Polypeptide random library and its construction method, and method for screening polypeptide capable of penetrating cell from the library
A technology for constructing methods and libraries, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as no random library, and achieve the effect of wide use and simple screening method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Random library construction.
[0064] The first step: construction of pET-14bMCS vector. This step is to add four enzyme cutting sites Apa I (GGGCCC), Kpn I (GGTACC), Sma I (CCCGGG) and Not I (CGGCCG) between the multiple cloning sites Nde I and Xho I of the pET-14b vector. The method of introducing mutations by PCR was used to complete the vector construction. The upstream primer was 5′-GGGCGGCCGCTCGAGGGATCCGGCTGCTAACAAAGCCG-3′; the downstream primer was 5′-GGGGGTACCGGGCCCCATATGGCTGCCGCGCGGCACCAG-3′. Using the pET-14b plasmid as a template, a PCR reaction was performed with Pyrobest high-fidelity polymerase (TaKaRa Company), and the reaction conditions were: 95° C. for 30 s; 56° C. for 30 s; 72° C. for 5 min. Perform agarose gel electrophoresis on the PCR reaction solution, and cut the gel to recover the target DNA fragment. According to the operation guide of TaKaRa MutanBEST Kit, mix 17 μl of the target fragment, 2 μl of 10×Blunting Kination Buffer, 1 μl of Bluntin...
Embodiment 2
[0091] Random library construction.
[0092] The first step: construction of pET-14bMCS vector. Its construction method is as described in the first step of Example 1.
[0093] The second step: construction of pET-14bMCStop vector. Its construction method is as described in the first step of Example 1.
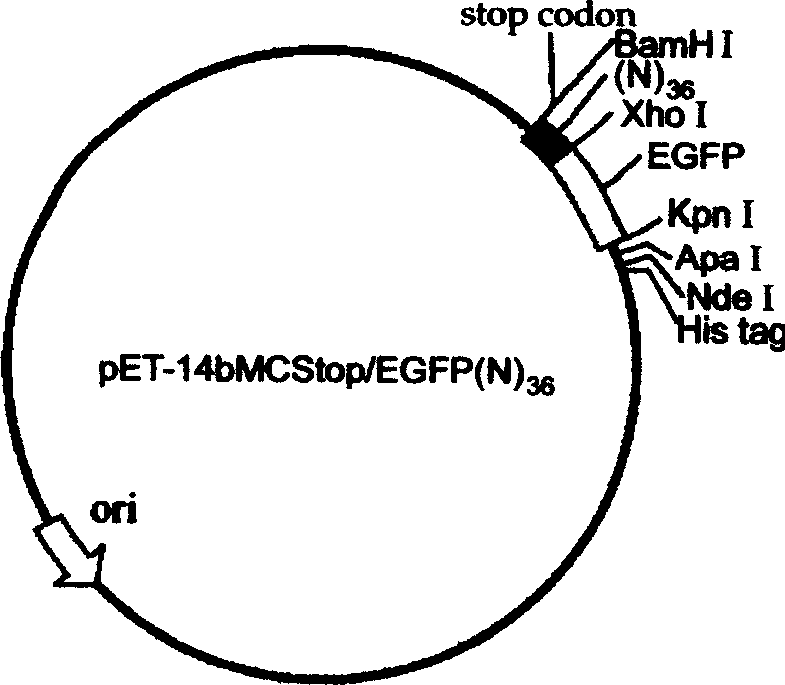
[0094] The third step: construction of pET-14bMCStop / EGFP vector. EGFP was subcloned into the pET-14bMCStop vector. The EGFP coding gene is obtained by using the pEGFP-C2 vector as a template, amplified by PCR technology, and adding a Kpn I site at the 5' end of the fragment, and adding an Xho I site at its 3' end.
[0095] Step 4: construction of random peptide library. Its construction method is as described in the first step of Example 1.
[0096] Step 5: transform to obtain a random expression library for screening cell-penetrating polypeptides. Its method is as described in the fifth step of Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0098] Construction of pET-14b / Tat-EGFP.
[0099] The first step: construction of pET-14b / Tat vector. Its construction method is as described in the first step of Example 1.
[0100] The second step: construction of pET-14b / Tat-EGFP vector. EGFP was subcloned into the pET-14b / Tat vector. The EGFP coding gene is obtained by using the pEGFP-C2 vector as a template, amplified by PCR technology, and adding a Kpn I site at the 5' end of the fragment, and adding an Xho I site at its 3' end.
[0101] The expression of pET-14b / Tat-EGFP and the positive result detection of the expressed protein His-Tat-EGFP penetrating the cell membrane:
[0102] Escherichia coli BL21 (DE 3), ampicillin plate selection, incubated overnight at 37°C, picked a single clone in the next morning and added 1.6ml LB / Amp + (100μg / ml) culture medium, use 48-well deep-well plates to shake at 37°C until the OD600 is about 0.6, then add a final concentration of 1mmol / LIPTG to the bacterial solution to induce p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com