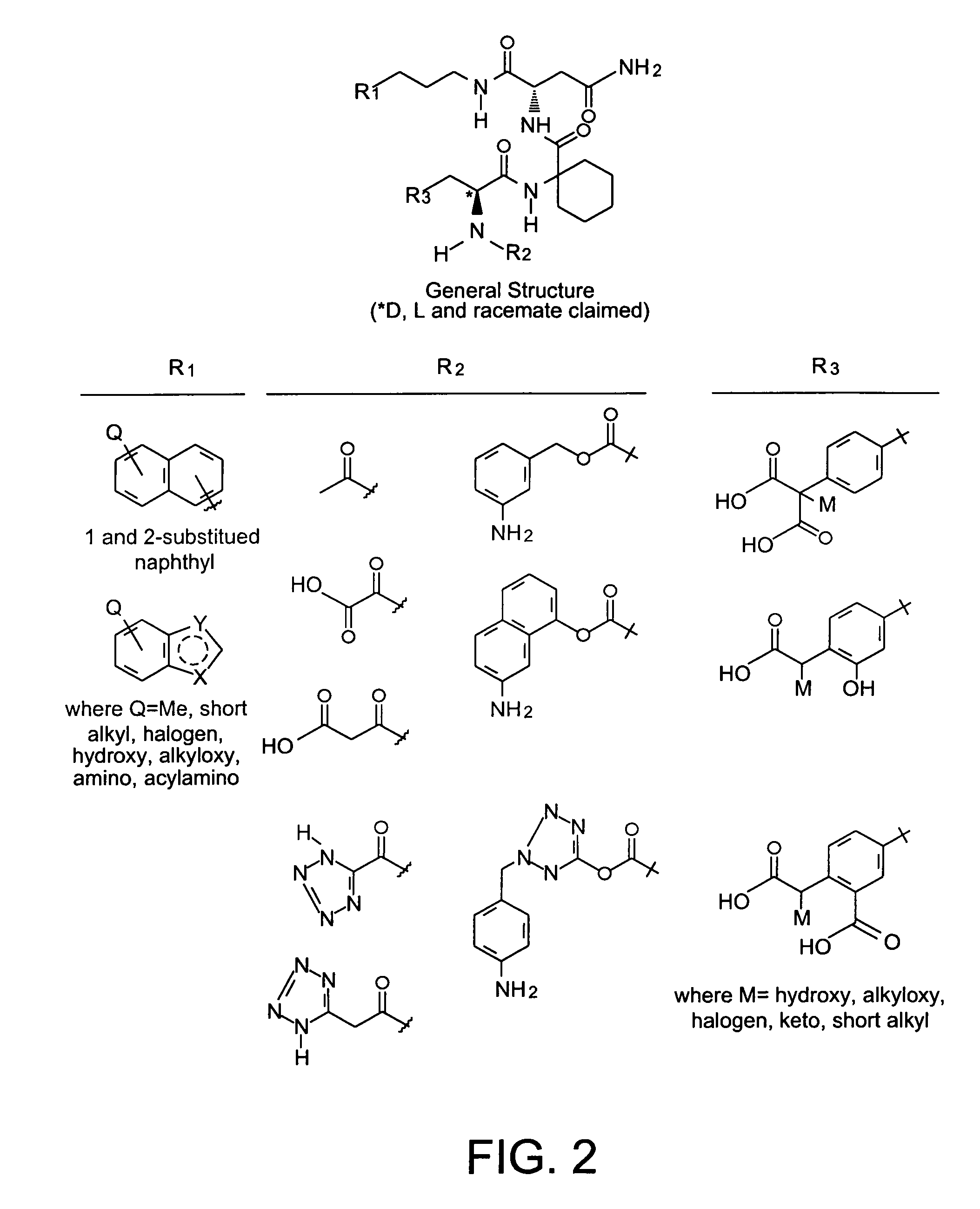
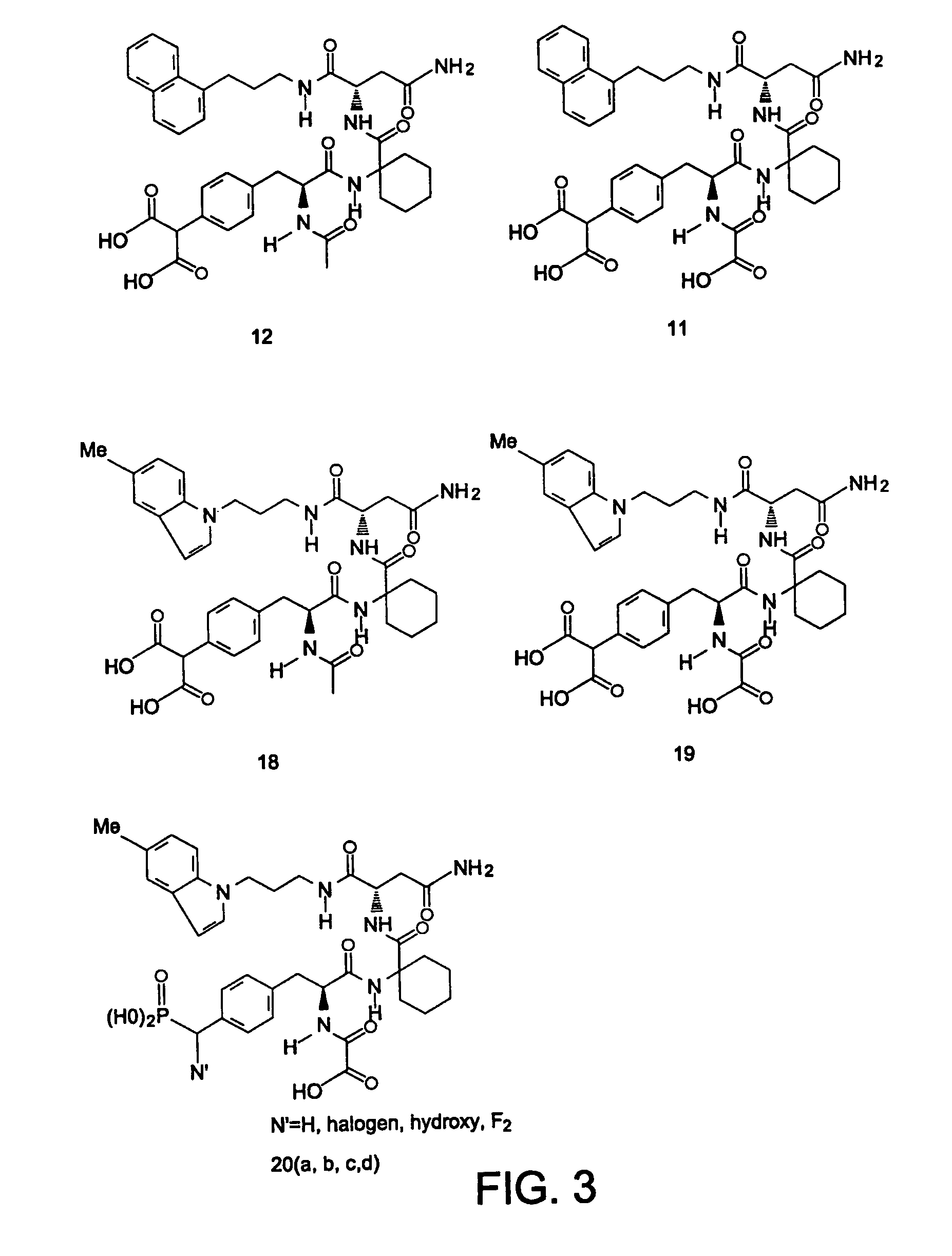
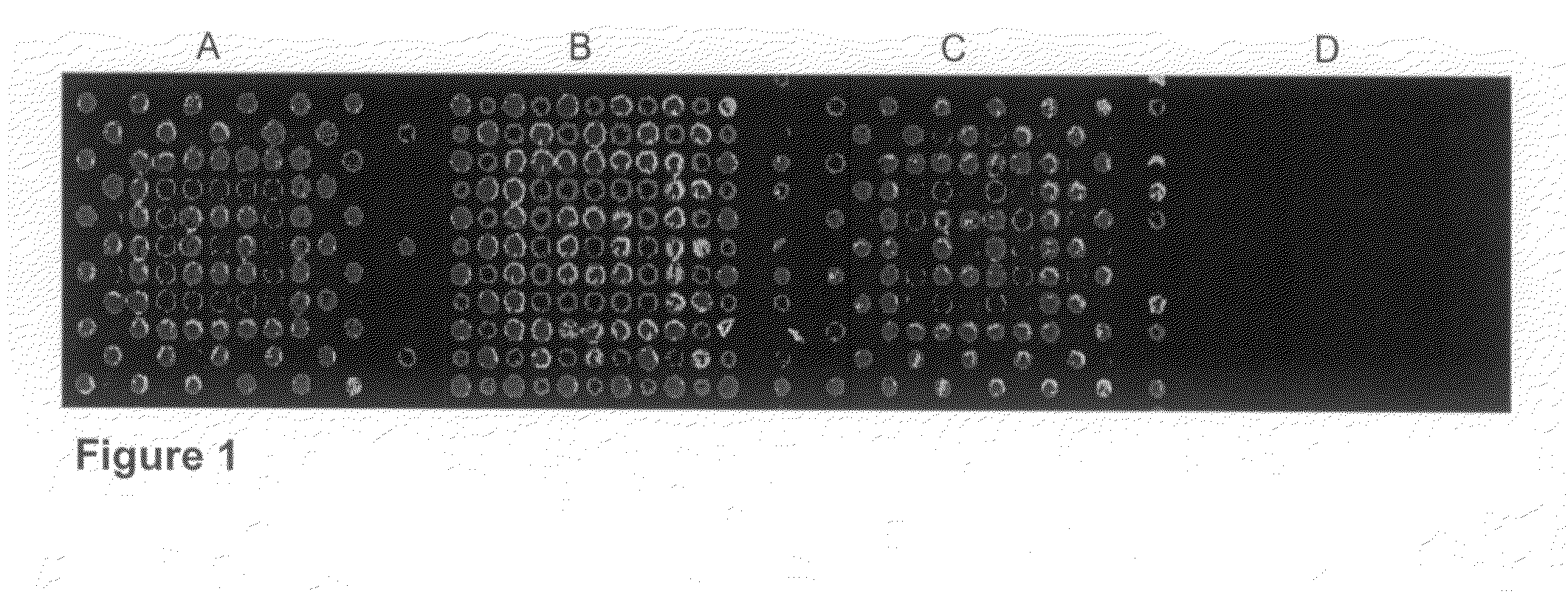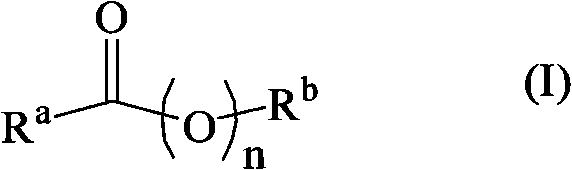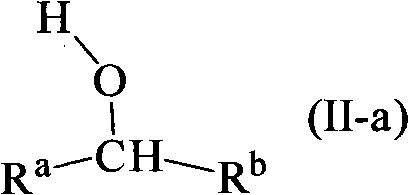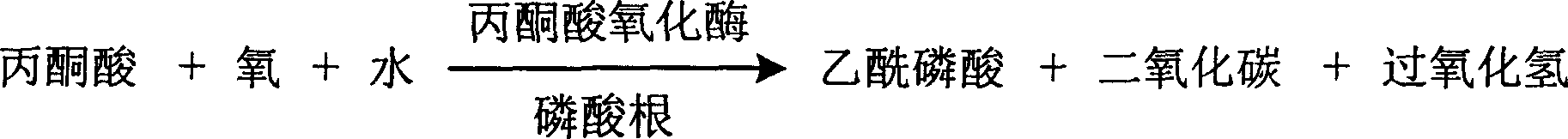Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Phosphagen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phosphagens, also known as macroergic compounds, are high energy storage compounds, also known as high-energy phosphate compounds, chiefly found in muscular tissue in animals. They allow a high-energy phosphate pool to be maintained in a concentration range, which, if it all were adenosine triphosphate (ATP), would create problems due to the ATP-consuming reactions in these tissues. As muscle tissues can have sudden demands for lots of energy; these compounds can maintain a reserve of high-energy phosphates that can be used as needed, to provide the energy that could not be immediately supplied by glycolysis or oxidative phosphorylation. Phosphagens supply immediate but limited energy.
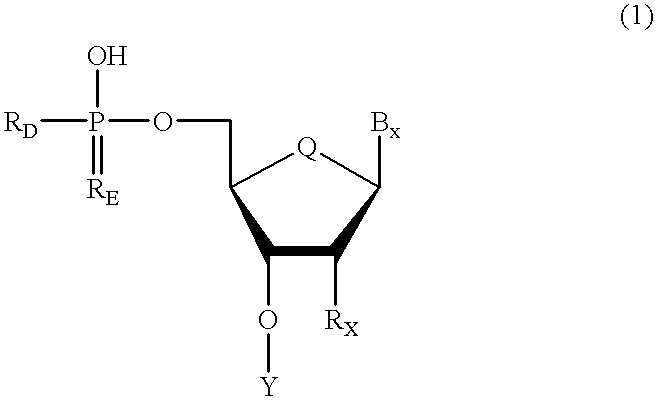
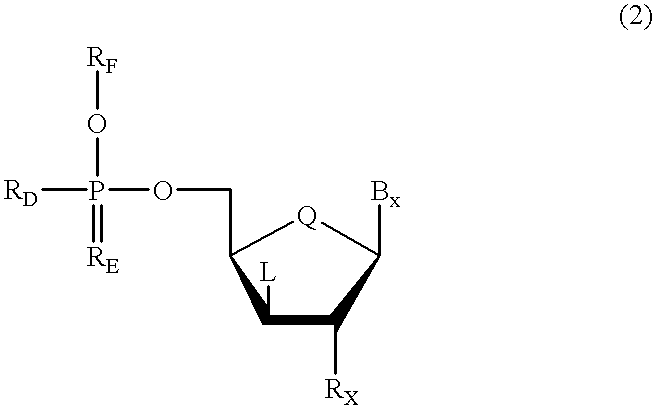
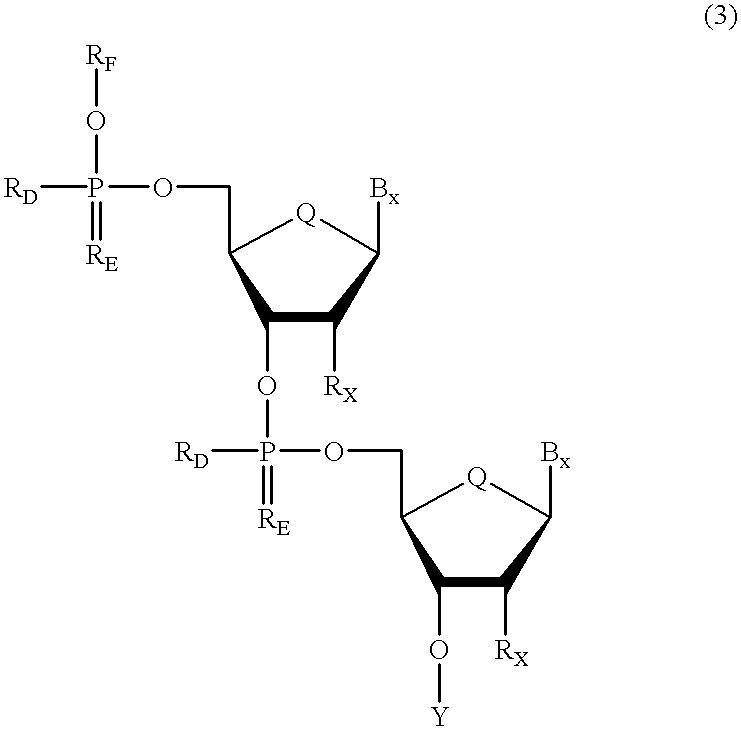
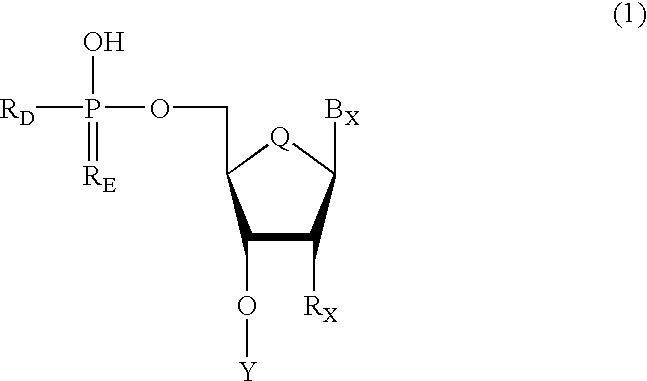
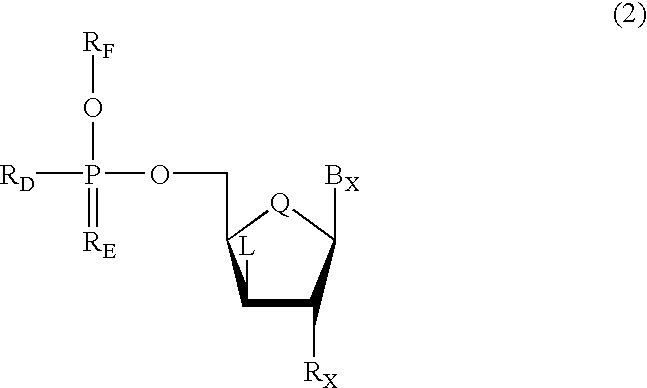
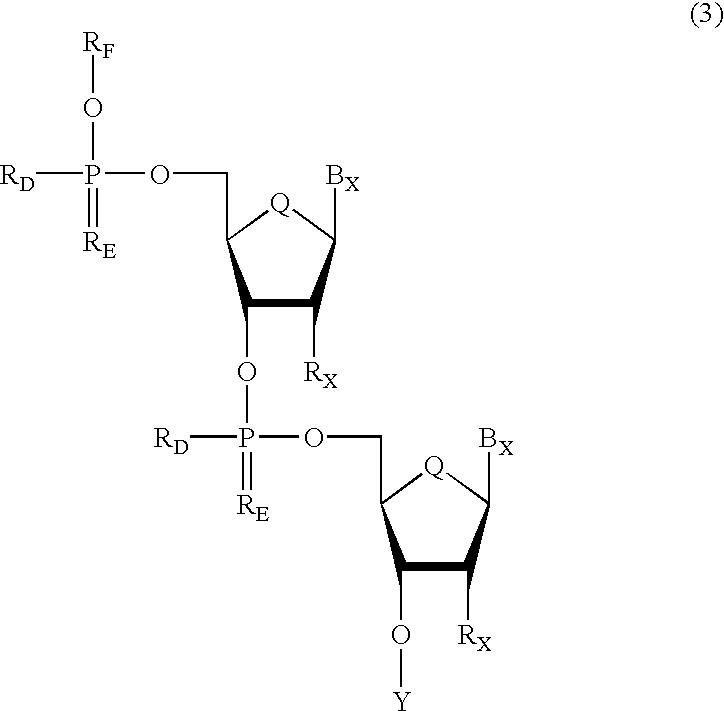
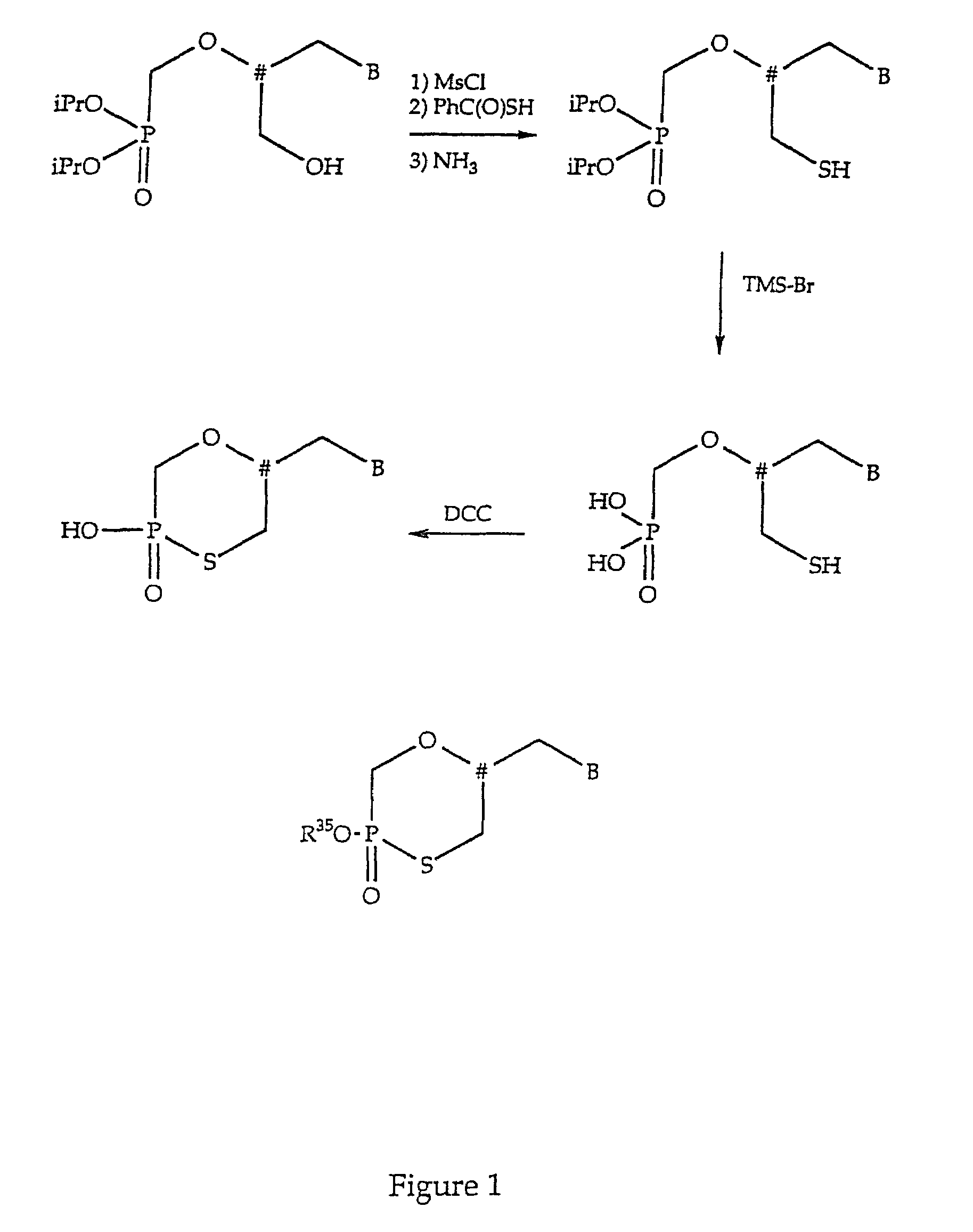
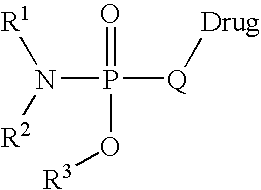
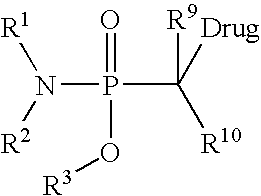
Oligonucleotides having chiral phosphorus linkages
InactiveUS6239265B1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesImprove propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSugar moietyPhosphoramidate
Sequence-specific oligonucleotides are provided having substantially pure chiral Sp phosphorothioate, chiral Rp phosphorothioate, chiral Sp alkylphosphonate, chiral Rp alkylphosphonate, chiral Sp phosphoamidate, chiral Rp phosphoamidate, chiral Sp phosphotriester, and chiral Rp phosphotriester linkages. The novel oligonucleotides are prepared via a stereospecific SN2 nucleophilic attack of a phosphodiester, phosphorothioate, phosphoramidate, phosphotriester or alkylphosphonate anion on the 3' position of a xylonucleotide. The reaction proceeds via inversion at the 3' position of the xylo reactant species, resulting in the incorporation of phosphodiester, phosphorothioate, phosphoramidate, phosphotriester or alkylphosphonate linked ribofuranosyl sugar moieties into the oligonucleotide.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
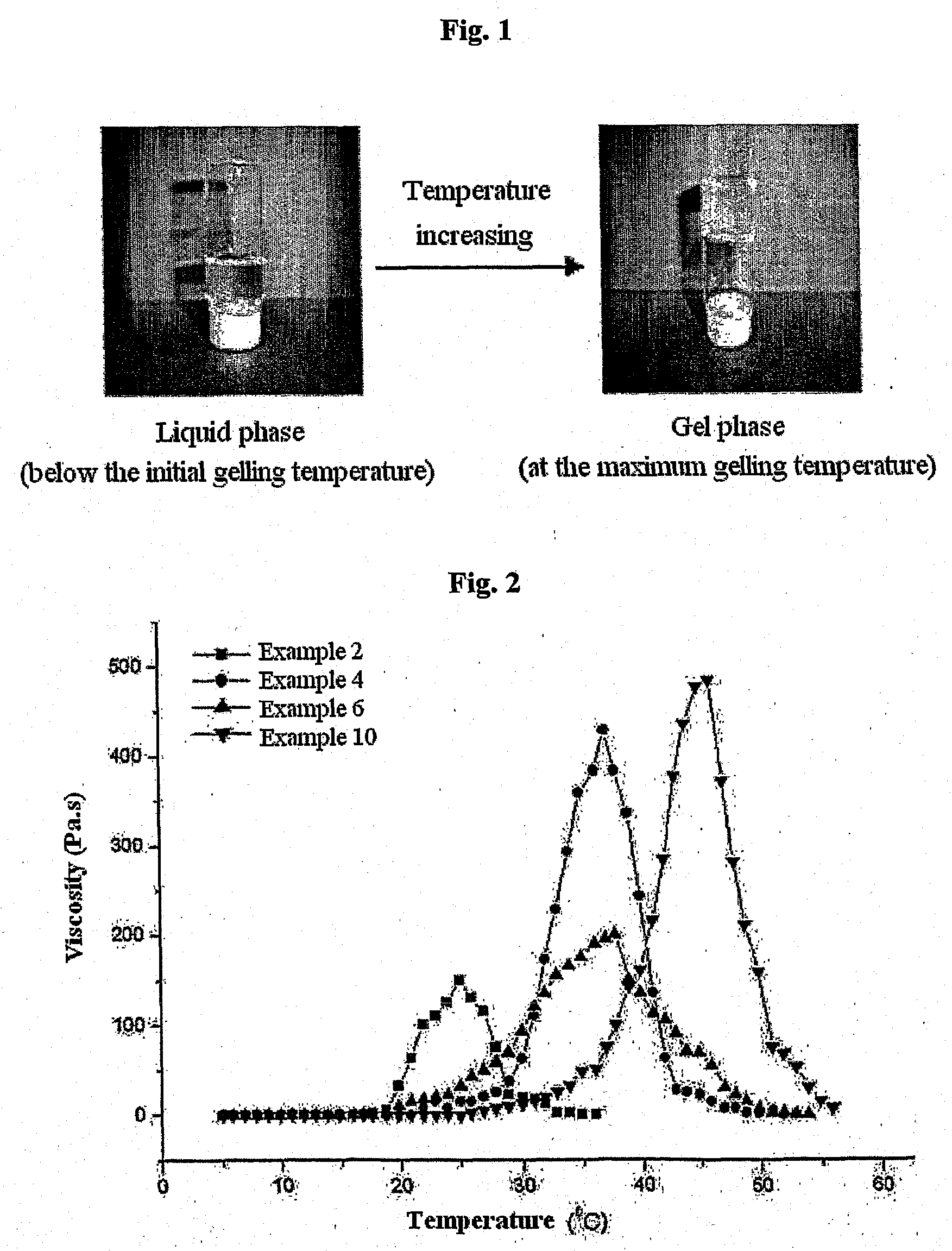
Biodegradable and Thermosensitive Poly(Organophosphazene) Hydrogel, Preparation Method Thereof and Use Thereof
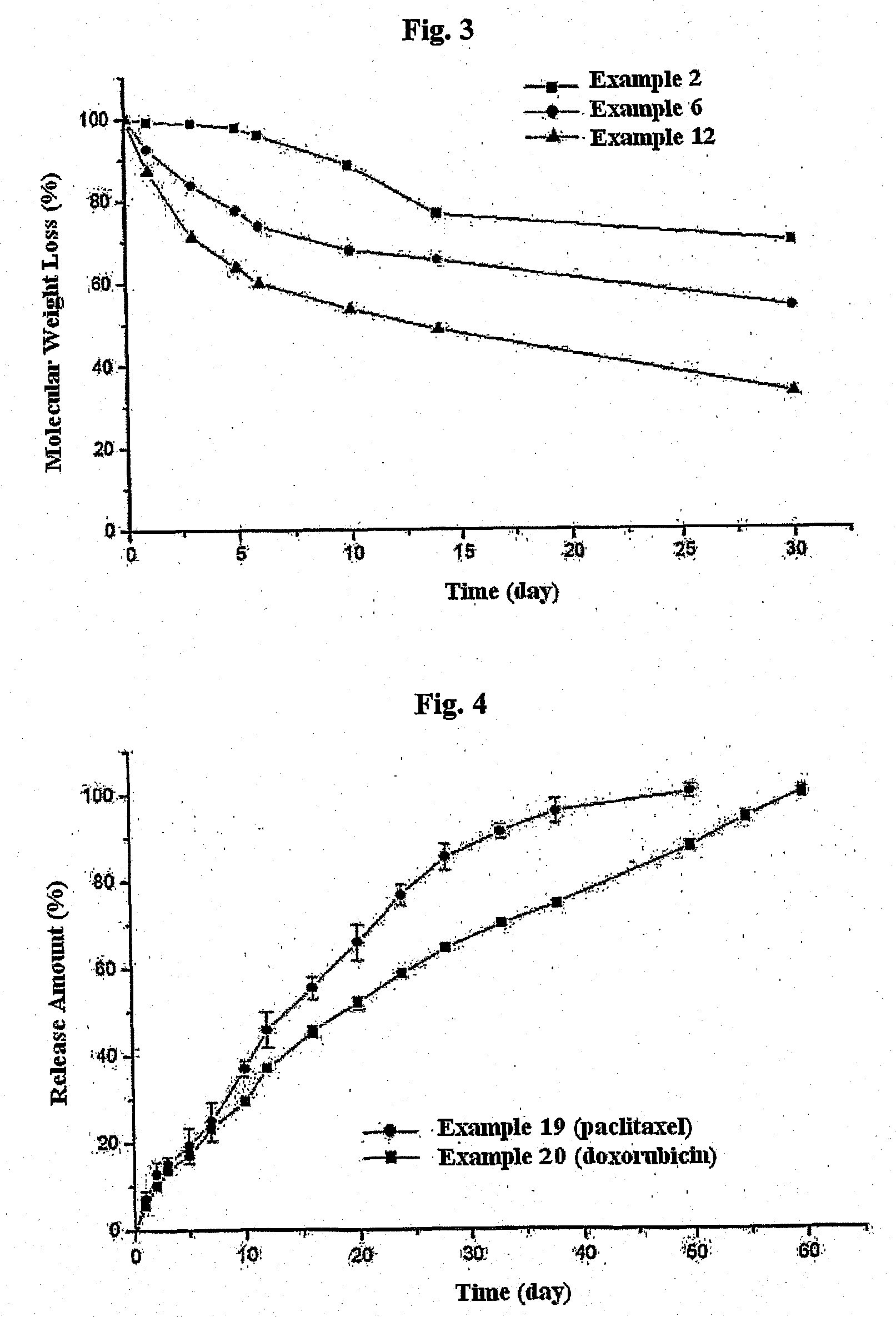
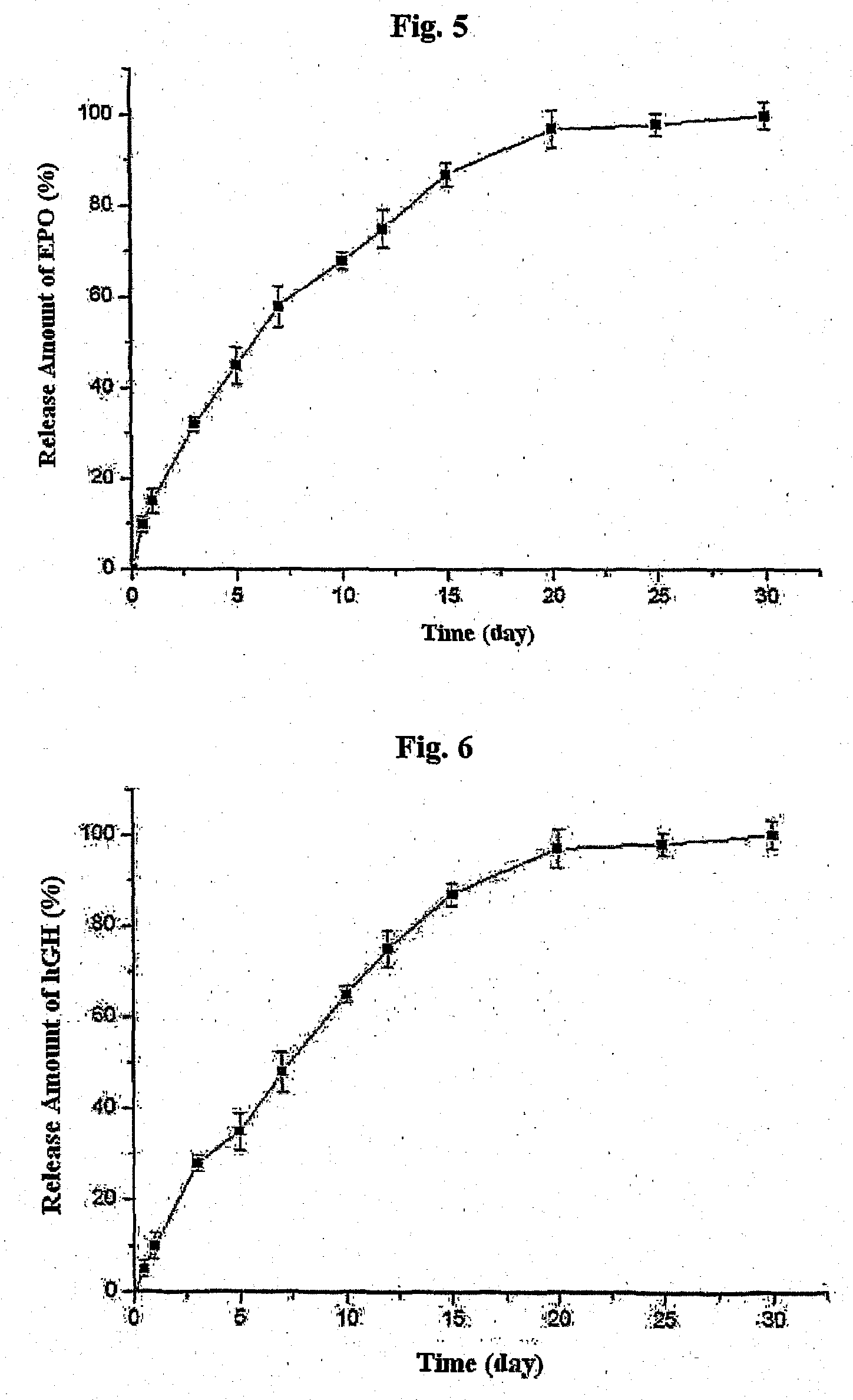
The present invention relates to a biodegradable and thermosensitive poly(organophosphazene) with a functional group, a preparation method thereof, and a use thereof for delivery of bioactive substances. According to the present invention, poly(organophosphazene) is a phosphagen-based polymer showing biodegradability, thermosensitivity, and sol-gel phase transition depending on temperature change, whereby when administered into a living body with bioactive substances such as drugs, the poly(organophosphazene) forms a gel-phase at body temperature to be capable of controlled release of the bioactive substances. Further, the poly(organophosphazene) has functional groups to chemically bind with bioactive substances through an ionic bond, covalent bond, or coordinate covalent bond to be capable of a sustained release of the bioactive substances due to its good binding property. Therefore, the poly(organophosphazene) is useful as a delivery material for bioactive substances.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing phosphatidylserine abundant in polyunsaturated fatty acid
InactiveCN101818179ANo emissionsImprove product qualityMicroorganism based processesFermentationUnsaturated fatty acid esterPhospholipid
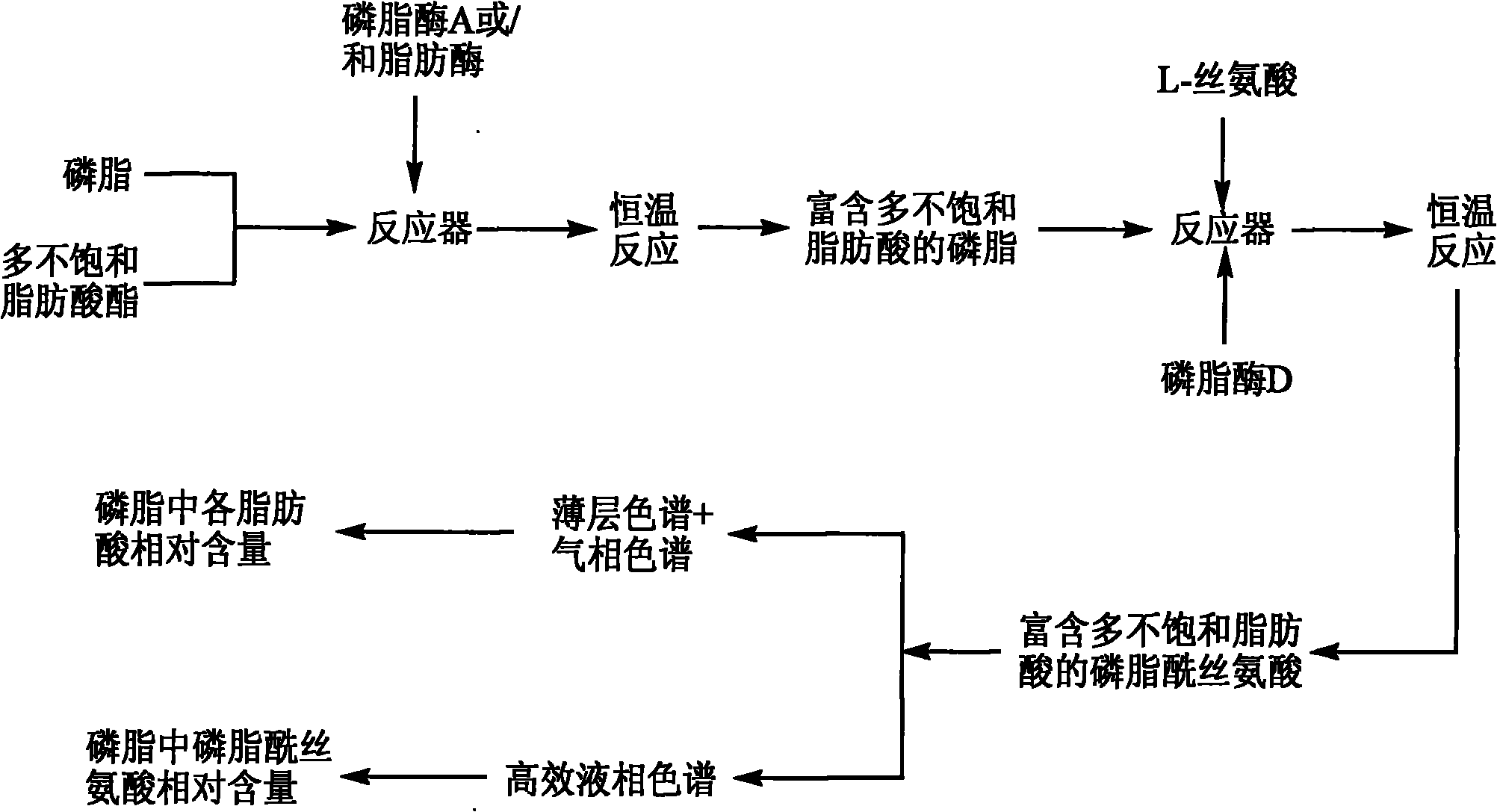
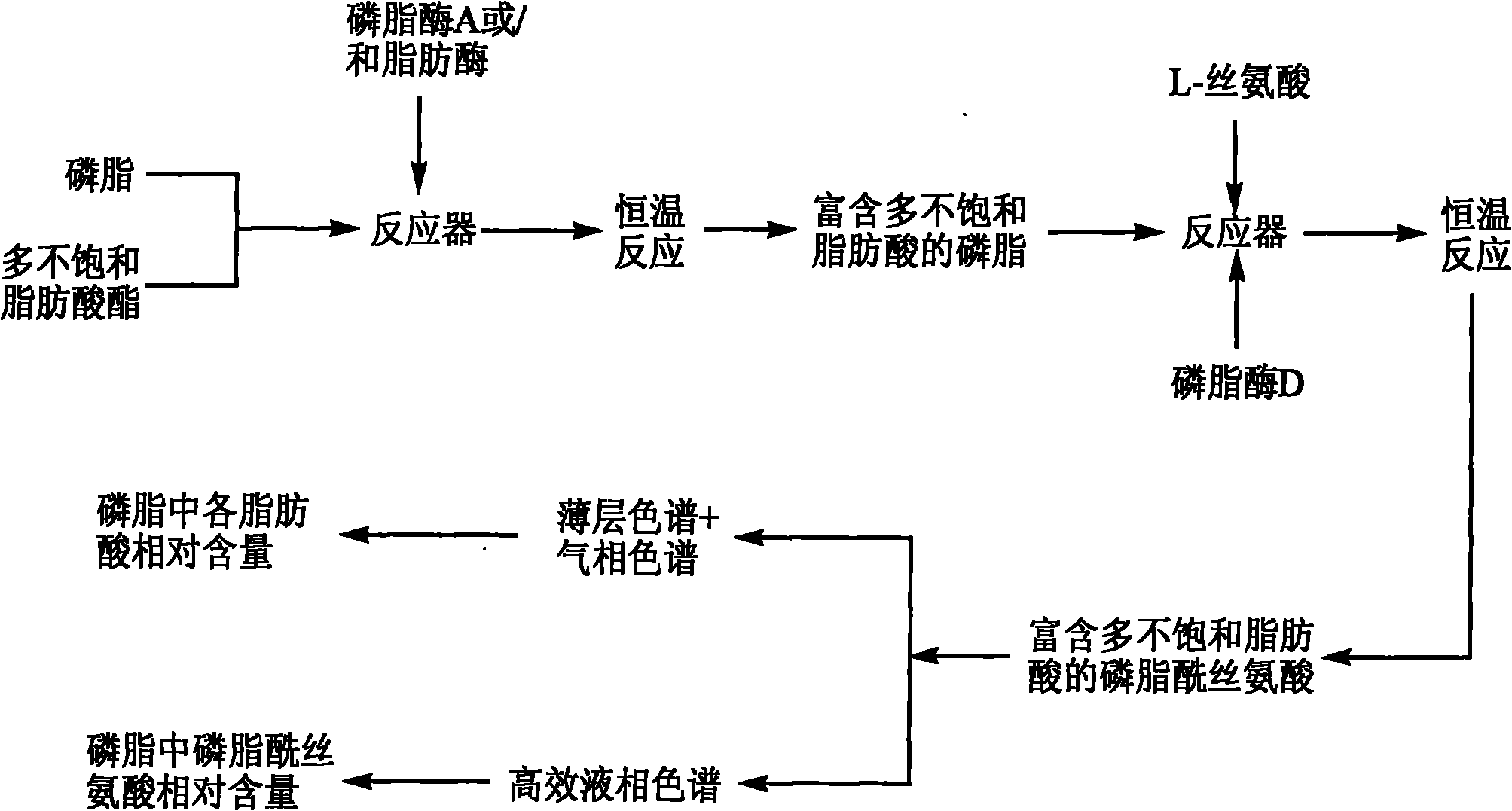
The invention relates to a method for preparing phosphatidylserine abundant in polyunsaturated fatty acid and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly, catalyzing ester exchange reaction between phosphatide and polyunsaturated fatty acid ester by utilizing one or a mixture of phosphatidase A and lipase to generate phosphatide abundant in polyunsaturated fatty acid; and then catalyzing phosphor-transfer esterification reaction between the phosphatide abundant in the polyunsaturated fatty acid and L-serine by utilizing phosphatidase D to generate the phosphatidylserine abundant in the polyunsaturated fatty acid. The method has the advantages of no discharge of waste water, good product quality, no solvent residue, safe process operation, few reaction byproducts, no waste generation, cost reduction, simple production process and easy realization of scale production because of utilizing two enzymes to perform sub-step catalysis and perform reaction in the same reactor, and completing the reaction process in a non-solvent system. Therefore, the invention provides a good and feasible method for preparing the phosphatidylserine abundant in the polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Oligonucleotides having chiral phosphorus linkages
InactiveUS20020137921A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesImprove propertiesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSugarSugar moiety
Sequence-specific oligonucleotides are provided having substantially pure chiral Sp phosphorothioate, chiral Rp phosphorothioate, chiral Sp alkylphosphonate, chiral Rp alkylphosphonate, chiral Sp phosphoamidate, chiral Rp phosphoamidate, chiral Sp phosphotriester, and chiral Rp phosphotriester linkages. The novel oligonucleotides are prepared via a stereospecific SN2 nucleophilic attack of a phosphodiester, phosphorothioate, phosphoramidate, phosphotriester or alkylphosphonate anion on the 3' position of a xylonucleotide. The reaction proceeds via inversion at the 3' position of the xylo reactant species, resulting in the incorporation of phosphodiester, phosphorothioate, phosphoramidate, phosphotriester or alkylphosphonate linked ribofuranosyl sugar moieties into the oligonucleotide.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Oligonucleotides having chiral phosphorus linkages
Sequence-specific oligonucleotides are provided having substantially pure chiral Sp phosphorothioate, chiral Rp phosphorothioate, chiral Sp alkylphosphonate, chiral Rp alkylphosphonate, chiral Sp phosphoamidate, chiral Rp phosphoamidate, chiral Sp phosphotriester, and chiral Rp phosphotriester linkages. The novel oligonucleotides are prepared via a stereospecific SN.sub.2 nucleophilic attack of a phosphodiester, phosphorothioate, phosphoramidate, phosphotriester or alkylphosphonate anion on the 3' position of a xylonucleotide. The reaction proceeds via inversion at the 3' position of the xylo reactant species, resulting in the incorporation of phosphodiester, phosphorothioate, phosphoramidate, phosphotriester or alkylphosphonate linked ribofuranosyl sugar moieties into the oligonucleotide.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
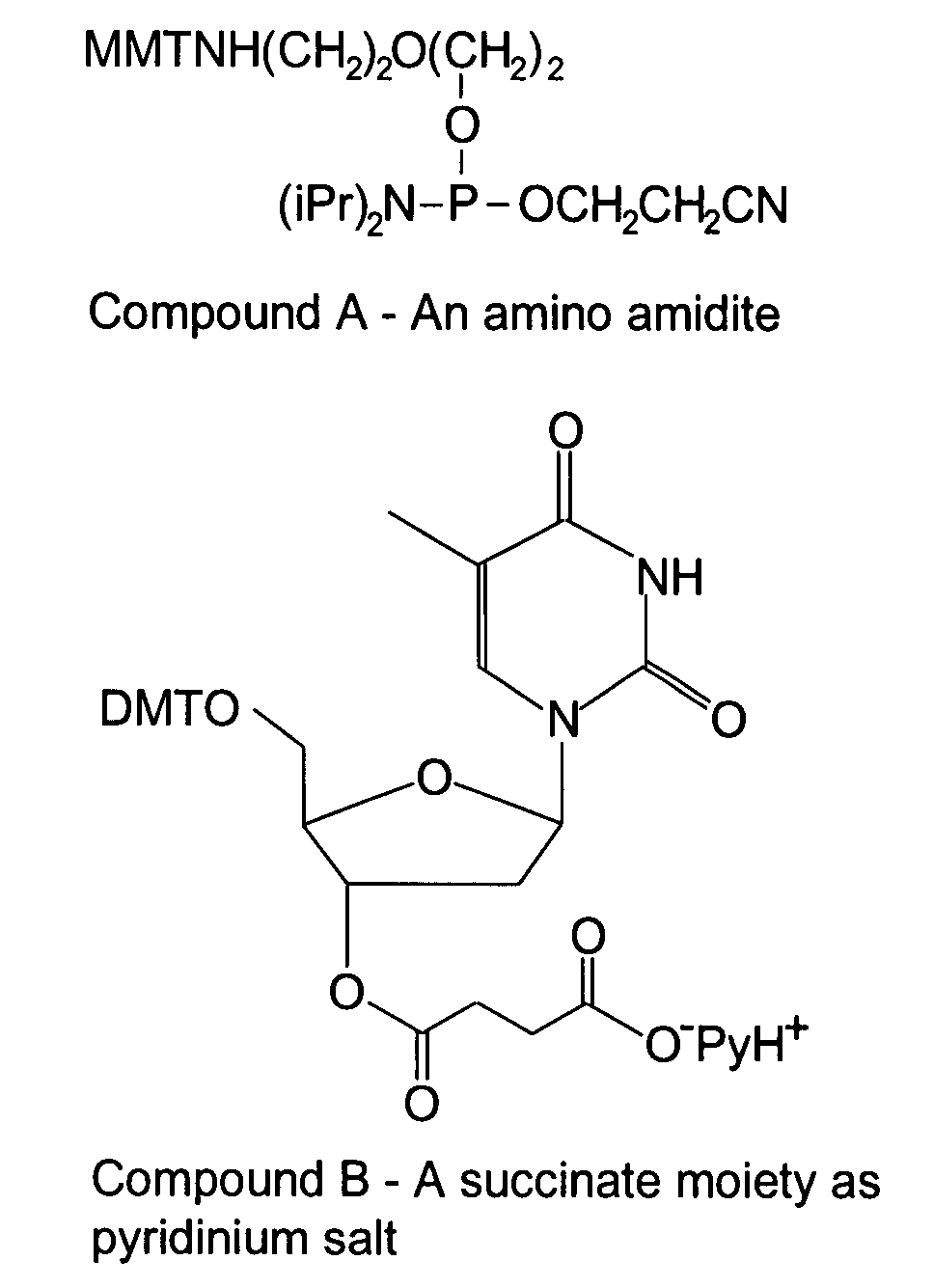
RNA sequences generated using a microarray having a base cleavable succinate linker
InactiveUS20080125327A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementSuccinic acidOxygen
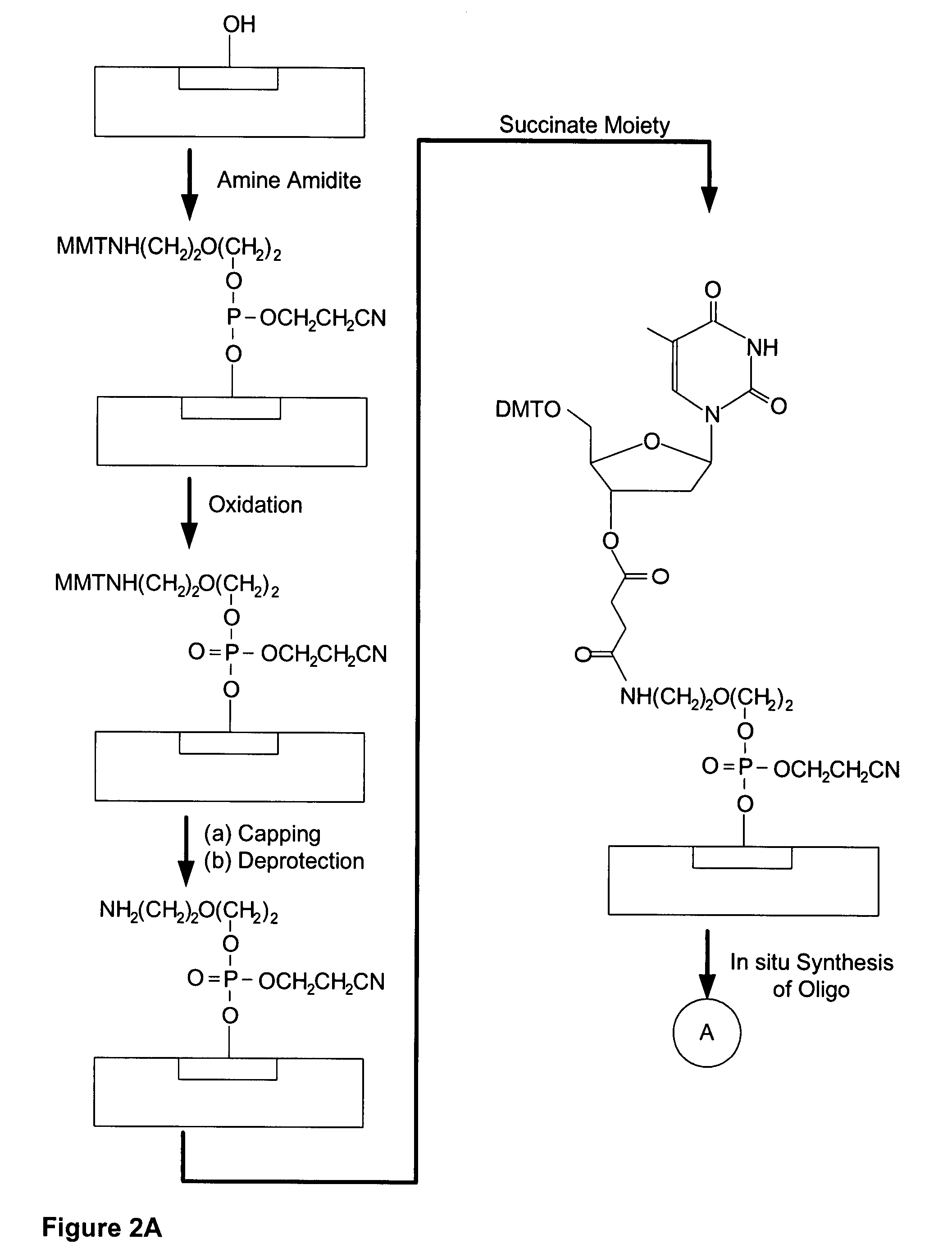
There is disclosed a microarray having base cleavable succinate linkers. The microarray has a solid surface with known locations, each having reactive hydroxyl groups. The density of the known locations is greater than approximately 100 locations per square centimeter. Amino moieties are attached to the reactive hydroxyl groups. Preferably the attachment is through a phosphorous-oxygen bond between the phosphorous of amino amidite moieties and the oxygen of the hydroxyl groups. Succinate moieties are attached to the amino moieties through amide bonds to form cleavable linkers attached to the microarray. Oligomers may be synthesis in situ onto the cleavable linkers and subsequently cleaved using a cleaving base. The cleaved oligomers are recoverable and include oligonucleotides.
Owner:CUSTOMARRAY INC
99mTc-labeled 19 amino acid containing peptide for use as phosphatidylethanolamine binding molecular probe and radiopharmaceutical
With only 19 amino acids, Duramycin is the smallest known polypeptide that has a defined 3-dimmensional binding structure. Duramycin binds Phosphatidylethanolamine (PtdE) at a 1:1 ratio with high affinity and exclusive specificity. As an abundant binding target, PtdE is a major phospholipid and accounts for about 20 % of the phospholipid content in mammalian cellular membranes. PtdE is externalized to the surface of apoptotic cells, and also becomes accessible in necrotic cells due to compromised plasma membrane integrity. Given the unique physicochemical properties of Duramycin and the availability of PtdE in acute cell death, the goal of this study is to develop and evaluate 99mTc-HYNIC-Duramycin as a novel molecular probe for imaging PtdE. 99mTc-HYNIC-Duramycin is a low-molecular weight, fast-clearing radiopharmaceutical that detects apoptosis / necrosis by binding to PtdE. The goal was to quantify the uptake of 99mTc-HYNIC-Duramycin in the area-at-risk after myocardial ischemia and reperfusion, and to determine the window of detection.
Owner:MCW RES FOUND INC
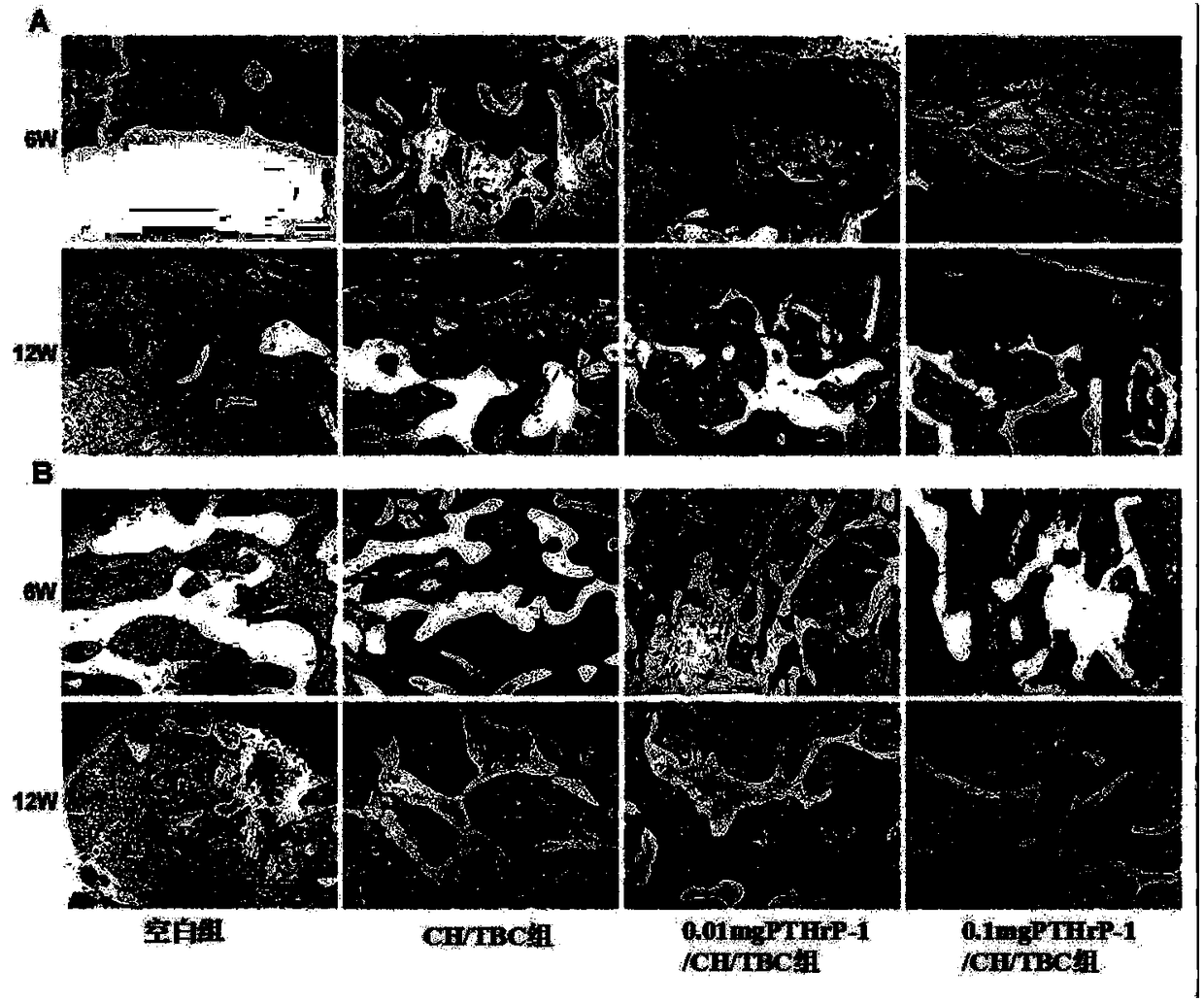
Active polypeptide capable of promoting osteogenesis and inhibiting osteoclast and application of active polypeptide
ActiveCN108276487AReduce osteoclastsReduce osteoporosisPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderViewpointsCalcium phosphate coating
The invention discloses an active polypeptide capable of promoting osteogenesis and inhibiting osteoclast and application of the active polypeptide. N-terminal serine is phosphorylated on the basis ofPTH1-34, and three repeated sequences of glutamic acid or aspartic acid are introduced at a C terminal; the sequence of the polypeptide is shown in SEQ ID NO:1 or SEQ ID NO:2, and the polypeptide hasosteoinductive activity similar to BMP2 and an osteoclast inhibiting effect similar to parathyroid hormones (PTH). Random coils of the polypeptide can be avoided by bonding the C-terminal repeated sequences of the polypeptide to the surface of a calcium phosphate material or a material with a calcium phosphate coating, no addition of organic reagents is needed, and therefore the activity of the polypeptide is protected effectively; furthermore, slow controlled release can be achieved through cleavage of peptide bonds, and long-term intermittent injection of the PTH1-34 can be avoided, so thatthe injection pain of patients is reduced, and effects of osteoblast promotion and osteoporosis inhibition are achieved; a conventional viewpoint that the PTH1-34 cannot be administered locally is changed.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
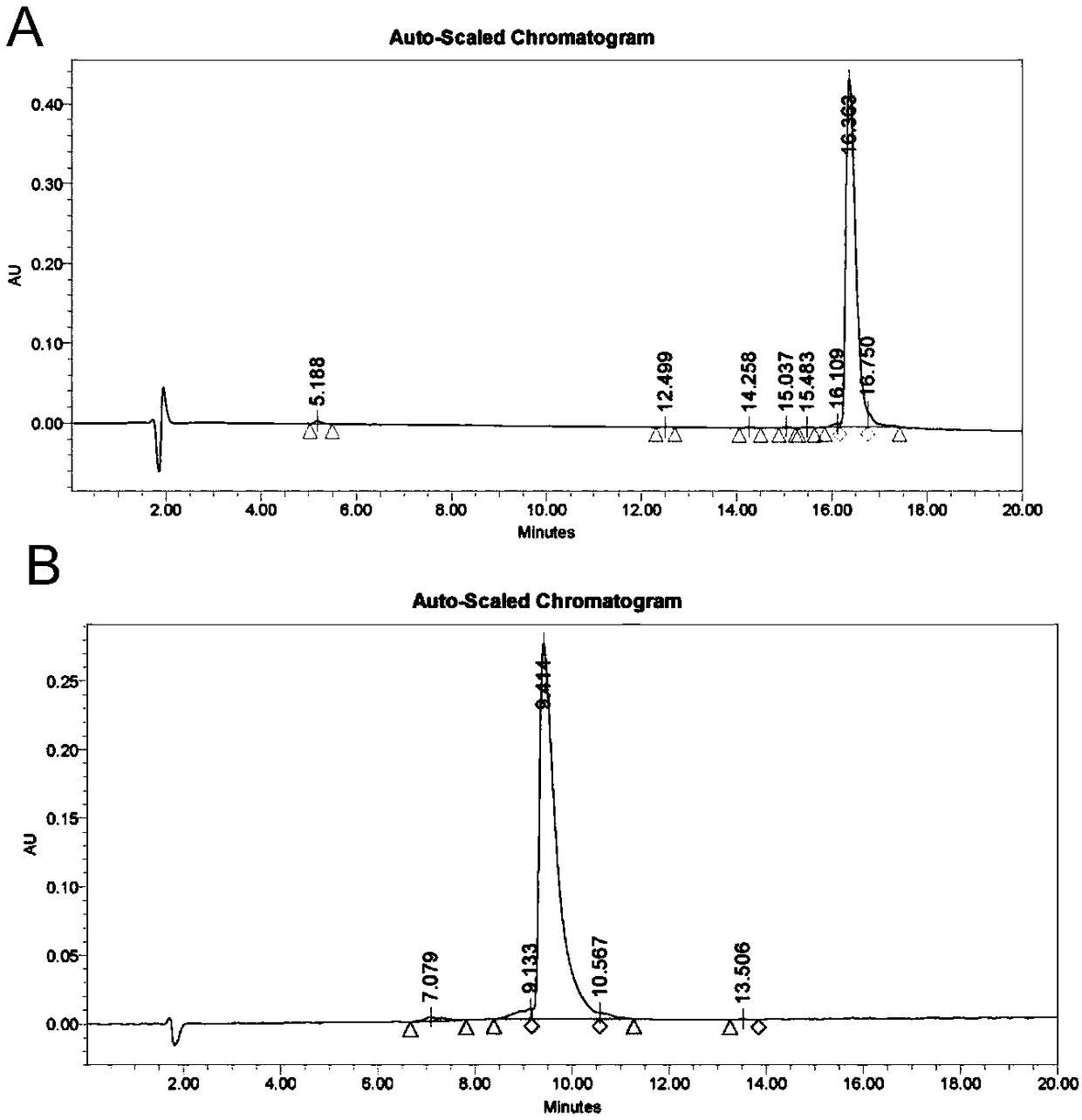
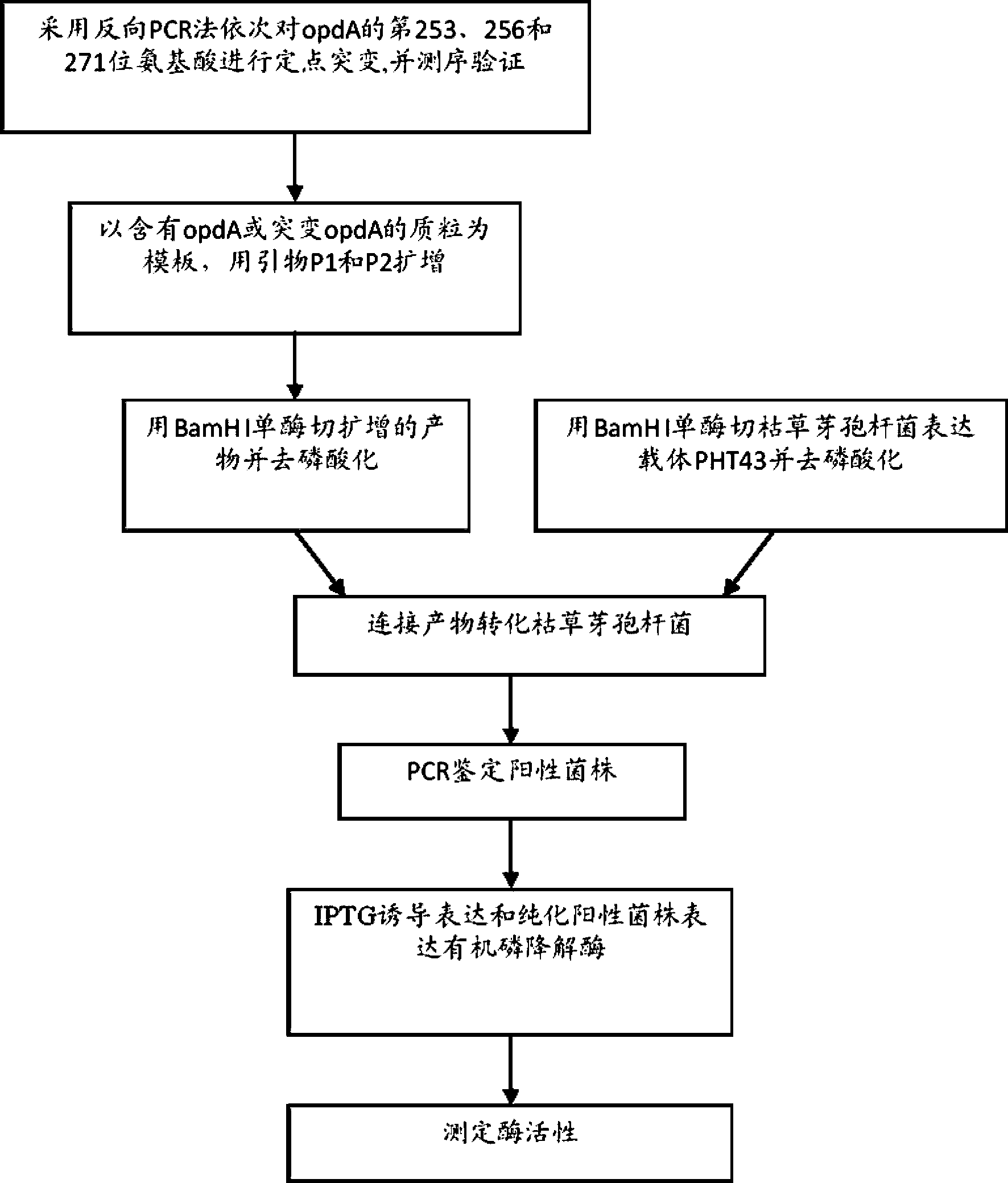
Organophosphorus pesticide degrading enzyme gene and application thereof
The invention discloses an organophosphorus pesticide degrading enzyme gene and application thereof. The gene is obtained through site-specific mutagenesis on three amino acid coding loci, the 253rd locus, the 256th locus and the 271st, on the organophosphorus degrading enzyme gene. The nucleotide sequence with mutated organophosphorus pesticide degrading enzyme gene is connected to a pHT43 vector, then the expression vector is transferred into Bacillus subtilis host cells for expression, so as to isolate expression protein with organophosphorus pesticide degrading activity. The organophosphorus pesticide degrading enzyme expressed by mutant gene provided by the invention has obviously improved affinity and sensitivity with a substrate ethyl-parathion, and obviously improved enzyme activity; the invention can be used for degradation and elimination of organic phosphorus pesticide residues in agricultural products and opens up a novel path for the engineering enzymatic degradation of organophosphorus pesticide.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
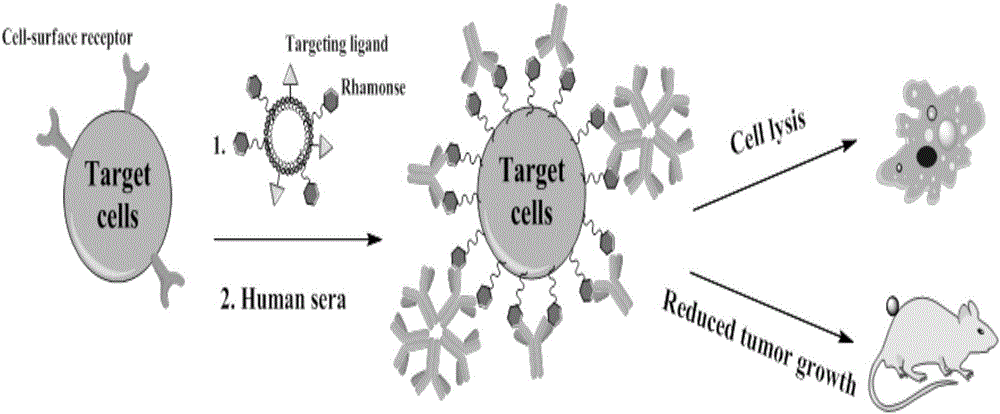
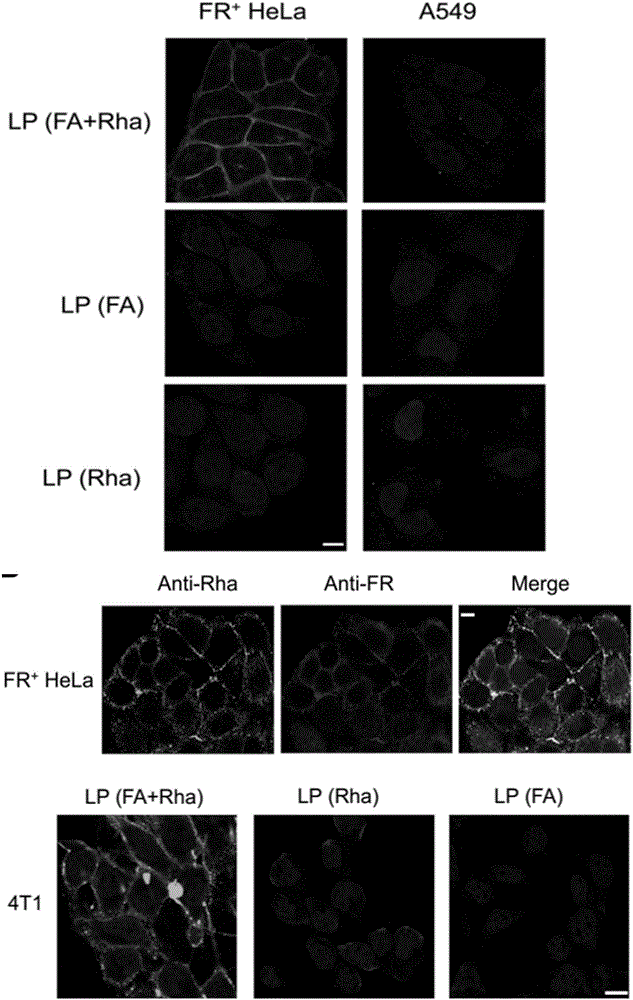
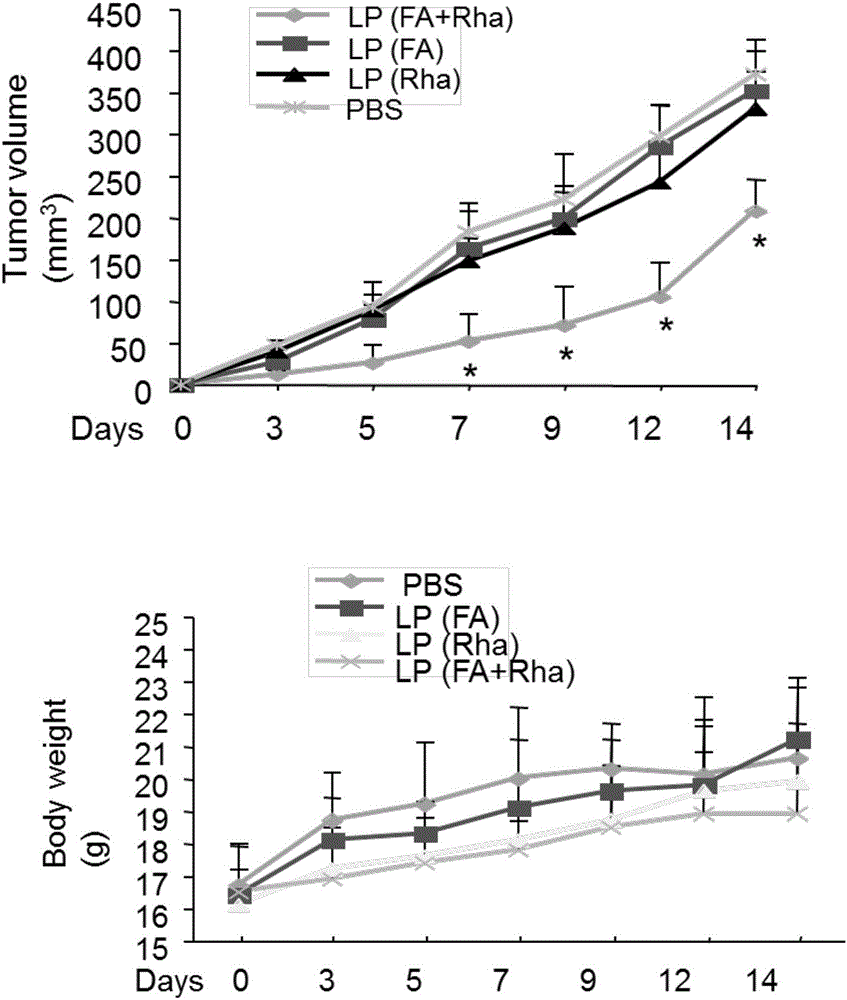
Liposome for cancer targeting immunotherapy by natural sugar antibody and preparation method of liposome
InactiveCN106146824AEfficient complement-dependent toxicityGood curative effectPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCancer targetingSide effect
The invention provides a novel phospholipid derived compound shaped like phospholipid-PEG (polyethylene glycol)-folic acid or phospholipid-PEG-rhamnose, and further provides a liposome medicine combination containing the phospholipid derived compound and a preparation method of the liposome medicine combination. The novel phospholipid derived compound can be used for cancer targeting immunotherapy, and cancer cells are killed by complement dependent toxicity immuno-targeting. Rhamnose and folic acid modified phospholipid is used as a raw material to prepare liposome, targeting property is fine, the cancer cells are efficiently killed by making full use of human natural immunity, toxic and side effects are small, and the liposome is suitable for clinical application research and industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Hydrogenation of ester, ketone or aldehyde groups with ruthenium complexes having di-amine and phosphorous-nitrogen bidentate ligand
InactiveCN102227261AHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsKetoneAldehyde formation
The present invention relates to the field of catalytic hydrogenation and, more particularly, to the use of specific ruthenium catalysts, or pre-catalysts, in hydrogenation processes with molecular H2 for the reduction of ketones, aldehydes and esters or lactones into the corresponding alcohol or diol respectively. Said catalysts are ruthenium complexes comprising a ligand of the type (N-N) type, in which at least one of said amino groups is a secondary or primary amine (i.e. a NH or NH2) and a ligand of the type (P-N) in which N belongs to a tertiary amino group, a N, N, N' trisubstituted carboxiamide (a C(=N)N moiety) or a N-substituted imidoate (a C(=N)O moiety).
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
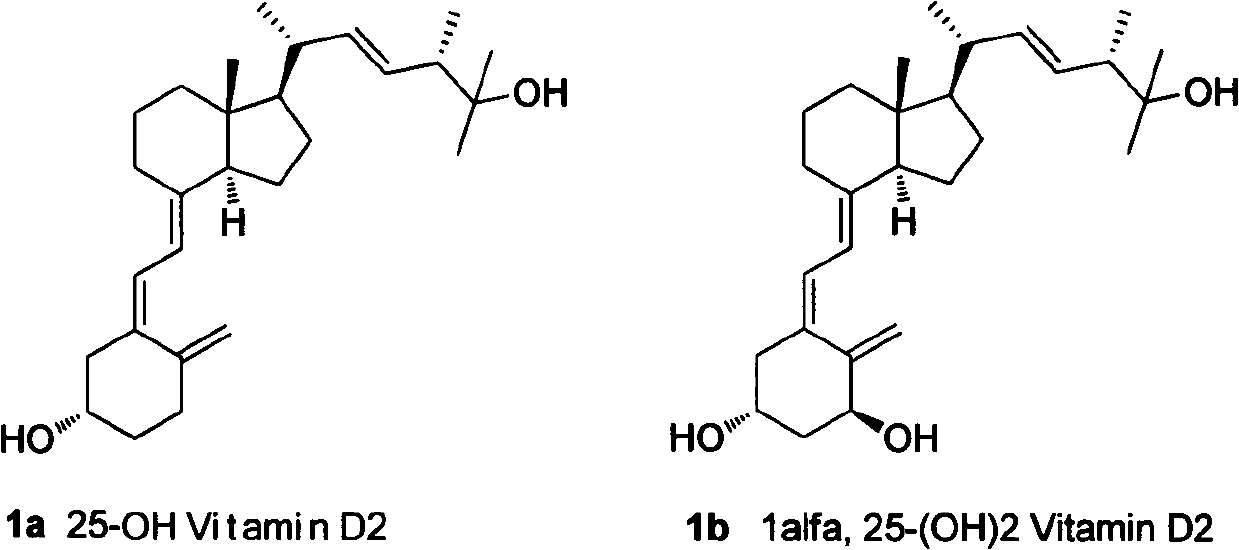
Method for preparing intermediates for synthesizing 25-hydroxyvitamin D2 and 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D2
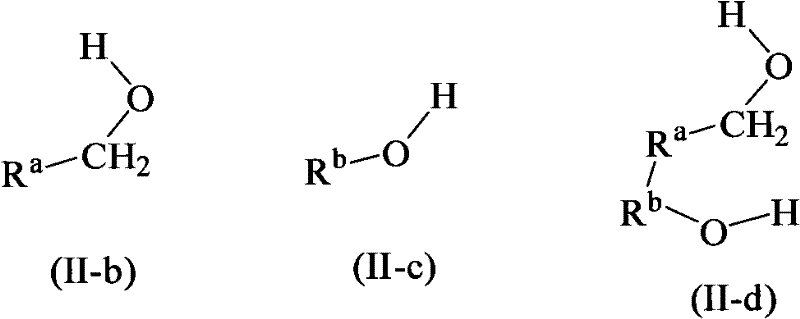
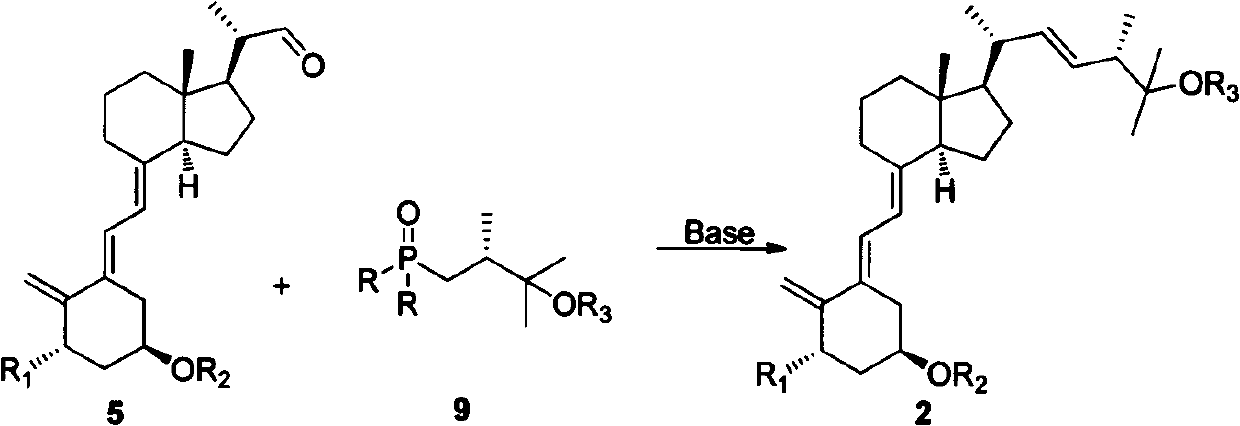
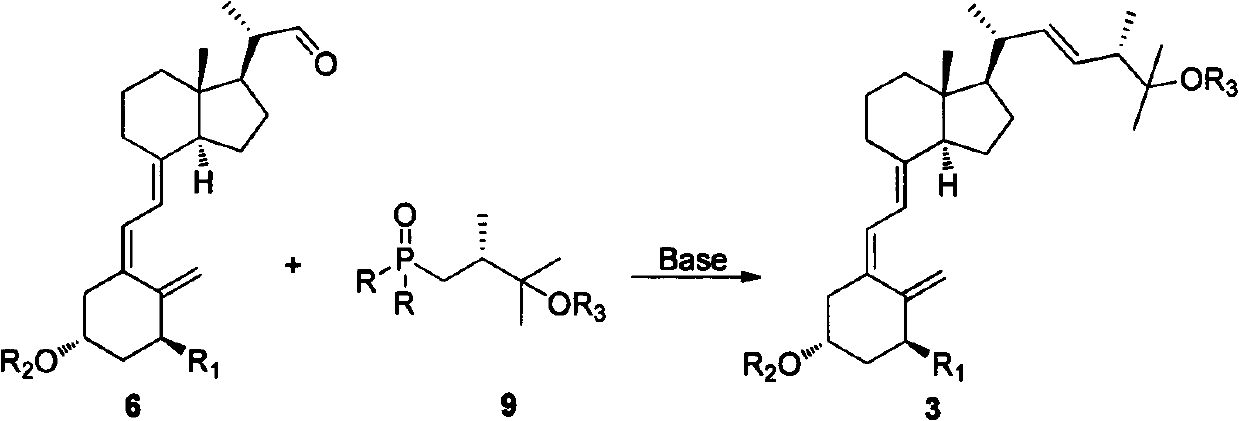
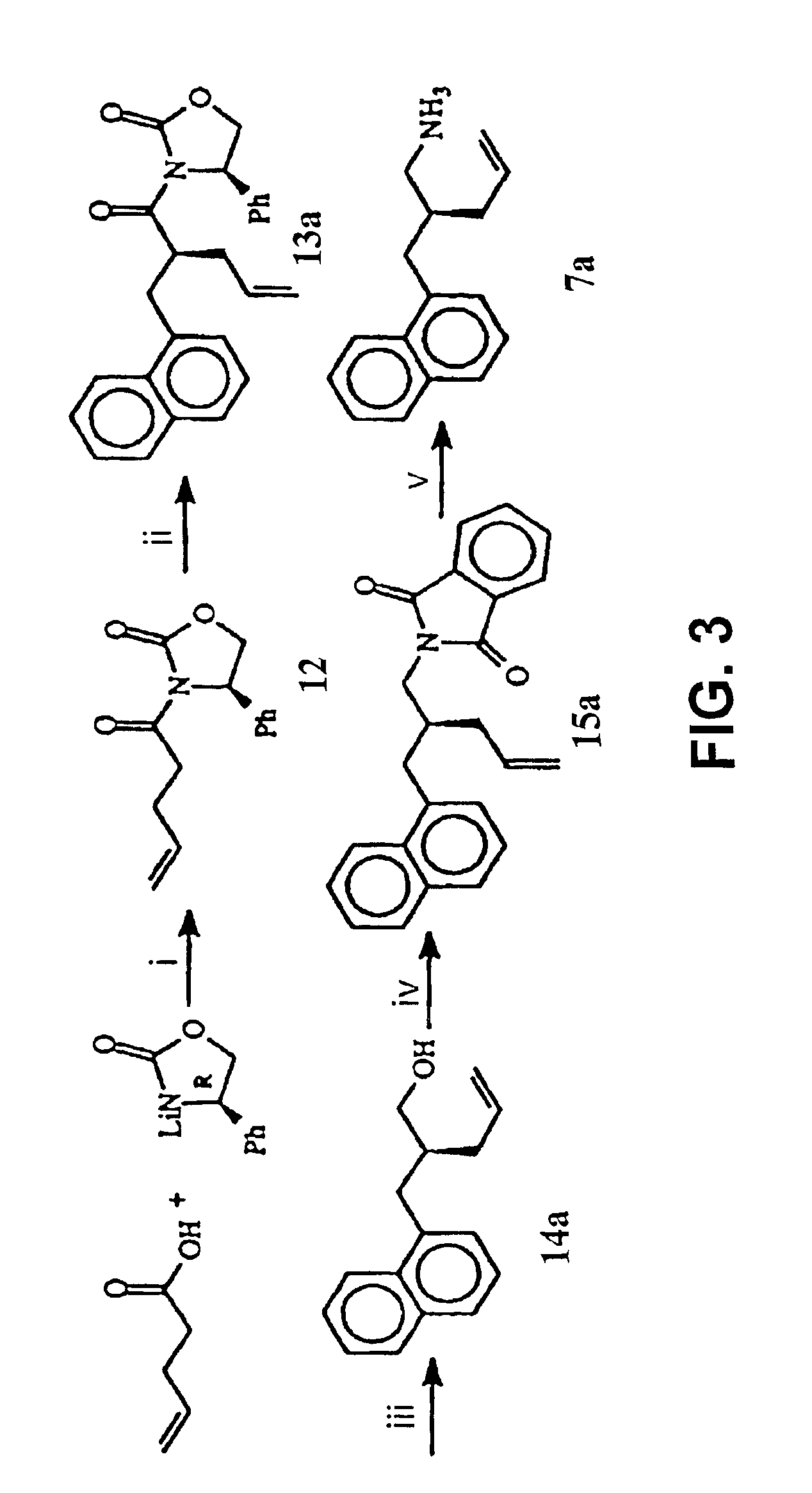
InactiveCN102643302AGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationStereochemistryPhosphagen
The invention discloses a method for preparing intermediates for 25-hydroxyvitamin D2 and 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D2. The structures of the intermediates are compounds 2 and 3 shown as the following formula 1. The preparation method is shown as the following formulas, and comprises the following steps of: treating a phosphorus oxide 9 by using strong base, and performing a Wittig-Hormer reaction with aldehyde 5 or 6. Formula 1.
Owner:SHANGHAI HAOYUAN CHEMEXPRESS
Phenol derivative containing (Rp)-2-chiral phosphinate substituent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103319526AHigh stereoselectivityHigh yieldGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic solventPhenol derivative
The invention provides a method for synthesizing a phenol derivative having a phosphorous chiral center and containing a (Rp)-2-chiral phosphinate substituent in a high stereoselectivity manner. According to the method, with small organic molecules as a catalyst and a (Rp)-2-chiral phosphinate compound containing P-H bonds, and phenol as reaction substrates, an organic solvent is added into a reaction system. The method has the advantages that the catalyst is low in cost and easy to obtain; reaction conditions are mild, safe and reliable; the stereoselectivity of the obtained target product is close to 100 percent and the yield of the obtained target product is up to 90 percent. According to the method provided by the invention, the defects of poor stereoscopic enantioselectivity, fussy reaction steps, low yield and the like of an organic phosphine compound containing the phosphorous chiral center, which is synthesized by adopting a traditional method, are overcome, and the method has a favorable industrial prospect. The invention further provides the phenol derivative having the phosphorous chiral center and containing the (Rp)-2-chiral phosphine substituent.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
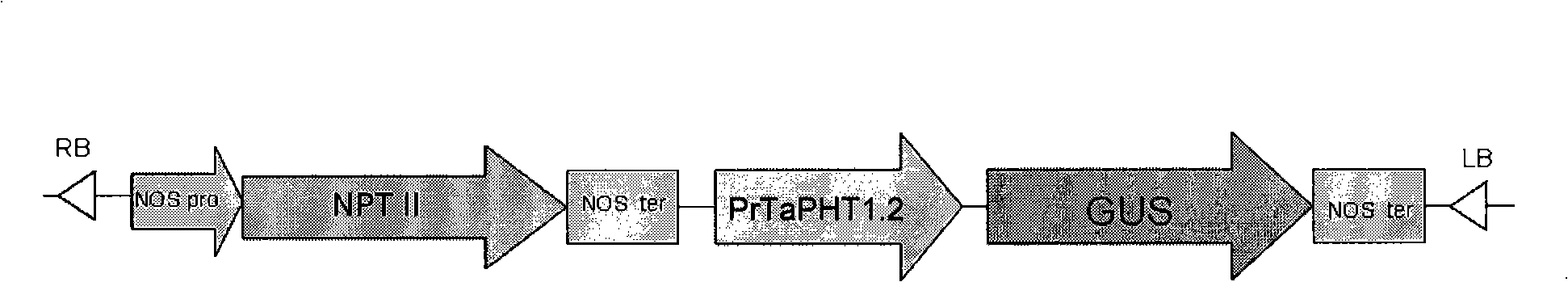
Promoter for expressing phosphor deficiency speciality induction in root and use thereof
The invention discloses a phosphorus deficiency specific inducement root-expression promoter and applications thereof. The promoter can be a DNA molecule as the following 1), 2) or 3): (1) the ribonucleotide sequence thereof is a DNA molecule in the 1st-serial in a sequence list; (2) a DNA molecule which can be hybridized with the DNA molecule of the 1st-serial in the sequence list under a strict condition and can drive targeted genes to be expressed specially in root in case of phosphorus deficiency; (3) a DNA molecule which has the homeology with the DNA by more than 90 percent and can drive targeted genes to be expressed specially in root in case of phosphorus deficiency. The promoter of the invention can be applied to the construction of carriers with economic value and the constructed carriers can be used for breeding transgenic plants with economic value.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
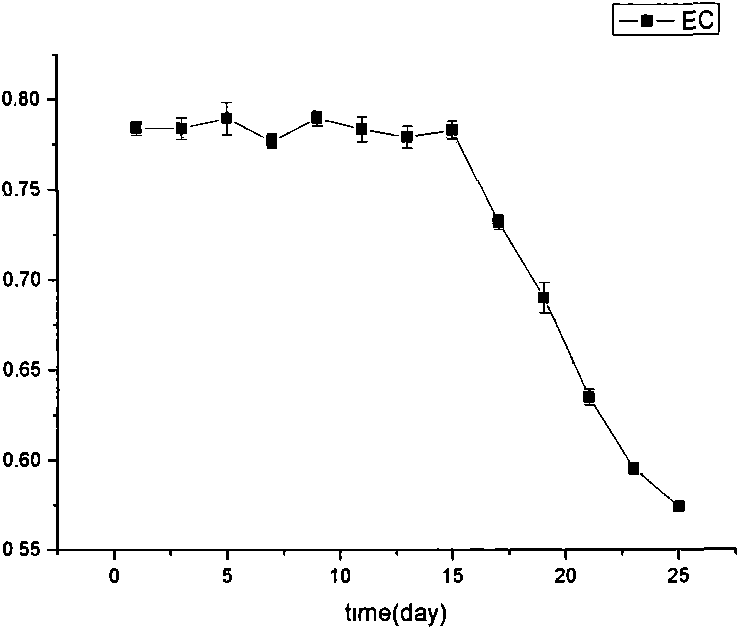
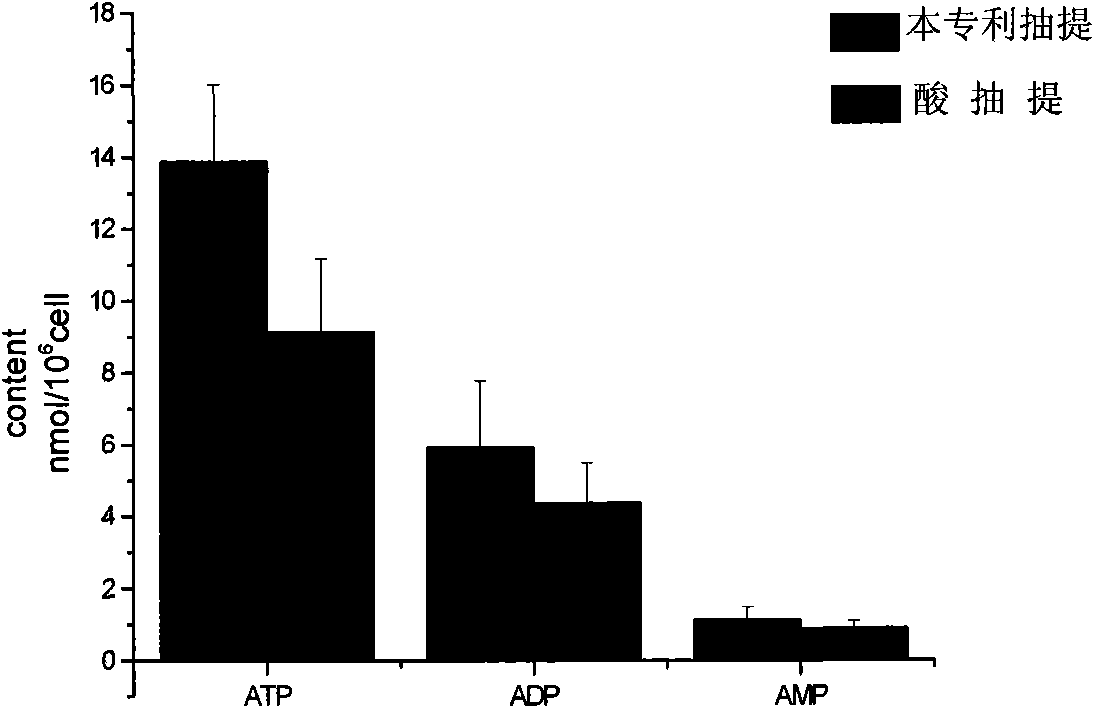
Method for detecting activation of microencapsulated cells
InactiveCN102053123ACorrectly reflect activityAvoid the influence of experimental resultsComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological activationRepeatability
The invention relates to a method for detecting activation of microencapsulated cells. The detection comprises the steps of sample extraction and phosphagen separation and quantification. The activation of the cell in a representation microcapsule is calculated through energy charge. The invention designs an operation scheme for the phosphagen quantification of microencapsulated cells to such special microcapsule system, which can accurately quantify the phosphagen content in the microencapsulated cells, and avoids the defects in the prior art such as large sample loss during extraction, unstable test, bad repeatability, etc., and the test results can be regarded as the evaluation indexes for the activation of the microencapsulated cells.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
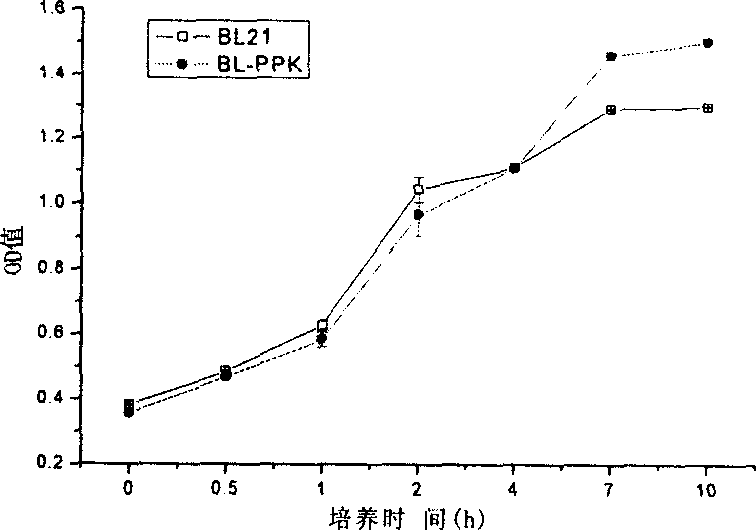
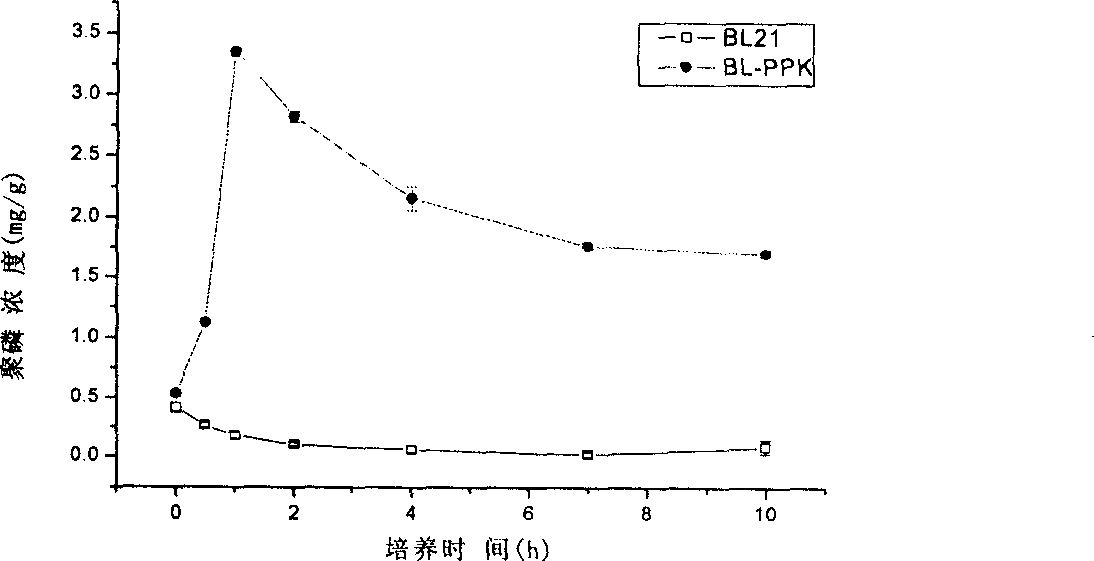
Construction method for polyphosphate kinase gene transformed Escherichia coli
InactiveCN1876809AProof of feasibilityEfficient removalBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBamHIGene clone
The invention discloses a construction approach for bacillus coli of transpolyphosphokinase gene, in which the said method includes gene-clone and carrier-construction; the clone includes extracting master DNA of bacillus coli; designing primers; augmenting ppk gene; restructuring the augmented object gene into clonic carrier pMD18-T and converting bacillus coli DH5 alpha; the construction includes adopting restriction enzymes of BamHI and HindIII bisenzyme to cut pMD18-T plasmid with ppk object gene and idle expression carrier pET-28a(+); directionally connecting the object gene by T4 to the expression carrier pET-28a(+), then converting the DH5 alpha; by the PCR and bisenzyme pressure methods screening and verifying the positive recon; extracting the recombination plasmid Pet28a-PPK and converting the acceptor strain BL21(DE3). The invention is of simple process and the obtained gene has efficient phosphorous removal ability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
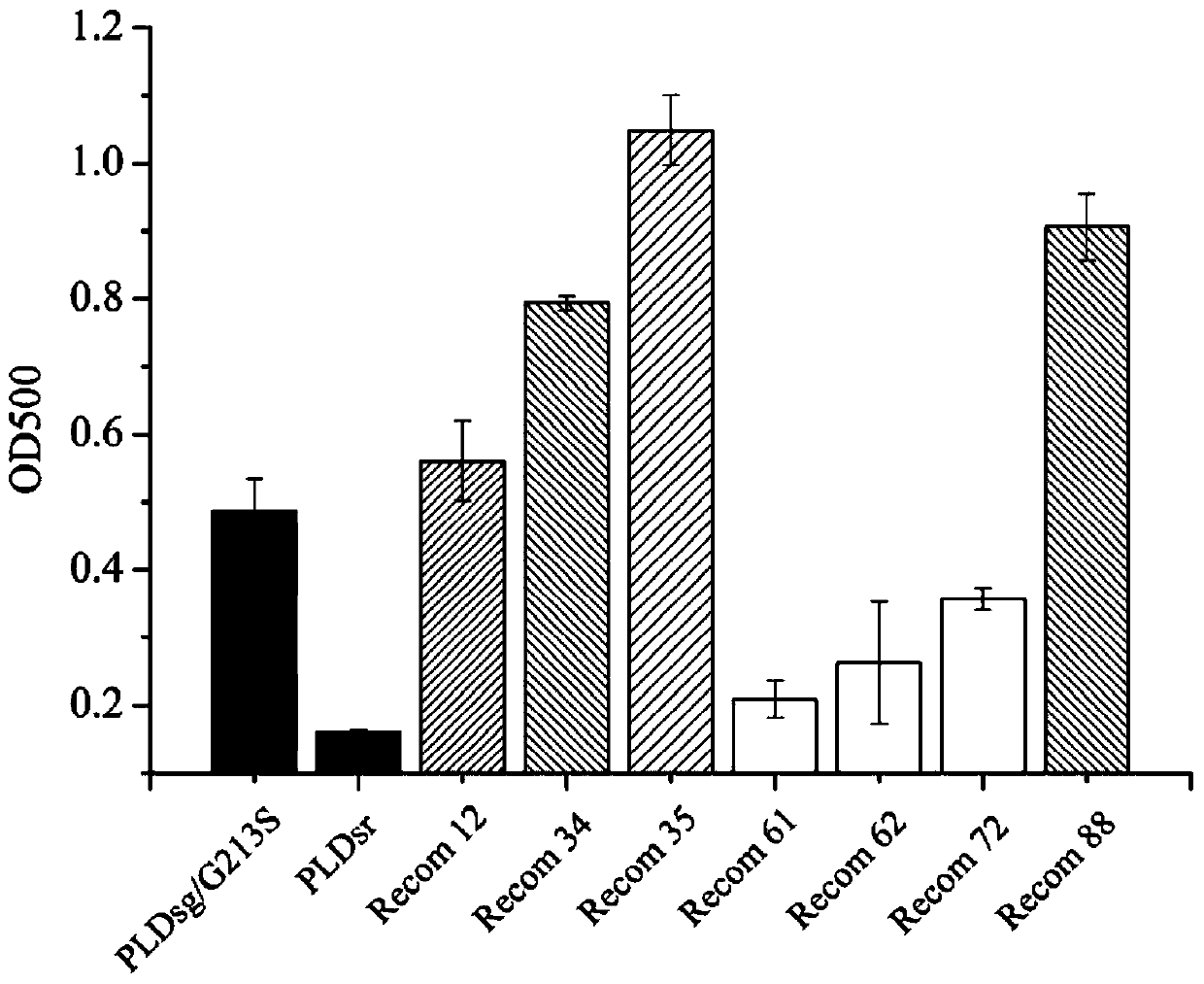
Recombinant phospholipase D and application thereof for synthesizing phosphatidylserine or other phospholipids
ActiveCN110564708AIncreased transesterification activityBacteriaHydrolasesSurface displayEscherichia coli
The invention provides a recombinant phospholipase D, which is a novel PLD (phospholipase D) screened through an escherichia coli surface display technology, a high throughput screening technology anda DNA gene recombination technology. The amino acid sequence of the recombinant phospholipase D provided by the invention is SEQ ID NO:1. The transesterification vitality of the recombinant phospholipase PLDr34 is improved by 3.24 times, a conversion rate is 80.3%, selectivity is 86.8%, and the recombinant phospholipase D is an ideal catalyst synthesized by PS (phosphatidylserine), DHA-PS and other rare phospholipids.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
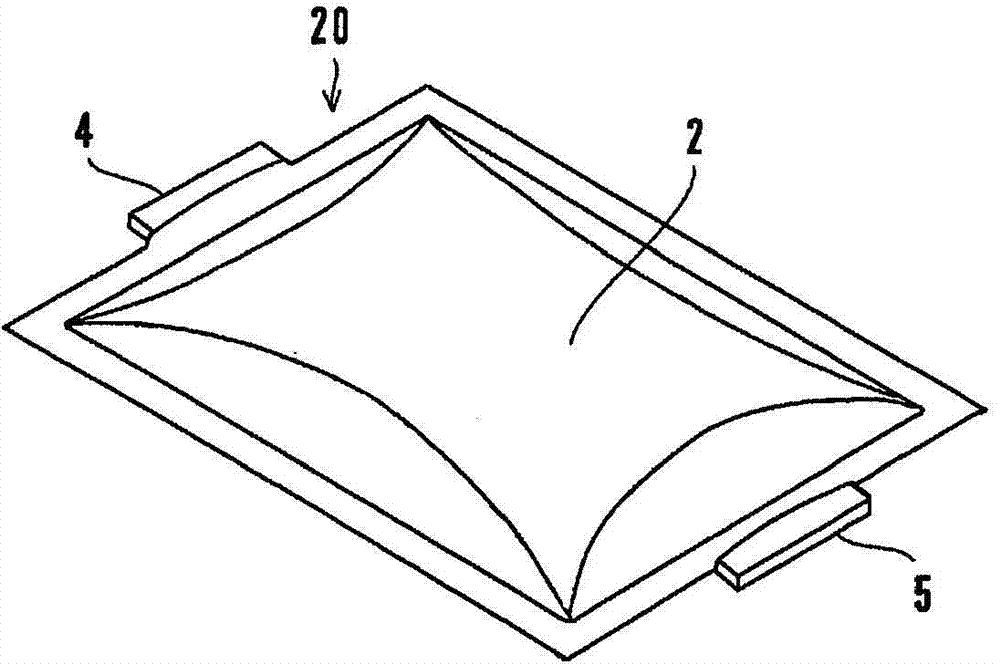
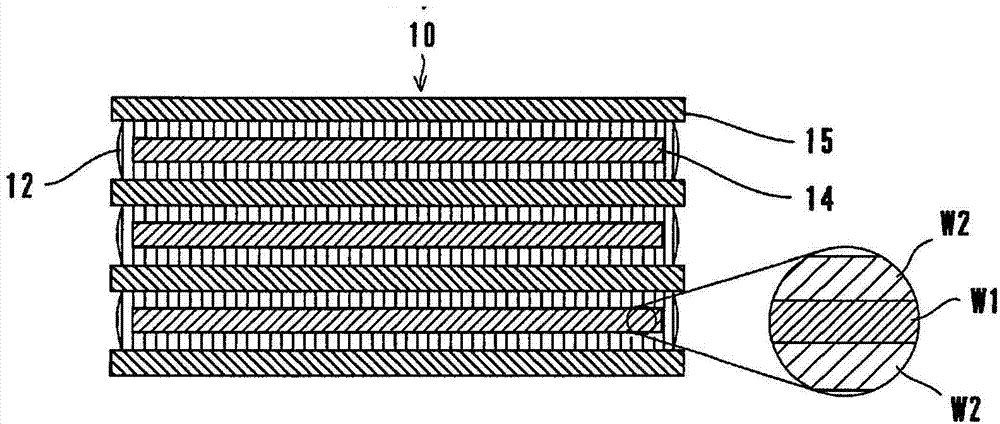
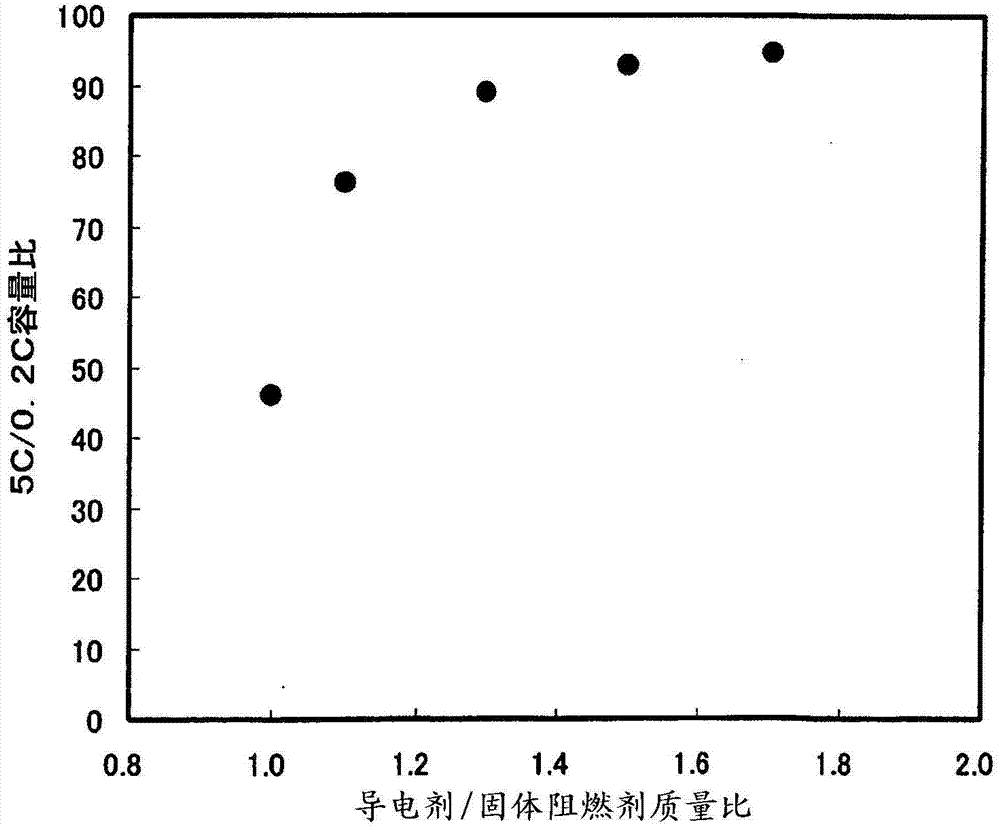
Nonaqueous electrolyte secondary cell
InactiveCN103782427AAvoid burnsSuppresses discharge capacity reductionCell electrodesLi-accumulatorsLithiumMass ratio
Provided is a nonaqueous electrolyte secondary cell with which high-performance discharge properties can be improved while guaranteeing safety. A lithium ion secondary cell has a stacked electrode group (10) sealed inside the laminated film of an outside casing. The stacked electrode group (10) is obtained by alternate stacking of positive pole plates (14) and negative pole plates (15). The positive pole plate (14) is obtained by forming, on both surfaces of an aluminum foil (W1), a positive electrode mix layer (W2) containing a lithium manganese compound oxide as the positive electrode active substance. In addition to the positive electrode active substance, a carbonaceous material as conductor and a phosphagen compound as a flame retarder are uniformly dispersed and mixed in the positive electrode mix layer (W2). The mass ratio of conductor with respect to the mass of flame retarder is adjusted to 1.3 or more. The negative pole plate (15) is obtained by forming, on both surfaces of rolled copper foil, a negative electrode mix layer containing a negative electrode active substance. Electron conductivity of the positive pole plate (14) is ensured by the conductor.
Owner:NTT FACILITIES INC +1
Nucleotide analogs
Nucleotide analogs characterized by the presence of an amidate linked amino acid or an ester linked group which is bonded to the phosphorus atom of phosphonate nucleotide analogs are disclosed. The analogs comprise a phosphoamidate or ester bond that is hydrolyzed in vivo to yield a corresponding phosphonate nucleotide analog. Methods and intermediates for their synthesis and use are described.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Determination of inorganic phosphorus and its diagnostic reagent kit
InactiveCN1778955AReflect contentHighlight substantive featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementUltravioletWavelength
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
SH2 domain binding inhibitors
InactiveUS6977241B2High affinityDipeptide ingredientsTetrapeptide ingredientsHydrogenPhosphoprotein binding
Disclosed are compounds for SH2 domain binding inhibition. For example, disclosed is a compound of formula (I) wherein R1 is a lipophile; R2, in combination with the phenyl ring, forms a phenylphosphate mimic group or a protected phenylphosphate mimic group; R3 is hydrogen, azido, amino, carboxyalkyl, alkoxycarbonylalkyl, aminocarbonylalkyl, or alkylcarbonylamino, wherein the alkyl portion of R3 may be optionally substituted with a substituent selected from the group consisting of halo, hydroxy, carboxyl, amino, aminoalkyl, alkyl, alkoxy, and keto; R6 is a linker; AA is an amino acid; and n is 1 to 6; or a salt thereof. Also disclosed are a pharmaceutical composition, a method for inhibiting an SH2 domain from binding with a phosphoprotein and a method of treating breast cancer.
Owner:DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES US SEC OF THE
Infusion preparation for dialysis patient
InactiveCN102600138AReduce dosageReduce drug costsOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsArginineTryptophan
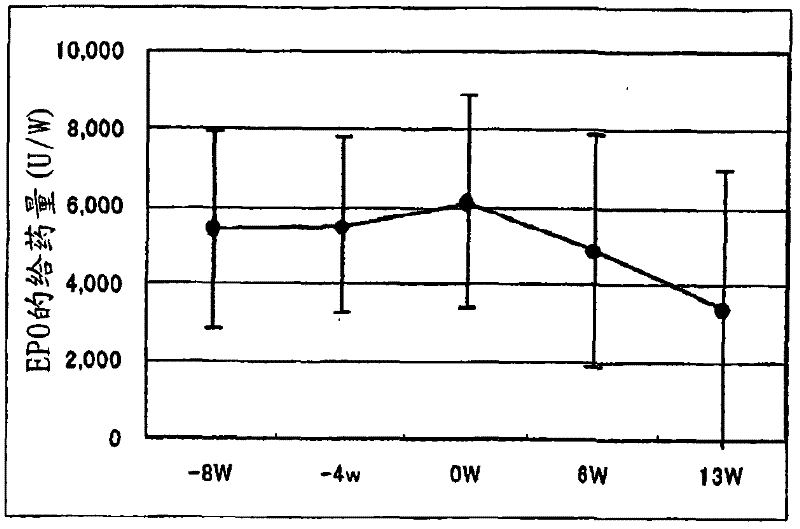
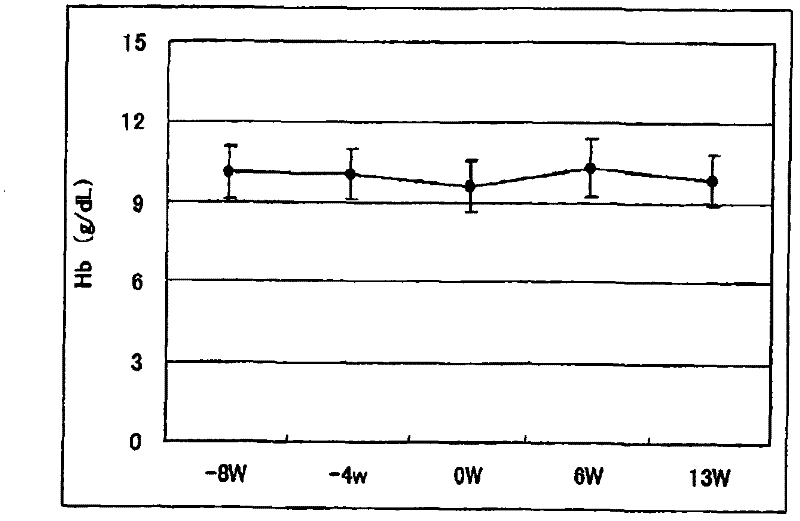
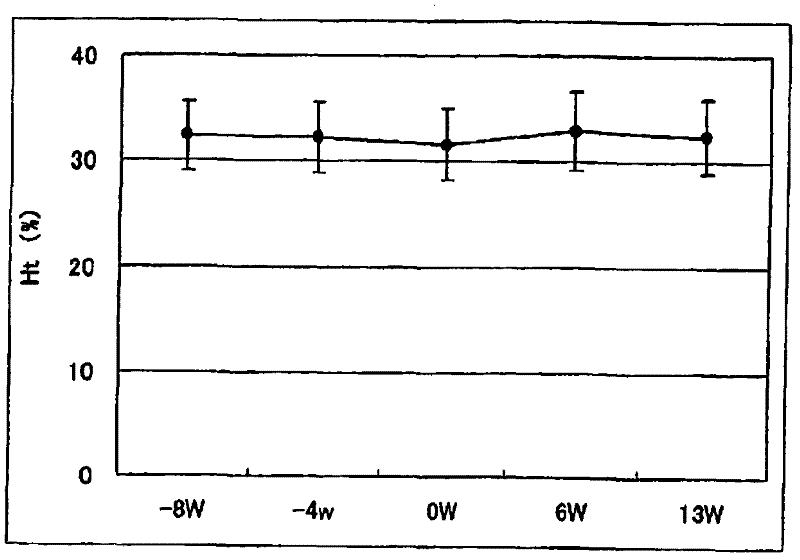
An infusion preparation which is to be used in dialyzing a dialysis patient for ameliorating the anemic state by improving nutritional conditions, thus reducing the dosing amount of erythropoietin, controlling the serum phosphorus level to thereby regulate the serum phosphorus level within a definite range and inhibiting the protein catabolism and which contains at least essential amino acids, characterized in that the amino acids are composed of at least L-isoleucine, L-leucine, L-lysine, L-methionine, L-phenylalanine, L-threonine, L-tryptophan, L-valine, L-alanine, L-arginine, L-aspartic acid, L-glutamic acid, L-histidine, L-proline, L-serine, L-tyrosine, glycine and L-cysteine and the ratio of essential amino acids : non-essential amino acids is 2.5 or higher.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
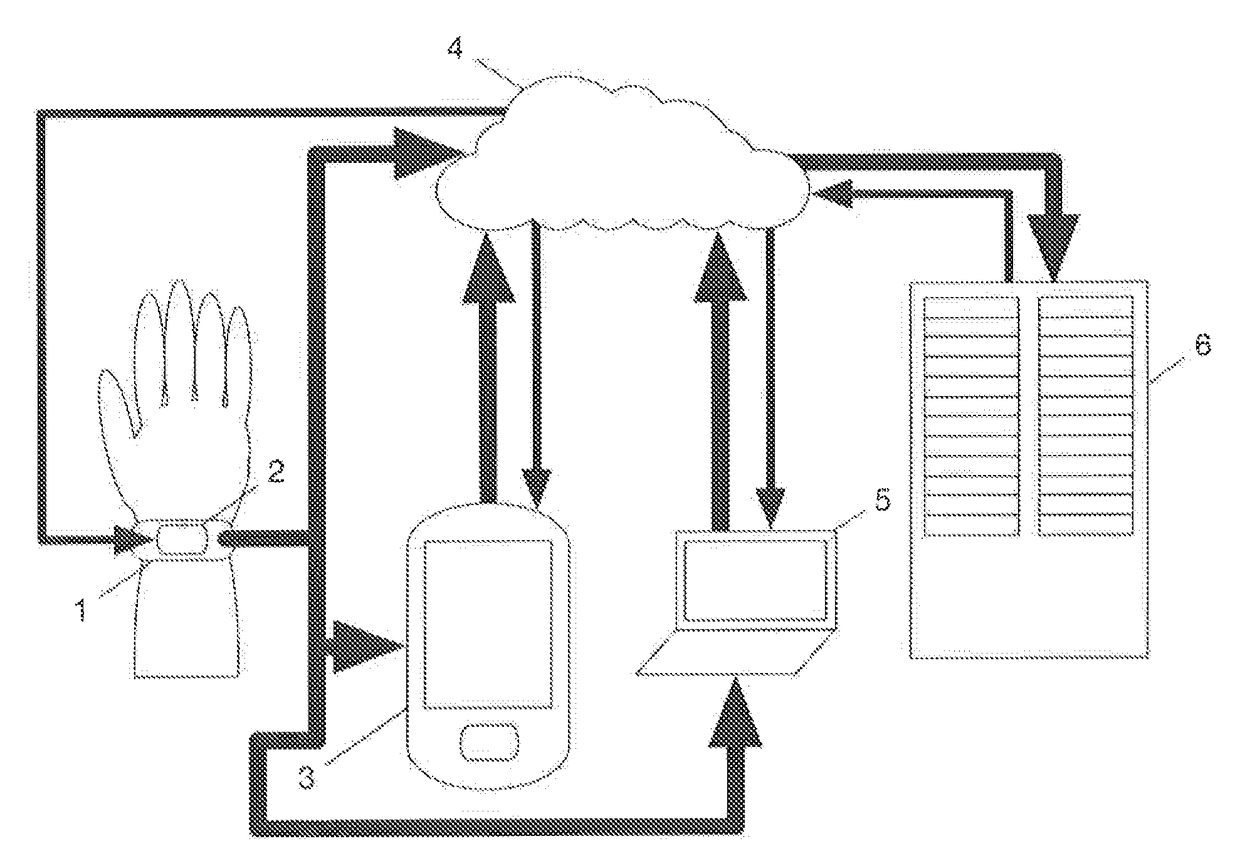
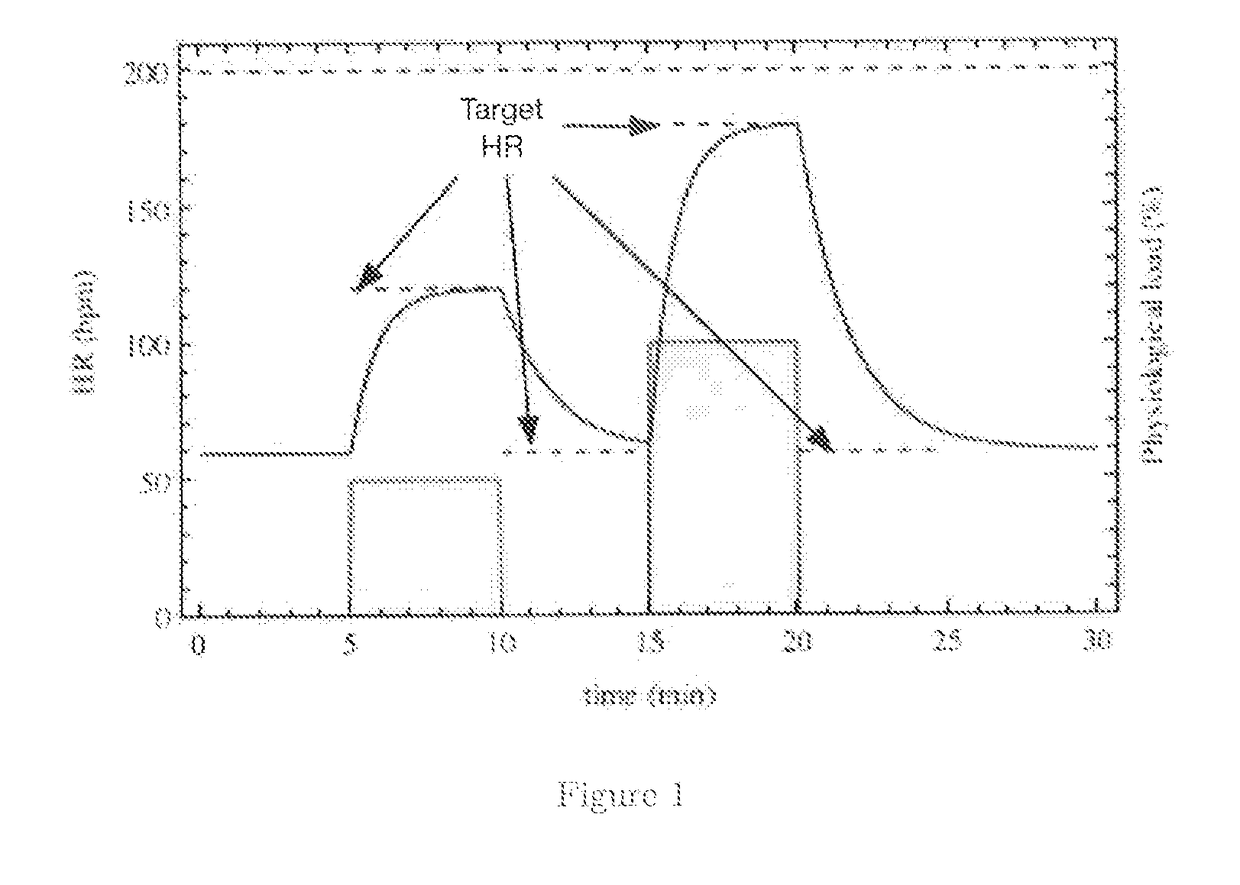
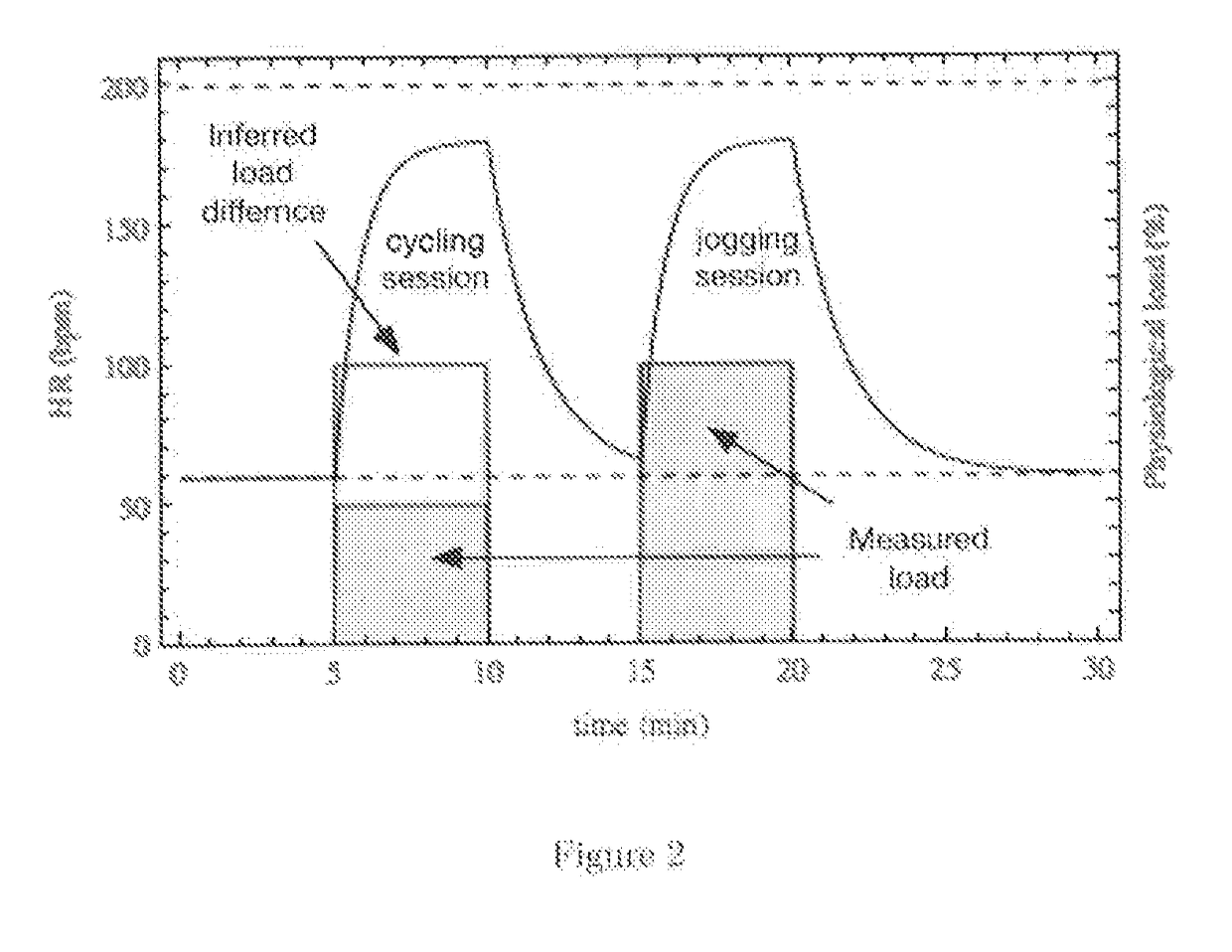
Biologically Inspired Motion Compensation and Real-Time Physiological Load Estimation Using a Dynamic Heart Rate Prediction Model
PendingUS20170238875A1Improve bindingMedical simulationElectrocardiographyPhysiologic StatesAnaerobic glycolysis
The current invention pertains to a method whereby the accuracy of a heart rate prediction gathered from sensor data can be improved during periods when motion corrupts the signal. The model utilized can also be inverted to infer information on the physiological state of a subject, such as real-time energy utilization or physiological load. In addition, this method can also be used to segment the contribution of each energy system, namely the phosphagen system, anaerobic glycolysis and aerobic respiration, to the physiological load experienced by the user. At the core of this approach lies a model describing the dynamic adjustment of human heart rate under varying physiological demands.
Owner:LIFEQ GLOBAL LTD
Phenylalanine derivatives
Disclosed herein are phenylalanine derivative compounds of the following formulaW—Y—(AA)n—Zwherein Y is a phenylalanyl radical, AA is an amino acid, n is an integer of 1 to 15, and substituent variables W and Z are as described herein. The compounds can be used to inhibit SH2 binding with phosphoproteins, and to inhibit proliferation of tumor cells.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA REPRESENTED BY SEC DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES +1
Phosphate solubilizing gene for promoting acetic acid secretion
InactiveCN103409437AProduce efficientlyAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaHeterologousAcetic acid
The invention provides a phosphate solubilizing gene psa A. The nucleotide sequence of the phosphate solubilizing gene psa A is as shown in SEQ ID No.1. The nucleotide sequence of a protein coded by the phosphate solubilizing gene psa A is as shown in SEQ ID No.2. The phosphate solubilizing gene psa A cloned through heterologous expression can be used for efficiently generating acetic acids, has a function of converting indissoluble phosphate into effective phosphate and provides a base material for increasing the utilization rate of a phosphate fertilizer by using a molecular biology means.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Prodrugs and conjugates of prenylation inhibitors
Described herein are neutral prodrugs of phosphorus-containing inhibitors of farnesyl transferase that include one or more phosphate fragments or analogs of phosphate fragments. Analogs of phosphate fragments include various linkers other than oxygen connecting the phosphate fragment to the remaining portion of the drug, such as but not limited to linkers forming phosphoramidates, phosphonates, difluorophosphonates, phosphordiamidates, and the like.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
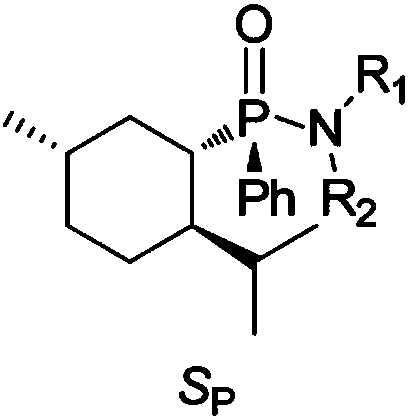
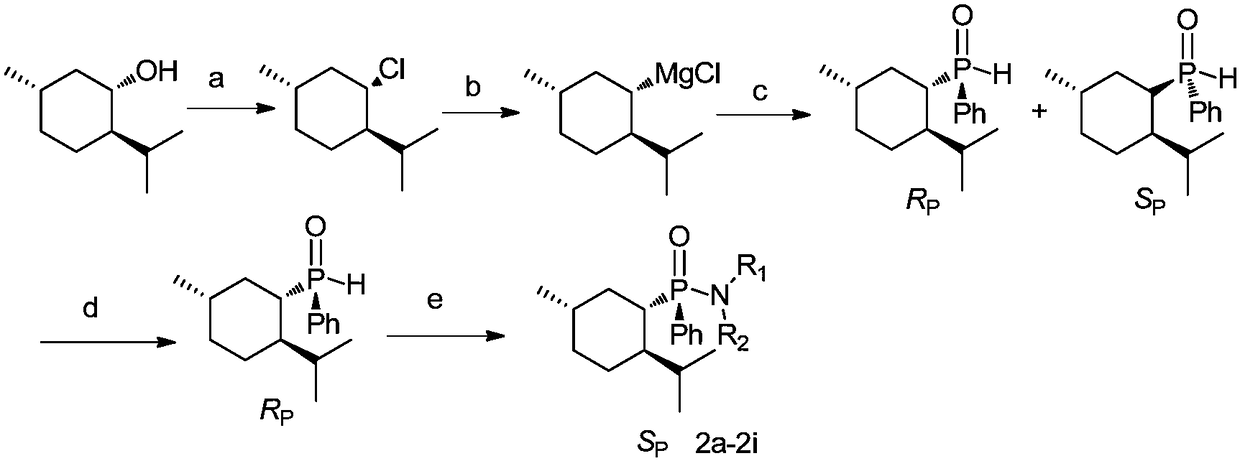
Chiral menthyl phenyl phosphonamide compound and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108164561AApparent chiral inductionGood chiralityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSynthesis methodsOrganic synthesis
The invention belongs to the field of organic synthesis, and particularly relates to a chiral menthyl phenylphosphonamide compound and a preparation method thereof. The chiral menthyl phenylphosphonamide compound has the following general formula (referring to the specification), wherein R1 is hydroxyl; R2 is hydroxyl, propyl, butyl, isopropyl, cyclopentyl, 2-chlorobenzyl, 2-methylidenefuran, 1-phenethyl or phenyl. The phosphonamide compound uses a phosphorus atom as a chiral source, has a more obvious chiral induction effect, and is more suitable for use in a chiral catalytic reaction; the phosphonamide compound has potentials of both drug activity and catalytic activity, and has development and application prospects; the phosphonamide compound is simple in synthesis method, easy to obtain and relatively good in application prospect.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
Application of acid phosphatase and related biological materials thereof in constructing phosphate-solubilizing engineering bacteria
ActiveCN105779408AHas phosphohydrolase activityIncrease contentBacteriaHydrolasesPhosphateProtein tag
The invention discloses application of acid phosphatase and related biological materials thereof in constructing phosphate-solubilizing engineering bacteria. The application refers to application of protein as shown in a) or b) or c) or d) in phosphohydrolase: a) protein constituted by amino acid sequences on 1st-203rd sites of SEQ ID N0.2; b) protein constituted by amino acid sequences on 26th-203rd sites of SEQ ID N0.2; c) fusion protein obtained by fusing a protein tag / protein tags on carboxyl terminal (C terminal) or / and amino terminal (N terminal) of the protein of a) or b); and d) protein which is obtained by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues of an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.2 or SEQ ID No.6 and has the activity of the acid phosphatase. According to the application disclosed by the invention, biological engineering bacteria, which can effectively activate soil phosphorus nutrients, can be cultivated.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Determination of inorganic phosphorus and its diagnostic reagent kit
InactiveCN1778941AHighlight substantive featuresSignificant progressMicrobiological testing/measurementPeroxidaseUltraviolet
The invention is about the measuring method of inorganic Phosphates and its diagnosis reagent box. Producing hydroperoxide by reacting pyruvate oxidase with pyruvate under the existence of Inorganic Phosphates , then causing enzyme-coupled reaction with peroxidase and oxidating the colorless reduced chromogen combination to quinoneimine chromogen or indamide chromogen dyer with color, testing the variation of dominant wave-length 400ú¡600nm absorbance during the reaction and finally measuring the content of Inorganic Phosphates . This method has high specificity and would not be contaminated by material of internal and exogenous sources, and the result is precise and accurate. Diving the diagnosis reagent box into double-dose or three-dose can reduces the cross interaction of each element, keeps the stability of the reagent and deposits chronically. Using this method can realize the fast testing in common ultraviolet / visible light analyzer or semiautomatic / automatic analyzer and doesní»t require special or additional apparatus, so the cost is low. Thus, this method can be easily promoted and applied in the whole industry.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Determination of inorganic phosphorus and its diagnostic reagent kit
InactiveCN1778943AContent reflectionHighlight substantive featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementPeroxidaseUltraviolet
The invention is about the measuring method of Inorganic Phosphates and its diagnosis reagent box. Producing hypoxanthine by reacting nucleoside phosphorylase with carnine under the existence of Inorganic Phosphates in the sample of plasma, serum and so on, then producing urate and hydroperoxide by reactinghypoxanthine withxanthine oxidase, and then reacting bimolecular hydroperoxide with peroxidaseand oxidating the colorless reduced chromogen combination to quinoneimine chromogen or indamide chromogen dyer with color, testing the variation of dominant wave-length400ú¡600nmabsorbance during the reaction and finally measuring the content of Inorganic Phosphates . This method has high specificity and would not be contaminated by material of internal and exogenous sources, and the result is precise and accurate. Using this method can realize the fast testing in common ultraviolet / visible light analyzer or semiautomatic / automatic analyzer and doesní»t require special or additional apparatus, so the cost is low. Thus, this method can be easily promoted and applied in the whole industry.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com