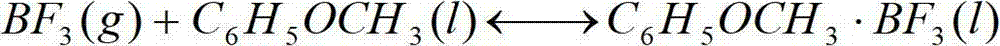Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
134results about "Boron halogen compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
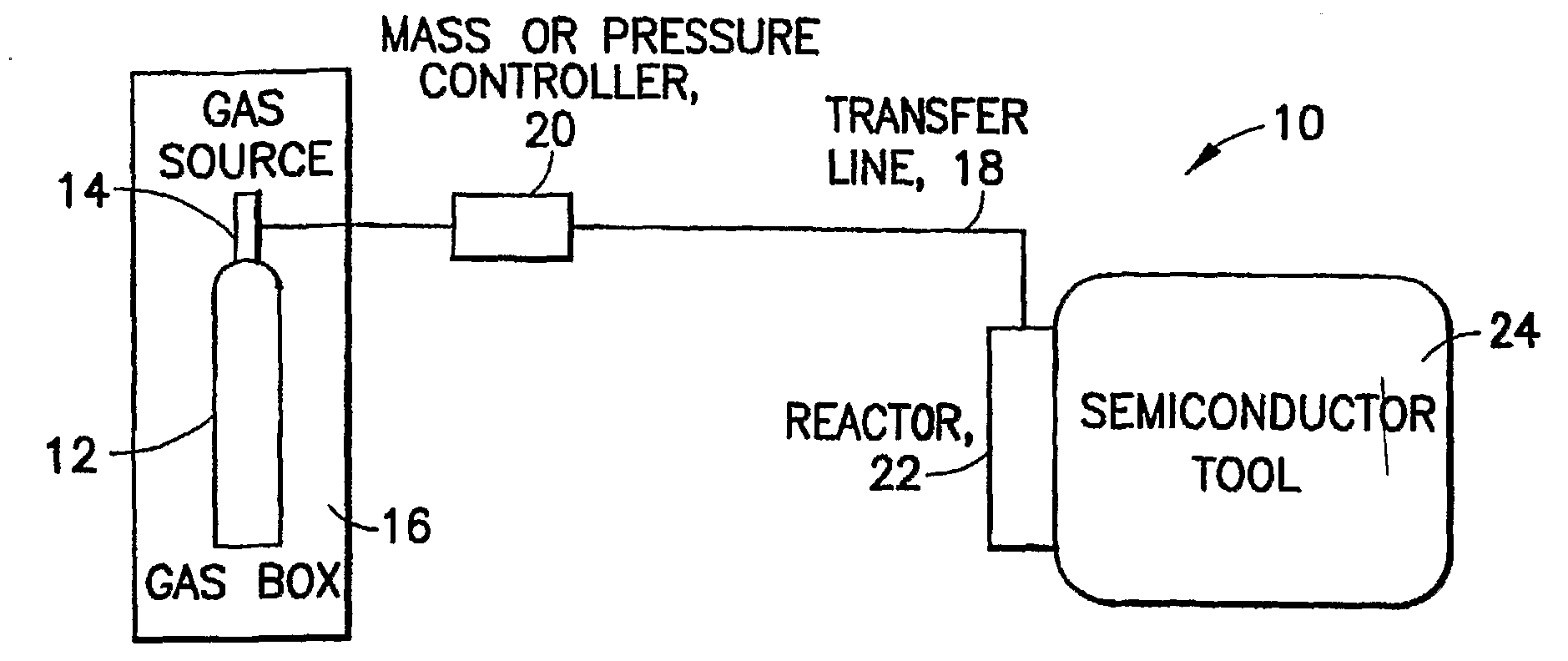
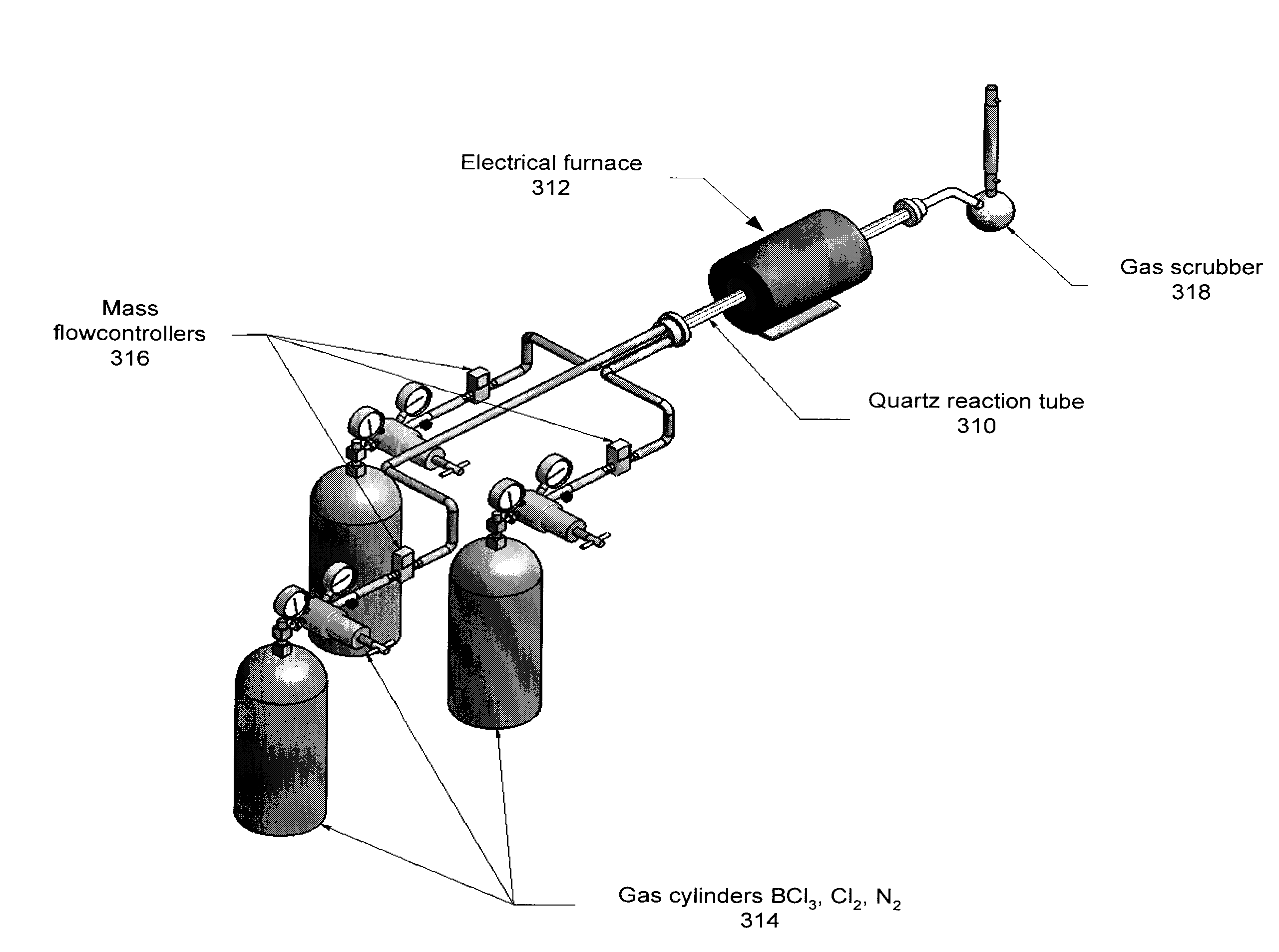
Boron Ion Implantation Using Alternative Fluorinated Boron Precursors, and Formation of Large Boron Hydrides for Implanation
ActiveUS20080248636A1Easy to cutImprove efficiencyOther chemical processesElectric discharge tubesBoron trifluorideIon implantation
Methods of implanting boron-containing ions using fluorinated boron-containing dopant species that are more readily cleaved than boron trifluoride. A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device including implanting boron-containing ions using fluorinated boron-containing dopant species that are more readily cleaved than boron trifluoride. Also disclosed are a system for supplying a boron hydride precursor, and methods of forming a boron hydride precursor and methods for supplying a boron hydride precursor. In one implementation of the invention, the boron hydride precursors are generated for cluster boron implantation, for manufacturing semiconductor products such as integrated circuitry.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
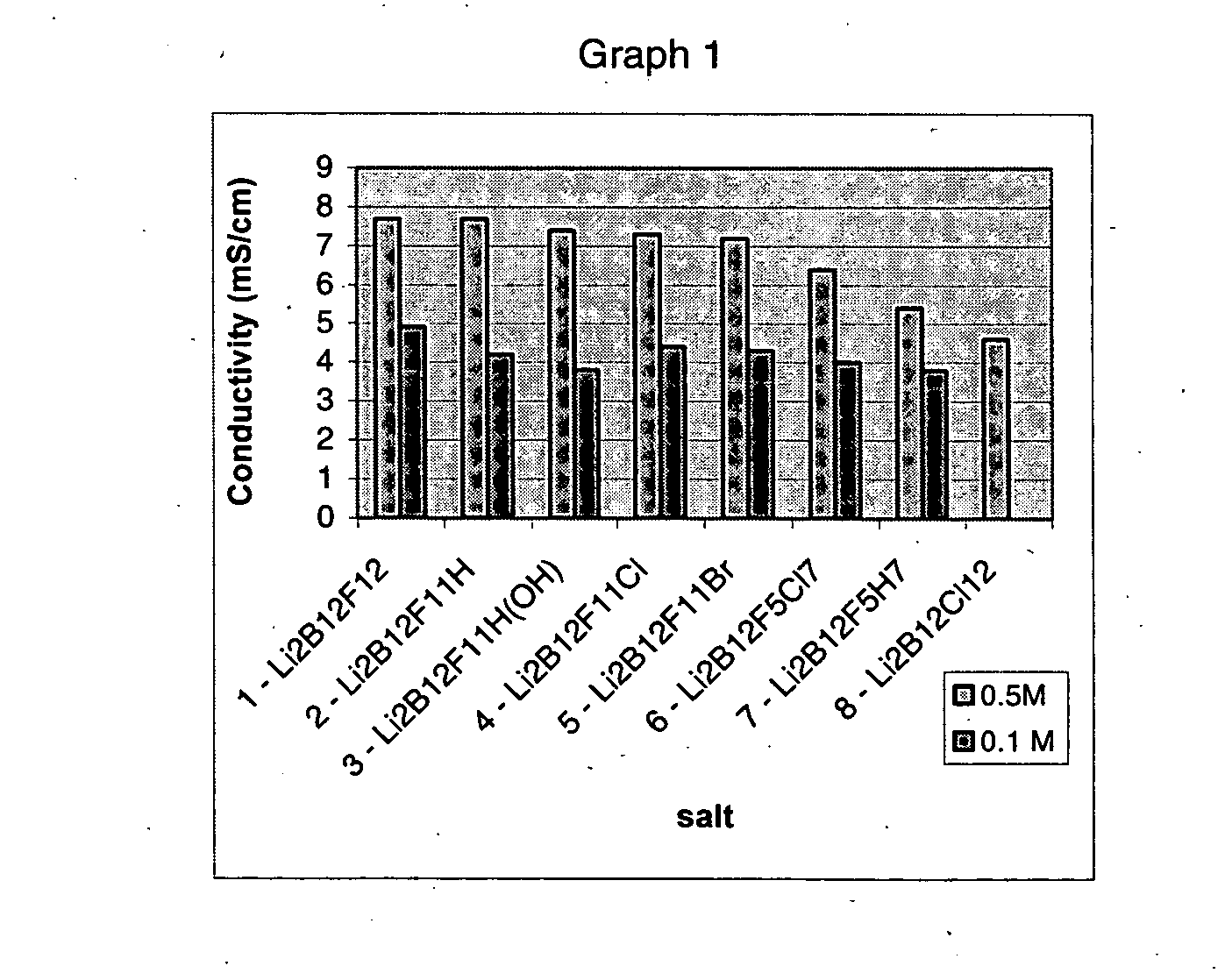
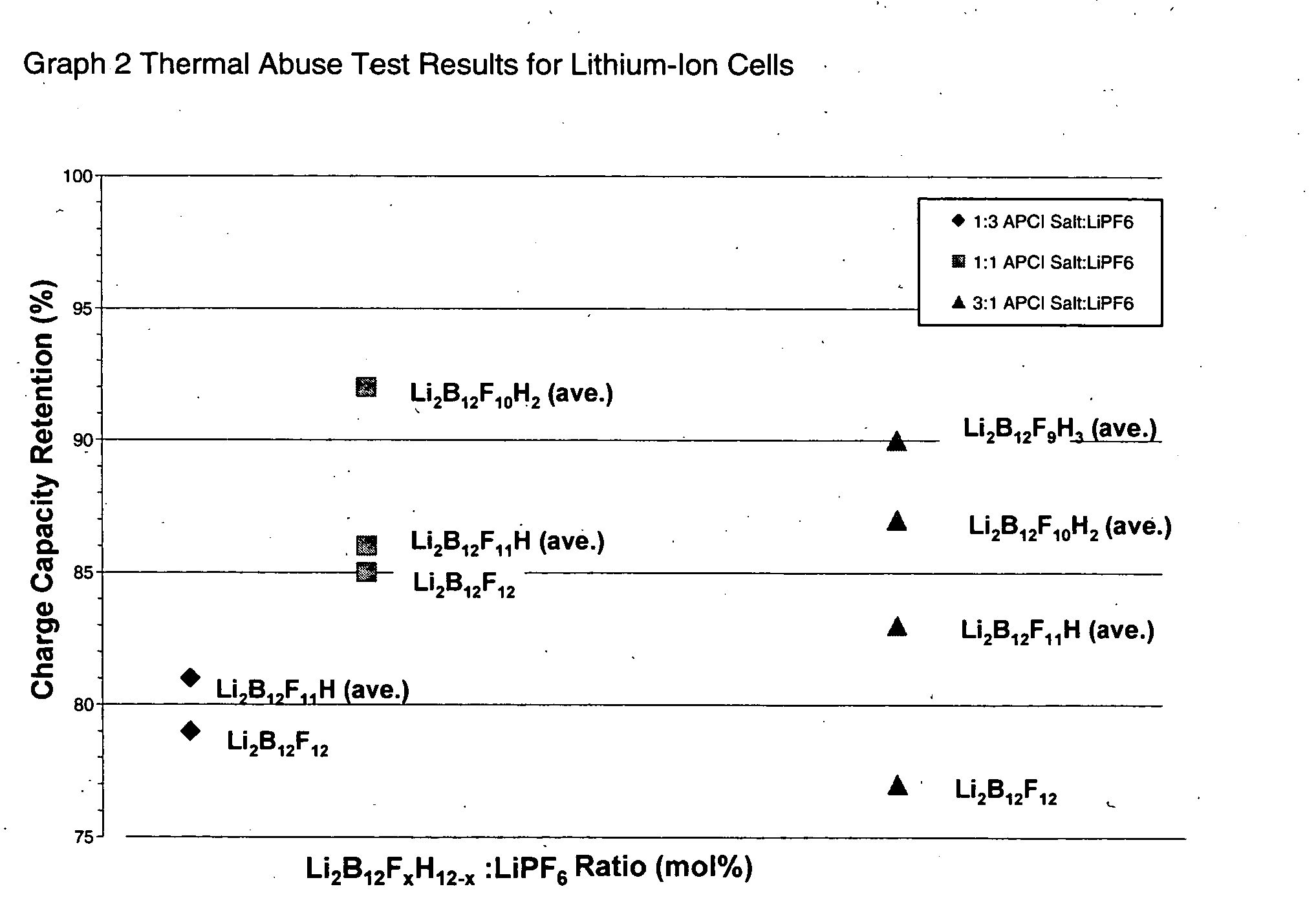
Polyfluorinated boron cluster anions for lithium electrolytes
ActiveUS20050064288A1Low viscosityLower impedanceOrganic electrolyte cellsBiochemical fuel cellsBoron clustersElectrolyte composition
The present invention relates to an improvement in lithium secondary batteries comprised of a negative electrode, a positive electrode, a separator, and a lithium-based electrolyte carried in an aprotic solvent and to the electrolyte compositions. The improvement resides in the use of a lithium salt of the formula: Li2B12FxZ12-x wherein x greater than or equal to 4 and Z represents H, Cl, and Br.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Synthesizing process for obtaining lithium difluoro-oxalato-borate and lithium tetrafluoroborate
InactiveCN101648963AImprove performanceSimple processGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsBoron halogen compoundsOrganic solventPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a synthesizing process for simultaneously obtaining lithium difluoro-oxalato-borate and lithium tetrafluoroborate with favorable performance, which comprises the following steps: (1) leading a fluorine-contained compound, a boron-contained compound, a lithium-contained compound and an oxalate-contained compound to react in a reaction medium at the reaction pressure of 0.1-1MPa and the temperature of 0-100 DEG C, wherein the molar ratio of lithium element, fluorine element, boron element and oxalate ion is (2-3):(5-6):6:2:1; generating reaction liquid containing the lithium difluoro-oxalato-borate and the lithium tetrafluoroborate; (2) carrying out initial separation on the lithium difluoro-oxalato-borate and the lithium tetrafluoroborate in the reaction liquid and then carrying out further extraction separation by an organic solvent which can extract the lithium difluoro-oxalato-borate or the lithium tetrafluoroborate; and (3) respectively carrying out recrystallization and vacuum drying to obtain the battery-grade lithium difluoro-oxalato-borate and the lithium tetrafluoroborate. The invention is suitable for industrially producing two lithium salts which have favorable performance and are used for a lithium ion battery.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG GUOTAI HUARONG NEW CHEM MATERIALS CO LTD
Nano-scale metal halide scintillation materials and methods for making same
Crystalline scintillator materials comprising nano-scale particles of metal halides are provided. The nano-scale particles are less than 100 nm in size. Methods are provided for preparing the particles. In these methods, ionic liquids are used in place of water to allow precipitation of the final product. In one method, the metal precursors and halide salts are dissolved in separate ionic liquids to form solutions, which are then combined to form the nano-crystalline end product. In the other methods, micro-emulsions are formed using ionic liquids to control particle size.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
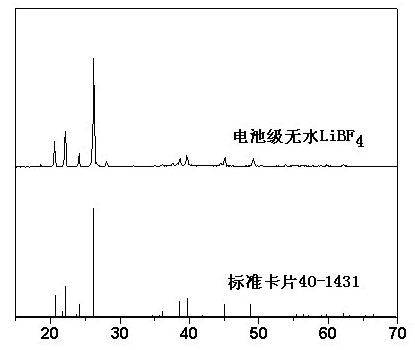
Preparation method of battery-grade anhydrous lithium tetrafluoroborate
The invention discloses a preparation method of battery-grade anhydrous lithium tetrafluoroborate. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: making hydrofluoric acid and boric acid react and adding lithium carbonate or lithium hydroxide to obtain a lithium tetrafluoroborate solution; then, filtering, evaporating, concentrating, crystallizing, separating and drying; and adding absolute ethanol to dissolve in a glove box and evaporating the ethanol to obtain a lithium tetrafluoroborate product. The invention improves an aqueous solution method, synthesizes in an inorganic medium, extracts with an organic solvent, further dries to obtain an anhydrous product, overcomes the difficulties in dehydration, extraction and separation because of the inorganic medium and has low cost and convenient operation.
Owner:XINJIANG RES INST OF NON FERROUS METALS
Co-production method for lithium oxalyldifluoroborate and lithium tetrafluoroborate
InactiveCN103374023AHigh purityHigh yieldGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsBoron halogen compoundsProtonSolvent
The invention discloses a co-production method for lithium oxalyldifluoroborate and lithium tetrafluoroborate. The co-production method comprises the following steps of: (1) uniformly mixing compounds containing lithium salts and BF3 in an aprotic nonpolar solvent or a solvent with a low aprotic polarity in a molar ratio of (1: 1: 3)-(1: 1.25: 3.75) of lithium to boron to fluorine; (2) refluxing for 1-48 hours at a temperature of 30-100 DEG C, then performing solid-liquid separation, and drying the obtained solid substance to obtain crude products LiODFB and LiBF4; and (3) performing purification and separation on the obtained crude products for one time, or performing purification for many times.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method and device for separately producing enriched boron-10 (10B) by using multiple serial towers
InactiveCN102773016ASatisfy the abundance requirementIsotope separationBoron halogen compoundsNuclear powerContinuous flow
The invention relates to a method and device for separately producing enriched boron-10 (10B) by using multiple serial towers. In the method, enriched production of 10B is realized through multiple chemical exchange towers which are connected in series. The production device mainly comprises a complexing tower, serial chemical exchange towers, and a cracking tower, wherein the tower top of the cracking tower is provided with a condenser; the tower bottom of the cracking tower is provided with a heating kettle; and continuous flow of a liquid phase is realized among the complexing tower, each chemical exchange tower and the cracking tower through a pump. A liquid phase sprayed out of the complexing tower is pumped to the top of the first chemical exchange tower through a pump, and is pumped to the top of the second chemical exchange tower after flowing out of the bottom of the first chemical exchange tower till the liquid phase flowing out of the bottom of the last exchange tower is pumped to the top of the cracking tower; and a liquid phase flowing out of the bottom of the cracking tower is subjected to heat exchange through a heat exchanger, and is pumped to the top of the complexing tower through a pump, so that circular flow of the liquid phase among serial towers is formed. Due to the adoption of the method and the device, production of enriched 10B is realized through multiple serial towers, the abundance of the boron-10 is over 95 percent, and the abundance requirement of an enriched 10B product in the fields of nuclear power, military industry, aerospace and the like is met.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
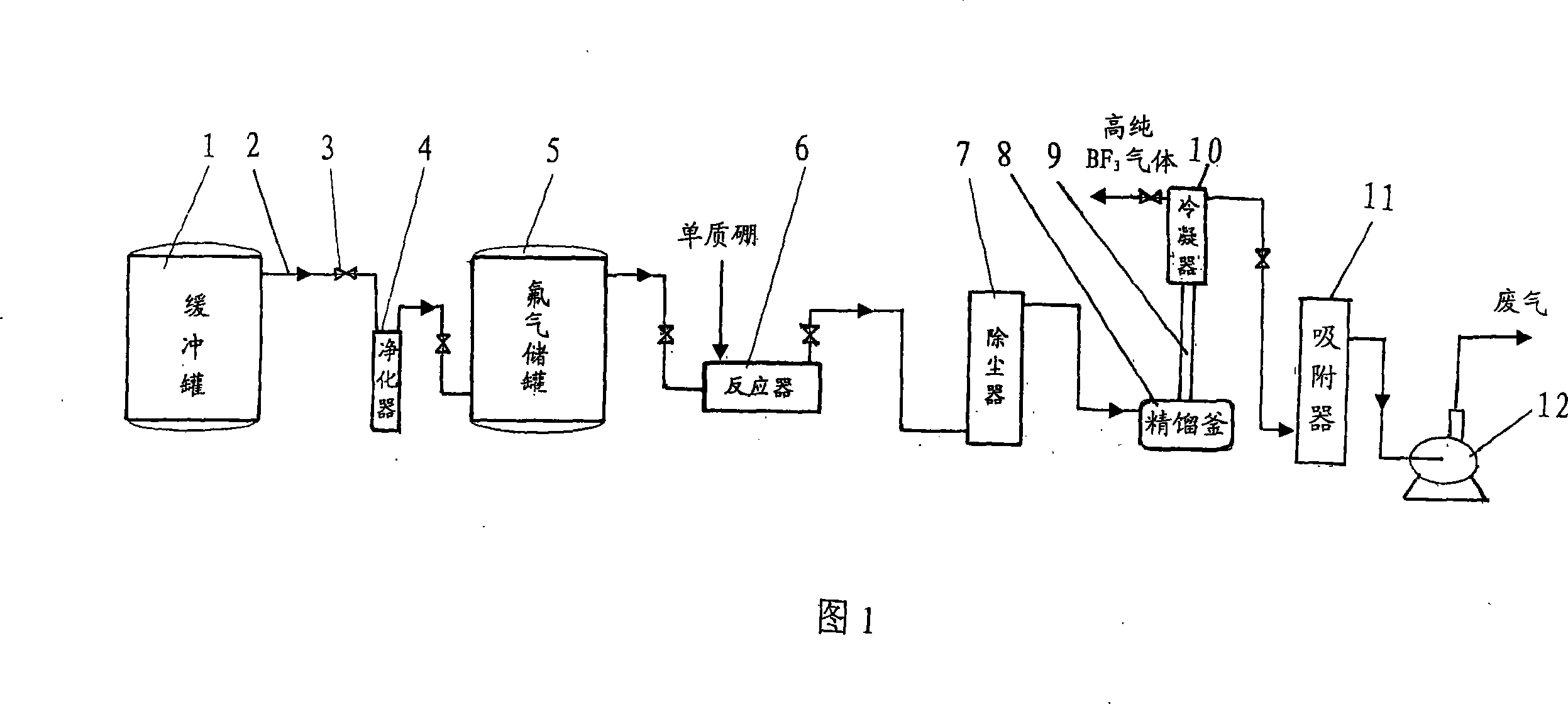
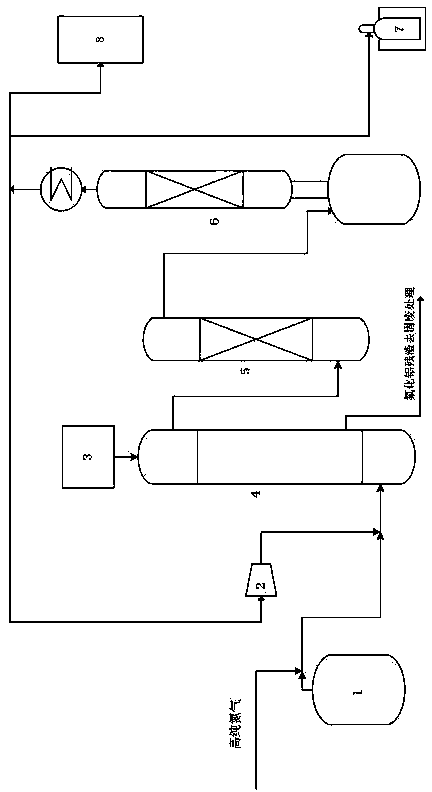
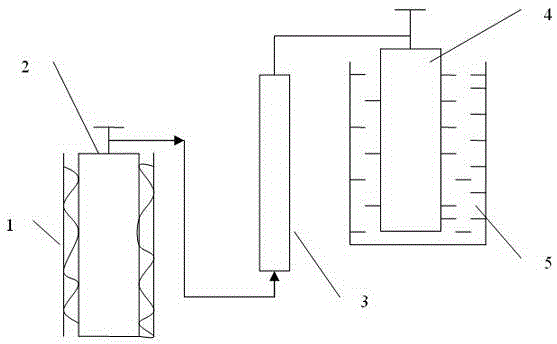
Technique and deice for preparing high purity boron trifluoride gas
The invention discloses a process for preparing a gas of high-purity boron trifluoride and an installation. The process comprises producing the gas of boron trifluoride by means of directly synthesizing fluoride and elemental boron and preparing the gas high-purity boron trifluoride through dedusting and rectifying the impure gas of boron trifluoride. The installation of the invention mainly comprises a buffer tank, a purifier, a fluoride storage tank, a reactor, a dust remover, a rectifying still, a condenser, an absorber and a vacuum group. The gas of boron trifluoride produced by employing the process and installation of the invention has the advantages of high purity, simple installation, convenient operation, safe operation of the installation, continual production and the like.
Owner:RES INST OF PHYSICAL & CHEM ENG OF NUCLEAR IND
Preparation method of high purity borane gas and application of borane gas
InactiveCN104086576AHigh purityNo pollutionGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsBoron halogen compoundsCooling towerFilter press
The invention relates to a preparation method of a high purity borane gas. The preparation method comprises the following steps: putting Lewis base in a reaction kettle and adding a neutral solvent to obtain a solution; adding the solution into Lewis acid to react to obtain a low purity borane gas and a reaction residue liquid; introducing the low purity borane gas into a buffer kettle, and then sequentially passing through a low temperature cooling tower, an acid gas absorption tower and a drying tower to obtain the high purity borane gas; and filter-pressing the quenched reaction residue liquid to obtain a filter solution and a solid, rectifying the filter solution to obtain a rectified product and recrystallizing the solid to obtain a recrystallized product. The invention further provides an application of the borane gas. By adopting the preparation of the borane gas and the application of the borane gas provided by the invention, the borane gas with the purity being over 99% can be obtained, and great improvement is made to effective utilization of post-treatment and treatment products for preparing the borane gas, so that the post-treatment is safer, the treatment products can turn waste into wealth, and the high purity product can be prepared.
Owner:SHANGHAI SCIENTIA PHARMA TECH
Device and method for producing boron trifluoride-11 electronic specific gas
InactiveCN102774845AFulfil requirementsMeet production requirementsBoron halogen compoundsCounter flowBoron trifluoride
The invention relates to a device and a method for producing boron trifluoride-11 (11BF3) electronic specific gas, wherein boron trifluoride raw gas is fed from the bottom of a synthesizer, anisole is downwards sprayed from the top of the synthesizer, and at the operation temperature of 10-25 DEG C, complex reaction is carried out to produce a boron trifluoride-anisole complex; a BF3 gas which is cracked from a cracking device is fed from the bottom of a chemical exchange tower, the gas and the liquid counter flow to fully contact with each other, and at the operation temperature of 15-30 DEG C, the chemical exchange reaction is carried out; heavier 11B isotope is enriched at the top of the tower in a gaseous state, and lighter 10B isotope is enriched in the liquid complex in the bottom of the tower; the enriched 11BF3 gas enters the synthesizer from the bottom, and is synthesized with the anisole again to form the liquid complex; the liquid complex of the enriched 10B isotope enters a decomposer, is heated to decompose into 11BF3 lean gas at 140-170 DEG C, and enters the chemical exchange tower to be subjected to chemical exchange; and the operation is repeated until the 11B abundance of the 11BF3 gas reaches above 99.7%, and the product is recovered from an 11BF3 product outlet.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
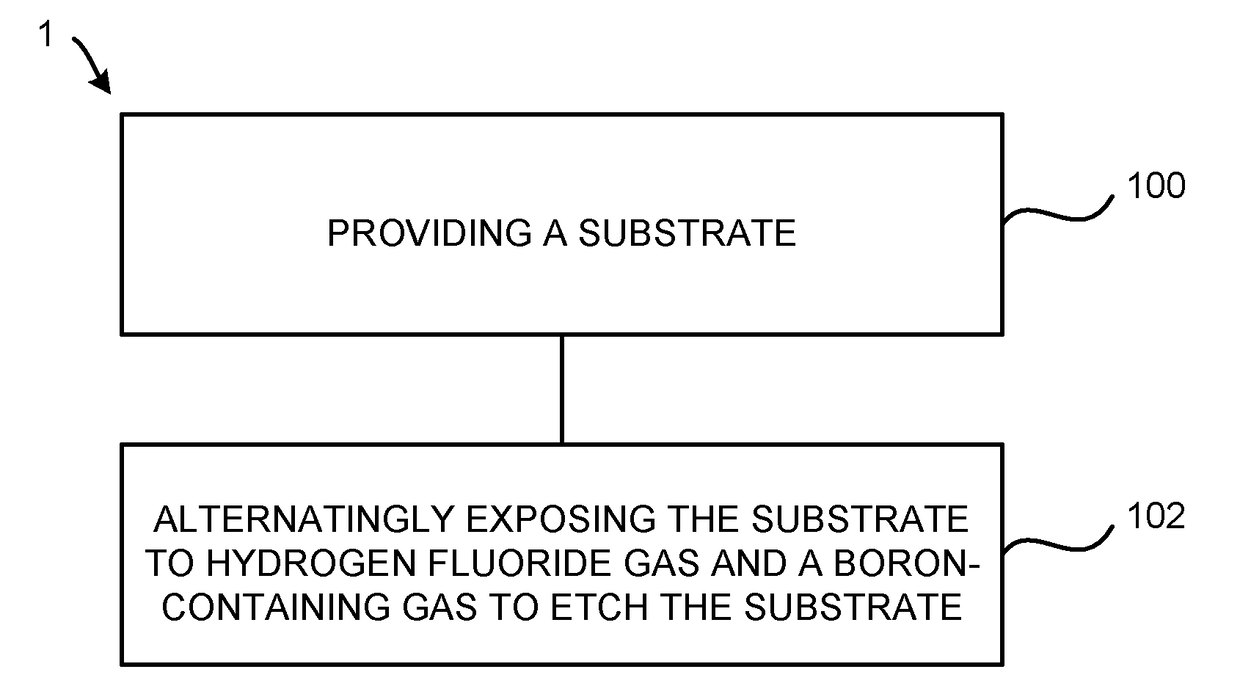
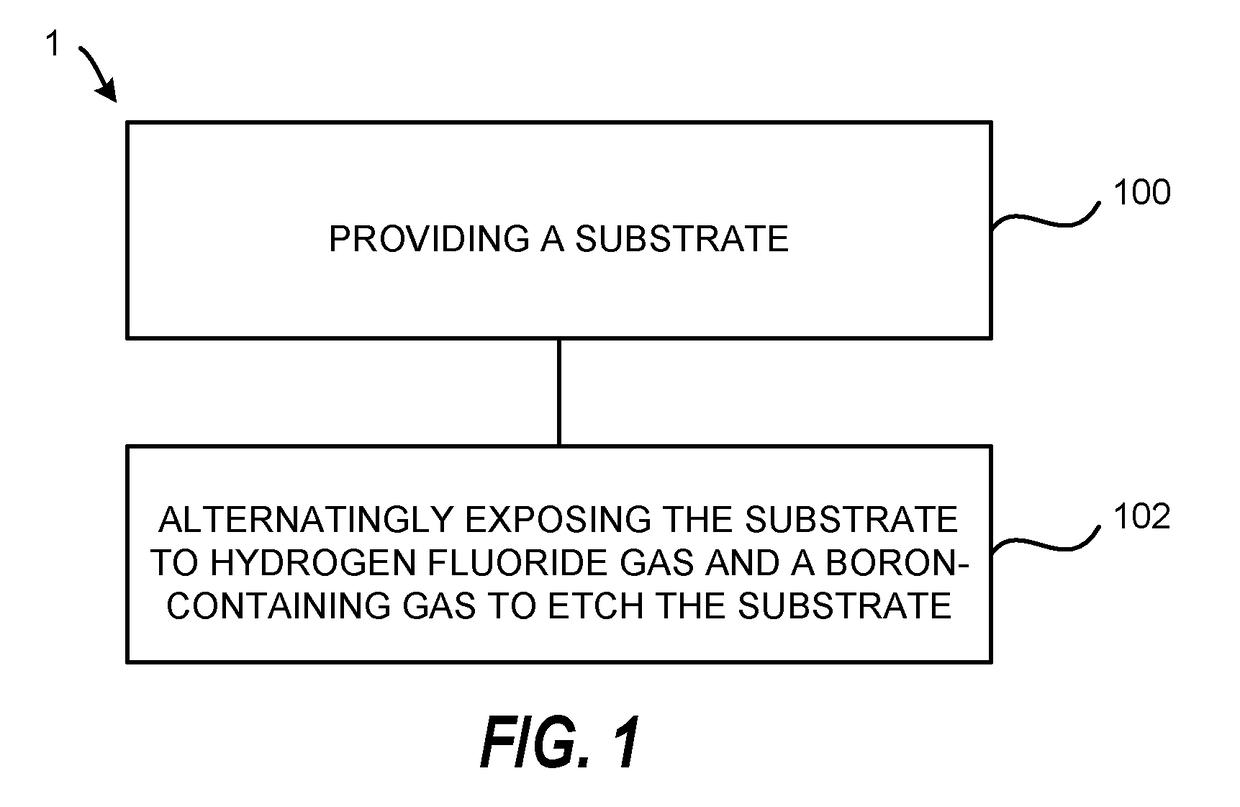
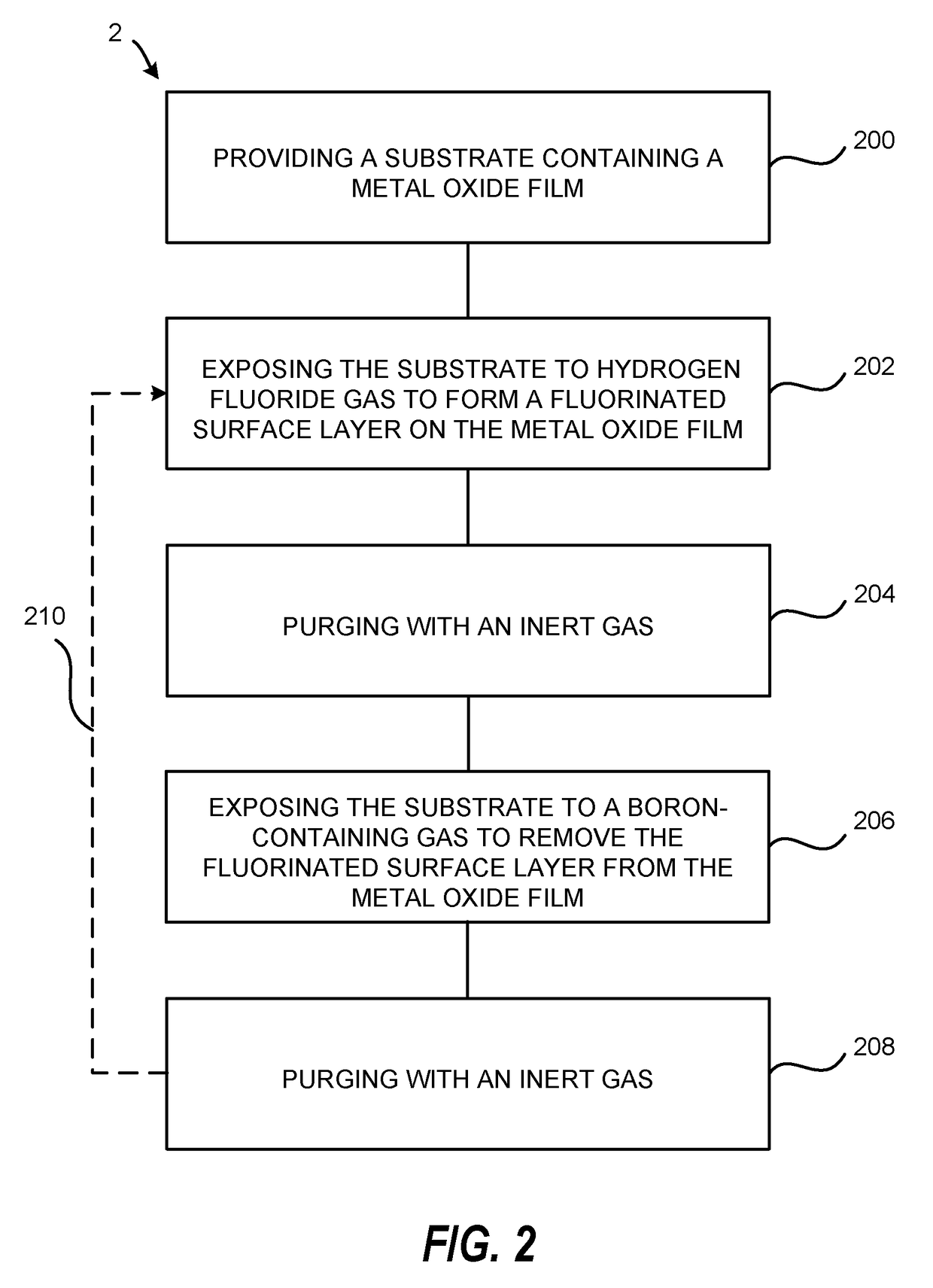
Atomic layer etching using a boron-containing gas and hydrogen fluoride gas
Embodiments of the invention provide a method for atomic layer etching (ALE) of a substrate. According to one embodiment, the method includes providing a substrate, and exposing the substrate to hydrogen fluoride (HF) gas and a boron-containing gas to etch the substrate. According to another embodiment, the method includes providing a substrate containing a metal oxide film, exposing the substrate to HF gas to form a fluorinated surface layer on the metal oxide film, and exposing the substrate to a boron-containing gas to remove the fluorinated surface layer from the metal oxide film. The exposures may be repeated at least once to further etch the metal oxide film.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method for preparing potassium borofluoride through fluorine-containing wastewater
ActiveCN103332700ARich sourcesReduce pollutionBoron halogen compoundsHydrogen fluorideAfter treatment
The invention relates to a method for preparing potassium borofluoride through fluorine-containing wastewater. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) utilizing water to regulate the hydrogen fluoride content of the fluorine-containing wastewater until the mass content of hydrogen fluoride is 12%-17%; (2) completely mixing the wastewater after treatment in the step (1) with potassium chloride saturated solution according to a mass ratio of (3-5):1 so as to fluorate; (3) mixing borax with the wastewater after treatment in the step (1) according to a mass ratio of 1: (3-5), and stirring so as to completely dissolve the borax; mixing solution in the step 2 with solution in the step 3 according to a mass ratio of (0.8-1.2):1, stirring to react, and continuously separating potassium fluoborate out in a reaction process so as to prepare potassium fluoborate suspension; and (5) solid-liquid separating, washing and drying the potassium fluoborate suspension in the step (4) so as to obtain a potassium fluoborate product. The potassium fluoborate product prepared by the method can satisfy the requirements of potassium fluoborate use factories.
Owner:MORITA NEW ENERGY MATERIALS ZHANGJIAGANG CO LTD
Process for preparing element halides
InactiveCN101061060AFast heating rateEfficient heatingBromide preparationChloride preparationTraffic accidentVehicle detection
To specify vehicles carrying persons who can be eyewitnesses in the event of a traffic accident. This vehicle detection apparatus is for detecting any vehicle located in the vicinity of an accident site at the time of occurrence of an accident and comprises a vehicle information storage part for storing vehicle identifiers; a one's own vehicle impact detection storage part for storing information about witnessing vehicles; a vehicle information reader part for obtaining vehicle identifiers from the vehicle information storage part of another vehicle detection apparatus; and an impact detection part for detecting impact and for obtaining the vehicle identifiers from the vehicle information reader part upon detection of the impact to store the vehicle identifiers as information about the eyewitnessing vehicles in the one's own vehicle impact detection storage part. Thus when detecting impact on a vehicle, the apparatus can obtain the identification numbers of nearby vehicles and specify any vehicles carrying persons who can be eyewitnesses of the traffic accident.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
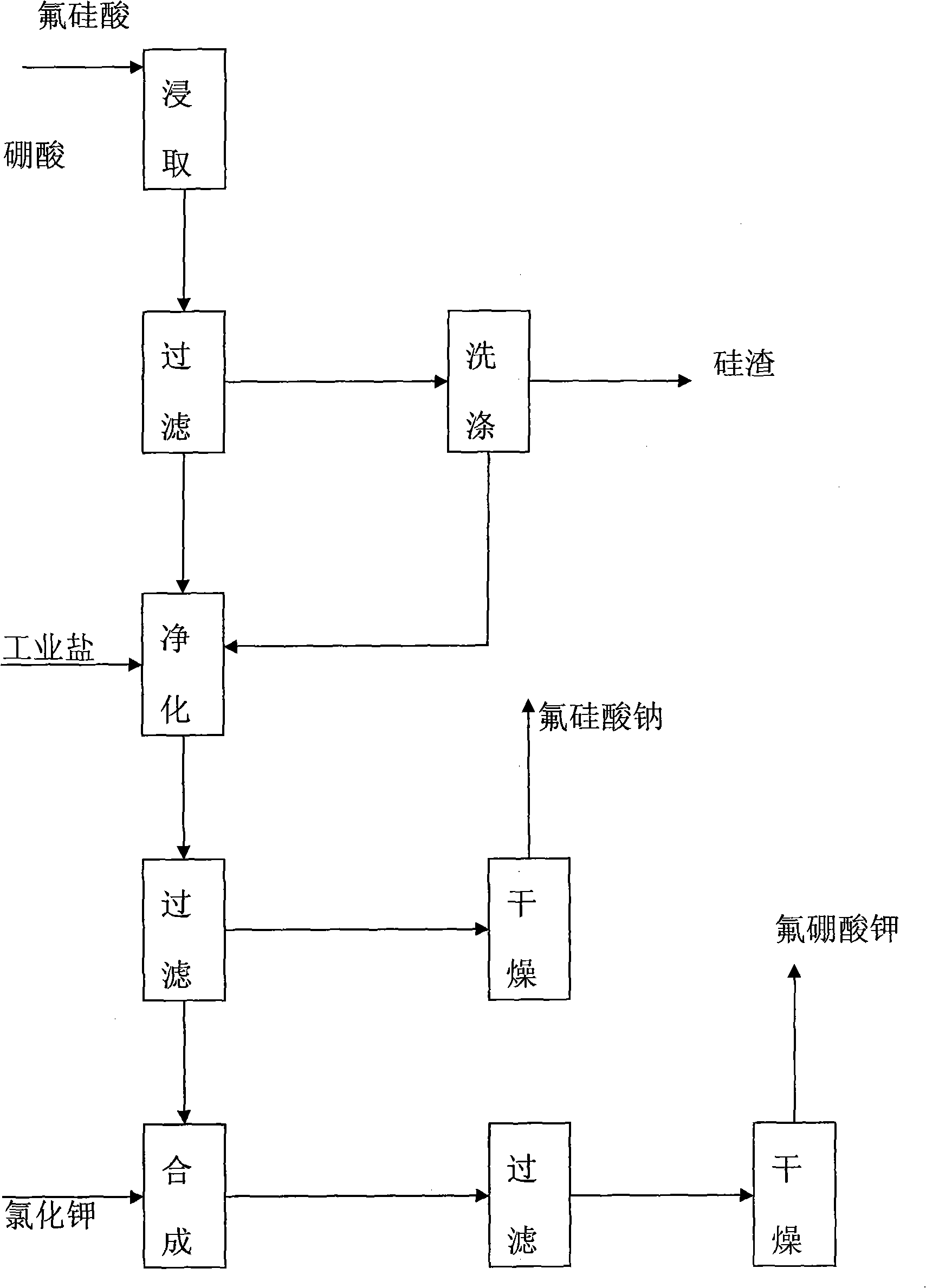
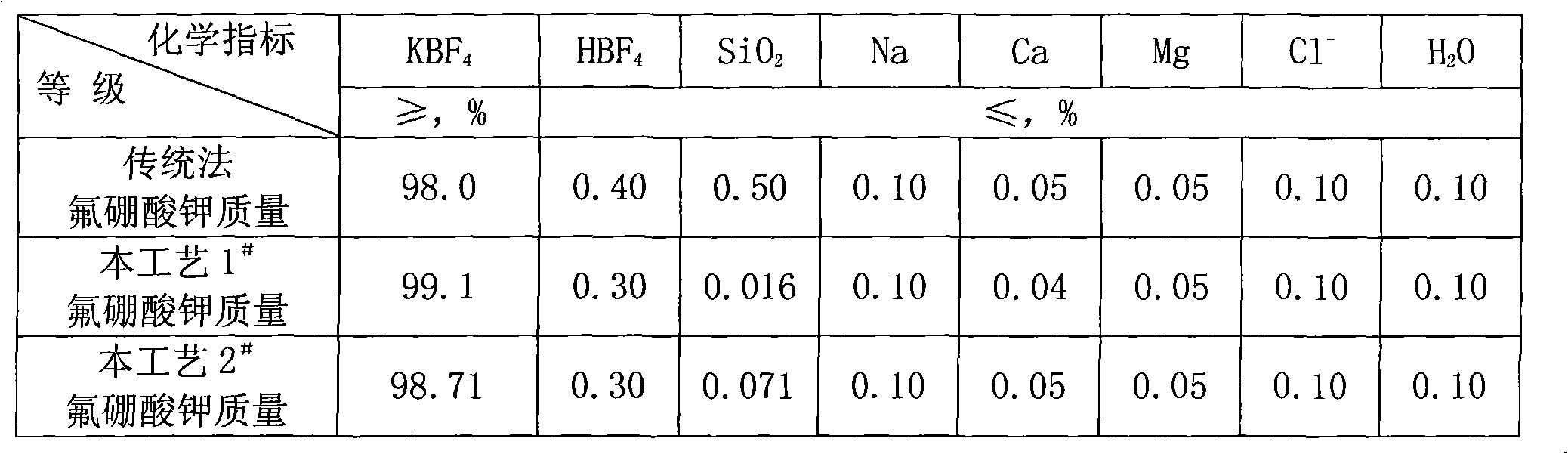
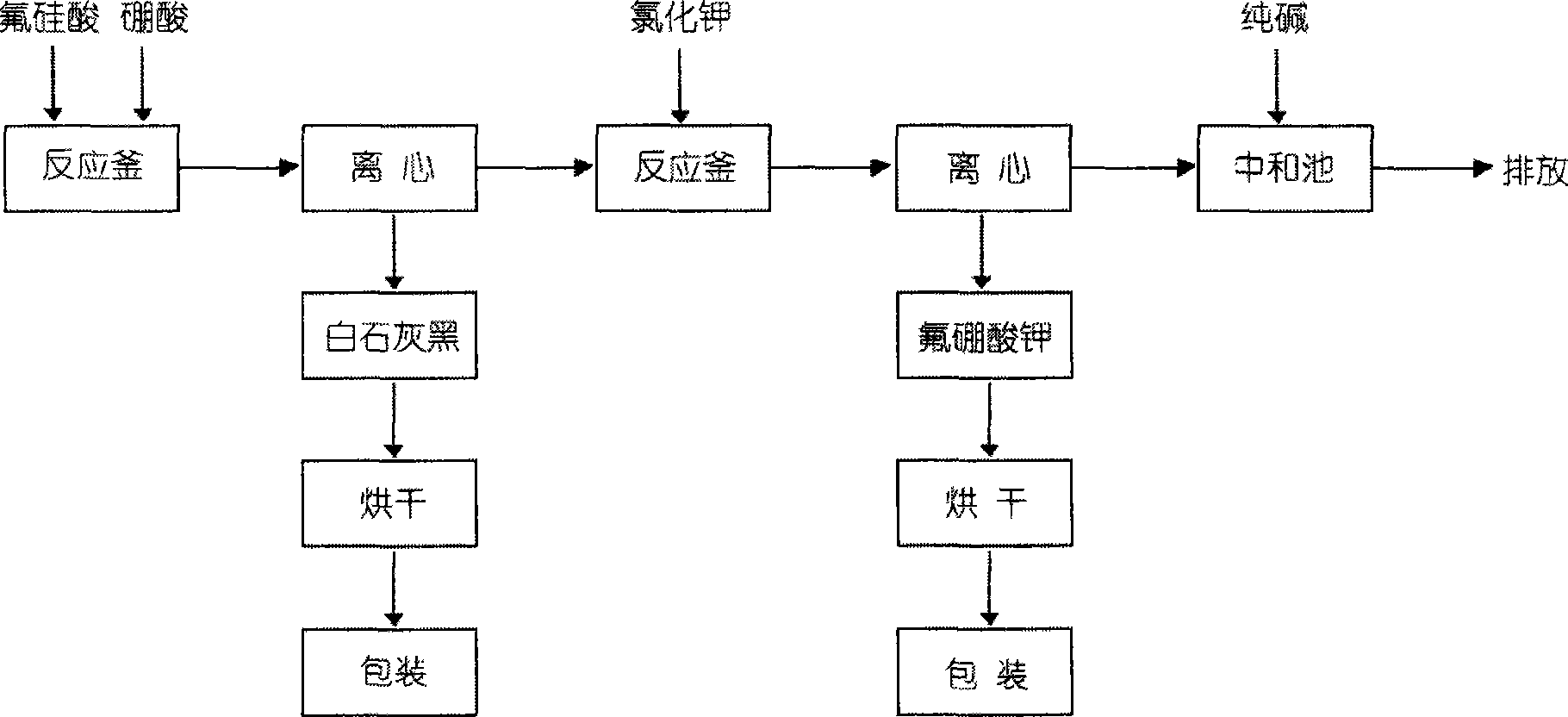
Process for preparing potassium borofluoride and co-production of white carbon black and sodium fluosilicate
InactiveCN101289195ARaw materials are easy to getLow costSilicaSilicon halogen compoundsPotassium borohydrideFiltration
The invention relates to a method for preparing potassium fluoborate with the co-product of white carbon black and sodium fluosilicate, which takes hydrofluosilicic acid, boric acid, industrial salt and potassium chloride as main raw materials and particularly comprises the steps as follows: (1) the hydrofluosilicic acid is firstly added into a leaching tank which is then preheated to 60 DEG C to 100 DEG C and then opened for carrying out stirring, theoretical quantity of boric acid is added into the hydrofluosilicic acid, then the leaching tank is obturated and reaction is carried out continuously for 2.0 hours to 6.0 hours, and leaching is carried out at the constant temperature of 60 DEG C to 100 DEC G; (2) qualified fluoboric acid solution after being leached is filtered, the white carbon black is dried after progressive concentration and washing by levels of water to produce the white carbon black; (3) the filtrate obtained and a first lotion are added with the industrial salt for purifying and disiliconization, then theoretical quantity of industrial salt is added for carrying out reaction for 10 minutes to 30 minutes to prepare sodium fluosilicate slurry; (4) the sodium fluosilicate slurry prepared is filtered, washed and dried to obtain sodium fluosilicate products, and the filtrate obtained is used for synthetizing the potassium fluoborate; (5) theoretical quantity of potassium chloride is added into the filtrate obtained in step (4) for carrying out reaction for 10 minutes to 30 minutes; (6) after the reaction in step (5) completes, filtration is carried out, an ointment is washed by primary water and dried to obtain the potassium fluoborate.
Owner:DO FLUORIDE CHEM CO LTD
Process for producing lithium-containing composite oxide for positive electrode for lithium secondary battery
ActiveUS20070298324A1Suppress gas productionImprove securitySilver accumulatorsPhosphatesAlkaline earth metalOxygen
To provide a cathode active material for a lithium secondary battery, which is low in gas generation and has high safety and excellent durability for charge and discharge cycles even at a high charge voltage. A process for producing a lithium-containing composite oxide represented by the formula LipLqNxMyOzFa (wherein L is at least one element selected from the group of B and P, N is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Co, Mn and Ni, M is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Al, alkaline earth metal elements and transition metal elements other than N, 0.9≦p≦1.1, 1.0≦q<0.03, 0.97≦x<1.00, 0≦y≦0.03, 1.9≦z≦2.1, q+x+y=1 and 0≦a≦0.02), wherein a lithium-containing composite oxide powder containing an N element and, if necessary, an M element and fluorine, is preliminarily prepared; the lithium-containing composite oxide powder is mixed with an aqueous solution containing the L element source; from the obtained mixture, an aqueous medium is removed, followed by the firing in an oxygen-containing atmosphere at from 300 to 1,050° C.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
A potassium fluoborate compound, a potassium fluoborate non-linear optical crystal, a preparing method of the crystal and uses of the crystal
ActiveCN106948003APromote growthStable physical and chemical propertiesPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltNonlinear optical crystalSpace group
A potassium fluoborate compound, a potassium fluoborate non-linear optical crystal, a preparing method of the crystal and uses of the crystal are provided. The chemical formula of the compound is KB4O6F, the molecular weight of the compound is 197.34, and the compound is prepared by a solid-phase synthetic method or a vacuum encapsulation method. The chemical formula of the crystal is KB4O6F, and the molecular weight of the crystal is 197.34. The crystal belongs to an orthorhombic system, and the space group of the crystal is Pna2<1>. According to cell parameters, a=7.4638 angstroms, b=11.2913 angstroms, c=6.5089 angstroms, alpha=beta=gamma=90 degrees, and the unit-cell volume is 548.54 angstrom<3>. The frequency-doubled effect of the crystal is 1.8 times of that of KH2PO4 (KDP), and the ultraviolet absorption edge is shorter than 190 nm. The crystal grows by adopting a melt method, a high-temperature melt method, a vacuum encapsulation method, a hydrothermal method or a room-temperature solution method. The crystal has good chemical stability, and can be applied as an ultraviolet and deep ultraviolet non-linear optical crystal in all-solid-state lasers.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing uranium oxide from uranium oxyfluoride
InactiveUS6096281AReduced thermodynamic stabilityAvoid vaporizationPhosphorus halides/oxyhalidesFluoride preparationUranium oxideOxidizing agent
A method for producing uranium oxide includes combining uranium oxyfluoride and a solid oxidizing agent having a lower thermodynamic stability than the uranium oxide after "oxide"; heating the combination below the vapor point of the uranium oxyfluoride to sufficiently react the uranium oxyfluoride and the oxidizing agent to produce uranium oxide and a non-radioactive fluorine compound; and removing the fluorine compound after "compound".
Owner:INT ISOTOPES
Fluorohaloborate salts, synthesis and use thereof
A composition is provided as a salt having the formula MBF3X where M is an alkali metal cation and X is the halide fluoride, bromide or iodide. A lithium salt has several characteristics making the composition well suited for inclusion within a lithium-ion battery. A process for forming an alkali metal trifluorohaloborate salt includes the preparation of a boron trifluoride etherate in an organic solvent. An alkali metal halide salt where the halide is chloride, bromide or iodide is suspended in the solution and reacted with boron trifluoride etherate to form an alkali metal trifluorohaloborate. The alkali metal trifluorohaloborate so produced is collected as a solid from the solution. The process is simple and yields alkali metal trifluorohaloborate of sufficient purity to be used directly in battery applications.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE
Preparation method of high-purity boron trichloride-11
ActiveCN103950947AHigh purityMeet the requirements of the processBoron halogen compoundsAluminium chlorideVery large scale integrated circuits
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-purity boron trichloride-11, and belongs to the field of preparation methods of boron compounds. The preparation method comprises the steps such as pretreating raw materials, synthesizing boron trichloride-11 through reaction of aluminum chloride and boron trifluoride-11, filtering, preliminarily separating, rectifying and purifying, collecting the high-purity boron trichloride-11 product, treating tail gas, and the like. The high-purity boron trichloride-11 prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention is high in purity which can reach over 99.9999%, can satisfy requirements of manufacturing integrated circuit semiconductor apparatuses on a large scale, effectively improves interference resistance and radiation resistance of an integrated circuit, and can be used as the raw material for manufacturing raw materials such as a high-purity boron-11 isotope material, a special boron fiber material and light-guide fiber.
Owner:方治文
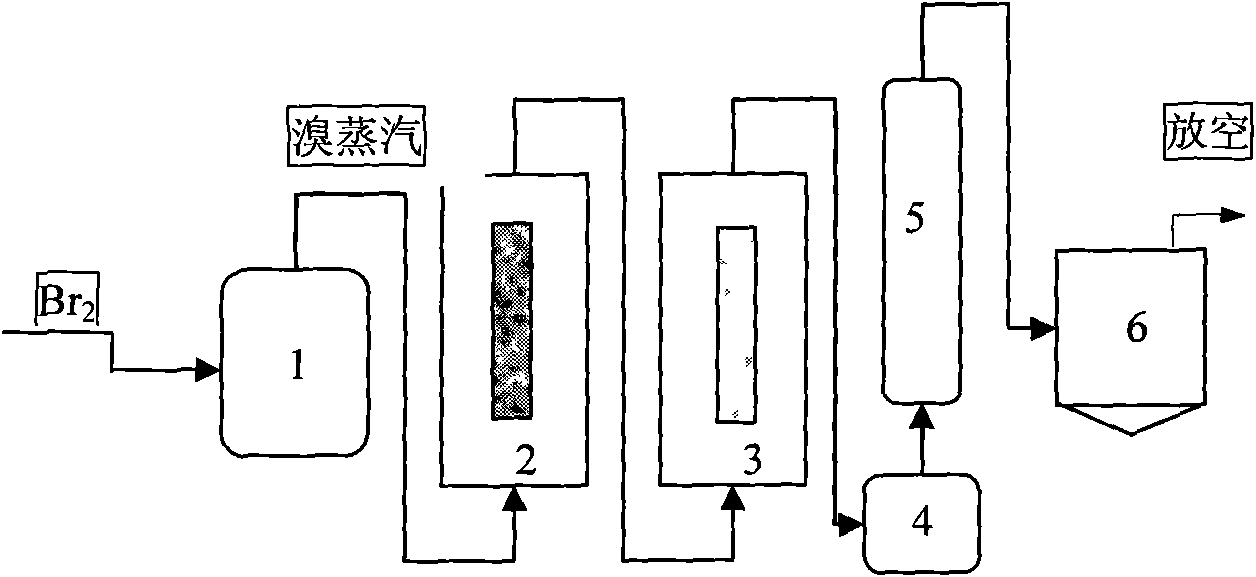
Method and device for preparing high-purity boron tribromide
InactiveCN101955189ALess impuritiesHigh purityBoron halogen compoundsAcid washingReaction temperature
The invention provides a method and a device for preparing high-purity boron tribromide. The method comprises the following steps of: performing acid-washing on industrial boron powder to prepare boron blocks; performing separatory purification on pure chemical liquid bromine, and performing a reaction on the purified liquid bromine and the industrial boron blocks at the high temperature of between 600 and 850 DEG C in a bromination furnace to obtain boron tribromide liquid containing impurities; removing redundant Br2 in boron tribromide by using high-purity aluminum serving as a debromination agent to obtain white boron tribromide gas, and hydrocooling the white boron tribromide gas to form white boron tribromide liquid; and removing high-boiling point and low-boiling point impurities through fractional distillation of a fractional column to obtain a BBr3 product of which the purity is more than 6N, wherein the fractionation temperature of the boron tribromide is between 85 and 120 DEG C. The device for preparing the high-purity boron tribromide is formed by connecting a vaporizer, the bromination furnace, a bromine removing furnace, a collector, the fractional column and a finished product storage tank sequentially through a pipeline made of high-purity quartz glass. The produced boron tribromide has a few impurities and high purity which can reach over 6N, and the method has the advantages of readily available materials, low cost, simple device, small equipment investment and industrialized production.
Owner:GRIMAT ENG INST CO LTD
Method for preparing potassium fluoborate
InactiveCN101397141AHigh puritySimple reaction conditionsBoron halogen compoundsTetrafluoroborateCentrifugation
The invention provides a method for preparing potassium tetrafluoroborate, comprising the steps as follows: a. fluosilicic acid content of fluosilicic waste material is gained by chemical analysis of the fluosilicic waste material; boric acid with suitable quantity is added to the fluosilicic waste material so as to carry out the reaction under the reaction temperature of 30-95 DEG C; preferably, the reaction temperature is 60 DEG C; when the reaction is completed, SiO2 solid and mother liquor are gained by centrifugation; b. KCl with suitable quantity is added in the mother liquor so as to carry out the reaction with the reaction temperature of 90-95 DEG C; preferably, the temperature is 60 DEG C; when the reaction is completed, the potassium tetrafluoroborate solid and centrifugal liquid are gained by centrifugation; the potassium tetrafluoroborate solid is dried; c. the centrifugal liquid is exhausted after being counteracted. The method for preparing the potassium tetrafluoroborate greatly reduces the production cost and has good economical benefits and environmental protection.
Owner:上海明煌实业发展有限公司
Production method for high-purity boron tribromide
The invention discloses a production method for high-purity boron tribromide, which comprises the following steps of: placing industrial grade boron tribromide into a container, adding 1 to 2 percent of decoloration adsorbent, keeping with slightly stirring for 60 to 80 minutes, and filtering by using a microfilter of below 0.05 micron; distilling the obtained filtrate by using a sub-boiling distiller, and adjusting the heating pipe voltage-stabilized liquid level temperature to be 60 to 75 DEG C; feeding the obtained distillate into a plate rectification column for distillation reflux, controlling the reflux time to be 5 to 6 hours, removing a low-boiling-point substance, feeding a boron tribromide pure product obtained from 89 to 93-degree centigrade distillate to another rectification column for rectification again, and controlling the reflux time to be 5 to 6 hours; and feeding 89 to 92.5-degree centigrade distillate into a finished product groove, and after the product is detected to be qualified, filtering and packing under the purification environment of which the whole is no more than a thousand level and of which the part is no more than a hundred level to obtain a high-purity boron tribromide product of 99.99999 percent. The method has the advantages of simple process, convenient operation, easy quality control and low finished product cost.
Owner:贵州威顿晶磷电子材料股份有限公司
Method for separating potassium chloride and potassium fluoride
ActiveCN102730710ASimple processLow costBoron halogen compoundsAlkali metal halide purificationWater contentAcetonitrile
The invention discloses a method for separating mixture of potassium chloride and potassium fluoride, which comprises the steps of: carrying out heat treatment on the mixture of the potassium chloride and the potassium fluoride at the temperature of 300-500 DEG C for 1-5h to remove organic waste in the mixture; then reacting with acetonitrile solution of boron trifluoride with the mass percent of 5-20wt% for 5-24h under the condition of refluxing to obtain mixed acetonitrile solution containing potassium fluoroborate and potassium chloride; filtering to remove potassium chloride; and concentrating, crystallizing, drying or spray-drying the filtrate containing potassium fluoroborate until the water content is lower than 1000ppm to finally obtain potassium fluoroborate. After the technical scheme disclosed by the invention is adopted, potassium chloride can be separated out, and potassium fluoroborate is obtained at the same time; and the separation method is simple in technology and low in cost, and the problems of safety, environmental protection and the like are basically solved.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG HUASHENG CHEM CO LTD
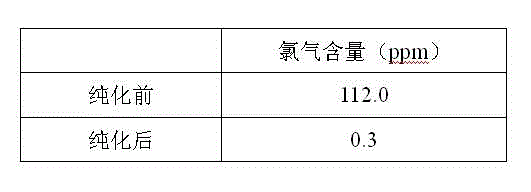
Purification method for boron trichloride
InactiveCN104098105AChlorine impurity levels are reducedBoron halogen compoundsReaction layerPurification methods
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical engineering and relates to a purification method for boron trichlorid. The purification method comprises the following steps: a heating tape at the temperature of 35 DEG C is adopted to heat a boron trichloride raw material steel bottle and the temperature is controlled at 25 DEG C- 35 DEG C; boron trichloride raw materials with chlorine gas content greater than 1 ppm are heated and fully vaporized and the gas flow rate of the boron trichloride is controlled at 10 L / min; micro-scale chlorine gas contained in the boron trichloride gas and boron carbide chlorine gas react with boron carbide at high-temperature through a boron carbide reaction layer which is 5 cm in diameter, 50 cm in height and 850 DEG C in temperature; after the reaction, the gas is cooled by a cryogenic box at the temperature of -20 DEG C and collected into product bottles. The purification method has the benefits that as the high-temperature boron carbide reaction layer is adopted by the technology, the raw materials and the boron carbide are subjected to deep contact reaction to enable the chlorine gas impurity content in the boron trichloride is reduced to less than 1 ppm.
Owner:大连科利德半导体材料股份有限公司
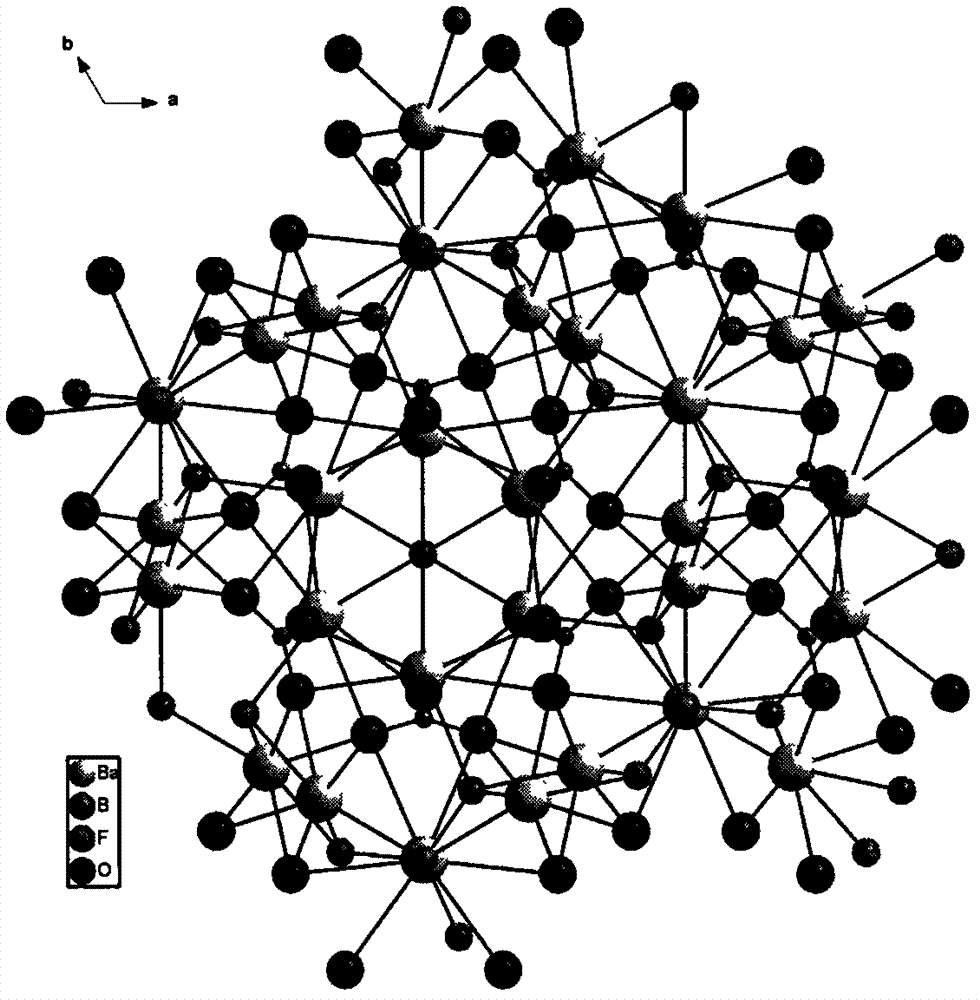
Compound barium boron oxyfluoride, barium boron oxyfluoride nonlinear optical crystal, and preparation methods and applications thereof
ActiveCN103088423APolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsNonlinear optical crystalHexagonal crystal system
The invention relates to a compound barium boron oxyfluoride, a barium boron oxyfluoride nonlinear optical crystal, and preparation methods and applications thereof. The barium boron oxyfluoride nonlinear optical crystal has a chemical formula of Ba7(BO3)3F5 and a molecular weight of 1232.81. The barium boron oxyfluoride nonlinear optical crystal belongs to a hexagonal crystal system, and a space group of P63mc. Lattice parameters are that a=11.1562(15)angstrom, c=7.2415(14)angstrom, Z=2 and V=780.5(2)angstrom<3>. A powder frequency-doubled effect reaches 1 / 3 of that of KDP, and a translucent band is 190nm to 2600nm. According to the invention, the compound is synthesized with a solid-phase reaction method, and the crystals are grown with a co-solvent method. The crystals has the advantages of simple preparation method, low cost, large crystal size, short growth period, less inclusion, high mechanical hardness, easy curing, easy polishing and processing, and easy storing. The compound barium boron oxyfluoride nonlinear optical crystal provided by the invention can be widely applied in frequency conversion and nonlinear optical devices such as optical parametric oscillators.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for separating potassium chloride and potassium fluoride
ActiveCN102730710BSimple processLow costBoron halogen compoundsAlkali metal halide purificationPotassium fluorideBoron trifluoride
The invention discloses a method for separating mixture of potassium chloride and potassium fluoride, which comprises the steps of: carrying out heat treatment on the mixture of the potassium chloride and the potassium fluoride at the temperature of 300-500 DEG C for 1-5h to remove organic waste in the mixture; then reacting with acetonitrile solution of boron trifluoride with the mass percent of 5-20wt% for 5-24h under the condition of refluxing to obtain mixed acetonitrile solution containing potassium fluoroborate and potassium chloride; filtering to remove potassium chloride; and concentrating, crystallizing, drying or spray-drying the filtrate containing potassium fluoroborate until the water content is lower than 1000ppm to finally obtain potassium fluoroborate. After the technical scheme disclosed by the invention is adopted, potassium chloride can be separated out, and potassium fluoroborate is obtained at the same time; and the separation method is simple in technology and low in cost, and the problems of safety, environmental protection and the like are basically solved.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG HUASHENG CHEM CO LTD
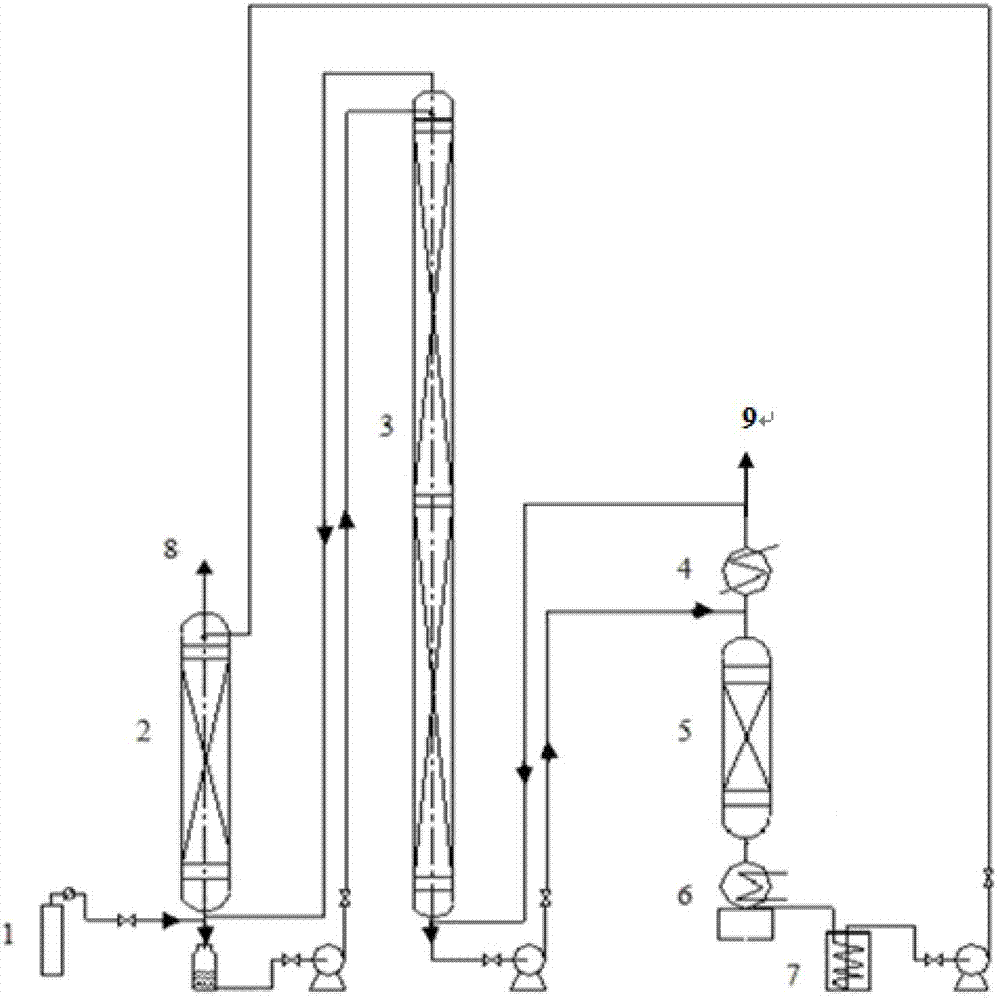
Construction method based on technology for producing boron isotope by anisole-boron trifluoride
ActiveCN104190256AImprove separation efficiencyReduce the amount requiredIsotope separationBoron halogen compoundsBoron trifluorideProduct gas
The invention discloses a construction method based on a technology for producing boron isotope by anisole-boron trifluoride, which belongs to the field of isotope separation, and mainly aims at solving the problems such as low yield of boron-10 and incapability of obtaining qualified boron-11 products at the same time in the existing construction method based on the technology for producing boron isotope by anisole-boron trifluoride. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: continuously purifying raw materials, namely boron trifluoride gas and an anisole liquid, as well as an anisole-boron trifluoride complex before entering a cracking tower, nitrogen gas coming out of the top of a complex gas stripping tower, boron trifluoride gas after cracking, and gas coming out of the top of a first exchange rectifying tower; adding the purified nitrogen gas into a second exchange rectifying tower; adding fresh boron trifluoride gas into the first exchange rectifying tower, wherein boron-10 is not discharged out from the top of the cracking tower and boron-11 is not discharged out from the top of a complexation tower; and after performing system rectification balance for 72-148 hours, converting to the normal production mode. The method has the advantage that the two qualified products, namely boron trifluoride-10 and boron trifluoride-11 can be produced at the same time.
Owner:浙江创世雷博科技有限公司
Gecl4 and/or sicl4 recovery process from optical fibers or glassy residues and process for producing sicl4 from sio2 rich materials
InactiveUS20100272625A1Reduce the temperatureSilicon halogen compoundsGermanium halidesBoronReducing agent
A method is provided for producing GeCl4 with or without SiCl4 from optical fibers, the method comprises the steps of: reacting comminuted optical fibers including germanium and optionally silicon oxides with a reagent including a solid carbonaceous reducing agent, chlorine and a boron compound to obtain a gaseous product including gaseous GeCl4, gaseous SiCl4, and gaseous BCl3 in accordance with the reactions: 2BCl3(g)+1.5GeO2=1.5GeCl4(g)+B2O3; 2BCl3(g)+1.5 SiO2=1.5 SiCl4(g)+B2O; B2O3+1.5C+3Cl2=2BCl3(g)+1.5CO2; and then condensing the gaseous GeCl4, BCl3 and optionally SiCl4 into liquid GeCl4, BCl3 and optionally SiCl4. The invention further provides a method for producing SiCl4 (and optionally GeCl4) from glass residues obtained from optical fiber manufacturing and wasted optical cables. The method includes the steps of: reacting comminuted glassy residues with a reagent including a solid carbonaceous reducing agent, a salt, a boron compound to obtain a gaseous product including SiCl4, BCl3, and optionally GeCl4; and then condensing the gaseous SiCl4, BCl3 (with or without GeCl4) into liquid SiCl4, BCl3 and GeCl4. There is also provided a method for producing SiCl4 from a SiO2 containing material.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE
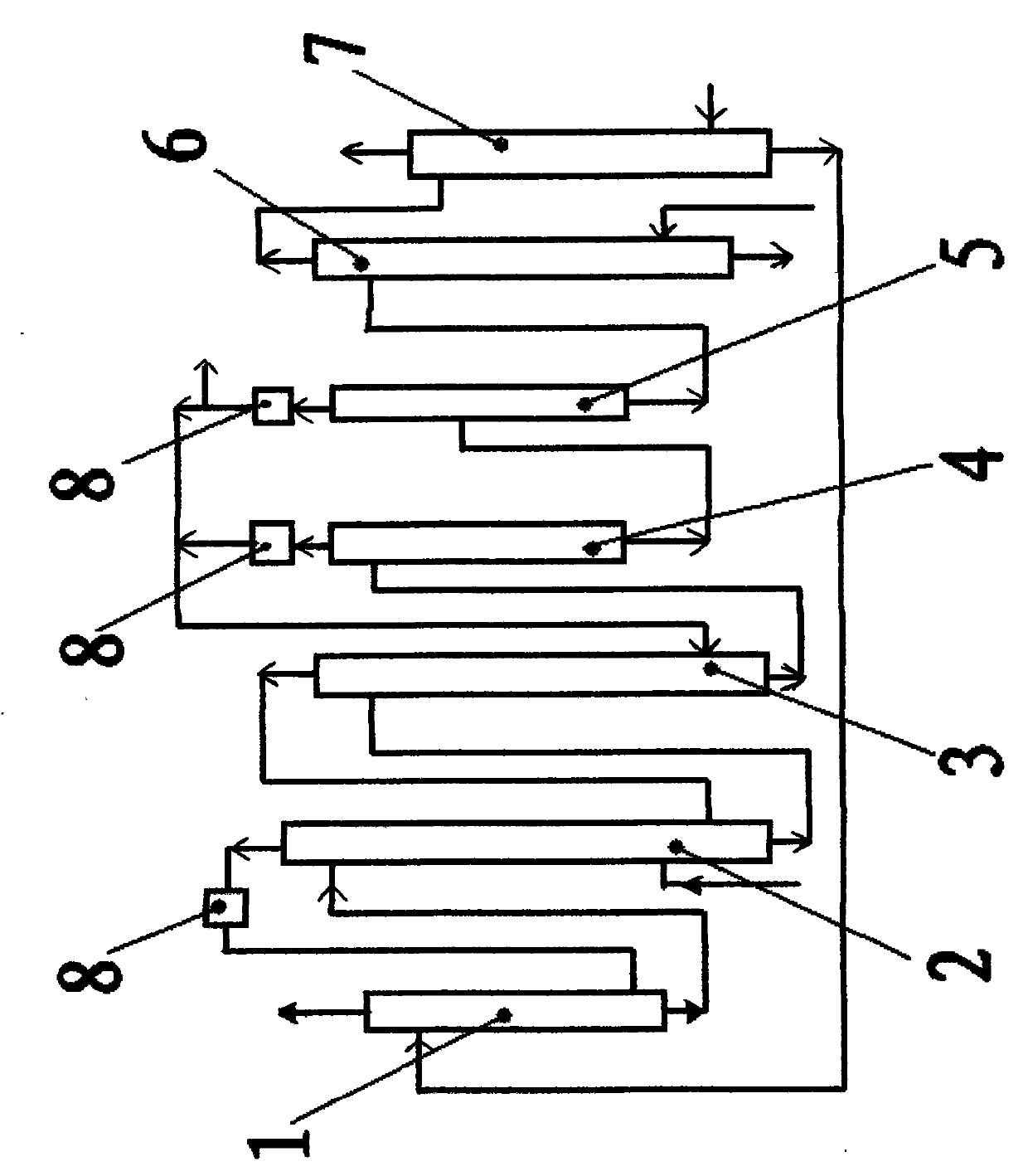
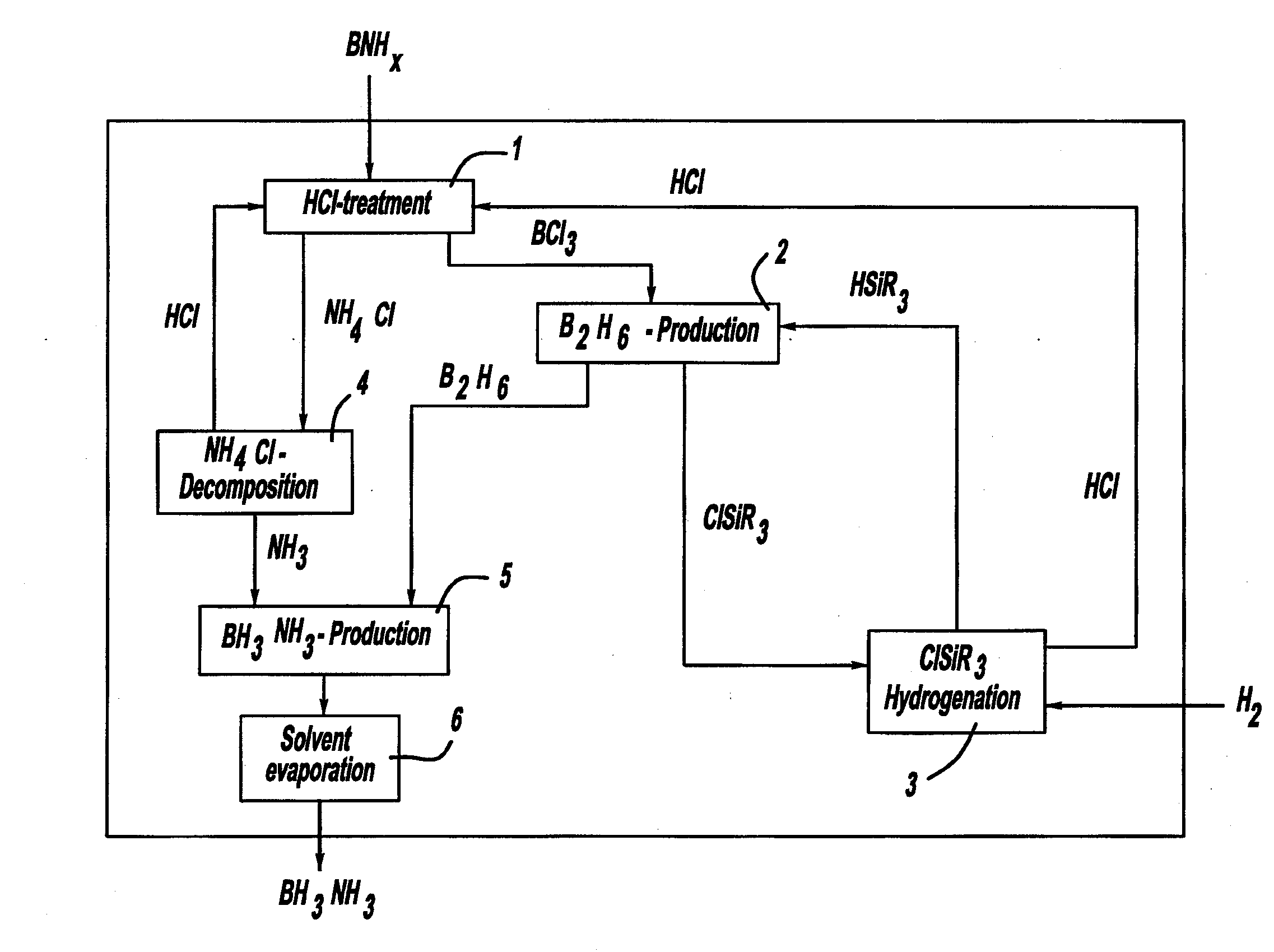
Procedure for the hydrogenation of bnh-containing compounds
InactiveUS20080193356A1Improve energy efficiencyNitrogen compoundsOther chemical processesHydrogen halideCompound a
A process for producing borazane from boron-nitrogen and boron-nitrogen-hydrogen containing BNH-waste products. The process includes reacting the BNH-waste products with a hydrogen halide, having the formula HX, wherein X is selected from the group consisting of F, Cl, Br, I, and combinations thereof, to form any of the following: a boron trihalide, having the formula BX3, an ammonium halide, having the formula NH4X, and hydrogen. The boron trihalide is then reacted with the hydrogen to form diborane, having the formula B2H6, and hydrogen halide. The ammonium halide is then converted to ammonia, having the formula NH3, and hydrogen halide. The diborane is then reacted with the ammonia to form borazane, having the formula BH3NH3.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
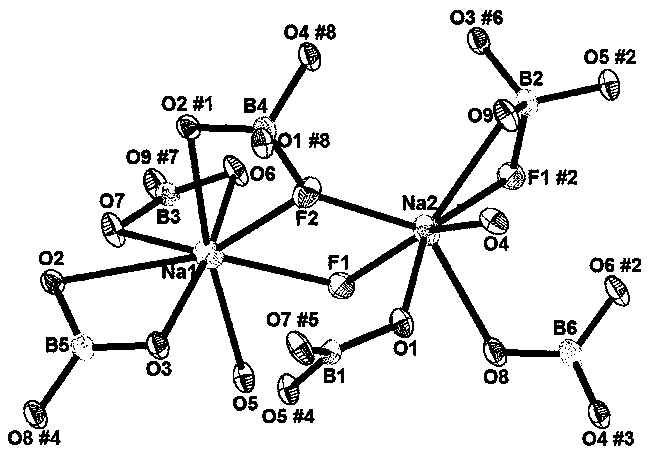
Sodium fluoborate compound, sodium fluoborate birefringent crystal as well as preparation method and application
ActiveCN108070902ASmall sizePolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltSpace groupBeam splitter
The invention relates to a sodium fluoborate compound, a sodium fluoborate birefringent crystal as well as a preparation method and an application. The compound has the chemical formula of Na2B6O9F2 and molecular weight of 292.84 and is prepared with a solid phase method. The sodium fluoborate birefringent crystal has the chemical formula of Na2B6O9F2 and molecular weight of 292.84 and belongs toa monoclinic system, the space group is P21 / c and the cell parameters are a=8.1964(12) angstrom, b=13.0005(19) angstrom, c=7.8955(11) angstrom, Z=4 and V=841.3(2) angstrom<3>, and the crystal is grownwith a flux method. The crystal is the birefringent crystal having centimeter-level large size and belonging to the monoclinic system, has birefringence of 0.080 at 589.3 nm and ultraviolet transmitting waveband cut-off edge of 169 nm and is suitable for the birefringent crystal. The crystal has the advantages that the operation is simple, the cost is low, used reagents are inorganic raw materials, the toxicity is low, the growth cycle is short, physical and chemical properties are stable and the like in the growth process. The crystal has important applications in preparation of Glan prisms,Wollaston prisms, Rochon prisms or polarizing beam splitter prisms, optoisolators, circulators and beam displacers.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com