Engineering bacteria and application thereof
A technology for engineering strains and genetically engineered bacteria, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of difficulty in efficiently producing tyrosol, being difficult to provide, increasing conversion costs, etc., and achieving good industrial application prospects, poor substrate specificity, and production process. simple effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Construction of four-gene co-expression system.
[0039] (1) Design primers
[0040] Design primers, the primer sequences are shown in Table 1
[0041] Table 1 Primers used in gene amplification
[0042]
[0043] (2) PCR amplification
[0044] According to the instructions provided by the manufacturer, Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Takara) was used to extract the genomic DNA of the strains in the logarithmic growth phase, and the primers in Table 1 were used for PCR amplification from the corresponding strains. The amplification system is: PrimeSTARHS DNA Polymerase (2.55U / μL) 0.5μL, 10×Prime STAR Buffer 10μL, dNTP Mixture (2.5mM each) 4μL, template DNA 1μL, Up primer (20μM) 1μL, Down primer (20μM) 1μL ,ddH 2 O to make up to 50 μL. The amplification program is: 94°C, 10min; 94°C, 30sec; 55°C, 30sec; 72°C, 2min, a total of 30 cycles; 72°C, 10min. PCR products were sent to BGI for sequencing.
[0045] Later, L-amino acid oxidase genes pmaao and cmaao were cloned...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Induced expression of the genetically engineered bacteria obtained in Example 1.
[0065] Pick the single bacterium colony of genetically engineered bacteria that has been constructed and inoculate in 10mL LB medium (containing 0.1g / L ampicillin), cultivate at 37 ℃ for 12 hours, inoculate in LB medium (200mL of 1000mL shake flask liquid) at a volume ratio of 2%. , containing 0.1g / L ampicillin), continue to cultivate at 37°C for 2.5hr, until the bacterial logarithmic growth phase (OD 600 0.6-0.8), add IPTG to a concentration of 0.4mM, and culture at 20°C and 200rmp for 8h. After induction of expression, the cells were collected by centrifugation at 20° C., 8000 rpm, and 20 minutes. According to the amount of cells required for transformation, the number of shake flasks can be increased to obtain sufficient cells.
Embodiment 3
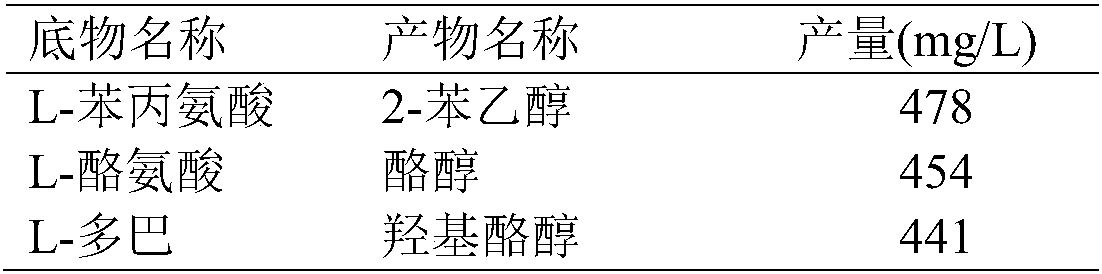
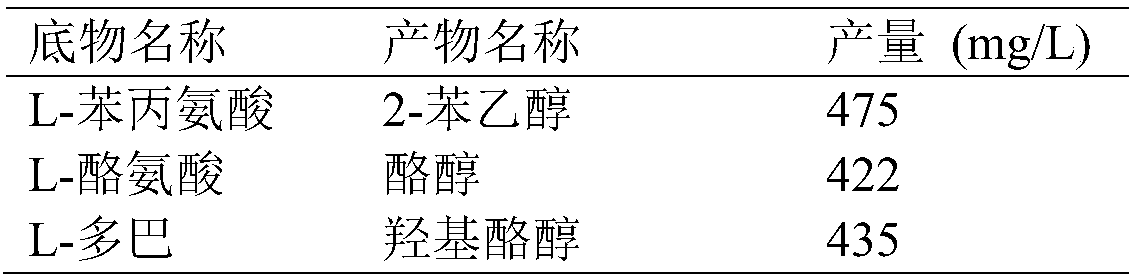
[0067] According to the inductive expression method described in Example 2, after the induction and expression of E.coli BL21 (pRSFDuet-cmaao-pmkdc, pETDuet-bsgdh-ecadh1) obtained in Example 1, the bacterial cells were collected, and different substrates were investigated in a 100ml reaction volume Transformation after mixing with whole cells, the final concentration of substrate is 0.5g / L, the concentration of glucose is 10g / L, the pH is adjusted to 7.0, the weight of fresh whole cells is added to 20g (wet weight), the temperature is 30°C, and the transformation is 24 Hours later, the results were measured, and the reaction conditions of various substrates were shown in the table below.
[0068] Table 2 Conversion of E.coli BL21(pRSFDuet-cmaao-pmkdc, pETDuet-bsgdh-ecadh1) to different substrates
[0069]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com