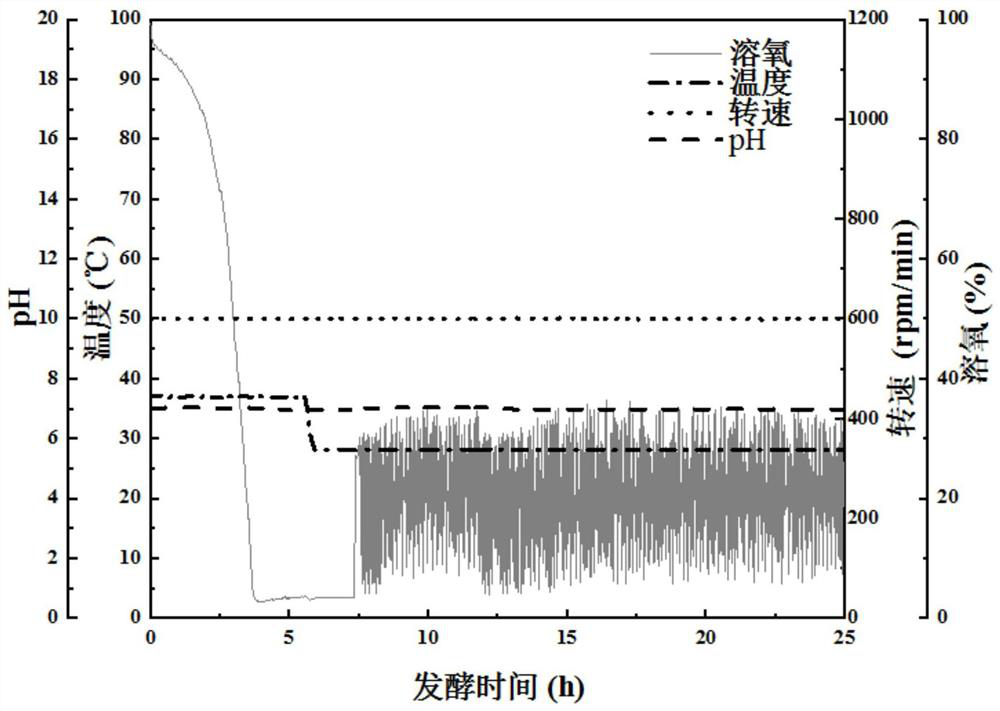
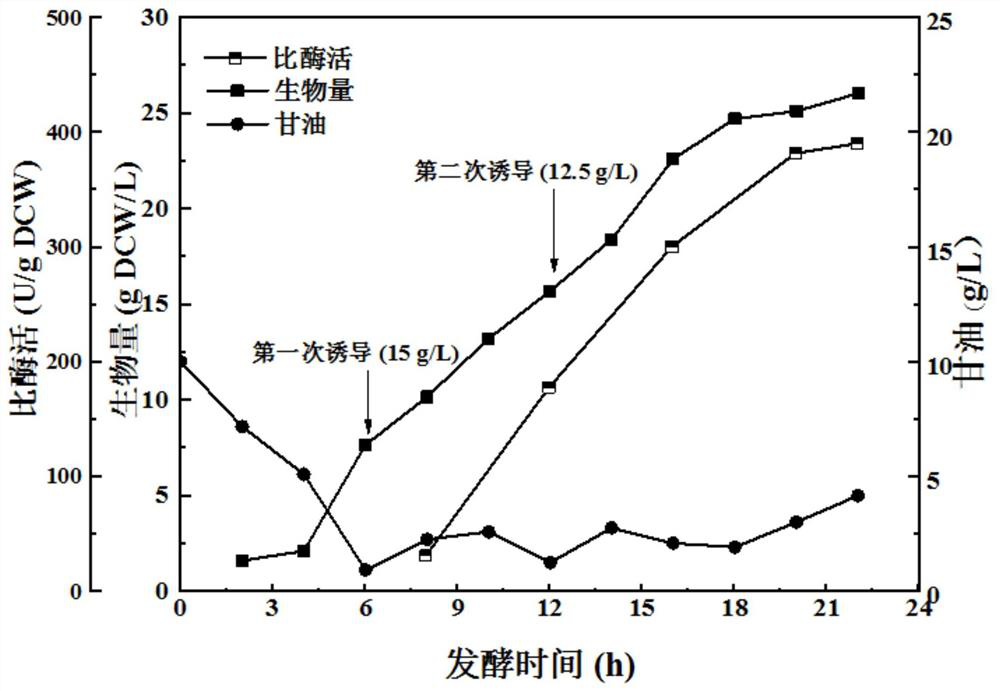
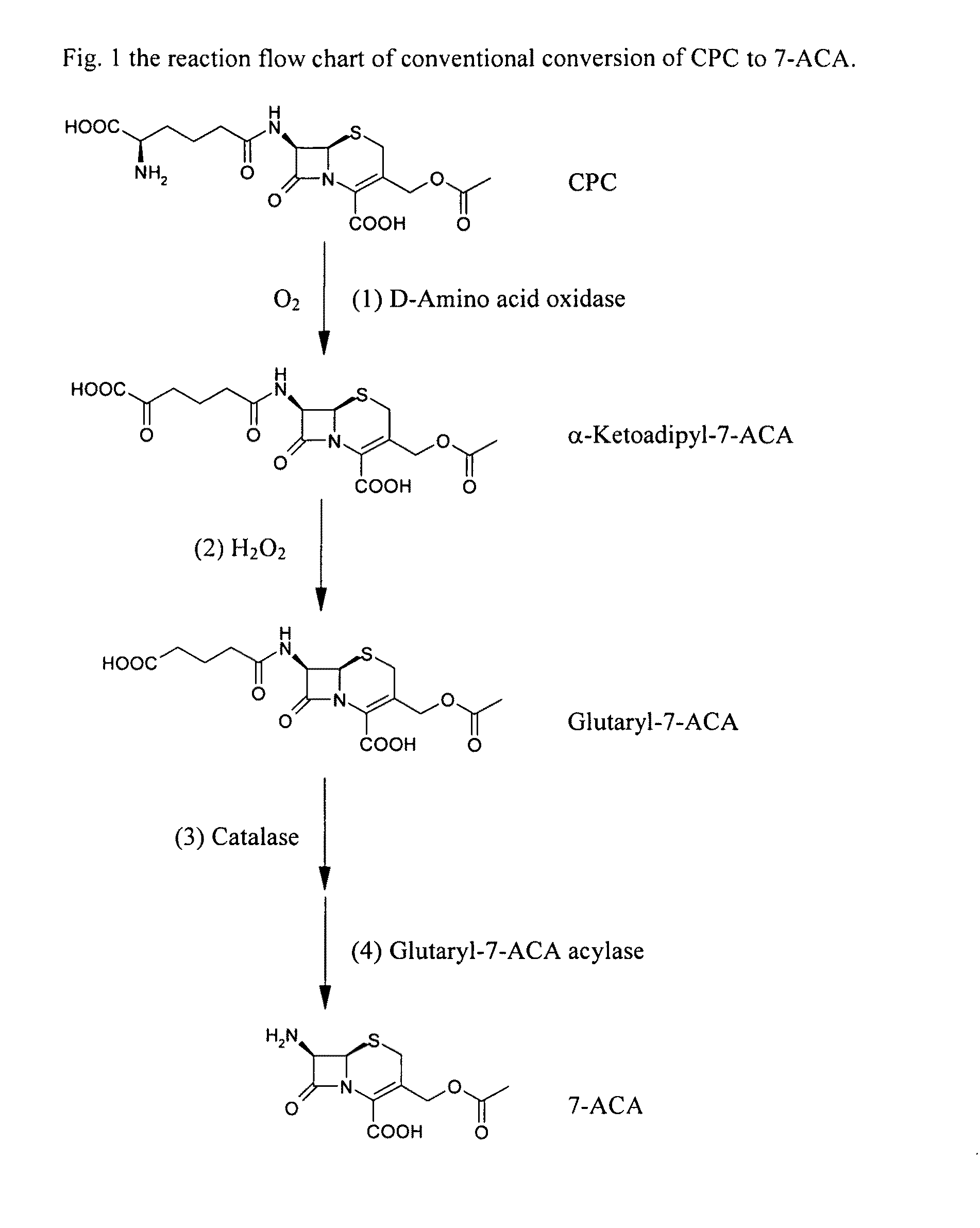
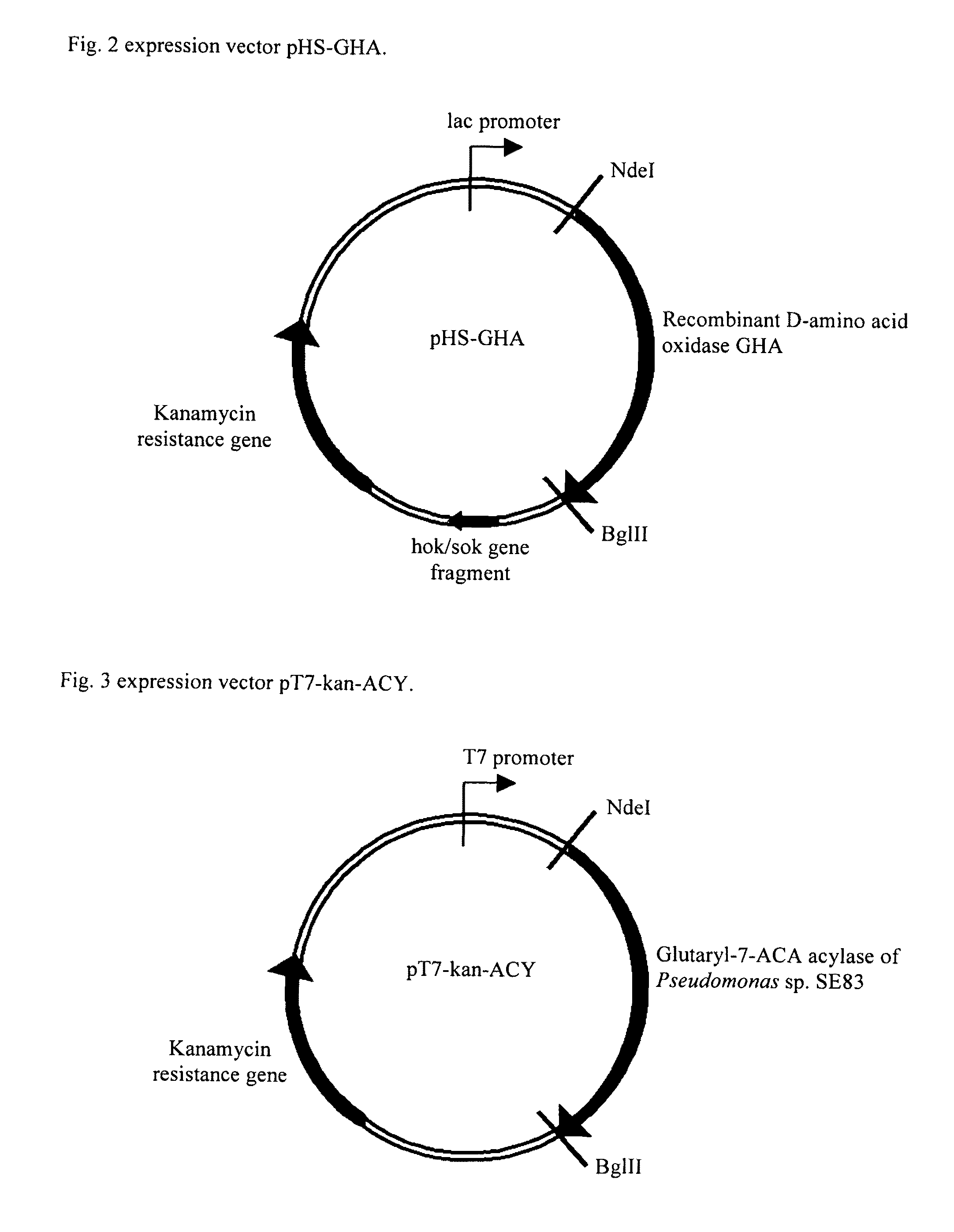
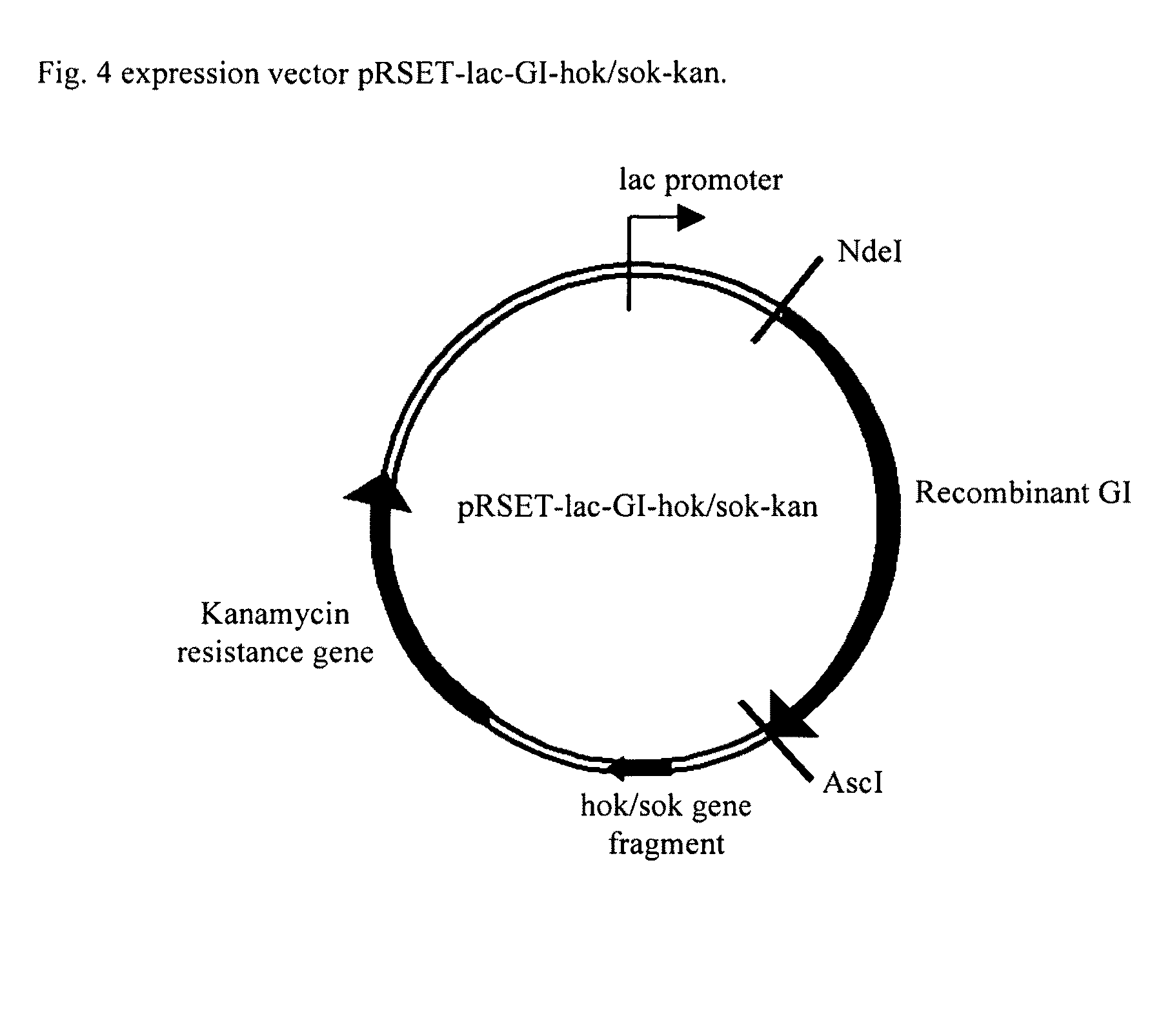
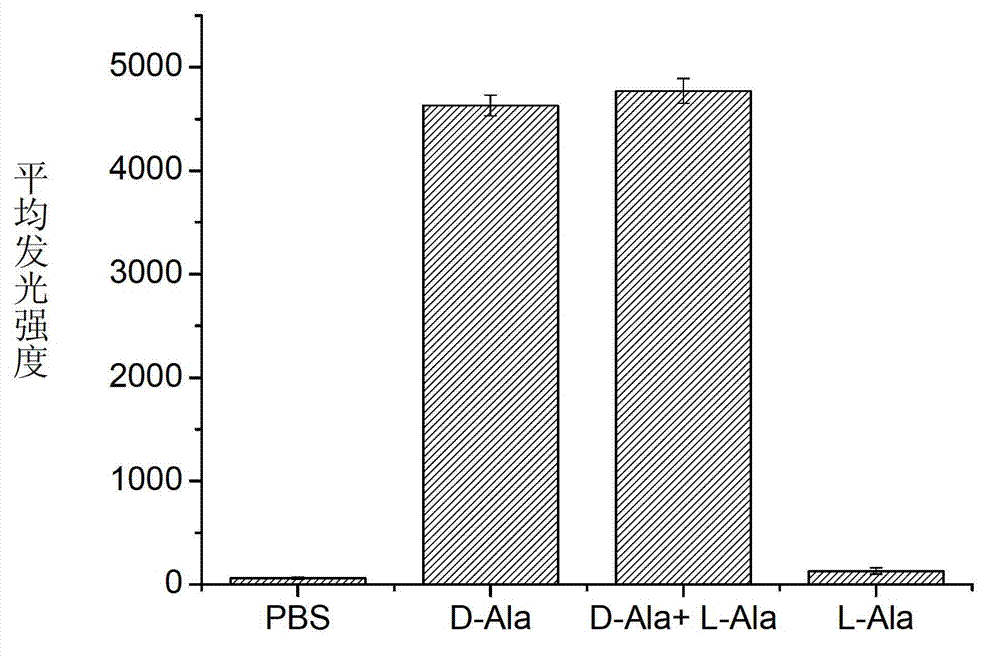
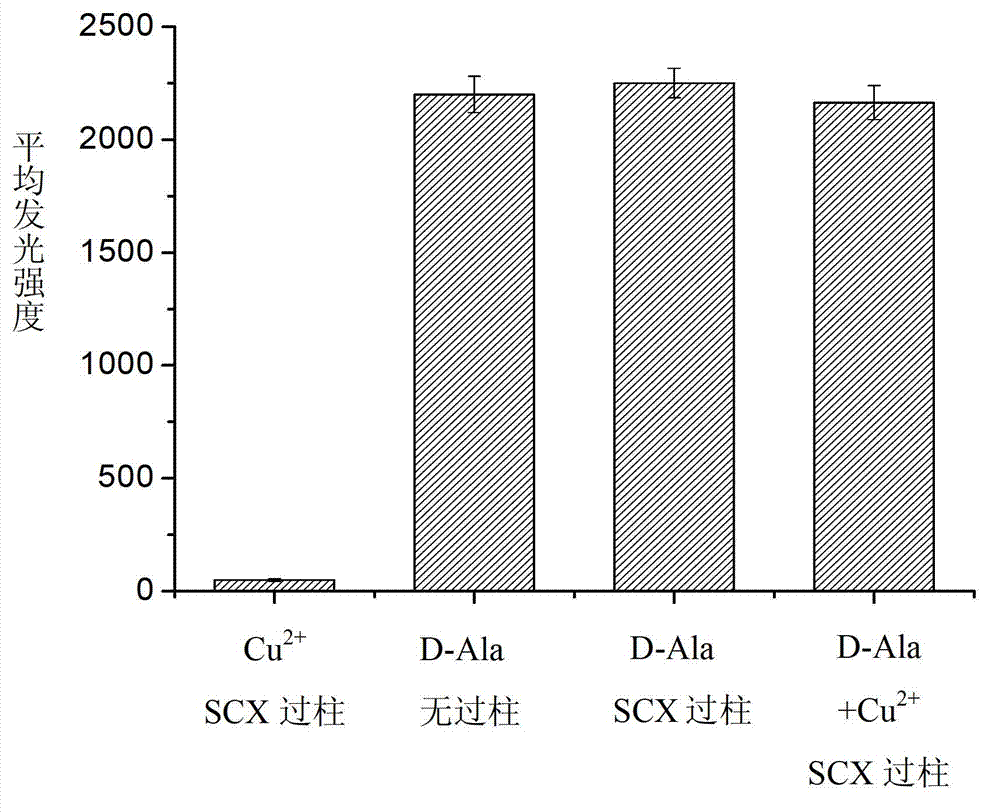
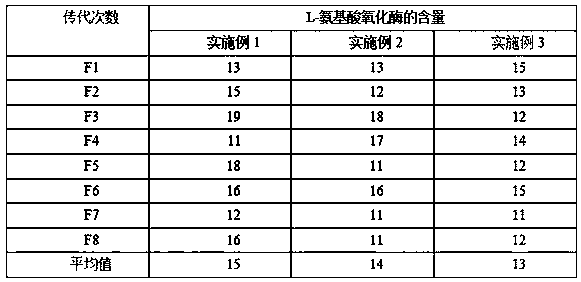
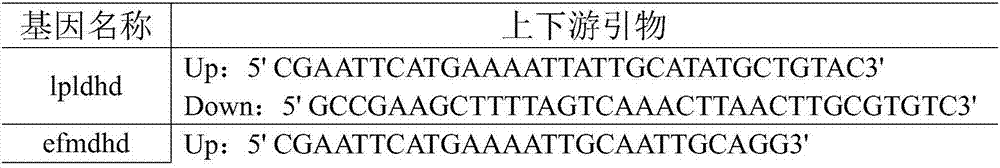Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "L-amino-acid oxidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
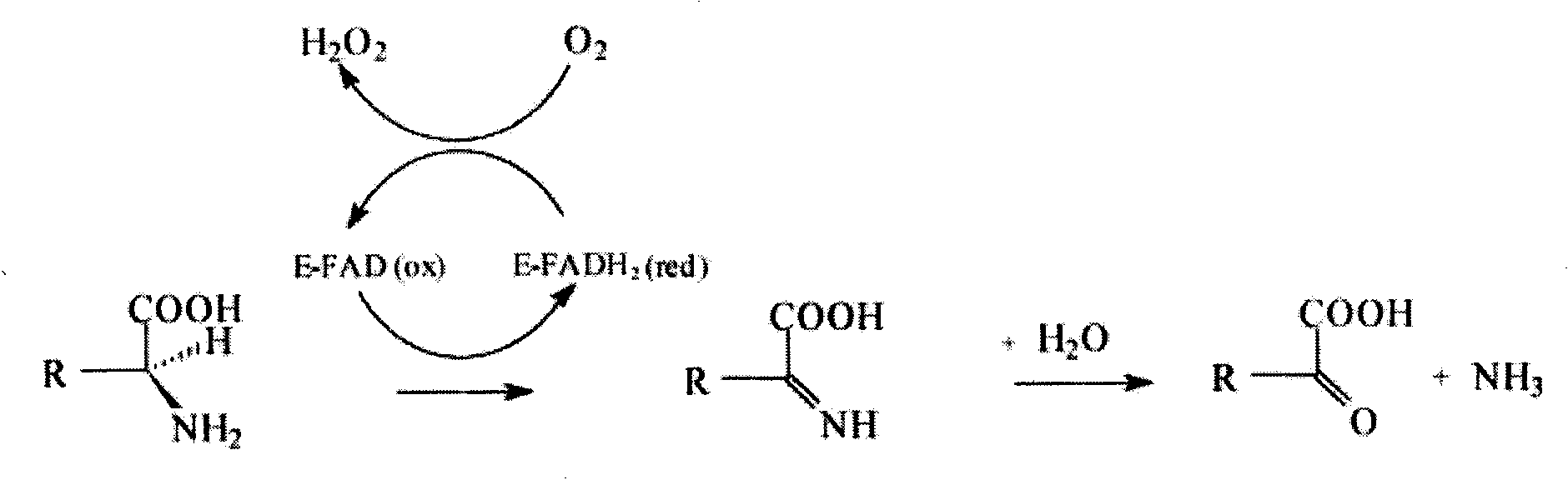
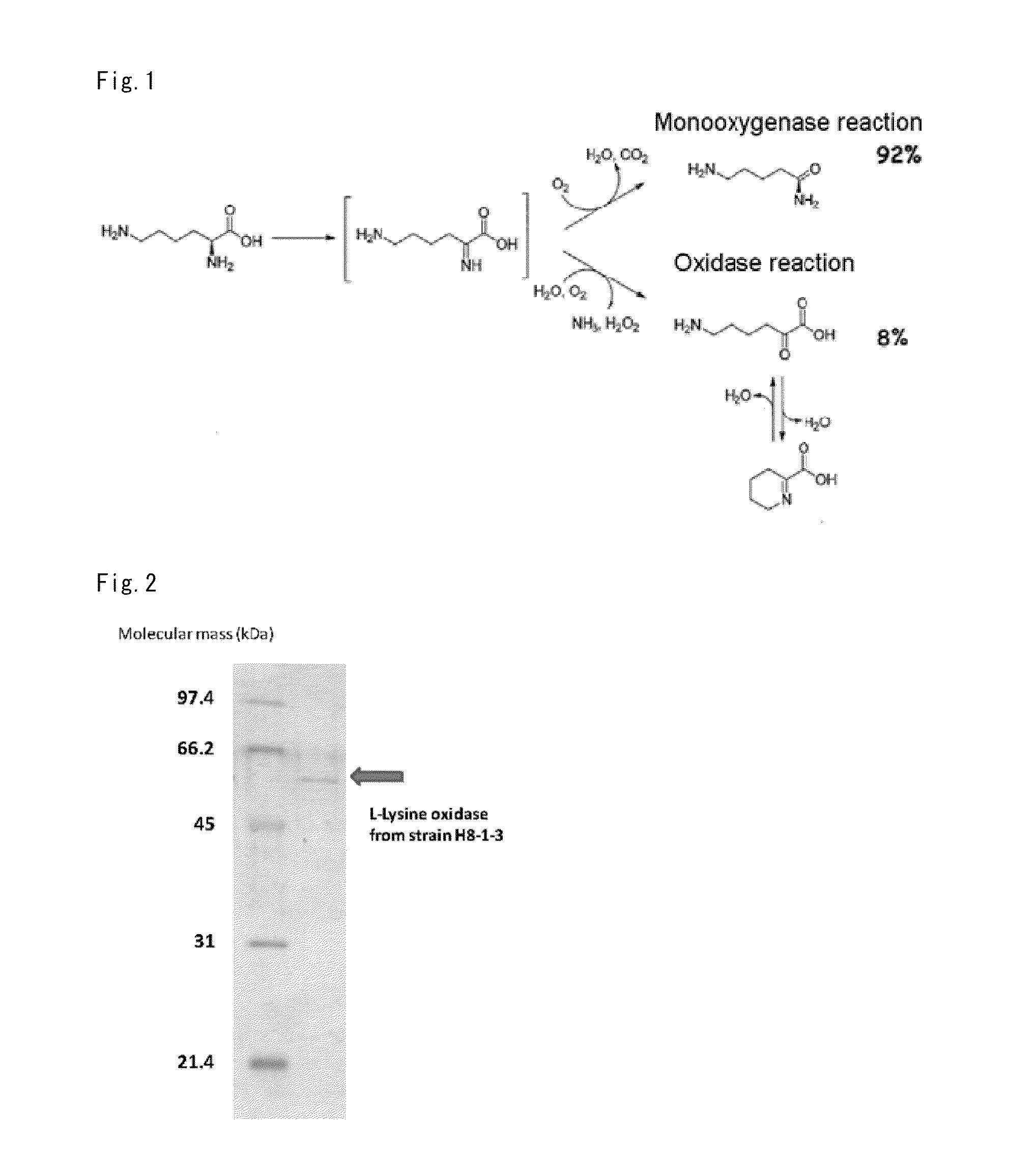
In enzymology, an L-amino acid oxidase (LAAO) (EC 1.4.3.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction an L-amino acid + H₂O + O₂ ⇌ a 2-oxo acid + NH₃ + H₂O₂ The enzyme was first described in 1944 by A. Zeller and A. Maritz. Not only are LAAOs quite variable in terms of molecular mass, they also vary widely regarding stability. In a similar vein, this enzyme performs in a myriad of biological activities including apoptosis-induction, edema-induction, hemorrhaging, and inhibition or induction of platelet aggregation.
Engineering bacteria and application thereof
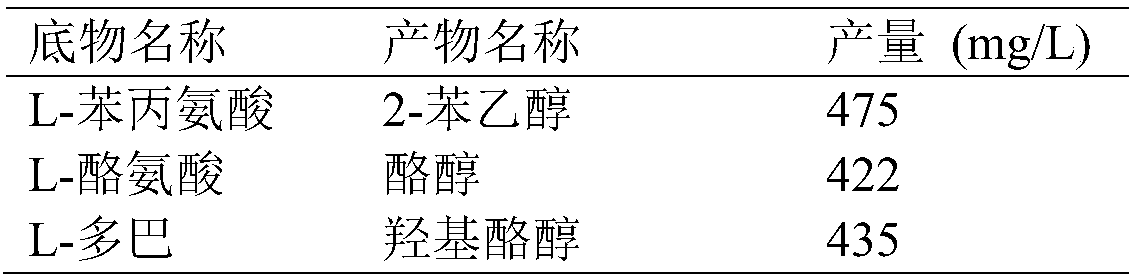
ActiveCN107299072AStrong substrate specificityEasy to produceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliL-amino-acid oxidase
The invention discloses escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria co-expressed by three enzymes. The escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria are characterized in that an L-amino-acid oxidase gene, a (D / L)-alpha-hydroxyl carboxylic acid dehydrogenase gene and a gene capable of reducing NAD(P) are imported. The invention also discloses a construction method and an application of the recombinant escherichia coli. The method is used to biologically synthesize optically pure alpha-hydroxyl carboxylic acid, has the characteristics of simple operation, low cost, high product synthesizing efficiency and high optical purity, and has a good industrial prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Fructose amino acid oxidase, preparation method and glycatedalbumin detection kit comprising oxidase
ActiveCN103695380AReduce performanceGood dilution linearityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisD-amino acid oxidaseGlutamic acid
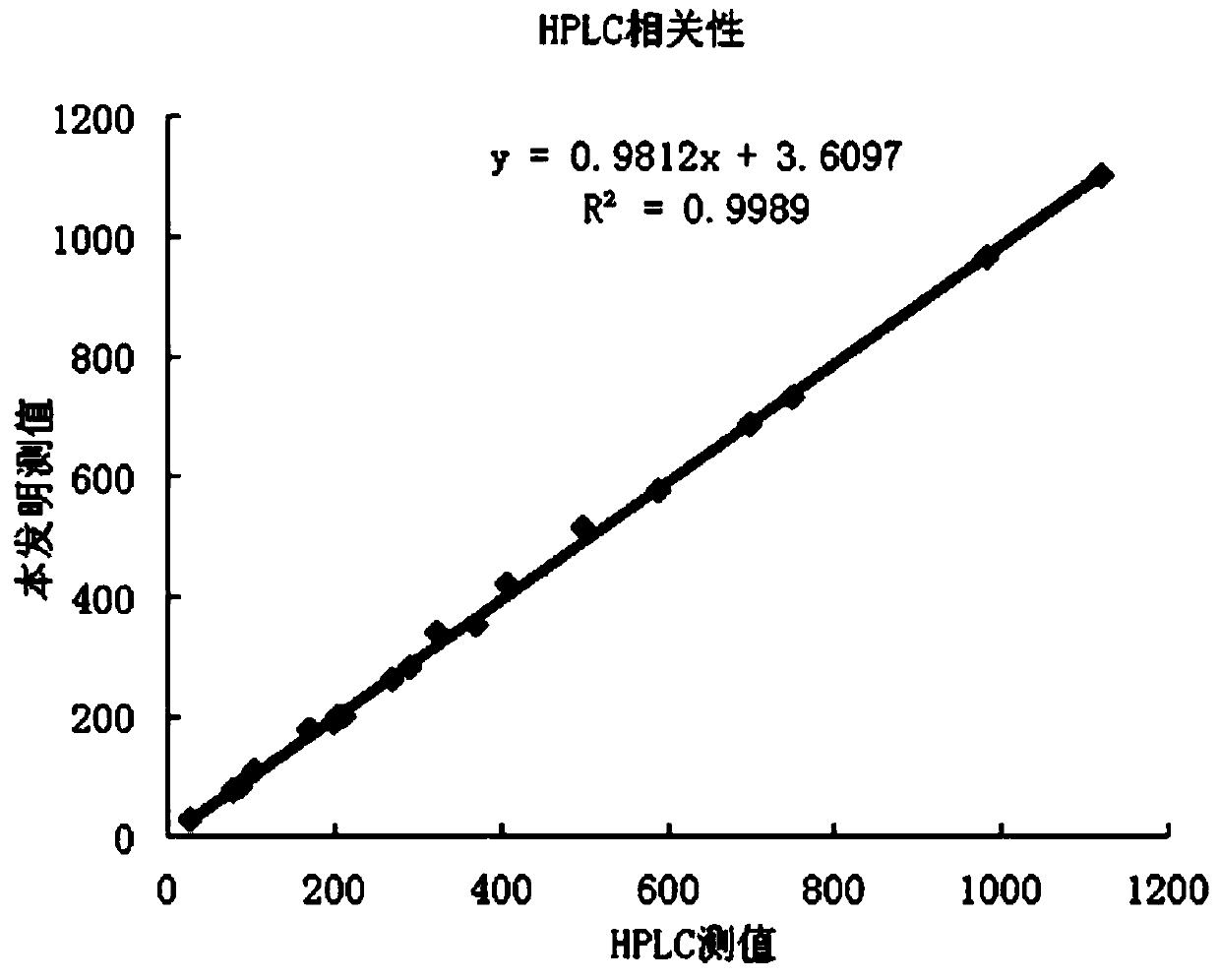
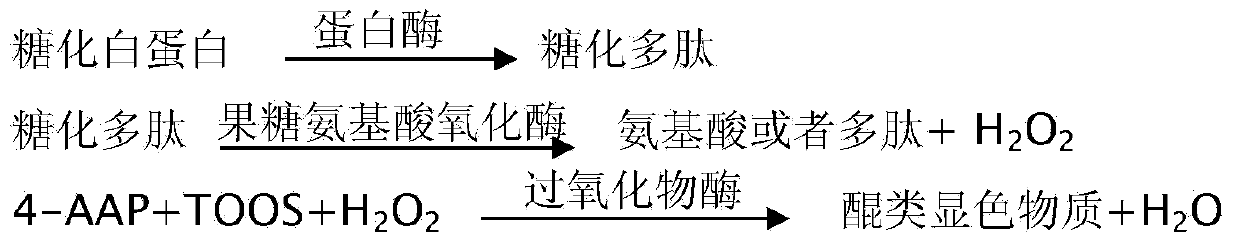
The invention discloses fructose amino acid oxidase which has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQID.No.1 (sequence identifier number 1) or has above 80% homology with the amino acid sequence. One or more amino acid residues in corresponding positions of amino acid selected from (a) to (f) are substituted. The obtained fructose amino acid oxidase has higher thermostability: (a) 59-site glutamic acid, (b) 98-site glutamic acid, (c) 225-site glycine, (d) 277-site lysine, (e) 283-site glutamic acid and (f) 355-site aspartic acid. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the oxidase and a kit comprising the oxidase and used for determining glycatedalbumin. The kit has higher thermostability and can accurately determine the glycatedalbumin.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Engineering bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN107586752APoor substrate specificityHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
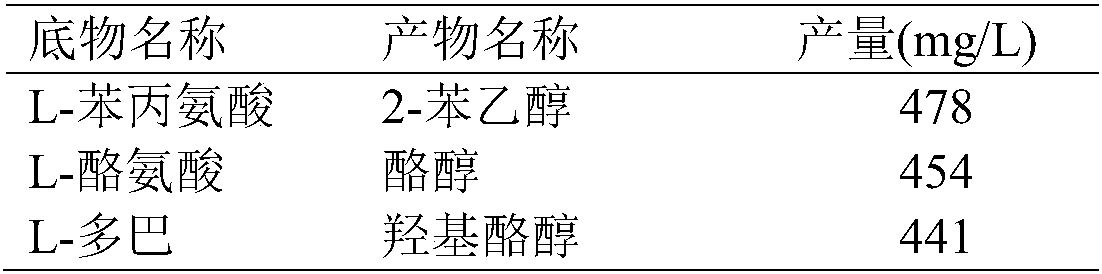
The invention discloses escherichia coli gene engineering bacteria for four enzyme co-expression. The engineering bacteria is characterized by introducing an L-amino acid oxidase gene, an alpha-ketonic acid decarboxylase gene, an alcohol dehydrogenase gene, and an enzyme gene capable of reducing NAD(P) to NAD(P)H. The invention further discloses a construction method and application of recombinantescherichia coli. The engineering bacteria is applied to biological synthesis of phenylethyl alcohol compounds, has the characteristics of simple operation, low cost, high product synthetic efficiency, and high optical purity, and has bright industrial prospects.
Owner:HONGTAOSIM RES INST OF ANALYCAL SCI & TECH LTD CO
Biocatalysis method for preparing Alpha ketoglutarate from L-soda glutamate
ActiveCN103352058AImprove conversion rateMicroorganism based processesFermentationL-amino-acid oxidaseSodium Glutamate
The invention expounds a biocatalysis method for preparing Alpha ketoglutarate from L-soda glutamate, and belongs to the biotechnological field. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing strains (Rhodococcus opacus) producing L-amino acid oxidase, performing fermentation for 48 hours, collecting thallus, weighing and pouring 12 g / L (calculating by dry weight) thallus into a 10 g / L L-soda glutamate contained conversion solution, performing conversion at the temperature of 35 DEG C and the pH of 8.4 for 10 hours, adding 4.3 g / L L-soda glutamate into a reaction system every 6 hours, and performing continuous conversion for 24 hours, where the output of Alpha-ketoglutarate reaches 16.8 g / L, and the conversion rate reaches more than 90 percent.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Biocatalysis method for preparing pyruvic acid from L-alanine
ActiveCN102586343ASimple separation processHigh chemical purityMicroorganism based processesFermentationL-amino-acid oxidaseAmmonia
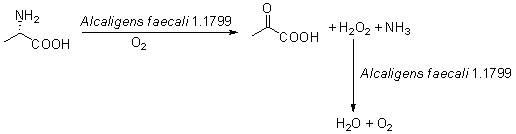
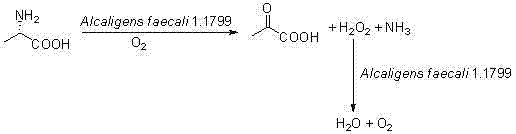
The invention provides a biocatalysis method for preparing pyruvic acid from L-alanine. The method comprises the steps of: carrying out permeability treatment on Alcaligens faecalisl.1799 cells; catalyzing oxidative deamination of L-alanine by utilizing L-amino acid oxidase in the cells in the presence of air to form pyruvic acid, ammonia and hydrogen peroxide; catalyzing the hydrogen peroxide formed in the reaction by utilizing catalase in the cells to realize pyruvic acid accumulation without producing by-products. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of low cost, high product yield and purity and environment friendliness, and is suitable for industrial production of pyruvic acid.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
Fructosyl amino acid oxidase
Disclosed is a mutant fructosyl amino acid oxidase modified at an amino acid residue involved in proton relay system. The mutant fructosyl amino acid oxidase has reduced oxidase activity while substantially maintaining its dehydrogenase activity. The invention also provides an assay device and assay method for measuring glycated protein.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG +1
Gene complete sequence of siganus oramin L-amino acid oxidase and application thereof
The invention discloses a gene complete sequence of siganus oramin L-amino acid oxidase and application thereof. The gene complete sequence of the siganus oramin L-amino acid oxidase is 1725bp, the length of an open reading frame is 1584bp, and the gene complete sequence is specifically in a 43-1626 region and is used for coding 527 amino acids. The siganus oramin L-amino acid oxidase is obtained from siganus oramin serum through separation and purification, and has a function of killing cryptocaryon irritans brown and a bactericidal activity on typical gram-positive bacteria (staphylococcus aureus) and gram-negative bacteria (escherichia coli). In an optimized high-definition enzyme PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) system, by using total siganus oramin spleen cDNA as a template and adopting a pair of designed specific primers, the gene sequence coding the protein can be rapidly accurately cloned and used for the subsequent genetic engineering.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method and kit for detecting concentration of chiral amino acid
InactiveCN102692409ALow light backgroundSuppress luminescenceChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLuminous intensityEnantiomer
The invention discloses a method and a kit for detecting concentration of chiral amino acid. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) adding D-amino acid oxidase or L-amino acid oxidase into a sample to be tested for carrying out an enzyme catalysis reaction; 2) sequentially adding buffer solution, luminol and horse radish peroxidase into the obtained reaction solution in the step 1) for carrying out a chemiluminiscence reaction; and 3) measuring the luminous intensity of the reaction solution in the step 2). The method can be used for measuring chiral amino acid in an enantiomer. The method is not interfered by another chiral amino acid in the enantiomer or is not interfered by common metal ions. The method is easy to operate and high in sensitivity, and the content of the chiral amino acid in the enantiomer can be detected.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
D-amino acid oxidase, and method for production of l-amino acid, 2-oxo acid, or cyclic imine
ActiveUS20110086396A1Efficient productionHigh activitySugar derivativesBacteriaD-Amino-Acid Oxidase GeneL-amino-acid oxidase
The present invention relates to novel D-amino acid oxidase isolated and purified from Candida intermedia, a gene encoding the D-amino acid oxidase, a recombinant plasmid containing the gene, and a transformant into which the D-amino acid oxidase gene has been introduced, as well as a production method of D-amino acid oxidase including culturing the transformant. Moreover, the present invention relates to a production method of L-amino acids, 2-oxo acids or cyclic imines, which include reacting racemic amino acids with the D-amino acid oxidase, more preferably, a production method of L-amino acids, which includes reacting racemic amino acid with the D-amino acid oxidase, amino acid dehydrogenase and an enzyme having a coenzyme-regenerating activity. According to the present invention, L-amino acids, 2-oxo acids or cyclic imines can be produced with good efficiency in an industrial scale.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Application of snake venom L-amino acid oxidase in preparing AIDS treating medicine
InactiveCN1526445ASignificant anti-HIV activityIncrease vitalityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsPeroxidaseCytotoxicity
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of Danshensu by using cheap substrate
ActiveCN108949648APoor substrate specificityEasy to produceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseL-amino-acid oxidase
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of Danshensu by using a cheap substrate, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium provided by the invention is a recombinant bacterium capable of producing Danshensu at a low cost; the recombinant bacterium can simultaneously express four enzymes which are tyrosinephenol lyase, L-amino acid oxidase, L-lactate dehydrogenase and alpha-hydroxycarboxylic acid oxidase respectively; and the recombinant bacterium knocks out a phenolic substance-decomposing gene, and can achieve enhanced expression of any one or more of a lactic acid transporter gene, a catechol transporter gene and a coenzyme synthesis-related gene. The engineering bacterium has the advantages ofrealization of the efficient production of Danshensu, simple process, few impurities and great industrial application values.
Owner:HONGTAOSIM RES INST OF ANALYCAL SCI & TECH LTD CO
Mutant of L-amino acid oxidase
ActiveCN109321541AHigh catalytic efficiencyMild reaction conditionsBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliHeterologous
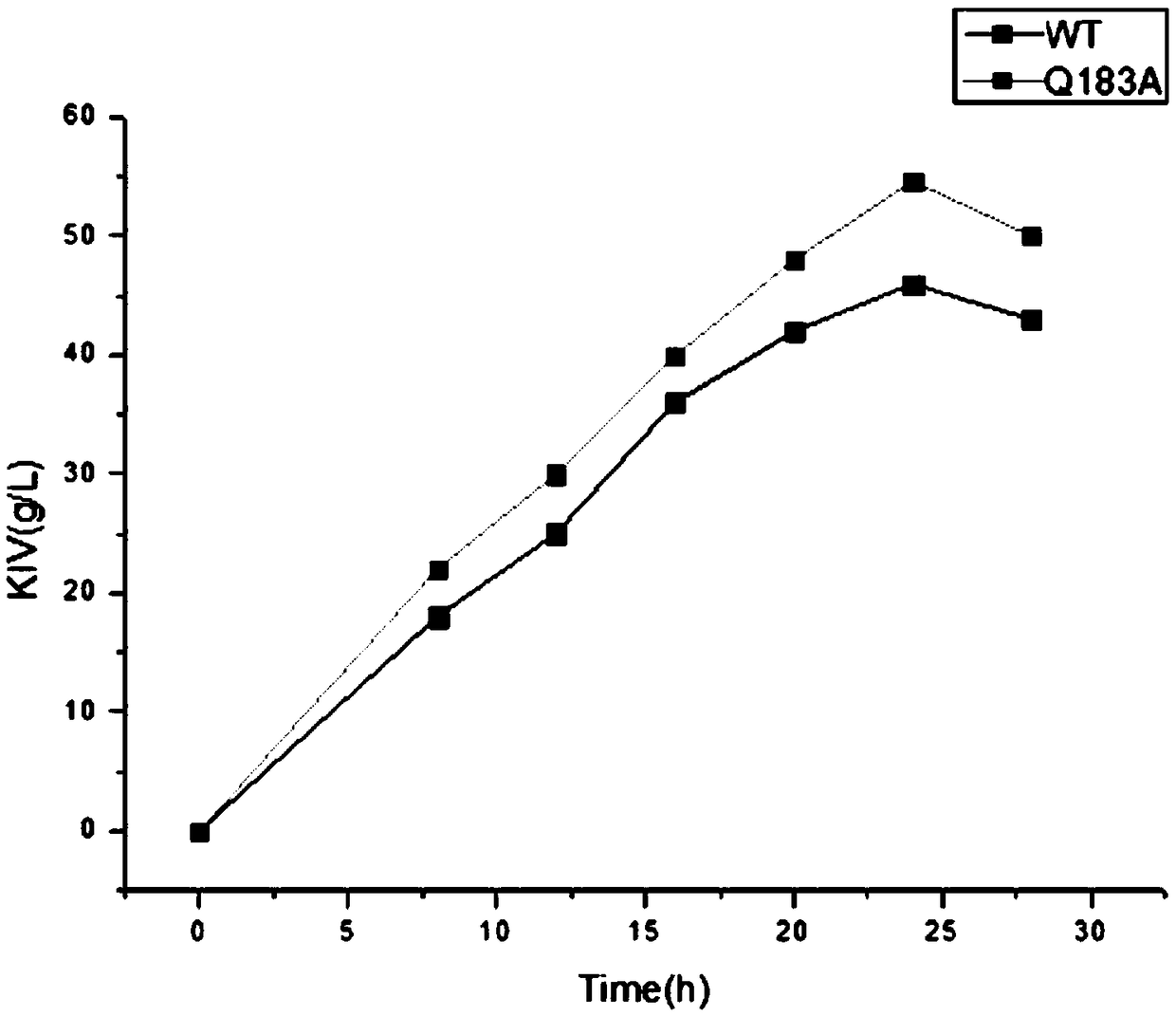
The invention discloses a mutant of L-amino acid oxidase and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. Through performing site-specific mutagenesis on the L-amino acid oxidase derived from corynebacterium glutamicum, a mutant Q183A is obtained. Heterologous expression is performed on escherichia coli through the mutant Q183A performs, catalytic efficiency of obtained recombinant bacteria to L-valine is improved by 18.7%, a yield of alpha-ketoisocaproic acid reaches 54.6 g / L, and a molar conversion rate of a substrate is 84.6%. Compared with a chemical method, the provided whole-cell transformation method has the advantages of moderate reaction condition, single target product, easy separation, environment-friendliness and the like, and is simple in process, easy to control, and easy for popularization and application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Method for producing alpha-ketoisovaleric acid with high yield
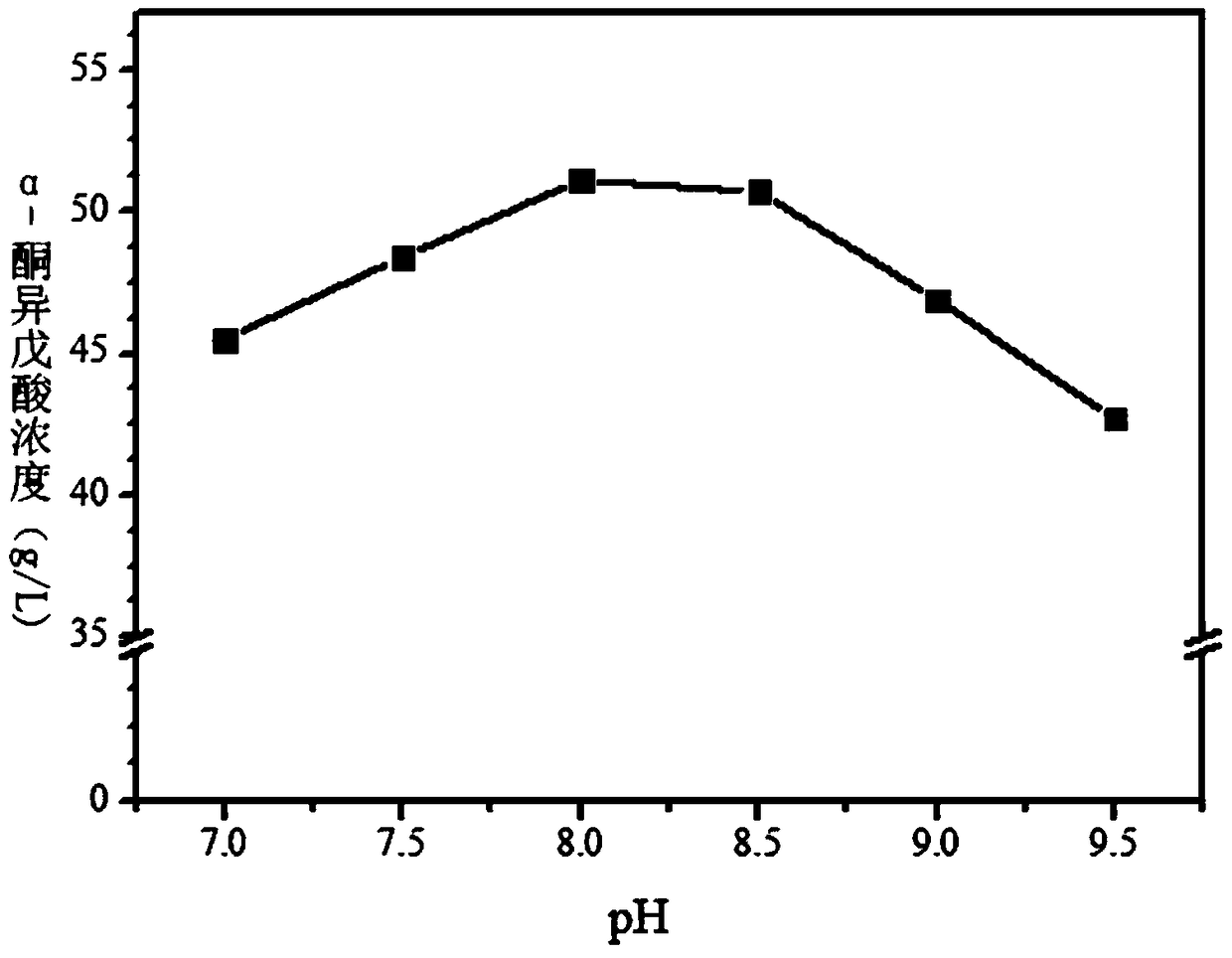
PendingCN109371070AHigh selectivityMild conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-amino-acid oxidaseAlpha-Ketoisovaleric acid
The invention discloses a method for producing alpha-ketoisovaleric acid with high yield, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The method includes connecting a gene derived from Corynebacterium glutamicum encoded L-amino acid oxidase to an expression vector by a molecular biological means; introducing constructed expression plasmids into E. coli BL21 (DE3) and screening with a kanamycin-resistant plate to obtain a recombinant L-amino acid oxidase-containing engineered bacterium which is used for conversion of L-valine to produce alpha- ketoisovaleric acid. High-efficiency production of the alpha-ketoisovaleric acid is achieved by controlling temperature and pH and metal ions. The yield of the alpha-ketoisovaleric acid is up to 51 g / L with the conversion rate of 79.1% underthe condition that the temperature is 25 DEG C, pH=8.0, the biomass is 30 g / L, and the substrate concentration is 65 g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
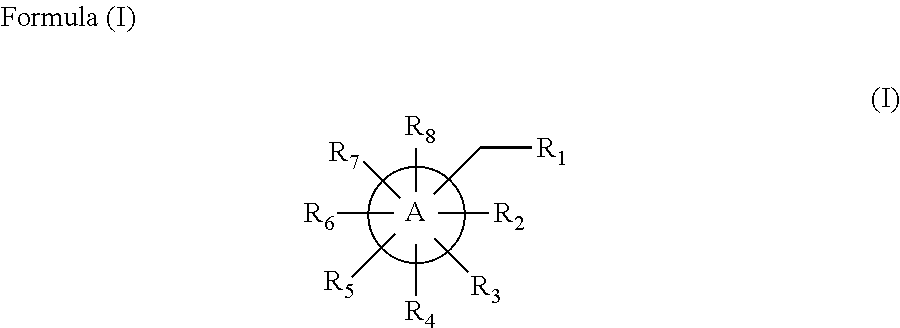
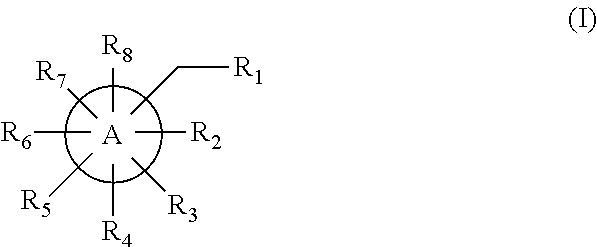
Inhibitors of d-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) and uses thereof
ActiveUS20190367549A1Esterified saccharide compoundsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseL-amino-acid oxidase
Provided herein are compounds of Formula (I) and uses thereof for inhibiting the activity of D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) or treating diseases or disorders associated with DAAO, such as a central nervous system (CNS) disorder, obesity, diabetes, or hyperlipidemia. Also provided in the present disclosure are methods of synthesizing the Formula (I) compounds described herein.
Owner:SYNEURX INT
Method for quantitatively determining activity of L-amino acid oxidase by using Prussian blue plate
ActiveCN102911999ALow costEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesL-amino-acid oxidaseRoom temperature
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting the activity of L-amino acid oxidase by using a Prussian blue agar plate, which comprises the following steps: with a punch, punching a small hole having a diameter of 4-10 mm on the Prussian blue agar plate; then, adding a liquid to be determined into the small hole, and standing at room temperature for 10-30 minutes, wherein hydrogen peroxide generated by the liquid to be determined forms a blue ring around the small hole; and determining the diameter of the blue ring, determining the release amount of hydrogen peroxide according to the hydrogen peroxide and a standard straight line made of the diameter of the blue ring, and then deducing to obtain the activity of L-amino acid oxidase, wherein the liquid to be determined is a reaction liquid obtained by reacting an enzyme source and a substrate under the conditions of a temperature of 25-50 DEG C and a pH value of 5-9 for 0.5-2 hours, the enzyme source is an enzyme obtained through the fermentation culture of Pseudoalteromonas sp. B3, and the substrate is L-amino acid. The method has the characteristics of low cost, simple and convenient operation process, wide applicability, high stability and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAILANG BIOTECHOLOGY
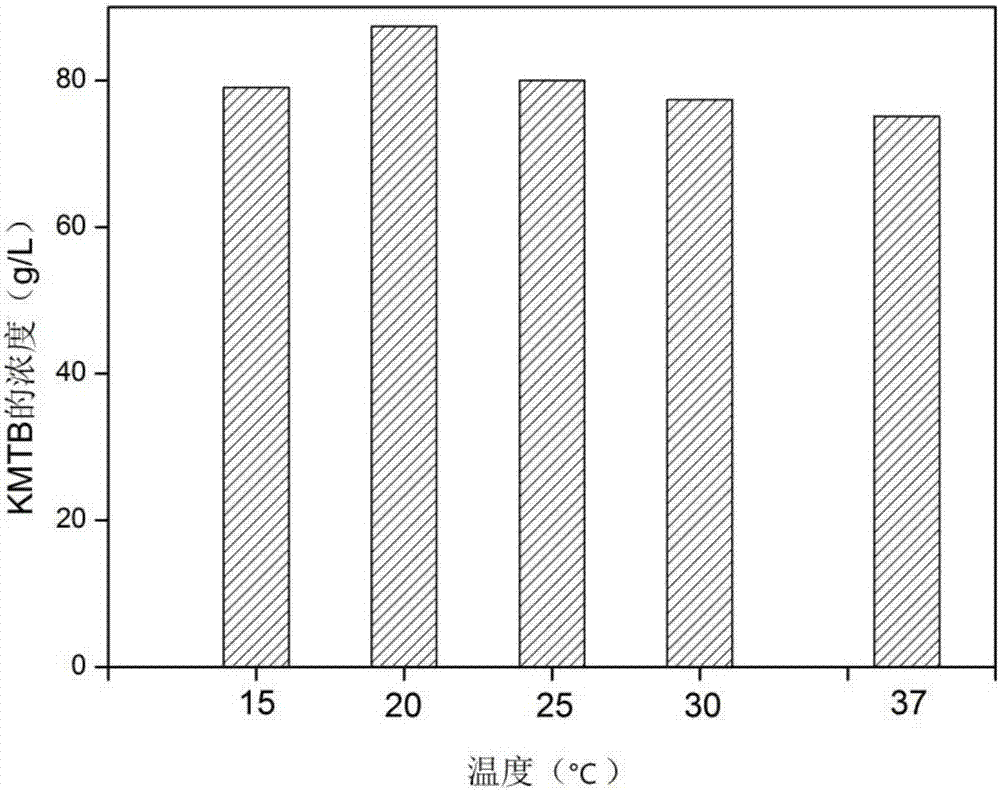
Method for efficiently producing KMTB (alpha-keto-gamma-methylthiobutyric acid)
ActiveCN107988131AIncrease vitalityMeet the needs of industrial scale productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-amino-acid oxidaseKetone
The invention discloses a method for efficiently producing KMTB (alpha-keto-gamma-methylthiobutyric acid) and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. A gene derived from rhodococcus erythropolis encoded L-amino acid oxidase is subjected to artificial synthesis and codon optimization with a molecular biology method and then connected with an expression vector. A constructed expression plasmid is introduced into E. coli BL21 (DE3), and expression vector high-copy recombinant engineering bacteria containing L-amino acid oxidase are obtained through kanamycin resistance plate screening.The engineering bacteria are used for converting L-methionine to produce KMTB. Efficient production of KMTB is realized by controlling bacterium quantity, temperature and pH. 30 g / L of wet bacteria are put under the conditions of 20 DEG C and pH of 7.5 to react for 24 h, the yield of KMTB can reach 95.18 g / L, the conversion rate is 95.84%, and the space time yield is 3.97 g / L / h.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for separating L-amino-acid oxidase from venin
InactiveCN1614012AAvoid influenceSimple methodOxidoreductasesL-amino-acid oxidaseGloydius ussuriensis
It was involved in separating L-amino acid oxidase from the snake venom of Agkistrodonhalysussuriensis. Through two steps of colum chromatography (i.e. heparin fast flow and qsepherose fast flow) L-amino acid oxidase was separated and purified from the snake toxin of Gloydius ussuriensis. Not including transfer between concentrating and buffer system. It could avoid the influence of freezing and the pH value change to enzyme activity. The method was found to be simple, rapid and convenient. The ratio of recovery was high.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV MEDICAL COLLEGE
Anti-IL-4R single-chain antibody and snake venom L-amino acid oxidase fusion protein and application thereof
The invention discloses anti-IL-4R single-chain antibody and snake venom L-amino acid oxidase fusion protein; the fusion protein is prepared by: connecting anti-IL-4R single-chain antibody and Trimeresurus stejnegeri venom LAAO (L-amino acid oxidase) gene into scFv-LAAO fusion gene by means of overlap extension PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology, constructing recombinant plasmid pET28-a-scFv-LAAO, transferring to BL21(DE3) prokaryotically-expressed bacterium, and inducing to express scFv-LAAO fusion protein. By using molecular biological techniques, an expression vector for anti-IL-4R single-chain antibody gene (scFv) and snake venom L-amino acid oxidase fusion gene is used to carry out in-vitro expression in order to recombine the anti-IL-4R single-chain antibody and snake venom L-amino acid oxidase fusion protein, and the anti-IL-4R single-chain antibody and snake venom L-amino acid oxidase fusion protein is applicable to the treatment of lung cancer, has good therapeutic effect and is substantially free of side effects.
Owner:贵州中医药大学
Construction method for recombinant baculovirus used for expressing L-amino acid oxidase of Siganus oramin
PendingCN107893084AHigh expressionNucleic acid vectorOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliRestriction enzyme digestion
The invention discloses a method for constructing a recombinant baculovirus for expressing L-amino acid oxidase of the macula macula. The gene whose DNA sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 is cloned into the vector pMD18-T to construct a recombinant plasmid; Restriction endonucleases EcoRI and XhoI cut the recombinant plasmid and the donor plasmid respectively, and ligated the digested products to obtain the recombinant donor plasmid; the recombinant donor plasmid was transformed into E. coli, so that the target gene and the bacillus contained in E. The virus shuttle vector is specifically transposed, and the recombinant bacmid is screened and extracted; the recombinant bacmid is transfected into insect cells by liposome transfection method, and the recombinant baculovirus is harvested after the insect cells are pathological.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
Preparation method of D-phenylalanine
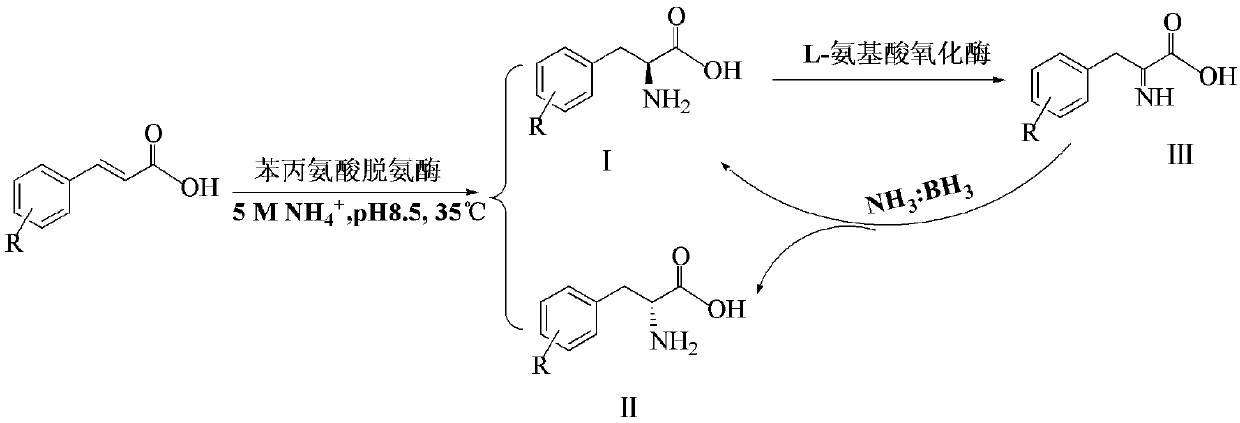
InactiveCN107653275AReduce manufacturing costRaw materials are cheap and easy to getFermentationD-PhenylalanineL-amino-acid oxidase
The invention discloses a preparation method of D-phenylalanine. The preparation method comprises the steps of mixing trans-cinnamic acid, phenylalanine deaminase, L-amino-acid oxidase, ammonia waterand ammonia borane and performing reaction to prepare the D-phenylalanine. Through the adoption of the technical scheme, the trans-cinnamic acid serves as a substrate raw material, ammonification of the trans-cinnamic acid is catalyzed by the phenylalanine deaminase, L-phenylalanine and D-phenylalanine are generated, the L-phenylalanine in the reaction system is under the oxidation action of the L-amino-acid oxidase to generate imidic acid, and the imidic acid is reduced into the L-phenylalanine and the D-phenylalanine under the existence of a reducing agent ammonia borane (NH3BH3), so that the L-phenylalanine generated in the reaction process is continuously converted into the D-phenylalanine. Through continuous circulating conversion, the yield of the D-phenylalanine is greatly increased, the yield reaches to 96 percent, and the optical purity of the D-phenylalanine exceeds 99 percent.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE
Pseudoalteromonas sp.B3 and application thereof in biological oxidation of L-amino acid
ActiveCN102367430BSubstrate Broad SpectrumMild responseBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismL-amino-acid oxidase
Owner:菏泽建数智能科技有限公司
Method for producing D-amino acid oxidase through fermentation
ActiveCN112852773AIncrease enzyme activityIncrease productivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHigh concentration
The invention discloses a method for producing D-amino acid oxidase through fermentation, and belongs to the technical field of biological enzyme preparation. The method comprises the following steps: taking recombinant escherichia coli for expressing D-amino acid oxidase as a production strain, inoculating the recombinant escherichia coli into a fermentation culture medium for fermentation culture, supplementing materials in batches in a DO-STAT mode after dissolved oxygen is reduced to 1%, and setting the DO value to be 10-50%; in the fermentation process, adding 10-50 g / L lactose serving as an inducer, meanwhile, adding D-amino acid into the fermentation liquor, continuing culture till fermentation is finished, and collecting thalli containing D-amino acid oxidase in cells. In the fed-batch fermentation process, high-concentration lactose is added to serve as an inducer to improve the enzyme activity of DAAO, meanwhile, a proper amount of D-amino acid is added to reduce inhibition of DAAO on growth of host cells, the production efficiency of DAAO is greatly improved, and conditions are provided for industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A kind of Bacillus xylosinolysine and its method for preparing α-keto acid
ActiveCN105316257BBroad substrate specificityHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisDecomposition
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and particularly relates to lysinibacillus xylanilyticus and a method for preparing alpha-ketoacid with the same. The lysinibacillus xylanilyticus XX-2 with a preservation number being CCTCC No:M2015520 is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection. Whole cells of the lysinibacillus xylanilyticus XX-2 are taken as a biocatalyst to realize oxidative deamination of L-amino acids to obtain corresponding alpha-ketoacid, ammonia gas and hydrogen peroxide in the presence of air by L-amino acid oxidase in the lysinibacillus xylanilyticus XX-2, and in-situ decomposition of the generated hydrogen peroxide is realized by co-expressed catalase in the cells. The method overcomes defects of chemical synthesis methods and fermentation methods for preparing the alpha-ketoacid, has advantages of mild reaction conditions, environment friendliness, low cost, wide product spectrum and the like and is applicable to industrial production of the alpha-ketoacid.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Two-step enzyme method for preparing 7-aminocephalosporanic acid
ActiveUS8003358B2Low production costThe production process is simpleBacteriaSugar derivativesTrigonopsis variabilisMutant
Owner:BIORIGHT WORLDWIDE
Method and kit for detecting concentration of chiral amino acid
InactiveCN102692409BLow light backgroundSuppress luminescenceChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLuminous intensityEnantiomer
The invention discloses a method and a kit for detecting concentration of chiral amino acid. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) adding D-amino acid oxidase or L-amino acid oxidase into a sample to be tested for carrying out an enzyme catalysis reaction; 2) sequentially adding buffer solution, luminol and horse radish peroxidase into the obtained reaction solution in the step 1) for carrying out a chemiluminiscence reaction; and 3) measuring the luminous intensity of the reaction solution in the step 2). The method can be used for measuring chiral amino acid in an enantiomer. The method is not interfered by another chiral amino acid in the enantiomer or is not interfered by common metal ions. The method is easy to operate and high in sensitivity, and the content of the chiral amino acid in the enantiomer can be detected.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A high-yield l-amino acid oxidase strain and its application
ActiveCN105087443BIncrease color valueImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliL-amino-acid oxidase
The invention relates to a strain with a high L-amino acid oxidase yield. The classification name of the strain is escherichia coli MZ505. The invention further provides a screening method of the strain, a method for producing L-amino acid oxidase with the strain, and application of L-amino acid oxidase produced by the strain to production of 5-aminovaleric acid.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Novel L-Amino Acid Oxidase, Method for Measuring L-Lysin, Kit and Enzyme Sensor
ActiveUS20140335553A1Increased substrate specificityConveniently and rapidly detectBacteriaSugar derivativesLysinL-amino-acid oxidase
Methods are provided measuring L-lysine using a variant enzyme, an L-lysine measurement kit, and an enzyme sensor. Variant L-amino acid oxidase having a predetermined amino acid mutation, and having oxidase activity that is highly substrate-specific for L-lysine; a method for measuring L-lysine using this variant enzyme; an L-lysine measurement kit; and an enzyme sensor are also provided.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC +1
Method for separating L-amino-acid oxidase from venin
It was involved in separating L-amino acid oxidase from the snake venom of Agkistrodonhalysussuriensis. Through two steps of colum chromatography (i.e. heparin fast flow and qsepherose fast flow) L-amino acid oxidase was separated and purified from the snake toxin of Gloydius ussuriensis. Not including transfer between concentrating and buffer system. It could avoid the influence of freezing and the pH value change to enzyme activity. The method was found to be simple, rapid and convenient. The ratio of recovery was high.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV MEDICAL COLLEGE
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of p-hydroxyphenyllactic acid by using cheap substrate
ActiveCN108949651APoor substrate specificityEasy to produceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseEscherichia coli
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of p-hydroxyphenyllactic acid by using a cheap substrate, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium constructed in the invention can simultaneously express four enzymes which are tyrosine phenol lyase, L-amino acid oxidase, alpha-hydroxycarboxylic acid oxidase and L-lactate dehydrogenase respectively. The knockout or enhanced expression of a related gene on the genome of the Escherichia coli can promote the transportation of the substrate and reduce the decomposition of the product. The method for producing the p-hydroxyphenyllactic acid has the advantages of simple process, few impurities and great industrial application values.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
Biocatalysis method for preparing pyruvic acid from L-alanine
ActiveCN102586343BSimple separation processHigh chemical purityMicroorganism based processesFermentationL-amino-acid oxidasePyruvic acid
The invention provides a biocatalysis method for preparing pyruvic acid from L-alanine. The method comprises the steps of: carrying out permeability treatment on Alcaligens faecalisl.1799 cells; catalyzing oxidative deamination of L-alanine by utilizing L-amino acid oxidase in the cells in the presence of air to form pyruvic acid, ammonia and hydrogen peroxide; catalyzing the hydrogen peroxide formed in the reaction by utilizing catalase in the cells to realize pyruvic acid accumulation without producing by-products. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of low cost, high product yield and purity and environment friendliness, and is suitable for industrial production of pyruvic acid.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com