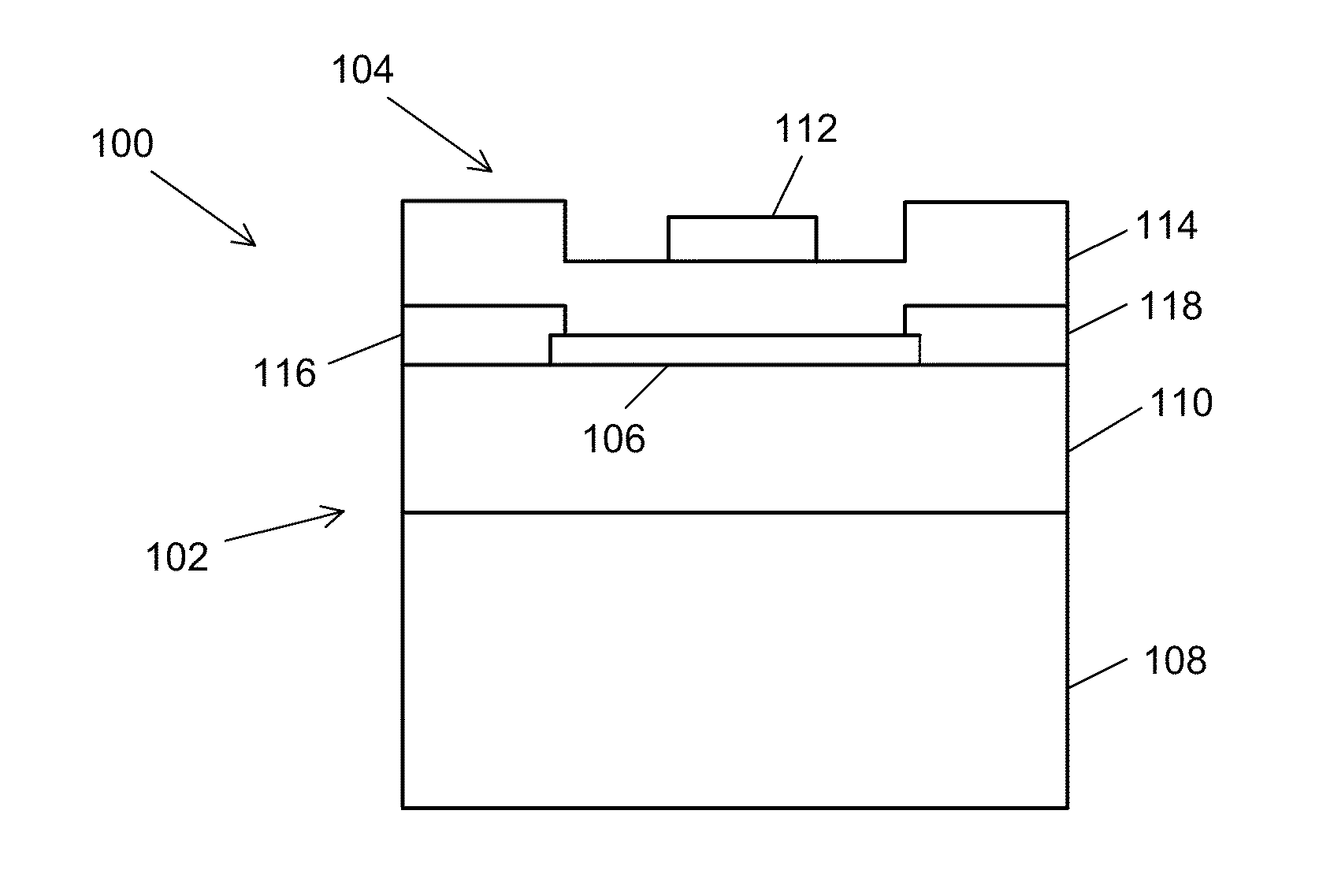
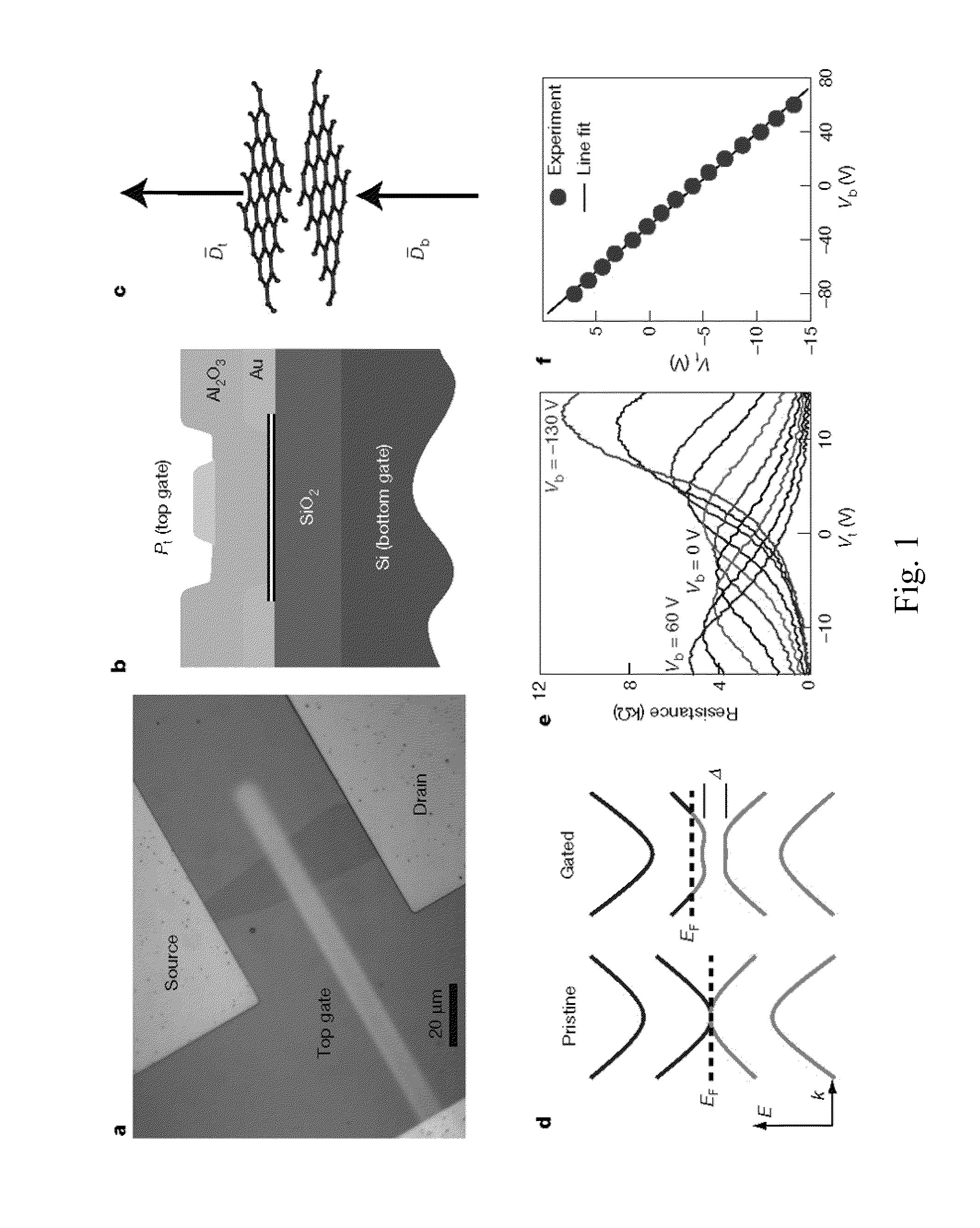
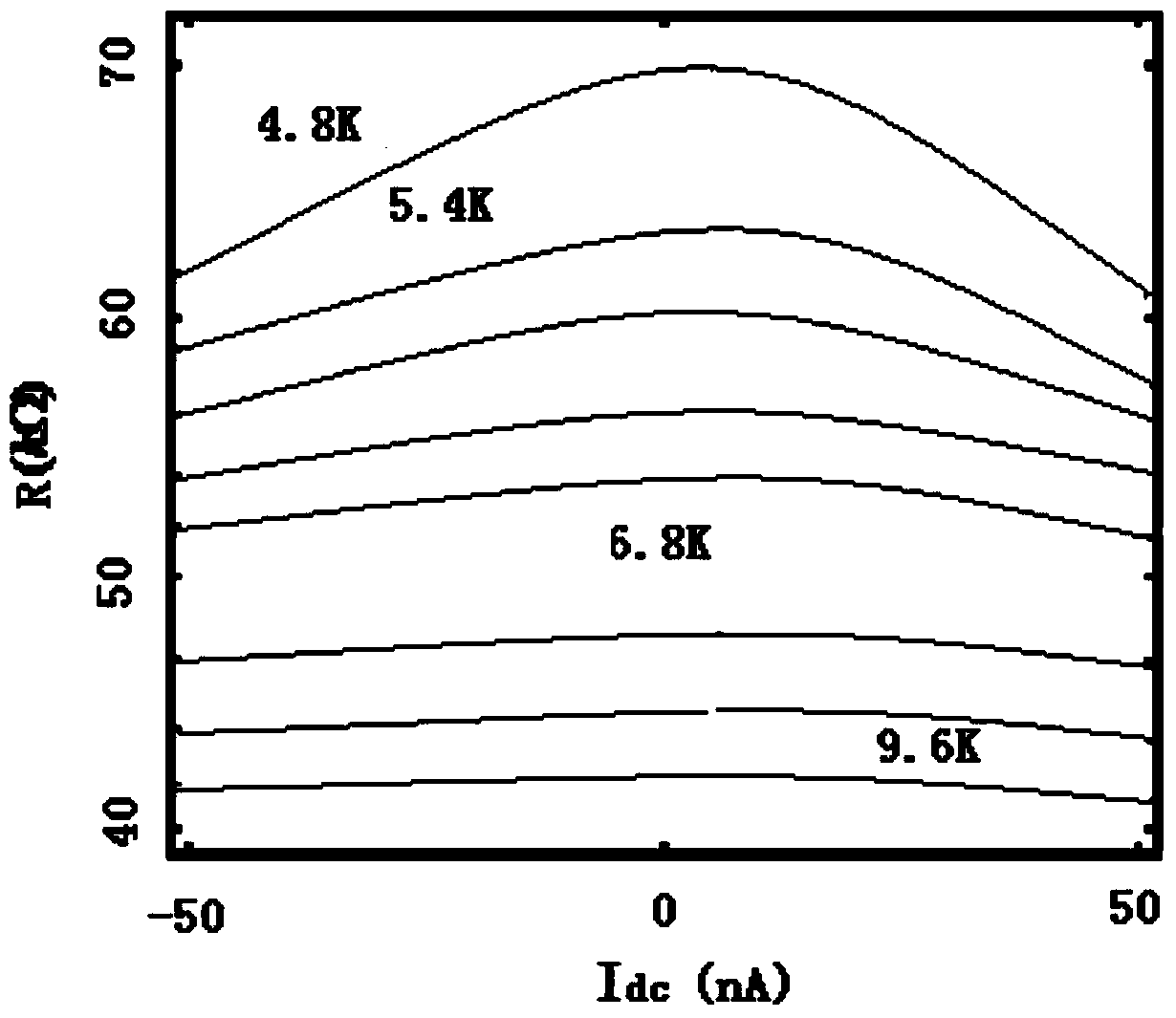
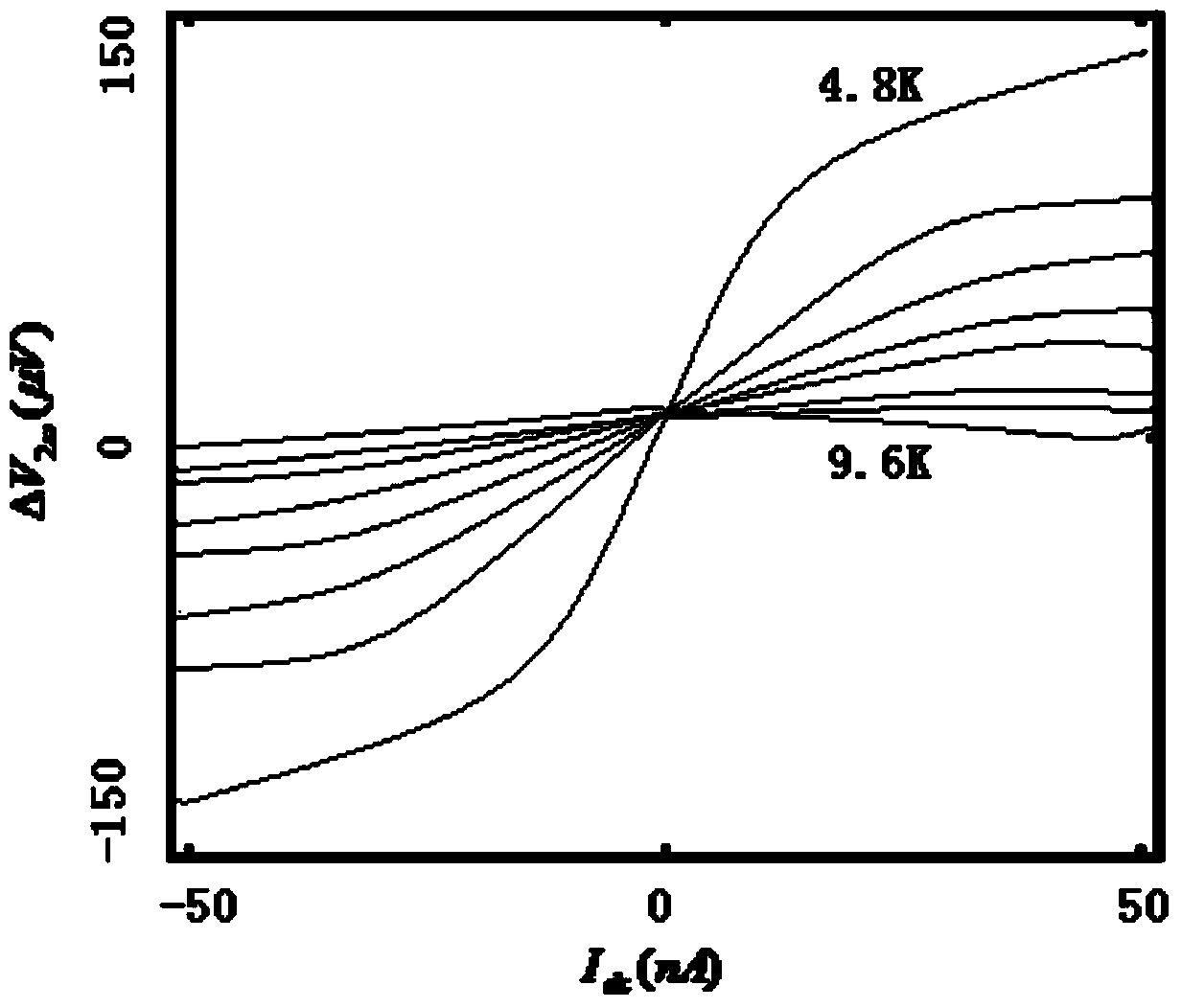
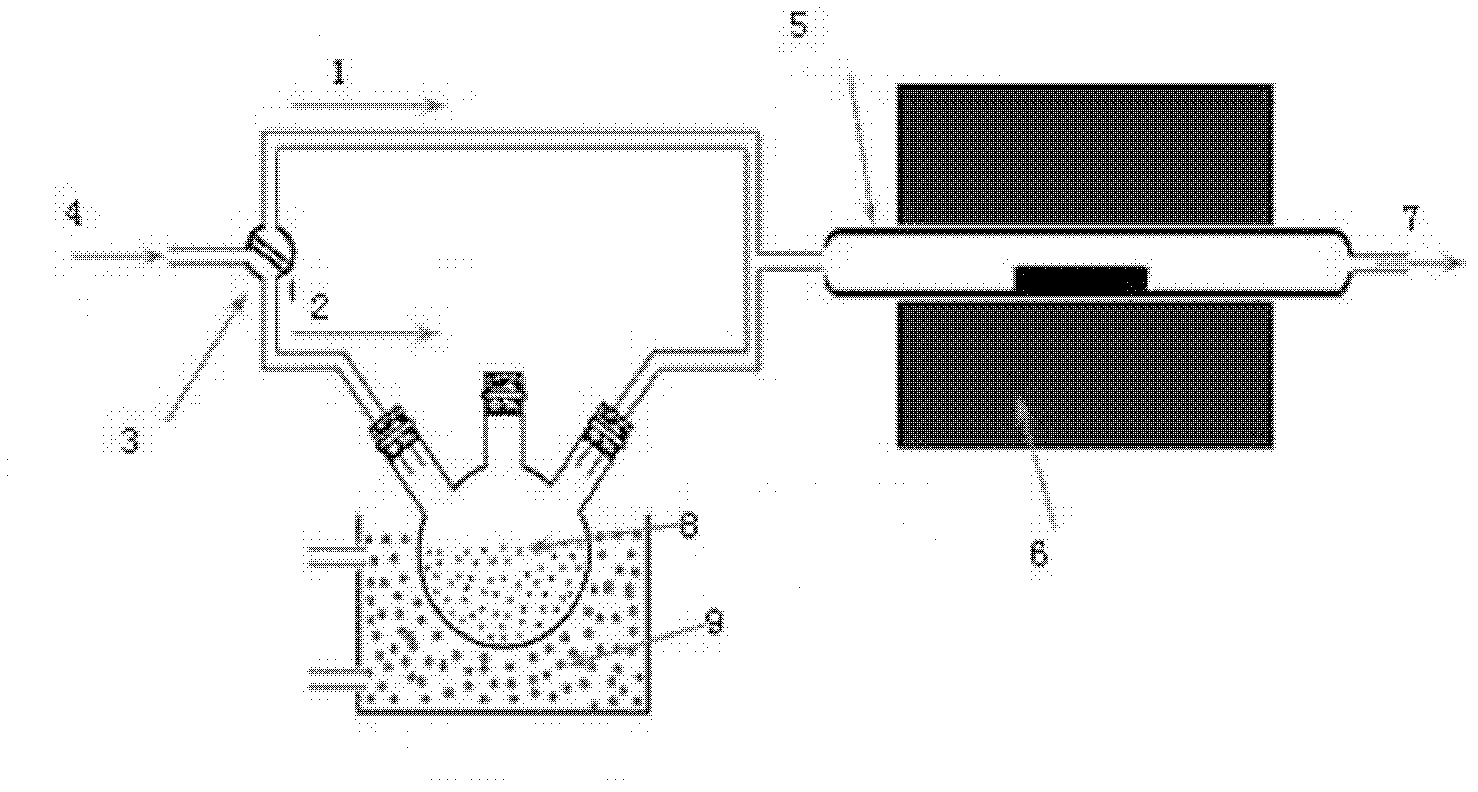
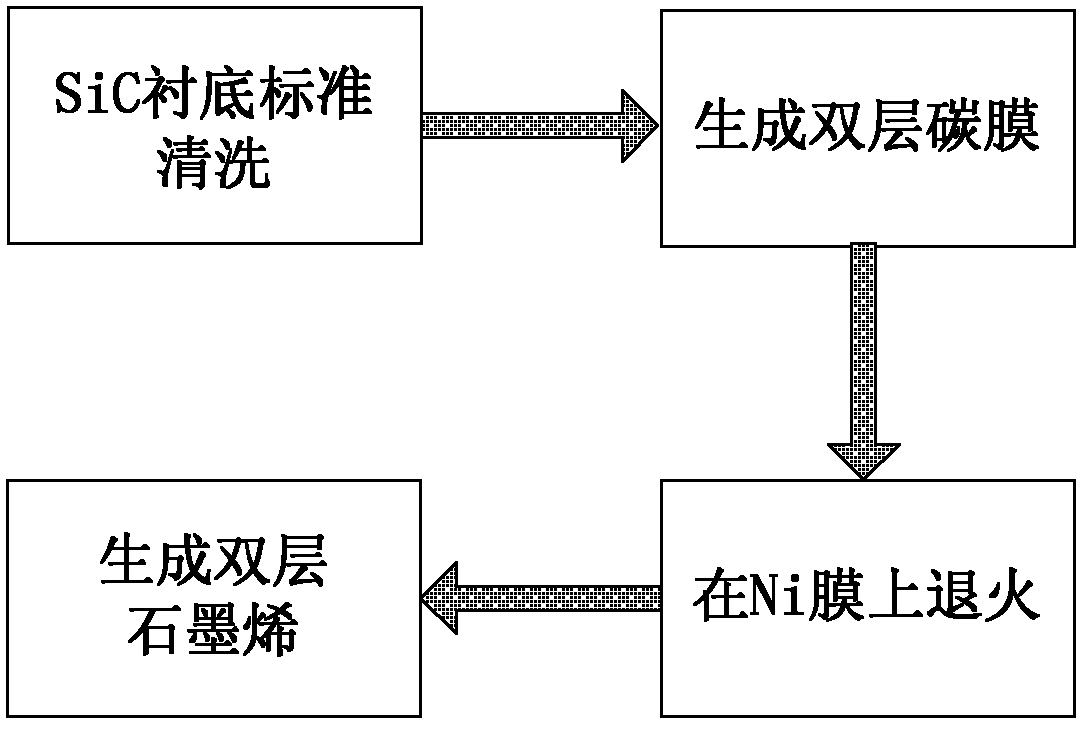
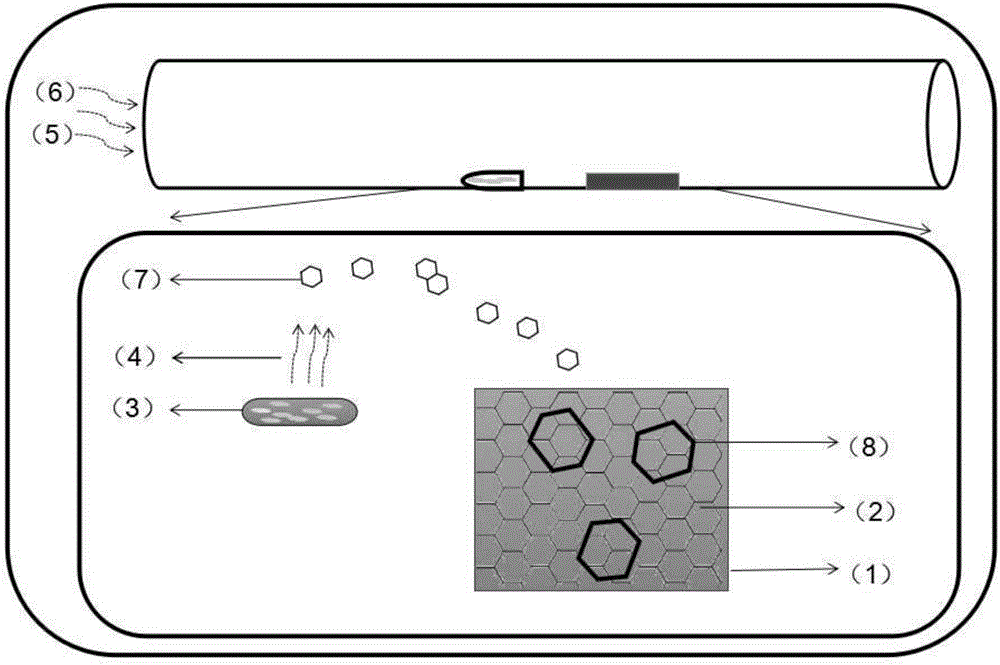
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
144 results about "Bilayer graphene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
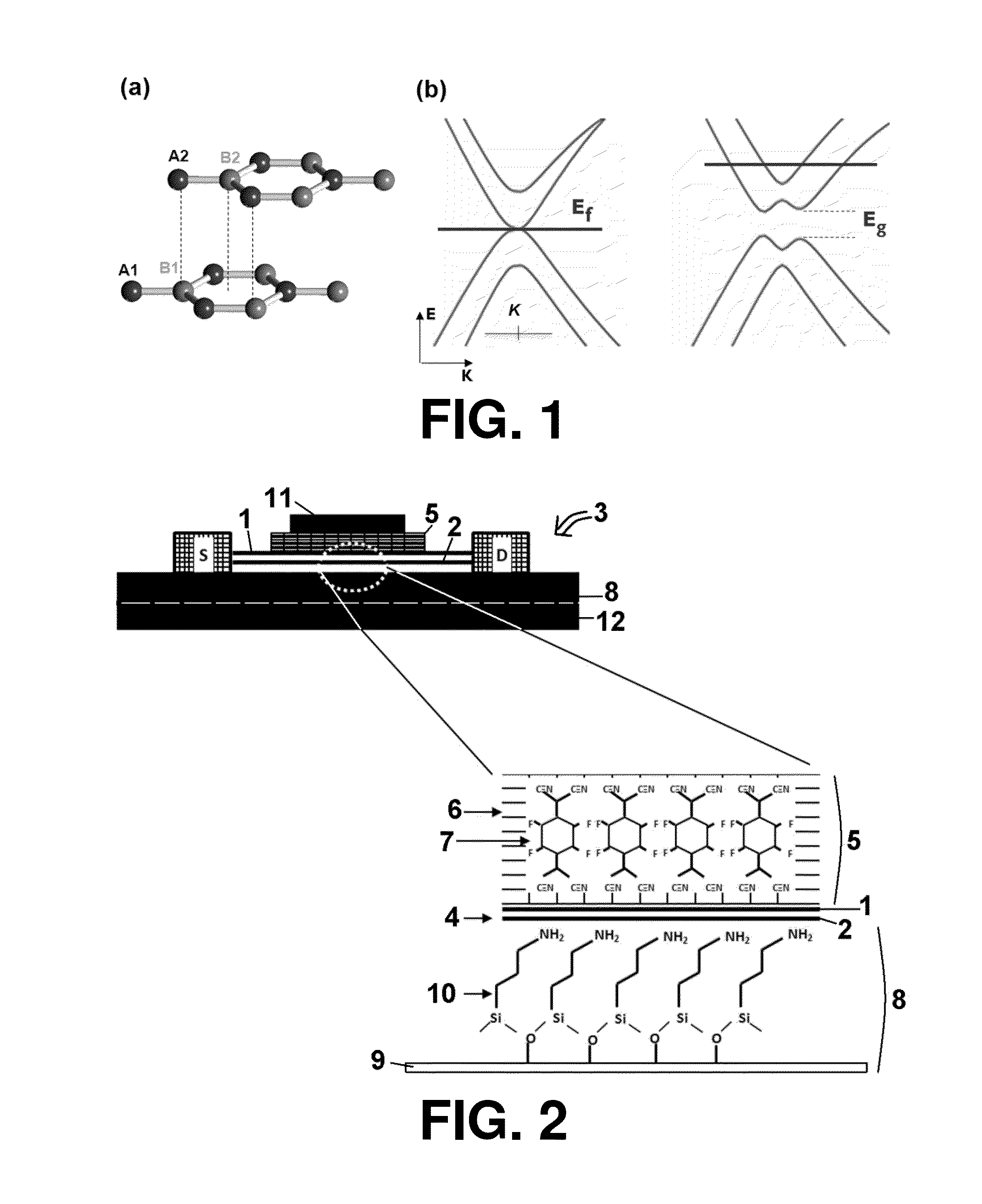
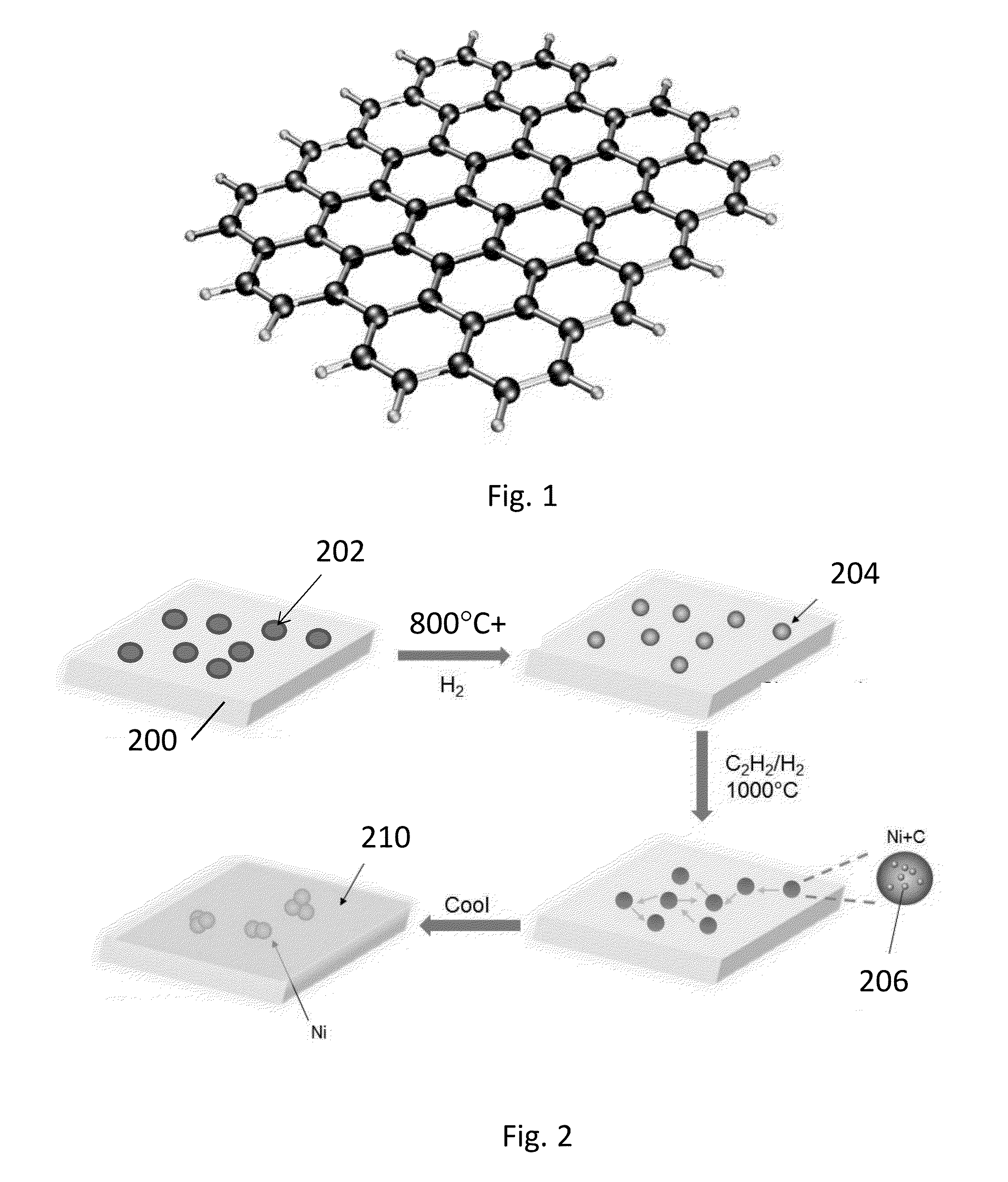
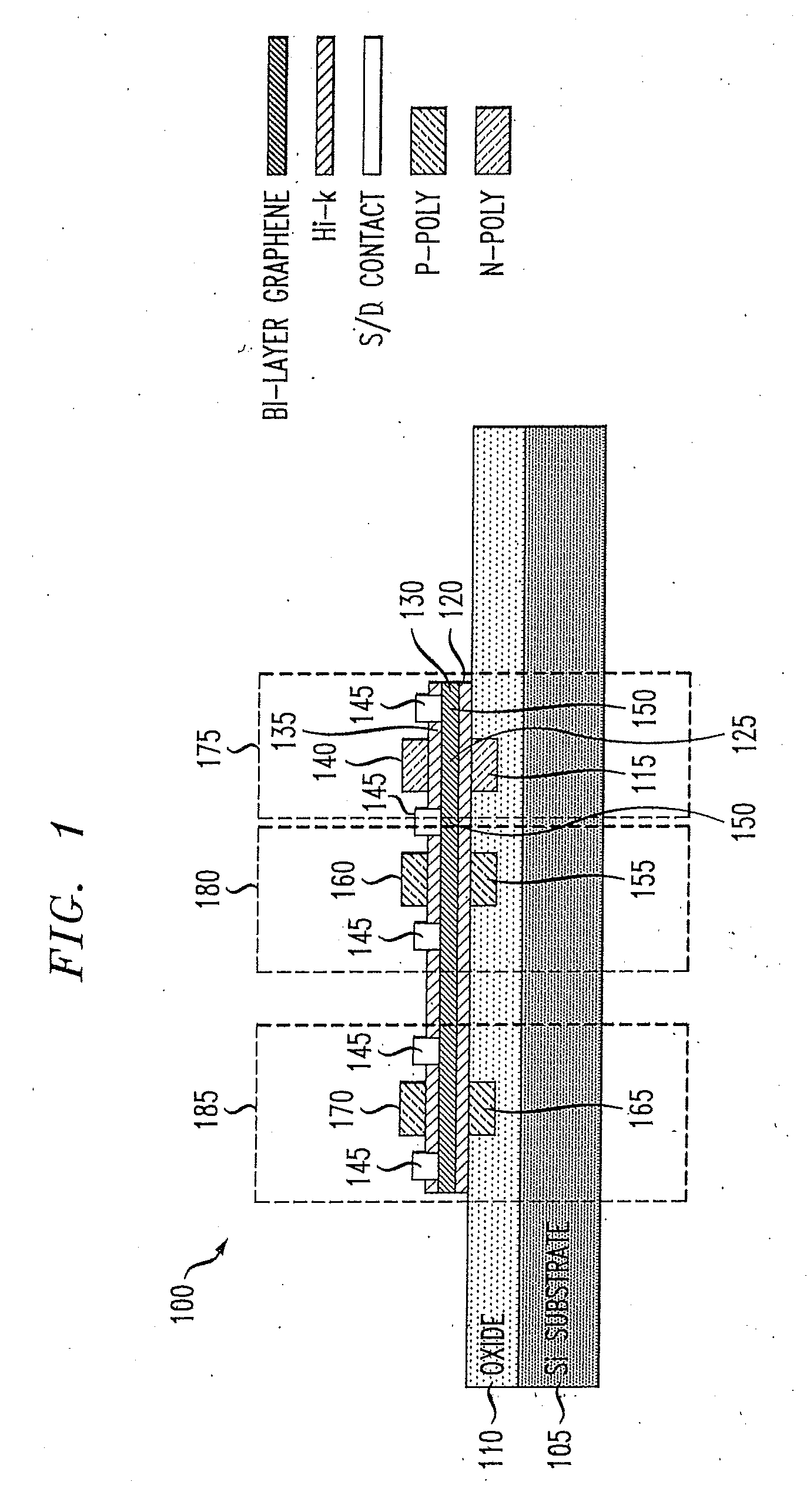
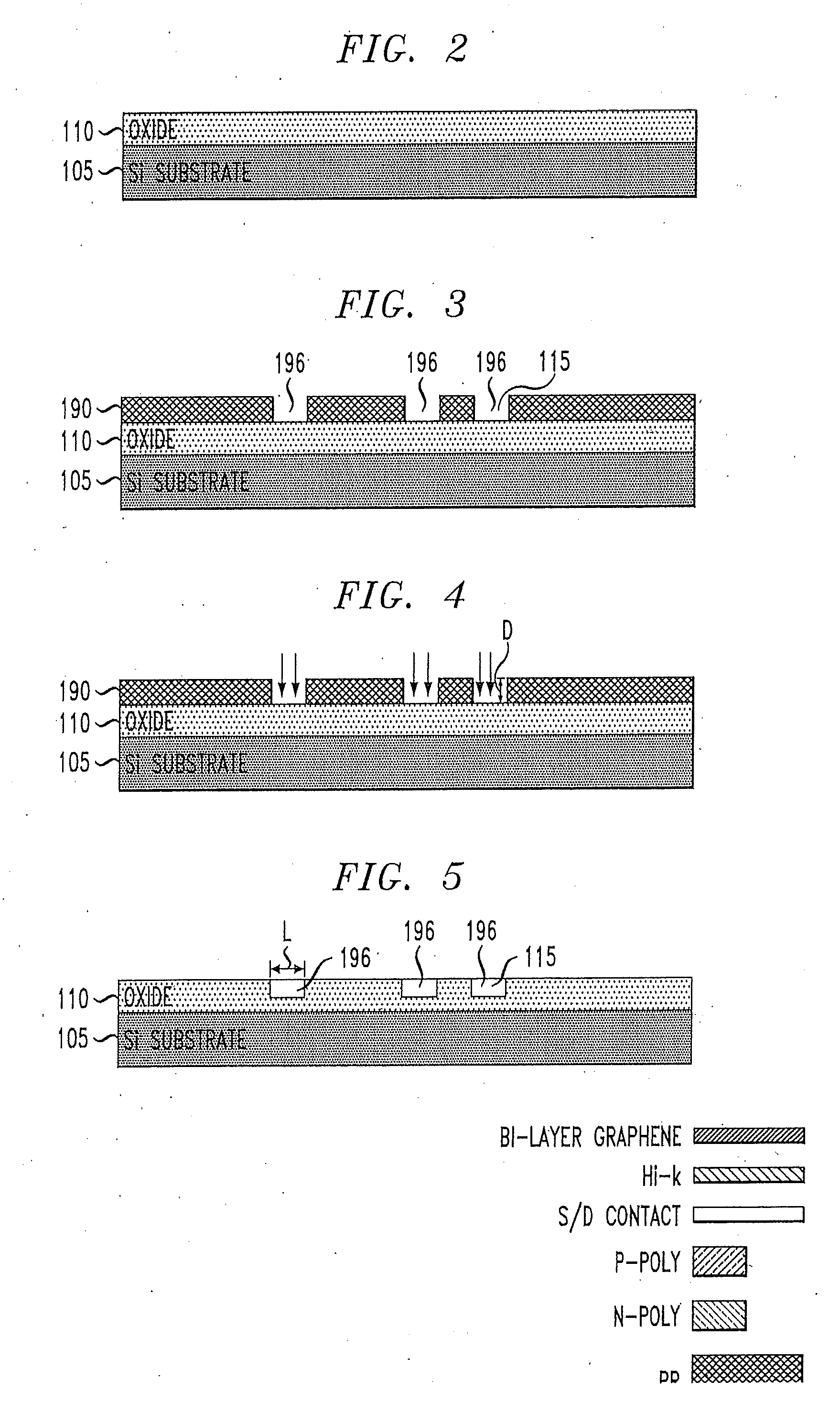
Bilayer graphene is a material consisting of two layers of graphene. One of the first reports of bilayer graphene was in the seminal 2004 Science paper by Geim and colleagues, in which they described devices "which contained just one, two, or three atomic layers"
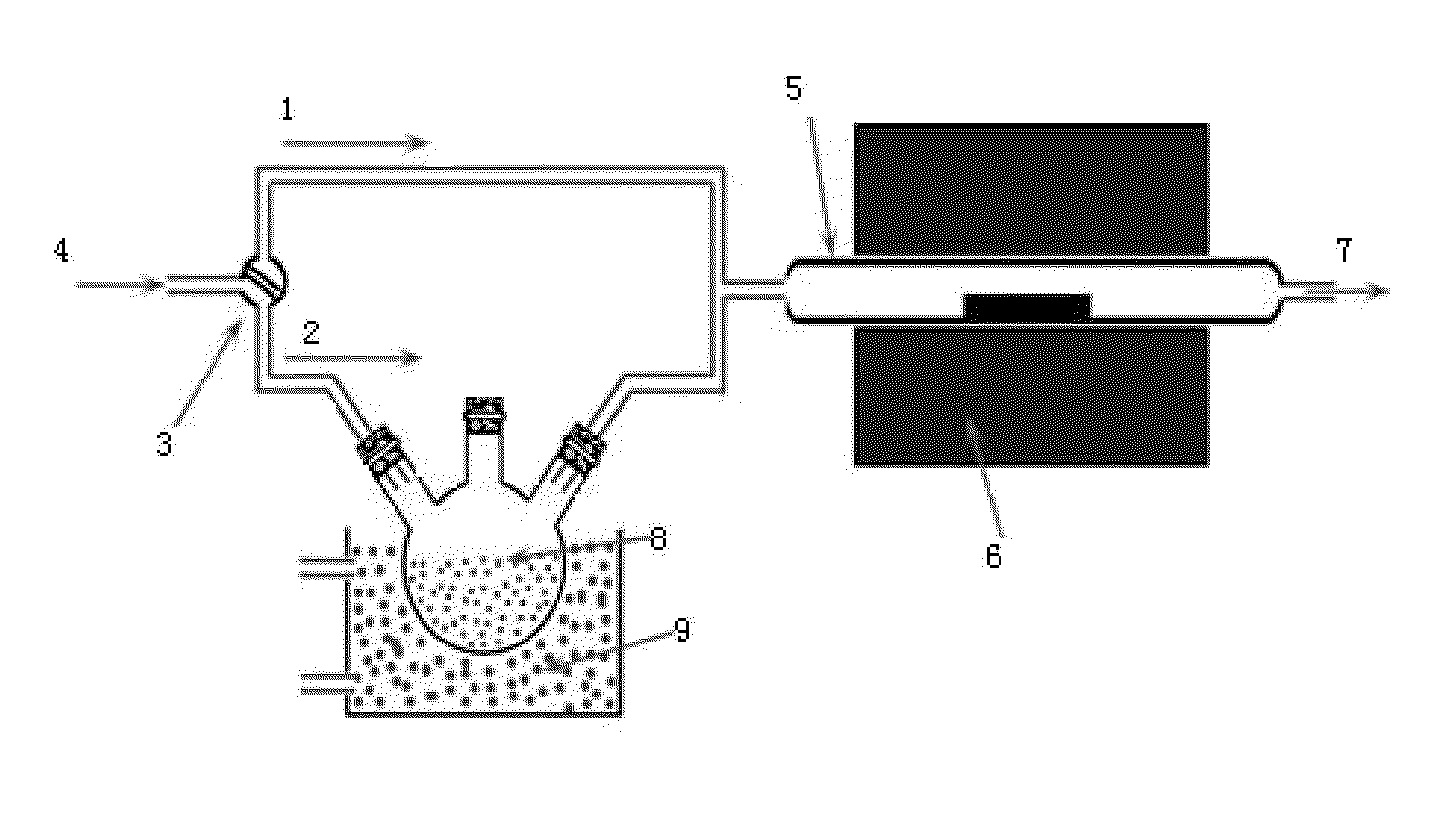
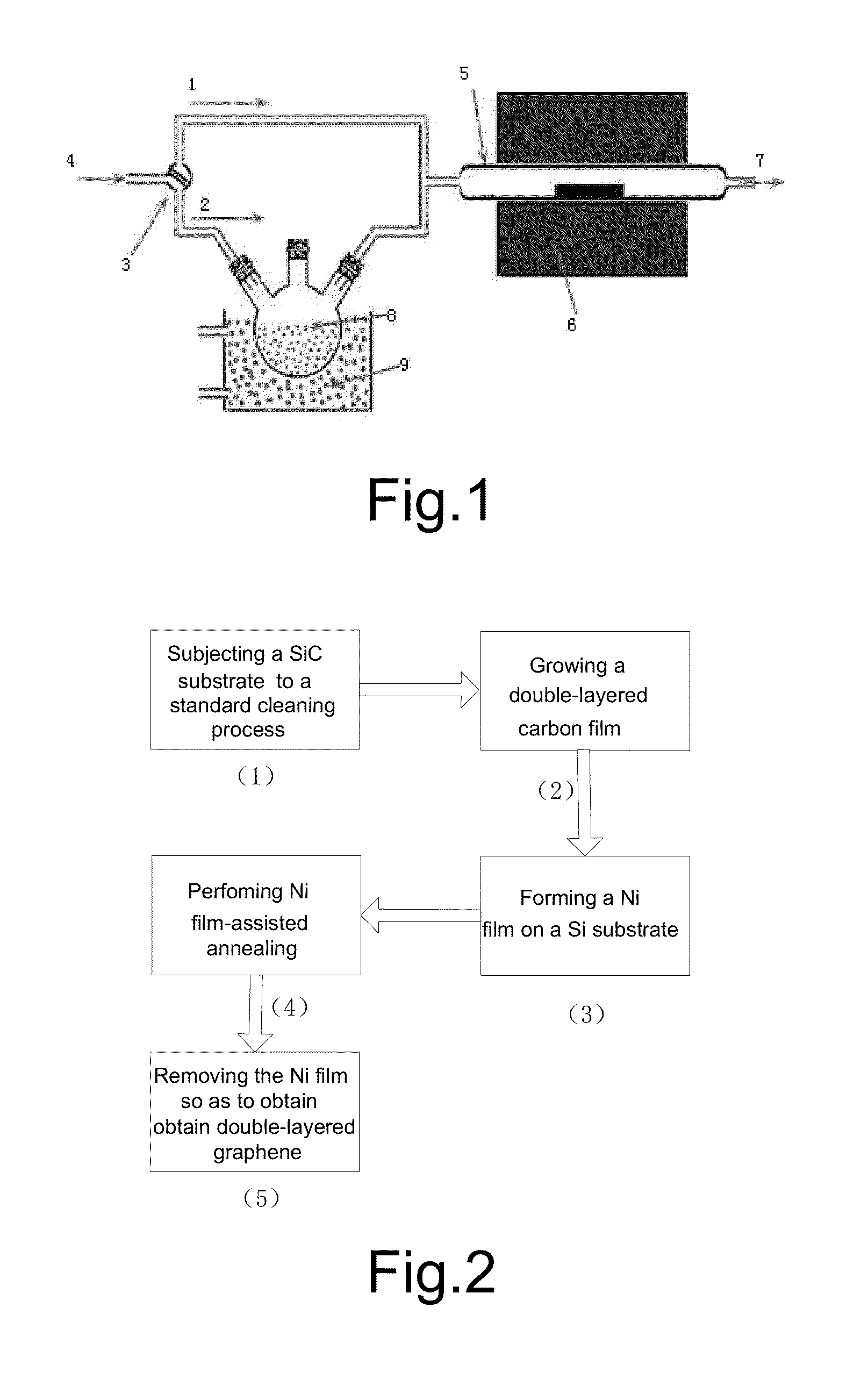
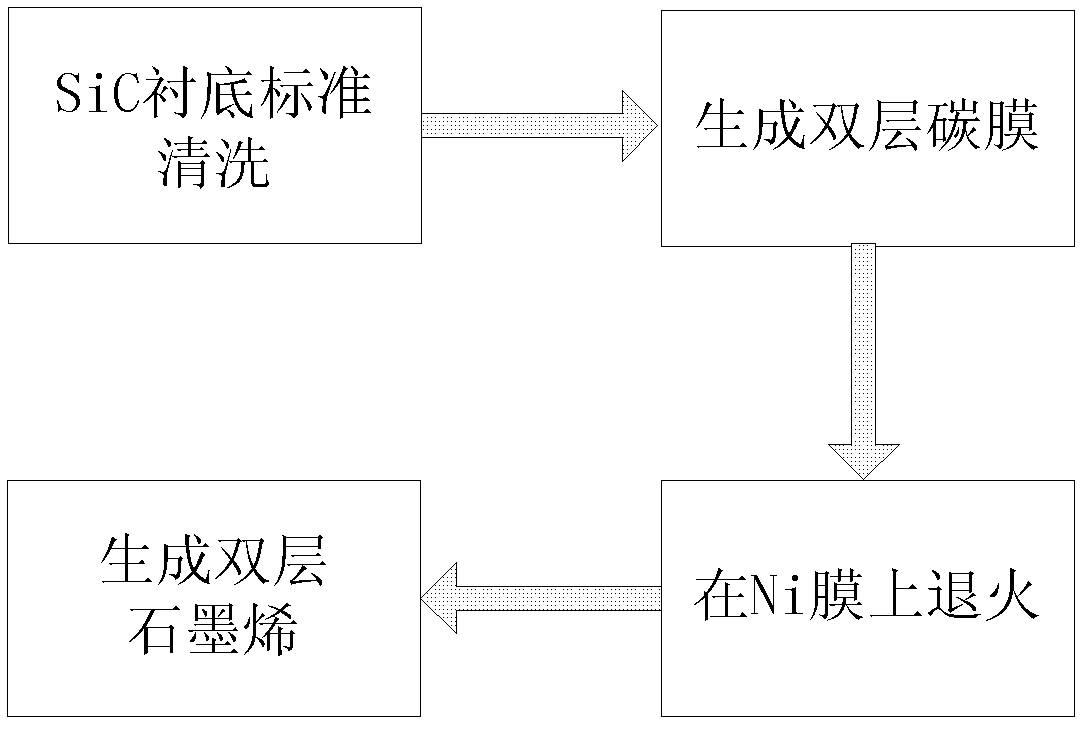
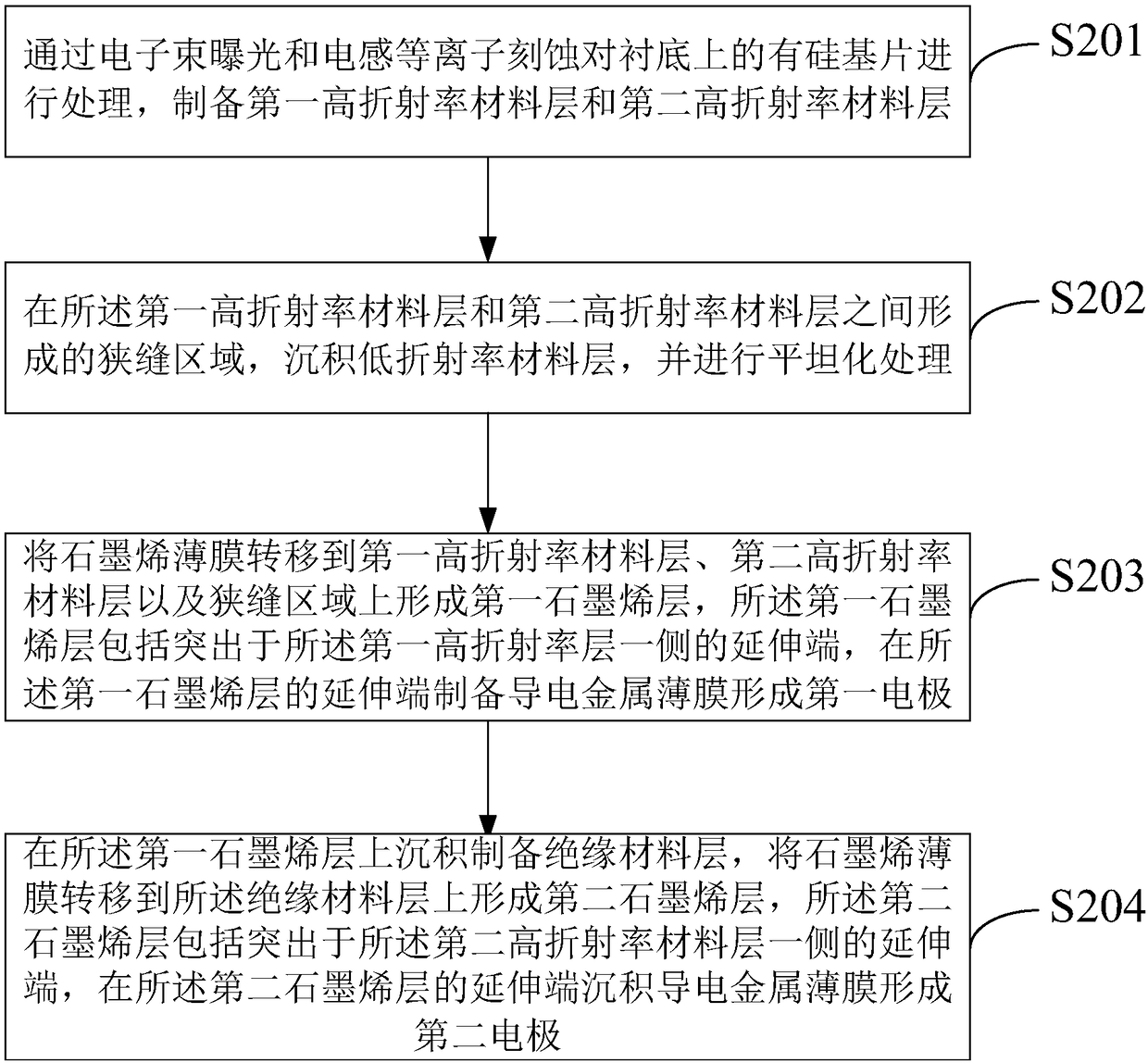
Process for Preparing Graphene on a SiC Substrate Based on Metal Film-Assisted Annealing
ActiveUS20140367642A1Simply and energy-efficientFlat surfaceMaterial nanotechnologyVacuum evaporation coatingCarbon filmElectron beam deposition
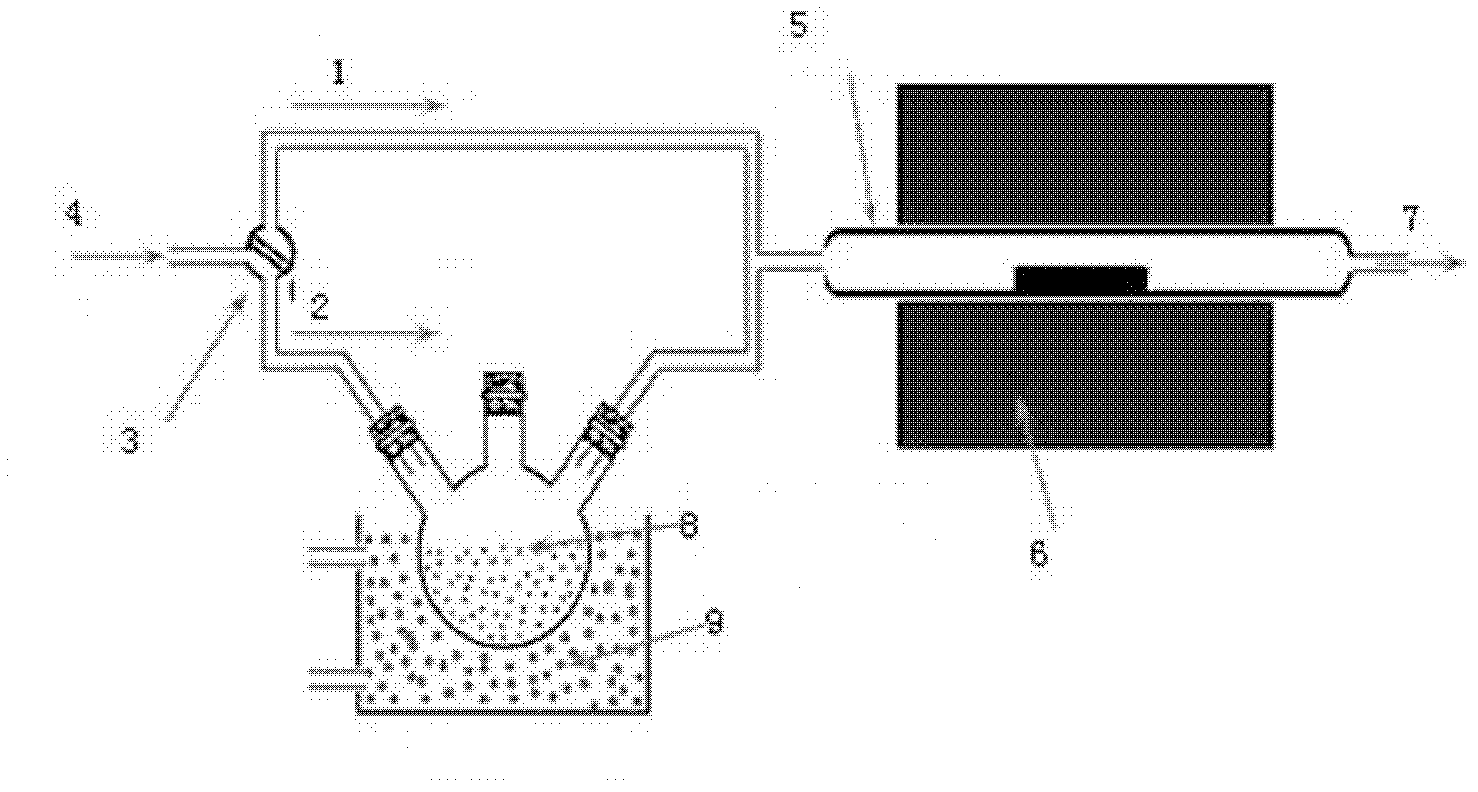
Provided is a process for preparing graphene on a SiC substrate, based on metal film-assisted annealing, comprising the following steps: subjecting a SiC substrate to a standard cleaning process; placing the cleaned SiC substrate into a quartz tube and heating the quartz tube up to a temperature of 750 to 1150° C.; introducing CCl4vapor into the quartz tube to react with SiC for a period of 20 to 100 minutes so as to generate a double-layered carbon film, wherein the CCl4 vapor is carried by Ar gas; forming a metal film with a thickness of 350 to 600 nm on a Si substrate by electron beam deposition; placing the obtained double-layered carbon film sample onto the metal film; subsequently annealing them in an Ar atmosphere at a temperature of 900 to 1100° C. for 10-30 minutes so as to reconstitute the double-layered carbon film into double-layered graphene; and removing the metal film from the double-layered graphene, thereby obtaining double-layered graphene. Also provided is double-layered graphene prepared by said process.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for preparing high-quality graphene through electrochemical high-efficiency exfoliation
The invention relates to a preparation method for graphene, especially to a method for preparing high-quality graphene through electrochemical high-efficiency exfoliation. The method mainly overcomes the technical problems that the honeycomb lattice structure of graphene is severely destroyed in the process of oxidation, an obtained membrane resistance is 1 K to 70 K omega / square (wherein light transmittance is less than 80%), the resistance is too high and much higher than requirements of ITO, etc. The method comprises the following steps: with graphite as a positive electrode and a platinum filament as a negative electrode, repeatedly applying high offset voltage and negative offset voltage on the graphite electrode, which enables graphite to be rapidly disassociated and decomposed into double-layer graphene floating on the surface of an electrolyte; collecting graphene and then filtering and drying graphene; dispersing obtained powder of a graphene film in a DMF solution; and carrying out water-bath ultrasonic treatment and centrifugation so as to obtain desired 1.5-nm-grade graphene flakes.
Owner:杭州金马新能源科技有限公司
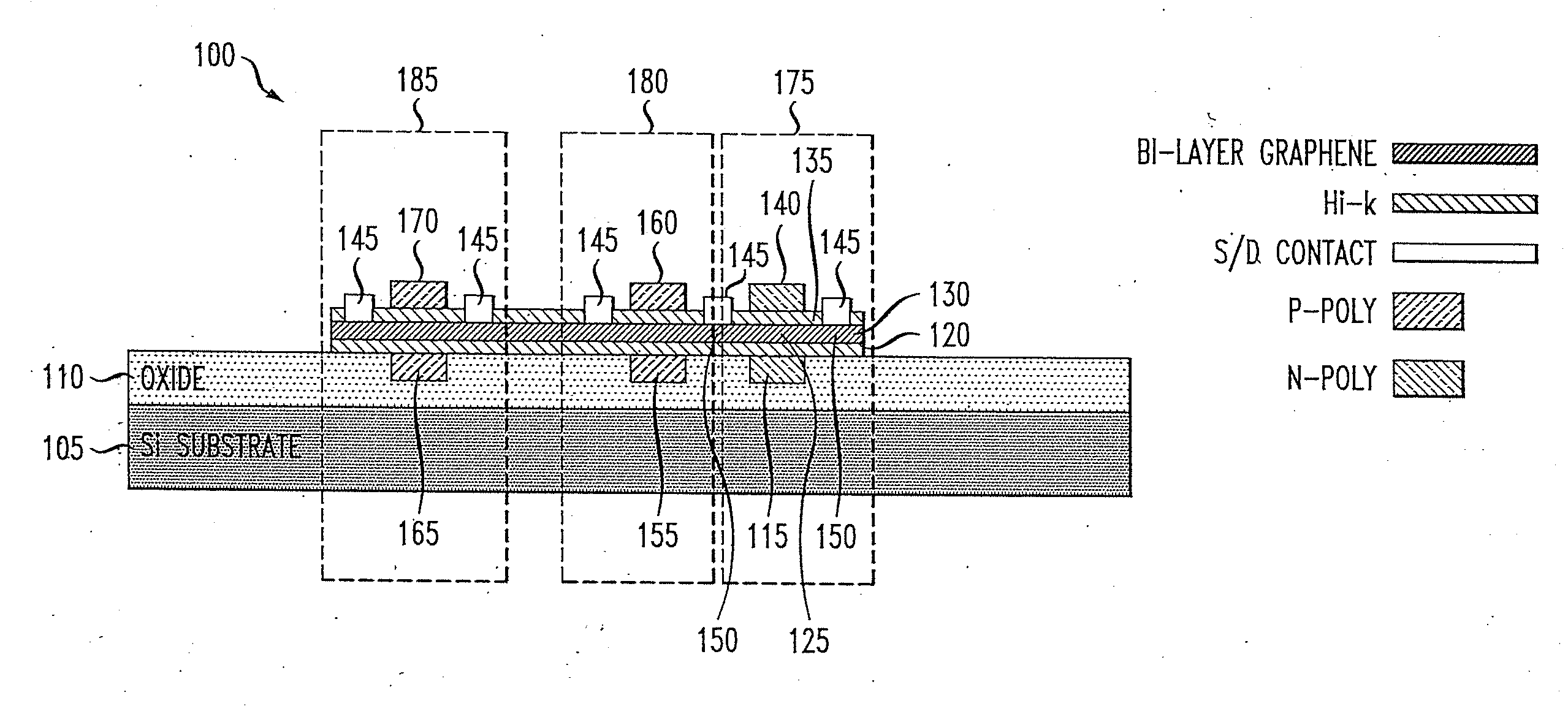
Graphene Device, Method of Investigating Graphene, and Method of Operating Graphene Device
InactiveUS20110006837A1Material analysis by optical meansElectric variable regulationBilayer grapheneSemiconductor properties
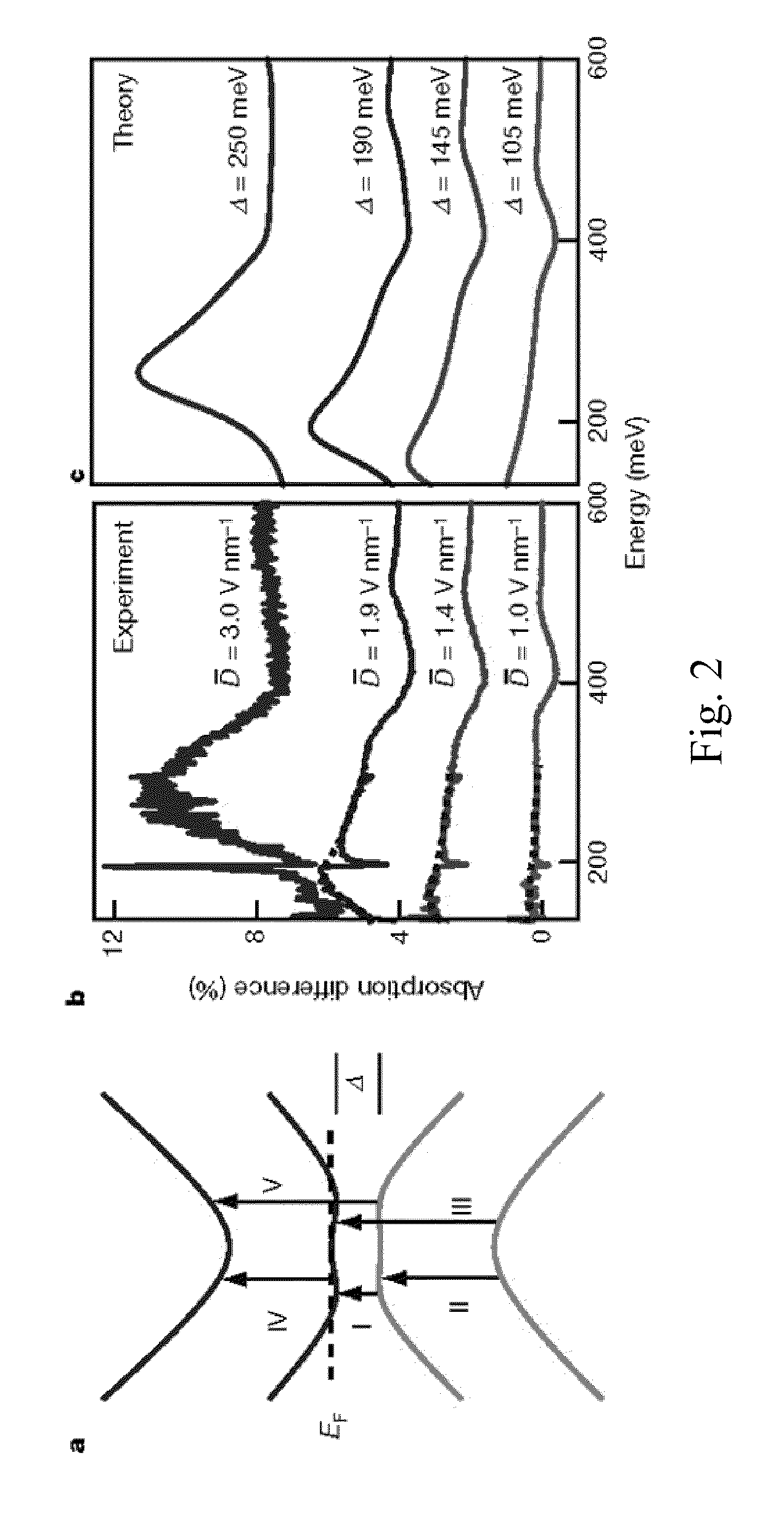
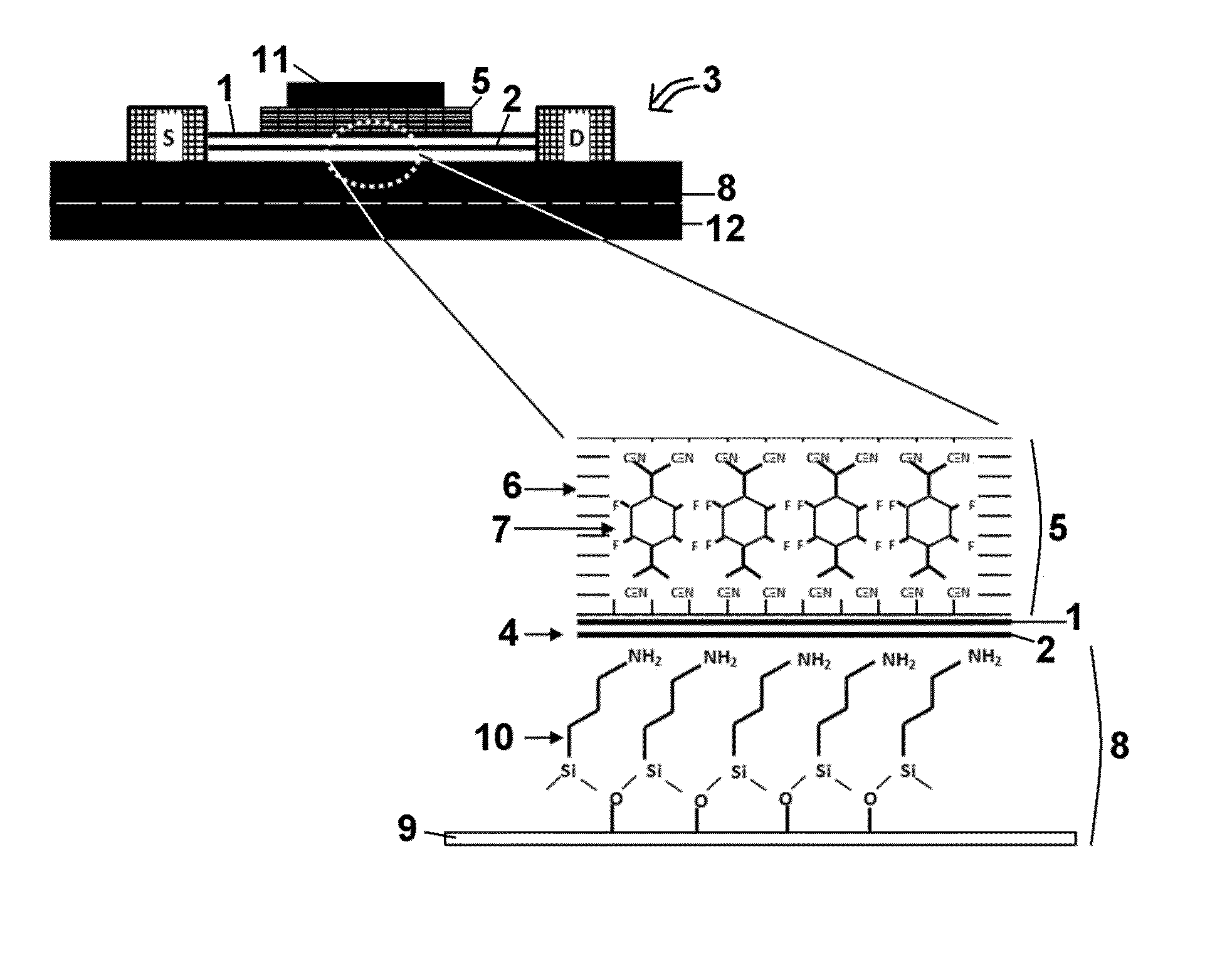
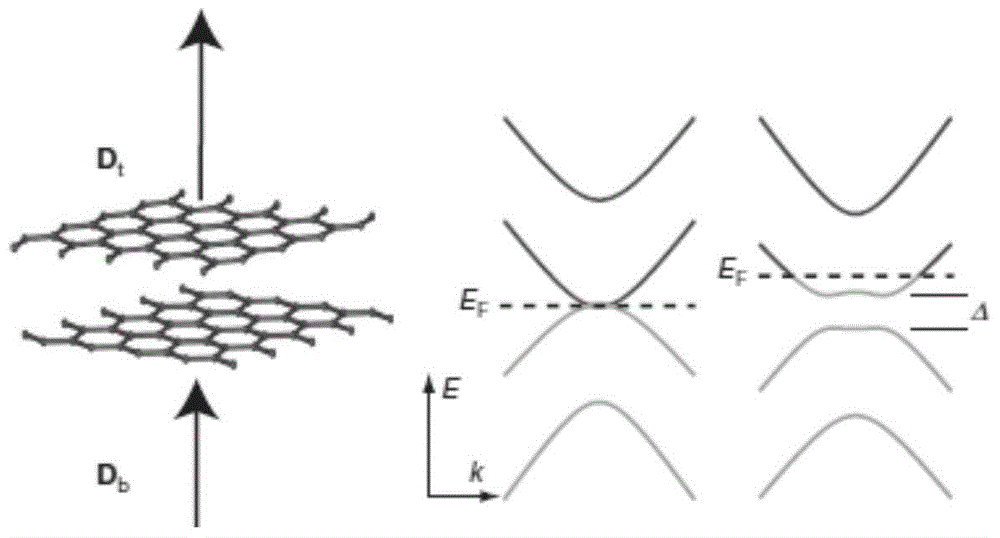
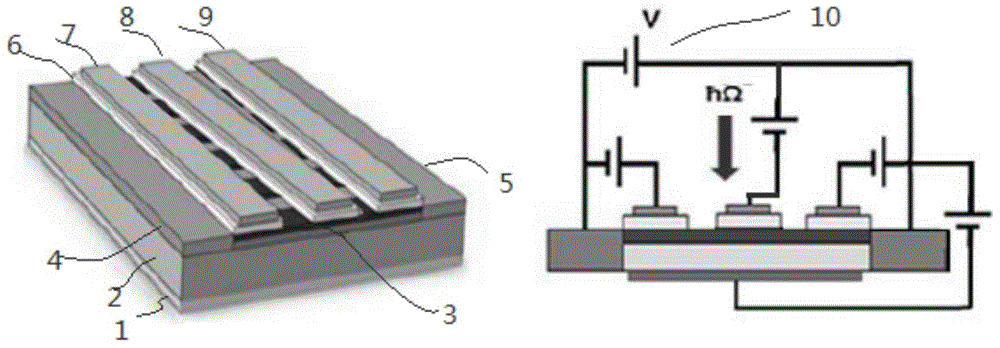
The present invention provides for a graphene device comprising: a first gate structure, a second gate structure that is transparent or semi-transparent, and a bilayer graphene coupled to the first and second gate structures, the bilayer graphene situated at least partially between the first and second gate structures. The present invention also provides for a method of investigating semiconductor properties of bilayer graphene and a method of operating the graphene device by producing a bandgap of at least 50 mV within the bilayer graphene by using the graphene device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Graphene Devices with Local Dual Gates
InactiveUS20120175594A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceDielectric layer
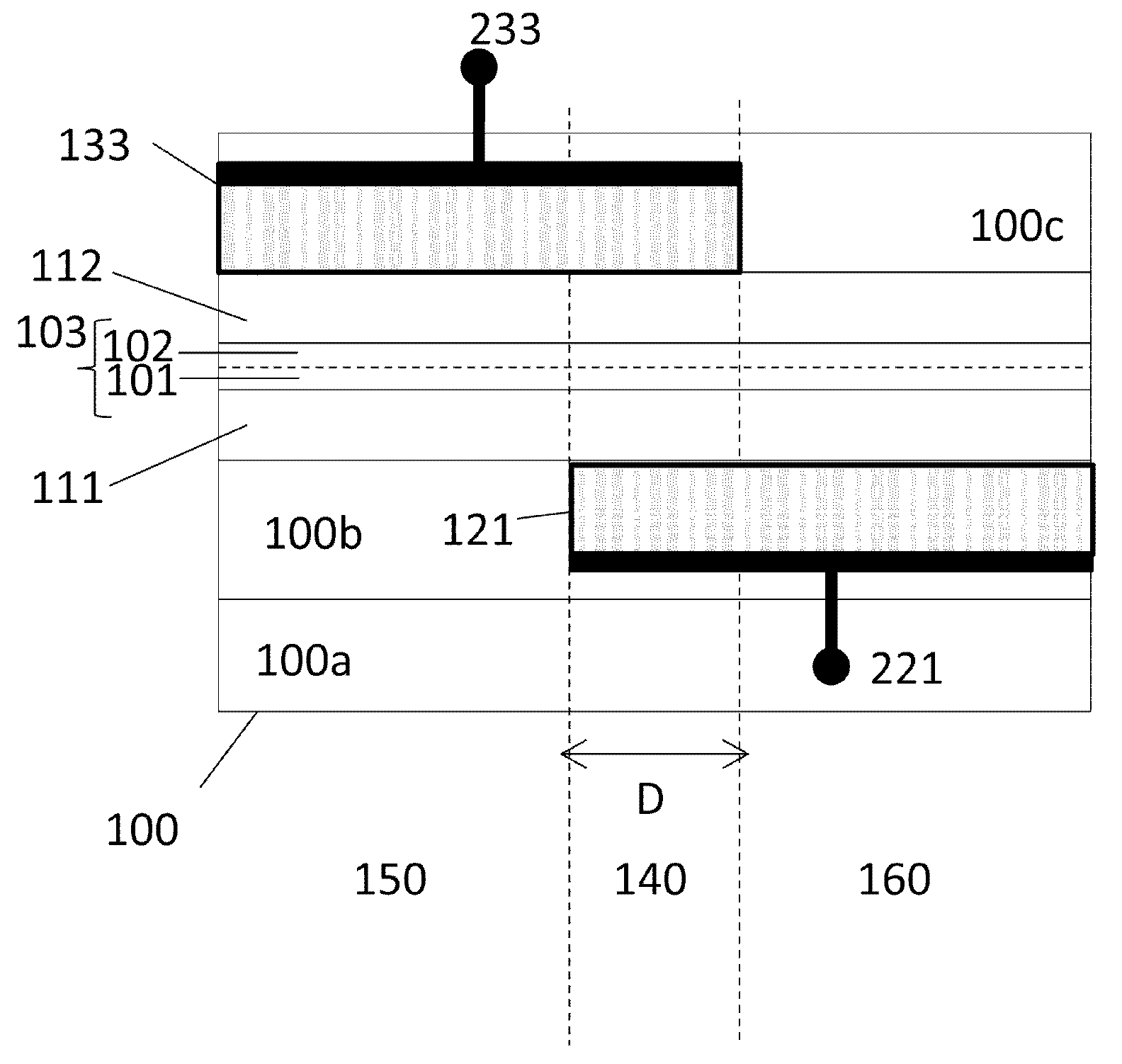
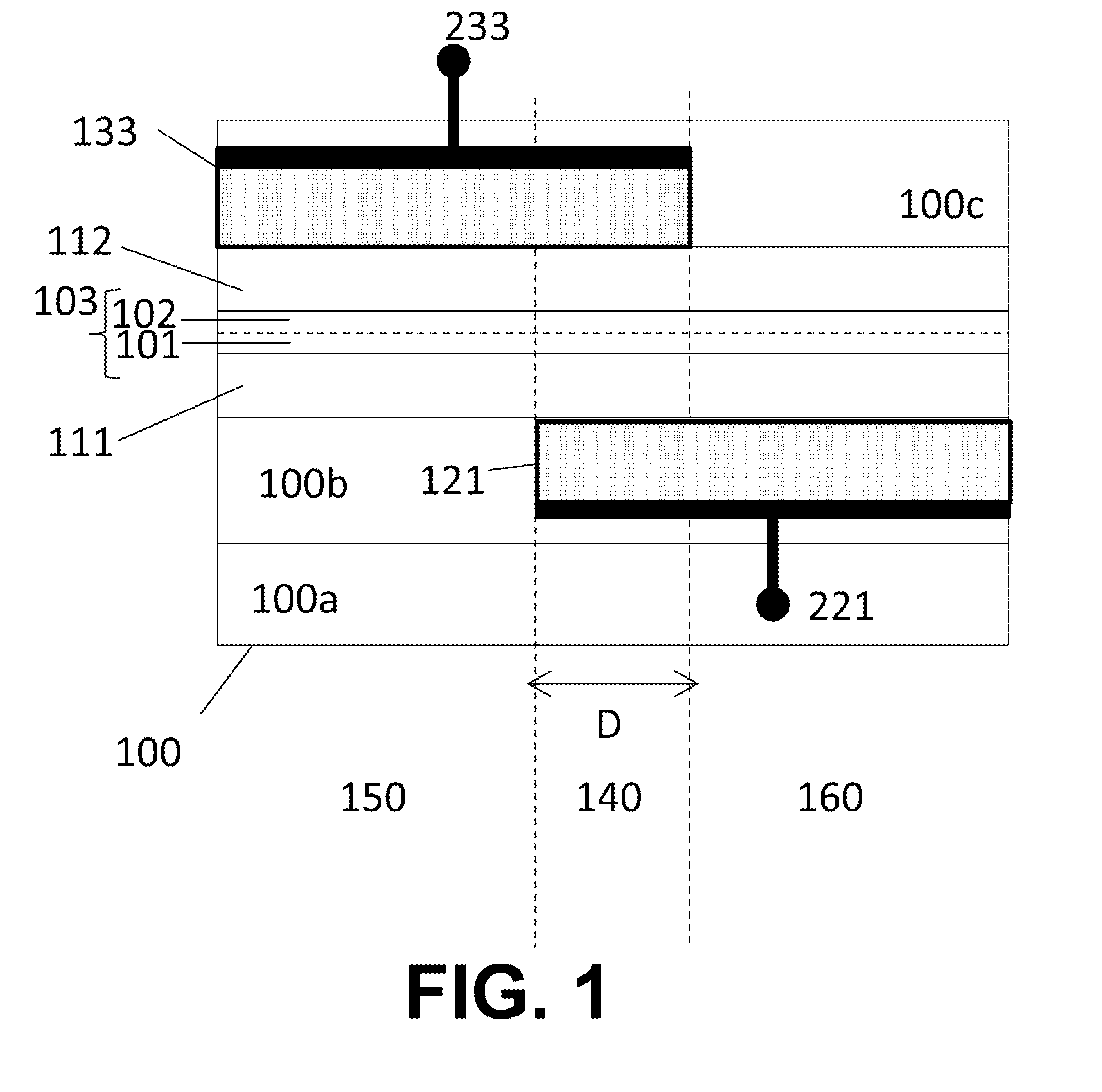
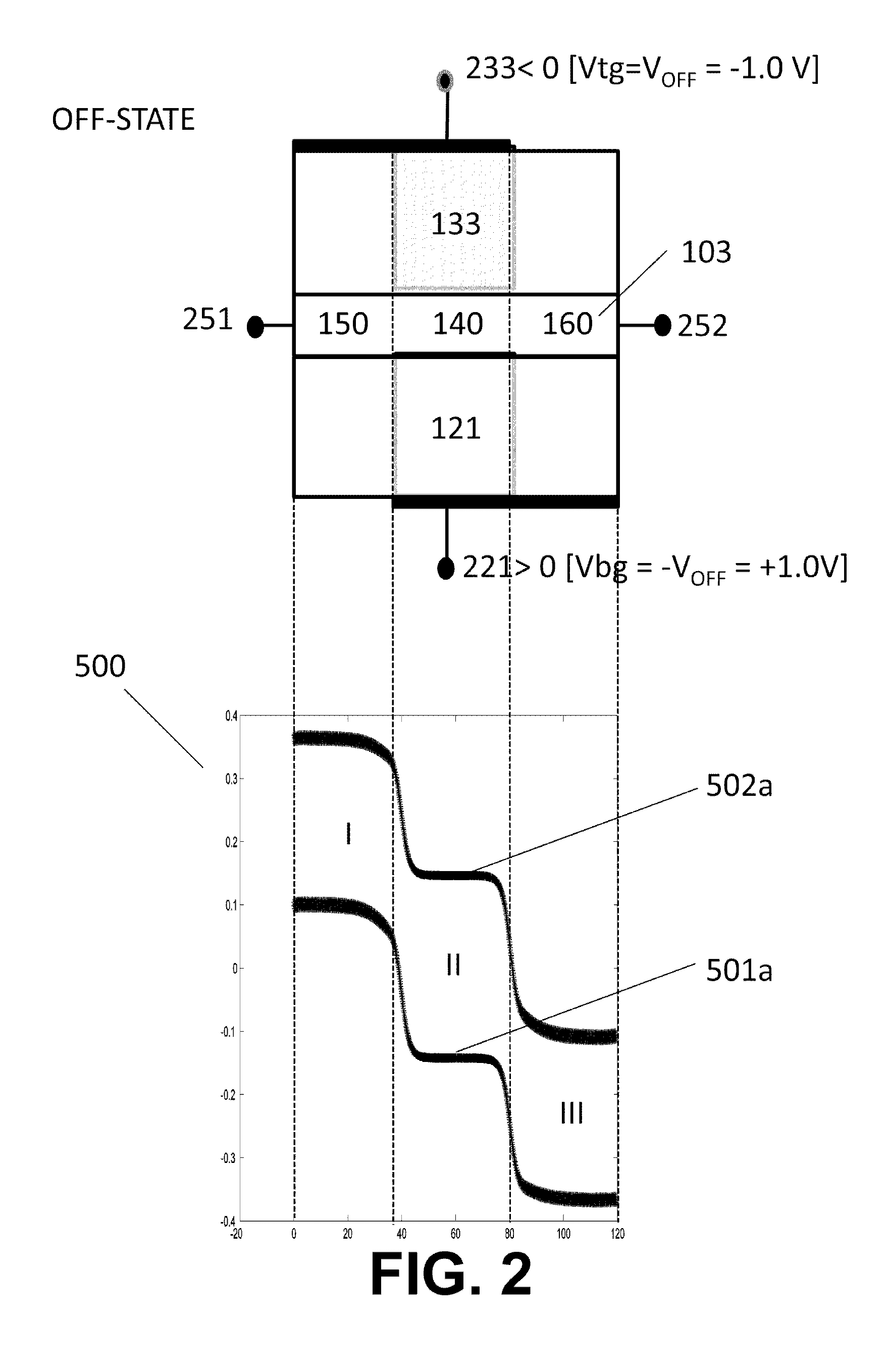
An electronic device comprises an insulator, a local first gate embedded in the insulator with a top surface of the first gate being substantially coplanar with a surface of the insulator, a first dielectric layer formed over the first gate and insulator, and a channel. The channel comprises a bilayer graphene layer formed on the first dielectric layer. The first dielectric layer provides a substantially flat surface on which the channel is formed. A second dielectric layer formed over the bilayer graphene layer and a local second gate formed over the second dielectric layer. Each of the local first and second gates is capacitively coupled to the channel of the bilayer graphene layer. The local first and second gates form a first pair of gates to locally control a first portion of the bilayer graphene layer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Graphene-based semiconductor device
ActiveUS20130313522A1Reduce impactSolve the stability is not highNanotechSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge carrierBilayer graphene
A semiconductor device is provided comprising a bilayer graphene comprising a first and a second adjacent graphene layer, and a first electrically insulating layer contacting the first graphene layer, the first electrically insulating layer comprising an electrically insulating material, and a substance suitable for creating free charge carriers of a first type in the first graphene layer, the semiconductor device further comprising an electrically insulating region contacting the second graphene layer and suitable for creating free charge carriers of a second type, opposite to the first type, in the second graphene layer.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
Graphene conductive ink
The invention discloses graphene conductive ink, which is composed of the following components in mass part: 20-50 parts of adhesive resin, 40-100 parts of alcohol solvent, 10-80 parts of graphene, 1-3 parts of dispersing agent, 1-3 parts of defoaming agent, and 1-3 parts of stabilizing agent, wherein the adhesive resin is one or two types from acrylic resin and polyurethane resin; the alcohol solvent is one or multiple types from ethyl alcohol, glycerin and isopropyl alcohol; the graphene is one or multiple types from single-layer graphene, double-layer graphene and three-layer graphene. The graphene conductive ink is simple in preparation procedure and low in cost; the graphene is selected as an electric conducting medium, so that the electric conducting performance is excellent, the stability is high and the mechanical property is good; the graphene conductive ink has excellent abrasive resistance and scratching resistance.
Owner:SUZHOU AITESI FURTHER MATERIALS CO LTD
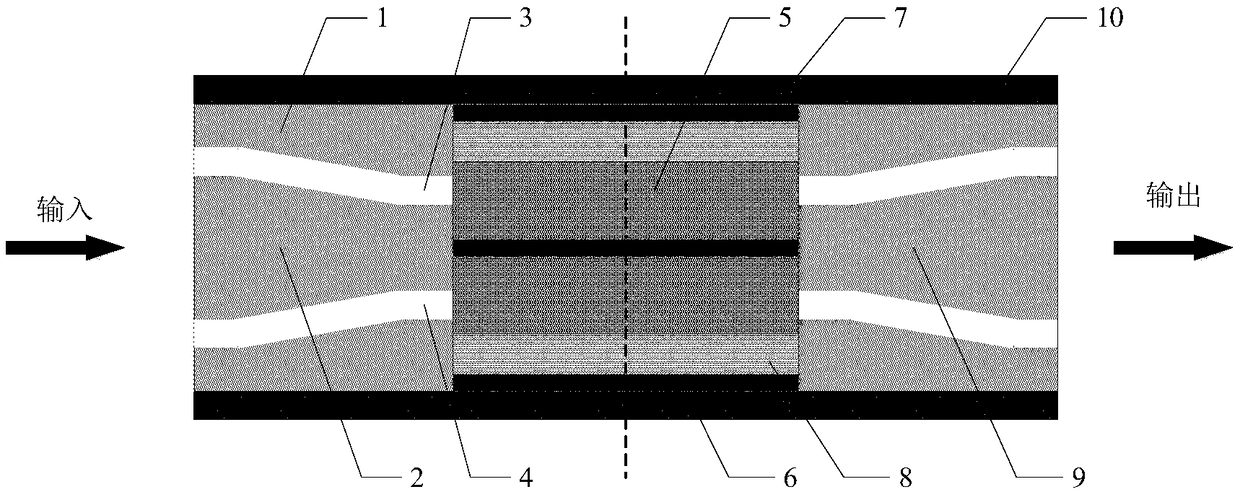
Grid-control graphene nano-ribbon array THz (terahertz) detector and tuning method
InactiveCN104795411AImprove mobilityHigh sensitivityRadiation controlled devicesSemiconductor devicesElectronBand width
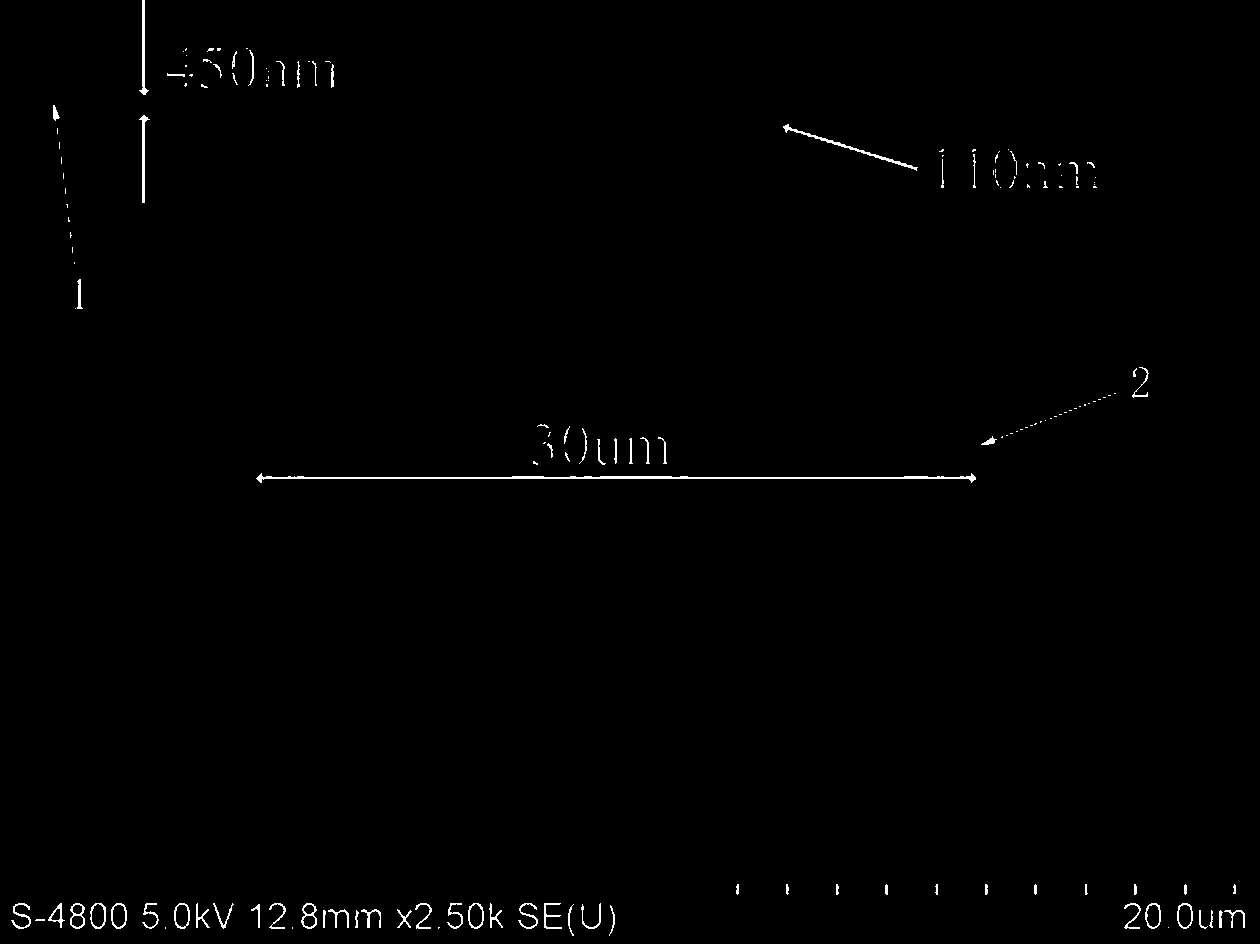
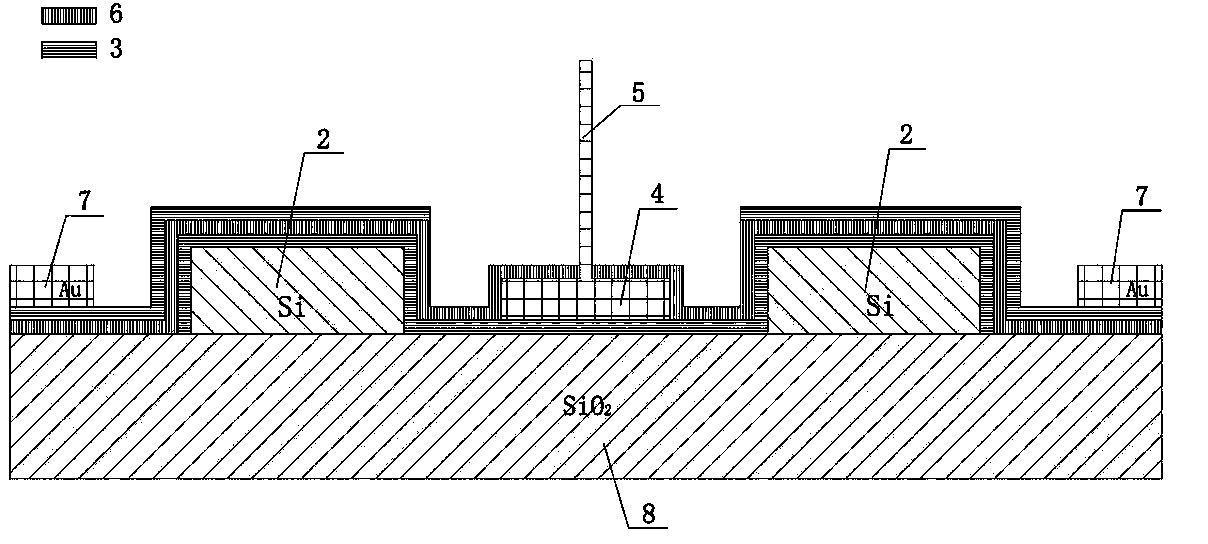
The invention relates to a terahertz detector, in particular to a grid-control graphene nano-ribbon array THz (terahertz) detector and a tuning method. The detector comprises a bottom grid 1, a low-resistivity silicon substrate 2, a double-layer graphene nano-ribbon array 3, source and drain electrodes 4 and 5, insulating layers 6, top grids 7, 8 and 9 and a driving circuit 10. The double-layer graphene nano-ribbon array 3, the source and drain electrodes 4 and 5, the insulating layers 6, the top grids 7, 8 and 9 and the driving circuit 10 are arranged on the substrate. The tuning method includes constructing grid-control double-layer graphene nano-ribbon arrays with different widths by the aid of energy gap double regulation and control mechanisms of double-layer graphene under the effects of lateral constraints and perpendicular electric fields; changing grid voltages; synchronously scanning terahertz waves in a subsection manner to achieve the purpose of detecting wide bands. The grid-control graphene nano-ribbon array THz detector and the tuning method have the advantages of high sensitivity, fast response, broad detection band widths, flexibility in regulation, simple structure, convenience in integration, small size and capability of working at room temperatures. Besides, the grid-control graphene nano-ribbon array THz detector and the tuning method can be widely applied to security inspection, drug enforcement, anti-terrorism, medical imaging, nondestructive examination, electronic countermeasure, radar, remote sensing and outer space wideband communication fields and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Bilayer graphene tunneling field effect transistor
A bilayer graphene tunnelling field effect transistor is provided comprising a bilayer graphene layer, and at least a top gate electrode and a bottom gate electrode, wherein the at least a top gate electrode and a bottom electrode are appropriately positioned relative to one another so that the following regions are electrically induced in the chemically undoped bilayer graphene layer upon appropriate biasing of the gate electrodes: a source region, a channel region, and a drain region.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
Uniform multilayer graphene by chemical vapor deposition
ActiveUS20120225296A1Reduce the temperatureIncrease temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyGrapheneElectrical conductorGas phase
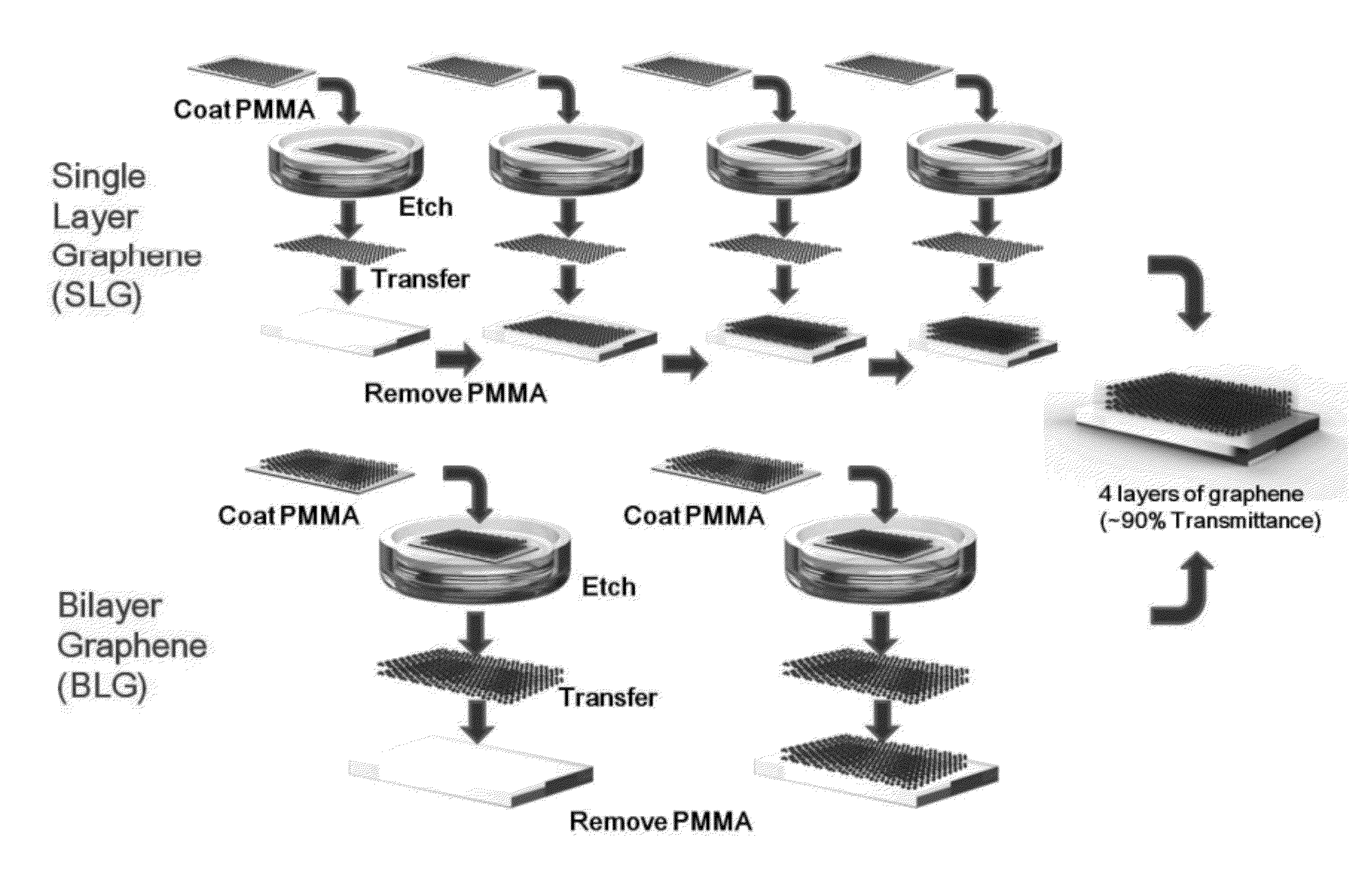
A method of producing uniform multilayer graphene by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is provided. The method is limited in size only by CVD reaction chamber size and is scalable to produce multilayer graphene films on a wafer scale that have the same number of layers of graphene throughout substantially the entire film. Uniform bilayer graphene may be produced using a method that does not require assembly of independently produced single layer graphene. The method includes a CVD process wherein a reaction gas is flowed in the chamber at a relatively low pressure compared to conventional processes and the temperature in the reaction chamber is thereafter decreased relatively slowly compared to conventional processes. One application for uniform multilayer graphene is transparent conductors. In processes that require multiple transfers of single layer graphene to achieve multilayer graphene structures, the disclosed method can reduce the number of process steps by at least half.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Preparation method of double-layer graphene films
InactiveCN103466609AHigh surface coverageUniform and stable structureGrapheneChemical vapor deposition coatingMetal foilHigh surface
The invention discloses a preparation method of double-layer graphene films, which belongs to the technical field of film materials. A catalyst promoter is coated on a cleaned metal foil by spin coating, and then, by using a chemical vapor deposition method, a double-layer graphene film is obtained on the metal foil. According to the method disclosed by the invention, graphene prepared on a metal foil and by using an introduced catalyst promoter is of a double-layer structure, and the coverage rate of the double-layer grapheme is greater than 90%, therefore, the method has the advantages of simple technological process, high controllability on the number of graphene layers, high surface coverage rate of double-layer grapheme, less defects, and the like. The method is applicable to the large-area mass controllable production and preparation of double-layer graphene films, and can be widely applied to the fields of microelectronic and optoelectronic devices.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
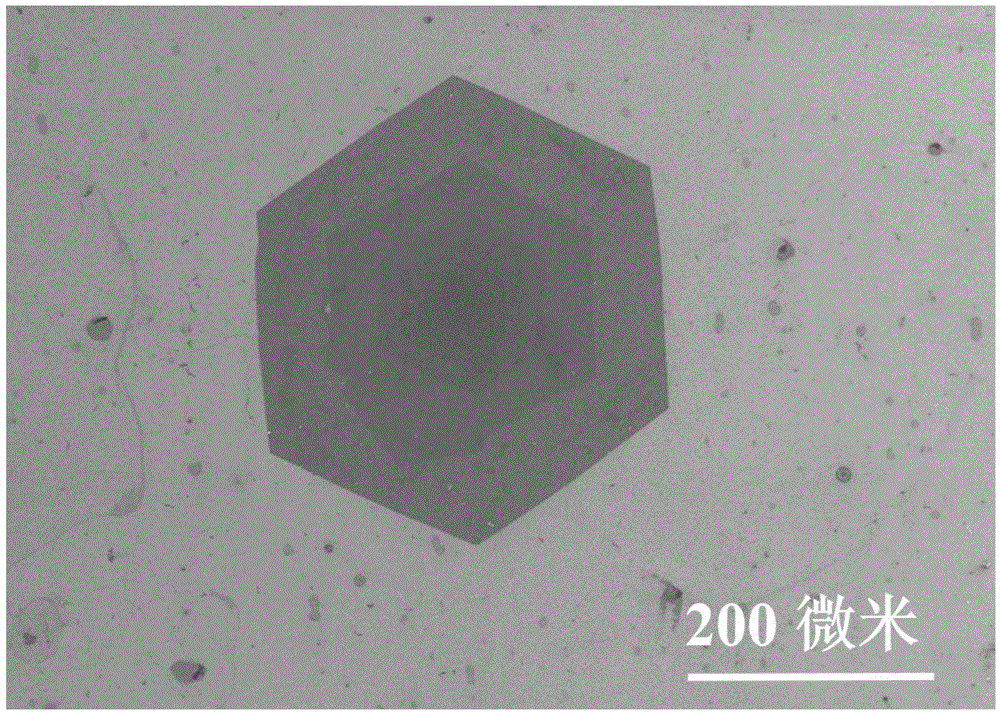
Large-dimension hexagonal bi-layer grapheme single-crystal domain and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102995119AQuality improvementSimple processPolycrystalline material growthGrapheneMicro nanoPhotonics
The invention belongs to the field of nano-materials, and relates to a novel large-dimension hexagonal bi-layer grapheme single-crystal domain and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that: elemental metal and a multi-element alloy thereof are adopted as a catalyst; and the hexagonal grapheme single-crystal domain is prepared with a chemical vapor deposition method. The grapheme single-crystal domain has a bi-layer structure, excellent quality, and bi-layer coverage higher than 90%. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple process and easy-to-control procedure. The large-dimension hexagonal bi-layer grapheme single-crystal domain and the preparation method thereof are suitable for the field of micro-nano-electronic and photonic devices such as transistor, light modulator, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Graphene temperature sensor and preparing process thereof
InactiveCN103630254AThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansNi cr alloyCvd graphene
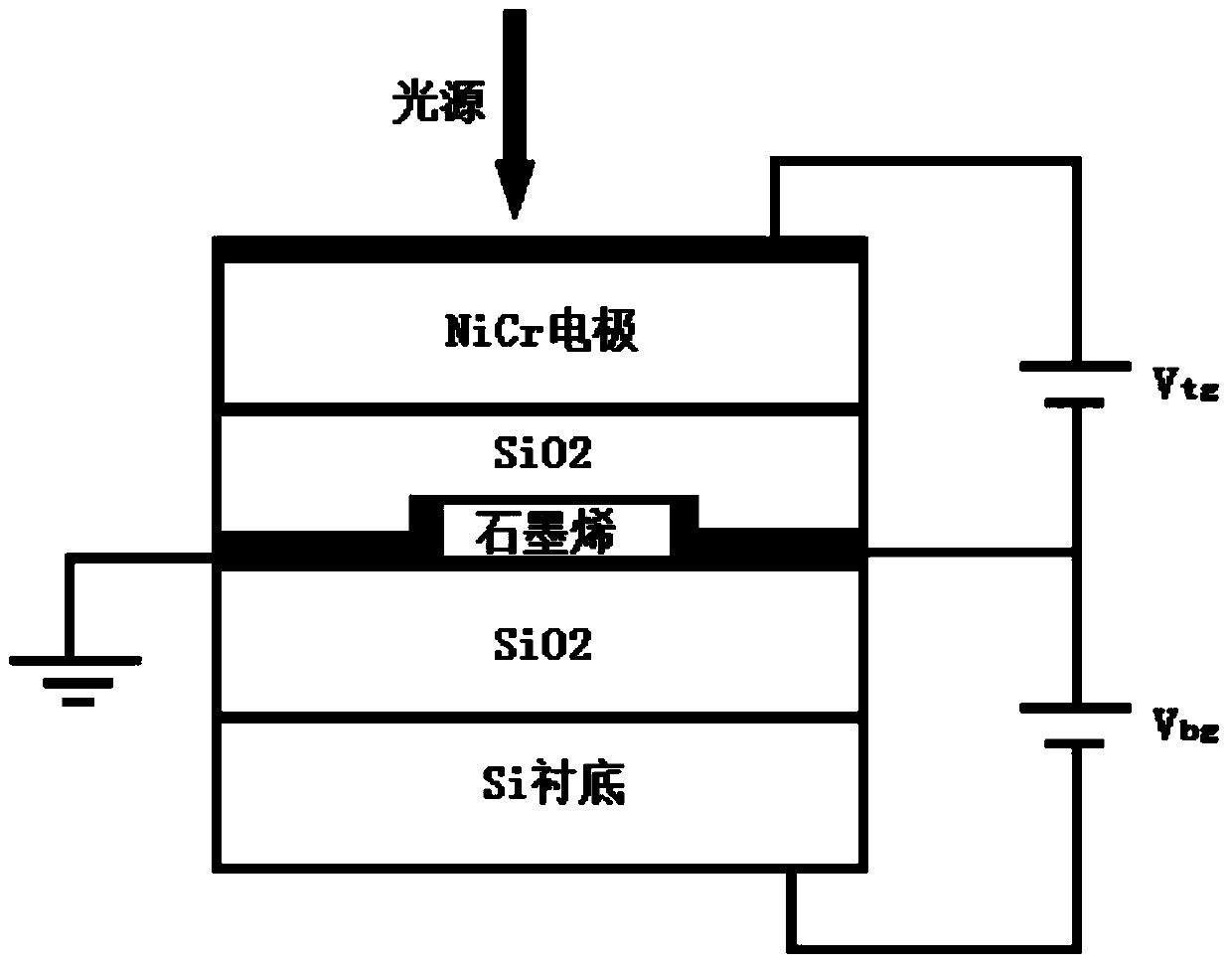
The invention discloses a graphene temperature sensor and a preparing process thereof. The structure of the graphene temperature sensor comprises a top gate electrode, a Ni-Cr alloy film, an upper SiO2 layer, hydrogen silsesquioxane, a dual-layer graphene and source and drain electrode, a lower SiO2 layer, a Si substrate and a back gate electrode from top to bottom. The method comprises the steps of depositing the dual-layer graphene obtained by mechanical stripping at the Si substrate with a SiO2 layer of 300nm thick, manufacturing electrodes at a source end and a drain end by an electronic beam photoetching technology, and thermally evaporating 5nmCr / 100nmAu. Compared with the existing sensor, the graphene temperature sensor has the advantages of very high sensitivity, lower intrinsic noise and very high detection speed and has well application prospect in the aviation field.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Preparation method of graphene on SiC substrate based on Ni film-aided annealing
InactiveCN102505114AThe method is simpleSimple processMaterial nanotechnologyVacuum evaporation coatingPorosityCarbon film
The invention discloses a preparation method of graphene on a SiC substrate based on Ni film-aided annealing, and is mainly used for solving the problems of non-smooth surface, low continuity and non-uniform layers of graphene prepared by the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of: performing standard cleaning of a SiC sample piece; placing the cleaned SiC sample piece in a quartz tube, carrying CCl4 vapor by Ar into the quartz tube, and reacting SiC with gaseous CCl4 at 750-1150 DEG C to generate a double-layer carbon film; performing electron beam deposition on the Si substrate to obtain a Ni film with thickness of 350-600 nm; placing the carbon surface of the generated double-layer carbon film sample piece on the Ni film, placing in Ar, and annealing at a temperature of 900-1100 DEG C for 10-20 minutes to generate double-layer graphene; and finally removing the Ni film from double-layer graphene sample piece. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple process and high safety; and double-layer graphene has smooth surface, good continuity and low porosity, and can be used for sealing gas and liquid.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
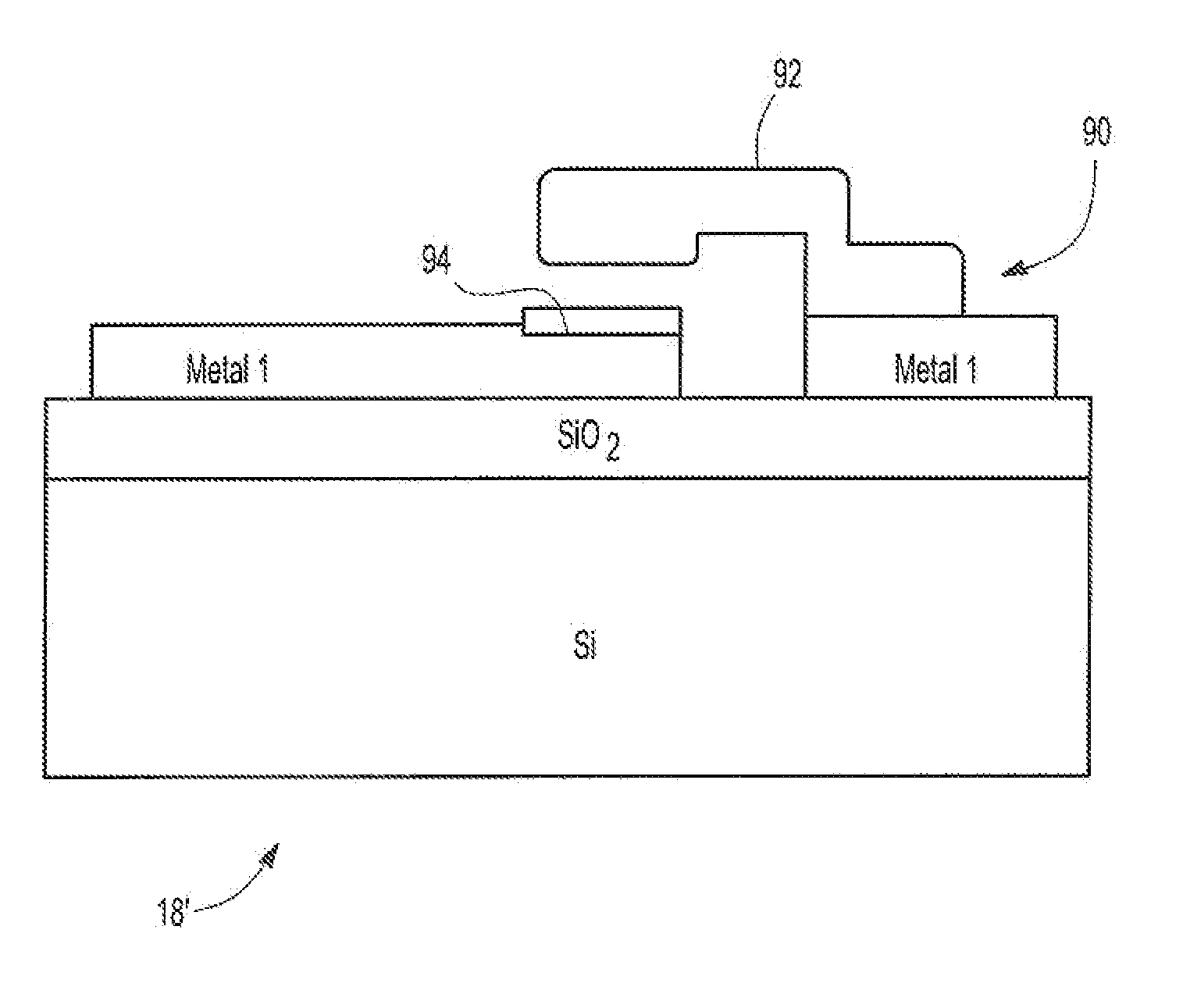
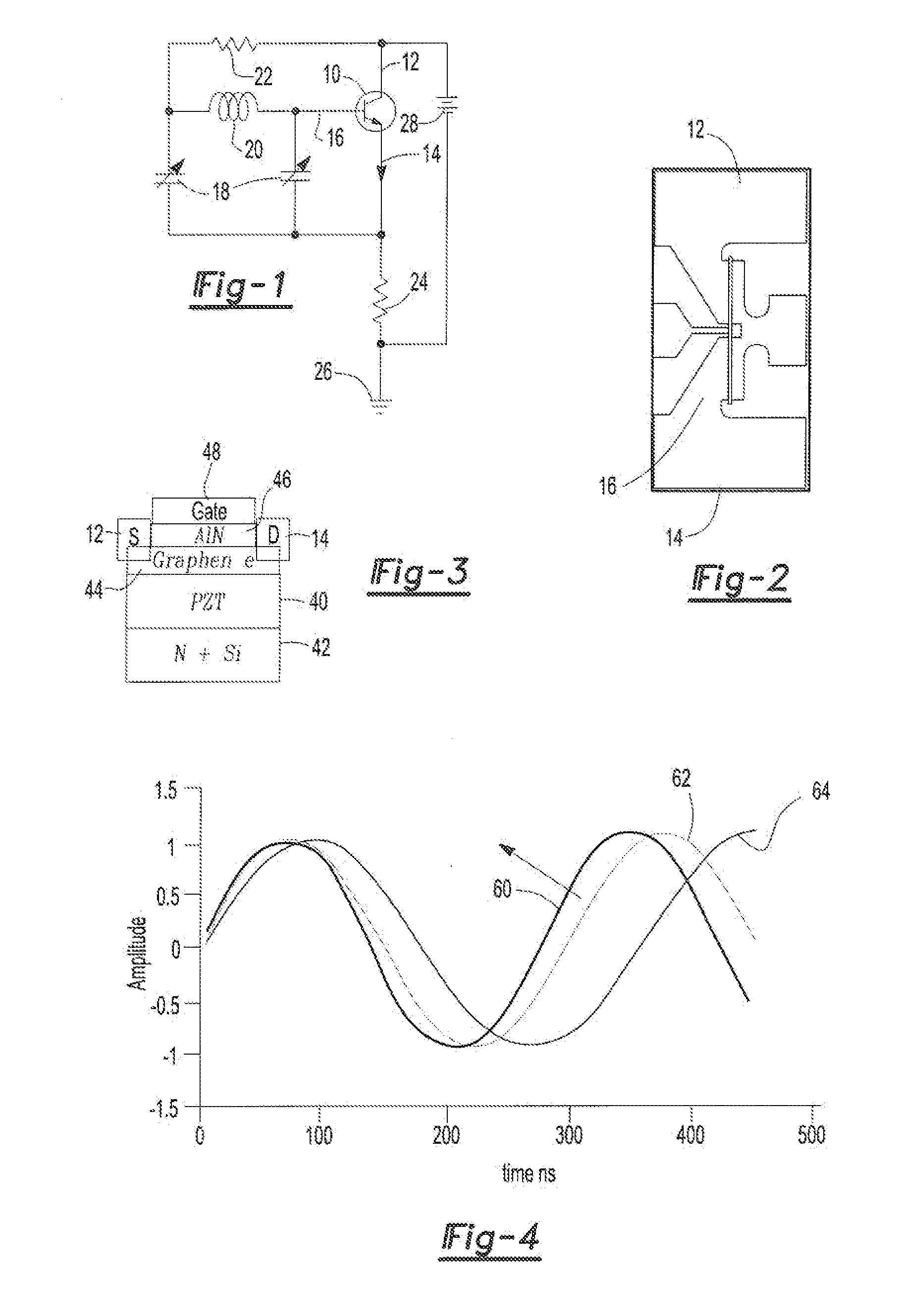
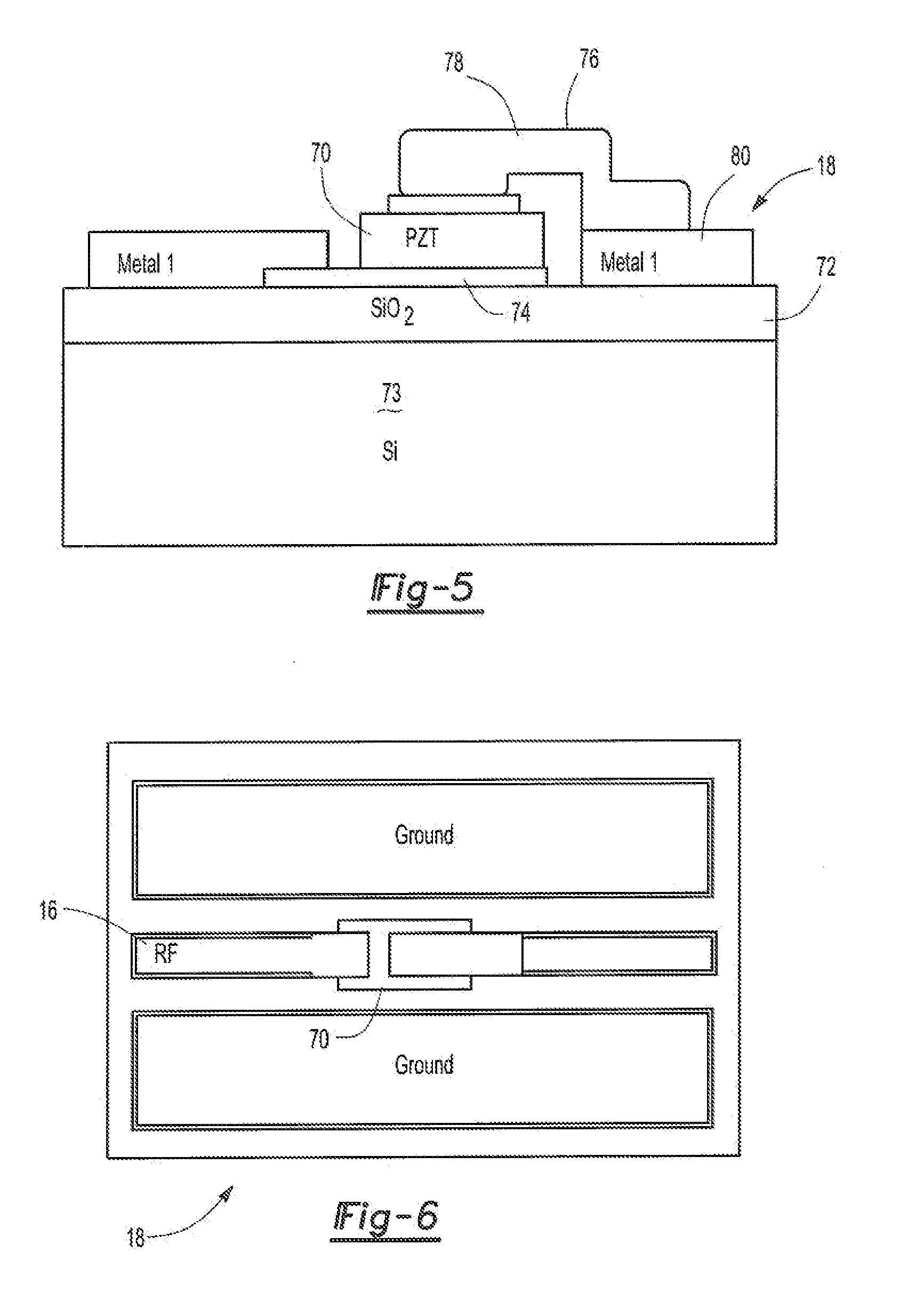
Voltage tunable oscillator using bilayer graphene and a lead zirconate titanate capacitor
ActiveUS20120293271A1Change frequencyNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesLead zirconate titanateMems capacitors
A voltage controlled oscillator comprising a substrate and a bilayer graphene transistor formed on the substrate. The transistor has two signal terminals and a gate terminal positioned in between the signal terminals. A voltage controlled PZT or MEMS capacitor is also formed on the substrate. The capacitor is electrically connected to the transistor gate terminal. At least one component is connected to the transistor and capacitor to form a resonant circuit.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
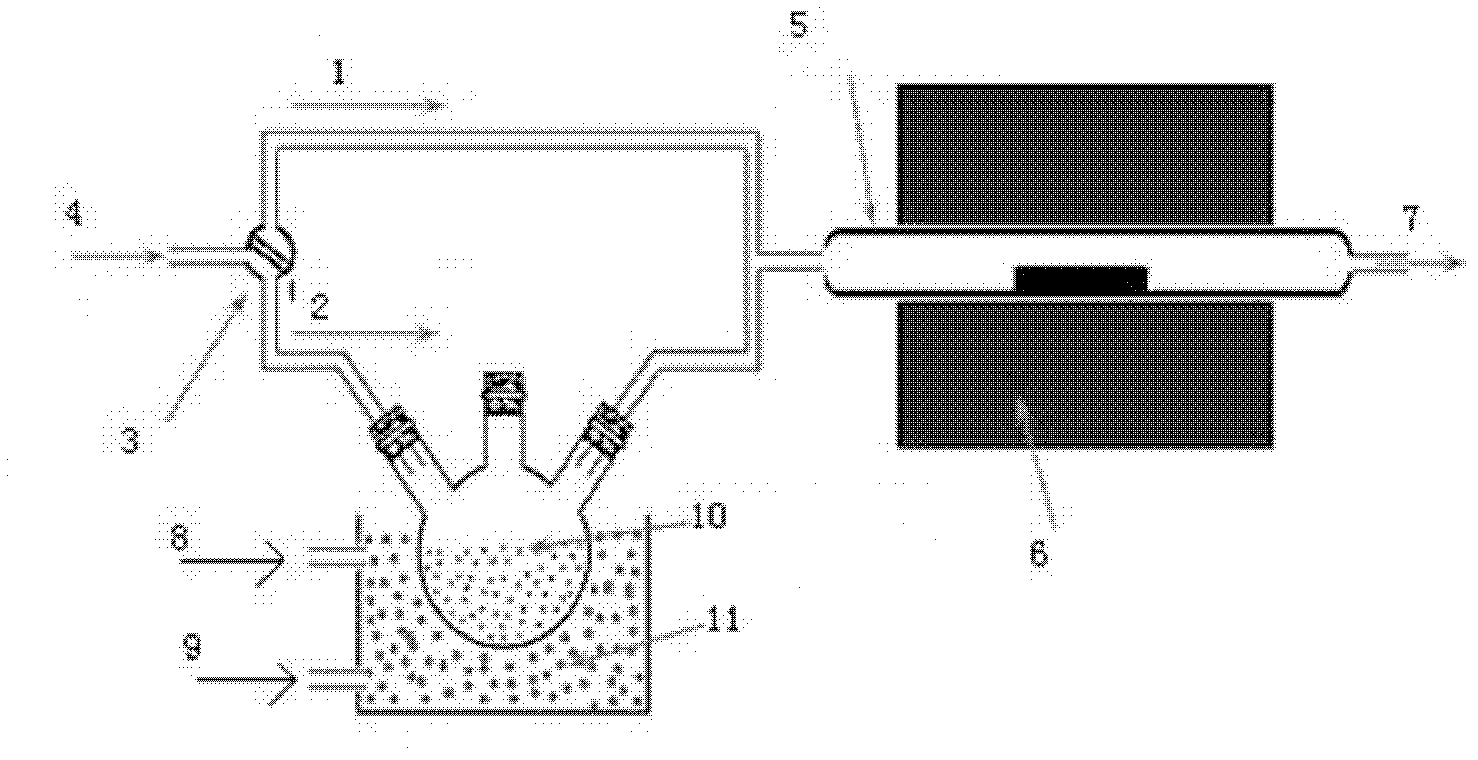
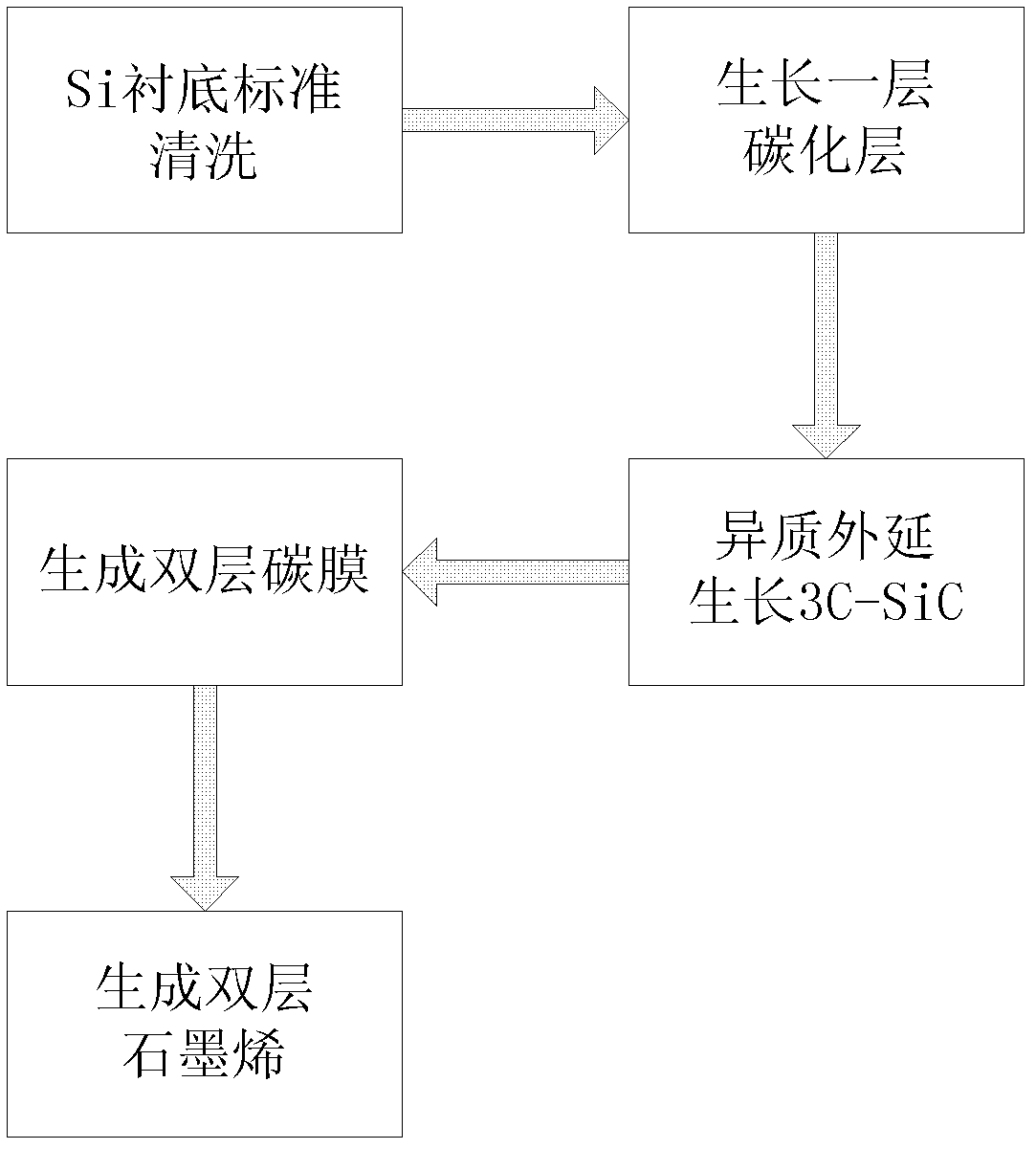
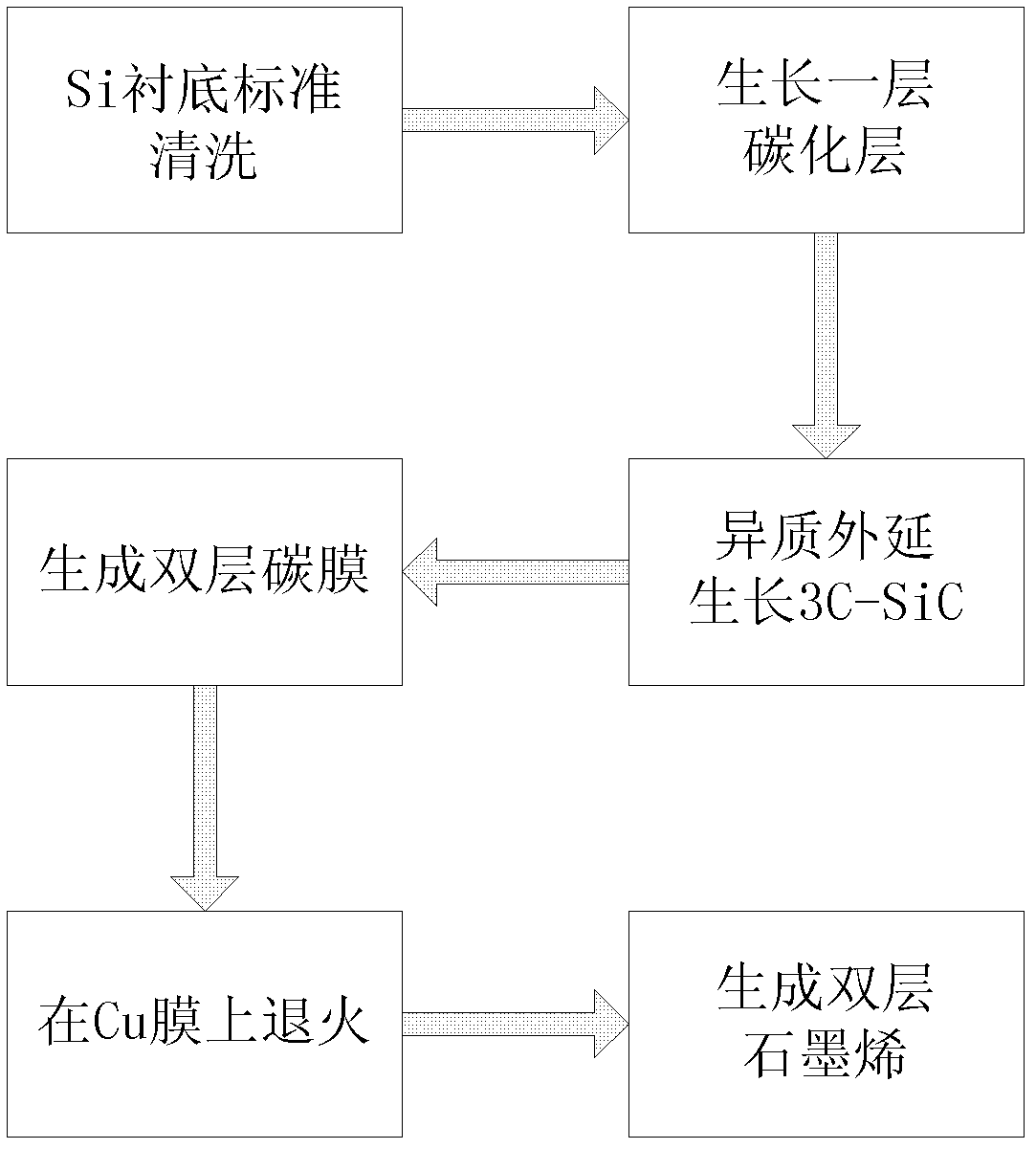
Method for preparing graphene on 3C-SiC substrate
InactiveCN102560414AQuality improvementLow pricePolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesCarbon filmVoid ratio
The invention discloses a method for preparing graphene on a 3C-SiC substrate, which mainly solves the problems that the graphene prepared by prior technology has small area and uneven layer numbers. The steps include: developing a layer of carbonization layer as a transition on a 4 to 12 inches of Si substrate base piece, performing a development of a 3C-SiC hetero-epitaxy film at the temperature between 1150 DEG C and 1300 DEG C, having C3H8 and SiH4 as development gas sources, subjecting the 3C-SiC at the temperature between 800 DEG C and 1000 DEG C and CCl4 in gas state to a reaction so as to produce a double layer carbon film, producing a double layer grapheme by annealing the double layer carbon film for 10 to 20 minutes in the Ar gas at the temperature between 1000 DEG C to 1100 DEG C. The method for preparing graphene on the 3C-SiC substrate has the advantages that the double layer graphene has a large area, smooth surface and low void ratio, and can be used for sealing gas and liquid.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Glass-ceramics substrates for graphene growth
An insulating glass-ceramic substrate for synthesizing graphene includes discrete, crystalline, nanophase metallic regions capable of catalyzing graphene growth. The nanophase regions may be formed by thermal treatment of a glass-ceramic substrate containing the corresponding metal oxide. Single layer and double layer graphene are prepared on the modified glass-ceramic substrate in a vacuum chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process from hydrocarbon precursors. The graphene-coated glass-ceramic substrate is electrically conductive.
Owner:CORNING INC
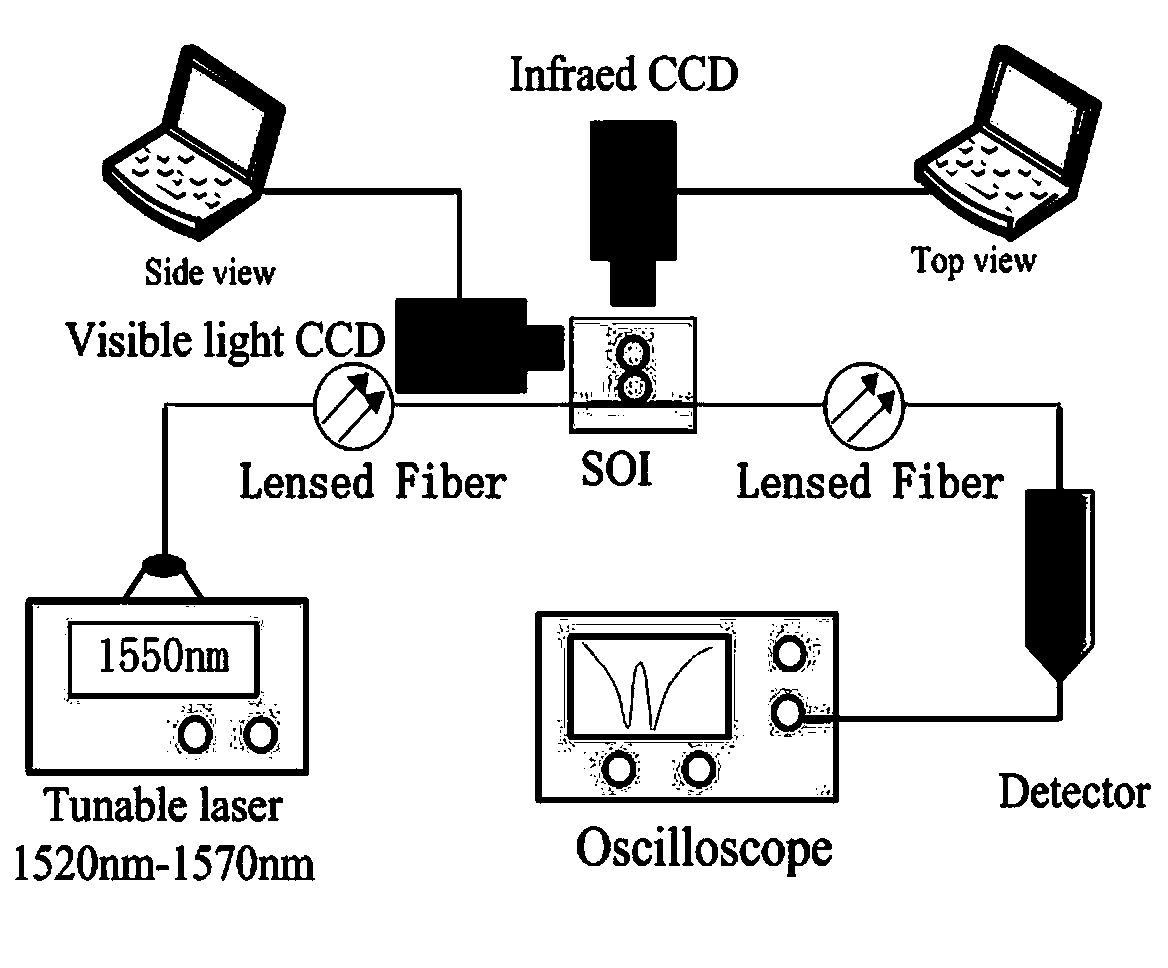
Method for manufacturing double-layer graphene electrooptical modulator on basis of silicon substrate optical waveguide micro-ring resonant cavity
InactiveCN103869504AAvoid insertion lossEnhance modulation strengthNon-linear opticsCharge carrier mobilityPicosecond
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a double-layer graphene electrooptical modulator on the basis of a silicon substrate optical waveguide micro-ring resonant cavity. The method comprises the steps that firstly, simulation and design of the silicon substrate optical waveguide micro-ring resonant cavity are conducted, and the design with a high Q value is selected, process tape-out is conducted; secondly, an existing SOI piece is taken out for process preparation of the silicon substrate optical waveguide micro-ring resonant cavity, and two layers of graphene and one layer of AL2O3 grow on the prepared silicon substrate optical waveguide micro-ring resonant cavity; finally, two electrodes which are symmetrically distributed are led. The method can provide very strong interaction of graphene and light and high-strength photovoltaic conversion. As light absorption of the graphene is unrelated to the light wavelength, broadband control can be conducted; meanwhile, carrier mobility of the graphene at room temperature is extremely high, and modulation time can be reduced to the picosecond level by exerting an external electric field; in addition, the method and a CMOS process can be compatible, and therefore the method is greatly meaningful to microminiaturization, high speed and low power consumption of later integrated optics chips.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Graphene electrooptical modulator and preparing method thereof
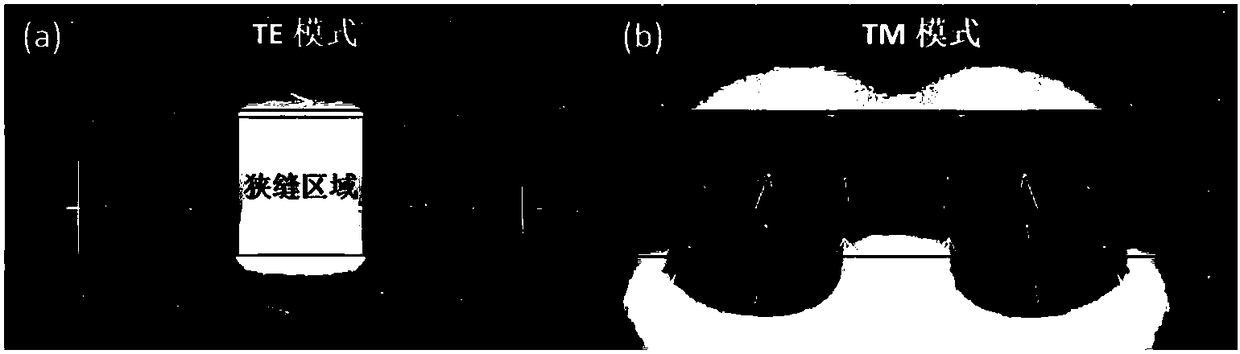
The invention is applicable to an electrooptical modulator, and provides a graphene electrooptical modulator and a preparing method thereof. The graphene electrooptical modulator comprises a substrate, a double-layer graphene perpendicular narrow slit optical waveguide structure, a first electrode, a second electrode, a light input end and a light output end, wherein the double-layer graphene perpendicular narrow slit optical waveguide structure, the first electrode, the second electrode, the light input end and the light output end are formed on the substrate, the double-layer graphene perpendicular narrow slit optical waveguide structure comprises a perpendicular narrow slit optical waveguide composed of a first high refractive index material layer, a low refractive index material layerand a second high refractive index material layer, a first graphene layer, an insulating material layer and a second graphene layer. The narrow slit optical waveguide can improve the limiting effect on a TE mode, so that mode fields distributed in the TE mode in a narrow slit area are increased, the mutual effect of double-layer graphene covering the upper layer is improved, and the modulating efficiency of the modulator is improved. By means of the light modulator made from double-layer graphene, since the transferring speed of a current carrier of the light modulator is high, the response speed of the modulator can be increased.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
Method for preparing monocrystal double-layer graphene
InactiveCN105483824ASmall sizeEasy to operatePolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesSingle crystalNon oxidative
The invention discloses a method for preparing monocrystal double-layer graphene. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a copper catalyst is put into a reactor, non-oxidative gas is introduced into the reactor to enable the reactor to be full of the non-oxidative gas, and monocrystal copper or polycrystalline copper or a copper film is adopted as the copper catalyst; 2, the copper catalyst is heated to the target temperature, and then the temperature is kept constant for 30-120 minutes, wherein the target temperature ranges from 1000 DEG C to 1070 DEG C; 3, the copper catalyst is cooled to enable the temperature to reach 900 DEG C-500 DEG C or be kept constant, in the cooling or constant temperature process, the non-oxidative gas carrying a carbon source is introduced into the reactor, and then the monocrystal double-layer graphene can be obtained on the surface of the copper catalyst. Accordingly, the large-size monocrystal double-layer graphene is prepared on the copper catalyst through an isothermal or non-isothermal atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition method, and the method is convenient to operate, simple and practicable and can be applied to high-grade electronic devices and integrated circuits.
Owner:XINYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Double-graphene-layer tunneling field effect transistor and manufacturing method thereof
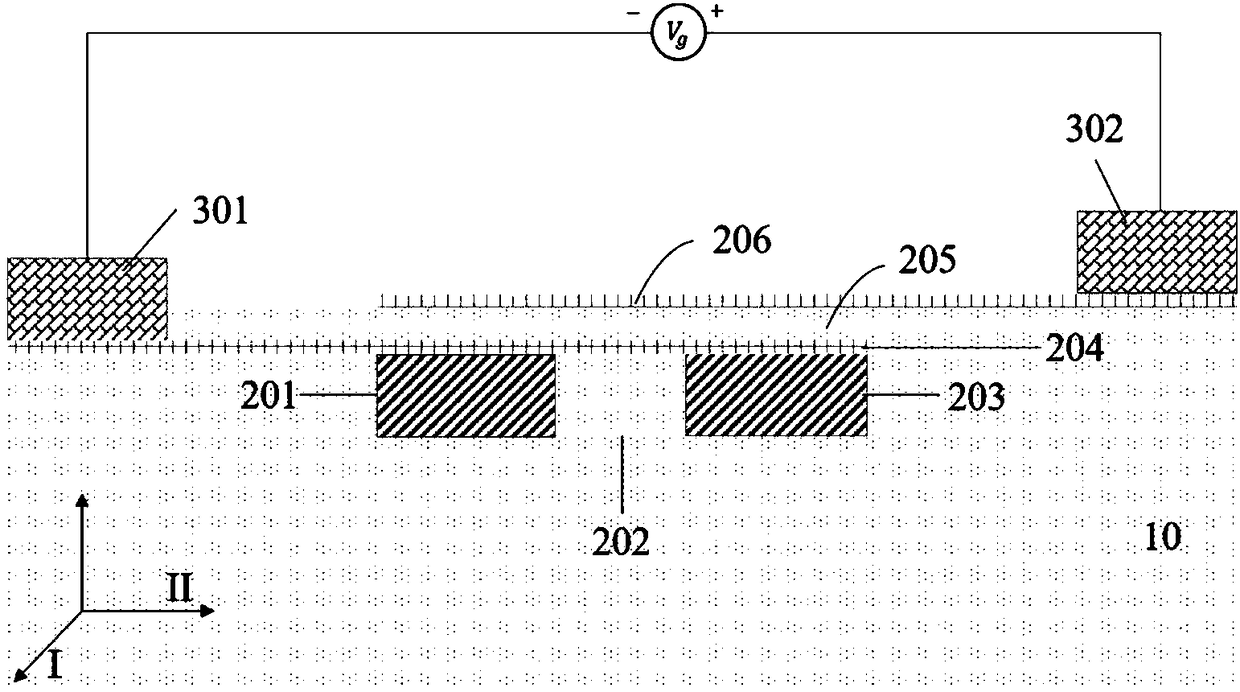
ActiveCN104241378AReduce off-state currentSimple preparation processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeGate dielectricManufacturing technology
The invention provides a double-graphene-layer tunneling field effect transistor. A bottom gate dielectric layer is located on a bottom gate electrode. A double-graphene-layer active area is located on the bottom gate dielectric layer. A metal source electrode and a metal drain electrode are located at the two ends of the double-graphene-layer active area respectively and respectively cover a part of the double-graphene-layer active area. The metal source electrode and the metal drain electrode are made of different materials. For an n-type device, the work function of the metal source electrode is larger, the graphene in contact with the metal source electrode is in p-type doping, the work function of the metal drain electrode is small, and the graphene in contact with the metal drain electrode is in n-type doping. The electrodes of a p-type device are opposite to those of the n-type devices. The metal source electrode, the metal drain electrode and the graphene between the metal source electrode and the metal drain electrode are covered with a top gate dielectric layer. A top gate electrode is located on the top gate dielectric layer and overlaps the metal source electrode and the metal drain electrode. The manufacturing technology of the double-graphene-layer tunneling field effect transistor is simple. Compared with a traditional double-graphene-layer field effect transistor, the metal source electrode and the metal drain electrode of the double-graphene-layer tunneling field effect transistor are completed independently.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Stepped gate-dielectric double-layer graphene field effect transistor and production method thereof
ActiveCN104218089AReduce the tunneling windowSuppresses off-state currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricBottom gate
A stepped gate-dielectric double-layer graphene field effect transistor comprises a bottom gate electrode, a bottom gate dielectric layer, a double-layer graphene active region, a metal source electrode, a metal drain electrode, a stepped top gate dielectric layer and a top gate electrode. The bottom gate dielectric layer is located on the bottom gate electrode, the double-layer graphene active region is located on the bottom gate dielectric layer, the metal source electrode and the metal drain electrode are located at two ends of the double-layer graphene active region respectively and cover the bottom gate dielectric layer and part of the double-layer graphene active region at the same time, the stepped top gate dielectric layer covers the metal source electrode, the metal drain electrode and graphene between the two electrodes, the top gate electrode only covers the top of the stepped top gate dielectric layer partially, and the distance between the top gate electrode and the edge of the metal source electrode is equal to that between the top gate electrode and the edge of the metal drain electrode. By introduction of the stepped top gate dielectric layer, a tunneling window between a source region and a gate-controlled trench under an off state is reduced effectively, so that small off-state current is obtained, and on-off ratio of a device is increased.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
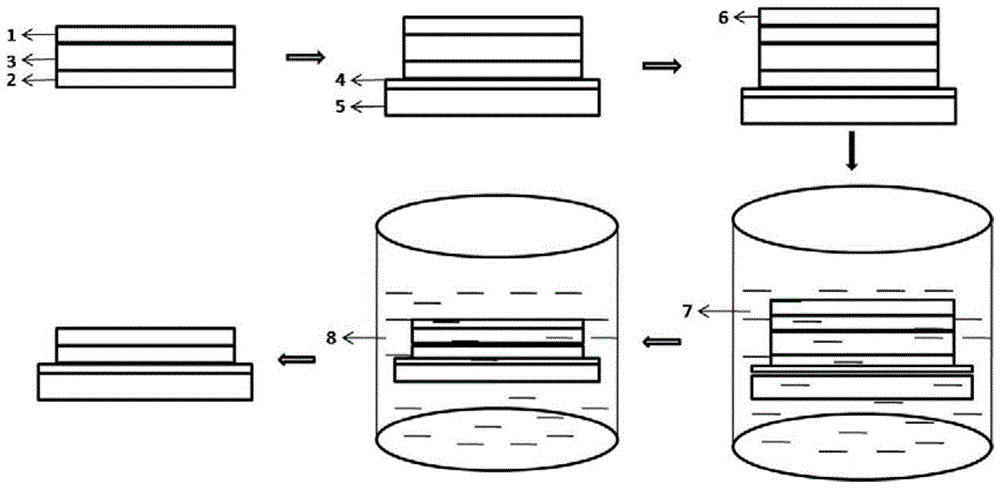
Preparation method of twist angle-controllable multilayer graphene structure
ActiveCN104029431AControl Twist AngleCarbon compoundsLayered productsPolymethyl methacrylateSingle crystal
The invention provides a preparation method of a twist angle-controllable multilayer graphene structure, belonging to the technical field of material, and relates to the preparation of a double-layer or multilayer graphene structure with controllable twist angle(s) between or among layers. The method comprises the steps of firstly, cutting a signal layer of graphene single crystal on an SiO2 / Si substrate into two parts, and carrying out spin coating on polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) on the two parts; after that, removing the SiO2 layer by corrosion, and enabling the two parts of PMMA films carrying the graphene to fall off; transferring one of the two parts of PMMA films onto a new SiO2 / Si substrate, removing PMMA, and fixing the other part of PMMA film onto a glass sheet; respectively fixing the new substrate and the glass sheet; adjusting the angles and the positions of the two pieces of graphene under a micromainpulator system, and stacking the two pieces of graphene together; removing the PMMA to obtain the double-layer graphene structure with a certain twist angle; repeating the process to obtain the twist angle-controllable multilayer graphene structure. After the method is used, the angle-controllable multilayer graphene structure can be flexibly and conveniently obtained, and foundation is laid for the application of the graphene on a photoelectronic device.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Graphene devices with local dual gates
InactiveUS20130001519A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceDielectric layer
An electronic device comprises an insulator, a local first gate embedded in the insulator with a top surface of the first gate being substantially coplanar with a surface of the insulator, a first dielectric layer formed over the first gate and insulator, and a channel. The channel comprises a bilayer graphene layer formed on the first dielectric layer. The first dielectric layer provides a substantially flat surface on which the channel is formed. A second dielectric layer formed over the bilayer graphene layer and a local second gate formed over the second dielectric layer. Each of the local first and second gates is capacitively coupled to the channel of the bilayer graphene layer. The local first and second gates form a first pair of gates to locally control a first portion of the bilayer graphene layer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Preparation method for synchronous-grown wafer-level AB-stack double-layer graphene and equipment for preparation method
ActiveCN106087051AAchieve synchronous growthImprove mobilityPolycrystalline material growthGrapheneSolid carbonCharge carrier mobility
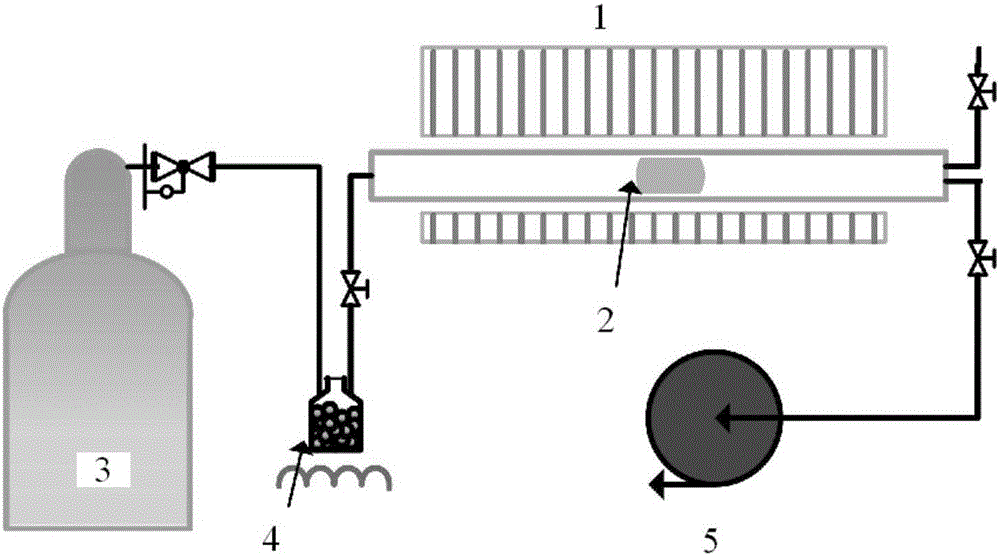
The invention relates to a preparation method for AB-stack double-layer graphene and equipment for the preparation method. A solid or liquid hydrocarbon compound is adopted as a carbon source, the amount of volatilization is controlled, the solid or liquid hydrocarbon compound is brought to the surface of copper foil through inert carrier gas containing high hydrogen partial pressure, and the growth of double-layer graphite is catalyzed by using a normal-pressure chemical vapor deposition method. The hydrocarbon compound is a solid carbon source, i.e., a solid hydrocarbon compound or hydrocarbon derivative; the amount of volatilization of the carbon source is controlled through heating the solid carbon source; or, the hydrocarbon compound is a liquid carbon source, i.e., a liquid hydrocarbon compound or hydrocarbon derivative; and the amount of volatilization of the liquid carbon source is controlled through controlling the volume of inert gas introduced. According to the preparation method and the equipment for the preparation method, the synchronous growth of the double-layer graphene is achieved, the high-quality wafer-level AB-stack double-layer graphene is obtained, the coverage of the AB-stack double-layer graphene can reach 100%, and the single-crystal field-effect carrier mobility reaches up to 5,300 cm<2> / v / s. Experimental parameters are conveniently controlled, and the operation is simple, environmentally friendly and efficient, so that the preparation method and the equipment for the preparation method are very easily extended to industrial large-scale reel-to-reel production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Etching method for directly forming multi-layer graphene film in graphene prepared through CVD method
The invention discloses an etching method for directly forming a multi-layer graphene film in graphene prepared through a CVD method. The etching method comprises the following steps: 1) bonding any side of a growth substrate where grapheme is grown through the CVD method with a substrate; 2) coating a protective glue solution at the other side of the growth substrate treated in the step 1), and then, roasting the growth substrate; 3) putting the growth substrate treated in the step 2) into an etching solution to etch, and removing the growth substrate clamped between graphene layers at the two sides, enabling the graphene layers, which are originally positioned at the two sides of the growth substrate separately, to automatically and tightly fit to form a double-layer graphene film, and getting out the double-layer graphene film; 4) cleaning the double-layer graphene film formed in the step 3 with water, roasting the double-layer graphene film, removing surface protective glue, cleaning the double-layer graphene film, and drying the double-layer graphene film, thereby obtaining the multi-layer graphene film.
Owner:WUXI GRAPHENE FILM +1
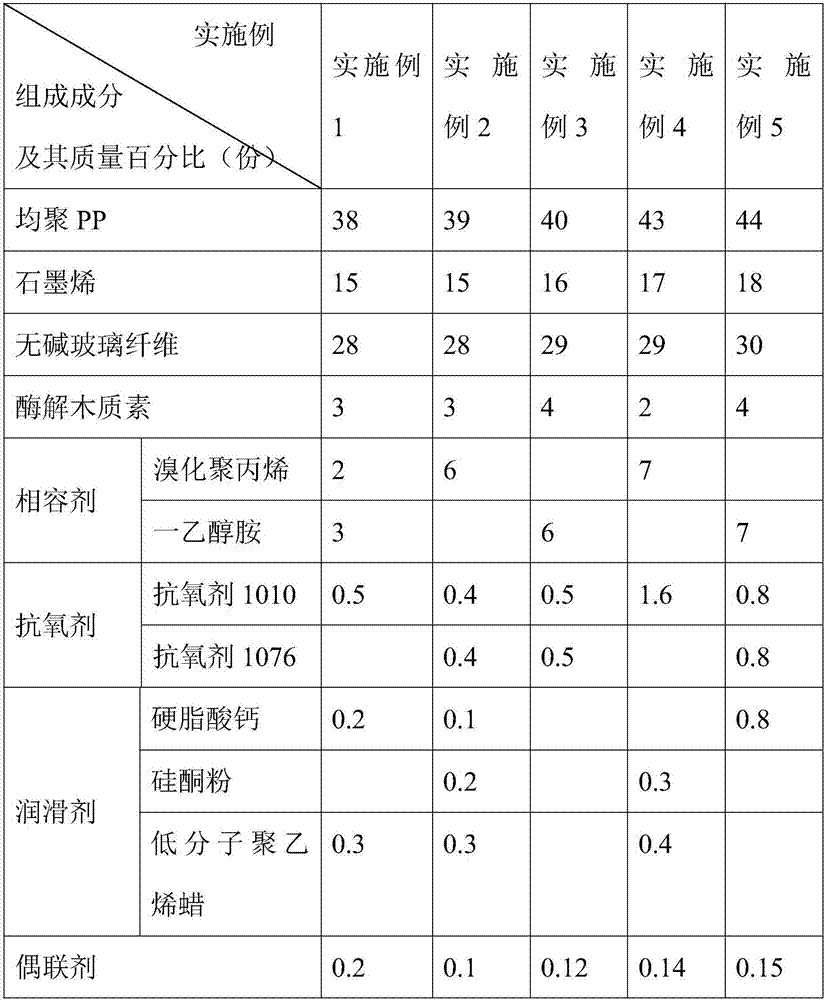
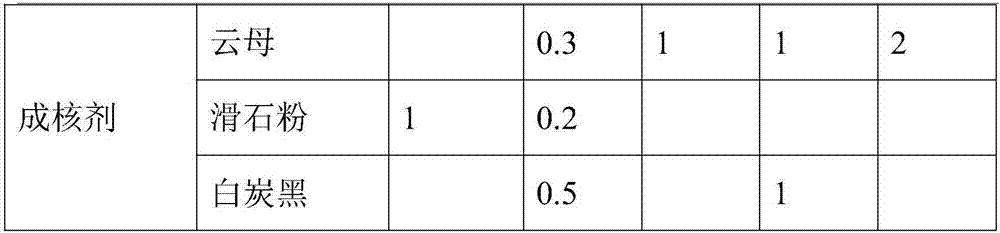
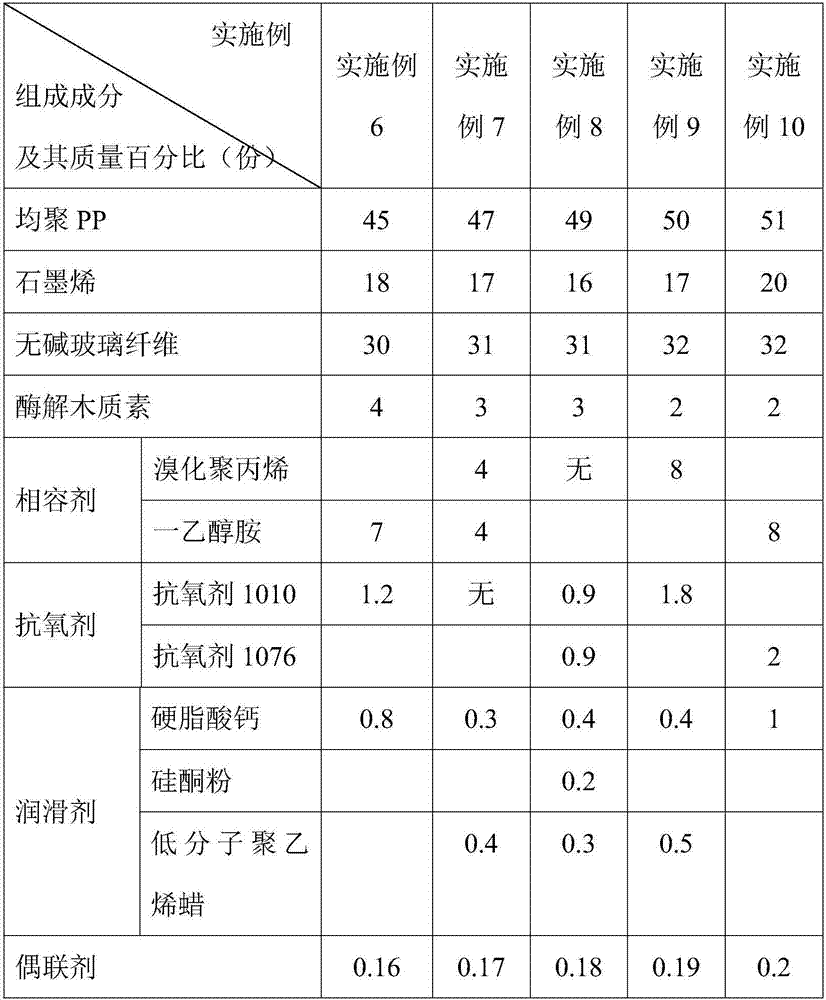
High-strength high-rigidity graphene modified polypropylene and preparation method therefor
The invention relates to modified polypropylene, particularly relates to high-strength high-rigidity graphene modified polypropylene and belongs to the technical field of macromolecular materials. The modified polypropylene material is prepared from the following ingredients in parts by weight: 38-51 parts of homopolymerized polypropylene, 15-20 parts of graphene, 28-32 parts of alkali-free glass fibers, 2-4 parts of enzymolysis lignin, 5-8 parts of compatibilizer, 0.5-2 parts of antioxidant, 0.5-1.0 part of lubricant and 0.1-0.2 part of couplant. The high-strength high-rigidity graphene modified polypropylene is prepared through adding the high strength glass fiber inorganic matter into the homopolymerized polypropylene, which serves as a carrier, then, introducing a conductive medium, i.e., double-layer graphene, and then, adding the enzymolysis lignin. Compared with the ordinary polypropylene, the high-strength high-rigidity graphene modified polypropylene disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being high in tensile strength and flexural strength, being not prone to breakage, being good in rigidity, resistant to corrosion and resistant to aging and having the characteristic of electric conduction.
Owner:NINGBO HAIYU ADVANCED MATERIALS TECH
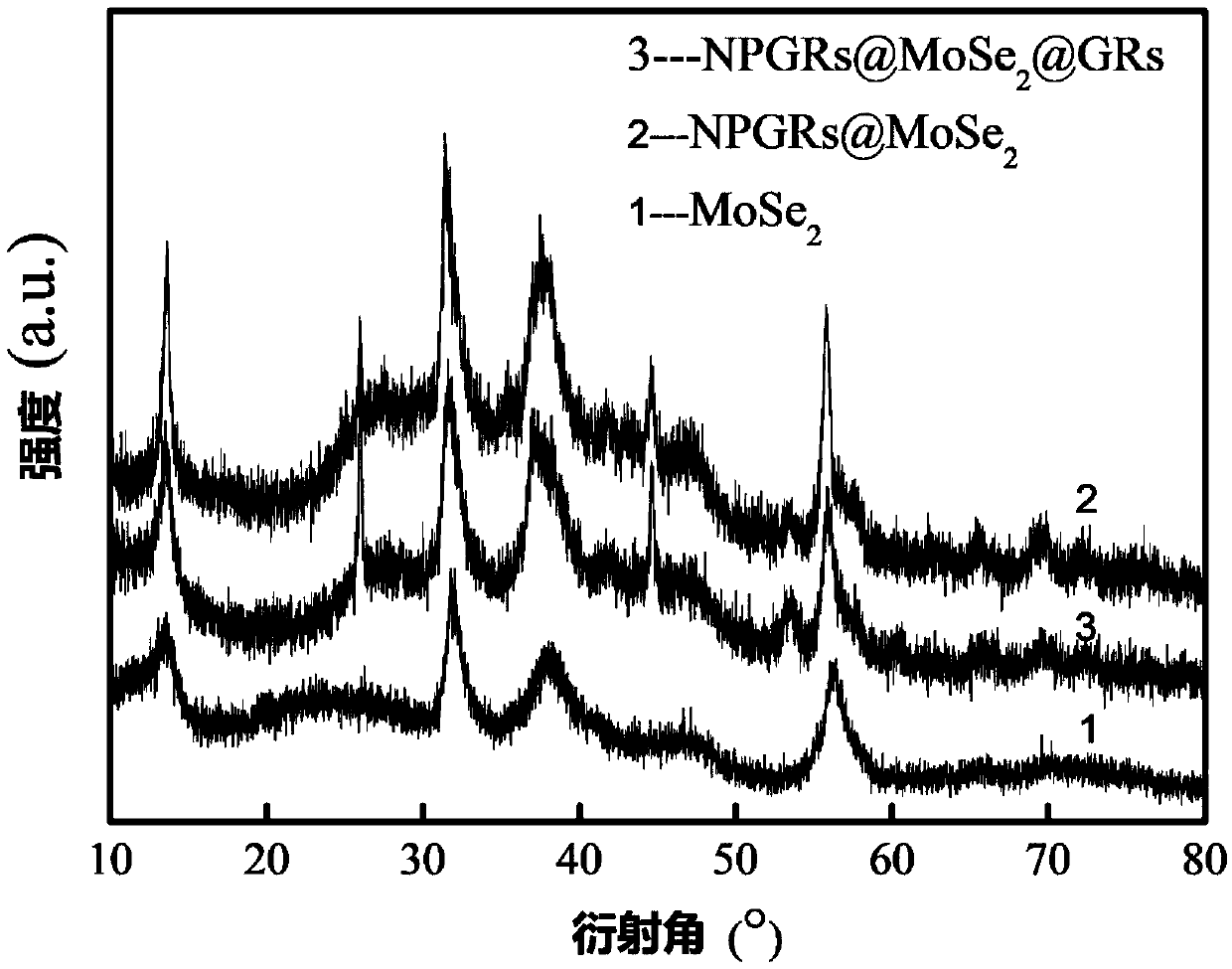
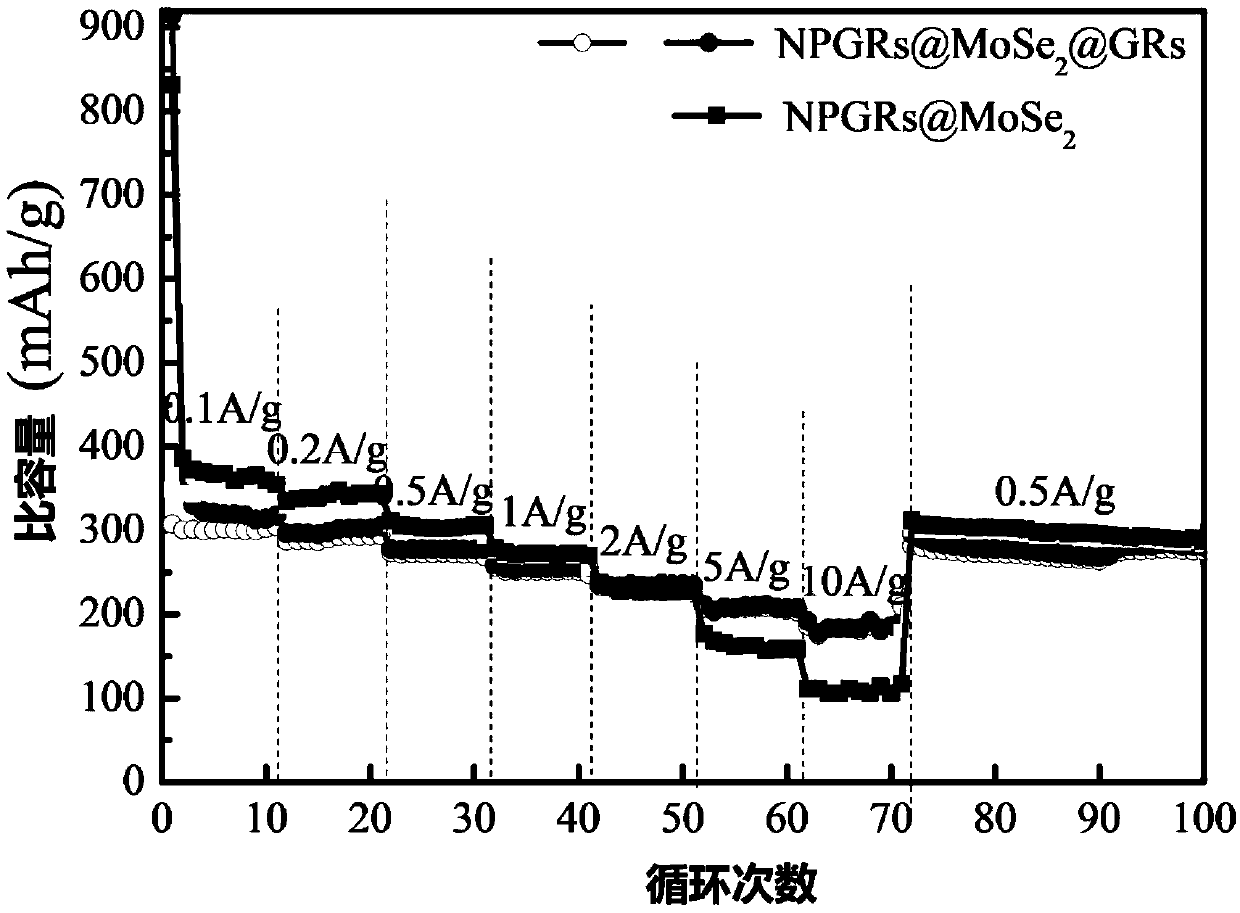
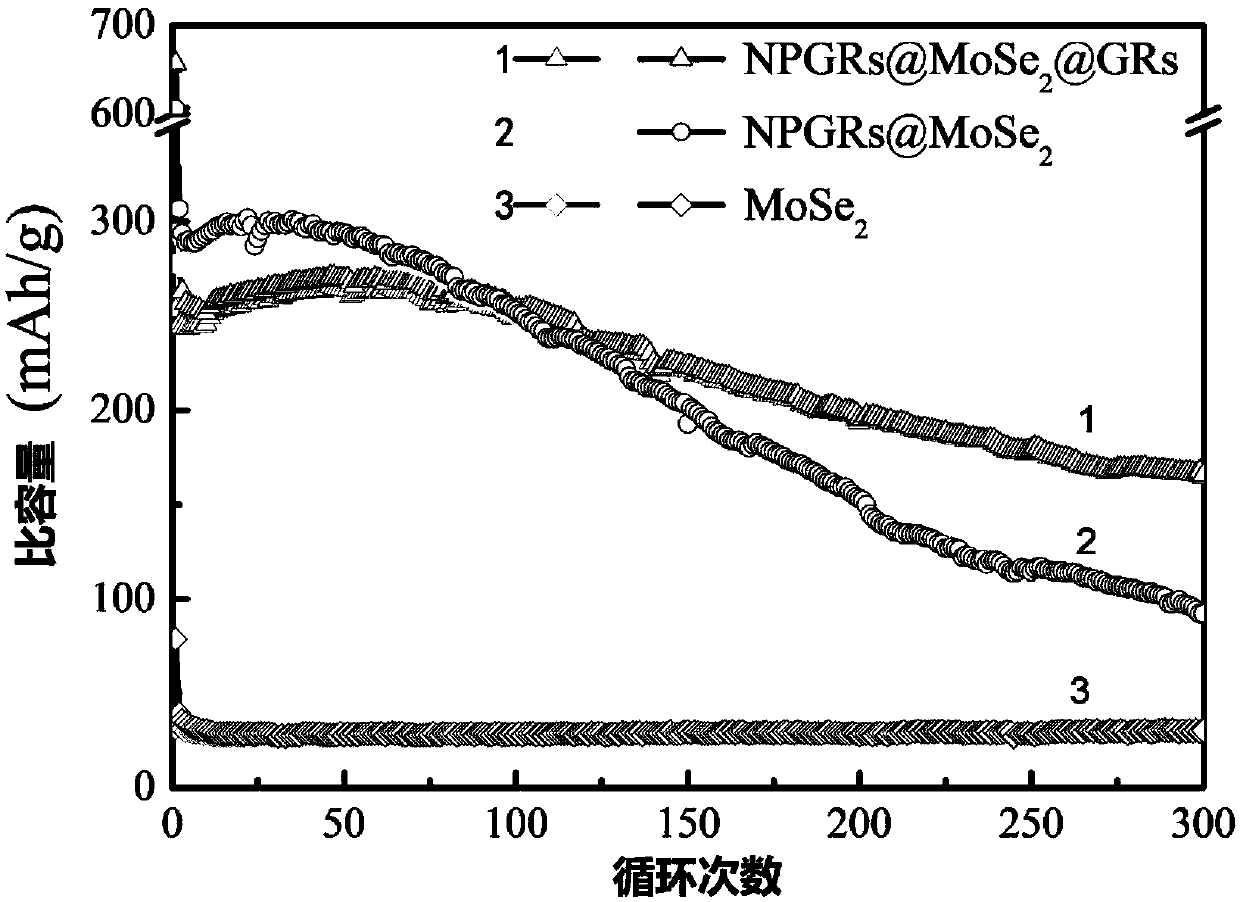
Sandwich-structured graphene/molybdenum selenide/nitrogen-doped porous graphene composite material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109546133AStable structureLow costSecondary cellsNegative electrodesPorous grapheneDissolution
The invention discloses a sandwich-structured graphene / molybdenum selenide / nitrogen-doped porous graphene composite material and a preparation method and an application thereof. The structure unit includes a nitrogen-doped porous graphene layer of a substrate, a molybdenum selenide layer growing on the substrate, and a graphene layer as an outer protective film on the molybdenum selenide layer. Molybdenum selenide is grown in the middle of two graphene layers by using structural similarity. The inner nitrogen-doped porous graphene has good conductivity and a porous structure, which is conducive to electron transport and electrolyte infiltration. The graphene protective film on the surface can reduce the dissolution and destruction of molybdenum selenide and improve the stability and rate performance of materials. Therefore, technical problems such as serious self-agglomeration, weak conductivity, large volume deformation and low capacity caused by the use of pure molybdenum selenide asa negative material of sodium ion batteries are solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
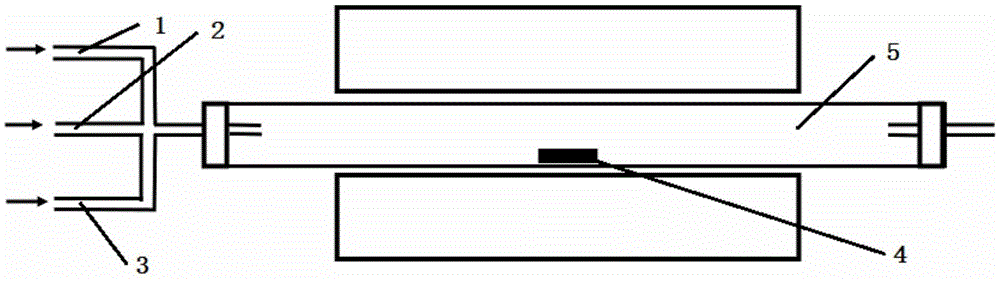
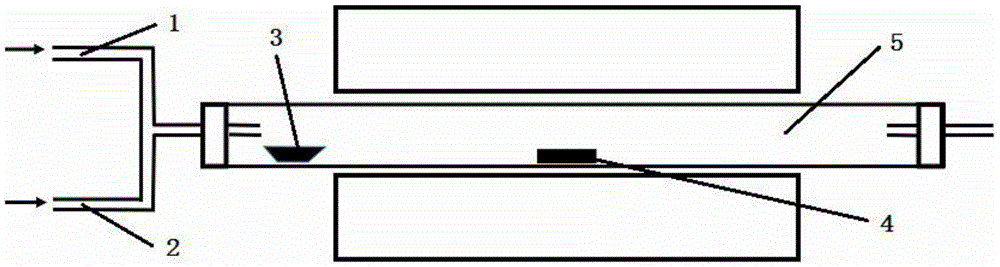
Graphene photoeletric modulator based on slot waveguide
The invention discloses a graphene photoelectric modulator based on a slot waveguide, which belongs to the field of integrated photons and silicon-based photonics. An optical modulator includes substrate layer, silicon optical waveguide, dielectric filling layer and electrode structure. The silicon optical waveguide structure is buried in the substrate layer, and the silicon optical waveguide is aMach-Zehnder interference structure composed by a silicon slot waveguide, including a slot waveguide splitter, a first slot waveguide, a second slot waveguide and a slot waveguide combiner. The firstslit waveguide consists of a first silicon waveguide and a second silicon waveguide; the second slot waveguide consists of a second silicon waveguide and a third silicon waveguide; a first graphene layer and a third graphene layer are covered on the first slot waveguide; a second graphene layer and a third graphene layer are covered on the second slot waveguide; the third graphene layer is separated from the first graphene layer and the second graphene layer through the dielectric filling layer; The electrode structure includes a first metal layer, a second metal layer and a third metal layer, and the three metal layers are respectively deposited on the first graphene layer, the second graphene layer and the third graphene layer. The double-layer graphene only overlaps on the slot of theslot waveguide, thereby enhancing the interaction between the graphene and the light and increasing the modulation rate. The graphene photoelectric modulator based on the slot waveguide has the advantages of large bandwidth, high modulation rate and compact structure, thereby providing an effective solution for building large bandwidth, high density and high speed on-chip system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Graphene preparation method based on Cu film assisted annealing
InactiveCN102505141AQuality improvementLow pricePolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsPorosityCarbon film
The invention discloses a graphene preparation method based on Cu film assisted annealing, which is used mainly for solving the problems of small area, poor continuity and nonuniform layering of graphene preparation in the prior art. The method includes: firstly, growing a carbonized layer for transition on a Si substrate 4-12 inches in size; secondly, growing a 3C-SiC heteroepitaxal film at the temperature of 1100 DEG C to 1250 DEG C, and using C3H8 and SiH4 as growth source gases; thirdly, allowing 3C-SiC to react with gaseous CCl4 at 800-1000 DEG C to generate a double-layer carbon film; fourthly, placing a carbon side of the double-layer carbon film sample on a Cu film; and fifthly, placing the double-layer carbon film and the Cu film in Ar atmosphere, and annealing at 900-1100 DEG C for 10-25 minutes to generate double-layer graphene. The double-layer graphene generated by the method has smooth surface, is large in area and low in porosity, and can be used for sealing gases and liquids.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Large single crystal double layer graphene and the preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a large single crystal double layer graphene and the preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps of selecting a single layer graphene as the seed layer, applying the chemical vapor deposition to cultivate graphene on the edge liner to obtain the double layer graphene on the insulated liner. The invention applies the single layer graphene as the seed layer of the double layer graphene and controls the development of the extensive growth of the double graphene by the chemical vapor deposition, thus achieving the control of the pile structure of the double layer graphene. The use of copper powder of nano scale and other catalysts can steam out the copper particulates, which is transported to the reactor liner by the steam, the catalyst decomposes the carbon source to acquire the carbon atoms or carbon atom groups which floats to the liner of the full layer of the single layer graphene to cultivate the double layer graphene on the extension of the single layer graphene. The method enhances the cultivation efficiency and achieves the top-to-bottom-piling preparation.
Owner:RENMIN UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com