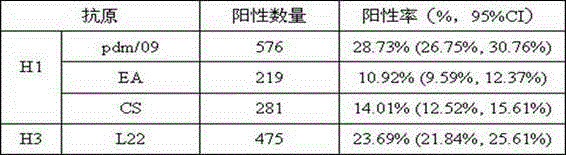
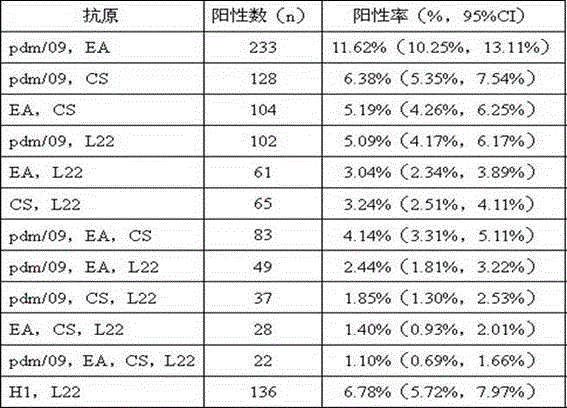
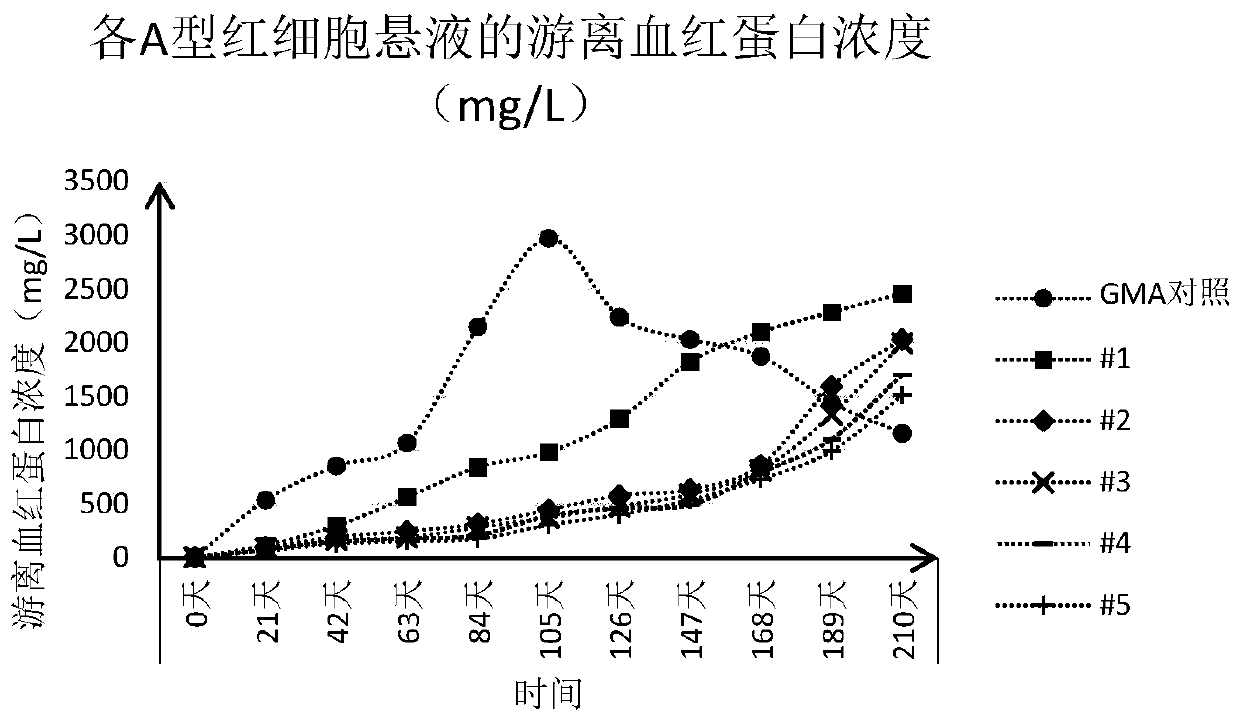
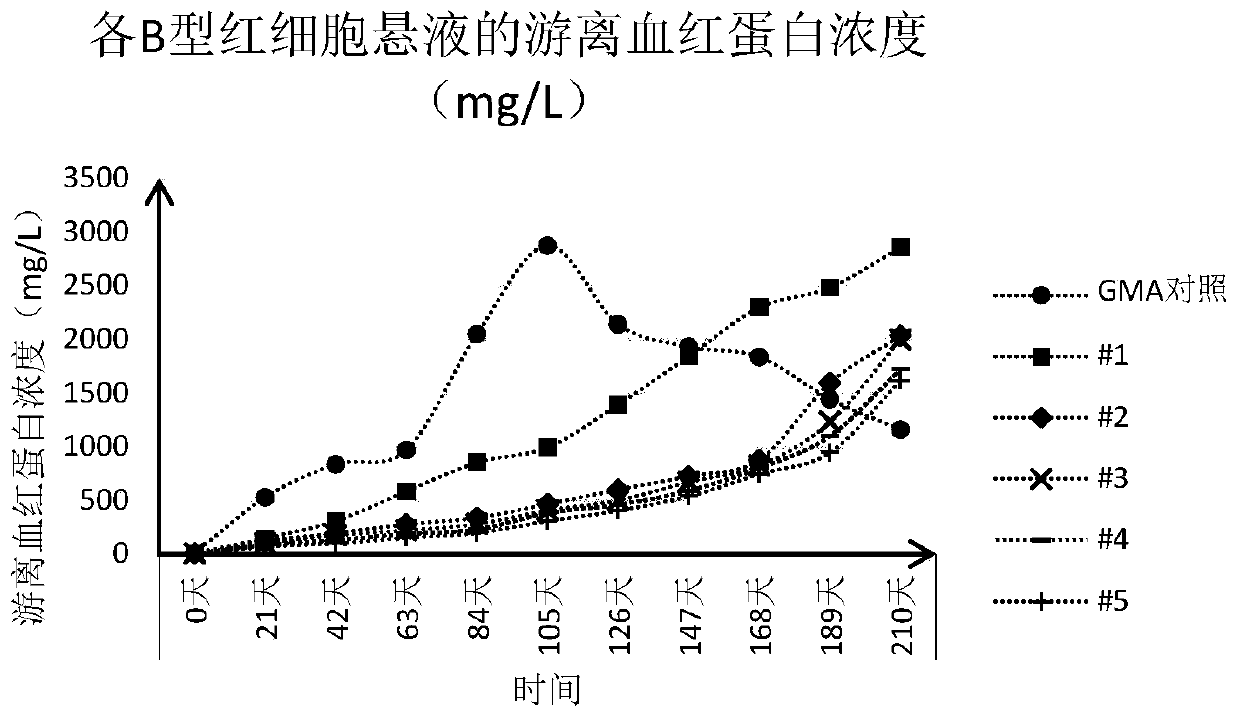
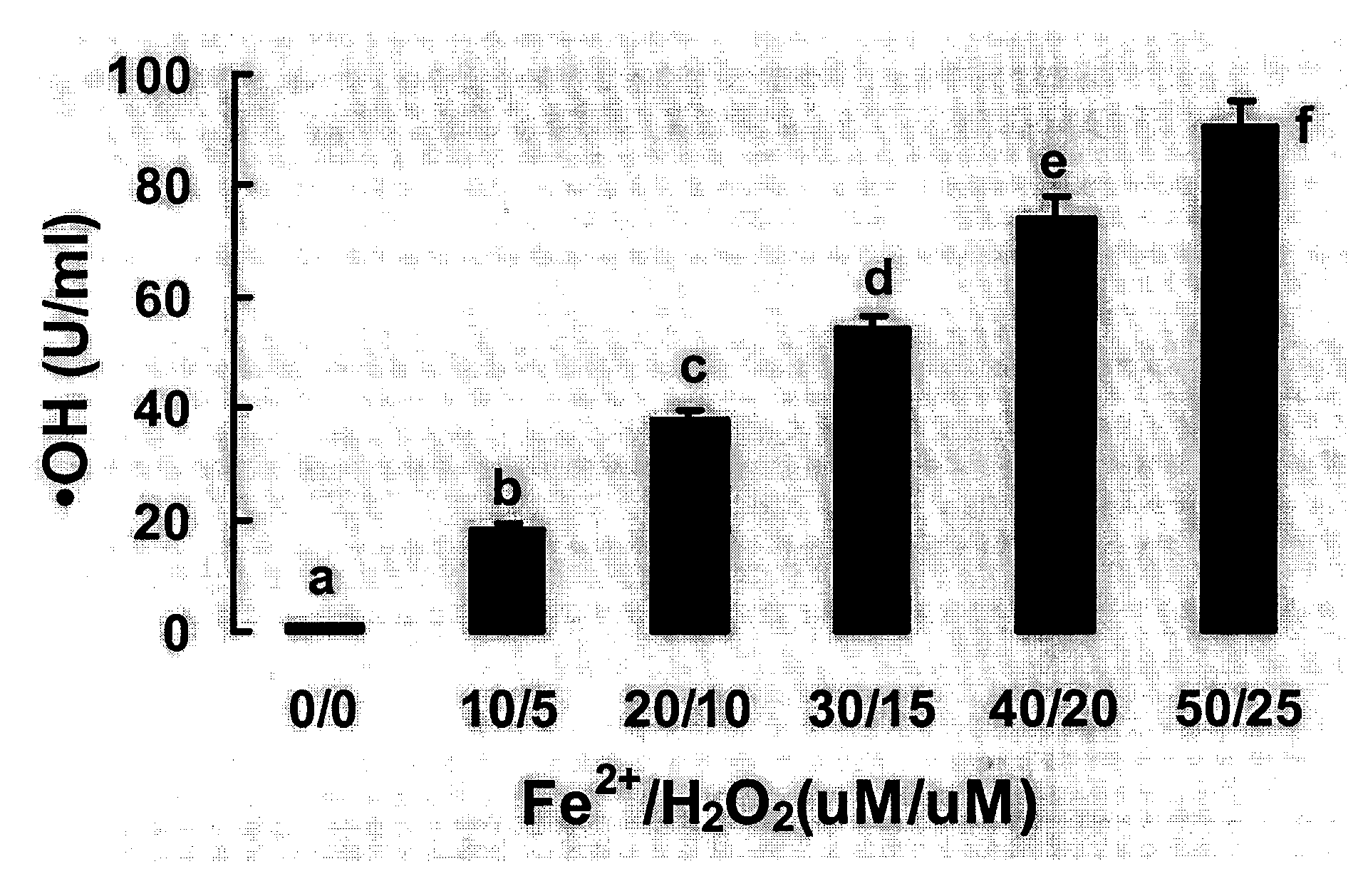Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "Erythrocyte suspension" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Erythrocyte preservative solution
ActiveCN105028389APrevent invasionProtect normal metabolismDead animal preservationBiological testingAntigenInosine
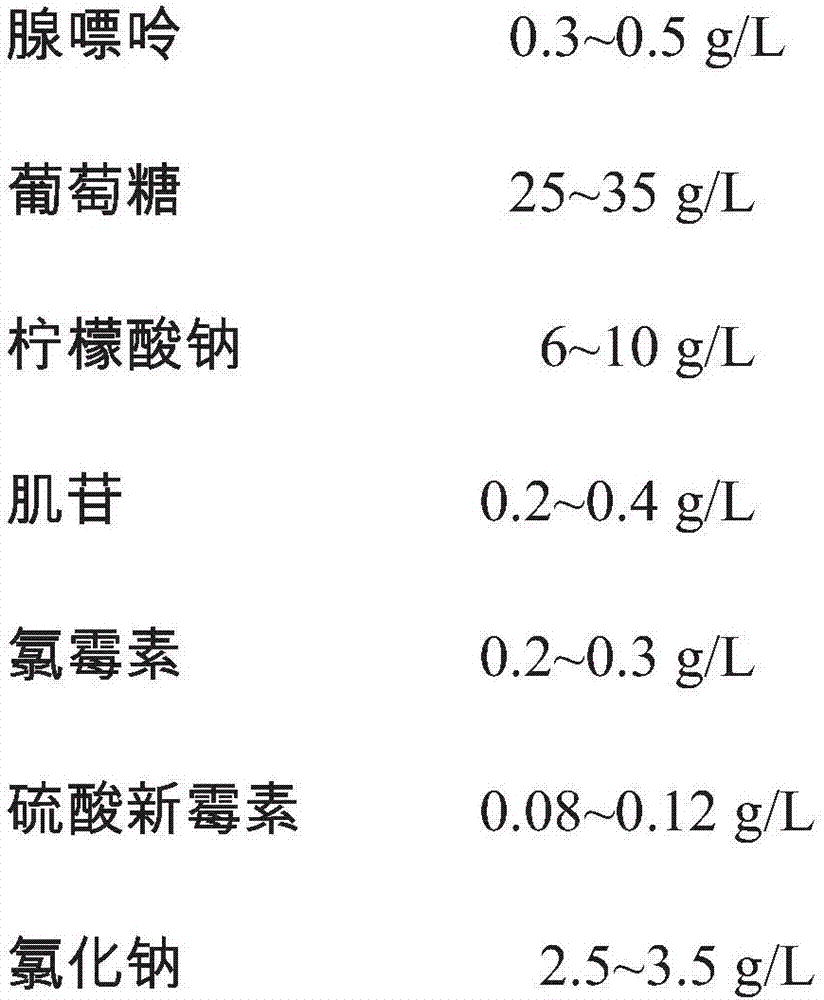
The invention provides an erythrocyte preservative solution. The solution comprises the following components by content: 0.3-0.5g / L of adenine, 25-35g / L of glucose, 6-10g / L of sodium citrate, 0.2-0.4g / L of inosine, 0.2-0.3g / L of chloramphenicol, 0.08-0.12g / L of neomycin sulfate, 2.5-3.5g / L of sodium chloride and 0.04-0.06g / L of sodium dihydrogen phosphate. According to the preservative solution, the preservation period of erythrocytes can be 14 weeks, and the erythrocyte suspension preserved in the solution has a relatively high antigen titer in the preservation period.
Owner:苏州苏大赛尔免疫生物技术有限公司
Lysis/resealing process and device for incorporating an active ingredient in erythrocytes
ActiveCN101031339AOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiochemical engineeringBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
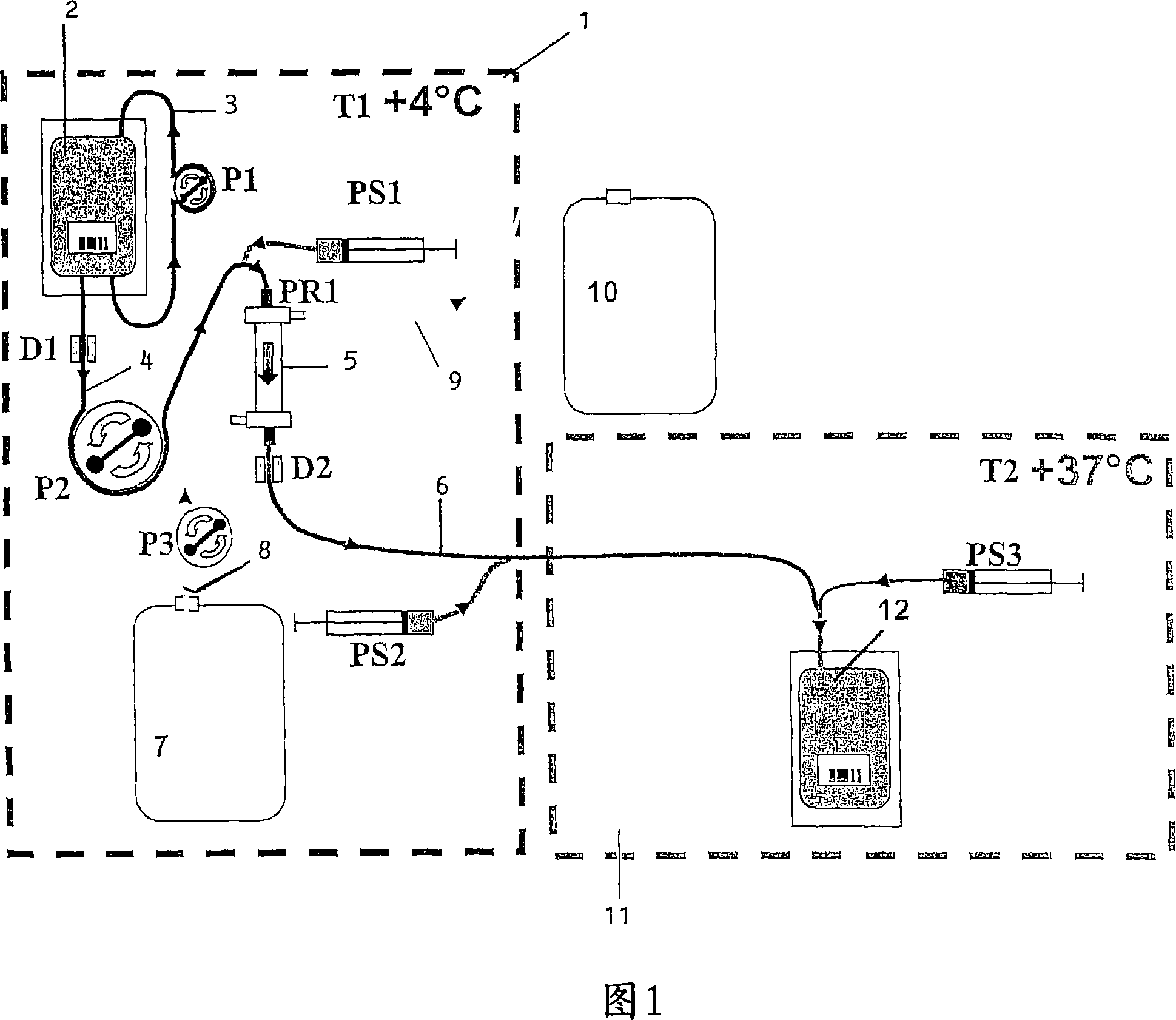
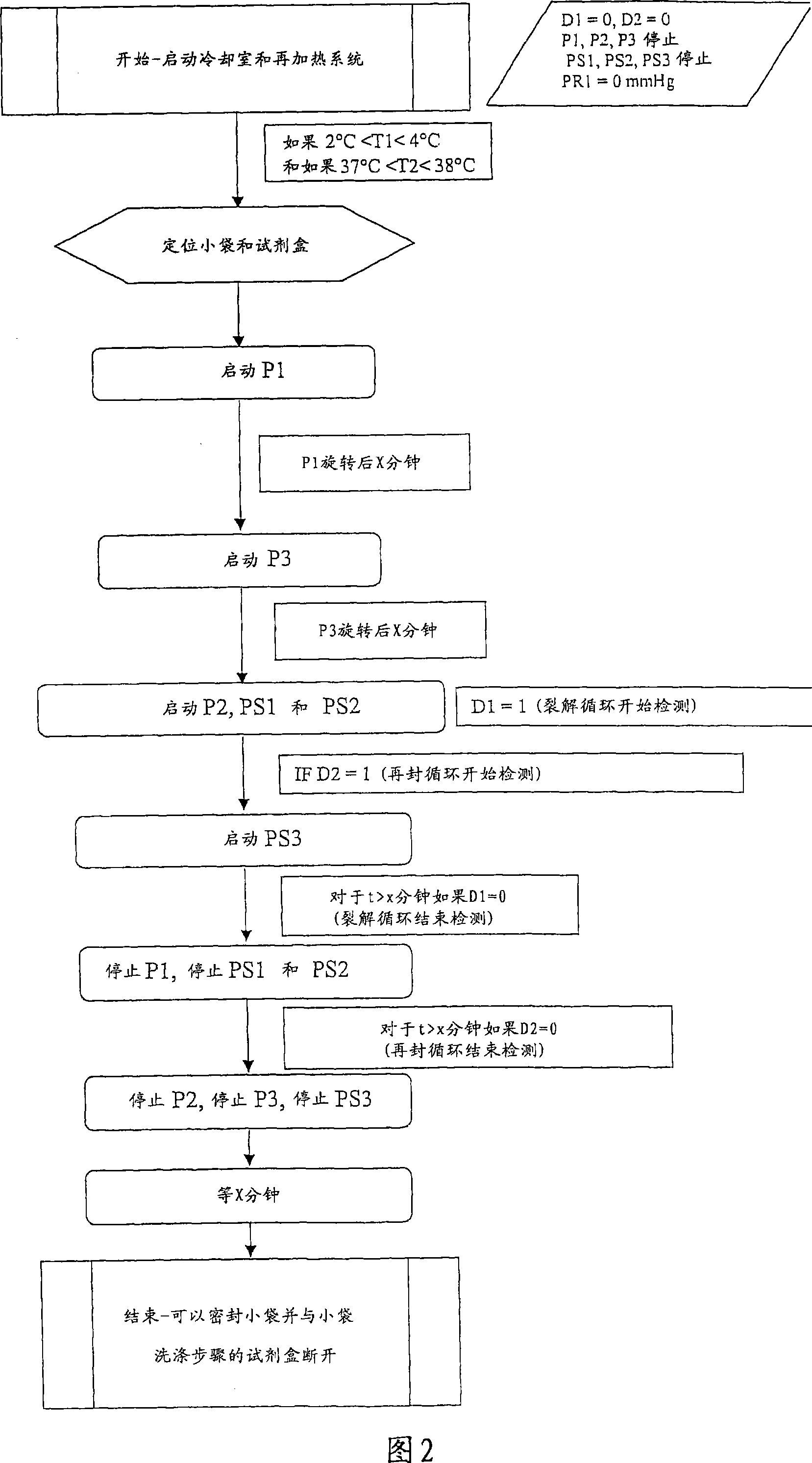
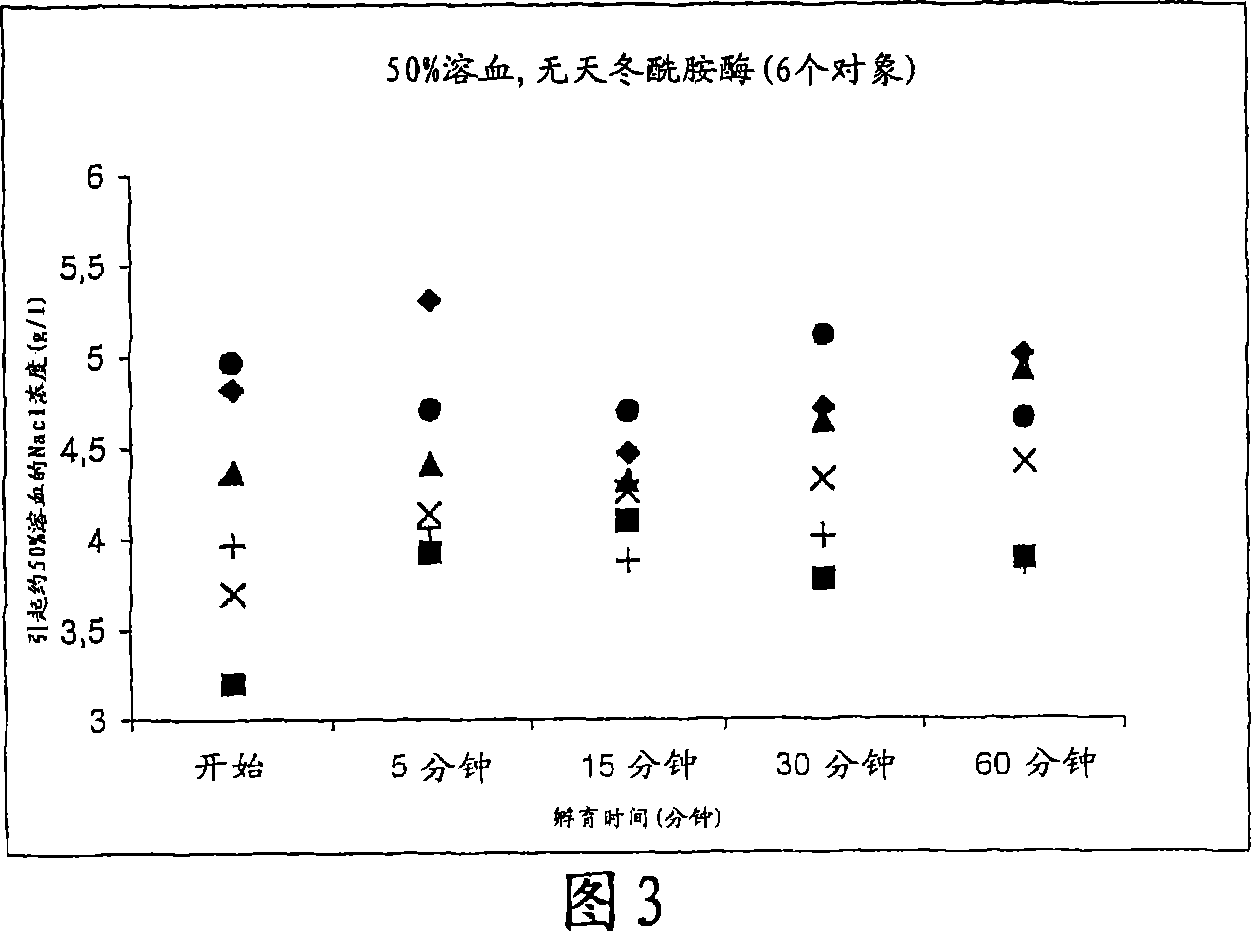
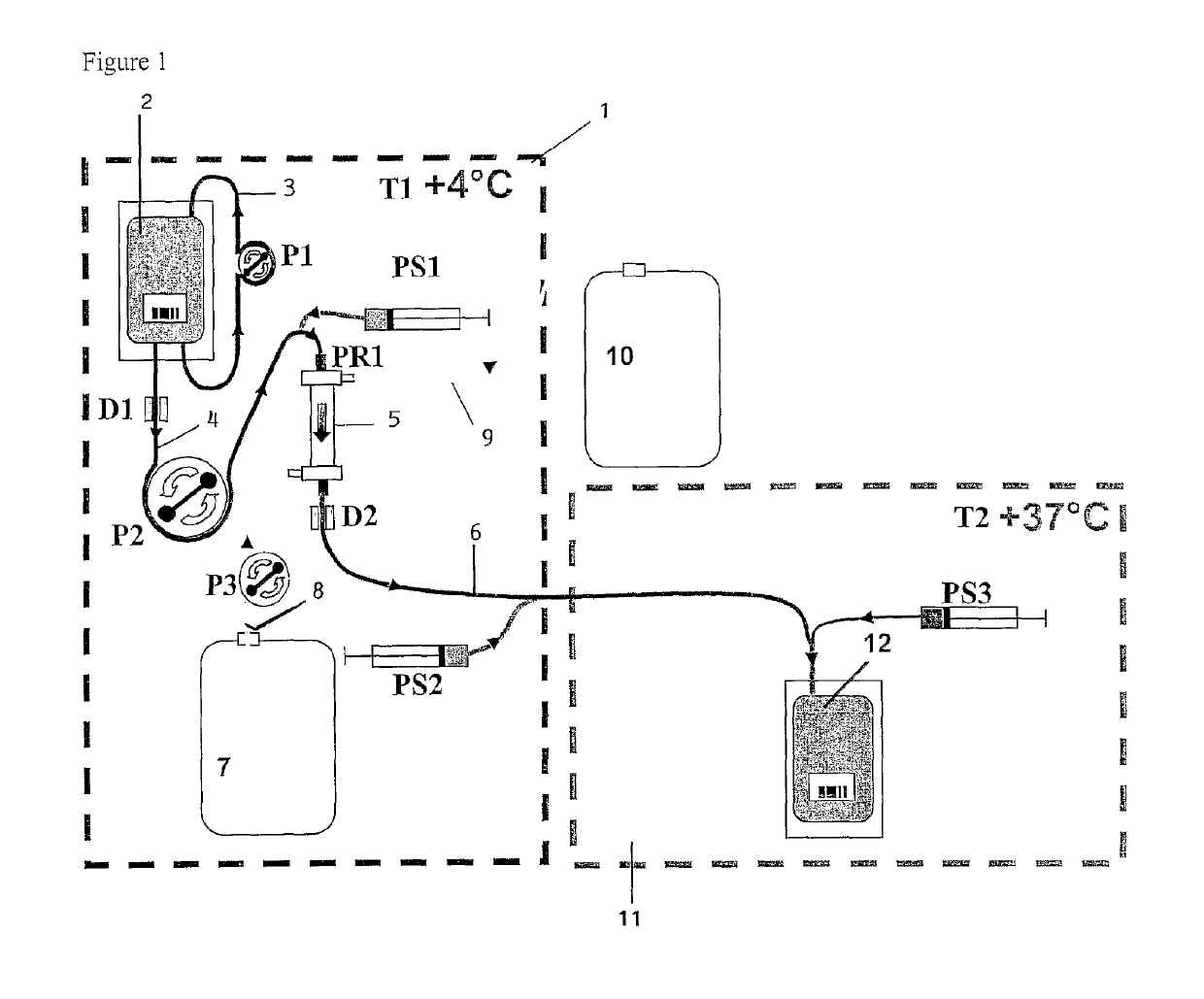
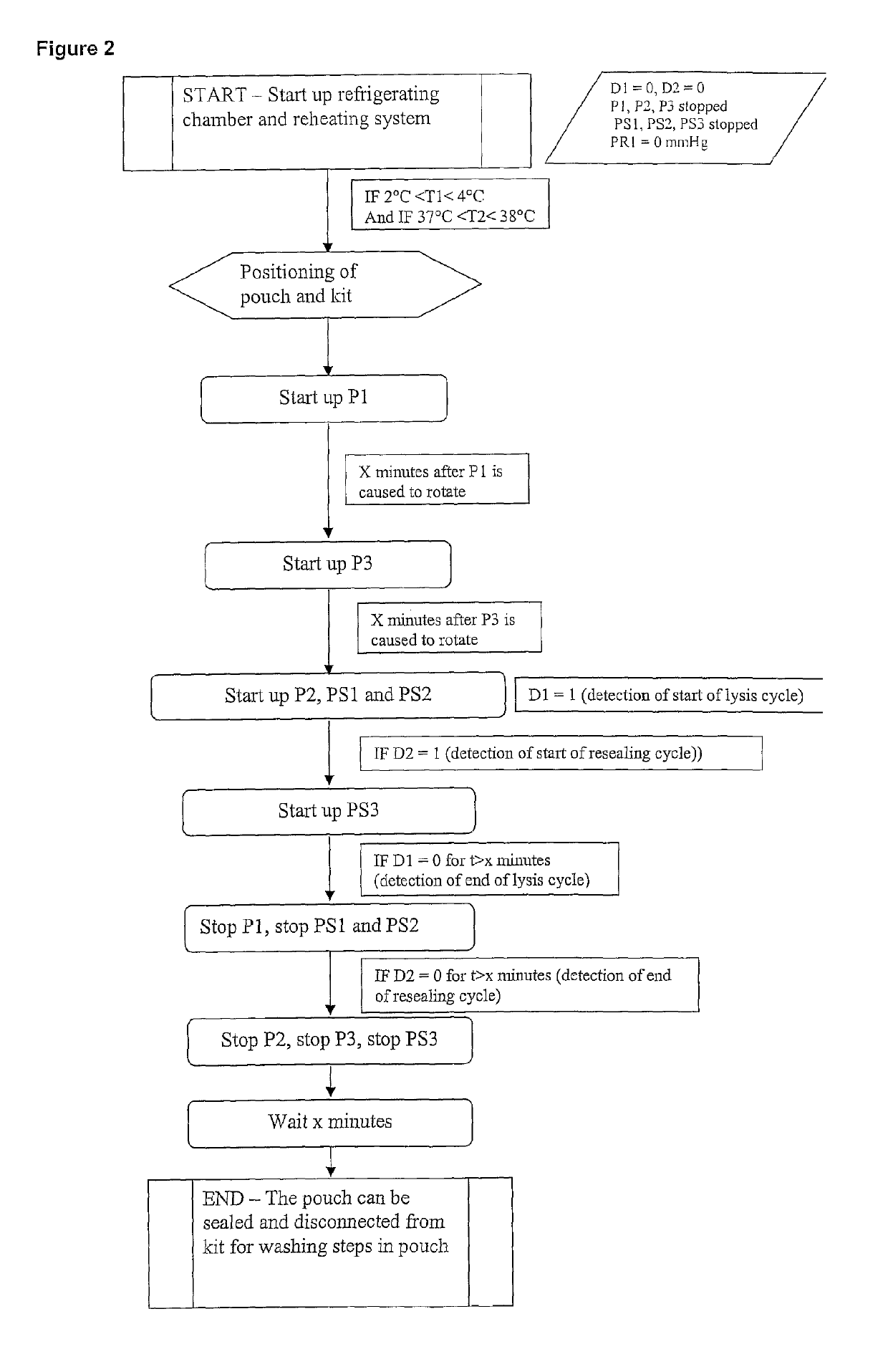
Lysis / resealing process for incorporating an active ingredient, the process comprising the following steps: (1) - placing a globular concentrate in suspension in an isotonic solution having a haematocrit level which is equal to or greater than 65 %, with refrigeration at from + 1 to + 8 DEG C, (2) - measuring the osmotic fragility based on a sample of erythrocytes from that same globular concentrate, preferably on a sample of the suspension obtained in step (1), (3) - lysis and internalisation procedure of the active ingredient, inside the same chamber, at a temperature which is constantly maintained at from + 1 to + 8 DEG C, comprising allowing the erythrocyte suspension having a haematocrit level which is equal to or greater than 65 % and a hypotonic lysis solution which is refrigerated at from + 1 to + 8 DEG C, to circulate in a dialysis cartridge; the lysis parameters being adjusted in accordance with the osmotic fragility previously measured; and (4) - resealing procedure carried out in a second chamber at a temperature of from + 30 to + 40 DEG C by means of a hypertonic solution. Figure 1.
Owner:ERYTECH PHARMA
Sperm antibody testing reagent
The sperm antibody testing reagent includes sensitized sheep erythrocyte suspension of 2-3 % concentration and rabbit antihuamn IgG in the concentration of 1 to 2 to the (8-10)-th power. The sensitized sheep erythrocyte suspension of 2-3% concentration is prepared through taking sheep blood, washing, hydroformylation, tanning, sensitizing and other steps. The preparation of rabbit antihuman IgG in the concentration of 1 to 2 to the (8-10)-th power includes taking rabbit blood, separating blood serum and other steps. The reagent has strong specificity, high detection sensitivity, no false positive and no false negative phenomenon, high stability, and storage life as long as one year. Using the reagent can obtain easy-to-judge detection result sipmle and fast.
Owner:ANHUI ANKE BIOTECHNOLOGY (GRP) CO LTD
Hemin production process, and health-care composition for making iron and zinc made thereof
ActiveCN1580061AMeet iron needsMeet the need for zinc supplementationOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderHeminGluconic acid
The invention refers to a kind of iron-adding agent and especially refers to the production technique of the hemin. The technique includes the following steps: a) get rid of the blood serum and fibrin in the fresh blood of livestock and birds for the red cell suspension; b) put the 1-3g / 1000ml sodium chloride into the acetate solution with the thickness between 60% and 100% and heat the solution to between 100deg.C and 110deg.C; c) add the red cell suspension got from the a) to the acetate solution with sodium chloride got from the b) and get the mixed solution; d) filter press the mixed solution got from the c) to get the solid materials and wash them with hot spirit of vinegar and hot distilled water respectively; e) dry the solid materials got from the d) between 110deg.C and 130deg.C to constant weight and then get the turnoff of hemin. If we mix the hemin of the invention with the zinc-adding agent (such as zinc gluconate) in reasonable proportion, we can get the iron-adding and zinc-adding health protection combination.
Owner:SHANGHAI HONGRU SCI TECH DEV
Method for detecting substances inhibiting the bacterial type III secretion mechanism and function of secretory proteins thereof
InactiveUS6586200B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisRed blood cellSecreted substance
The present invention relates to a method for detecting substances specifically inhibiting a type III secretion mechanism and functions of the type III secretory proteins, within short time and large amounts thereof, without depending upon animal infectious experiments. Namely it relates to the method for detection of a type III secretory mechanism inhibitor comprising mixing a bacterium having the type III secretory mechanism and an erythrocyte suspension, adding the type III secretory mechanism inhibitor thereto, and detecting changes in the thus formed hemolytic activity. The method for detecting substances can be treated large amount of samples within short time by exhibiting the substances inhibiting the type III secretion mechanism or the functions of the type III secretory proteins as numerical index of the hemolytic activity of erythrocytes. Consequently, the present invention is useful for development of drugs.
Owner:THE KITASATO INST
Method for evaluating eye irritation by using miniature pig erythrocytes
InactiveCN102359946ASmall batch-to-batch varianceClear genetic backgroundColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingFormularyOphthalmology
The present invention discloses an experimental method for evaluating eye irritation by using miniature pig erythrocytes. The method mainly comprises: (1) preparing a suspension of miniature pig erythrocytes; (2) carrying out a miniature pig erythrocyte hemolysis test; (3) carrying out a protein denaturation experiment; (4) predicting a model; (5) carrying out classification and judgment. According to the present invention, the source of the erythrocytes is reliable and safe; the tested material is easy to obtain, and has good uniformity; the test system is simple and cheap, and no special equipment is required; the detection method is rapid, sensitive and universal; the method of the present invention can be directly applicable for safety evaluations of chemicals, cosmetics, pesticides, eye medicines and other substances possibly contacting the eyes, wherein the chemicals comprise surfactants, disinfection products, detergent and the like, the cosmetics comprise shampoo, bath foam, eye cream and the like; the method further can be applicable for rapidly screening, classifying and identifying the eye irritations of the raw materials, the formulas or the products.
Owner:程树军 +1
Hybridoma cell strain capable of secreting anti-human AB blood type IgM type monoclonal antibodies, monoclonal antibodies, and application
ActiveCN110903396AImmunoglobulins against blood group antigensTissue cultureBALB/cAntiendomysial antibodies
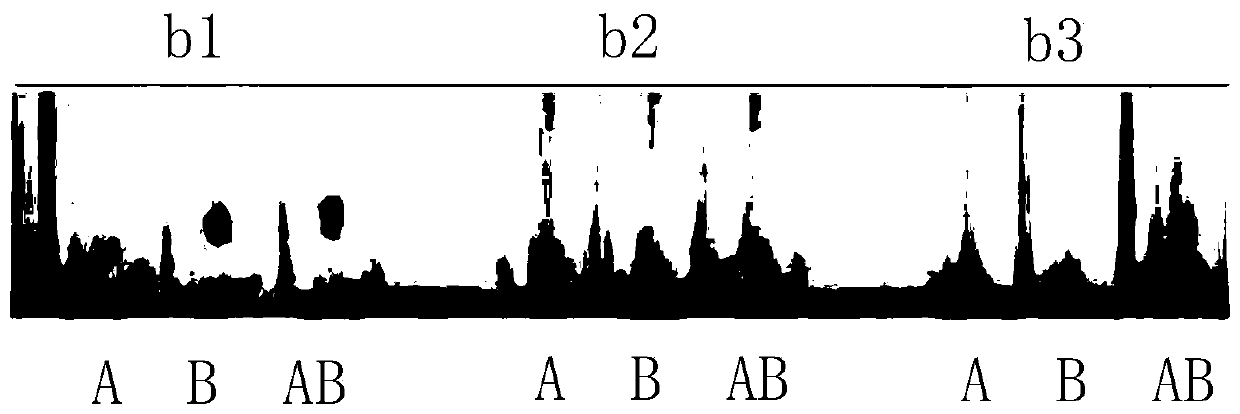
The invention provides a hybridoma cell strain capable of secreting anti-human AB blood type IgM type monoclonal antibodies. The preservation number of the hybridoma cell strain is CGMCC NO. 18535. The invention also provides the monoclonal antibody secreted by the hybridoma cell strain capable of secreting anti-human AB blood type IgM type monoclonal antibodies, and application of the monoclonalantibody. A preparation method comprises following steps: taking a human AB type erythrocyte suspension as an antigen to immunize BALB / c mice; carrying out immunization, cell fusion, screening and cloning to obtain a hybridoma cell strain 2D12 capable of stably subculturing and secreting anti-human AB blood type IgM type monoclonal antibodies; the secreted 2D12 antibody can agglutinate with humanA-type red blood cells, B-type red blood cells and AB-type red blood cells, no agglutination reaction with human O-type red blood cells is caused, the secreted 2D12 antibody is an anti-AB-type blood type monoclonal antibody, and has antibody titer of 512.
Owner:苏州国科思倍达生物技术有限公司
Method for quantitatively detecting coagulant activity of bean phytohemagglutinin
ActiveCN103558176AThe detection method is simpleThe results are relatively consistentPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsPhytohemagglutininsActivity concentration
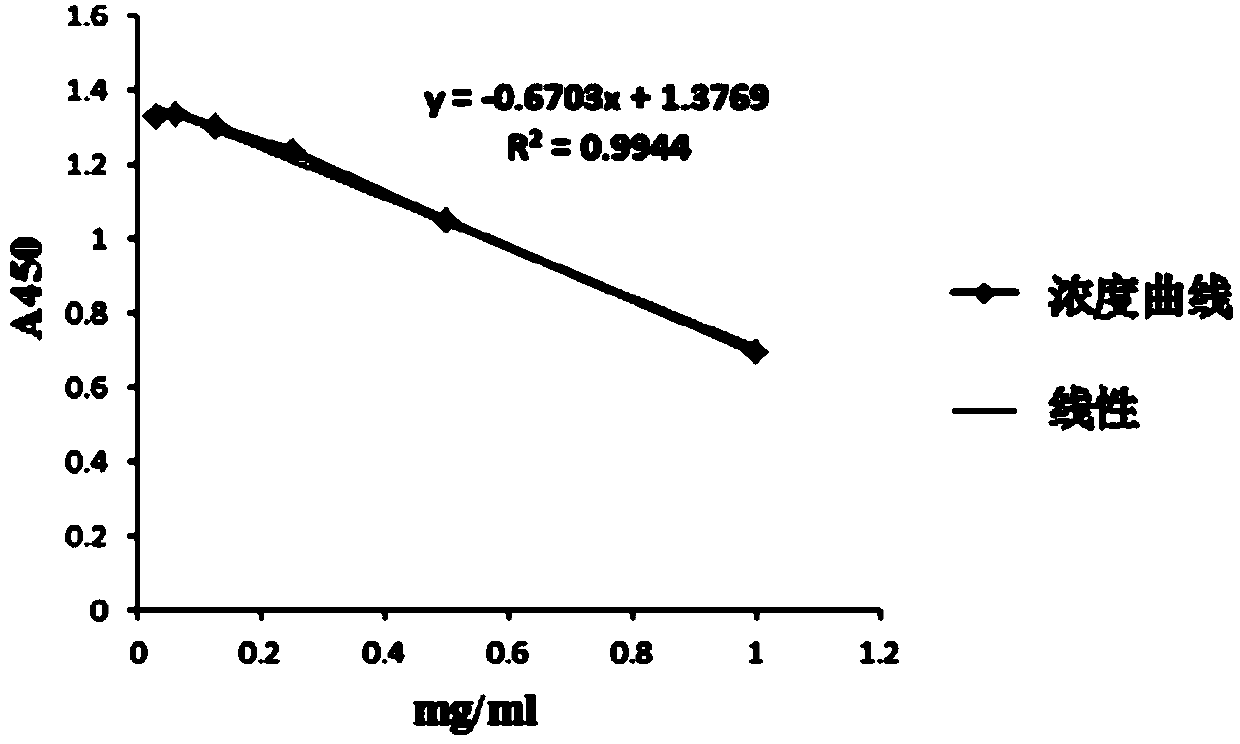
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting the coagulant activity of bean phytohemagglutinin and belongs to the technical field of plant component detection. According to the method, a red cell suspension for detection is subjected to cell quantification; meanwhile, a coagulant activity concentration standard curve is drawn by using the bean phytohemagglutinin with the known concentration as a standard substance, and the coagulant activity concentration of the bean phytohemagglutinin is further calculated, so that the coagulant activity of the bean phytohemagglutinin is quantified.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Lysis/resealing process and device for incorporating an active ingredient, in particular asparaginase or inositol hexaphosphate, in erythrocytes
ActiveUS10273444B2Reproducible and reliable and stable mannerIncrease oxygenationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOrganic active ingredientsRed blood cell samplePhosphoric acid
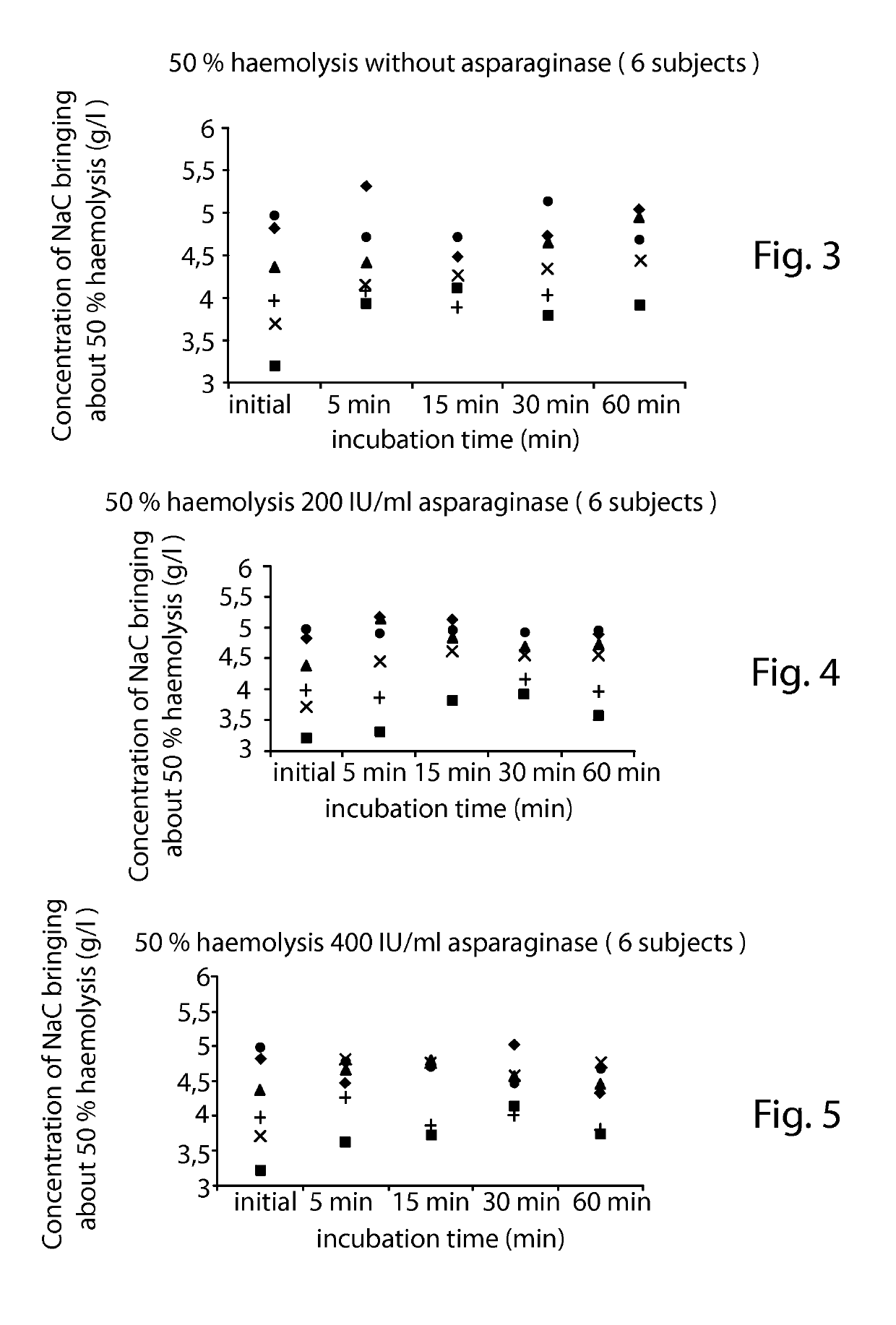
A lysis / resealing process for preparing erythrocytes containing active ingredient is provided comprising placing a globular concentrate in suspension in an isotonic solution having a haematocrit level which is equal to or greater than 65%, with refrigeration at 1 to 8° C.; measuring the osmotic fragility based on a sample of erythrocytes from that same globular concentrate, preferably on a sample of the suspension; lysis and internalization procedure of the active ingredient, inside the same chamber, at a temperature maintained at 1 to 8° C., comprising allowing the erythrocyte suspension having a haematocrit level equal to or greater than 65% and a hypotonic lysis solution which is refrigerated at 1 to 8° C., to circulate in a dialysis cartridge; the lysis parameters being adjusted in accordance with the osmotic fragility previously measured; and resealing in a second chamber at a temperature of from 30 to 40° C. by means of a hypertonic solution.
Owner:ERYTECH PHARMA
Red blood cell preserving fluid, preparation method thereof and red blood cell suspension
ActiveCN114732008AExtended shelf lifeImprove performance and stabilityDead animal preservationHydroxyethyl starchRed blood cell
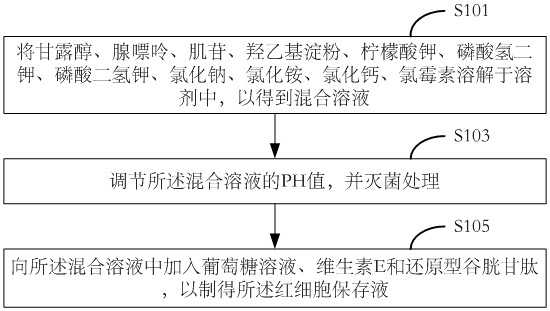
The invention provides a red blood cell preserving fluid, a preparation method thereof and a red blood cell suspension. The erythrocyte preserving fluid comprises a solvent, glucose, adenine, inosine, potassium citrate, dipotassium phosphate, monopotassium phosphate, hydroxyethyl starch, mannitol, sodium chloride, ammonium chloride, calcium chloride, chloramphenicol, vitamin E and reduced glutathione. According to the red blood cell preserving fluid, the components are mutually contained and have a synergistic effect, so that the storage life of red blood cells is prolonged, and the performance stability of the red blood cells is enhanced.
Owner:深圳瑞亚力集团有限公司
Method for detecting mechanical characteristics of red blood cells based on atomic force microscope
InactiveCN108037320AReal physical characteristicsFirmly attachedScanning probe microscopyMaterial analysisMagnetic force microscopeAtomic force microscopy
The invention provides a method for detecting the mechanical characteristics of red blood cells based on an atomic force microscope, which relates to the technical field of biophysics. The technical scheme adopted in the invention is as follows: a round coverslip is used to fix red blood cells; and the method specifically includes the following steps: preparing red blood cell suspension, preprocessing the round coverslip, preparing an atomic force microscope sample, and using the atomic force microscope to detect the mechanical characteristics of the red blood cells in a liquid environment. The red blood cells are fixed by the round coverslip, so that the red blood cells can still be maintained in a physiological state, and the maintenance of the normal morphology and function of the red blood cells is very obvious. Necessary disinfection and innocuous treatment is carried out on the commonly used round coverslip, so that there is no additional drug effect and toxic effect on the red blood cells, and the morphology and function of the cells will not be affected. The red blood cells treated by the round coverslip can be stably attached, the mechanical characteristics of the red blood cells can be independently detected without any other influence or interference, and the real physiological characteristics of the cells can be reflected.
Owner:KUNMING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
a red blood cell preservation solution
ActiveCN105028389BLong storage timeHigh antigen titerDead animal preservationBiological testingAntigenErythrocyte suspension
The invention provides a erythrocyte preservation solution. The composition and content of the erythrocyte preservation solution are as follows: adenine 0.3-0.5g / L, glucose 25-35g / L, sodium citrate 6-10g / L, inosine 0.2-0.4 g / L, chloramphenicol 0.2~0.3g / L, neomycin sulfate 0.08~0.12g / L, sodium chloride 2.5~3.5g / L, sodium dihydrogen phosphate 0.04~0.06g / L. The present invention can make the storage period of red blood cells reach 14 weeks, and within the storage period, the preserved red blood cell suspension of the present invention has higher antigen titer.
Owner:苏州苏大赛尔免疫生物技术有限公司
Detection method for avian influenza hemagglutination inhibition test
InactiveCN108088995AMonitor antibody levelsMonitor uniformityImmunoassaysSerum igeAvian influenza virus
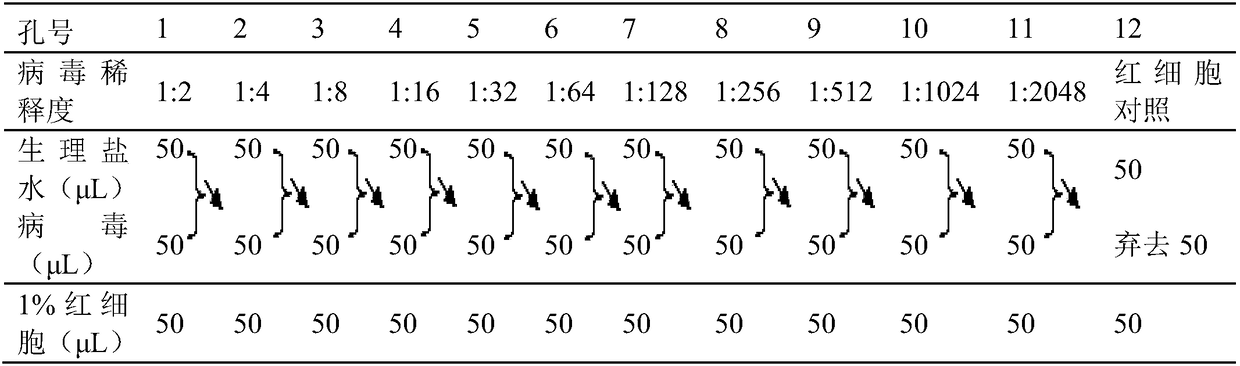
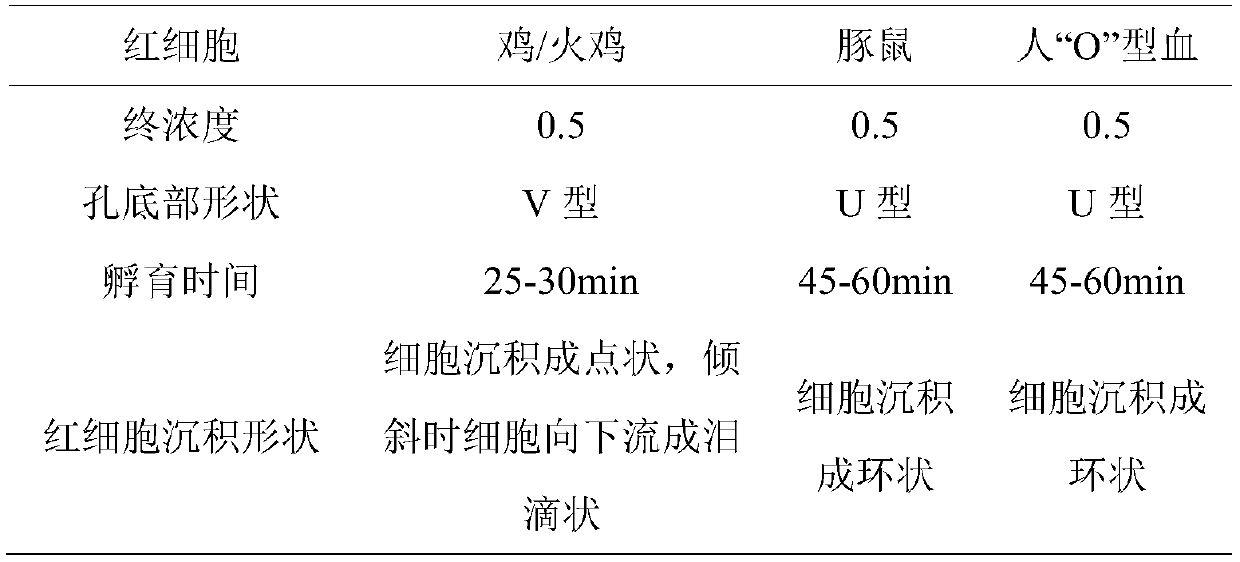
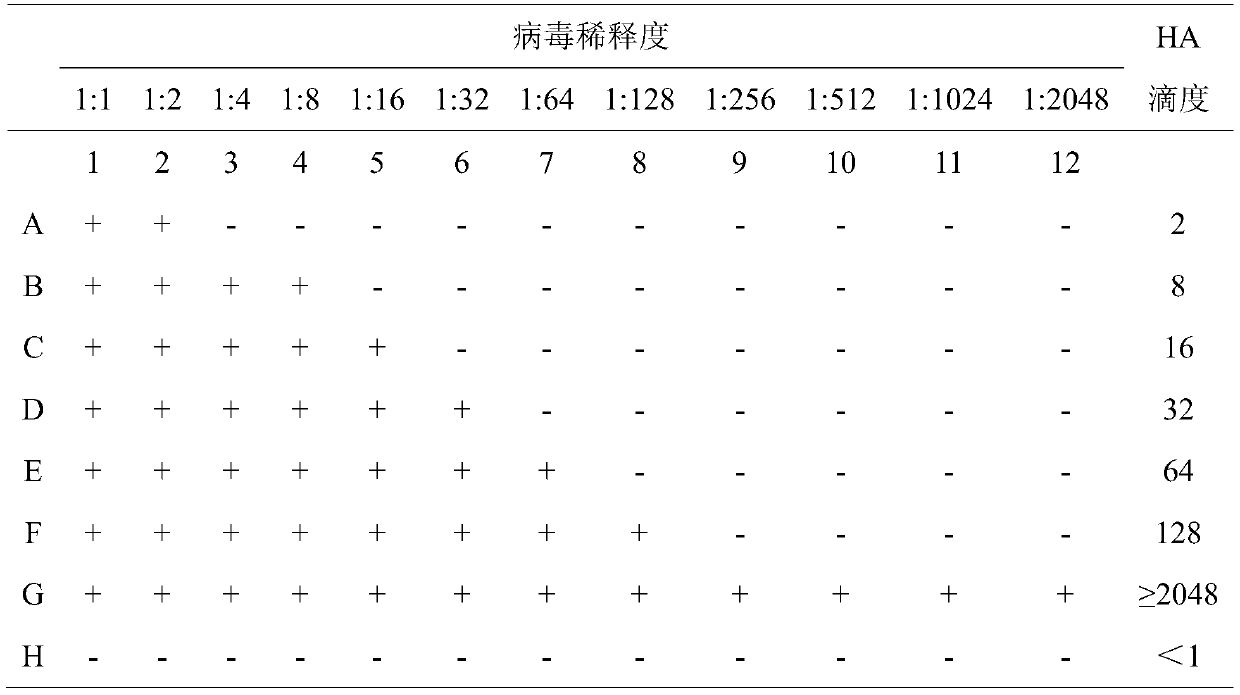
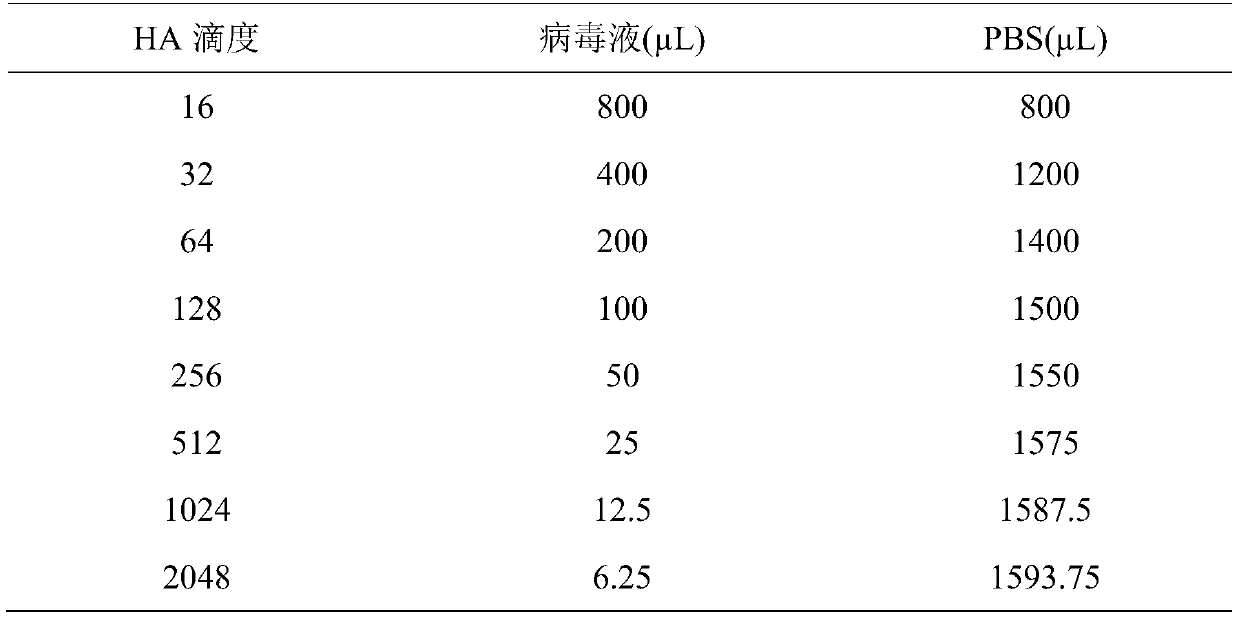
The invention discloses a detection method for an avian influenza hemagglutination inhibition test. The detection method comprises the following steps: S1, sequentially numbering a V-shaped micro-reaction plate from 1 to 12, sequentially adding 50 [mu]L of 4 units of an avian influenza virus antigen solution into each of the holes from 1 to 11; S2, respectively adding 50 [mu]L of detected serum into the first hole and the twelfth hole, mixing evenly, then absorbing 50 [mu]L to the second hole from the first hole, sequentially diluting to the tenth hole at multiple proportions, abandoning 50 [mu]L in the tenth hole; S3, sequentially adding 50 [mu]L of 1% chicken erythrocyte suspension into each hole from the twelfth hole to the first hole; S4, oscillating the V-shaped micro-reaction plate on a microoscillator, allowing standing still, incubating, and judging the agglutination condition of each hole when erythrocyte in the twelfth hole forms a button shape and sinks to the bottom of thehole. The detection method is efficient and fast, is high in accuracy, and is suitable for monitoring large chicken flocks by an enterprise.
Owner:广西凤翔集团股份有限公司
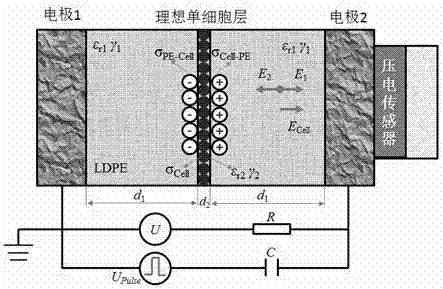
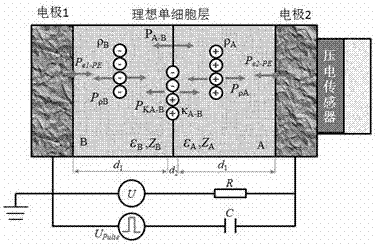
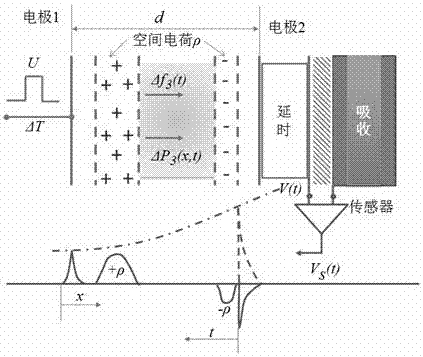
Method for measuring electrical characteristics of cell suspension by using pulsed electro-acoustic method
ActiveCN106872825ANo damageEasy to operateElectrical testingElectrostatic field measurementsElectricityNon destructive
The invention relates to a method for measuring the electrical characteristics of a cell suspension by using a pulsed electro-acoustic method. According to the method of the invention, the fundamental principles of a traditional pulsed electro-acoustic method (PEA) for measuring the space charges of a solid thin film or a cable material are adopted to detect the charged characteristics of the cell suspension. The method includes the following steps that: 1) a three-layer composite media model is established, and the use conditions of the three-layer composite media model are defined; 2) red cells are separated from venous blood obtained from the tail of an SD rat, and the red cells are diluted to an appropriate concentration; 3) an obtained red cell suspension is injected into a measuring chamber; 4) direct-current bias voltage and pulse electrical signals are applied to the sample; and 5) acoustic waves are detected and converted into electrical signals through a piezoelectric sensor, so that the charged characteristics of the cell suspension can be calculated. The method of the invention has the advantages of simplicity, quickness and convenient operation. With the method adopted, the charged characteristics of various kinds of cells can be measured in a non-destructive manner, and a new measurement means can be provided for the study of electrophysiology.
Owner:XIJING UNIV
Three-dimensional microfluidic chip capable of driving deterministic lateral displacement on basis of centrifugal force and Euler force
ActiveCN108251297AEasy to controlRealize non-contactBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWhite blood cellEngineering
A three-dimensional microfluidic chip capable of driving deterministic lateral displacement on the basis of centrifugal force and Euler force comprises more than two groups of centrically-symmetric flowing channels, wherein each flowing channel comprises a whole blood input type blood storing chamber; an outlet of each blood storing chamber is connected to an inlet of a leukocyte filtering chamberfor filtering leukocyte of the whole blood; an outlet of the leukocyte filtering chamber is connected to an inlet of a centrifugal chamber for separating blood into red cell suspension and blood plasma; an outlet of the centrifugal chamber is connected to an inlet of a liquid storing chamber for temporarily storing the blood plasma or providing a reaction environment; an outlet of the liquid storing chamber is connected to an inlet of a small-inside-diameter flowing channel for supplying cell screening or chromatography environment through a spiral flowing channel. With the adoption of the three-dimensional microfluidic chip, the liquid in the radial direction (centrifugal force), tangential direction (Euler force) and normal direction (gravity) can be controlled by simply controlling thespeed, the acceleration and the direction of a motor of a centrifugal system in rotating; the noncontact operation is realized; high driving powder can be supplied; moreover, the control accuracy isensured.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Influenza hemagglutination inhibition test detection method
PendingCN111323581ASolve the difficulty that the experiment cannot be carried outAvoid difficultiesBlood/immune system cellsBiological testingAntigenic analysisSpecific lectin
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbiological detection, and discloses an influenza hemagglutination inhibition test detection method which comprises the following steps: pretreatingstandard reference antiserum to remove non-specific inhibin and non-specific lectin in the serum; preparing an erythrocyte suspension; determining the hemagglutination titer of the influenza virus strain; preparing four hemagglutination unit antigens for an erythrocyte agglutination inhibition test; rechecking and titrating four hemagglutination unit antigens; and performing influenza virus identification and antigen analysis by using an HAI method to obtain the serum titer of the detected serum. According to the detection method, chicken erythrocyte, turkey erythrocyte and guinea pig erythrocyte are used as raw materials to prepare erythrocyte suspension, animal erythrocyte is used for replacing human erythrocyte, and the difficulty that an experiment cannot be conducted due to lack of erythrocyte is solved.
Owner:广州鸿泉生物科技有限公司
Method for monitoring benzo(a)pyrene pollution of seawater by utilizing fish blood cells
InactiveCN102087277AEasy to prepareEasy to operateIndividual particle analysisBiological testingRed blood cellPyrene
The invention provides a method for monitoring benzo(a)pyrene in seawater by utilizing fish blood cells. The method comprises the following steps: taking 50mu L of staphylococcus aureus suspension obtained through treatment of buffer solution on ice and mixing the staphylococcus aureus suspension with isovolumetric paralichthys olivaceus erythrocyte suspension exposed in the seawater containing benzo(a)pyrene and incubating the mixture at the constant temperature of 20 DEG C for 30 minutes, wherein the ratio of the cell number is 20:1; shaking the mixture to mix the mixture uniformly every 10 minutes to prevent precipitates; terminating reaction after completion of incubation, adding 20mu L of 0.25% of precooled glutaraldehyde solution to each tube, immobilizing the tube in a refrigerator at the temperature of 4 DEG C for 15 minutes, taking incubation solution to prepare smears and immobilizing the smears with methanol after airing the smears; dying each smear with Wright's dye solution for 3 minutes, washing the smear with distilled water until the smear becomes colorless, carrying out observation under an oil lens after airing the smear and computing the erythrocyte C3b receptor rosette rate; and forming a rosette by adhering two or more staphylococcus aurei to each erythrocyte. The detection method is completed in one hour and whether the seawater is polluted by benzo(a)pyrene can be better monitored and analyzed by the method.
Owner:张振冬
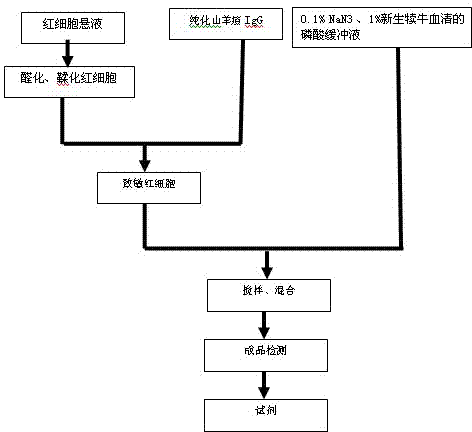
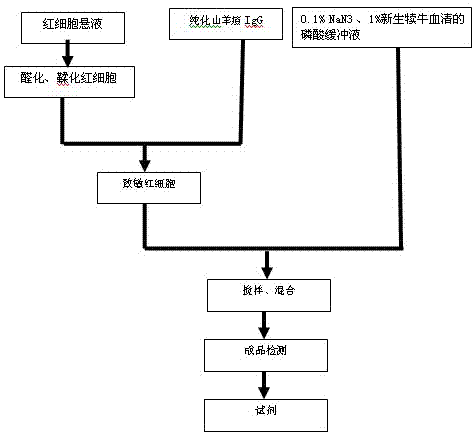
Preparation method and detection method of goat pox reverse indirect hemagglutination diagnostic reagent
InactiveCN102288756AThe detection process is fastIncreased sensitivityMaterial analysisRed blood cellReaction temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method and a detection method of a goat pox reverse indirect hemagglutination diagnostic reagent capable of detecting goat pox antigen. The preparation method is: mix glutaraldehyde and sheep red blood cells to prepare red blood cell suspension, mix with the same amount of purified goat pox IgG, stir, centrifuge, wash, and use PBS containing 1% newborn calf serum to make 1% sensitization Red blood cells, this is the diagnostic reagent for goat pox reverse indirect hemagglutination. The optimized preparation conditions are: use glutaraldehyde monoformylation method to fix red blood cells, the concentration of sensitized red blood cells is 0.8%-1.0%, and the IgG content is controlled at 1.5-1.55mg.ml-1, which can achieve a better labeling effect; The reagent is used to detect goat pox virus antigen according to the conventional reverse indirect hemagglutination test method, the reaction temperature is 20-25°C, and the reaction time is 50min. The method has good specificity, sensitivity and repeatability, and can be used for rapid detection of goat pox antigen in veterinary clinic.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
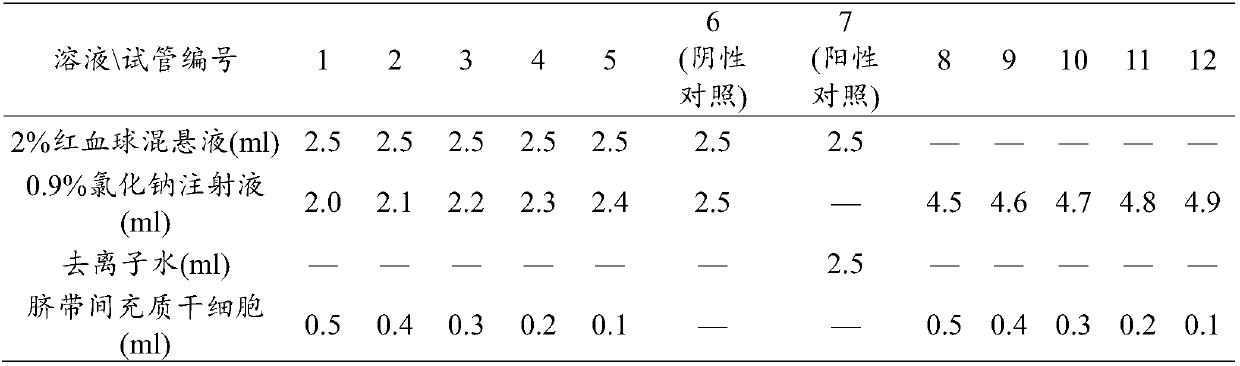
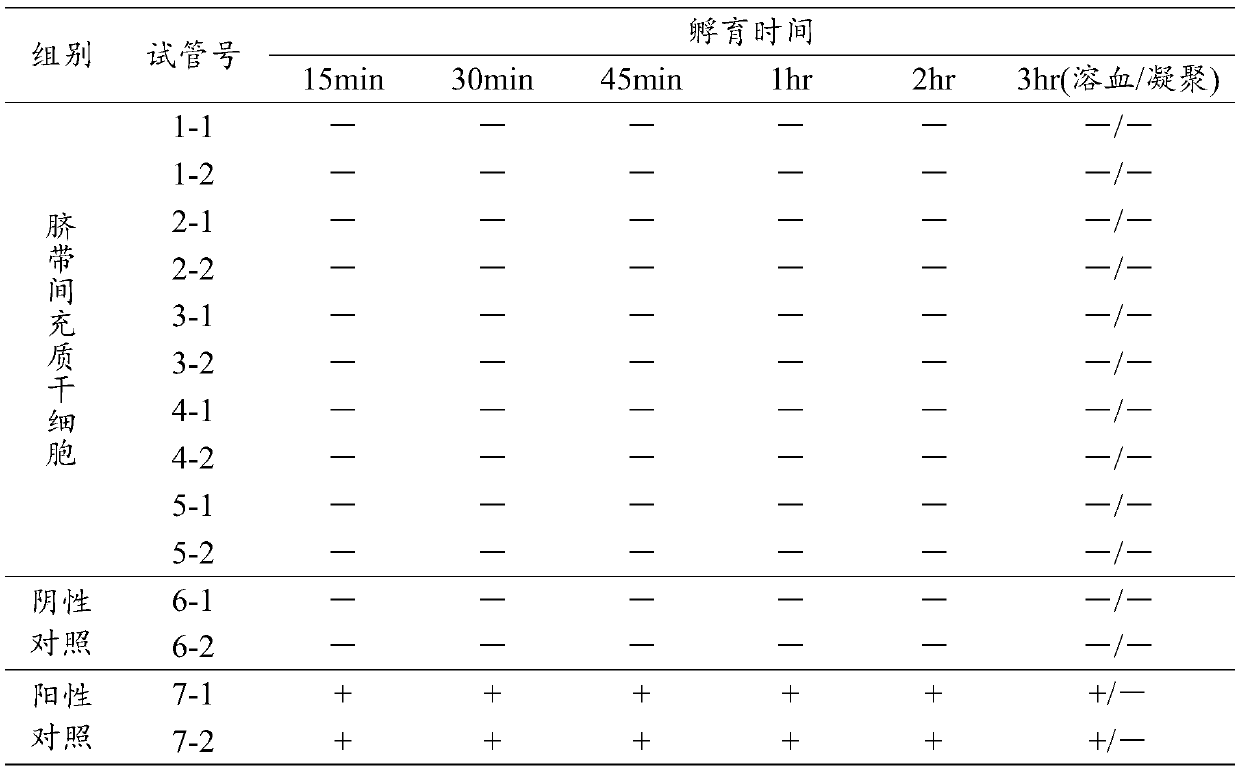
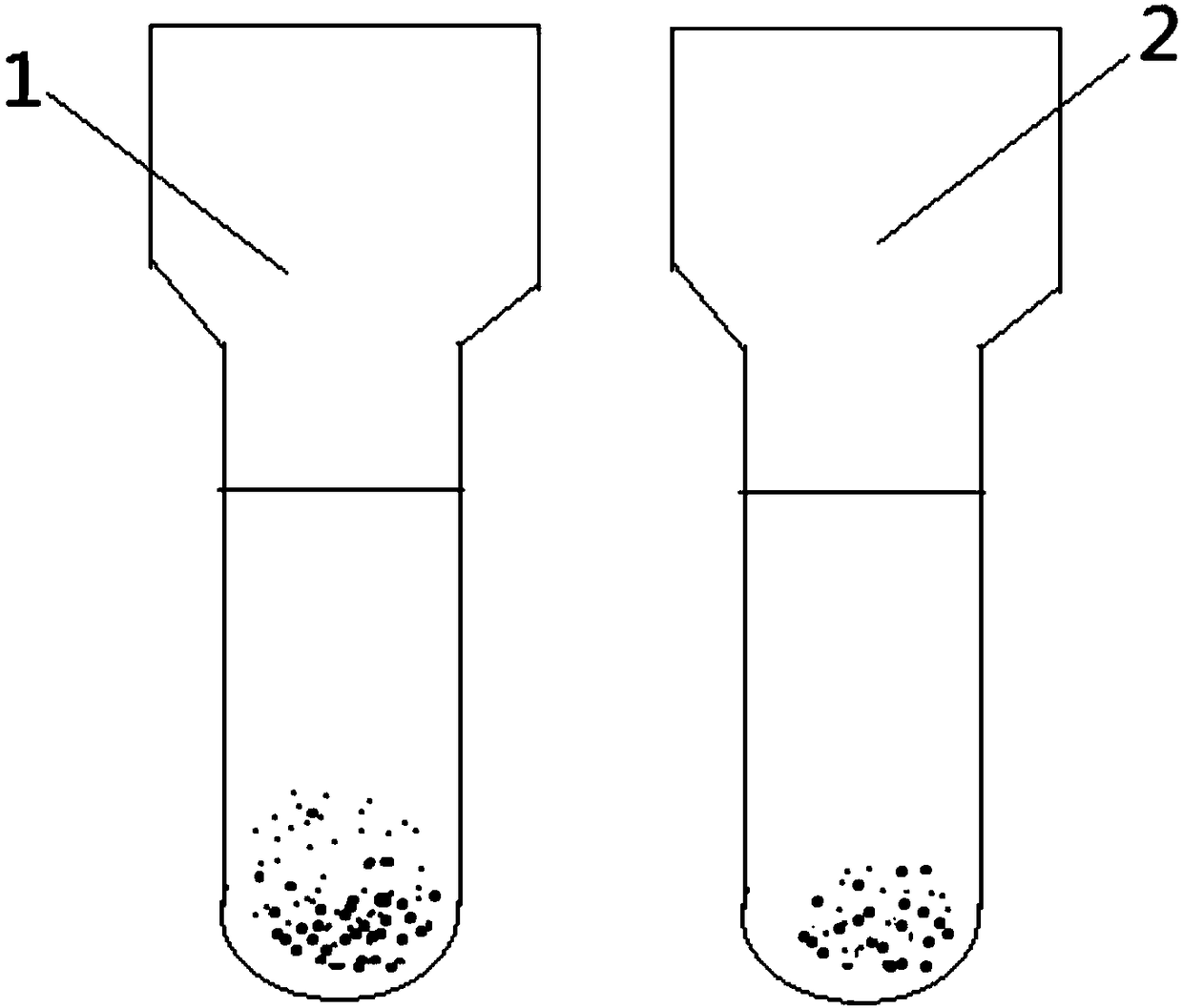
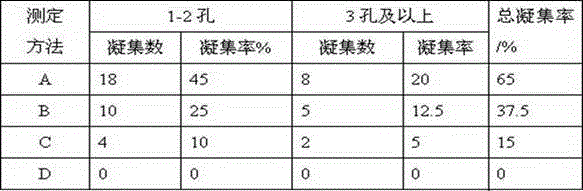
Evaluation method of hemolysis of mesenchymal stem cell preparation and application
InactiveCN109576335AReduce the risk of inaccurate resultsAvoid the problem of inaccurate evaluation resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisEvaluation resultHemolysis
Owner:TIANJIN CHANGHE BIOLOGICAL TECH
Indirect anti-human globulin accelerated blood matching test method
InactiveCN108548921AQuick checkoutSafe Blood Transfusion QualityMaterial analysisMatching testBlood plasma
The invention discloses an indirect anti-human globulin accelerated blood matching test method, which comprises: adding physiological saline to red blood cells, washing, uniformly mixing, carrying outcentrifugal separation, removing the supernatant, adding physiological saline, preparing a red blood cell suspension, adding plasma or serum, uniformly mixing, adding an indirect anti-human globulintest acceleration enhancer, uniformly mixing, incubating, adding physiological saline, carrying out centrifugal separation, slightly shaking the test tube, observing the result, and judging the resultaccording to the red blood cell agglutination or dispersion condition. According to the present invention, the cross matching test and / or the red blood cell irregular antibody screening test before the blood transfusion is accelerated and enhanced by using the indirect anti-human globulin test acceleration enhancer, and the indirect anti-human globulin test acceleration enhancer has characteristics of short incubation time, high sensitivity and strong accuracy, can be quickly detect various weak red blood cell irregular antibodies, and is suitable for emergency rapid cross-matching and red blood cell irregular antibody screening.
Owner:SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV
Method for detecting regional SIV (swine influenza virus) subtype distribution
ActiveCN106442986AEliminate distractionsEliminate the effects of agglutinationMaterial analysisDiseaseMicrotiter plate
The invention relates to a method for detecting regional SIV (swine influenza virus) subtype distribution and belongs to the technical field of animal hygiene examination. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: acquiring serum samples firstly, processing the serum samples with a pancreatin-sodium ferrate-hydrogen peroxide-polyethylene glycol method, and removing non-specific clotting factors from the serum samples to obtain to-be-detected serum; determining the concentration of four hemagglutination units of antigens with a double-dilution method; reacting the to-be-detected serum, the to-be-detected antigens and chicken erythrocyte suspension on a V-shaped microtiter plate, and determining the to-be-detected serum with positive titer of serum antibodies by taking the highest dilution ratio, completely inhibiting the four hemagglutination units of the to-be-detected antigens, of the to-be-detected serum as the titer of the serum antibodies. The method is simple, effective and low in cost, can be used for performing positive rate analysis of a larger number of serum samples and lays a foundation for treatment and prevention of animal diseases.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method of detecting red cell antigen-antibody reactions
InactiveUS7919266B2High test sensitivityAntibody uptake by the red cells is noticeably increasedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSerum igeTest sample
A process for the detection of antibodies in a test sample by preparing a suspension of erythrocytes with a test serum or plasma by mixing a test serum or plasma with erythrocytes; incubating the suspension of erythrocytes at a temperature of from 37° C. to 45° C. to bind any antibodies in the test serum or plasma to the surface of said erythrocytes; combining the suspension of erythrocytes with an amount of a solution of a macromolecule which is effective to agglutinate the erythrocytes; packing the resultant red cell agglutinates by centrifuging the suspension of erythrocytes; and, determining the presence of anti-erythrocyte antibodies by observing if antibody-dependent erythrocyte agglutination has occurred.
Owner:CLAVINA DIAGNOSTICS
Erythrocyte preserving fluid and application thereof
ActiveCN111513059AExtended shelf lifeDead animal preservationColor/spectral properties measurementsRed blood cellGallic acid
The present invention provides an erythrocyte preserving fluid comprising 5 to 15 [mu] mol / L of an epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). The invention also provides a method for preserving erythrocytes andan erythrocyte suspension. The preservation period of the red blood cell suspension can be prolonged to 168 days by utilizing the red blood cell preservation solution.
Owner:TIANJIN DEXIANG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Serum pre-dilution method for HI test
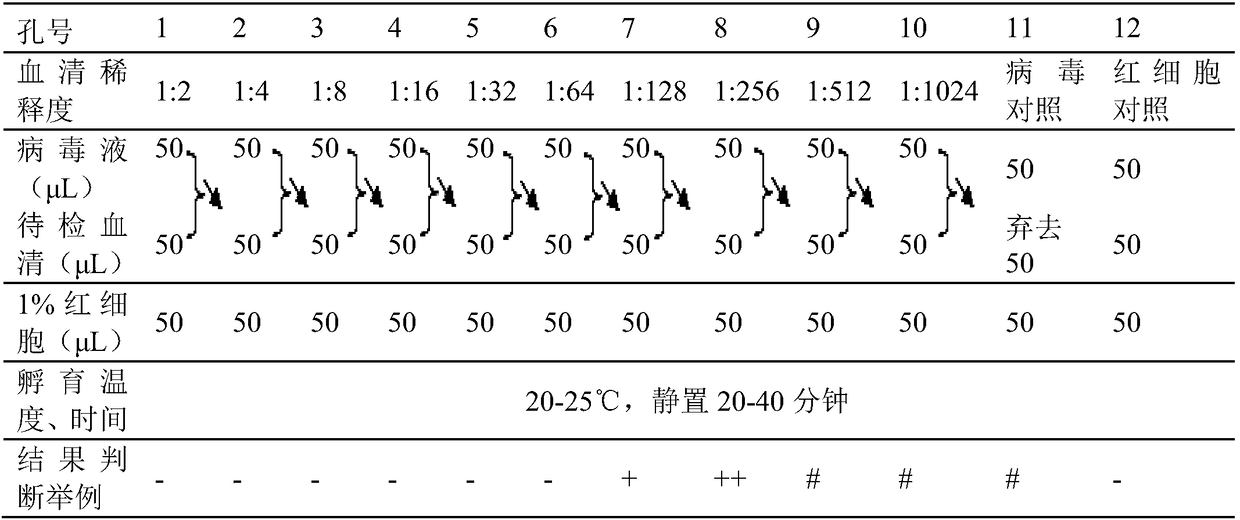
InactiveCN110007070AData error is smallReduce retest ratePreparing sample for investigationBiological testingAntigenPre-Dilution
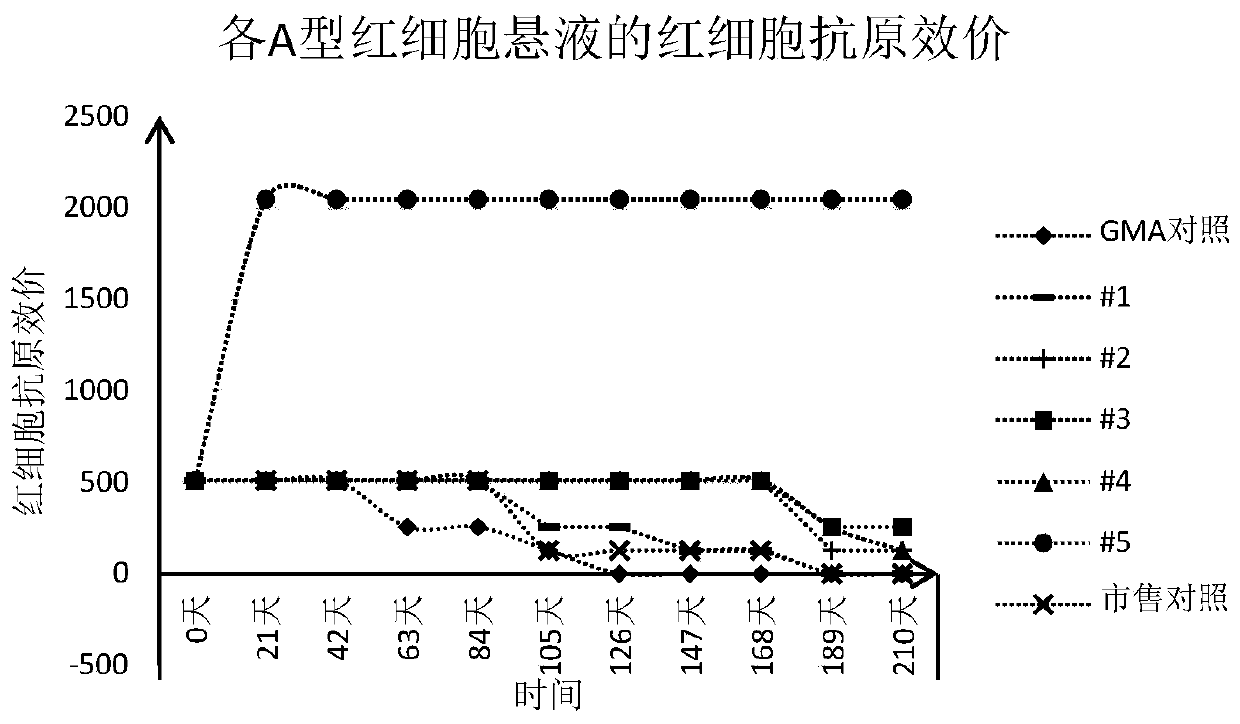
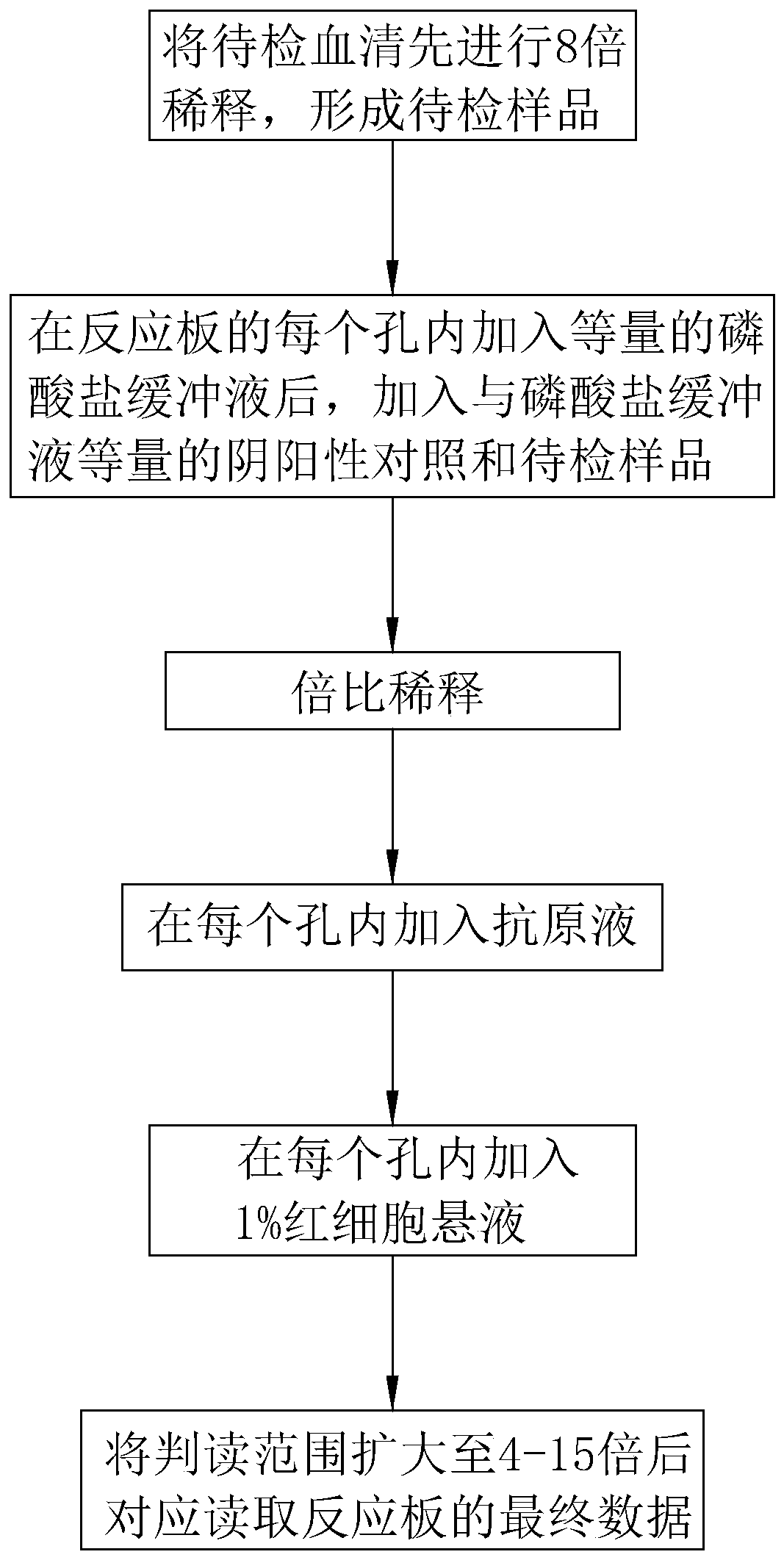
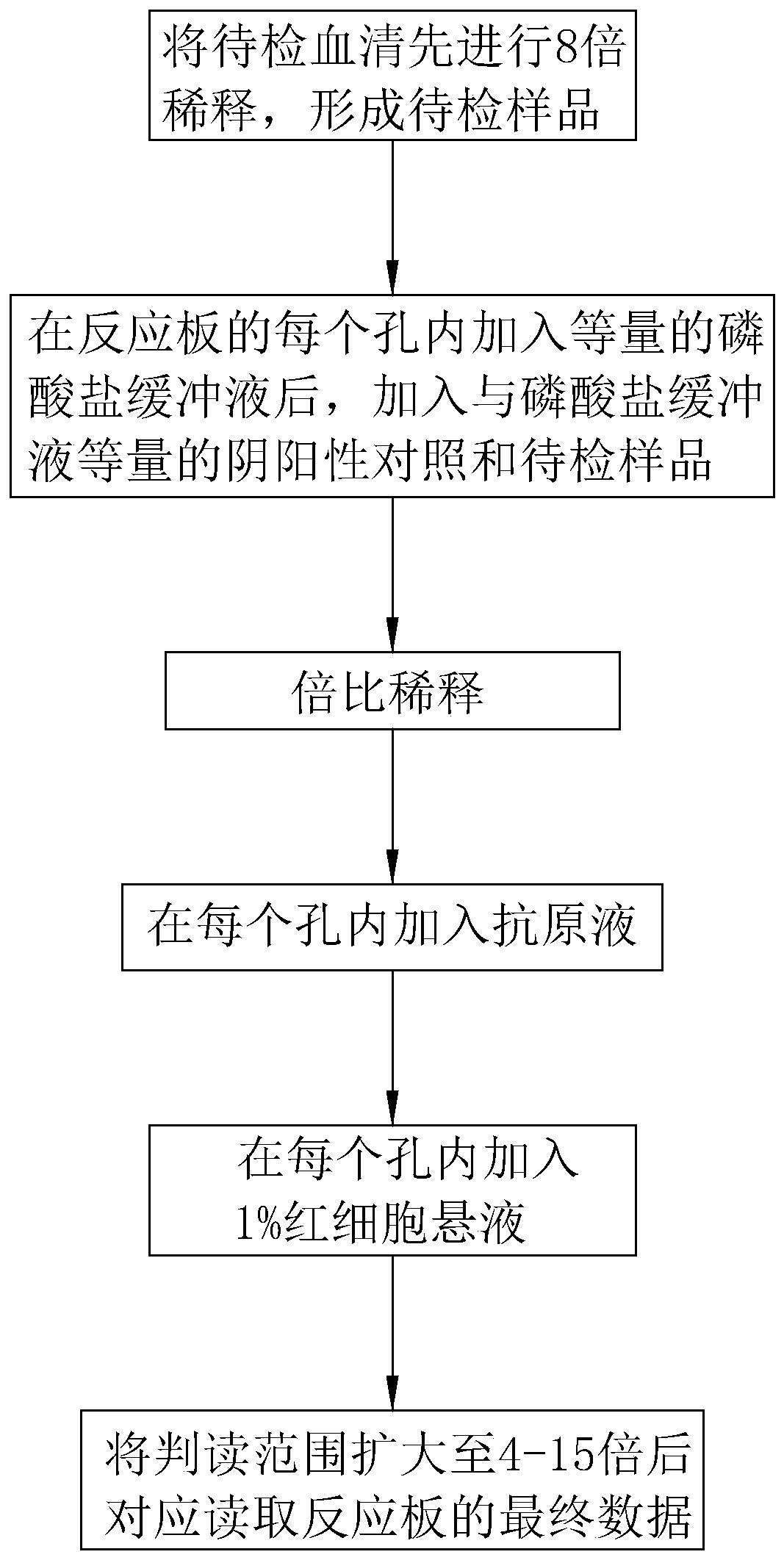
A serum pre-dilution method for an HI test comprises the following steps: diluting serum to be detected by 8 times to form a sample to be detected; adding an equal amount of phosphate buffer solutioninto each hole of a reaction plate, and then adding a positive-negative control and the sample to be detected which are equal to the phosphate buffer solution in amount; carrying out double-ratio dilution; adding an antigen solution into each hole; adding 1% of erythrocyte suspension into each hole; expanding the interpretation range to 4-15 times, and correspondingly reading the final data of thereaction plate. The serum to be detected is diluted by 8 times in advance; according to the serum pre-dilution method for an HI test, after an HI experiment pre-dilution is carried out, the concentration of a sample in each hole of the reaction plate is reduced by 8 times, and the original interpretation range is expanded by 8 times, so that a re-detection step is avoided, operation steps in theHI experiment serum pre-dilution process are reduced, and the detection cost of an HI test sample is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING POULTRY BREEDING
Compound application
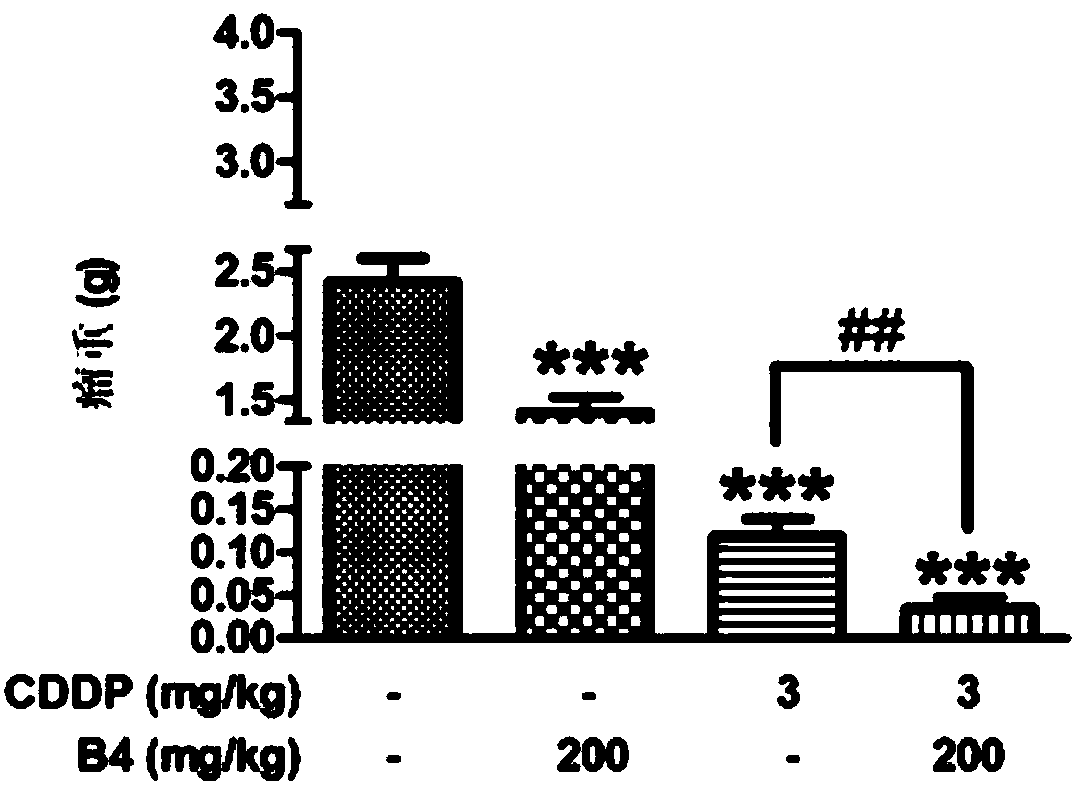
InactiveCN107929298AGrowth inhibitionDoes not inhibit growthOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsIn vitro stimulationAcute toxicity testing
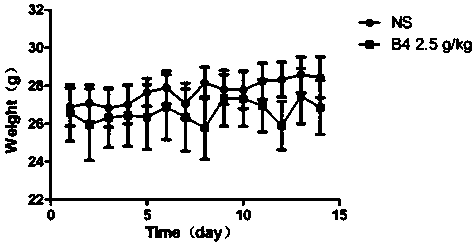
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, and in particular relates to application of pulsatilla saponin B4 to preparation of medicine for preventing and / or treating tumor. Results ofhemolysis tests show that the pulsatilla saponin B4 does not have the obvious hemolysis phenomenon during incitation by in vitro addition in rabbit 2-percent erythrocyte suspension for stimulation. According to the evaluation on toxicity of the pulsatilla saponin B4 to the in vitro cell, the condition that the pulsatilla saponin B4 does not have the obvious cell toxicity to the in vitro culturedRD cells is discovered through study. The acute toxicity tests are used for evaluating the safety of the pulsatilla saponin B4; test results show that the pulsatilla saponin B4 is safe and non-toxic.Through MTT experiments, the condition that the pulsatilla saponin B4 does not have the cell toxic effects on S180 and Lewis cancer cells, and cannot be used for inhibiting the tumor cell multiplication is discovered; but the results of mice in vivo transplantation tumor tests show that the pulsatilla saponin B4 obviously inhibits the growth of the S180 sarcoma growth in the bodies of the mice, and the anti-tumor effect is achieved in the bodies.
Owner:四川睿麒源医药科技有限公司
Method for building oxidative stress model of carp red blood cells
InactiveCN102559592BOptimum use concentrationSuitable incubation timeBlood/immune system cellsCarpApoptosis
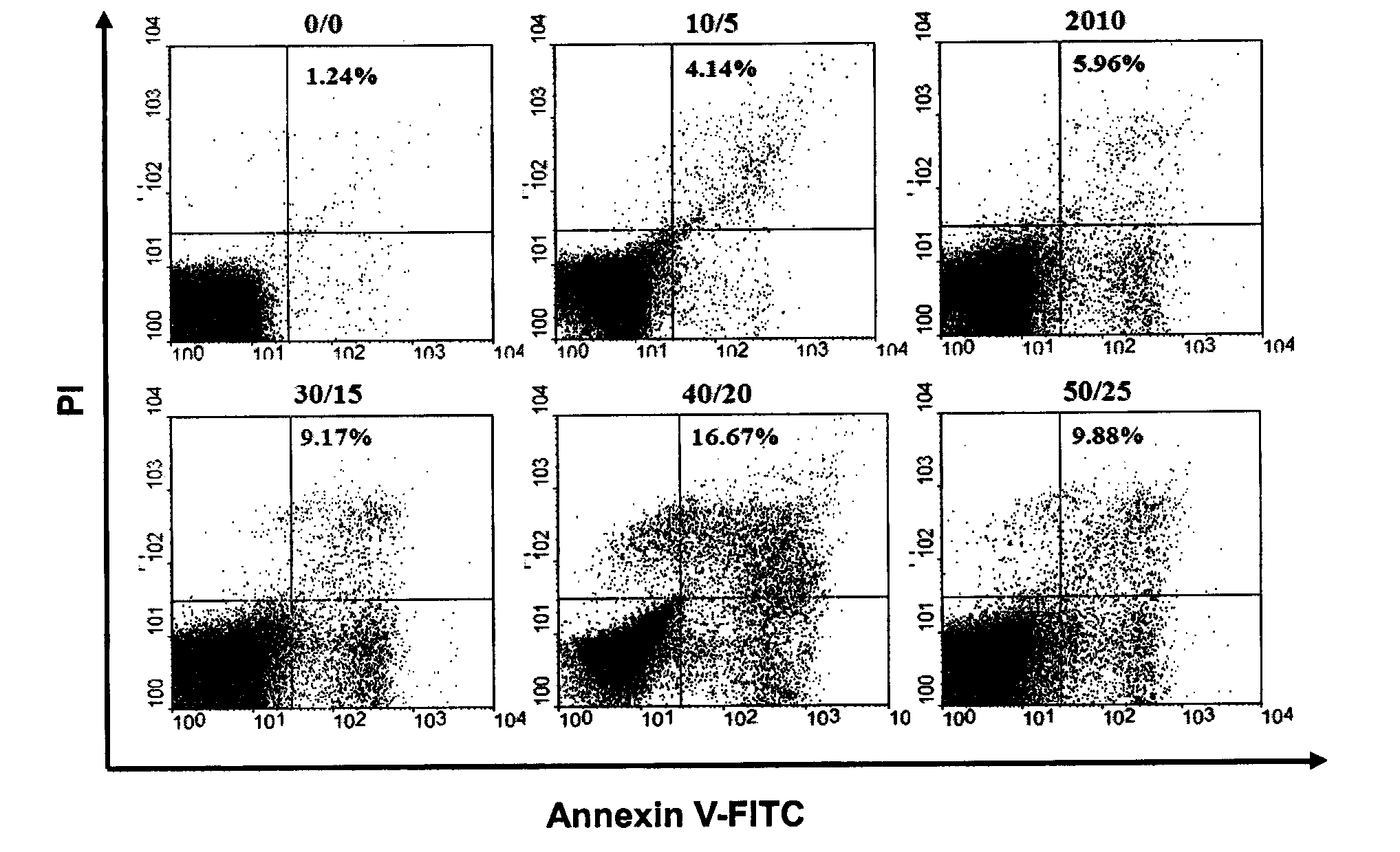
The invention discloses a method for building an oxidative stress model of carp red blood cells, which comprises sterilizing the tail of a carp, drawing about 1 millimeter of blood from the tail of each carp; putting the blood into 6 millimeters of carp saline solution containing heparin, centrifuging 900 grams of a blood sample at a temperature of 4 DEG C for 10 minutes, rejecting supernate; suspending red blood cell deposits in the 6 millimeters of carp saline solution, centrifuging 900 grams of sample at a temperature of 4 DEG C for 10 minutes; re-suspending the red blood cell deposits in the carp saline solution, washing suspending the red blood cell deposits in the 6 millimeters of carp saline solution after the red blood cell deposits are washed twice, preserving the red blood cell deposits at a temperature of 4 DEG C for reserve; drawing adequate red blood cell suspension, adding equal volume of Fe2+ mixture solution with a density of 40 mu M or H2O2 mixture solution with a density of 20 mu M, incubating the suspension at a temperature of 37 DEG C for 8 to 10 hours; centrifuging 1000 grams of sample at a temperature of 4 DEG C for 3 minutes, and detecting apoptosis of cell samples by a flow cytometry and agarose gel electrophoresis. The method for building the oxidative stress model of carp red blood cells utilizes the Fe2+ or H2O2 mixture solution as a source of free radical OH, for the first time, and a red blood cell oxidative stress model is built.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
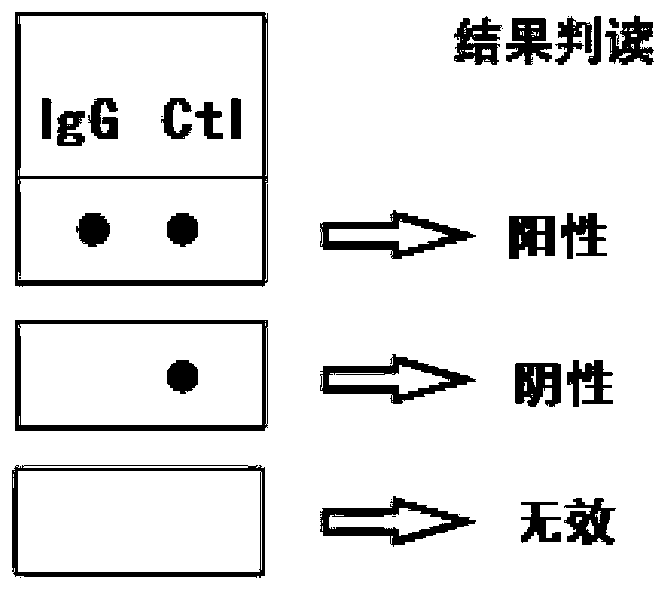
Rapid detection kit for IgG blood group antibody titer
PendingCN111458524AGet rid of distractionsBright redBiological testingAntiendomysial antibodiesTiter
The invention discloses a rapid detection kit for IgG blood group antibody titer. The rapid detection kit comprises a standard red blood cell suspension, a flushing fluid and a detection test strip; the detection test strip comprises a sample adding part, a reaction part and a water absorption part which are sequentially arranged in a contact manner from the upstream side to the downstream side; the sample adding part is sequentially provided with a washing sample adding area, an erythrocyte sample adding area and a sample adding area from the upstream side to the downstream side; the reactionpart is provided with at least one detection point and a contrast point, wherein at least one detection point is coated and cured with an anti-human IgG antibody, and the contrast point is coated andcured with an anti-RBC antibody. When the kit is used, only one-step sample adding, red blood cell adding and flushing fluid adding are needed, and a result can be obtained after 3-5 minutes.
Owner:INTEC PROD INC
Method for evaluating eye irritation by using miniature pig erythrocytes
InactiveCN102359946BSmall batch-to-batch varianceClear genetic backgroundColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingFormularyOphthalmology
The present invention discloses an experimental method for evaluating eye irritation by using miniature pig erythrocytes. The method mainly comprises: (1) preparing a suspension of miniature pig erythrocytes; (2) carrying out a miniature pig erythrocyte hemolysis test; (3) carrying out a protein denaturation experiment; (4) predicting a model; (5) carrying out classification and judgment. According to the present invention, the source of the erythrocytes is reliable and safe; the tested material is easy to obtain, and has good uniformity; the test system is simple and cheap, and no special equipment is required; the detection method is rapid, sensitive and universal; the method of the present invention can be directly applicable for safety evaluations of chemicals, cosmetics, pesticides, eye medicines and other substances possibly contacting the eyes, wherein the chemicals comprise surfactants, disinfection products, detergent and the like, the cosmetics comprise shampoo, bath foam, eye cream and the like; the method further can be applicable for rapidly screening, classifying and identifying the eye irritations of the raw materials, the formulas or the products.
Owner:程树军 +1
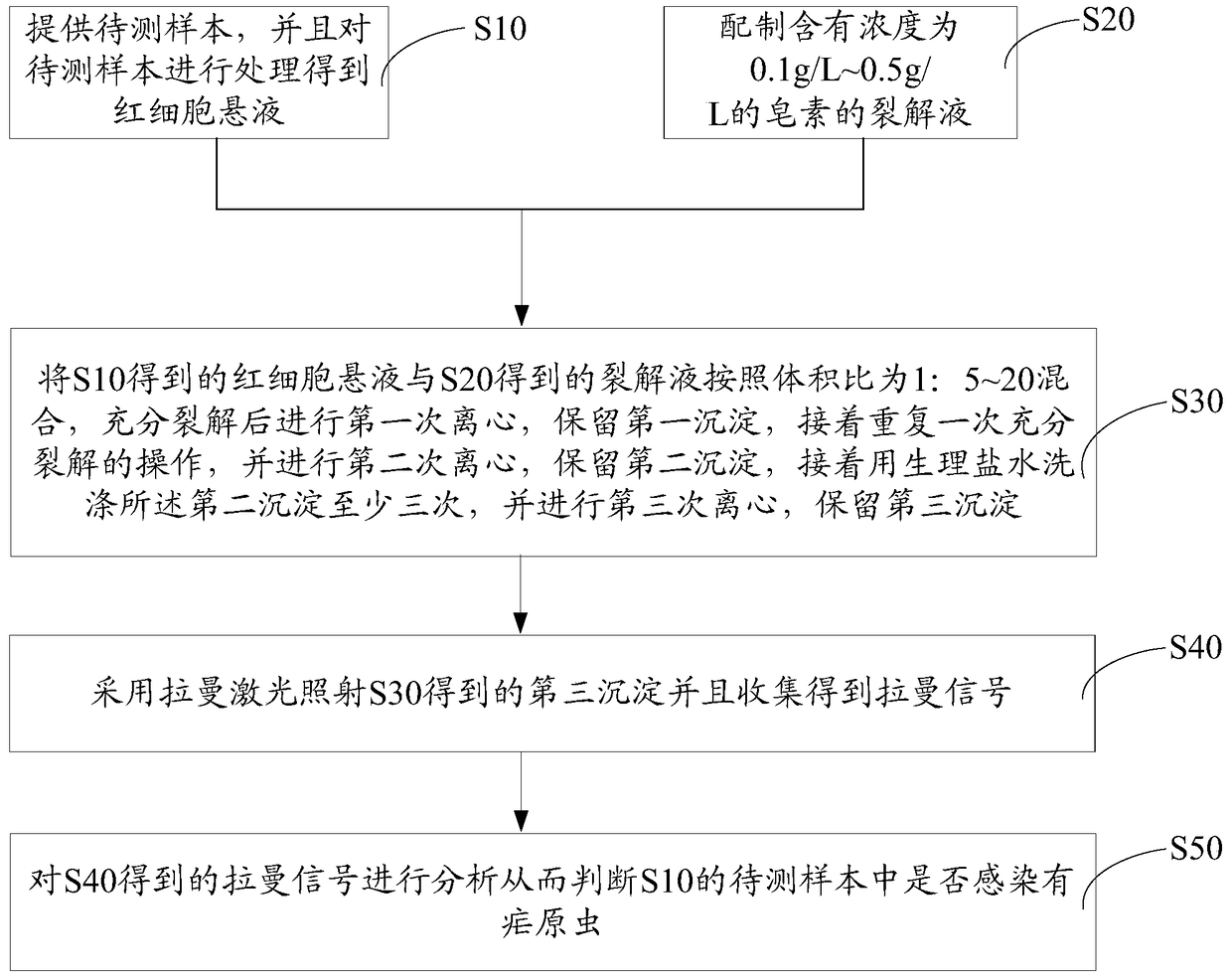
Plasmodium detection method and detection system
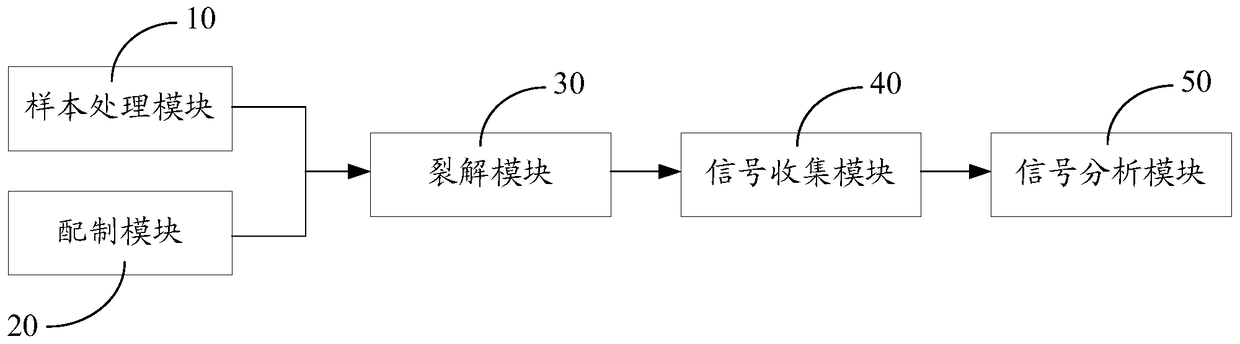
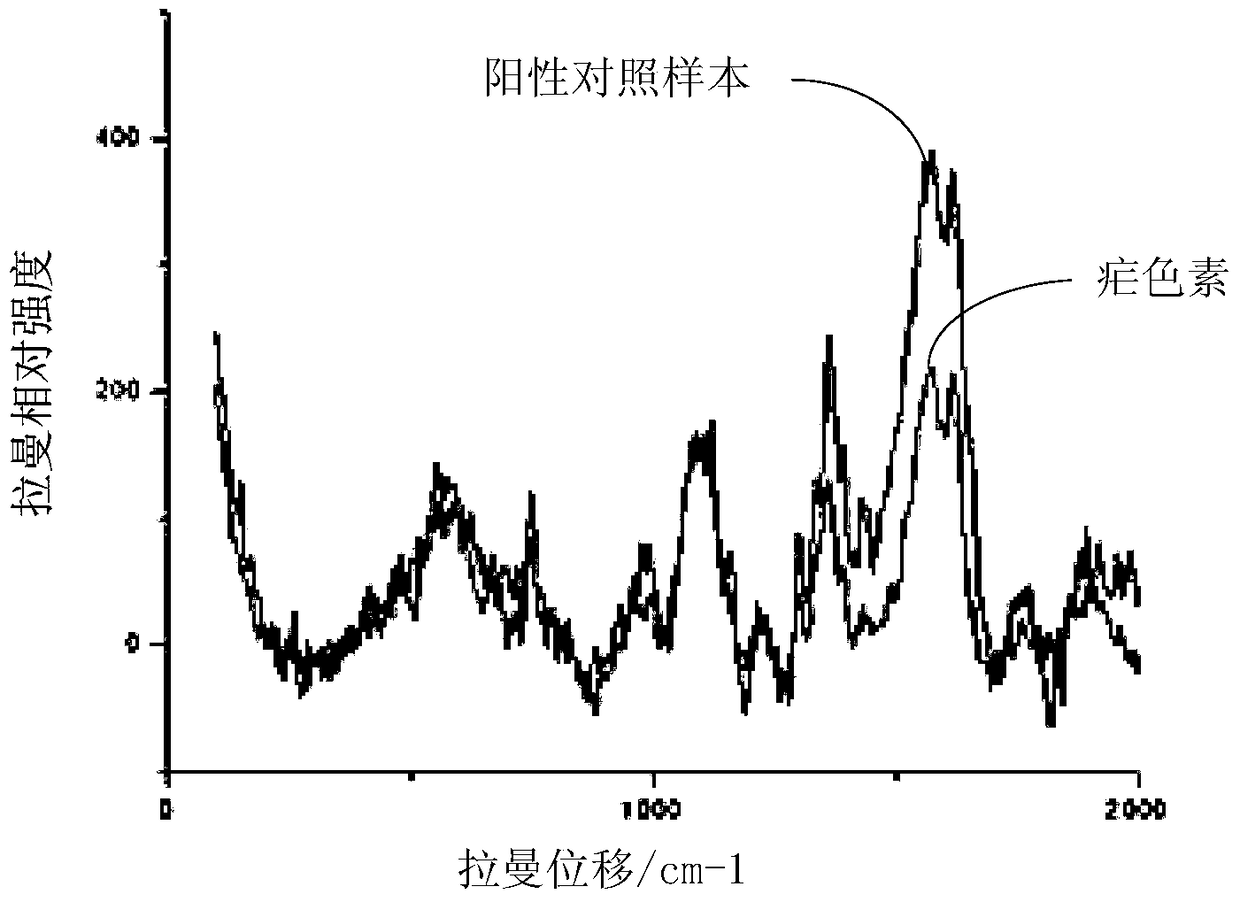
InactiveCN104897644BHigh detection sensitivityPreparing sample for investigationRaman scatteringMedicineCentrifugation
The invention discloses a method for detecting malaria parasites, which comprises the following steps: providing a sample to be tested, and processing the sample to obtain a red blood cell suspension; preparing a saponin-containing lysate; mixing the red blood cell suspension with the lyse and fully After lysis, centrifuge and retain the first precipitate, then fully lyse the first precipitate, then centrifuge and retain the second precipitate, then wash the second precipitate with saline at least three times, then centrifuge and retain the third precipitate; use Raman laser irradiation The third step is to precipitate and collect the Raman signal; and analyze the Raman signal to determine whether the sample to be tested contains Plasmodium. This method of detection of malaria parasites releases malaria parasites from red blood cells through saponin, and then obtains malaria pigment by lysing the plasma parasite cell membrane, and concentrates malaria parasites. Combined with Raman spectroscopy, the detection sensitivity is high. The invention also discloses a malaria parasite detection system.
Owner:SHENZHEN INT TRAVEL HEALTHCARE CENT
Combined rapid detection method for various avian antibodies
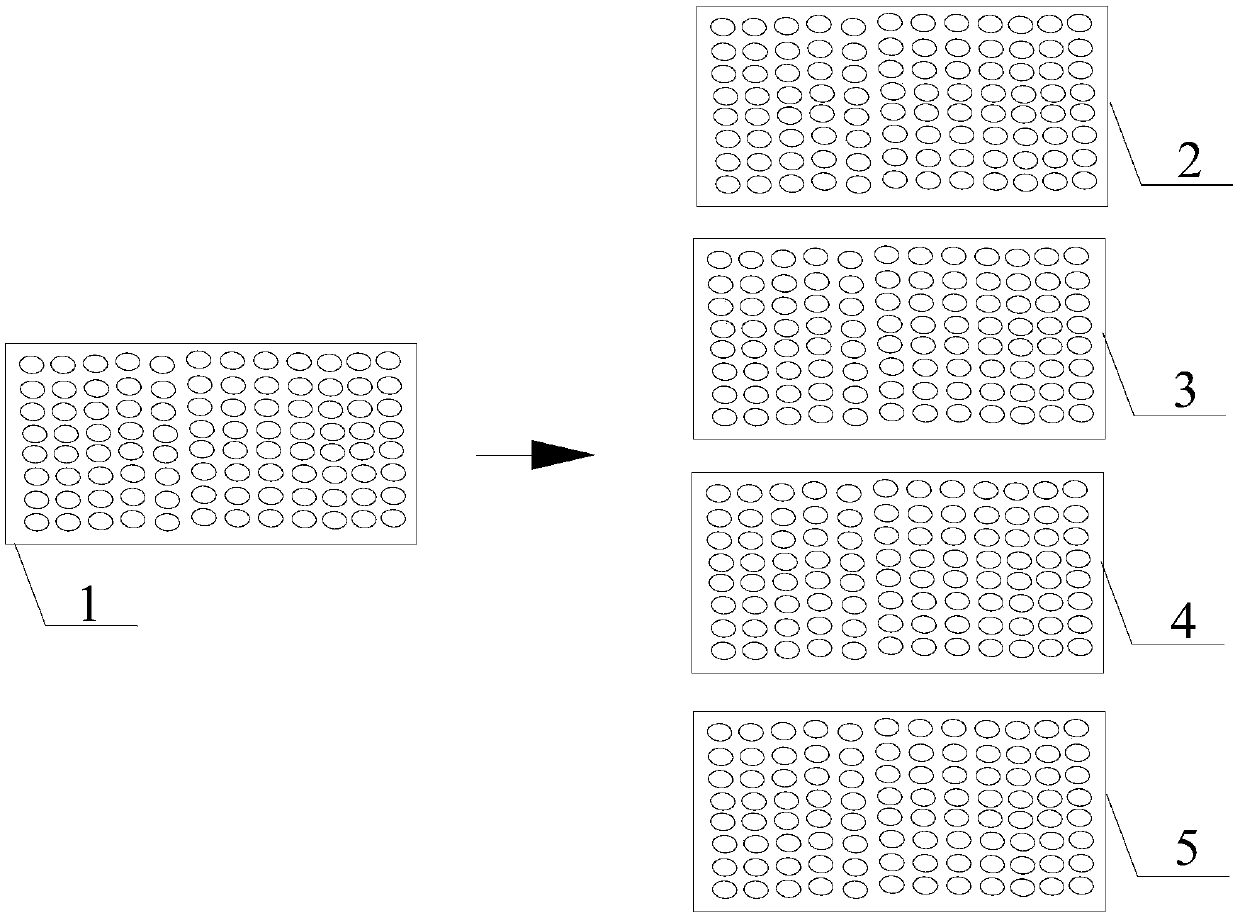
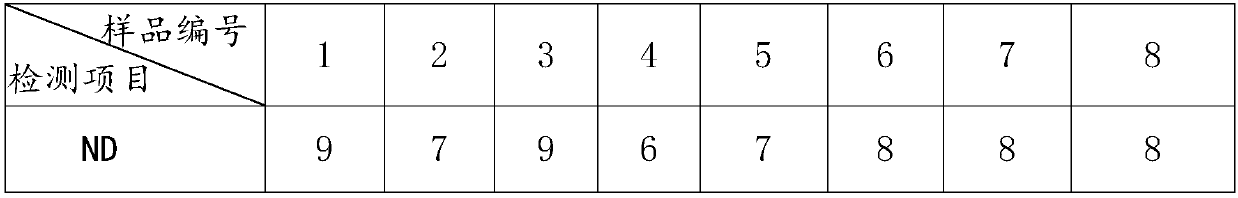
PendingCN111198265AImprove stabilityImprove work efficiencyBiological testingErythroid cellVirus antigen
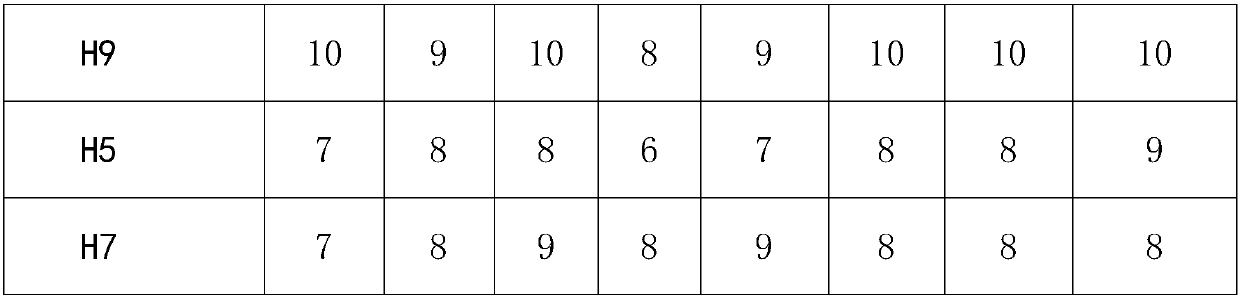
The invention belongs to the technical field of antibody detection, and provides a combined rapid detection method for various avian antibodies, which comprises: step 1, adding 0.1-0.2 mL of a diluentto all holes in first to tenth columns of an original reaction plate; step 2, adding 0.1-0.2 mL of serum liquid into each hole in the first column in the step 1; step 3, sucking 0.1-0.2 mL from eachhole in the first column in the step 2 into the holes in the second column; step 4, respectively transferring the serum liquid obtained in the step 3 into corresponding reaction holes of ND, H9, H5 and H7 reaction plates according to 0.02-0.04 mL per hole; step 5, respectively adding 0.02 to 0.04 mL of diluent into each hole in the eleventh column of each reaction plate in the step 4; step 6, adding 0.02-0.04 mL of ND, H9, H5 and H7 virus antigen solutions into the holes in the first to eleventh columns of the reaction plates in the step 5; step 7, adding 0.02-0.04 mL of chicken erythrocyte suspension into each hole of each reaction plate in the step 6, and judging the antibody titer of ND, H9, H5 and H7; meanwhile, the invention has the characteristic that multiple antibodies can be simultaneously detected by a single person.
Owner:内蒙古正大食品有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com