Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
131results about "Boron/borides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hexaboride particles, hexaboride particle dispersion, and article making use of hexaboride particles or hexaboride particle dispersion
ActiveUS20050161642A1Improve water resistanceImprove waterproof performancePigmenting treatmentBoron/boridesAlkoxy groupSide chain
In hexaboride particles having particles of a hexaboride of at least one element (X) selected from Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu, Sr and Ca, or a dispersion of such particles, the surfaces of the hexaboride particles have physically been coated with a surface treatment agent containing silicon, selected from a silazane type treatment agent, a chlorosilane type treatment agent, an inorganic treatment agent having at least one alkoxyl group in the molecular structure, and an organic treatment agent having at least one alkoxyl group at a molecular terminal or in the side chain, or have been coated with the surface treatment agent, having chemically combined with hexaboride particles on the surfaces of the hexaboride particles.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
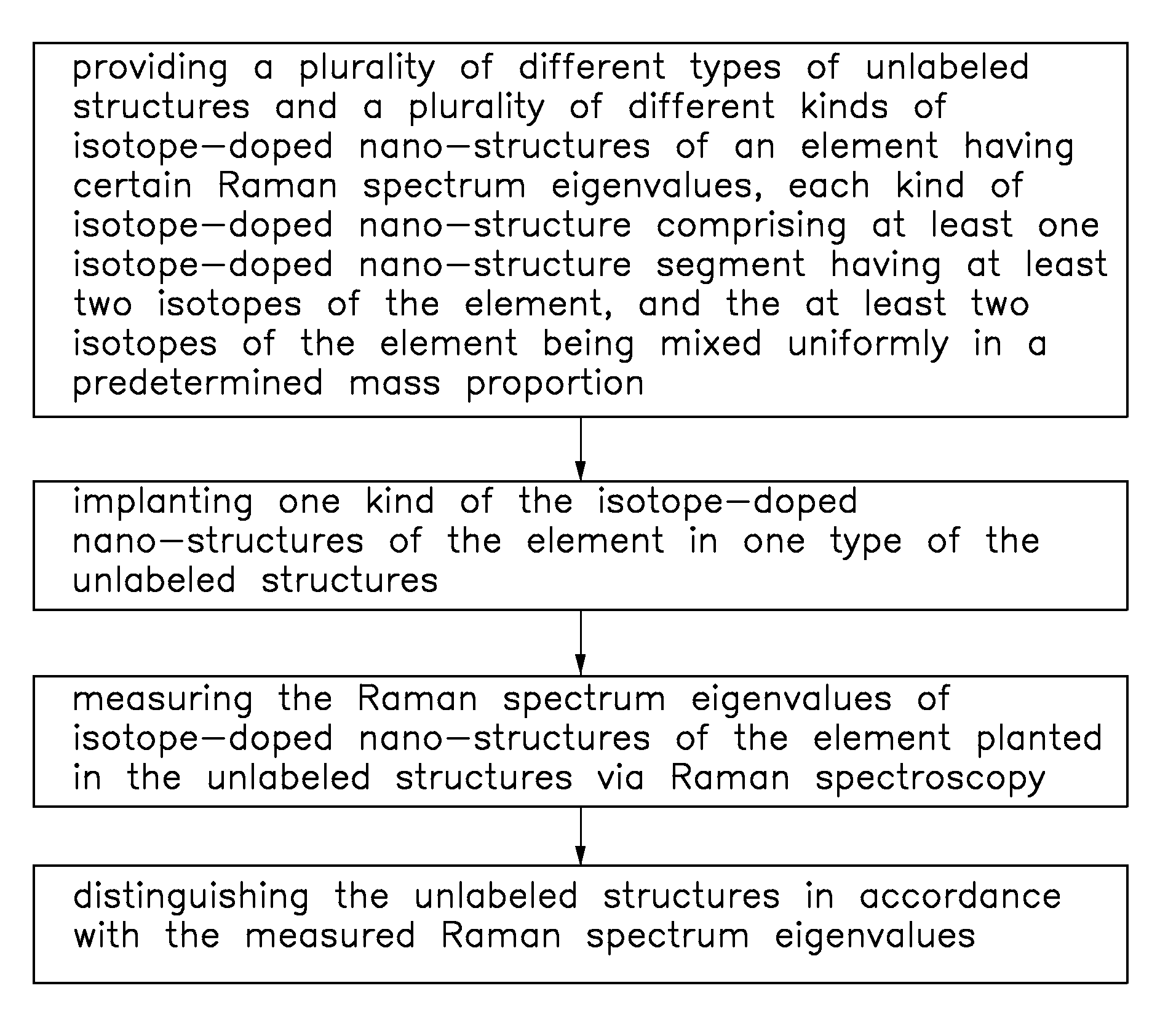
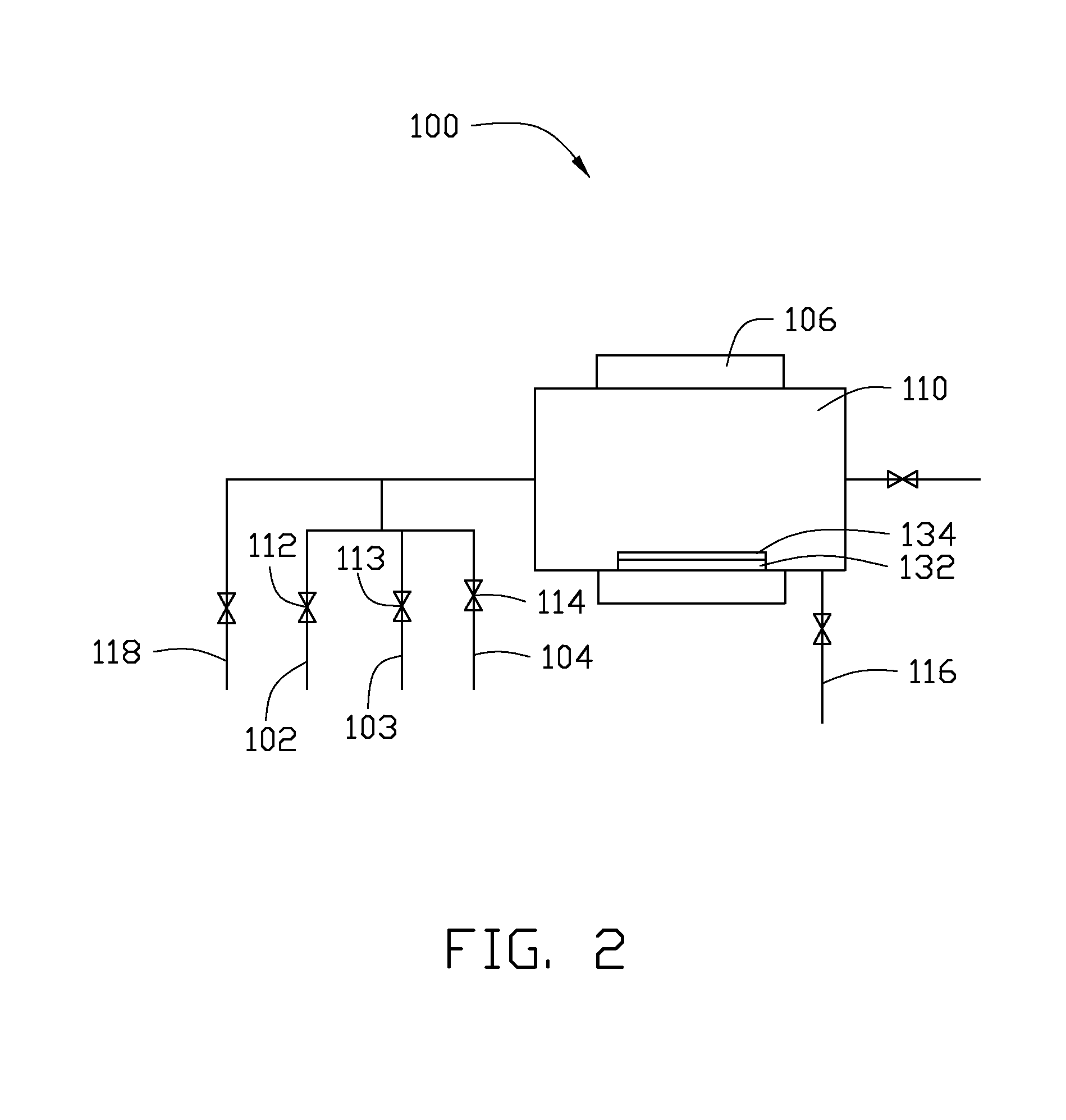
Isotope-doped nano-material, method for making the same, and labeling method using the same
An isotope-doped nano-structure of an element is provided. The isotope-doped nano-structure includes at least one isotope-doped nano-structure segment having at least two isotopes of the element, and the at least two isotopes of the element are mixed uniformly in a certain proportion. The present disclosure also provides a method for making the isotope-doped nano-structures, and a labeling method using the isotope-doped nano-structures.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
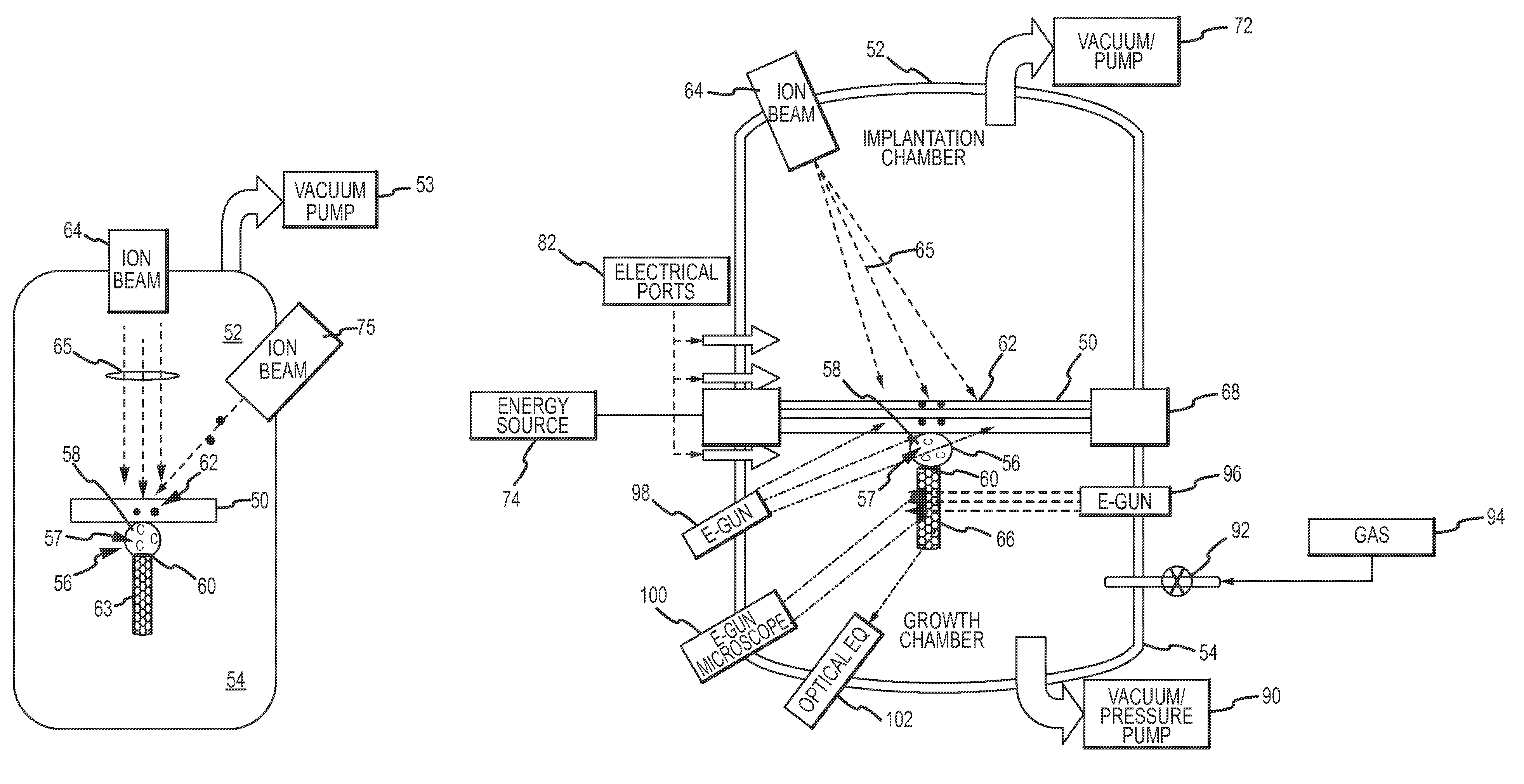
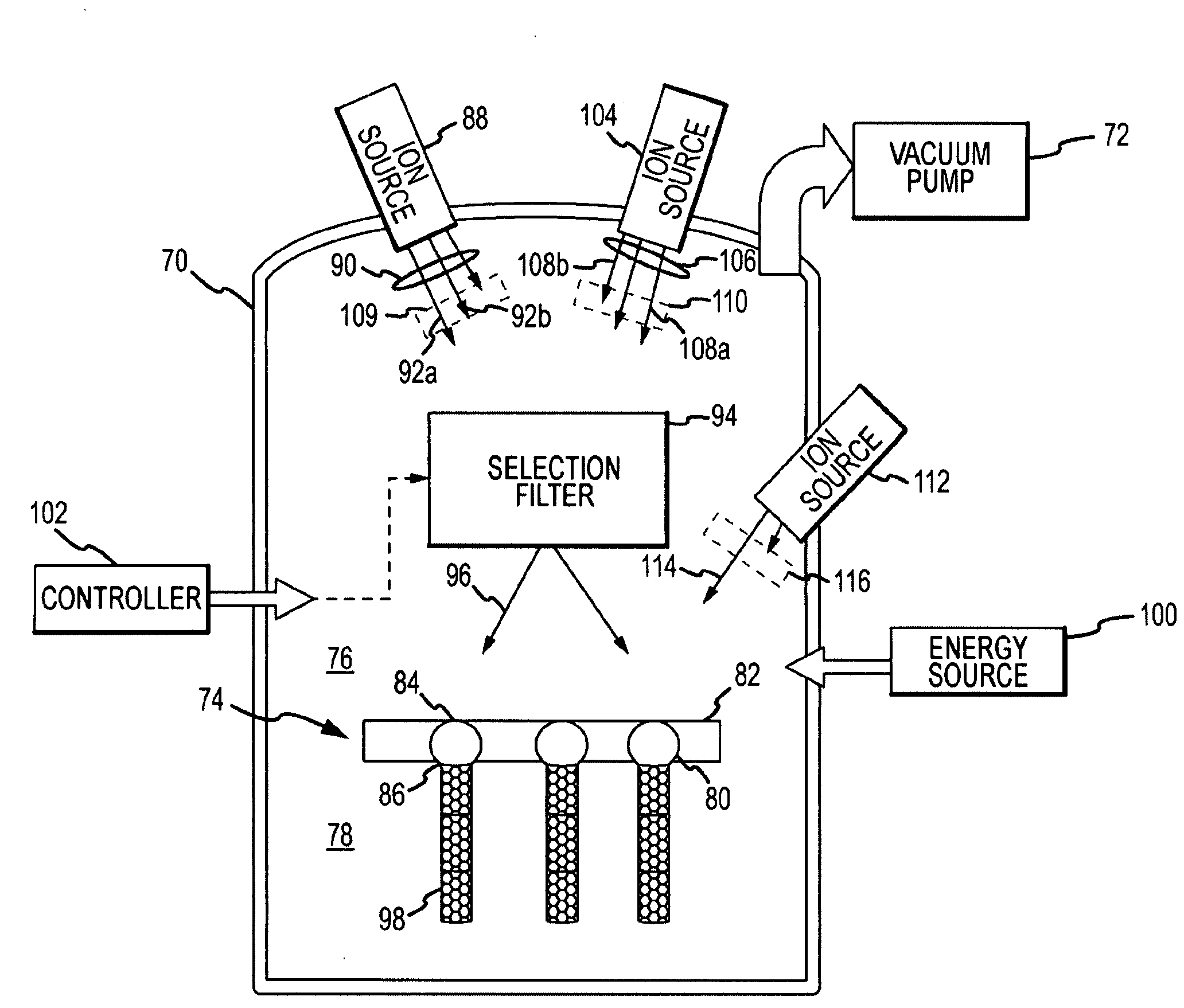
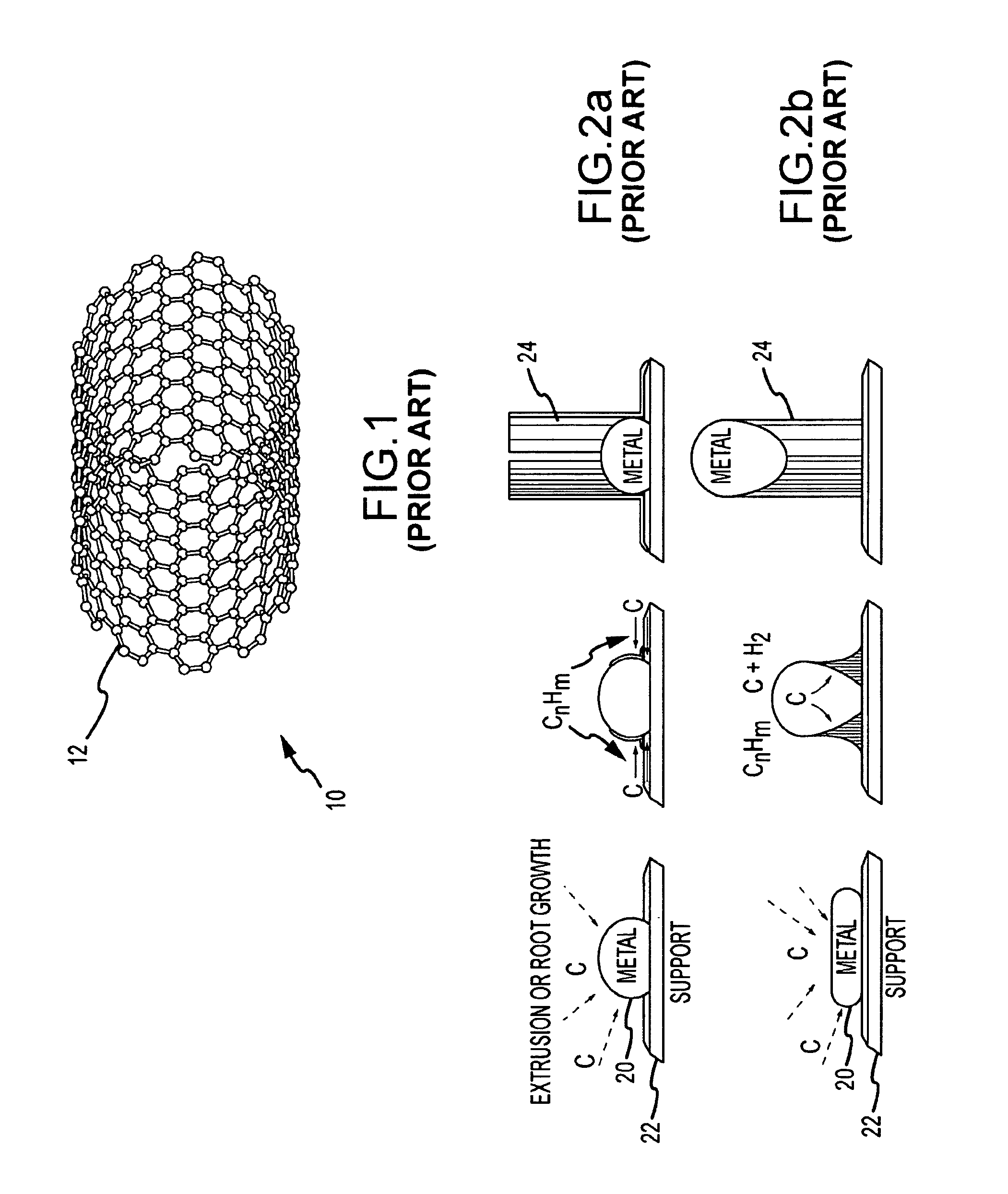
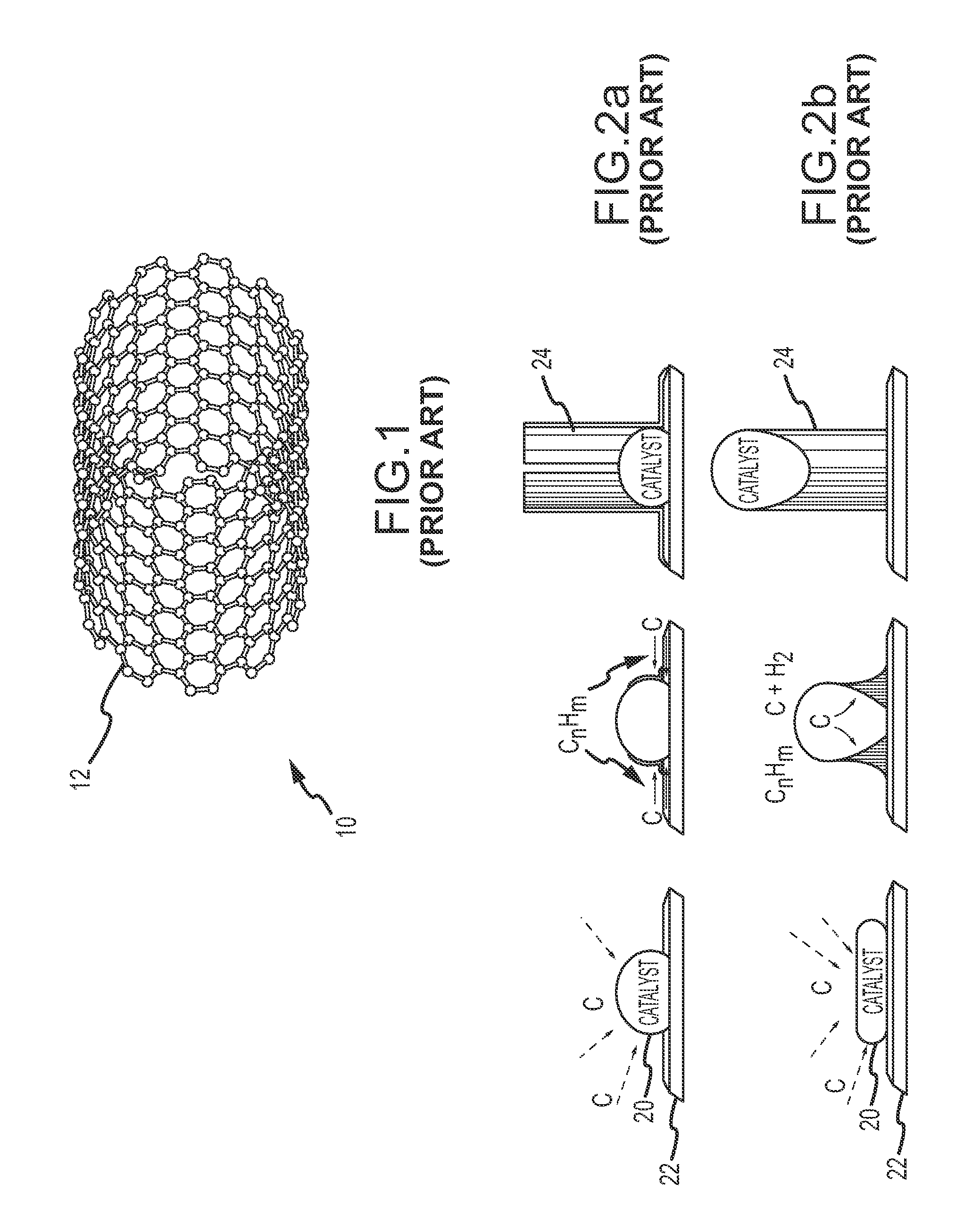
System and method for growing nanotubes with a specified isotope composition via ion implantation using a catalytic transmembrane
ActiveUS20090252887A1Avoid contaminationAvoid erosionMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen compoundsDopantIsotopic composition
An ion source(s) is configured to generate ions from one or more elements including a plurality of different isotopes or unique molecular combinations of two or more different isotopes from at least one of the selected elements. A selection filter(s) directs a subset of the ions onto a catalytic transmembrane to grow nanotubes of a specific isotope composition on the opposite side of the transmembrane. The nanotubes may be uniformly or selectively doped with dopant atoms. A controller can configure the selection filter(s) to sequentially pass different subsets of ions to form isotope, molecular or element junctions in the growing nanotubes.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +1
System and method for nanotube growth via ion implantation using a catalytic transmembrane
ActiveUS20090252886A1Promote continued growthGood flexibilityNanotechNitrogen compoundsHigh energyIon implantation
Ion implantation is used to grow nanotubes out of carbon and other materials. Catalytic material is placed on or in a membrane that physically and possibly environmentally separates an implantation chamber or region from a growth chamber or region. High-energy ions are implanted into the catalytic material from one side to grow nanotobes on an exposed surface in the growth chamber. Ion implantation via the membrane provides for greater flexibility to separate and independently control the implantation and growth processes.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
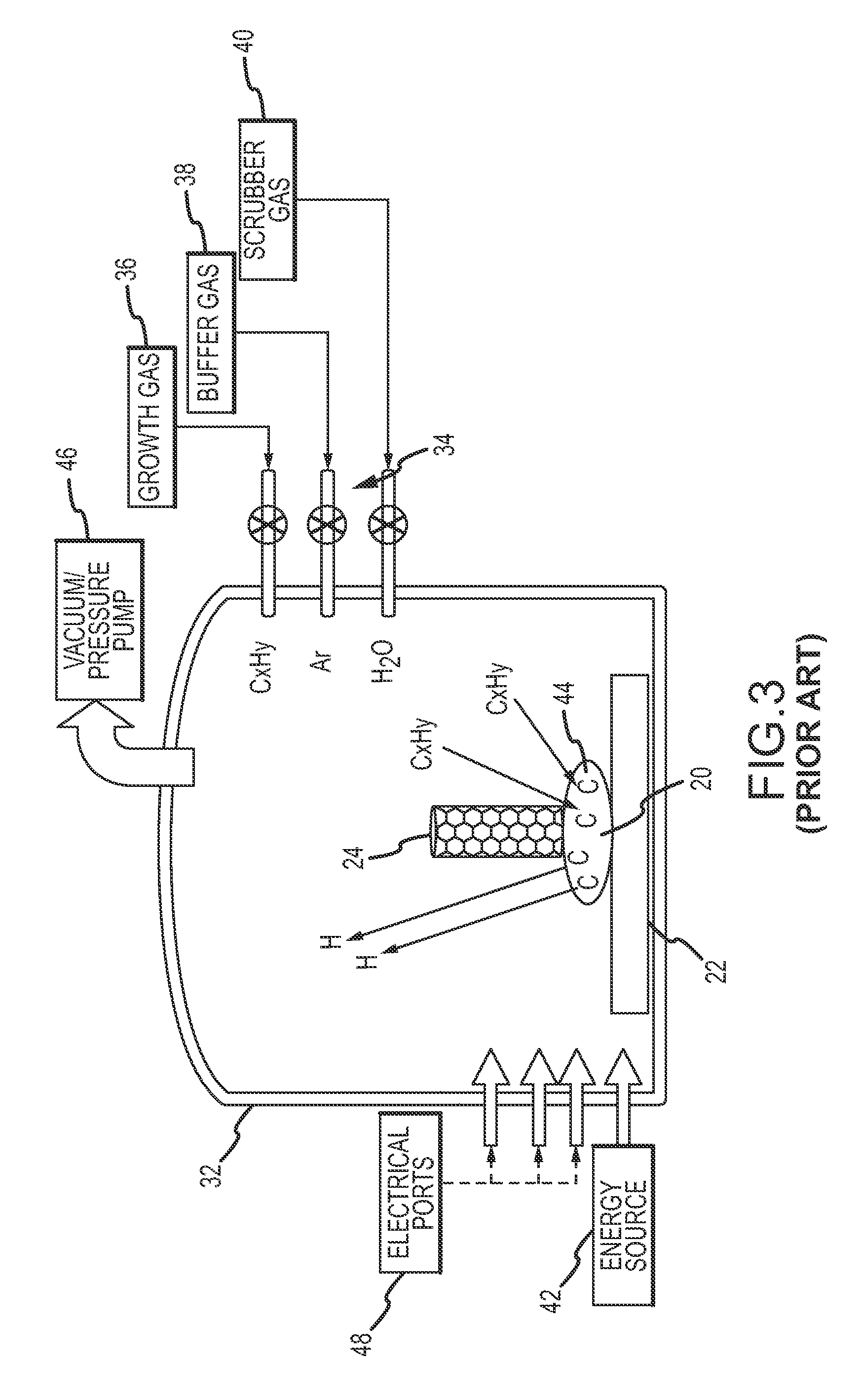
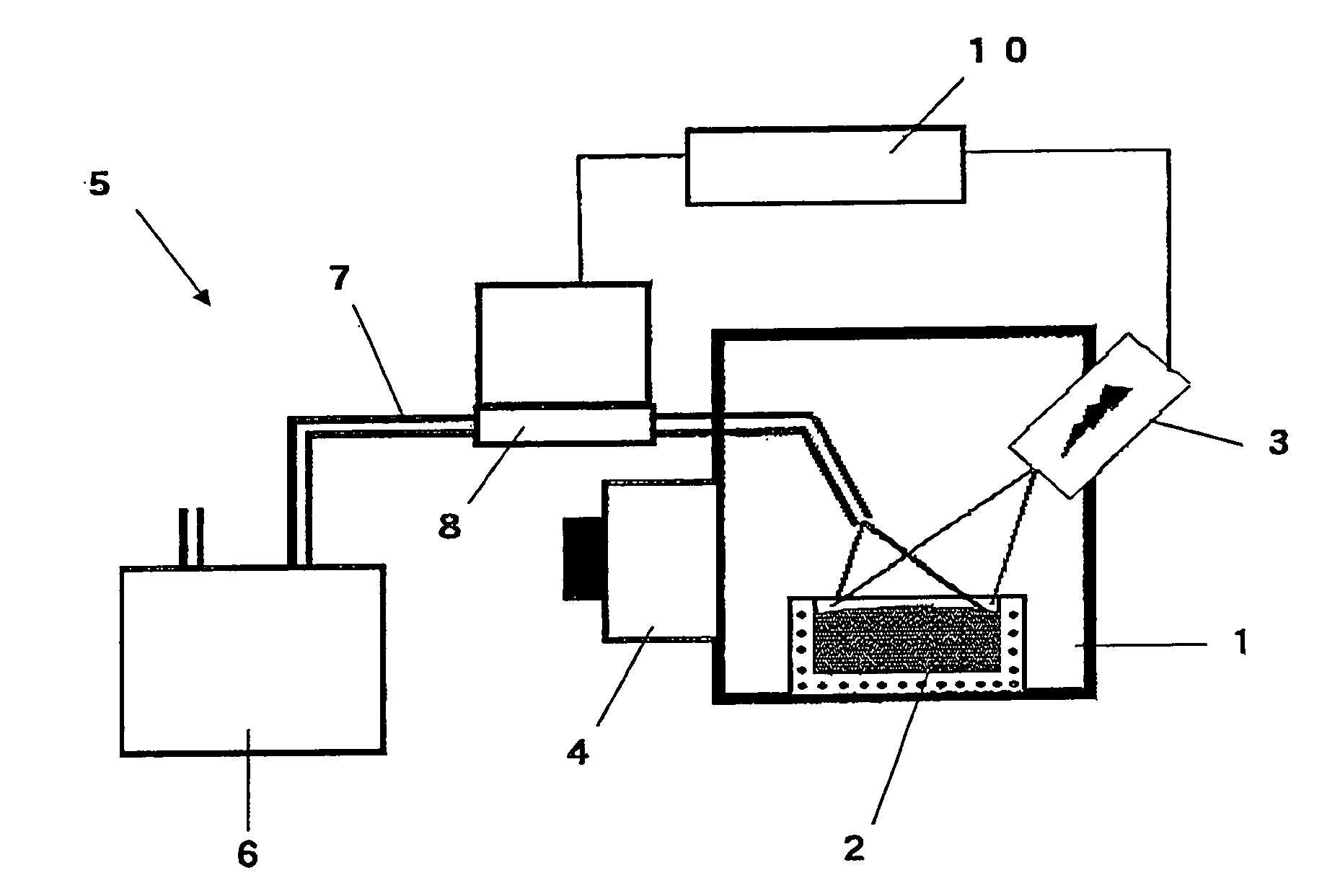
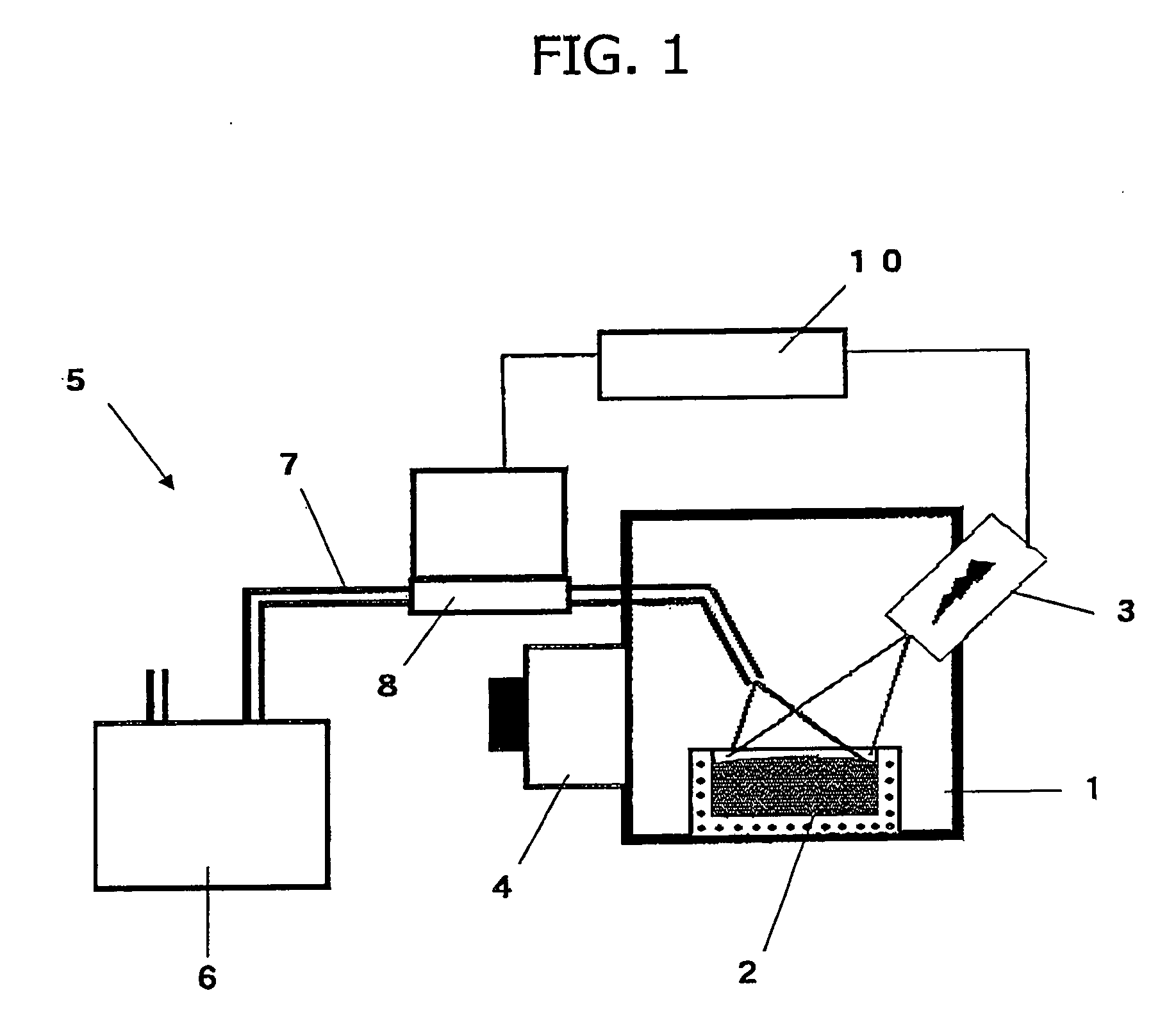
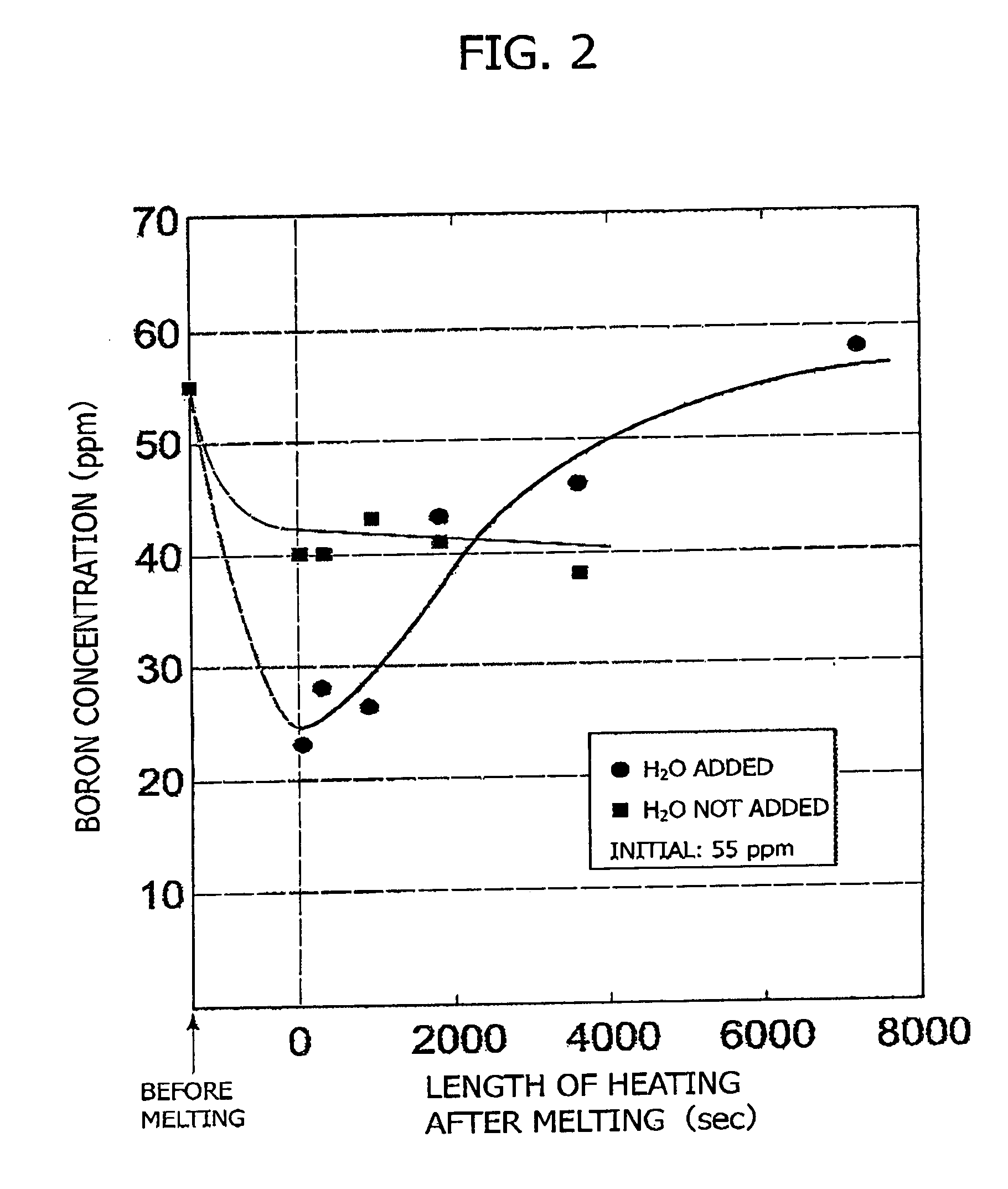
Method and apparatus for refining boron-containing silicon using an electron beam
InactiveUS20060123947A1Efficient removalInhibition formationBoron/boridesElectric furnaceBoron containingIrradiation
In a refining method for boron-containing silicon, boron-containing silicon is irradiated with an electron beam in a vacuum vessel to melt the boron-containing silicon. A boron compound-forming substance is introduced into the vacuum vessel, and boron contained in the molten silicon is formed into a boron compound. After at least a portion of the boron compound has vaporized, irradiation with the electron beam is stopped. The high-purity molten silicon can then be solidified.
Owner:IIS MATERIALS CORP
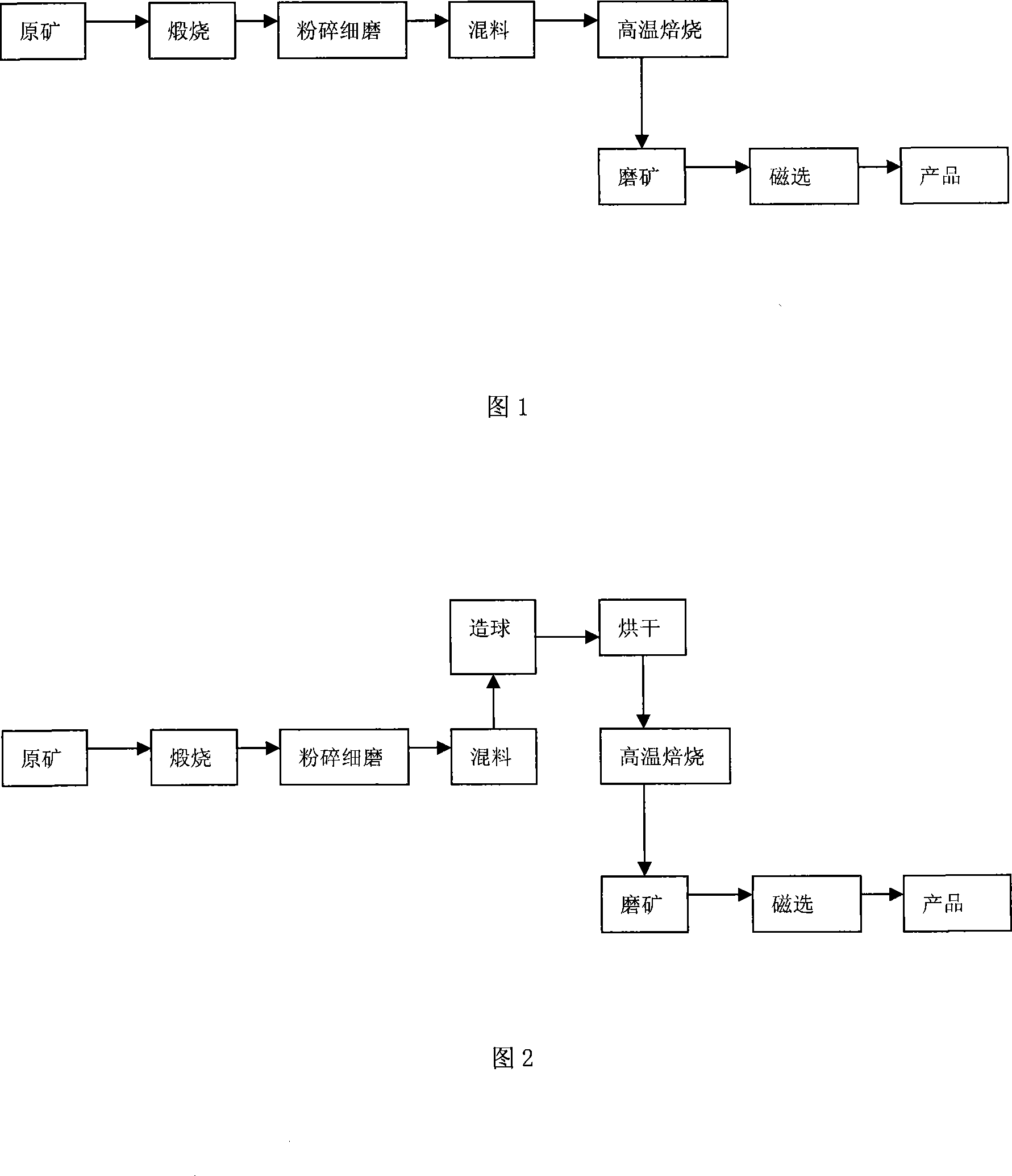
Concentration method for iron and boron in low-grade paigeite
InactiveCN101157977ATake advantage ofBoron/boridesMagnetic separationLimited resourcesEconomic benefits
An enriched method of iron and boron by using low-grade ferroboron ore pertains to the field of iron-smelting, in particular to an enriched method of iron and boron by using low-grade ferroboron ore, which applies for the exploitation and use of low-grade ferroboron ore. The method is characterized in that the low-grade ferroboron ore of boron content between 5 percent and 10 percent is taken as raw material and is calcined, cracked, grinded, mixed with solid reducer, baked and magnetic-picked to get the boron concentrate power of boron content between 12 percent and 15 percent and the iron concentrate power of iron content between 60 percent and 90 percent. Consequently, the limited resource of boron and iron is sufficiently used, which has great significance for both the society and economic benefit.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
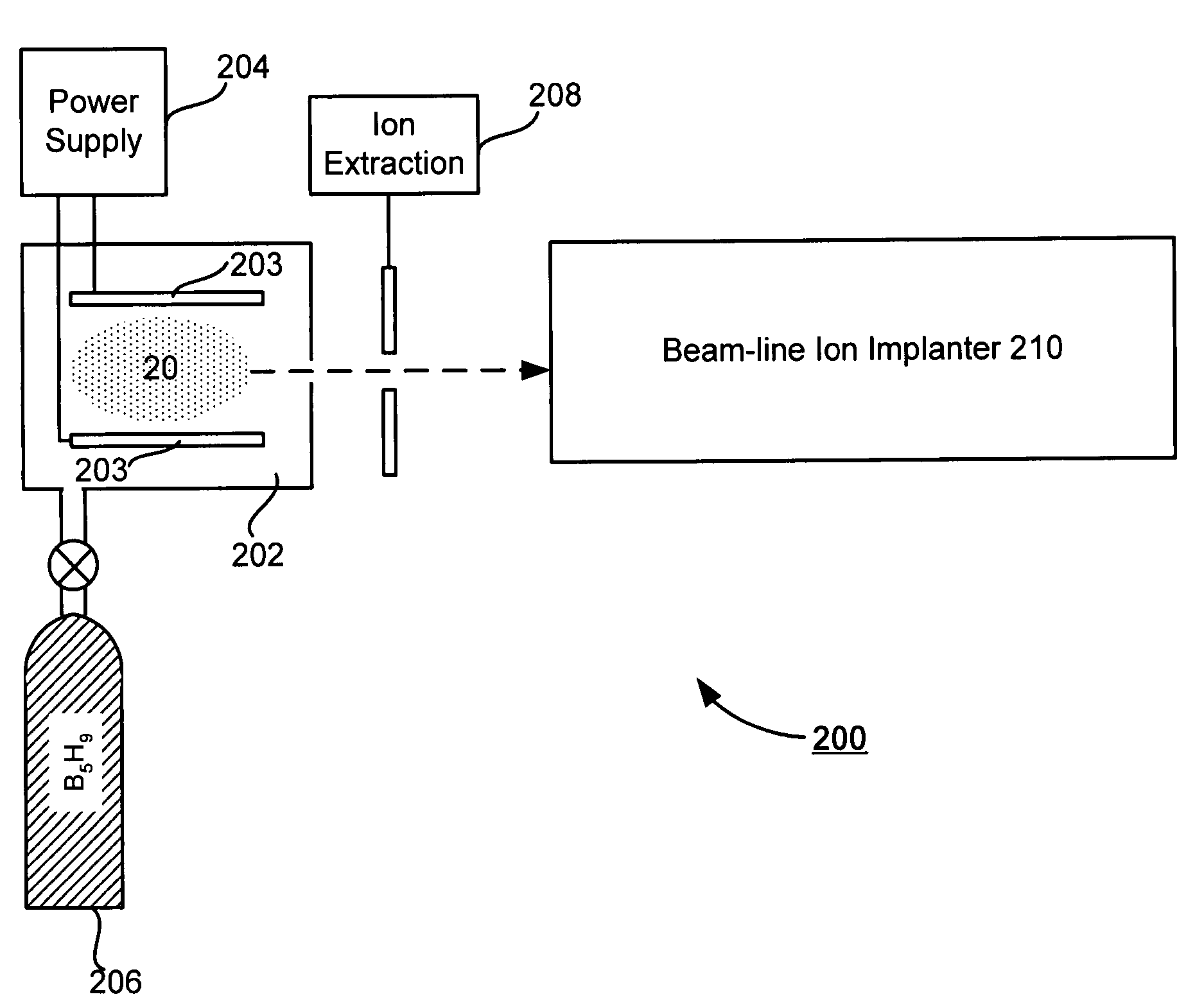
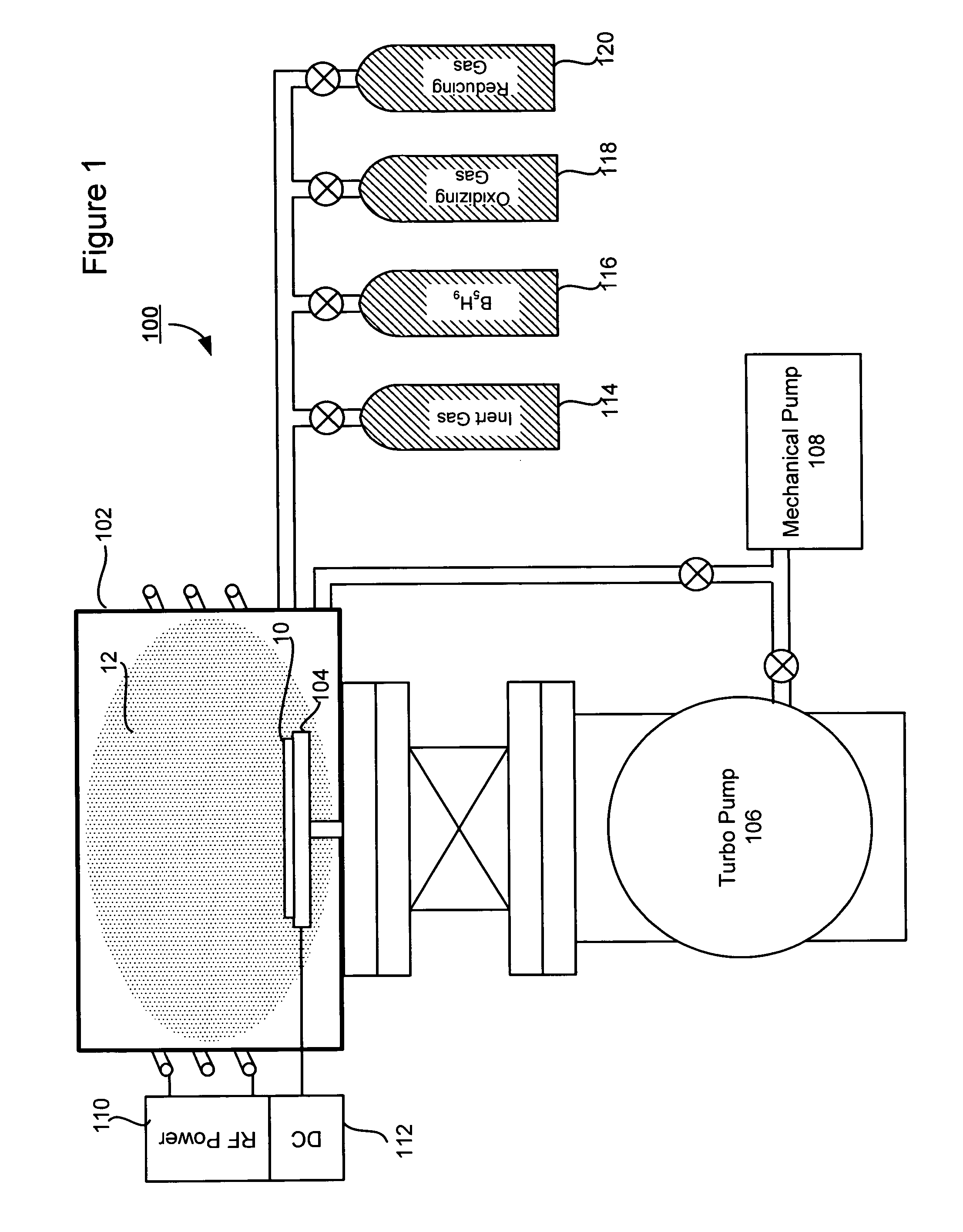
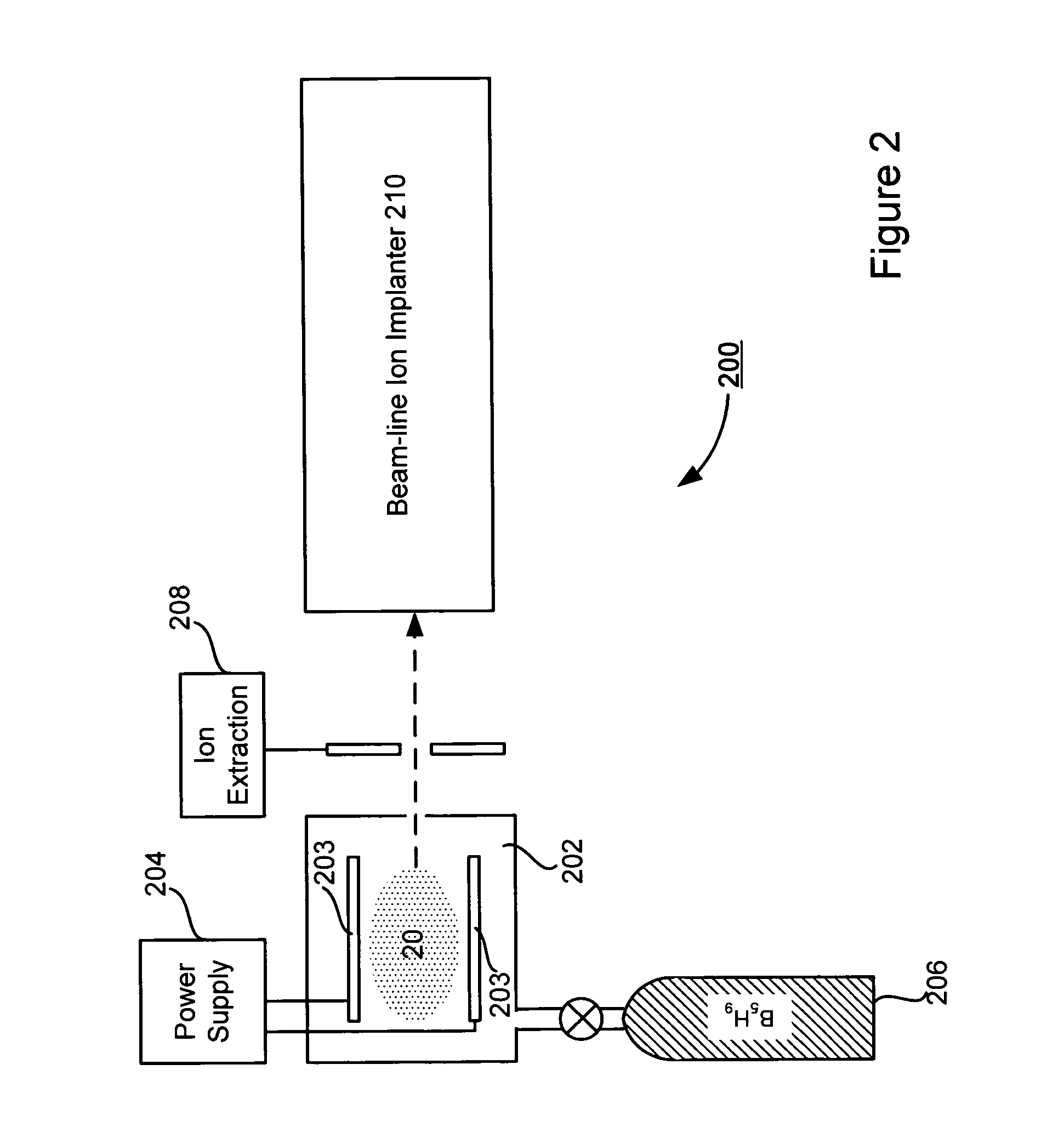
Technique for boron implantation
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Technique for separating boron isotope with boron specific resin ion-exchange chromatography
ActiveCN101274217AEasy to separateHigh separation factorCation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersIon exchangeIsotope
The invention provides a process for separating boron isotope with a boron special-effect resin ion exchange chromatography. The process adopts chelate-typed ion exchanging resin-boron special-effect resin, separates <10>B from boric acid solution, and uses hydrochloric acid or nitric acid as eluent to separate the boron isotope in the boric acid solution by the adsorption of the boric acid on resin columns and the washing of the eluent on the boric acid adsorbed on the resin. According to the process of the invention, the enrichment ratio of the <10>B can be enriched from natural 20 percent or so to 91 percent or so, with fast enrichment speed. The process of the invention is a simple and high-efficiency process which separates the boron isotope from the boric acid solution.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Technique for boron implantation
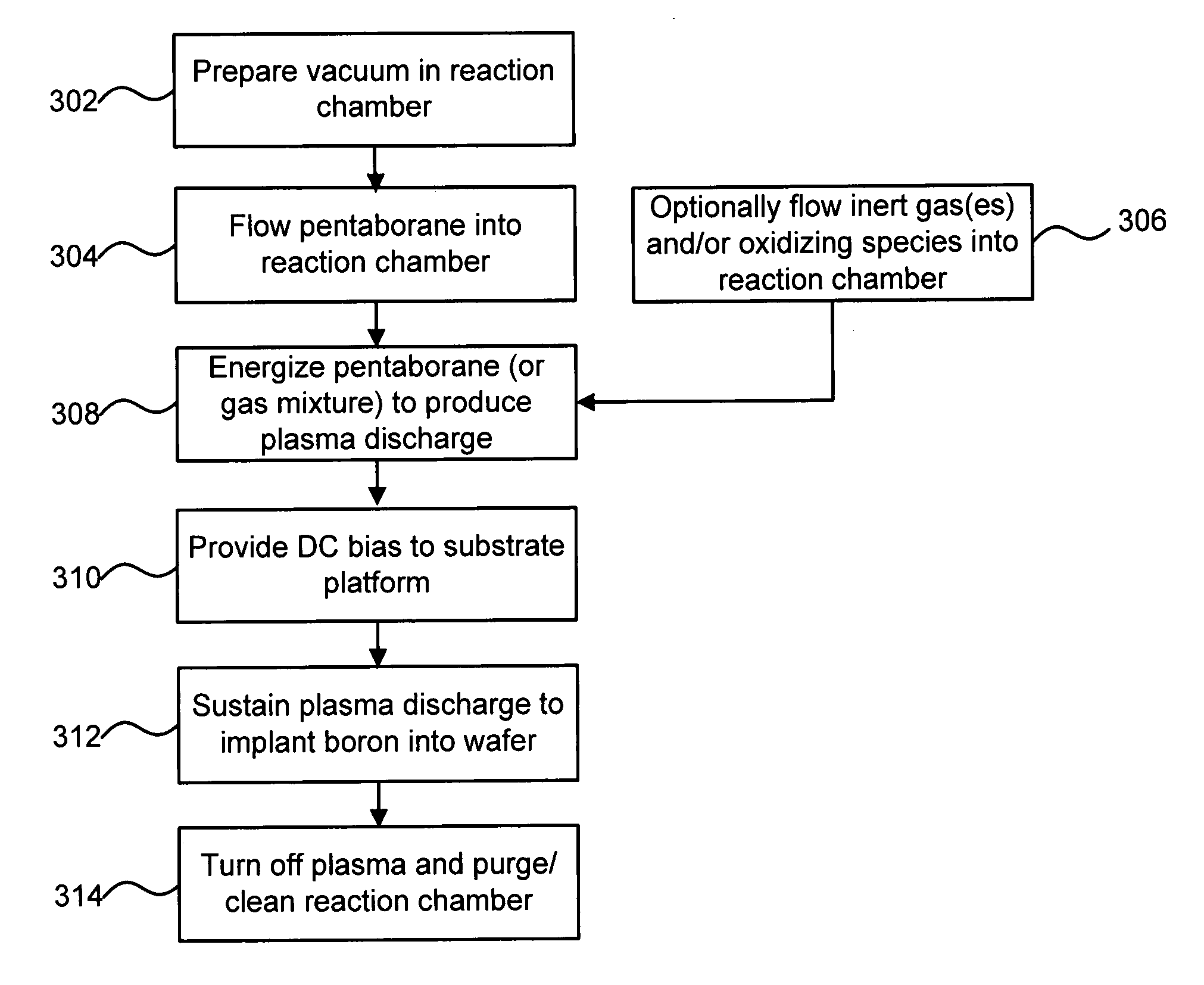
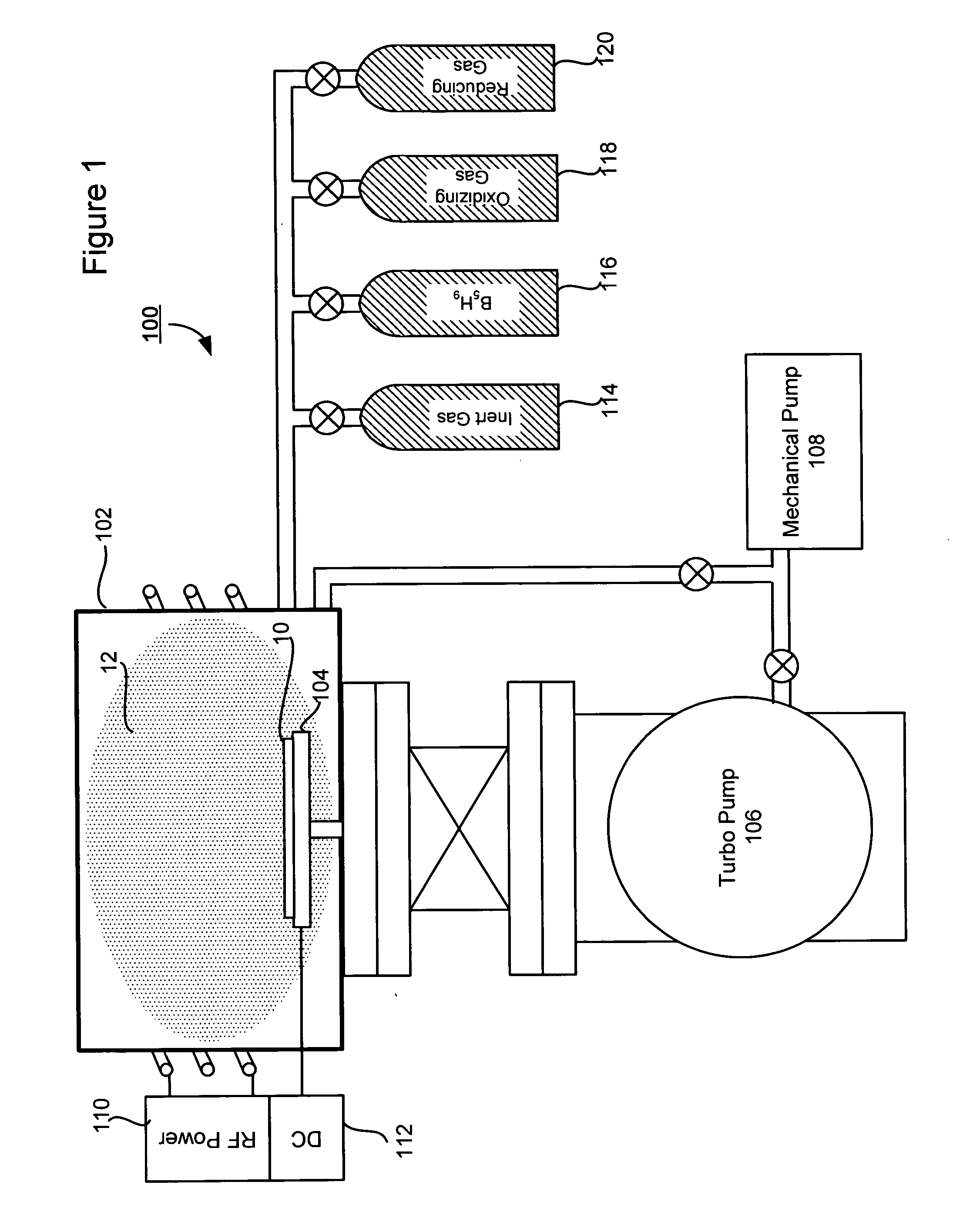
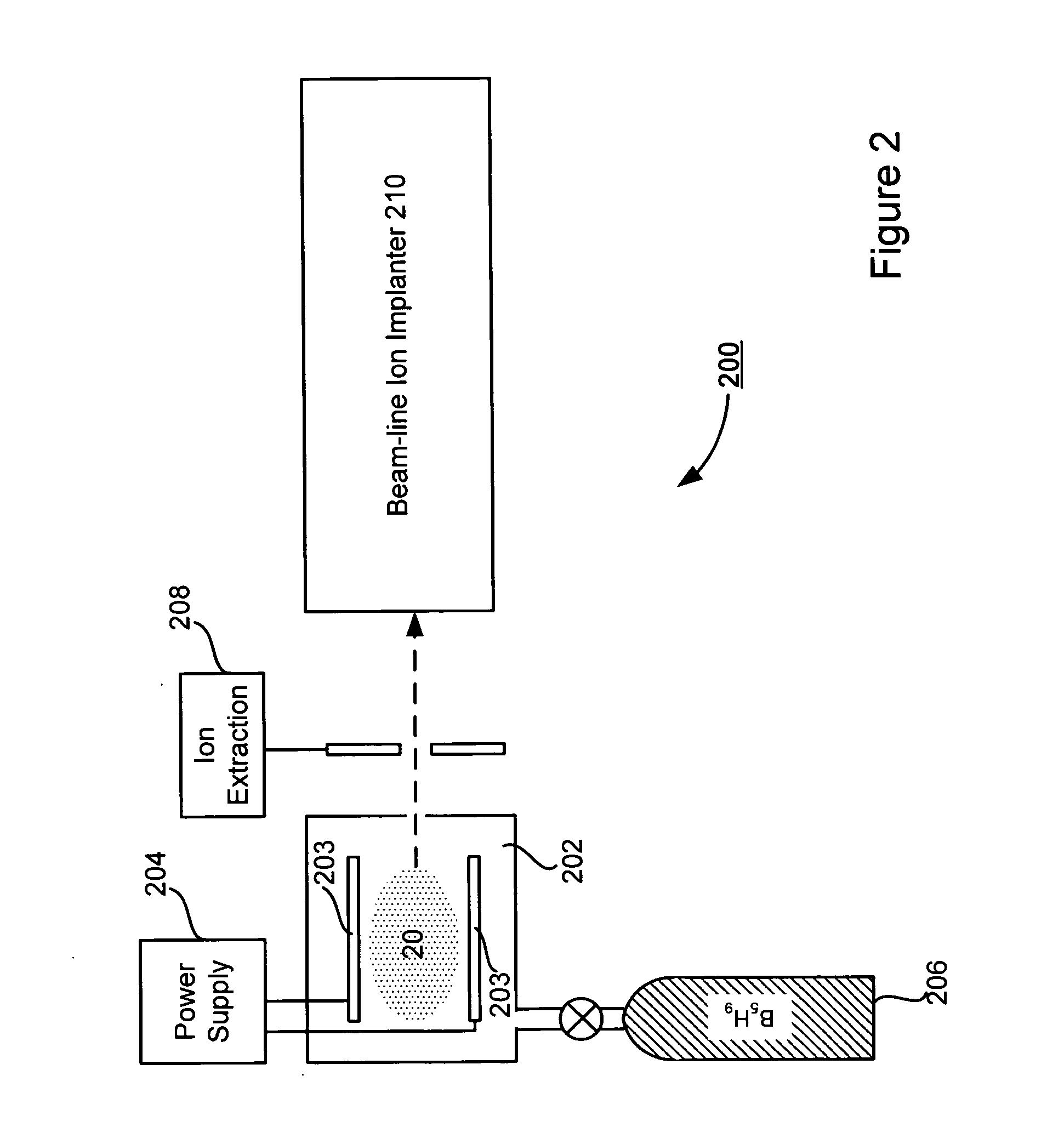
A technique for boron implantation is disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the technique may be realized by an apparatus for boron implantation. The apparatus may comprise a reaction chamber. The apparatus may also comprise a source of pentaborane coupled to the reaction chamber, wherein the source is capable of supplying a substantially pure form of pentaborane into the reaction chamber. The apparatus may further comprise a power supply that is configured to energize the pentaborane in the reaction chamber sufficiently to produce a plasma discharge having boron-bearing ions.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
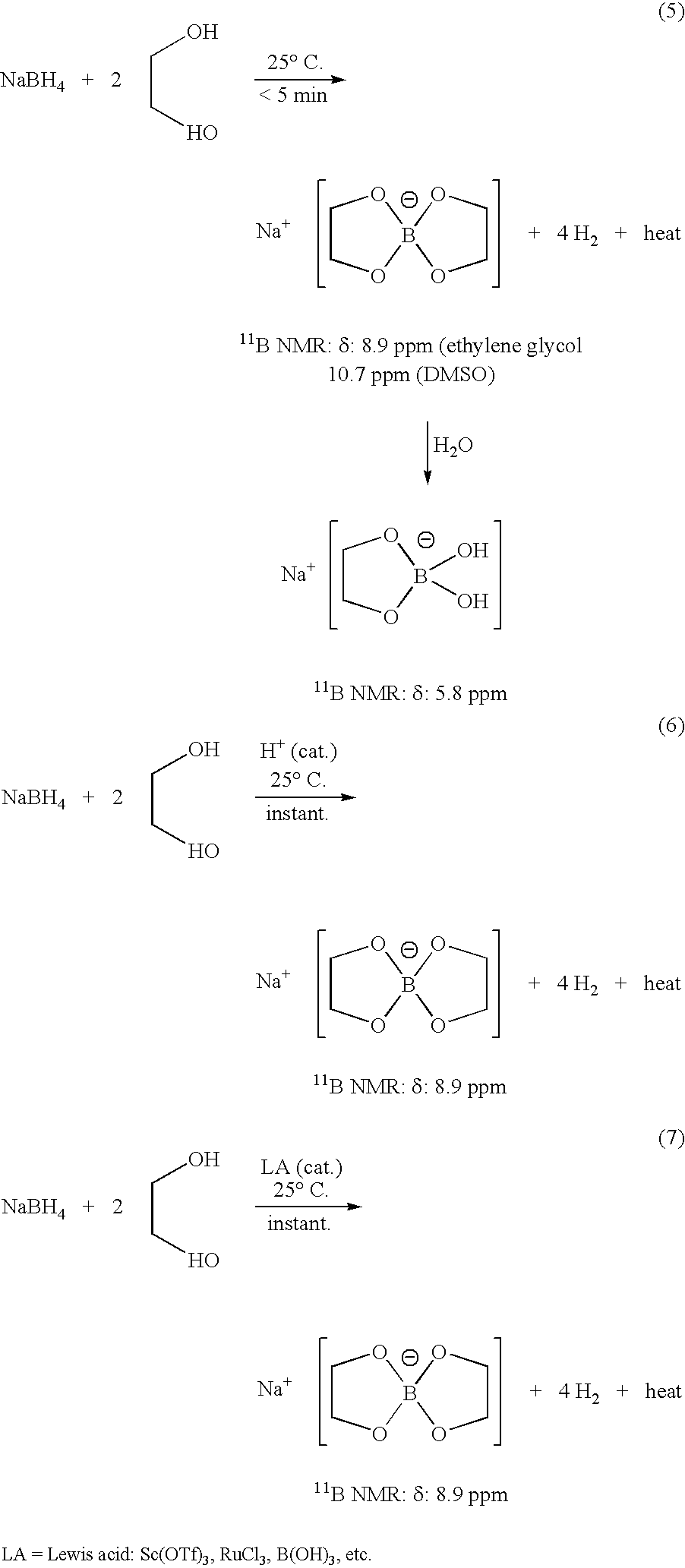
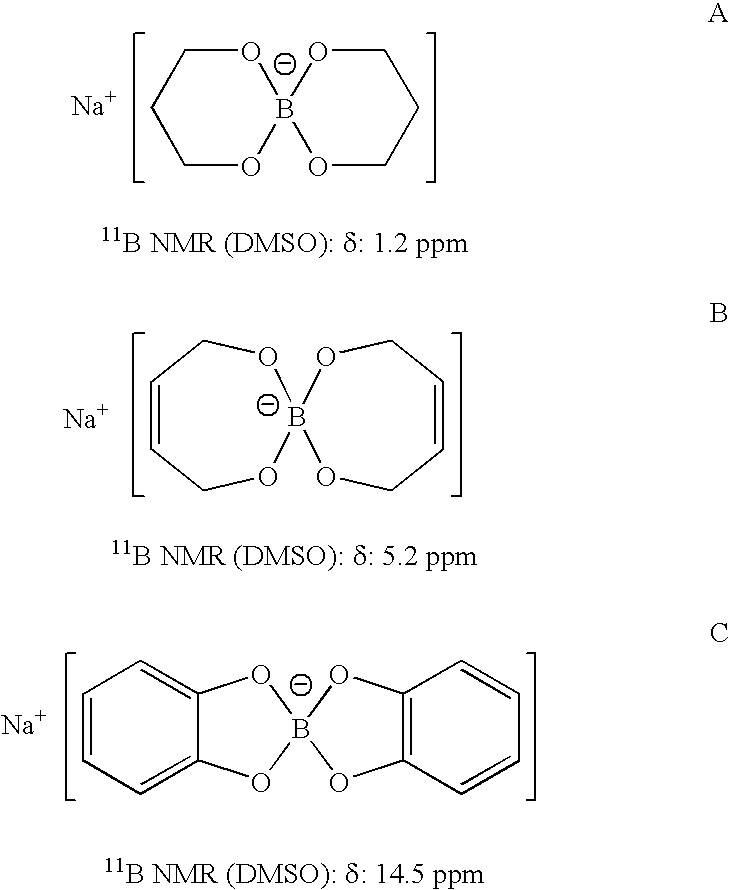
Method of controlled alcoholysis and regeneration of a borohydride
InactiveUS20050255024A1Efficient procedureEffective protocolMonoborane/diborane hydridesBoron/boridesSodium borohydrideBoric acid
Methods of controlled hydrolysis / alcoholysis and regeneration of a borohydride are disclosed. Examples of the present invention show that hydrolysis of sodium borohydride or lithium borohydride with dilute acid provides simultaneous generation of H2 and boric acid for recycling. Other examples of the present invention show methods for regenerating a borohydride by reacting an aluminum hydride to a borate compound to provide a regenerated borohydride.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
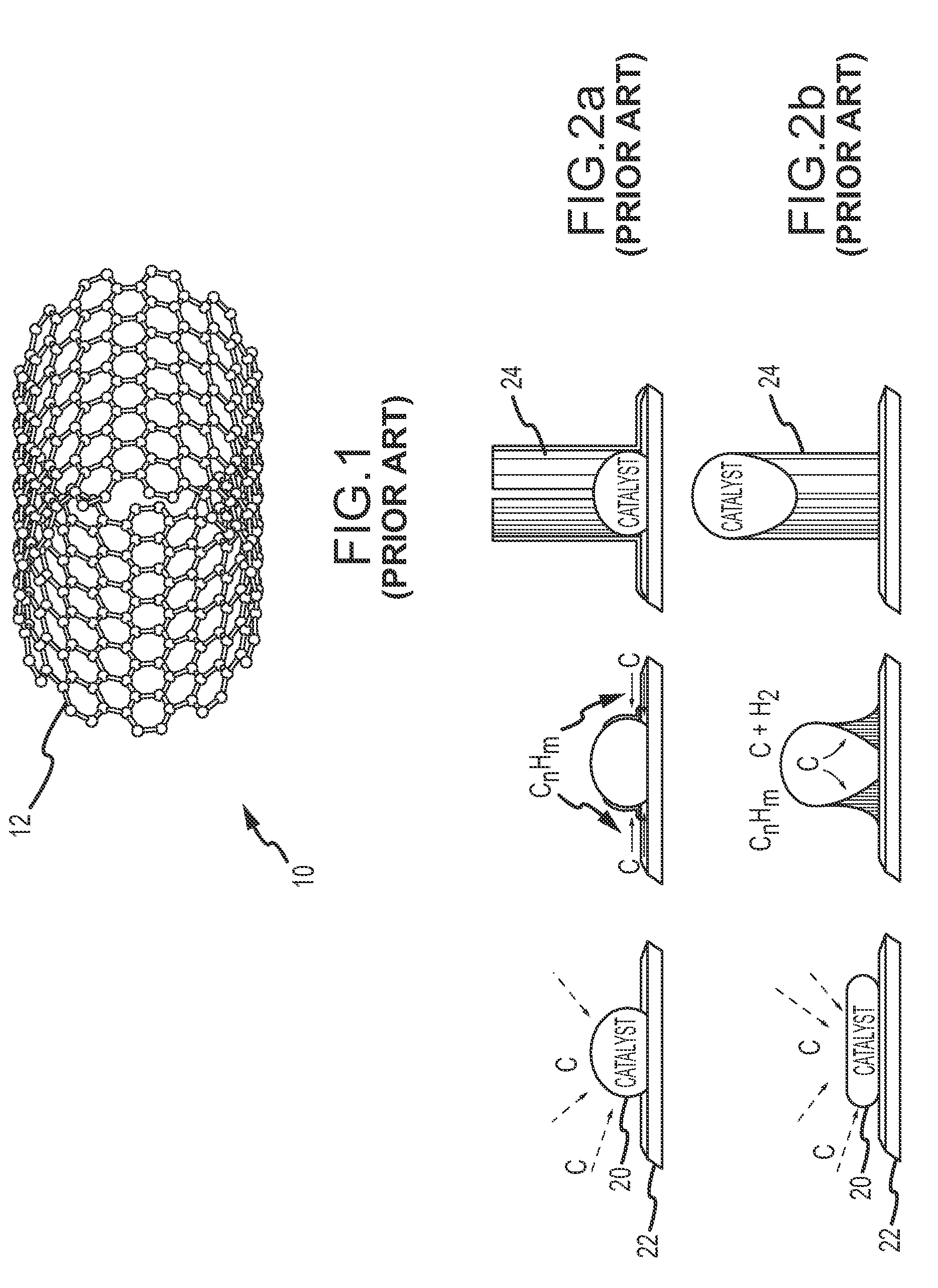
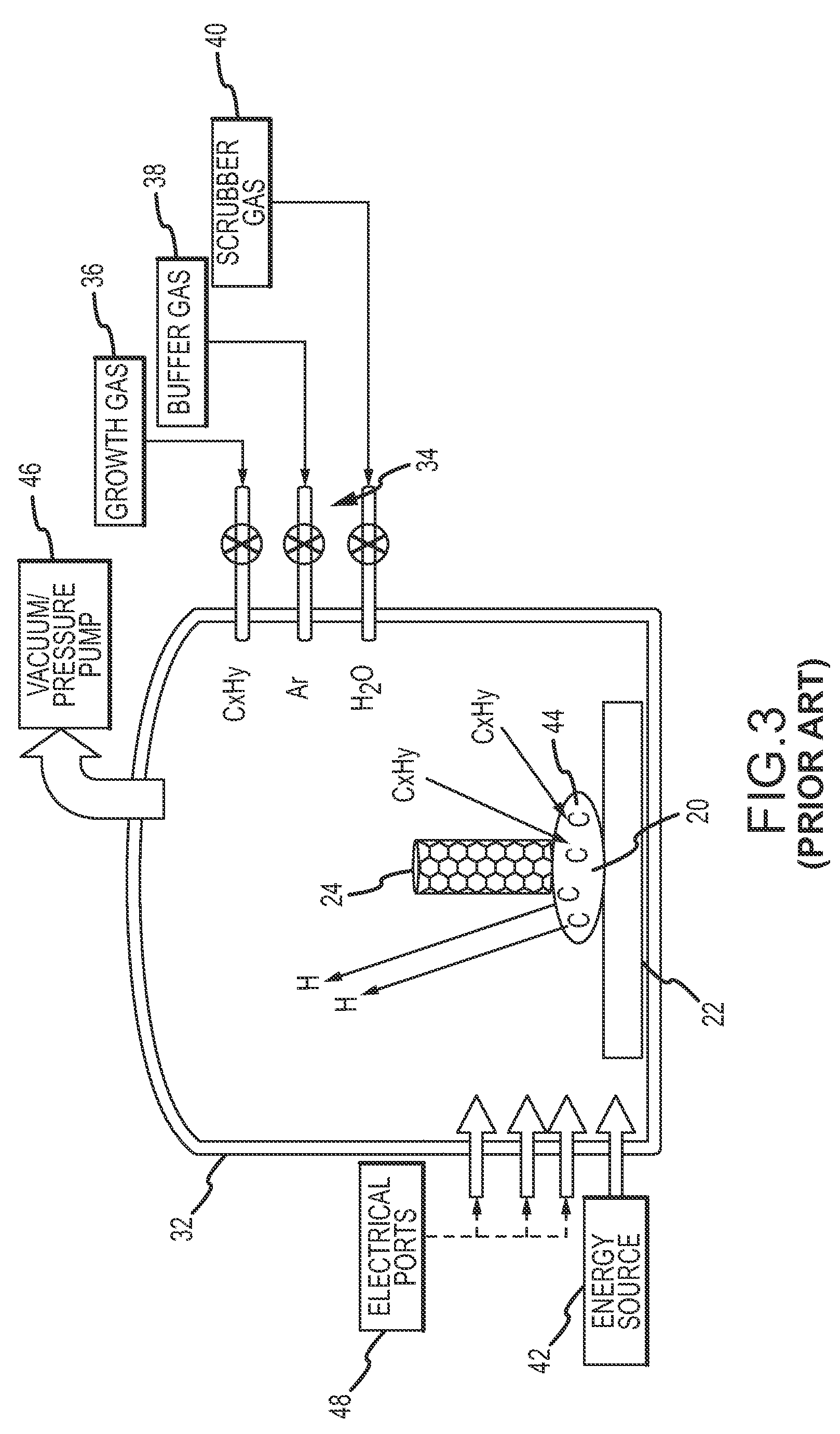
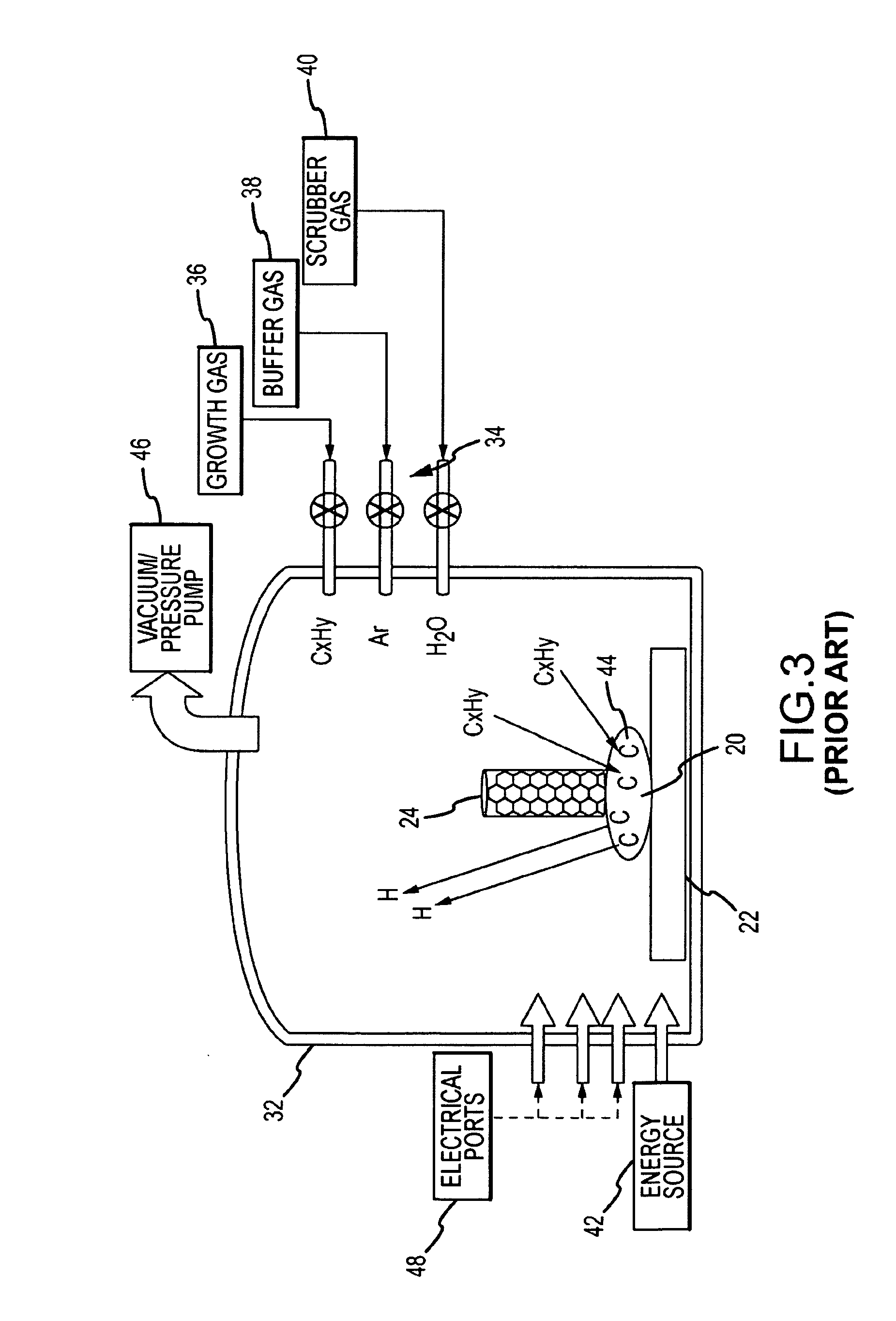
Device and method for producing nanotubes
InactiveUS20100072429A1Increase sublimation areaEfficiently conveyedMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureProcess engineeringMulti-Walled Nanotube
Owner:BENEQ OY
Boron extraction technology
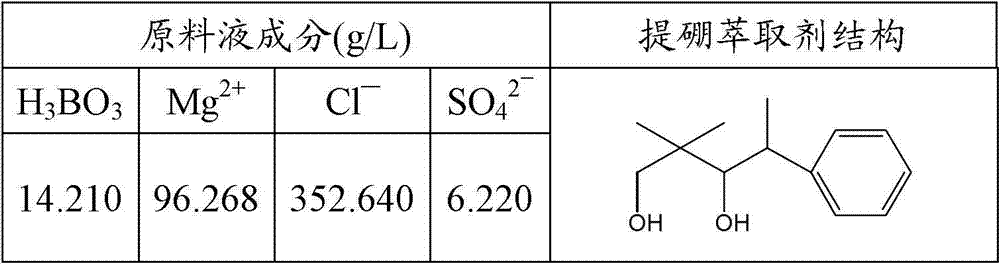
The invention discloses a boron extraction technology. Brine water after extracting lithium from salt lake is used as raw paderial and 2-thyl-1,3-hexanediol respectively with mixture alcohol of isooctal alcohol and isoamyl alcohol extracts borone from the brine water and optimum processing condition for extracting boron from brine water using the mixture alcohol is obtained after performing experiments from the aspects of extractant volume fraction, acidity, phase ratio, extraction time, extraction temperature, saturation extraction volume, back washing agent concentration and back washing time: extractant volume fraction 30%, water phase pH 3, phase ratio 1:1, extraction time 10min, maximum saturation capacity 61.4g / L(B2O3).
Owner:于网林
Method for enriching boron and lithium elements in sulfate type salt lake brine
ActiveCN103194622AReduce manufacturing costReduce the ratio of magnesium to lithiumBoron/boridesChemical industrySalt lakePotassium
The invention relates to a method for enriching boron and lithium elements in sulfate type salt lake brine. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) introducing the sulfate type salt lake brine into a pre-sunning pool, and regulating the concentration of sodium ions to a saturation state of sodium chloride; (2) introducing the brine with the sodium chloride in the saturation state into a mirabilite pool, and freezing in winter to precipitate mirabilite; (3) evaporating the brine after the precipitation of the mirabilite in spring and summer to precipitate the sodium chloride; (4) performing potassium removal treatment on the brine after the precipitation of the sodium chloride; (5) introducing the brine after potassium removal into an epsomite pool, and precipitating epsomite to obtain the brine with high content of magnesium chloride; and (6) mixing the brine with high content of magnesium chloride with the mirabilite for reaction, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain a solution which is rich in boron and lithium elements.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Cleaner production method for preparing superfine powder through self-propagating metallurgy method
ActiveCN103466648ALow raw material costReduce energy consumptionMaterial nanotechnologyBoron/boridesHydrogen chlorideCleaner production
A cleaner production method for preparing superfine powder through a self-propagating metallurgy method is carried out according to the following steps: (1) mixing and conducting ball-milling on the powdery oxide and magnesium powder, then compacting into a blank, putting the blank into a self-propagating reaction furnace to cause a self-propagating reaction, and naturally cooling to the room temperature to obtain a coarse product; (2) using hydrochloric acid to leach and separate magnesium oxide in the coarse product after breaking, and filtering to obtain a solid phase and a leaching agent; (3) washing and drying the solid phase and making the solid phase into ultrafine powder; (4) processing the leaching agent through a spray-pyrolysis mode to obtain a nanoscale magnesium oxide and pyrolysis tail gas, wherein the hydrogen chloride in the pyrolysis tail gas is absorbed to form hydrochloric acid and is circularly used back in the leaching process. The cleaner production method producing the ultrafine powder through the self-propagating metallurgy mode has the characteristics of low material cost, low energy consumption, simple operation, low requirement on process conditions and the like, and the product is high in purity, small in particle size and high in powder activity.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Hydrogen Gas Generation system
InactiveUS20060236606A1Avoid heat exchangeLower the volumePressurized chemical processLevel controlHydrogenAqueous solution
A system for generating hydrogen gas utilizes a volume exchange housing for the storage of a fuel material that reacts to generate hydrogen gas and a hydrogen separation chamber. The system includes a gas permeable membrane or membranes that allow hydrogen gas to pass through the membrane while preventing aqueous solutions from passing therethrough. The system is orientation independent. A throttle valve is also used to self regulate the reaction generating the hydrogen gas.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
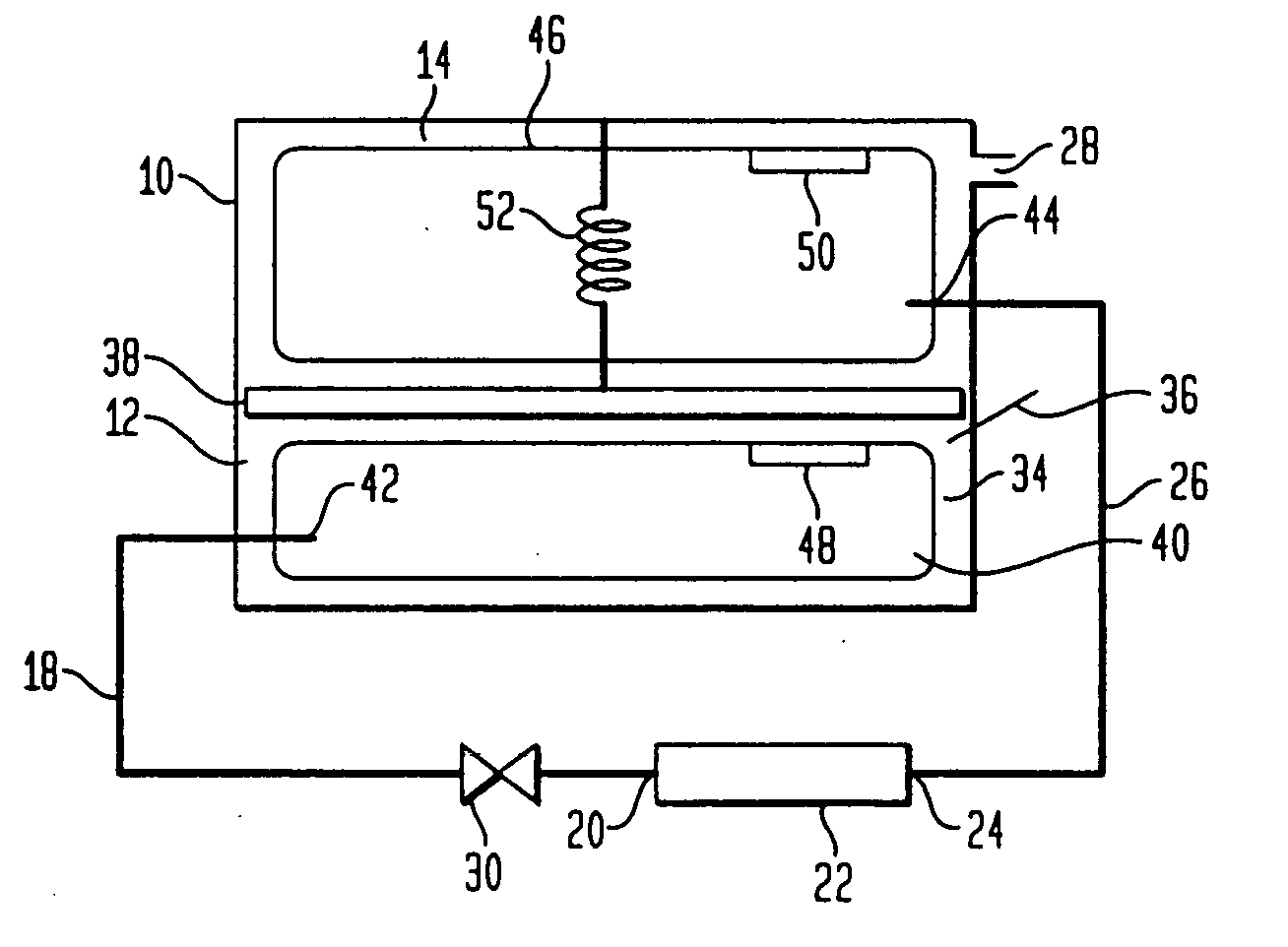
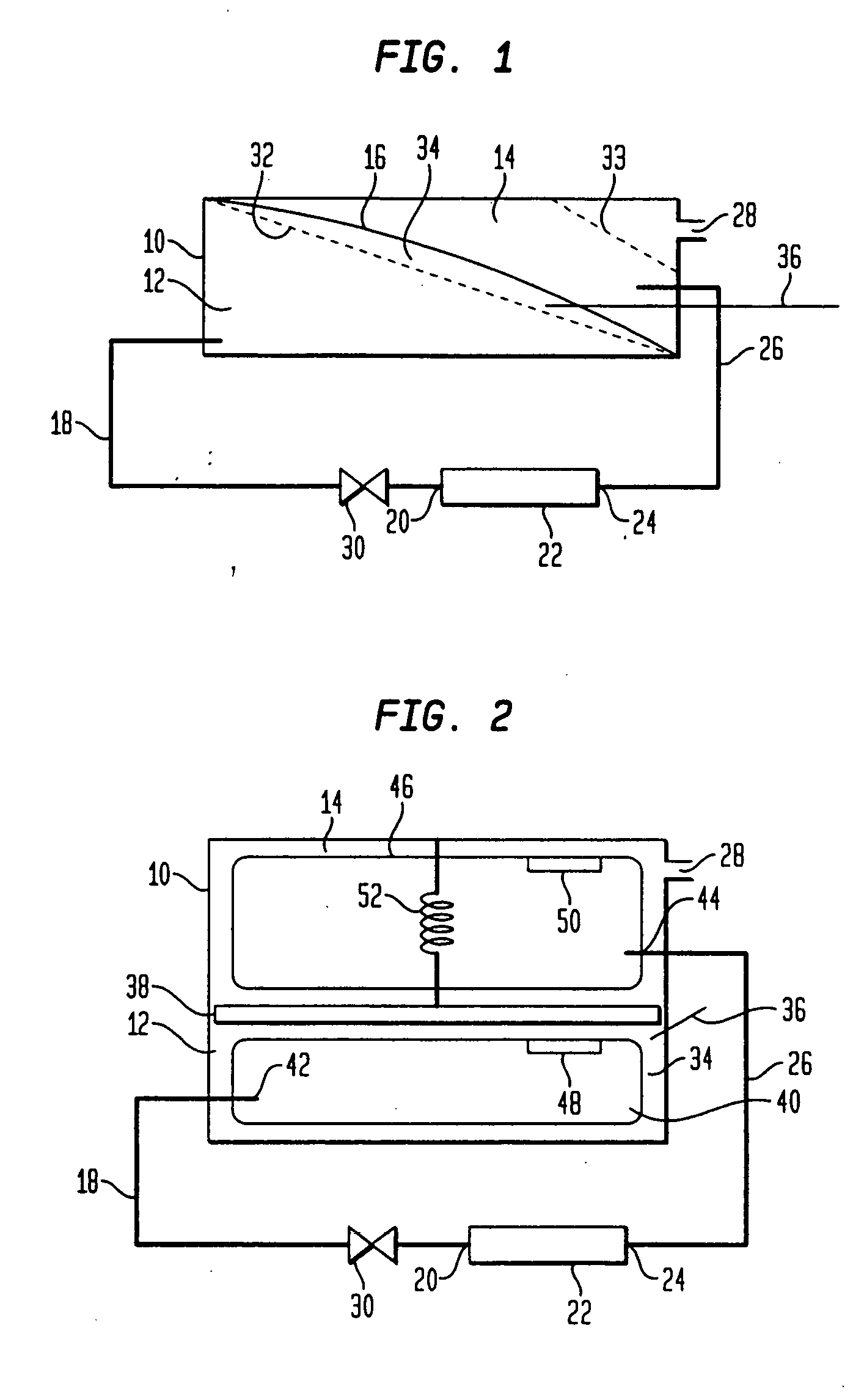
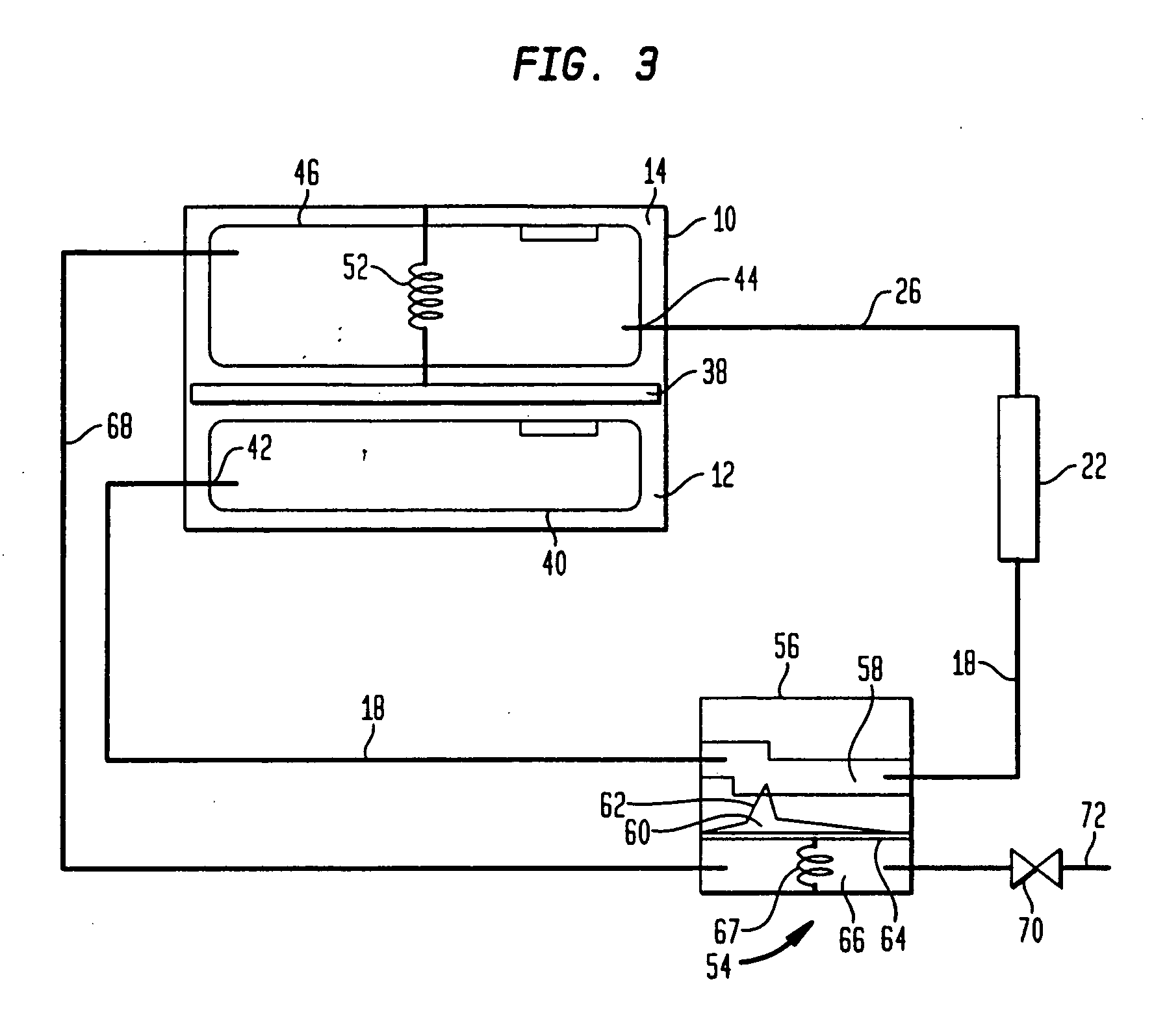
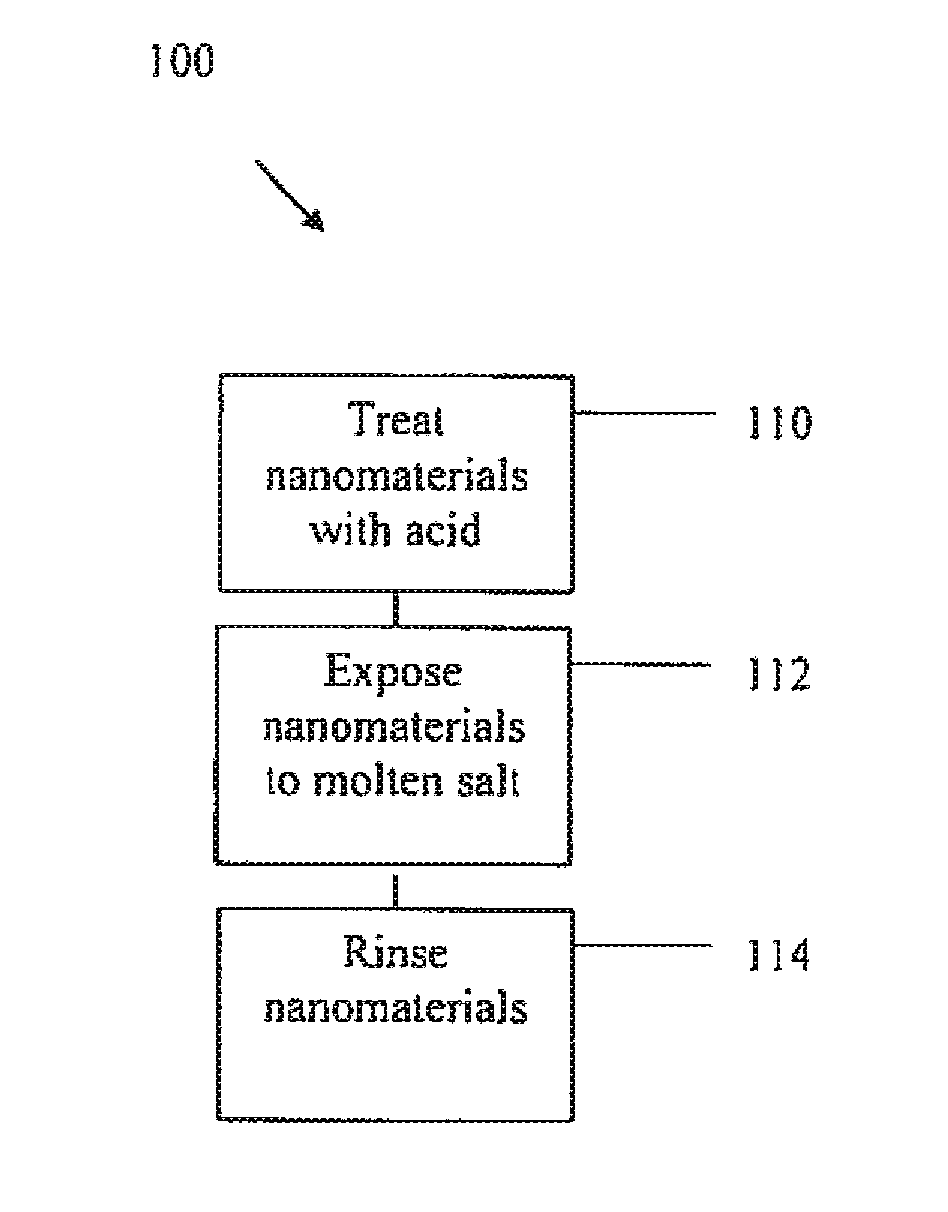
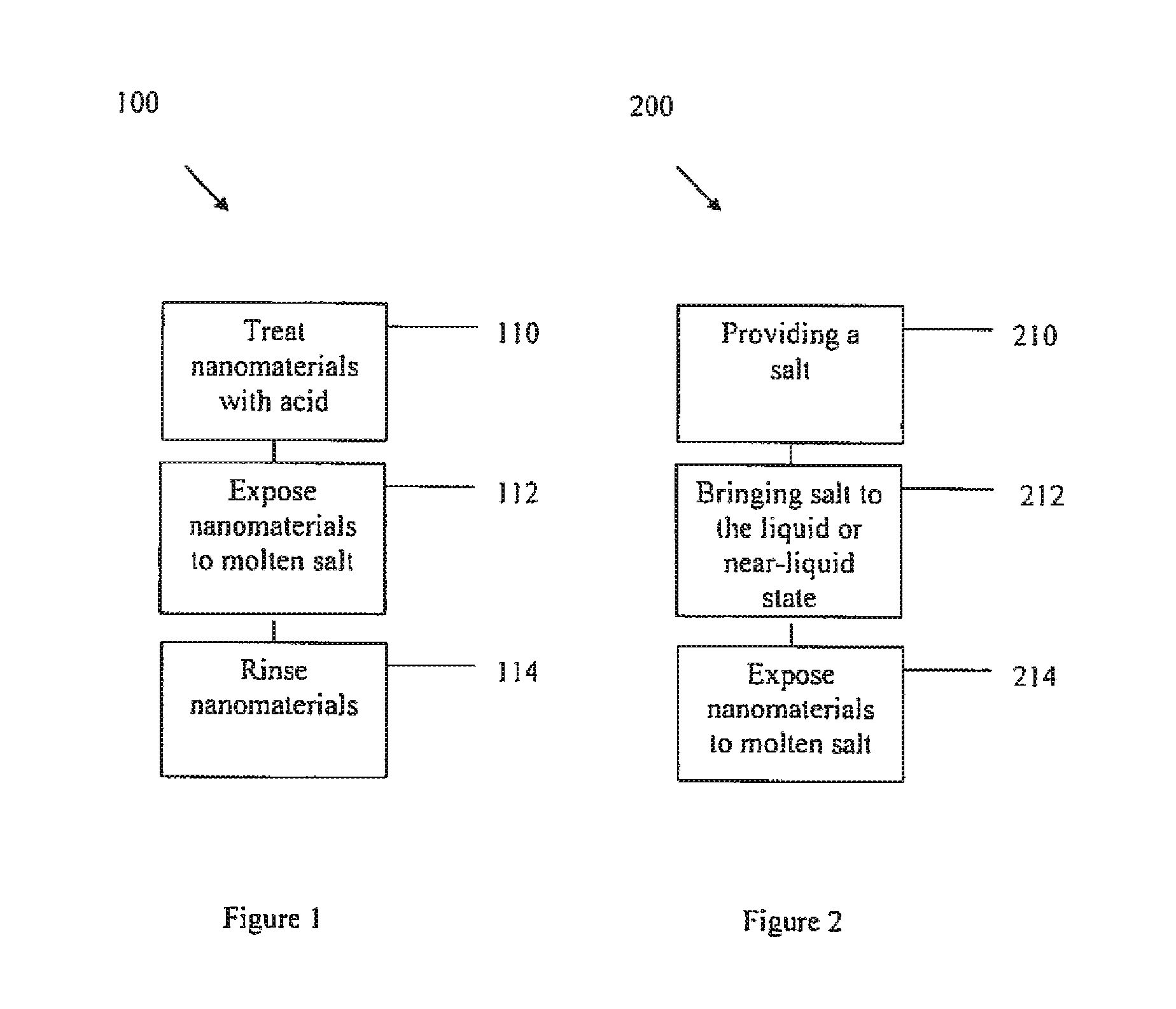
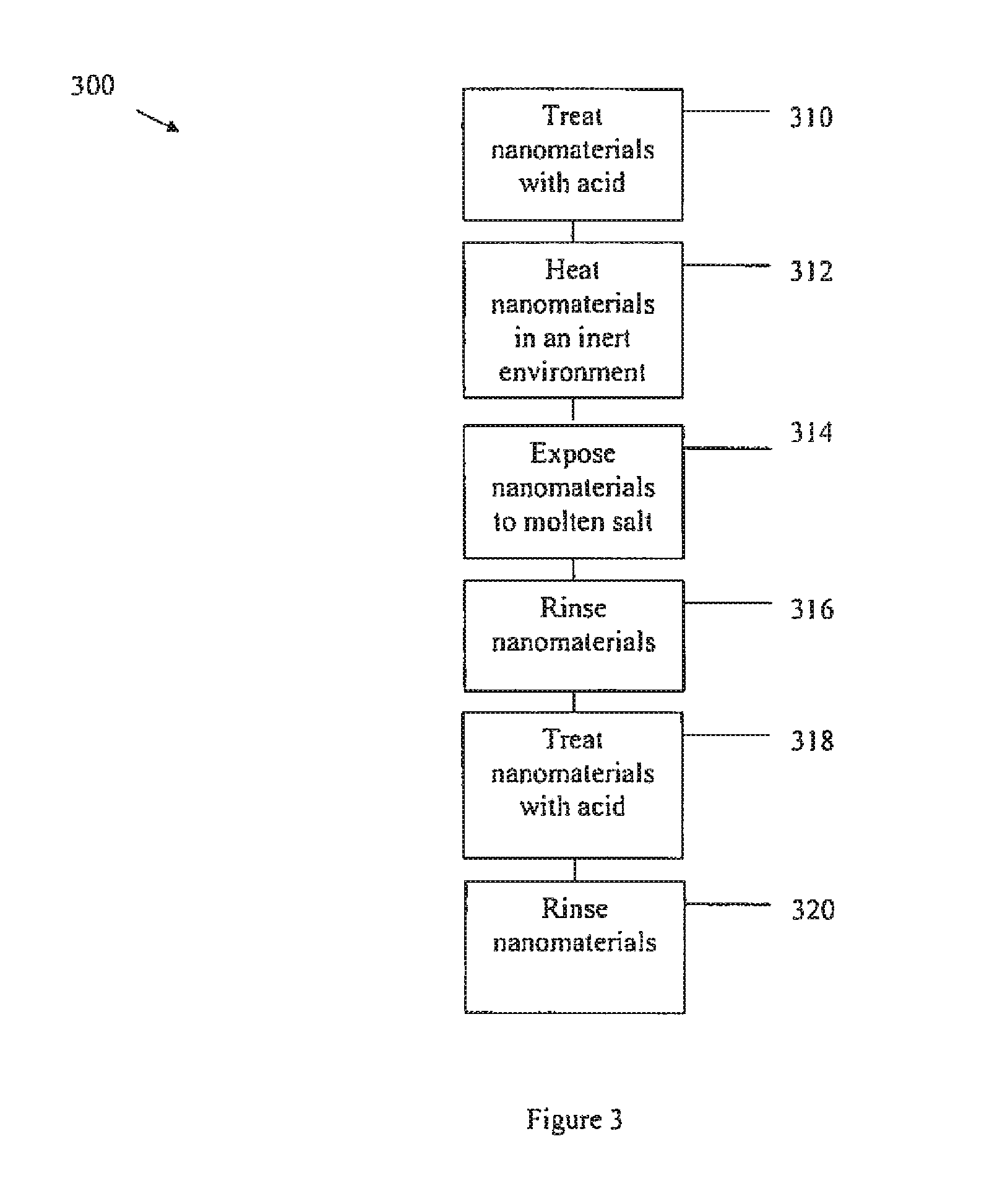
Purifying nanomaterials
A method of purifying a nanomaterial and the resultant purified nanomaterial in which a salt, such as ferric chloride, at or near its liquid phase temperature, is used to penetrate and wet the internal surfaces of a nanomaterial to dissolve impurities that may be present, for example, from processes used in the manufacture of the nanomaterial.
Owner:NASA
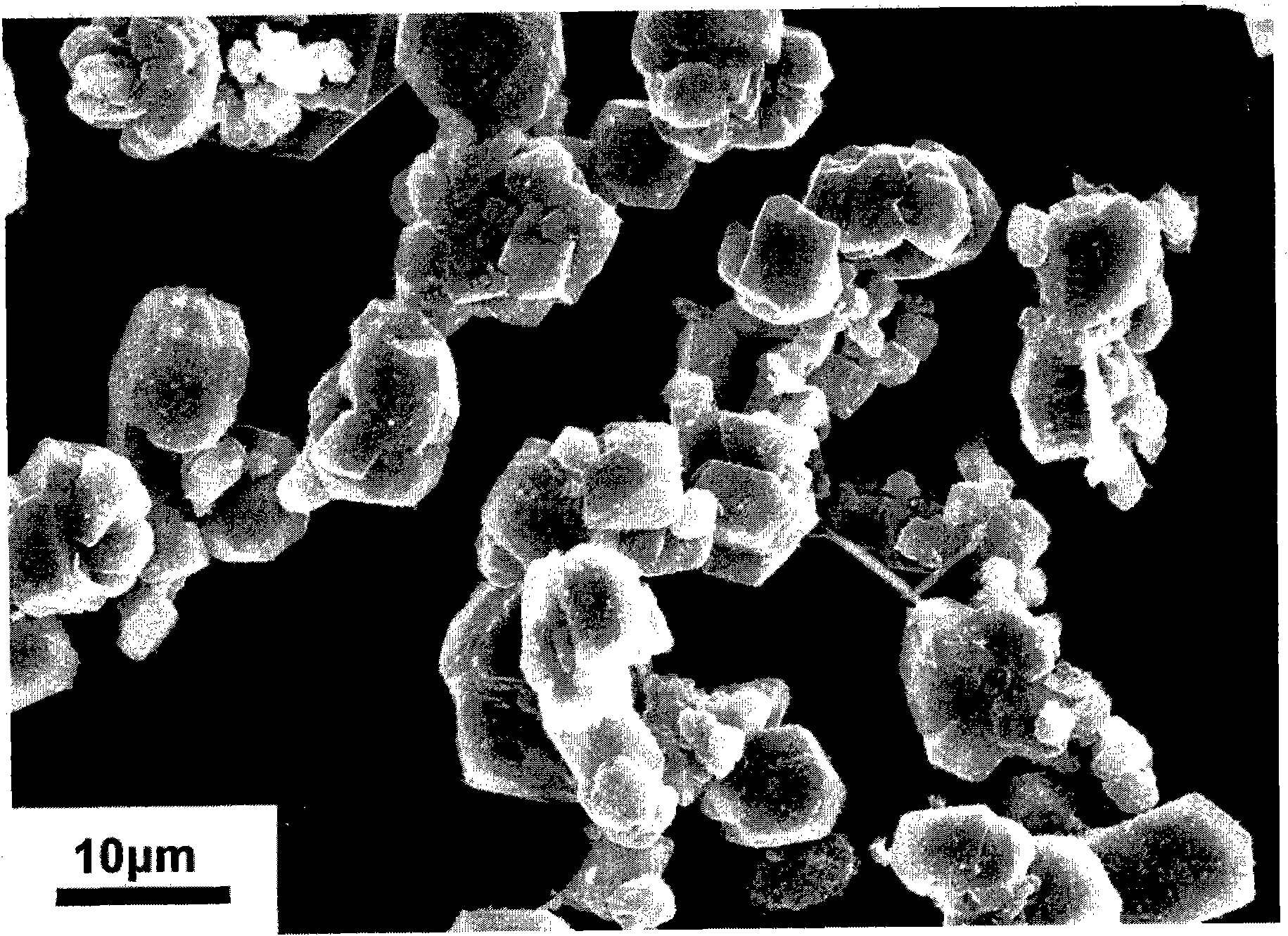
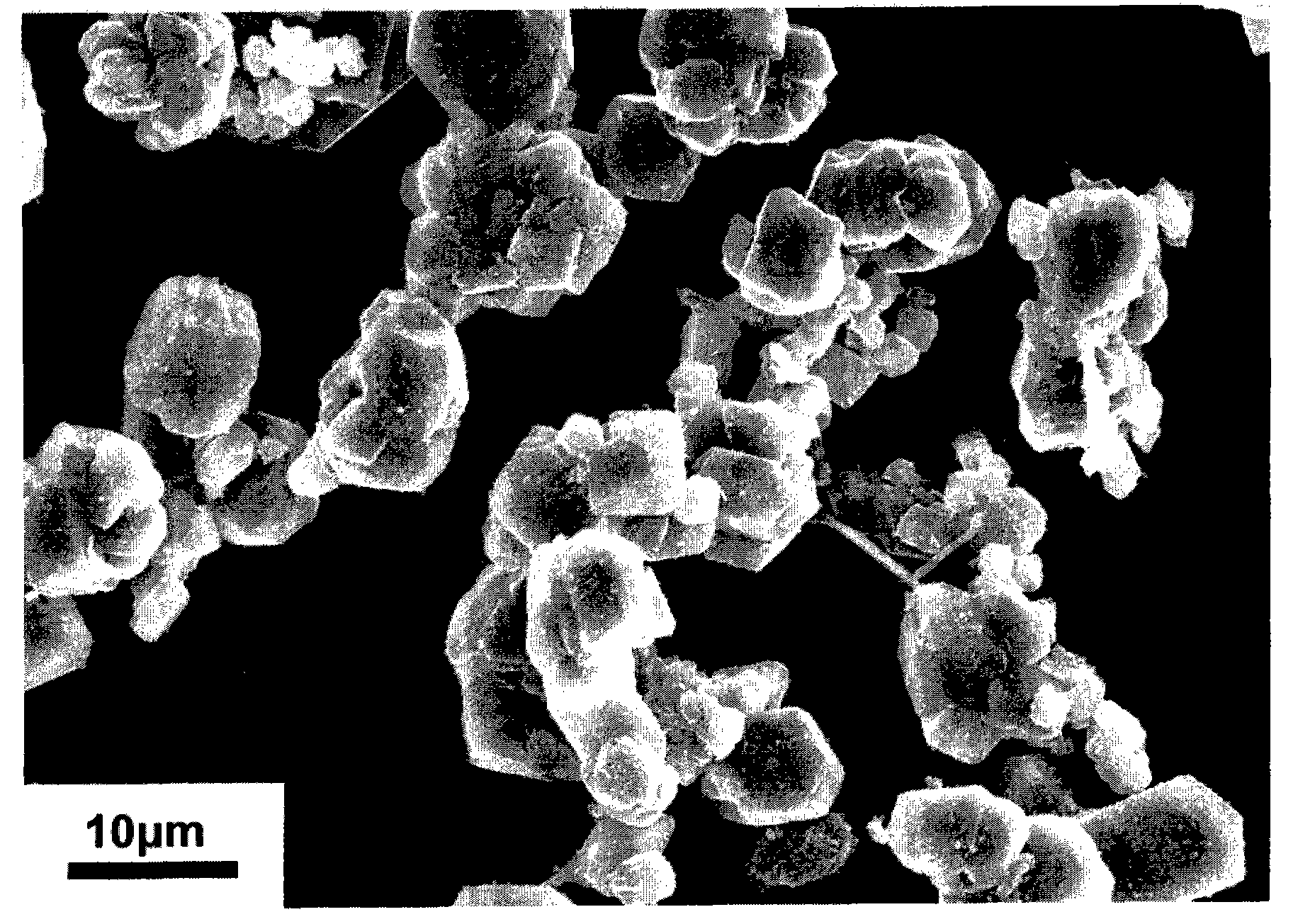
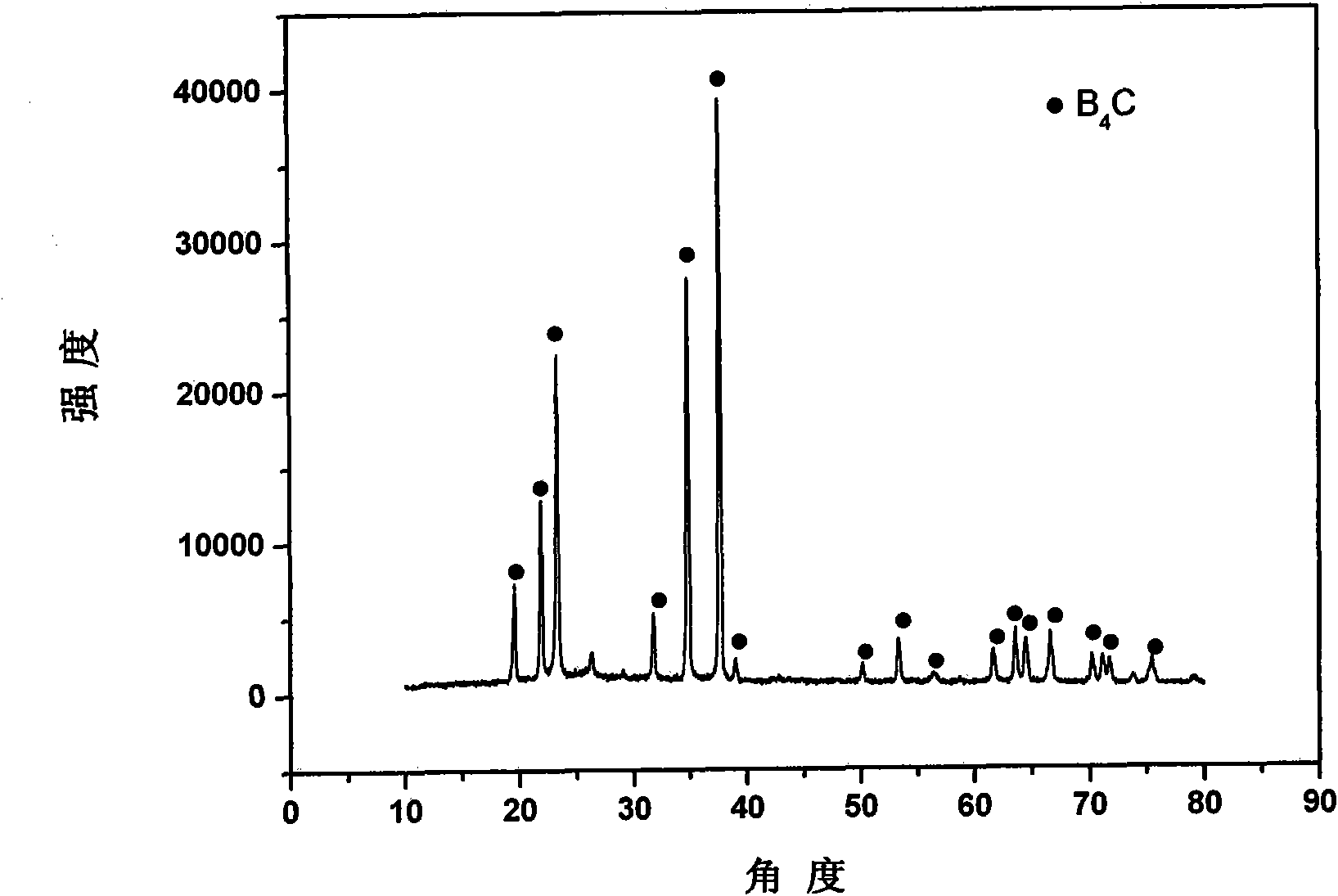
Preparation method for synthesizing boron carbide powder at low temperature
InactiveCN101891214ASave energyReduce manufacturing costBoron/boridesActivated carbonArgon atmosphere
The invention discloses a preparation method for synthesizing boron carbide powder at a low temperature, and belongs to the field of boron carbide ceramic material. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing boric acid, glycerol and nano active carbon powder in a certain ratio by using an ultrasonic cleaner; heating the mixed liquid in a tube furnace under the condition of the heating temperature of 450 to 700 DEG C, the heat preservation time of 0.5 to 3 hours and the heating rate of 5 to 10 DEG C per minute; grinding the heated product by using an agate mortar to form granules with a granule diameter less than 1 millimeter; filling the granules into a graphite jar with screw threads, and screwing down the graphite jar; treating the graphite jar in a vacuum or argon atmosphere at a high temperature, heating the graphite jar to between 1,400 and 1,500 DEG C at a heating rate of 10 to 20 DEG C per minute, preserving the heat for 1 to 5 hours, and cooling the product along with the furnace; and screening the obtained product to obtain the boron carbide powder with the granule diameter less than 10 microns. The whole process has low energy consumption and low preparation cost, and does not introduce exogenous impurities.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for extracting boron from magnesium-containing saline lake bittern
The invention discloses a method for extracting boron from magnesium-containing saline lake bittern. The method comprises the following steps of: performing multi-stage counter-current extraction on an extract organic phase and raw material liquid by using magnesium-containing saline lake bittern as the raw material liquid, the aryl-containing1.3-binary fatty alcohol as a boron extracting agent and using mixed solution which consists of the boron extracting agent and diluent as the extract organic phase to prepare an extract phase containing boric acid; and performing multi-stage counter-current reextraction on a stripping agent and the extract phase containing boric acid by using aqueous alkali as the stripping agent to prepare boron-containing water solution. According to the method, the content of the boric acid in the magnesium-containing bittern is reduced to be below 30mg / L, while a borax product can be obtained; the extraction ratio of single-stage boric acid is up to over 90 percent, and the boric acid yield ratio is up to over 95 percent; and the method has the advantages of good boron extraction effect, reduced consumption of solvent, simple processes, easiness for industrialization and application and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
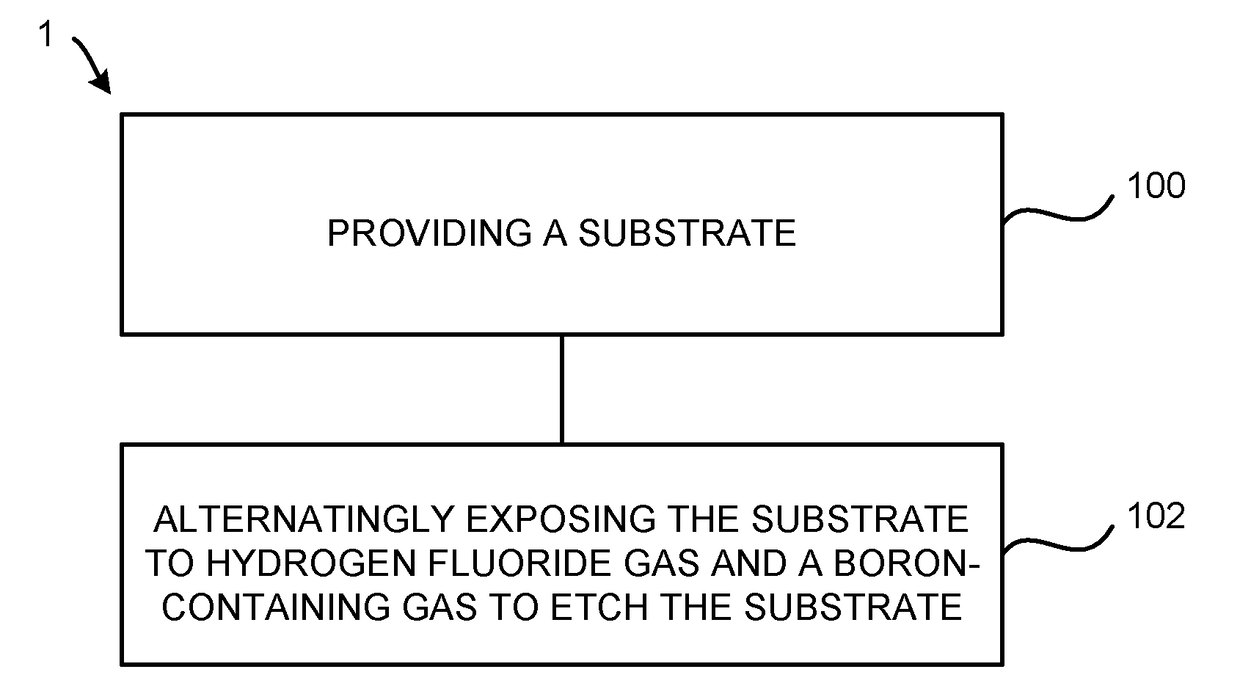
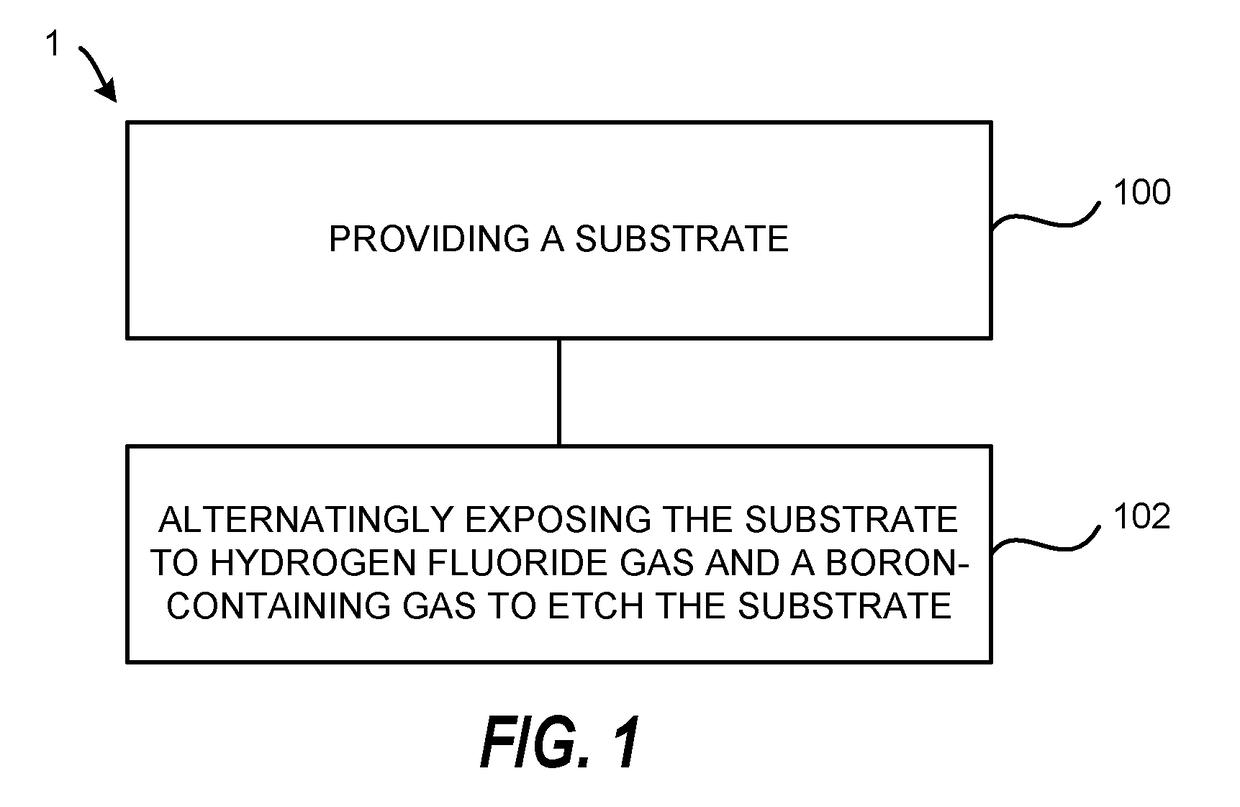
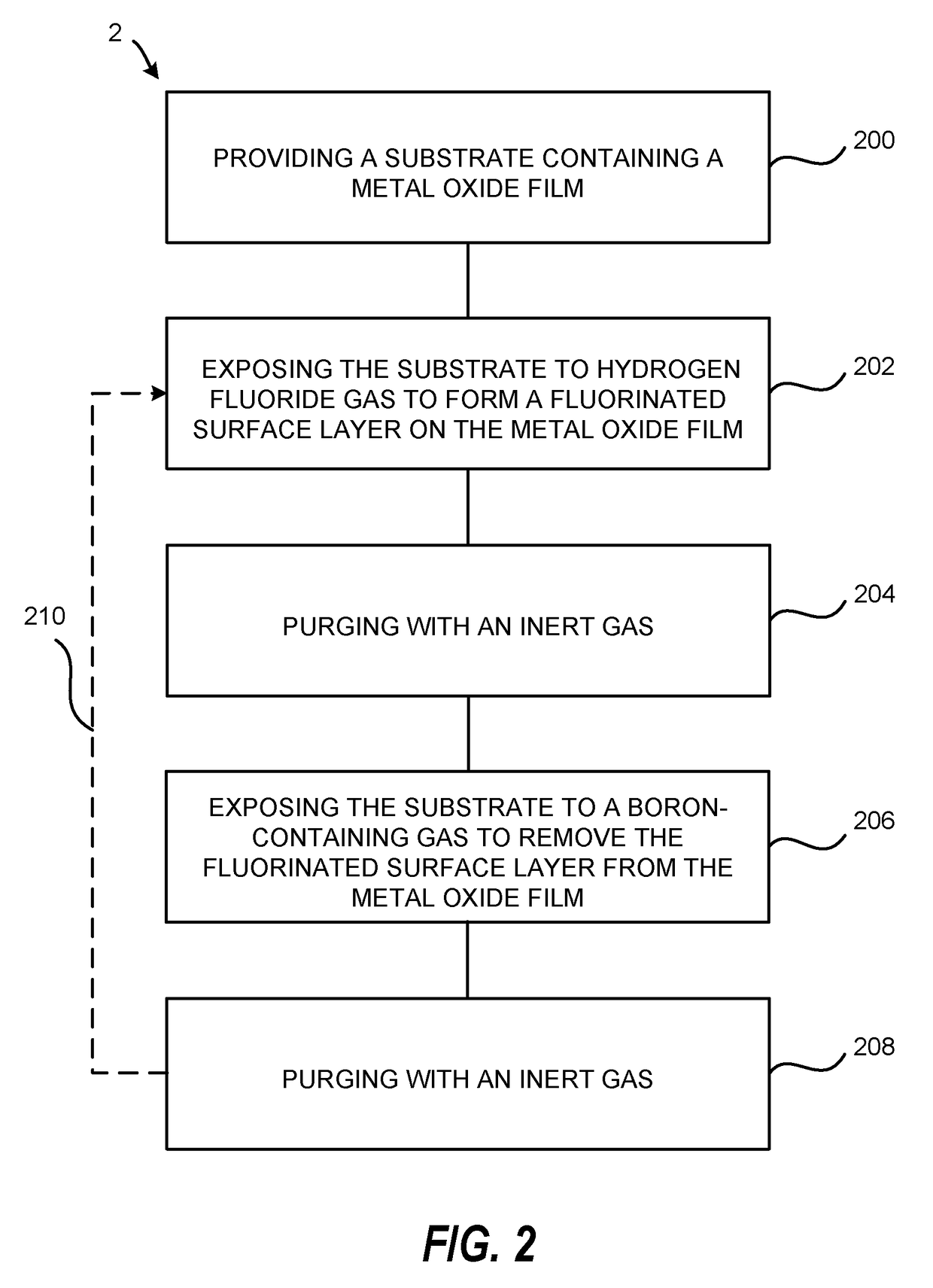
Atomic layer etching using a boron-containing gas and hydrogen fluoride gas
Embodiments of the invention provide a method for atomic layer etching (ALE) of a substrate. According to one embodiment, the method includes providing a substrate, and exposing the substrate to hydrogen fluoride (HF) gas and a boron-containing gas to etch the substrate. According to another embodiment, the method includes providing a substrate containing a metal oxide film, exposing the substrate to HF gas to form a fluorinated surface layer on the metal oxide film, and exposing the substrate to a boron-containing gas to remove the fluorinated surface layer from the metal oxide film. The exposures may be repeated at least once to further etch the metal oxide film.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method for preparing pure boron
The invention discloses a method for preparing pure boron, which comprises the following steps of: weighing corresponding powdery materials in a weight ratio of B2O3 to Mg of 1 to 2-3; performing ball milling and mixing on the materials for 8 to 16 hours; putting the mixture in a mould and compacting the mixture under the pressure of between 10 and 60 MPa; putting ignition powder on the surface of the mixture; then reacting the mixture in a high pressure kettle; blowing the high pressure kettle with argon gas at room temperature so as to discharge the air therein; discharging the air again when the temperature of the container is raised to 180 DEG C; introducing the argon gas of 1 to 6MPa into the container and continuing to raise the temperature of the container; raising the temperature in the container to about 260 DEG C to perform reaction on the ignition powder and release a large amount of heat so as to initiate the reaction between the reaction materials; and finally cooling the reaction product along with the furnace under the protection of the argon gas to room temperature so as to prepare the boron-containing material, wherein the boron content is more than 90 to 98 percent and the particle size is 0.1 to 10 mu m.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
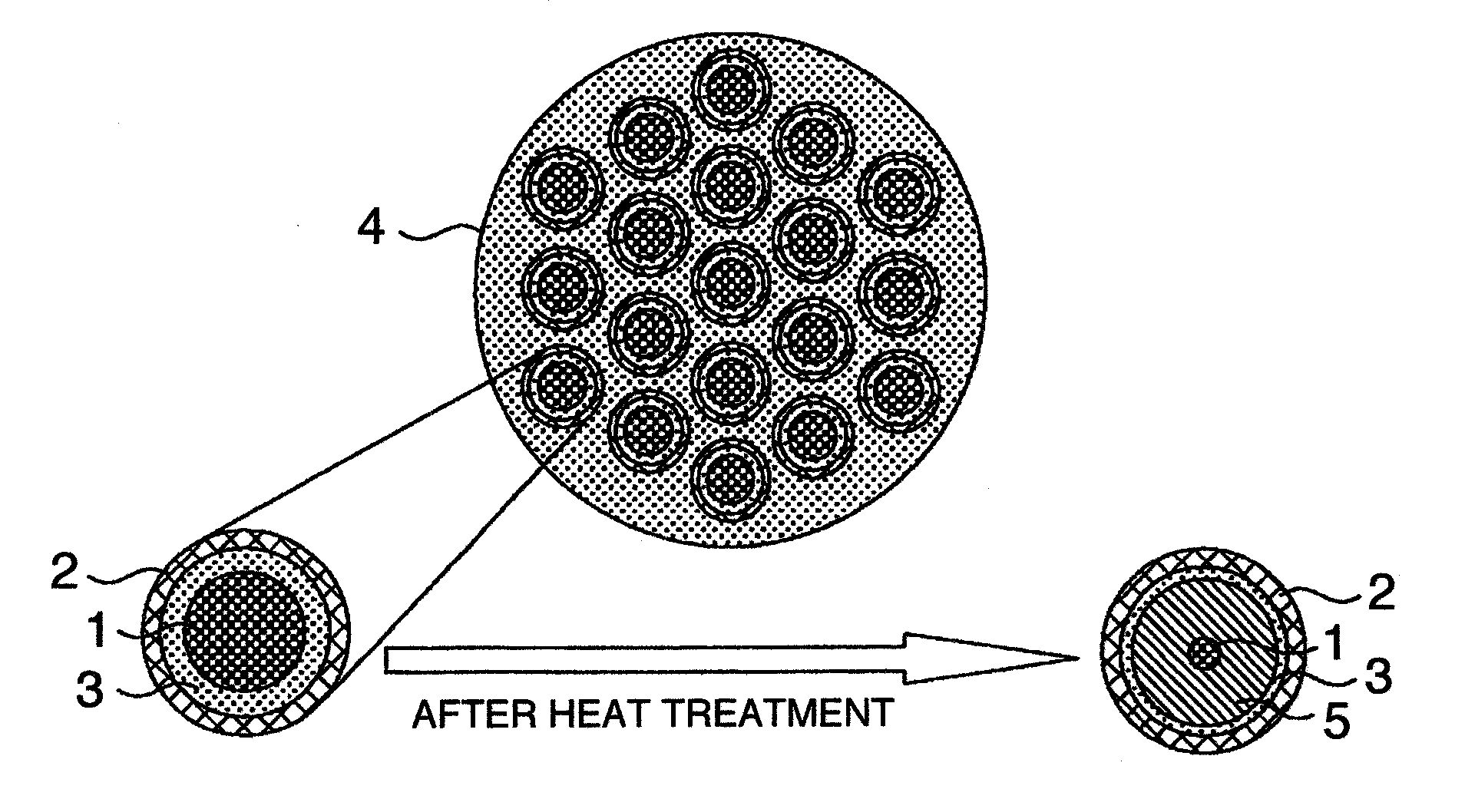
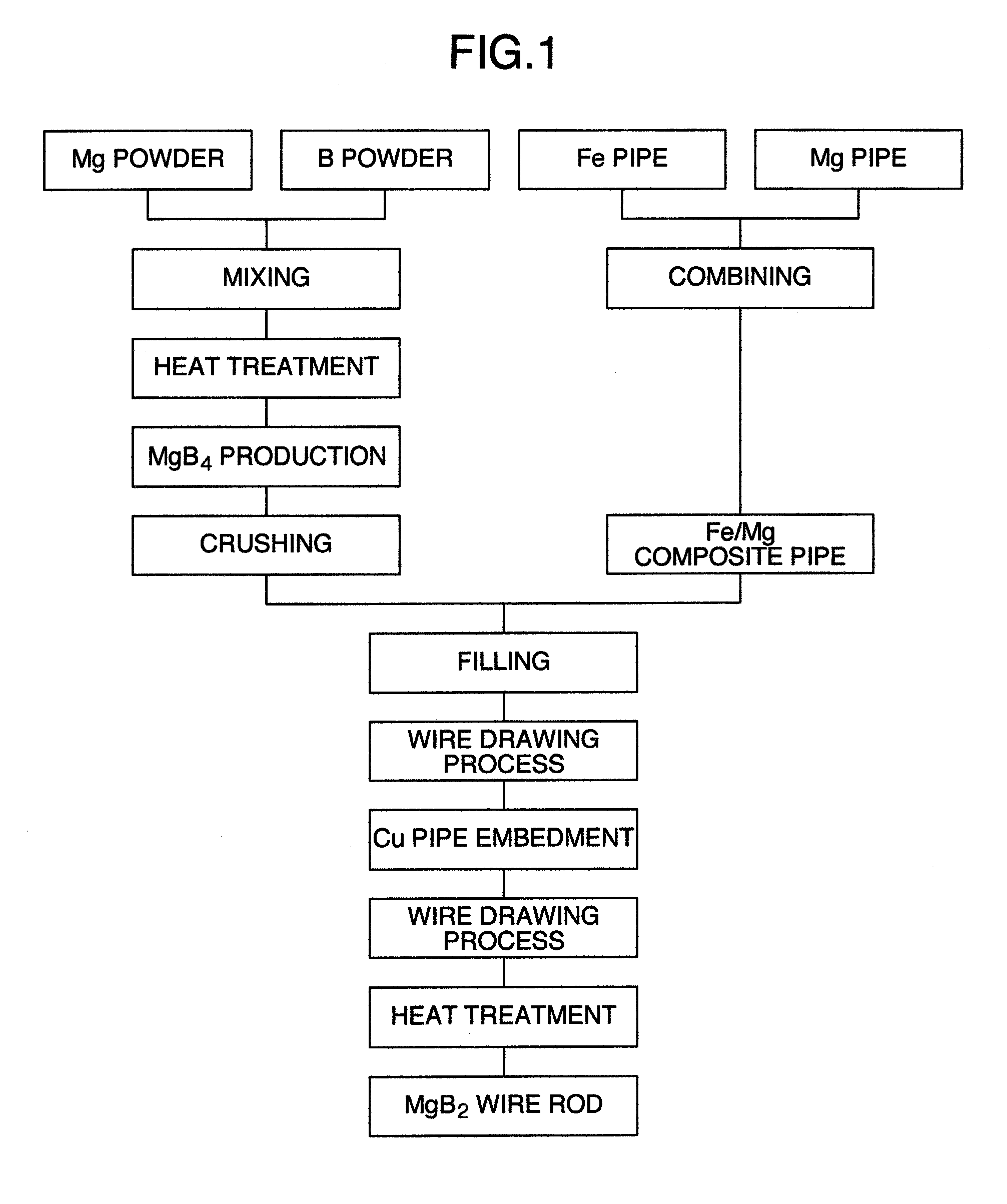
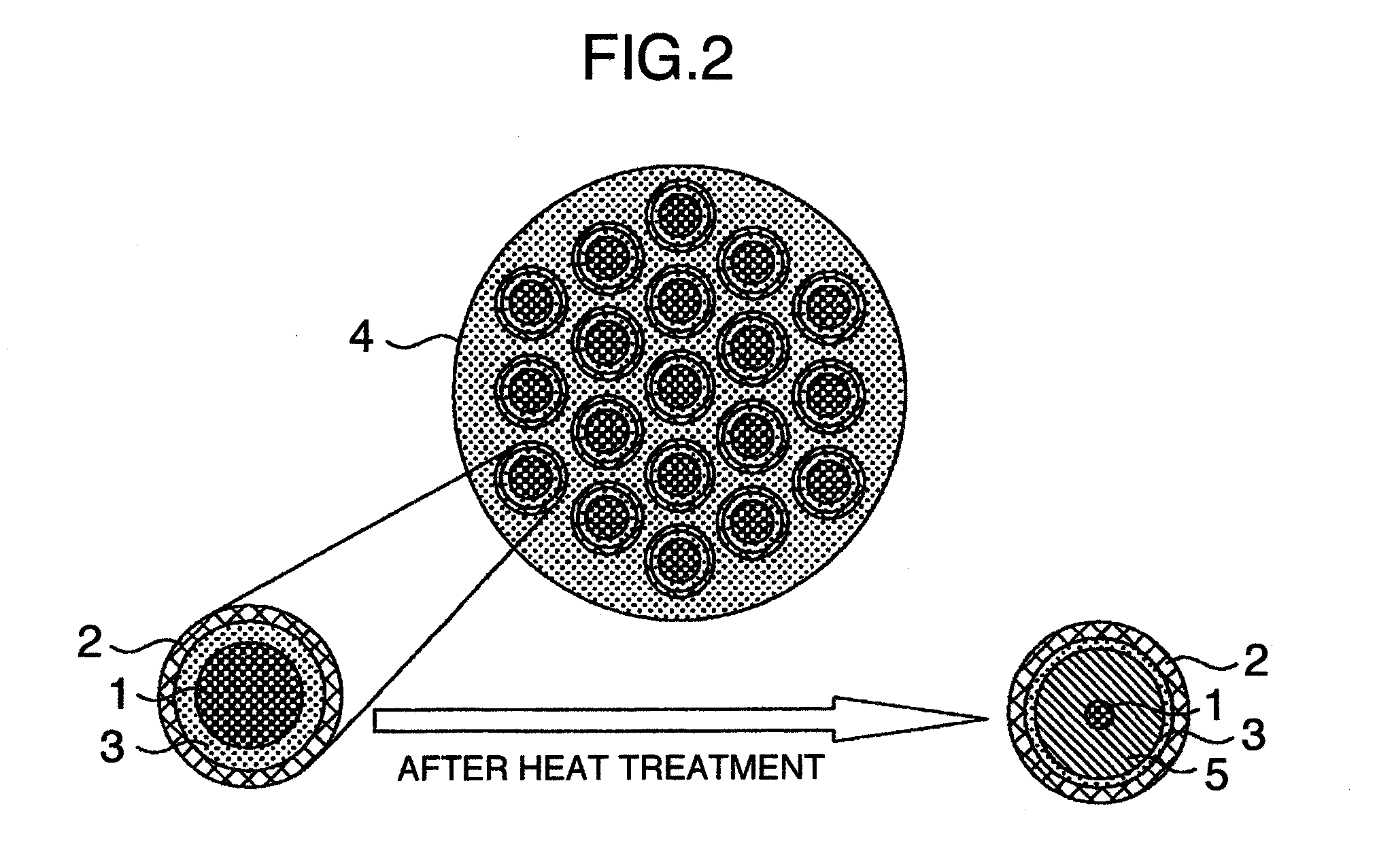
MgB2 SUPERCONDUCTIVE WIRE
The invention provides a MgB2 superconductive wire which is long and has a high critical current density. The invention provides a manufacturing method of a superconductive wire in which a magnesium or a magnesium alloy is reacted with a magnesium boride expressed by MgBx (x=4, 7, 12) by carrying out a heat treatment. A superconductive wire is characterized by the magnesium boride expressed by the MgBx (x=4, 7, 12) is included in a part.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
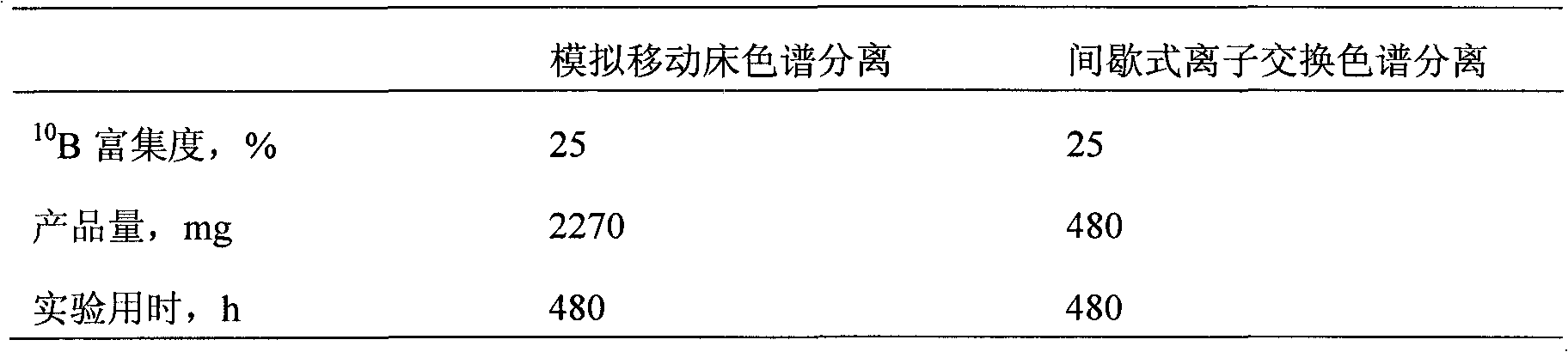
Method for separating boron isotopes by simulated moving bed chromatography
ActiveCN102145256AReduce manufacturing costImprove separation efficiencyBoron/boridesIsotope separationSimulated moving bedEvaporation
The invention discloses a method for separating boron isotopes by simulated moving bed chromatography. The method is used to selectively separate isotopes 10B with high thermal-neutron-absorption cross section from boric acid by simulated moving bed chromatograph with a sassolite solution as a raw material, deionized water as a mobile phase, and weak-base anion-exchange resin as a stationary phase. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a boric acid aqueous solution with certain concentration, filtering the boric acid aqueous solution for removing impurities to obtain a sampleinjection solution for a simulated moving bed, then loading samples by the simulated moving bed, collecting condensed boric acid rich in isotopes 10B at an extraction port, and then obtaining a target product by evaporation concentration. The method for separating the boron isotopes is continuous and has high separation efficiency.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
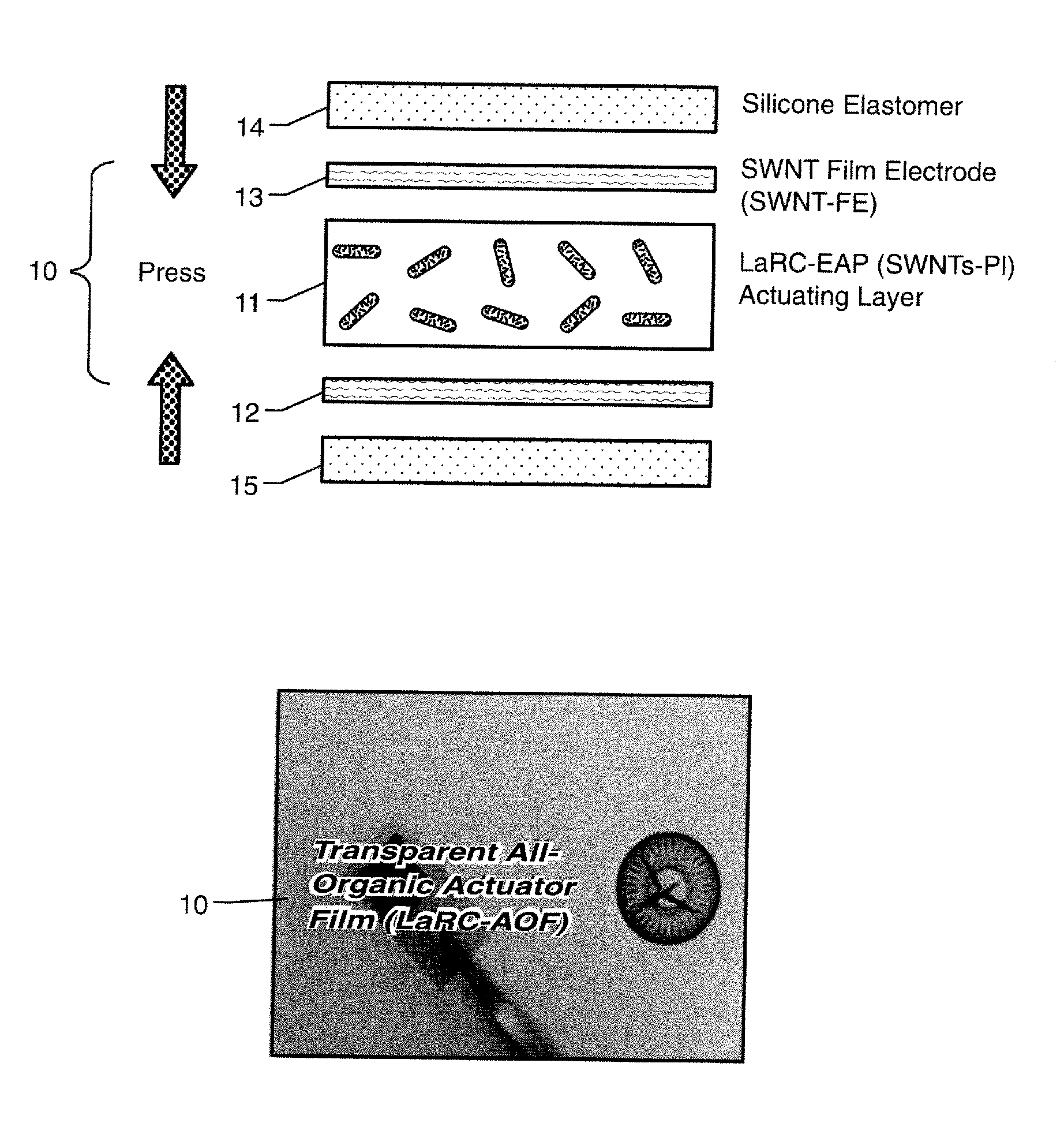
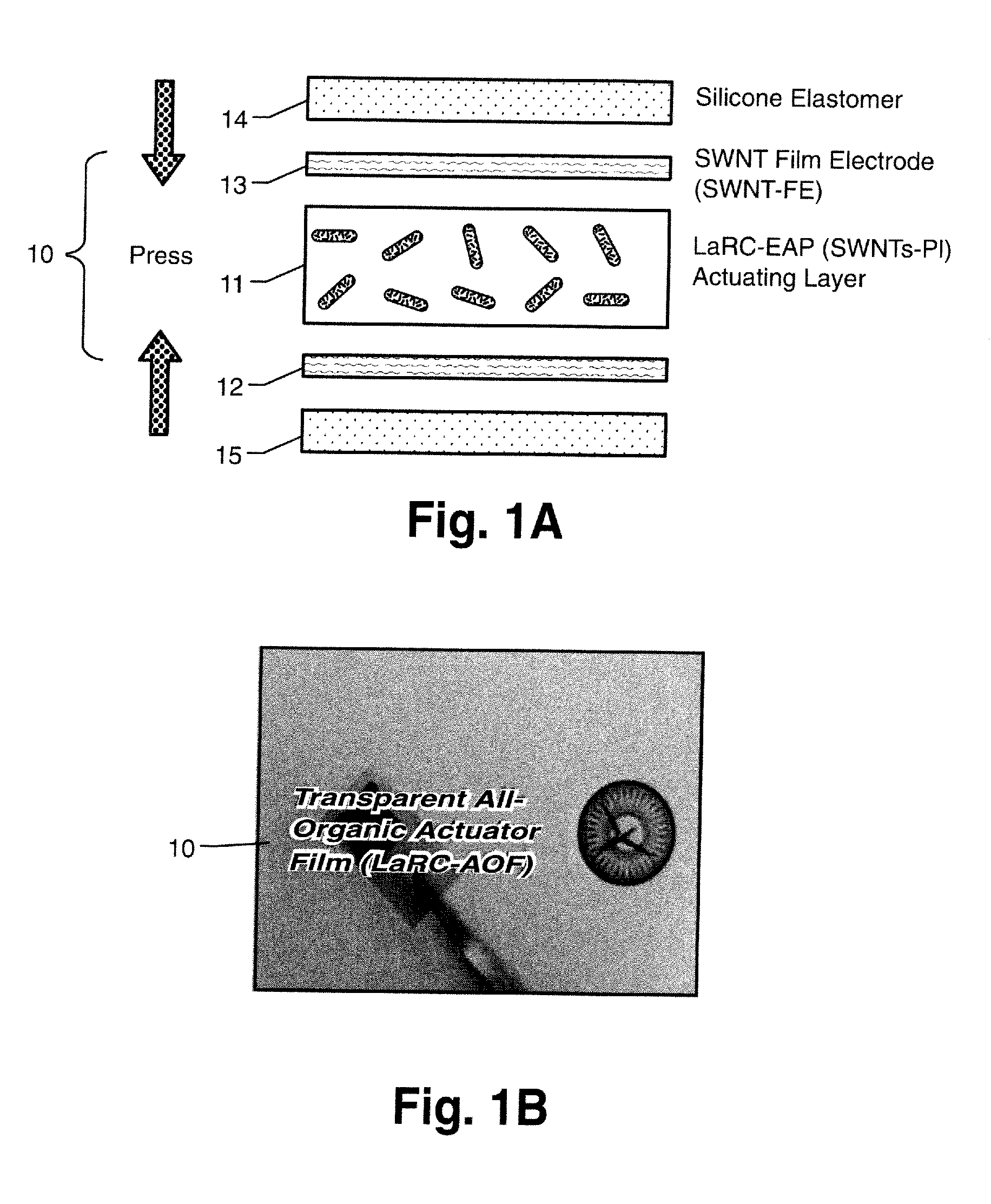
Nanotube Film Electrode and an Electroactive Device Fabricated with the Nanotube Film Electrode and Methods for Making Same
Disclosed is a single wall carbon nanotube (SWCNT) film electrode (FE), all-organic electroactive device systems fabricated with the SWNT-FE, and methods for making same. The SWCNT can be replaced by other types of nanotubes. The SWCNT film can be obtained by filtering SWCNT solution onto the surface of an anodized alumina membrane. A freestanding flexible SWCNT film can be collected by breaking up this brittle membrane. The conductivity of this SWCNT film can advantageously be higher than 280 S / cm. An electroactive polymer (EAP) actuator layered with the SWNT-FE shows a higher electric field-induced strain than an EAP layered with metal electrodes because the flexible SWNT-FE relieves the restraint of the displacement of the polymeric active layer as compared to the metal electrode. In addition, if thin enough, the SWNT-FE is transparent in the visible light range, thus making it suitable for use in actuators used in optical devices.
Owner:NASA
Superconductor compositions operable at high temperatures
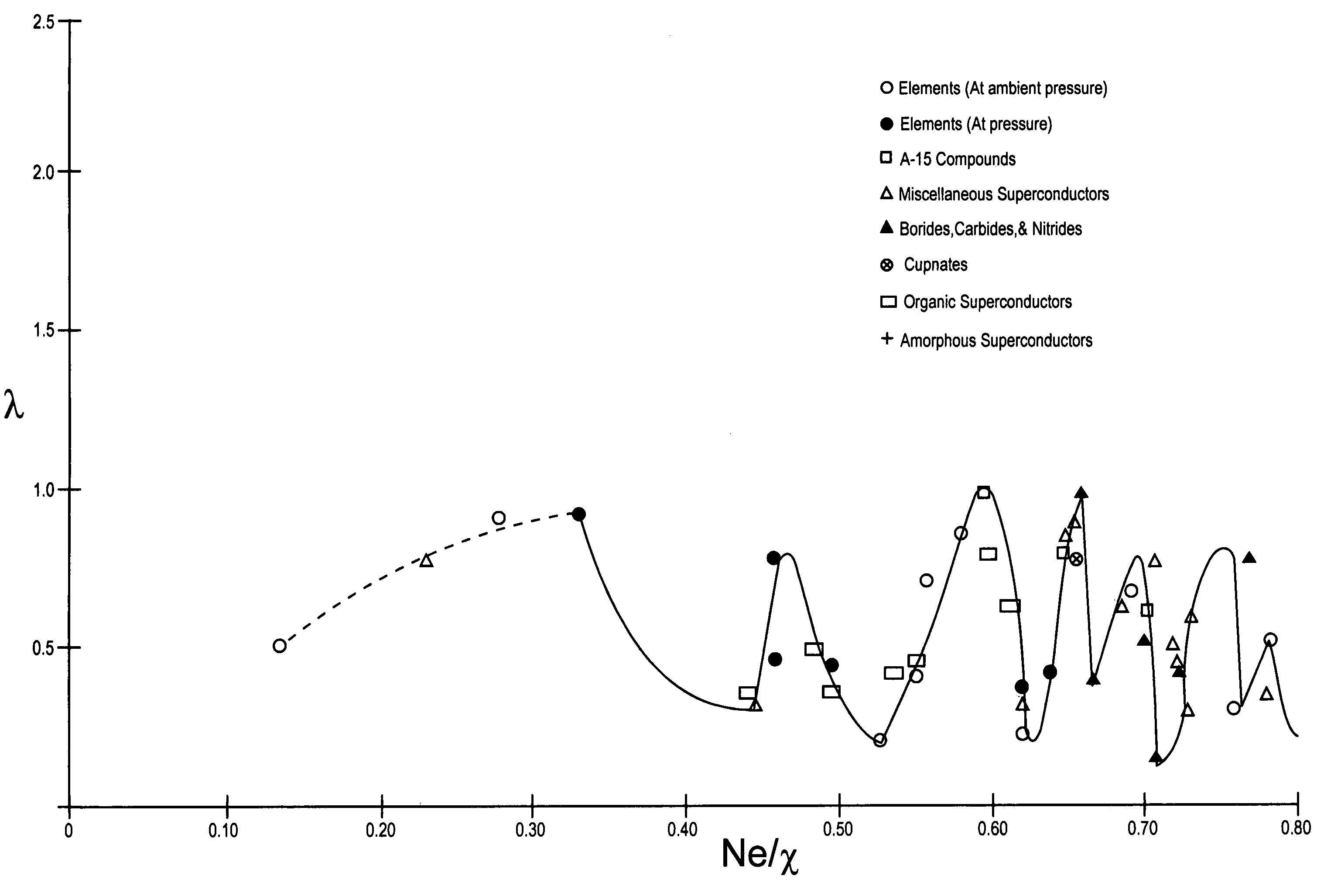
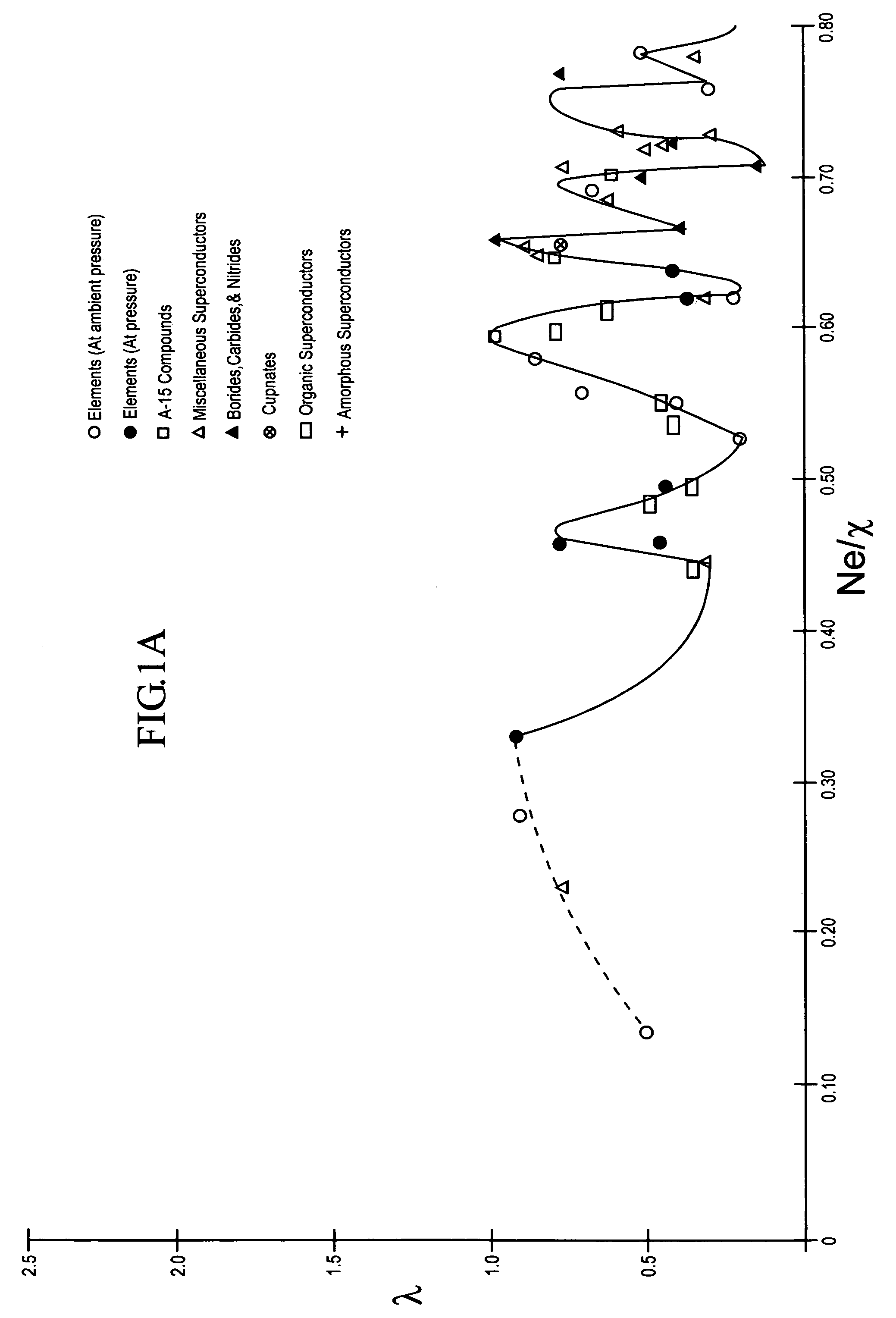
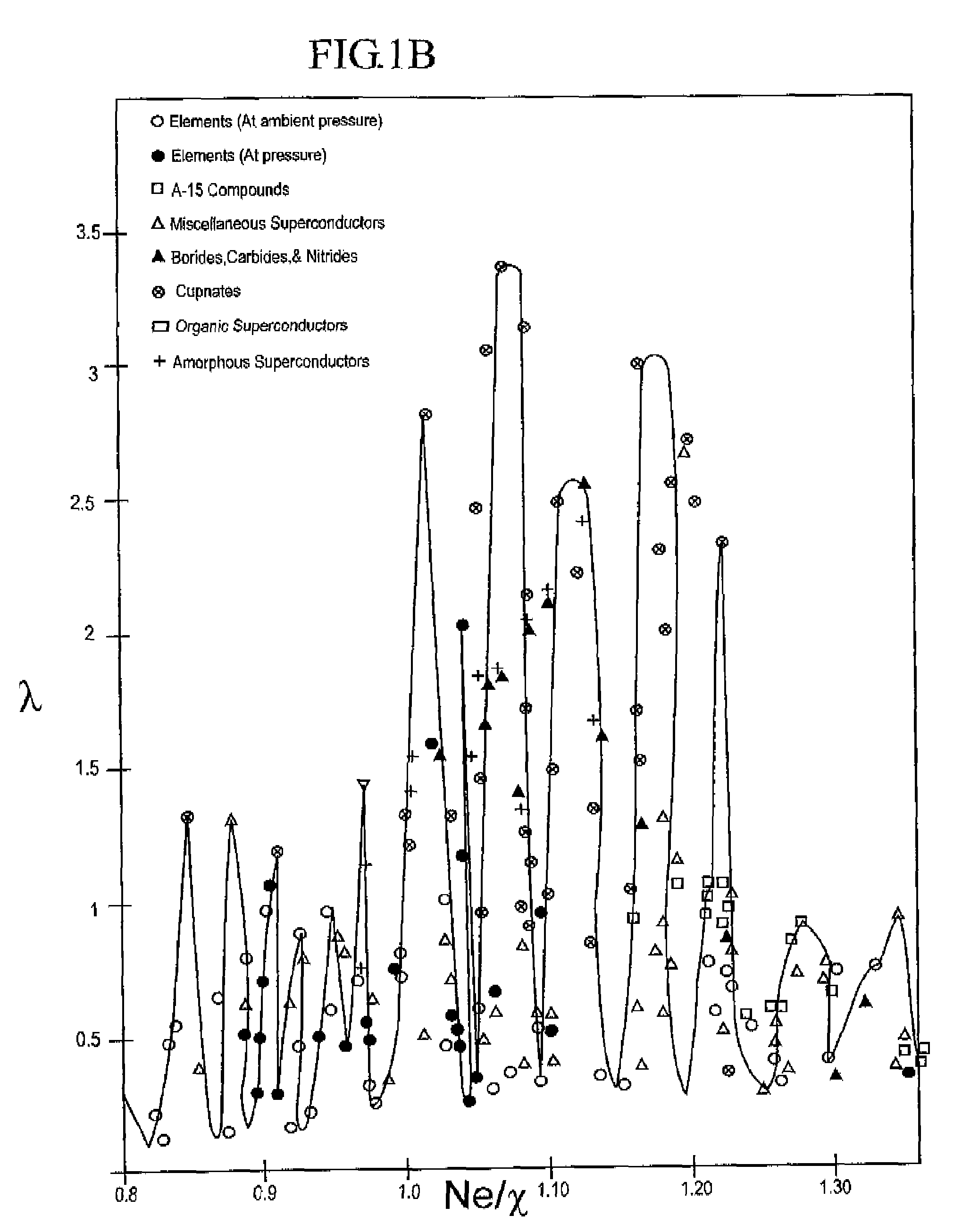
InactiveUS7482298B2Calcium/strontium/barium compoundsBoron/boridesElectron phonon couplingElectron phonon
The composition of compounds containing a multiplicity of different elements are optimized in general by full or partial substitutions of one or more of the atoms in such compounds so as to effect an Ne / χ value which represents a peak or near peak value in λ (the electron-phonon coupling constant) so as to maximize Tc for such compositions of matter.
Owner:NEPELA DANIEL A
Plasma synthesis of nanopowders
ActiveUS8859931B2Improve scalabilityReduce the possibilityBoron/boridesNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsPlasma flowNanometre
A process and apparatus for preparing a nanopowder are presented. The process comprises feeding a reactant material into a plasma reactor in which is generated a plasma flow having a temperature sufficiently high to vaporize the material; transporting the vapor with the plasma flow into a quenching zone; injecting a preheated quench gas into the plasma flow in the quenching zone to form a renewable gaseous condensation front; and forming a nanopowder at the interface between the renewable controlled temperature gaseous condensation front and the plasma flow.
Owner:TEKNA PLASMA SYST INC
Synthesis method of boron hydride [NH3BH2NH3]B3H8
InactiveCN107416856AEasy to operateSuitable for large-scale productionBoron/boridesSynthesis methodsOxygen
The invention discloses a synthesis method of boron hydride [NH3BH2NH3]B3H8 and belongs to the technical field of synthesis of boron hydride. The technical scheme is characterized in that ammonia borane is added to a reaction container under waterless and oxygen-free conditions, a tetrahydrofuran solution THF.B3H7 of B3H7 is added and stirred at the temperature of 0-50 DEG C for a reaction, and the target product boron hydride [NH3BH2NH3]B3H8 is prepared. The method is simple to operate, low-toxicity, harmless, safe, reliable and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for preparing boron powder by combustion synthesis
InactiveCN1508070ASmall granularityHigh reactivityBoron/boridesElectrical resistance and conductanceCombustion
The method for preparing boron powder by using combustion synthesis process includes the following steps: mixing boron oxide and magnesium powder according to the ratio of 1-2.5:1 (weight), under the protection of argon gas grinding them for 3-30 hr. by using high-energy mill, making the said material into blank or directly using powder material and placing it into combustion synthesis reactor, using detonating process or using resistance wire to make initiation and implement combustion synthesis reaction, after the reaction is completed, using acid to wash and remove magnesium oxide so as to obtain the boron powder whose purity can be up to 90-97%.
Owner:丹东市化工研究所有限责任公司
System and method for nanotube growth via Ion implantation using a catalytic transmembrane
ActiveUS7883580B2Promote continued growthGood flexibilityNanotechNitrogen compoundsHigh energyIon implantation
Ion implantation is used to grow nanotubes out of carbon and other materials. Catalytic material is placed on or in a membrane that physically and possibly environmentally separates an implantation chamber or region from a growth chamber or region. High-energy ions are implanted into the catalytic material from one side to grow nanotubes on an exposed surface in the growth chamber. Ion implantation via the membrane provides for greater flexibility to separate and independently control the implantation and growth processes.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Preparation method of boron nano-particles
InactiveCN102849752ASmall sizeUniform size distributionMaterial nanotechnologyBoron/boridesHydrogenPlasma technology
The invention discloses a preparation method of boron nano-particles. The preparation method comprises the following steps: letting a mixed gas containing an inert gas and a boron-containing gas source into a plasma chamber, and exciting the mixed gas through using a radio frequency source to decompose the boron-containing gas source to generate the boron nano-particles, wherein the boron nano-particles are separated and collected through taking out of the plasma chamber through a gas flow. The method for preparing the boron nano-particles through utilizing a plasma technology in the invention has the following beneficial effects: 1, the dimension in a range of 1-100nm is adjustable, and the dimension distribution standard deviation is less than 30% of an average dimension; 2, the surfaces of the particles are passivated by hydrogen, and the purities of the boron nano-particles are not less than 99.99wt%; and 3, the production technology is simple, so it is convenient to realize large-scale production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for purifying amorphous rough boron powder through pressurizing and leaching
InactiveCN102491359ASolve the problem of too low puritySimple purification processBoron/boridesRoom temperatureHydrometallurgy
The invention provides a method for purifying amorphous rough boron powder through pressurizing and leaching. The method comprises the following steps of: adding diluted hydrochloric acid of a certain proportion to the amorphous rough boron powder, heating and pressurizing during mixing, and carrying out leaching reaction; and naturally cooling down to room temperature to obtain a mixture, filtering the mixture, cleaning filter residue by water, drying and sieving to obtain amorphous boron powder with purity of more than 97%, wherein the contents of impurities, such as Mg, O, Si, Fe and the like are respectively below 0.9%, 0.2%, 1.0% and 0.3%. According to the method for purifying the amorphous rough boron powder through pressurizing and leaching, disclosed by the invention, the purification of rough boron is carried out by a hydrometallurgy pressurizing leaching method, thus the purification process is simple, the cost is low, the additional value is high and the purity of boron power can be over 97%. The method for purifying the amorphous rough boron powder through pressurizing and leaching, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of novel technique, innovativeness and high additional value, and can solve a problem that the purity of the amorphous boron powder prepared by the current thermal magnesium reduction method is too low.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
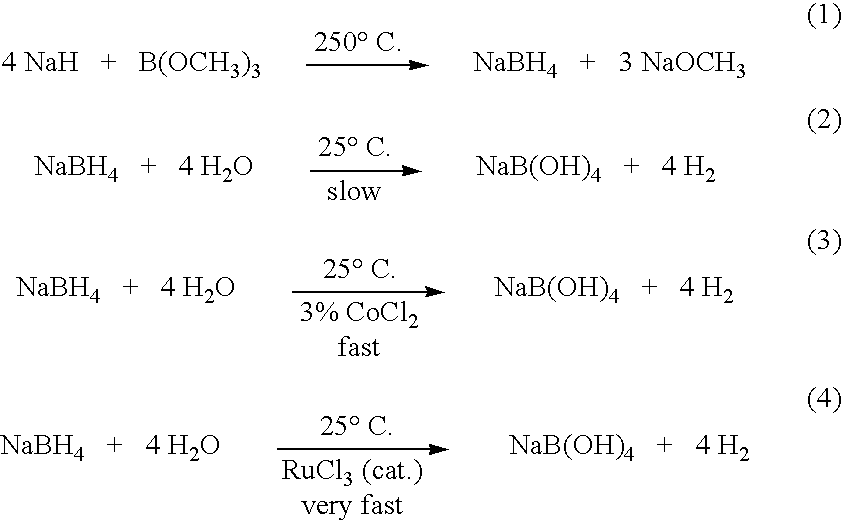





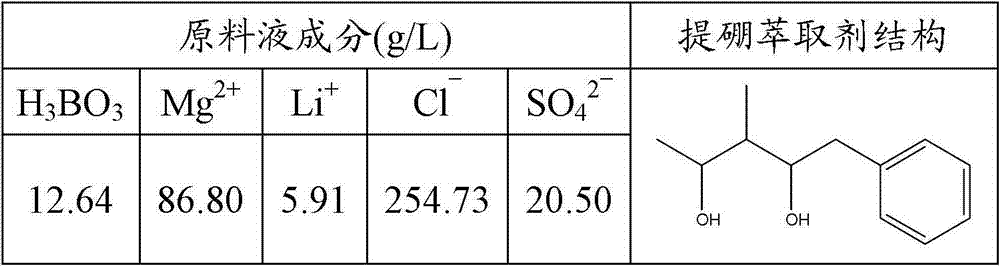

![Synthesis method of boron hydride [NH3BH2NH3]B3H8 Synthesis method of boron hydride [NH3BH2NH3]B3H8](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/99085d6f-050f-4662-8f30-645c61371345/170802164819.png)