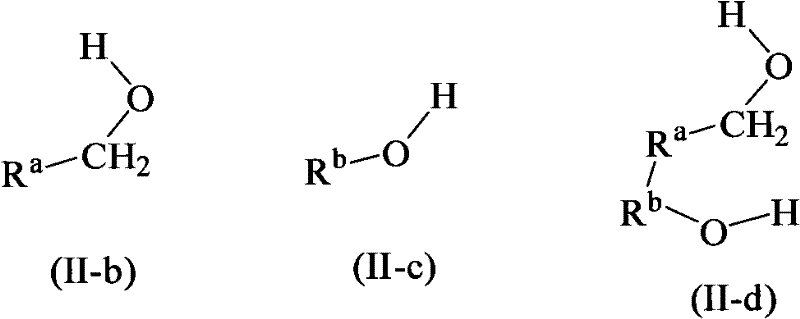
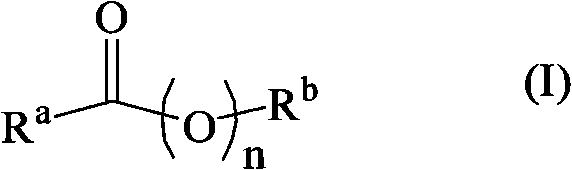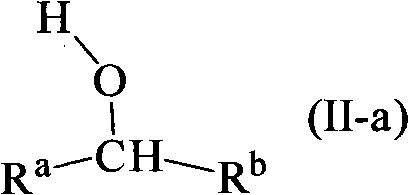Hydrogenation of ester, ketone or aldehyde groups with ruthenium complexes having di-amine and phosphorous-nitrogen bidentate ligand
A technology of ruthenium complexes and bidentate ligands, which is applied in the field of catalytic hydrogenation and can solve problems such as poor reactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0233] Catalytic hydrogenation of acetophenone using various ruthenium complexes of the invention:
[0234] Using various oxazoline derivatives as (P-N), (1R,2R)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine) (R,R-Le) as (N-N), from Ru(COD)(C 4 h 7 ) 2 As the Ru precursor is formed in situ, the hydrogenation process is carried out in the absence of a base.
[0235] Typical experimental steps are as follows:
[0236] In a glove box under argon atmosphere, equipped with a magnetic stirring bar and containing Ru(COD)(C 4 h 7 ) 2 (6.4mg, 0.02mmol, 0.1mol%), phosphine-oxazoline La (8.2mg, 0.02mmol, 0.1mol%), (1R, 2R)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine (R, R A solution of acetophenone (2.404 g, 20 mmol) and n-tridecane (187.8 mg, 1 mmol) in iPrOH (2 ml) was added to a Keim autoclave of -Le) (4.7 mg, 0.02 mmol, 0.1 mol%) and iPrOH (6 ml) , then iPrOH (2 x 1 ml) was added. The autoclave was pressurized to 50 bar with hydrogen and placed in a constant temperature oil bath at 60°C. After 1 hour, the au...
Embodiment 2
[0252] Catalytic hydrogenation of acetophenone using various ruthenium complexes of the invention:
[0253] Using (R)-2-[2-(diphenylphosphino)phenyl]-4-(1-methylethyl)-4,5-dihydrooxazole as (R-La)(P-N), A variety of diamines (Le-Lr) as (N-N), from Ru(COD)(C 4 h 7 ) 2 As precursors are formed in situ, the hydrogenation process is carried out in the absence of a base.
[0254] Typical experimental steps are as follows:
[0255] In a glove box under argon atmosphere, equipped with a magnetic stirring bar and containing Ru(COD)(C 4 h 7 ) 2 (6.4mg, 0.02mmol, 0.1mol%), phosphine-oxazoline La (8.4mg, 0.02mmol, 0.1mol%), (1R,2R)-1,2-bis(2,4,6-trimethyl Acetophenone (2.415 g, 20 mmol) and n-tridecane (179.1 mg, 1 mmol) in iPrOH were added to a Keim autoclave of ethylenediamine (6.3 mg, 0.02 mmol, 0.1 mol%) and iPrOH (6 ml). (2ml) solution, and then iPrOH (2 x 1ml) was added. The autoclave was pressurized to 50 bar with hydrogen and placed in a constant temperature oil bath at ...
Embodiment 3
[0269] Catalytic hydrogenation of acetophenone using various ruthenium precursors of the invention:
[0270] The use of oxazoline derivatives (R-La) as (P-N) and diamines (R,R-Le) as (N-N) were formed in situ from various Ru precursors, optionally in the presence of bases.
[0271] Typical experimental steps are as follows:
[0272] In a glove box under argon atmosphere, equipped with a magnetic stirring bar and containing [RuCl 2 (COD)] n (5.6mg, 0.02mmol, 0.1mol%), (R)-2-[2-(diphenylphosphino)phenyl]-4-(1-methylethyl)-4,5-dihydrooxane Azole (7.7mg, 0.02mmol, 0.1mol%), (1R, 2R)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine (4.4mg, 0.02mmol, 0.1mol%), potassium tert-butoxide (4.5mg, 0.04 mmol, 0.2mol%) and iPrOH (6ml) into the Keim autoclave, add acetophenone (2.407g, 20mmol) and n-tridecane (188.6mg, 1mmol) in iPrOH (2ml) solution, then add iPrOH (2× 1ml). The autoclave was pressurized to 50 bar with hydrogen and placed in a constant temperature oil bath at 60°C. After 30 min, the autocl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com