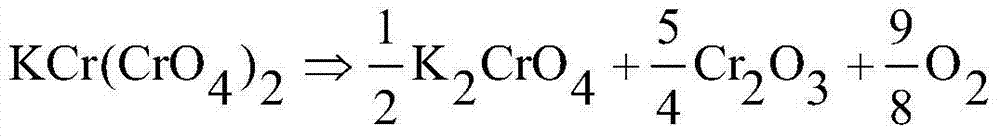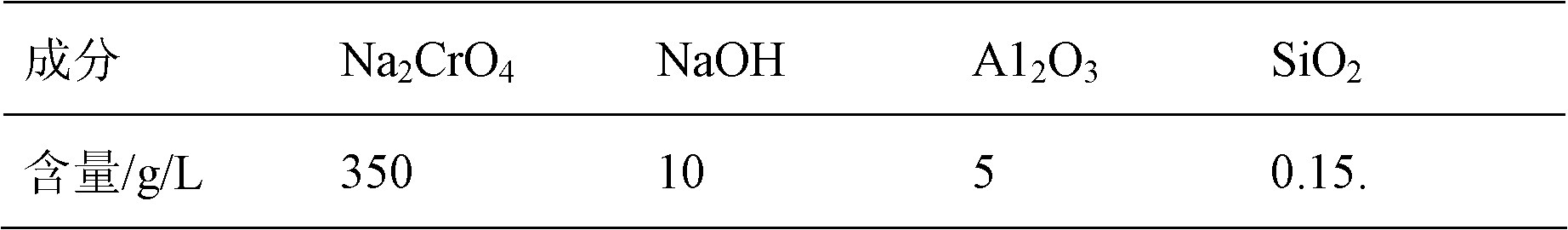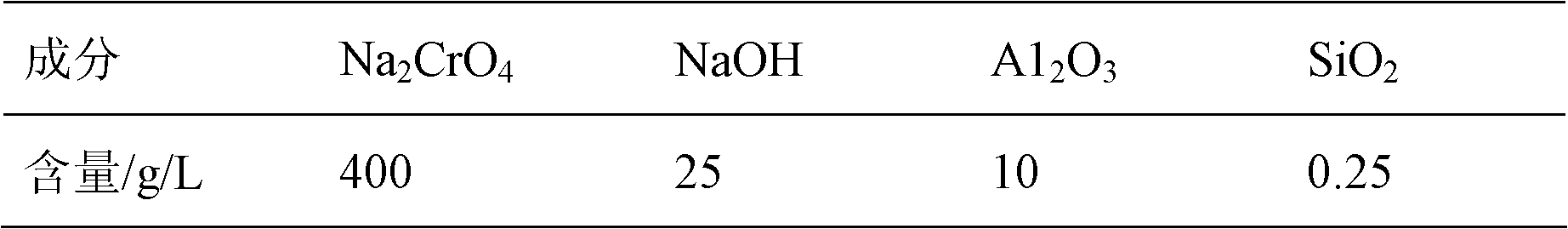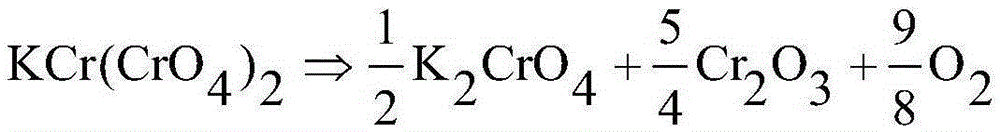Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35results about How to "Coarse particles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mixed salt process to preparing in-situ reinforced Mg-based composite material
The present invention relates to material technology and is mixed salt process to prepare in-situ reinforced Mg-base composite material. The process includes determining the alloy element components in the composite material, selecting the reinforcing phase based on the wettability between the substrate and the reinforcing phase whith ic controlled in 2-15 wt%, compounding and pretreating mixed salt system, smelting the magnesium substrate material and adding the pretreated mixed salt into the magnesium melt at proper temperature via stirring, and final casting after being let stand to form. The reinforcing phase is fine, homogeneously distributed and excellent in interface bindnig, and the Mg-base composite material has excellent mechanical and physical performance and may be used widely.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method of high-stability high-purity extra-coarse tungsten carbide powder
InactiveCN102557028ANarrow particle size distributionImprove stabilityTungsten/molybdenum carbideGranularityCarbonization
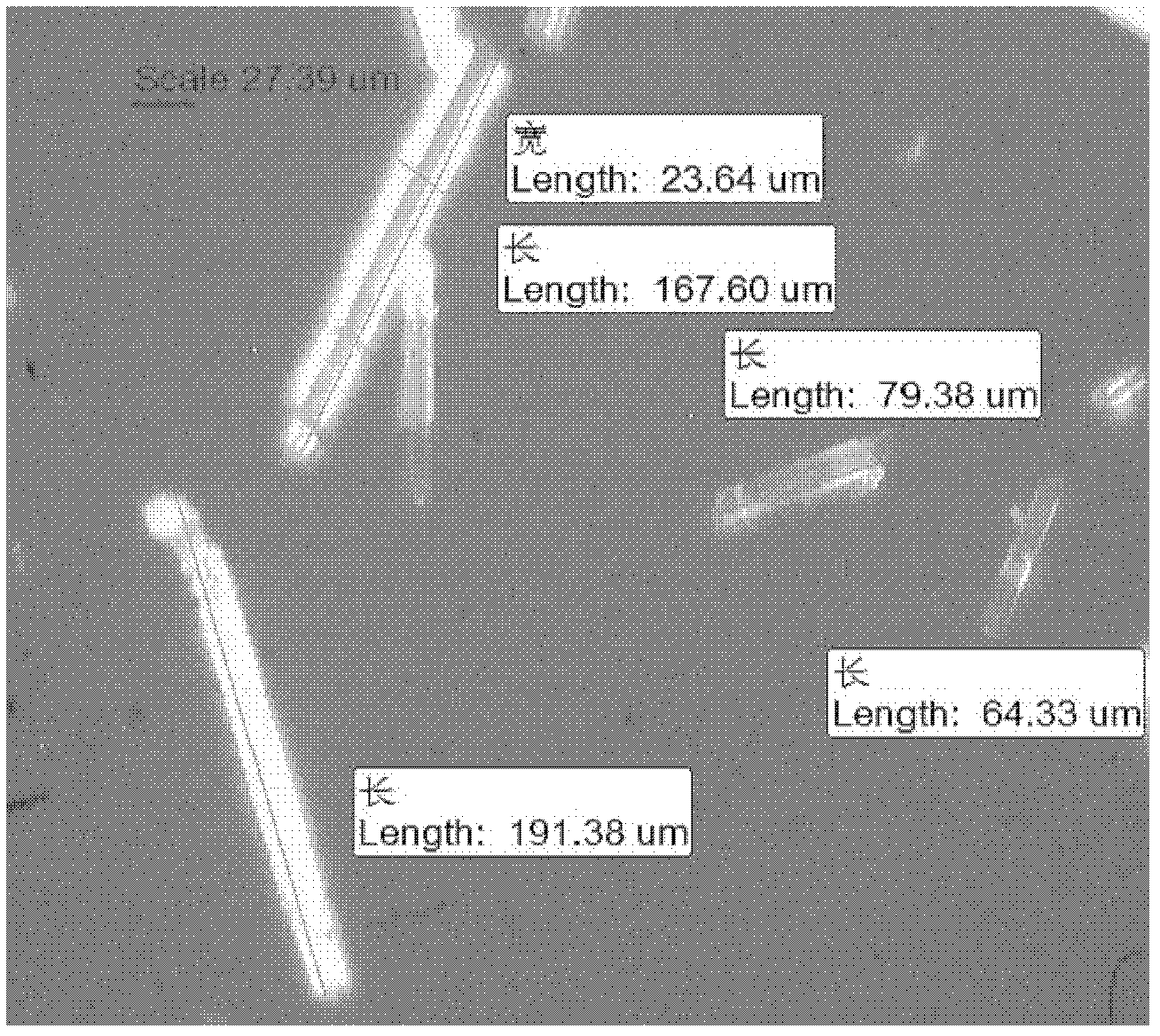
A preparation method of a high-stability high-purity extra-coarse tungsten carbide powder contains the following steps of: (1) grinding a high-purity extra-coarse tungsten carbide powdered raw material with its chemical purity being greater than or equal to 99.98 wt%, and carrying out size grading to obtain the required average granularity and a high-purity extra-coarse tungsten powder according to the particle size distribution; (2) carrying out carbon addition by the use of carbon black according to the total carbon content of the obtained tungsten carbide powder being 6.13+ / -0.05%, followed by ball milling and mixing to obtain a ball-milling mixture; (3) filling the obtained ball-milling mixture into a graphite boat and a carbide furnace, and carrying out high-temperature carbonization at 1600-2500 DEGC for the carbonization time of 1-10 hours; and (4) carrying out coarse crushing on the obtained carbonized material, followed by grinding and crushing, and carrying out size grading to obtain the high-purity extra-coarse tungsten carbide powder. The method provided by the invention can be adopted to produce the high-purity extra-coarse tungsten carbide powder with good crush resistance, morphology and structure and excellent thermal stability. The high-purity extra-coarse tungsten carbide powder is used to prepare an extra-coarse crystal cemented carbide product with high performance.
Owner:江西耀升钨业股份有限公司 +1
Method for preparing small-particle-size cerium-activated yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) florescent powder
ActiveCN105062482AImprove luminous efficiencyCrystallization perfectEnergy efficient lightingLuminescent compositionsCeriumCrystallinity
The invention discloses a method for preparing small-particle-size cerium-activated yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) florescent powder. According to the method, first, in fused salt, a wrapping structure of nanometer yttrium oxide (cerium oxide) @ aluminum oxide particles is obtained through controlled synthesis, then the aggregate of small-particle YAG florescent powder particles is generated through reaction in high-temperature fused salt, and finally the small-particle-size YAG: Ce florescent powder is obtained through weak ball milling. It is avoided that in the reaction process, the aluminum oxide particles and intermediate-phase particles abnormally grow, and while the high crystallinity of the particles is kept, final YAG is effectively controlled; the particle size of the Ce florescent powder has important significance for improving light-color quality of white-light LEDs, lowering the complexity of a white-light LED packaging technology and increasing the yield.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for preparing rare-earth phosphorate
InactiveCN106315536ACoarse particlesEasy to filter washPhosphorus compoundsSolid reactionPhosphoric acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of rare earth chemical engineering and particularly relates to a method for preparing rare-earth phosphorate. The method for preparing rare-earth phosphorate comprises the following steps that firstly, a rare-earth carbonate or rare-earth oxide suspension with the concentration of 10-1000 g / L is prepared; secondly, a precipitator is added into the suspension under continuous stirring at the room temperature until the pH value is smaller than or equal to 5; thirdly, stirring continues for 5-30 min, the reaction endpoint is reached when it is observed that the pH does not rise any more, if in the stirring process, the pH rises to 2 or above, the precipitator is supplemented until the pH is smaller than or equal to 5, and stirring and observation are carried out until the reaction endpoint is reached; fourthly, precipitation, dehydration and washing are carried out, and rare-earth phosphorate is obtained. According to the method, rare-earth phosphorate obtained through precipitation is large in particle size and easy to filter and wash with water; compared with preparation with a hydrothermal reaction and a solid-phase reaction, the method is relatively easy to implement, and certain industrial popularization meaning is achieved.
Owner:淄博包钢灵芝稀土高科技股份有限公司
Crystallization method of ammonium paratungstate
InactiveCN101182039AUniform crystallizationCoarse particlesTungsten compoundsAmmonia compoundsIsothermal crystallizationChemistry
The invention discloses a crystallization method of ammonium paratungstate and relates to a production method of ammonium tungstate by adopting hydrometallurgy. The method is characterized in that the invention has a crystallization process that ammonium paratungstate crystal seeds are added into ammonium tungstate solution when the solution is evaporated and concentrated to appear microcrystalline particles for isothermal crystallization under the solution temperature of 90-95 DEG C for 20-40mins; the solution is then heated up to boil and added with weak aqua ammonia to adjust the pH value of the ammonium tungstate solution to 8.0-8.5 and then treated with feeding and filtering when the density of mother liquor reaches 10.8 to 1.10 g / cm <3>; the solution is again washed with the weak aqua ammonia and deionized water and dried to obtain the ammonium paratungstate crystals with large particle size and uniform distribution. The method of the invention effectively controls the crystallization of the ammonium paratungstate through the measures of removing fine crystals through the weak aqua ammonia, adding the crystal seeds, controlling the evaporation speed, etc.; in addition, the produced ammonium paratungstate crystals with large and controllable particle size are uniform and smooth; and the technology is simple and easy to be operated.
Owner:JINDUICHENG MOLYBDENUM CO LTD
Method for converting neodymium oxide into neodymium acetate crystal
InactiveCN103360233ACoarse particlesHigh purityCarboxylic acid salt preparationAcetic acidFree cooling
The invention relates to a method for converting neodymium oxide into a neodymium acetate crystal. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: pumping analytically-pure glacial acetic acid and deionized water into a reaction kettle according to the volume ratio of 1:1, uniformly stirring and heating until the mixture is boiled; rotating a stirring paddle, and slowly adding the weighted neodymium oxide into the reaction kettle, wherein the mole rate of the addition of the neodymium oxide to the addition of acetic acid is 1:3.9; after the reaction is ended completely, heating a liquid material to 110-125 DEG C, and then, stopping heating to enable the liquid material in the reaction kettle to naturally cool and crystallize; when the liquid material is cooled to the temperature below 50 DEG C, enabling the stirring paddle to stop stirring, filtering a liquid through a filter tank, and centrifugally dewatering; and airing the dewatered reactant in a dust-free room to realize natural evaporation. The rare earth neodymium oxide is used for manufacturing the neodymium acetate crystal, so that the method is simple in process flow, high in production efficiency, low in energy consumption and capable of reducing the production cost and environment pollution; and the neodymium acetate crystal product is high in purity and total rare earth quantity, large in crystal particle and pure in color and luster, and the added value of a product can be increased.
Owner:YIXING XINWEI LEESHING RARE EARTH +1
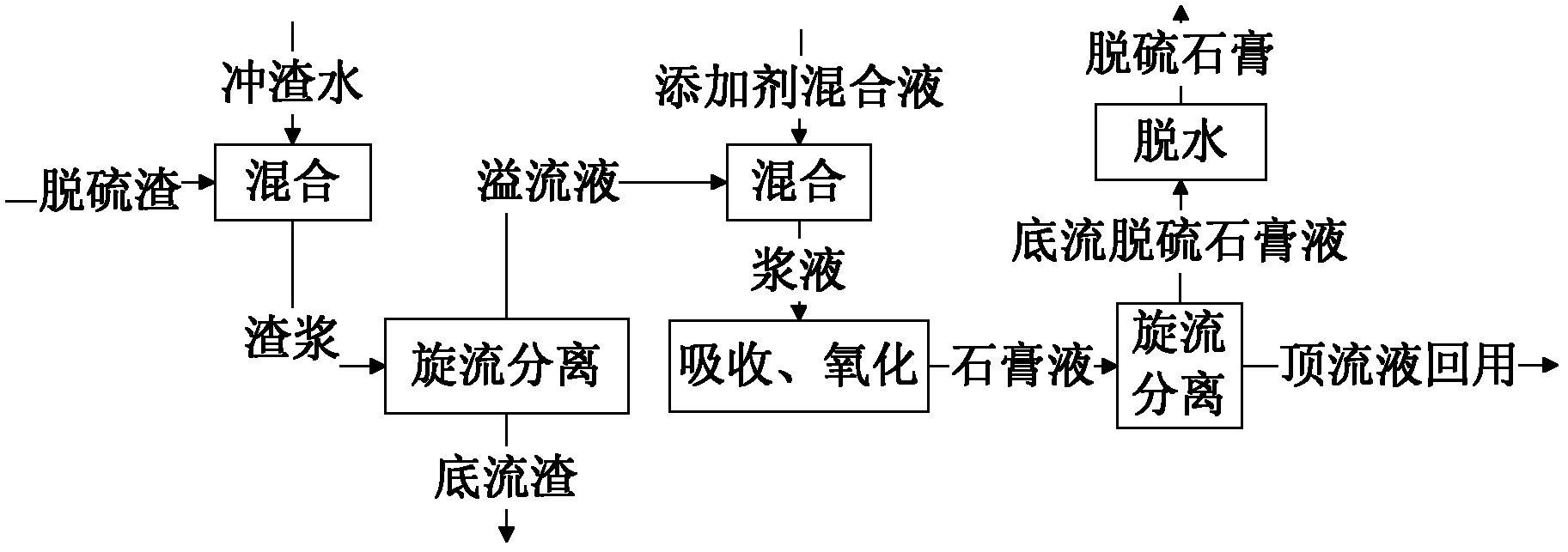
Gypsum crystallization regulator suitable for wet type calcium-based flue gas desulphurization poisoning slurry
InactiveCN104147910AReduce mass transfer rateImprove the crystallization processDispersed particle separationSlurryContamination
The invention discloses a gypsum crystallization modifier suitable for wet type calcium-based desulphurization of a thermal power generating unit, and the gypsum crystallization modifier can effectively eliminate the impact of heavy metal ions and oil contaminations in gypsum slurry on gypsum crystallization process to obtain gypsum crystals with coarse and large particles and low water content, increases stability of the desulfurization system, and belongs to the technical field of environmental protection. The gypsum crystallization modifier comprises the following components by weight: 0.1-5% of an oil-removing agent, 85-95% of a metal complexing agent and 5-10% of a surfactant, and is characterized in that the gypsum crystallization modifier can be directly added into an absorption tower or an absorption tower filtrate pit, then mixed evenly and dissolved for pumping. The gypsum crystallization modifier can accelerate the oxidation of sulfites and the gypsum crystallization process, is appropriate to improve the efficiency of the desulfurization system. In the embodiment, the gypsum crystallization modifier concentration is increased from 0% to 0.1%, the by-product gypsum purity is improved from 78% to 93%, the gypsum water content is reduced from 19% to 10%, the crystal size distribution is more uniform, acicular gypsum crystals are decreased, rhombic crystal share and columnar crystal share increase, the crystal specific surface area increases, and the gypsum dewatering performance is better.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
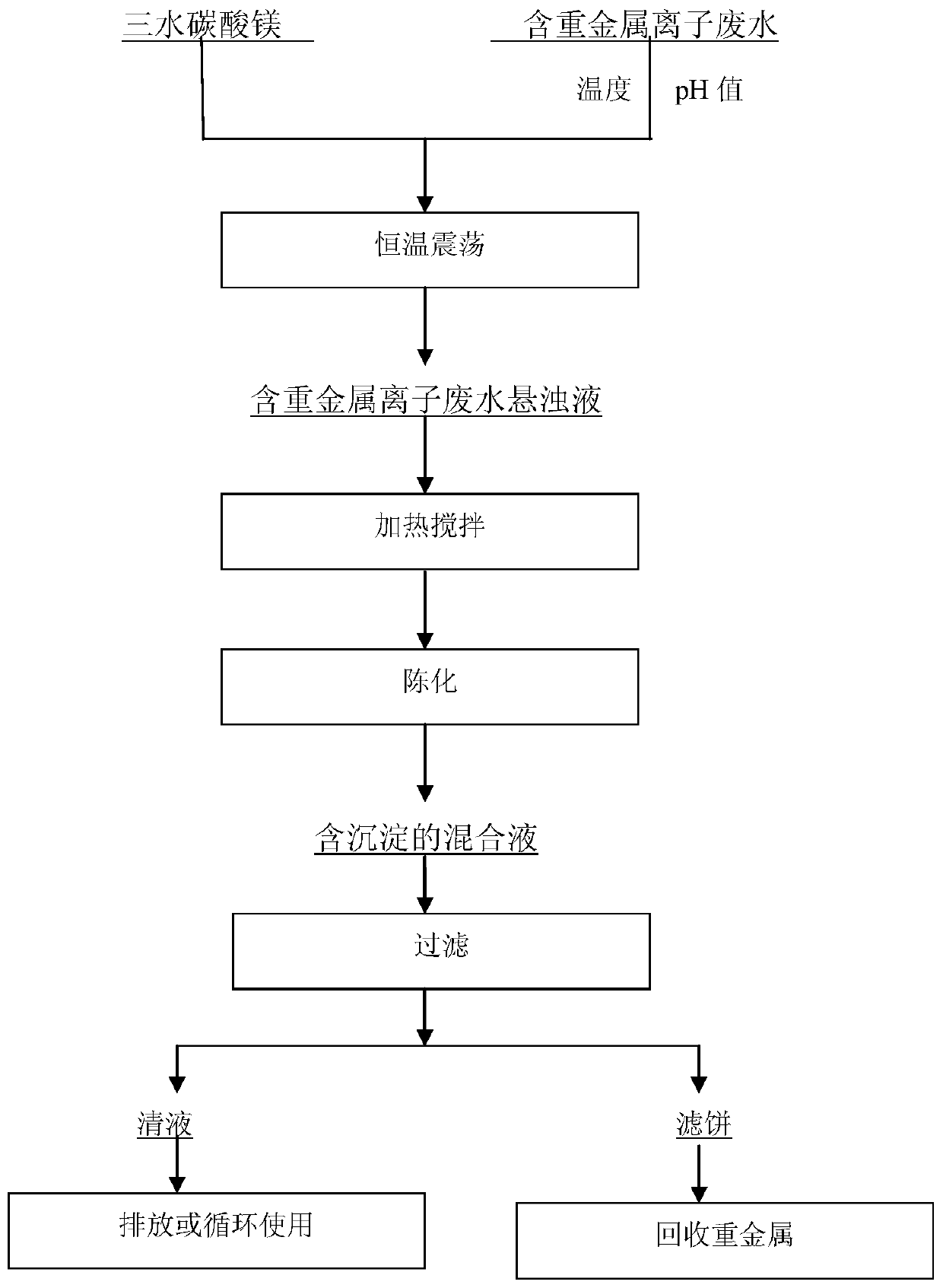
Method for treating wastewater containing heavy metal ions through phase transformation of MgCO3.3H2O
ActiveCN108117145AHigh purityNon-corrosiveWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationResource recoveryPhysical chemistry
The invention provides a method for treating wastewater containing heavy metal ions through phase transformation of MgCO3.3H2O, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The method comprises the following steps: taking wastewater solution containing heavy metal ions, regulating the temperature to 50-60 DEG C, regulating the pH value to 4-8, adding MgCO3.3H2O into the wastewater solution containing the heavy metal ions, and oscillating the solution at constant temperature, so as to obtain wastewater turbid liquid containing the heavy metal ions; heating the wastewater turbid liquid to 55-90 DEG C, stirring at constant temperature for 30-90min, standing, aging, and filtering obtained mixed solution containing precipitation, so as to obtain clear liquid and a filter cake, wherein the mass ratio of MgCO3.3H2O to the heavy metal ions is (4-50):(0.01-1); the heavy metal ion(s) is / are one or more heavy metal ions of Cr<3+>, Pb<2+>, Ni<2+>, Cu<2+>, Zn<2+> and Cd<2+>. According to the method, the wastewater containing the heavy metal ions is treated, the treatment cost is lowered, and the secondary resource recycling of heavy metals can be realized.
Owner:SHENYANG LIGONG UNIV
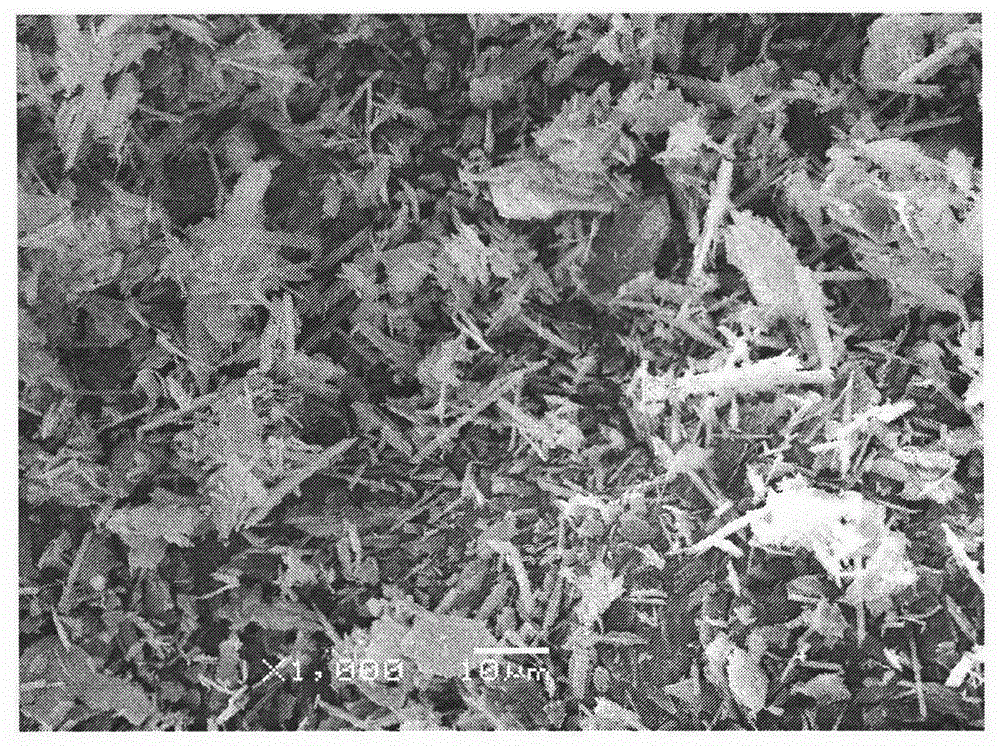
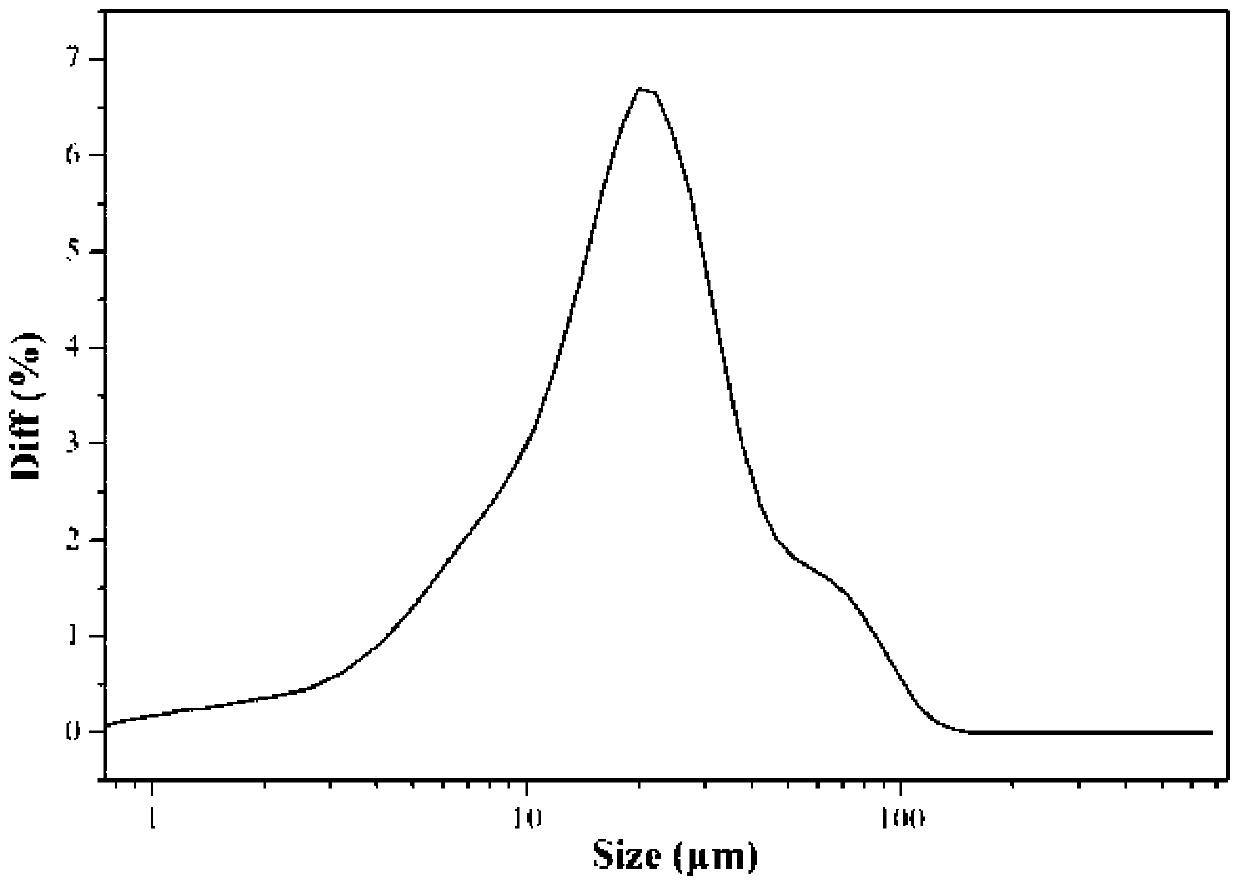
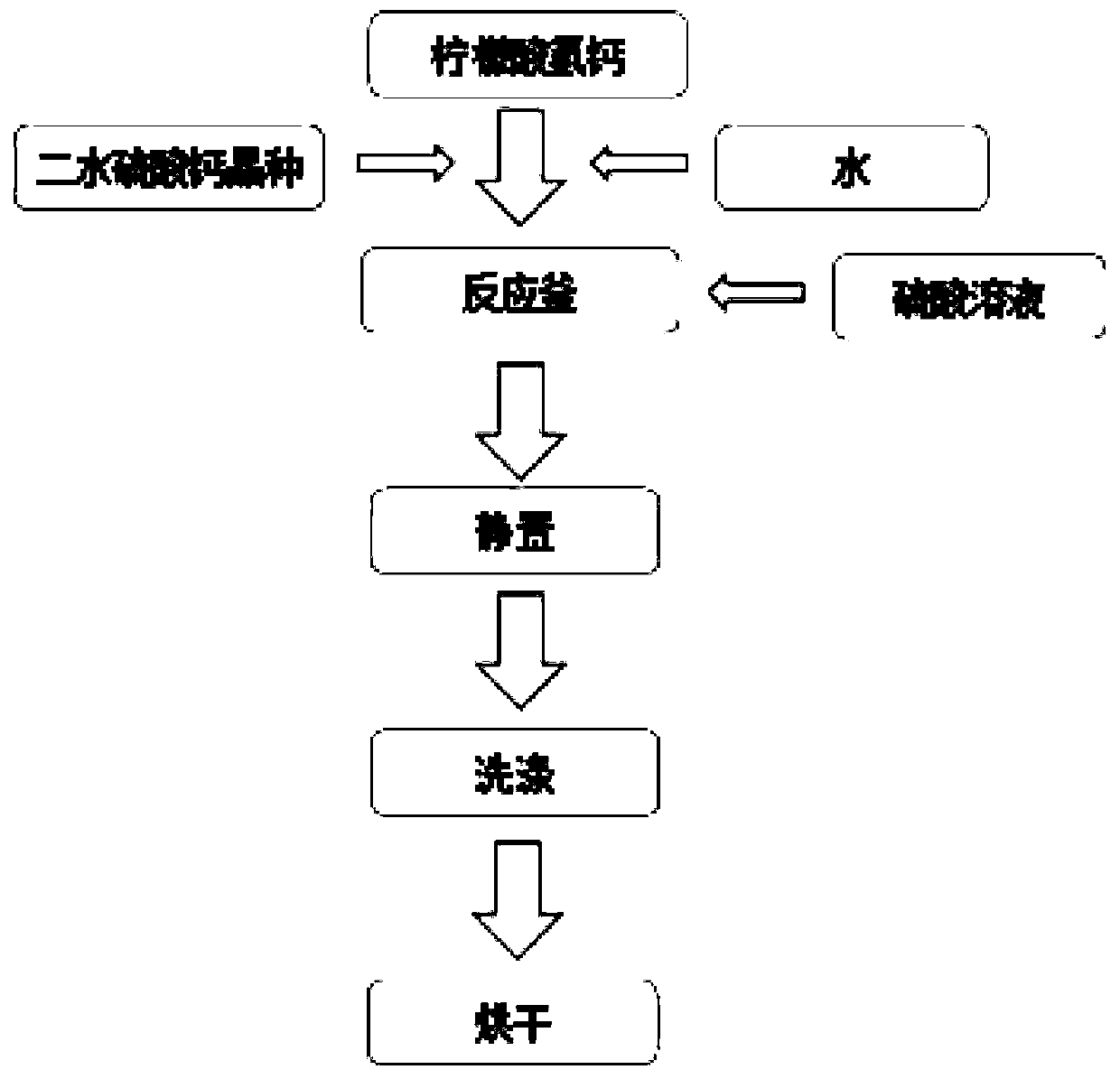
Synthetic method of citric acid gypsum
ActiveCN110282648ACoarse particlesCrystal Structure RulesCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesGypsumSeed crystal
The invention belongs to the field of dihydrate gypsum synthesis and relates to a synthetic method of citric acid gypsum. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a suspension from calcium hydrogen citrate, calcium sulphate dihydrate seed crystal and water; heating the suspension until the temperature of the suspension is 20-80 DEG C, stirring the suspension and simultaneously adding a sulfuric acid solution into the suspension until sulfuric acid and calcium hydrogen citrate completely react; standing and taking a bottom solid after the reaction, cooling and washing and drying. By the technical scheme, the problem of low strength of building gypsum powder due to fine citric acid gypsum particles and irregular crystal structure is solved.
Owner:JIANGSU EFFUL SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Process for improving quality of phosphorus chemical industry waste smoke desulfurization gypsum
InactiveCN102527196BImprove stabilityCoarse particlesDispersed particle separationChemical industrySlag
Owner:ZHEJIANG TIANLAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
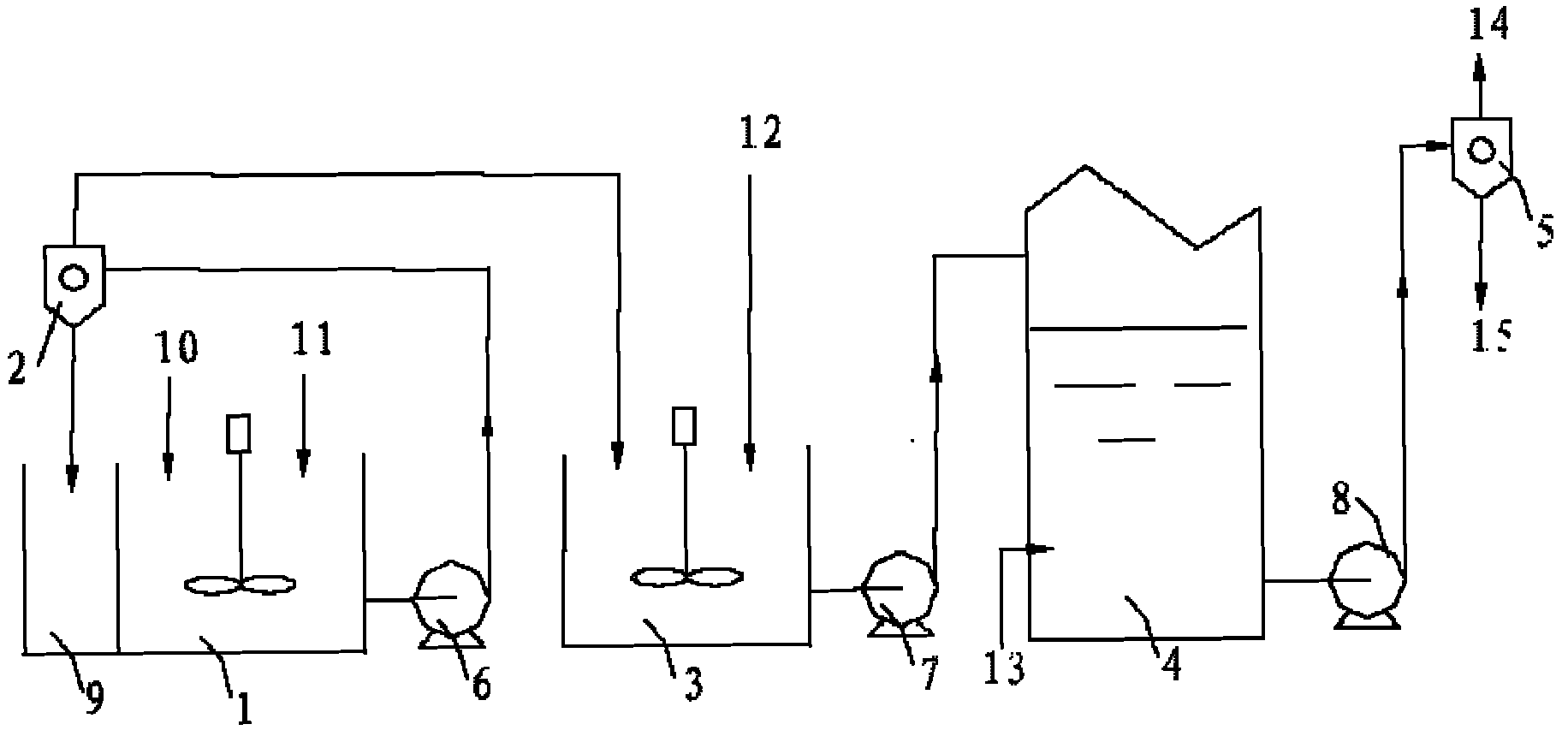
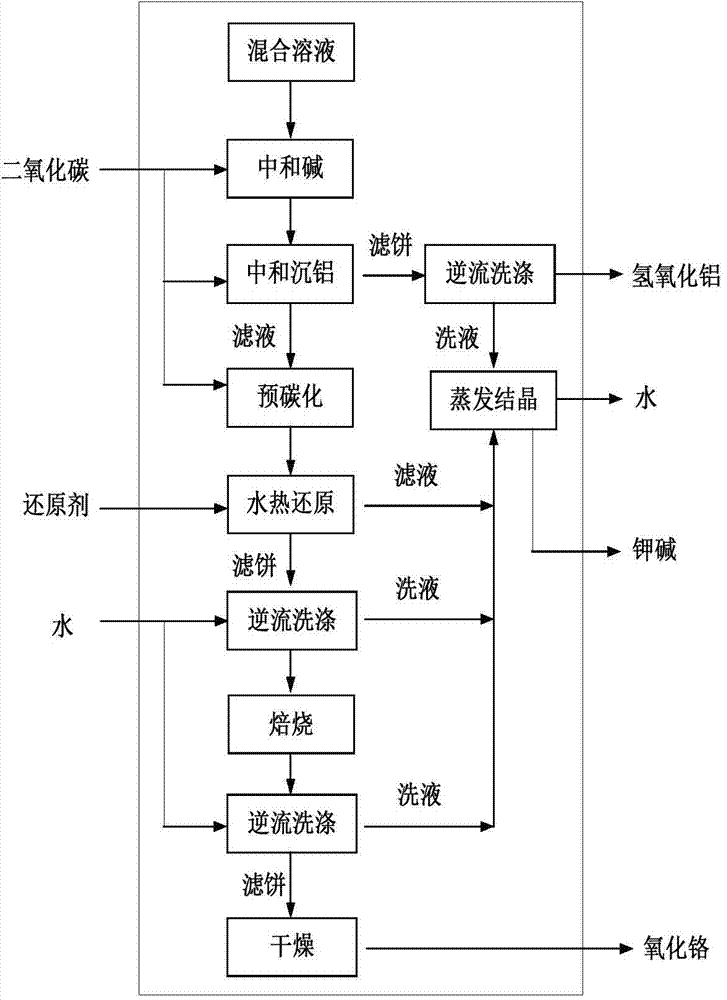
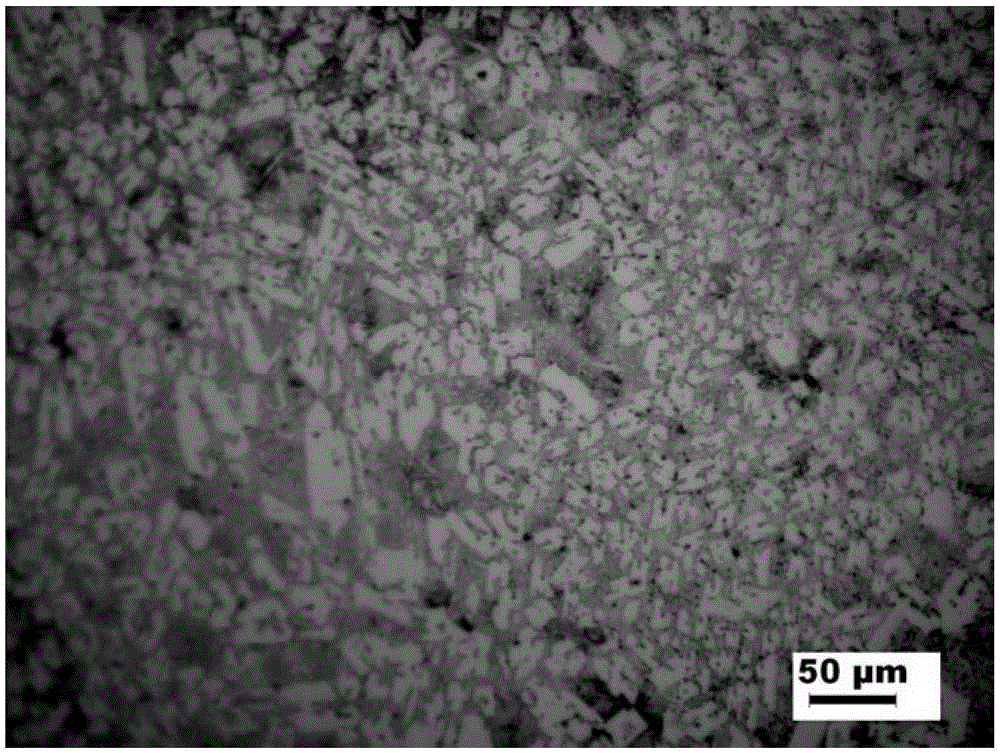
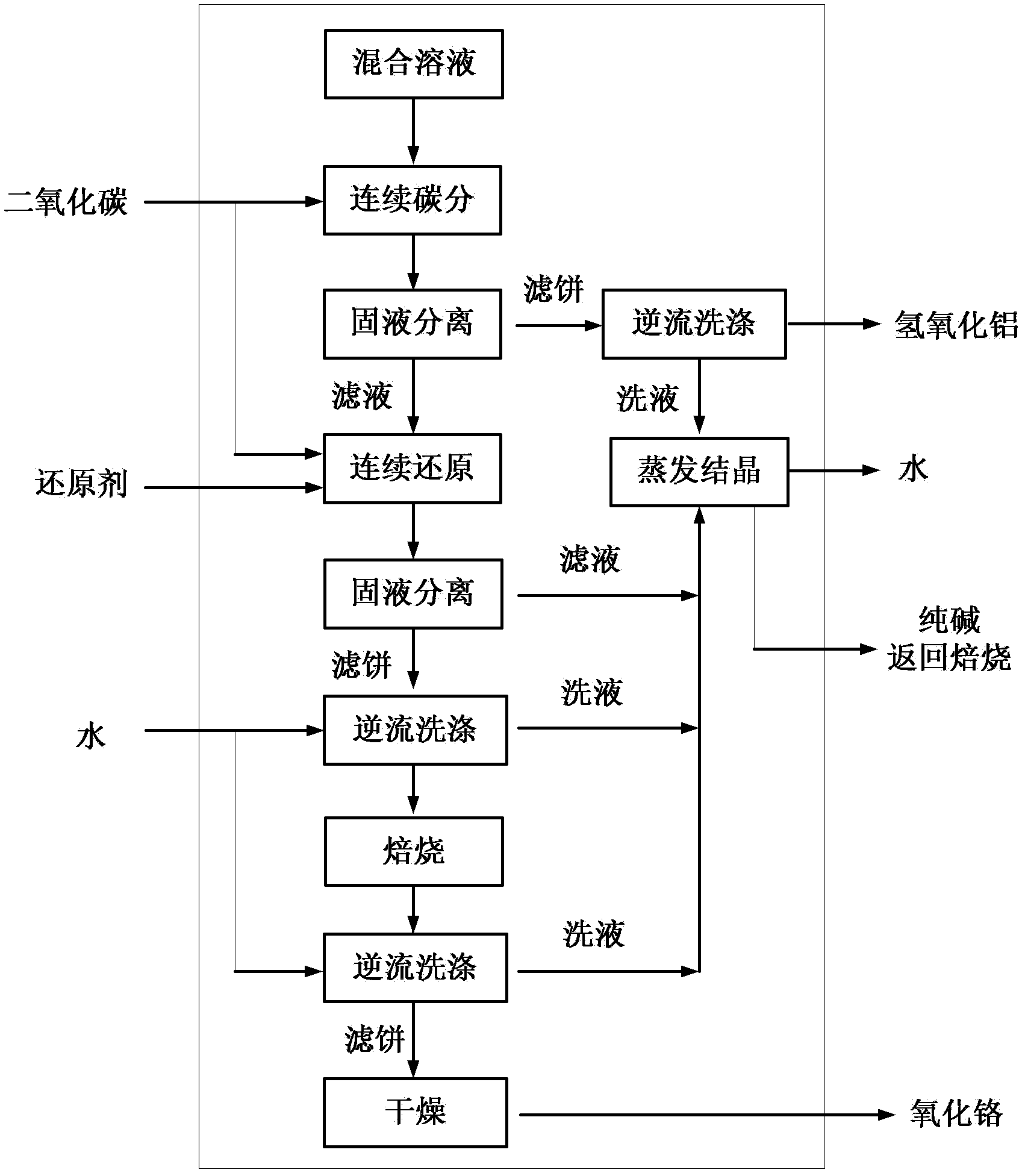
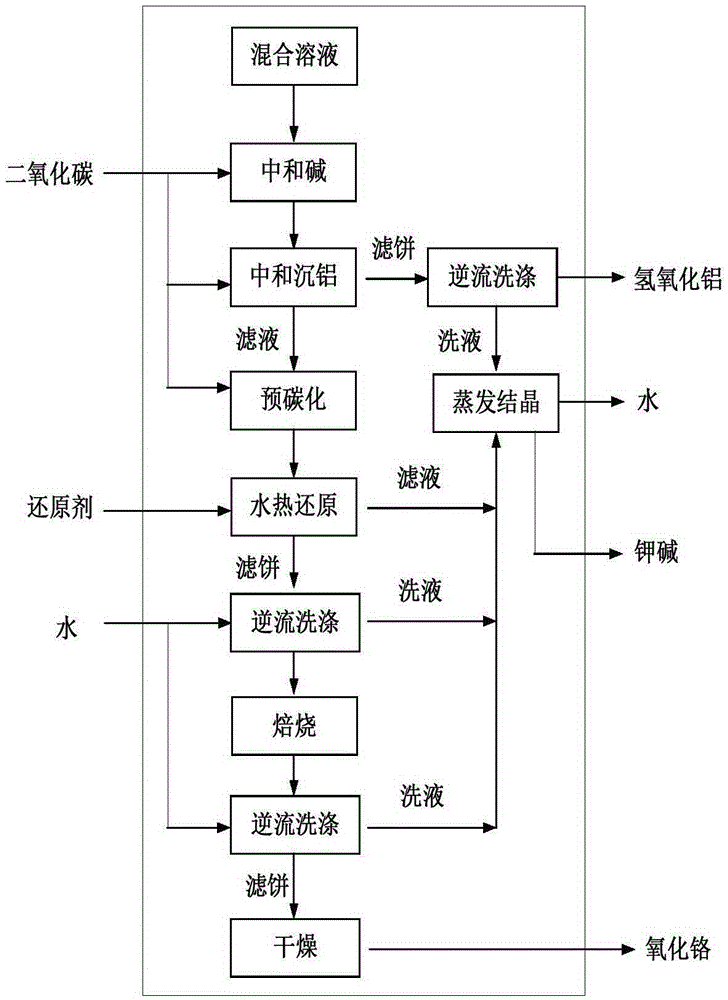
Method for decontaminating potassium sub-molten salt soluble crystal liquid and preparing chromic oxide
The invention discloses a method for decontaminating potassium sub-molten salt soluble crystal liquid and preparing chromic oxide. The method comprises the following steps: (1) introducing CO2 to potassium sub-molten salt soluble crystal liquid, neutralizing potassium hydroxide in the solution, then adding seed crystals, controlling the temperature of the solution at 30-90 DEG C and removing aluminum and silicon; (2) introducing CO2 to the solution obtained in the step (1) to carry out room-temperature pre-carbonation; (3) adding a reducing agent to pre-carbonated feed liquid obtained in the step (2), heating to 120-170 DEG C, and carrying out heat preservation and solid-liquid separation after reaction is ended, so as to obtain a chromium hydroxide filter cake; and (4) drying and calcining the chromium hydroxide filter cake obtained in the step (3), so as to obtain a chromium sesquioxide product. By adopting a pre-acidification mode, the reducing agent is not added in pre-carbonation; no CO2 is introduced after the pre-carbonated feed liquid and the reducing agent are mixed; the method is high in conversion rate of hydrothermal reduction, fewer in intermediate products, high in total yield of chrome, high in purity of the sintered chromic oxide and fewer in impurities by controlling a proper pre-carbonation condition.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation technology of zinc sulfate heptahydrate by cold liquid hot flushing method
InactiveCN107098376ACoarse particlesEasy to dryZinc sulatesSolution crystallizationChemistryZINC SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE
The invention discloses a preparation technology of zinc sulfate heptahydrate by a cold liquid hot flushing method. The preparation technology comprises the following steps of quickly cooling a saturated zinc sulfate solution for the first time, crystallizing, quickly cooling for the second time, adding a hot saturated solution, quickly cooling for the third time, cooling by cooling water, and crystallizing, so as to obtain a zinc sulfate heptahydrate product. The preparation technology has the advantages that when the zinc sulfate heptahydrate is applied to the industrial production, the large-particle zinc sulfate crystal can be obtained; the content of free water in the product is obviously reduced, the crystallizing time is shortened, and the production efficiency and the product quality are improved.
Owner:SHANDONG DAZHENG ENERGY SAVING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Method of water treatment process
InactiveCN108862728AReduce dosageDeep purificationWater contaminantsTreatment involving filtrationLiquid wasteWastewater
The invention belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment in zinc hydrometallurgy process, and provides a method of water treatment process. The method comprises the following steps: (1) addinga neutralizing agent to acidic wastewater containing heavy metals to adjust the pH value to 7.0 to 8.0 till the reaction stops and precipitates are generated, and then filtering to separate the precipitates to obtain first filtrate with residue at the bottom; (2) adding a neutralizing agent to the first filtrate again to adjust the pH value to 8.0 to 9.0 till the reaction stops and precipitates are generated, then adding Na2S to the filtrate till the reaction stops and precipitates are generated, wherein the weight ratio of Na2S added to heavy metals in the first filtrate is (1.2-1.5) to 1, and finally, filtering to separate the precipitates in the first filtrate, so as to obtain second filtrate with residue at the bottom. The method is highly efficient, the consumption of a precipitatingagent is small, the degree of purification is deep, and the amount of residue is small, and thus the method is suitable for large-scale industrial treatment.
Owner:四川四环锌锗科技有限公司
Method for extracting iodine from iodine enriched solution
ActiveCN101041422BHigh purityGrowth appearance is regularIodineMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystIodine solutions
The invention discloses a method to extract iodine from enriched iodine solution, which comprises the following steps: fetching iodine reclaiming liquid as raw material with density at 15.00g / L-50.00g / L; adding into autoclave incorporating stirring device and condensing unit; operating stirring device; heating to 25-80 deg.c; setting the rotary speed of regulating stirrer at 300-600 / min; adding into activator; making the ratio of the weight of activator and iodine in the iodine reclaiming liquid at 0.1-0.3 per mill ; adjusting the flow quantity of oxidation agent; adding into autoclave in 15-40 min with 1-1.4 double oxidation agent of iodine in the iodine reclaiming liquid; keeping the reacting temperature at 30 min; adopting gradient cooling; setting the cooling amplitude at 5-15 deg.c per time; keeping 20-30 min; cooling into indoor temperature; getting rough iodine. The invention possesses short dealing cycle and high purity.
Owner:WENGFU (GRP) CO LTD
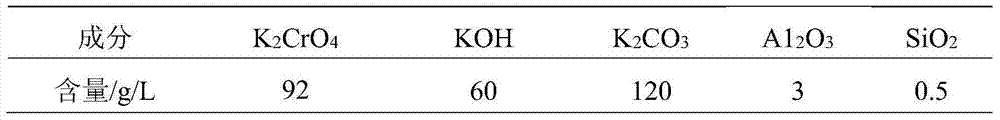
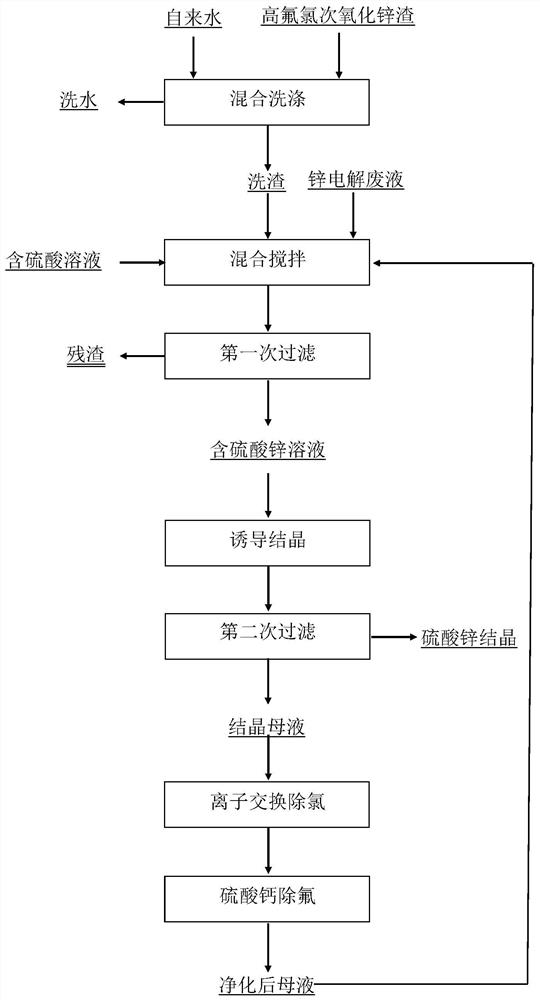
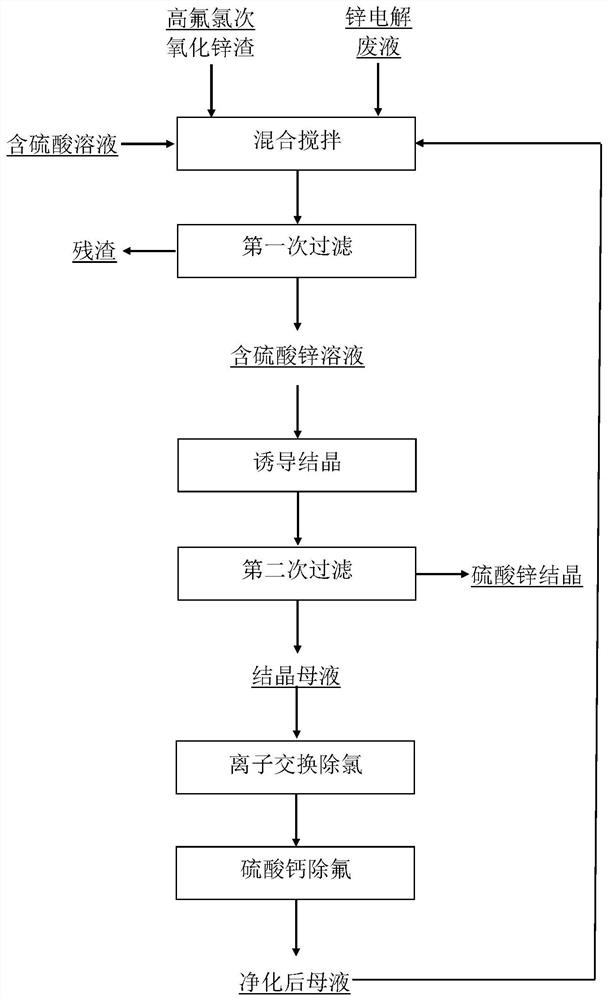
Treatment method of high-fluorine-chlorine secondary zinc oxide slag
ActiveCN112779424AHigh purityHigh saturationPhotography auxillary processesZinc sulatesSulfate zincSlag
The invention provides a treatment method of high-fluorine-chlorine secondary zinc oxide slag. The treatment method comprises the following steps: S1) washing the high-fluorine-chlorine secondary zinc oxide slag with water to obtain washing slag and washing water; S2) mixing and stirring the washing slag, zinc electrolysis waste liquid and a sulfuric acid-containing solution, and filtering to obtain a zinc sulfate-containing solution and slag; and S3) performing cooling crystallization on the zinc sulfate-containing solution to obtain zinc sulfate and crystallization mother liquor. Compared with the prior art, the treatment method has the advantages that the secondary zinc oxide waste slag is washed with water, fluorine and chlorine in part of secondary zinc oxide can be removed in advance, and a foundation is laid for fluorine and chlorine purity control of subsequent zinc sulfate crystallization; then the washing slag of secondary zinc oxide, which is obtained after washing, the zinc electrolysis waste liquid and the sulfuric acid-containing solution are mixed and stirred, and the temperature is controlled to improve the saturation of zinc sulfate in the solution, thereby laying a foundation for subsequent induced crystallization and precipitation of zinc sulfate; and finally, zinc sulfate crystals generated through cooling induced crystallization are coarse in particle and high in purity, only a small amount of fluorine and chlorine are adsorbed on the surfaces of the crystals, and the recycling quality requirement can be met.
Owner:湖南中金岭南康盟环保科技有限公司
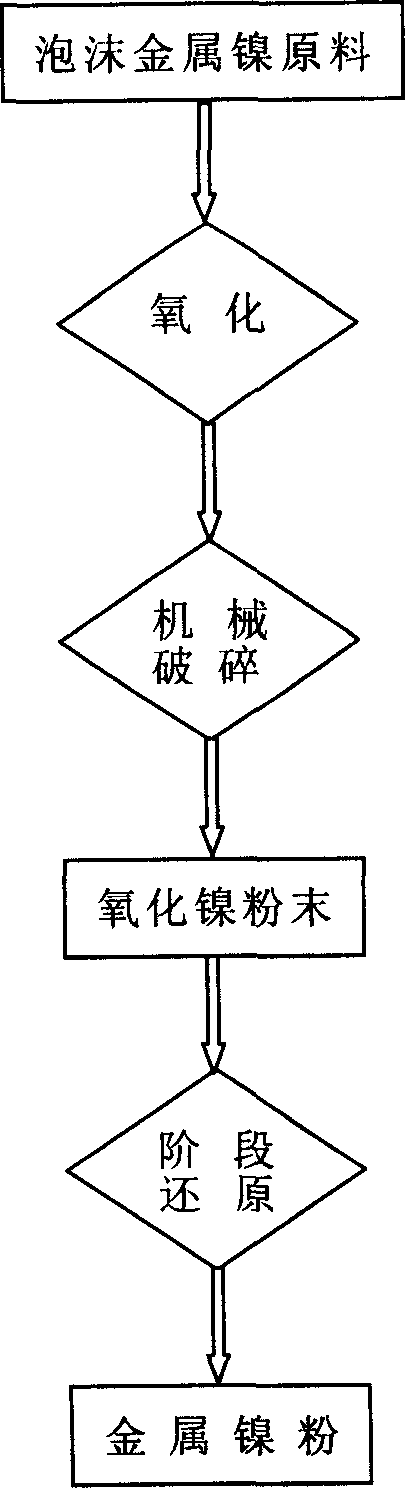
Method for manufacturing specified nickel powder for welding electrode by machinery crushing method
The invention is an electric welding rod special nickel powder production technique by machine fragmenting. Fragment an oxidating production with brittle nickel oxide surfacing layer outside and nickel inside which obtained by dynamically continuously oxidating the foam nickel raw material, with multi-level fragmenting machine. Secondary oxidating the fragmented powder obtaining large particle nickel oxide powder and then take the powder into phasing deoxidation so to obtain high performance nickel powder with high purity and large particles which is also the advantages of the invention and the powder is a fine material of electric welding rod coating. The production technique is simple, of low cost and high efficiency which adapted to mass production. The preparation processes is without any additions and any pollutions which is environmetal.
Owner:长沙市维优金属材料有限公司
Method for producing sandy alumina through decomposing seeds in low concentration
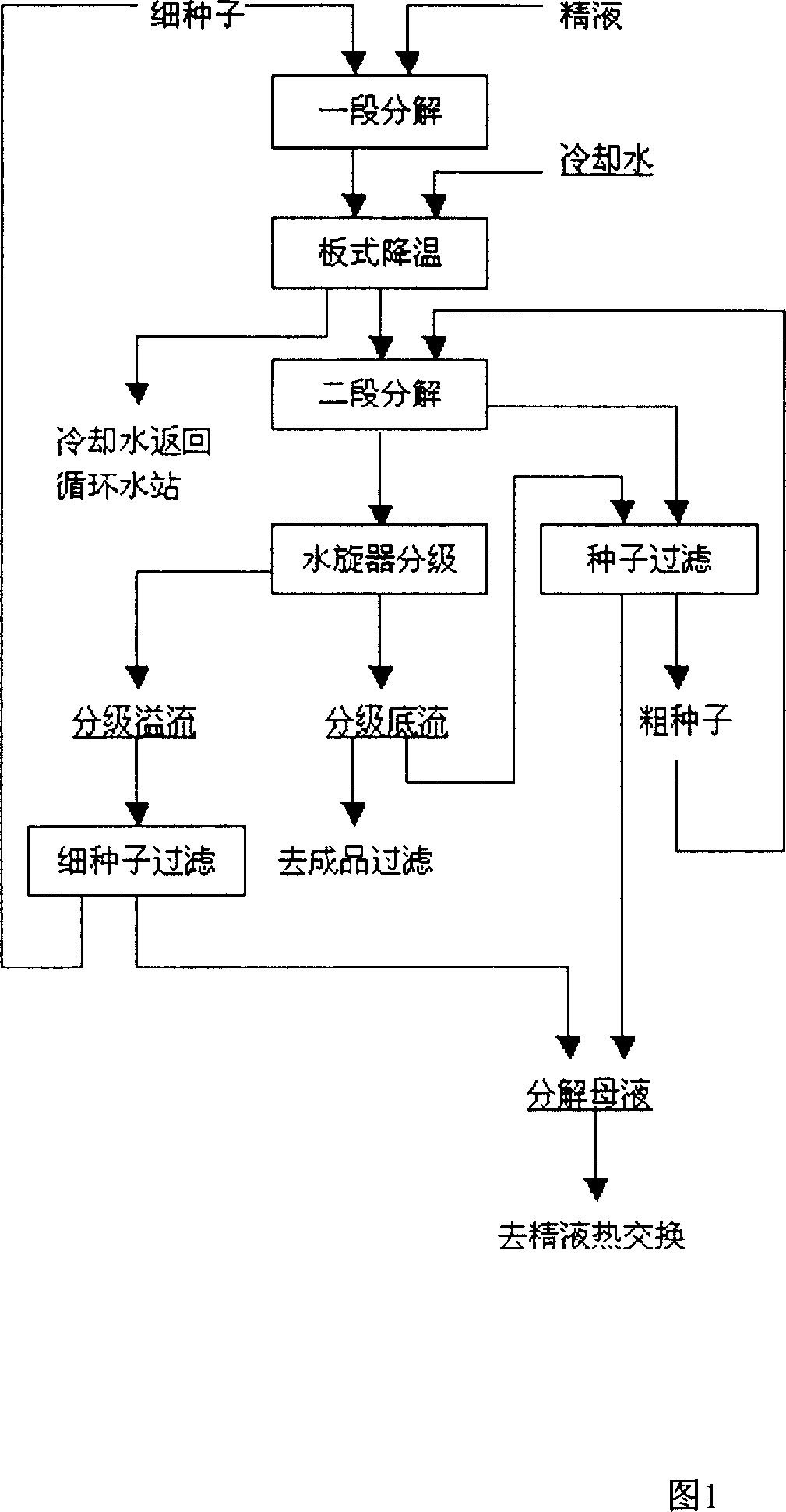
InactiveCN1329300CSolve the problem of decomposition process in the process of extracting aluminaCoarse particlesClimate change adaptationAlkali-metal aluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide preparationEngineeringFilter press
A process for preparing sandy alumina by decomposing low-concentration seed includes such steps as mixing the refined liquid from settling workshop with the fine seeds from plate-and-frame filter press, stage-one decomposing, stage-two decomposing, classifying by hydraulic cyclone bed, filtering part of bottom stream to obtain finished product, filtering the rest to obtain seeds, filtering overflow liquid to obtain fine seeds, adding fine seeds to the stage-one decomposing reactor, adding coarse seeds to the stage-two decomposing reactor, and heat exchange between mother liquid and refined liquid.
Owner:GUIYANG AL-MG DESIGN & RES INST
Method for producing holmium acetate crystal
InactiveCN103360234AHigh purityHigh Total Rare EarthCarboxylic acid salt preparationAcetic acidHolmium
The invention relates to a method for producing a holmium acetate crystal. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: pumping analytically pure glacial acetic acid and deionized water at the volume ratio of 1:0.5 into a reactor, stirring uniformly, and heating to the temperature of 50 DEG C; rotating a stirring paddle, and adding the weighed holmium carbonate into the reactor slowly, wherein the molar ratio of the added holmium carbonate to the glacial acetic acid is 1:3.3; heating a liquid material to the temperature of 110-125 DEG C after the materials react completely, and stopping heating to naturally cool the liquid material in the reactor to crystallize; cooling the liquid material to the temperature below 50 DEG C, discharging the liquid material into a filtering box, removing liquid by filtering, and dehydrating centrifugally; and airing the dehydrated product of reaction in a dust-free room to evaporate naturally. The method for producing the holmium acetate crystal from the carbonate holmium (rear earth) is simple in technological process, high in production efficiency and low in production cost, consumes less energy and causes less pollution to the environment. In addition, the holmium acetate crystal is high in purity, high in content of rear earth, high in additional value, large in particle size and pure in color.
Owner:YIXING XINWEI LEESHING RARE EARTH +1
Neutralization aluminum removing method for sodium chromate alkali solution
InactiveCN101723461BCoarse particlesReduce moisture contentChromates/bichromatesHydrogen SulfateAluminium hydroxide
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A wear-resistant surfacing alloy containing ceramic phases of mo and cr elements and its preparation process
InactiveCN103769765BHigh temperature hardnessImprove wear resistancePlasma welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsWear resistantBall mill
A wear-resistant surfacing alloy containing ceramic phases of Mo and Cr elements and its preparation process are characterized in that: the alloy composition is Cr15-30%, Mo3-12%, Ni0.5-1%, C6-10%, The balance is Fe and unavoidable impurities; the preparation process is to mechanically mix ferrochromium powder, molybdenum powder, nickel powder, graphite and reduced iron powder, and then use a ball mill to dry-type ball mill to mix evenly, and coat the powder on carbon after cooling. On the steel plate, and then uniformly mixed with water glass to form a coating layer with a thickness of 4mm; stand at room temperature, dry in a drying furnace, cool to room temperature in the furnace, and perform plasma surfacing. The preparation process of the present invention is simple, there are few kinds of alloys to be added, and the cost is low. Compared with other iron-based surfacing wear-resistant alloys, it has a significant effect on resisting adhesive wear.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
An ionic membrane salt separation concentration crystallization freeze crystallization salt production device and process
ActiveCN105712553BHigh purityImprove the mixing effectAlkali metal sulfite/sulfate purificationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisSystem recoveryFresh water
The invention discloses a device and a process for preparing salt through ionic membrane salt separation, concentration crystallization and freezing crystallization. The device for preparing salt through ionic membrane salt separation, concentration crystallization and freezing crystallization comprises a monovalent ionic membrane salt separation device, a heating and heat exchanging device with a water inlet connected with a concentrated water outlet of the monovalent ionic membrane salt separation device, a concentration crystallization device with a water inlet connected with a water outlet of the heating and heat exchanging device, a special ionic membrane salt concentration device with a water inlet connected with a fresh water outlet of the monovalent ionic membrane salt separation device, a cooling and heat exchanging device with a water inlet connected with a concentrated water outlet of the special ionic membrane salt concentration device as well as a freezing crystallization device with a water inlet connected with a water outlet of the cooling and heat exchanging device. The system recovery rate is increased, the salt separation effect is enhanced, high-purity NaCl crystal salt and mirabilite are obtained according to different qualities, the system is stable and reliable, the operation cost is low, and the investment cost is low.
Owner:岳阳锦能环境绿色能源有限公司
Sodium chromate alkali solution impurity removal method and preparation method of chromic oxide
ActiveCN102583541BRich sourcesLow priceChromium trioxideChromates/bichromatesDecompositionCalcination
The invention discloses a sodium chromate alkali solution impurity removal method and a preparation method of chromic oxide. According to sodium chromate alkali solution impurity removal, CO2 with rich resources and low cost serves as acidulant, aluminium and silicon are removed by continuous carbonating decomposition, and the removal rates of the aluminium and the silicon are high; new impurities are not introduced; and aluminium mud after sedimentation has thick and large particles, is low in chromium belt loss, and can be used in alumina industries after being filtered and washed, thus having a high added value. Impurities and sodium chromate solution are separated to obtain solution, cheap and rich starch and derivatives of the starch serve as reductants, and hydrated chromium hemitrioxide is prepared under a hydrothermal reducing condition, and then pigment-level chromium hemitrioxide is generated after dehydration and calcination. The reducing condition is mild, the conversion rate is higher than 90%, slurry easy to filter and wash, and final filtrate and alkaline rinse in production process can be returned to mix with chromite to enter a calcination process, thereby recycling sodium carbonate. According to the invention, the process adopted for generating the chromium hemitrioxide is simple and environment-friendly, the cost is low, and industrialization is easy to realize.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for analyzing lithium ion battery electrolyte salt LiBF4
InactiveCN102937558AStable in natureReduce solubilityWeighing by removing componentBoronic acidLithium-ion battery
The invention relates to a method for analyzing lithium ion battery electrolyte salt LiBF4. The method includes steps of preparing and calibrating a Na2S2O3 5H2O standard solution; preparing and calibrating a K13 standard solution; preparing and calibrating a (C6H5) As4Cl standard solution; preparing 1mol / L of a LiBF4 solution; preparing 0.01 mol of mol / L of the LiBF4 solution; determining a main content four fluorine boric acid roots by a weighting method: placing the LiBF4 solution in a water bath thermostatic bath, adding the (C6H5) As4Cl solution dropwise after 15 minutes to 30 minutes, mixing the mixture during dropwise adding, and obtaining sediment (C6H5) 4AsBF4 after dropwise adding; and ageing the sediment (C6H5) 4AsBF4 in a constant temperature water bath for 30 minutes to 60 minutes and then performing leaching, cleaning and drying to a constant weight, and performing content calculation. According to the method, the operation is simple and rapid, and defects that errors are increased for the increase of the sample dilution ratio as the ion selective electrode method is used are effectively overcome.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for converting yttrium oxide into yttrium acetate crystal
The invention relates to a method for converting yttrium oxide into an yttrium acetate crystal. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: pumping analytically-pure glacial acetic acid and deionized water into a reaction kettle according to the volume ratio of 1:1, uniformly stirring and heating until the mixture is boiled; rotating a stirring paddle, and slowly adding the weighted yttrium oxide into the reaction kettle, wherein the mole rate of the addition of the yttrium oxide to the addition of acetic acid is 1:3.9; after the reaction is ended completely, heating a liquid material to 110-125 DEG C, and then, stopping heating to enable the liquid material in the reaction kettle to naturally cool and crystallize; when the liquid material is cooled to the temperature below 50 DEG C, enabling the stirring paddle to stop stirring, filtering a liquid through a filter tank, and centrifugally dewatering; and airing the dewatered reactant in a dust-free room to realize natural evaporation. The rare earth yttrium oxide is used for manufacturing the yttrium acetate crystal, so that the method is simple in process flow, high in production efficiency, low in energy consumption and capable of reducing the production cost and environment pollution; and the yttrium acetate crystal product is high in purity and total rare earth quantity, large in crystal particle and pure in color and luster, and the added value of a product can be increased.
Owner:YIXING XINWEI LEESHING RARE EARTH +1
Method for treating waste water containing heavy metal ions by phase transformation of magnesium carbonate trihydrate
ActiveCN108117145BHigh purityNon-corrosiveWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationAqueous solutionFilter cake
Owner:SHENYANG LIGONG UNIV
A method for removing impurities and preparing chromium oxide in a potassium-based sub-molten salt solution
The invention discloses a method for decontaminating potassium sub-molten salt soluble crystal liquid and preparing chromic oxide. The method comprises the following steps: (1) introducing CO2 to potassium sub-molten salt soluble crystal liquid, neutralizing potassium hydroxide in the solution, then adding seed crystals, controlling the temperature of the solution at 30-90 DEG C and removing aluminum and silicon; (2) introducing CO2 to the solution obtained in the step (1) to carry out room-temperature pre-carbonation; (3) adding a reducing agent to pre-carbonated feed liquid obtained in the step (2), heating to 120-170 DEG C, and carrying out heat preservation and solid-liquid separation after reaction is ended, so as to obtain a chromium hydroxide filter cake; and (4) drying and calcining the chromium hydroxide filter cake obtained in the step (3), so as to obtain a chromium sesquioxide product. By adopting a pre-acidification mode, the reducing agent is not added in pre-carbonation; no CO2 is introduced after the pre-carbonated feed liquid and the reducing agent are mixed; the method is high in conversion rate of hydrothermal reduction, fewer in intermediate products, high in total yield of chrome, high in purity of the sintered chromic oxide and fewer in impurities by controlling a proper pre-carbonation condition.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for preparing cerium hydroxide
InactiveCN1289699CCoarse particlesImprove filtering effectRare earth metal compoundsProcess efficiency improvementCeriumCe element
The invention belongs to wet method metallurgy field of rare earth production, especially relates to a preparation method for cerium hydroxide. The method comprises: (1) adding raw cerium material into alkali liquor with stirring for creating precipitate Ce(OH)3 ensuring that the mol ratio of OH ion and cerium ion is 0.5-4:1; (2) adding oxidizing agent with stirring under normal temperature with mol ratio of oxidizing agent and Ce(OH)3 as 0.1-4:1 for creating Ce(OH)4 or Ce(OH)3OOH; (3) washing the Ce(OH)4 obtained in step (2), separating the solid from liquid, airing, and obtaining the cerium hydroxide product. The invention has a wide range of application. According to different purposes, cerium hydroxide products with different purities (80~99.9999%(CeO2 / sigma RE2O3)) depending to the raw material.
Owner:北京方正稀土科技研究所有限公司
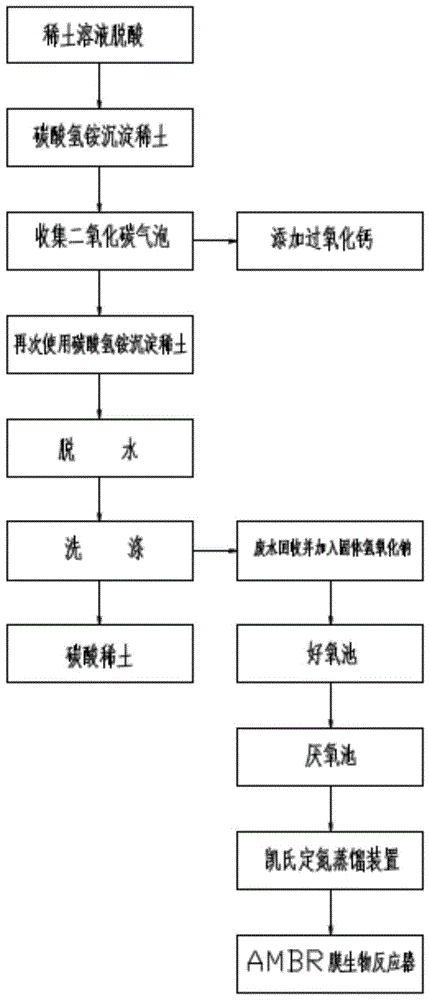
A kind of preparation method of rare earth carbonate that does not produce ammonia nitrogen wastewater
InactiveCN104211106BIncrease profitCoarse particlesRare earth metal compoundsChemical reactionRare earth
The invention discloses a preparation method of rare earth carbonate free of generation of ammonia-nitrogen wastewater, and belongs to the technical field of production of rare earth carbonate. The method comprises the following steps: deacidifying by a rare-earth solution; precipitating rare earth by using ammonium bicarbonate; collecting carbon dioxide bubbles generated during rare earth participation; carrying out chemical reaction on carbon dioxide and calcium peroxide to release oxygen and water; participating rare earth by using ammonium bicarbonate again; dewatering and washing a rate block which is crystallized when the pH value is greater than 7 until the rare earth carbonate is obtained; and carrying out environmental-friendly and energy-saving treatment on the left ammonia-nitrogen wastewater, thereby achieving pollution-free production when the deamination rate and the denitrification rate reach 99.9%. The preparation method has the advantages of fully utilizing the ammonium bicarbonate to participate the rate earth, and effectively processing non-environmental-friendly processes in the production process, and therefore, cyclic utilization of resources and environmental-friendly production are achieved.
Owner:GANZHOU XINLONGKANG RARE EARTH
Mixed salt process to preparing in-situ reinforced Mg-based composite material
The present invention relates to material technology and is mixed salt process to prepare in-situ reinforced Mg-base composite material. The process includes determining the alloy element components in the composite material, selecting the reinforcing phase based on the wettability between the substrate and the reinforcing phase whith ic controlled in 2-15 wt%, compounding and pretreating mixed salt system, smelting the magnesium substrate material and adding the pretreated mixed salt into the magnesium melt at proper temperature via stirring, and final casting after being let stand to form. The reinforcing phase is fine, homogeneously distributed and excellent in interface bindnig, and the Mg-base composite material has excellent mechanical and physical performance and may be used widely.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
A kind of method for preparing sodium dichromate
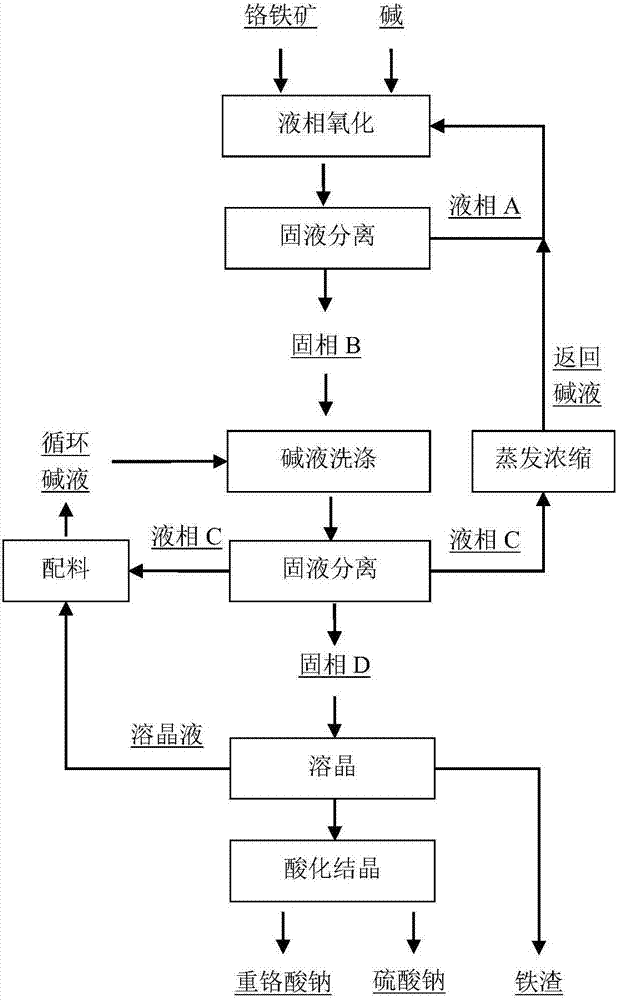
ActiveCN106219607BLow costReduce energy consumptionSulfate/bisulfate preparationChromates/bichromatesDissolutionSlurry
The invention discloses a method of preparing sodium dichromate, comprising the steps of (1), subjecting chromite and alkali solution to liquid oxidation, subjecting slurry to solid-liquid separation after reacting to obtain liquid phase A and solid phase B; (2), washing the solid phase B with circulatory alkali liquid, subjecting post-washing slurry to solid-liquid separation to obtain liquid phase C and solid phase D; (3), crystal-dissolving the solid phase D with sodium chromate crystal with water and iron residue washing liquid, carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain crystal-dissolved liquid and iron residue, washing the iron residue with water, and returning the washing liquid to crystal dissolution; (4), preparing circulatory alkali liquid with the liquid phase C and crystal-dissolved liquid, adding an acid solution to the remaining crystal-dissolved liquid to adjust pH, and carrying out aluminum-silicon removal, acidifying, crystallizing and separating to obtain sodium dichromate and sodium sulfate; preparing. The process of the invention is simple, the flow is short, and the method is highly operable, low in cost and free of wastewater and is an effective way of chromium salt industry to make recycle use and reduce pollution.
Owner:格润过程(北京)科技有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com