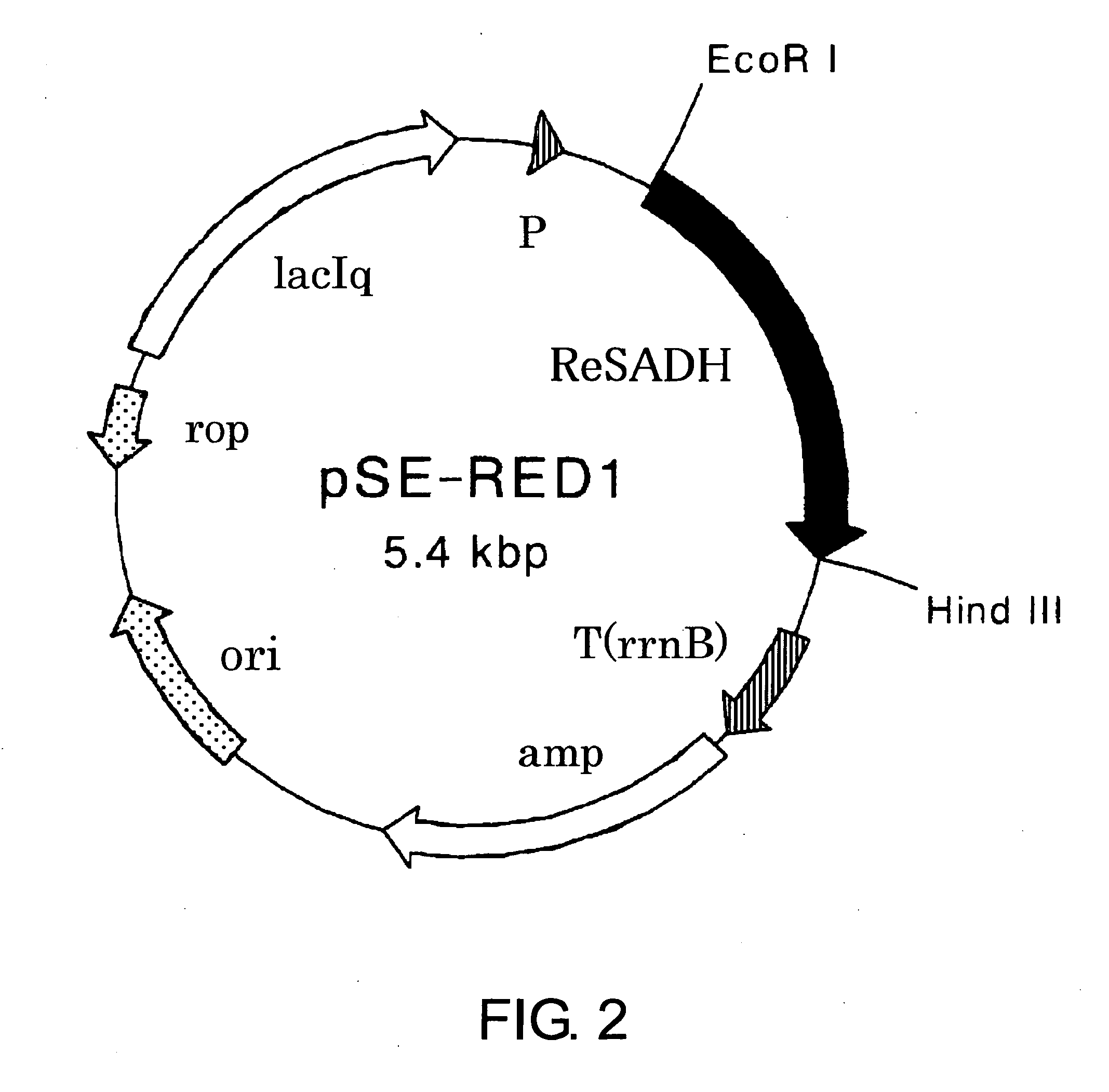
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
228 results about "Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP+)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetically modified cyanobacteria for the production of ethanol, the constructs and method thereof
InactiveUS6306639B1Inhibit transcriptionAlgae productsBacteriaPhylum CyanobacteriaKetoacid decarboxylase
The invention relates to the genetic modification of Cyanobacteria for the production of ethanol, and more particularly, to the genetic modification of Cyanobacteria by incorporating the genetic information encoding for pyruvate decarboxylase (pdc) and alcohol dehydrogenase (adh).
Owner:ENOL ENERGY
Modified alcohol dehydrogenases for the production of fuels and chemicals
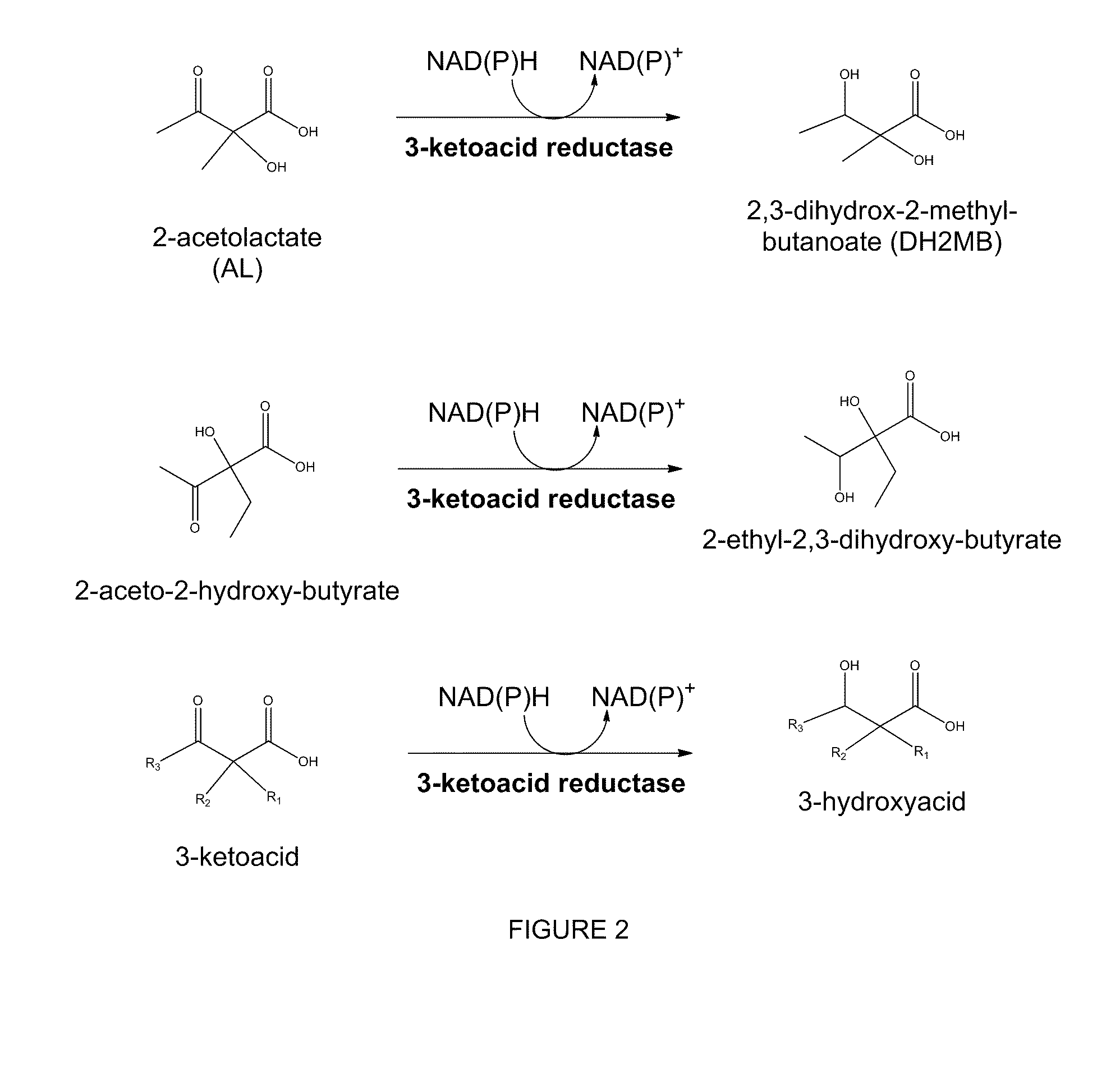
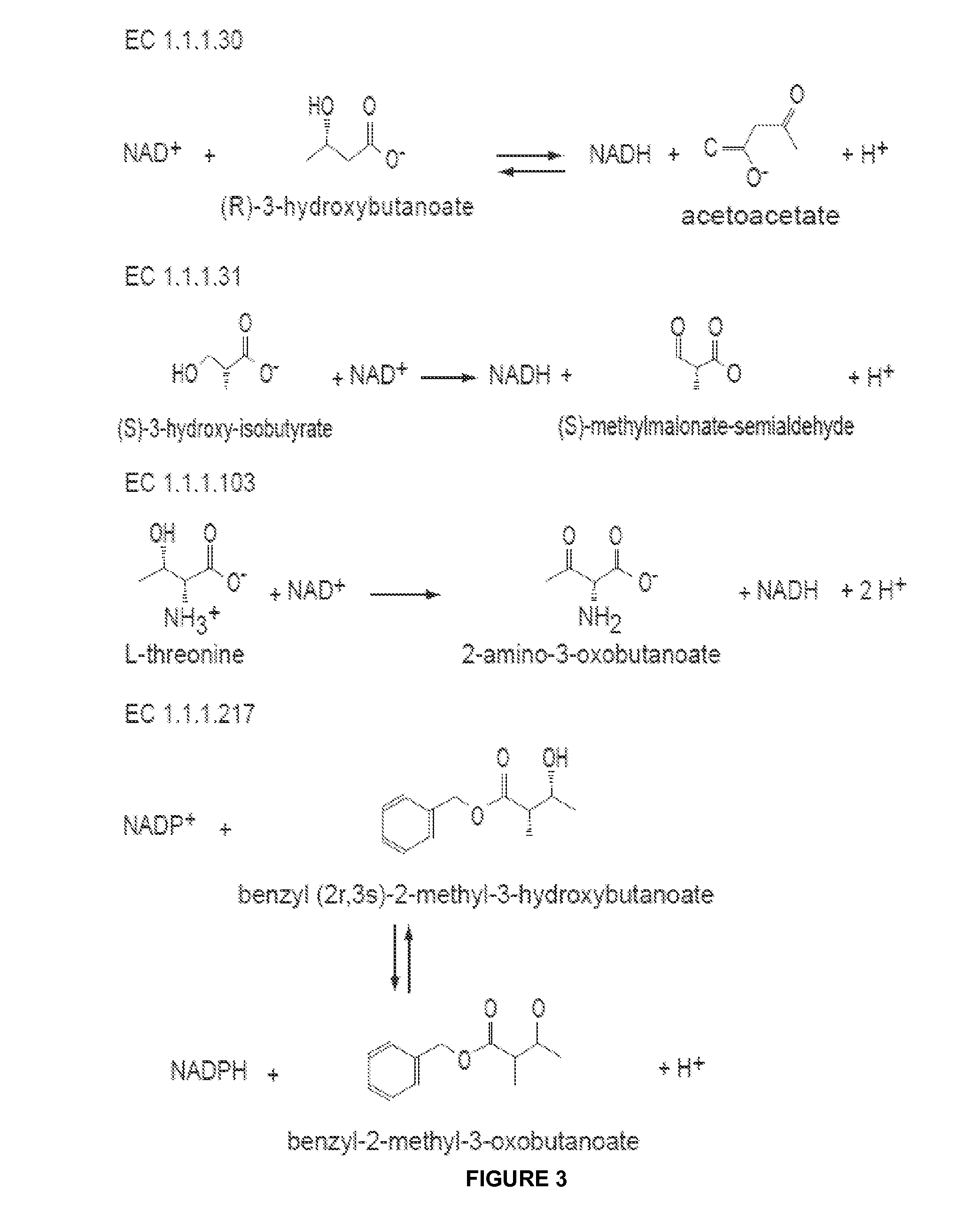
The present invention relates to recombinant microorganisms comprising biosynthetic pathways and methods of using said recombinant microorganisms to produce various beneficial metabolites. In various aspects of the invention, the recombinant microorganisms may further comprise one or more modifications resulting in the reduction or elimination of 3 keto-acid (e.g., acetolactate and 2-aceto-2-hydroxybutyrate) and / or aldehyde-derived by-products. In various embodiments described herein, the recombinant microorganisms may be microorganisms of the Saccharomyces clade, Crabtree-negative yeast microorganisms, Crabtree-positive yeast microorganisms, post-WGD (whole genome duplication) yeast microorganisms, pre-WGD (whole genome duplication) yeast microorganisms, and non-fermenting yeast microorganisms.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Application of alcohol dehydrogenase in catalytic generation of ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate
InactiveCN103160547AHigh yieldHigh optical activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydroxybutyric acidPtru catalyst
The invention discloses application of alcohol dehydrogenase with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2 in preparing ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate from ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate by asymmetric reduction. By using alcohol dehydrogenase with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2 as a catalyst, ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate as a substrate and NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) as a cofactor, asymmetric reduction is carried out to prepare the ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate. The invention applies the alcohol dehydrogenase with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2 in preparing ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate from ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate by asymmetric reduction for the first time, and has favorable effect. The enzyme activity is up to 5.6 U / mg, the yield of the substrate is up to 94%, and the enantiomeric excess value of the product is 100%. The yield is high, and the production cost is greatly lowered.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Alcohol dehydrogenase, gene and recombinase thereof, and application of alcohol dehydrogenase in synthesis of chiral diaryl secondary alcohol
InactiveCN105936909AImprove expression levelIncrease enzyme activityOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringDiaryl ketoneGenus Kluyveromyces
The invention discloses an alcohol dehydrogenase, a gene thereof, a recombinant expression vector and a recombinant expression transformant respectively containing the gene, a recombinase of the alcohol dehydrogenase, and an application of the alcohol dehydrogenase in asymmetric reduction synthesis of chiral diaryl secondary alcohol as a catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The alcohol dehydrogenase is from Kluyveromyces sp. CCTCCM2011385, has a carbonyl group reduction function, and also has a hydroxy group oxidation function. Extra addition of glucose dehydrogenase and other enzymes used for cofactor circulation is not needed when the alcohol dehydrogenase is used in the reduction of diaryl ketone into the chiral diaryl secondary alcohol as a biocatalyst, and the alcohol dehydrogenase has the advantages of high catalysis efficiency, mild reaction conditions, easy product recovery and low cost, so the alcohol dehydrogenase has very good application and exploitation prospect in the production of antihistamine medicines.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Isolated alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes and uses thereof
Bacterial polynucleotides and polypeptides are provided in which the polypeptides have a dehydrogenase activity, such as an alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) activity, an uronate, a 4-deoxy-L-erythro-5-hexoseulose uronate (DEHU) ((4S,5S)-4,5 dihydroxy-2,6-dioxohexanoate) hydrogenase activity, a 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-gluconate dehydrogenase activity, a D-mannuronate hydrogenase activity, and / or a D-mannnonate dehydrogenase activity. Methods, enzymes, recombinant microorganism, and microbial systems are also provided for converting polysaccharides, such as those derived from biomass, into suitable monosaccharides or oligosaccharides, as well as for converting suitable monosaccharides or oligosaccharides into commodity chemicals, such as biofuels. Commodity chemicals produced by the methods described herein are also provided.
Owner:BIO ARCHITECTURE LAB
Method for producing 1,3-propylene glycol through fermentation via recombinant microbes
PendingCN106906248AAddressing Biosecurity IssuesLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationPhosphoric acidBacterial strain
The invention provides a method for producing 1,3-propylene glycol through fermentation via recombinant microbes. According to the invention, an endogenous dihydroxypropanone phosphatein phosphatase gene hdpA is over-expressed in Corynebacterium glutamicum to reinforce removal of phosphoric acid from dihydroxypropanone phosphatein so as to produce dihydroxypropanone; exogenous glycerol dehydrogenase is introduced to convert dihydroxypropanone into glycerin; and glycerin finally produces 1,3-propylene glycol under the action of exogenous glycerol dehydratase and an activator thereof and alcohol dehydrogenase. Corynebacterium glutamicum can use different cheap raw materials for fermentation, and cheap corn steep liquor can be used as a nutritional component to replace expensive yeast powder, so cost for raw materials is further reduced, and the problems in biosecurity and tolerance of the bacterial strain to a substrate and a product are overcome; and thalli obtained in the process of fermentation can be used as a product for a feed additive. The method provided by the invention produces few by-products and can further simplify the separating process of 1,3-propylene glycol.
Owner:GUANGDONG TSINGDA SMART BIOTECH CO LTD
Recombinant microorganisms and uses therefor
The invention provides, inter alia, methods for the production of acetone, isopropanol and / or precursors of acetone and / or isopropanol by microbial fermentation of substrates comprising CO, genetically modified microorganisms of use in such methods, nucleic acids suitable for preparation of genetically modified microorganisms, a novel alcohol dehydrogenase and nucleic acids encoding same.
Owner:LANZATECH NZ INC
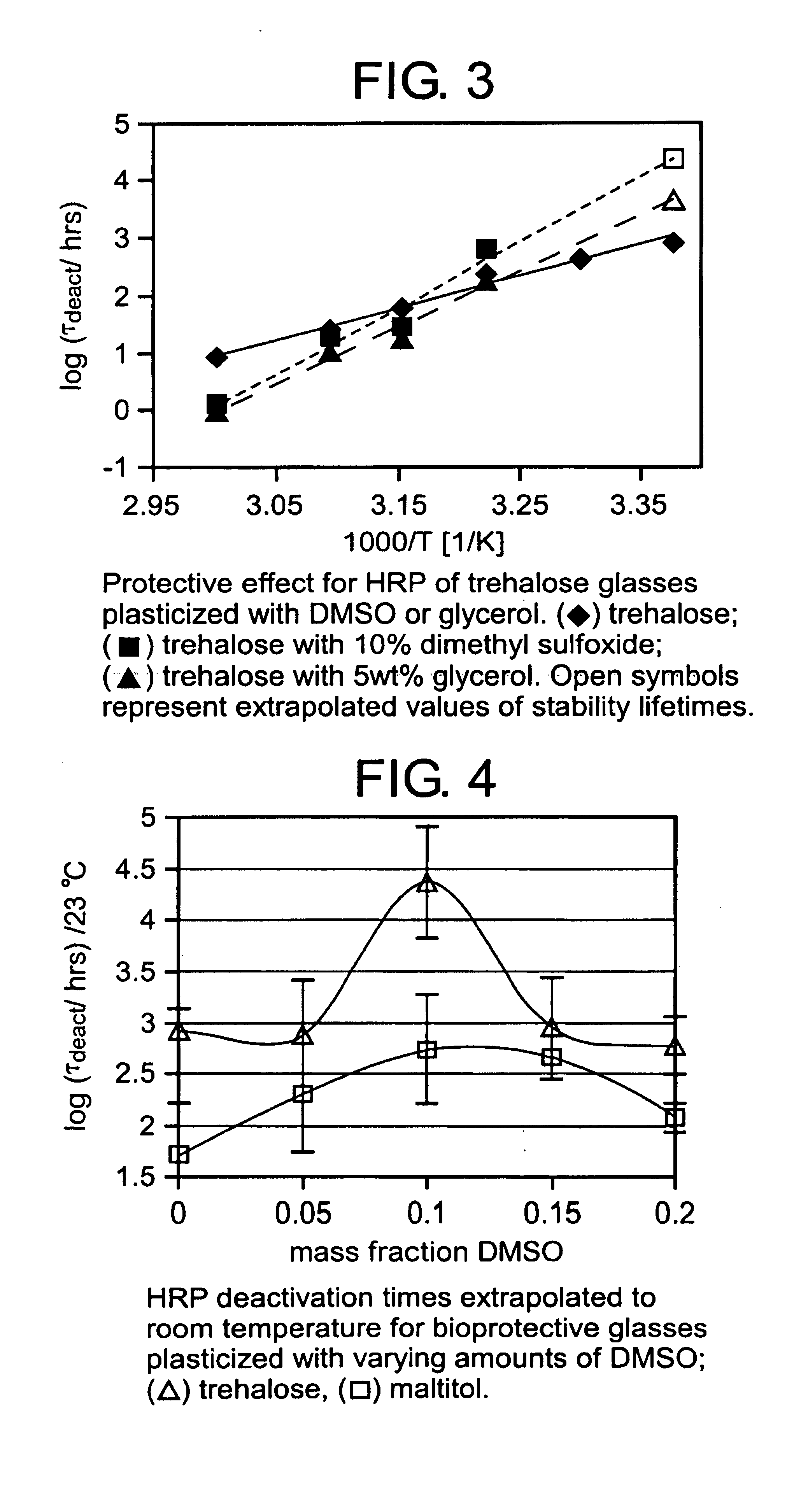
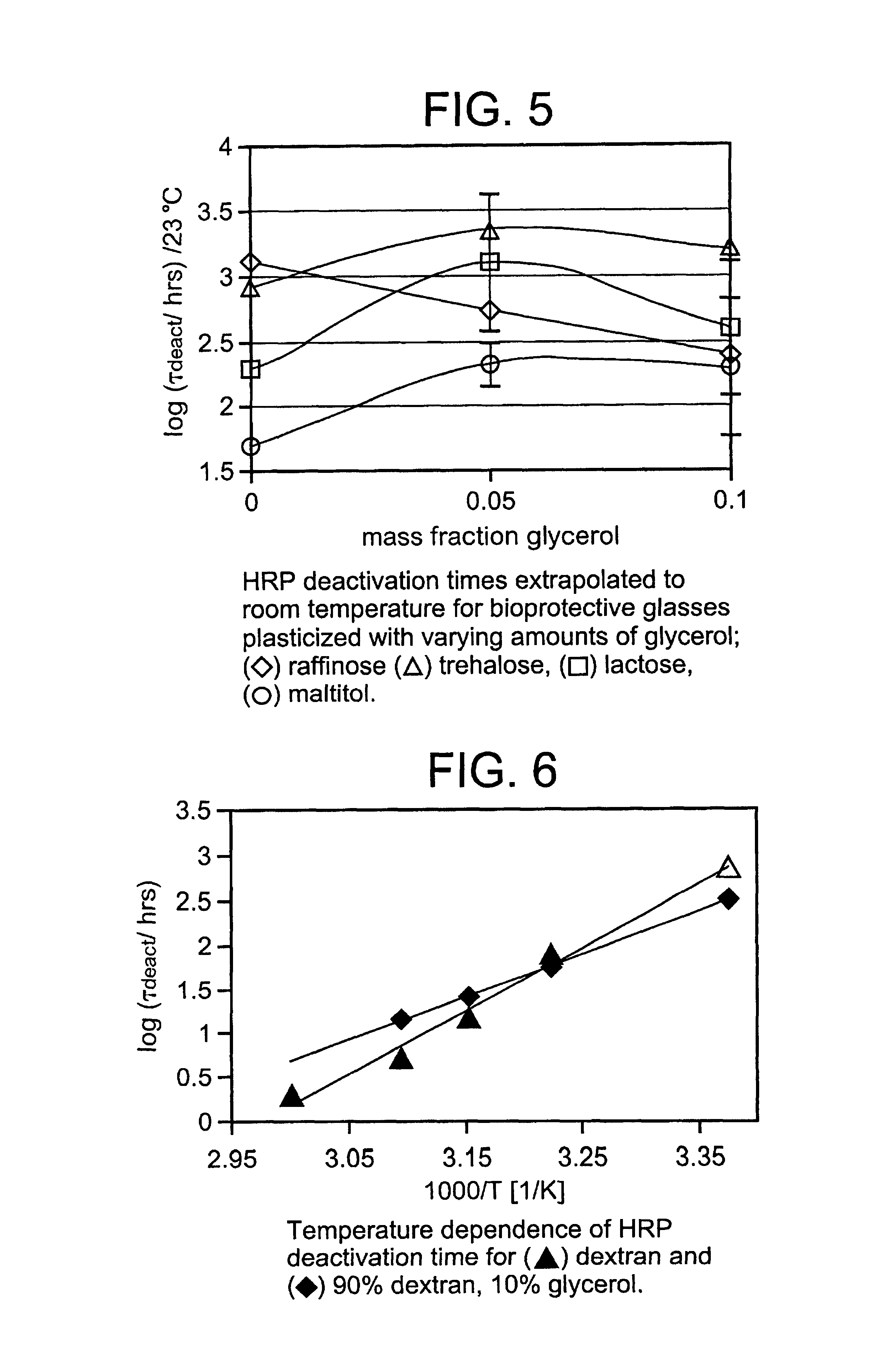
Plasticized hydrophilic glasses for improved stabilization of biological agents
InactiveUS7101693B2Slow dynamicReducing lengthscaleBiocidePowder deliveryBiological materialsGlass transition
The stabilization of biomaterials such as proteins in a nominally dry, hydrophilic glassy matrix is vastly improved by the addition of an appropriate amount of a small-molecule pasticizer such as a glycol or DMSO to the formulation, while maintaining a glass transition temperature (Tg) that is above the storage temperature. By plasticizing the glasses, their ability to preserve proteins is improved by as much as 100 times over the unplasticized glass at room temperature. The plasticizer confers the greatest beneficial effect when it is dynamically coupled into the bulk glass, and this coupling occurs over a fairly narrow range of plasticizer concentration. Methods are described in which a small-molecule plasticizer can be incorporated into a glass made of much larger molecules (e.g. a polymeric glass), with desired dynamic coupling, via a molecule that is believed to act as a dynamic linker. Protein preservation data was obtained from two enzymes, horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH).
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
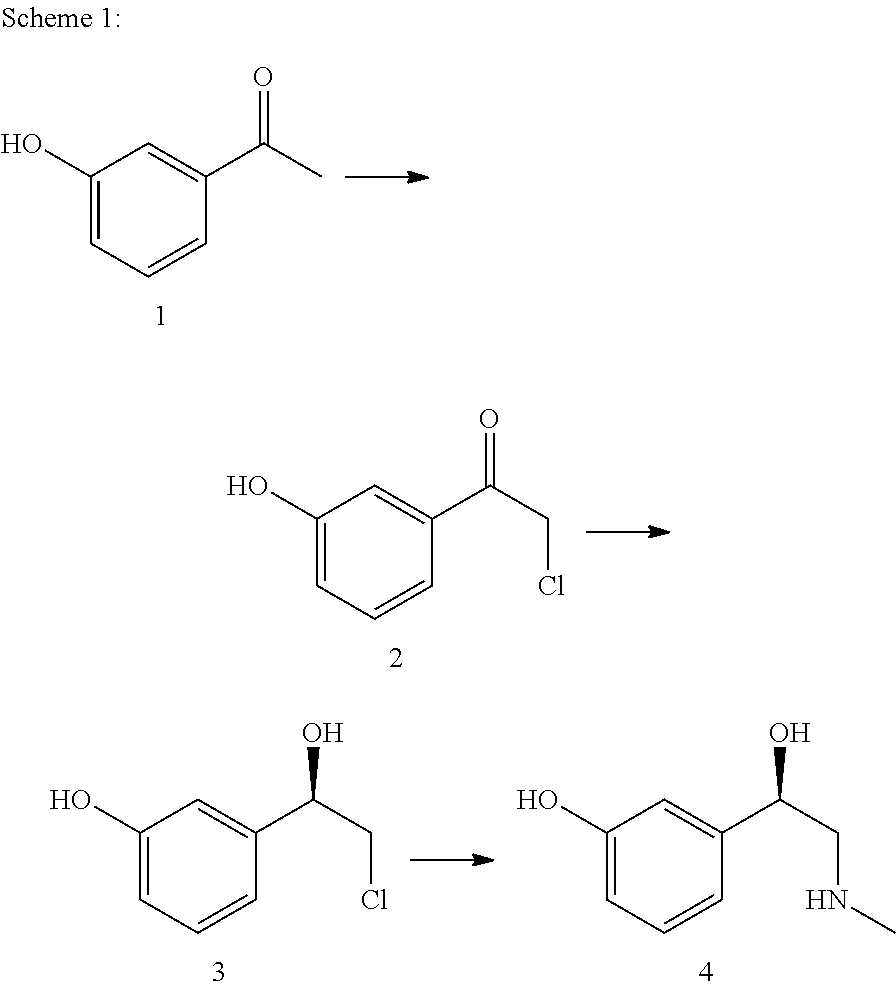
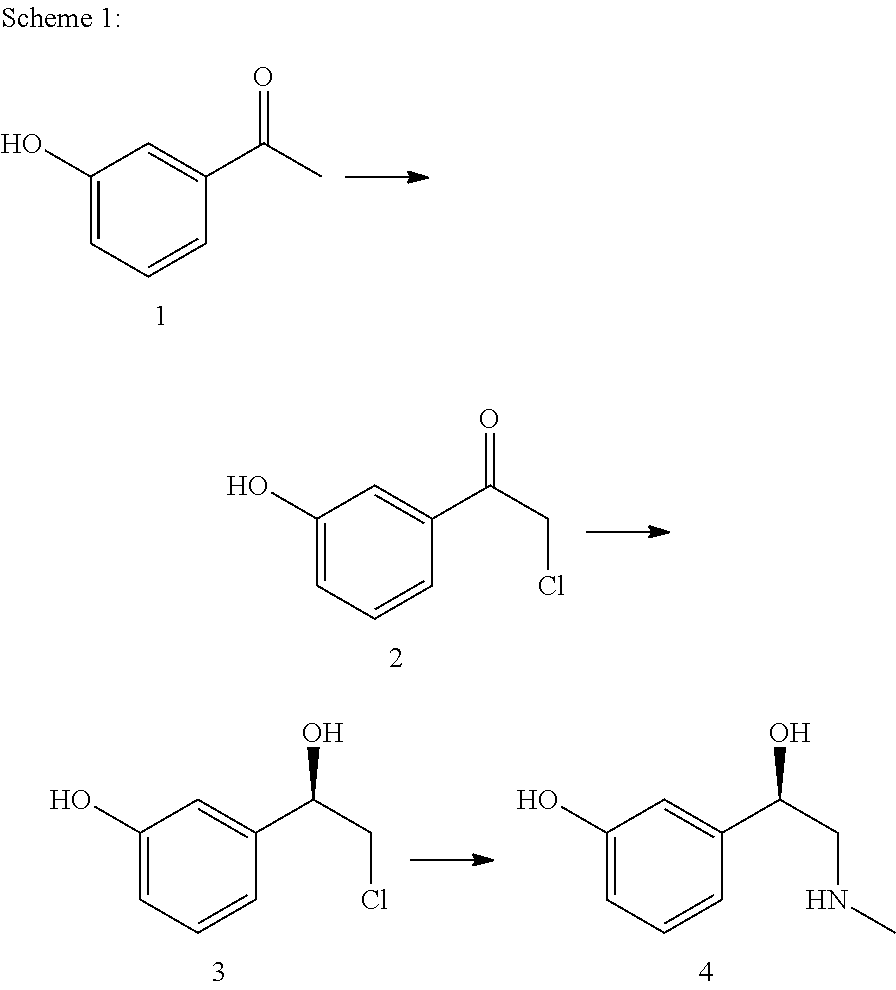
Method for producing l-phenylephrine using an alcohol dehydrogenase of aromatoleum aromaticum ebn1 (azoarcus sp. ebn1)
ActiveUS20110171700A1High stereoselectivityMoreOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationAlcoholAzoarcus sp.
The present invention relates to a multi-stage process for producing substituted, optically active alcohols, comprising an enzyme-catalyzed synthesis step, in particular a synthesis step which is catalyzed by an alcohol dehydrogenase. The inventive method is particularly suitable for producing phenylephrine, i.e. 3-[(1R)-1-hydroxy-2-methylamino-ethyl]-phenol.
Owner:BASF AG
Engineering bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN107586752APoor substrate specificityHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
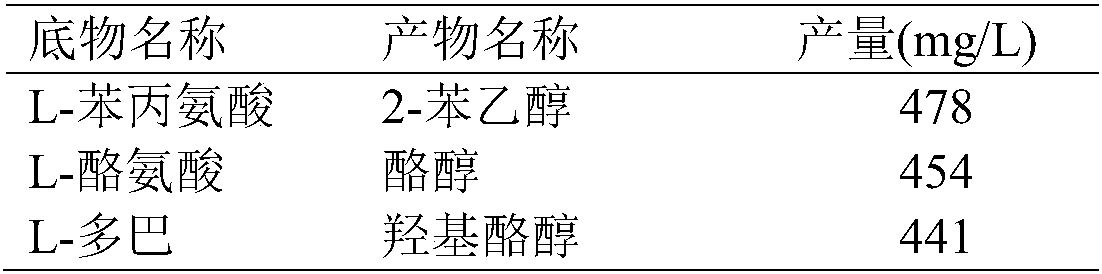
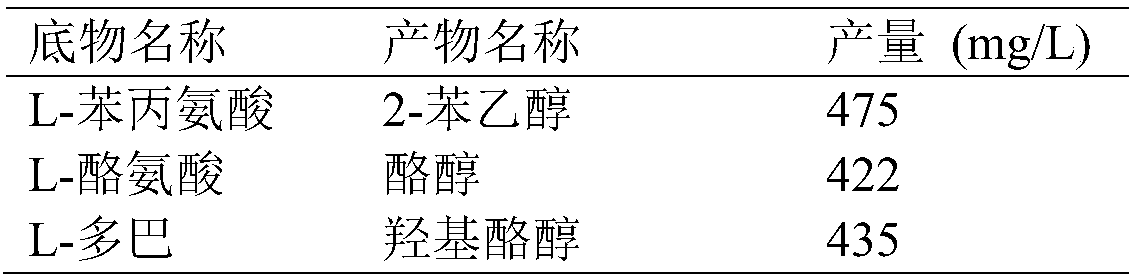
The invention discloses escherichia coli gene engineering bacteria for four enzyme co-expression. The engineering bacteria is characterized by introducing an L-amino acid oxidase gene, an alpha-ketonic acid decarboxylase gene, an alcohol dehydrogenase gene, and an enzyme gene capable of reducing NAD(P) to NAD(P)H. The invention further discloses a construction method and application of recombinantescherichia coli. The engineering bacteria is applied to biological synthesis of phenylethyl alcohol compounds, has the characteristics of simple operation, low cost, high product synthetic efficiency, and high optical purity, and has bright industrial prospects.
Owner:HONGTAOSIM RES INST OF ANALYCAL SCI & TECH LTD CO
Alcohol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof to synthesis of diaryl chiral alcohol
InactiveCN108384765AHigh stereoselectivityIncrease vitalityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFormate dehydrogenase HGlycol synthesis
The invention discloses an alcohol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof to synthesis of diaryl chiral alcohol and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The alcohol dehydrogenase mutant disclosed by the invention has good catalytic activity and stereoselectivity, and a series of chiral diaryl alcohol with R- and S- configurations can be prepared through efficient catalysis. According to the alcohol dehydrogenase mutant, alcohol dehydrogenase is coupled with glucose dehydrogenase or formate dehydrogenase, and can be used for synthesizing various antihistamine drugs, i.e., a chiral diaryl alcohol intermediate. Compared with an existing report, a method for preparing the diaryl chiral alcohol through asymmetric catalysis of the alcohol dehydrogenase has the advantages of simplicity in operation, high substrate concentration, complete reaction and high product purity and has a very good industrial application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Protein and amorphous metal organic framework compound and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111909924AHigh embedding rateImprove stabilityOxidoreductasesCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesKetoneOxidative enzyme
The invention discloses a protein and amorphous metal organic framework compound and a preparation method thereof. The organic framework compound has a 2 nm-50 nm mesoporous structure. The preparationmethod comprises the following step of enabling a protein, zinc ions and an organic ligand to react in a solvent, wherein the organic ligand is a compound containing an imidazole group; the protein is one or a combination of several kinds of cytochrome C, cytochrome P450, horse radish peroxidase, alcohol dehydrogenase, lipase, acetylcholin esterase, laccase, a green fluorescent protein, glucose dehydrogenase, glucose oxidase, trypsin, bacillus subtilis protease, carbonic anhydrase, aldehyde ketone reductase, amylase, saccharase, superoxide dismutase, urease and catalase. The preparation method of the protein and amorphous metal organic framework compound provided by the invention is simple to operate and mild in condition, the obtained product is high in protein embedding rate and good inprotein stability, and the biologic al activity of the protein is reserved to a greater extent.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Nucleic Acid Molecules Conferring Enhanced Ethanol Tolerance And Microorganisms Having Enhanced Tolerance To Ethanol
The present invention provides isolated nucleic acid molecules which encode a mutant acetaldehyde-CoA / alcohol dehydrogenase or mutant alcohol dehydrogenase and confer enhanced tolerance to ethanol. The invention also provides related expression vectors, genetically engineered microorganisms having enhanced tolerance to ethanol, as well as methods of making and using such genetically modified microorganisms for production of biofuels based on fermentation of biomass materials.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC +1
Gene combination, primer and probe for detecting alcoholic liver disease susceptibility and application
InactiveCN101962669AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAlcoholic liver diseaseLiver disease
The invention discloses a gene combination, a primer and a probe for detecting alcoholic liver disease susceptibility and application. The gene combination comprises a combination of three genes closely related with an alcoholic liver disease, namely an ADH2 gene of alcohol dehydrogenase, an ALDH2 gene of acetaldehyde dehydrogenase and a CYP2E1 gene of cytochrome P4502. The gene combination comprises the following SNP sites: rs1229984 site of the ADH2 gene, rs671 site of the ALDH2 gene and rs2031920 site of the CYP2E1 gene. Whether the detected crowds carry 'alcoholic liver disease susceptible genes' are comprehensively detected and analyzed by detecting a group of genes and sites related with the alcoholic liver disease susceptibility, using the specific primer and the probe and combining a mononucleotide extending technique and a micro array chip technique so as to screen the alcoholic liver disease susceptible crowd from the crowds, change unhealthy lifestyles and fulfill the purpose of preventing.
Owner:NANJING WEIYU GENETIC ENG
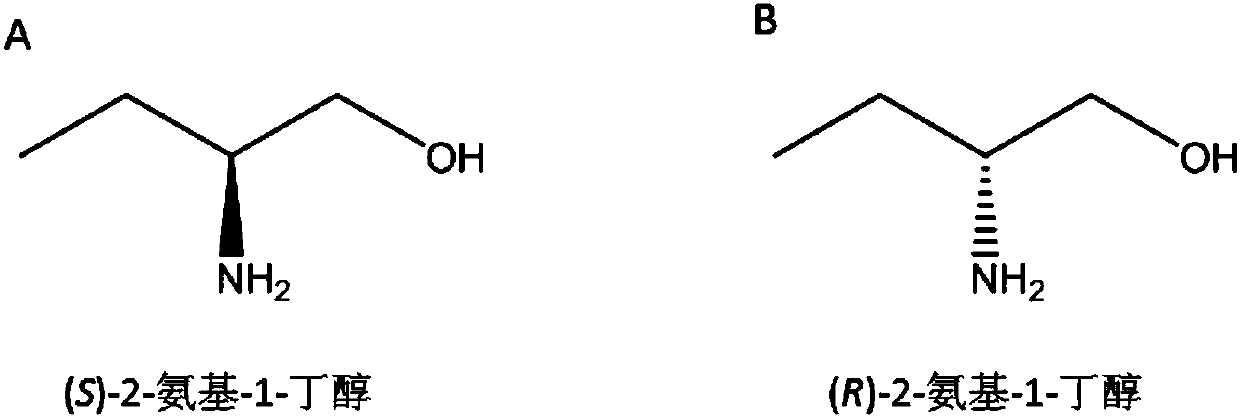
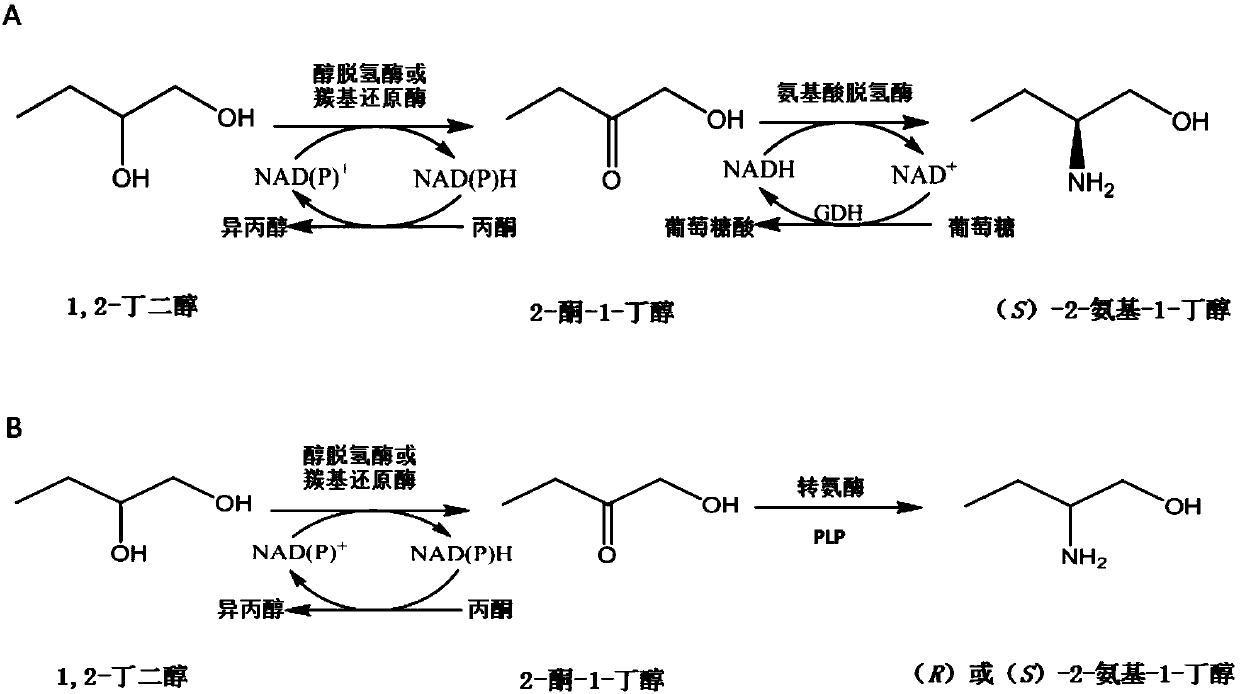
Method for synthesizing chiral 2-amino-1-butanol
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing chiral 2-amino-1-butanol. The method comprises the following steps: 1,2-butanediol is used as a substrate and is catalyzed by enzyme A and coenzyme thereof to generate 2-ketone-1-butanol; the 2-ketone-1-butanol serves as a substrate, and the 2-amino-1-butanol is generated through catalytic reaction of enzyme B and coenzyme thereof. The enzyme A isselected from alcohol dehydrogenase, carbonyl reductase or mutants of the two enzymes; the enzyme B is selected from amino acid dehydrogenases, transaminases or mutants of the two enzymes. The invention provides a brand-new green biosynthesis route. The cheap 1,2-butanediol is used as a raw material, and the chiral 2-amino-1-butanol is synthesized through multi-enzyme co-expression or cascade or step-by-step catalysis, namely (S)-2-amino-1-butanol and (R)-2-amino-1-butanol.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Enzyme combination for producing L-phosphinothricin, and production method of L-phosphinothricin
InactiveCN111139270AReduce manufacturing costTake full advantage of catalytic activityOxidoreductasesFermentationPhosphorous acidPhosphite dehydrogenase
The invention discloses an enzyme combination for producing L-phosphinothricin. The enzyme combination comprises glutamate dehydrogenase and a coenzyme regenerating enzyme, wherein the coenzyme regenerating enzyme is alcohol dehydrogenase, formate dehydrogenase and phosphite dehydrogenase. The invention also discloses a production method of L-phosphinothricin, 4-(methylhydroxyphosphinyl)-2-oxobutyric acid is used as a raw material, NH<4><+>, a coenzyme NADP<+> / NADP, and a coenzyme regeneration substrate are added, and then the enzyme combination is used for catalysis, wherein the glutamate dehydrogenase is used to catalyze a reaction of 4-(methylhydroxyphosphinyl)-2-oxobutyric acid to obtain L-phosphinothricin, and the coenzyme regenerating enzyme is used to reduce NADP<+> to NADP. According to the enzyme combination and the production method of L-phosphinothricin provided by the invention, by-products produced are very easy to remove, a post-treatment process of the product is simplified, the total yield of the product is greater than 95%, and the production cost of L-phosphinothricin is reduced, so that the method is a green, environment-friendly, and low-carbon process route, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production applications.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
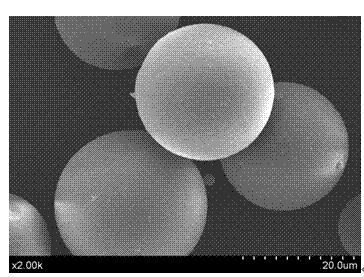
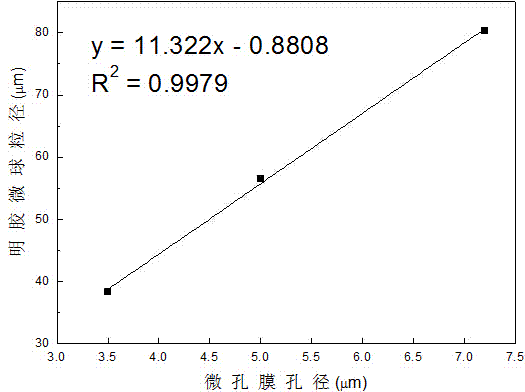
Preparing method for gelatin microsphere of fixed alcohol dehydrogenase by micro-porous membrane permeation and emulsification
InactiveCN104762289AEasy to fixGood acid and alkali toleranceOn/in organic carrierGelatin microspheresMembrane permeabilization
The invention relates to a preparing method for a gelatin microsphere of fixed alcohol dehydrogenase by micro-porous membrane permeation and emulsification. The method comprises the following steps that solid gelatin and alcohol dehydrogenase are dissolved in deionized water, and a gelatin / alcohol dehydrogenase solution called as a water phase is prepared; oil soluble emulsifier span-80 is added into liquid paraffin, and liquid paraffin oil called as an oil phase is prepared; a micro-porous membrane is immersed into the liquid paraffin oil, according to the volume ratio of the gelatin / alcohol dehydrogenase solution and the liquid paraffin oil, the gelatin / alcohol dehydrogenase solution is pressed to penetrate through the micro-porous membrane and enter into the liquid paraffin oil, and W-shaped or O-shaped emulsion is formed by the emulsification; glutaraldehyde is added into the W-shaped or O-shaped emulsion, and after cross linking, solidifying, washing and drying are carried out, the gelatin microsphere of the fixed alcohol dehydrogenase is obtained. The preparing method for the gelatin microsphere of the fixed alcohol dehydrogenase by the micro-porous membrane permeation and emulsification has the advantages that the preparing condition is warm, the preparing technology is simple and easy to carry out, the granularity of the prepared microsphere is even, the size is controllable, the storing stability is good, the leakage rate of the alcohol dehydrogenase in the using process is low, and the anti-acid-base environment capacity is strong.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
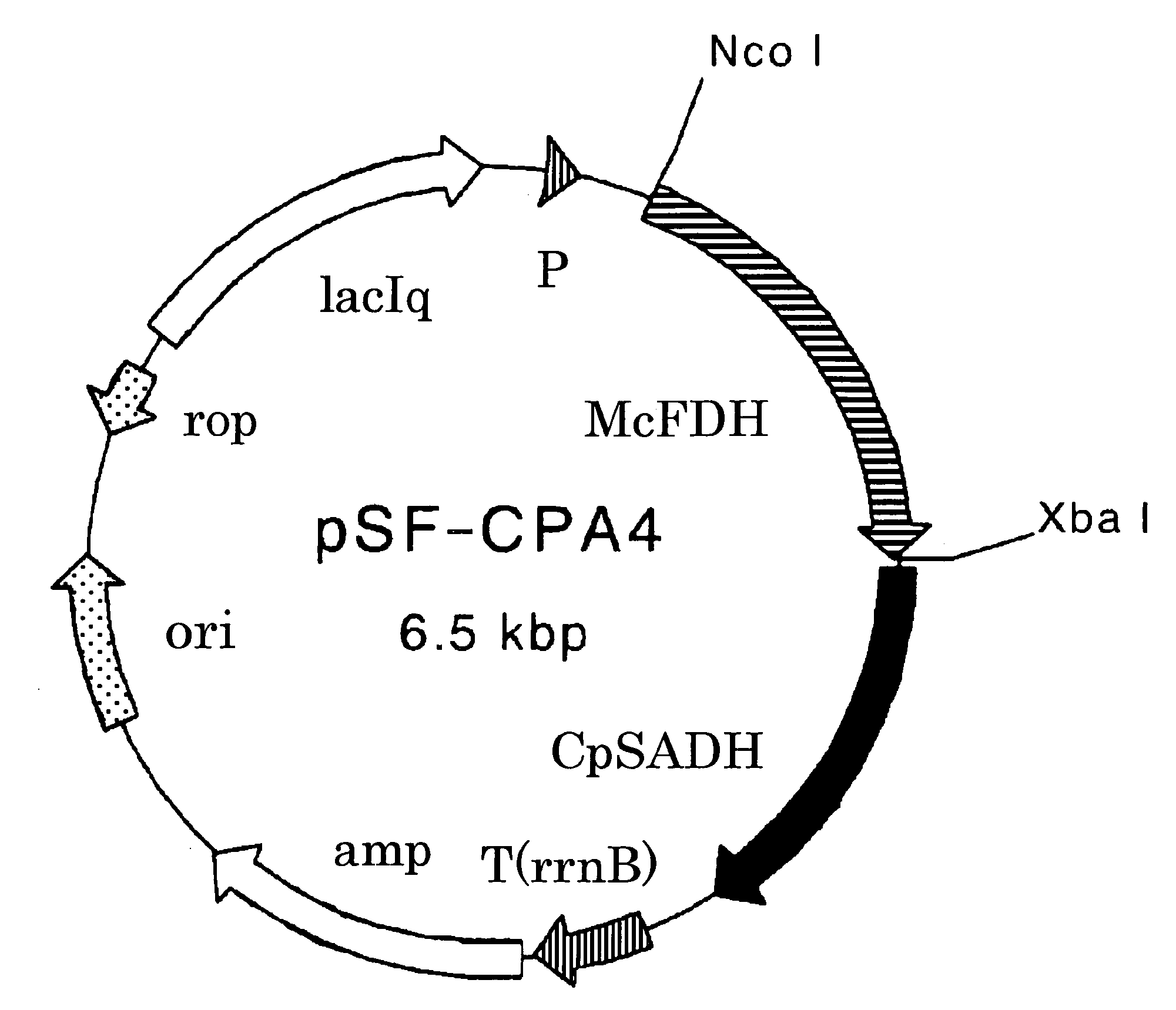
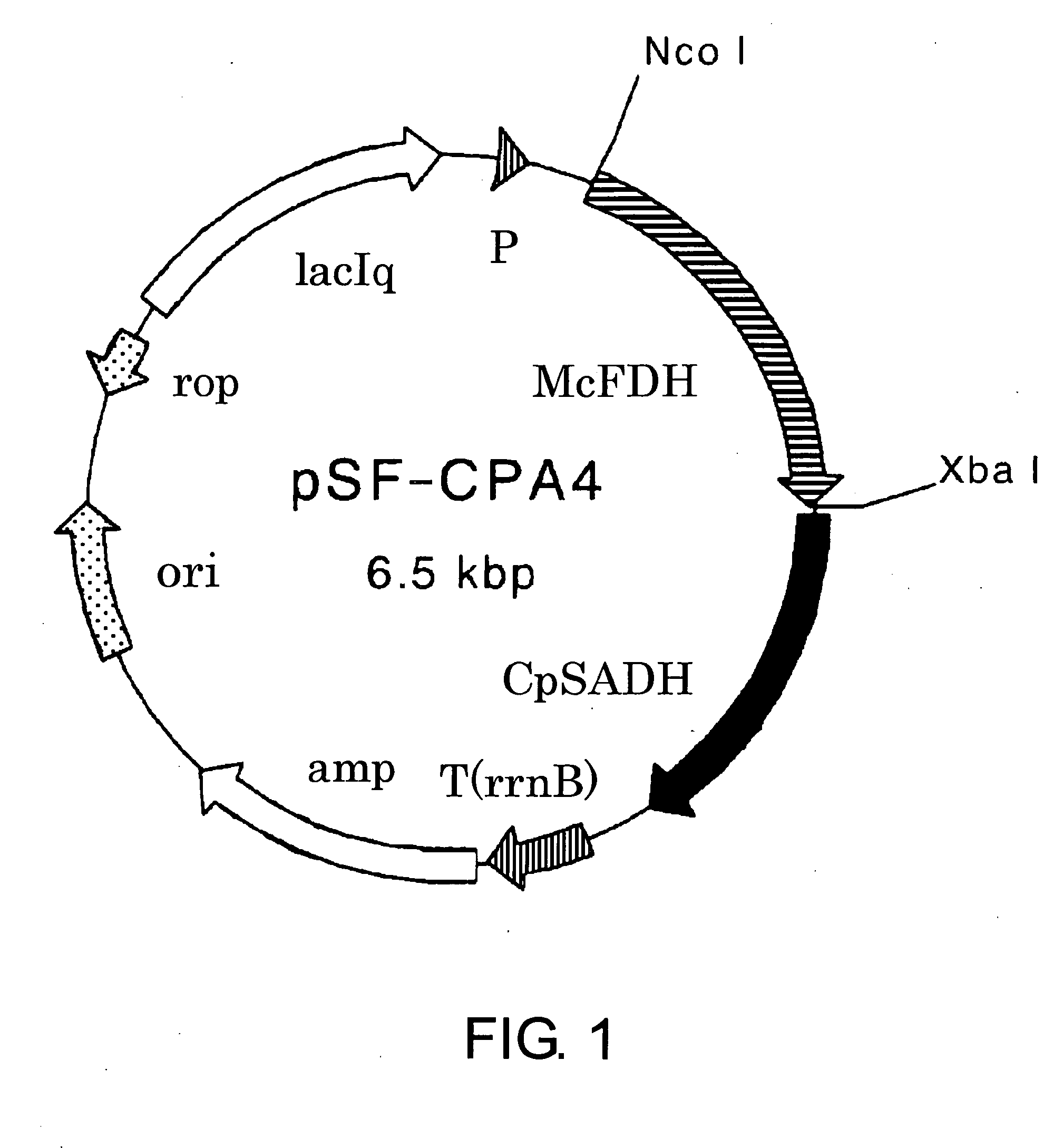
Process for Production of Optically Active Alcohol
The present invention provides methods for producing (S)-1,1,1-trifluoro-2-propanol, which include the step of reacting an enzyme of any one of alcohol dehydrogenase CpSADH, alcohol dehydrogenase ReSADH, carbonyl reductase ScoPAR, (2S,3S)-butanediol dehydrogenase ZraSBDH, carbonyl reductase ScGCY1, tropinone reductase HnTR1, tropinone reductase DsTR1, or alcohol dehydrogenase BstADHT, a microorganism or a transformant strain that functionally expresses the enzyme, or a processed material thereof, with 1,1,1-trifluoroacetone. The present invention also provides methods for producing (R)-1,1,1-trifluoro-2-propanol, which include the step of reacting alcohol dehydrogenase PfODH, a microorganism or a transformant strain that functionally expresses the enzyme, or a processed material thereof, with 1,1,1-trifluoroacetone.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Method for synthesizing chiral bisaryl alcohol compound
ActiveCN109837317AReduce usageHigh yieldOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringAlcoholSporobolomyces species
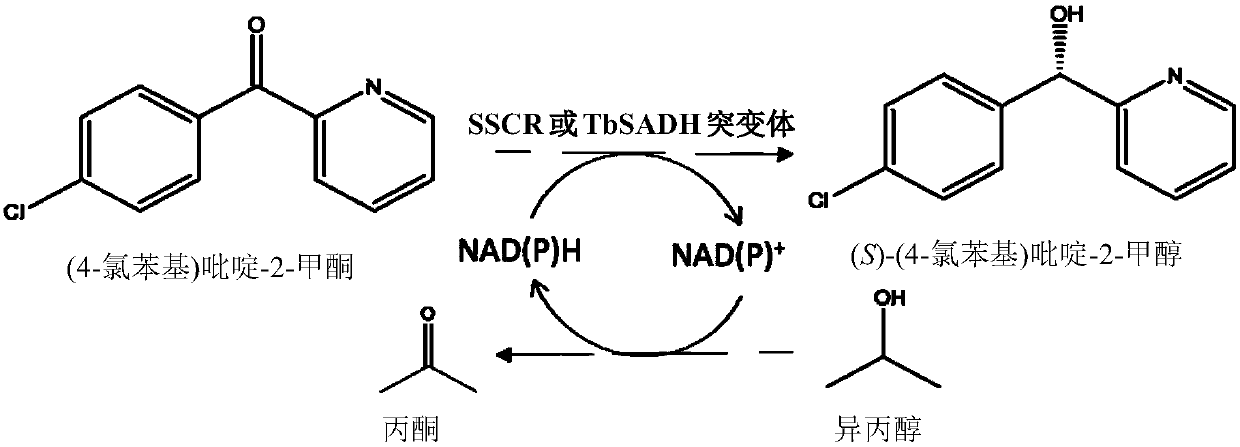
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a chiral bisaryl alcohol compound. The method provided by the present invention specifically uses a mutant of a carbonyl reductase SSCR derived from Sporobolomyces Salmonicolor and a mutant of alcohol dehydrogenase TbSADH derived from Thermoanaerobacter brockii to catalyze asymmetric reduction of (4-chlorophenyl)pyridine-2-ketone to form (S)-(4-chlorophenyl) pyridine-2-methanol. The experiment proves that the method provided by the invention has high yield and high ee value, can reduce the addition amount of coenzyme, and does not need to add enzyme such as glucose alcohol dehydrogenase for cofactor circulation, the reaction condition is mild, and the operation is simple.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for efficiently producing 3-hydroxypropionic acid(3HP) and derivatives thereof based on halophilic bacteria
A 3-hydroxypropionic acid(3HP) degradation way of halophilic bacteria is analyzed for the first time by a transcriptomics method, the inventor finds that the 3-hydroxypropionic acid can degrade genesdddA and dddC, and recombination halophilic bacteria TD delta dddA which cannot degrade 3HP is obtained. Based on this, an alcohol dehydrogenase gene AdhP and an aldehyde dehydrogenase gene AldDTD, which are from the halophilic bacteria endogenous and responsible for production and metabolism of the 3HP are further utilized, and a synthetizing biology means is taken for adjusting and controlling the expression level of the metabolic way. Through screening, the recombination halophilic bacteria high in yield of the 3HP is obtained, and the yield and the productivity are respectively 0.93g / g ofthe 1,3-propylene glycol(PDO) and 2.4g / L / h, which are the highest 3HP yield and productivity reported so far.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
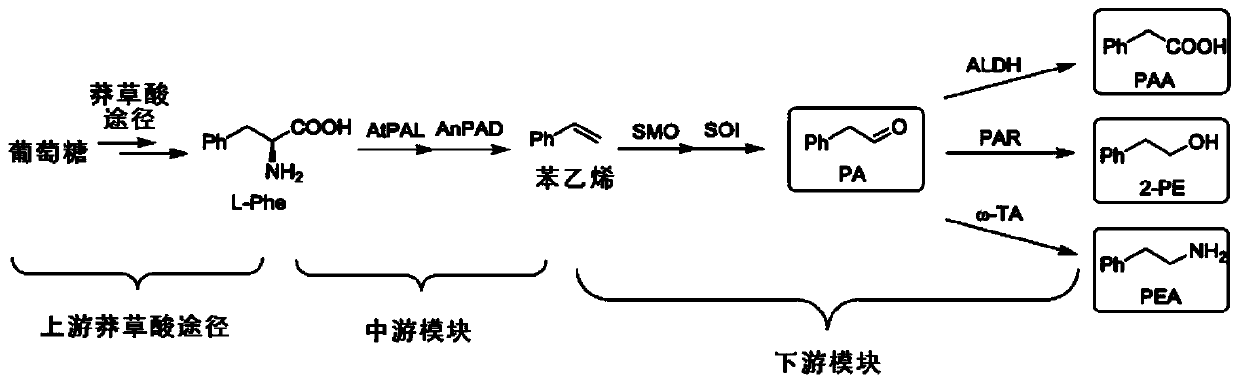
Bioproduction of phenethyl alcohol, aldehyde, acid, amine, and related compounds
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Alcohol dehydrogenase gene of acetic acid bacterium
InactiveUS20070026104A1FunctionHigher acetic acid concentrationFungiBacteriaAcetobacter sp.Acetate fermentation
A novel gene having a function of improving acetic acid fermentation in practical level was cloned from a practical acetic acid bacterium belonging to the genus Gluconacetobacter by a method for obtaining a gene having a growth-promoting function in acetic acid-containing medium from the chromosomal DNA library of the acetic acid bacterium. It was made possible to significantly shorten the growth induction period and significantly improve the acetic acid fermentation rate of transformants obtained by introducing the gene into acetic acid bacteria, when such transformants are cultured in the presence of ethanol.
Owner:MITSUKAN GROUP CORP +1
Alcohol dehydrogenase LC3 and gene and application thereof
The invention provides an alcohol dehydrogenase LC3 and a gene and application thereof. An amino acid sequence of the alcohol dehydrogenase LC3 is shown in SEQ ID NO:2. An alcohol dehydrogenase gene lc 3 is extracted from lactobacillus curieae, a gene engineering strain is established, the heterologous expression of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene lc 3 is realized, and the enzymatic characteristic of the produced alcohol dehydrogenase LC3 is excellent. A co-expression gene engineering strain containing a glucose dehydrogenase gdh gene and the alcohol dehydrogenase gene lc3 is also successfully established, so as to realize the co-expression of glucose dehydrogenase and alcohol dehydrogenase. The alcohol dehydrogenase LC3 has the characteristics that the alcohol dehydrogenase LC3 and the gene engineering strain are applied to the production of chiral alcohol(R)-4-chloride-3hydroxy ethyl butyrate and other chiral alcohol products by a biological enzyme synthesizing method; the substrate concentration is high, the reaction rate is high, and the convenience is realized.
Owner:百开盛(上海)生物科技有限公司
Process for enantioselective enzymatic reduction of keto compounds
InactiveUS20060177913A1High space time throughputLow consumptionBiofuelsFermentationAlcohol dehydrogenaseKetone
Chiral secondary alcohols may be produced enzymatically in high space-time yields while minimizing enzyme use, by reducing a keto compound in an aqueous reaction medium containing water, reducing agent, alcohol dehydrogenase and coenzyme, extracting the secondary alcohol formed by means of a further phase containing a water-immiscible organic solvent, and removing the phase used for extraction and reusing the aqueous reaction medium in step a).
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
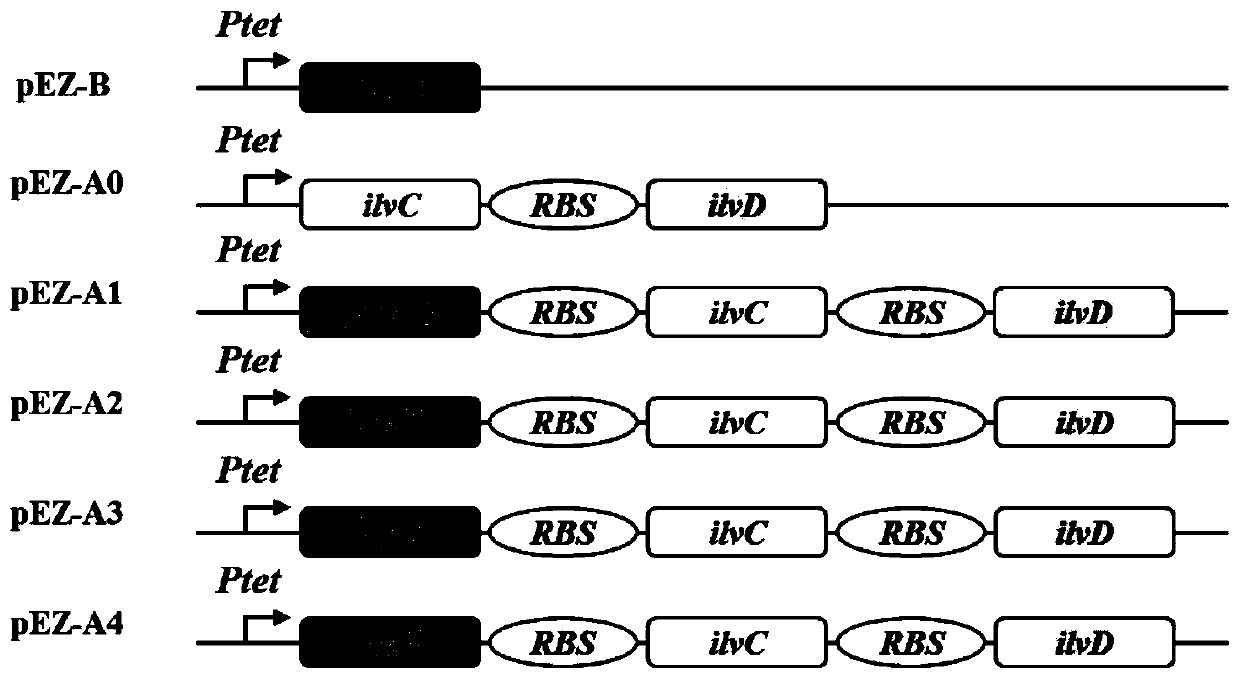
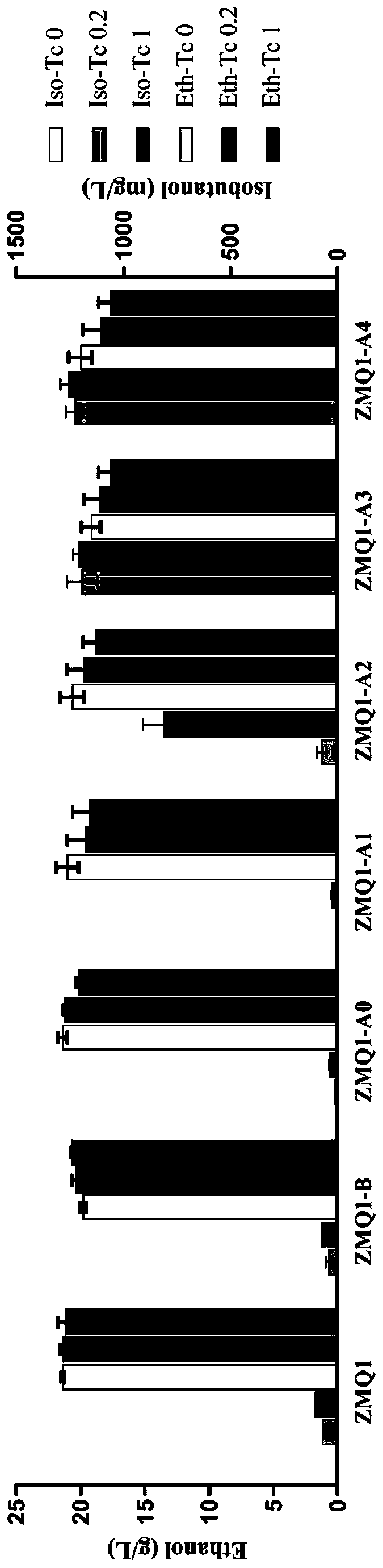
Zymomonas mobilis recombination strain producing isobutanol, construction method and application thereof
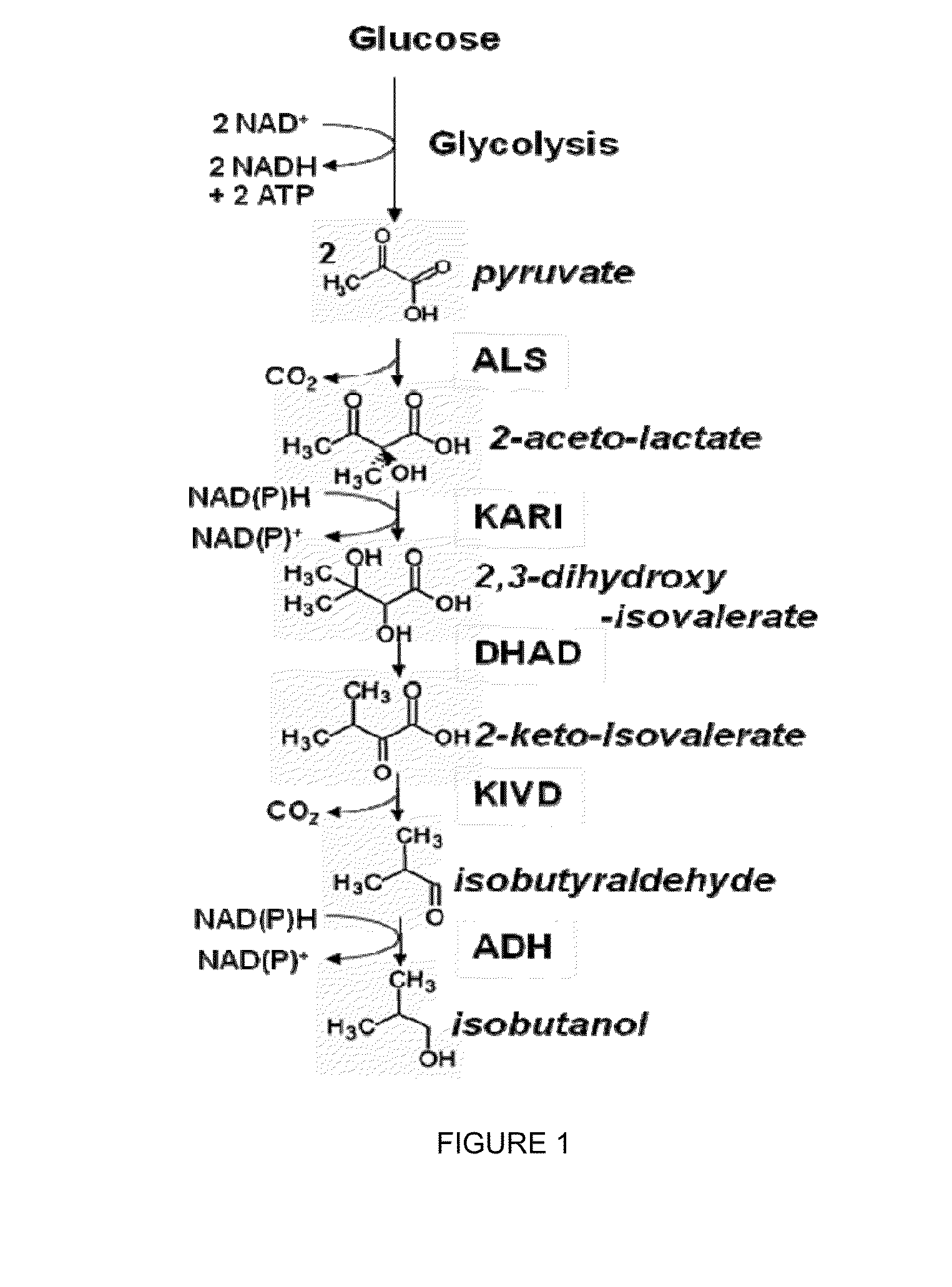
ActiveCN110358720ATo achieve the purpose of increasing productionPowerful Restriction Modification SystemBacteriaBiofuelsIsobutanolAcetolactate synthase
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a zymomonas mobilis recombination strain producing isobutanol, a construction method and application thereof. Zymomonas mobilis ZM4 serves as a model strain, firstly, the strain is transformed by means of genetic engineering, a metabolic intermediate in the synthesis pathway of valine of zymomonas mobilis is utilized for introducing a KDCA gene, 2-ketoisovalerate in the valine pathway is converted into a precursor isobutyraldehyde of isobutanol, and then isobutanol is generated under thehelp of alcohol dehydrogenase; secondly, the purpose of increasing the yield is achieved by overexpressing genes in the L-valine synthesis pathway and screening acetolactate synthase in the metabolicpathway;finally, by adjusting the expression quantity of different genes in the metabolic pathway, the purpose of high yield is finally achieved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Alcohol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN110982799AImprove thermal stabilityImprove conversion efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChlorobenzeneAlcohol dehydrogenase (NADP+)
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering and microbial engineering, discloses an alcohol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof. The alcohol dehydrogenase mutantdisclosed by the invention is high in thermal stability, and high in catalytic efficiency and conversion efficiency (namely space-time yield) of asymmetric reduction of prochiral diarylketone to produce chiral diarylalcohol. Therefore, the alcohol dehydrogenase mutant disclosed by the invention has the extremely broad application prospects in production of chiral diarylalcohol such as (S)-(4-chlorphenyl)-(pyridine-2-yl)-methanol, (R)-(4-chlorphenyl)-(pyridine-2-yl)-methanol and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Specific primer pair and probe for detecting ALDH2 (alcohol dehydrogenase 2) gene chip
InactiveCN103540675AGood signal to noise ratioStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAlcoholALDH2 gene
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, and discloses a specific oligonucleotide probe for detecting an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) site of ALDH2 (alcohol dehydrogenase 2)gene, wherein the probe is capable of hybridizing with the 504th different genetype of the ALDH2 gene. The invention further discloses a specific primer pair for amplifying the ALDH2 gene when detecting the SNP site, and the primer pair can be used for specifically amplifying a target area containing a detection target site in the ALDH2 gene. The specific oligonucleotide probe and the specific primer pair provided by the invention can be used for detecting the ALDH2 genetype and providing information for people to learn individual alcohol metabolism detoxification ability and correctly use nitroglycerin.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAIO TECH
Metabolically enhanced cyanobacterial cell for the production of ethanol
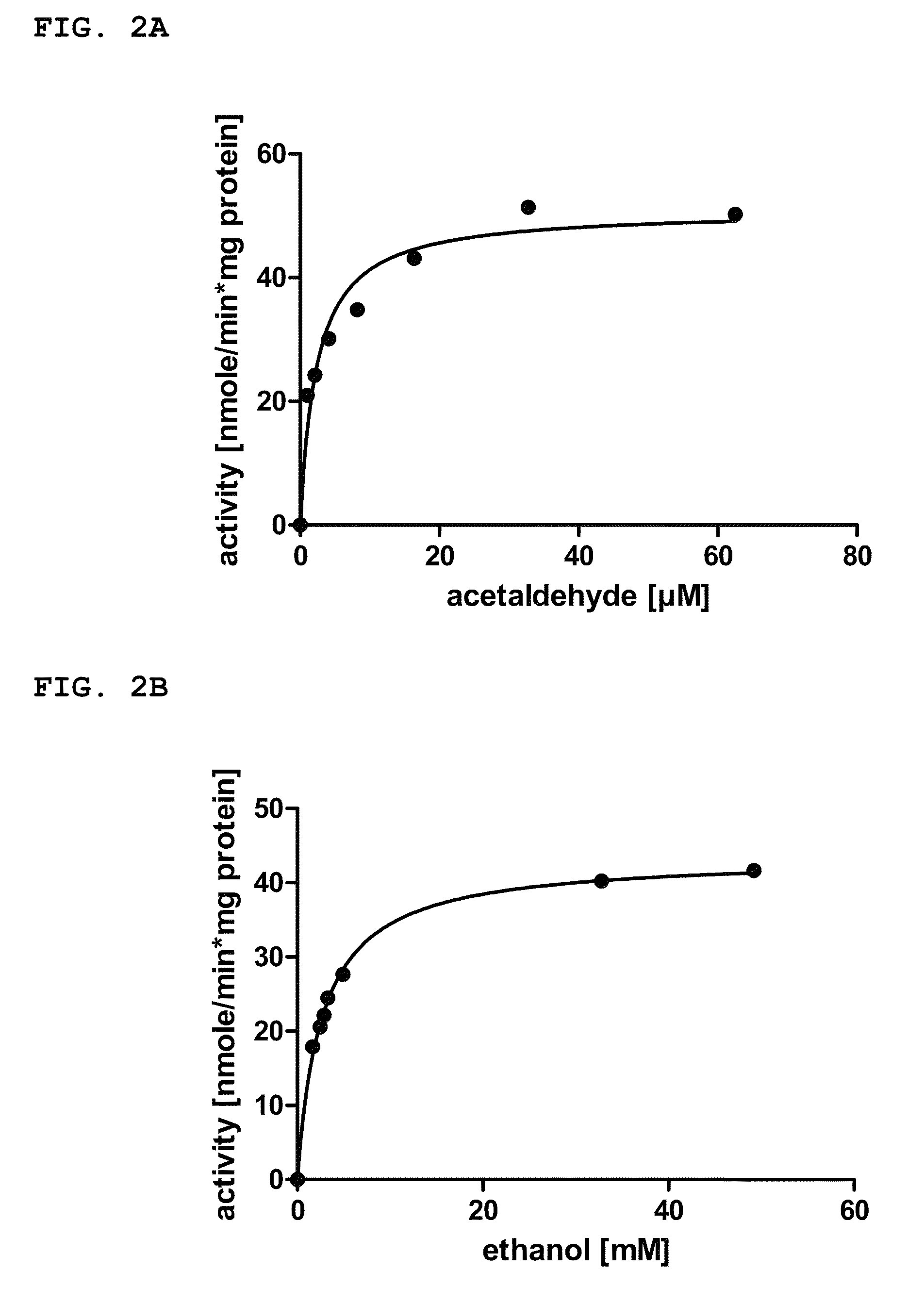
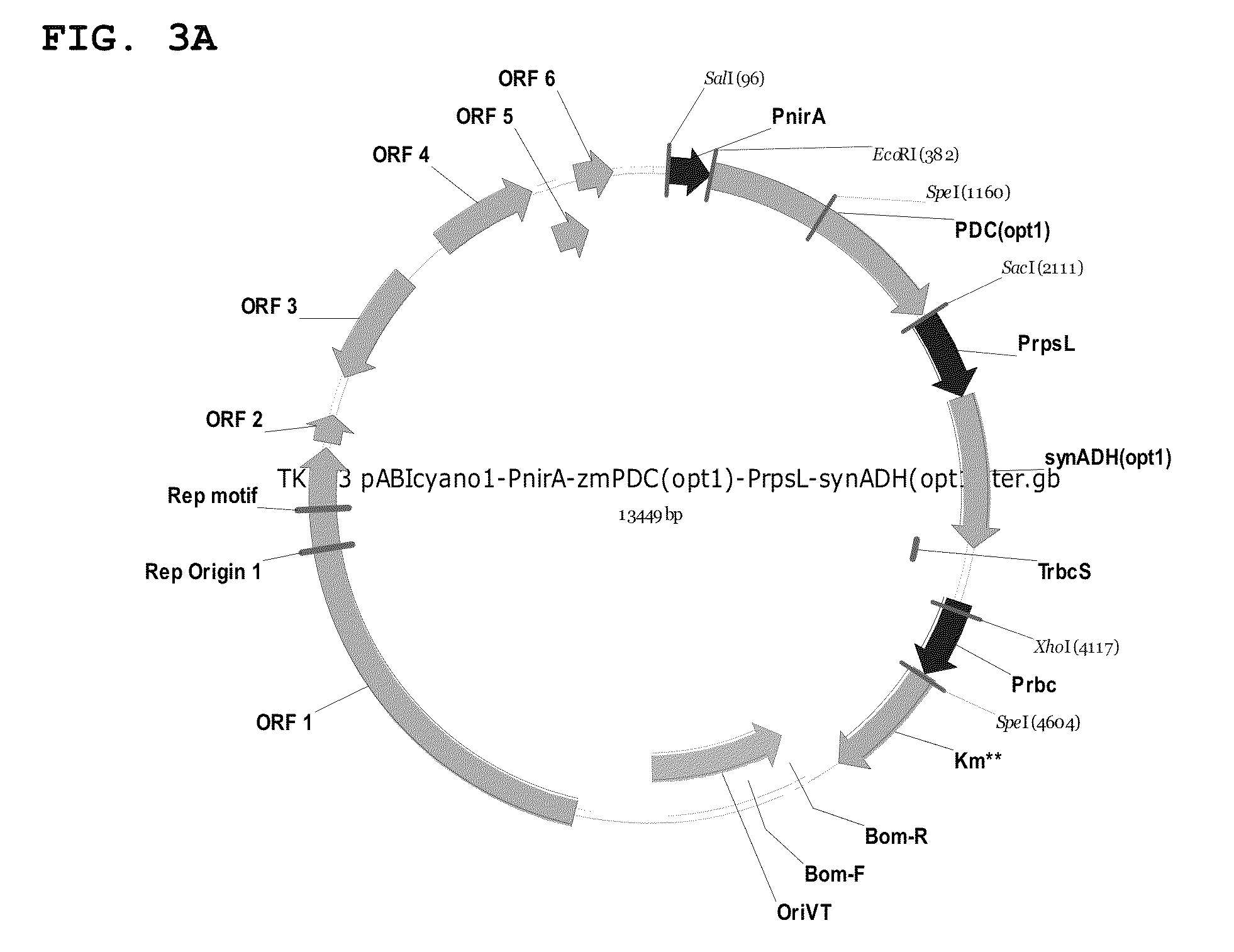
A metabolically enhanced cyanobacterial cell for the production of ethanol is provided. The metabolically enhanced cyanobacterial cell for the production of ethanol comprises at least one recombinant gene encoding a pyruvate decarboxylase enzyme (Pdc) converting pyruvate to acetaldehyde, and at least one recombinant gene encoding a first Zn2+ dependent alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme (Adh) converting acetaldehyde to ethanol. The invention also provides a method for producing the metabolically enhanced cyanobacterium, a method for producing ethanol with the metabolically enhanced cyanobacterium, and a method for screening of alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme expressing cyanobacterial strains for the presence of NADPH-dependent native alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes.
Owner:ALGENOL BIOTECH
Efficient preparation method of intermediate of heterocyclic drugs
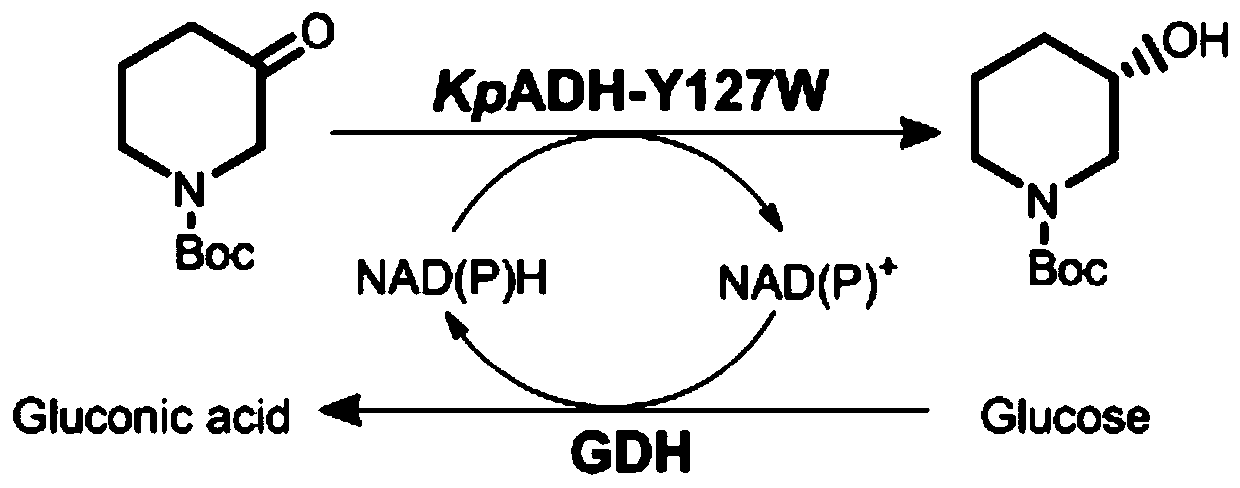
ActiveCN110777125AHigh catalytic efficiencyHigh stereoselectivityOxidoreductasesFermentationTyrosineTryptophan
The invention discloses an efficient preparation method of an intermediate of heterocyclic drugs. According to the efficient preparation method of the intermediate of the heterocyclic drugs, the intermediate of the heterocyclic drugs are produced by catalyzing a heterocyclic substrate by coupling an alcohol dehydrogenase mutant and glucose dehydrogenase; and the alcohol dehydrogenase mutant is prepared by mutating tyrosine at position 127 of a alcohol dehydrogenase female-parent with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 2 into tryptophan. The alcohol dehydrogenase mutant, namely mutant Y127W, utilized in the efficient preparation method of the intermediate of the heterocyclic drugs is capable of reducing product inhibition effects in a single aqueous system without addition of any co-solvent, thereby achieving a conversion rate higher than 99% within 12 hours. Being coupled with the glucose dehydrogenase (BmGDH), the mutant Y127W is capable of realizing gram-level preparation ata scale of 50 ml in a single aqueous system without addition of any exogenous coenzyme or organic co-solvent when substrate concentration is up to 600g x L<-1>; and the catalyst loading capacity is 3.3%. As for a final product, namely (S)-NBHP, the e.e. value is up to 99.4%; the space-time yield is about 1400g x L<-1> x d<-1>; and the product purity is 99.58%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing L-phenylephrine using an alcohol dehydrogenase of Aromatoleum aromaticum EBN1 (Azoarcus sp. EBN1)
ActiveUS8617854B2MoreHigh stereoselectivityOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationAlcoholAzoarcus sp.
The present invention relates to a multi-stage process for producing substituted, optically active alcohols, comprising an enzyme-catalyzed synthesis step, in particular a synthesis step which is catalyzed by an alcohol dehydrogenase. The inventive method is particularly suitable for producing phenylephrine, i.e. 3-[(1R)-1-hydroxy-2-methylamino-ethyl]-phenol.
Owner:BASF AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com