Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
93results about How to "Reduce leaching costs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Treatment method of nickel-cobalt material
The invention provides a treatment method of a cobalt-containing material, belonging to the technical field of non-ferrous metal smelting. In the treatment method, through six steps such as peroxidation roasting, sulfuric acid leaching, N902 extraction of copper, chemical iron calcium magnesium removal, P204 extraction and impurity removal, P507 extraction and separation of nickel-cobalt, nickel,cobalt and copper in the nickel-cobalt material are extracted in high recovery, and impurities such as iron, zinc, manganese, calcium, magnesium and the like in the nickel-cobalt material are removed, thereby achieving nickel-cobalt-copper separation and resource comprehensive utilization. According to the treatment method provided by the invention, the process is simple and production cost is relatively low; the adaptability of the method on raw materials is strong and can be used for treating the nickel-cobalt material with complicated components and high copper-zinc-magnesium contents.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Method for extracting tungsten from scheelite
ActiveCN102021328AReduce lossesLow costProcess efficiency improvementWater dischargeReaction temperature
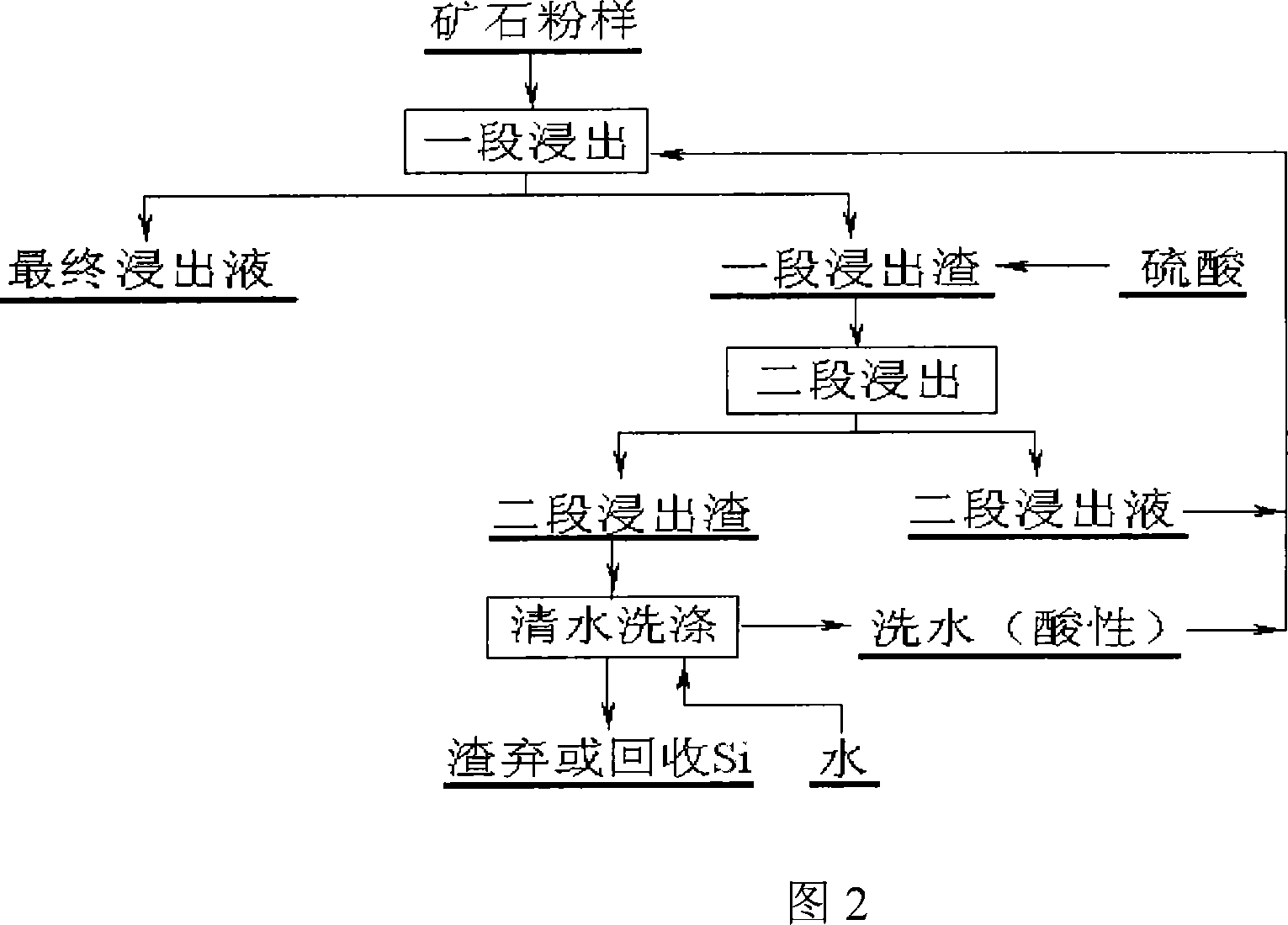
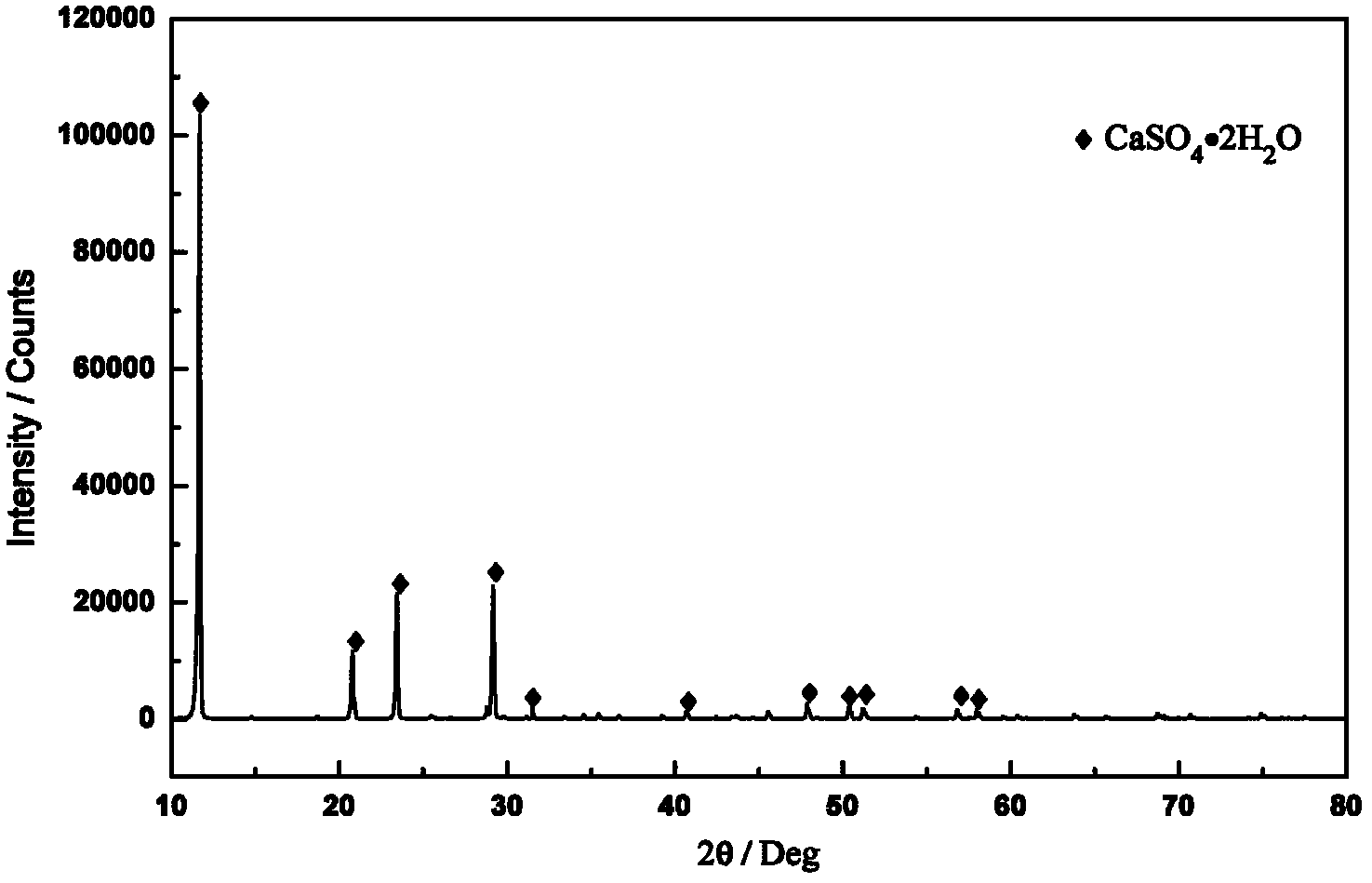
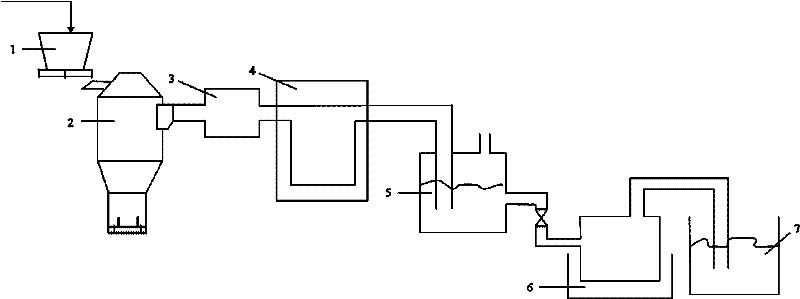
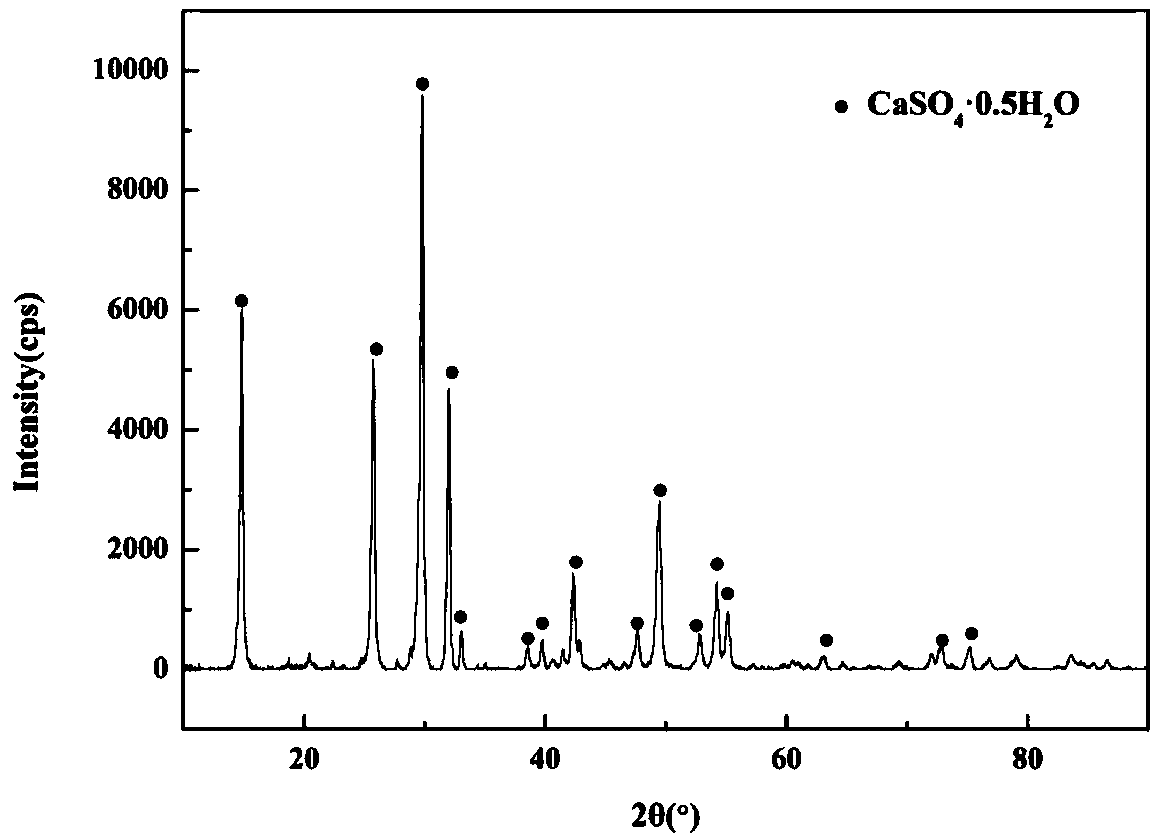
The invention discloses a method for extracting tungsten from scheelite, comprising the following steps of: mixing the scheelite with a mixed solution of phosphoric acid and sulfuric acid for reaction, adding dihydrate gypsum as seed crystals, and controlling the concentration of SO4<2->, the content of P2O5 and the reaction temperature to obtain the dihydrate gypsum with good filtering and washing properties. The invention has the advantages that one-step efficient normal pressure leaching of the scheelite is achieved, thus resources and energy consumption are saved, and the resolution ratio of the scheelite is up to above 98%; the problems of Cl<-> corrosion and serious HCl volatilization are overcome; the cyclic utilization of phosphoric acid is basically achieved, and the leaching cost and waste water discharge are greatly reduced; leaching equipment is simple, is convenient for operation and is easy to realize industrialization; the single and stable dihydrate gypsum is obtained, the filter efficiency of the dihydrate gypsum is high, the washing property of the dihydrate gypsum is good, and the P2O5 content in the washed dihydrate gypsum is reduced to be below 2%, thereby reducing the loss of phosphoric acid; and the passivation phenomenon of calcium sulfate solid film when the tungsten ore is leached is avoided.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Flotation and metallurgy method of high-bonding-ratio carbonate gangue-type oxygen-sulfur mixed copper ore
ActiveCN101831559AAvoid lostReduce consumptionFlotationProcess efficiency improvementCopper oxideOxygen
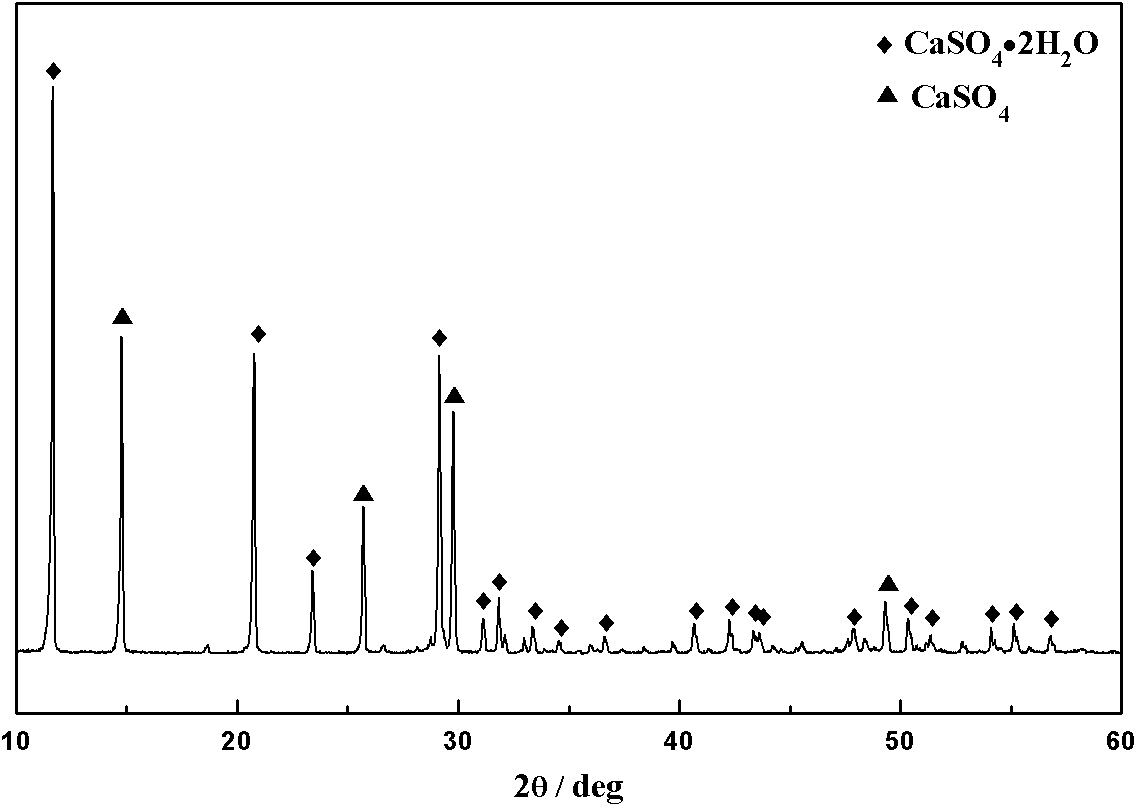
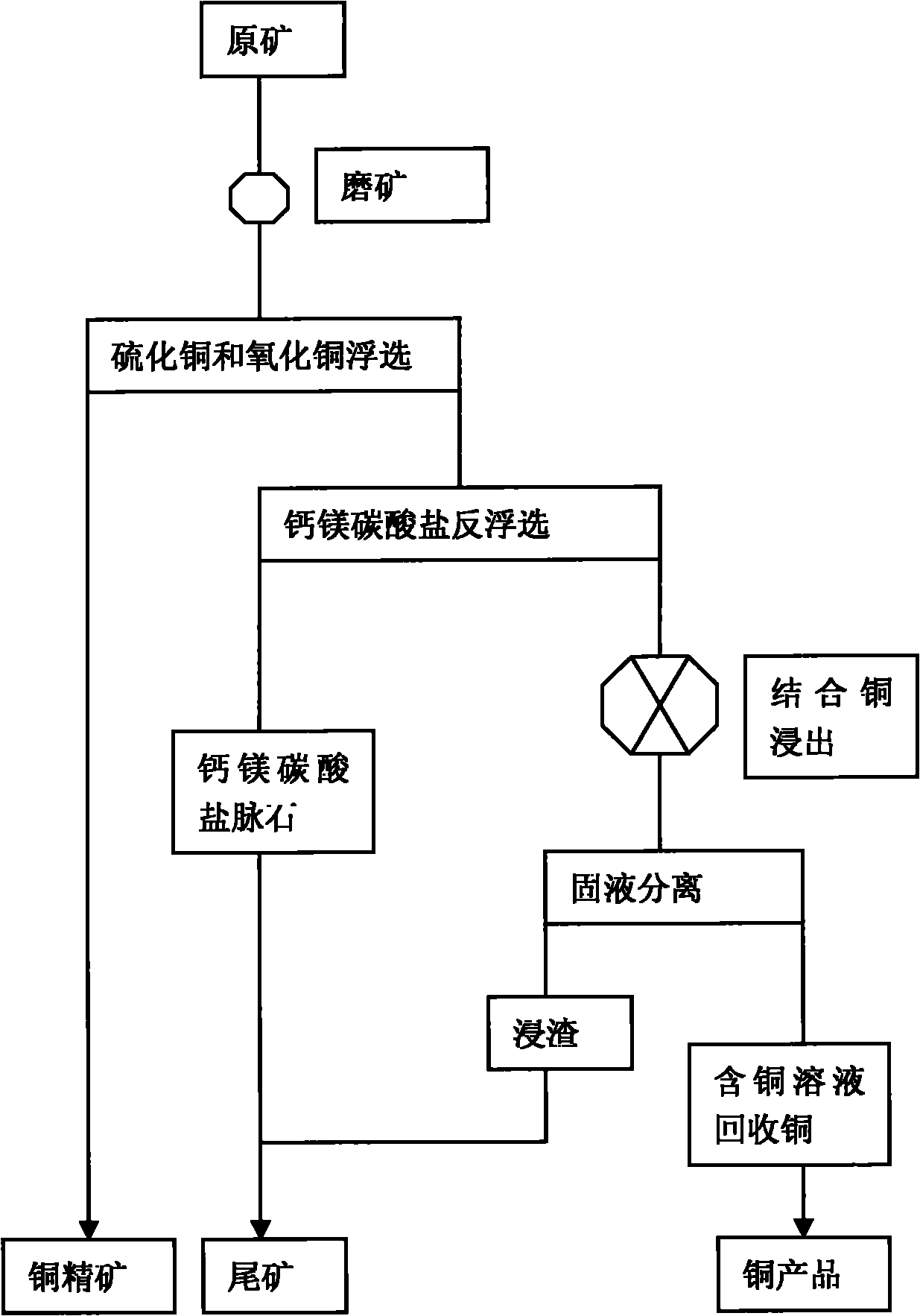
The invention relates to a flotation and metallurgy method of high-bonding-ratio carbonate gangue-type oxygen-sulfur mixed copper ore. The flotation and metallurgy method comprises the following steps of: firstly, recovering copper sulfide minerals and free copper oxide minerals in the high-bonding-ratio oxygen-sulfur mixed copper ore with high calcium-magnesium carbonate gangue mineral content by flotation; carrying out reverse flotation on calcium-magnesium carbonate ore in tailings obtained after floatation with fatty acid to obtain middlings containing combined copper and less calcium-magnesium carbonate minerals; then, adding sulphuric acid and stirring to leach out combined copper; and processing a copper-contained solution obtained after solid-liquid separation to obtain a copper product by a metallurgy method. The method combines the flotation and the metallurgy for complementary advantages, efficiently recovers and utilizes high-bonding-ratio carbonate gangue-type oxygen-sulfur mixed copper ore resources incapable of being processed at present, lessens the emission of castoff, such as carbon dioxide, magnesium calcium sulfate, and the like and has favorable economic benefits and environmental benefits.
Owner:YUNNAN TIEFENG MINING CHEM NEW TECH CO LTD
Method for extracting tungsten from scheelite and producing high-quality calcined gypsum
ActiveCN102021329AReduce lossesLow costCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesProcess efficiency improvementPhosphoric acidSeed crystal
The invention provides a method for extracting tungsten from scheelite and producing high-quality calcined gypsum, comprising the following steps: adding a mixed acid of phosphoric acid and sulphuric acid to decompose scheelite; and after decomposition, adding hydrated gypsum seed crystals to finish the dewatering conversion process of dihydrate gypsum to obtain hydrated gypsum with good properties. The invention has the following advantages: the efficient atmospheric pressure leaching of scheelite is realized, the resource and energy consumption is saved, and the decomposition rate of scheelite can reach over 98%; the serious problems of Cl<-> corrosion and HCl volatilization in the traditional acid decomposition process can be overcome; the recycling of phosphoric acid is basically realized, and the leaching cost and the wastewater discharge are greatly reduced; the leaching device is simple, the operation is convenient and industrialization is easy to realize; the obtained byproduct gypsum has pure quality and can be used to produce gypsum boards, and can be used in retarder, plaster and the like produced by using cement; and due to the recrystallization process, the P2O5 content in gypsum is further reduced to below 0.5%.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for continuously leaching sulfide ore by using synergy of autotrophic ore leaching bacteria and heterotrophic ore leaching bacteria
ActiveCN102329957AEliminate static clingImprove leaching efficiencyPregnant leach solutionSulfidation
The invention discloses a method for continuously leaching sulfide ore by using the synergy of autotrophic ore leaching bacteria and heterotrophic ore leaching bacteria, which comprises two main steps of preparing a compound ore leaching strain and leaching ore by using the compound strain. The step of preparing the compound ore leaching strain comprises the steps of selecting a strain, preparing a culture medium, compositely culturing the strain and domesticating the compound ore leaching strain. The step of leaching ore by using the compound strain comprises the steps of pretreating an ore sample, preparing an ore leaching culture medium, leaching the ore by using the compound ore leaching strain, selecting and adding semiconductor sulfide ore and extracting metals in the leaching liquids. In the method, the characteristic of the semiconductor sulfide ore to provide electrons to promote the ore leaching action of microbes in the electron transition process is utilized, so that the operating cost of the whole process is lowered, the ore leaching efficiency of the process is improved, and the method has broad application prospect in the field of metallurgy.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for recovering valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries
ActiveCN102534223AHigh recovery rateReduce leaching costsProcess efficiency improvementCooking & bakingManganese
The invention discloses a method for recovering valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. The valuable metals comprise nickel, cobalt, manganese, copper and ferrum. According to the method, the valuable metals, such as the nickel, the cobalt, the manganese, the copper and the ferrum, are recovered through the following steps of baking, sieving, magnetic separation, leaching, purification, crystallization and the like by taking the spent lithium-ion batteries as raw materials. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics that the disposal cost is low; the recovery rate of the nickel, the cobalt, the manganese, the copper and the ferrum is high; and greater economic benefits and social benefits can be generated.
Owner:HUNAN BRUNP RECYCLING TECH
Multistage counter current acid leaching process containing nickel serpentine ore
InactiveCN101058852AReduce leachingReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionReverse current
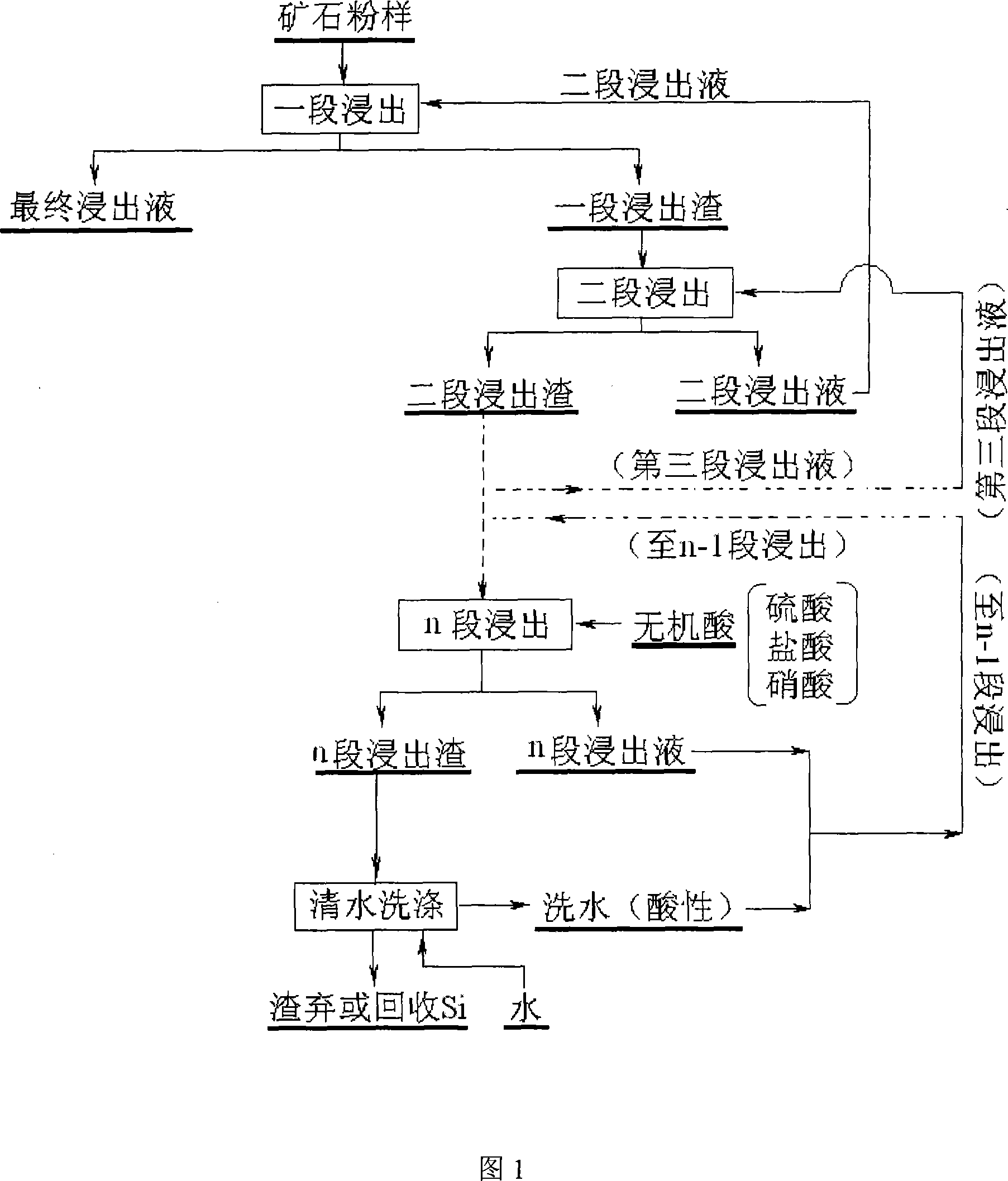
The invention discloses a nepouite with the multi-stage reverse-current acid-dipping technology, which comprises the following steps : grinding the nepouite; reacting with mixing the primary immersion liquid and water; reacting the leach residues a plurality of times endlessly; getting the K extract after finishing filtering the reaction of the k times; making the K extract liquor and the K extract react cyclically the k+1 times; regarding the k extract liquor as the extract liquor of the k-1 leaching reaction; regarding a corrosive acid as the extract liquor of the last leaching reaction; regarding the last extract liquor as a liquor containing Ni and Mg after n times reaction (k is between 1 and n and n is not less than 2). The invention reduces the cost, which recovers the Ni and Mg highly effectively.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for quickly leaching gold and silver by using mixed leaching agent
The invention discloses a method for quickly leaching gold and silver by using a mixed leaching agent, which comprises the following steps of: crushing gold-containing pyrite smelting slag, a sulfide-containing visible gold ore or / and a gold-containing oxidized ore serving as raw materials, conditioning the raw materials with water to form slurry, adding ammonium thiocyanate, thiocarbamide, urea and an oxidant, namely manganese dioxide or ferric chloride, into the ore slurry and stirring and leaching the mixed slurry to leach the gold and silver out. The method has the advantage that: the mixed leaching agent formed by adding the urea into the ammonium thiocyanate can quickly leach the gold and the silver out of the sulphur and arsen-containing gold ore by adding the urea with a low cost, particularly the gold and the silver which are contained in pyrolusite can be leached out with a lower cost. At the same time, beneficial elements in the ores can be comprehensively used.
Owner:梁伟基 +1
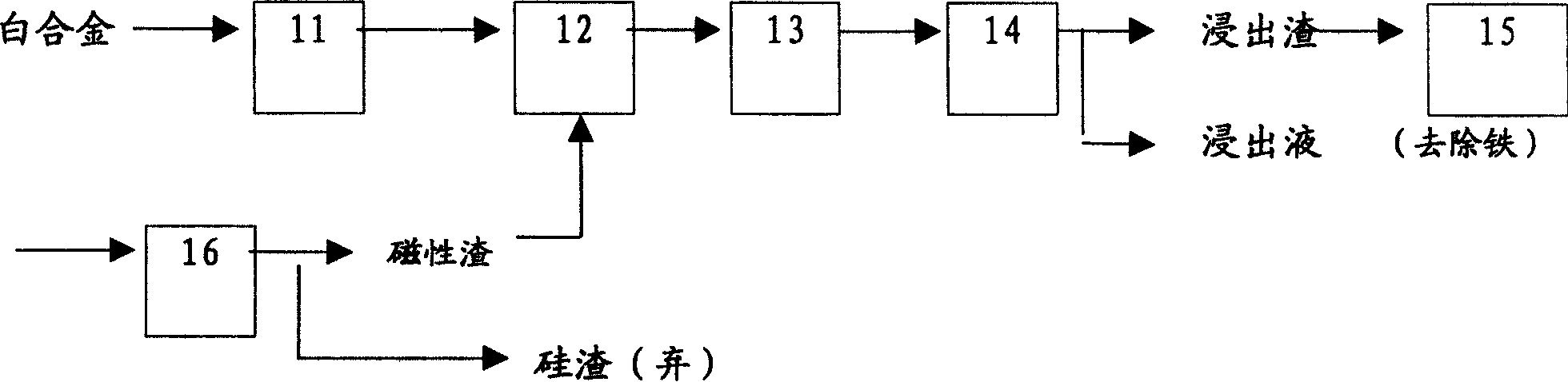
Method for leaching bidery metal by sulfuric acid and inflation agitation leaching trough
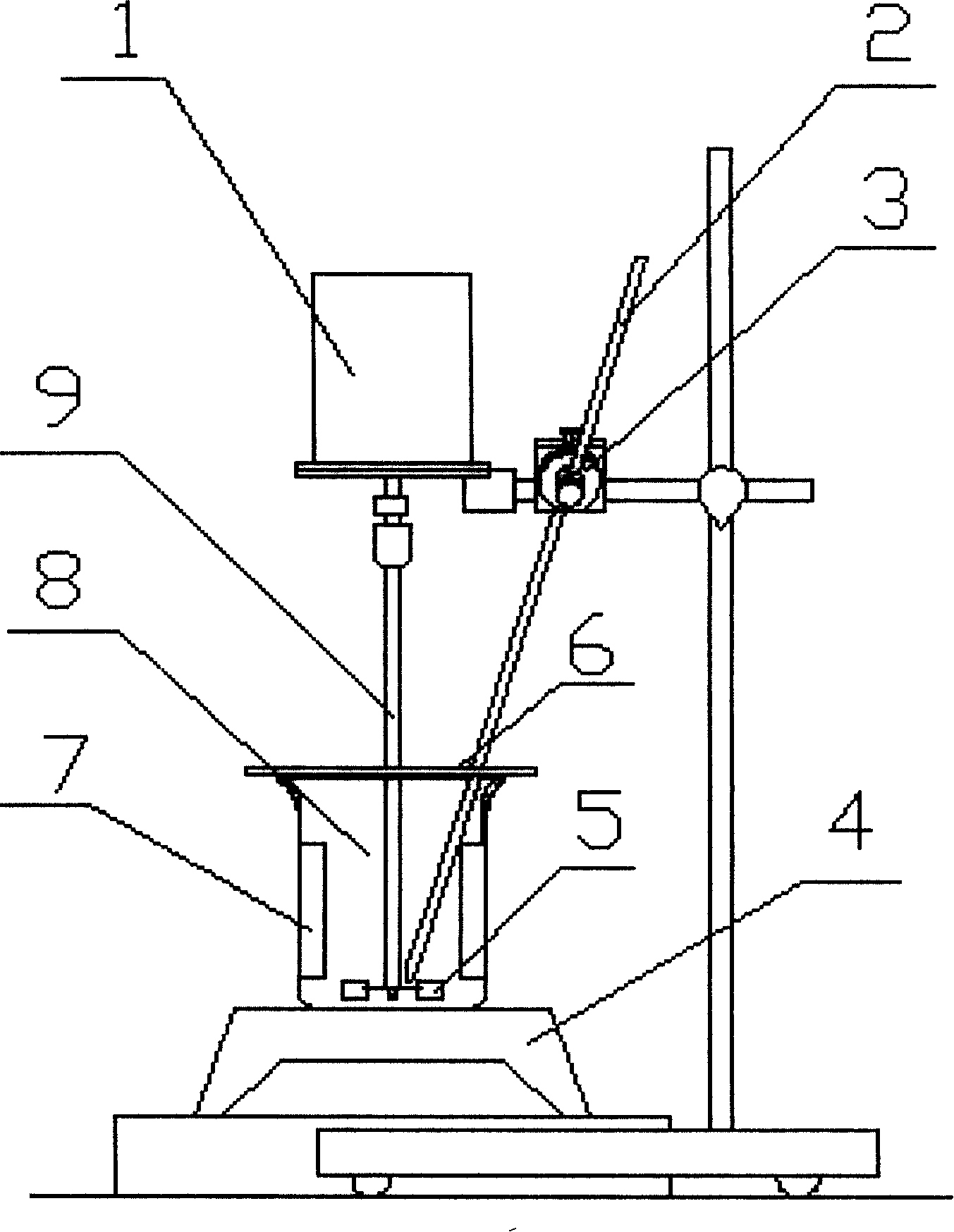
The invention relates to a method of lixiviating a white metal with vitriol and a charged churn of lixiviation tank. The method is as follows; the white metal is ground subtly as a lixiviation raw material; in lixiviation phase 1, add certain amount of white metal into a reactor, confect lixiviation solution with a liquid / solid ratio of 5:1 using H2SO4; churn lixiviate under the temperature of 85 - 100 DEG C; in lixiviation phase 2, lead the air to oxidize a lixiviated copper, under the temperature of 80- 85 DEG C, charge a turbine and churn lixiviate; slag and filtrate are generated after a filtration and rinse of pulp, magnetic material is selected and return to lixiviation phase 1; slag and filtrate are generated after the filtration and rinse of pulp, and the pulp is recycled; the lixiviation solution is used as the stock solution for the recycle of Cu and CO. Charge-churn the lixiviation tank comprises a stirrer, a beaker, the lixiviation tank is placed upon an electric cooker, a churn shaft and a blade are made of titanium, two pieces of PTFE baffles are arranged inside the beaker, a charging tube is a glass tube with a nozzle, the nozzle is positioned between the blade and the shaft, a lid is supplied on the beaker.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
Method for decomposing scheelite
ActiveCN103276208AReduce leaching costs and waste water dischargeSimple equipmentProcess efficiency improvementIon exchangeSolvent
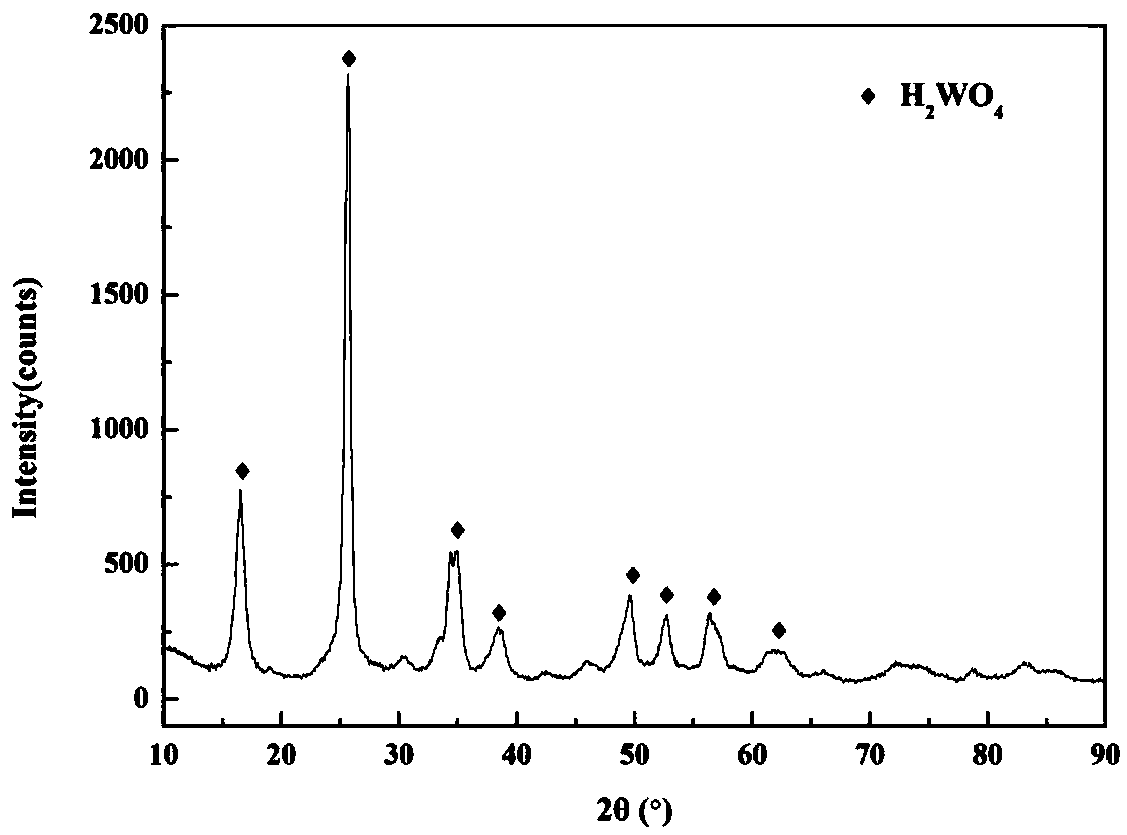
The invention provides a method for decomposing scheelite. The scheelite is decomposed by employing nitric acid, so that Ca in the scheelite can enter the solution in a form of soluble calcium nitrate; meanwhile, phosphoric acid or phosphorite (the phosphorite is decomposed into phosphoric acid through the nitric acid) serve as a tungsten complexing agent, so that WO3 in the scheelite enters the solution in a form of soluble phosphotungstic acid, the generation of solid tungstic acid membrane and slightly soluble calcium salt is avoided in the whole decomposition process, the calcium nitrate solution containing phosphotungstic acid, which is generated after decomposition, is extracted by employing a solvent and is subjected to ion exchange or ammonium salt precipitation method so that the phosphotungstic acid is recovered from the calcium nitrate solution; and sulfuric acid is added into the calcium nitrate solution from which tungsten is extracted and is combined with calcium ion in the solution so as to generate slightly soluble calcium sulfate precipitate, so that the nitric acid is regenerated; and the regenerated nitric acid return to a new round of mineral leaching process. The method has the advantages that tungsten in the tungsten mineral can be completely decomposed; the regenerated nitric acid is recycled, and the leaching cost and wastewater discharge are greatly reduced; and moreover, the treatment equipment is simple, the operation is convenient, and industrialization is easily realized.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
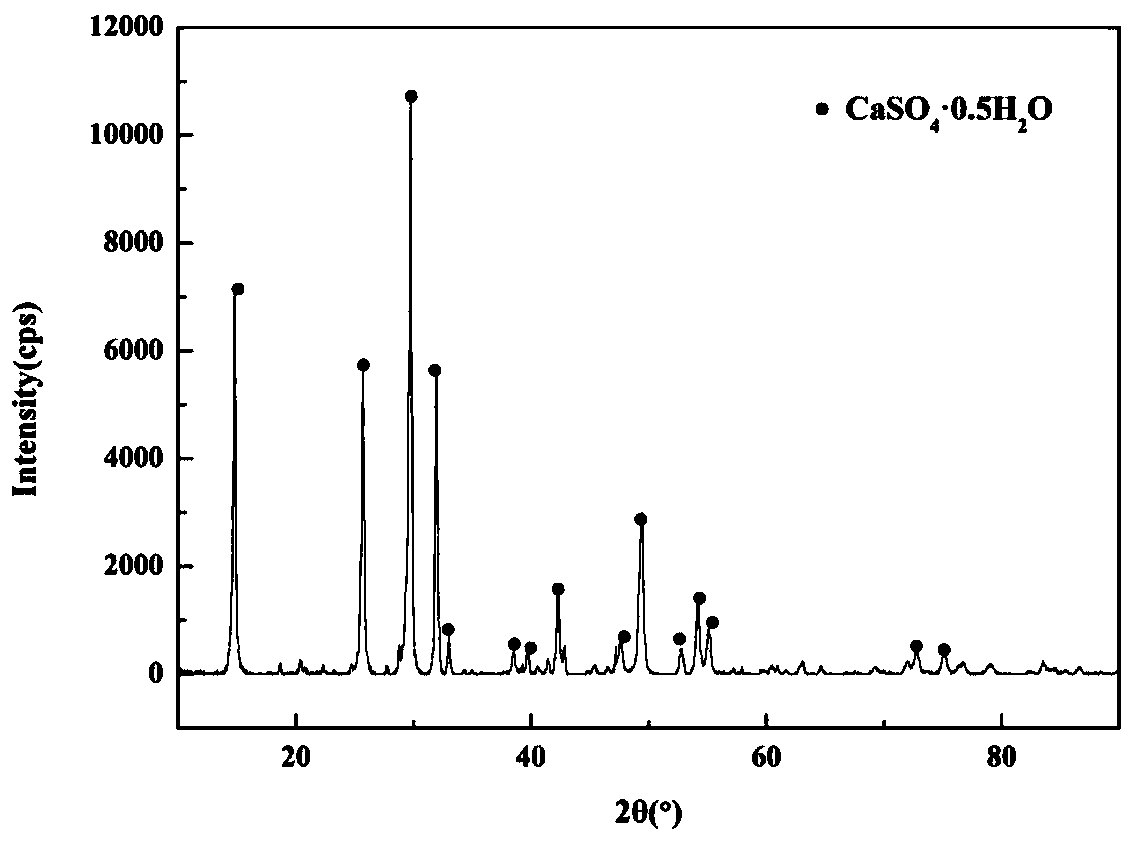
Method for comprehensively recycling tin and tungsten from high-tin-tungsten concentrates
ActiveCN107267782AEasy to handleImprove leaching rateCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesSulfur compoundsSlagFlue gas
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recycling tin and tungsten from high-tin-tungsten concentrates. The method comprises the steps that firstly, evenly-mixed high-tin-tungsten concentrates and vulcanizing agent gypsum are added into a fuming furnace for blowing; the furnace temperature and atmosphere are controlled by adjusting the coal-air ratio of the furnace; in the blowing process, tin volatilizes in a SnS gas manner to enter dust-containing flue gas, and the high-temperature dust-containing flue gas enters a settling chamber; and the high-grade tin concentrates are obtained in an electric dust collection manner, tungsten enters furnace slag, and the furnace slag is used for recycling tungsten. The method has the beneficial effects that tin is preferentially recycled through sulfidization of the fuming furnace, the tin recycling rate is greatly increased, and efficient separation of tungsten and tin is achieved; conversion of black tungsten into white tungsten in associated ore is achieved, and subsequent tungsten efficient extraction is facilitated; meanwhile, associated potassium-containing minerals are decomposed and can be removed through washing, and therefore the impurity removal pressure in the subsequent tungsten APT extraction and preparation process is relieved; generated gypsum residues are cyclically utilized, and residue discharge is reduced; and SO2-containing flue gas discharged in the fuming process is absorbed and prepared into sulfuric acid to be used for a subsequent tungsten leaching agent, and leaching cost is reduced.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Nickel oxide ore acid leaching solution two-step iron removal method
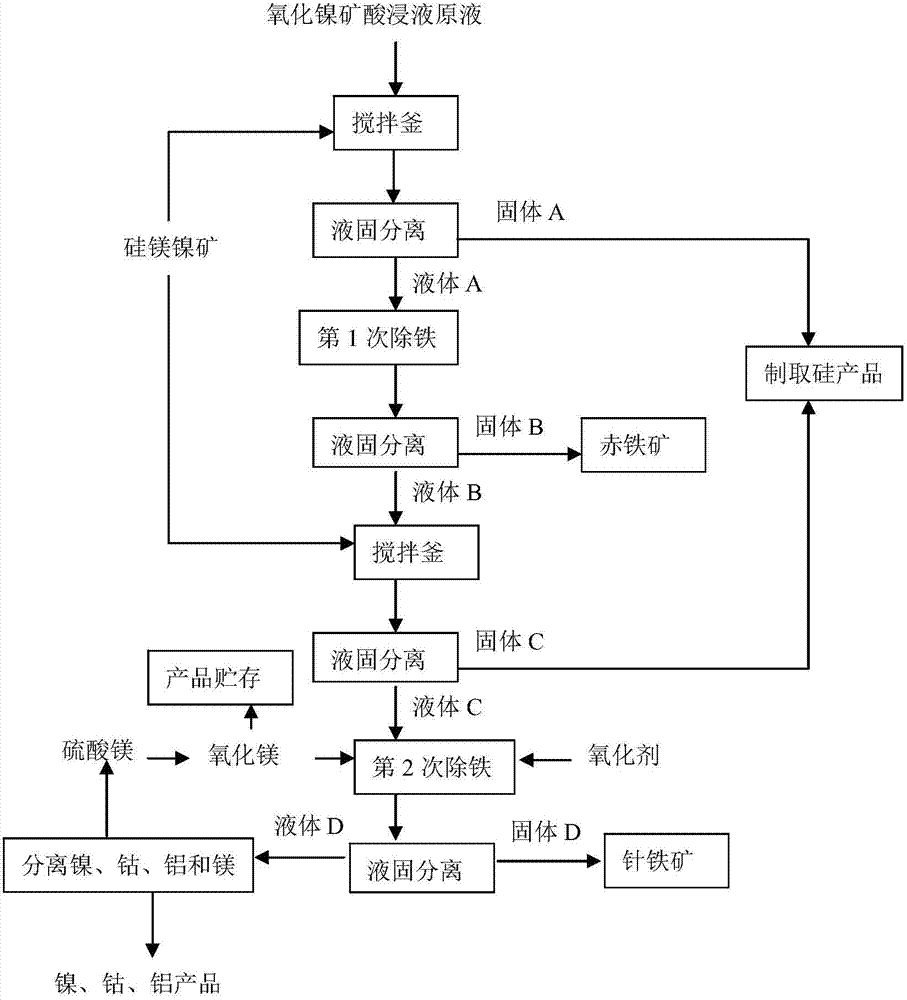
ActiveCN104120259ADeposit completelyAvoid interferenceProcess efficiency improvementDissolutionCobalt
The invention discloses a nickel oxide ore acid leaching solution two-step iron removal method. The method comprises the following steps: adding garnierite ore pulp into a nickel oxide ore acid leaching solution, stirring and reacting until the dissolution is completed and the pH value of the solution is more than or equal to 1.6, performing liquid-solid separation, raising the temperature of obtained liquid to 130-170 DEG C, stirring and reacting for 1-3 hours, performing liquid-solid separation, and drying a solid to obtain a hematite product; adding the garnierite ore pulp into the collected liquid for the second time, stirring and reacting until the dissolution is completed and the pH value of the solution is about 2, performing liquid-solid separation, and adding magnesium oxide and an oxidizing agent into the obtained liquid, or only adding the oxidizing agent; stirring and reacting for 0.5-4 hours, performing liquid-solid separation, and drying the solid to obtain a goethite product. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, complete iron removal can be achieved under a relatively mild condition; hematite and goethite which can be directly sold can be obtained; meanwhile, residual acid in the acid leaching solution and acid released in the iron deposition process are recycled; loss of nickel, cobalt, aluminum and magnesium in the leaching solution can not be generated.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Roasting-ammonia leaching processing method for brown iron type laterite nickel ore
A roasting-ammonia leaching processing method for brown iron type laterite nickel ore includes the steps that firstly, suspension fluidized roasting is performed on ore powder of the brown iron type laterite nickel ore and reduction gas, nickel oxide and cobalt oxide in the ore powder are fast and dynamically reduced into metal nickel and metal cobalt within 20-120 s, brown iron is reduced into magnetic iron, roasted ore is obtained, and according to the technological condition of roasting, temperature is 600-900 DEG C, and the volume percentage of CO in reducing gas is 2-7%; secondly, magnetic separation is performed on the roasted ore, and magnetite concentrate containing metal nickel and metal cobalt is obtained through separation; and thirdly, ammonia leaching is performed on the magnetite concentrate, and nickel and cobalt leaching agents and magnetic iron leaching slag are obtained. The method achieves the purpose of extracting and purifying nickel and cobalt and comprehensively recovering iron.
Owner:湖南长拓高科冶金有限公司
Cobalt copper sulfide ore processing method
ActiveCN102465202AImprove leaching efficiencyLow costProcess efficiency improvementChloric acidSulfite
The invention which is suitable for the technical field of mineral processing provides a cobalt copper sulfide ore processing method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, grinding the cobalt copper sulfide ore, mixing the cobalt copper sulfide ore with sulfurous acid or a sulfite according to a ratio of the total mass of cobalt and copper in the cobalt copper sulfide ore to the mass of sulfurous acid or the sulfite of 1:1-3, adding an acidic solution to adjust the pH value of the obtained system to 0.5-1, and reacting for more than 1h at 65-80DEG C; and 2, maintaining the pH value andthe temperature of the system, adding chloric acid or a chlorate according to a ratio of the total mass of residual cobalt and residual copper in the system to the mass of chloric acid or the chlorate of 1:1-3, and continuously reacting for more than 1h. The cobalt copper sulfide ore processing method of the invention, which allows cobalt and copper in the cobalt copper sulfide ore to be fully leached by carrying out primary leaching with sulfurous acid or the sulfite and carrying out secondary leaching with chloric acid or the chlorate, allows the leaching efficiency of cobalt and copper in the cobalt copper sulfide ore to be substantially improved. Sulfurous acid or the sulfite is used as an oxidant and a reductant in the primary leaching process, and chloric acid or the chlorate is used as an oxidant in the secondary leaching process, so the processing cost is substantially reduced.
Owner:GEM CO LTD +1
Method for producing hydrofluoric acid from fluorite as raw material
InactiveCN102556973ADecompose thoroughlyQuality improvementFluorine/hydrogen-fluorideDecompositionPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a method for producing hydrofluoric acid from fluorite as a raw material. The preparation process of the hydrofluoric acid is carried out in airtight reaction equipment. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing fluorite mineral powder and a mixed solution of phosphoric acid and sulfuric acid to form a mixed solution; adding the new mixed solution into an airtight reactor and reacting; adding dihydrate gypsum as a seed crystal and controlling the concentration of the phosphoric acid, the content of P2O5 and the reaction temperature to obtain favorable dihydrate gypsum with excellent filtering and washing performances; vacuumizing HF gas generated in the reaction process, exhausting and condensing; carrying out absorption and dehydration on the condensed HF gas by concentrated sulphuric acid; further rectifying the dehydrated gas to obtain the hydrofluoric acid; and complementing and decomposing the consumed sulfuric acid by using the defluorinated concentrated sulphuric acid and enabling the defluorinated concentrated sulphuric acid and filtrate to return to a new round of leaching step of the fluorite mineral powder. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that high-efficiency decomposition of fluorite mineral is realized and the leaching rate of fluorine reaches over 98 percent; the recycling of the sulfuric acid is basically realized, so that the leaching cost is greatly reduced; and the leaching equipment is simple in structure, convenient to operate and easy to realize the industrialization.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for leaching positive-negative pole material mixture of waste lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide battery
InactiveCN103757298AReduce leaching costsReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementBenzenePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for leaching a positive-negative pole material mixture of a waste lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide battery. The method comprises the steps of adding the positive-negative pole material mixture which is separated from the waste lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide battery and is subjected to roasting pretreatment, and high-concentration organic wastewater which does not contain benzene-ring substances into a reaction kettle which is resistant to pressure and the corrosion of sulfuric acid and nitric acid, adding a mixed solution of sulfuric acid and nitric acid, and leaching while stirring under closed conditions.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
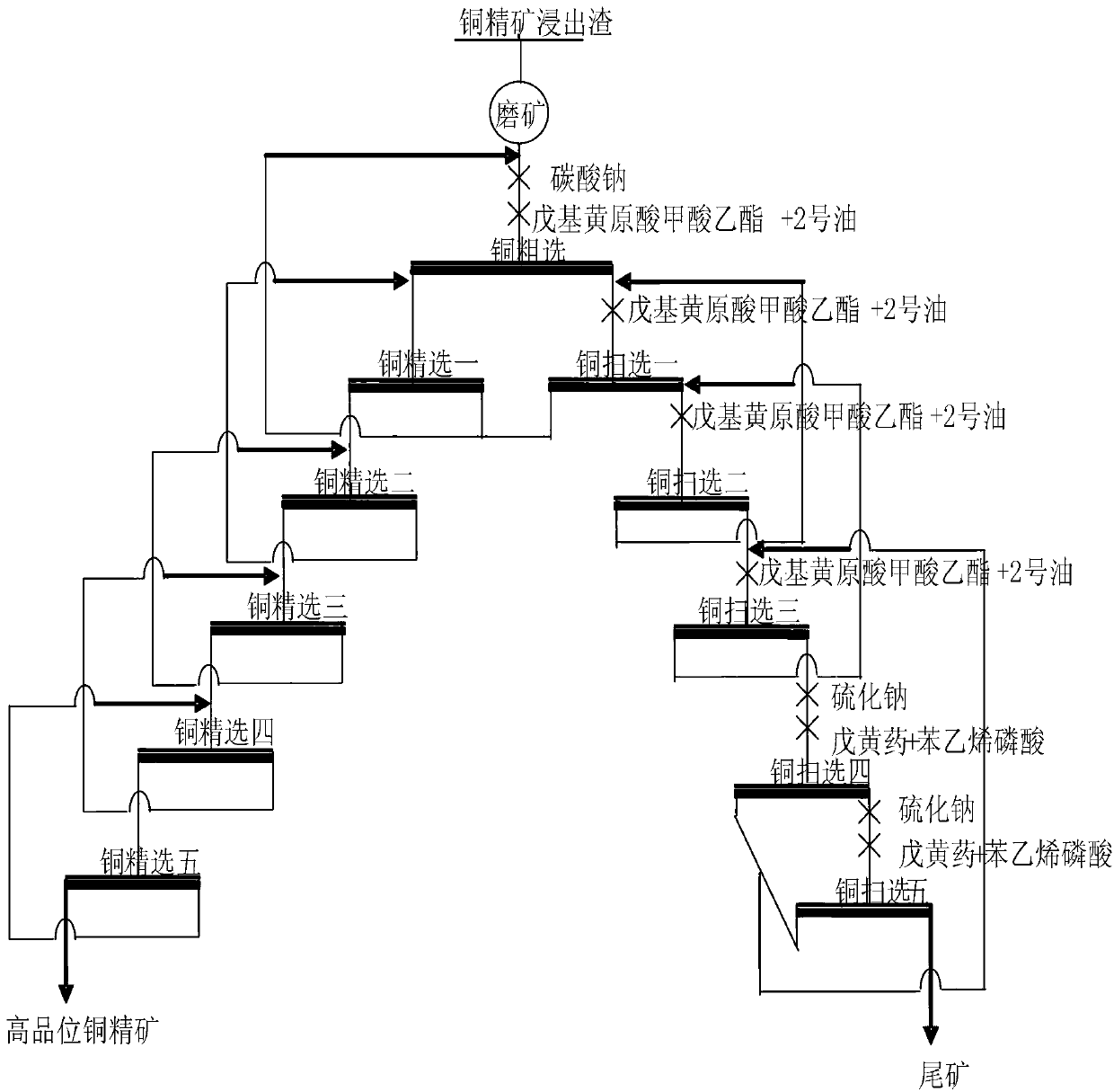
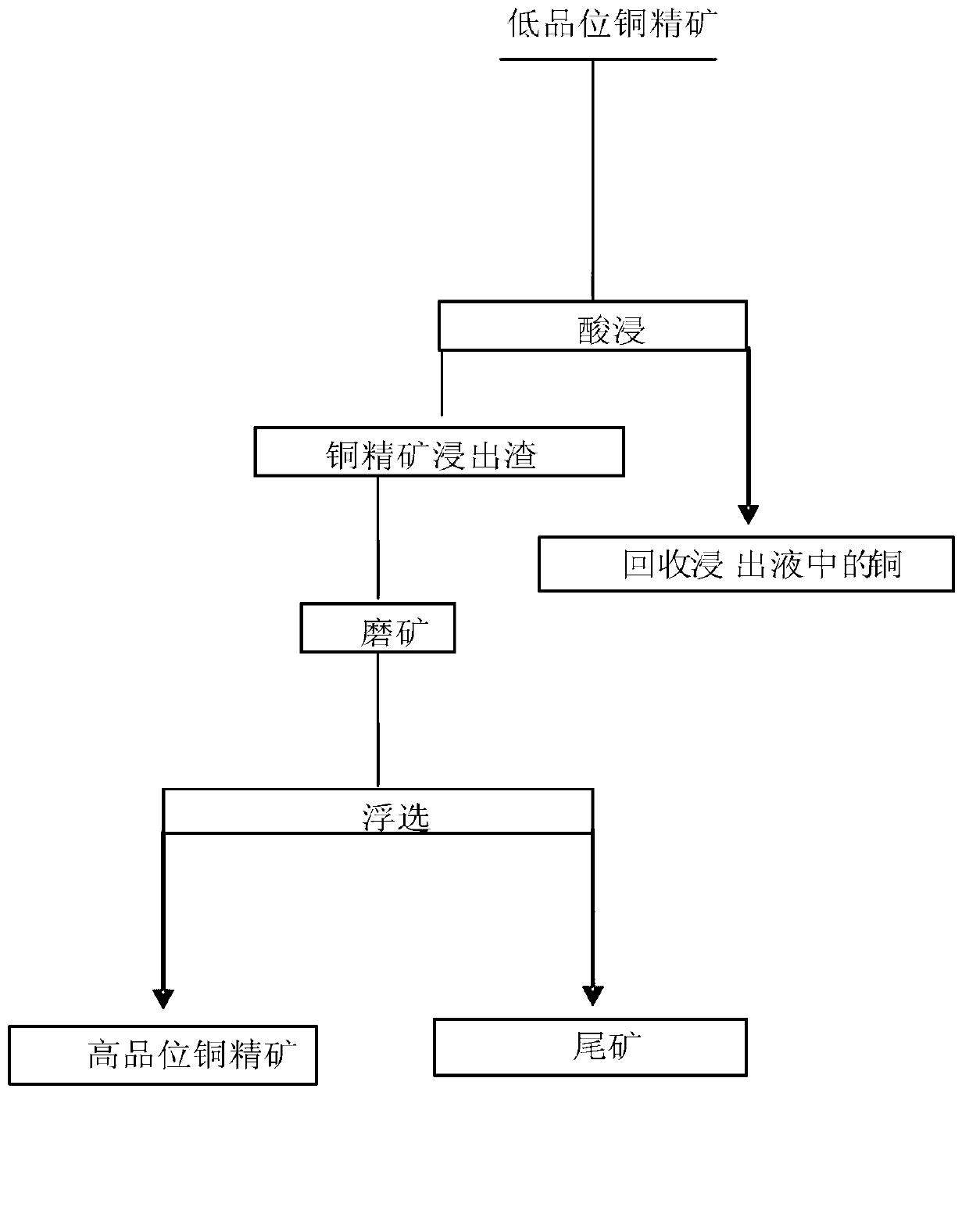
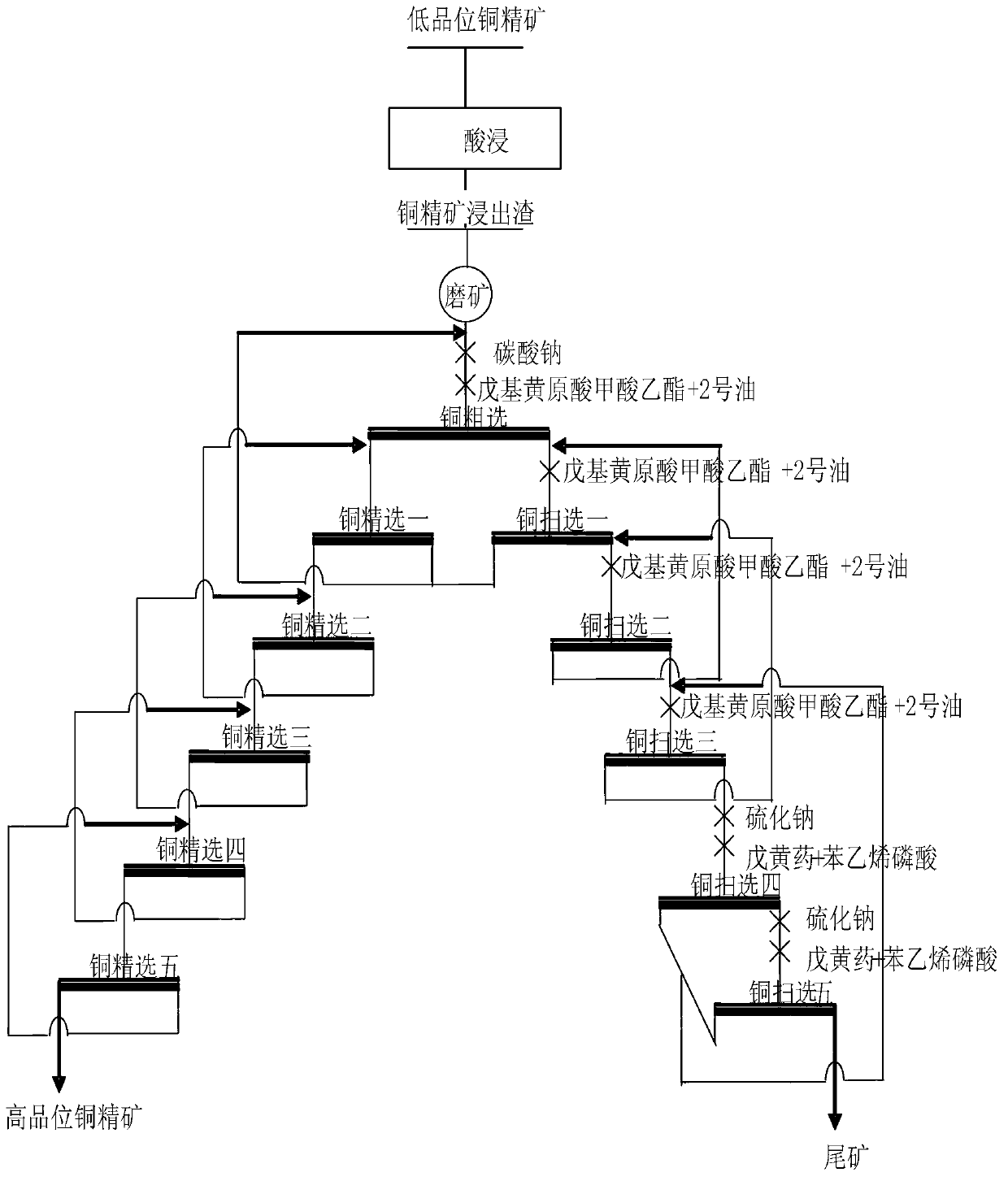
Treatment method for copper concentrate leached residues
The invention discloses a treatment method for copper concentrate leached residues. The method comprises the following steps of grinding and preparing ore pulp, and grinding a mixture of the copper concentrate leached residues and water to prepare the ore pulp, wherein particles of which particle sizes are smaller than 0.074mm in the ore pulp account for 90-95 percent of total particle weight; and performing flotation treatment on the ore pulp. Through adopting an ore grinding process, a rough concentration process and a refined concentration on the copper concentrate leached residues, copper sulfide ore which is relatively difficult to leach but is easy to float in copper ore are effectively recovered; copper in finally obtained copper concentrate reaches up to 69.86 percent in grade; and the recovery rate of the copper reaches up to 98.72 percent. For oxygen and sulfur mixed copper ore which is changeable in property, the process flows are very strong in adaptability. The leaching cost is effectively reduced, and the recovery rate of the copper is improved. Through treating low-grade copper concentrate leached residues, the copper content in finally obtained tailings is extremely low, and the waste of copper resources is avoided. The treatment method for the copper concentrate leached residues is simple in process, low in energy consumption, small in investment and high in recovery rate.
Owner:HUNAN RES INST FOR NONFERROUS METALS +1
Method for melting and solidifying heavy metal in waste burning fly ash
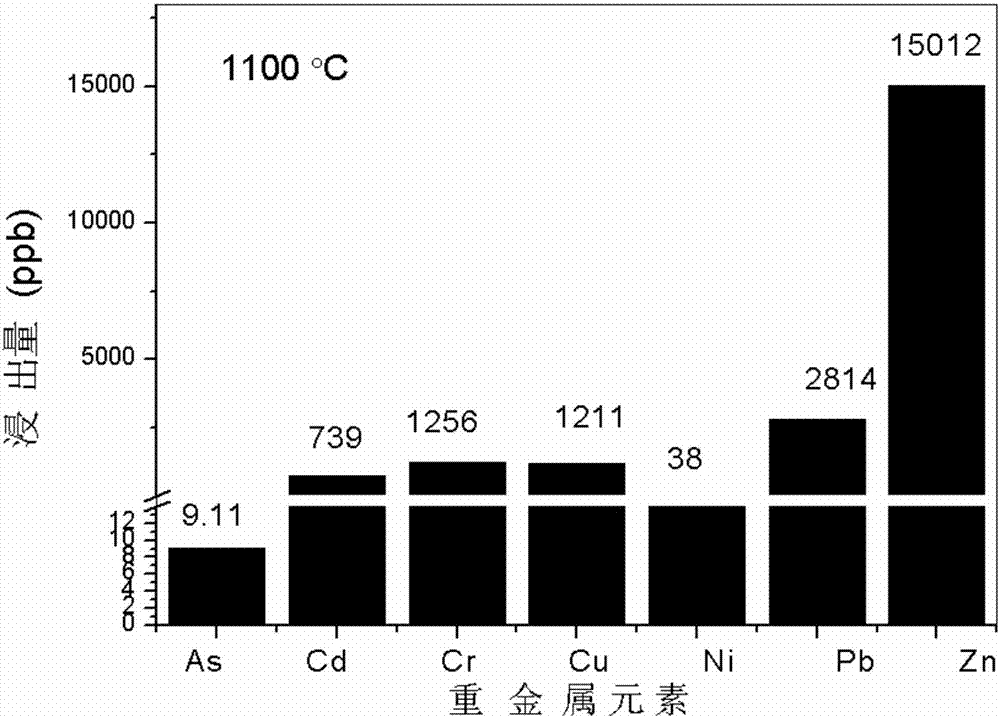
InactiveCN107252810AReduce leaching costsReduce control leaching costsTransportation and packagingSolid waste disposalMetal leachingResource utilization
The invention discloses a method for melting and solidifying heavy metal in waste burning fly ash and belongs to the technical field of solid waste utilization and pollution control. According to the method, the waste fly ash and blast furnace gas mud are mixed with the proportion being 9-1:1 and heated to 800-1200 DEG C, heat preservation is conducted for 0. 5-3 hours, and finally a molten solidified product is obtained. According to the national standard, the molten solidified product is subjected to leaching test of the heavy metal of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pd and Zn, and the result shows that the solidified product completely meets the national emission standard. Compared with a traditional method, the blast furnace gas mud is utilized to melt and solidify the heavy metal in the waste burning fly ash at the high temperature, leaching of the heavy metal in the fly ash and environmental pollution can be effectively reduced, thus the limit that an existing heavy metal solidifying technology solely relies on first resources and chemical reagents is overcome, and a new way is also provided for harmlessness and resource utilization of the blast furnace gas mud while heavy metal pollution of the waste burning fly ash is reduced.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
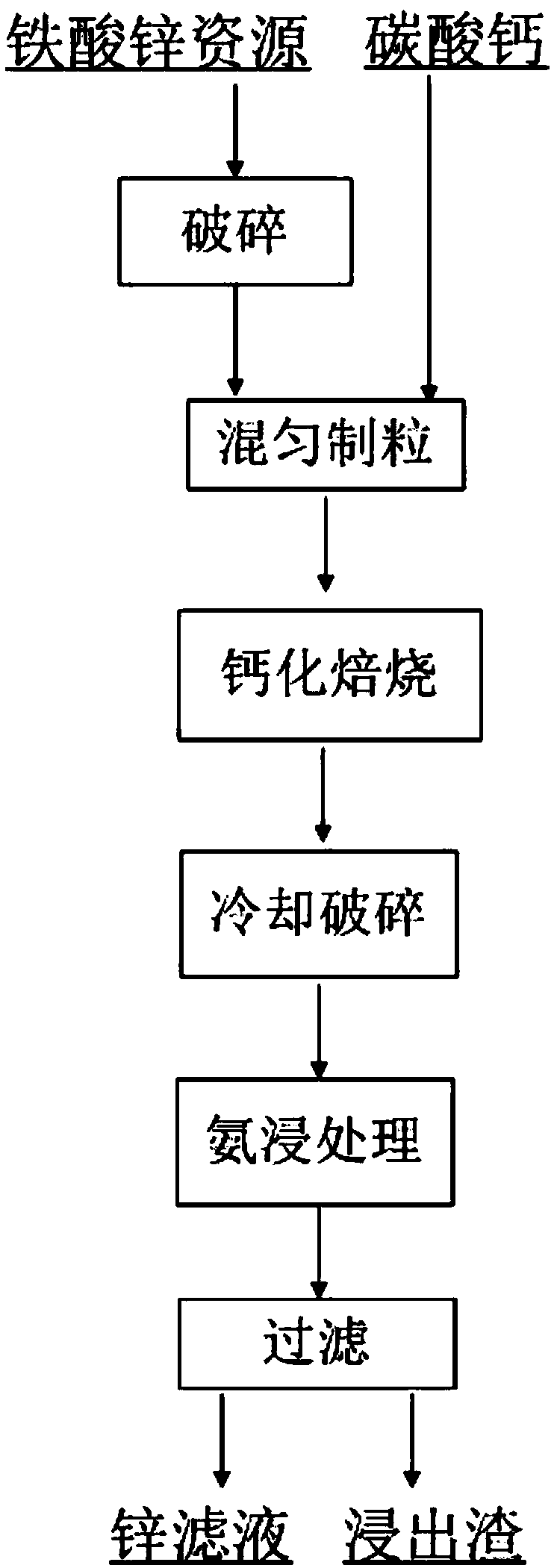
Method of recycling zinc from zinc ferrite resource by using calcium roasting-ammonia leaching process
InactiveCN108913907AReduce leaching costsGood choiceProcess efficiency improvementReaction rateCarbonization
The invention discloses a method of recycling zinc from a zinc ferrite resource by using a calcium roasting-ammonia leaching process, belonging to the technical field of mineral processing. The methodof recycling the zinc from the zinc ferrite resource by using the calcium roasting-ammonia leaching process comprises the following steps of: step (1) crushing raw ores to obtain the zinc ferrite resource with the predetermined fineness; step (2) adding a calcifying agent to the zinc ferrite resource, fully mixing, then pelletizing, and carrying out calcium roasting on the mixture in an oxidizingatmosphere, so that zinc ferrite is subjected to mineral phase reconstruction and is transformed into zinc oxide, thereby obtaining a calcium roasting product; and step (3) crushing the calcium roasting product, dissolving and leaching the zinc oxide by ammonia-leaching treatment, and obtaining zinc filtrate and leached residues after solid-liquid separation. According to the method, the zinc ferrite is subjected to mineral phase reconstruction and is transformed into the zinc oxide by the calcium roasting, and thus, the follow-up ammonia leaching extraction is facilitated; the leaching costis low; the selectivity is good; the calcifying agent adopted is low in cost and easily available; and compared with pyrogenic process carbonization reduction, the method has the advantages that cokeor reducing coal does not need to be added as a reducing agent, the reaction rate is fast, and the zinc leaching rate can reach above 90%.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for leaching valuable metal
InactiveCN102534247AReduce leaching costsImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementNickelOxidizing agent
The invention discloses a method for leaching valuable metal. The valuable metal is either nickel or cobalt or both; and the method comprises the following steps of: mixing two nickel-cobalt-containing materials with oxidizability and reducibility according to a certain ratio, and leaching the valuable metal from the mixed raw materials by using acid. According to the method, the nature that the oxidizability and the reducibility of the two nickel-cobalt-containing materials are complementary is fully utilized, the consumption of substances, such as a reductant and an oxidant and the like, is reduced, the method is environment-friendly and energy-saving, and the leaching efficiency of the valuable metal is high and the processing cost is low, so that the method has greater social and economic benefits.
Owner:HUNAN BRUNP RECYCLING TECH
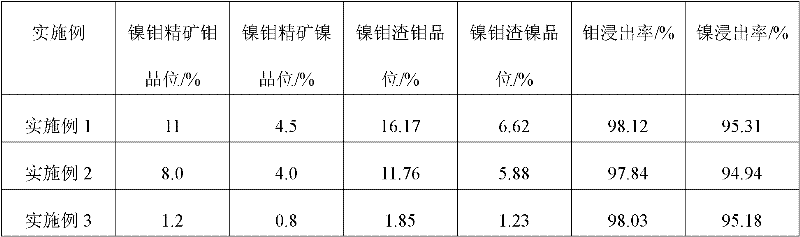
Fluidized furnace device for roasting nickel-molybdenum concentrate and method for roasting nickel-molybdenum concentrate
InactiveCN102268538ARaise the gradeAddressing high organic carbon contentEffective solutionFluidized bed
The invention discloses a fluidized furnace device for roasting nickel-molybdenum concentrate and a method for roasting nickel-molybdenum concentrate, comprising a feeder, a fluidized furnace body, a dust removal device, a condensing device, and an organic amine SO2 absorption device connected sequentially through pipelines, Water area heating device and contact acid making device. The technical effect of the present invention is that the nickel-molybdenum slag whose nickel-molybdenum grade is increased by about 45% can be obtained from the nickel-molybdenum concentrate obtained by flotation; for smelting, the leaching cost is greatly reduced and the processing capacity is increased; It effectively solves the problem of high organic carbon content in black rock series nickel-molybdenum concentrate; after roasting, the arsenic in nickel-molybdenum concentrate is released, which solves the harm caused by arsenic in the subsequent leaching process; the sulfur released by roasting is directly made into Sulfuric acid has become the main reagent for leaching nickel and molybdenum slag.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for extracting tungsten through scheelite decomposing
ActiveCN109680148AReduce emissions and reagent costsIncreased thermodynamic driving forceProcess efficiency improvementCorrosionHydrogen peroxide
The invention discloses a method for extracting tungsten through scheelite decomposing. The method mainly comprises the following steps that a sulfuric acid-hydrogen peroxide mixed solution is prepared, after the temperature is increased to the temperature required by a reaction, scheelite is added into a reactor to be decomposed, after the reaction is finished, the tungsten is extracted from obtained filtrate, and after hydrogen peroxide and sulfuric acid are supplemented, the leaching step is conducted. The method has the advantages that efficient normal-pressure leaching of the scheelite isachieved, no impurity is brought into the leaching process, energy sources are saved, follow-up impurity removal burden is lowered, and the tungsten leaching rate reaches 98% or above; hydrochloric acid volatilization and corrosion in the traditional acid decomposing process are avoided; influence of tungstic acid generation on the leaching process is overcome; the leaching agent can be recycled,the leaching cost is greatly reduced, and waste water emission is decreased; the leaching process is easy to operate, and industrialization is easy to achieve; and the obtained leached residues are gypsum good in filtering performance.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
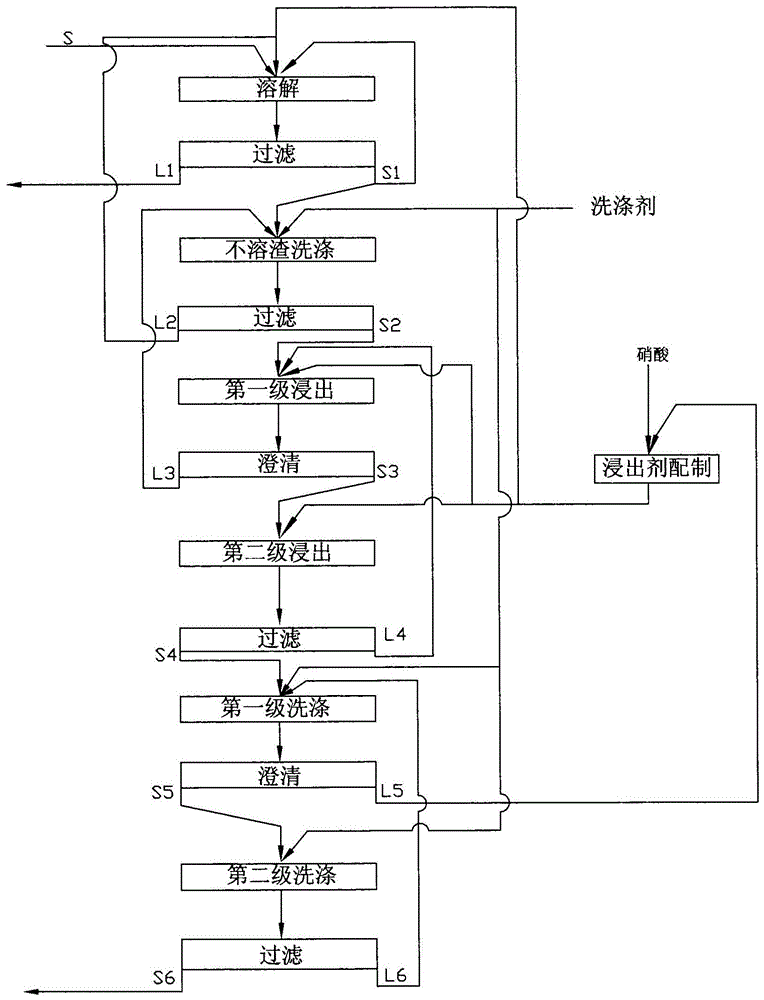
Method for leaching uranium in radioactive alkali residues
ActiveCN105969987AImprove leaching rateReduce leaching costsProcess efficiency improvementRefluxWastewater
The invention provides a method for leaching uranium in radioactive alkali residues. The radioactive alkali residues are dry alkali residues which are finally formed after uranium-containing waste residues obtained through precipitation under alkaline conditions are filtered and forged at 800 DEG C in the uranium-containing wastewater treatment process. Multi-stage reflux dissolving leaching is adopted in the method, the method mainly includes the steps of alkali residue circulating dissolving, filtering, undissolved residue washing, filtering, undissolved residue first-stage leaching, clarifying, undissolved residue second-stage leaching, filtering, leached residue first-stage washing, clarifying, leached residue second-stage washing and filtering, leached tailings S6 are obtained after filtering, and the leached tailings S6 are subjected to neutralizing treatment and are conveyed to a disposal site. The method for leaching uranium in the radioactive alkali residues is simple in technical process, process solutions can be recycled, the uranium leaching rate is high, leaching cost is low, no wastewater is generated, and the content of uranium in the leached tailings S6 is lower than 0.1%.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV +1
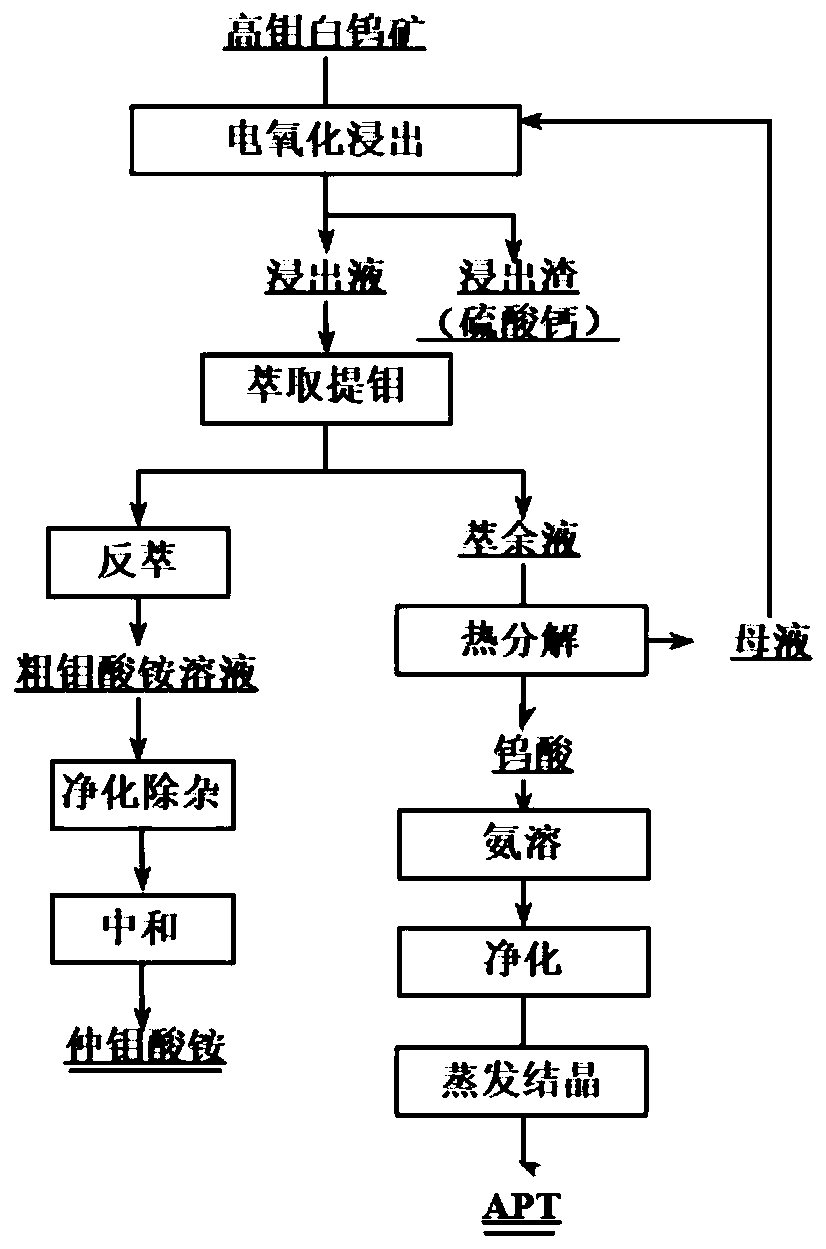
Method for extracting tungsten and molybdenum by decomposing high-molybdenum scheelite by electro-oxidation method
ActiveCN109763003AReduced activityAchieve separationProcess efficiency improvementDecompositionAmmonium paratungstate
The invention relates to a method for extracting tungsten and molybdenum by decomposing high-molybdenum scheelite by an electro-oxidation method. The method comprises the steps that electro-oxidationleaching of the high-molybdenum scheelite is carried out in a sulfuric acid system, coordination of tungsten and molybdenum with active oxygen generated by an anode to form soluble peroxy tungstic acid and peroxy molybdic acid, solid-liquid separation is carried out after complete decomposition, and ammonium paramolybdate is obtained after filtrate is subjected to processes of extraction of molybdenum-back extraction-removing impurities, raffinate is subjected to high temperature decomposition or SO2 reduction to obtain powdery tungstic acid, after hydrogen peroxide and sulfuric acid are addedinto mother liquor for supplement to initial concentration, returning leaching is carried out, and ammonium paratungstate is obtained after tungstic acid is subjected to processes of ammonia neutralization-removing impurities and the like. The method realizes high-efficiency normal-pressure leaching of the high-molybdenum scheelite, any impurities does not be introduced in the leaching process, energy is saved, subsequent purification burden is reduced, and the leaching rates of tungsten and molybdenum in the leaching process can reach more than 98%; the separation process of tungsten and molybdenum can realize extraction and molybdenum extraction without additional reagents, and the separation efficiency is high; the produced tungstic acid has less impurity content, a leaching agent canbe recycled, and the leaching cost and wastewater discharge are reduced; and the process is easy to operate.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
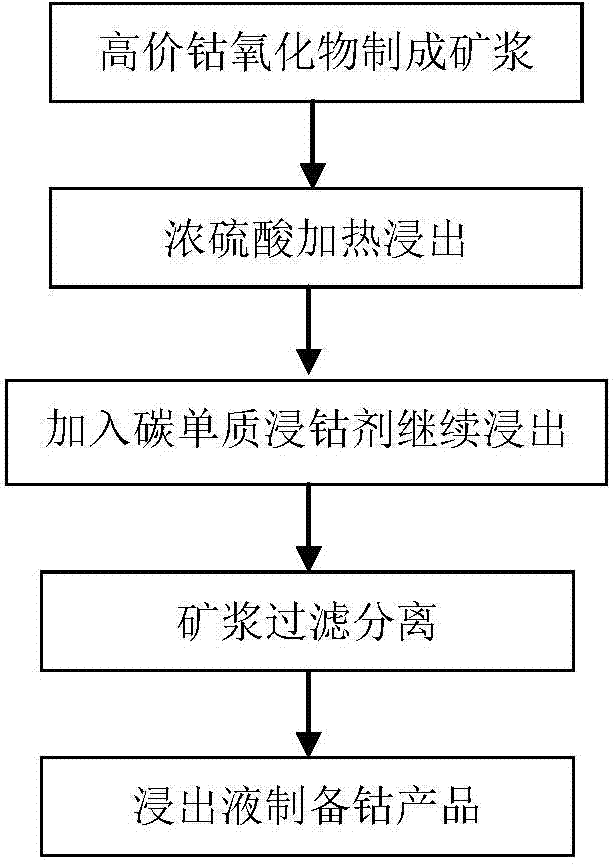
Economical, clean, simple and convenient method for leaching cobalt from high-valence cobalt oxides
ActiveCN103882226ASimplify the leaching processReduce production energy consumptionProcess efficiency improvementSlagLeaching rate
The invention discloses an economical, clean, simple and convenient method for leaching cobalt from high-valence cobalt oxides, and relates to a technology of leaching cobalt from cobalt oxide ores such as asbolite. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a carbon elementary-substance cobalt leaching agent without environmental pollution, which is not used yet at home and abroad, is used by aiming at shortages existing in the prior art, the cobalt leaching agent is low in price, material-saving, ubiquitous, and capable of leaching the high-valence cobalt oxides until the cobalt content of slag is about 0.02% in case of being simply poured in a leaching tank, and the cobalt leaching rate achieves 98%. During the leaching process, gases harmful to environment, such as SO2 and Cl2 are not generated, and the technical process is simplified, so that the method is an economical, clean, simple and convenient method for leaching cobalt from high-valence cobalt oxides.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY +1
Method for efficiently leaching lithium from lithium-containing clay rock
InactiveCN111575504AReduce leaching costsGood economic foundationProcess efficiency improvementMuffle furnaceHeat conservation
The invention discloses a method for efficiently leaching lithium from lithium-containing clay rock. The method comprises the following steps of: crushing raw ore, adding the crushed raw ore into a rod mill for grinding, filtering, drying, scattering, uniformly mixing a sample and concentrated sulfuric acid according to a ratio, putting the mixture into a muffle furnace for heat preservation, taking out the sample, naturally cooling, scattering, stirring and leaching according to a ratio of the sample to water, and filtering after stirring to obtain a leaching solution. The leaching method disclosed by the invention is low in energy consumption, simple in process, low in production cost and convenient for subsequent industrial production.
Owner:贵州锂电新能源科技有限公司 +1
Method for extracting tungsten and molybdenum by decomposing high-molybdenum scheelite
InactiveCN109628737AAchieve separationReduce the burden onProcess efficiency improvementTungsten compoundsAmmonium paratungstateRaffinate
The invention discloses a method for extracting tungsten and molybdenum by decomposing high-molybdenum scheelite. The method comprises the steps that a sulfuric acid-hydrogen peroxide mixed solution is prepared, the high-molybdenum scheelite is added into a reactor to be decomposed after the temperature rises to the temperature needed by reacting, filtrate obtained after reacting is subjected to the processes of molybdenum extraction, reverse extraction, impurity removal and the like to obtain ammonium paramolybdate, raffinate is decomposed at high temperature or reduced through SO2 to obtainpowdery tungstic acid, mother liquid is added into hydrogen peroxide and sulfuric acid till the initial concentration is obtained and then returns to the leaching process, the tungstic acid is subjected to the processes of ammonia neutralization, impurity removal and the like, and then ammonium paratungstate is obtained. According to the method, efficient normal-pressure leaching of the high-molybdenum scheelite is achieved, no impurity is introduced in the leaching process, energy sources are saved, the subsequent purification burden is reduced, and the tungsten and molybdenum leaching rate in the leaching process can reach 98% or above; molybdenum extraction can be achieved without adding a reagent in the tungsten and molybdenum separating process, and the separating efficiency is high;the thermal decomposition or reduction process achieves the impurity removal effect, the content of produced tungstic acid impurities is low, a leaching agent can be cyclically used, and the leachingcost and wastewater drainage are reduced; and the technological process is easy to operate.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Leaching method of uranium in radioactive alkali slag
ActiveCN105969987BImprove leaching rateReduce leaching costsProcess efficiency improvementWastewaterLeaching rate
The invention provides a method for leaching uranium in radioactive alkali residues. The radioactive alkali residues are dry alkali residues which are finally formed after uranium-containing waste residues obtained through precipitation under alkaline conditions are filtered and forged at 800 DEG C in the uranium-containing wastewater treatment process. Multi-stage reflux dissolving leaching is adopted in the method, the method mainly includes the steps of alkali residue circulating dissolving, filtering, undissolved residue washing, filtering, undissolved residue first-stage leaching, clarifying, undissolved residue second-stage leaching, filtering, leached residue first-stage washing, clarifying, leached residue second-stage washing and filtering, leached tailings S6 are obtained after filtering, and the leached tailings S6 are subjected to neutralizing treatment and are conveyed to a disposal site. The method for leaching uranium in the radioactive alkali residues is simple in technical process, process solutions can be recycled, the uranium leaching rate is high, leaching cost is low, no wastewater is generated, and the content of uranium in the leached tailings S6 is lower than 0.1%.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV +1
Method for reduction leaching of manganese oxide ore through cassava starch
The invention belongs to the technical field of manganese metallurgy, and particularly relates to a method for reduction leaching of manganese oxide ore through cassava starch. According to the method, the cassava starch is used as a reducing agent, and reduction leaching of the manganese oxide ore is achieved in a sulfuric acid water solution medium. By adoption of the method, reduction leachingof the manganese oxide ore is conducted, the adopted cassava starch is low in cost and wide in source, the leaching cost is reduced, the manganese oxide ore is high in reduction leaching speed, high in efficiency and high in manganese leaching rate, and the manganese leaching rate reaches 92% or above. Lixivium obtained by adopting the method for reduction leaching of the manganese oxide ore through the cassava starch is small in impurity content, components are simple, and influences on the later electrolysis technology efficiency are weak.
Owner:DAXIN MANGANESE MINE BRANCH OF CITIC DAMENG MINING IND
Method for leaching metal in vanadium titano-magnetite through full acid method
InactiveCN108165741ALarge specific surface areaChange shapeProcess efficiency improvementResource utilizationSlag
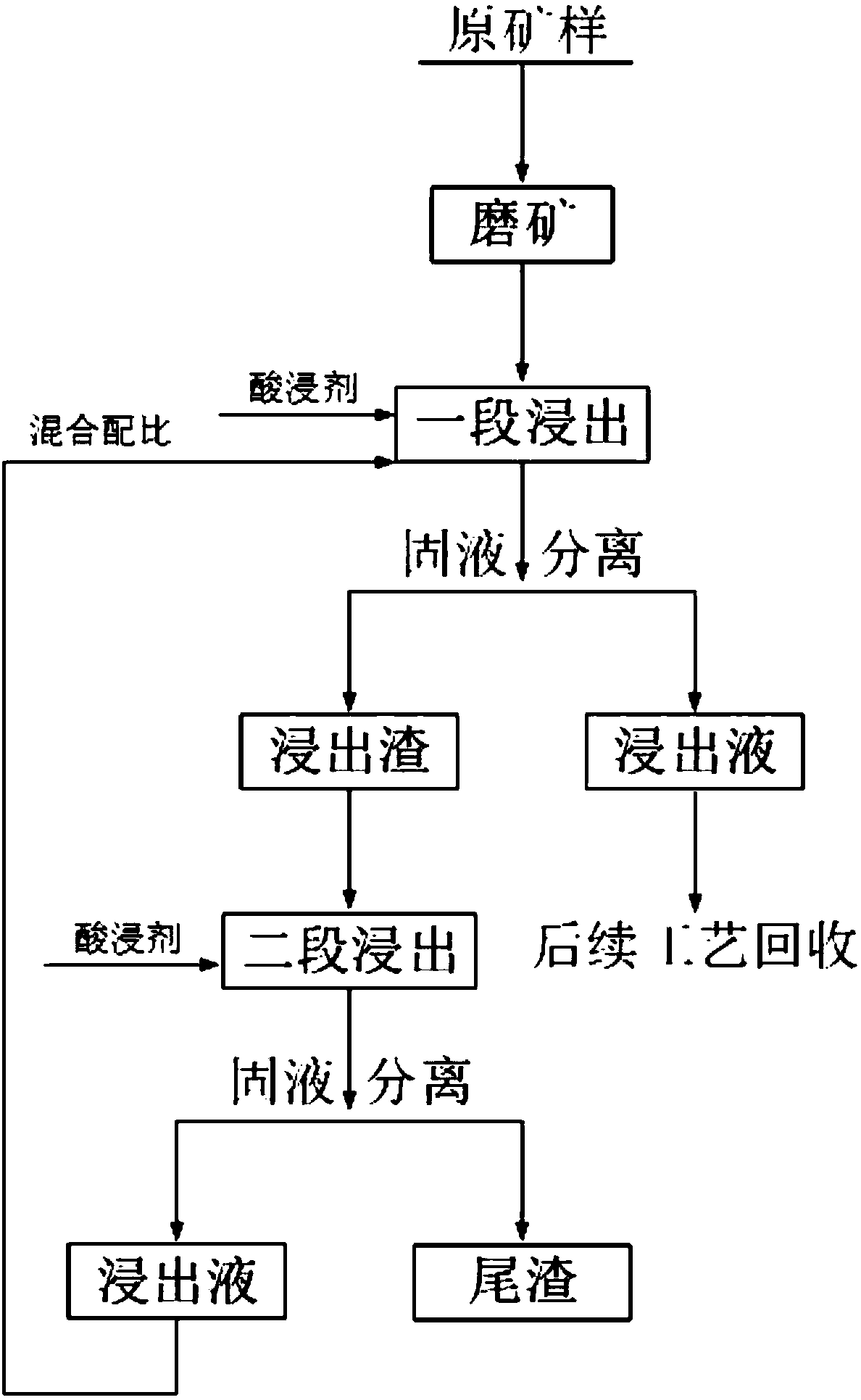
The invention discloses a method for recycling valuable metal in vanadium titano-magnetite through acid high-pressure leaching. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a vanadium titano-magnetiteconcentrate is mechanically activated; secondly, first acid liquid is provided as a leaching agent, the leaching agent is added into the vanadium titano-magnetite concentrate treated in the first step, and first-segment leaching is carried out; thirdly, solid-solution separation is carried out to obtain first leaching liquid and first leaching slag; fourthly, second acid liquid is provided as a leaching agent, and is added into first leaching slag to be subject to second-segment leaching; fifthly, solid-solution separation is carried out to obtain tailings and second leaching liquid, and thesecond leaching liquid is subject to certain proportion treatment to be circularly used as the first acid liquid; sixthly, the first leaching liquid is subject to subsequent extraction-separation-step-by-step crystallization and sedimentation-separation process recycling. Two-segment leaching is adopted to sufficiently recycle valuable metal in ore, the recycling effect is good, the leaching rateis stable, and the recycling rate of valuable metal elements of vanadium, titanium and iron can reach 95% or above, and the resource utilization rate is high.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com