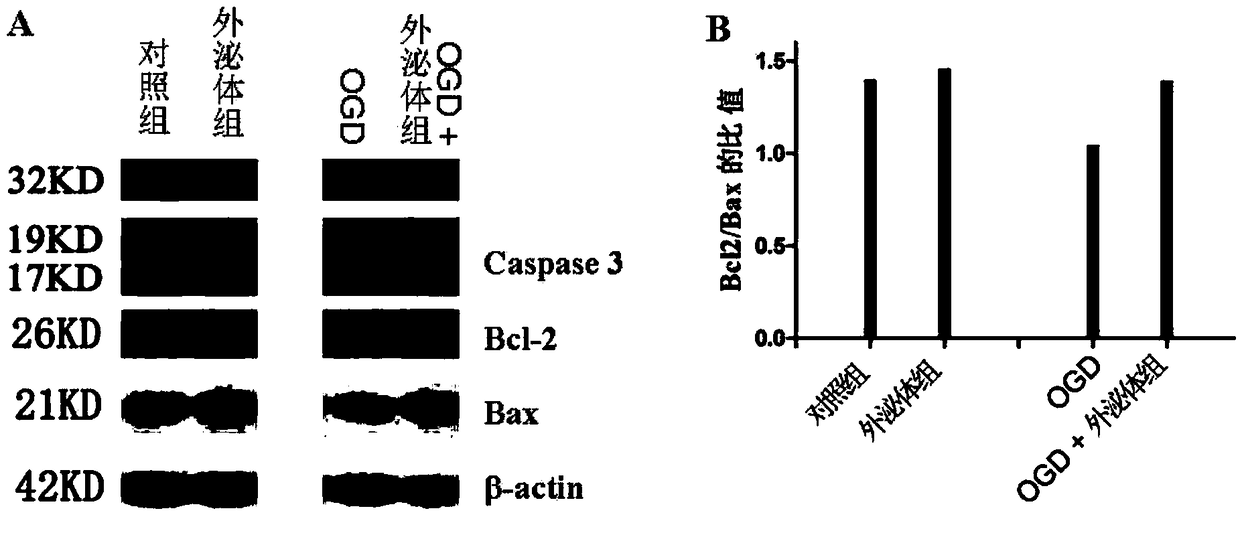
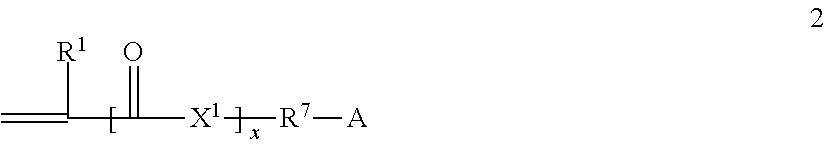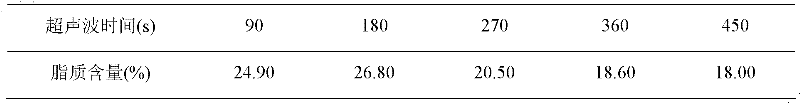Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
304 results about "CELL DEBRIS" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
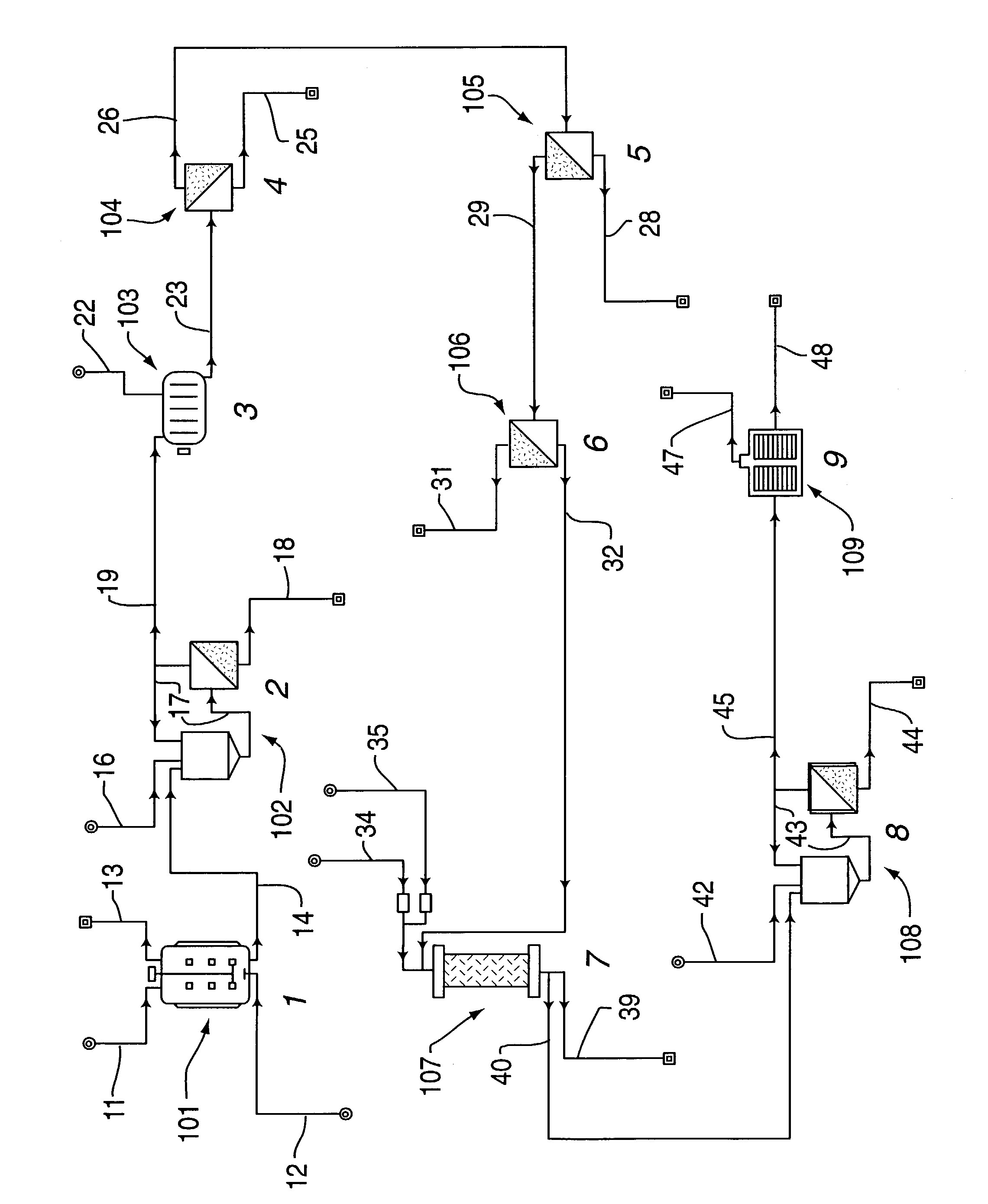
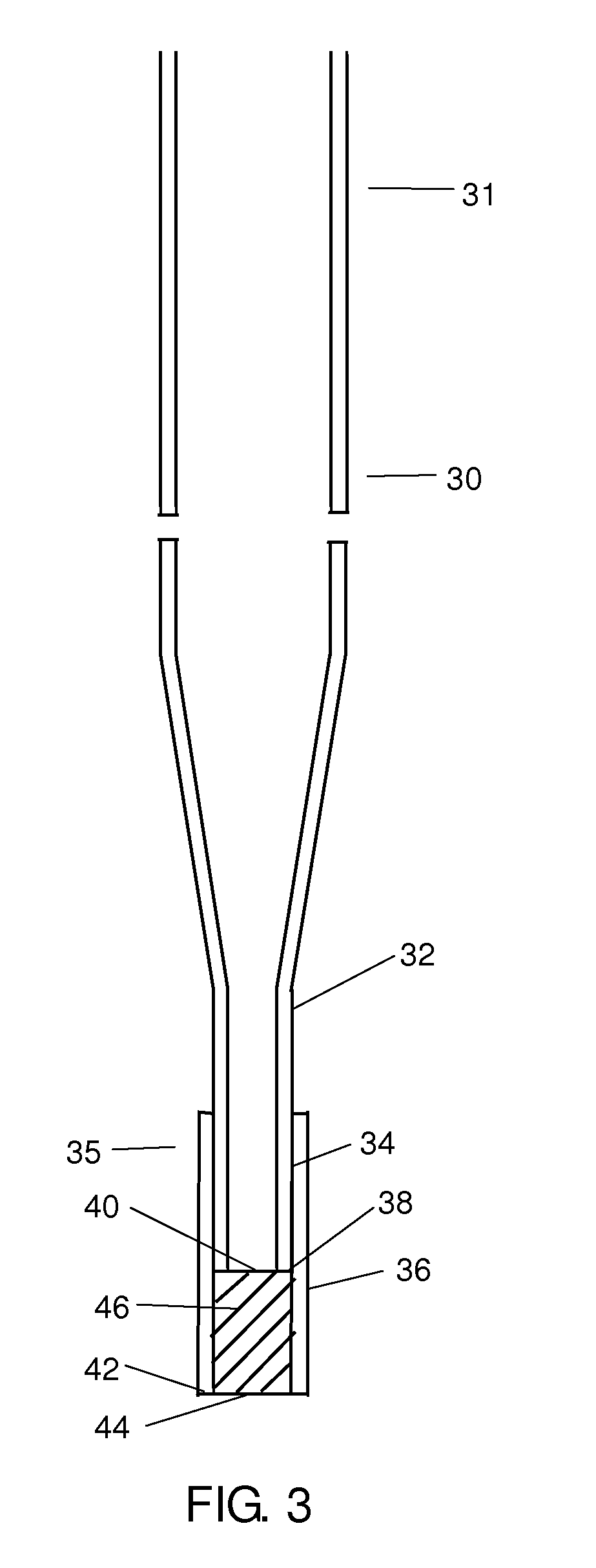
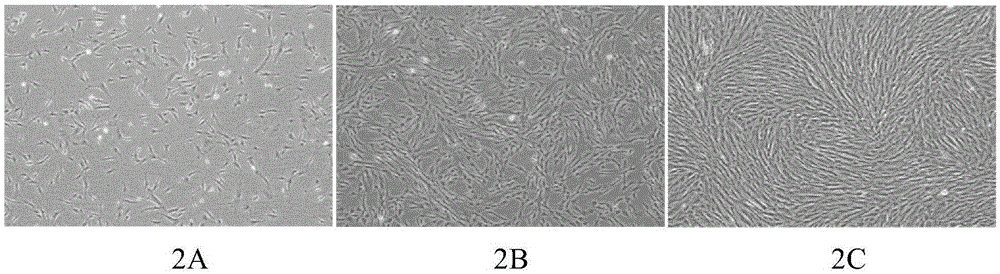
Rapid cell block embedding method and apparatus
ActiveUS6913921B2Maximize efficiencyReduce amountBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringReagent
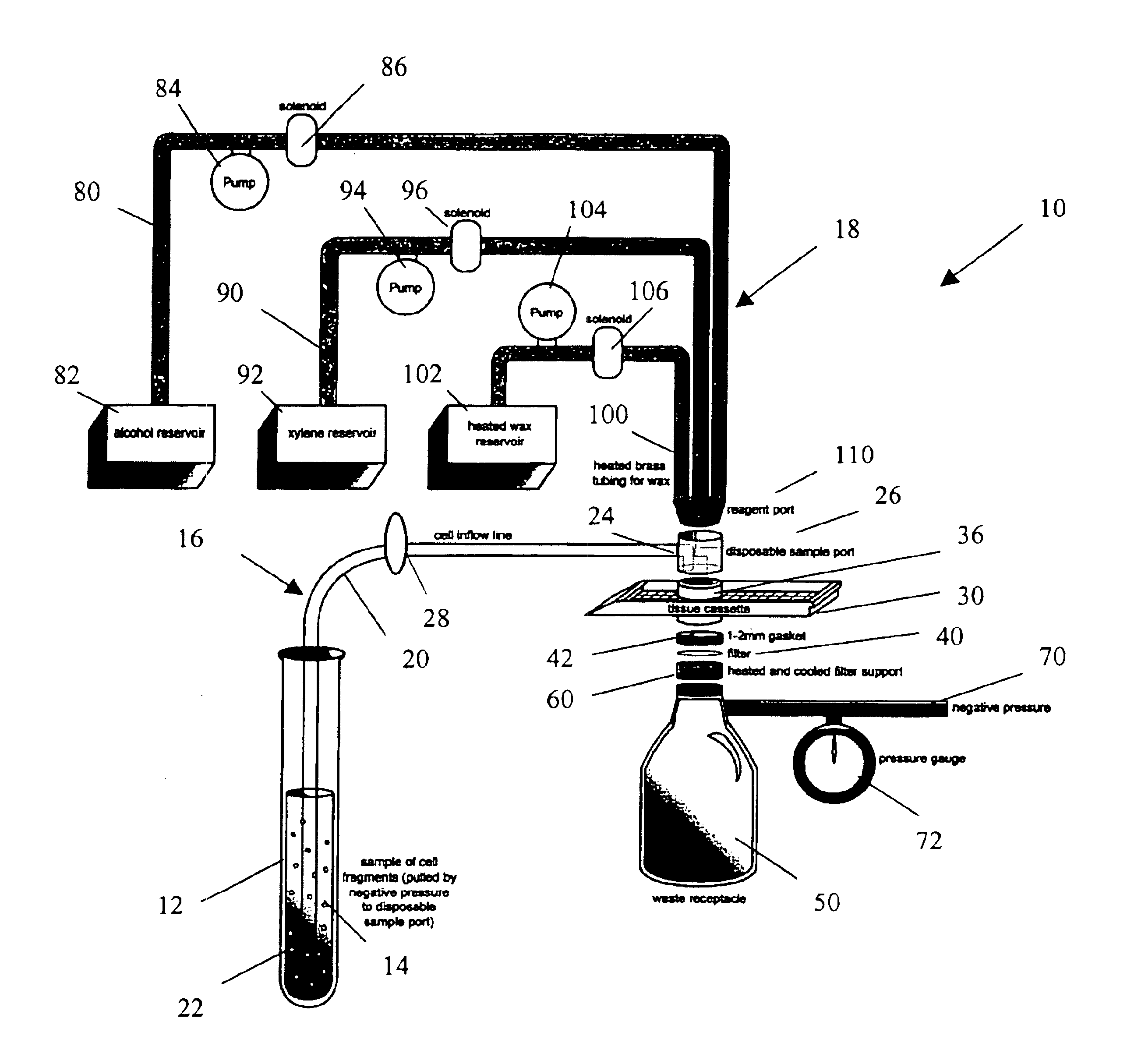
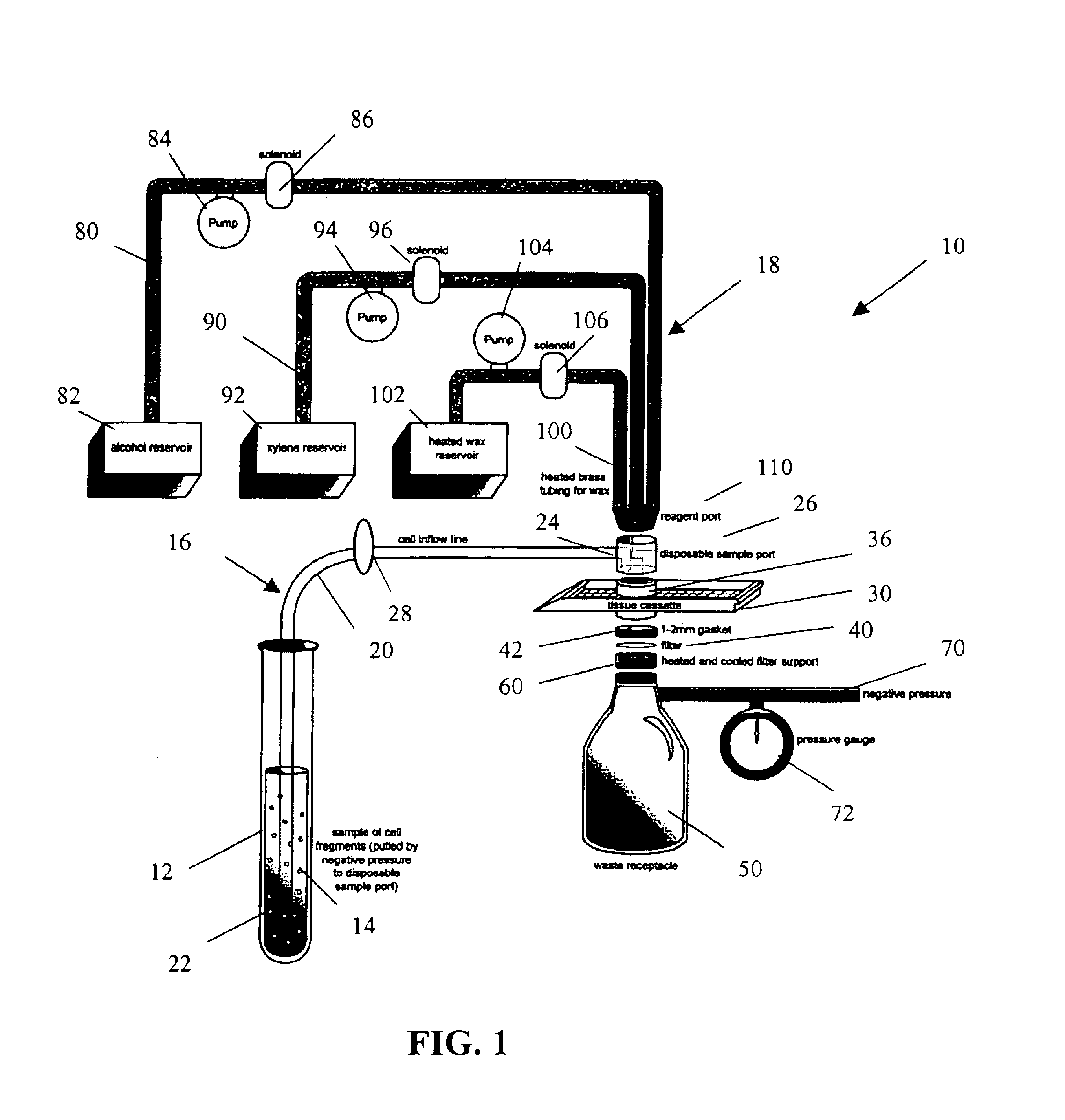
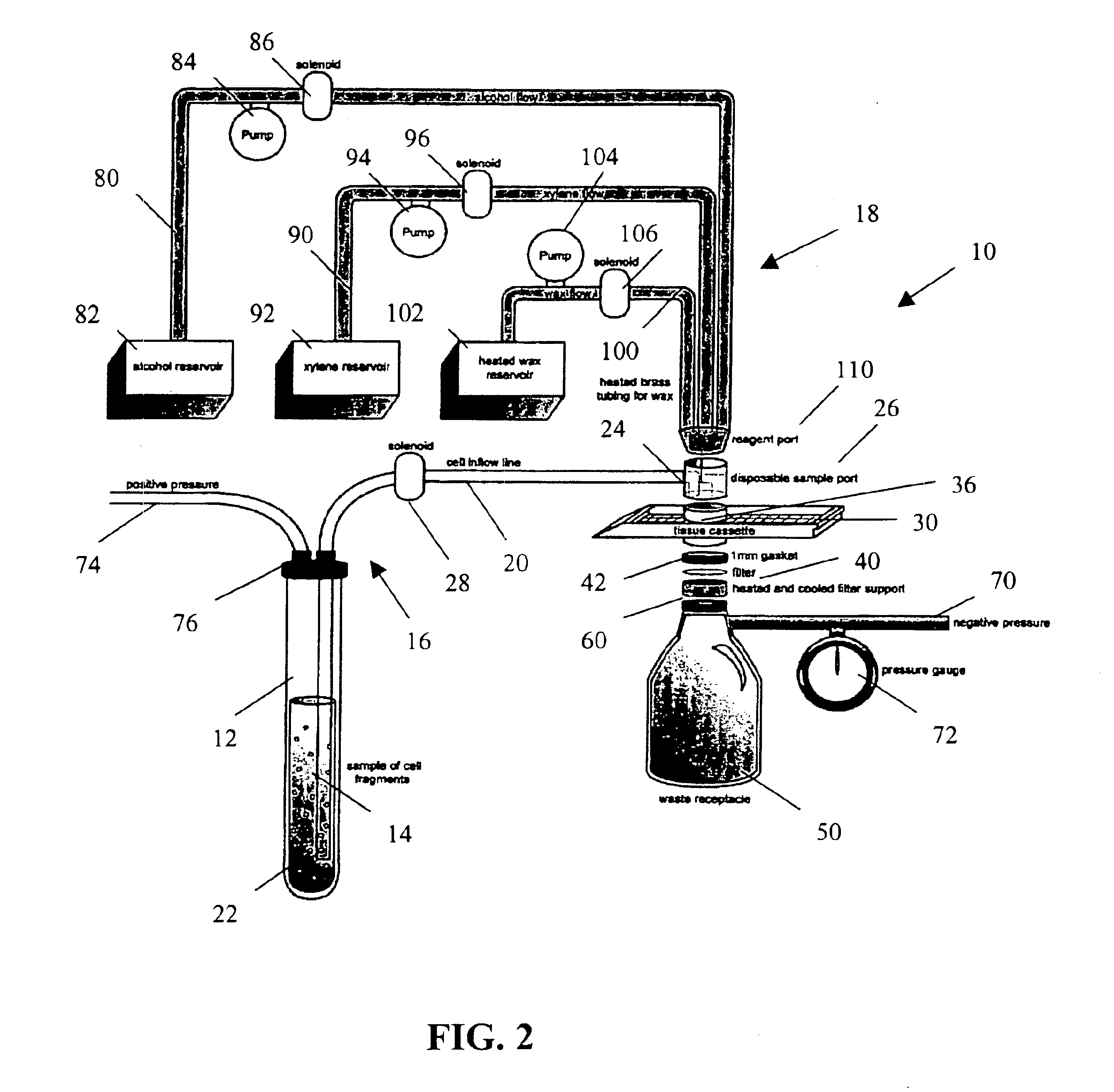
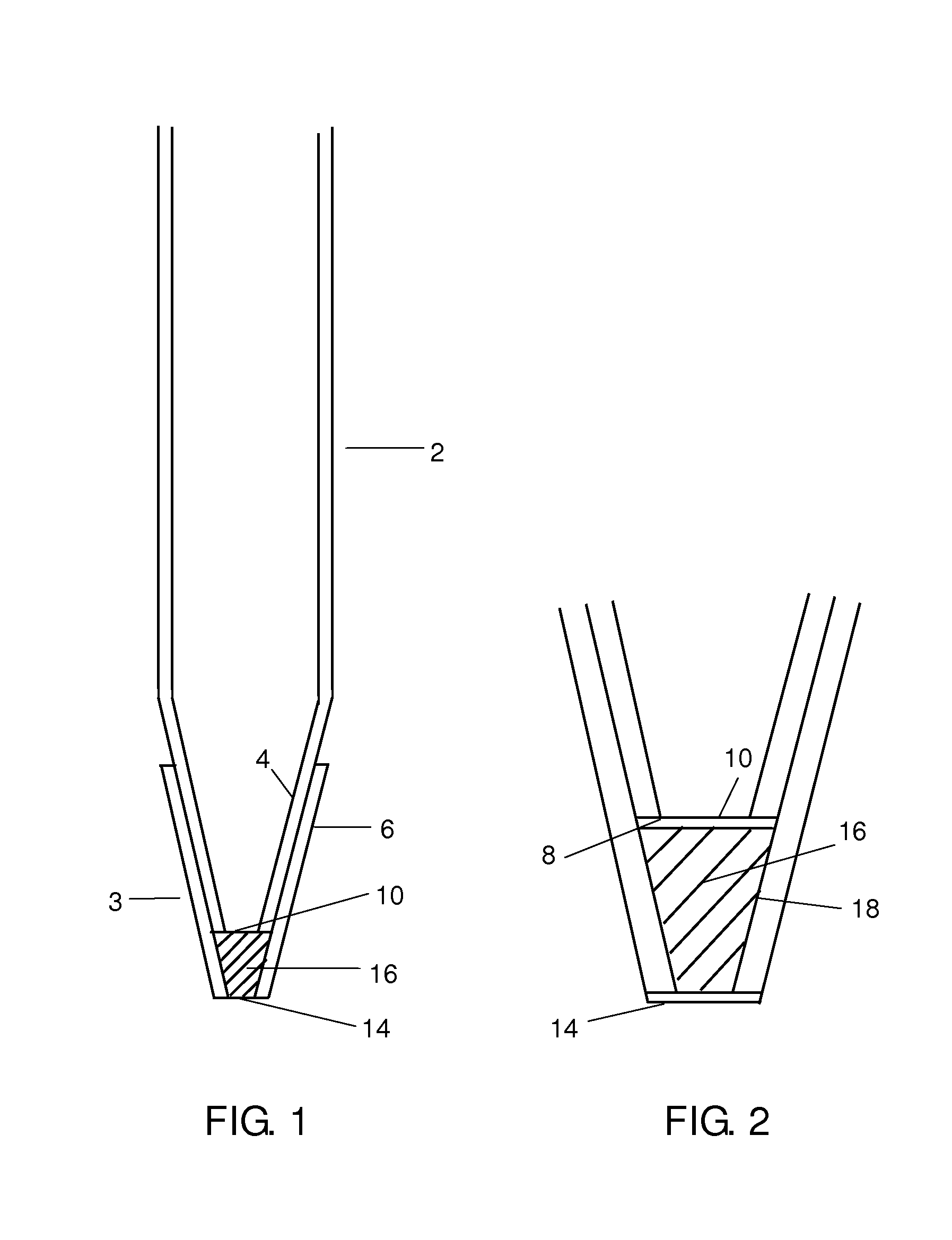
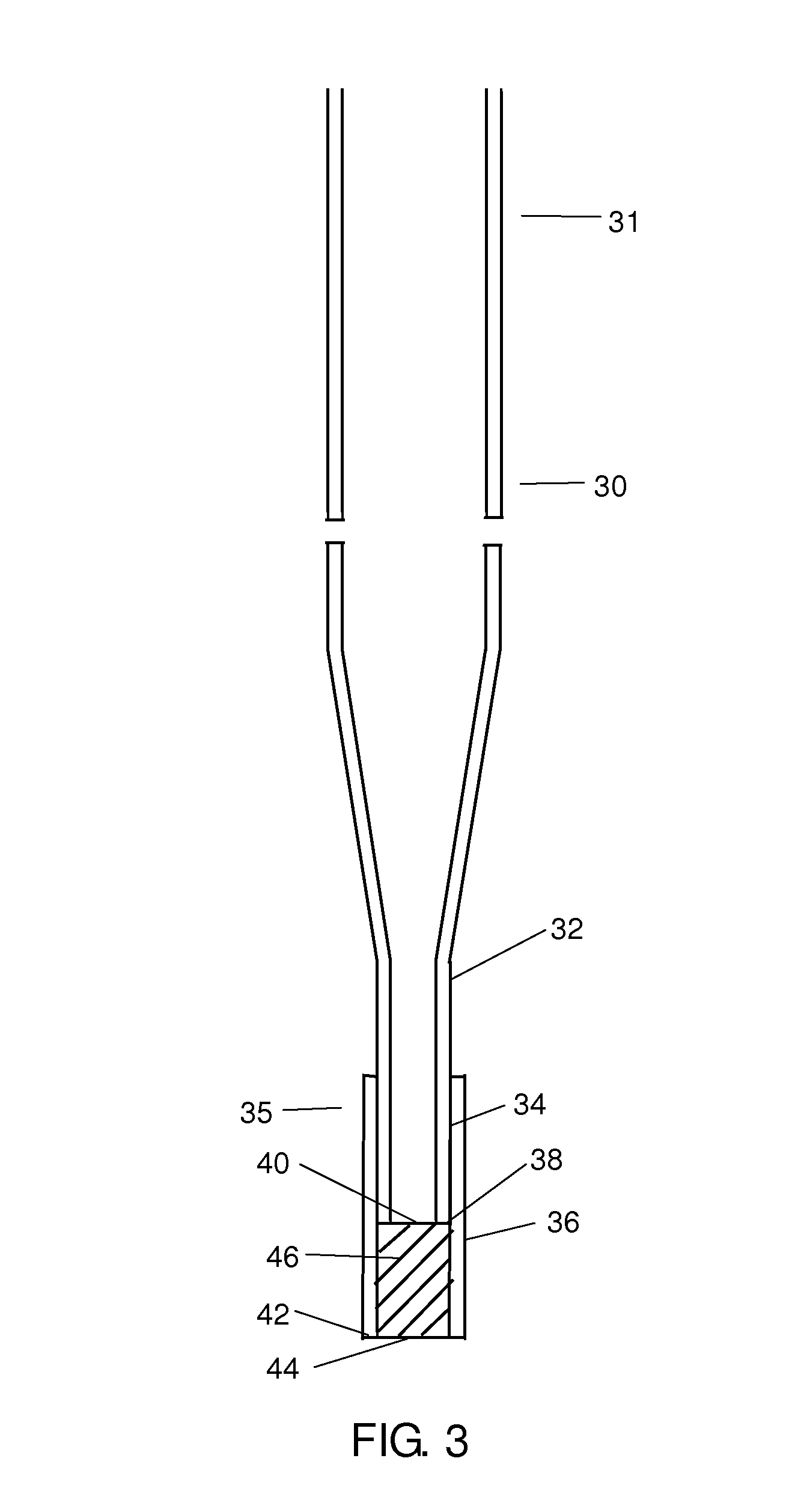
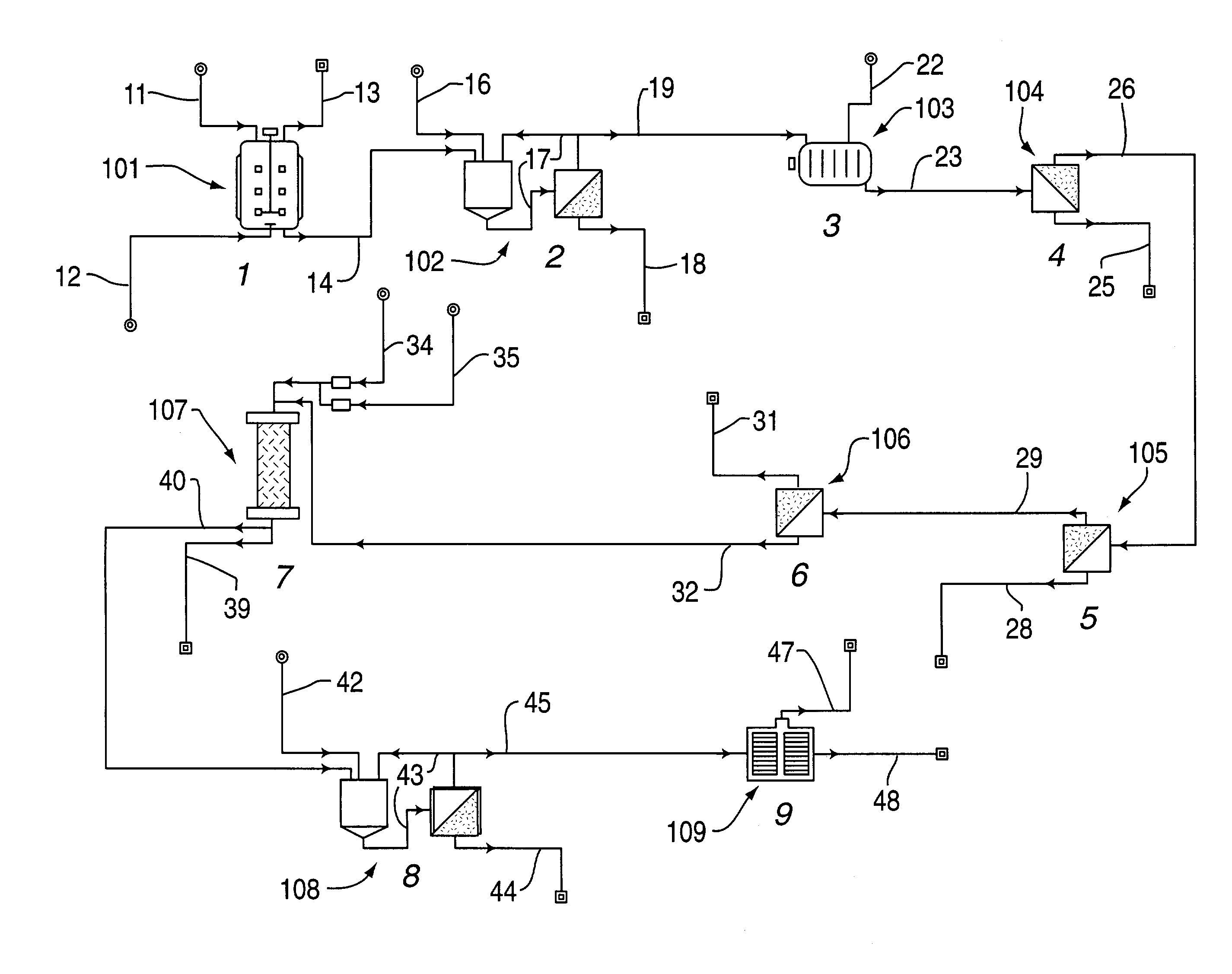
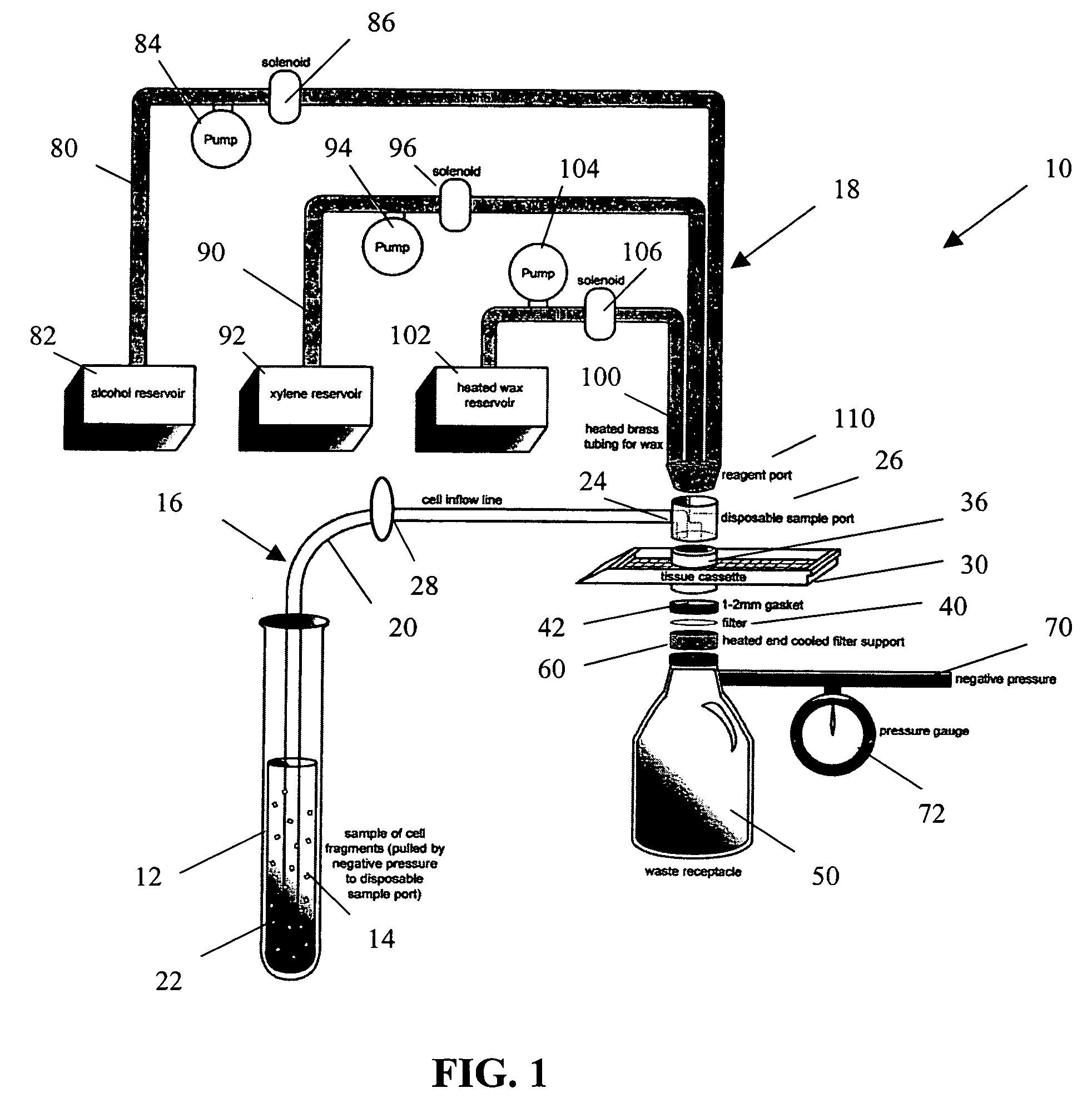
A method and apparatus for embedding cells that utilizes a flow-through embedding technique maximizes the efficiency of extractions and decreases time for embedding the cell fragments, minimizes cell loss, and automatically positions cell samples at the position in which a microtome blade will section them. The apparatus includes a cell flow pathway defined by an inflow tube for delivering cell fragments from a cell sample to a sample port. The sample port is in fluid communication with a tissue cassette having attached thereto a filter. The cell flow pathway is in communication with a reagent flow pathway for delivering the reagents through the sample port to the cassette. The apparatus is configured such that the application of pressure directs the cell fragments from the cell sample through the cell flow pathway, and effects delivery of the reagents through the reagent flow pathway. The apparatus produces an embedded cell block having concentrated cells near the plane of the block to be sectioned in a quick and efficient manner.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF
Processes for removing cells and cell debris from tissue and tissue constructs used in transplantation and tissue reconstruction
InactiveUS20070123700A1Improve inflammatory responseImprove responseHeart valvesDead animal preservationPresent methodFresh Tissue
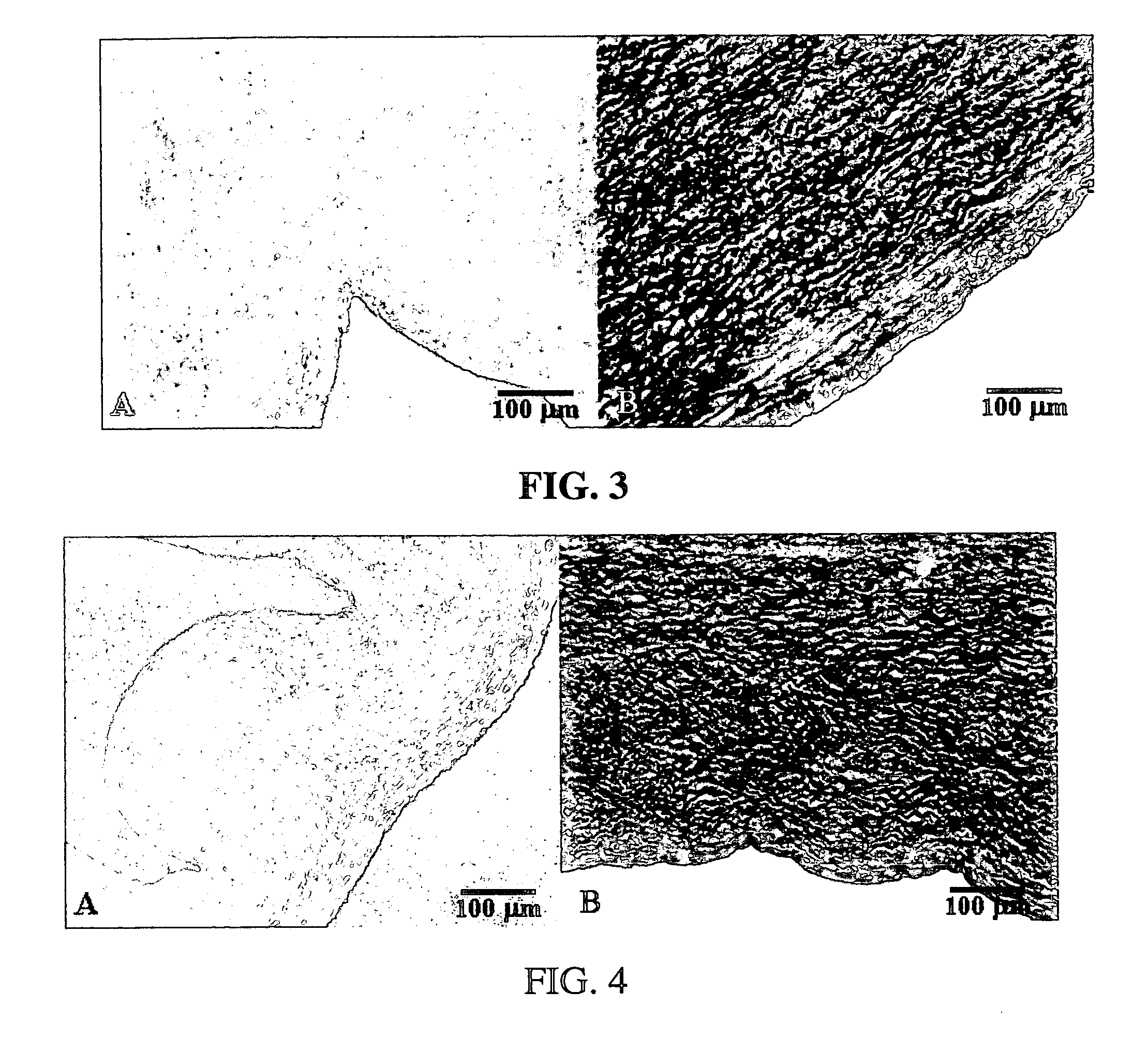
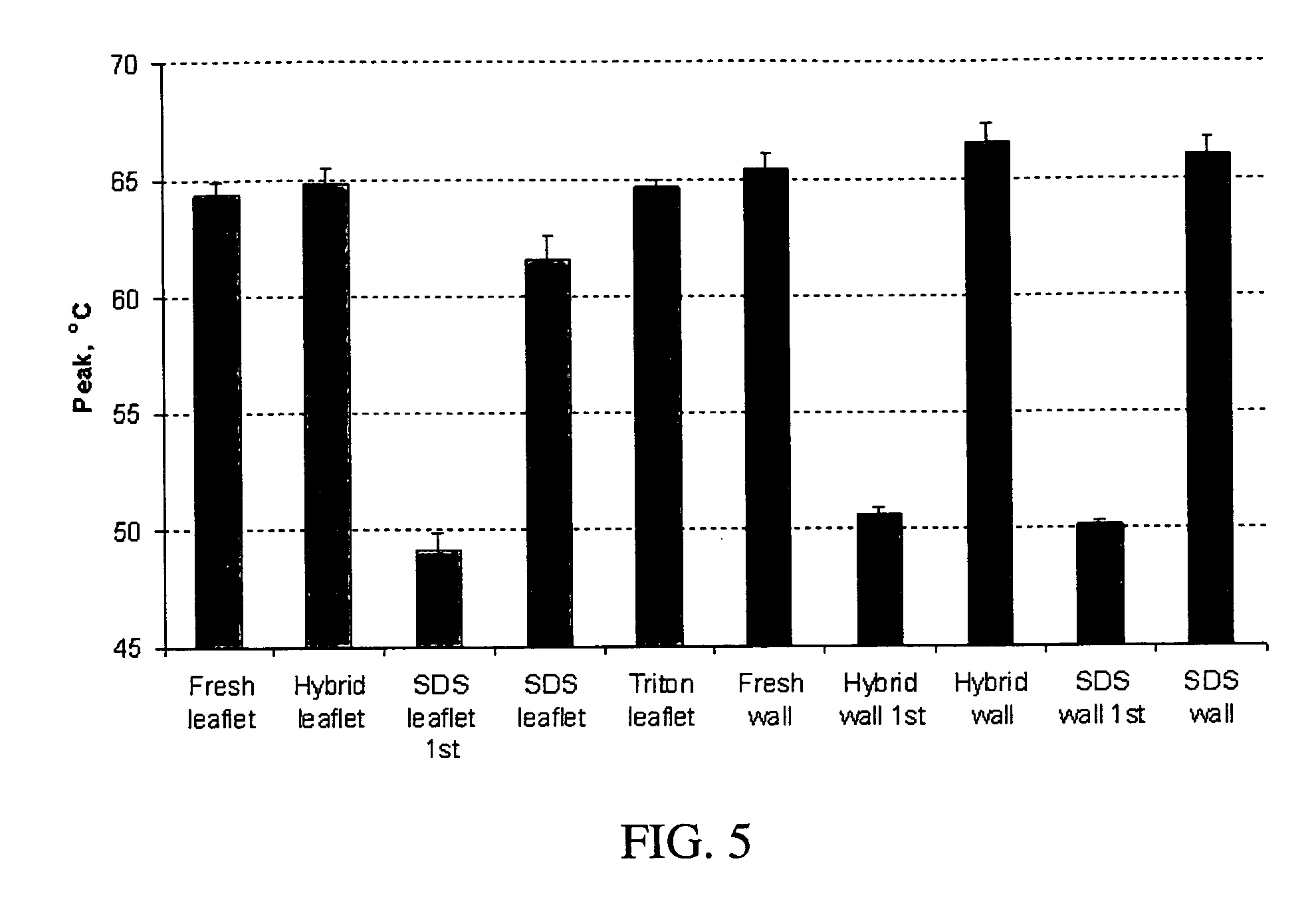
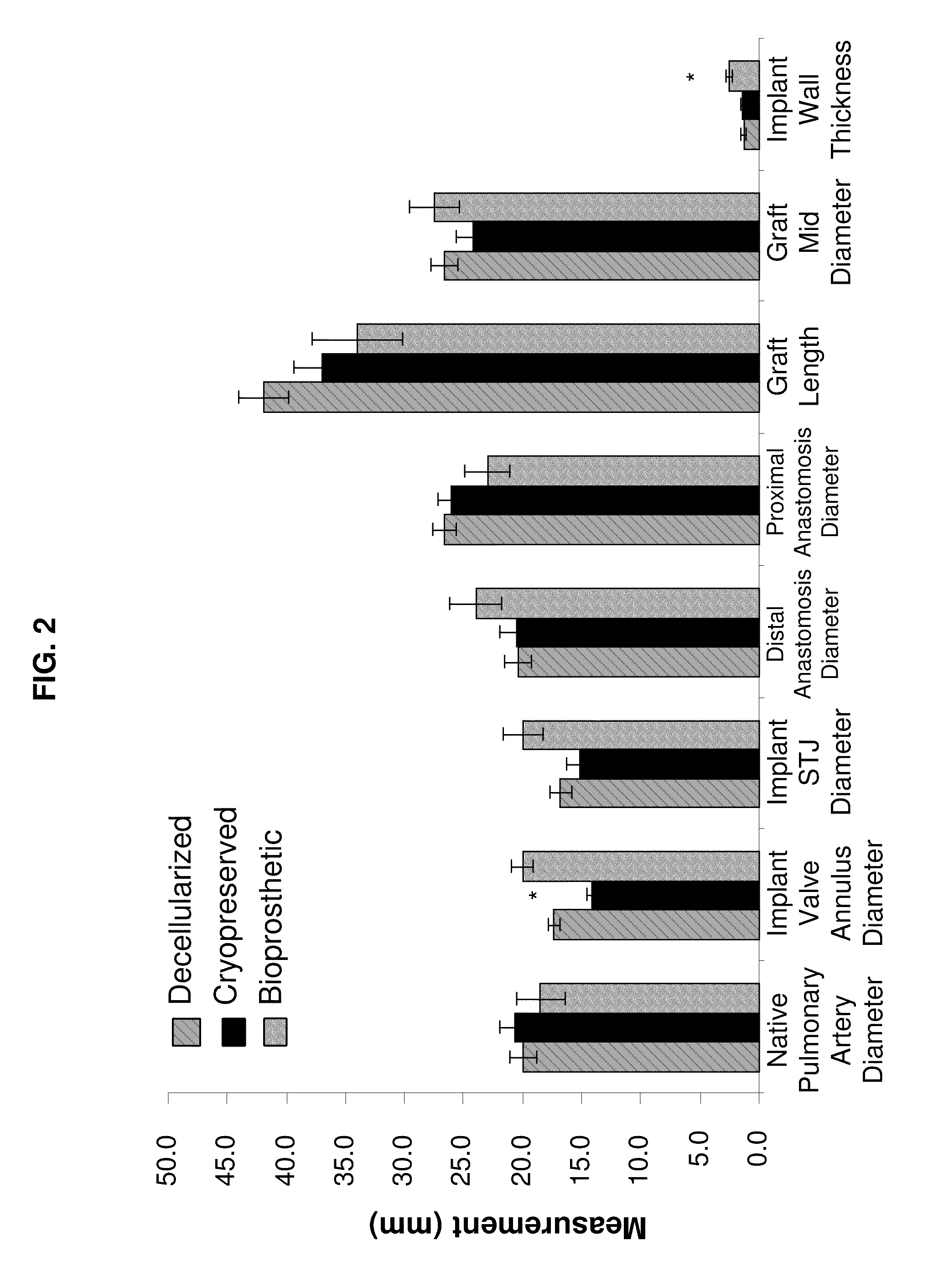
Methods for decellularizing mammalian tissue for use in transplantation and tissue engineering. The invention includes methods for simultaneous application of an ionic detergent and a nonionic detergent for a long time period, which may exceed five days. One method utilizes SDS as the ionic detergent and Triton-X 100 as the nonionic detergent. A long rinse step follows, which may also exceed five days in length. This long duration, simultaneous extraction with two detergents produced tissue showing stress-strain curves and DSC data similar to that of fresh, unprocessed tissue. The processed tissue is largely devoid of cells, has the underlying structure essentially intact, and also shows a significantly improved inflammatory response relative to fresh tissue, even without glutaraldehyde fixation. Significantly reduced in situ calcification has also been demonstrated relative to glutaraldehyde fixed tissue. Applicants believe the ionic and non-ionic detergents may act synergistically to bind protein to the ionic detergent and may remove an ionic detergent-protein complex from the tissue using the non-ionic detergent. The present methods find one exemplary use in decellularizing porcine heart valve leaflet and wall tissue for use in transplantation.
Owner:UEDA YUICHIRO +1
Ligand functional substrates
A substrate comprising a crosslinked polymer primer layer, and grafted thereto a ligand-functionalized polymer is provided. The grafted polymer has the requisite affinity for binding neutral or negatively charged biomaterials, such as cells, cell debris, bacteria, spores, viruses, nucleic acids, and proteins, at pH's near or below the pI's of the biomaterials.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
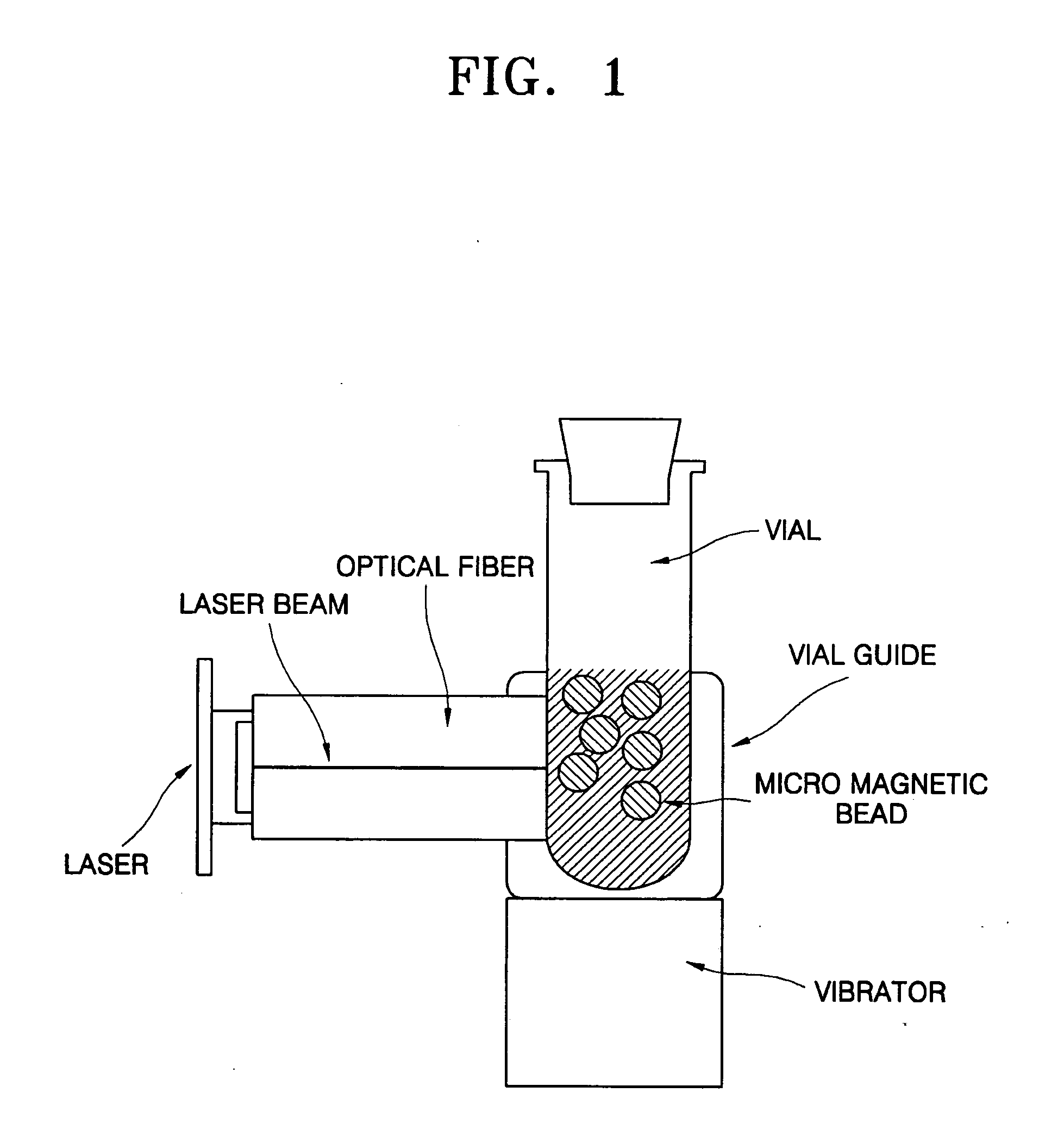
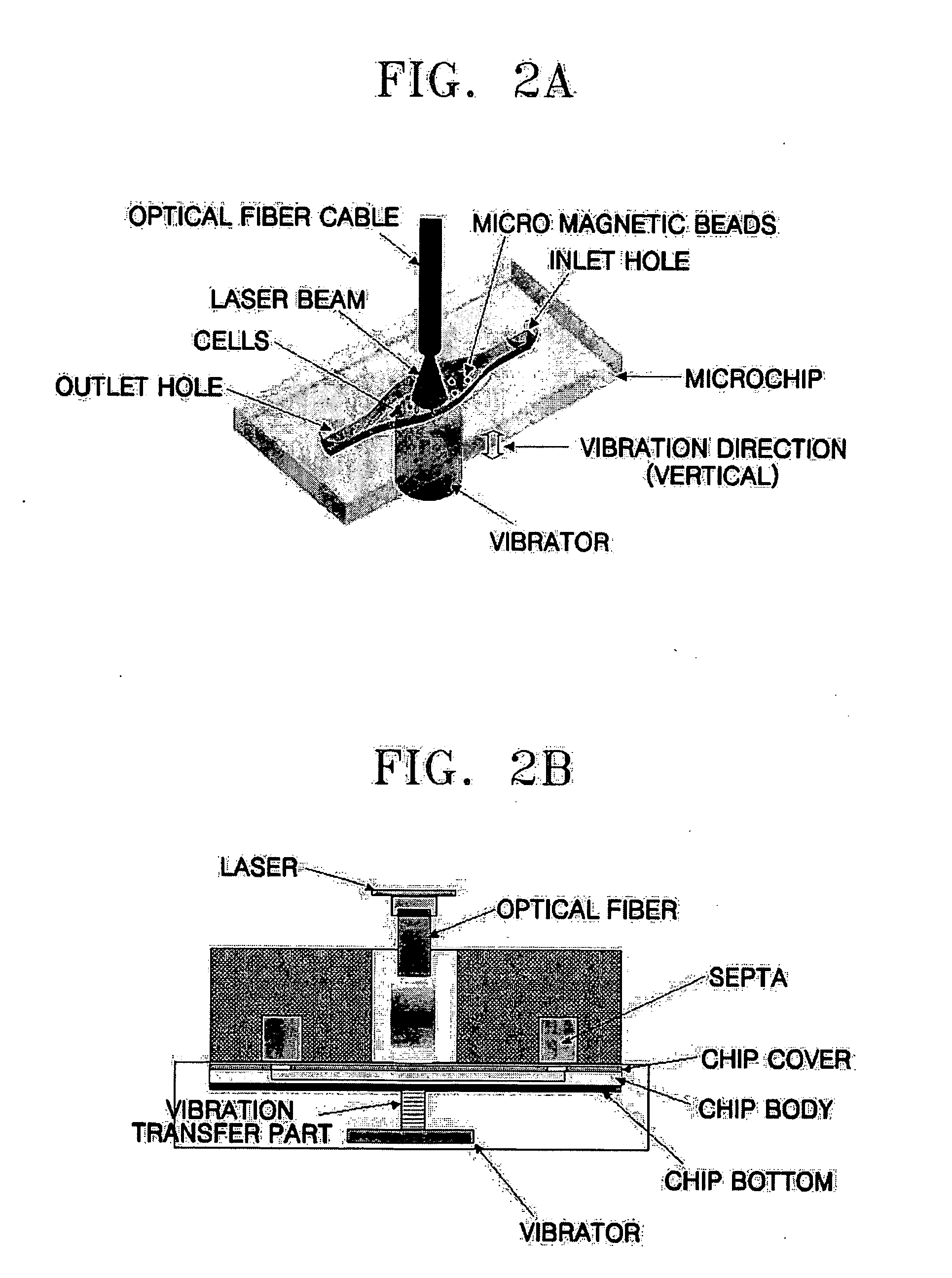
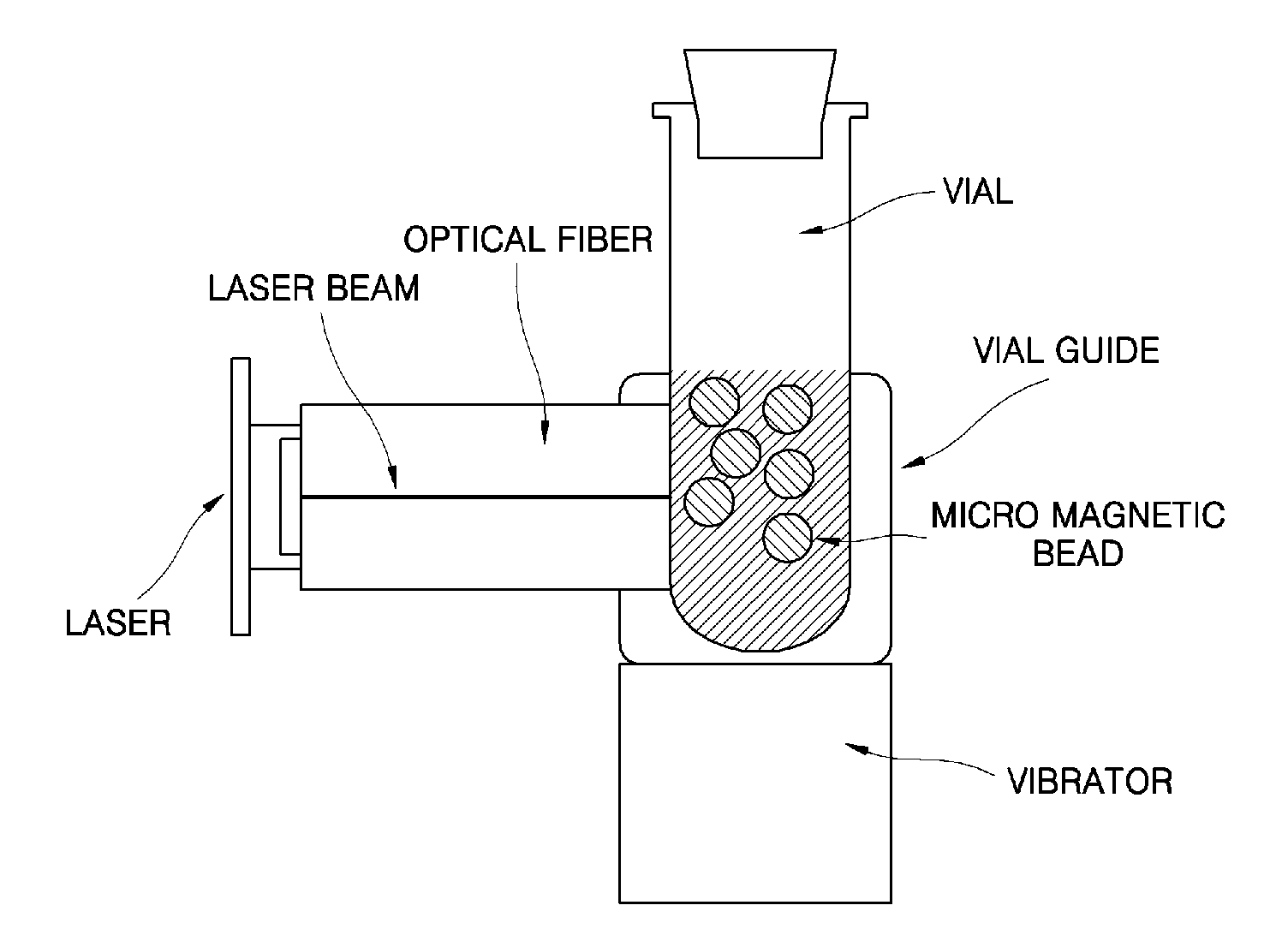
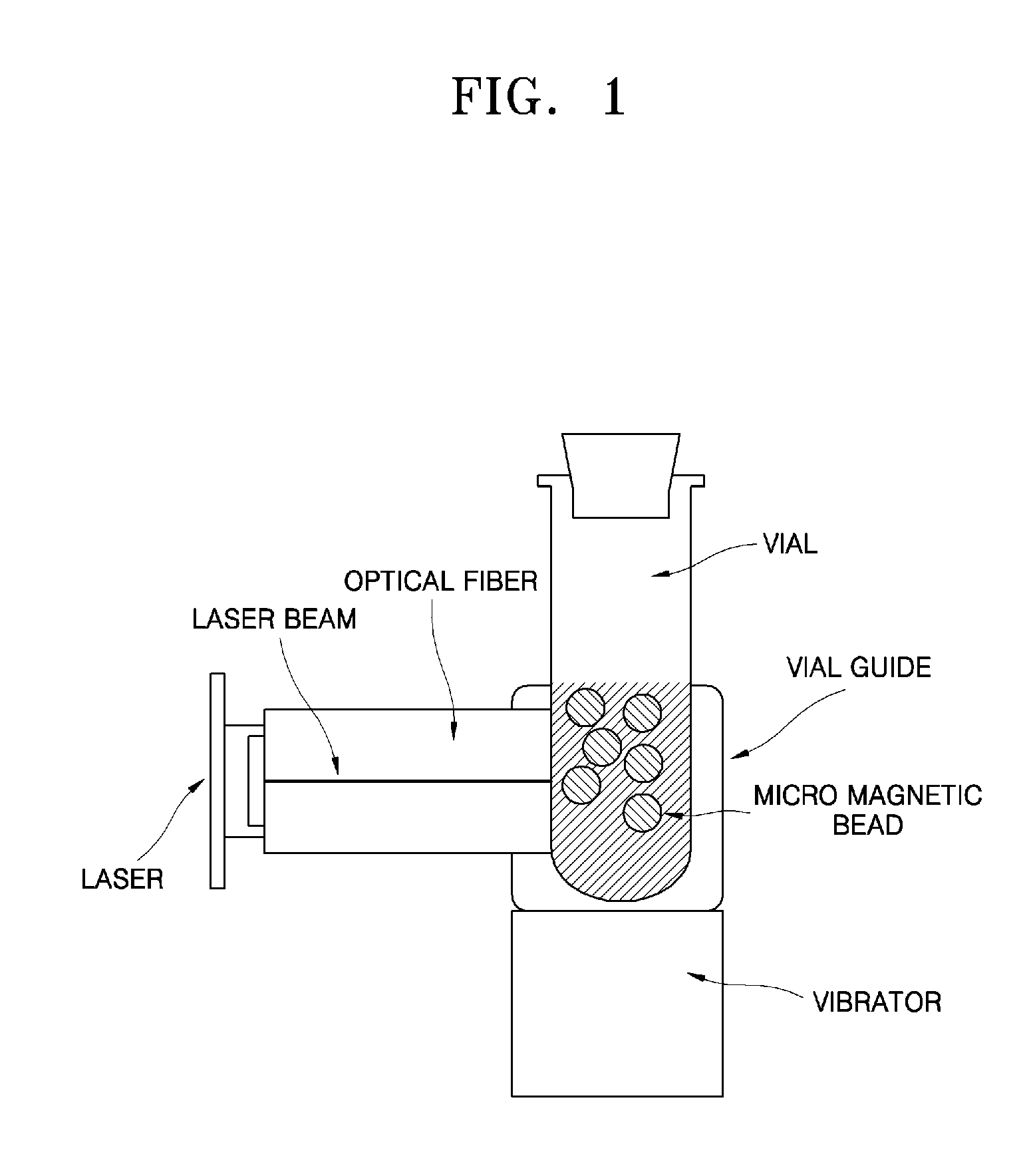
Method and apparatus for the rapid disruption of cells or viruses using micro magnetic beads and laser
ActiveUS20060084165A1Efficient releaseEfficient amplificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersRough surfaceLysis
A method and apparatus for a rapid disruption of cells or viruses using micro magnetic beads and a laser are provided. According to the method and apparatus for a rapid disruption of cells or viruses using micro magnetic beads and a laser, cell lysis within 40 seconds is possible, the apparatus can be miniaturized using a laser diode, a DNA purification step can be directly performed after a disruption of cells or viruses, and a solution containing DNA can be transferred to a subsequent step after cell debris and beads to which inhibitors of a subsequent reaction are attached are removed with an electromagnet. In addition, by means of the cell lysis chip, an evaporation problem is solved, vibrations can be efficiently transferred to cells through magnetic beads, a microfluidics problem on a rough surface is solved by hydrophobically treating the inner surface of the chip, and the cell lysis chip can be applied to LOC.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
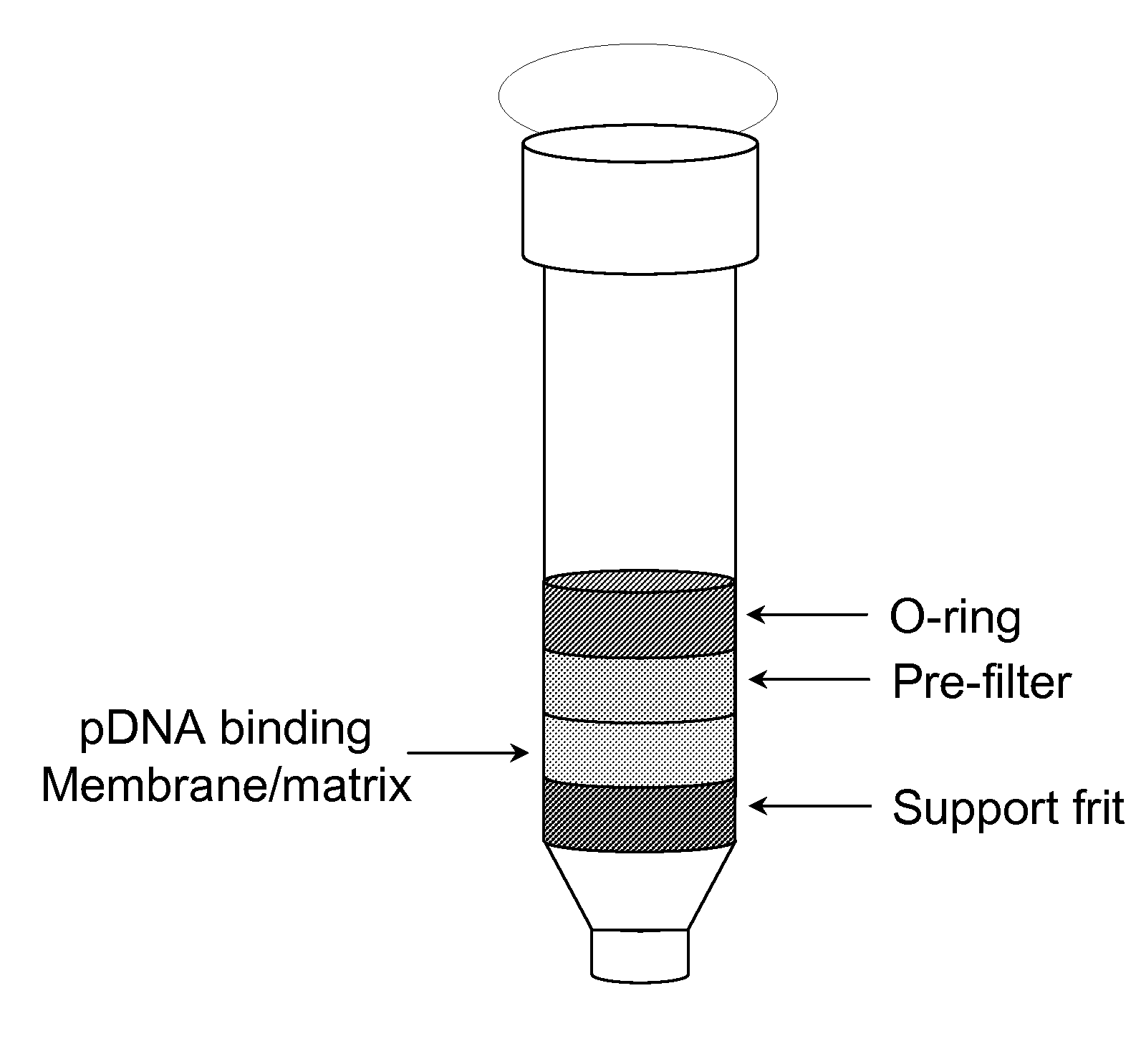
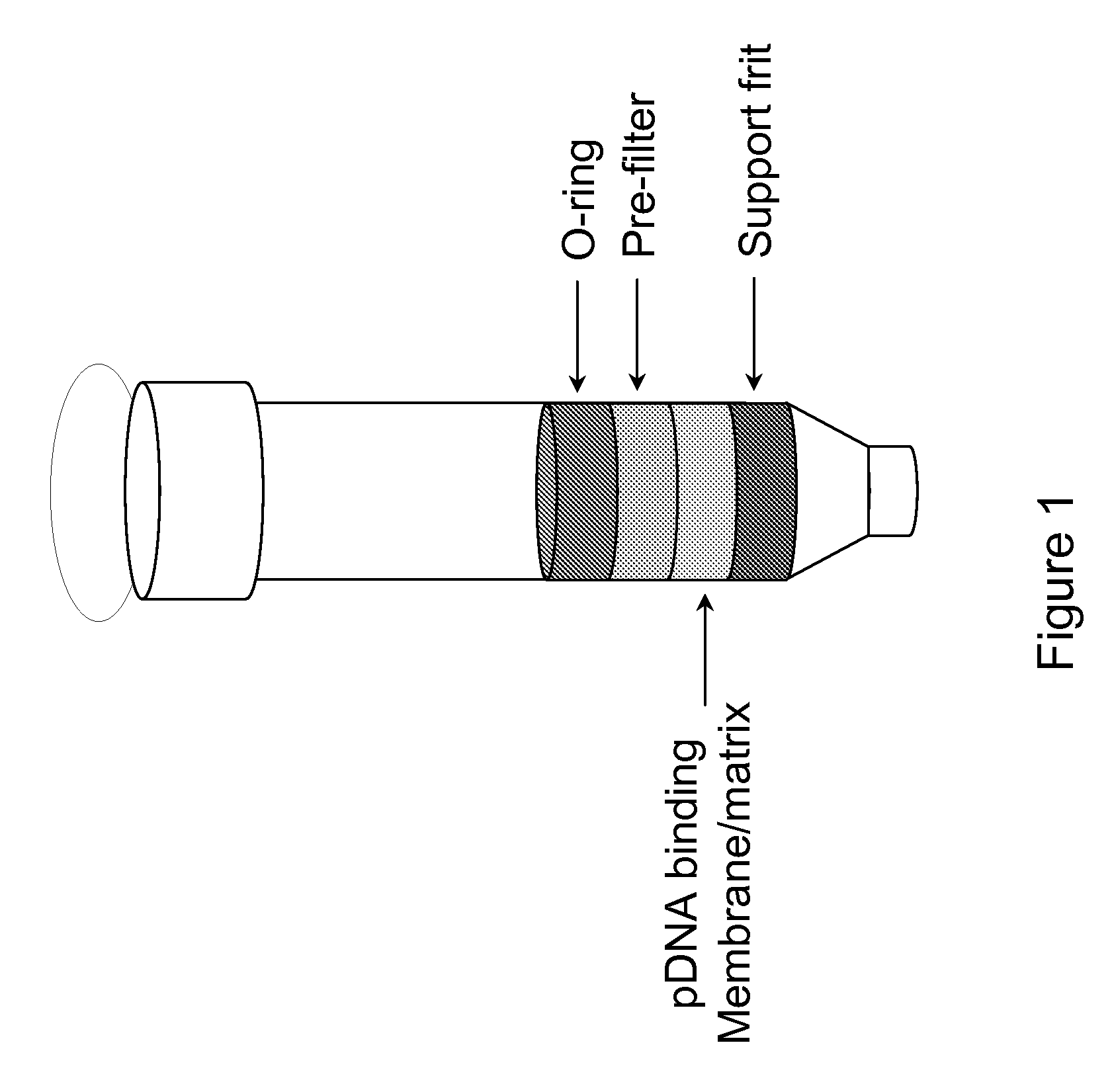
Modified spin column for simple and rapid plasmid DNA extraction
InactiveUS20080300397A1Rapid isolationImprove system performanceSamplingSugar derivativesCellular DebrisSpins
The invention relates to a modified spin column for the isolation and purification of plasmid DNA. A pre-filtration disc is included in a traditional spin column. During plasmid DNA isolation, the lysate can be loaded directly to the modified spin column, eliminates the need to first remove the flocculants containing cellular debris. This results in a much shortened process. Variation of the invention includes a depth filter in between the pre-filtration disc and the main separation matrix. Also provided are kits for isolation of plasmid DNA including the modified spin columns.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Method for decellularization
InactiveUS20110165676A1Less calcificationReduce inflammationHeart valvesNucleic acid reductionMedicineTissue Decellularization
The present invention provides for decellularized tissue and method for decellularizing tissue. The method generally comprises the steps of obtaining a harvested tissue, performing a muscle shelf debridement, treating the tissue with an enzyme, washing the tissue with a detergent, and performing an organic solvent extraction on the tissue. The tissues decellularized according to the present invention have several advantages including removing more of the residual cell debris, dsDNA, and chemicals, as well as exhibiting less calcification and better ultimate tensile strength than tissues prepared not according to the method of the present invention.
Owner:CHILDRENS MERCY HOSPITAL
Acellular amnion derived therapeutic compositions
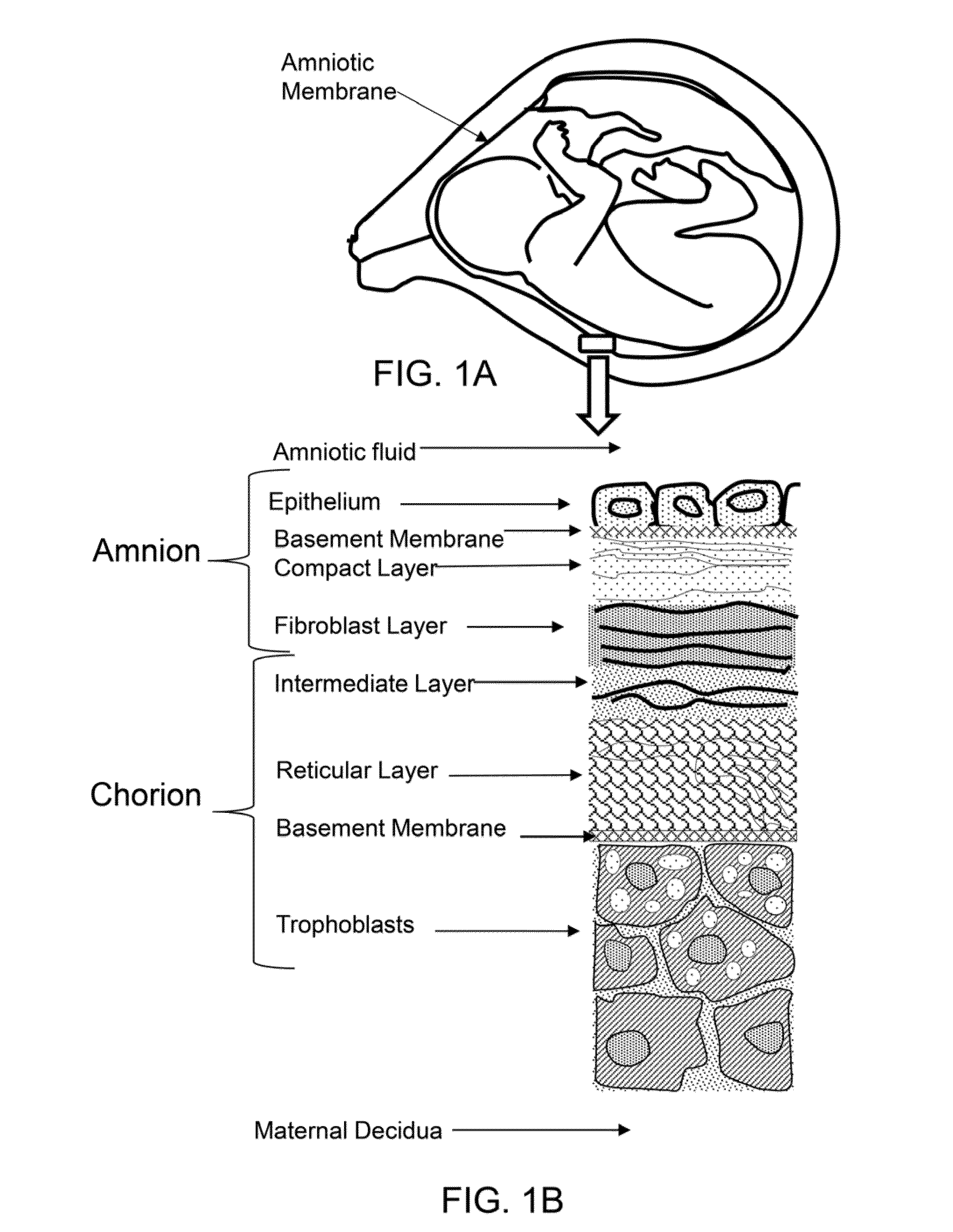
ActiveUS9132156B1Reduce in quantityInduce and responsePowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsAmniotic fluidViable cell
Acellular amnion derived therapeutic compositions are described having a number of various compositional embodiments. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition has essentially no live or active amniotic stems cells. The amniotic stem cells may be destroyed, and the cells and cell debris may be removed from the acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may comprise micronized amniotic membrane particles, and / or amniotic fluid. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may be a dispersion of micronized amniotic membrane combined with a fluid, such as plasma, saline, amniotic fluid, combinations thereof and the like. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may be combined with a matrix component to form a composite. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may be used in conjunction with a composition comprising viable cells, such as stem cells.
Owner:AMNIO TECH +1
Graft copolymer functionalized article
Guanidinyl ligand-functionalized polymers, methods of making the same, and substrates bearing a grafted coating of the ligand-functional polymers are described. The grafted polymer has the requisite affinity for binding neutral or negatively charged biomaterials, such as cells, cell debris, bacteria, spores, viruses, nucleic acids, endotoxins and proteins, at pH's near or below the pI's of the biomaterials.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method and device for sample preparation
InactiveUS20100200509A1Easily plug columnAvoid purificationMaterial nanotechnologyComponent separationPipetteFrit
The invention provides pipette tip extraction columns for the purification of a DNA vector from un-clarified cell lysate containing cell debris as well as methods for making and using such columns. The columns typically include a bed of extraction media positioned in the pipette tip column, above a bottom frit and with an optional top frit.
Owner:PHYNEXUS
Extraction method of specific mesenchymal stem cell exosome
InactiveCN109097328AReduce mechanical damageImprove separation efficiencyCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSerum freeFiltration
The invention discloses an extraction method of a specific mesenchymal stem cell exosome. The method comprises the following steps: collecting supernatant of serum-free mesenchymal stem cells: firstly, culturing mesenchymal stem cells, changing a culture medium for culturing, centrifuging, and removing cell debrises to obtain initial supernatant; taking the initial supernatant for carrying out further gradient centrifugation, transferring the centrifuged supernatant into a sterile centrifugal tube, centrifuging and collecting supernatant containing micro vesicles; centrifuging the supernatantcontaining the micro vesicles to obtain precipitate containing an exosome, washing and then centrifuging to obtain exosome precipitate; adding the obtained exosome precipitate into sterile PBS and filtering to obtain the specific mesenchymal stem cell exosome. The exosome collected in the extraction method disclosed by the invention adopts a filter membrane for filtration, so the extracted exosomeis enabled to be nanoscale; meanwhile, the rotational speed is reduced and optimized, high-speed mechanical damage is reduced, separation efficiency is high and the cost is low.
Owner:深圳市浊安认证生物技术有限公司
Method and apparatus for the rapid disruption of cells or viruses using micro beads and laser
InactiveUS20080199930A1Prevent evaporationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersRough surfaceLysis
A method and apparatus for rapid disruption of cells or viruses using beads and a laser are provided. According to the method and apparatus for rapid disruption of cells or viruses using beads and a laser, cell lysis within 40 seconds is possible, the apparatus can be miniaturized using a laser diode, a DNA purification step can be directly performed after a disruption of cells or viruses, and a solution containing DNA can be transferred to a subsequent step after cell debris and beads to which inhibitors of a subsequent reaction are attached are removed with an electromagnet. In addition, by means of the cell lysis chip, an evaporation problem is solved, vibrations can be efficiently transferred to cells through magnetic beads, a microfluidics problem on a rough surface is solved by hydrophobically treating the inner surface of the chip, and the cell lysis chip can be applied to LOC.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
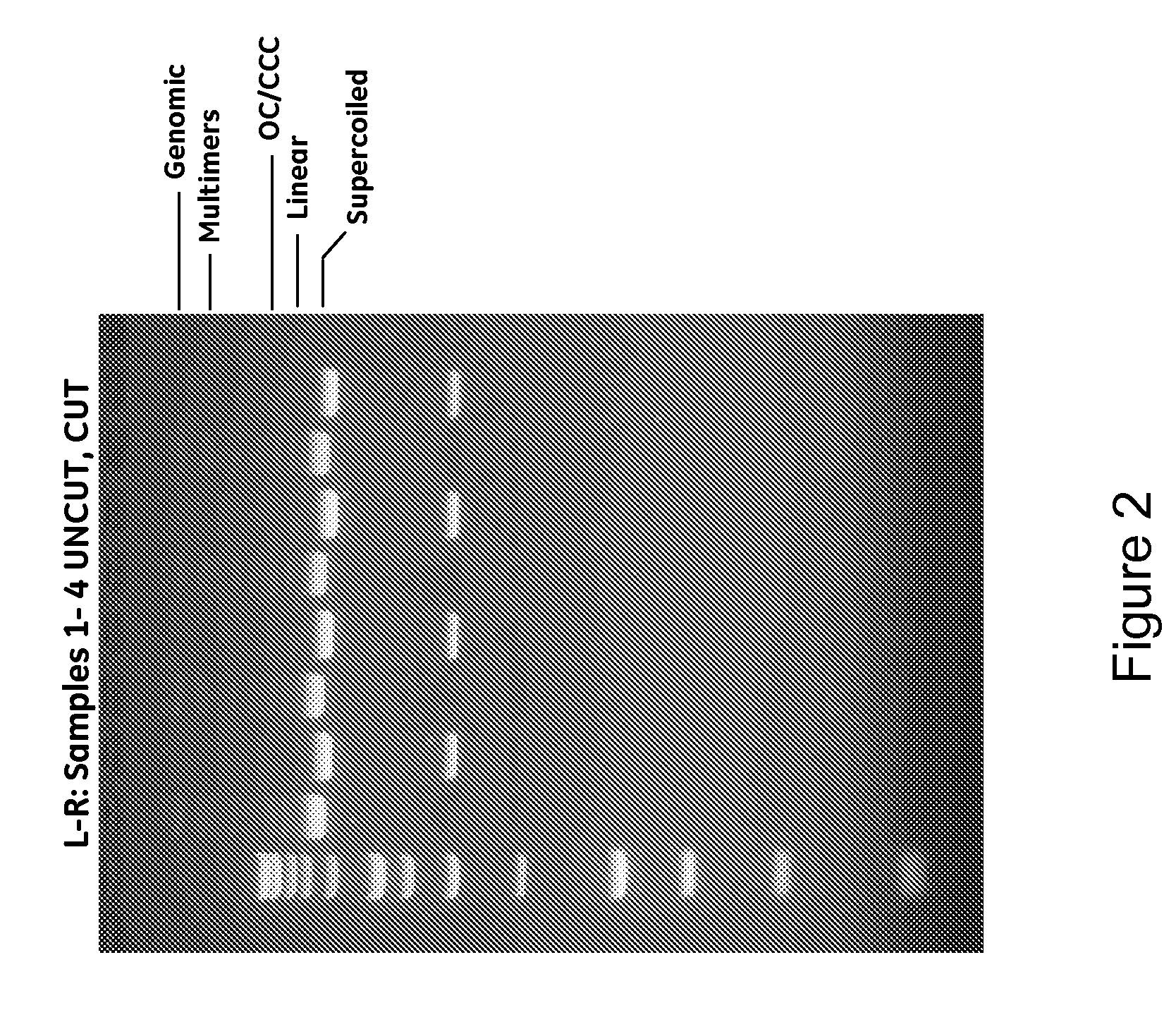
Method for extracting DNA from organisms
InactiveUS20060188967A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansFermentationBiological bodyElectrophoresis
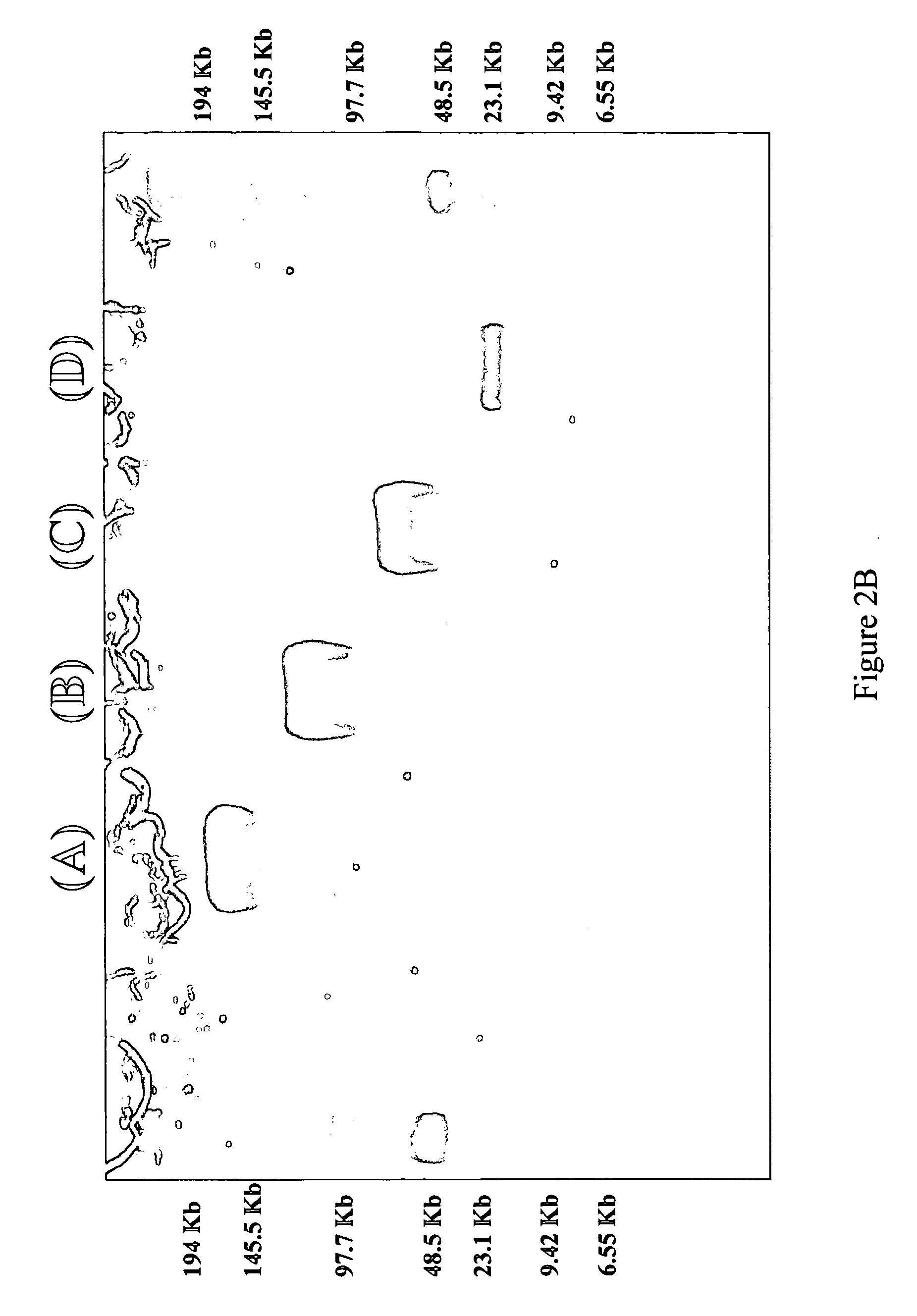
A method for the indirect extraction of DNA greater than 300 kb in size from non-cultivatable organisms contained in an environmental sample is disclosed. The method comprises isolating the organisms from the sample and embedding the isolated organisms in a block of agarose where the organisms are subsequently lysed and the DNA subjected to a first alternating field electrophoresis to extract DNA fragments which are large in size and separate them from the cell debris. The first electrophoretic migration is followed by an enzymatic restriction step and additional electrophoretic migrations. The invention also encompasses DNA obtained by the method.
Owner:NALIN RENAUD +2
Method of treatment utilizing an acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition
ActiveUS20160199417A1Reduce harmMaintain their viabilityCosmetic preparationsAerosol deliveryCELL DEBRISCompound s
Acellular amnion derived therapeutic compositions are described having a number of various compositional embodiments. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition has essentially no live or active amniotic cells. The amniotic cells may be destroyed, and the cells and cell debris may be removed from the acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may comprise micronized placental tissue particles, and / or amniotic fluid. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may be a dispersion of micronized amniotic membrane combined with a fluid, such as plasma, saline, amniotic fluid, combinations thereof and the like. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may be combined with a matrix component to form a composite. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may be used in conjunction with a composition comprising viable cells, such as stem cells.
Owner:AMNIO TECH
Bioprocess for the production of recombinant anti-botulinum toxin antibody
A process for producing recombinant anti-botulinum toxin antibody comprising the steps of fermenting recombinant E. Coli cells in broth, concentrating the cells by removing the broth, crushing the concentrated cells, separating a permeate derived from the crushed cells from cell debris, purifying a recombinant antibotulinum antibody (Fab) from said permeate, and separating said Fab from impurities by diafiltration.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Method for separating exosome from cell culture medium
InactiveCN103468642AEfficient extractionAvoid restrictionsBlood/immune system cellsTumor/cancer cellsCell culture mediaMicrobiology
The invention provides a method for separating an exosome from a cell culture medium. The method comprises the following steps of: collecting fresh cell culture medium, centrifuging the collected cell culture medium to remove the suspended cell, other cell fragments and impurities in the culture medium, transferring the supernatant into a concentration tube for concentration, and adding Total Exosome Isolation (invitrogen) into the concentrated culture medium for the final extraction of the exosome. By adopting the method provided by the invention, the exosome in the cell culture medium can be conveniently obtained, and the separation cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Plant lactobacillus M1-UVs29 and uses thereof
InactiveCN101402923AImprove securitySmall side effectsMilk preparationBacteriaFood additiveMetabolite
The invention discloses a Lactobacillus plantarum M1-UVs29 with an accession number of CGMCC No.2591. The Lactobacillus plantarum M1-UVs29 can be isolated from fermented meat products of various resources, such as preserved ham, sausage, salami, Xuanwei ham and the like, and is obtained after induced mutation and optimization. The Lactobacillus plantarum M1-UVs29 is a new strain of the induced mutation and isolation and has superior safety and minimal toxic and side effects, and can relieve classical clinical symptoms of coronary heart diseases, atherosclerosis, hyperlipemia and the like and treat cardiovascular diseases of various coronary heart diseases, atherosclerosis, hyperlipemia and the like incurred by hyperlipemia in a safe and effective way. The Lactobacillus plantarum M1-UVs29 is applied to the production of beverages, and health products of dairy products, fermented milk, acidsoy milk and the like and food additives. The obtained products of beverages, health products and food additives, containing the fermented Lactobacillus plantarum M1-UVs29 or metabolins, cell debris or secretions thereof, can effectively degrade cholesterol self-cumulated by human bodies and self-contained by food.
Owner:于长青
Method for producing biological flocculant by using sewage treatment plant residual active sludge
InactiveCN101186366AGood turbidity removalEfficient removalWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationActivated sludgeMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method to produce bio-flocculant from residual activated sludge of a sewage treatment plant, pertaining to sludge treatment and disposition technique field in environmental engineering. The method is characterized in that: the residual activated sludge of the sewage treatment plant is used as material which is pre-treated for preparing purified sludge, and the purified sludge is cell-disrupted for preparing extraction serosity, which is solid-liquid separated to respectively obtain rough microorganism flocculant solution and cell debris residues. The rough microorganism flocculant solution is post-treated to prepare the concentrate solution of the microorganism flocculant or an finished product of a solid microorganism flocculant, and the cell debris residues is post-treated to realize the zero discharge of the residual activated sludge. The effects and benefits of the invention are that: sludge is regarded as a resource to be effectively employed; compared with other recycling way of the residual activated sludge, the invention has comparatively high added value of resource utilization. The generated bio-flocculant has good effects for removing the turbidity, the organic substances and the heavy metals of waste water.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
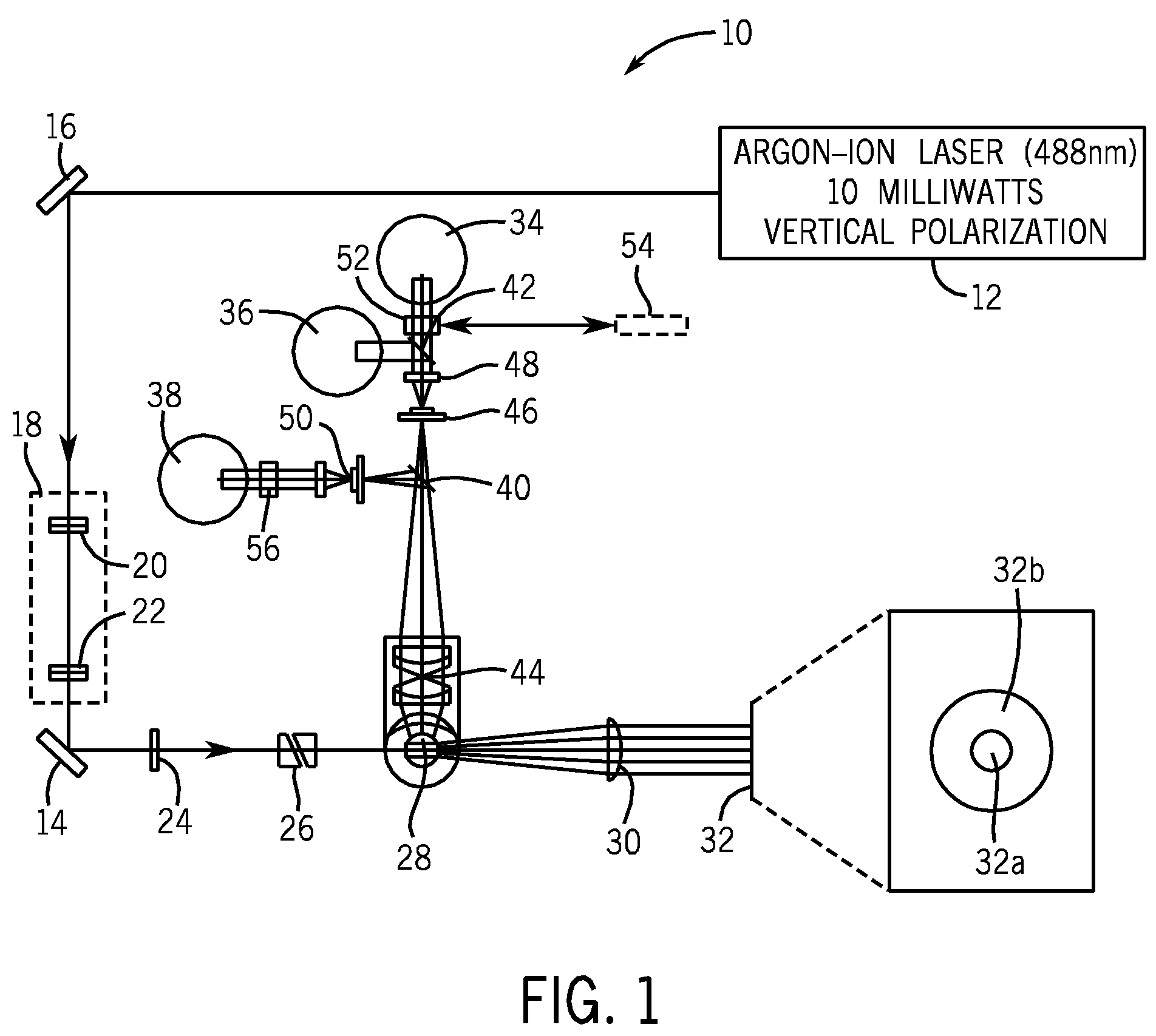
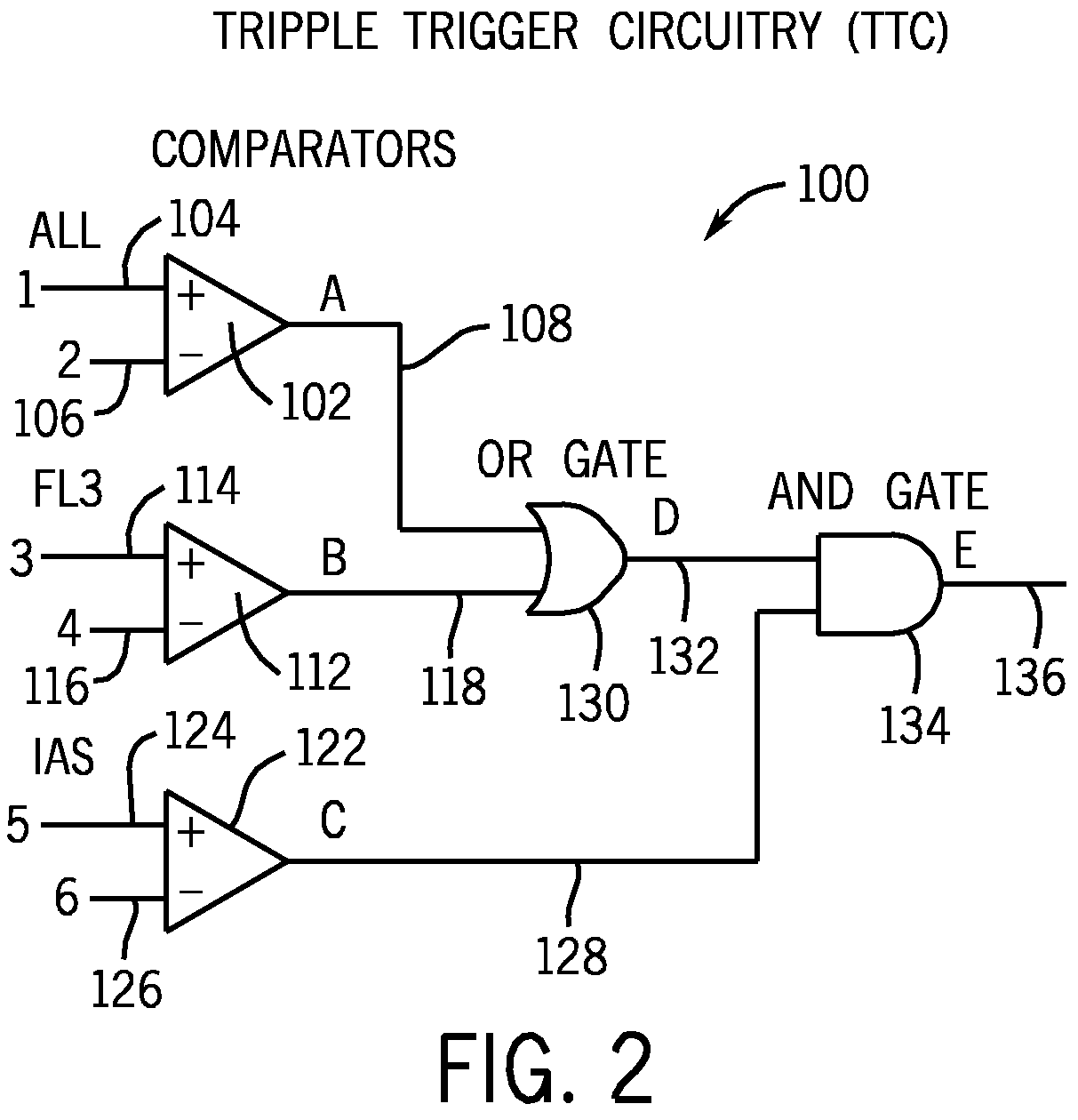
Method for classifying and counting bacteria in body fluids
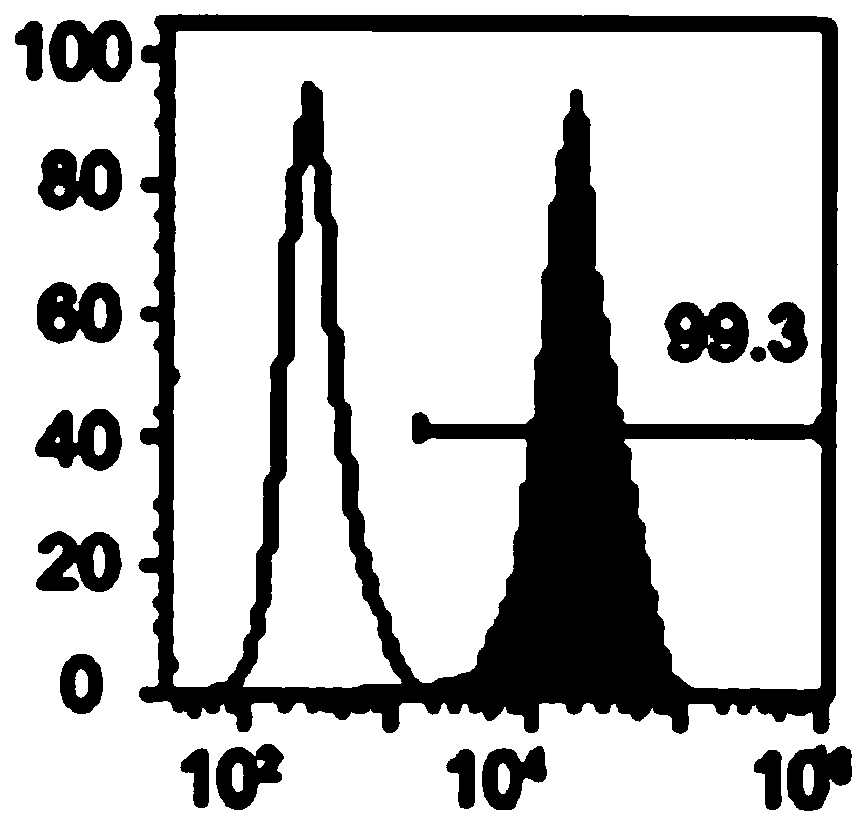
InactiveUS20100021878A1Easy to distinguishRemove noise signalMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological particle analysisFluorescenceWhite blood cell
A method for distinguishing erythroblasts from bacteria by automated hematology analyzers, such as, for example, the CELL-DYN® 4000 automated hematology analyzer and the CELL-DYN® Sapphire™ automated hematology analyzer. Bacterial cells scatter light and fluoresce differently than do red blood cells, white blood cells, erythroblast nuclei, and platelets. Signals generated by bacteria are distinguishable from those of erythroblasts because the signals generated by erythroblast nuclei are sufficiently unique that erythroblast nuclei can be distinguished from signals generated by bacteria. Signals generated by platelets, lysed red blood cell ghosts, and other cell debris are blocked by the triple-trigger circuitry of the hematology analyzer, because all of the signals generated by noise are below the AND / OR thresholds. Algorithm(s) in the software of the system detect and count signals generated by bacteria by means of the location and the shape of the signals generated by bacteria and calculate the concentration of bacteria per unit of body fluid. In addition, certain body fluids, such as, for example, synovial fluid, can be pretreated with a viscosity reducing agent for a short period of time to reduce the viscosity of the body fluid prior to analyzing a sample of the body fluid by an automated hematology analyzer.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Method for preparing mesenchymal stem cell exosome and application thereof
InactiveCN109097326AReduce volumeFacilitated releaseCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsUmbilical cord tissueCuticle
The invention provides a method for preparing a mesenchymal stem cell exosome. The method comprises the steps that human umbilical cord tissue surface blood is cleaned to remove epidermal and vasculartissues, Wharton jelly is taken out for cleaning, then the tissues are cut into pieces, and inoculation is performed for culture; subculturing is performed; second generation of umbilical mesenchymalstem cells are inoculated and cultured; a cell stimulator factor for promoting secretion of the exosome is added; when the cells grow to the fusion degrees 90%, first cell supernate is sucked out forseparating the exosome; the first cell supernate is centrifuged to remove cell debris, and second cell supernate is collected; the first time of ultrafiltration and concentration is conducted on thesecond cell supernate, excessive moisture is removed, and a first concentrated solution is obtained; the first concentrated solution is subjected to the second time of ultrafiltration and concentration, excessive moisture is removed, and a second concentrated solution is obtained; the first time of ultracentrifugation is conducted on the second concentrated solution, and the supernate is taken andsubjected to the second time of ultracentrifugation, the supernate is removed, and precipitation is performed to obtain the exosome for stem cell secretion; normal saline is added for cleaning and centrifugation, the supernate is removed, and the exosome precipitate is obtained.
Owner:GUANGDONG VITALIFE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for separating exosomes from animal plasma and for detecting purity
InactiveCN105779586AFast and Efficient Separation MethodsEfficient separationMicrobiological testing/measurementCellular componentCentrifugation
The invention provides a method for separating exosomes from animal plasma and for detecting purity. The method mainly comprises the following steps: first, thinning the plasma by virtue of a PBS (phosphate buffer solution) at the ratio of 1 to 1; removing cell components and cell debris in the plasma through centrifuging; precipitating the exosomes through ultrahigh-speed centrifugation; suspending the exosomes by virtue of 250[mu]l of the PBS solution; extracting total RNA in an exosome suspension by virtue of Trizol LS; and conducting poly (A) reversing and related gene quantification on the extracted total RNA, and detecting the purity. The method disclosed by the invention is conducive to researches on plasma exosome contents and exosome related functions in the future.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Method for extracting lipid from Chlorella sorokiniana CS-01
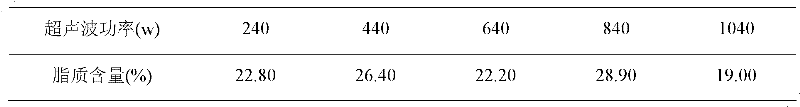
The invention discloses a method for extracting lipid from Chlorella sorokiniana CS-01 (CCTCC M209220), namely an ultrasonic-assisted chloroform / methanol extraction method. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: collecting algae, drying, extracting by using chloroform / methanol, performing ultrasonic crushing, washing, and drying. Through the certification, compared with a Soxhlet extraction method, an acid heat extraction method, and a chloroform / methanol extraction method, the method has the advantages that: the extraction ratio of the lipid is improved by 1.4, 1.7 and 0.5 timesrespectively; meanwhile, a lipid extraction phase is positioned under a cell debris solid phase, so the method is favorable for the subsequent direct separation of the lipid, and meets the requirements of mass industrialized production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
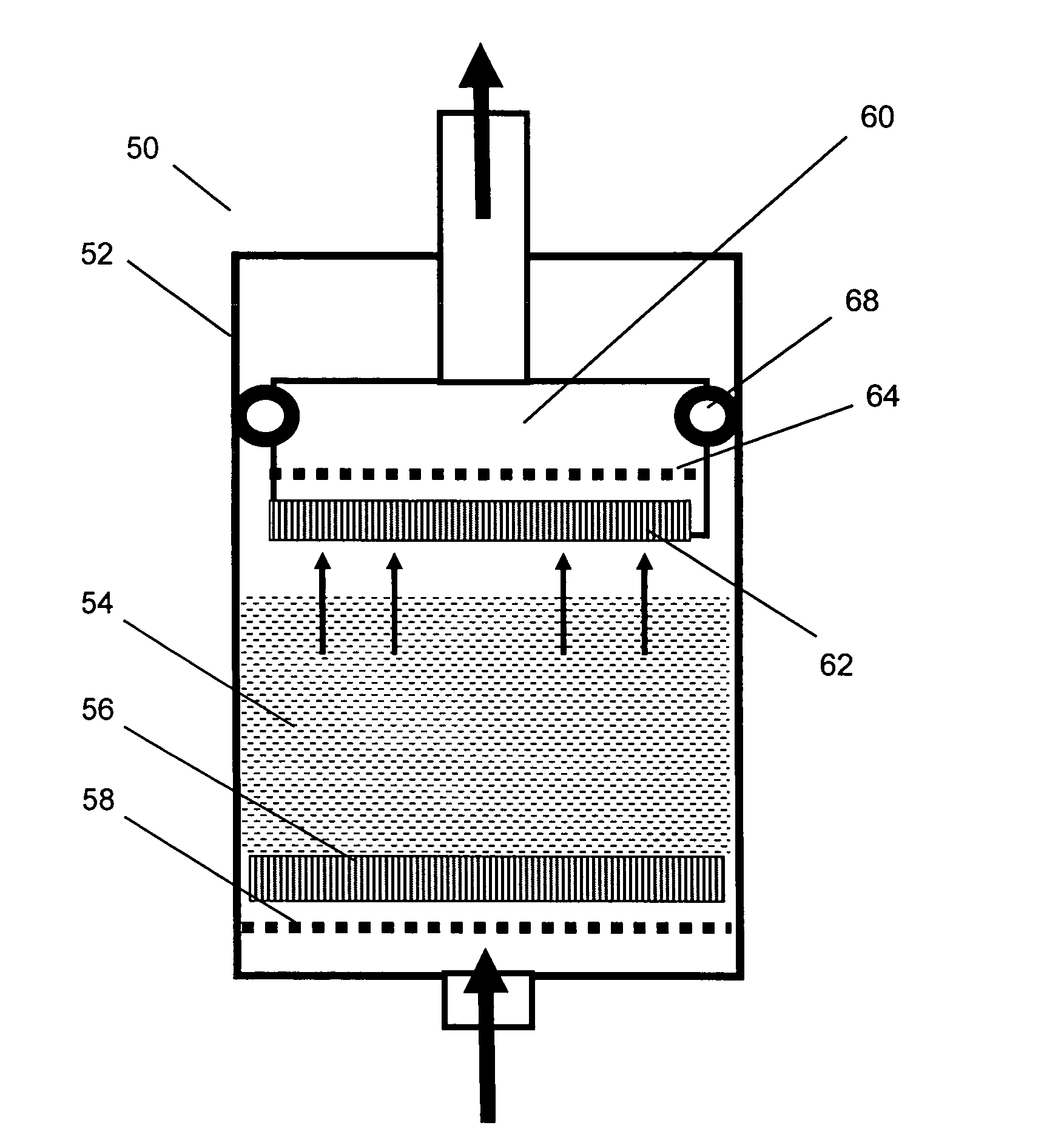
Method and apparatus for preparing cells for microtome sectioning and archiving nucleic acids and proteins
InactiveUS7541161B2Maximize efficiencyReduce amountBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringCELL DEBRIS
A method and apparatus for embedding cells that utilizes a flow-through embedding technique maximizes the efficiency of extractions and decreases time for embedding the cell fragments, minimizes cell loss, and automatically positions cell samples at the position in which a microtome blade will section them. The apparatus includes a cell flow pathway defined by an inflow tube for delivering cell fragments from a cell sample to a sample port. The sample port is in fluid communication with a tissue cassette having attached thereto a filter. The cell flow pathway is in communication with a reagent flow pathway for delivering the reagents through the sample port to the cassette. The apparatus is configured such that the application of pressure directs the cell fragments from the cell sample through the cell flow pathway, and effects delivery of the reagents through the reagent flow pathway. The apparatus produces an embedded cell block having concentrated cells near the plane of the block to be sectioned in a quick and efficient manner.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Method and device for sample preparation
InactiveUS8377715B2Easily plug columnsAvoid purificationMaterial nanotechnologyComponent separationFritPipette
The invention provides pipette tip extraction columns for the purification of a DNA vector from un-clarified cell lysate containing cell debris as well as methods for making and using such columns. The columns typically include a bed of extraction media positioned in the pipette tip column, above a bottom frit and with an optional top frit.
Owner:PHYNEXUS
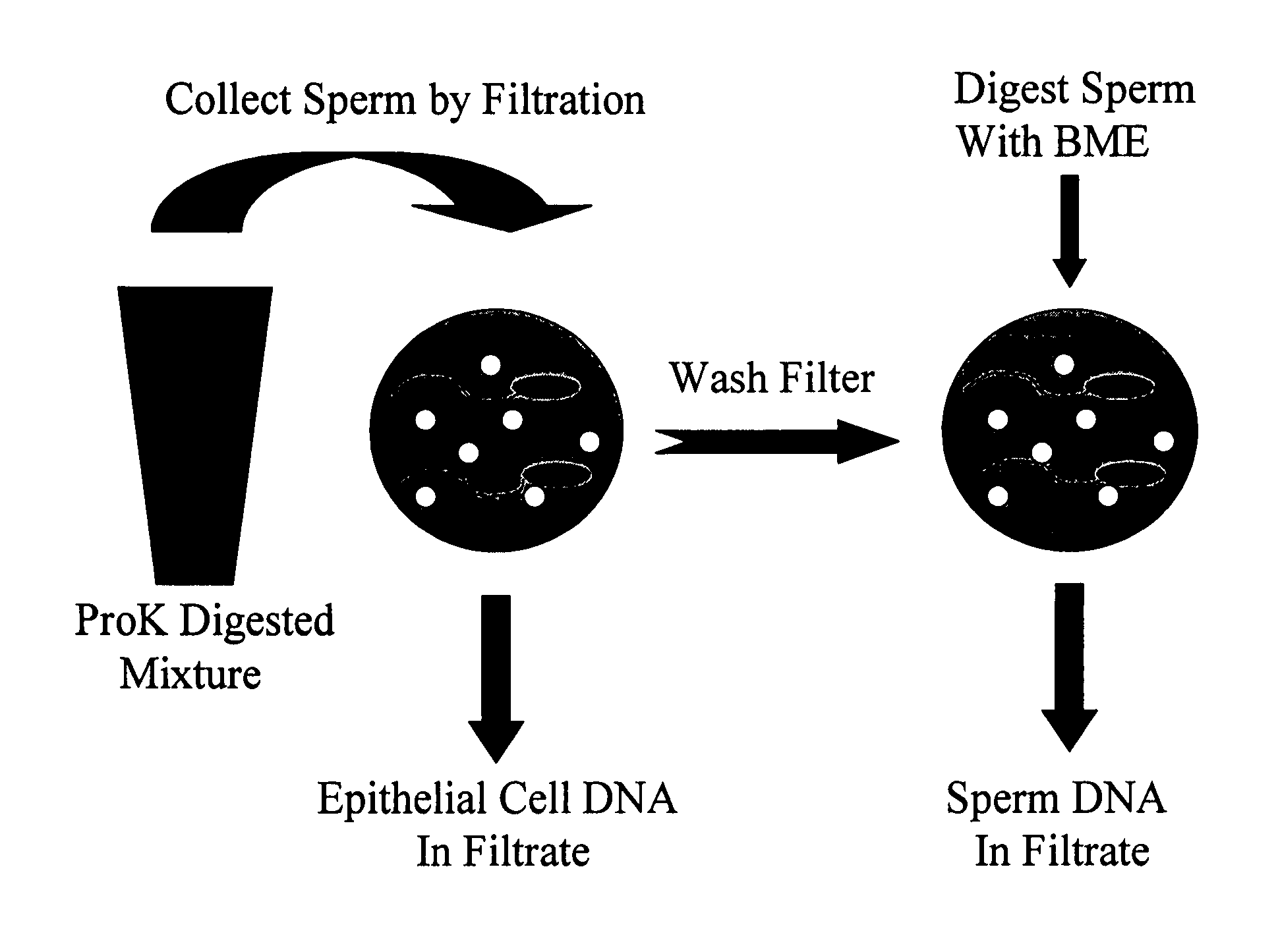
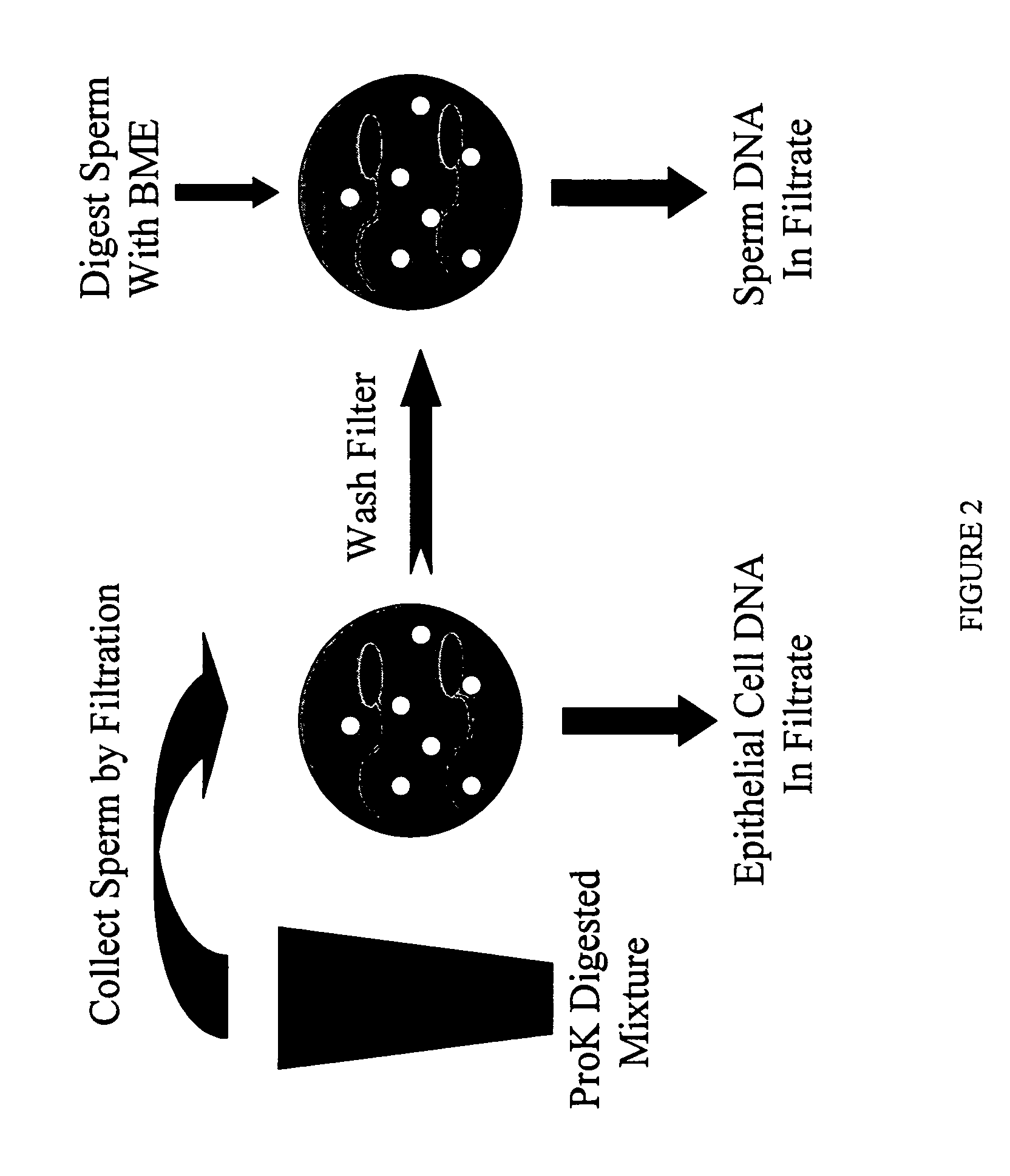
Method for processing samples containing sperm and non-sperm cells for subsequent analysis of the sperm DNA
InactiveUS20050032097A1Suitable for automationReliable resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid reductionFiltrationBiology
In various aspects, the present invention provides novel and effective methods and kits for the isolation of sperm and sperm DNA from samples having at least one other cell type, or having the DNA of one other cell type. More specifically, a process for isolating sperm DNA from a mixture of sperm and non-sperm cells by filtration is provided. DNA from non-sperm cells is solubilized by selective lysis, and the intact sperm are retained on a filter, washed, and then treated in situ with a reducing agent to solubilize the sperm DNA. Significantly, centrifugation steps are not required, the process can be easily automated, and can be performed on many samples in parallel. The novel methods and kits are based on filtering selectively solubilized samples through filters that retain sperm by virtue of having uniform pore diameters that: are smaller than sperm, large enough to allow passage of cell debris and solubilized DNA; and are stable to pressure. The inventive methods and kits have broad utility, particularly in the forensic art.
Owner:GARVIN ALEX M
Concentration and enrichment of microbial cells and microbial nucleic acids from bodily fluids
ActiveUS8481265B2Improve concentrationEfficient extractionSugar derivativesBacteriaMicrobial fuel cellMicrobiology
The present invention relates to a method for isolating microorganisms and / or microorganisms nucleic acids from a bodily fluid that may comprise or may be suspected to comprise microorganisms and / or host cells and / or host cells debris. Microorganisms nucleic acids may further be isolated by lysing the isolated microorganisms. The present invention also relates to a method for detecting microorganisms in a bodily fluid. The present invention further relates to a saponin formulation and its use.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Preparation method and application of mesenchymal stem cell exosome
InactiveCN108624557AImprove mitochondrial damageFunction increaseCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsReperfusion injuryApoptosis
The invention relates to a preparation method of a mesenchymal stem cell exosome. The preparation method comprises the following steps: culturing mesenchymal stem cells for several hours by using a serum-free conditioned culture medium, centrifuging and removing the cells, collecting a liquid supernatant crude product, then re-centrifuging, filtering, and removing the residual cells as well as cell debris to prepare liquid supernatant containing an exosome; preparing the exosome by stepwise centrifugation of polyethylene glycol adopted by the liquid supernatant containing the exosomes. Exosome-expressed specific proteins CD63 prepared by the preparation method provided by the invention can effectively improve the mitochondria damage of the myocardial cells, prevent the cell apoptosis and improve the functions of the myocardial cells and are used for preparing a drug for treating myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury.
Owner:章毅 +7
Spirulina phatensis polysaccharide and extraction method thereof
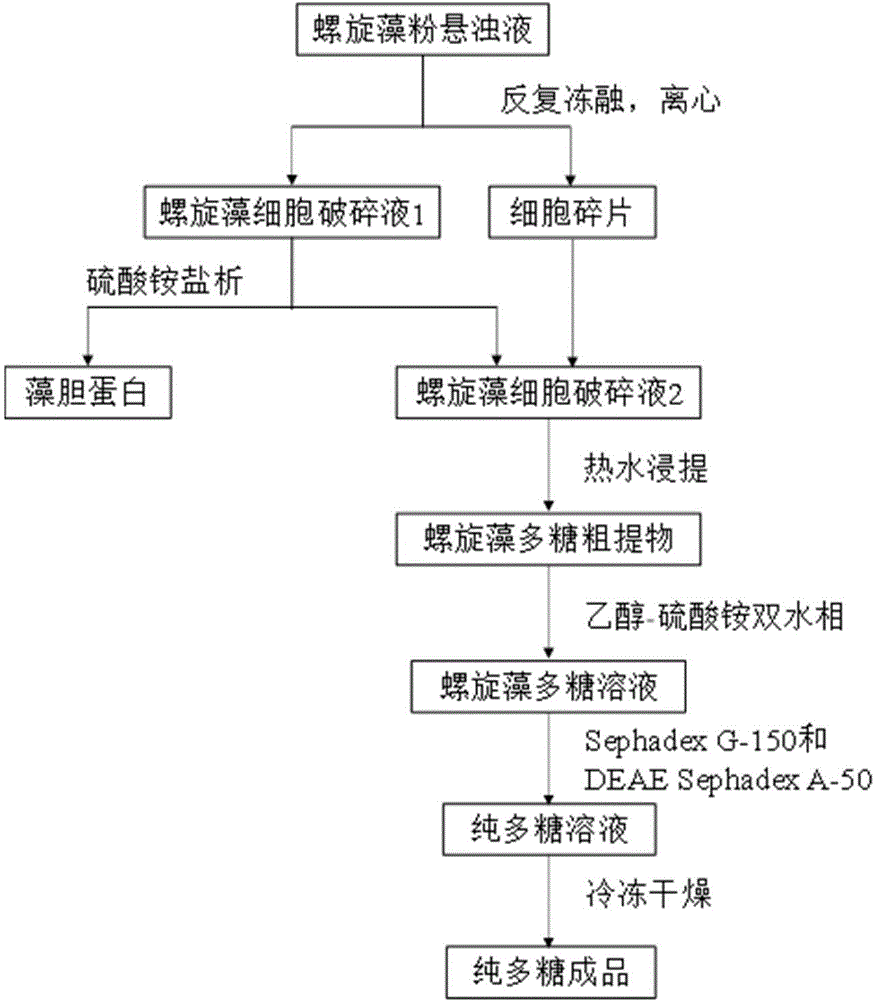
The invention relates to a spirulina phatensis polysaccharide and an extraction method thereof. The extraction method comprises the following steps: after multigelation and wall breaking of a spirulina phatensis powder suspension, centrifuging to obtain a cell lysate 1 and cell debris; adding ammonium sulfate in the cell lysate 1 until the saturation is 50%, after salting-out precipitation, centrifuging to remove phycobiliprotein to obtain a supernatant, and evenly mixing the supernatant and the cell debris to obtain a cell lysate 2; obtaining a spirulina phatensis polysaccharide crude extract by using a hot water extraction method; adding the crude extract to an ethanol / ammonium sulfate aqueous two-phase system, and extracting to obtain a bottom-phase solution of spirulina phatensis polysaccharide with higher purity; after the bottom-phase solution is desalted by dialysis, eluting by using a Sephadex G-150 chromatographic column and a DEAE Sephadex A-50 anion exchange column to obtain a pure spirulina phatensis polysaccharide solution; and freeze-drying, thereby obtaining a pure spirulina phatensis polysaccharide finished product. The extraction method can be used for avoiding the traditional complicated protein removal operation steps, has low cost, high yield, and high purity and activity of polysaccharide, and is suitable for intermittent and large-scale production and processing.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
Serum-free medium and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN105420189AAvoid situations where the growth process is unstableSolve the shortcomings of poor adhesion ability and slow proliferationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSerum free mediaFiltration membrane
The invention discloses a novel serum-free medium. The serum-free medium comprises, by volume, 0.05-0.2 part of beta-mercaptoethanol, 0.5-2 parts of a non-essential amino acid aqueous solution, 4-6 parts of human mesenchymal stem cell cultural concentrated supernatant and 90-95 parts of a-MEM / DMEM-F12 and recombination human basic fibroblast growth factors with the final concentration of 5-15 ng / ml. A preparing method of the cultural concentrated supernatant includes the following steps that umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell cultural supernatant is collected; cells, cell debris, impurities and the like are centrifugally removed; filtering is carried out through a micro-filtration membrane; ultrafiltration and concentration are carried out. When cultured through the medium, stem cells still keep the multi-directional differentiation potential and the high multiplication capacity under the long-time culturing condition.
Owner:郭镭 +2
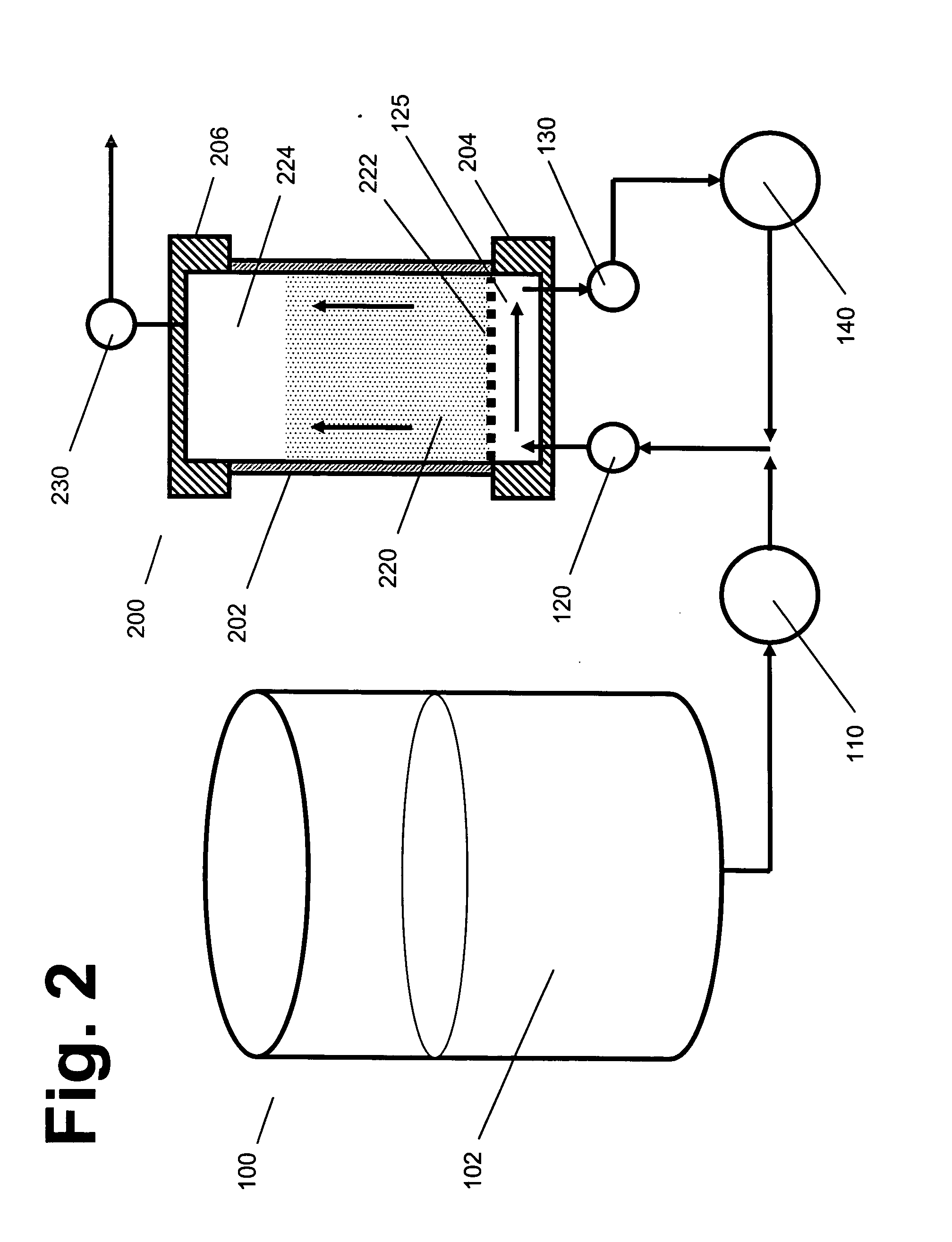
Sweep-flow methods and clogging disrupters, for expanded bed chromatography of liquids with suspended particulates
InactiveUS20070199899A1Prevent and reduce formationPrevent and reduce and growthIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationParticulatesSorbent
Devices for expanded bed chromatography use inlet and outlet ports beneath a mesh that supports sorbent beads in a column. Placement of both ports beneath the mesh provides a horizontal “sweep flow” tangential to the mesh, to suppress the formation of particulate cakes on the lower surface of the mesh when liquids containing high particulate loads (such as cells or cell debris) are being processed. This design can be used with vibrators, hammering devices, intermittent reverse flow, or other means for disrupting the formation of particulate cakes or aggregates. Disrupters can also be used during elution, to accelerate the release of the valuable molecules from the sorbent. Initial tests indicate that these systems can efficiently handle heavily loaded liquids that would rapidly clog other systems previously known in the art.
Owner:ALASKA ANDREW
Tumor-targeted delivery carrier based on cell-derived micro-vacuoles, preparation method and application
ActiveCN106692984AGood biological stabilityHigh biosecurityEnergy modified materialsGenetic material ingredientsDspe pegCell culture supernatant
The invention discloses a tumor-targeted delivery carrier based on cell-derived micro-vacuoles, a preparation method and an application. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (A) preparing a conditioned medium: supplementing fetal bovine serum, antibiotics, DSPE-PEG-Biotin and DSPE-PEG-Folate into a basal medium; (B) using the obtained conditioned medium in cell culture, and collecting cell culture supernatant for subsequent separation; (C) carrying out low-speed centrifugation on the obtained culture supernatant to remove cell debris and apoptotic bodies, then adding SA-IONPs, mixing uniformly, incubating, then separating by a magnet, using PBS for re-suspension, eluting for multiple times to obtain the cell-derived micro-vacuoles with membrane surfaces modified by folic acid and iron oxide nano-particles, and freezing for storage; and (D) loading chemotherapeutic drugs or therapeutic genes into the functionalized micro-vacuoles doubly-modified by an electroporation mode, and carrying out re-suspension after separation with the magnet. The tumor-targeted delivery carrier based on cell-derived micro-vacuoles, the preparation method and the application disclosed by the invention are applicable to specific targeting delivery of multiple chemotherapeutic drugs and therapeutic genes, and have the advantages of enhancing the anti-tumor effect, reducing the systemic toxicity and improving the clinical effect of the current therapeutic selection, so that a new hope is brought for clinical therapy of tumors.
Owner:珈泌生物科技(武汉)有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com