Cement produced by utilizing industrial solid wastes and preparation method of cement
A waste, solid-state technology, applied in the field of cement and its preparation, can solve the problems affecting the ecological protection of Hezhou City, the single utilization of waste residues, and the occupation of land resources by high-magnesium waste rocks, so as to improve the comprehensive utilization range, increase the processing difficulty, The effect of prolonging the setting time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
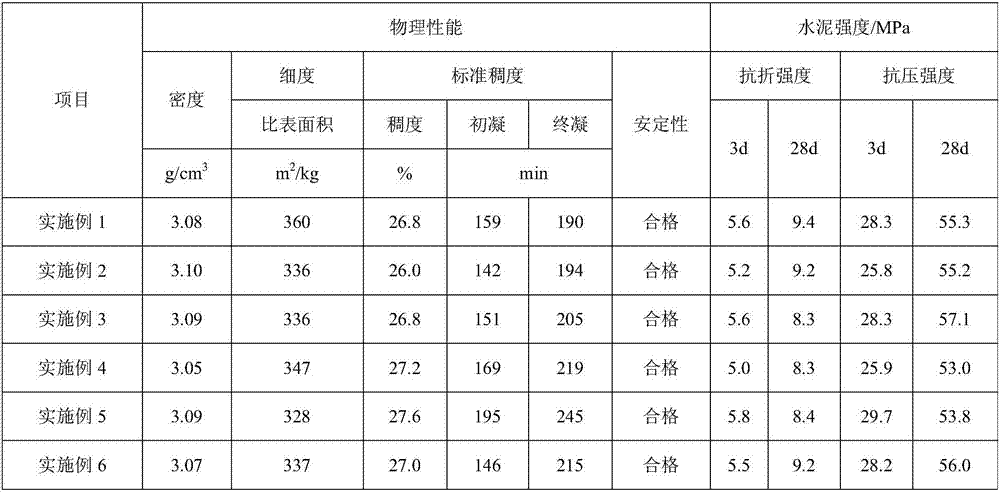
Embodiment 1
[0037] A cement produced from industrial solid waste, made of the following raw materials in weight percentages:
[0038] Clinker 80.50%, furnace bottom slag 3.40%, desulfurization gypsum 2.10%, mining waste rock 4.70%, high silica sandstone 1.00%, fly ash 0.90%, high magnesium waste rock 5.00%, phosphogypsum 2.10%, titanium gypsum 0.30% ;
[0039] Wherein said clinker is made from the raw material of following weight percent:
[0040] Ordinary limestone 73.90%, marble sawdust 4.70%, marble scrap 6.40%, high-magnesium waste rock 2.00%, sandstone 10.60%, laterite 1.90%, wet discharge fly ash 0.50%.
[0041] A preparation method for producing cement by utilizing industrial solid waste, comprising the following steps:
[0042] (1) Press-filter the water content of natural marble or artificial marble sawdust to ≤25%, then mix and grind marble sawdust, marble scraps, high-magnesium waste rock, ordinary limestone, sandstone and laterite according to the mass percentages mentioned ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] A cement produced from industrial solid waste, made of the following raw materials in weight percentages:
[0048] Clinker 82.50%, furnace bottom slag 0.30%, desulfurization gypsum 2.60%, mining waste rock 5.00%, fly ash 6.70%, high magnesium waste rock 2.20%, titanium gypsum 0.70%;
[0049] Wherein said clinker is made from the raw material of following weight percent:
[0050] Ordinary limestone 75.00%, marble sawdust 2.50%, marble scrap 3.50%, high magnesium waste rock 2.00%, sandstone 10.00%, laterite 4.00%, wet discharge fly ash 3.00%.
[0051] In this embodiment, in the clinker, marble waste accounts for 6.00%, high-magnesium waste rocks account for 2%, and when preparing cement, other solid wastes account for 17.50%, of which high-magnesium waste rocks account for 2.20%, and titanium gypsum 0.70%.
[0052] The preparation method is the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0054] A cement produced from industrial solid waste, made of the following raw materials in weight percentages:
[0055] Clinker 77.00%, furnace bottom slag 2.50%, desulfurization gypsum 5.55%, mining waste rock 7.60%, fly ash 5.90%, high magnesium waste rock 0.40%, phosphogypsum 0.55%, titanium gypsum 0.70%;
[0056] Wherein said clinker is made from the raw material of following weight percent:
[0057] Ordinary limestone 80.24%, marble sawdust 2.00%, high-magnesium waste rock 4.10%, sandstone 11.60%, laterite 1.70%, wet discharge fly ash 0.36%.
[0058] In this embodiment, in the clinker, marble wastes accounted for 2.00%, high-magnesium waste rocks accounted for 4.10%, and when preparing cement, other solid wastes accounted for 23.00%, of which high-magnesium waste rocks accounted for 0.40%, titanium gypsum 0.70%.
[0059] The preparation method is the same as in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com