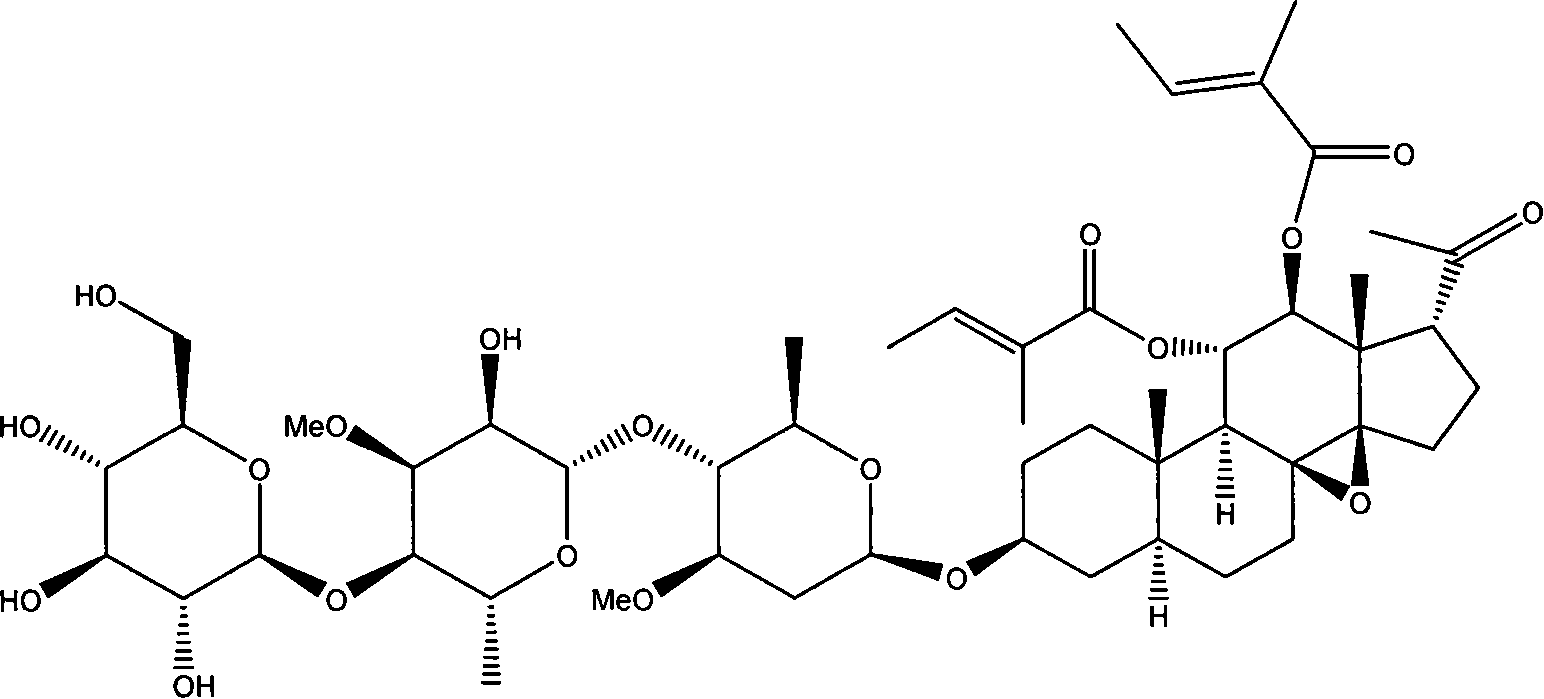
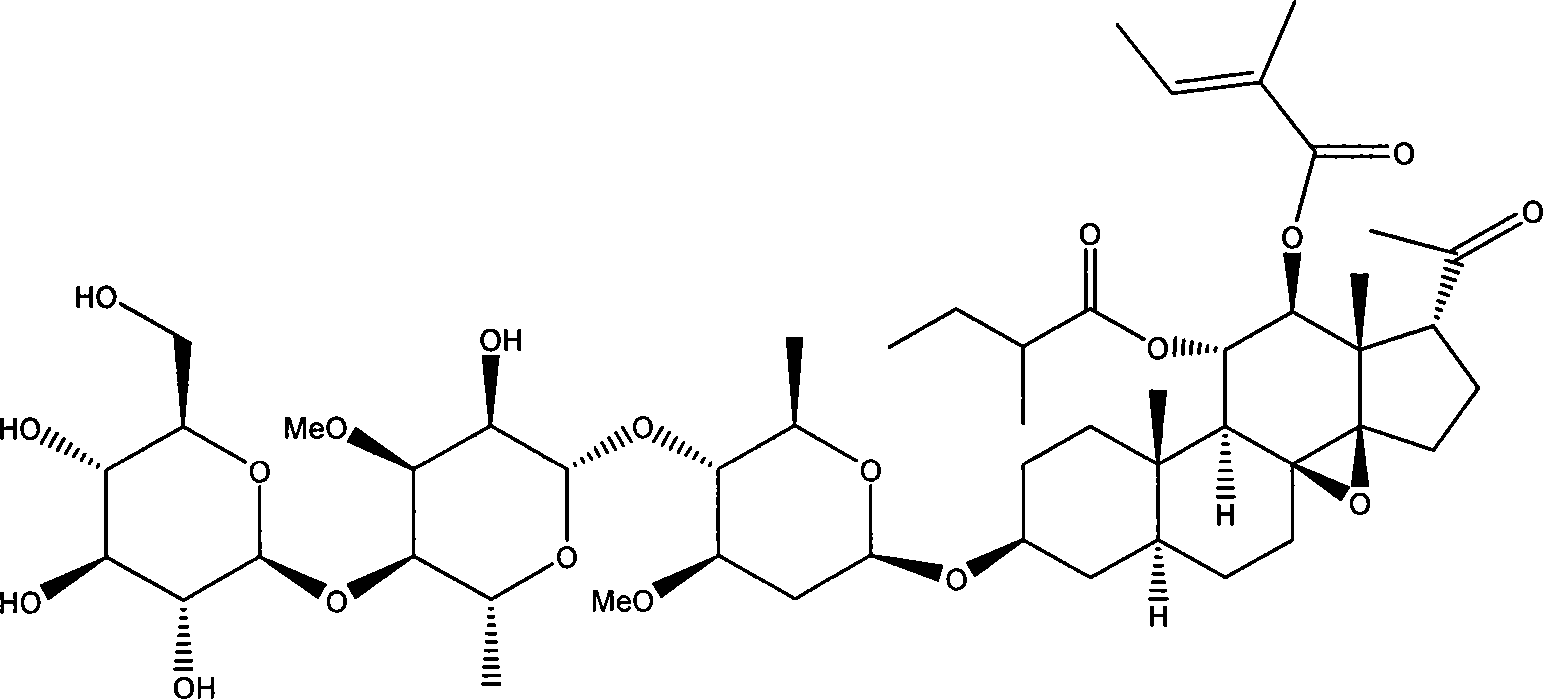
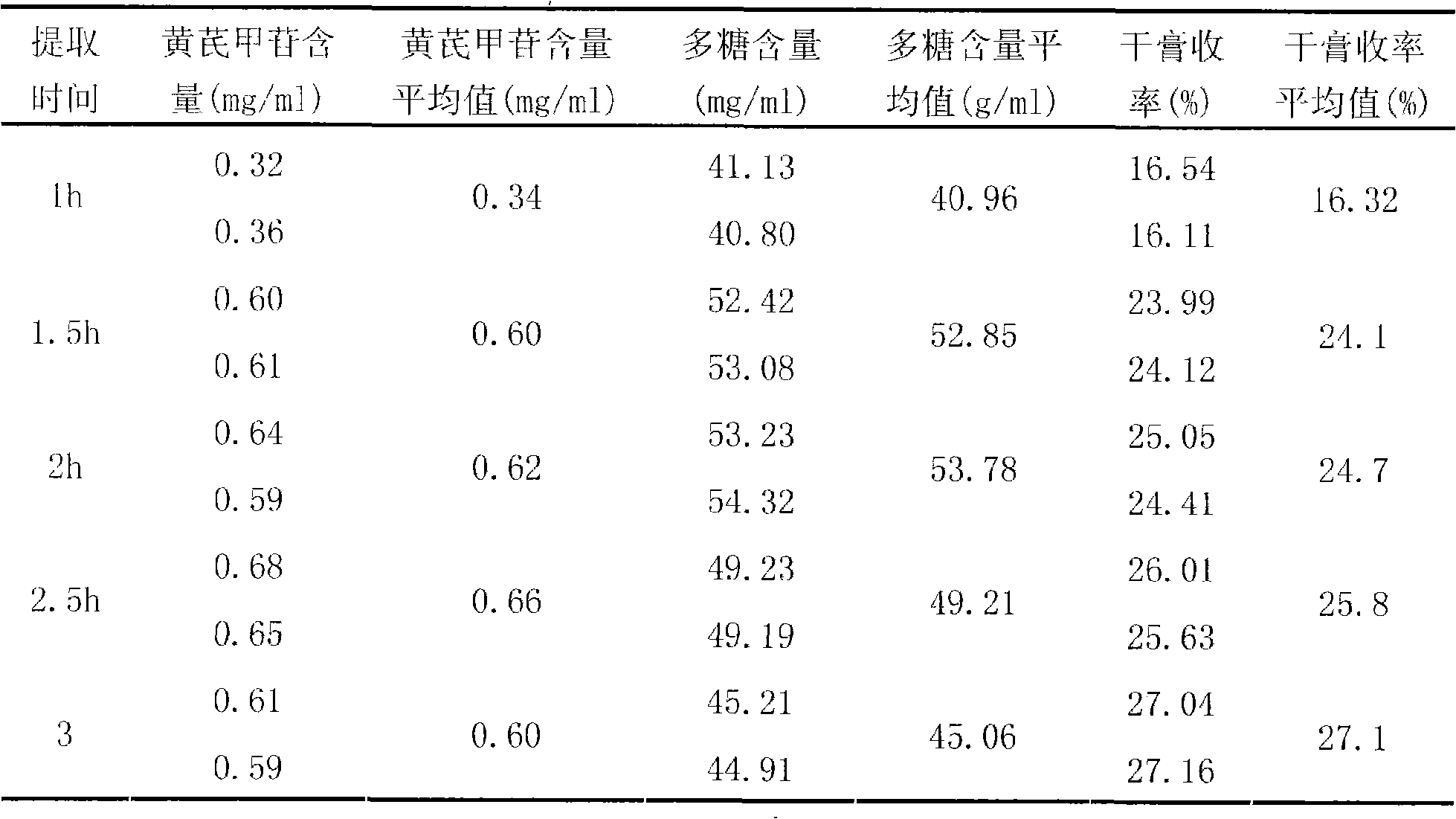
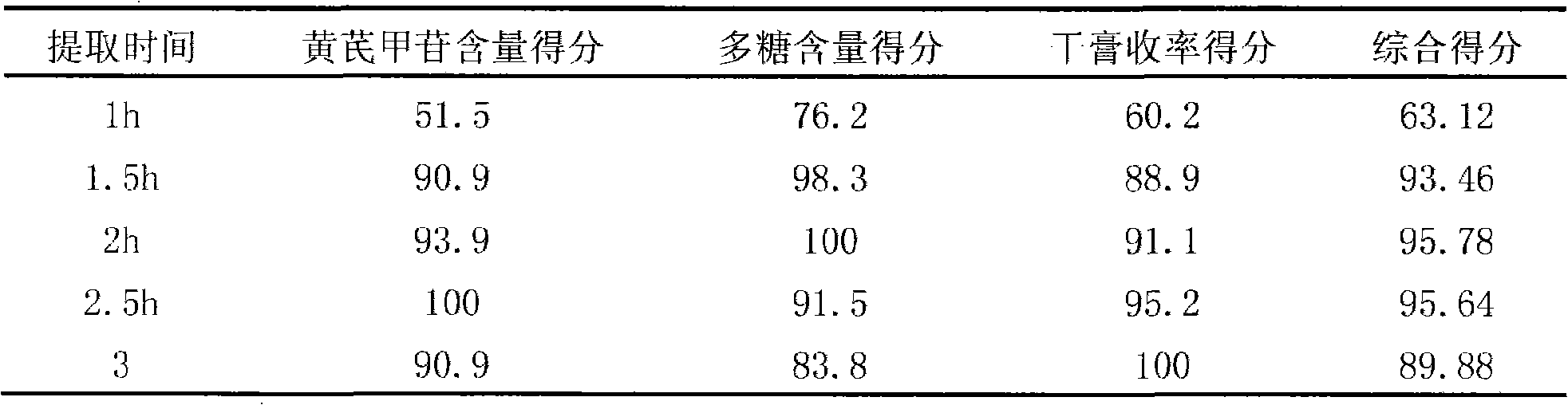
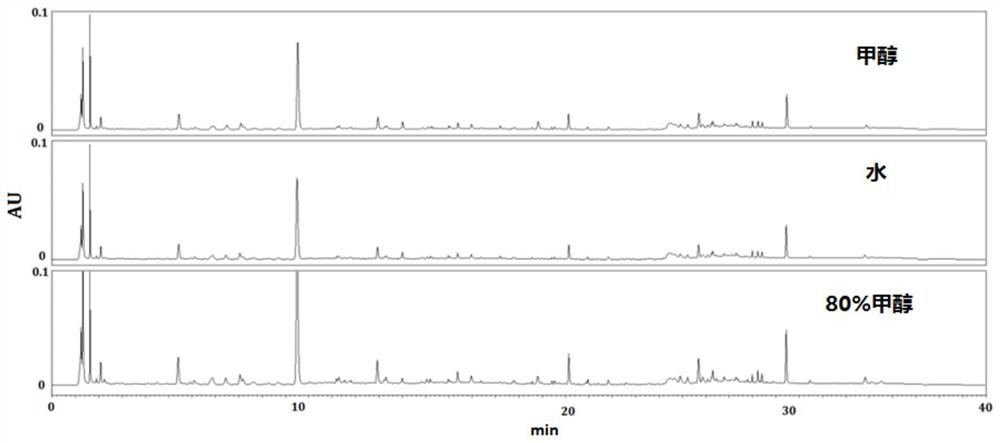
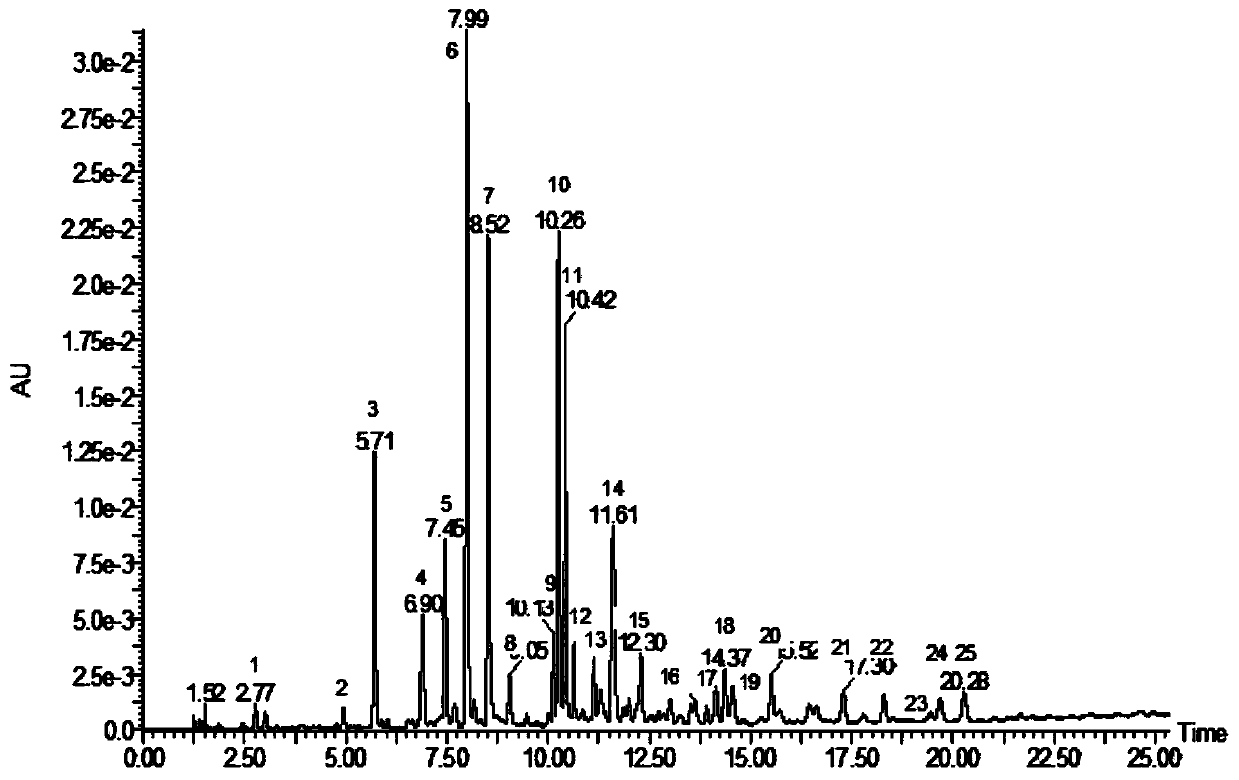
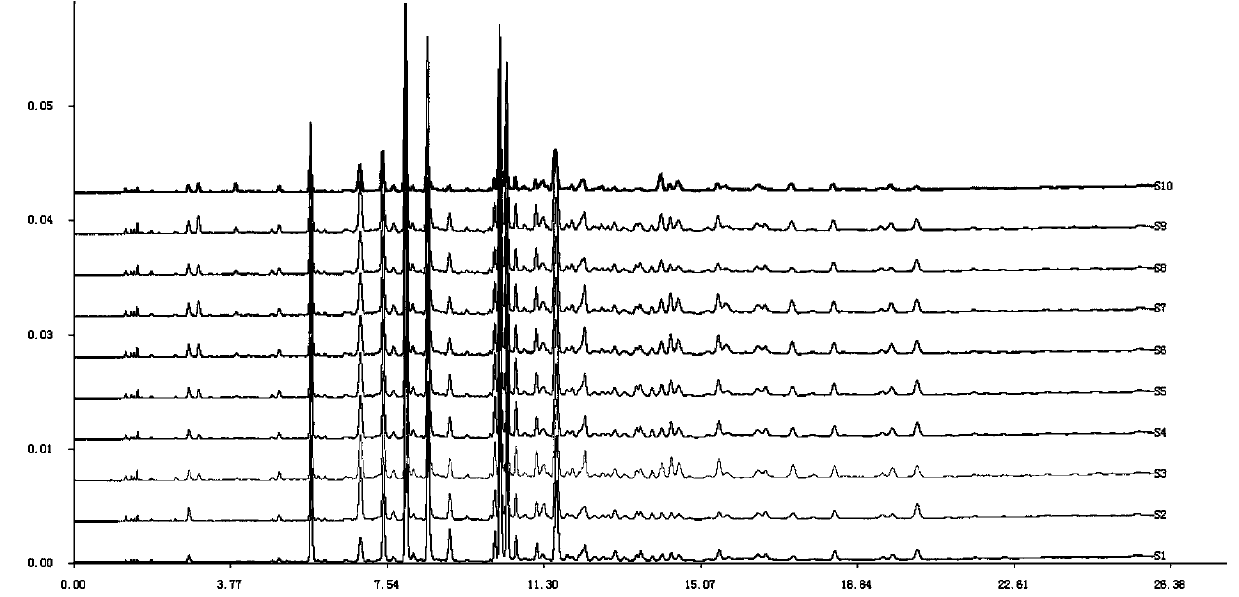
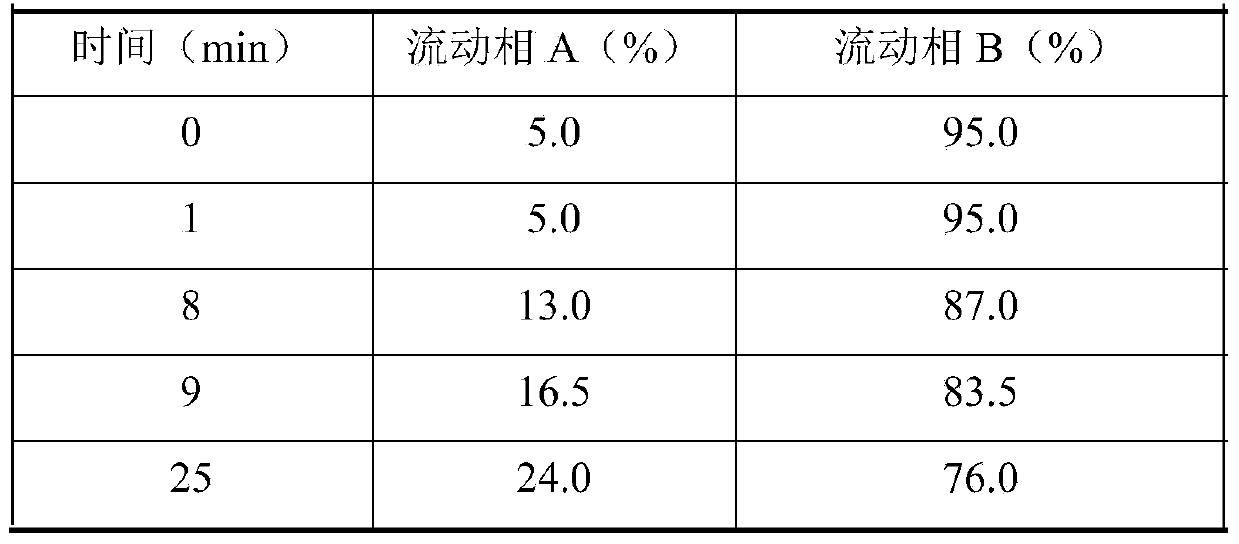
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58results about How to "Control internal quality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
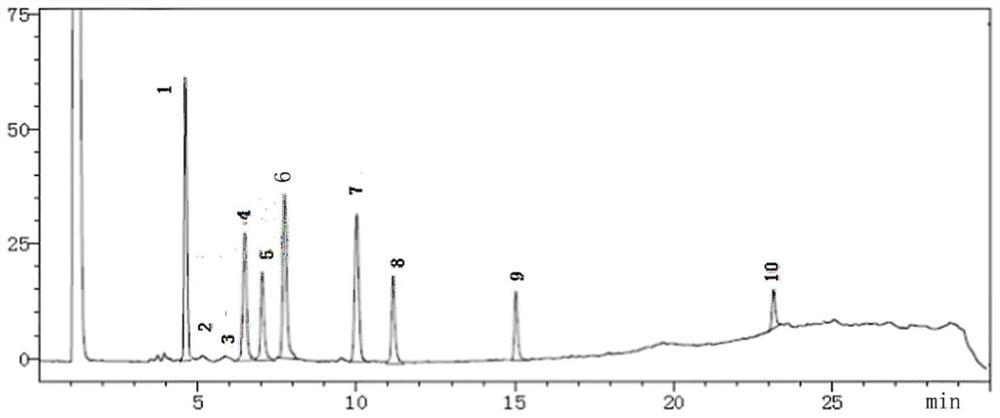
HPLC (high-performance liquid chromatography) detection method capable of simultaneously detecting contents of six amino acids in donkey-hide glue blood-supplementing preparation
ActiveCN102406749ASolve the technical problems of content determinationIncrease varietyComponent separationUnknown materialsPhenyl isothiocyanateAcetonitrile
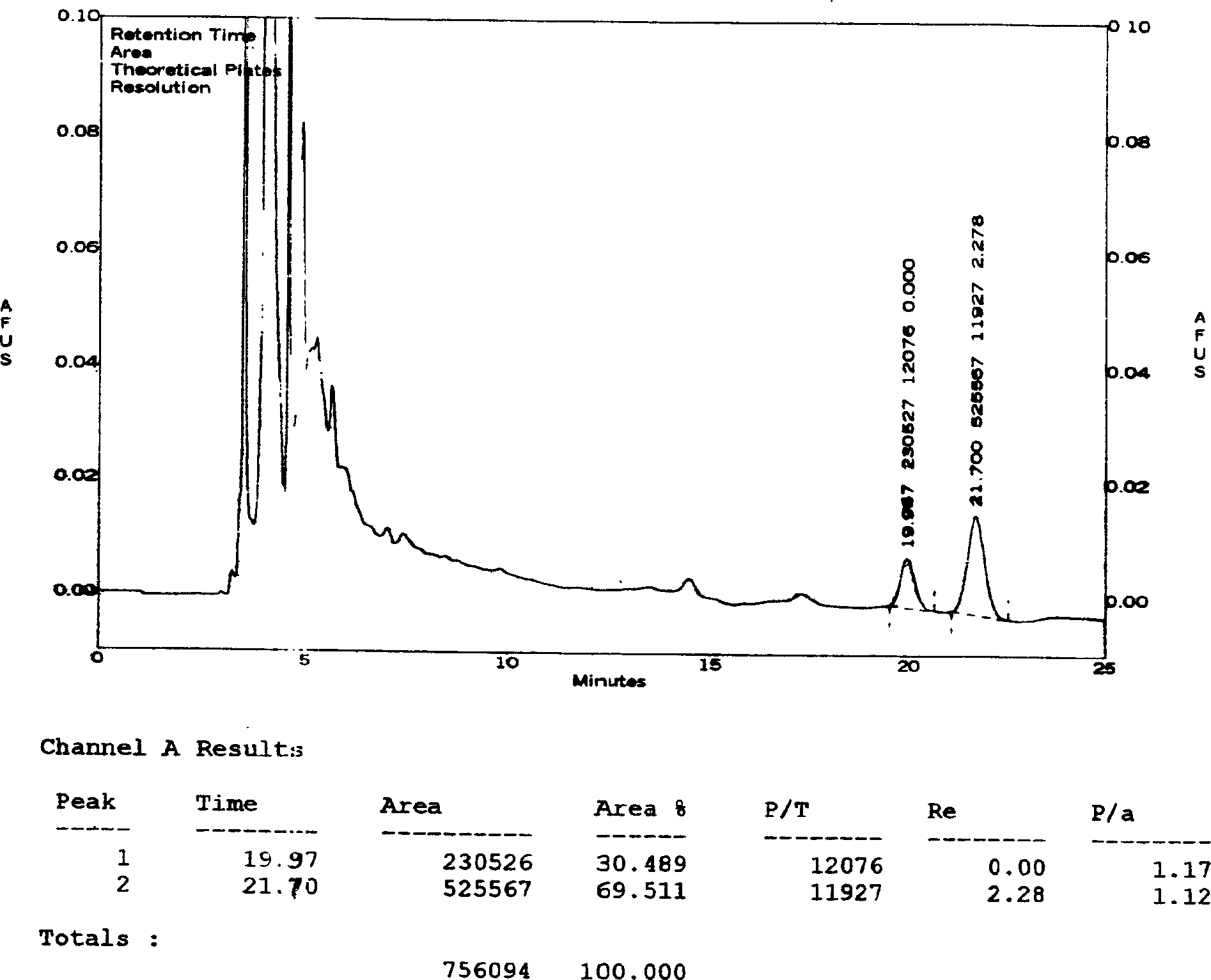
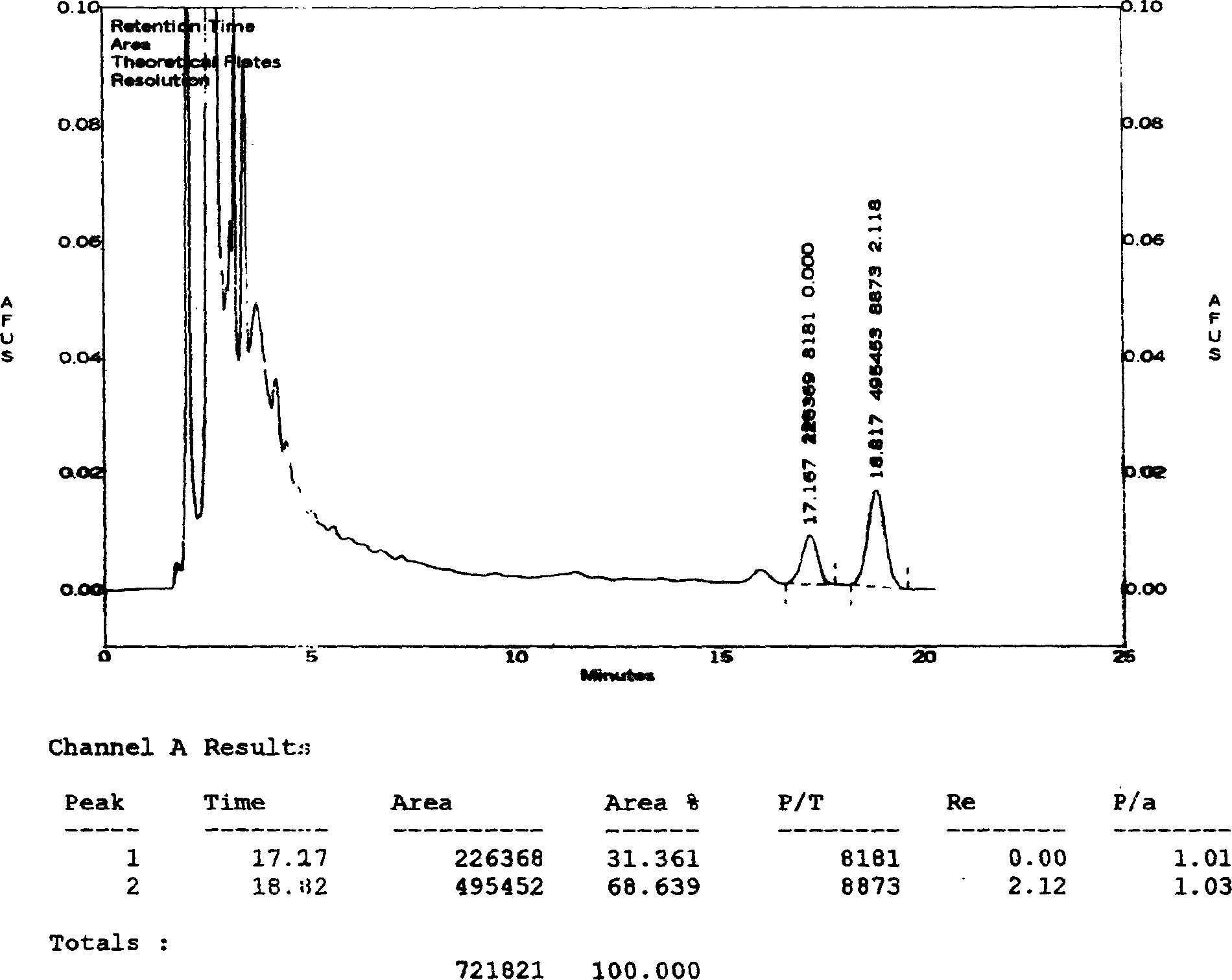
The invention relates to a HPLC (high-performance liquid chromatography) detection method capable of simultaneously detecting contents of six amino acids in a donkey-hide glue blood-supplementing preparation. The method comprises the following steps: providing a donkey-hide glue blood-supplementing preparation sample; providing an amino acid standard sample; respectively adding the donkey-hide glue blood-supplementing preparation sample and the amino acid standard sample into phenylisothiocyanate-acetonitrile solution; uniformly mixing and standing, and respectively adding n-hexane; uniformlymixing and standing once again, respectively extracting lower-layer solutions, and filtering to obtain a derivatized donkey-hide glue blood-supplementing preparation sample solution and a derivatizedamino acid standard sample solution; sucking the derivatized donkey-hide glue blood-supplementing preparation sample solution and the derivatized amino acid standard sample solution, and injecting into a liquid chromatograph to perform amino acid detection. According to the invention, the contents of six major amino acids in the donkey-hide glue blood-supplementing preparation are detected by adopting reversed-phase high-performance liquid-phase, the sample treatment method is simple, the detection method has good specificity, repeatability and accuracy, and the internal quality of donkey-hide glue blood-supplementing granules can be well controlled.
Owner:JIUZHITANG
Glaucescent fissistigma root saponin pharmaceutical composition and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101612183AClear ingredientsStable qualityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDrugSaponin
The invention relates to an extract of a single Chinese medicament, in particular to a glaucescent fissistigma root saponin extract and a preparation method thereof, a pharmaceutical composition, anti-tumor application thereof and the like.
Owner:CHIA TAI TIANQING PHARMA GRP CO LTD
Radix astragali particle and quality control method thereof
InactiveCN101342230AImprove clinical effectivenessPromote dissolutionComponent separationUrinary disorderAstragalus polysaccharideAlcohol
The invention discloses a raidx astragali particle. The radix astragali particle is prepared by a following method: the medicinal materials of the radix astragali are decocted with water and extracted twice; the medicinal materials of the radix astragali are decocted for 1.5 to 2.5hours every time; decoctions are put together and filtered; filtrate is concentrated into a clear paste with relative density of 1.20 to 1.30 (70 to 80 DEG C); auxiliary materials are added and mixed evenly; then the medicinal materials of the radix astragali and the auxiliary materials are processed by granulation, drying, sub-package and sterilization; and the raidx astragali particle is made. The radix astragali particle is prepared by the new method and the procedures of alcohol precipitation is reduced. That decoction time is changed is beneficial to the dissolution and preservation of effective components. As a result, the effective components of the medicinal materials of the radix astragali, including astragalus polysaccharides and total saponin, and the like, are reserved in the radix astragali particle as much as possible, thus greatly improving the content of the effective components so as to improve the clinical effectiveness of the raidx astragali. Meanwhile, production period is greatly shortened; energy consumption is decreased; and cost is lowered. The invention also provides a quality control method of the raidx astragali particle.
Owner:SICHUAN BAILI PHARM CO LTD
Method for measuring content of amino acid in black-bone chicken milk increasing preparation
InactiveCN105223280AAccurate determination of contentControl internal qualityComponent separationHydrolysateTotal nitrogen
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of amino acid in a black-bone chicken milk increasing preparation. The method comprises the following steps: subjecting a black-bone chicken milk increasing preparation to a protein hydrolysis treatment; and then using an amino acid analyzer to analyze the hydrolysate so as to measure the amino acid content. In the conventional standards, the protein content can be only represented by total nitrogen content, the provided method can overcome the shortage, moreover, the method can precisely measure contents of 17 amino acids in the preparation, has the advantages of simple pretreatment, strong specificity, good repeatability, and high precision, can well control the quality of the black-bone chicken milk increasing preparation, and improves the safety and effectiveness of the preparation.
Owner:天津飞鹰玉川药业有限公司
Detection method of traditional Chinese medicinal composition for treating waist and knee pains and sciatica
ActiveCN106918674AIncrease quantitative detectionControl internal qualityComponent separationSciaticaBoswellia
The invention provides a detection method of a traditional Chinese medicinal composition for treating waist and knee pains and sciatica. Raw materials of the traditional Chinese medicinal composition comprise Rhizoma Cibotii, Fructus Rosae Laevigatae, Caulis Spatholobi, Philippine flemingia root, Kadsura coccinea, Millettia specisoa Champ, Ligustri Lucidi Fructus, Chinese Taxillus Twig, semen cuscutae, Rhizoma Corydalis, Zanthoxylum nitidum, Boswellia carteri and myrrh. The detection method comprises the following steps: detecting the content of (2'S)-Kadsura longepedunculata lignin J in the Kadsura coccinea through high performance liquid chromatography; and detecting the content of specnuezhenide in the Ligustri Lucidi Fructus through the high performance liquid chromatography, and detecting the Kadsura coccinea, the Rhizoma Cibotii and the Chinese Taxillus Twig through thin layer chromatography. The invention also concretely discloses conditions and concrete operating steps of all above detection technologies. The detection method allows five raw materials to be qualitatively and quantitatively detected, and the quantity of the detected raw materials is 1 / 3 of the total quantity of the raw materials, so the quality of medicines is effectively guaranteed, and medical demands are met.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CHEN LI JI PHARMA FACTORY
Lead-free and preferably arsenic-free dense optical crown glass
The lead-free, Li2O-free, CuO-free and preferably arsenic-free optical glass is suitable for applications in the fields of imaging, projection, telecommunications, optical communication technology and / or laser technology, and has a refractive index nd of 1.55≦nd≦1.60, an Abbe number Vd of 54≦Vd≦63 and a transformation temperature Tg≦500° C. This optical glass has good production and processing properties and crystallization stability, and, at the same time, advantageously does not contain PbO and As2O3. These glasses contain, in percent by weight based on oxide content: P205, 43-56; ZnQ, 21-36; Al2O3, 0-6; Na2O, 0-16; K2O, 0-8; ΣM2O ≦16; MgO, 0-5; CaO, 0-5; BaO, 3-14; B2O3, 0-8; La2O3, 0-7. In addition, it may also contain standard refining agents.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Method for identifying glossy privet fruit medicinal material or derivative
ActiveCN103868943AControl internal qualitySolve the identification problemComponent separationAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceFingerprint detection
The invention relates to a method for identifying a glossy privet fruit medicinal material or a derivative. The method comprises the following steps: extracting the glossy privet fruit medicinal material or the derivative to obtain a glossy privet fruit iridoid glycoside characteristic extract containing an active ingredient group; performing IGD (Inverted Gated Decoupling) nuclear magnetic resonance carbon spectrum fingerprint detection on the glossy privet fruit iridoid glycoside characteristic extract, and obtaining characteristic peak intensities of a plurality of active ingredients in the glossy privet fruit iridoid glycoside characteristic extract according to the fingerprint; measuring the characteristic peak intensity of a standard reference object corresponding to each active ingredient in the same manner; measuring the absolute content of the standard reference object through a quantitative analysis method; calculating the content of each active ingredient and the content of the active ingredient group in the glossy privet fruit medicinal material or a derivative by using the ratio of the characteristic peak intensities and the absolute content of the standard reference object. According to the method, the glossy privet fruit iridoid glycoside compounds contained in the glossy privet fruit and the ratio of the compounds can be reflected so as to achieve the aims of variety identification and quality determination of the glossy privet fruit medicinal material.
Owner:河南省科高植物天然产物开发工程技术有限公司 +1
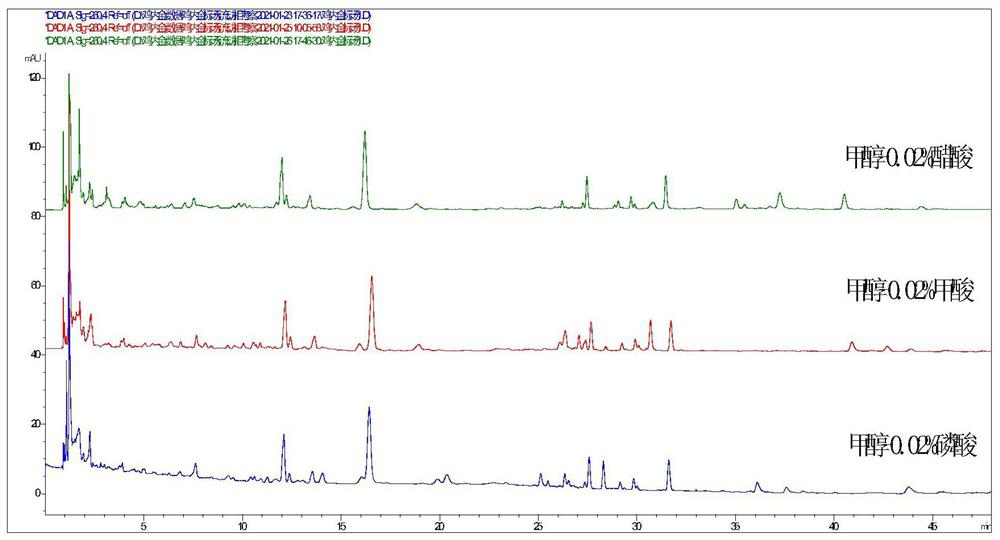
Construction method, detection method and application of fingerprint spectrum of Juanbi decoction composition
ActiveCN114200046AAvoid product qualityQuality improvementComponent separationAgainst vector-borne diseasesChlorogenic acidLoganic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and particularly relates to a construction method, a detection method and application of a fingerprint spectrum of a Juanbi decoction composition. The construction method of the fingerprint spectrum comprises the following steps: taking a Juanbi decoction composition, adding an extraction solvent, weighing, carrying out ultrasonic treatment, cooling, weighing again, complementing the lost weight by using the extraction solvent, uniformly shaking, filtering, and taking a subsequent filtrate to obtain a test solution; 11 reference substances such as loganic acid, mulberroside A, chlorogenic acid and gentiopicroside are taken and prepared into reference substance solutions of the reference substances; respectively and precisely sucking 1-2mu L of the reference solution and the test solution, injecting the reference solution and the test solution into a liquid chromatograph for chromatographic analysis, measuring and recording chromatograms to respectively obtain a test fingerprint spectrum and a reference chromatogram spectrum, and formulating a standard fingerprint spectrum of the Juanbi decoction composition. According to the present invention, the quality information of the Juanbi decoction can be comprehensively reflected by the fingerprint so as to achieve the purpose of more comprehensively and effectively controlling the quality of the Juanbi decoction preparation product.
Owner:SINOPHARM GUANGDONG GLOBAL PHARMA CO LTD
HPLC fingerprint determination method of cough relieving Bulbus fritillariae cirrhosae and loquat dripping pills
ActiveCN103487528AGuaranteed stabilityGuarantee the safety of useComponent separationHplc fingerprintHplc method
An HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) fingerprint determination method of cough relieving Bulbus fritillariae cirrhosae and loquat dripping pills comprises the following steps: 1, cough relieving Bulbus fritillariae cirrhosae and loquat dripping pill tested substance solution preparation: preciously weighing the cough relieving Bulbus fritillariae cirrhosae and loquat dripping pills, and carrying out ultrasonic extraction of the cough relieving Bulbus fritillariae cirrhosae and loquat dripping pills by using 30-100% ethanol as an extraction solvent to prepare a tested substance solution; and 2, injecting the solution obtained in step 1 into a high performance liquid chromatograph, and determining to obtain a cough relieving Bulbus fritillariae cirrhosae and loquat dripping pill fingerprint. An HPLC method is adopted to establish the fingerprint according to the self characteristics of the cough relieving Bulbus fritillariae cirrhosae and loquat dripping pills, and optimal chromatogram conditions are found, so the determination result is precious, and has a good reappearance and a good stability.
Owner:津药达仁堂集团股份有限公司第六中药厂
Quality detection and control method for south Schisandrol extract
InactiveCN1866026AControl internal qualityColor/spectral properties measurementsTesting foodAlcoholLignan
The disclosed quality control method for longipeduncle kadsura alcohol extract comprises: with dry extract weight as base, determining total lignans content not less than 5.6% with ultraviolet spectrophotometry, or the ester content not less than 0.7% by HPLC, or lignans not less than 1.0% by HPLC. This invention has well control effect.
Owner:SICHUAN HEZHENG PHARM CO LTD
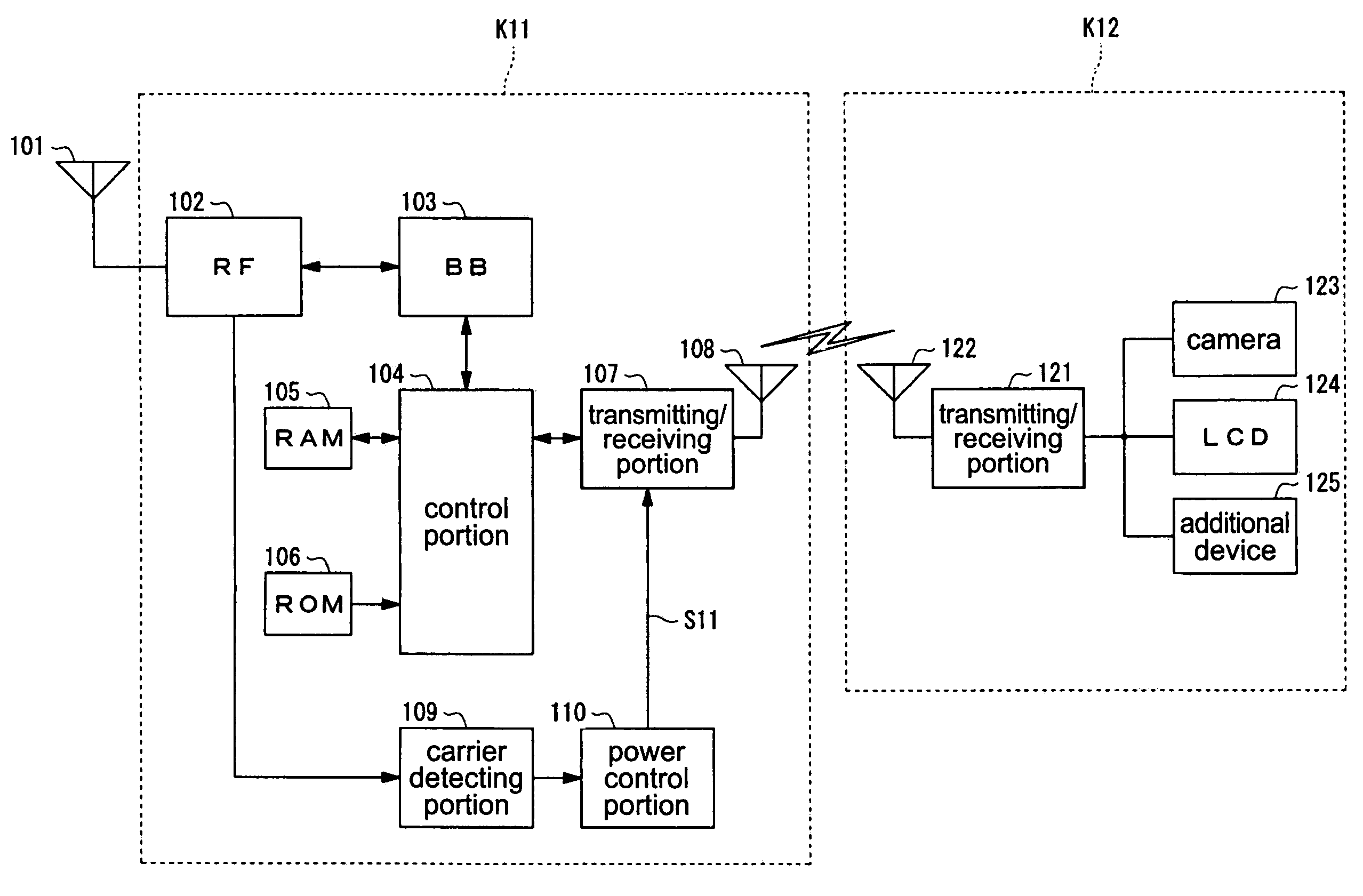
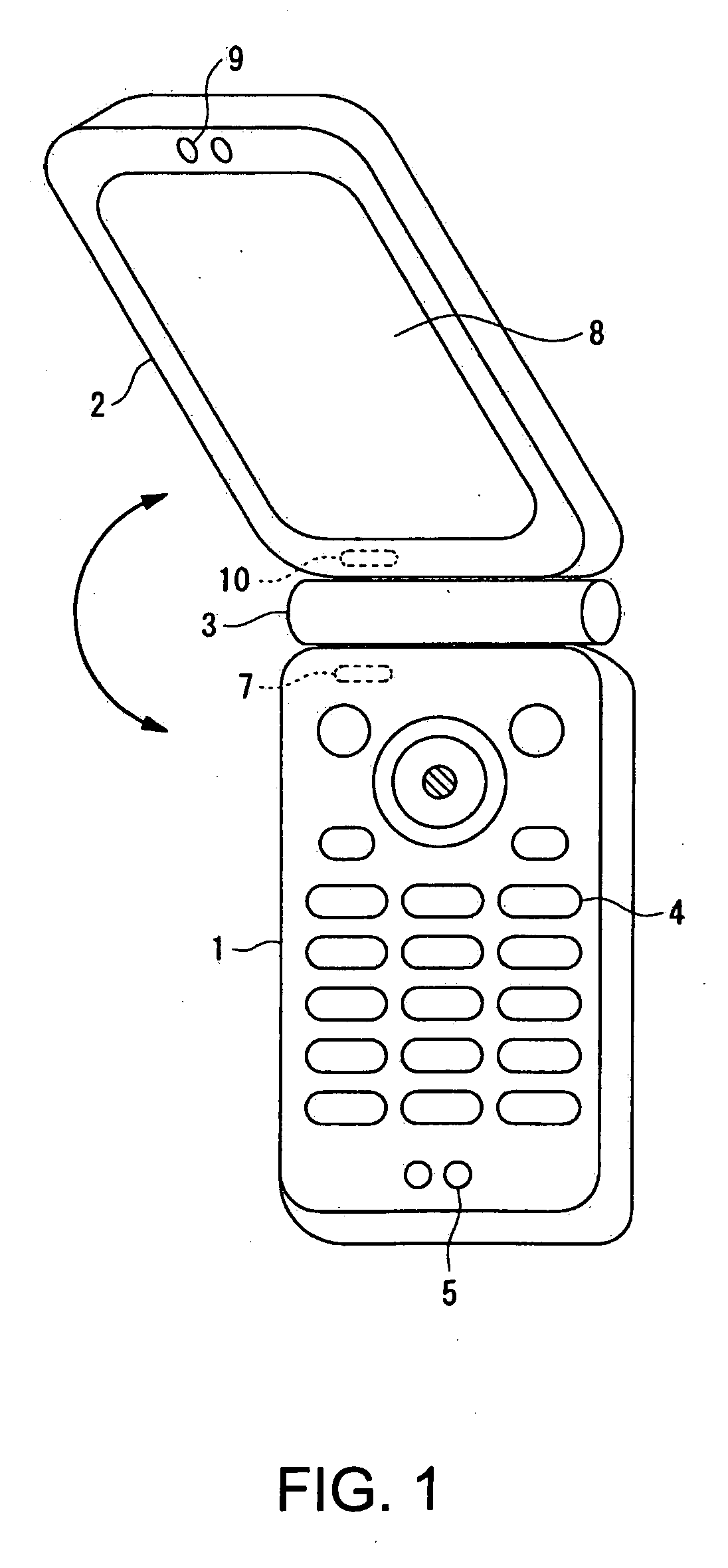
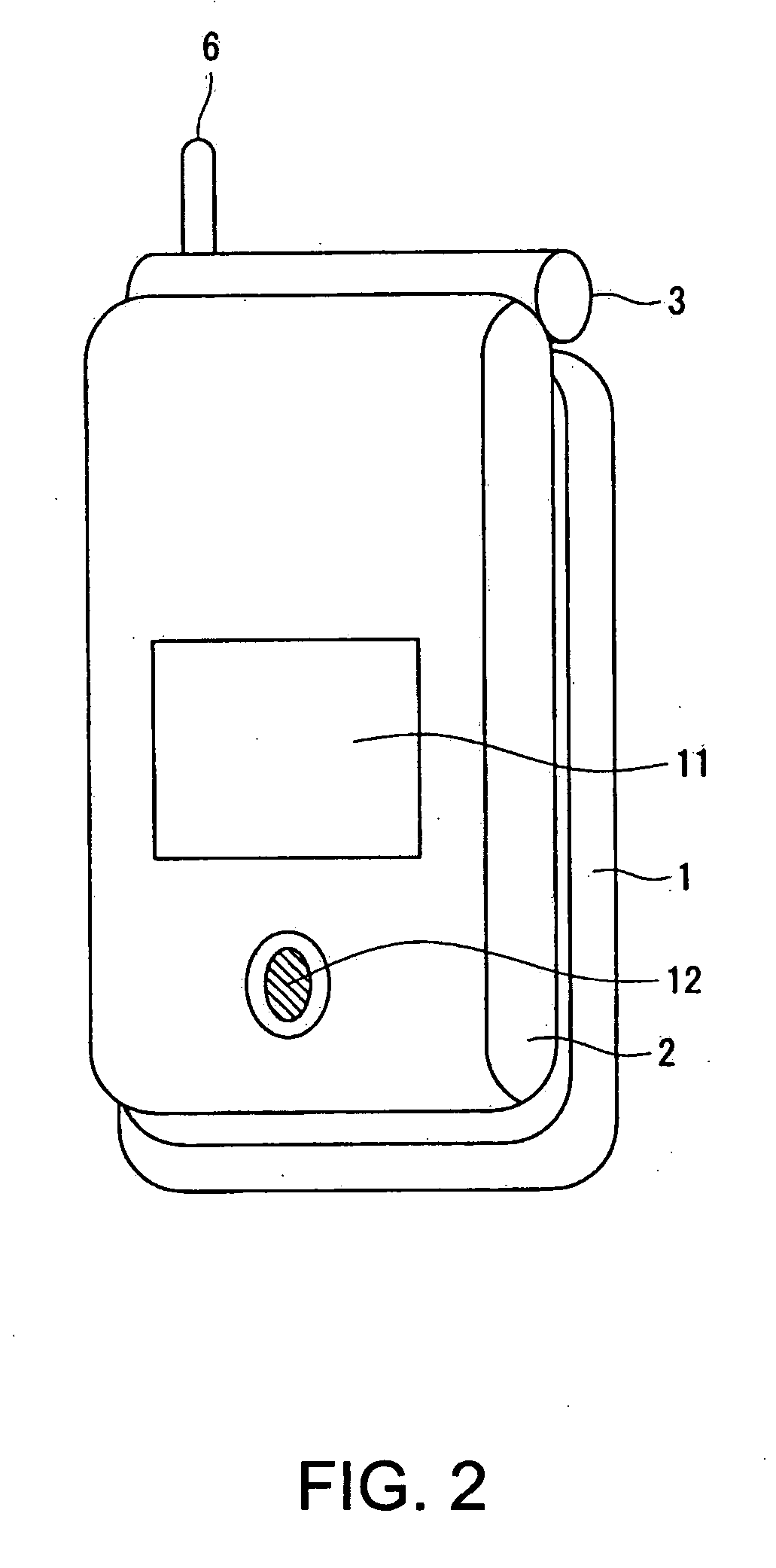
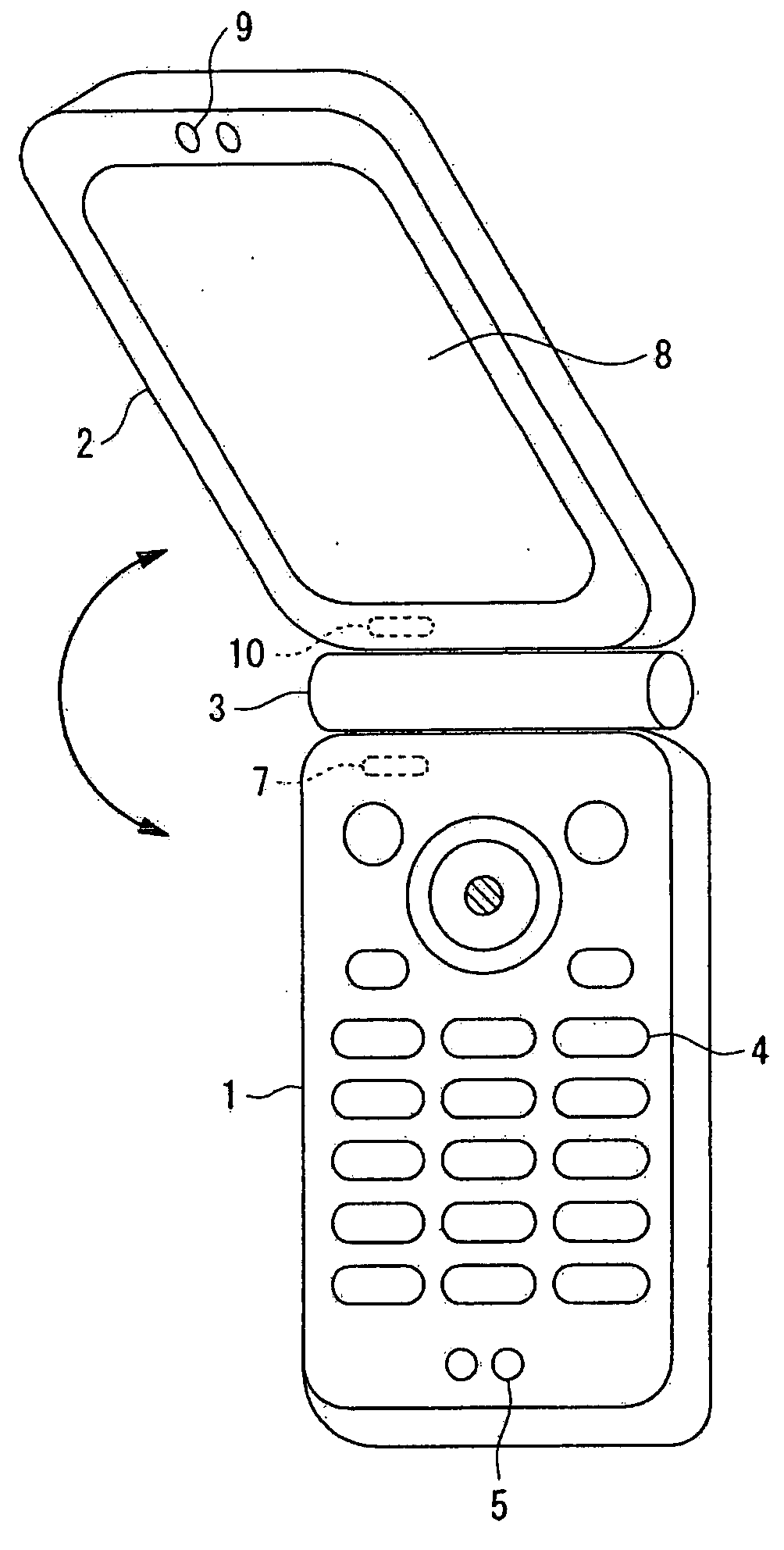
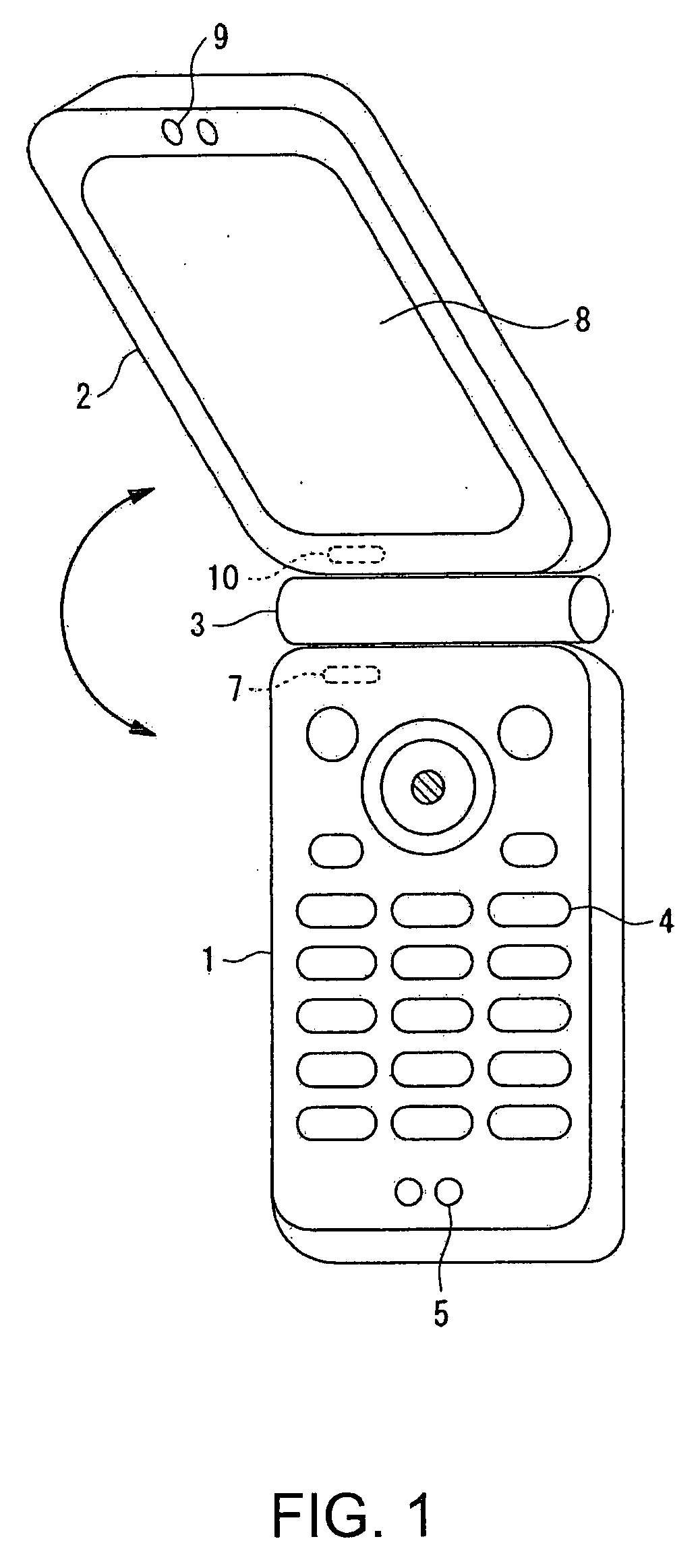
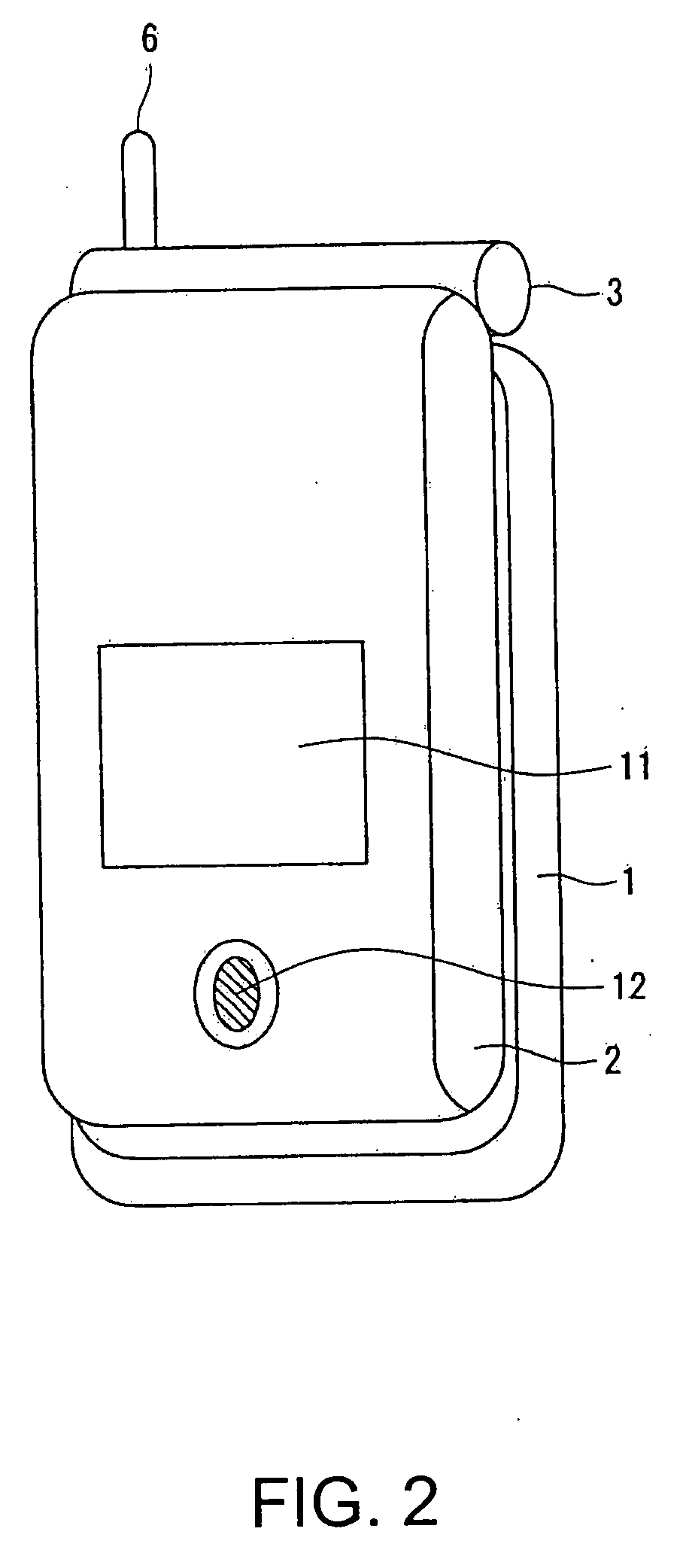
Wireless communication terminal and mobile type wireless communication terminal
InactiveUS7251510B2Quality improvementControl internal qualityEnergy efficient ICTInterconnection arrangementsCouplingCommunication control
A wireless communication terminal includes first and second case members coupled together by a coupling portion so that the positional relation therebetween can be changed, an external wireless communication antenna provided at the first case member, an external wireless communication control portion mainly controlling external wireless communication carried out through the external wireless communication antenna, a first internal wireless communication antenna, a first internal wireless communication control portion controlling internal wireless communication carried out through the first internal wireless communication antenna, a display part provided at the second case member, a second internal wireless communication antenna, a second internal wireless communication control portion controlling internal wireless communication carried out through the second internal wireless communication antenna, and an output power control portion controlling the output power of waves transmitted by the internal wireless communication based on the timing of transmitting waves transmitted through the external wireless communication antenna.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Wireless communication terminal and mobile type wireless communication terminal
InactiveUS20050288073A1Quality improvementControl internal qualityEnergy efficient ICTInterconnection arrangementsCouplingCommunication control
A wireless communication terminal includes first and second case members coupled together by a coupling portion so that the positional relation therebetween can be changed, an external wireless communication antenna provided at the first case member, an external wireless communication control portion mainly controlling external wireless communication carried out through the external wireless communication antenna, a first internal wireless communication antenna, a first internal wireless communication control portion controlling internal wireless communication carried out through the first internal wireless communication antenna, a display part provided at the second case member, a second internal wireless communication antenna, a second internal wireless communication control portion controlling internal wireless communication carried out through the second internal wireless communication antenna, and an output power control portion controlling the output power of waves transmitted by the internal wireless communication based on the timing of transmitting waves transmitted through the external wireless communication antenna.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
HPLC (high-performance liquid chromatography) fingerprint spectrum measurement method for standard Yunujian decoction
ActiveCN107643343AGuaranteed stabilityGuarantee the safety of useComponent separationHplc fingerprintMedicine
The invention provides an HPLC (high-performance liquid chromatography) fingerprint spectrum measurement method for a standard Yunujian decoction, and belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicine. The HPLC fingerprint spectrum measurement method includes (1), preparing a sample solution for test; (2), preparing a mixed reference substance solution; (4), accurately sucking the sample solution for test and the mixed reference substance solution, and injecting the solutions into a high-performance liquid chromatograph for measurement to acquire liquid chromatograms of the samplesolution for test and the mixed reference substance solution; (5), matching data of the liquid chromatograms of the sample solution for test and the mixed reference substance solution by traditionalChinese medicinal chromatography fingerprint spectrum similarity evaluation system software made by Chinese Pharmacopeia Commission to acquire a standard fingerprint spectrum. The HPLC fingerprint spectrum measurement method for the standard Yunujian decoction has the advantages that quality of standard Yunujian particles is controlled effectively, curative effect of the medicine is guaranteed, and the classic prescription is enabled to be under standard quality control.
Owner:天津同仁堂集团股份有限公司
Finger-print quality determination method on wuji powder preparation and intermediate thereof
ActiveCN101920001AGuaranteed stabilityGuarantee the safety of useComponent separationDigestive systemPhosphoric acidGradient elution
The invention discloses a finger-print quality determination method on wuji powder preparation and intermediate thereof. The finger-print quality determination method includes the following steps: quantitative wuji powder preparation or intermediate thereof is weighed, at least one of solvents of water, methyl alcohol or ethyl alcohol is used for extraction, constant volume is carried out, so as to obtain test solution; the test solution is sucked and injected into a liquid chromatograph, and high efficiency liquid chromatography and gradient elution are adopted for carrying out determination, so as to obtain the finger-print of wuji powder preparation or intermediate thereof; wherein the chromatographic conditions of the high efficiency liquid chromatography include that the filler of chromatographic column is octadecylsilane chemically bonded silica, mobile phase A is methyl alcohol, mobile phase B is phosphoric acid aqueous solution, the volume ratio of the mobile phase A and the mobile phase B is gradually increased along with time, and detection wavelength is 285-305nm. The invention has the characteristics that method is simple and stable, has high precision and good reproducibility and is easy to grasp.
Owner:JIUZHITANG
Quality control method for vatility source preparation
InactiveCN1857602AControl internal qualityGood curative effectNervous disorderComponent separationClinical efficacyMedicine
The present invention discloses quality control method for vitality source preparation. The quality control method includes the identification of ophiopogon, ginsenoside, schisandra and astragalus in the vitality source preparation; the limit inspection of aconitine; and the measurement of ginsenoside content. The identification, the inspection and the measurement may be adopted alone or in combination in the quality control. The present invention makes it possible to raise the quality of vitality source preparation so as to ensure the stable and reliable curative effect of vitality source preparation and reduce adverse reaction.
Owner:CHENGDU ZHONGHUI PHARM CO LTD
Method for simultaneously detecting contents of four components of traditional Chinese medicine for treating children cough
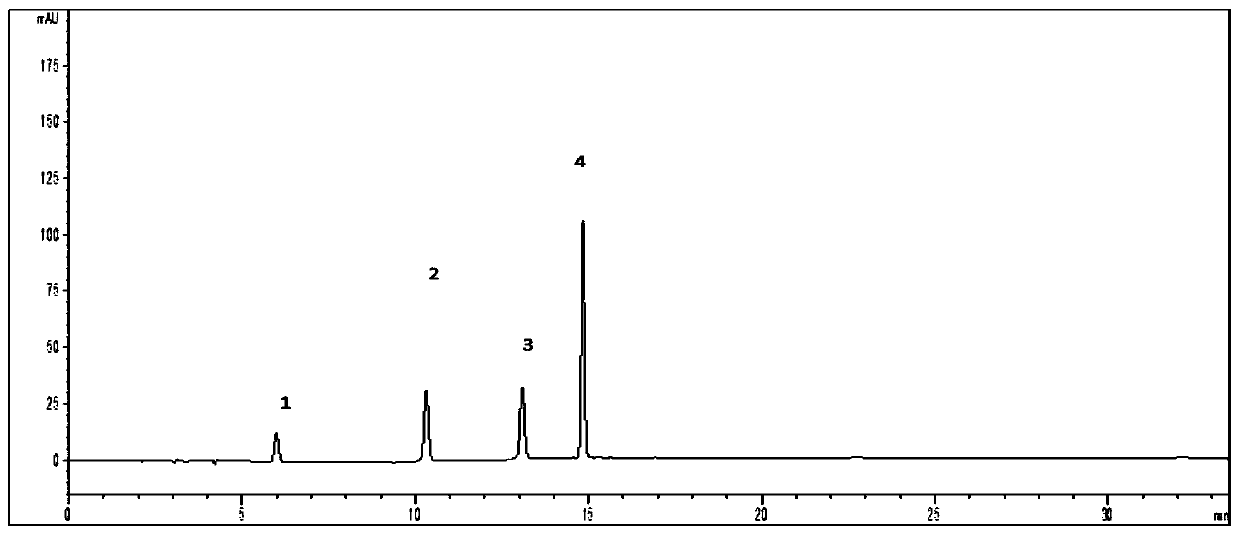
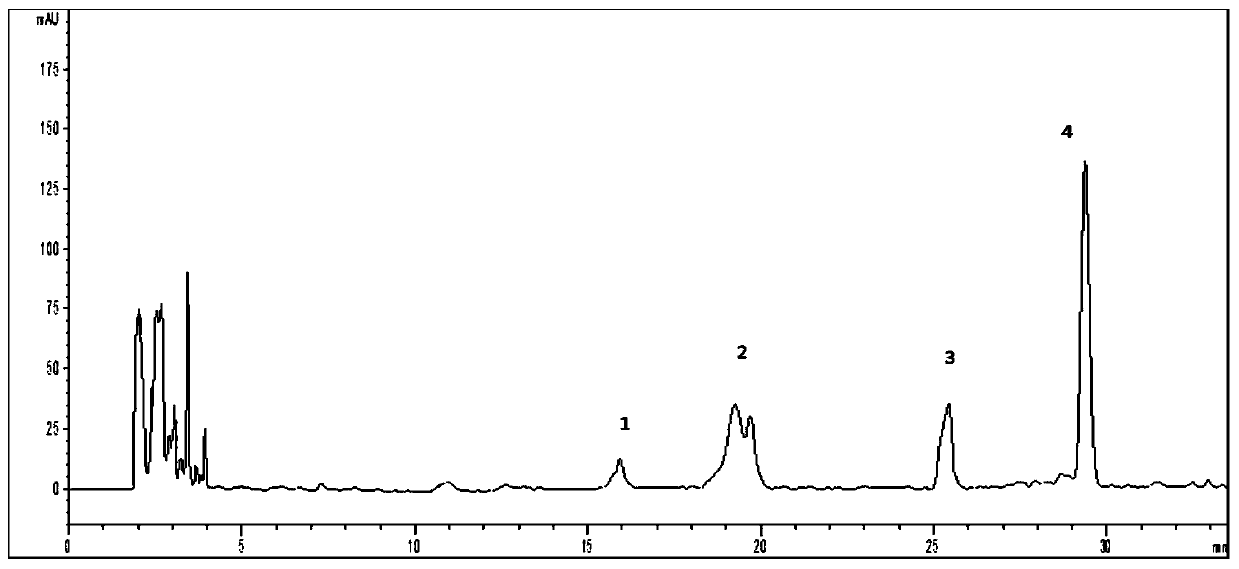
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously detecting the contents of four components of a traditional Chinese medicine for treating children cough. The traditional Chinese medicine for treating children cough is prepared from burdock, mulberry leaves, bulbus fritillariae cirrhosae, mint, radix isatidis, schizonepeta spike, fructus aurantii, radix peucedani, aster and liquorice, the four components are liquiritin, naringin, neohesperidin and arctiin, and the method comprises the following steps: extracting a sample to be detected with an extraction solvent, and detecting with a high performance liquid chromatograph. According to the method, the contents of the four substances can be detected at the same time, the adopted chromatographic conditions are good in separation effect, short in peak appearance time, good in detection result reproducibility and high in accuracy, and the quality of the traditional Chinese medicine is more controllable.
Owner:JIANMIN PHARMA GRP CO LTD
Determination of Chinese patent drug Chinese magnoliavine fruit content made from Chinese magnoliavine fruit extract
InactiveCN1895358AControl internal qualityHigh sensitivityComponent separationPlant ingredientsAlcoholMedicine
A method for measuring the content of schizandrin A in the Chinese medicine prepared from the alcohol extract of schisandra fruit includes such steps as experiment of chromatographic condition and system adaptivity, preparing the solution of reference, preparing the solution of specimen, and measuring.
Owner:SICHUAN HEZHENG PHARM CO LTD
Jintangning capsule quality detection method
ActiveCN105004829AFully reflect the quality informationControl internal qualityComponent separationFingerprintTraditional Chinese medicine
The present invention relates to a Jintangning capsule quality detection method, wherein a high performance liquid chromatography method is used to prepare the control characteristic map of the Jintangning capsule and the characteristic map of the Jintangning capsule to be tested, the mobile phase comprises acetonitrile, dimethylformamide and 0.025 mol / L sodium acetate according to a volume ratio of 24:0.5:76, the detection wavelength is 390 nm, the flow rate is 0.8 ml / min, and the similarity comparison is performed on the characteristic map of the Jintangning capsule and the control characteristic map of the Jintangning capsule, and the qualified standard is that the similarity is greater than 0.90. According to the present invention, the control characteristic map prepared by the method can completely reflect the quality information of the Jintangning capsule so as to effectively control the inherent quality of the Jintangning capsule; the established method has characteristics of good stability, good precision and good reproducibility; and the traditional Chinese medicine chromatography fingerprint similarity evaluation system software specified by the Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission is used, such that the operation is convenient and the result is objective and accurate.
Owner:ZHANGZHOU PIEN TZE HUANG PHARM
Quality control method of intestine astringe antidiarrheic preparation
InactiveCN102866213AThe determination method is accurateStability determination methodWeighing by removing componentComponent separationFluid phaseBiochemistry
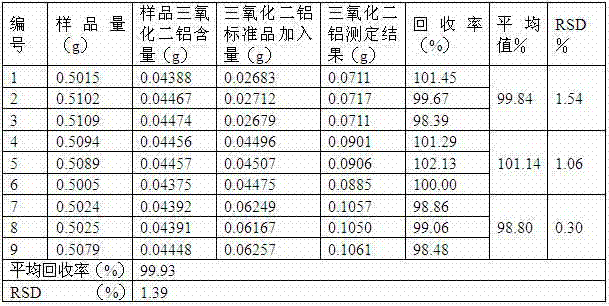
The invention discloses a quality control method of intestine astringe antidiarrheic preparation. The intestine astringe antidiarrheic preparation consists of 7 to 18 parts by weight of featherleaf rodgersflower extract, 700 to 800 parts by weight of bentonite and auxiliary materials with appropriate quantity. The quality control method of the intestine astringe antidiarrheic preparation comprises the following steps of utilizing high-efficient liquid-phase chromatography to determine content of bergenin in the preparation; determining content of aluminum oxide in the intestine astringe antidiarrheic preparation; and determining content of silicon dioxide in the intestine astringe antidiarrheic preparation. The quality control method is characterized in that on the basis of the traditional standard, the main active component bergenin is quantitatively detected, and main active components such as aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide in the preparation are quantitatively detected. The method is operable, simple, feasible and capable of effectively controlling the quality of the intestine astringe antidiarrheic preparation.
Owner:YUNNAN SHIPURUI BIOLOGICAL ENG
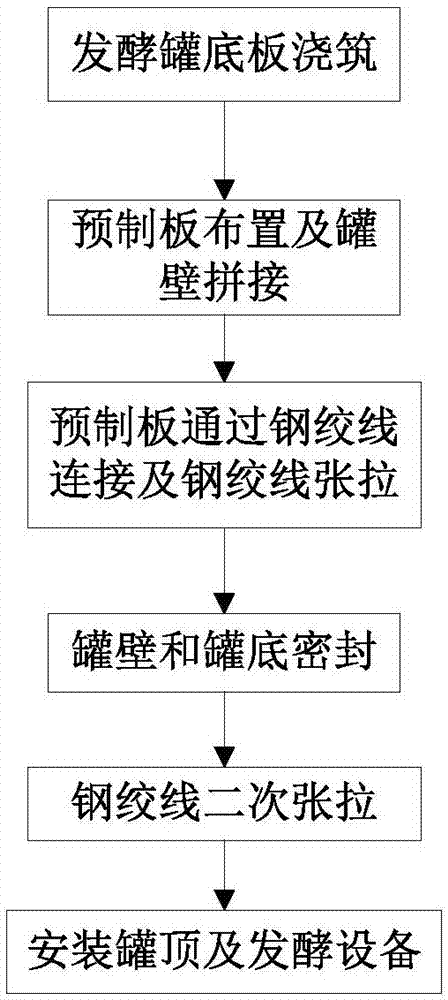
Construction method for fermentation tank assembled by precast slabs
ActiveCN106906125AControl appearanceControl internal qualityGas production bioreactorsBuilding material handlingFermentationBuilding construction
The invention relates to a construction method for fermentation tank assembled by precast slabs. The construction method comprises the following steps that: a base plate of the fermentation tank is poured; first precast slabs are circumferentially arranged on a base plate of the fermentation tank in a positioned way at intervals; each second precast slab is arranged between every two neighbouring first precast slabs in a positioning mode, so as to make each first precast slab and each second precast slab assemble into a closed tank wall together; each first precast slab is connected with each second precast slab through steel strands to make the first precast slab and the second precast slab connected as a whole by stretching the steel strands; a seam between each first precast slabs and each second precast slab is sealed, and the seams of the base plate of the fermentation tank and the first precast slab and the second precast slab are sealed; the steel strands are stretched for a second time, and finally the tank top and the relevant fermentation equipment are arranged. According to the construction method for fermentation tank assembled by precast slabs, the closed wall of the fermentation tank is assembled by multiple first precast slabs and multiple second precast slabs, therefore, the construction speed and working efficiency of the fermentation tank are increased.
Owner:恩威泰科环能股份有限公司
Wireless communication terminal and mobile type wireless communication terminal
InactiveUS20070270106A1Quality improvementControl internal qualityEnergy efficient ICTInterconnection arrangementsCouplingCommunication control
A wireless communication terminal includes first and second case members coupled together by a coupling portion so that the positional relation therebetween can be changed, an external wireless communication antenna provided at the first case member, an external wireless communication control portion mainly controlling external wireless communication carried out through the external wireless communication antenna, a first internal wireless communication antenna, a first internal wireless communication control portion controlling internal wireless communication carried out through the first internal wireless communication antenna, a display part provided at the second case member, a second internal wireless communication antenna, a second internal wireless communication control portion controlling internal wireless communication carried out through the second internal wireless communication antenna, and an output power control portion controlling the output power of waves transmitted by the internal wireless communication based on the timing of transmitting waves transmitted through the external wireless communication antenna.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Guanxinshutong capsule content detection method using quantitative analysis of multi-components by single-marker
ActiveCN106950289AGuaranteed stabilityGuaranteed uniformityComponent separationInjection volumeGallic acid ester
The invention provides a Guanxinshutong capsule content detection method using quantitative analysis of multi-components by single-marker (QAMS). According to the present invention, the chromatographic conditions comprise that the chromatographic column uses an octadecyl-bonded silica gel column as a filler, methanol is adopted as a mobile phase A, a 0.4% formic acid aqueous solution is adopted as a mobile phase B, a volume ratio of the mobile phase A to the mobile phase B is 3-90:97-10, linear gradient elution is performed, the detection wavelength is 280 nm, the column temperature is 35 DEG C, and the sample injection volume is 5 [mu]L; the content detection method can simultaneously determine the contents of gallic acid, danshensu sodium, protocatechuic acid, protocatechuic aldehyde, vanillin, rosmarinic acid, salvianolic acid B, eugenol, cryptotanshinone and tanshinone IIA in the Guanxinshutong capsule; and the detection method has characteristics of simpleness, accuracy, efficiency, good reproducibility, and good stability.
Owner:SHAANXI BUCHANG PHARMA
Processing method of high-quality bombyx mori linnaeus
PendingCN109985066AControl internal qualityEasy to operateAnthropod material medical ingredientsBiologyAir drying
The invention provides a processing method of high-quality bombyx mori linnaeus. The processing method comprises the following steps of a, taking fresh bombyx mori linnaeus which is dead due to infection of beauveria assiana (Bals.)Vuillant, wherein the infection mode involves artificial breeding infection or natural infection; b, harvesting, wherein the bombyx mori linnaeus is harvested within 24-48 hours after 80% of the bombyx mori linnaeus is dead; c, conducting pretreatment, wherein bombyx mori linnaeus bodies are spread flat, and subjected to ventilation and dehydration treatment for atleast 6 hours for ossification; d, conducting processing, wherein two-section-type circular drying is adopted for scale production, hot-air drying is conducted for 2 hour at 80 DEG C, and after dehydration, low-temperature drying is conducted at 60 DEG C; drying in the sun or drying in the shade is adopted for production site preliminary processing. The processing method is high in operability, the cost is reduced, the method is suitable for scale production and processing of the bombyx mori linnaeus, and the quality is high.
Owner:SICHUAN GUANGYUAN MINJIANG CHINESE HERBAL MEDICINE PLANTING CO LTD
Method for establishing fingerprint spectrum of volatile components of musk wind-dispelling and pain-relieving paste, standard fingerprint spectrum and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicine preparation identification, in particular to a method for establishing a fingerprint spectrum of volatile components of musk wind-dispelling and pain-relieving paste, a standard fingerprint spectrum and application thereof. The method comprises a reference substance solution preparation step, a test solution preparation step and a detection step. In the test solution preparation step, N, N-dimethylformamide is used as a solvent to extract volatile components in a musk wind-dispelling and pain-relieving paste sample, and a liquid phase part is taken to obtain the test solution. According to the scheme, the technical problem of lack of a quality control method for volatile components of the musk wind-dispelling andpain-relieving ointment can be solved. The standard fingerprint spectrum established by the scheme and the detection method can be applied to identification of volatile components of rubber plasters,gel plasters and powdery premixed plasters of musk wind-dispelling and pain-relieving plasters.
Owner:重庆希尔安药业有限公司
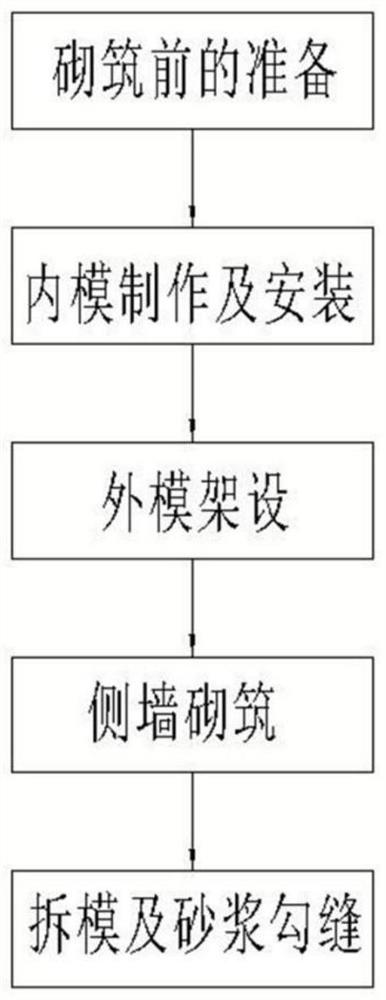
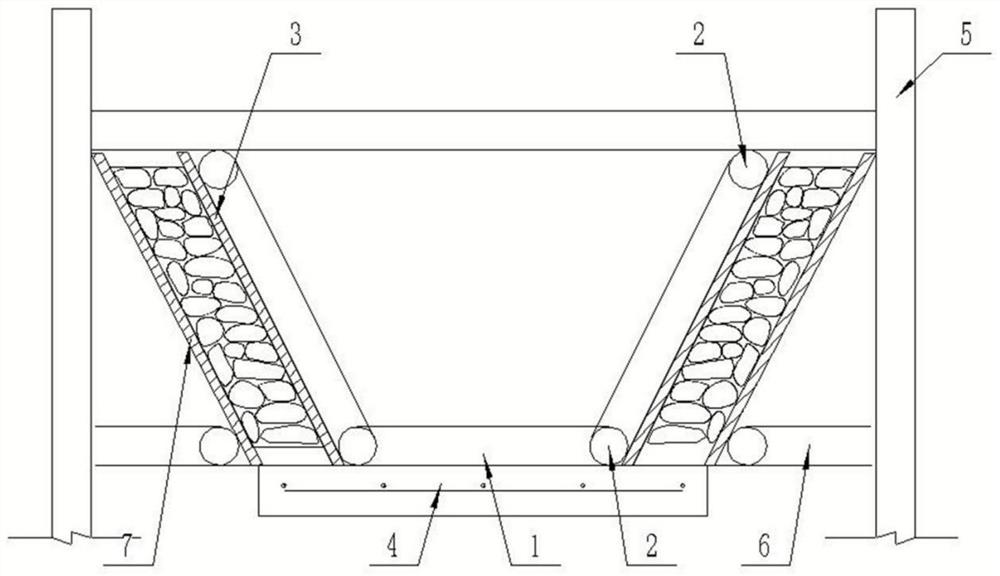
Open drainage ditch process by internal mold method mortar masonry
InactiveCN112031120AExquisite structureImprove appearance qualitySewer pipelinesArchitectural engineeringStructural engineering
The invention relates to an open drainage ditch process by internal mold method mortar masonry. The process comprises the following specific steps: preparation before masonry; internal mold manufacturing and installation: manufacturing a supporting internal mold according to the shape of a drainage ditch; placing a plurality of internal mold trapezoidal supports on the upper surface of a concretebottom plate; external mold erection: after the internal mold of the drainage ditch is placed, manufacturing external molds for supporting, and positioning and erecting the external molds on both sides of the internal mold according to the required side wall thickness; side wall masonry: adopting a mortar squeezing method for layered and segmented masonry of mortar masonry; and mold removal and mortar jointing. The process solves the problems that the masonry line type of a traditional open drainage ditch is not easy to control, the surface is uneven, and the masonry thickness is uneven, the line type of the drainage ditch structure is attractive, the mortar jointing thickness is uniform, and the appearance quality is good; the masonry thickness is uniform, a sand joint is full of mortar,material waste can be avoided, and the internal quality can be well controlled; the construction is simple, and skills and work types are saved; and the weight of a template is light, the template canbe manually disassembled and supported, and the mechanical use is reduced.
Owner:CCCC FIRST HARBOR ENG +1
A niobium-titanium-chromium-boron alloy wear-resistant steel and preparation method thereof
Owner:MAGANG (GROUP) HOLDING CO LTD +1
UPLC characteristic spectrum construction method and application of endothelium corneum gigeriae galli, fried endothelium corneum gigeriae galli and vinegar endothelium corneum
ActiveCN114778731AControl internal qualityGuaranteed clinical efficacyComponent separationAgainst vector-borne diseasesAcetic acidEthylic acid
The invention provides a UPLC characteristic chromatogram construction method of endothelium corneum gigeriae galli decoction pieces, fried endothelium corneum gigeriae galli decoction pieces, vinegar endothelium corneum gigeriae galli decoction pieces, standard decoction of the endothelium corneum gigeriae galli decoction pieces and formula granules of the endothelium corneum gigeriae galli decoction Determining the liquid to be detected by adopting a high performance liquid chromatography to obtain UPLC characteristic chromatograms of the endothelium corneum gigeriae galli decoction pieces, the fried endothelium corneum gigeriae galli decoction pieces, the vinegar endothelium corneum gigeriae Chromatographic conditions of the high performance liquid chromatography are as follows: a chromatographic column is a C18 column; a mobile phase A is a methanol solution, a mobile phase B is a 0.02% acetic acid aqueous solution, and gradient elution is carried out. According to the method, the UPLC characteristic chromatogram for distinguishing the endothelium corneum gigeriae galli decoction pieces, the fried endothelium corneum gigeriae galli decoction pieces, the vinegar endothelium corneum gigeriae galli decoction pieces, the standard decoction and the formula granules of the endothelium corneum gigeriae galli decoction pieces, the fried endothelium corneum gigeriae galli decoction pieces and the vinegar endothelium corneum gigeriae galli decoction pieces is established,
Owner:SICHUAN NEO GREEN PHARMA TECH DEV
Method for simultaneously detecting contents of five components of traditional Chinese medicine for treating infantile enuresis
ActiveCN111398505AControl internal qualityHigh detection sensitivityComponent separationOfficinalGinkgo nut
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously detecting contents of five components of a traditional Chinese medicine for treating infantile enuresis. The traditional Chinese medicine for treating infantile enuresis is prepared from six traditional Chinese medicinal materials including ephedra, cinnamon, alpinia oxyphylla, ginkgo, semen cuscutae and endothelium corneum gigeriae galli, the five components include ephedrine hydrochloride, cinnamaldehyde, cinnamic acid, quercetin and ginkgolide C. The detection method comprises the steps that the traditional Chinese medicine is extracted through an extraction solvent and then detected through a high performance liquid chromatograph. Compared with the methods in the prior art, the method has the advantages of high detection sensitivity,high speed, simplicity in operation and the like, the detection efficiency and the detection accuracy are greatly improved, and the internal quality of the traditional Chinese medicine can be more comprehensively controlled.
Owner:JIANMIN PHARMA GRP CO LTD
Fingerprint determination method and quality control method of Guyin decoction
ActiveCN113125569BGuaranteed curative effectFormal quality controlComponent separationChemical compositionBiochemical engineering
The invention provides a fingerprint spectrum determination method and a quality control method for the reference substance of Guyin decoction. The invention confirms 12 common characteristic peaks in the process of establishing the fingerprint spectrum of the Guyin decoction substance reference, solves the problems of difficulty in separating the fingerprint characteristic peaks and the interference of impurity peaks, and ensures the chemical composition stability and use safety of the substance reference , which provides an important reference for the quality control of the subsequent preparations, effectively controls the quality of the Guyin decoction substance benchmark, and enables the classic prescriptions to get more formal quality control.
Owner:HUNAN YINENG BIOLOGICAL PHARMA
Detection method of traditional Chinese medicine ingredients in Chenxianglubailu tablets
InactiveCN108362796AControl internal qualityProtect against Alzheimer'sComponent separationProduct inspectionAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a detection method of traditional Chinese medicine ingredients in Chenxianglubailu tablets. Under the same chromatographic condition, quality control is performed on liquiritin, narirutin and hesperidin in a Chenxianglubailu preparation simultaneously, and thin-layer qualitative discrimination is performed on rhizoma acori graminei. The product quality can be effectively controlled, the method is simple and convenient to operate, high in accuracy and high in specificity, and the working efficiency of product inspection is improved.
Owner:贵州省科晖制药有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com