Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41results about How to "Lower magnesium levels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
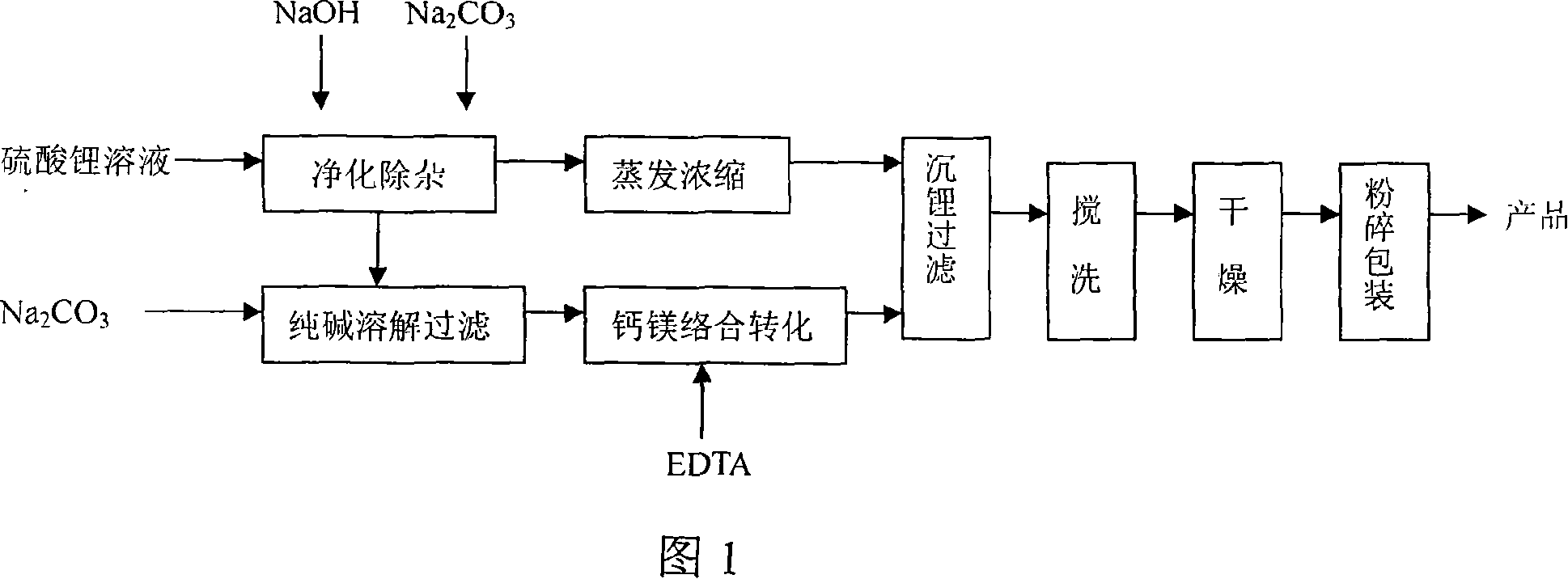
Method for producing low-magnesium battery-stage lithium carbonate from lithium sulfate solution
ActiveCN101125668ALower magnesium levelsAchieve preparationCarbonate preparationLithium carbonateChemistry
The invention provides a method to produce a low-magnesium battery grade lithium carbonate from lithium sulfate solution. The method comprises the steps that: (1) purification treatment of lithium sulfate solution as following: lithium sulfate solution is co-precipitated to lower the impurities ions Fe3+, Mg2+, Al3+ and Ca2+, and condensed and filtered to further eliminate impurities, and obtain purification residues and a pure finish solution of lithium sulfate; (2) soda is dissolved and added with purification residues obtained from the purified lithium sulfate solution, and used for a filtering media to filter calcium and magnesium and obtain purified soda solution; (3) the purified soda solution is added with complexant EDTA, and stirred for complexation reaction, and slowly added with condensed and impurities eliminated pure finish solution of lithium sulfate, and a crude lithium carbonate is prepared; (4) the crude lithium carbonate is stirred, cleaned, dried and smashed, thus obtaining the low-magnesium battery grade lithium carbonate. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple production technique, stable product quality and low cost, and expertly employs the waste residues in the process, not only solves the difficulty of impurities elimination for soda, but also enhances the recycling ratio of lithium, which is suitable for the production application of the positive pole material of Li-ion battery.
Owner:TIANQI LITHIUM CORP
Process for preparing phosphate concentrate and by-products calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide from mid and low-grade phosphate rocks
InactiveCN104876197AEfficient recyclingSolve pollutionCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesRaw phosphate material treatmentAmmonium nitrateAmmonium sulfate
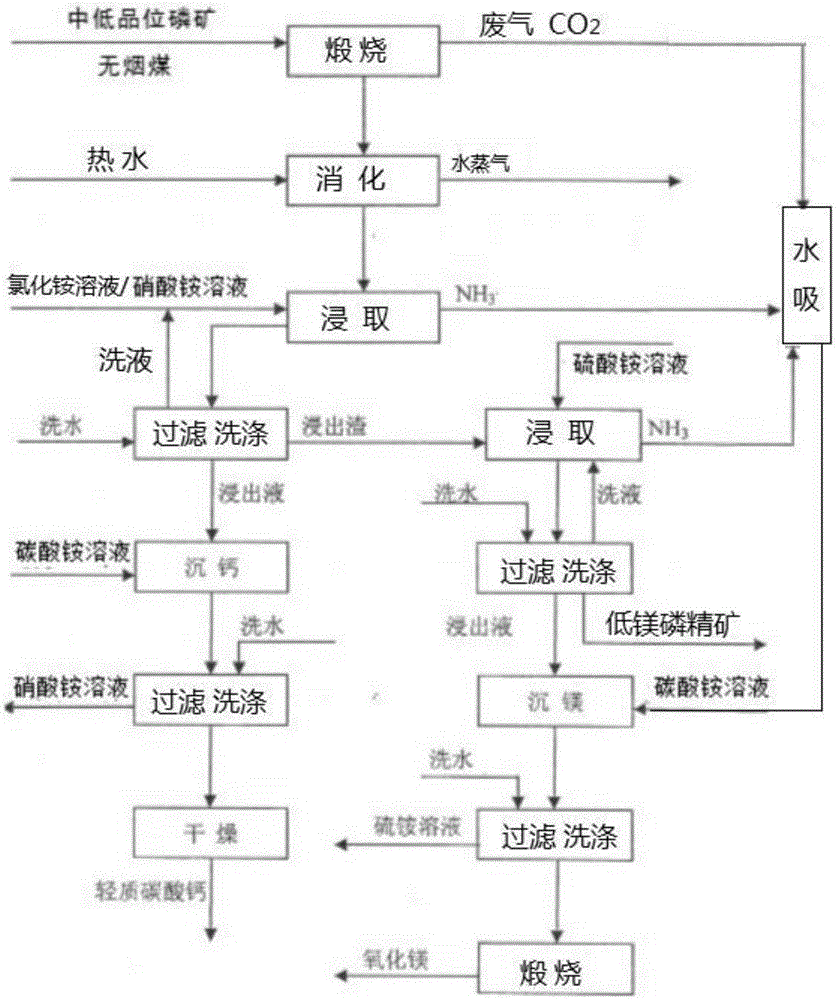
The invention provides a process for preparing phosphate concentrate and by-products calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide from mid and low-grade phosphate rocks, and belongs to the technical field of inorganic chemical industry. The process comprises the following steps: burning mid and low-grade phosphate rocks at 900-1100 DEG C; and then carrying out a series of treatment including digesting, leaching and participating to obtain phosphate concentrate, calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide. By virtue of the process, the phosphorus element is reserved in the prepared phosphate concentrate to the maximal extent; meanwhile, the by-products calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide are generated; calcium elements, magnesium elements and phosphorus elements in the mid and low-grade phosphate rocks are fully utilized; and meanwhile, ammonium nitrate and ammonium sulfate are recycled in the treatment process, so that the target of saving raw materials is reached.
Owner:GUIZHOU RES INST OF CHEM IND
Integrated nitrogen and phosphorus recovery device with low energy consumption
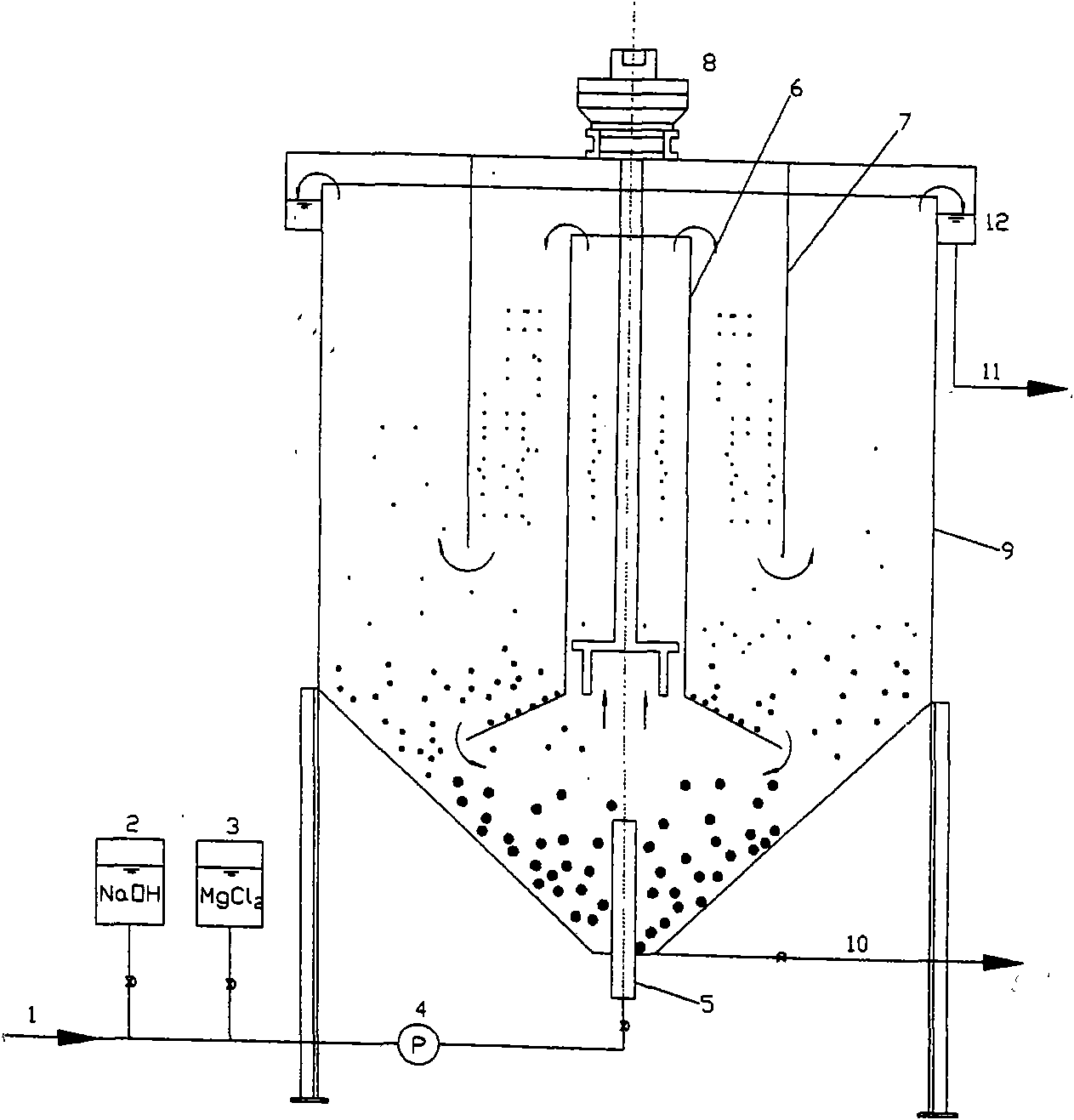
InactiveCN101560001AGood processing effectReduce loadWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationRefluxFrequency conversion
The invention relates to an integrated nitrogen and phosphorus recovery device with low energy consumption, which comprises a vertical tank body; the bottom of the vertical tank body is provided with a water inlet ejector; a dosage adding device and a water inlet pipe are connected with the water inlet ejector; one end of a clear water outlet pipe is communicated with the top of the vertical tank body; and the integrated nitrogen and phosphorus recovery device is characterized in that: a fluidization area is arranged on the middle and lower part in the vertical tank body; struvite seed crystal particles are arranged in the fluidization area; the center of the fluidization area is provided with a guide mixer; a space of the tank body under the guide mixer is a water distribution area which is communicated with the water inlet ejector; the top of the vertical tank body is provided with a lifting device; and the guide mixer is arranged on the output shaft of the lifting device. The integrated nitrogen and phosphorus recovery device has the advantages that the integrated nitrogen and phosphorus recovery device quickens the mass transfer process of a system, greatly reduces running cost and operation difficulty, improves interception efficiency and recovery effect of nitrogen and phosphorus, has simple and convenient engineering design and short installation period of construction, does not need external reflux, and has low energy consumption of internal reflux, frequency conversion and speed regulation, easy control of magnesium source externally added, and low content of magnesium in the outlet water.
Owner:SHANGHAI RUNDE ENVIRONMENT ENG
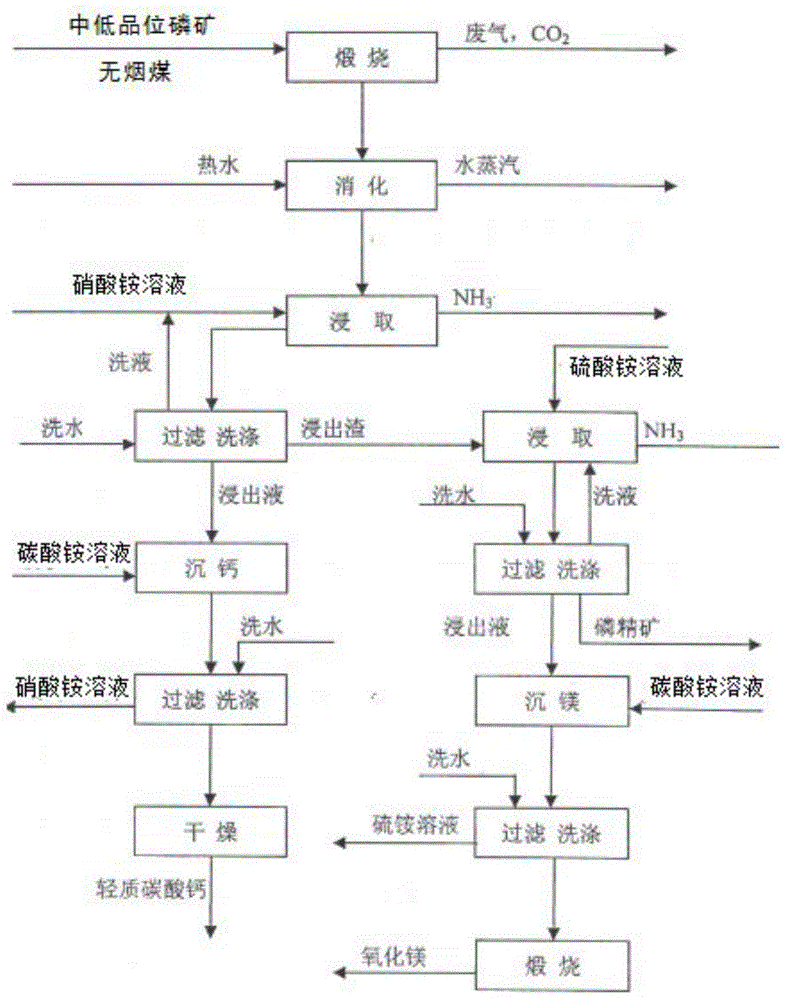
Technology for preparation of low-magnesium phosphate concentrate and byproducts calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide from medium and low grade phosphate rock
ActiveCN105540560AEfficient recyclingSolve pollutionCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesRaw phosphate material treatmentInorganic ChemicalPhosphorite
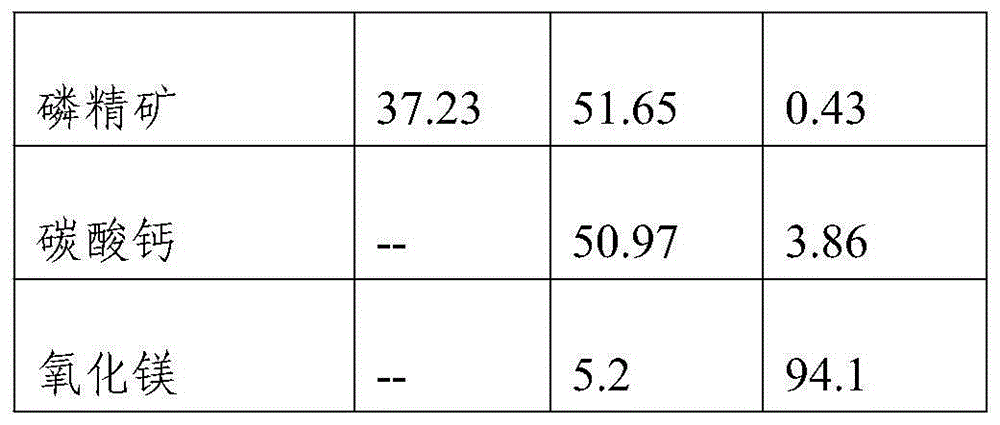
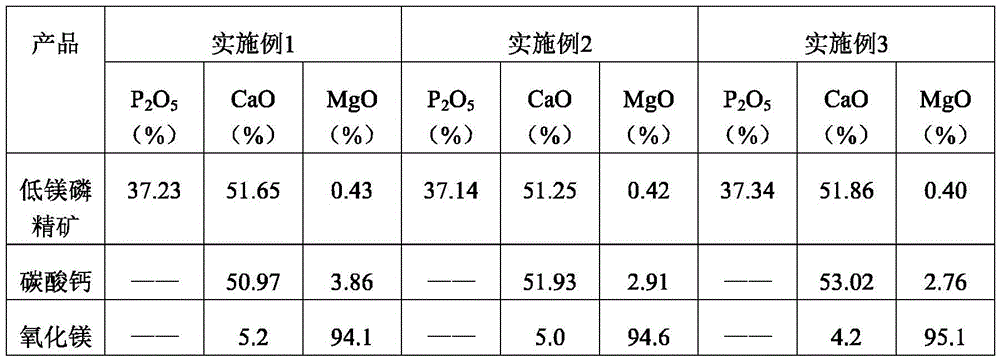
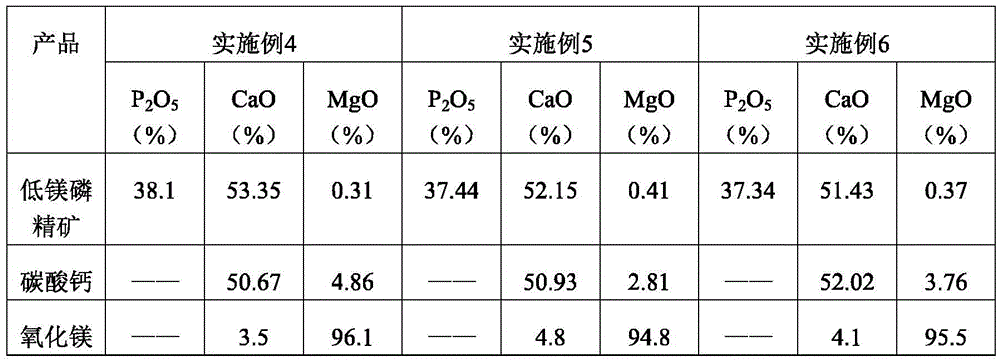
Belonging to the technical field of inorganic chemical industry, the invention provides a technology for preparation of low-magnesium phosphate concentrate and byproducts calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide from medium and low grade phosphate rock. The technology includes the steps of: calcining medium and low grade phosphate rock at 900-1100DEG C; and then carrying out slaking, leaching, precipitation and a series of treatment to obtain low-magnesium phosphate concentrate, calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide. The technology maximumly retains phosphorus element in the prepared low-magnesium phosphate concentrate, and produces calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide as the byproducts, so that the calcium, magnesium and phosphorus elements in the medium and low grade phosphate rock can be fully utilized. In the obtained low-magnesium phosphate concentrate, calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide products, the low-magnesium phosphate concentrate has a phosphorus pentoxide content of more than 37% and a magnesium oxide content of less than 0.5%, the calcium carbonate has a calcium oxide content of more than 50%, and the magnesium oxide has purity of over 94%. Therefore, the increase percentage point of phosphorus pentoxide in the low-magnesium phosphate concentrate is over 10.13.
Owner:贵州盛源新材料股份有限公司
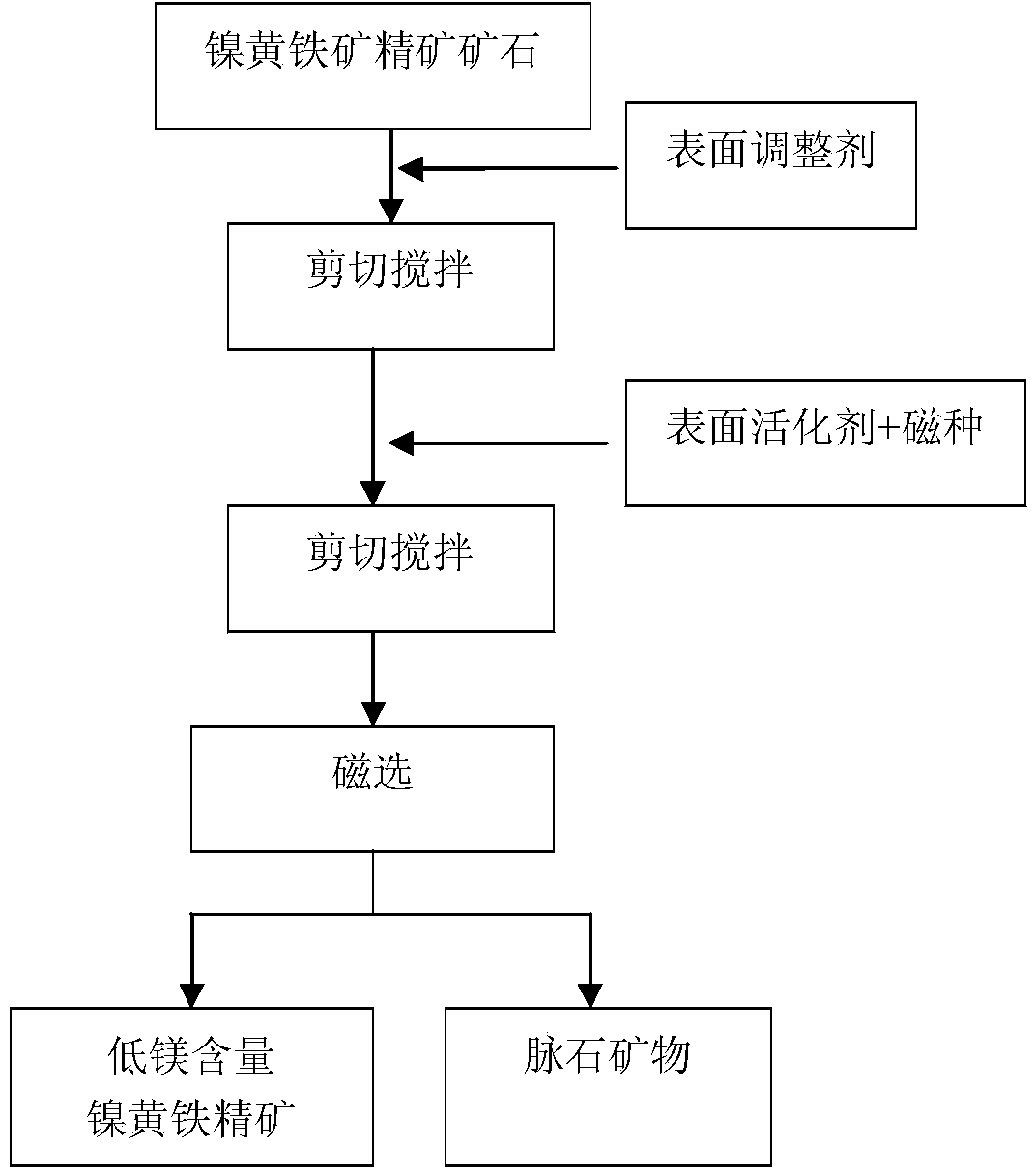
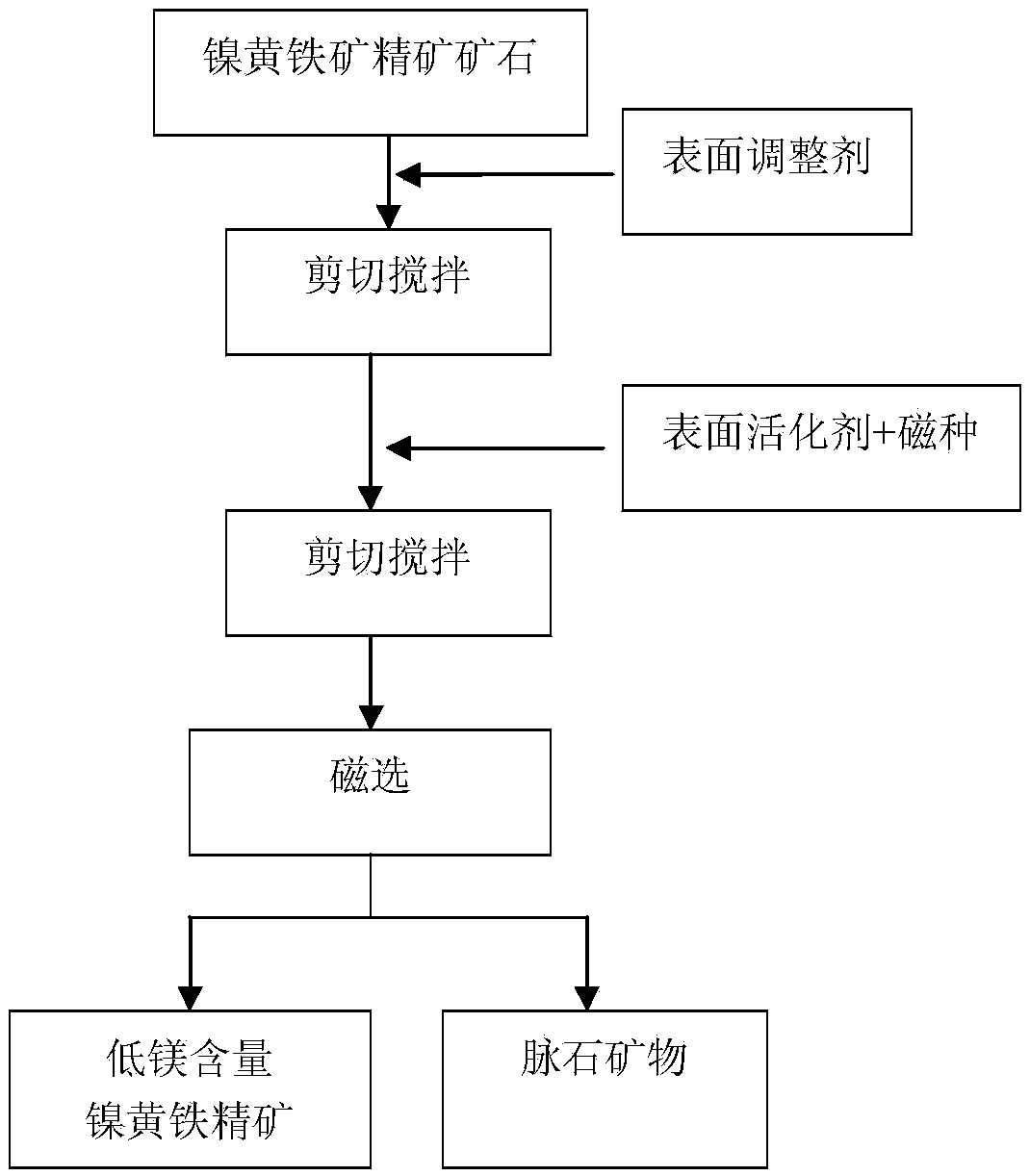
Method for lowering content of magnesium in pentlandite concentrate
ActiveCN103934099ALarge specific surface areaReduce repulsion energyMagnetic separationHigh magnesiumCorrosion
Nickel sulfide in low-grade ores is mainly recycled by a flotation method, but the defect is that the content of MgO in concentrate is high. As magnesium-containing minerals are high in smelting point and poor in mobility, when the content of MgO in concentrate is higher than 6.5%, adverse effects such as furnace body nodulation and furnace body corrosion are brought to a follow-up novel flash smelting process of nickel. In order to solve a problem that the content of magnesium in concentrate is high during separating of magnesium-nickel containing minerals, the invention provides a method for lowering the content of magnesium in pentlandite concentrate. The method comprises the following steps: adding surface conditioning agents such as sodium hexametaphosphate into the pentlandite concentrate, and uniformly dispersing ore pulp by stirring; then, adding magnetic seeds and a surfactant, and stirring to ensure that the magnetic seeds and the pentlandite concentrate generate adhesion agglomeration; and performing magnetic separation, thereby obtaining the pentlandite concentrate with the content of magnesium being lower than 6.5% (in terms of MgO). The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being good in pentlandite separation selectivity, environmentally friendly, low in energy consumption, easy to operate, high in efficiency, and the like, and solves a problem that the content of magnesium in nickel concentrate is high.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
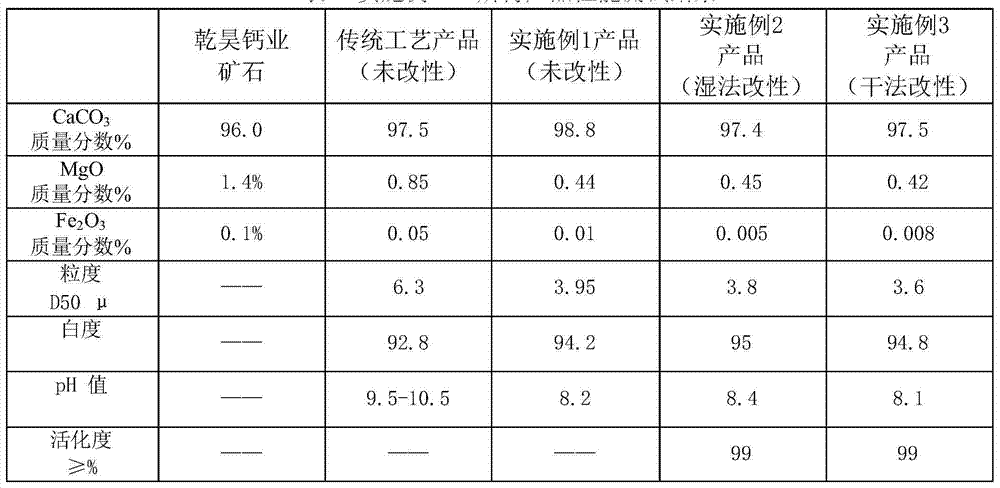
Precipitated calcium carbonate production technology for reducing magnesium and increasing calcium
InactiveCN103880058AAbundant raw material resourcesLow costCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCarbonationCalcium EDTA
The invention discloses a precipitated calcium carbonate production technology for reducing magnesium and increasing calcium. The technology comprises the steps as follows: 1) a desulfurizing tower is serially connected with a washing tower in kiln gas purification, and a desulfurizer is added to a liquid phase of the desulfurizing tower, so that the purification effect of a kiln gas is improved, and meanwhile, the dosage of circulating water is reduced; 2) a raw slurry pre-ageing process and a dynamic ageing process are adopted, the "back-mixing" phenomenon is avoided, and the ageing time of the raw slurry is ensured; 3) a carbonation reaction kettle adopts a stirring apparatus with three layers of paddles, so that the carbonation reaction time is shortened, and the utilization rate of the kiln gas is increased; 4) magnesium is separated out from mother liquor from which calcium carbonate is separated out by adopting a steam pyrolysis method, filtrate is returned to a digestive process, and cyclic utilization of water is achieved. The precipitated calcium carbonate product obtained by the technology is small in grain size (D50 is approximate to 4mu), high in whiteness (greater than or equal to 94), low in magnesium content (MgO is smaller than or equal to 0.5%), and low in alkalinity (pH is smaller than or equal to 9), and is more applicable to the industries of plastic steel and the like with special demands on the magnesium content, the whiteness, the alkalinity and the like besides of meeting the industries such as rubber, plastic, papermaking and coatings.
Owner:云南和铄投资管理有限公司
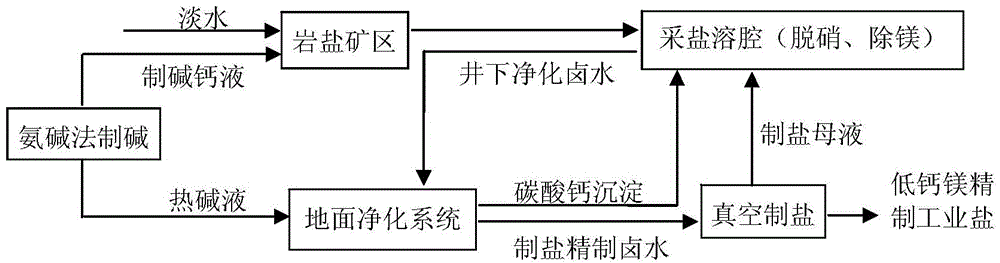
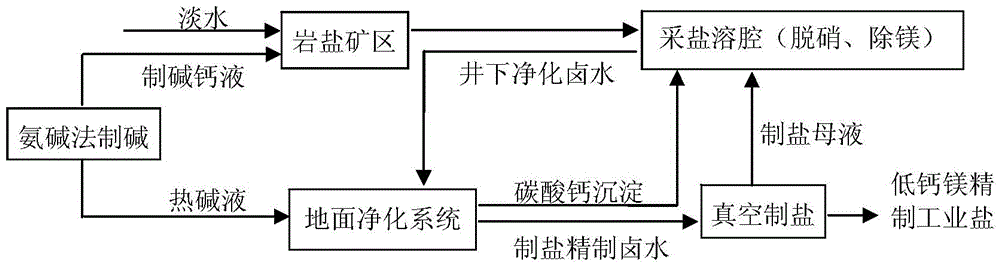
Method for preparing refined salt low in calcium and magnesium by utilizing underground denitration process
ActiveCN103979579AReduce emissionsReduce production energy consumptionAlkali metal chloridesCalciums magnesiumMagnesium
The invention discloses a method for preparing refined industrial salt low in calcium and magnesium by utilizing an underground denitration process. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: (1), injecting alkali production calcium liquid in a well and extracting brine; (2), underground removing sulfate radicals and magnesium; (3), surfacely removing calcium; (4), producing salt in vacuum; and (5), returning salt production mother liquid in the well and denitrating. The content of calcium and magnesium in industrial salt produced by the method disclosed by the invention is less than or equal to 0.05%, and therefore, the content of calcium and magnesium is far less than that in industrial salt produced by the traditional methods.
Owner:江苏苏盐井神股份有限公司 +1
Sodium fluosilicate production-phosphorite demagging combined treatment method
InactiveCN104876198ATake advantage ofLow costSilicon halogen compoundsRaw phosphate material treatmentSulfurPhosphoric acid
The invention relates to the technical field of phosphorite quality improvement, particularly a sodium fluosilicate production-phosphorite demagging combined treatment method. Sodium sulfate and wastewater generated in the wet-process phosphoric acid sodium fluosilicate coproduction process are utilized and returned to the phosphorite demagging treatment technique so as to utilize the residual sulfuric acid and fluosilicic acid and remove the magnesium element in the phosphorite, thereby enhancing the phosphorite grade. In the treatment process, since the content of sulfuric acid in the wastewater in the fluosilicic acid coproduction process is lower and the fluosilicic acid content is lower, the raw materials added into the reaction kettle for phosphorite treatment have low corrosiveness to the equipment, thereby lowering the cost for the phosphorite grade enhancement treatment. The sulfur element and fluorine element in the sodium fluosilicate sewage can not be abundantly discharged into the environment, thereby providing a new way for sodium fluosilicate sewage treatment, relieving the sodium fluosilicate wastewater treatment load and lowering the environmental pollution.
Owner:贵州开磷氟硅化工有限责任公司
Method for green-producing high-quality calcium superphosphate co-generated magnesium chloride by low-level collophanite
InactiveCN106517124AReduce contentSolve problems such as poor qualitySuperphosphatesMagnesium chloridesDecompositionCarbonate
The invention relates to a method for green-producing high-quality calcium superphosphate co-generated magnesium chloride by low-level collophanite, comprising steps of a, performing acid splitting on carbonate in the phosphorite by hydrochloric acid and preparing phosphorus concentrate; b, preparing high-purity calcium sulfate; c, preparing magnesium chloride; after concentrating the filter fluid to a certain volume, preparing magnesium chloride. The invention has the advantages that the method is applicable to prepare high-efficient phosphatic fertilizer by directly producing high-quality low-magnesium phosphorite in hydrochloric acid decomposition, carbonate of low-level phosphorite and in particular to high-magnesium phosphorite; no waste discharges during the whole technical flow; by applying the invention, the phosphorus pentoxide content of phosphorite is promoted through one acidolysis while content of magnesium oxide in the phosphorite is also reduced; thus the problem of agglomeration and poor phosphatic fertilizer quality caused by high magnesium content during the ordinary calcium production can be solved; the phosphorite therefrom is directly reacted with sulfuric acid, thus high-quality phosphatic fertilizer of which available phosphorus is improved to 16-18% P2O5 can be obtained.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
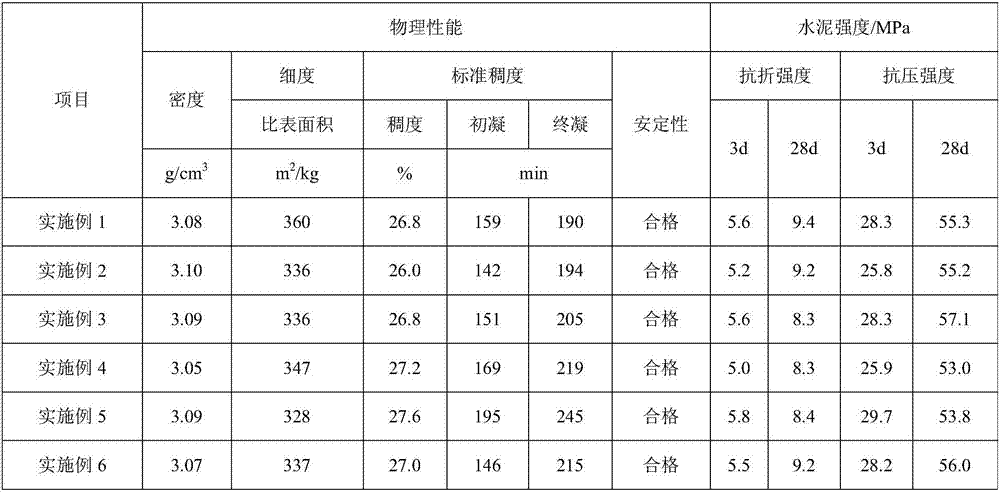
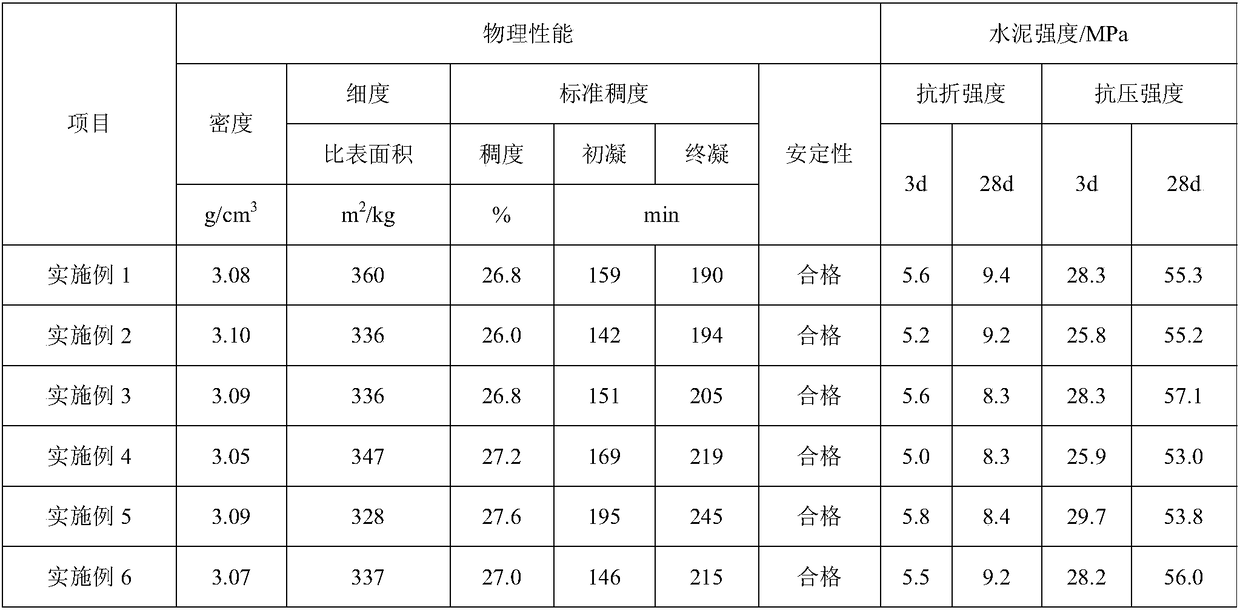
Cement produced by utilizing industrial solid wastes and preparation method of cement
The invention provides cement produced by utilizing industrial solid wastes. The cement is prepared from the following raw materials: 77.00-82.50% of clinker, 0.30-7.90% of blaster furnace slag, 1.60-5.55% of desulfurization gypsum, 2.90-7.60% of waste rocks, 0-1.00% of high-silicon sandstone, 0.70-6.70% of fly ash, 0-12.00% of high magnesium waste rock, 0-2.40% of phosphogypsum and 0-0.80% of titanium gypsum, wherein the clinker is prepared from the following raw materials: common limestone, marble sawdust, marble leftover material, high magnesium waste rock, sandstone, red clay and wet-discharged fly-ash. According to the cement, the cement raw material is prepared by using the marble sawdust and leftover material, the waste residue utilization rate is high, and lots of natural resources and energy can be saved. Meanwhile, the high magnesium waste rock is used for preparing the raw material and serves as a mixed material of the cement to be simultaneously used, and the utilization rate of the high magnesium waste rock is greatly improved.
Owner:华润水泥(富川)有限公司 +1
Method for purifying manganese sulfate in magnesium-rich manganese sulfate solution
The invention provides a method for purifying manganese sulfate in a magnesium-rich manganese sulfate solution. The purification method comprises the following steps: S1, performing primary high-temperature crystallization on a magnesium-rich manganese sulfate solution to obtain primary crystallized crystals; and S2, carrying out secondary high-temperature crystallization on the primary crystallized crystal to obtain a secondary crystallized crystal. The smaller the mass ratio of manganese to magnesium in the manganese sulfate solution is, the more difficult the manganese and the magnesium areseparated, and when the temperature is higher than 100 DEG C, the solubility of manganese sulfate is negatively related to the temperature. Most magnesium in the manganese sulfate solution with the mass ratio of manganese to magnesium being lower than 5 is removed through a high-temperature crystallization method, so that the method for purification of the magnesium-rich manganese sulfate solution is simple in process and low in production cost.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
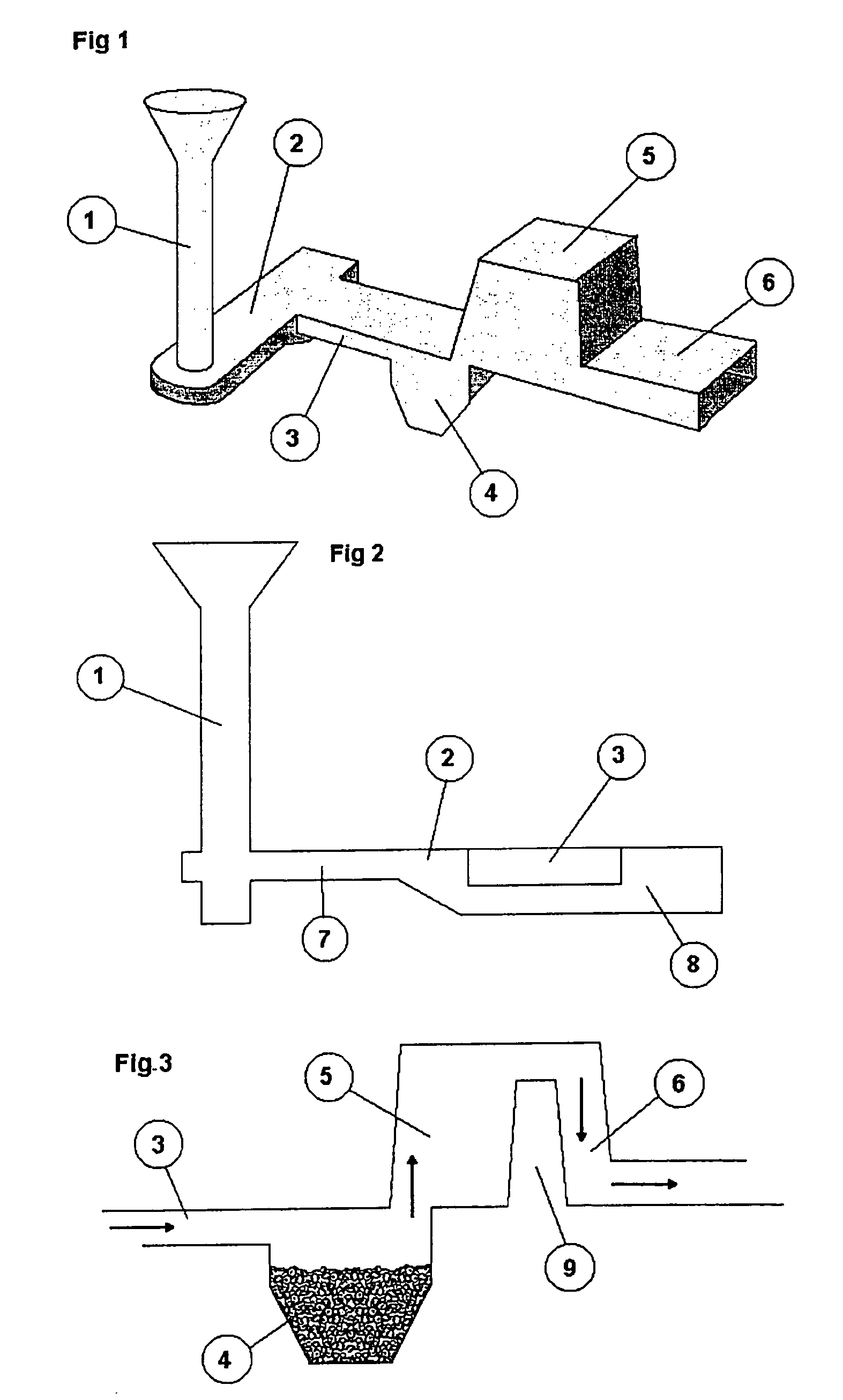
Process for Production of Compacted Graphite Iron
InactiveUS20090183848A1Lower magnesium levelsCasting defects such as dross and micro-shrinkage are minimizedCompacted graphite ironCerium
A process for production of compacted graphite iron using in-mould addition of a magnesium alloy is disclosed. The process is characterised by a step of pre-treating the base iron in a ladle or in a furnace with an alloy containing cerium and performing a structure forming treatment in a reaction chamber in the mould using an alloy containing magnesium and lanthanum.
Owner:NOVACAST
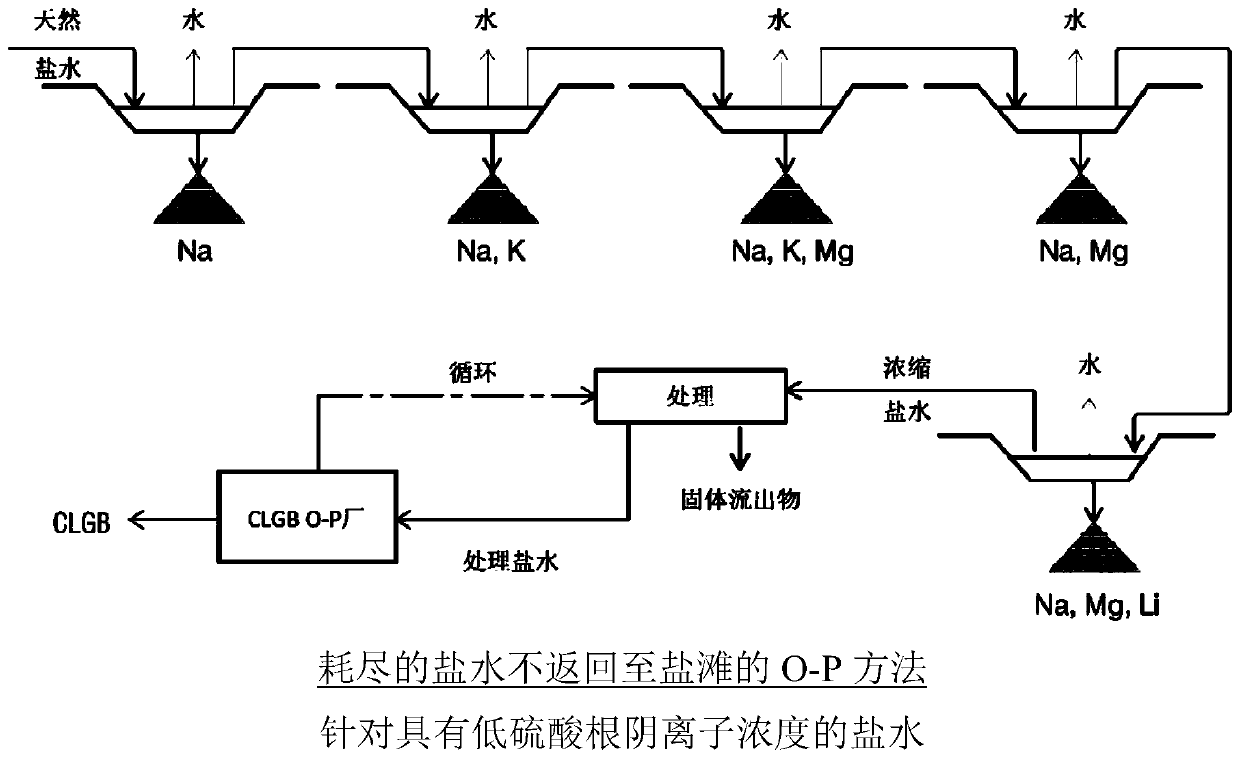
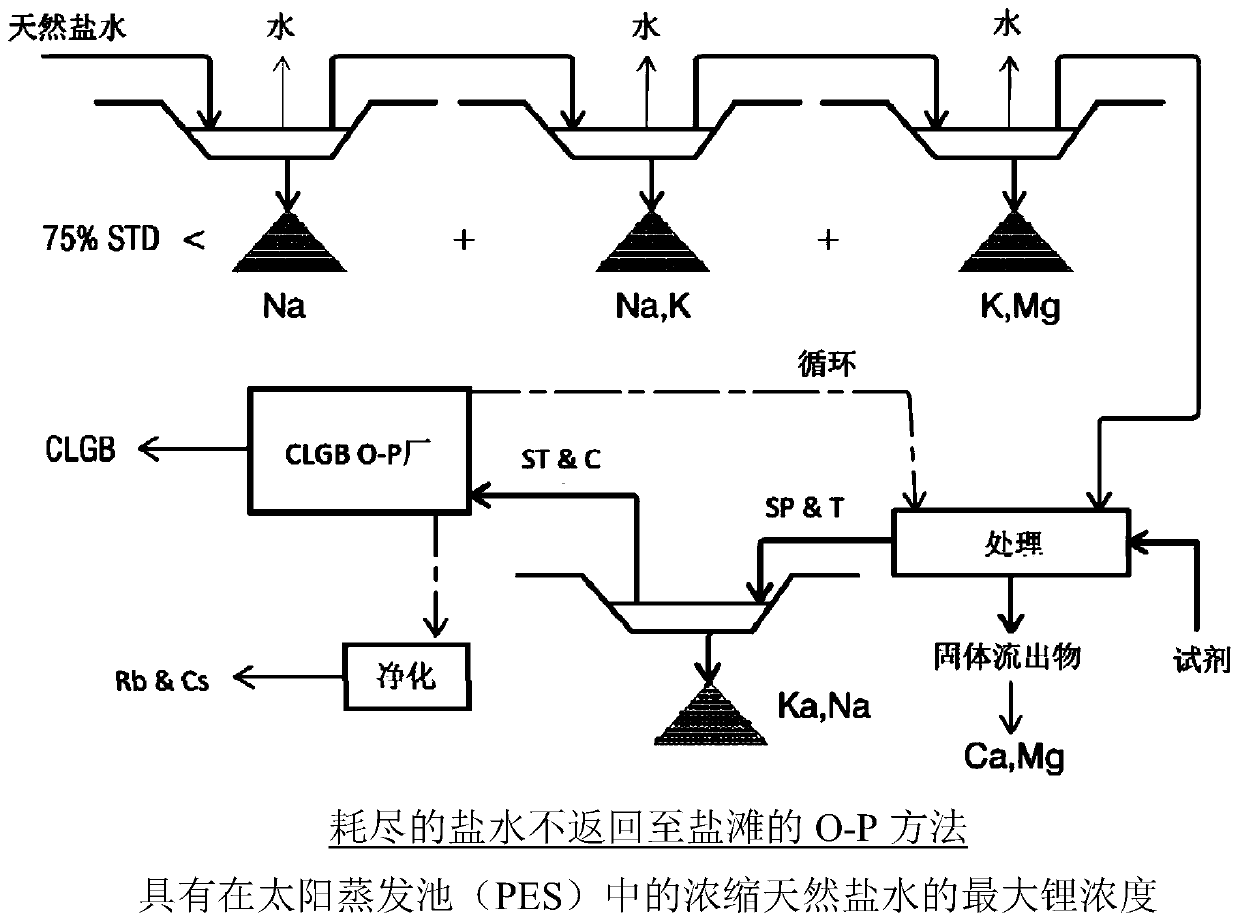
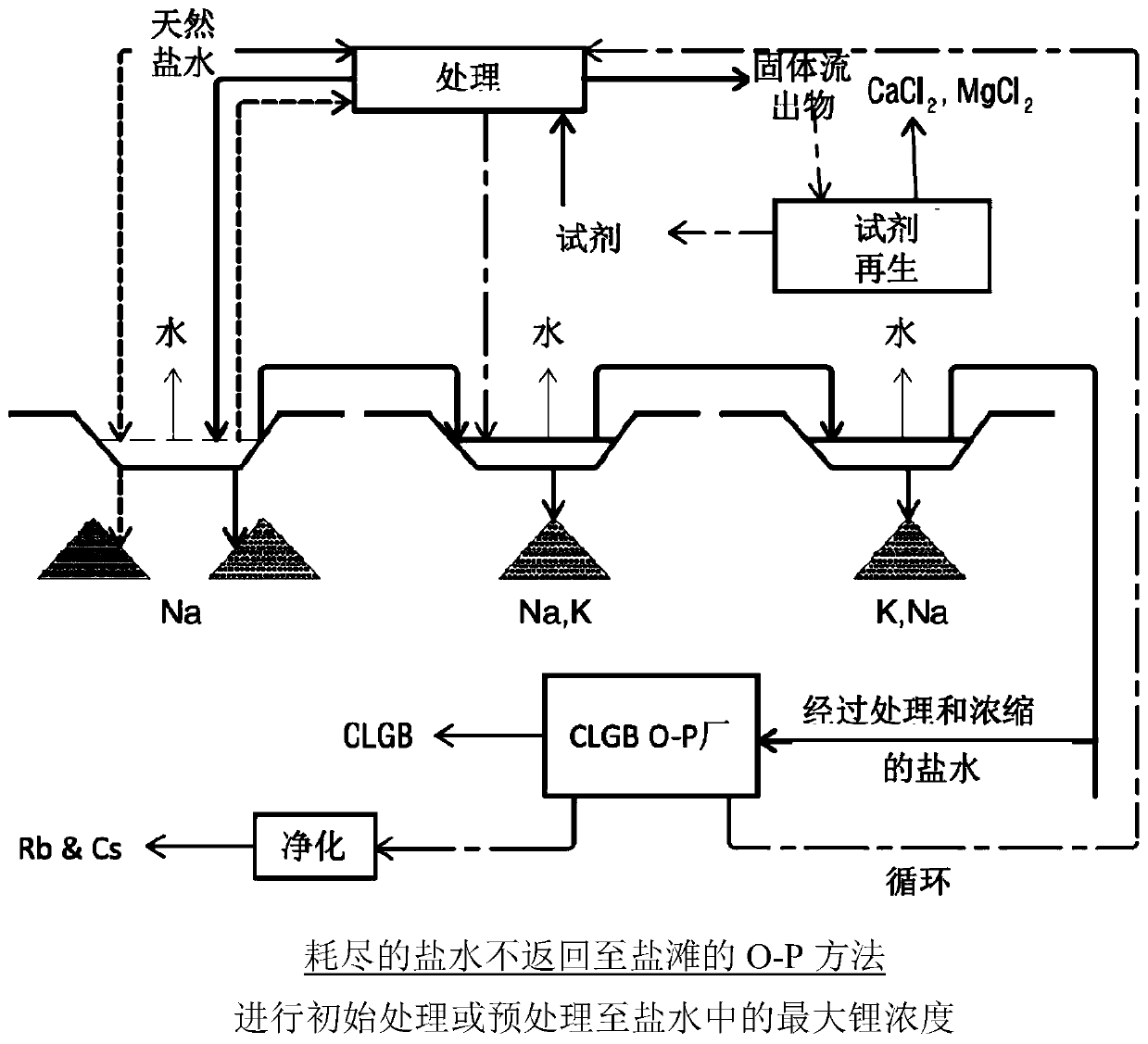
Method for obtaining concentrated brine of minimum impurity content from brine found in natural salt flats and salt marshes, said method having minimum environmental impact and maximum lithium recovery
PendingCN111448164AReduce contentLower magnesium levelsMagnesium carbonatesCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesSaline waterLithium
The invention relates to a method for obtaining concentrated brine of minimum impurity content from brine found in natural salt flats and salt marshes, said method having minimum environmental impactand maximum lithium recovery. The method is characterised in that it comprises the steps of: a) constructing ponds for fractional crystallisation based on solar evaporation; b) filling the ponds withnatural brine; c) initially pre-concentrating the natural brine until the maximum possible lithium concentration in the liquid phase is obtained, without lithium-containing salts being precipitated; d) cooling the pre-concentrated brine obtained in step (c), ensuring the maximum precipitation of salts containing sulphate anion; e) chemically pre-treating the liquid phase of the brine separated from the salts precipitated by means of cooling in order to minimise sulphate anions in the liquid phase after cooling; f) finally pre-concentrating the pre-treated liquid phase until the maximum possible lithium concentration in the liquid phase is obtained, without lithium-containing salts being precipitated; g) chemically treating the liquid phase of the brine separated from the salts precipitatedin step (f) in order to minimise the concentration of magnesium, calcium, boron and sulphate in the liquid phase; and h) concentrating the liquid phase obtained in step (g).
Owner:丹尼尔恩内斯托加利
Method for preparing low calcium and magnesium refined salt by downhole denitration process
The invention discloses a method for preparing refined industrial salt low in calcium and magnesium by utilizing an underground denitration process. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: (1), injecting alkali production calcium liquid in a well and extracting brine; (2), underground removing sulfate radicals and magnesium; (3), surfacely removing calcium; (4), producing salt in vacuum; and (5), returning salt production mother liquid in the well and denitrating. The content of calcium and magnesium in industrial salt produced by the method disclosed by the invention is less than or equal to 0.05%, and therefore, the content of calcium and magnesium is far less than that in industrial salt produced by the traditional methods.
Owner:江苏苏盐井神股份有限公司 +1
Method for comprehensively recovering copper and cobalt from copper cobalt oxide ore
PendingCN113388741AImprove leaching rateLow costPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSulfite saltSlag
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recovering copper and cobalt from copper cobalt oxide ore. The method comprises the steps of size mixing, leaching, concentration thickening and washing, copper recovery, cobalt recovery from low-copper raffinate and the like. According to the method, under the conditions that the ore pulp concentration is high and the temperature of the ore pulp is increased to 60-85 DEG C through heat release of concentrated sulfuric acid, sulfide minerals and the copper sulfide slag obtained by treating the copper-containing solution through a sulfide precipitation method are adopted, and smelting soot obtained after the sulfide minerals are not completely oxidized replaces sodium pyrosulfite or sodium sulfite to serve as a cobalt leaching reducing agent; on one hand, the cost of the reducing agent is greatly reduced, and on the other hand, environmental unfriendliness caused by SO2 generated when sodium pyrosulfite or sodium sulfite is adopted as the cobalt leaching reducing agent in an acid environment is avoided. More importantly, under the conditions of high ore pulp concentration and high-temperature leaching, the leaching rate of copper and cobalt is increased, the leaching rate of harmful impurity silicon is greatly reduced, and the adverse effects of generation of silica gel on the subsequent procedures of sedimentation, extraction and the like are reduced.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP +1
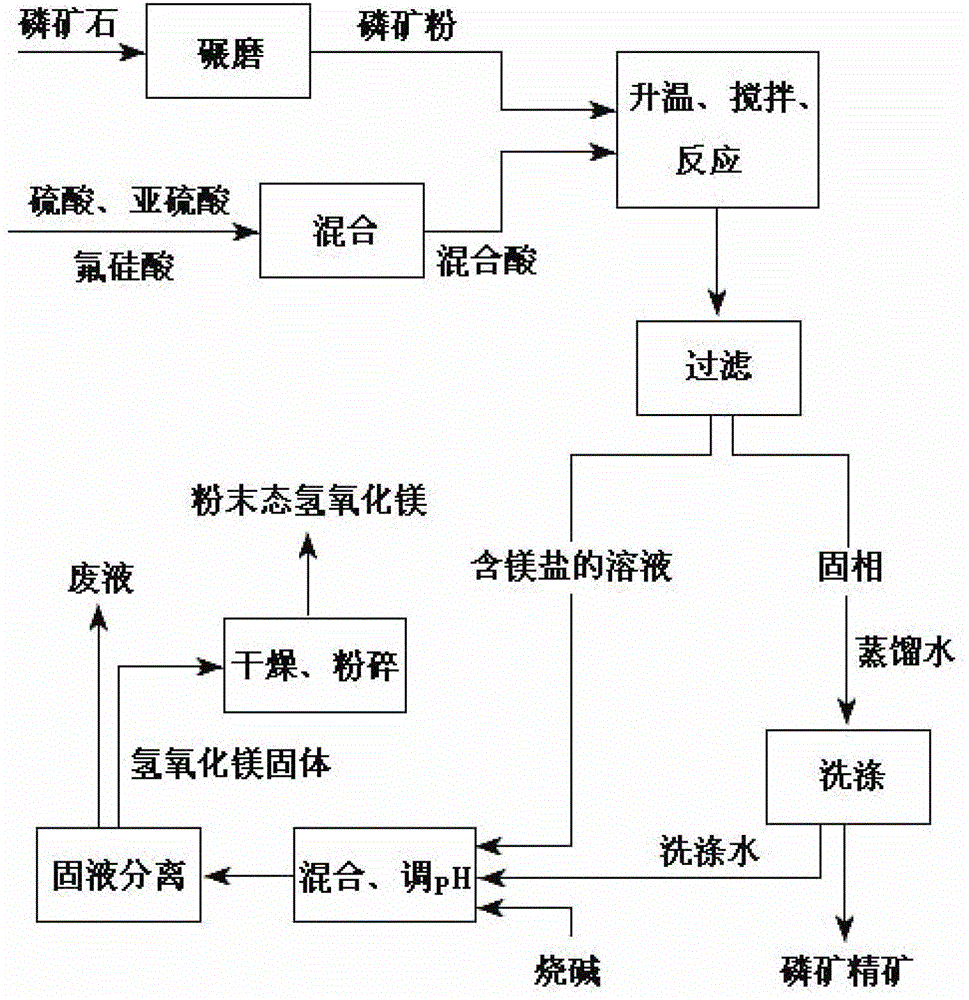
Method for removing magnesium from ultralow-quality phosphate rock and producing magnesium hydroxide
InactiveCN103073034BReduce lossesLower magnesium levelsMagnesium hydroxidePhosphateProcess conditions
The invention discloses a method for removing magnesium from an ultralow-quality phosphate rock and producing magnesium hydroxide. The method comprises the steps as follows: mixing phosphate rock powder with a magnesium remover for magnesium removal reaction, carrying out solid-liquid separation, obtaining solid-phosphate concentrate, and adding a neutralization and sedimentation agent into liquid to obtain a magnesium byproduct. The method is characterized by taking the ultralow-quality phosphate rock as a raw material and mixed acid of sulphurous acid, sulfuric acid and fluorosilicic acid as the magnesium remover, carrying out solid-liquid separation, mixing washing water for washing a solid phase with a solution obtained after separation, and carrying out neutralization and sedimentation reaction. According to the method, mixed acid of sulphurous acid, sulfuric acid and fluorosilicic acid is adopted as the magnesium remover, so that the P2O5 loss is reduced; the process route is short, the operation is simple and the one-time investment cost is low; the magnesium removal rate can reach more than 80% and the content of magnesium in the obtained concentrate is lower than 1%; and the obtained phosphate concentrate is good in quality, the quality is improved by 5-10%, the P2O5 yield is high and can reach more than 99% under the optimal process conditions, and the P2O5 content is increased by 3-5% in general.
Owner:GUIZHOU KAILIN GRP MINERAL FERTILIZER CO LTD
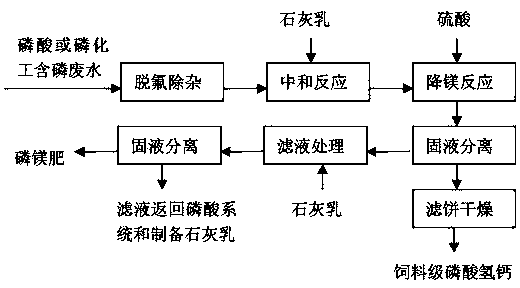
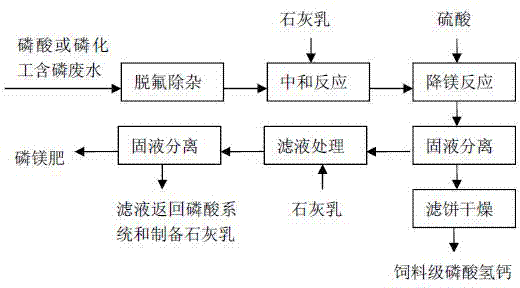
Method for reducing content of magnesium in feed grade calcium hydrophosphate
A method for reducing content of magnesium in feed grade calcium hydrophosphate is characterized in that a purified liquid obtained after defluorination and purification of phosphoric acid by a wet process with sulfuric acid or phosphorus wastewater of the phosphorus chemical industry is subjected to neutralization reaction with lime cream, sulfuric acid is added after reaction to reduce the content of magnesium in a reaction slurry solid phase, the adding amount of sulfuric acid is 0.5-1.3 times of stoichiometric ratio of the magnesium content in a reaction endpoint slurry solid phase, slurry is filtered after the reaction, and a feed grade calcium hydrophosphate product is obtained after a filter cake is dried; and a separated liquid phase is added into the lime cream, neutralized to the pH value of 8-10 and then filtered, and filtrate is recycled. The method can effectively reduce the content of magnesium in feed grade calcium hydrophosphate, the calcium content can be improved, and the method has the characteristics of simple and effective process, easiness in reaction operation and good economic benefit.
Owner:WENGFU (GRP) CO LTD
Low-magnesium barium-containing spheroidized cored wire
InactiveCN111690790ASolve the problem of unstable absorptionLower magnesium levelsMetallic materialsWaste product
The invention discloses a low-magnesium barium-containing spheroidized cored wire, and belongs to the technical field of ferrous metal materials. The core powder comprises the components of, in percentage by mass, 8%-12% of Mg, 45%-60% of Si, 1.5%-2.5% of RE, 5%-10% of Ba, 1.5%-3% of Ca, 0.5%-1.5% of MgO, 1.0%-1.5% of Al and the balance Fe. According to the low-magnesium barium-containing spheroidized cored wire, the spheroidizing function and the inoculation function are integrated, inoculation of cored wires is not needed any more, thus the magnesium content is reduced, the wire feeding timeof a small ladle with the weight being 500 kg or below is stably controlled to be 24-32 s, and the problem that due to the fact that the wire feeding time is too short, magnesium absorption is unstable in the small ladle spheroidizing process is solved; and the nodulizing cored wire is used for wire feeding and nodulizing, the content of residual Mg in molten iron is more stable than that of an in-ladle pouring method, and nodulizing of ductile iron is poor and pore waste is lower.
Owner:DONGFENG PRECISION CASTING CO LTD
A kind of cement produced by utilizing industrial solid waste and its preparation method
The invention provides cement produced by utilizing industrial solid wastes. The cement is prepared from the following raw materials: 77.00-82.50% of clinker, 0.30-7.90% of blaster furnace slag, 1.60-5.55% of desulfurization gypsum, 2.90-7.60% of waste rocks, 0-1.00% of high-silicon sandstone, 0.70-6.70% of fly ash, 0-12.00% of high magnesium waste rock, 0-2.40% of phosphogypsum and 0-0.80% of titanium gypsum, wherein the clinker is prepared from the following raw materials: common limestone, marble sawdust, marble leftover material, high magnesium waste rock, sandstone, red clay and wet-discharged fly-ash. According to the cement, the cement raw material is prepared by using the marble sawdust and leftover material, the waste residue utilization rate is high, and lots of natural resources and energy can be saved. Meanwhile, the high magnesium waste rock is used for preparing the raw material and serves as a mixed material of the cement to be simultaneously used, and the utilization rate of the high magnesium waste rock is greatly improved.
Owner:华润水泥(富川)有限公司 +1
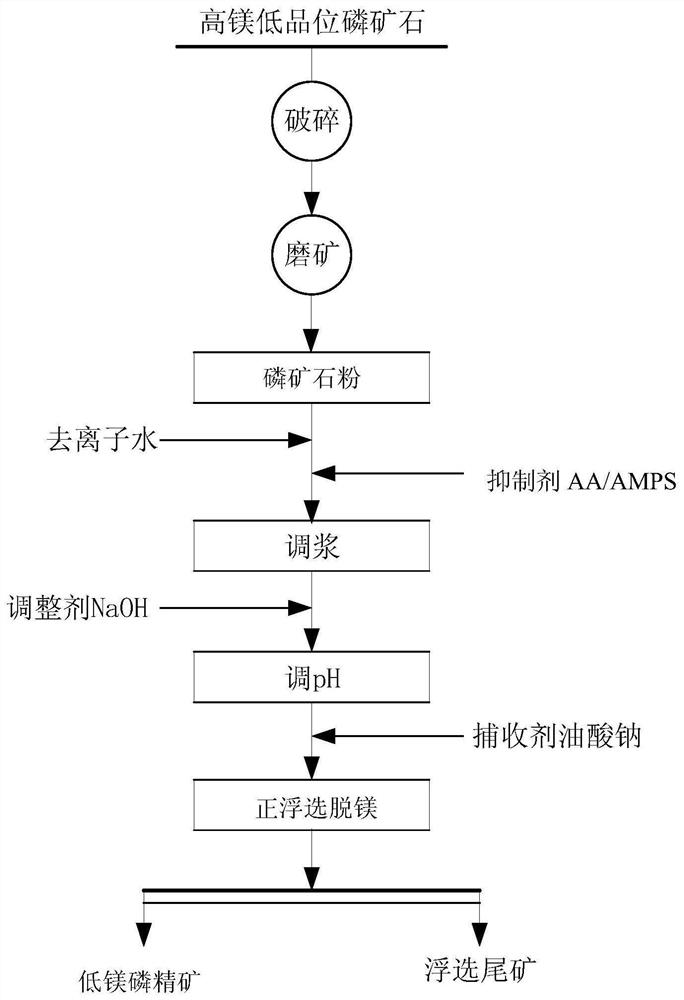
Application of a kind of inhibitor aa/amps in positive flotation demagnesization of phosphate rock
The invention relates to the application of an inhibitor AA / AMPS in positive flotation demagnesization of phosphate rock, which belongs to the field of mineral processing and purification technology of phosphate rock. This application is to add inhibitor AA / AMPS in the process of positive flotation demagnesification of phosphate rock. Specifically, the inhibitor AA / AMPS is used to prepare phosphate rock pulp, wherein the mass concentration of the phosphate rock pulp is 20-25%; the inhibitor AA / AMPS accounts for 100-140 g / t of the phosphate rock pulp. Inhibitor AA / AMPS (acrylic acid-2-acrylamide-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid copolymer), for phosphate rock containing a lot of dolomite, under alkaline conditions, inhibits the flotation of dolomite by positive flotation process It can effectively increase the difference in flotation performance between apatite and dolomite, and facilitate the efficient removal of dolomite. In addition, the inhibitor AA / AMPS has the characteristics of strong selectivity of inhibitory performance, low cost, and simple use, etc. It can effectively reduce the magnesium content of phosphate concentrate, improve the quality of concentrate, and realize the flotation of high-magnesium and low-grade phosphate rock to reduce magnesium. Target.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
Process for enriching lithium in salt lake brine
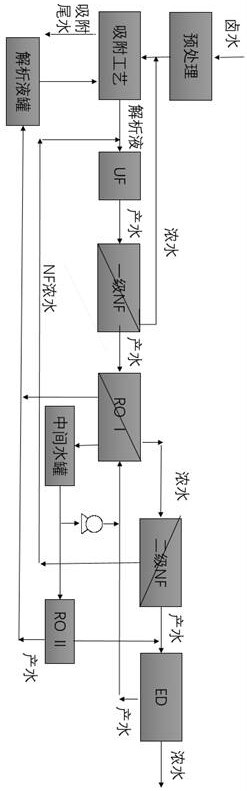
ActiveCN114870633AAchieve separationEfficient enrichmentSemi-permeable membranesLithium compoundsUltrafiltrationReverse osmosis
The invention belongs to the technical field of solution purification and separation, and discloses a process for enriching lithium in salt lake brine. After being pretreated, salt lake brine respectively passes through an adsorption device, an ultrafiltration device, a primary nanofiltration device, a reverse osmosis device I, a secondary nanofiltration device and an electrodialysis device to obtain a solution which can be directly used for preparing high-purity lithium. In order to reduce the pressure difference of the two sides of a reverse osmosis membrane and improve the recovery rate of lithium ions, electrodialysis produced water is conveyed to a reverse osmosis device I and mixed with reverse osmosis produced water I to serve as rear-end effluent of the reverse osmosis device I; an independent reverse osmosis device II is arranged to concentrate outlet water at the rear end of the reverse osmosis device I, and reverse osmosis concentrated water II and secondary nanofiltration produced water are mixed and then enter an electrodialysis device. The enrichment process provided by the invention is low in energy consumption and high in lithium recovery rate.
Owner:BEIJING WANBANGDA ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
High-performance aluminum alloy ingot for electric vehicle and preparation method
PendingCN113278852AImprove performance indicatorsLower magnesium levelsElectric vehicleElectric cars
The invention relates to the technical field of aluminum alloy preparation, in particular to a high-performance aluminum alloy ingot for an electric vehicle and a preparation method. By adjusting an existing aluminum alloy ingot formula, the magnesium content is greatly reduced, the silicon content is improved, the original performance can be met, the performance is higher than the original performance, and the performance index is improved; in the aspect of cost saving, the cost per ton can be saved by more than 200 yuan, the tensile strength is improved to 220 MPa from original 180 MPa and is improved by 22% through the adjustment of the new formula, the ductility is improved to 3% from original 2% and is improved by 50% through the adjustment of the new formula, and the hardness is improved to more than 65 from original 50 HB and is improved by 30% through the adjustment of the new formula; and the problems that the reject ratio of an existing aluminum alloy die-casting product is up to 25% or above, the follow-up remelting loss is large due to the high magnesium content proportion, the requirement for the die-casting technology after remelting is strict, and the yield is low are solved.
Owner:帅翼驰(河南)新材料科技有限公司 +1
A combined treatment method for sodium fluorosilicate production and magnesium removal from phosphate rock
InactiveCN104876198BRaise the gradeReduce pollutionSilicon halogen compoundsRaw phosphate material treatmentMagnesium phosphatePhosphoric acid
The invention relates to the technical field of phosphorite quality improvement, particularly a sodium fluosilicate production-phosphorite demagging combined treatment method. Sodium sulfate and wastewater generated in the wet-process phosphoric acid sodium fluosilicate coproduction process are utilized and returned to the phosphorite demagging treatment technique so as to utilize the residual sulfuric acid and fluosilicic acid and remove the magnesium element in the phosphorite, thereby enhancing the phosphorite grade. In the treatment process, since the content of sulfuric acid in the wastewater in the fluosilicic acid coproduction process is lower and the fluosilicic acid content is lower, the raw materials added into the reaction kettle for phosphorite treatment have low corrosiveness to the equipment, thereby lowering the cost for the phosphorite grade enhancement treatment. The sulfur element and fluorine element in the sodium fluosilicate sewage can not be abundantly discharged into the environment, thereby providing a new way for sodium fluosilicate sewage treatment, relieving the sodium fluosilicate wastewater treatment load and lowering the environmental pollution.
Owner:贵州开磷氟硅化工有限责任公司
Potassium magnesium sulphate composite crystal slow-release salt product for improving milk yield of dairy cows and preparation method thereof
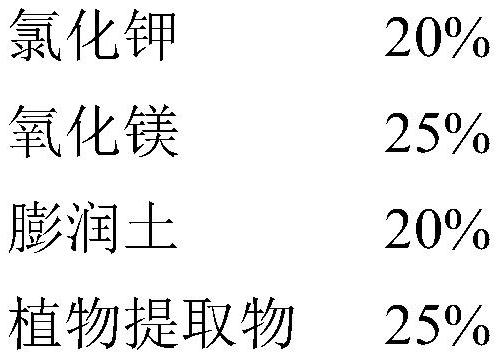
PendingCN112544802AHigh biological valueImprove qualityAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsBiotechnologyRuminant animal
The invention provides potassium magnesium sulphate composite crystal slow-release salt for improving the milk yield of dairy cows, and belongs to the technical field of livestock feed. The potassiummagnesium sulphate composite crystal slow-release salt comprises the following main components in percentage by weight of 50-60% of potassium magnesium sulphate crystal salt, 5-40% of a carrier and 5-40% of plant extract. The specific preparation method comprises the following steps of stirring and mixing the potassium magnesium sulphate crystal salt and the carrier, then adding the carrier, performing stirring and mixing uniformly, adding the plant extract, performing stirring and mixing for 5-10 hours, and finally performing drying to obtain the potassium magnesium sulphate composite crystalslow-release salt product. As a supplement of potassium and magnesium for ruminants, the the potassium magnesium sulphate composite crystal slow-release salt is consistent with body requirements, hasthe characteristics of no heavy metal residues, stable performance, uniform granularity, good fluidity, good palatability and the like, and can significantly improve the milk yield of the dairy cows.
Owner:WUXI ZHENGDA POULTRY
Method for reducing content of magnesium in feed grade calcium hydrophosphate
ActiveCN103723698BLower magnesium levelsSimple processPhosphorus compoundsChemical industryPhosphoric acid
Owner:WENGFU (GRP) CO LTD
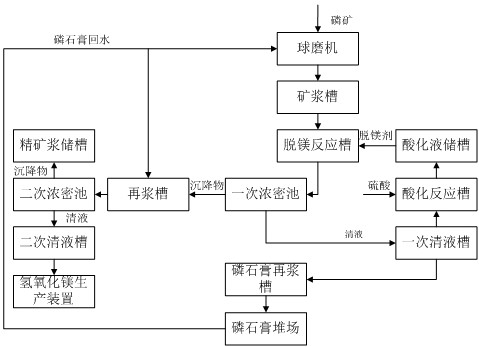
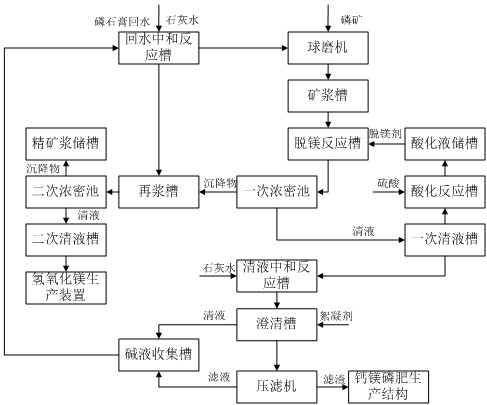
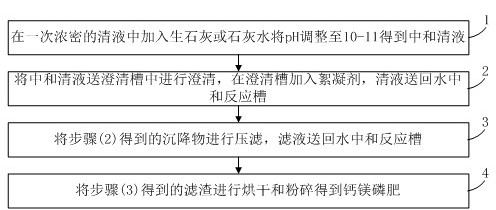
Method and device for producing calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer from magnesium-removed clear liquid
PendingCN113800956AIncrease profitHigh yieldFertilisers by pryogenic processesPhosphoric acidO-Phosphoric AcidLiquid storage tank
The invention discloses a method and a device for producing a calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer from magnesium-removed clear liquid, and belongs to the technical field of wet-process phosphoric acid. The device comprises a primary clear liquid tank, an acidification reaction tank, an acidification liquid storage tank, a ball mill, an ore pulp tank, a magnesium removal reaction tank, a primary thickening tank, a repulping tank, a secondary thickening tank, a concentrate pulp storage tank, a return water neutralization reaction tank, a clear liquid neutralization reaction tank, a clarifying tank, a filter press and a calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer production structure; a clear liquid outlet of the primary thickening tank is connected with the primary clear liquid tank; the primary clear liquid tank, the acidification reaction tank, the acidification liquid storage tank and the magnesium removal reaction tank are connected in sequence; the ball mill and the repulping tank are connected with the return water neutralization reaction tank, the primary clear liquid tank is also connected with the clear liquid neutralization reaction tank, and the clear liquid neutralization reaction tank is connected with the clarifying tank; a clear liquid outlet of the clarifying tank is connected with the return water neutralization reaction tank, and a sediment outlet of the clarifying tank is connected with the filter press; and a filter residue outlet of the filter press is connected with the calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer production structure, and a filtrate outlet of the filter press is connected with the return water neutralization reaction tank.
Owner:HUBEI XIANGYUN GROUP CHEM
A method for reducing magnesium content in pentlandite concentrate
Nickel sulfide in low-grade ores is mainly recovered through flotation, but its disadvantage is that the MgO content in the concentrate is high. Due to the high melting point of magnesium-containing minerals, the fluidity is poor. When the MgO content in the concentrate is higher than 6.5% , which will bring adverse effects such as furnace body nodulation and furnace body corrosion to the subsequent new nickel flash smelting process. Aiming at the problem of high magnesium content in magnesium-containing nickel ore sorting concentrates, the present invention provides a method for reducing the magnesium content in pentlandite concentrates. In this method, surface adjusters such as sodium hexametaphosphate are added to the pentlandite concentrate, and the slurry is evenly dispersed through stirring; magnetic seeds and surfactants are then added, and after stirring, the magnetic seeds and the pentlandite concentrate are Adhesion agglomeration occurs; and through magnetic separation, a pentlandite concentrate with a magnesium content of less than 6.5% calculated as MgO is obtained. This method has the advantages of good selectivity for nickel pyrite minerals, environmental protection, low energy consumption, easy operation, and high efficiency, and solves the problem of high magnesium in nickel concentrate.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
A kind of precipitation calcium carbonate production process that reduces magnesium and increases calcium
InactiveCN103880058BSmall particle sizeHigh whitenessCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesPapermakingSlurry
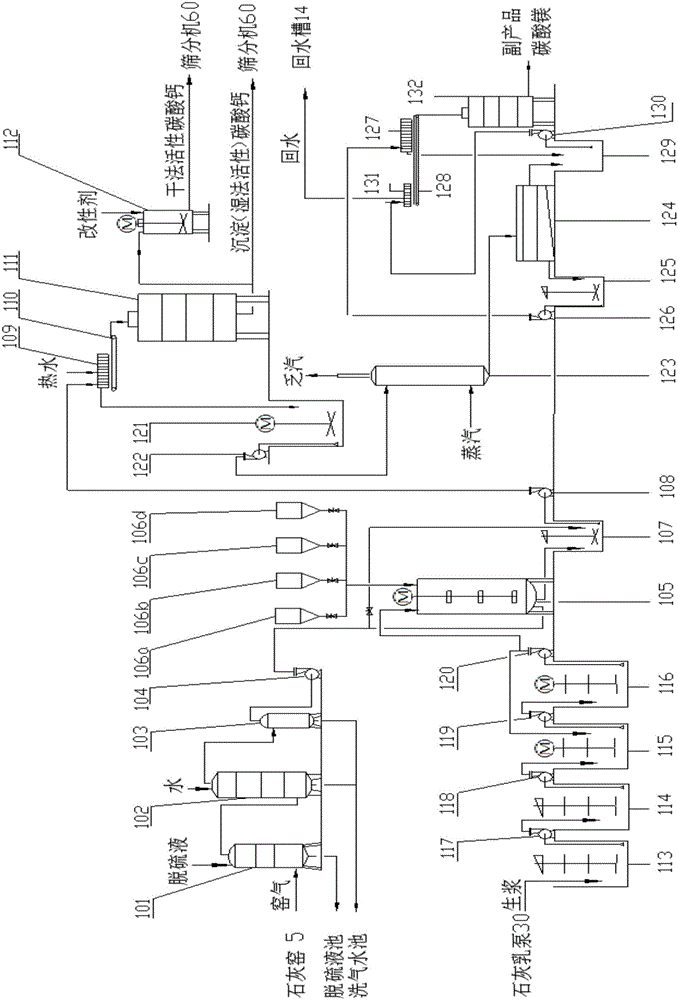
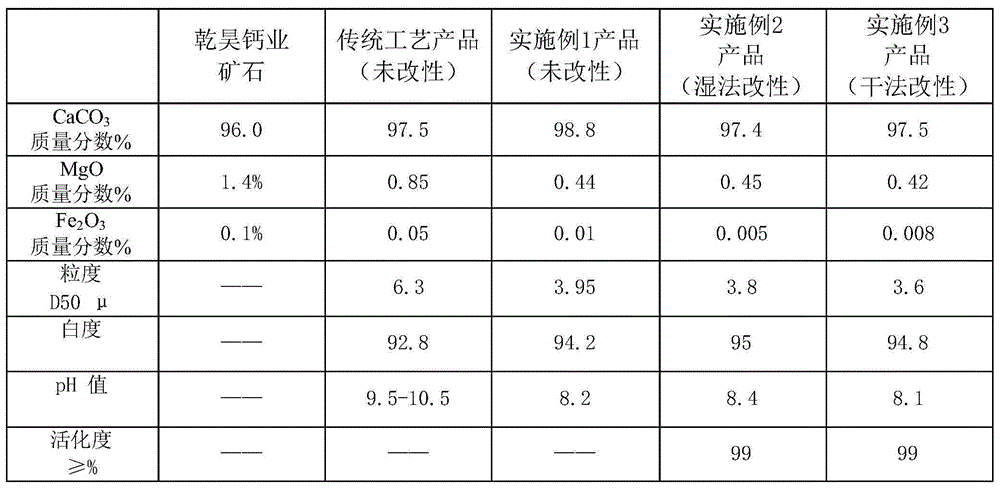
The invention discloses a precipitated calcium carbonate production technology for reducing magnesium and increasing calcium. The technology comprises the steps as follows: 1) a desulfurizing tower is serially connected with a washing tower in kiln gas purification, and a desulfurizer is added to a liquid phase of the desulfurizing tower, so that the purification effect of a kiln gas is improved, and meanwhile, the dosage of circulating water is reduced; 2) a raw slurry pre-ageing process and a dynamic ageing process are adopted, the "back-mixing" phenomenon is avoided, and the ageing time of the raw slurry is ensured; 3) a carbonation reaction kettle adopts a stirring apparatus with three layers of paddles, so that the carbonation reaction time is shortened, and the utilization rate of the kiln gas is increased; 4) magnesium is separated out from mother liquor from which calcium carbonate is separated out by adopting a steam pyrolysis method, filtrate is returned to a digestive process, and cyclic utilization of water is achieved. The precipitated calcium carbonate product obtained by the technology is small in grain size (D50 is approximate to 4mu), high in whiteness (greater than or equal to 94), low in magnesium content (MgO is smaller than or equal to 0.5%), and low in alkalinity (pH is smaller than or equal to 9), and is more applicable to the industries of plastic steel and the like with special demands on the magnesium content, the whiteness, the alkalinity and the like besides of meeting the industries such as rubber, plastic, papermaking and coatings.
Owner:云南和铄投资管理有限公司
A method for producing slag micropowder from copper smelting secondary slag
ActiveCN104446041BPlay a grinding roleHigh slag calcium and magnesium contentCement productionSlagMirabilite
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
A method for preparing magnesium-based hydrotalcite and co-producing boric acid with high magnesium-lithium ratio salt lake brine
ActiveCN105217644BReduce utilizationLow costIron oxides/hydroxidesChromium compoundsResource utilizationMagnesium salt
The invention relates to the field of comprehensive utilization of salt lake resources. Specifically, the invention relates to a method for preparing magnesium-based intercalation functional materials and co-producing boric acid by using salt lake brine with a high magnesium-lithium ratio. The invention uses high-magnesium-lithium salt lake brine as raw material, adds certain soluble trivalent metal salts, fully utilizes magnesium resources in high-magnesium-lithium ratio salt lake brine by synthesizing magnesium-based layered functional materials, and then uses low-magnesium-lithium ratio hydrotalcite mother liquor to prepare boric acid. The preparation method of the magnesium-based functional material and boric acid provided by the present invention can not only effectively solve the problem of complex process, high cost, low utilization rate of salt lake resources, and "magnesium damage" formed in the production process of potash fertilizer in the previous methods, but also greatly reduce the cost of preparing boric acid Moreover, the abandoned magnesium resources can be fully utilized, the production cost of magnesium-based functional materials is reduced, and the high-value and comprehensive utilization of magnesium-boron resources in salt lakes is realized, which has good industrialization prospects.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com