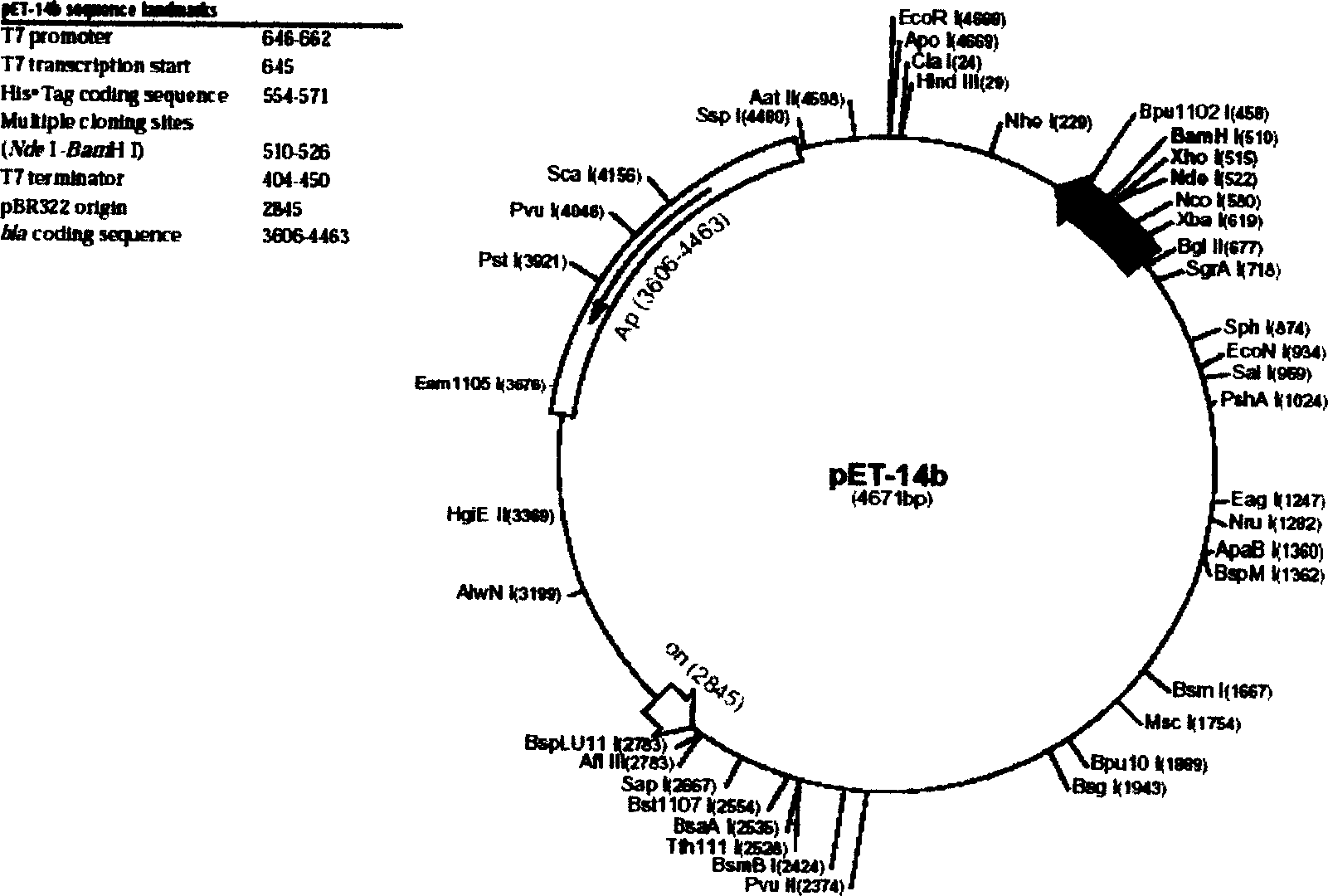
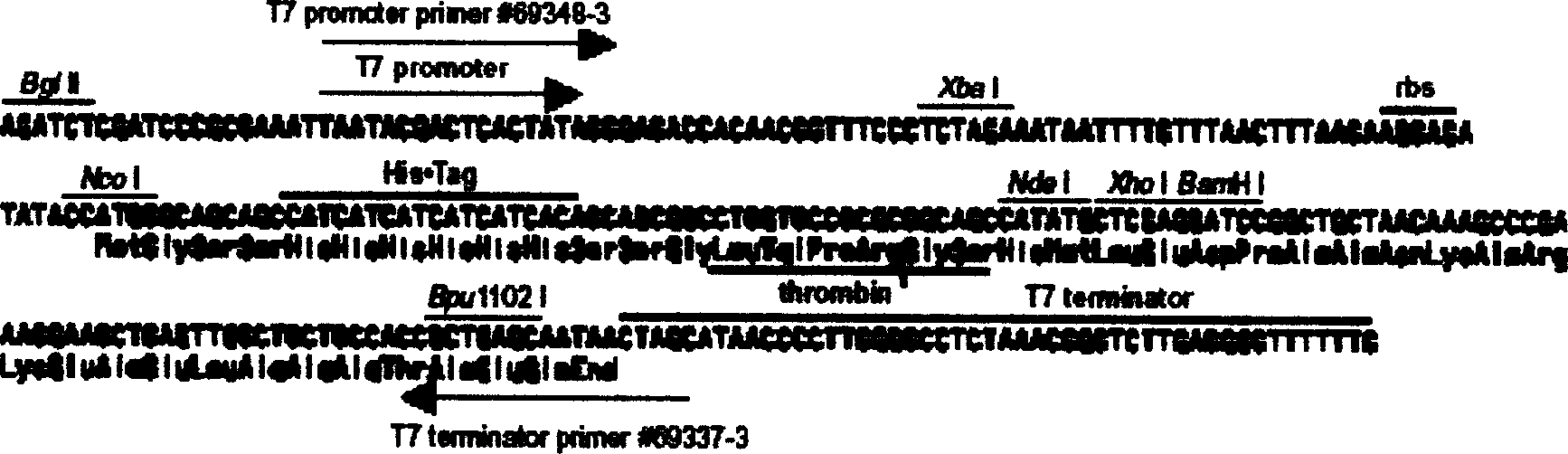
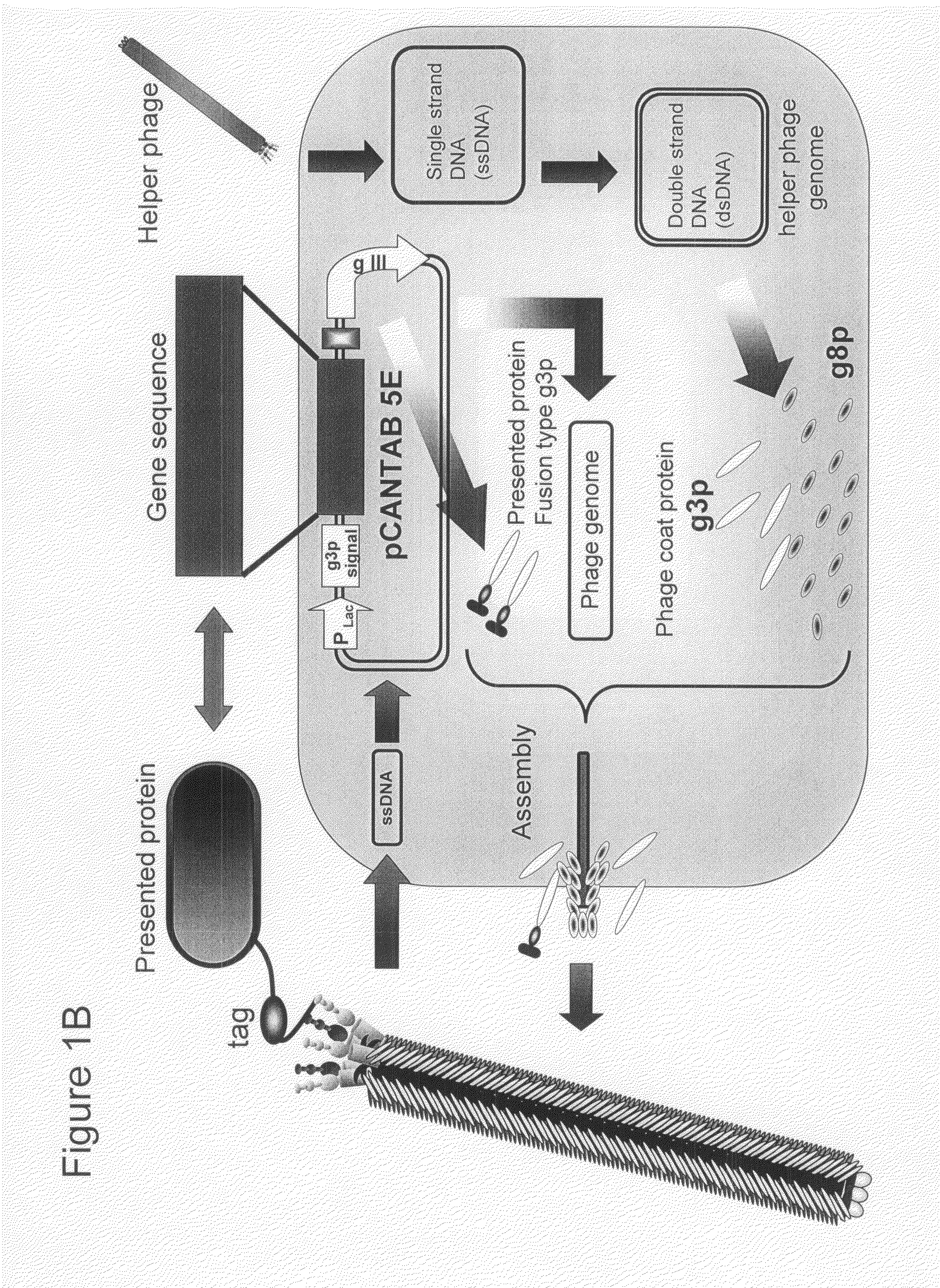
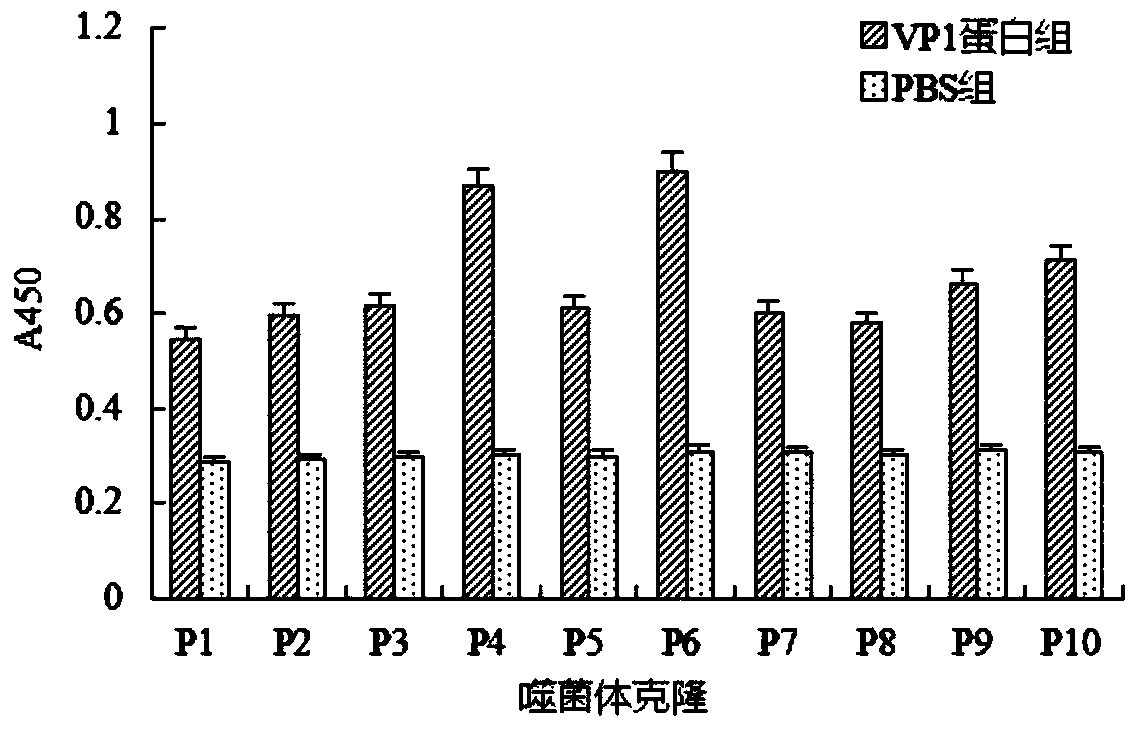
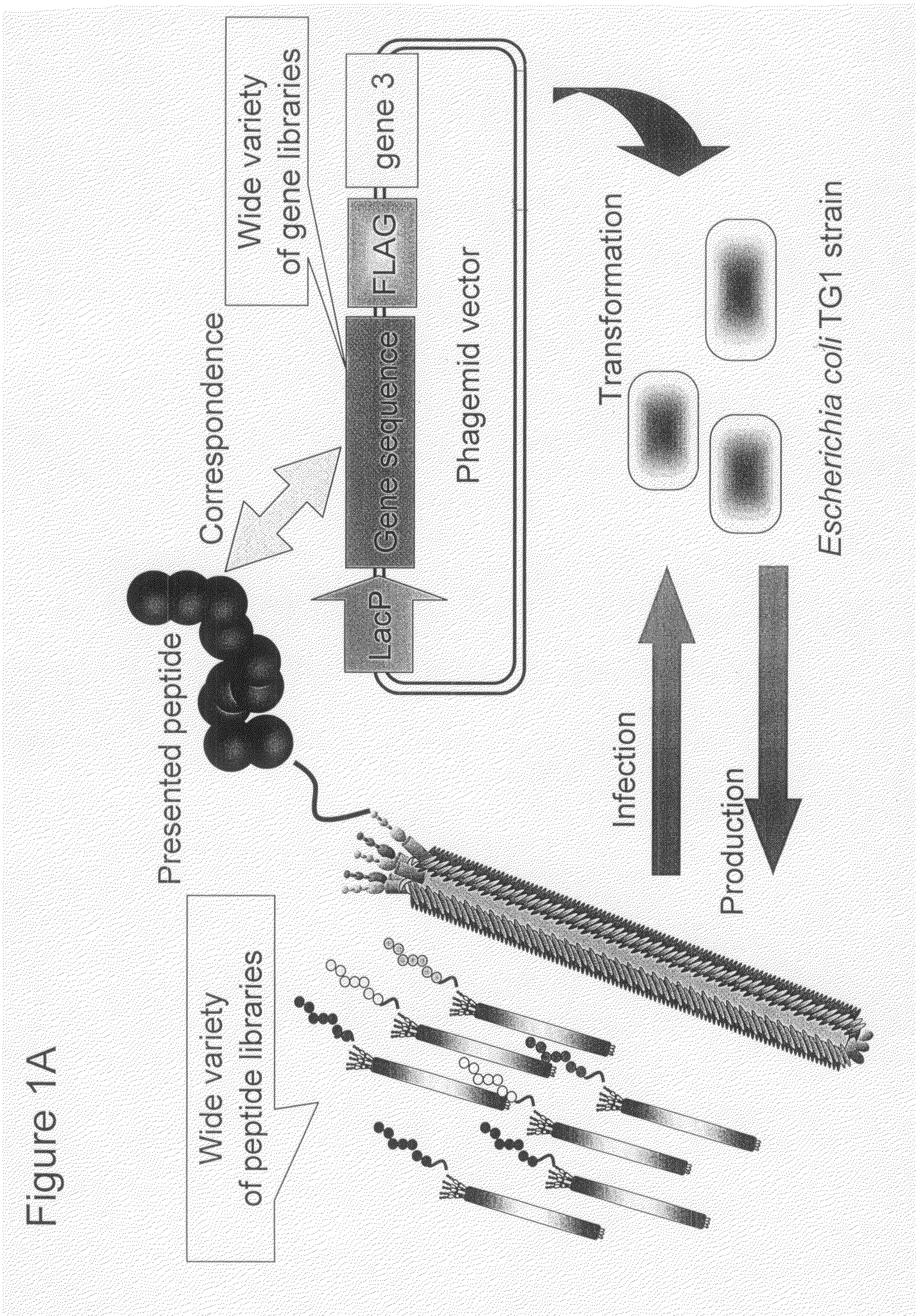Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
59 results about "Random Peptide Library" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
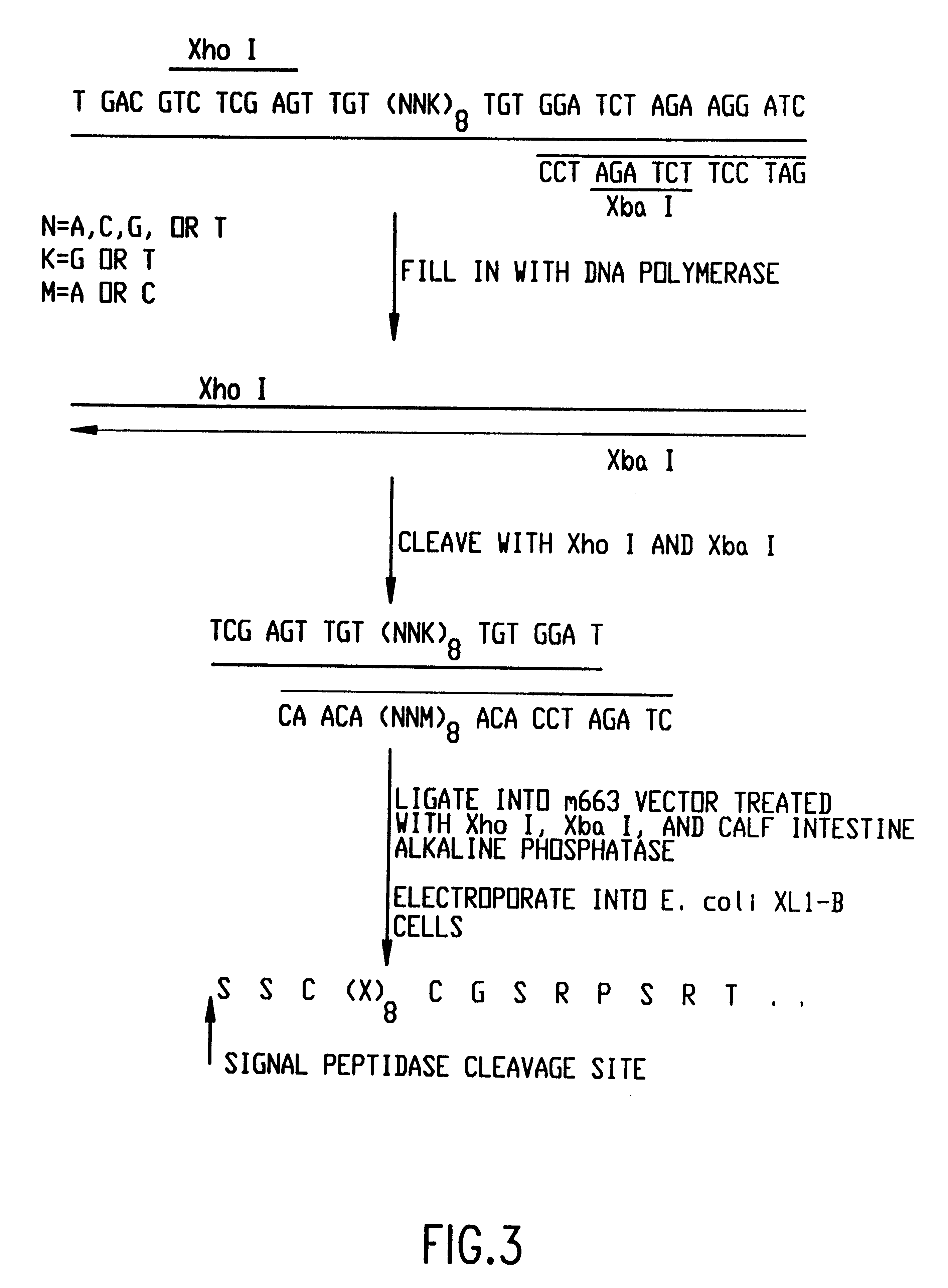
Random peptide library displayed on aav vectors
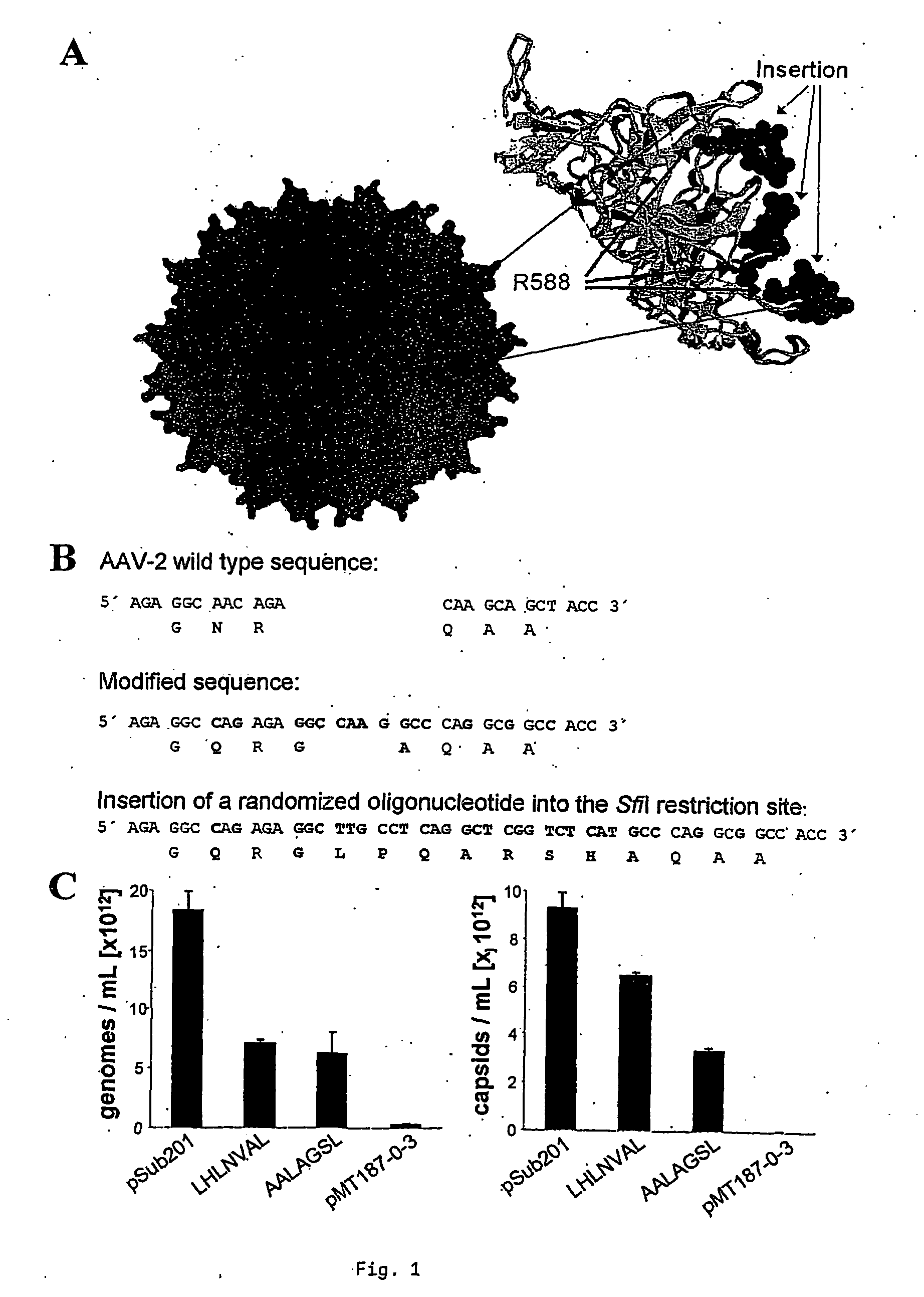
Described is a method of producing a repertoire of random peptides on the surface of AAV particles wherein said random peptides are expressed as a fusion with an AAV capsid protein of an AAV particle which displays at its surface said random polypeptides. Also described is a peptide library obtainable by said method as well as a method of selecting a gene therapy vector specific for a desired cell type comprising the steps of (a) infecting the desired cell type with a peptide library of the invention and (b) harvesting AAV library particles from the supernatant and / or cell lysates. Finally, AAV vectors obtained by said method are described which are useful for gene therapy, e.g., AAV vectors targeting primary human coronary artery endothelial cells which are suitable for the treatment of diseases associated with a dysfunction of said cells.
Owner:KLEINSCHMIDT JURGEN +4
GRB2 SH3 binding peptides and methods of isolating and using same
InactiveUS6184205B1Increase ratingsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRandom Peptide LibraryADAMTS Proteins
Peptides having general and specific binding affinities for the Src homology region 3 (SH3) domains of proteins are disclosed in the present invention. In particular, SH3 binding peptides have been isolated from phage-displayed random peptide libraries which had been screened for isolates that bind to bacterial fusion proteins having an SH3 domain and glutathione S-transferase (GST). Preferred peptides are disclosed which comprise a core 7-mer sequence (preferably, a consensus motif) and two or more, preferably at least six, additional amino acid residues flanking the core sequence, for a total length of 9, preferably at least 13, amino acid residues and no more than about 45 amino acid residues. Such peptides manifest preferential binding affinities for certain SH3 domains. The preferred peptides exhibit specific binding affinities for the Src-family of proteins. In vitro and in vivo results are presented which demonstrate the biochemical activity of such peptides.
Owner:CYTOGEN CORP +1
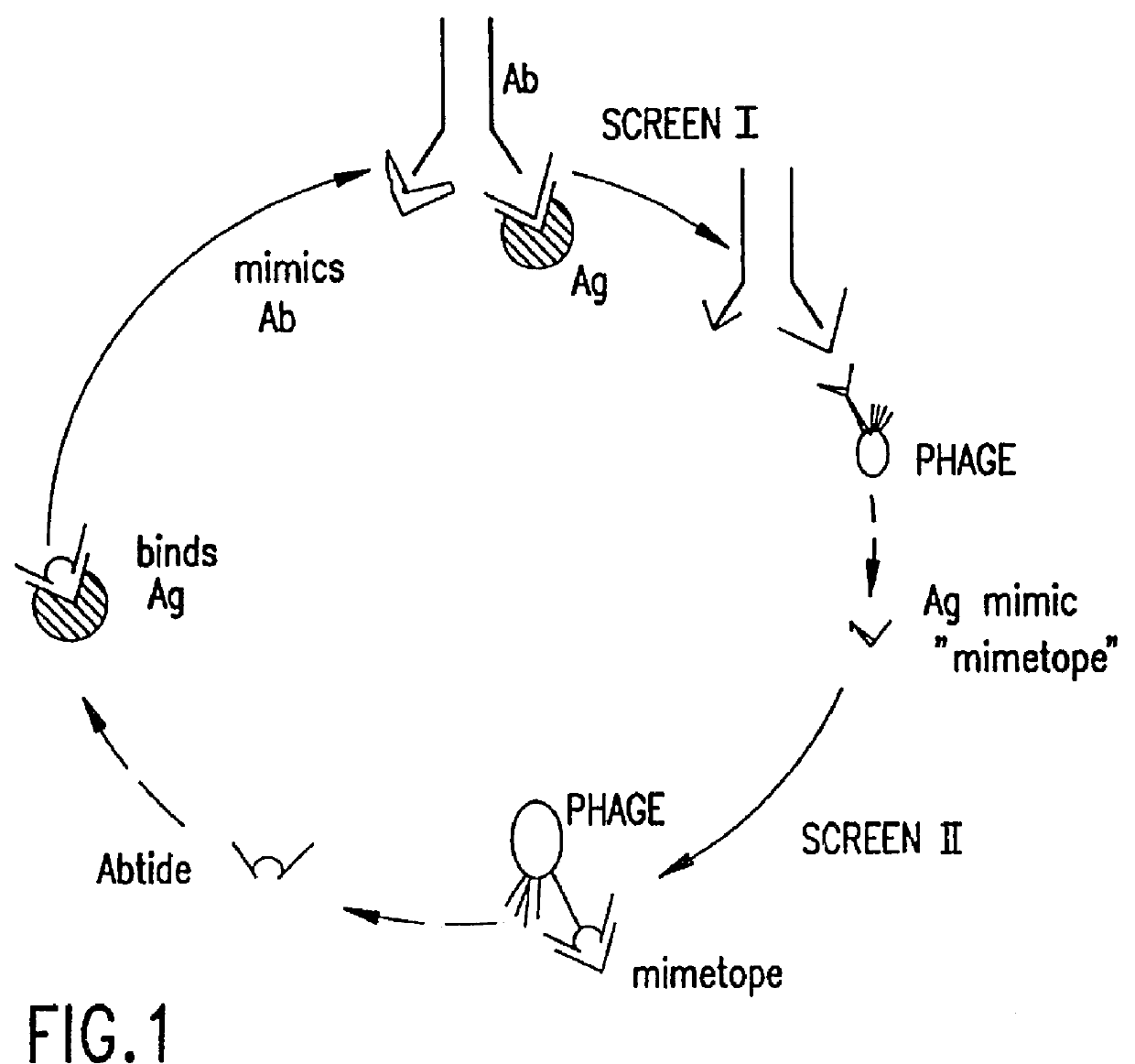
Antigen binding peptides (abtides) from peptide libraries
InactiveUS6015561AEasy to produceLow costPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRandom Peptide LibraryBinding peptide
Abtides are provided. Abtides are peptides identified by a two-step process of screening random peptide libraries. In the first step, the target ligand is an antibody or receptor (or derivative thereof). The peptides identified in the first screening step are used as target ligands in the second screening step. The peptides identified in the second screening step are abtides. Abtides possess binding specificities that are similar to the binding specificities of the antibodies or receptors that are used in the first screening step. Abtides may be used in place of antibodies in many assays or therapeutic applications. Abtides binding to polymorphic epithelial mucin (PEM) are provided. Also provided are methods of obtaining abtides as well as diagnostic and therapeutic compounds containing abtides.
Owner:CYTOGEN CORP
Polypeptide composition for detecting serum marker of autoimmune disease patient and application of polypeptide composition
The invention discloses a polypeptide composition for detecting a serum marker of an autoimmune disease patient and an application of the polypeptide composition and belongs to the technical field of medicines. Polypeptide with bonding capability on the serum marker of an autoimmune disease is screened out from a phage random peptide library, and is applied to immunological detection of the serum marker through artificial synthesis. The polypeptide composition comprises all or partial sequences as shown in SEQID NO.1-19. In addition, the invention further discloses a chip comprising the polypeptide composition, an enzyme-linked immune response plate and a kit. The obtained polypeptide sequences have good bonding capability on the serum marker of the autoimmune disease patient, and can be applied to diagnosis and evaluation of the autoimmune disease.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Targetted polypeptide for specificity of liver cancer blood vessel
InactiveCN1552727APeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemRandom Peptide LibraryVascular endothelium
A liver cancer blood vessel specific target polypeptide LCI-X7 able to specific binding with liver cancer blood vessel is extracted from the naked mouse model of human liver cancer by the showing technique of phage random peptide library in body and microscopic laser cutting technique. It provides important theory and practical basis for the diagnosis to liver cancer transfer recurrence and target therapy.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Identification of molecular targets
InactiveUS6897028B1Peptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementSide effectRandom Peptide Library
Identification of the molecular targets of a drug or toxin is the first step in understanding how the drug or toxin works, an important advance in learning how to improve a drug or assess the risks due to a toxin. The primary action of a drug usually involves binding to a protein; secondary actions may express themselves in the form of side effects and in some cases may be due to binding to other proteins. Consequently, it is useful to identify all physiologically relevant sites of action of a drug or toxin. A simple method for obtaining a list of the potential targets of a drug, toxin or other biologically active substance (referred to collectively as ligands) involves a multistep process. The first step is screening a protein or peptide library to identify library members that exhibit high affinity for a particular ligand. The second step involves searching of sequence data bases for proteins that contain the sequences of the library members shown to have high affinity for the ligand. The proteins thus identified constitute a list of potential targets for the ligand. If random peptide libraries have been used, the position of identified consensus sequences within the identified protein constitutes an identification of the potential ligand binding site on the target.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIVERSITY
Src SH3 binding peptides and methods of isolating and using same
InactiveUS20020091085A1Increase ratingsPeptide-nucleic acidsPeptide/protein ingredientsRandom Peptide LibraryBinding peptide
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
High-efficiency binding peptide in DNA binding region protein of FoxM1c and method for acquiring polypeptide structure sequence
The invention discloses a high-efficiency binding peptide in a DNA binding region protein of FoxM1c, a method for acquiring a polypeptide structure sequence and application of a target product. In the invention, protein obtained by inducing and expressing with a pronucleus recombinant plasmid in the DNA binding region of the FoxM1c is used as a target, and a set of targeted FoxM1c high-efficiency binding polypeptides are screened and obtained from a phage random peptide library. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing the pronucleus recombinant plasmid in the DNA binding region of the FoxM1c, carrying out induction expression and protein purified preparation; and screening and analyzing the phage random peptide library on the basis of the DNA binding region protein of the FoxM1c; and screening for four rounds to obtain the binding peptide phage and the polypeptide structure sequence of the enriched and targeted FoxM1c. The target product used as a precursor molecule is used for developing medicaments and diagnosing for treating related diseases of tutors, and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Liver cancer cell specificity internalization short peptide and its in vitro screening and identification
InactiveCN101033251AStrong specificityGood effectLibrary screeningPeptidesSequence analysisWilms tumour
This invention relates to the special short peptide of hepatoma cell internalization and its screen and identification in vitro, belonging to the technology of tumor cell peptides screening and identification. It takes hepatoma cell BEL-7404 as the screening target cell, displays the random 12-peptide library for bacteria invader to conduct affinity panning. Through three times of screen, it randomly selects twenty negative colonies for amplification and sequence, to deduct the amino acid sequence of random peptide. Through cell ELISA, immunofluorescence, flow cytometry and other method, it further identifies the combination and internalization of bacteria invader clones and hepatoma cells. From sequencing and sequence analysis of the positive clones, four obtained different sequences have good combination with hepatoma cells, and the screened monoclone can internalize cells.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Structure and application of influenza virus hemagglutinin protein binding polypeptide
InactiveCN102268072ACytopathic inhibitionNo obvious toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesDiseaseHemagglutinin
Belonging to the technical field of biomedicine, the invention relates to a sequence and structure of a polypeptide able to specifically bind with influenza virus hemagglutinin protein, and application of the polypeptide in anti-influenza viruses. By expressing purified influenza virus hemagglutinin protein and screening a random peptide library with a phage display technology, a polypeptide specifically bound with influenza virus hemagglutinin and equipped with sequences numbered 1-18 can be obtained. As a hemagglutinin-binding peptide can hinder the combination of hemagglutinin and a host cell receptor, so the influenza virus can be inhibited from infecting the host cell. Thus, the invention also conducts an anti-influenza virus activity study to the hemagglutinin-binding peptide selected from the phase peptide library, and finds that a polypeptide H17, with a sequence of NH2-SHGRITFAYFAN-COOH, can effectively inhibit the influenza virus from infecting the host cell and is of small toxicity. Therefore, the hemagglutinin-binding peptide of the invention and the H17 polypeptide therein with an anti-influenza virus activity are expected to become novel treatment medicaments for treating diseases caused by influenza virus infection and reducing the hazards of diseases caused by influenza viruses.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
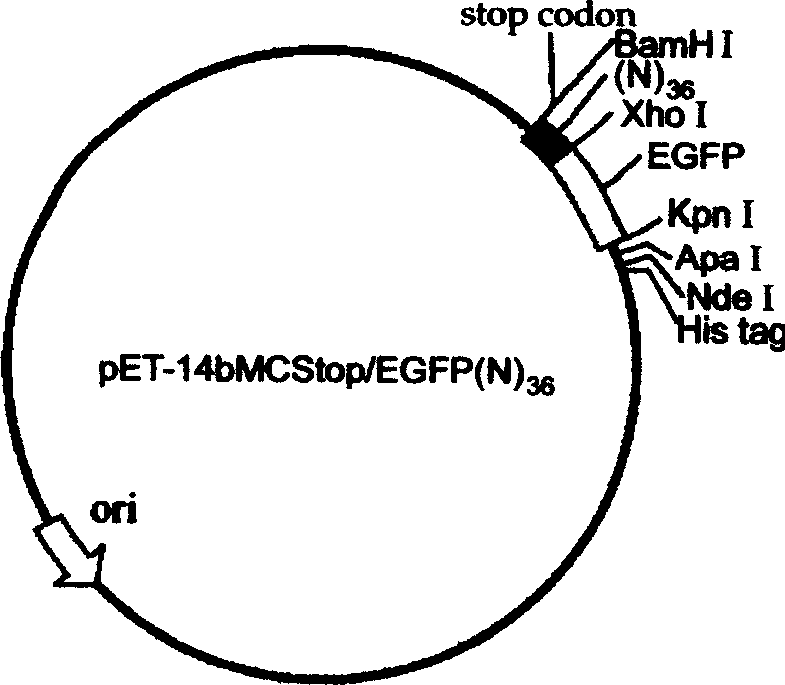
Structurally biased random peptide libraries based on different scaffolds
InactiveUS6936421B2BacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGreen fluorescent proteinRandom Peptide Library
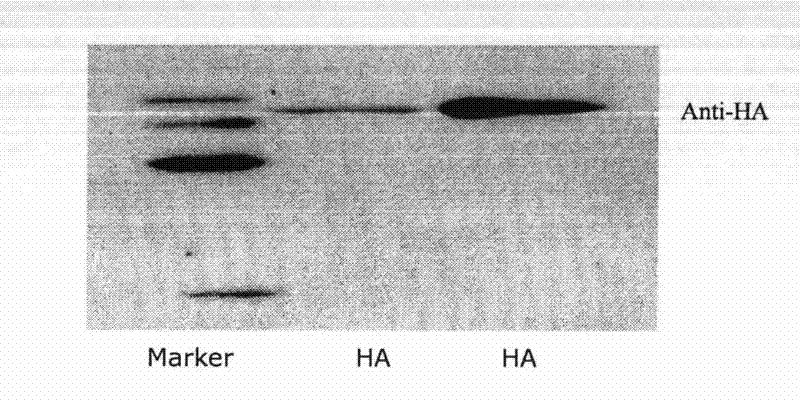
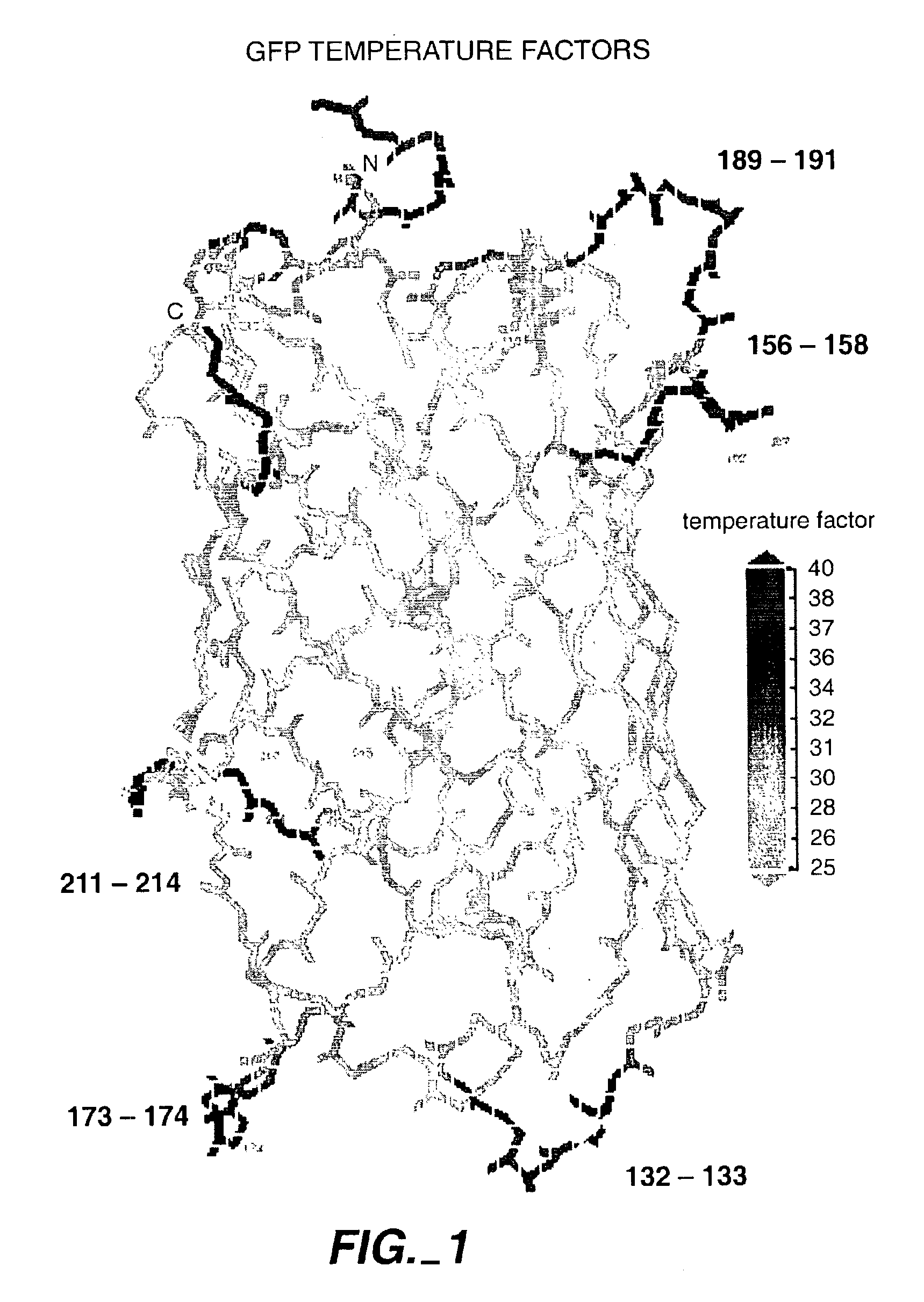
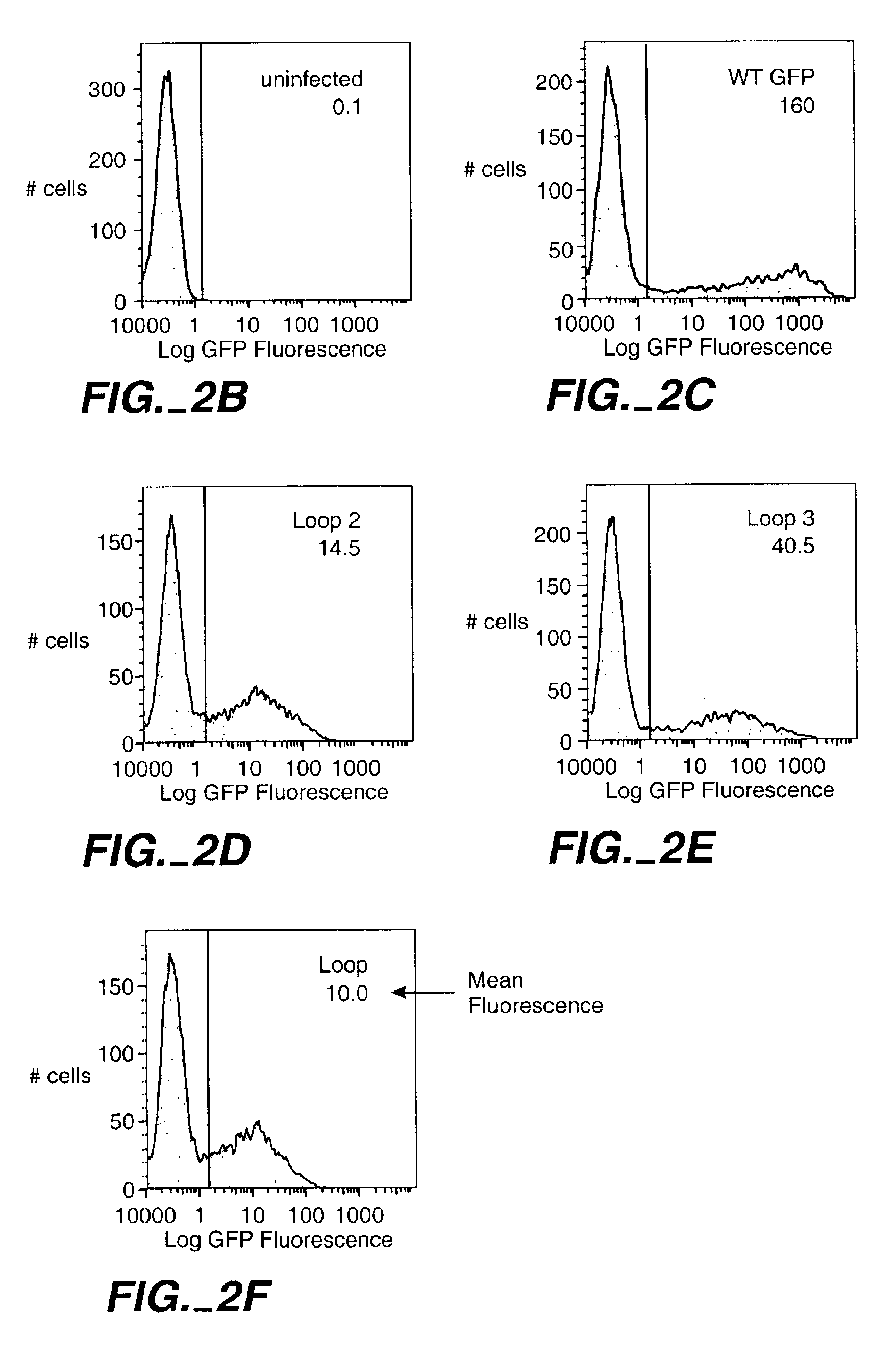
The invention relates to the use of scaffold proteins, particularly green fluorescent protein (GFP), in fusion constructs with random and defined peptides and peptide libraries, to increase the cellular expression levels, decrease the cellular catabolism, increase the conformational stability relative to linear peptides, and to increase the steady state concentrations of the library peptides and peptide library members expressed in cells for the purpose of detecting the presence of the peptides and screening peptide libraries. N-terminal, C-terminal, dual N- and C-terminal and one or more internal fusions are all contemplated. Novel fusions utilizing self-binding peptides to create a conformationally stabilized fusion domain are also contemplated.
Owner:RIGEL PHARMA
Nck SH3 binding peptides
InactiveUS6432920B1Increase ratingsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRandom Peptide LibraryBinding peptide
Peptides having general and specific binding affinities for the Src homology region 3 (SH3) domains of proteins are disclosed in the present invention. In particular, SH3 binding peptides have been isolated from phage-displayed random peptide libraries which had been screened for isolates that bind to bacterial fusion proteins having an SH3 domain and glutathione S-transferase (GST). Preferred peptides are disclosed which comprise a core 7-mer sequence (preferably, a consensus motif) and two or more, preferably at least six, additional amino acid residues flanking the core sequence, for a total length of 9, preferably at least 13, amino acid residues and no more than about 45 amino acid residues. Such peptides manifest preferential binding affinities for certain SH3 domains. The preferred peptides exhibit specific binding affinities for the Src-family of proteins. In vitro and in vivo results are presented which demonstrate the biochemical activity of such peptides.
Owner:CYTOGEN CORP +1
Dendritic cell targeted peptide, coding gene and application
InactiveCN104387453APrecise positioningEfficient presentationMacromolecular non-active ingredientsHybrid peptidesDendritic cellRandom Peptide Library
The invention discloses a dendritic cell targeted peptide, a coding gene and an application. The dendritic cell targeted peptide is named NP. The amino acid sequence of the dendritic cell targeted peptide is shown in SEQ ID NO.1 in a sequence table. One efficiently targeted dendritic cell targeted peptide is screened out of numerous short peptides by using a dendritic cell as the target cell and reducing and screening phage random peptide libraries in a subtractive manner. The antigen presenting capacity of the dendritic cell and the capacity of the dendritic cell in killing most tumors, such as cervical cancers and breast cancers are obviously improved through fusion of the dendritic cell targeted peptide and a tumor-associated antigen MUC1. The dendritic cell targeted peptide has wide application value in diagnosis and treatment of most cancers.
Owner:SHENZHEN TONGKANG BIOLOGICAL PHARMA
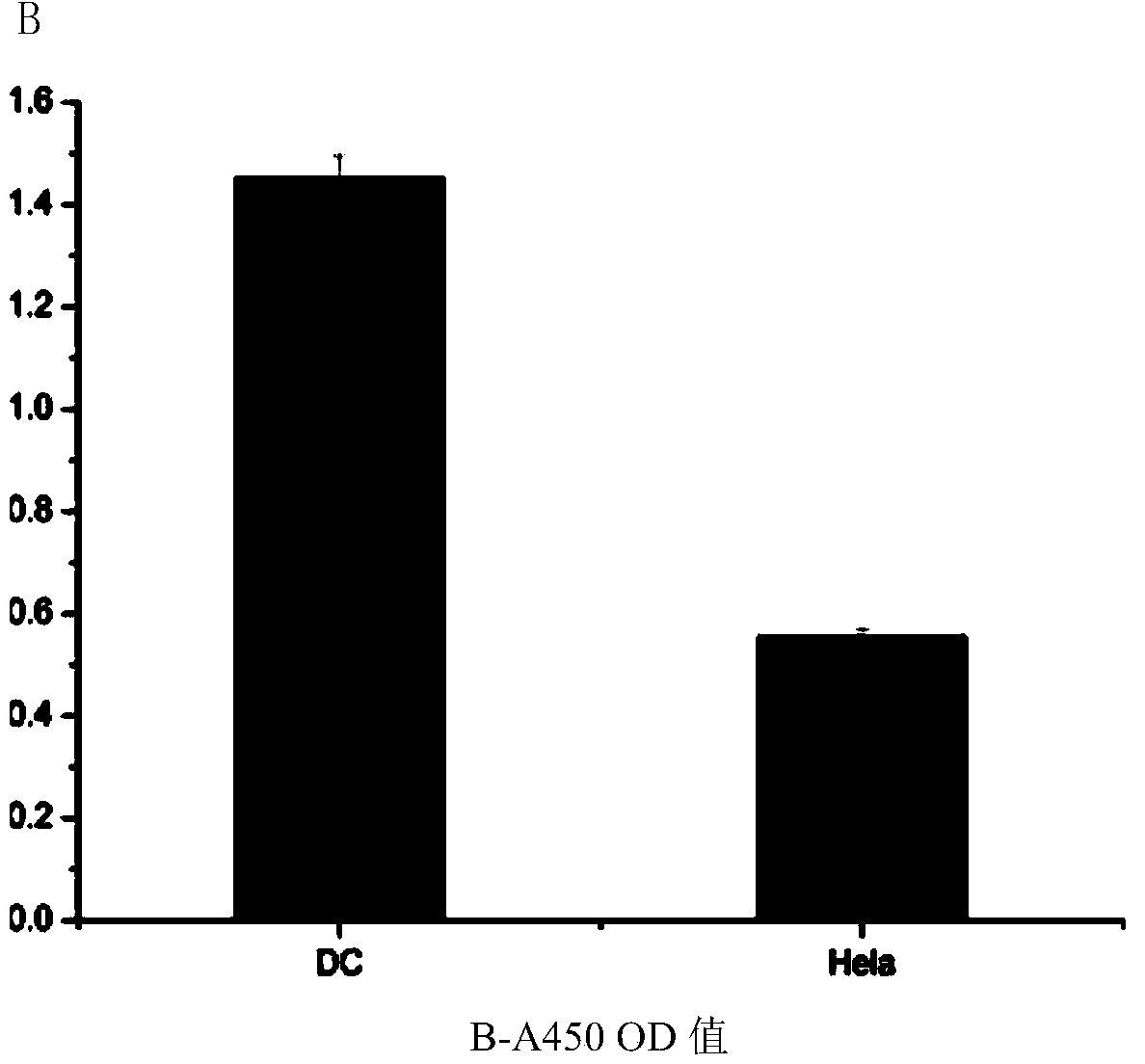
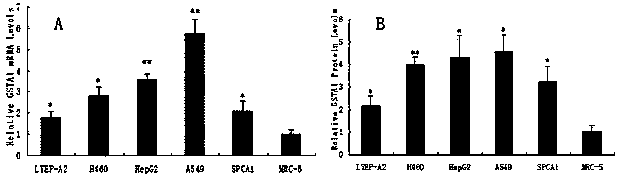
Novel tumor marker GSTA1 for lung caner as well as screening method and application thereof
InactiveCN104198722APrevent proliferationGenetic material ingredientsDisease diagnosisCDNA libraryAntigen
The invention discloses a novel tumor marker GSTA1 for lung cancer as well as a screening method and application thereof, belonging to the field of molecular biology and medical science. The marker is characterized in that on the basis of the novel lung cancer specific binding polypeptide acquired by utilizing a bacteriophage random peptide library screening technology at the earlier stage, the polypeptide is used as a probe to select lung cancer associated antigen GSTA1 from a lung cancer cDNA library. The occurrence and development of the lung cancer have a complicated mechanism, the lung cancer involves to the alteration of a lot of lung cancer associated genes and expressions thereof in the primary stage, a plurality of adhesion molecules as well as receptors or ligands can be expressed in a patient body under the effect of a carcinogenic factor, the content of the marker released by the tumor at different development stages is also different, the variation of the specific molecular marker of the tumor cancer is detected from peripheral blood and sputum, advantages of simplicity, rapidness, little pain and easiness in reviewing can be achieved, the novel tumor marker GSTA1 is easy to receive by the patient, and an important significance on the clinical diagnosis for the lung cancer can be achieved. The molecular marker can be provided for the diagnosis and targeted therapy of the lung cancer, a candidate antigen can be provided for the research of the lung cancer tumor vaccine, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Polypeptide random library and its construction method, and method for screening polypeptide capable of penetrating cell from the library
InactiveCN1733806AWide range of usesSimple screening methodFluorescence/phosphorescenceFermentationGreen fluorescent proteinRandom Peptide Library
The invention provides a random peptide library, wherein any one fusion protein in the random peptide library comprises a label for purifying the fusion protein, a labeling protein and random polypeptide, wherein the labeling protein is linked to the end of the carboxyl of the label, the random polypeptide is linked to the end of the carboxyl of the labeling protein. The invention also provides a method for constructing the random polypeptide library and a method for screening cells from the library to penetrate polypeptides.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Epitope of spring viraemia of carp
The invention relates to an antigenic epitope of spring viraemia of carp and belongs to the technical field of biology. According to the invention, by virtue of phage display technique, a positive clone is screened out by the use of spring viraemia of carp virus (SVCV) monoclonal antibody, a conserved sequence binding to the SVCV monoclonal antibody is found out, a clinical diagnosis reagent is prepared by the screened antigenic epitope, and spring viraemia of carp is prevented and treated by a small molecular antigen peptide as a vaccine. The gene sequence of the invention is SEQ ID NO:1. The phage display technique is utilized to screen the positive clone by SVCV monoclonal antibody and find out the conserved sequence which can bind to the monoclonal antibody with the ability of SVCV activity neutralization in a random peptide library. The site of the antigenic determinant is determined, and the relationship of its sequence, structure and function is analyzed. The study of inhibition effect to SVCV generated from the competitive binding of small peptide to SVCV receptor will have a huge application value for taking small molecular antigen peptide as vaccine in the future.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Immunoregulatory molecules for costimulatory signal transduction
InactiveUS6429286B1Improve developmentImprove screening efficiencyImmunoglobulin superfamilySnake antigen ingredientsAntigenRandom Peptide Library
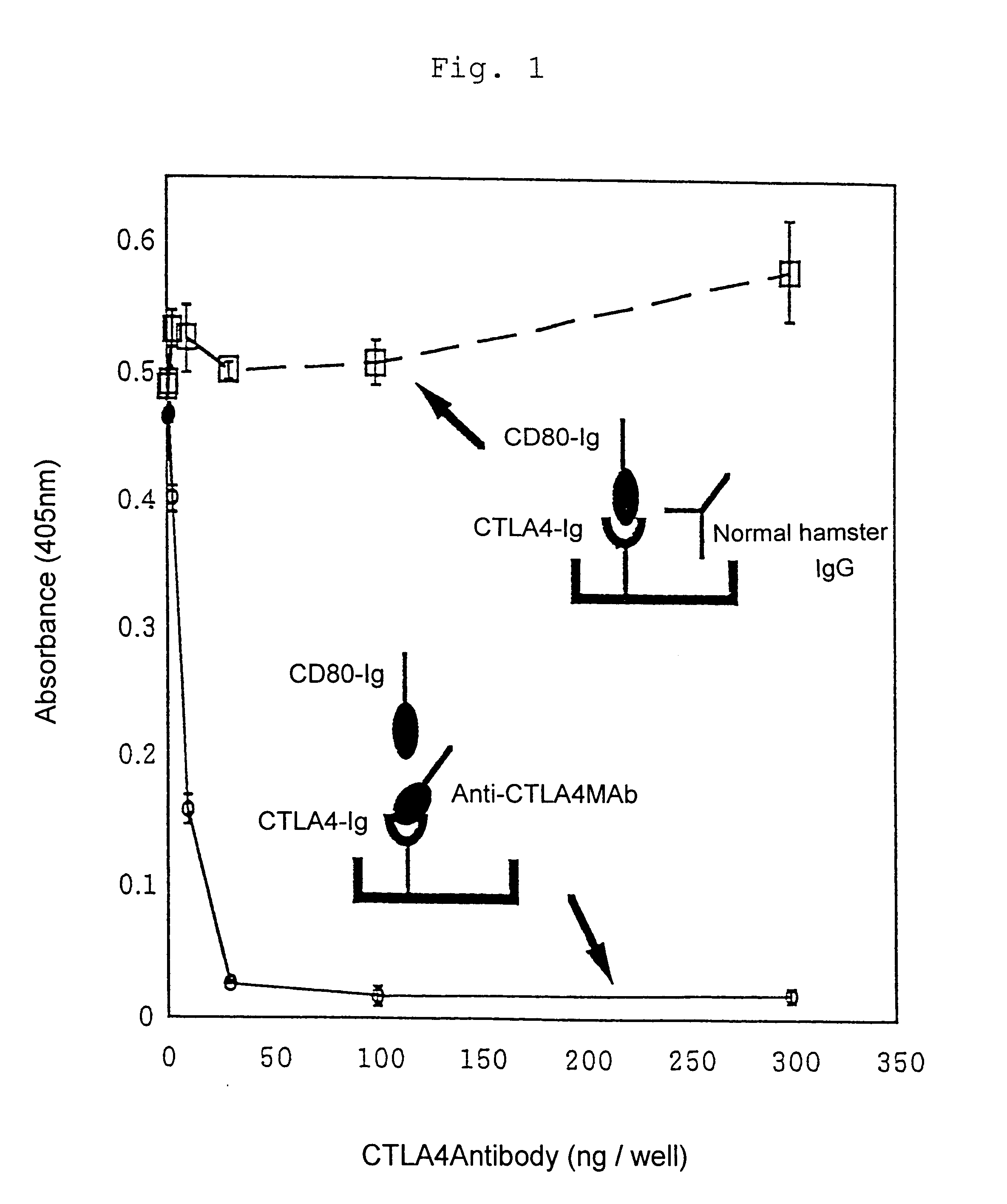
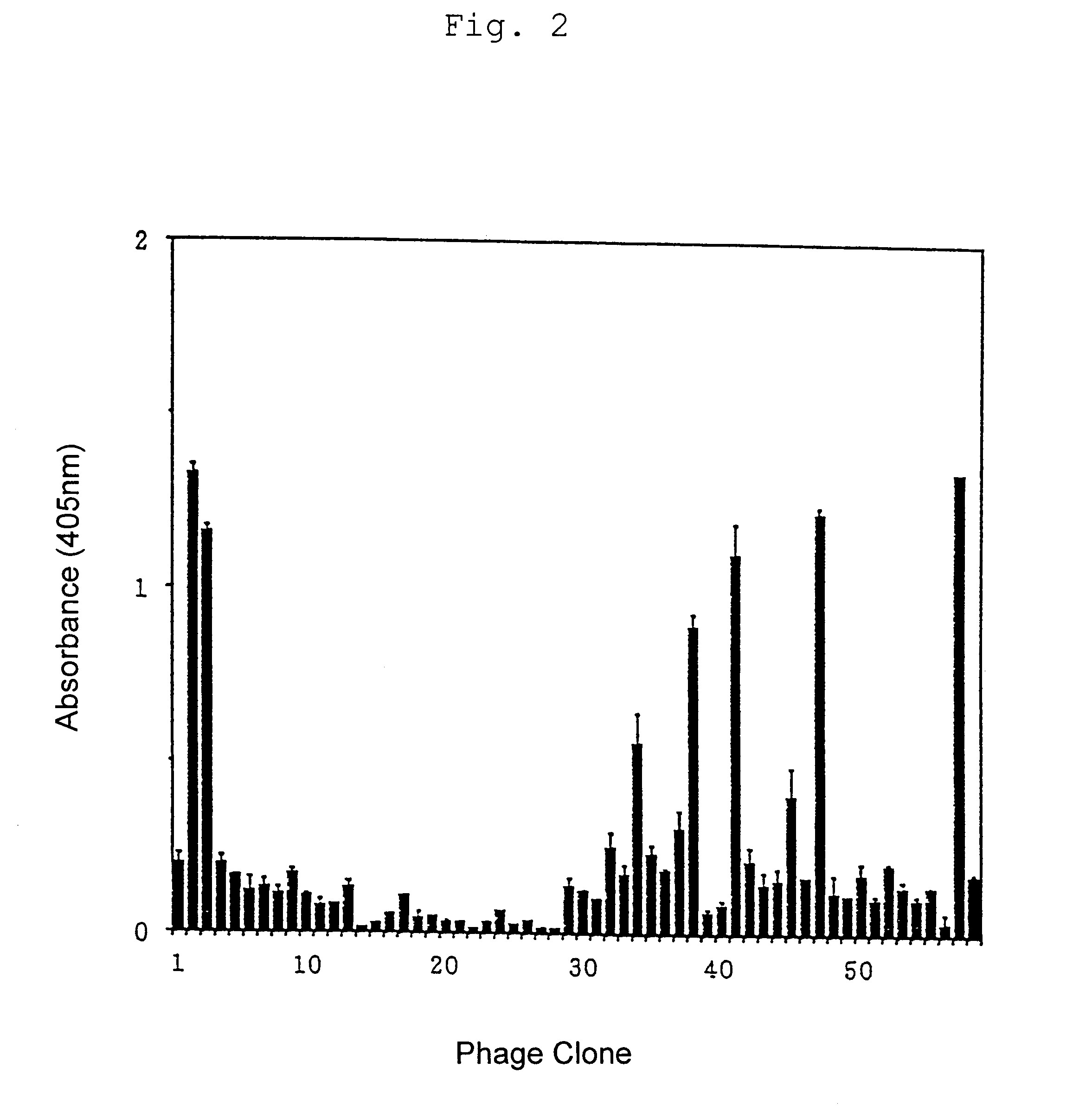
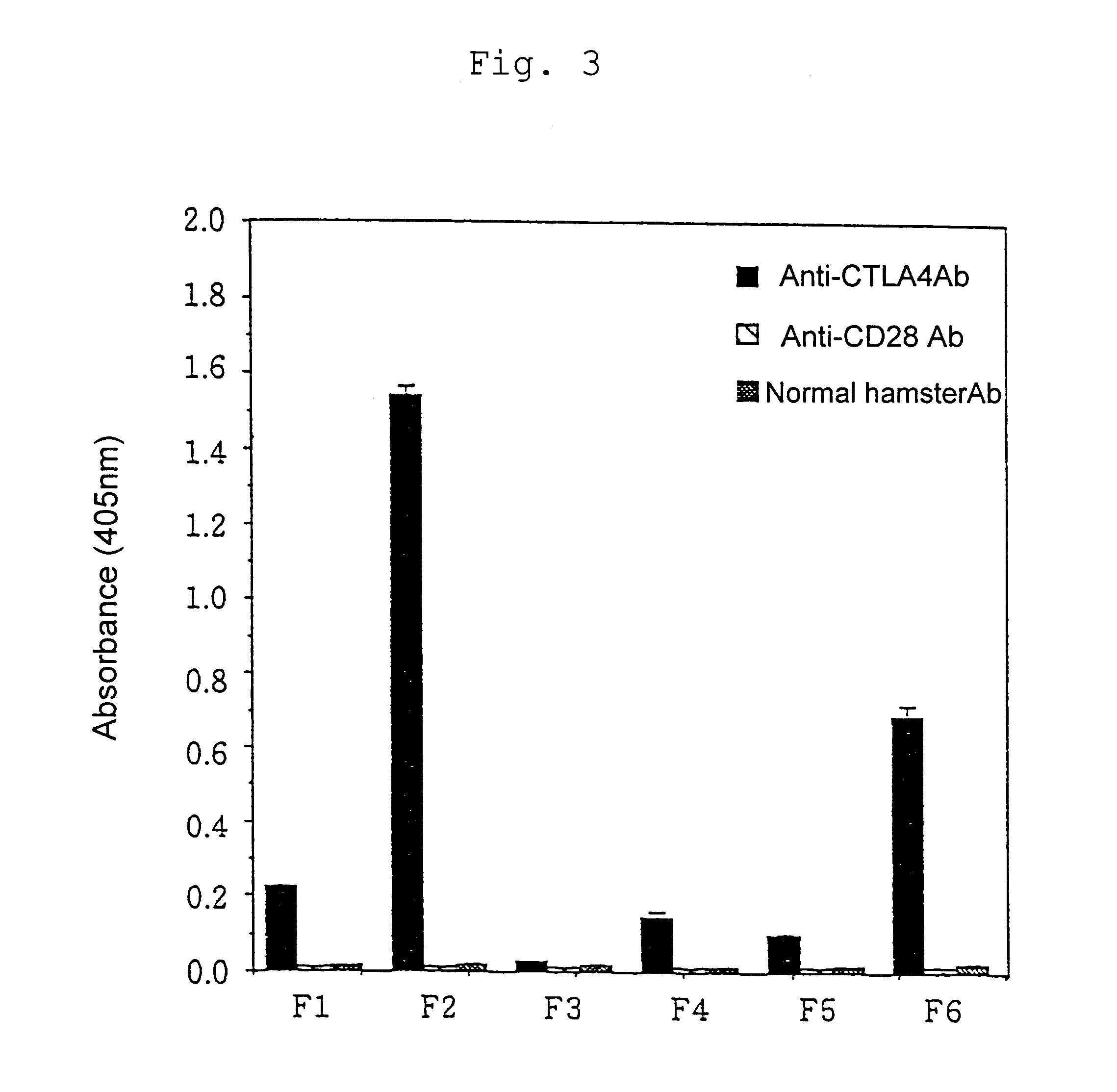
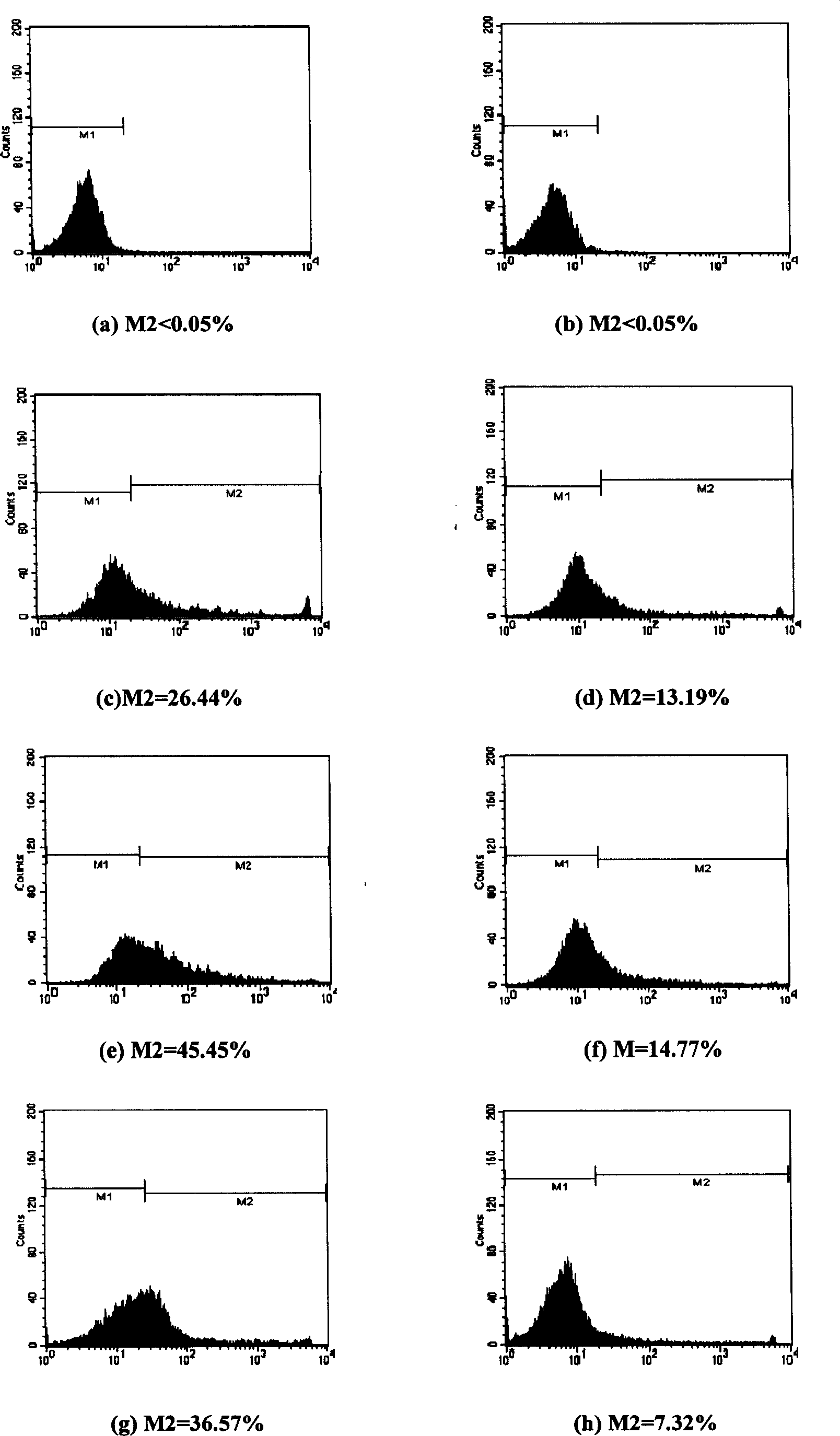
An immunoregulatory molecule that regulates costimulatory signal transduction through interaction with the molecules involved in costimulatory signal transduction present on antigen presenting cells and / or T cells in the activation of T cells by antigen presenting cells and a process for preparing the same are provided. Said immunoregulatory molecule comprises a peptide which has two cysteine (Cys) residues forming Cys-Cys linkage and comprises at least six amino acid residues between said Cys-Cys linkage. Said immunoregulatory molecule is obtained by screening a phage random peptide library with a monoclonal antibody to CTLA-4 on T cells involved in costimulatory signal transduction.
Owner:JURIDICAL FOUND THE CHEMO SERO THERAPEUTIC RES INST
Chronic myelogenous leukemia cell KT-1/A3 specific targeting short peptide series and its sieving
InactiveCN1900108AIncrease the number ofPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesRandom Peptide LibraryPeptide sequence
The present invention belongs to the field of biomedicine technology, and is especially short peptides specifically conjugated with chronic myelogenous leukemia cell KT-1 / A3 and their screening process. The four short peptides specifically conjugated with chronic myelogenous leukemia cell KT-1 / A3 of the present invention have the sequences of KMSNSIY, KLWVIPQ, KLYTPVD and QHLWAPR separately. These four short peptides are obtained through bacteriophage exhibiting process with interferon insensitive KT-1 / A3R cell strain as pre-adsorbing cell and interferon insensitive KT-1 / A3 cell strain as target cell to screen out bacteriophage random peptide library, and the subsequent screening out the four short peptides from the random peptide library. These four short peptides are identified to have specificity of conjugating with chronic myelogenous leukemia cell KT-1 / A3, and have important latent application in the diagnosis, treatment, etc of leukemia.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Chicken marrow-derived dendritic cell (DC) targeting peptide AH and application thereof
ActiveCN108276475AImprove bindingStrong targetingPeptidesMacromolecular non-active ingredientsFowlDendritic cell
The invention discloses a chicken marrow-derived dendritic cell (DC) targeting peptide AH and an application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the chicken marrow-derived DC targeting peptide AH is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. A chicken marrow-derived DC dominant binding peptide AH is sieved by using a phage random peptide library and a whole cell differential screening technology, the peptide can be relatively strongly bound to a chicken marrow-derived DC to show good targeting properties and specificity, and therefore, the targeting peptide can be used as a lead molecule of a drug such as a gene leading carrier to lay the foundation for specific small molecular therapy of a cell or can be combined with a vaccine to increase the immunization efficiency of an avian vaccine and promote organismsto generate immunities in advance.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
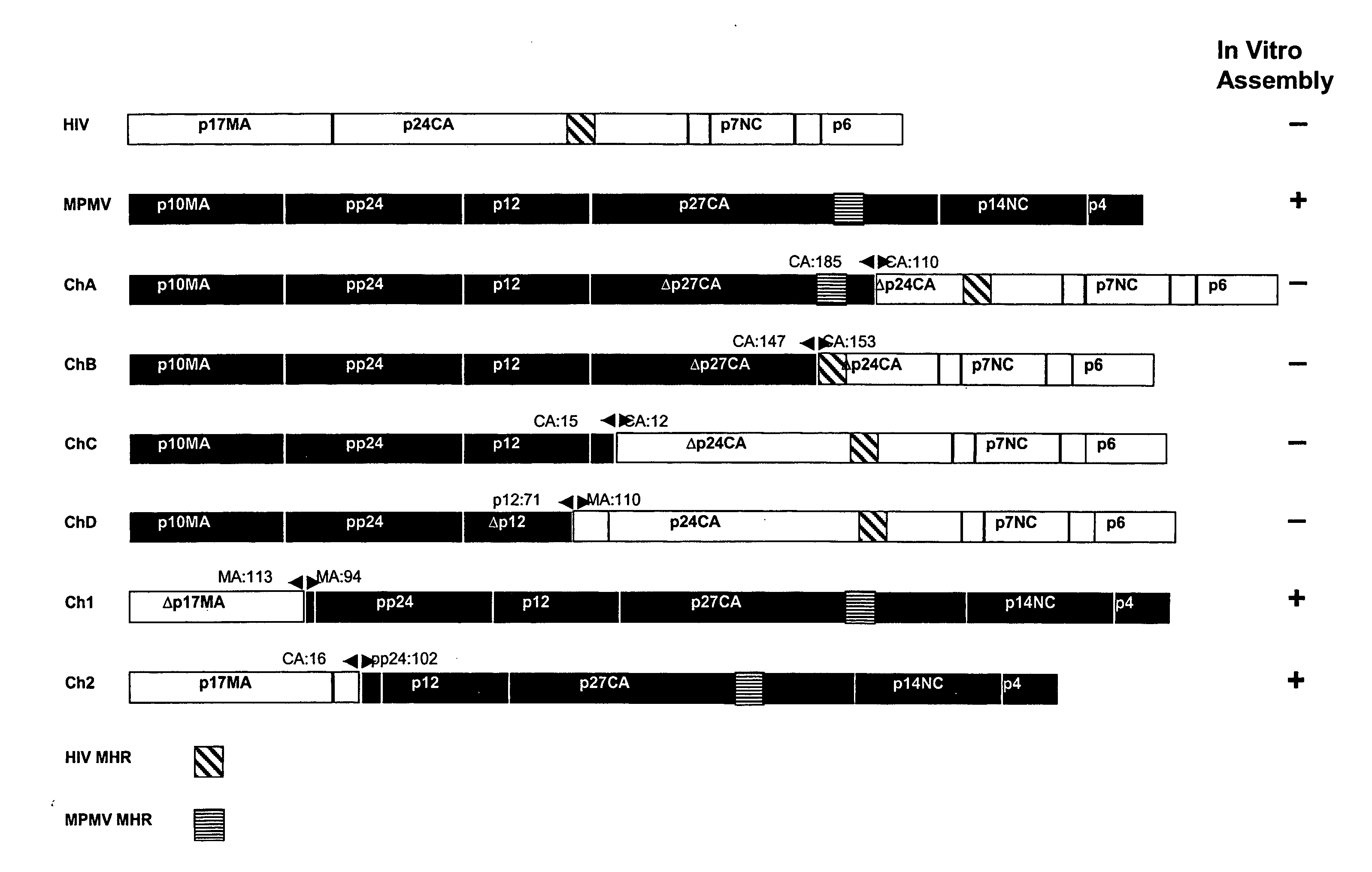
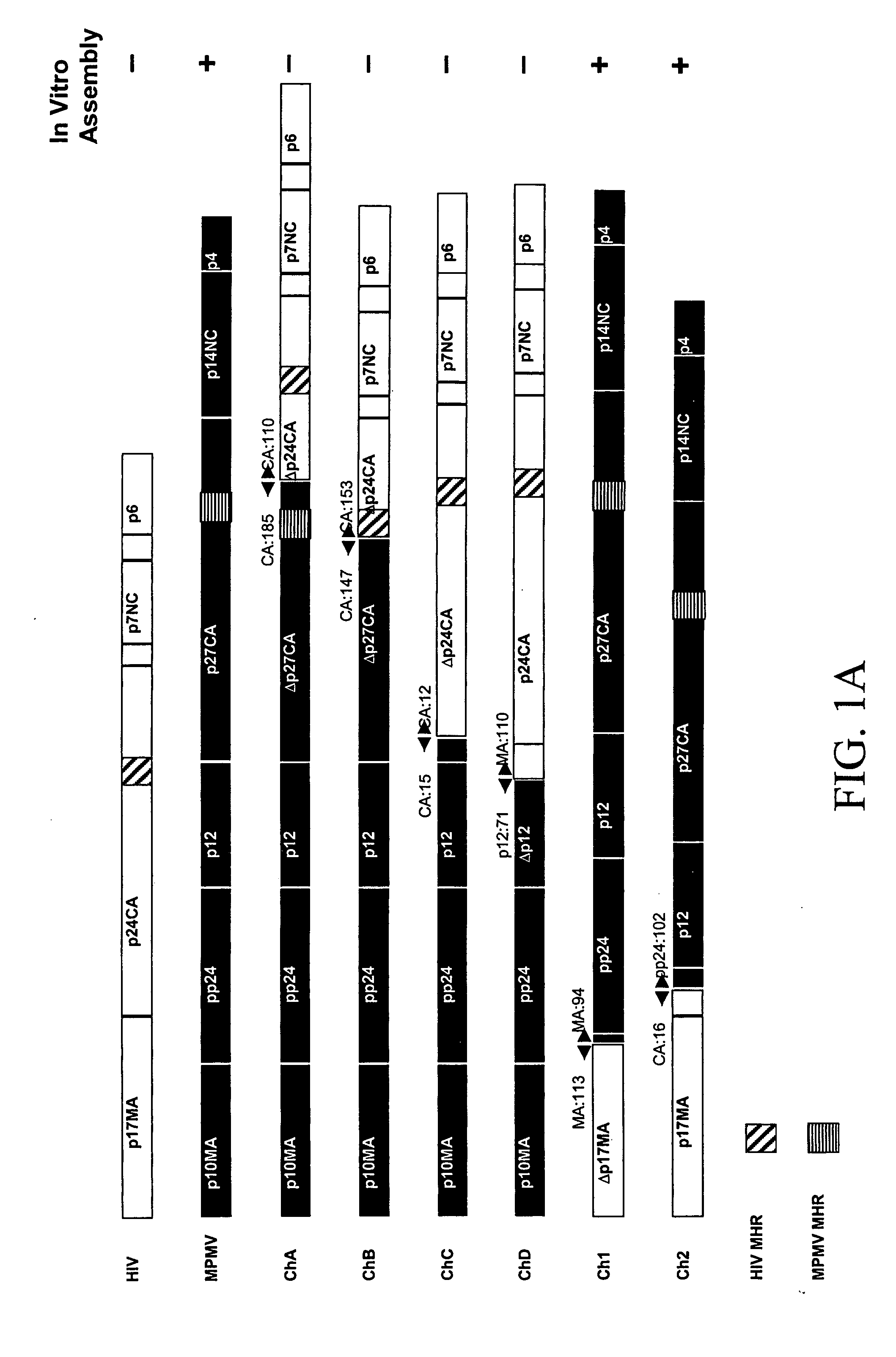
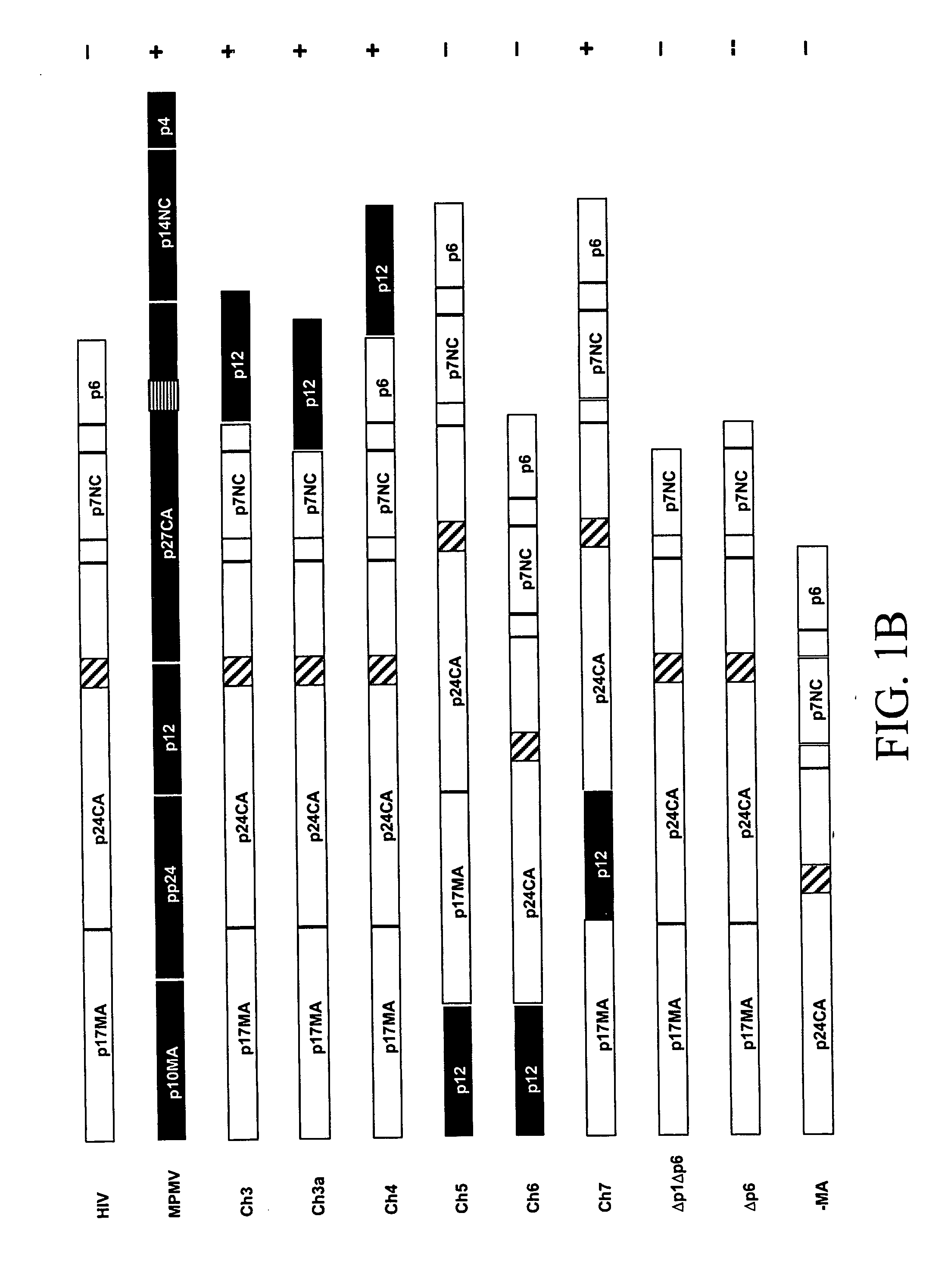
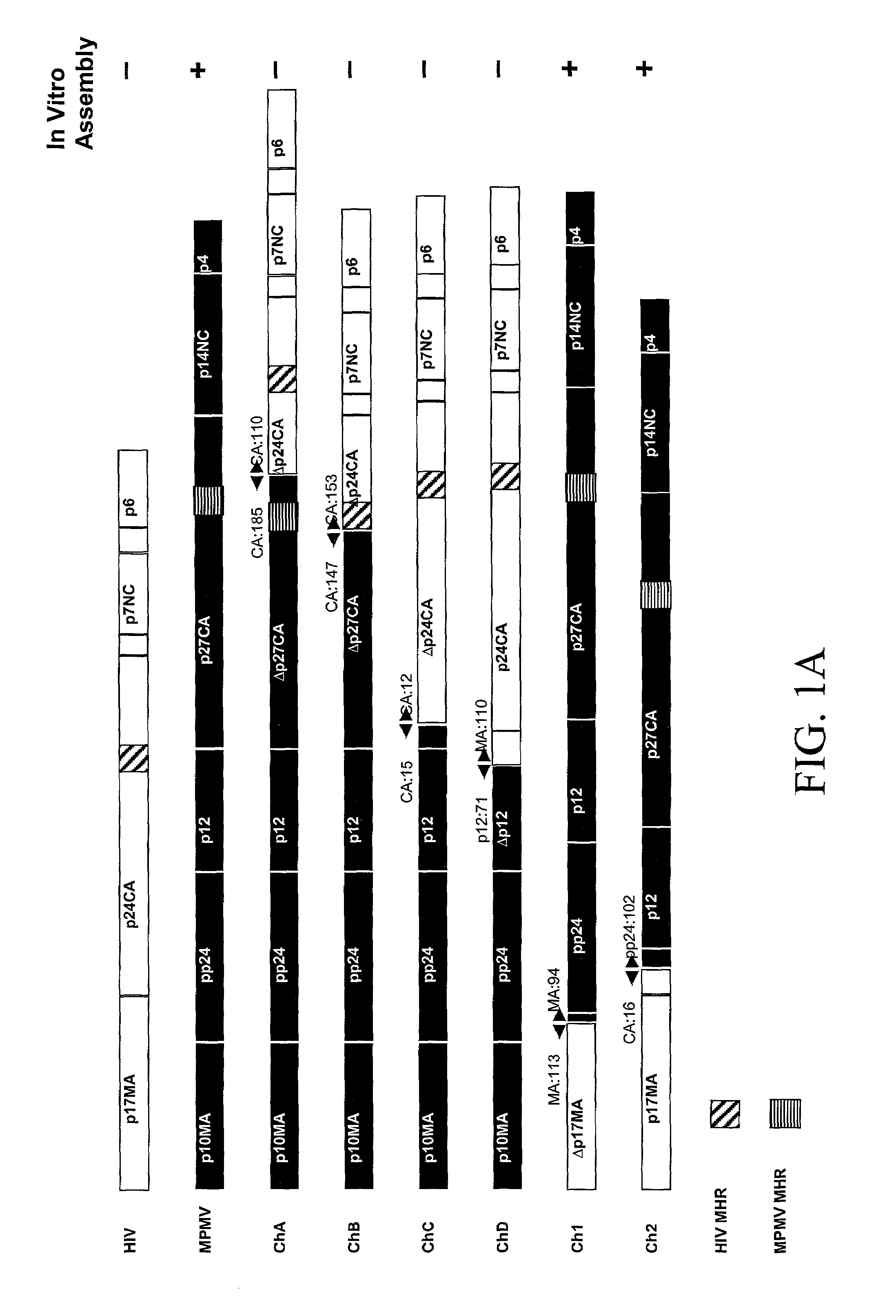
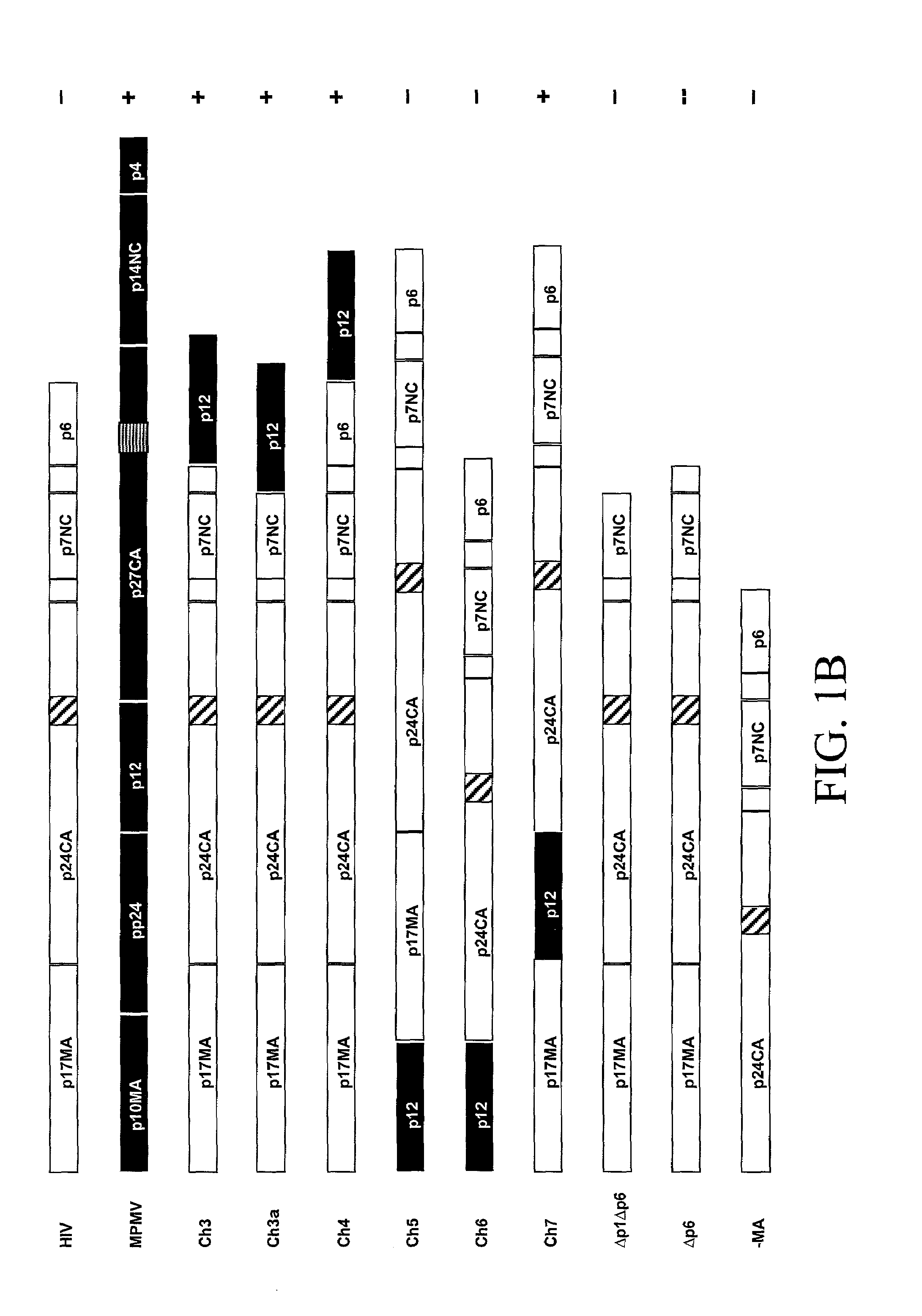
Chimeric retroviral Gag genes and screening assays
InactiveUS20070032636A1Peptide/protein ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsRandom Peptide LibraryCompetitive inhibitor
The subject invention provides novel and advantageous methods for identifying amino acid sequences in random peptide libraries that can bind to Gag polypeptides. The subject invention also establishes a novel in vitro system that can be used to test competitive inhibitors of retroviral capsid assembly. Also provided are peptides, and compositions containing these peptides, which are inhibitors of the retrovirus Gag protein(s) function. Chimeric Gag polypeptides are also provided.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
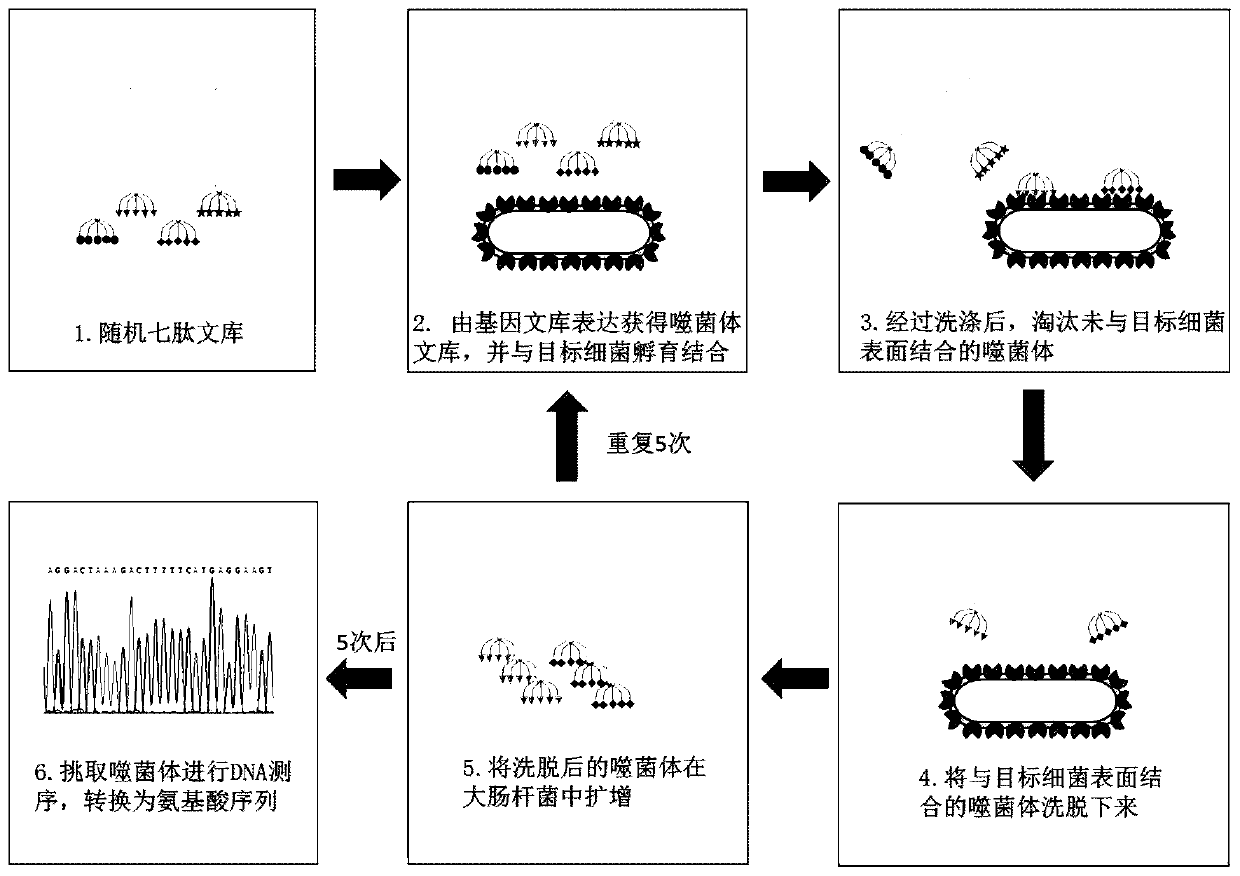
Screening method of antimicrobial peptide and application of screening method
ActiveCN110734474ASmall molecular weightReduce manufacturing costAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical synthesisRandom Peptide Library
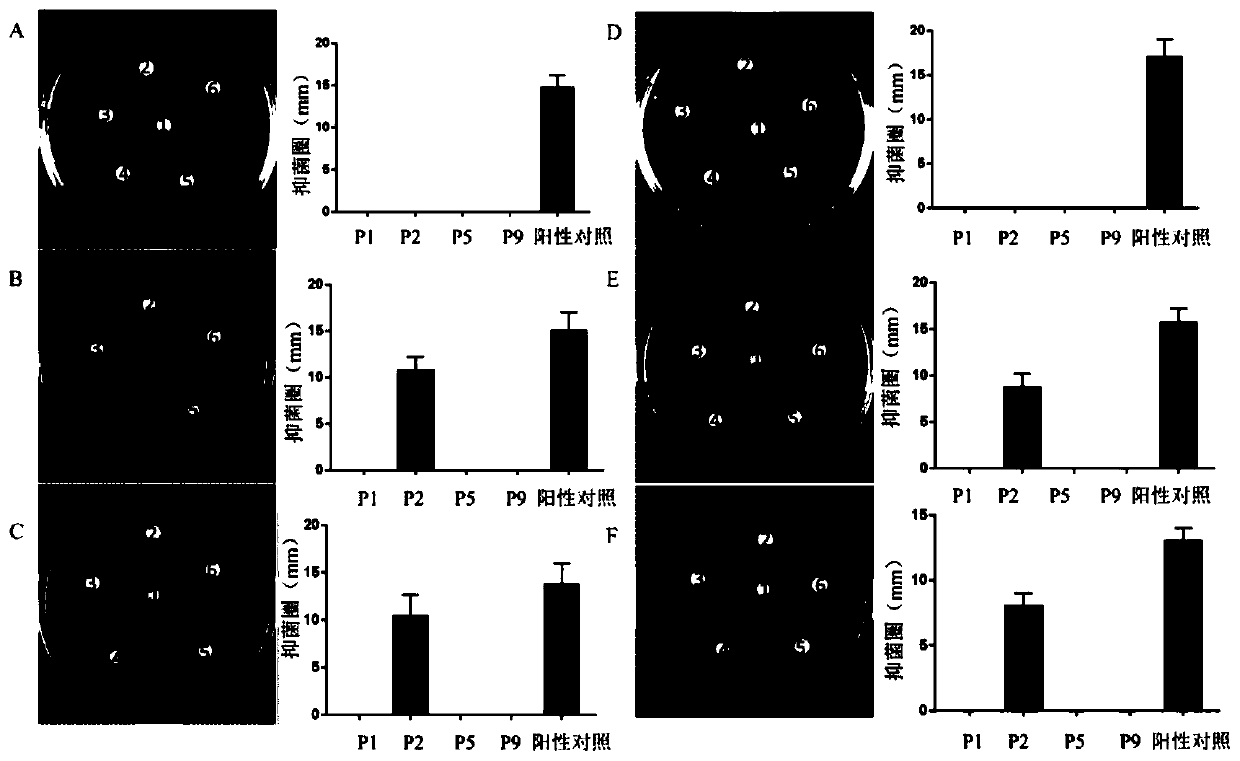
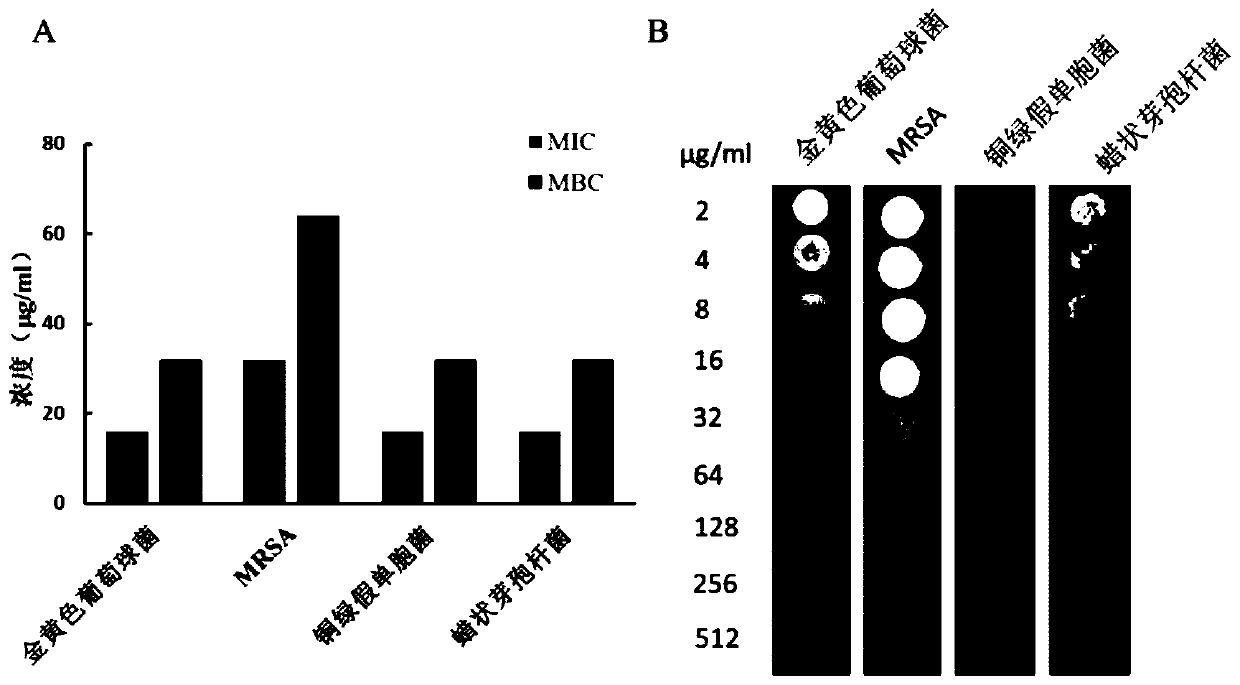
The invention relates to the technical field of antibacterial peptide, in particular to a screening method of the antimicrobial peptide and an application of the screening method, and discloses a screening method of the antimicrobial peptide. In accordance with specific pathogenic bacteria, the screening method can quickly screen the antibacterial peptide having excellent resistance. The polypeptide molecular weight in a bacteriophage random peptide library selected in the screening method is small, so that the screened antibacterial peptide is small in molecular weight, and easy to obtain bya chemosynthesis method, and the production cost of the antibacterial peptide is reduced. The antibacterial peptide screened by the screening method has high bactericidal activity for pathogenic bacteria, and the cytotoxicity and the hemolytic activity are low.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Surface display of selenocysteine-containing peptides
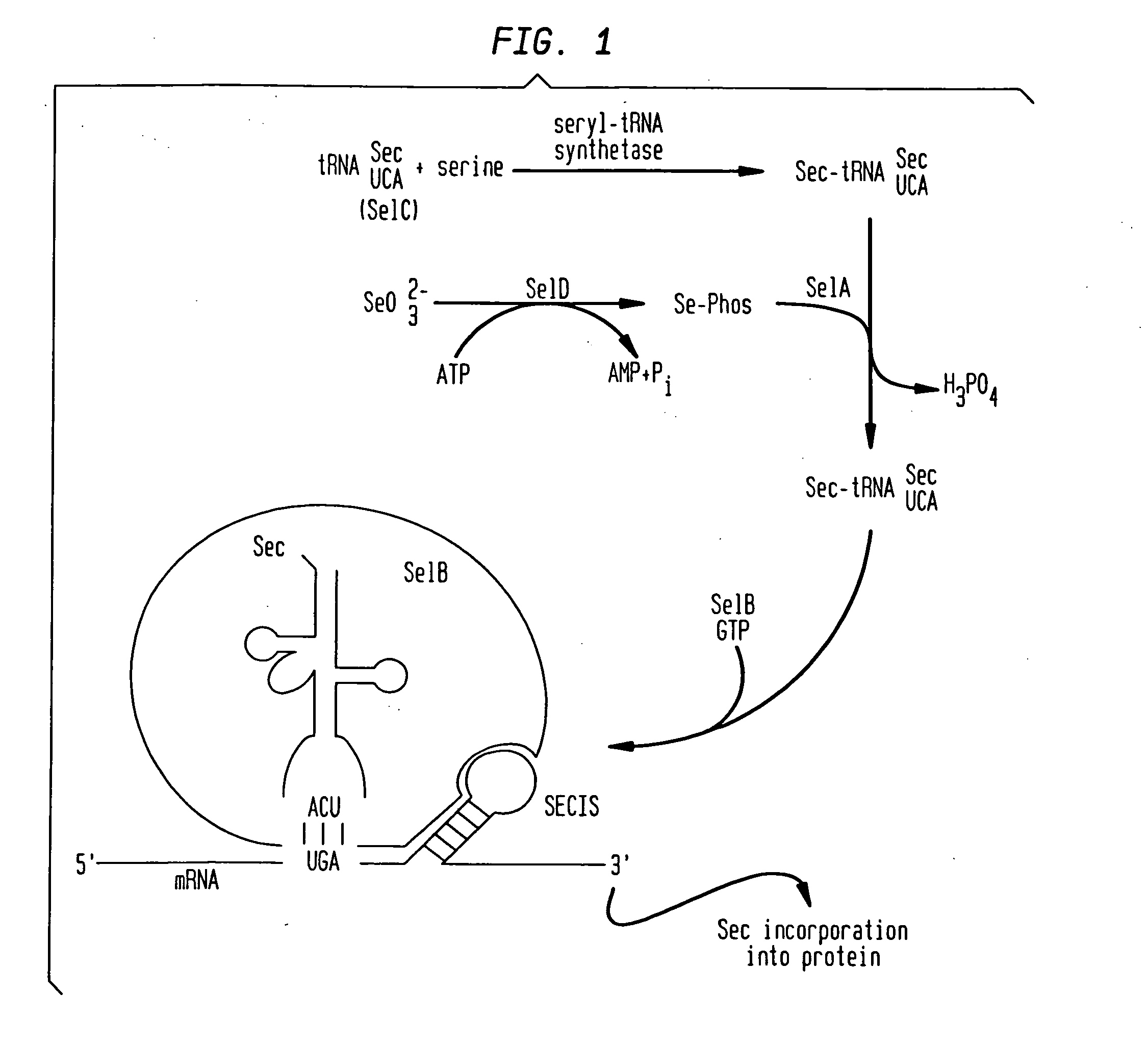
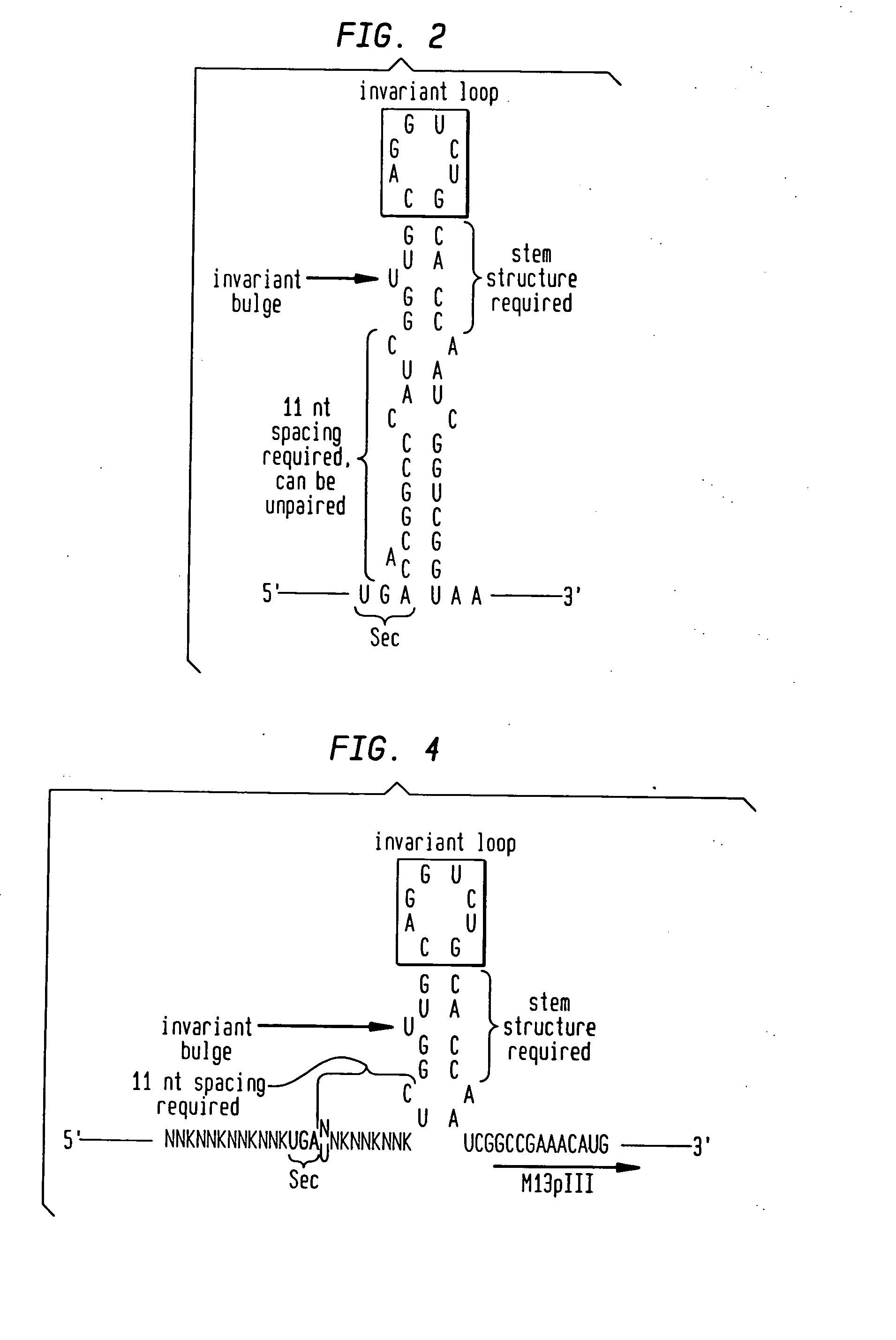
InactiveUS20050048548A1High binding activityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism librariesSurface displayRandom Peptide Library
The naturally-occurring amino acid selenocysteine (Sec) is incorporated uniquely and specifically in the context of a polypeptide displayed on the surface of an amplifiable genetic particle (phage, cell or spore) in response to incorporation signals engineered in the encoding DNA. In addition to conferring the unique activities of the selenol group to the chemistry of the displayed peptide, Sec also provides a unique handle for specific chemical modification of the displayed peptide. In addition to increasing the palette of available residues in a random peptide library to 21 possibilities, the present invention also provides a means of tethering virtually any desired chemical functionality to the incorporated Sec.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Low-cost high throughput screening method of antibacterial peptide lead compound
InactiveCN103590116AIncrease the speed of creationImprove efficiencyLibrary screeningPeptide preparation methodsRandom Peptide LibraryHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention belongs to the technical field of polypeptide drugs, and particularly relates to a low-cost high throughput screening method of an antibacterial peptide lead compound. The method is characterized in that a bacterial cell is taken as a target cell, polypeptide specifically bonded with the surface of the bacterial cell is panned from a phage display random peptide library, and the antibacterial peptide lead compound is screened in a high throughput manner after positive clone, ssDNA (single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid) sequencing, synthesis of affinity peptides and determination of antibacterial activity; an escherichia coli cell is taken as a target, polypeptide specifically bonded with the surface of the bacterial cell is panned from the phage display random peptide library, and the amino acid sequence of a decapeptide affinity peptide is QKRPRVRLSA. According to the method, polypeptide with specific biological activity, such as an antimicrobial peptide and the like, can be obtained through high throughput screening from random peptides with specific lengths with an affinity screening method in a phage peptide library, the antibacterial peptide lead compound can be rapidly screened with the method, and the development speed of new medicine for the antimicrobial peptide is increased.
Owner:刁有江
Targetted polypeptide for specificity of liver cancer blood vessel
A liver cancer blood vessel specific target polypeptide LCI-X7 able to specific binding with liver cancer blood vessel is extracted from the naked mouse model of human liver cancer by the showing technique of phage random peptide library in body and microscopic laser cutting technique. It provides important theory and practical basis for the diagnosis to liver cancer transfer recurrence and target therapy.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Cell Permeable Peptide
InactiveUS20110045009A1Highly efficiently introducePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSurface displayRandom Peptide Library
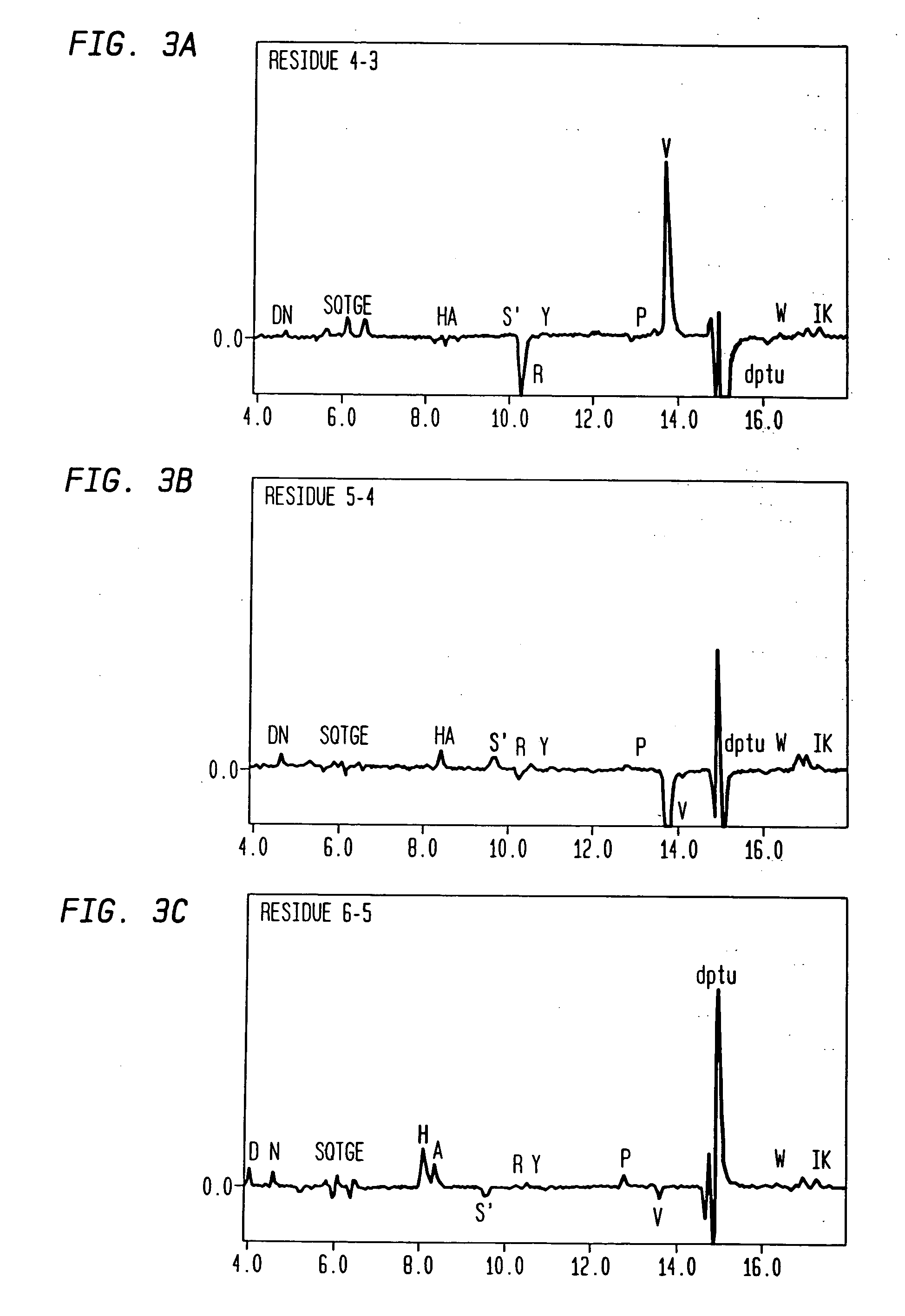
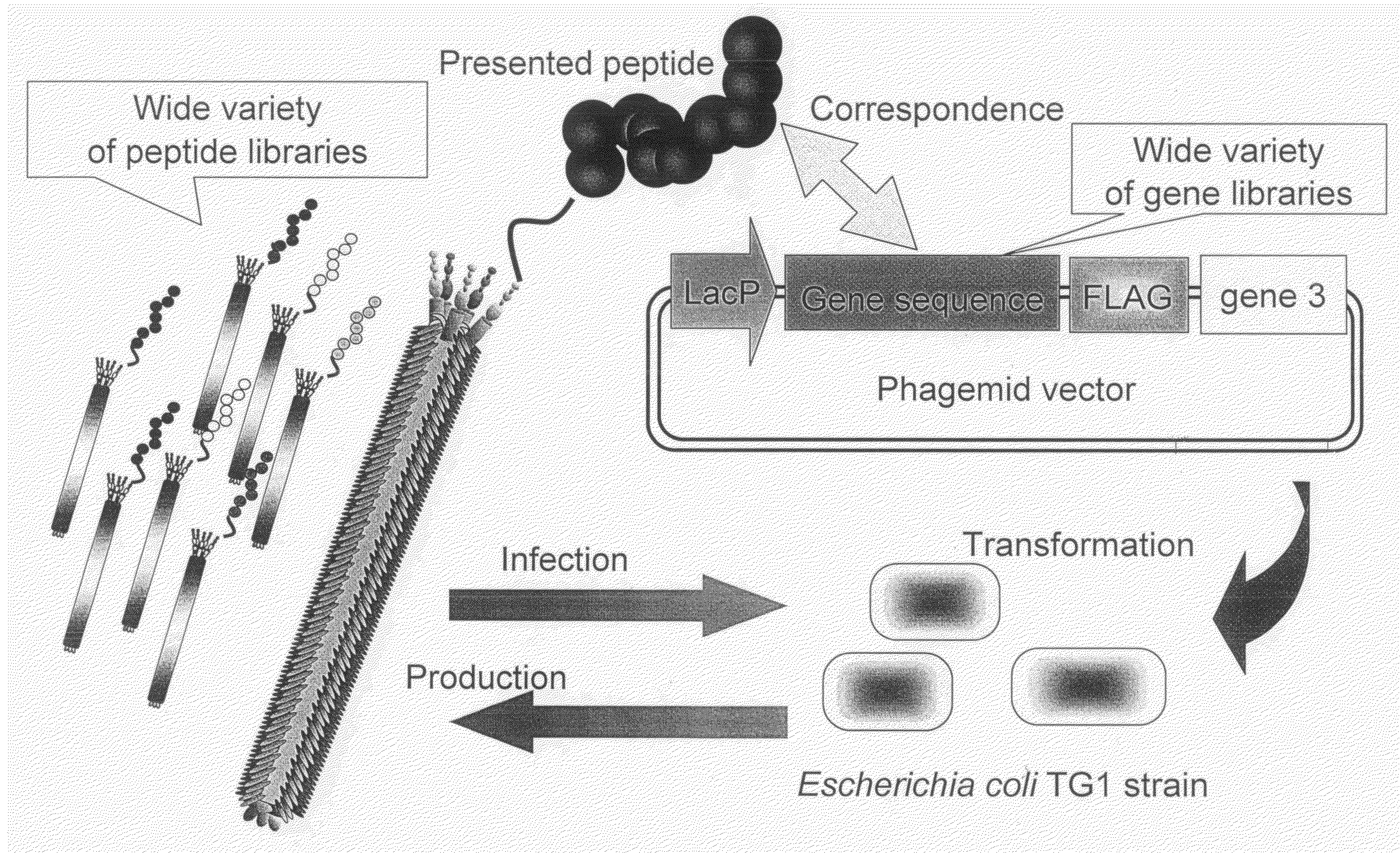
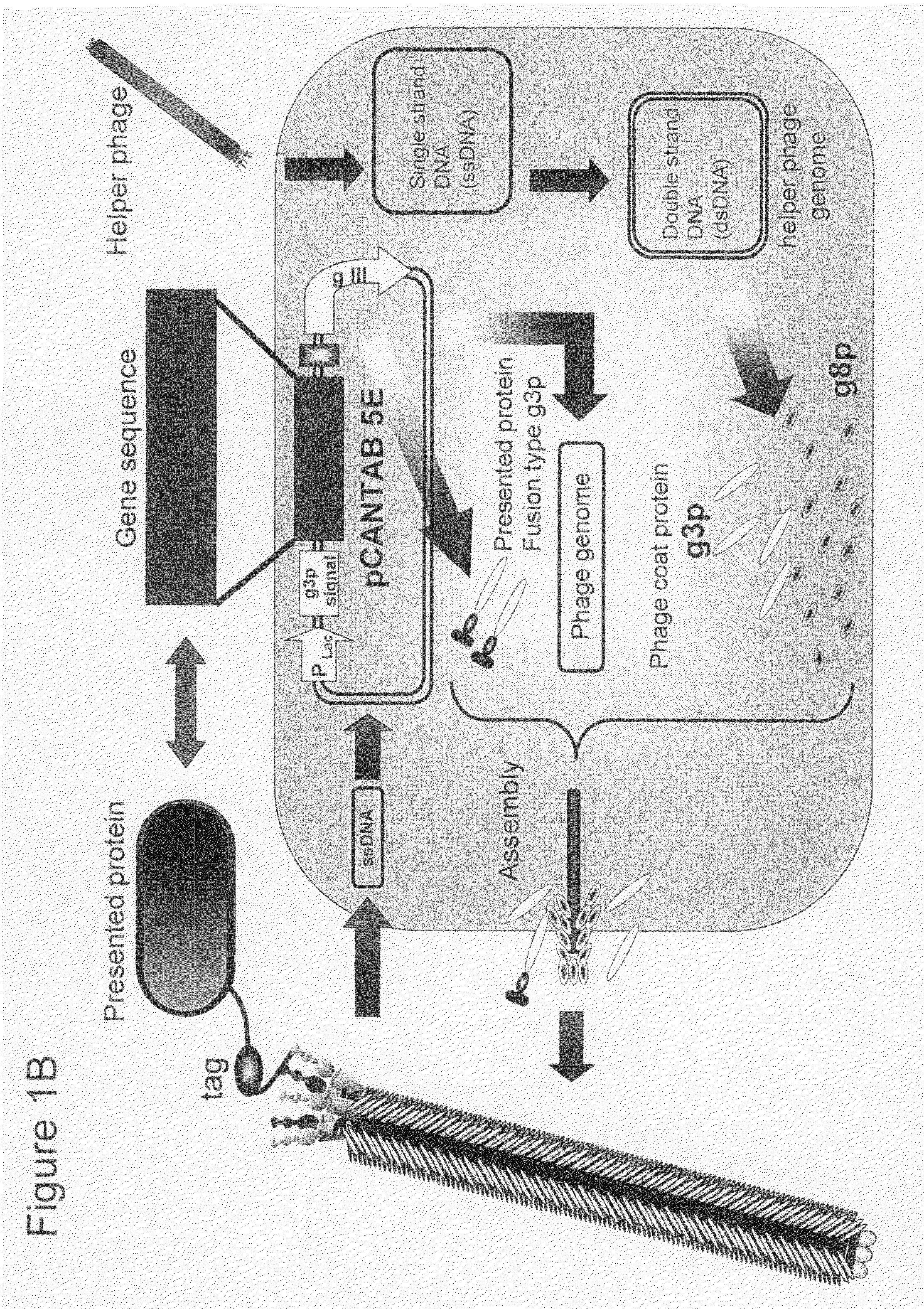
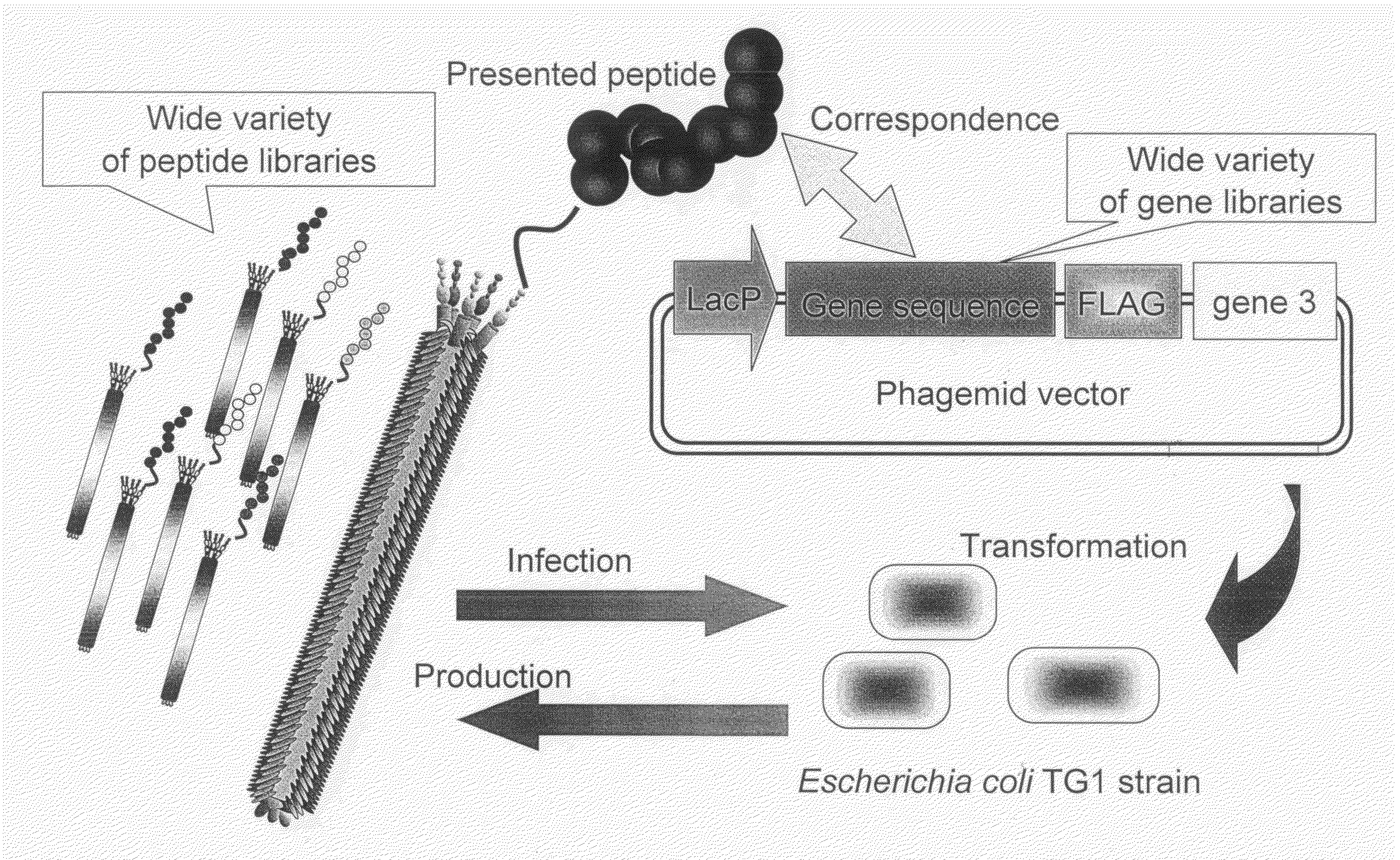
The number of peptides having an ability to bind to a cell or penetrate into a cell is narrowed down by being selectively enriched from a random peptide library with a diversity of not less than one hundred millions of peptides using a phage surface display technique, and then cytoplasmic transfer is evaluated by using protein synthesis inhibition as an indicator by adding to a cell, a fusion body of the selectively enriched peptide and a protein synthesis inhibitory factor (PSIF) that cannot solely penetrate into the cell.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV +1
Cell permeable peptide
InactiveUS7989588B2Highly efficiently introducePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSurface displayCytoplasmic transfer
Owner:OSAKA UNIV +1
Duck hepatitis virus (DHV) I type VP1 protein inhibitory peptide and application thereof
InactiveCN104193803APrevent proliferationDownregulation of viral copy numberPeptide/protein ingredientsAnimal feeding stuffAnimal virusDuck hepatitis A virus
The invention discloses a duck hepatitis virus (DHV) I type VP1 protein inhibitory peptide and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of animal virus molecular biology. The inhibitory peptide is characterized in that DHV-1VP1 protein is obtained by means of a gene engineering method; and the DHV-1VP1 protein is used as a target, and a phage 12 peptide library is utilized for screening, so that the inhibitory peptide specifically bound with the DHV-1VP1 is obtained, and the amino acid sequence of the inhibitory peptide is LLADTTHHRPWT. Tests prove that the DHV I type VP1 protein inhibitory peptide is capable of inhibiting proliferation of DHV-1 in duck embryo fibroblasts, remarkably reducing the virus copy number of the DHV-1 in the duck embryo fibroblasts under different concentrations, and remarkably reducing the virus titer of the DHV-1 in the duck embryo fibroblasts. The DHV I type VP1 protein inhibitory peptide can be used for preparing anti-DHV medicines or feed additives, and has excellent application prospects in prevention and treatment of DHV-1.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Construction method for double-promoter yeast random peptide library for screening protein dissociation peptide
InactiveCN1827763ARealize complementary advantagesEasy to filterFungiPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseDNA-binding domain
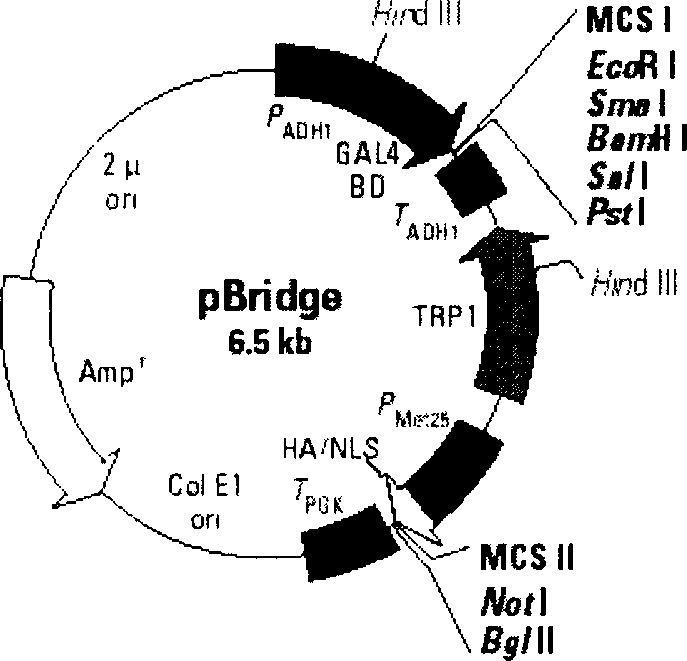
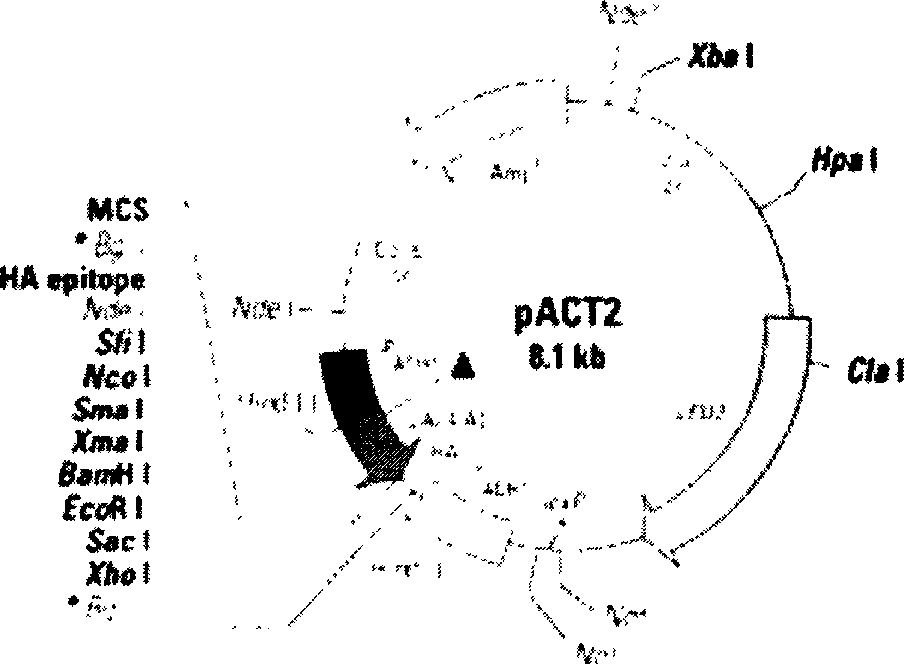
The invention discloses a method for construction of double-activation subyeast random peptide library for screening dissociating peptide of protein, which belongs to the molecular biology and biopharmaceutics categories. Making use of characteristic that the DNA binding domain (BD) and the activation domain (AD) of the yeast activator of transcription can separate in space, the method consists of inserting gene X in domain BD of Bridge particles, inserting random 10 peptide library with thioredoxin as framework in second conditional methilanin promoter (PMET25) downstream and inserting gene Y in pACT2 containing domain AD, co-transforming yeast host cell, finally screening small peptide molecule which can promote X-Y dissociation by using the expression of auxotrophic gene and the corresponding narrative gene. The method provides a new approach for studying dissociation of protein complex; the obtained peptide of protein can effectively block up the important protein complex in the signal path, which provides a target point for medicines which can cure diseases caused by abnormal signal transduction path.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Chimeric retroviral gag genes and screening assays
The subject invention provides novel and advantageous methods for identifying amino acid sequences in random peptide libraries that can bind to Gag polypeptides. The subject invention also establishes a novel in vitro system that can be used to test competitive inhibitors of retrovrial capsid assembly. Also provided are peptides, and compositions containing these peptides, which are inhibitors of the retrovirus Gag protein(s) function. Chimeric Gag polypeptides are also provided.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Chicken bone marrow-derived dendritic cell targeting peptide SP and application thereof
ActiveCN108276476AImprove bindingImprove targetingPeptidesCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsCell specificDendritic cell
The invention discloses a chicken bone marrow-derived dendritic cell targeting peptide SP and an application thereof. An amino acid sequence of the chicken bone marrow-derived dendritic cell targetingpeptide is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. According to the SP provided by the invention, a phage random peptide library and a whole-cell differential screening technology are utilized to screen out the chicken bone marrow-derived DC preferential binding polypeptide SP, compared with a published human DC targeting peptide, the SP provided by the invention can strongly bind to a chicken source DC and showsgood targeting and specificity, so that the targeting peptide SP can be used as a leading molecule of medicines such as a gene guide vector, and lays a foundation for therapy of cell-specific small molecules, or the SP is used in combination with vaccines to improve the immune efficiency of poultry vaccines and promote a body to produce immunity in advance.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com