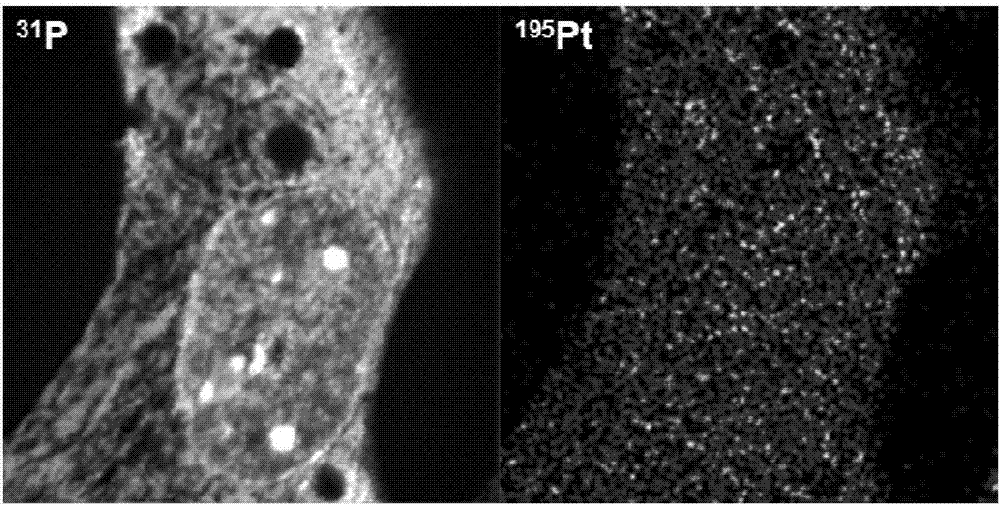
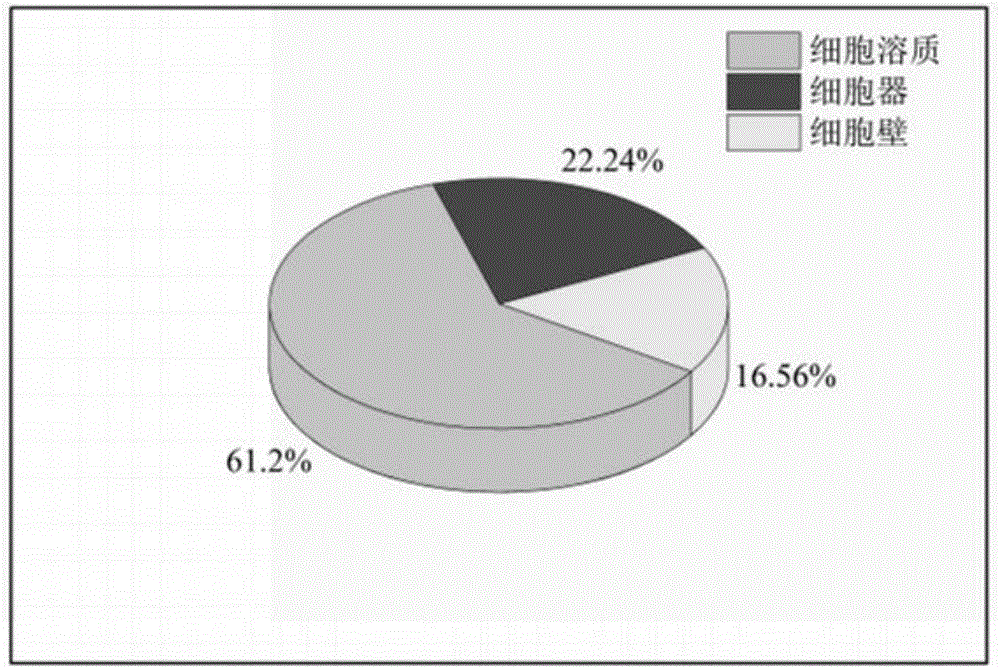
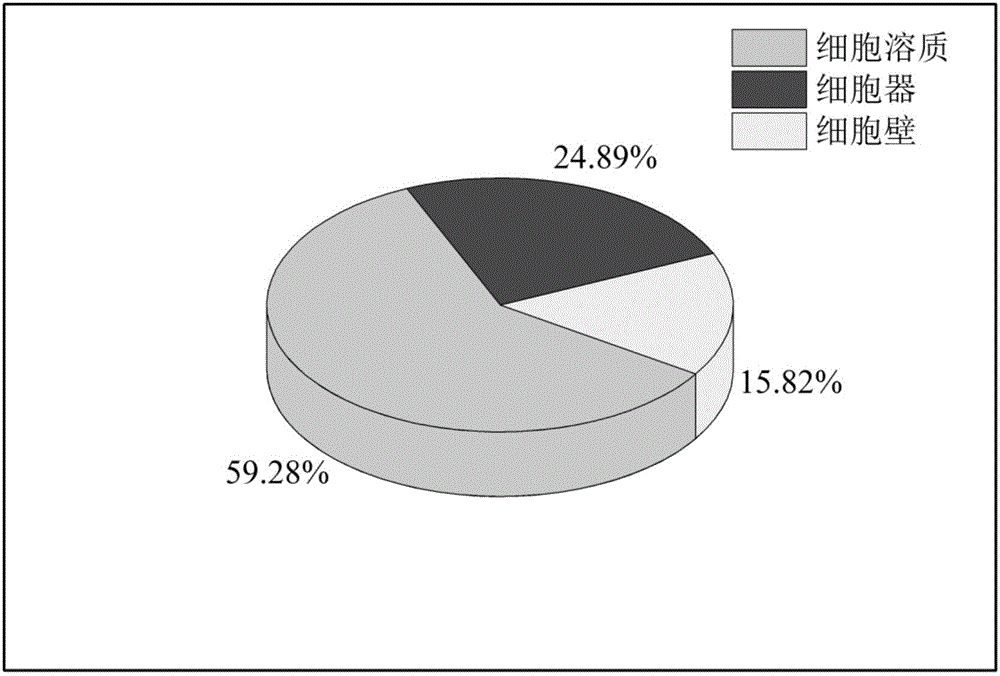
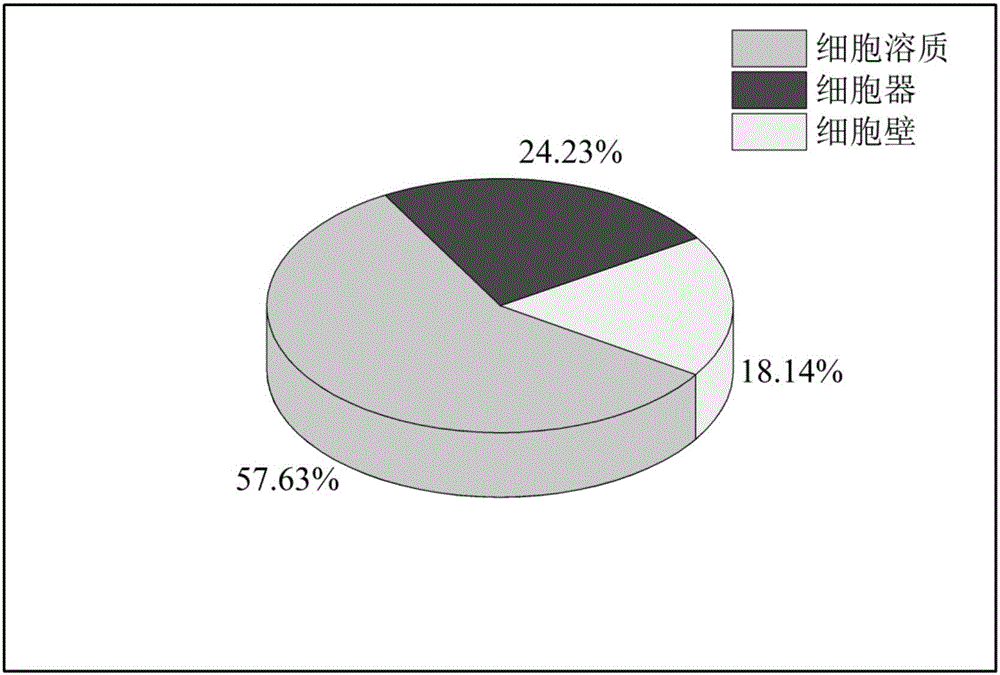
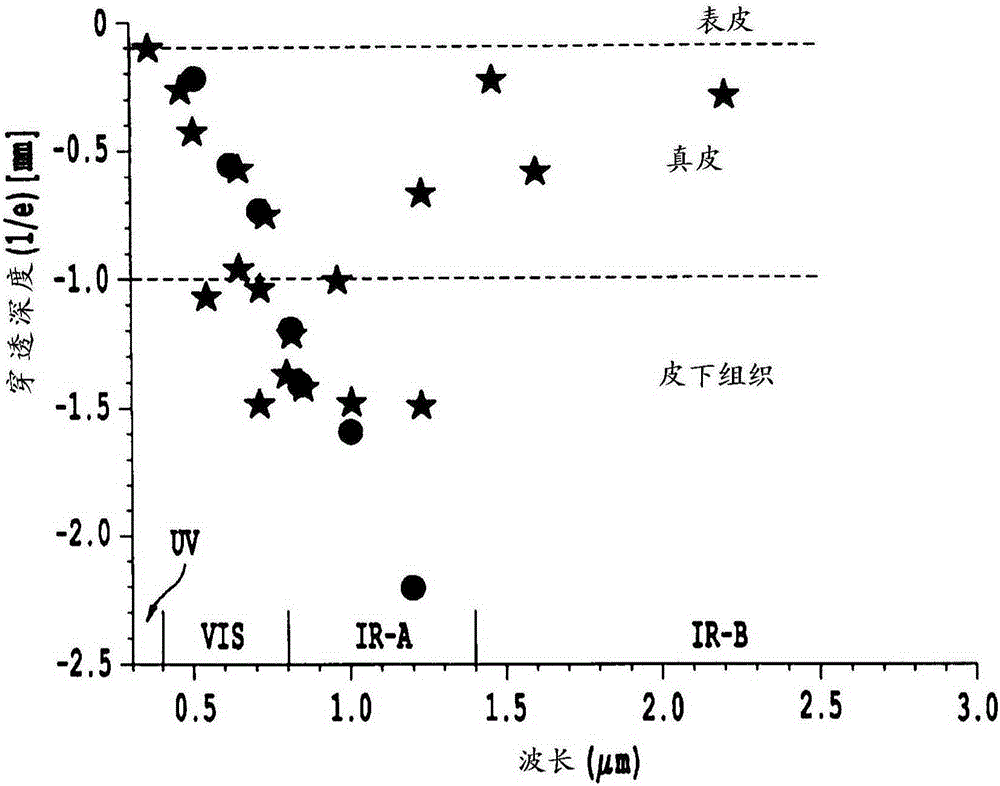
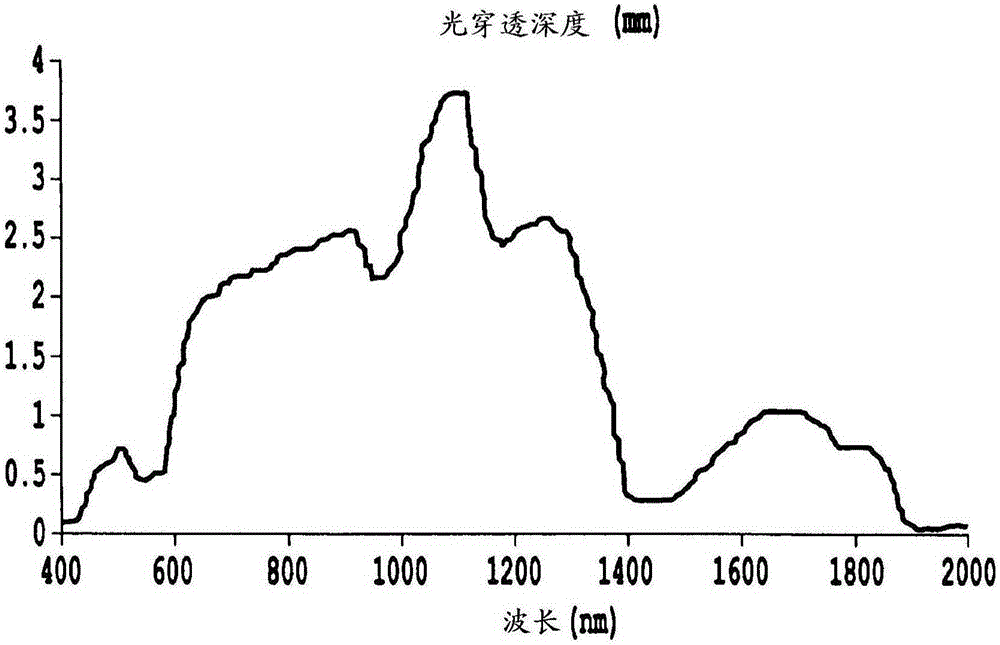
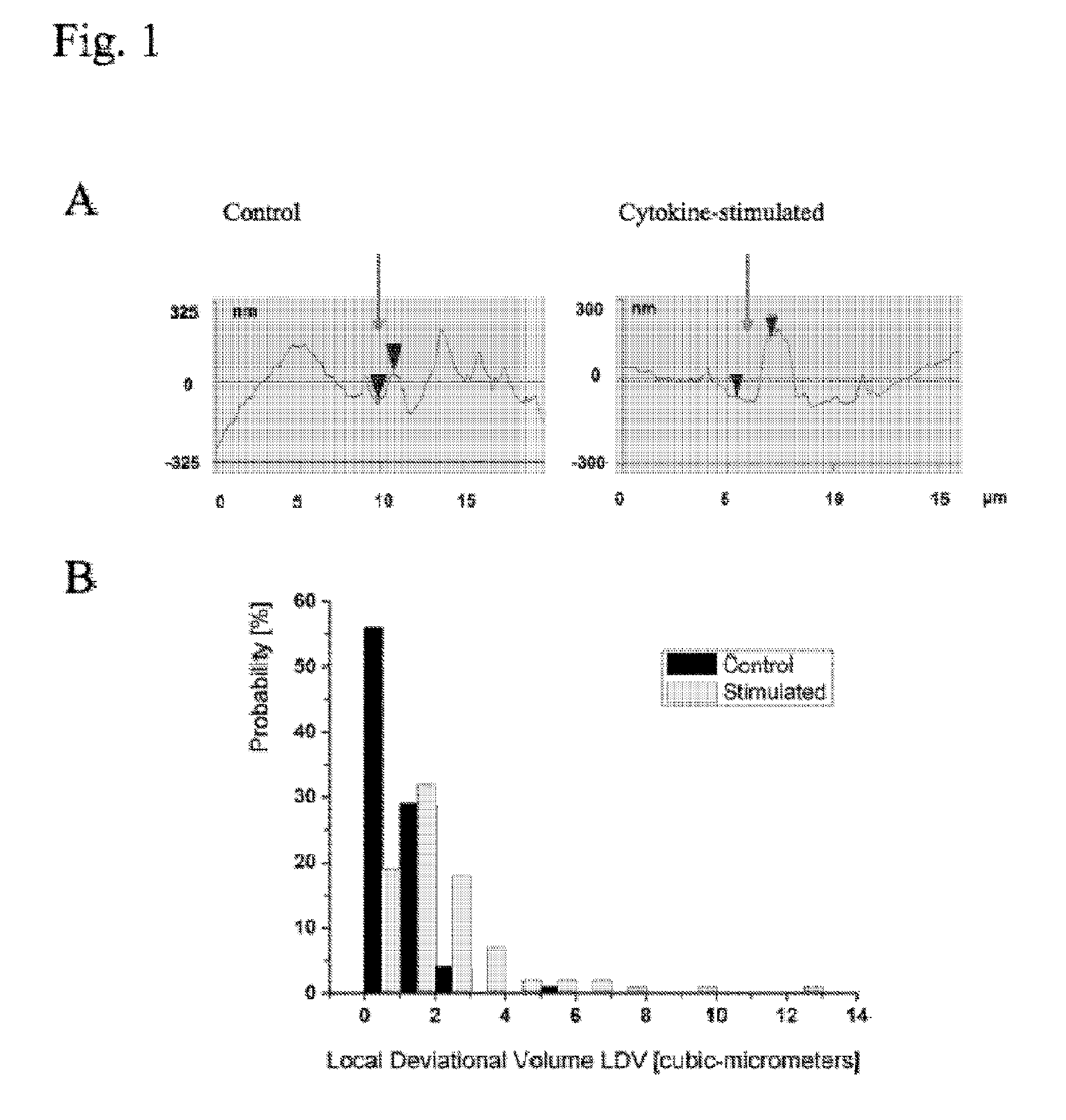
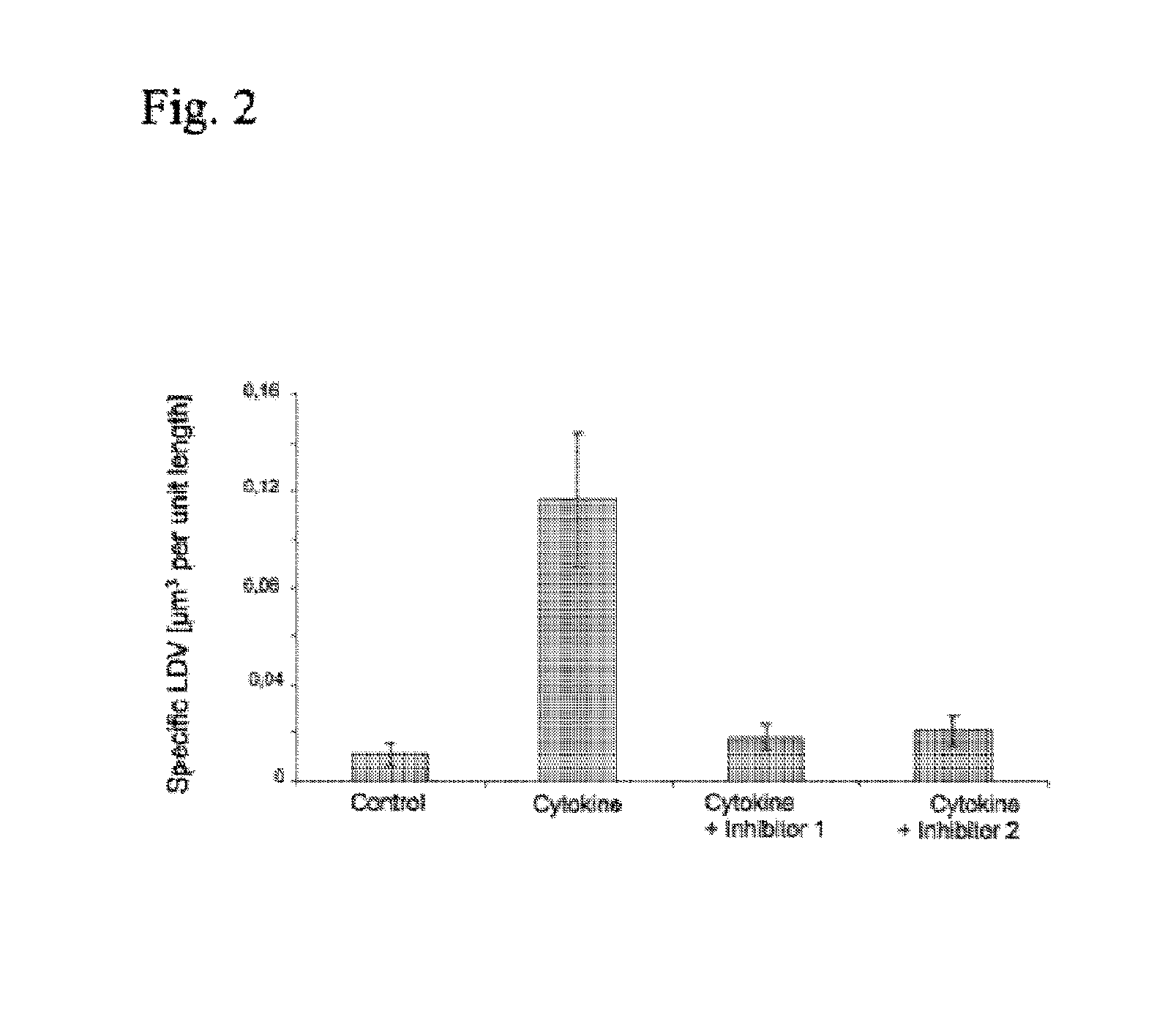
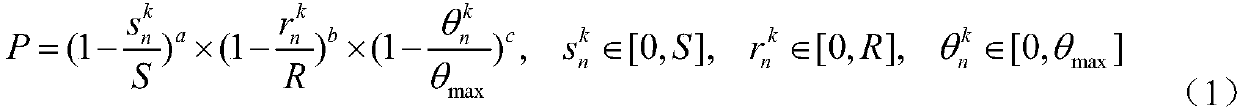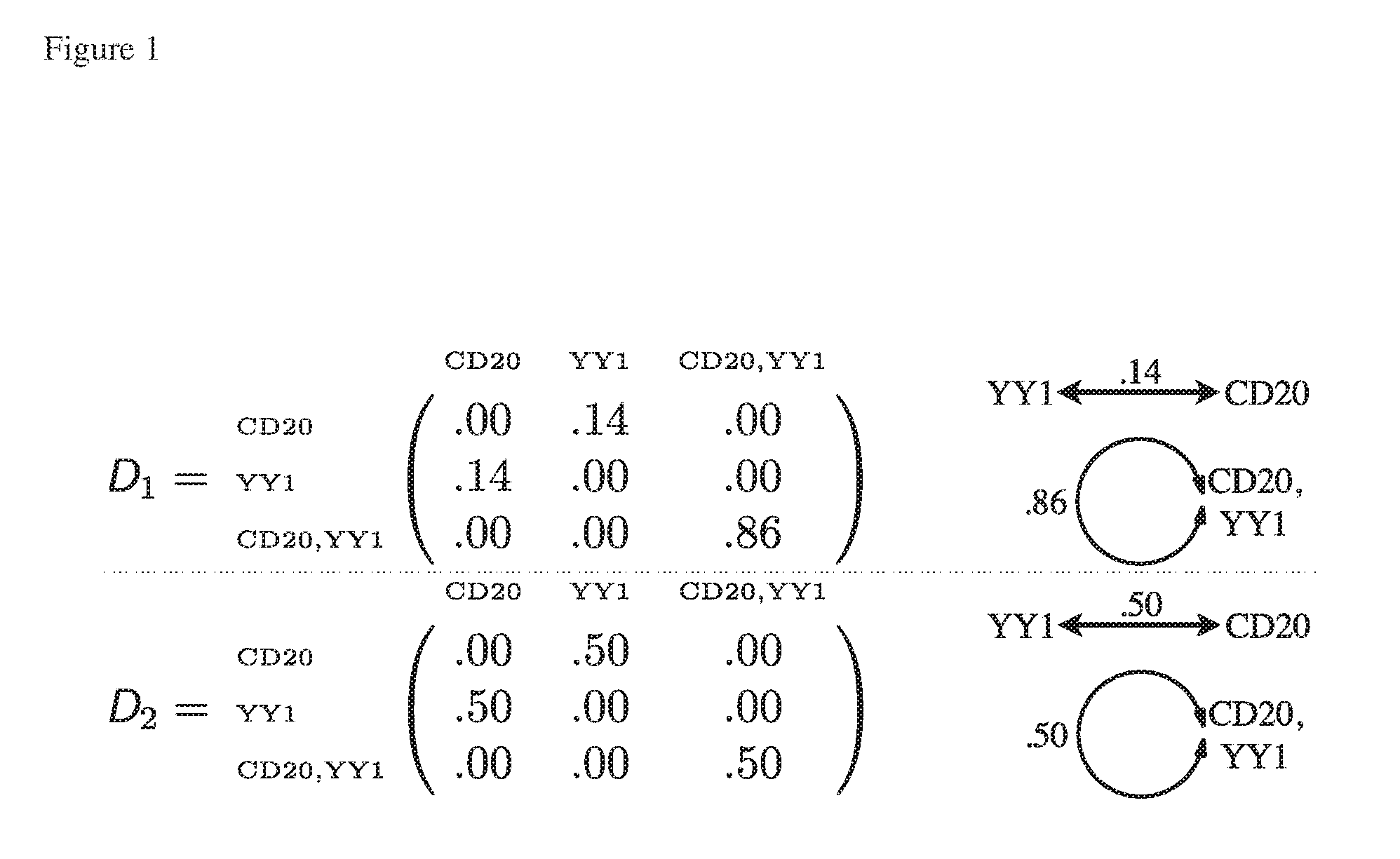Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57 results about "Subcellular structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
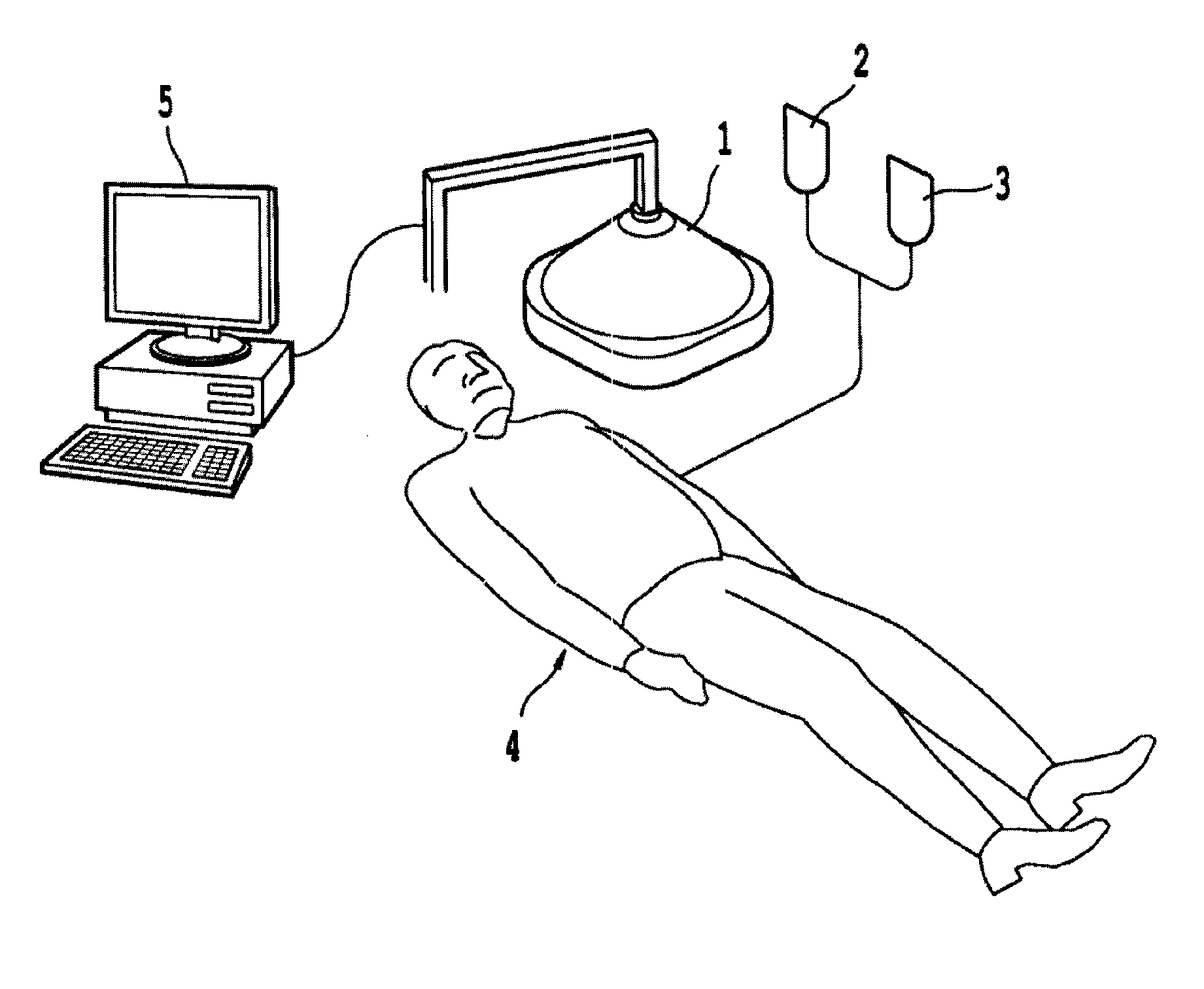
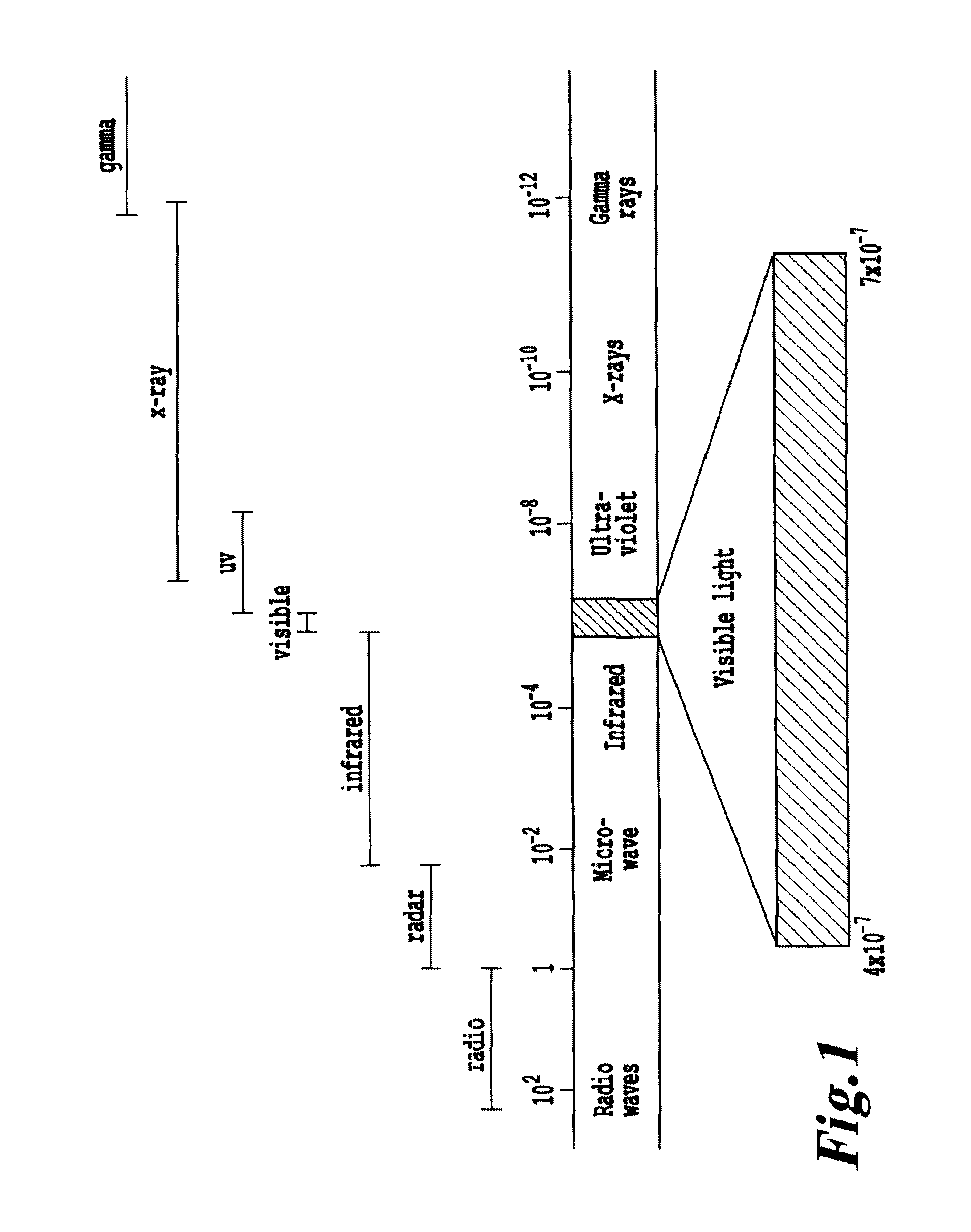
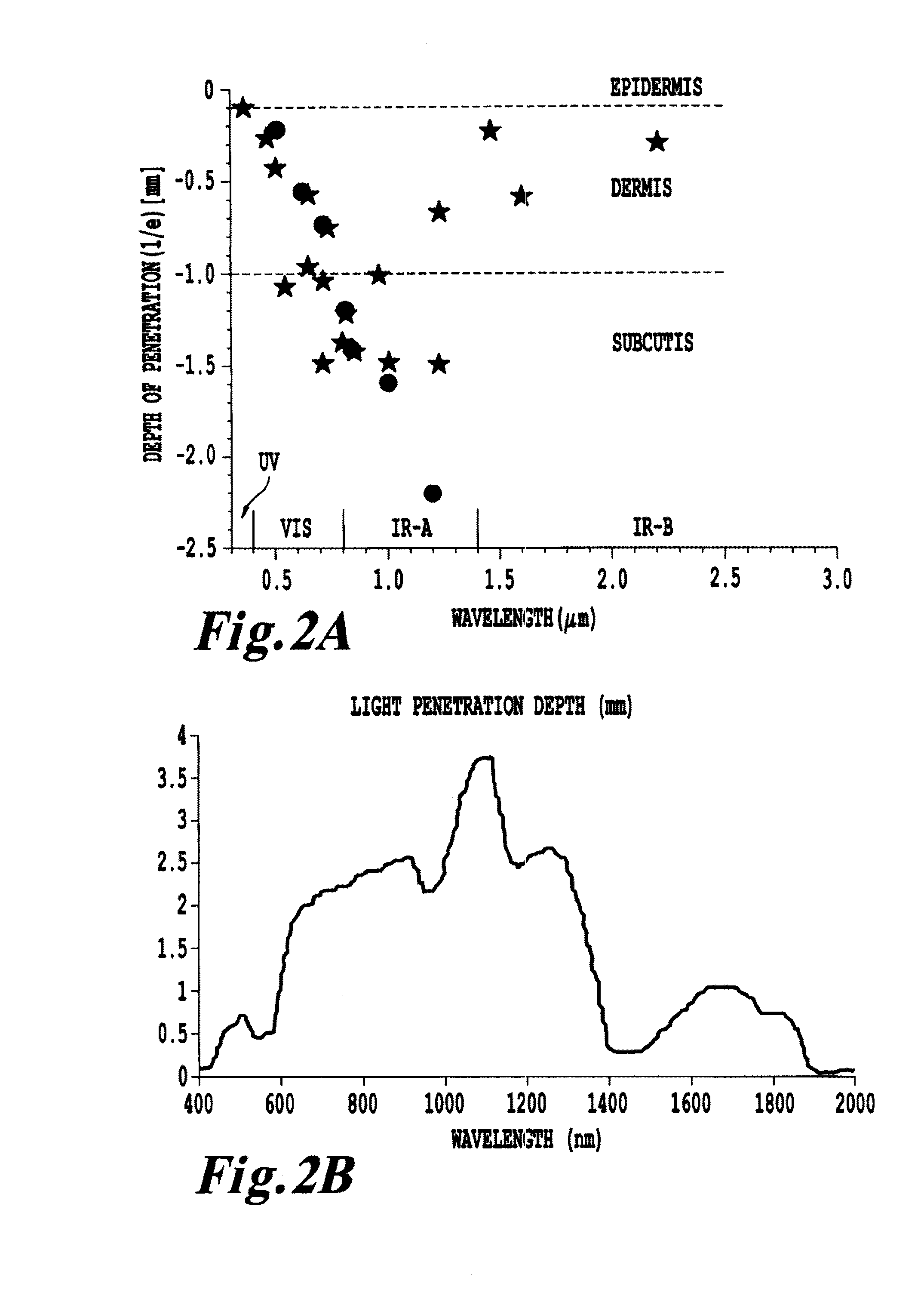
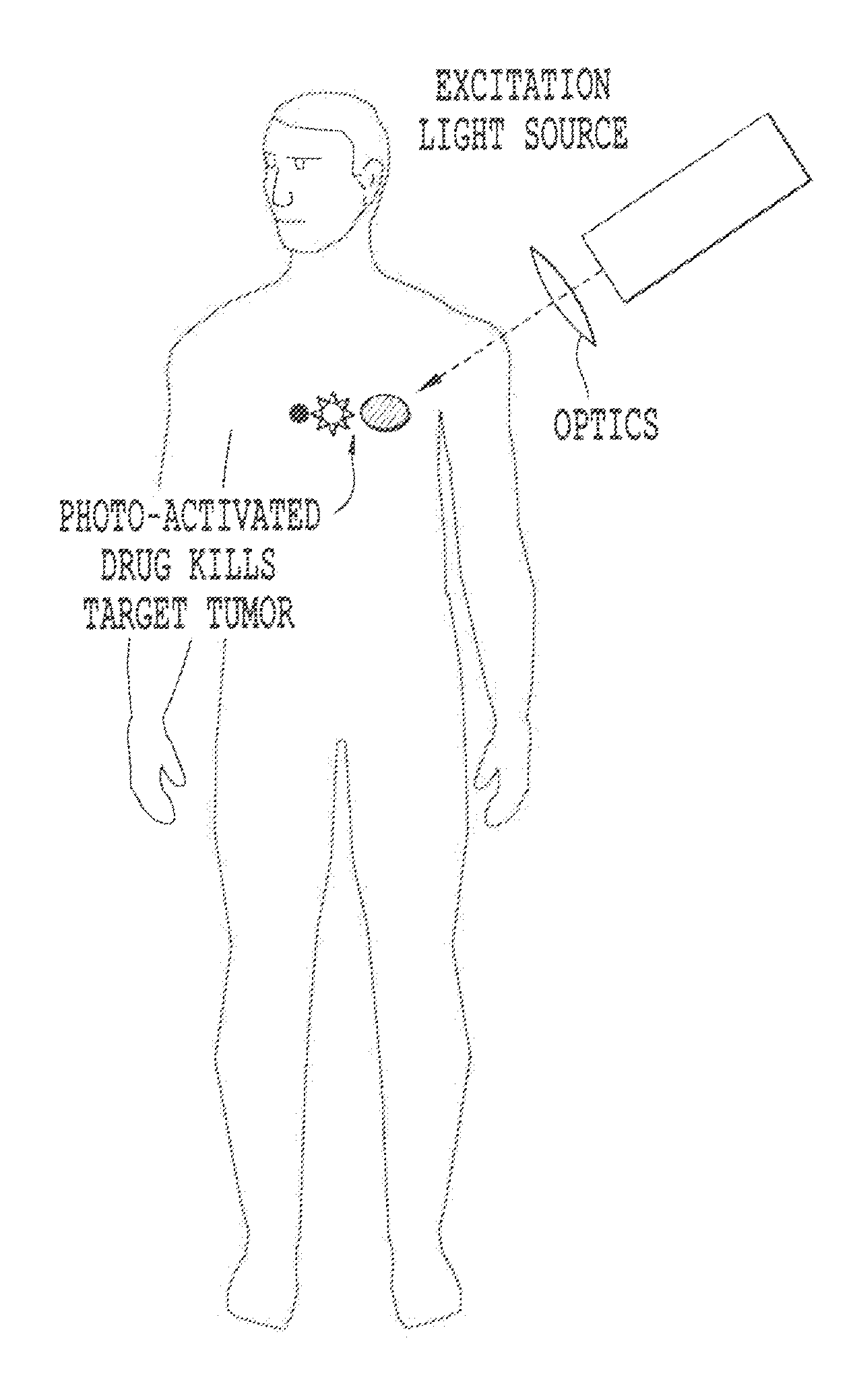
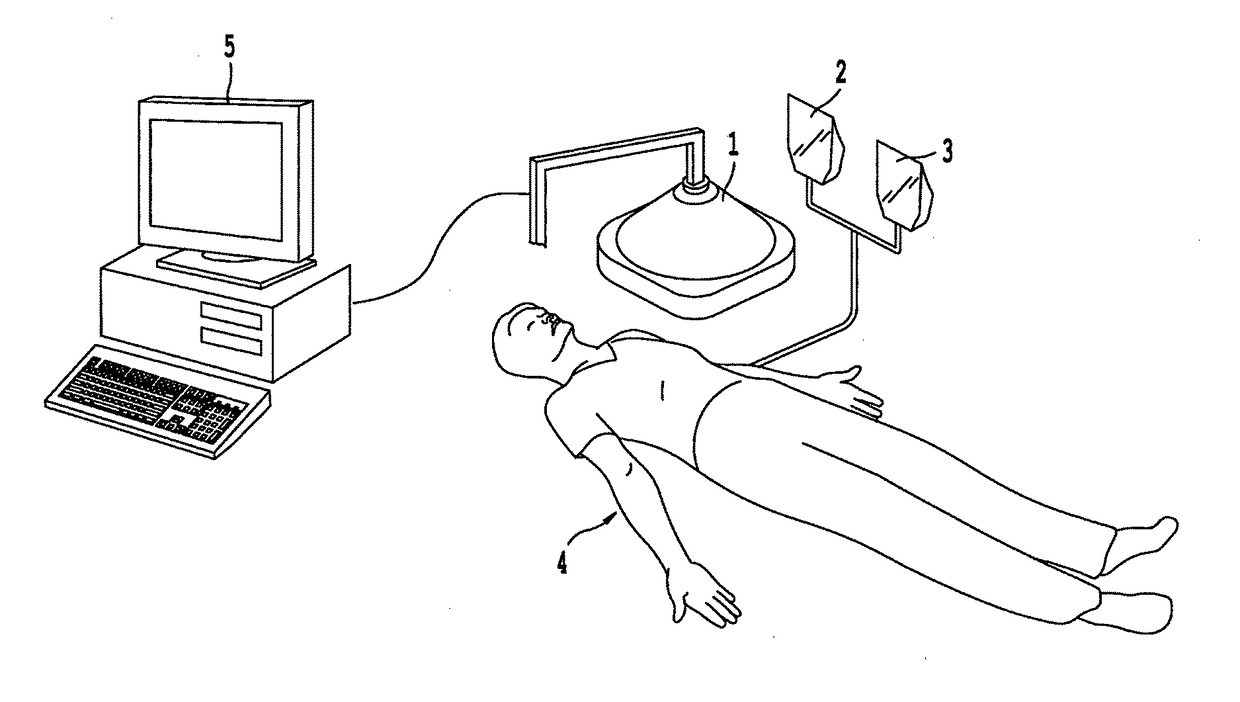
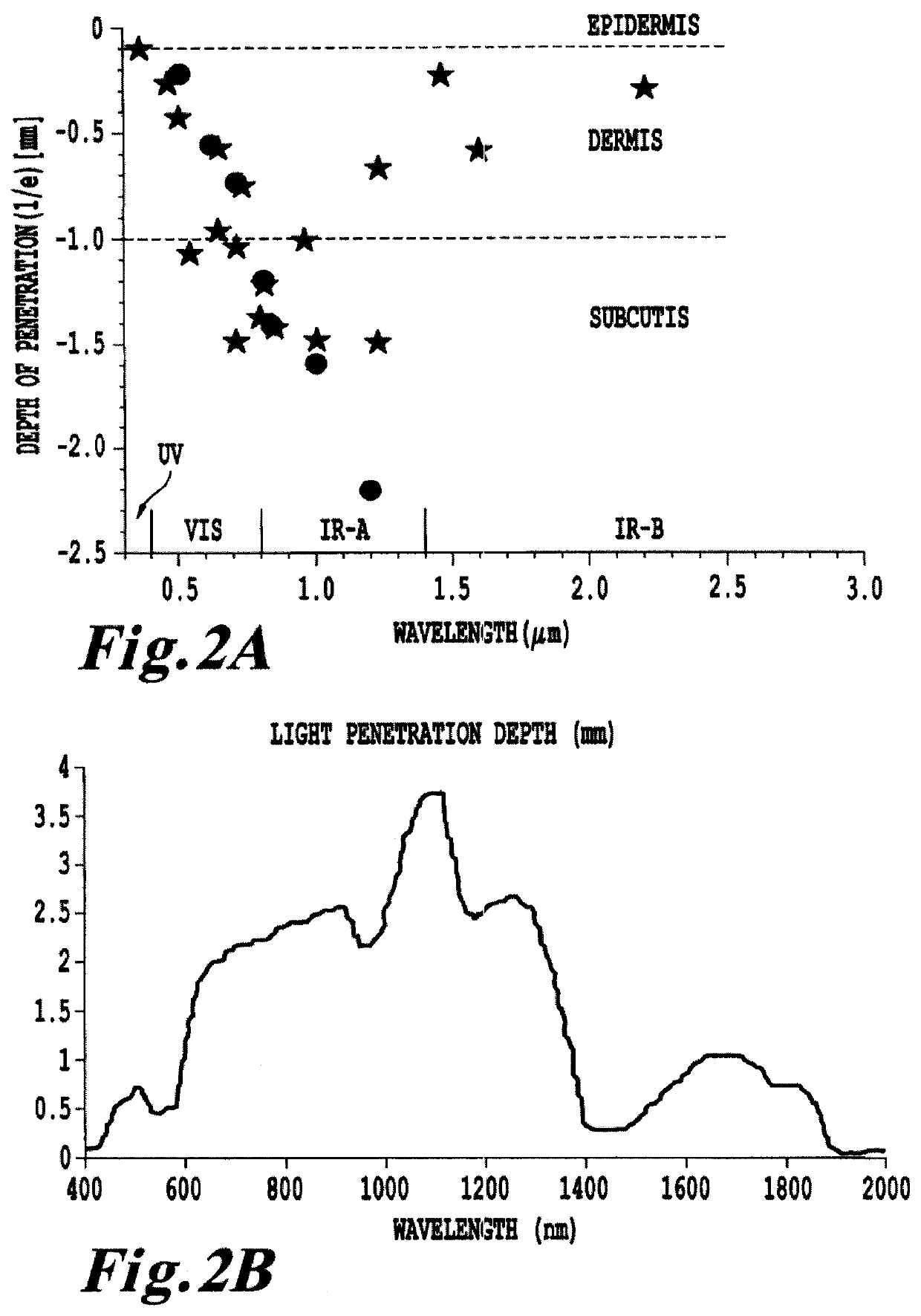
Non-invasive systems and methods for in-situ photobiomodulation
InactiveUS20100016783A1High selectivityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryDiseaseBiological regulation
Products, compositions, systems, and methods for modifying a target structure which mediates or is associated with a biological activity, including treatment of conditions, disorders, or diseases mediated by or associated with a target structure, such as a virus, cell, subcellular structure or extracellular structure. The methods may be performed in situ in a non-invasive manner by application of an initiation energy to a subject thus producing an effect on or change to the target structure directly or via a modulation agent. The methods may further be performed by application of an initiation energy to a subject in situ to activate a pharmaceutical agent directly or via an energy modulation agent, optionally in the presence of one or more plasmonics active agents, thus producing an effect on or change to the target structure. Kits containing products or compositions formulated or configured and systems for use in practicing these methods.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Non-invasive energy upconversion methods and systems for in-situ photobiomodulation
ActiveUS20110021970A1High selectivityAvoid the needAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDiseaseHigh energy
Products, compositions, systems, and methods for modifying a target structure which mediates or is associated with a biological activity, including treatment of conditions, disorders, or diseases mediated by or associated with a target structure, such as a virus, cell, subcellular structure or extracellular structure. The methods may be performed in situ in a non-invasive manner by placing a nanoparticle having a metallic shell on at least a fraction of a surface in a vicinity of a target structure in a subject and applying an initiation energy to a subject thus producing an effect on or change to the target structure directly or via a modulation agent. The nanoparticle is configured, upon exposure to a first wavelength λ1, to generate a second wavelength λ2 of radiation having a higher energy than the first wavelength λ1. The methods may further be performed by application of an initiation energy to a subject in situ to activate a pharmaceutical agent directly or via an energy modulation agent, optionally in the presence of one or more plasmonics active agents, thus producing an effect on or change to the target structure. Kits containing products or compositions formulated or configured and systems for use in practicing these methods.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Functional imaging of cells with optical projection tomography
ActiveUS20120105600A1Well formedReconstruction from projectionScattering properties measurementsOptical projection tomographyOptical tomography
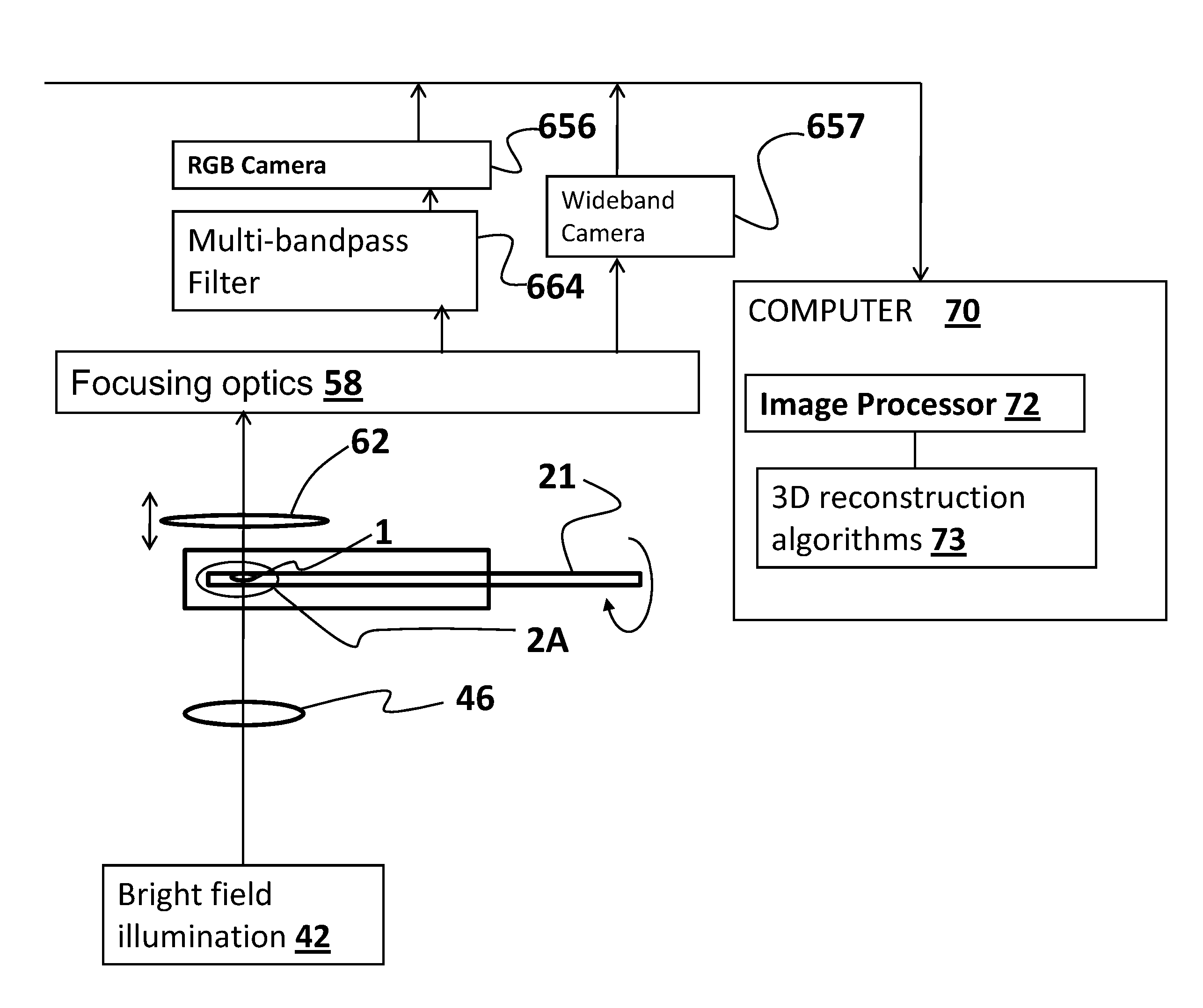
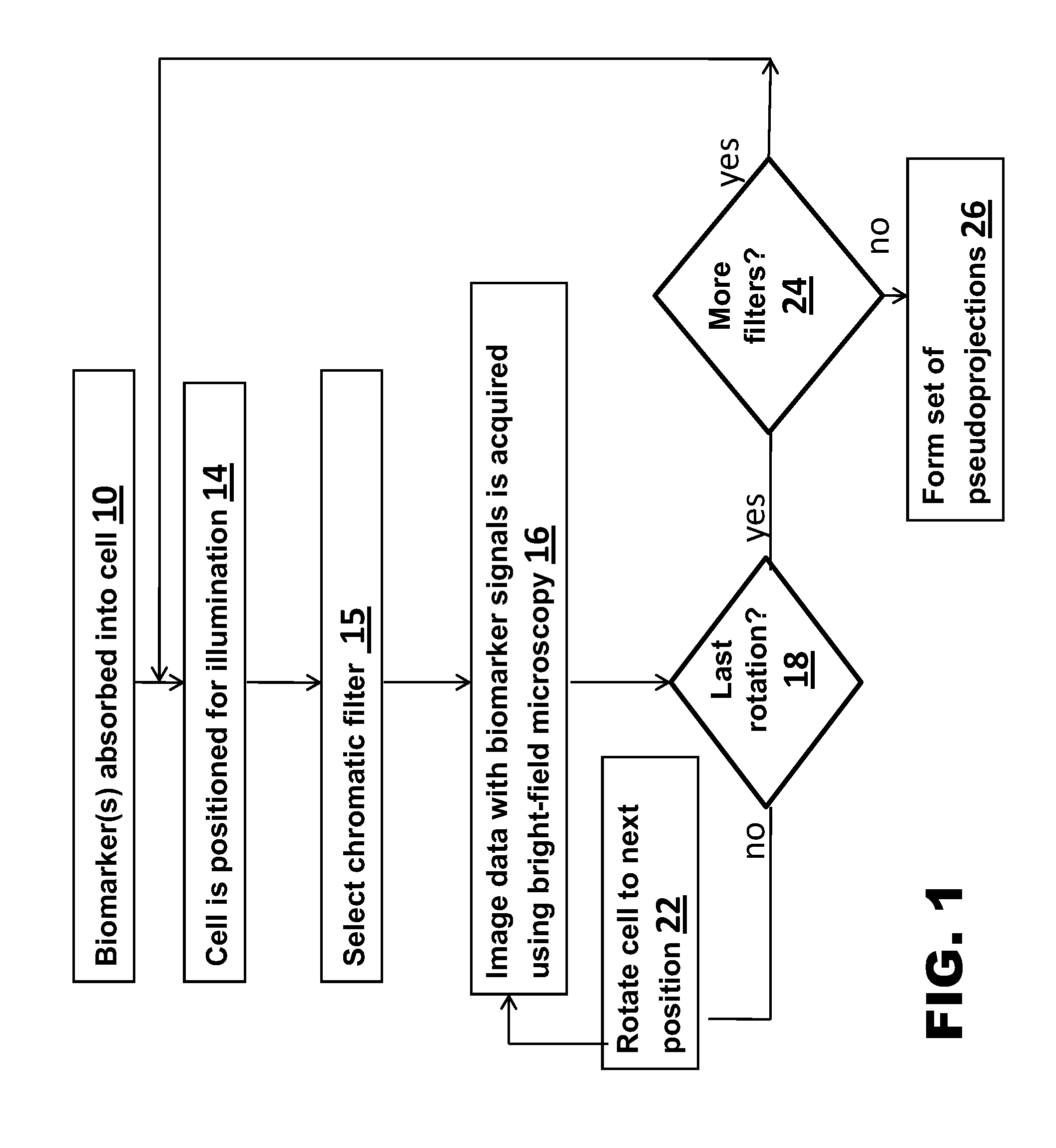
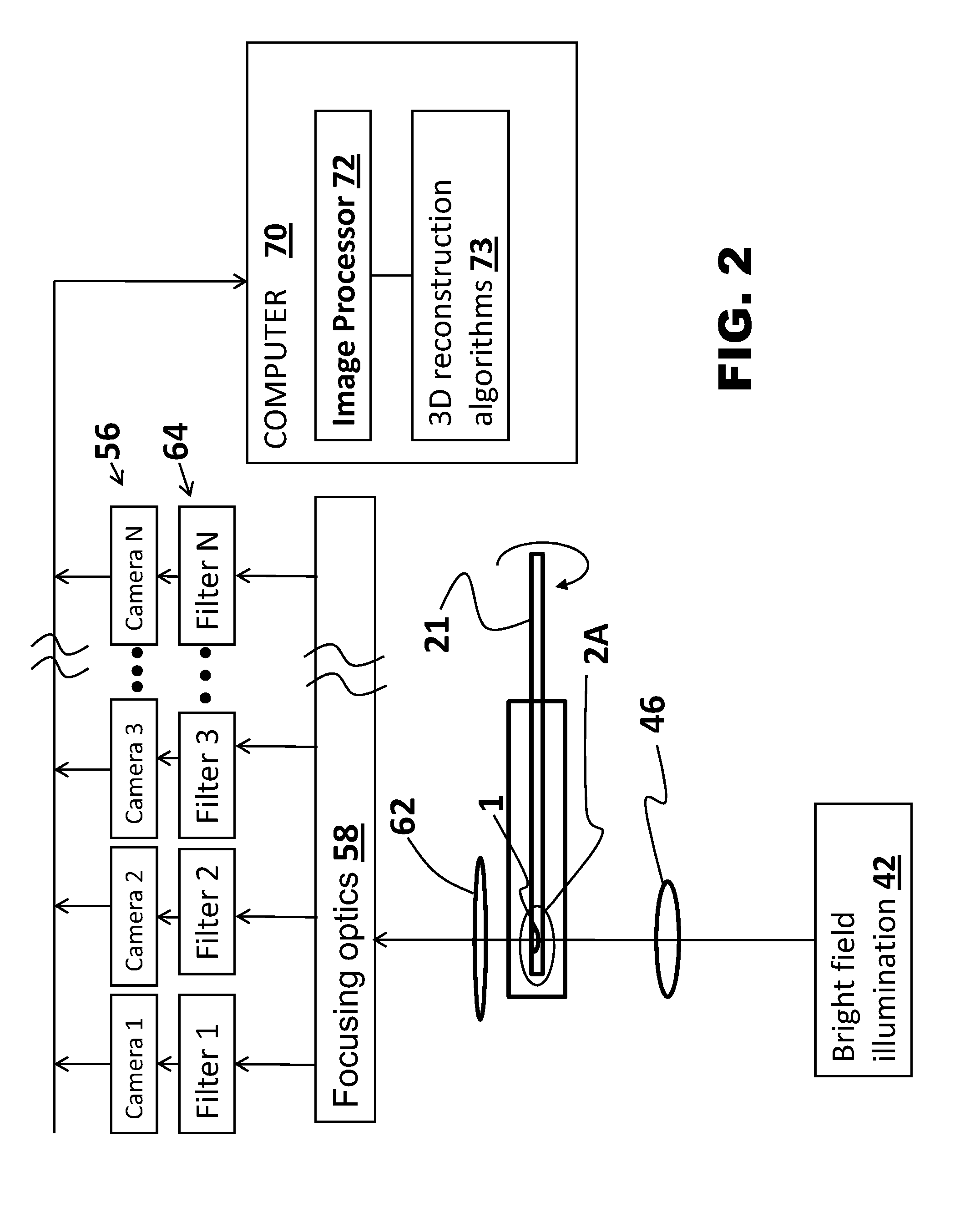
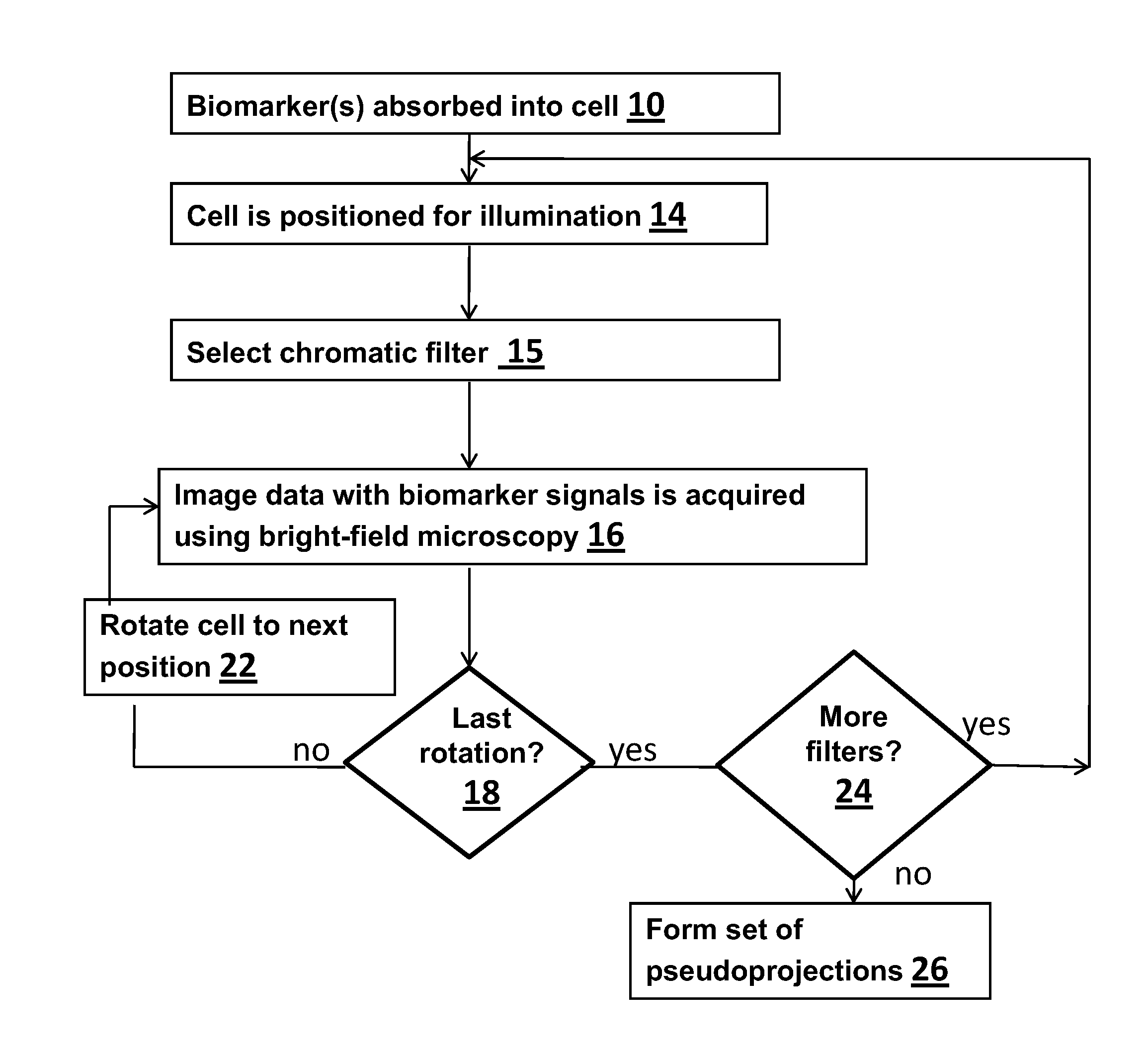
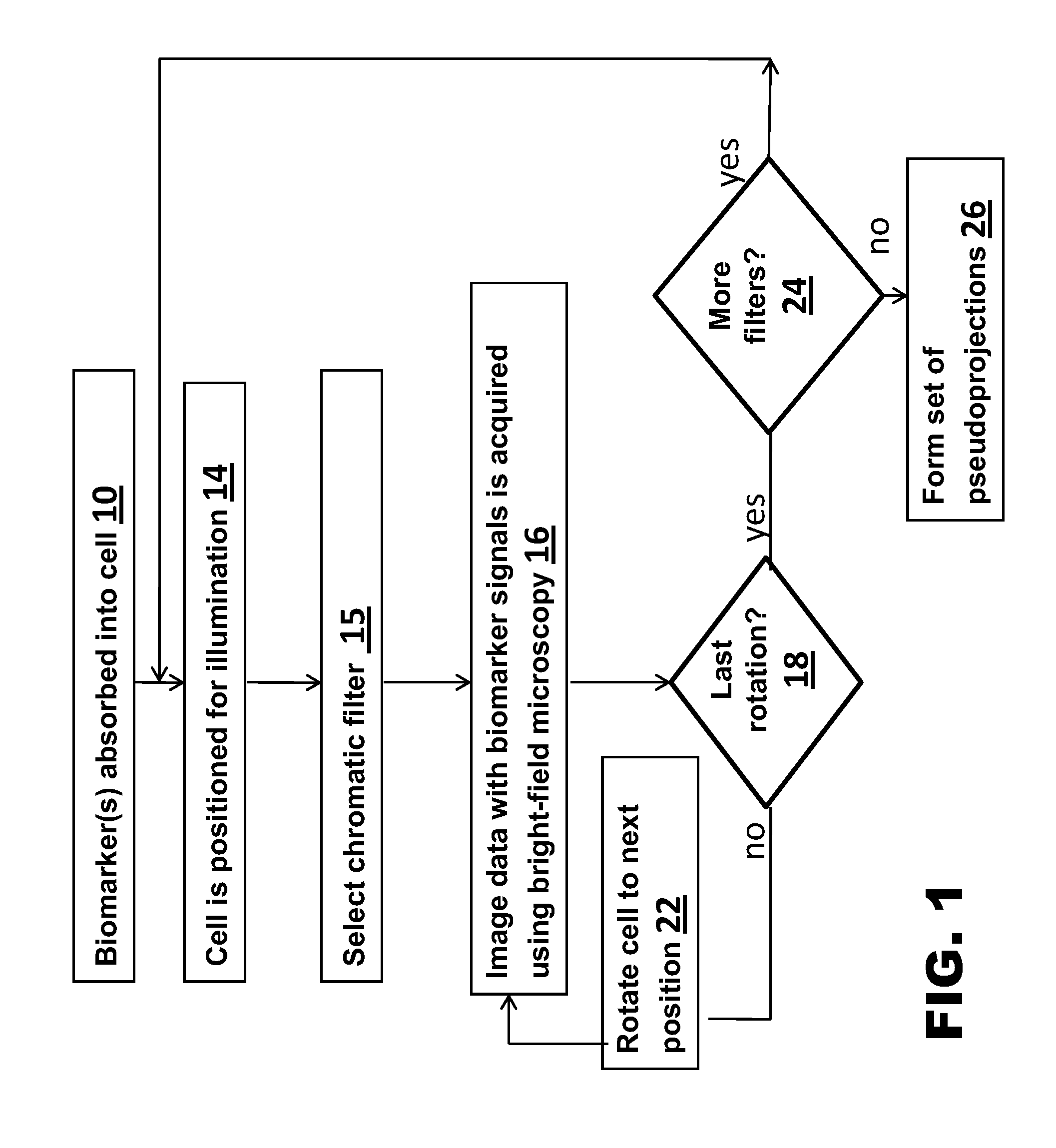
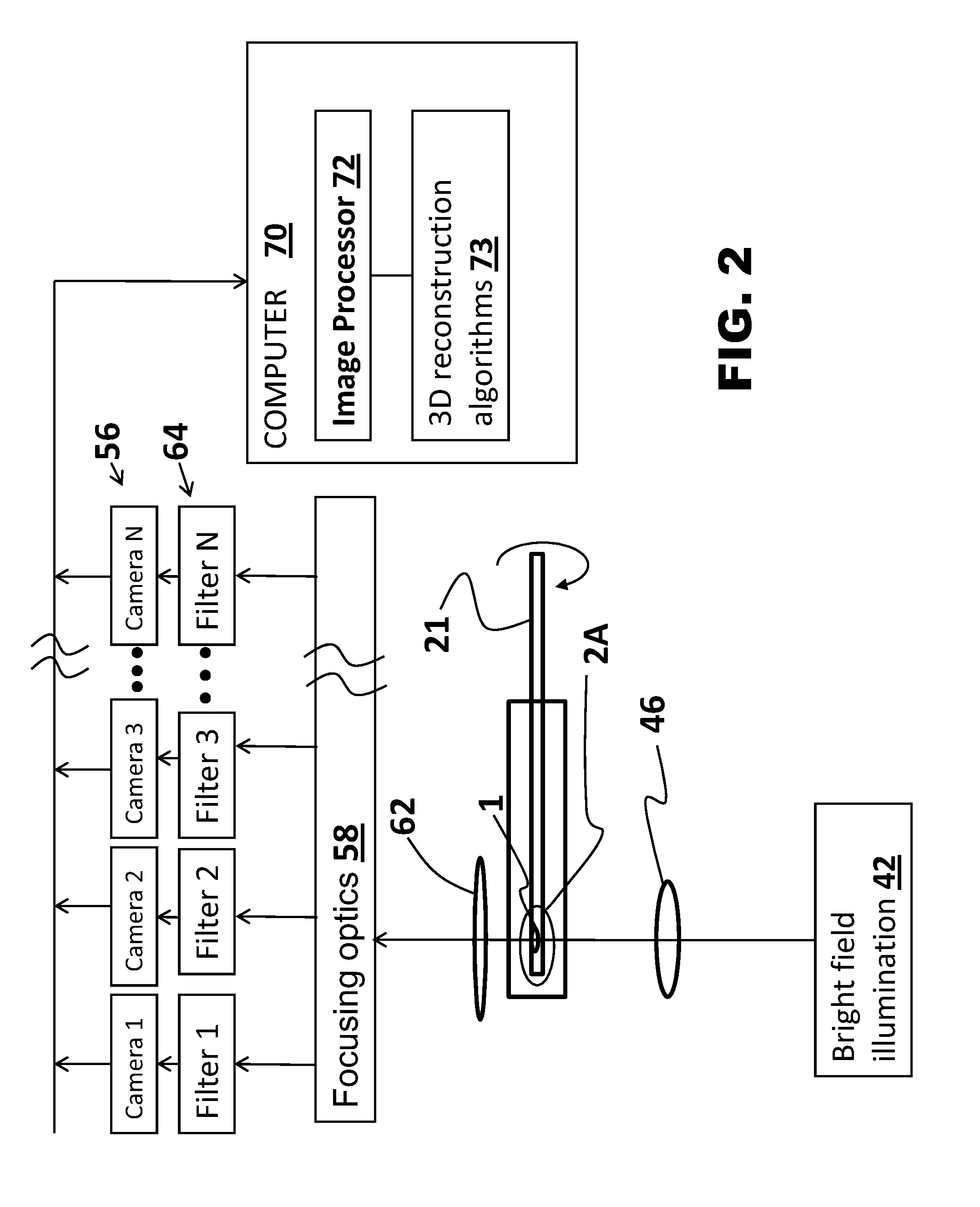
A method for 3D imaging of a biologic object (1) in an optical tomography system where a subcellular structure of a biological object (1) is labeled by introducing at least one nanoparticle-biomarker. The labeled biological object (1) is moved relatively to a microscope objective (62) to present varying angles of view and the labeled biological object (1) is illuminated with radiation having wavelengths between 150 nm and 900 nm. Radiation transmitted through the labeled biological object (1) and the microscope objective (62) within at least one wavelength bands is sensed with a color camera, or with a set of at least four monochrome cameras. A plurality of cross-sectional images of the biological object (1) from the sensed radiation is formed and reconstructed to make a 3D image of the labeled biological object (1).
Owner:VISIONGATE
Transmission electron microscope processing method for insect antenna samples
ActiveCN103115809AEffective immobilizationEffective preservationPreparing sample for investigationElectron microscopeBiology
The invention belongs to the field of experimental sample processing technologies, relates to insect antenna sample processing methods and particularly relates to a transmission electron microscope processing method for insect antenna samples. The method sequentially comprises the following steps of: (A) preparing fixing liquid; (B) preparing various embedding agents; (C) dissecting, fixing and rinsing; (D) dewatering and soaking; and (E) gathering, so as to obtain the samples. The method has the advantages that the problems of difficulty in fixing liquid soaking and insufficiency in embedding agent soaking during the process of insect antenna transmission processing are solved, finally-obtained sample slices can be relatively flat, the phenomena of sample wrinkling, damaging and losing are greatly reduced, internal structures of the sample slices are all effectively fixed, and subcellular structures are clearly visible.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
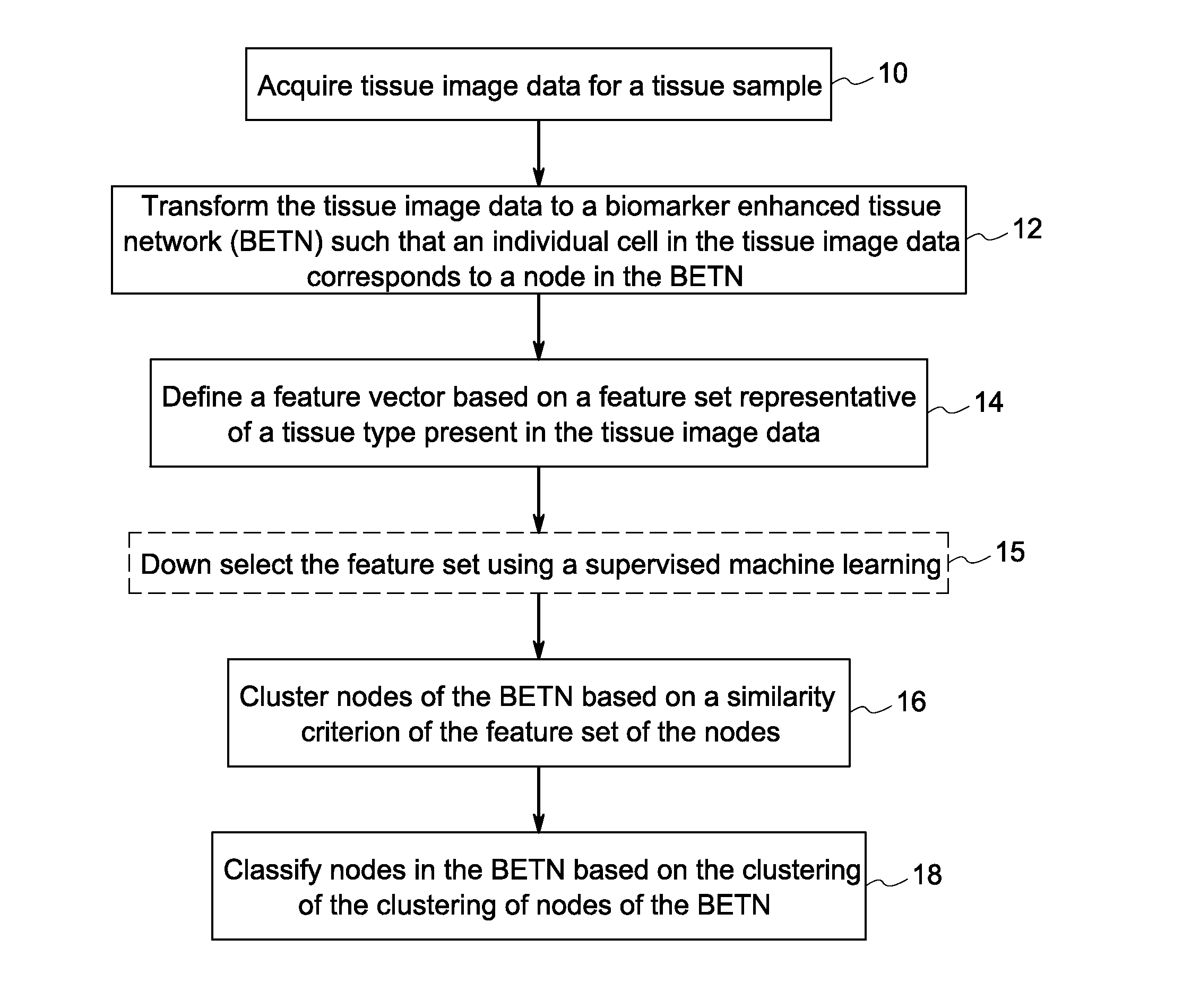
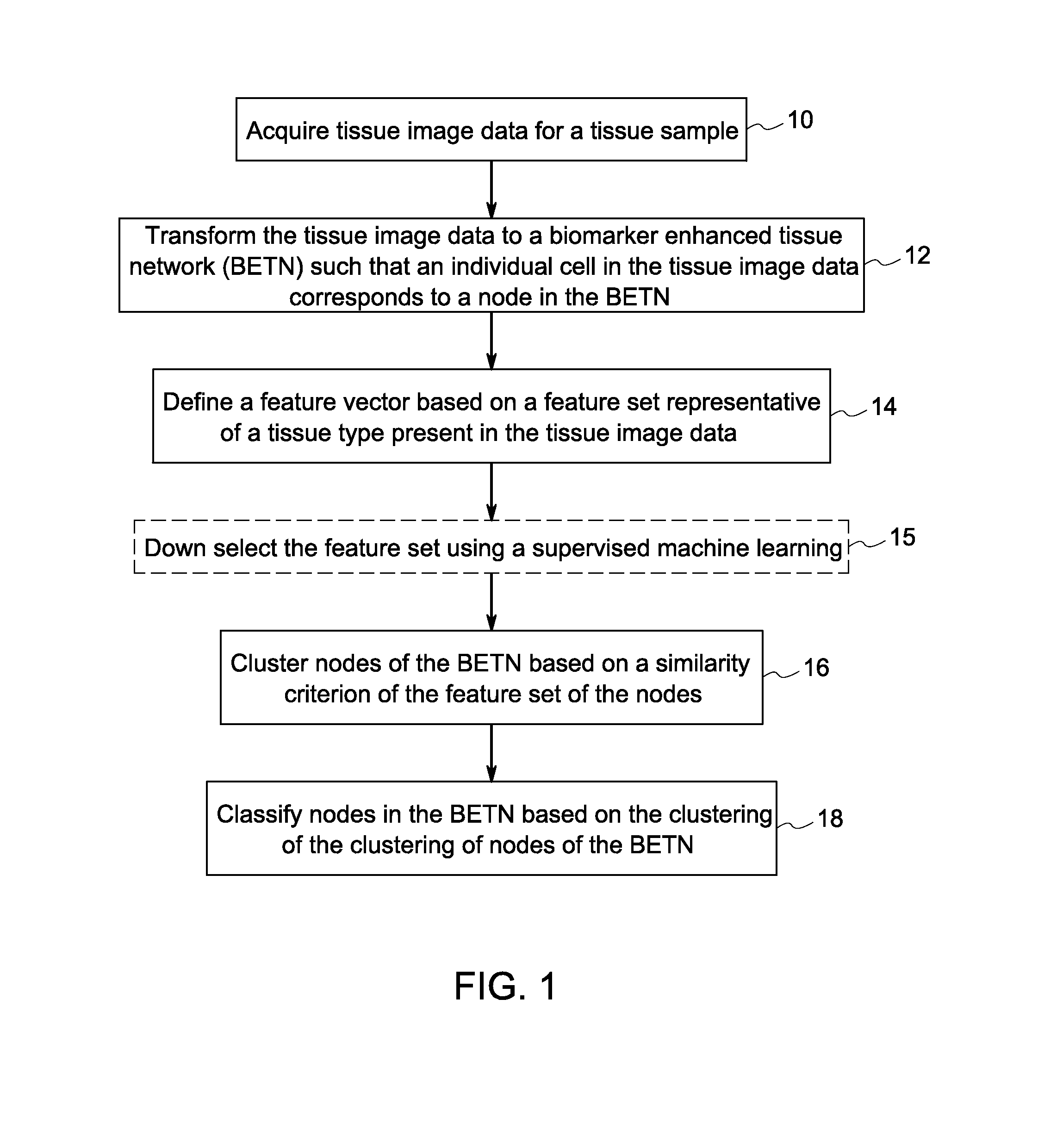
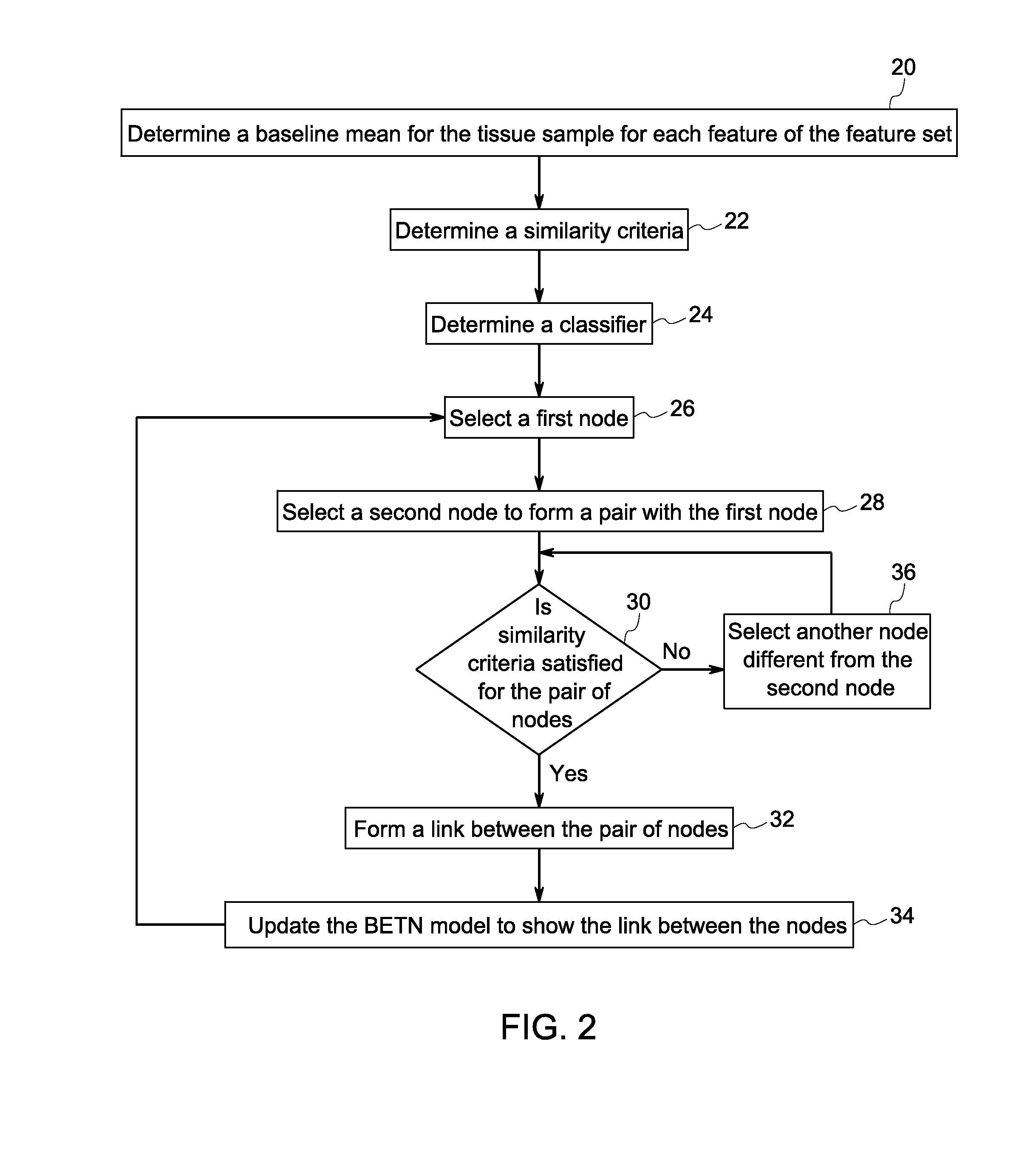
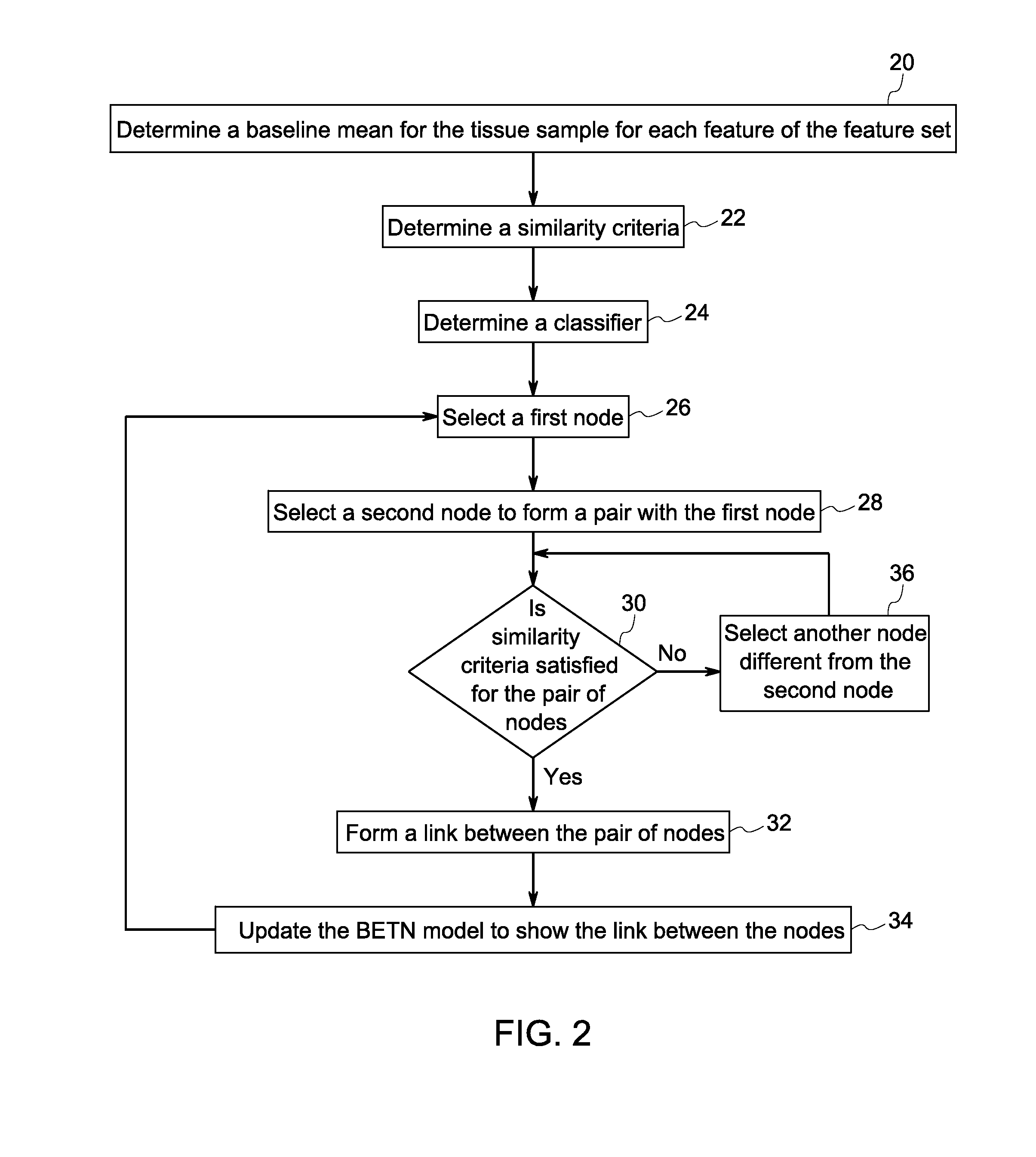
Systems and methods for tissue classification
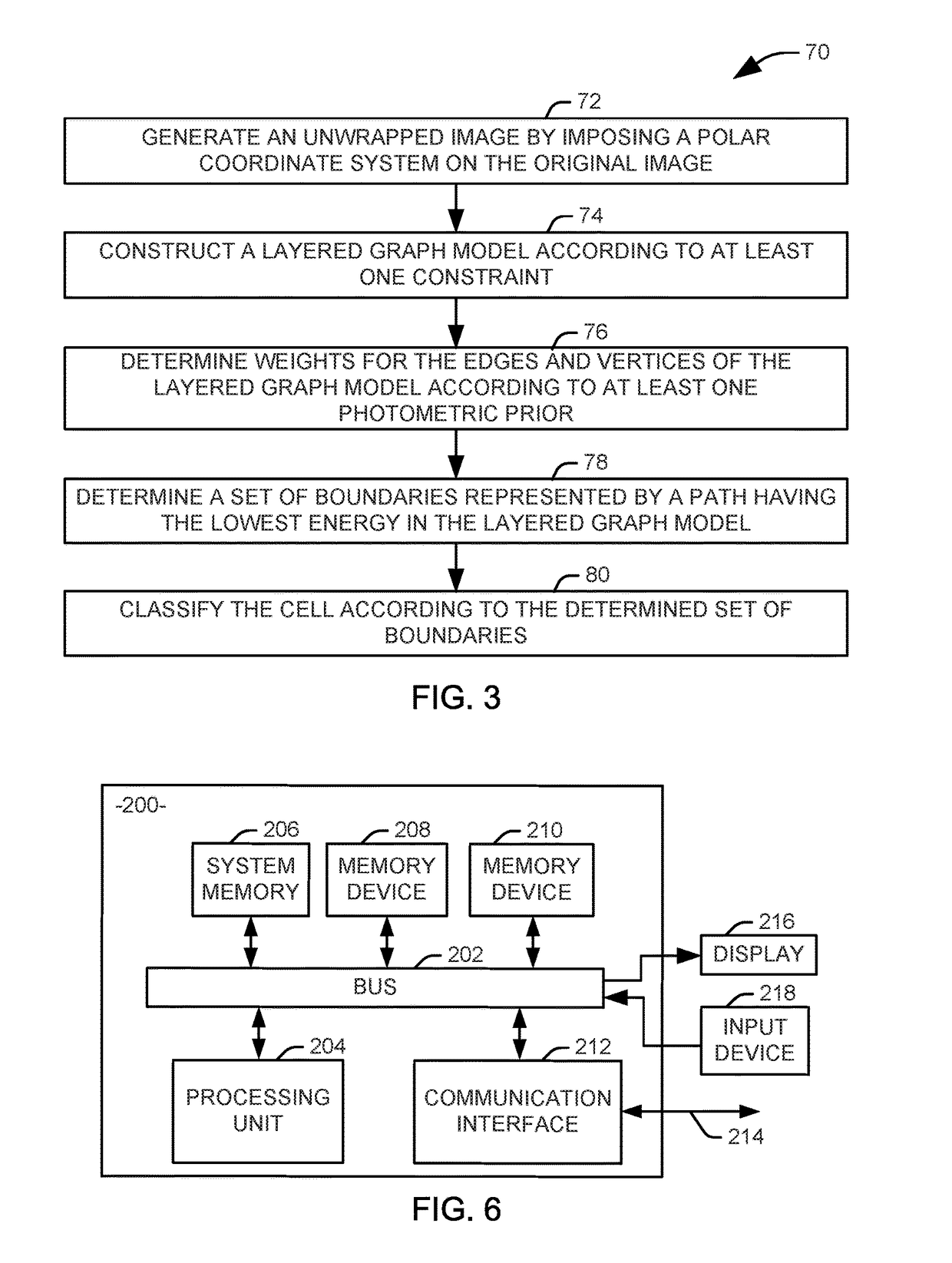
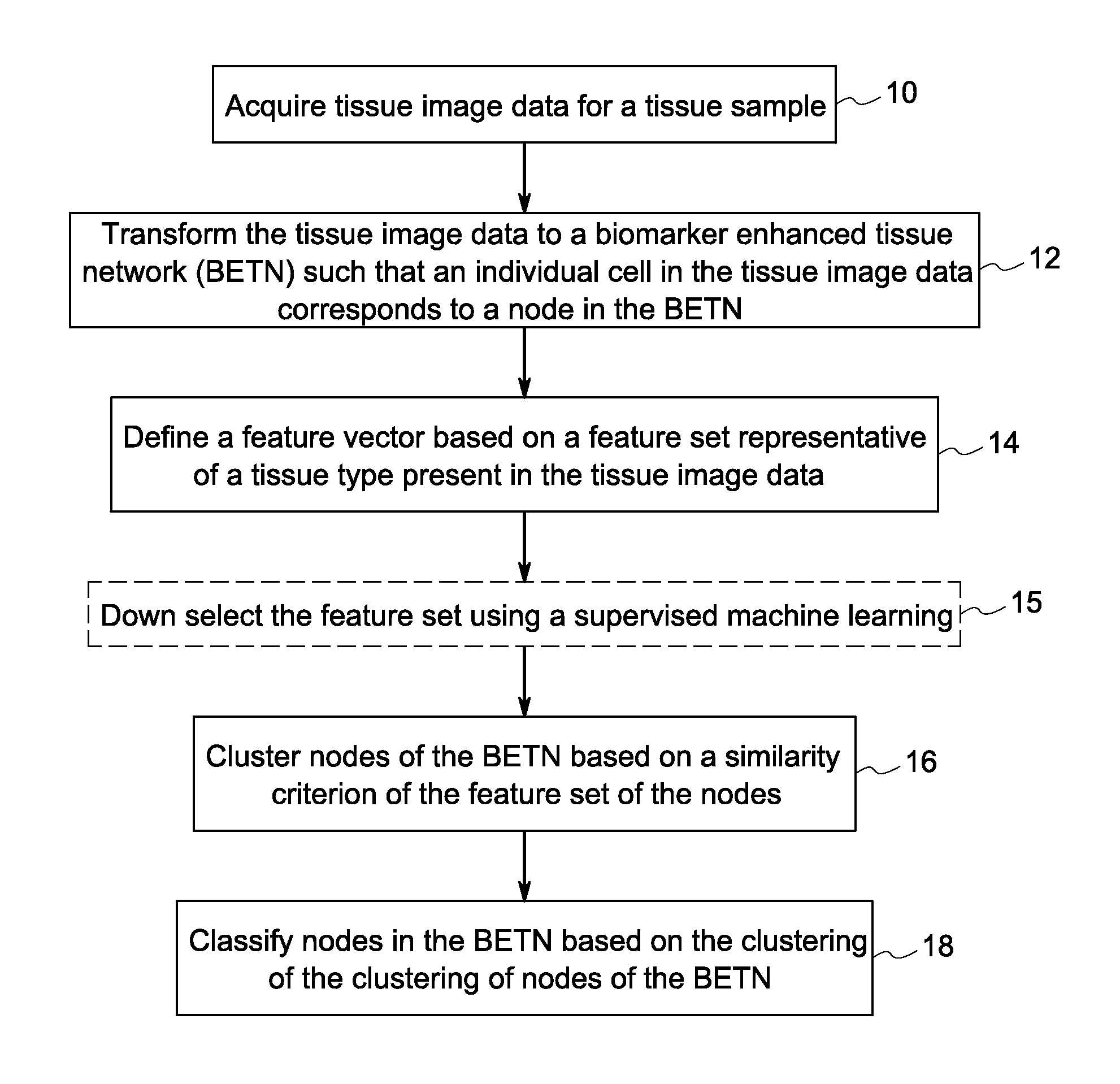
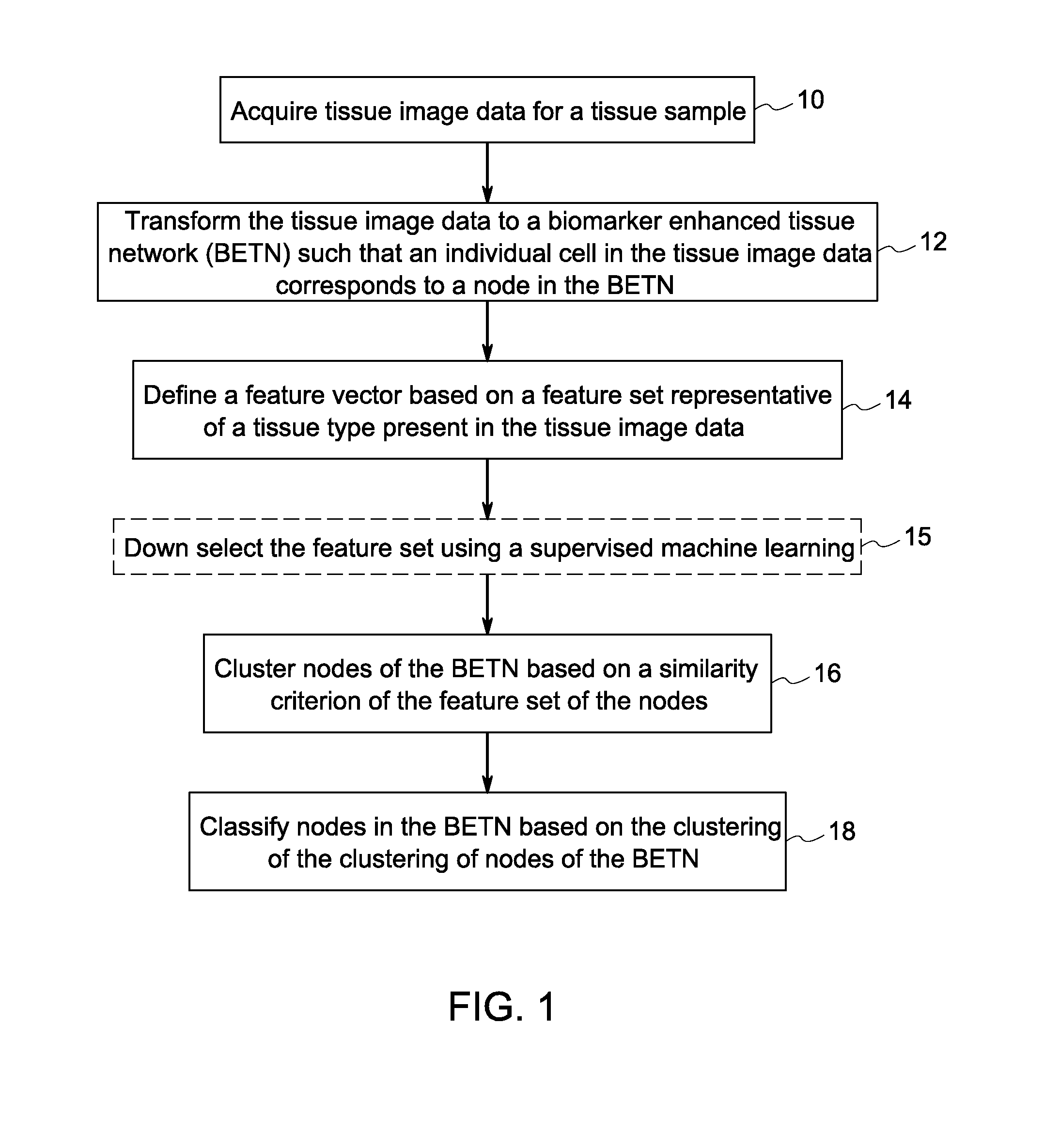
Methods and systems for tissue classification of a tissue sample are provided. The methods and systems transform the tissue image data to a biomarker enhanced tissue network (BETN) such that an individual cell or a sub-cellular structure in the tissue image data corresponds to a node in the BETN, define a feature vector based on a feature set representative of a tissue type of interest, cluster nodes of the BETN based on a similarity criterion of one or features of the feature vector, and classify the nodes in the tissue image data based on the grouping of the nodes of the BETN.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Non-invasive systems and methods for selective activation of photoreactive responses
Products, compositions, systems, and methods for modifying a target structure which mediates or is associated with a biological activity, including treatment of conditions, disorders, or diseases mediated by or associated with a target structure, such as a virus, cell, subcellular structure or extracellular structure. The methods may be performed in situ in a non-invasive manner by application of an initiation energy to a subject thus producing an effect on or change to the target structure directly or via a modulation agent. The methods may further be performed by application of an initiation energy to a subject in situ to activate a pharmaceutical agent directly or via an energy modulation agent, optionally in the presence of one or more plasmonics active agents, thus producing an effect on or change to the target structure. Kits containing products or compositions formulated or configured and systems for use in practicing these methods.
Owner:IMMUNOLIGTHT LLC
Optical clearing agent for bone tissue
ActiveCN102749231AUniform refractive indexReduce scatterPreparing sample for investigationSodium bicarbonateOptical clearing
The present invention discloses an optical clearing agent for bone tissue. The optical clearing agent comprises dimethyl sulfoxide, sodium bicarbonate, and at least two materials selected from polyethylene glycol-400, methyl salicylate, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, sodium diatrizoate, glycerol, glucose, sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate, sorbitol and laurinol, wherein a volume percentage of the dimethyl sulfoxide in the optical clearing agent for bone tissue is 40-80%, a mass percentage of the sodium bicarbonate in the optical clearing agent for bone tissue is 1-2%, the balance is other materials, and the pH value of the optical clearing agent for bone tissue is 6-11. After the optical clearing agent for bone tissue in the present invention acts on bone tissue, a refractive index inside the tissue can be quickly homogenized, and scattering inside the tissue can be reduced, such that the tissue provides improved transparency for light, the imaging depth is increased, and a new method for obtaining cortex neuron subcellular structures and microvascular information is provided. After the optical clearing agent for bone tissue is locally coated on the bone tissues or is adopted to soak the bone tissues, the bone tissue can provide improved transparency for light.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method, optical module and system for extended field depth three-dimensional nanoscale-resolution imaging
ActiveCN102980875AHigh resolutionLarge depth of fieldScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansMicro imagingGrating
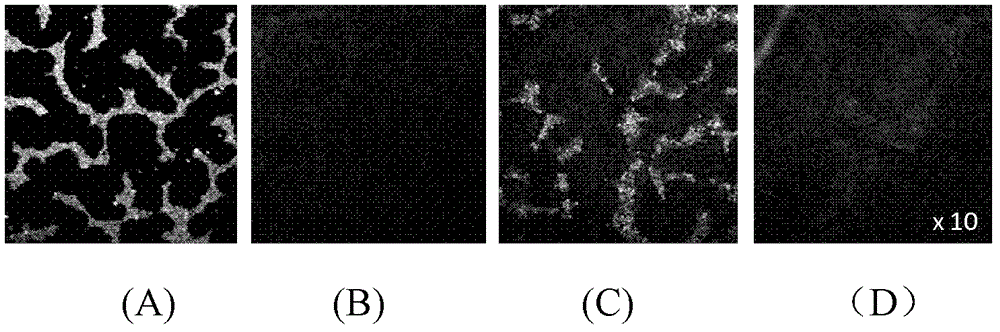
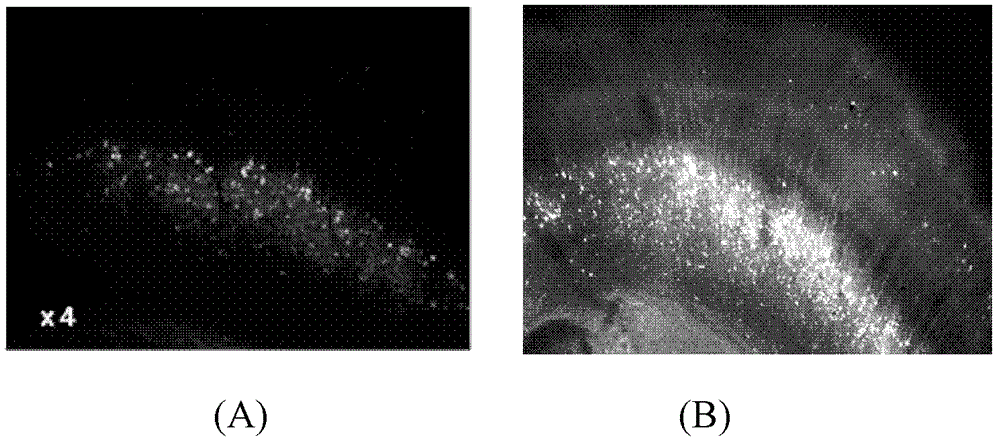
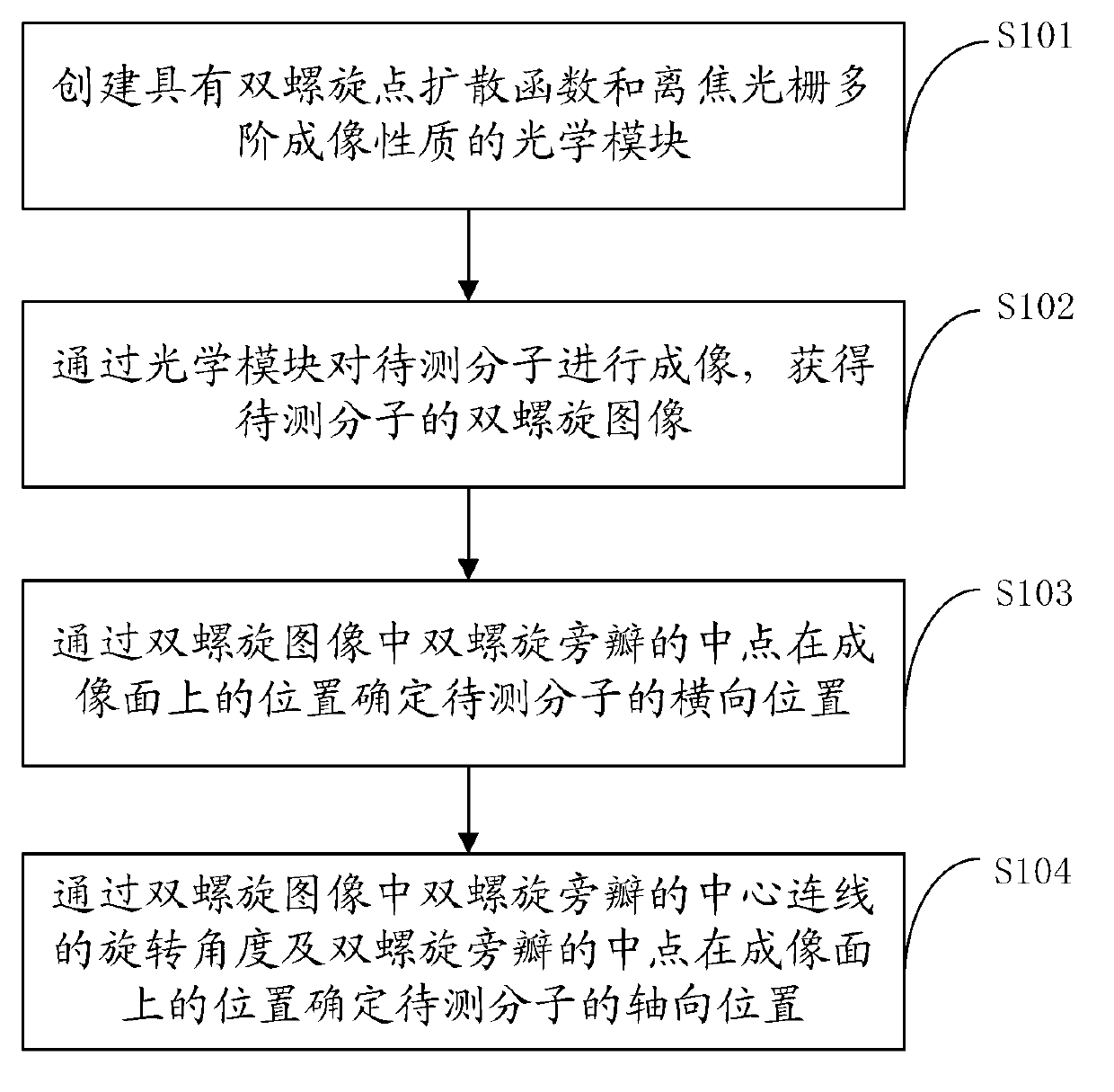
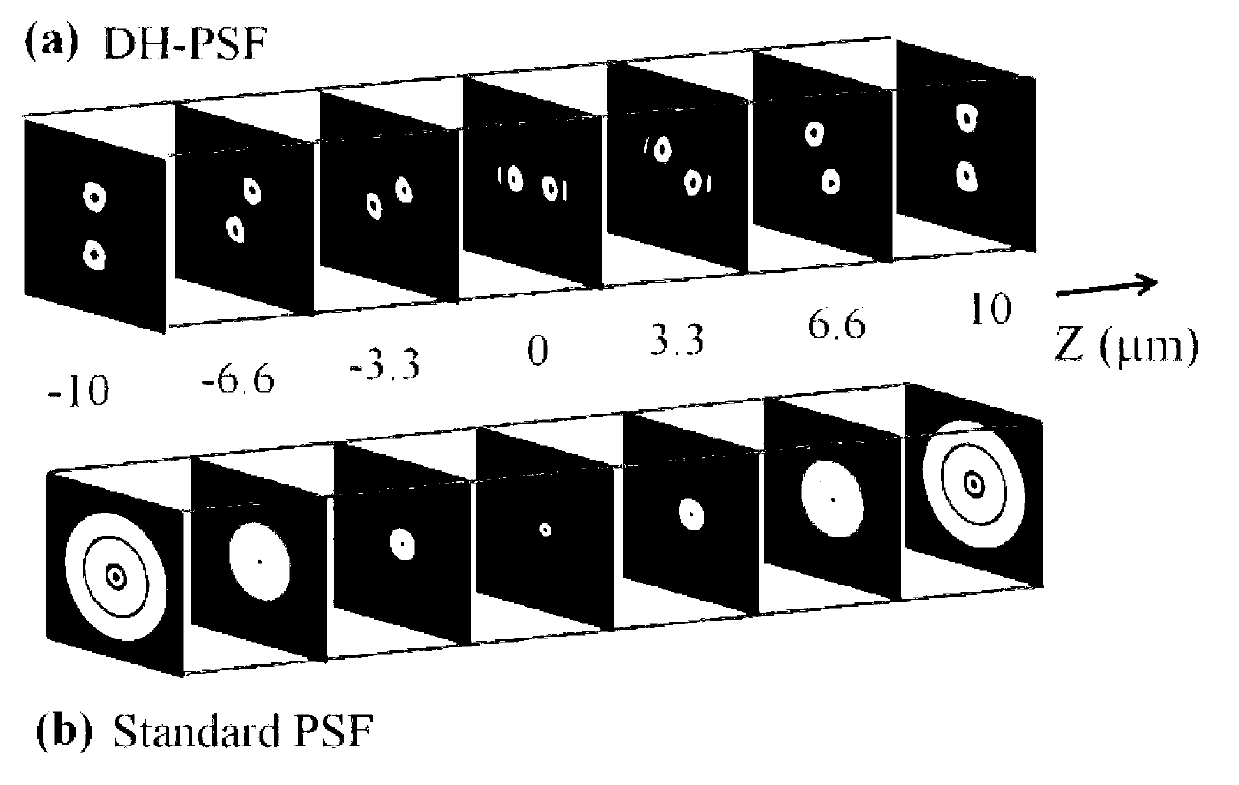
The invention belongs to the technical field of microimaging and provides a method, an optical module and a system for extended field depth three-dimensional nanoscale-resolution imaging. The method comprises the following steps of 1, building the optical module having a double-helix point spread function and defocusing grating multistage imaging properties, 2, carrying out imaging of a molecule needing to be detected by the optical module to obtain a double-helix image, 3, determining a horizontal position of the molecule needing to be detected according to positions of middle points of double-helix sidelobes of the double-helix image, and 4, determining an axial position of the molecule needing to be detected according to a rotation angle of a connection line of centers of the double-helix sidelobes of the double-helix image, and the positions of the middle points of the double-helix sidelobes. Through combination of double effects of the double-helix point spread function and the defocusing grating multistage imaging, the method extends a field depth and improves a resolution ratio. The method can be used for dynamic range imaging of subcellular fractions having any depth values in a whole cell, can produce dynamic function images of multiple moving molecules, and has an important meaning for high-level understanding of a rule and a relationship between a subcellular structure and a cell function change.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
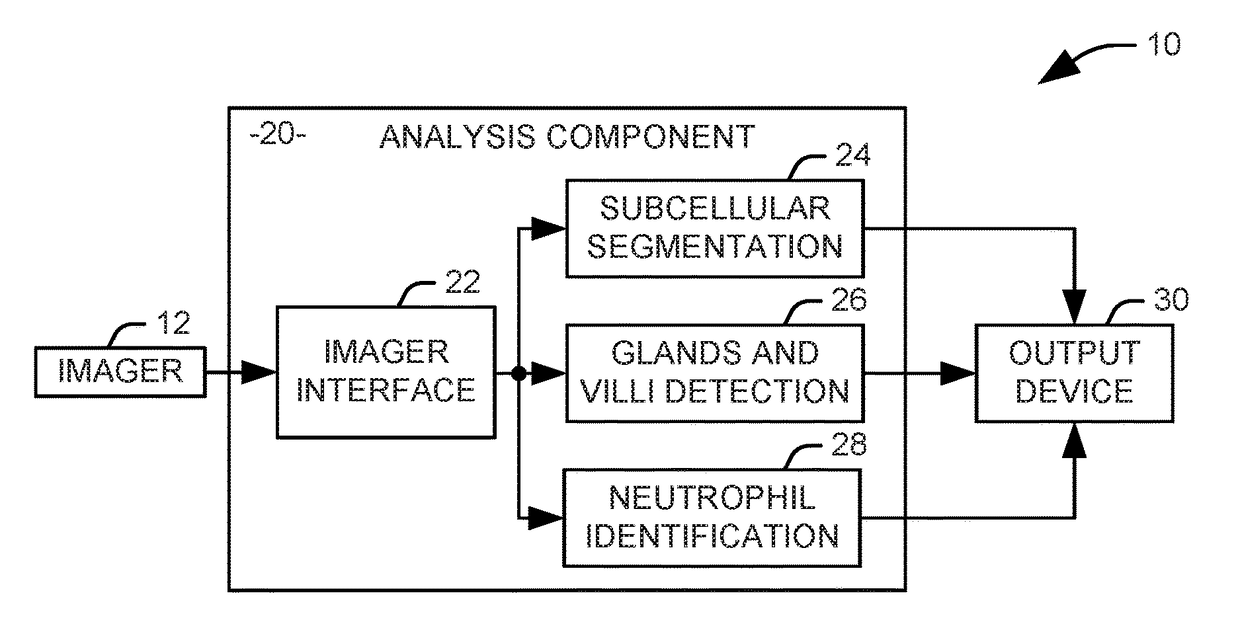
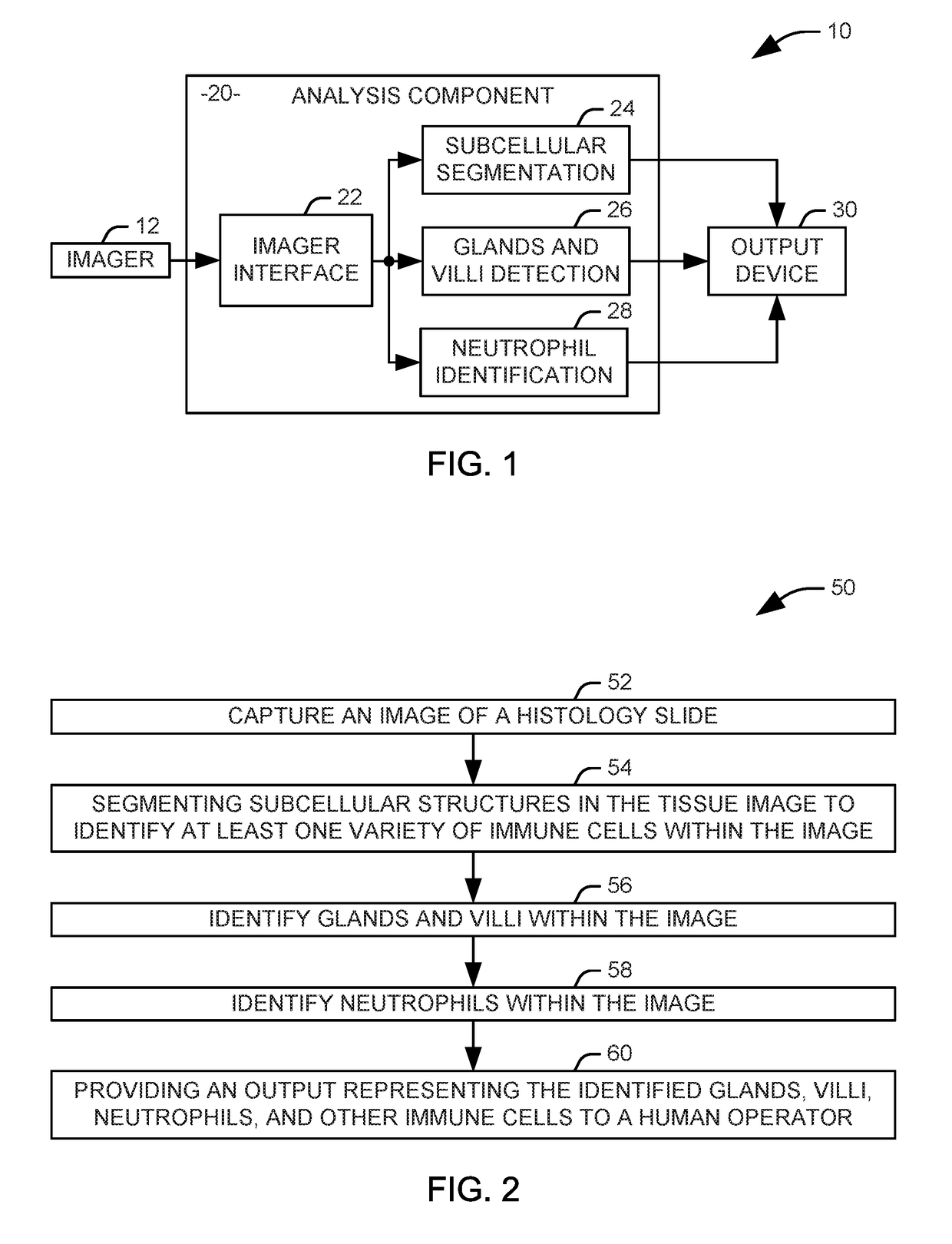
Identification of inflammation in tissue images
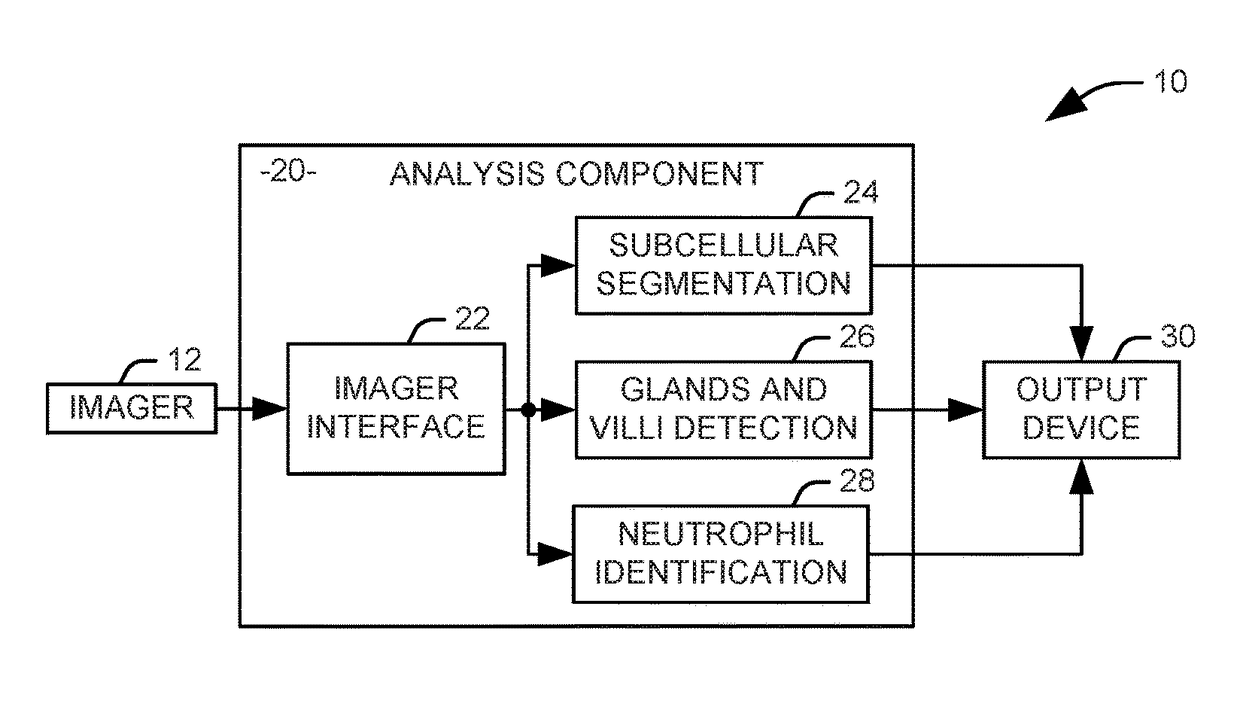
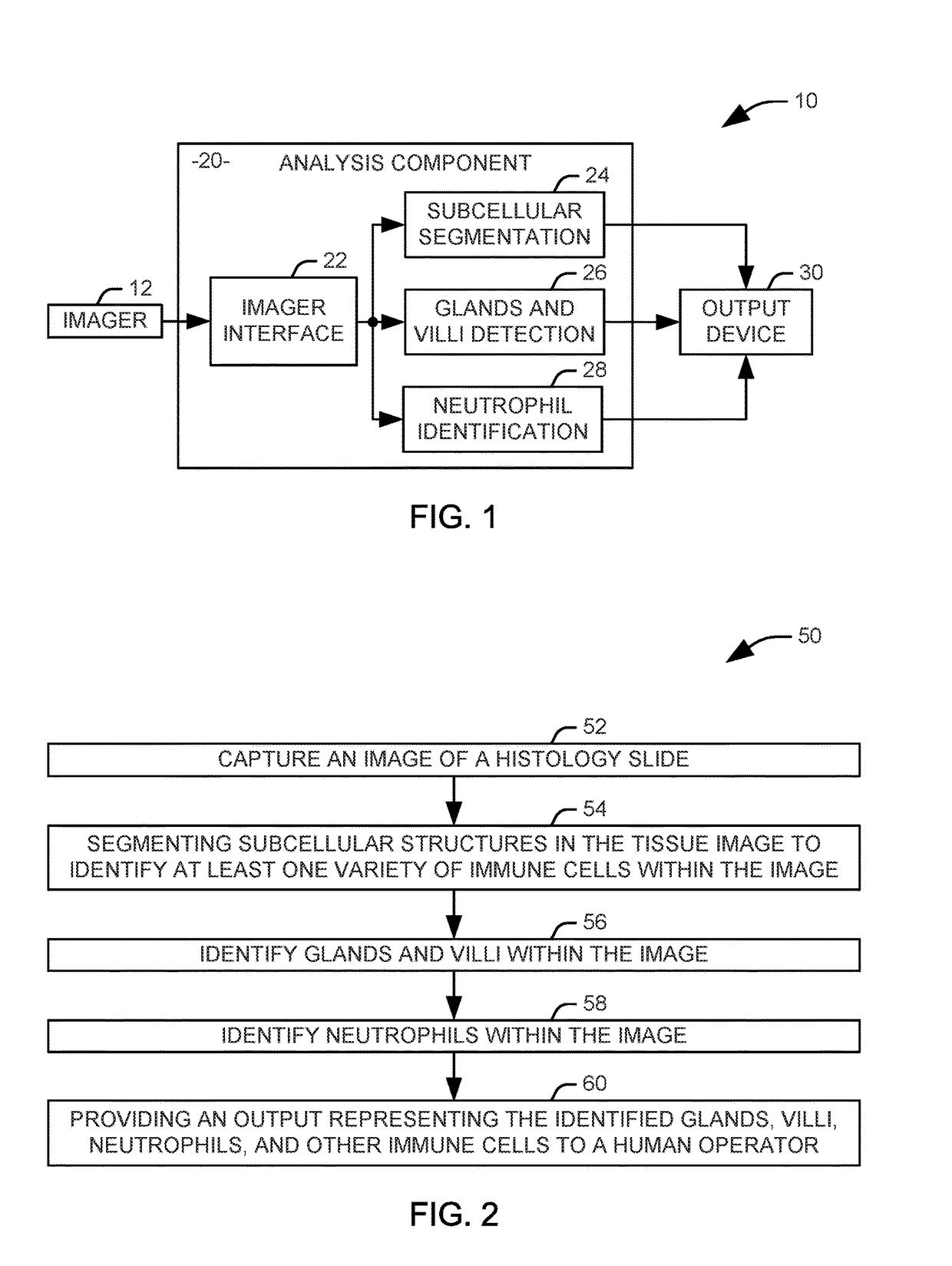
Systems and methods are provided for identifying markers for inflammation in a tissue image. The tissue image is captured as an image of a histology slide. Subcellular structures in the tissue image are segmented via a first automated process to identify at least one variety of immune cells within the image. Glands and vilii are identified within the tissue image via a second automated process. Neutrophils are identified within the tissue image via a third automated process. An output representing the identified glands, villi, neutrophils, and other immune cells is provided to a human operator.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Upconversion super-resolution imaging nanoprobe as well as preparation method and application thereof
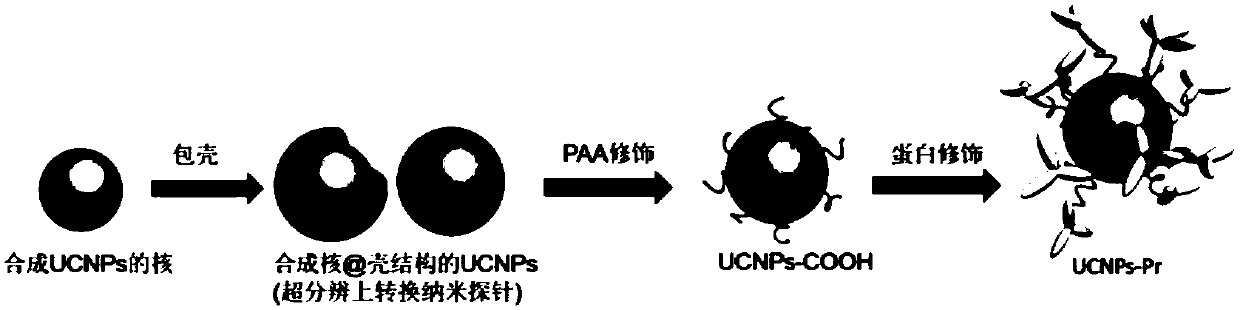
ActiveCN107629792AAchieve super-resolution optical imagingGood photochemical stabilityNanoopticsFluorescence/phosphorescenceImmunofluorescent labelingSubcellular structure
The invention discloses an upconversion super-resolution imaging nanoprobe as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The upconversion super-resolution imaging nanoprobe has a core@shellstructure. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing rare-earth upconversion nano-particles with controllable particle size and excellent dispersion property by adopting a solvothermal method; performing surface modification by polyacrylic acid; and finally performing protein modification. The upconversion super-resolution imaging nanoprobe is applied to immunofluorescent labeling of a subcellular structure of cells, so that fluorescent super-resolution imaging of the subcellular structure is realized. Compared with the traditional fluorescein-based super-resolution optical imaging method, the method disclosed by the invention is a fluorescence zero-bleaching and zero-flicker super-resolution microscopic imaging method based on the upconversion super-resolution imaging nanoprobe, and biological samples can be observed for a long time.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
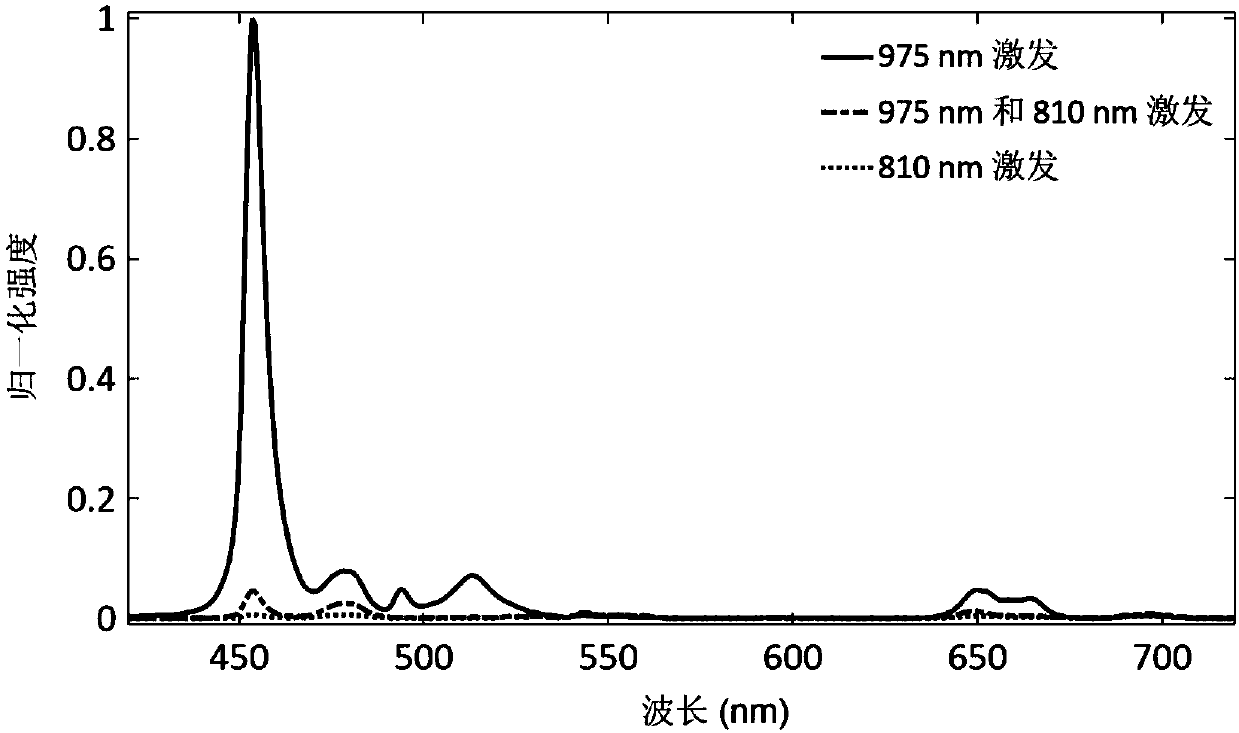
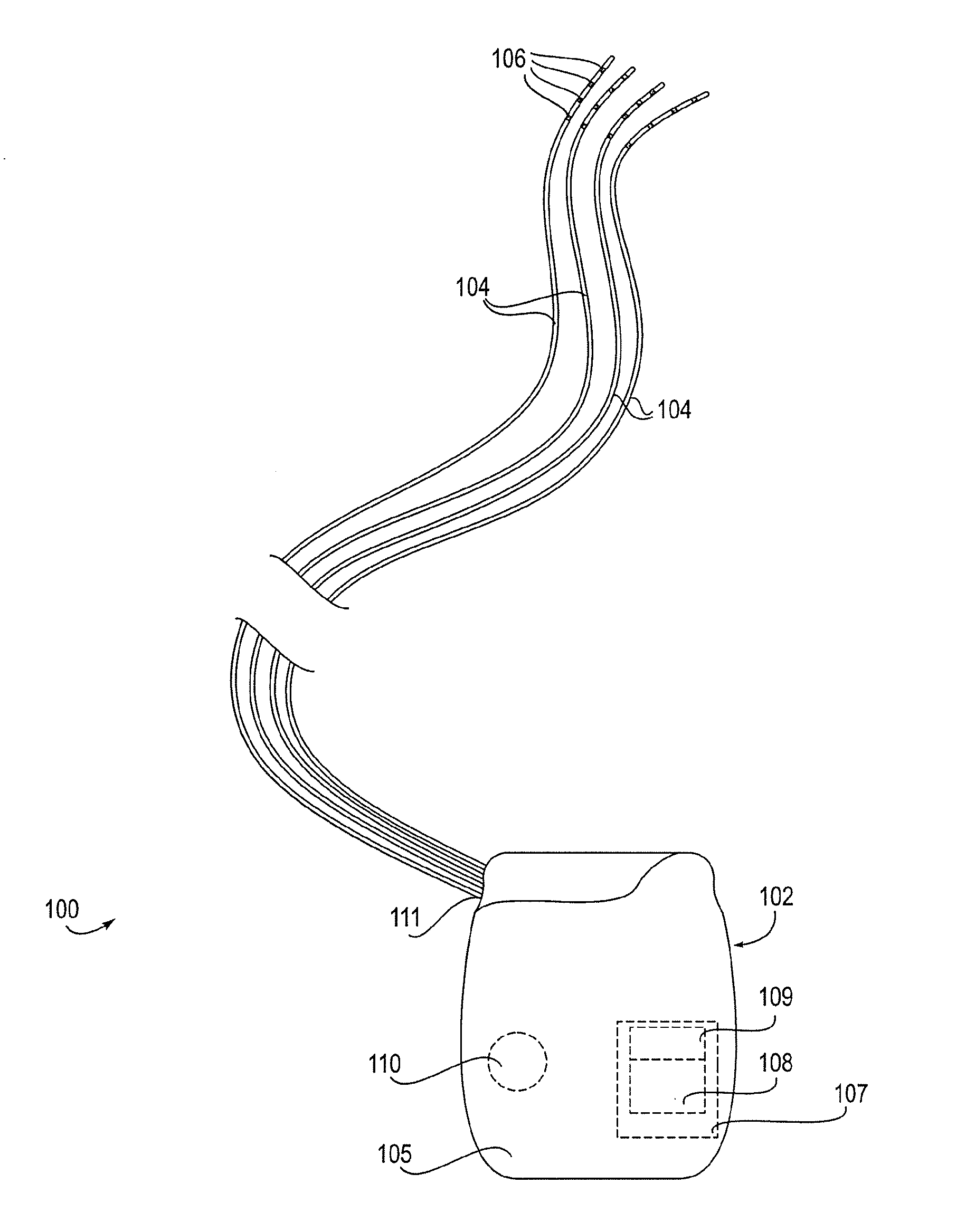
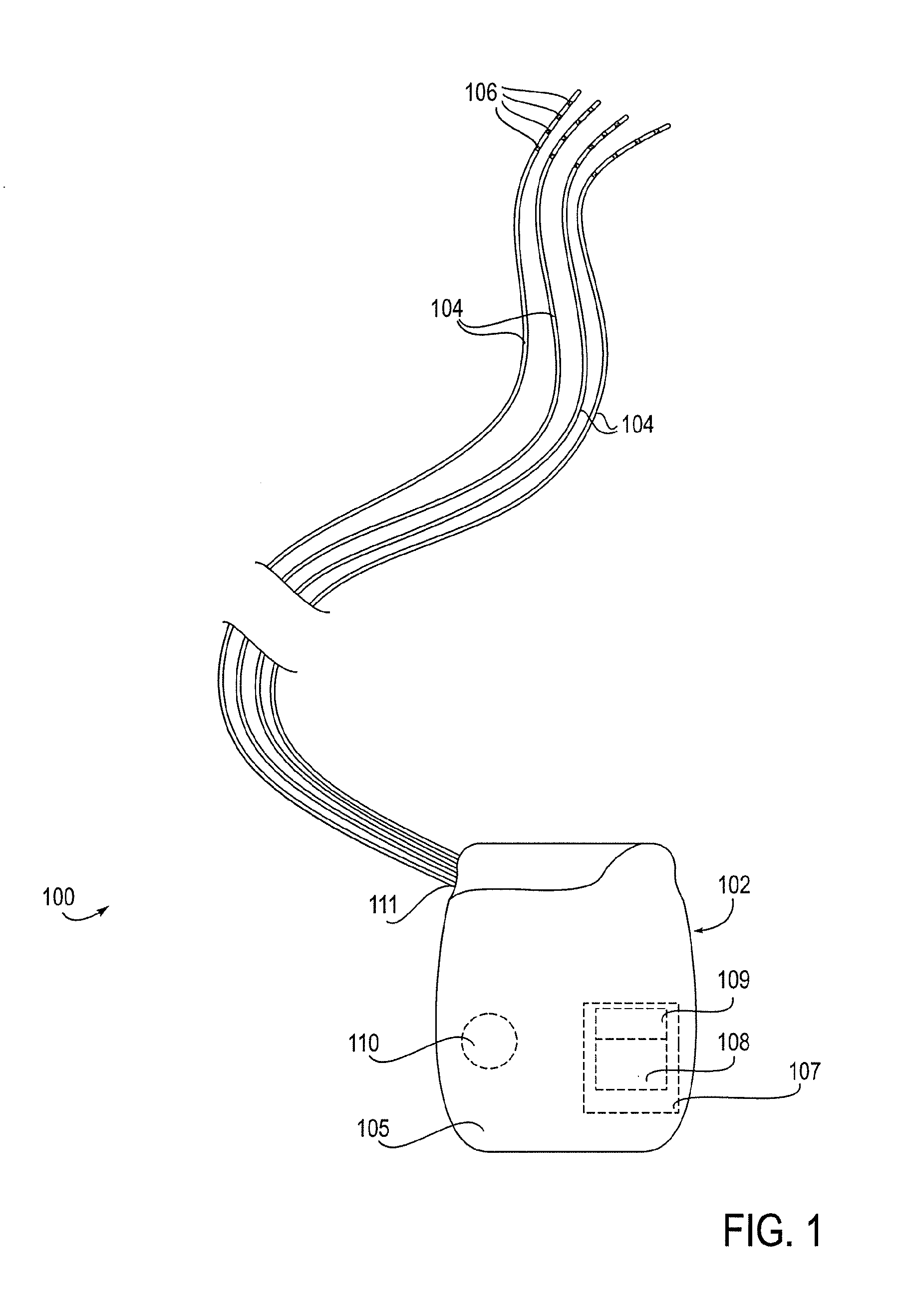
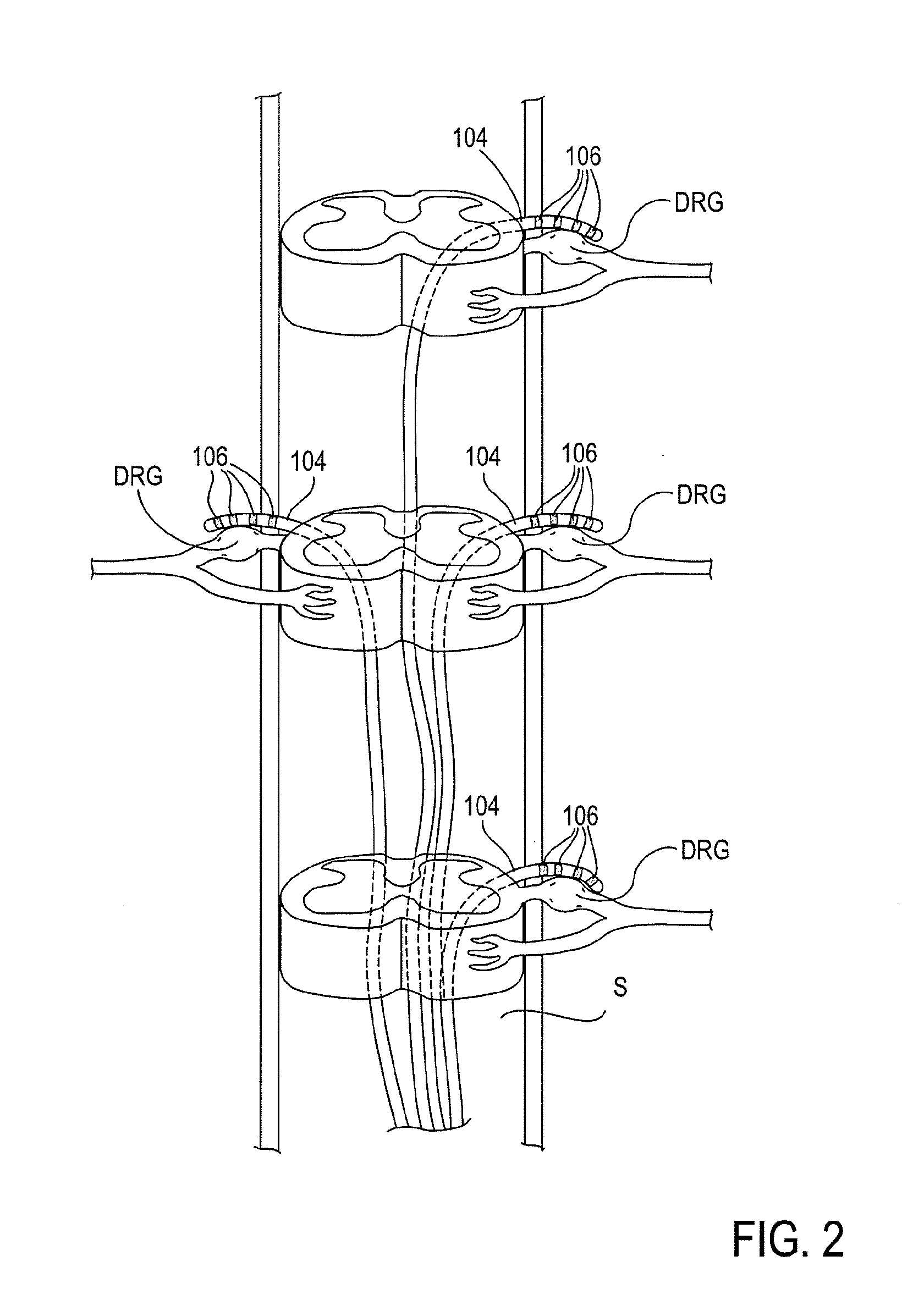
Neuromodulation of subcellular structures within the dorsal root ganglion
InactiveUS20140343624A1Suppressing action potential firingReduce conductionSpinal electrodesArtificial respirationPrimary sensory neuronSensory neuron
Devices, systems and methods are provided for the targeted treatment of abnormal sensory conditions. In such conditions, physical stimuli is transduced into neuronal impulses that are subsequently transmitted to the central nervous system for processing. Such transduction is achieved by primary sensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglions. Subcellular structures on primary sensory neurons can significantly modulate the function of these neurons, thereby affecting the transduction and reducing the abnormal sensory experiences. Thus, devices, systems and methods are provided for neuromodulating subcellular structures on primary sensory neurons of the dorsal root ganglions.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG SMI S A R L SJM LUX SMI
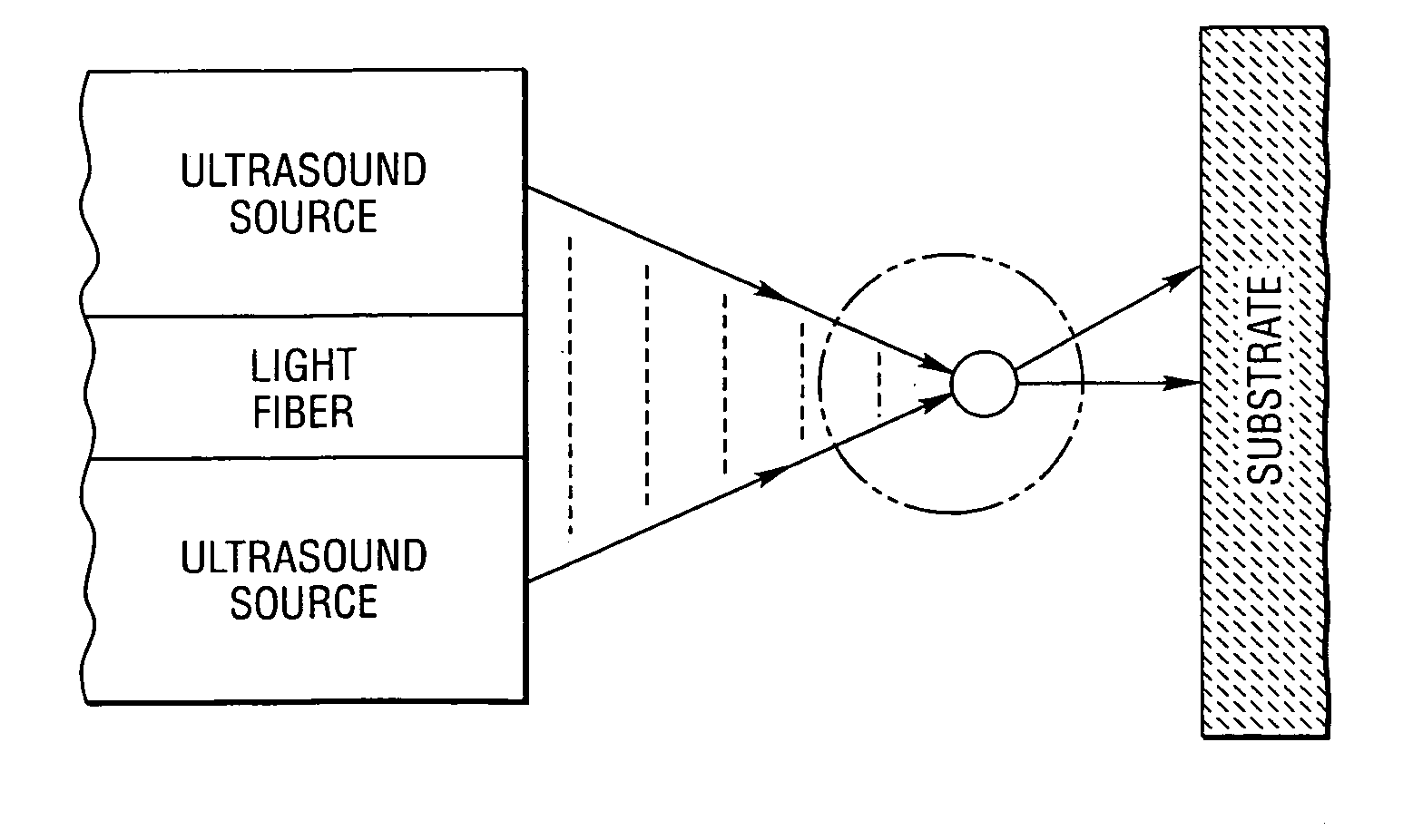
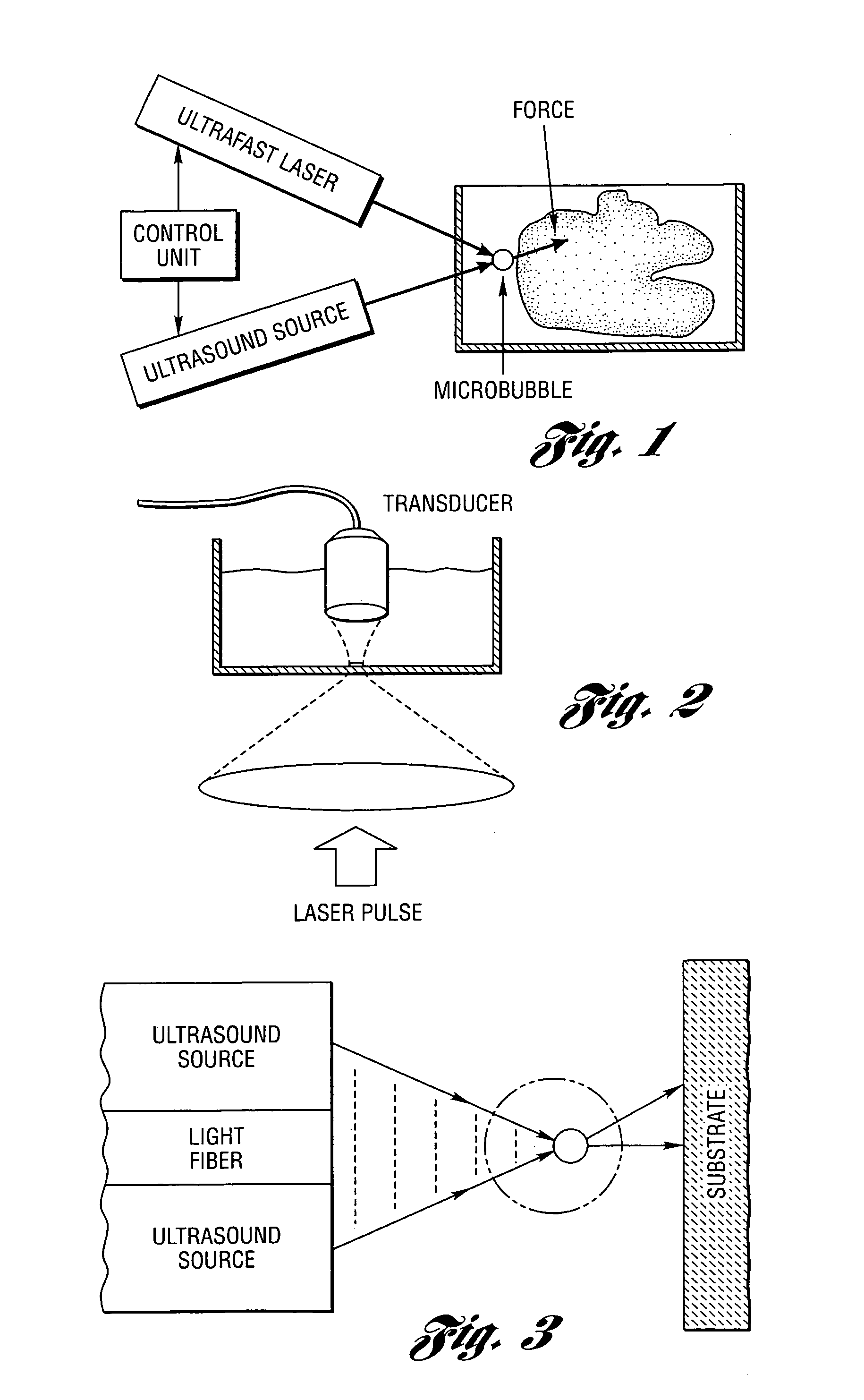
Method and system to create and acoustically manipulate a microbubble
InactiveUS7549985B2Radiation pyrometryMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEngineeringNanoscopic scale
A method and system to create and acoustically manipulate without destroying a microbubble which, in biological applications, can manipulate structures such as cells and subcellular structures at a nanoscopic scale.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Nanoelectrodes and nanotips for recording transmembrane currents in a plurality of cells
InactiveUS8232074B2Improve throughputMinimizing noise in measurementSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectricityPower flow
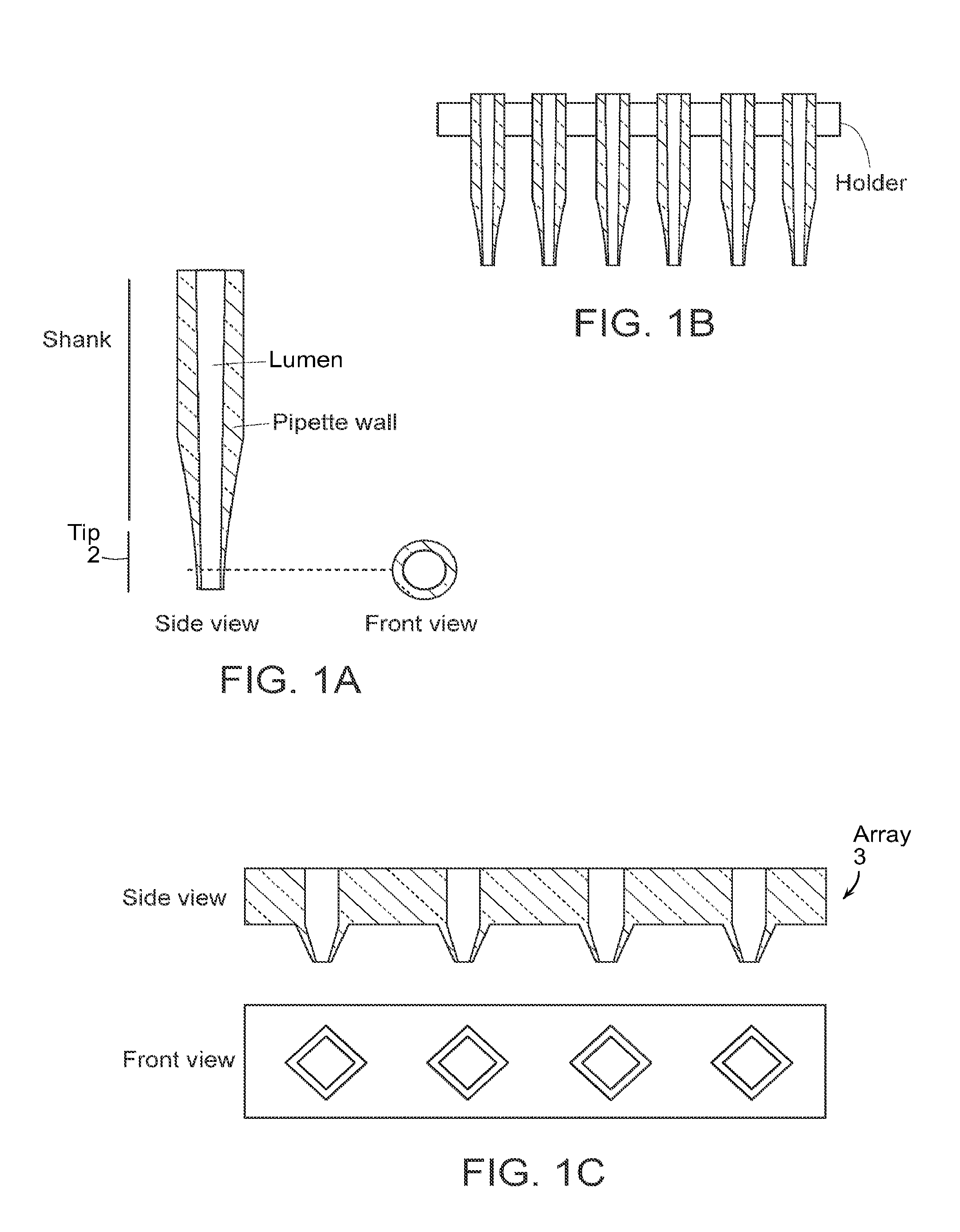
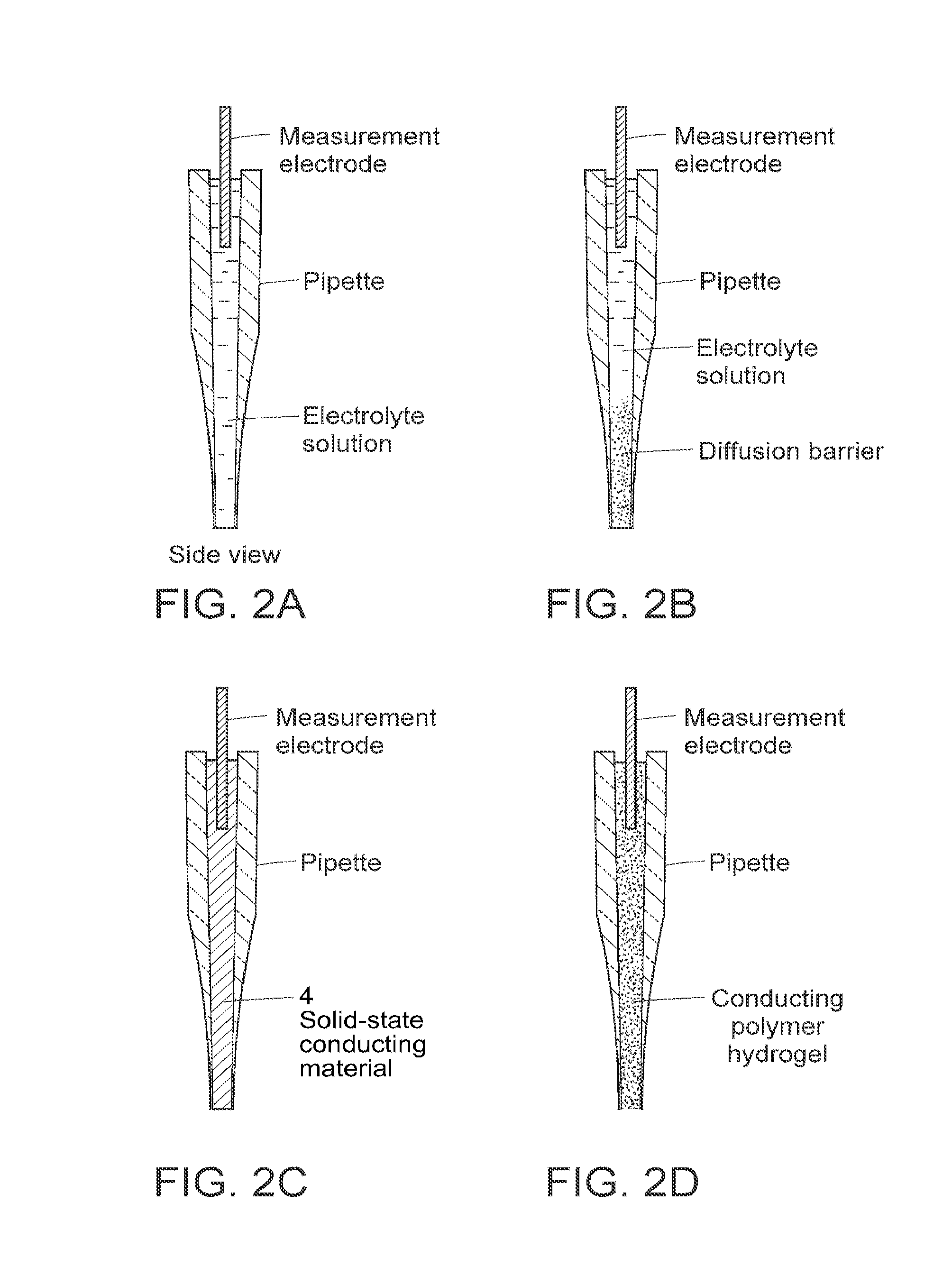
The present invention relates to methods of measuring electrical properties of a cell using electrode devices comprising tapered nanotips having submicrometer dimensions (“nanoelectrodes”) for insertion into a cell. The devices are used to measure electrical properties of the cell and, optionally, may be used to electroporate, the cell or subcellular structures within the cell. The invention also provides arrays of electrode devices having nanotips for simultaneously or sequentially measuring the electrical properties of cells (e.g., such as surface immobilized cells). The electrodes can be used to measure properties of ion channels and in HTS assays to identify drugs which affect the properties of ion channels. The invention additionally provides microfluidic systems adapted for use with the electrode devices having nanotips. In combination with the electrodes, the microfluidic systems provide cell-based biosensors for monitoring cellular responses to conditions, such as exposure to candidate drugs.
Owner:CELLECTRICON
Systems and methods for tissue classification using attributes of a biomarker enhanced tissue network (BETN)
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Research method for classifying endosperm tissues in detail by using morphological method
InactiveCN104390978AAbundant evidenceComplete informationScanning probe techniquesFluorescence/phosphorescenceSoftware development processFluorescence
The invention discloses a research method for classifying endosperm tissues in detail by using a morphological method. The research method comprises the following steps: planting corn, sorghum, wheat and rice, experimenting caryopsis developed for different days; examining size, shape and color changes of the caryopsis by using an integrated microscope, and observing position and distribution changes of the endosperm tissues; observing fluorescence characteristics of different tissues of the caryopsis by using a luminescence microscope, and analyzing ingredients of the caryopsis; observing microstructure change of caryopsis and endosperm tissue development by using a light microscope; observing a three-dimensional shape and distribution of cell walls, amyloid, protein body and aleurone cereal by using a scanning electron microscope; and observing characteristics and changes of subcellular structures in cells by using a transmission electron microscope. According to the research method, by using four main cereals as experiment materials, a total development process of the cereal endosperm is analyzed and verified by using various morphological observation technologies, an important role of the endosperm during development of the caryopsis is displayed, and important information is provided for evolution development by comparing structural difference of different grain endosperms.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Identification of inflammation in tissue images
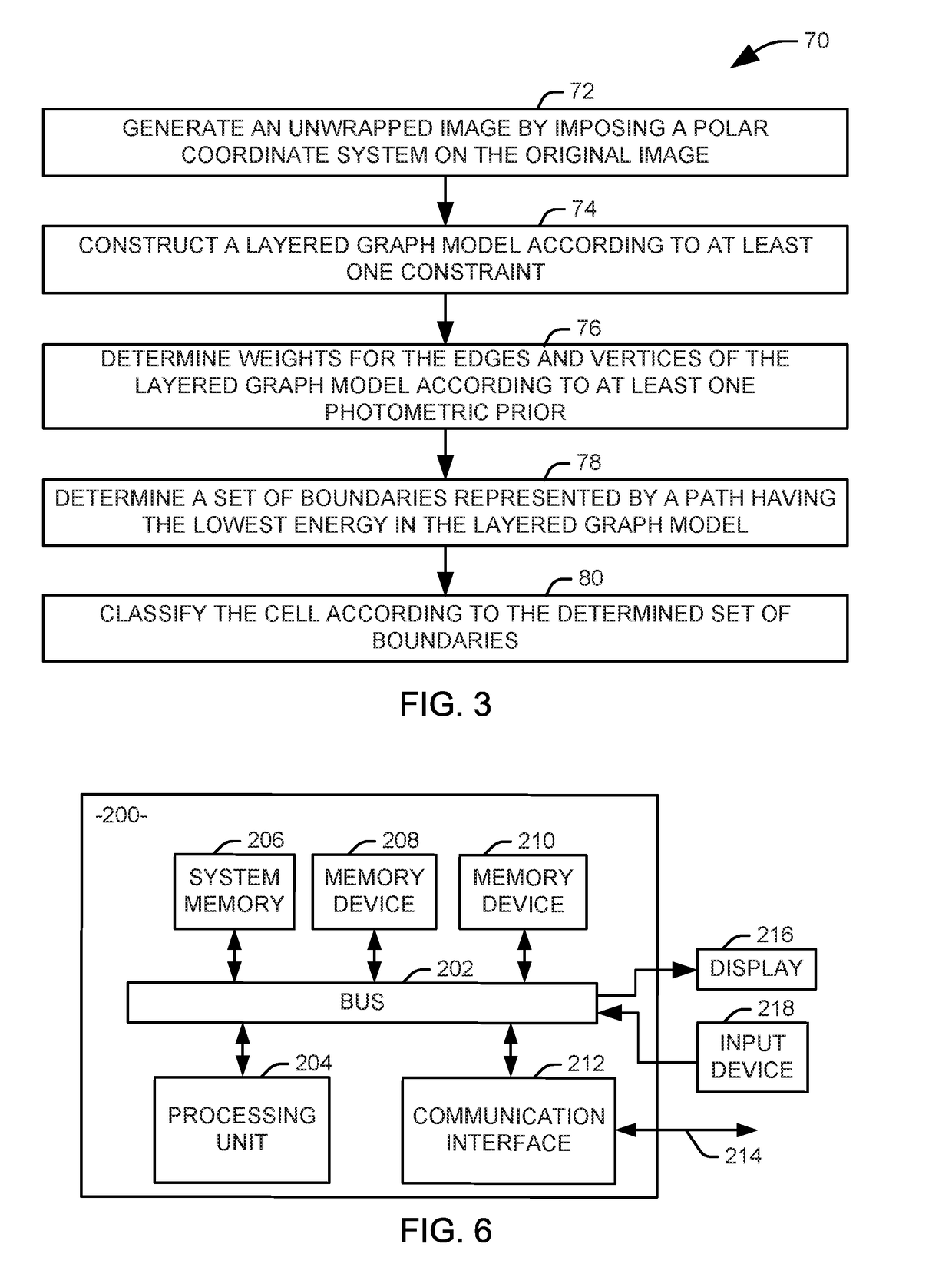
Systems and methods are provided for identifying markers for inflammation in a tissue image. The tissue image is captured as an image of a histology slide. Subcellular structures in the tissue image are segmented via a first automated process to identify at least one variety of immune cells within the image. Glands and vilii are identified within the tissue image via a second automated process. Neutrophils are identified within the tissue image via a third automated process. An output representing the identified glands, villi, neutrophils, and other immune cells is provided to a human operator.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Subcellular structure characteristic N-linked carbohydrate chain and application thereof
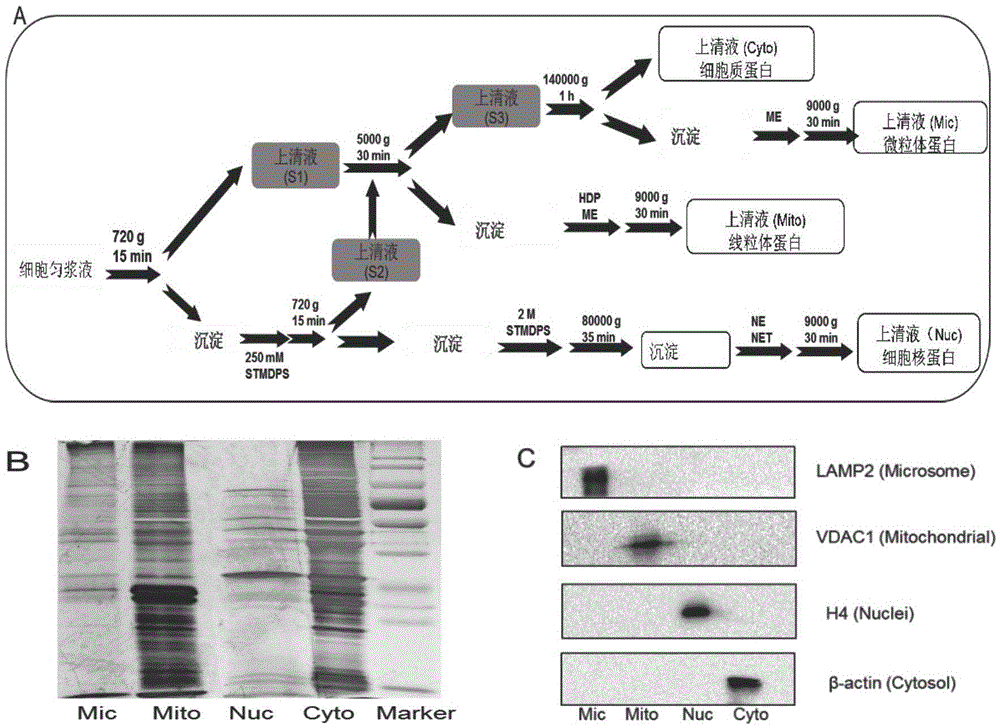
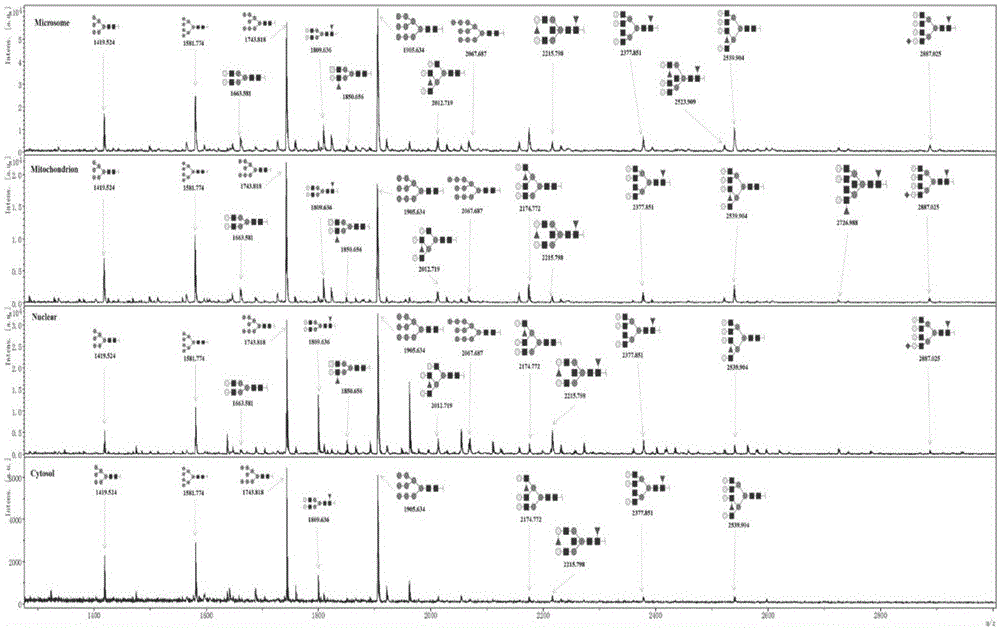
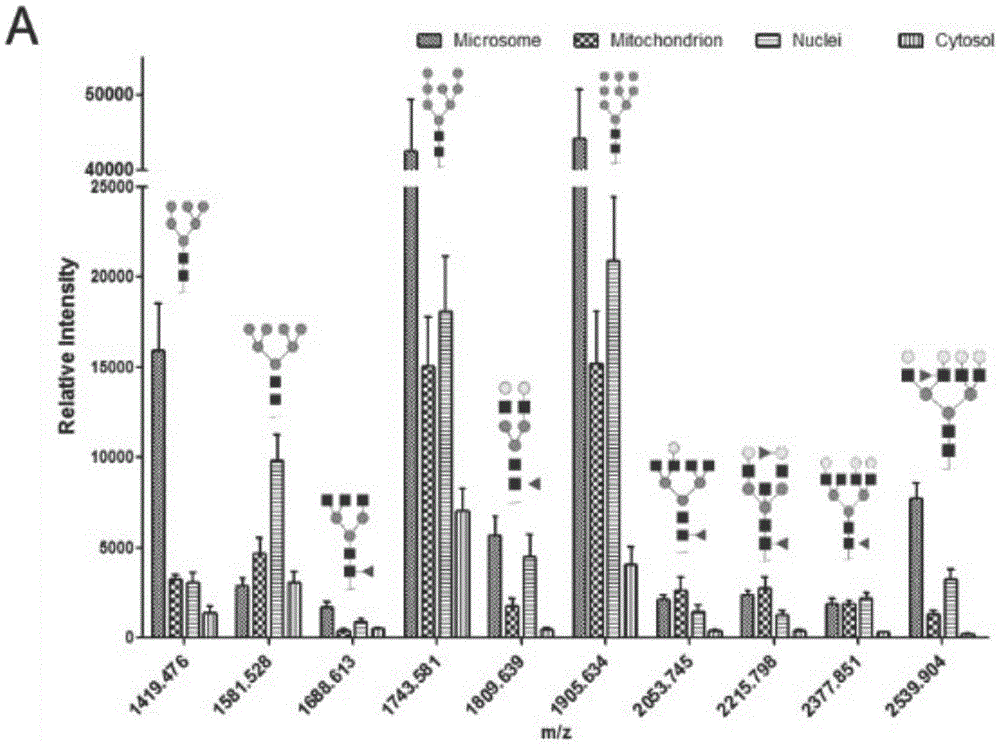
ActiveCN105651853AImplement indirect detectionEasy to detectMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDetection of post translational modificationsBiologySubcellular structure
The invention discloses a subcellular structure characteristic N-linked carbohydrate chain and the application thereof and belongs to the technical field of glycobiology. Bladder YTS1 cells are used as the experiment material, the protein components of four subcellular structures (microsome, chondriosome, cell nucleus and cytoplasm) are obtained with the differential centrifugation method, and subcellular structure difference carbohydrate chain distribution is displayed through the change of the type and structure of subcellular structure protein galactosylated modification identified through a united lectin chip and a mass spectrum (PS) respectively. Subcellular structure characteristic N-linked glycan of ten kinds of human bladder YTS1 cells is obtained. By means of characteristic N-linked glycan, indirect detection and qualitative or quantitative detection of other target substances in corresponding subcellular structures can be achieved.
Owner:上海微江生物技术有限公司
A method for determining the motion trajectory of subcellular structures based on microscopic images
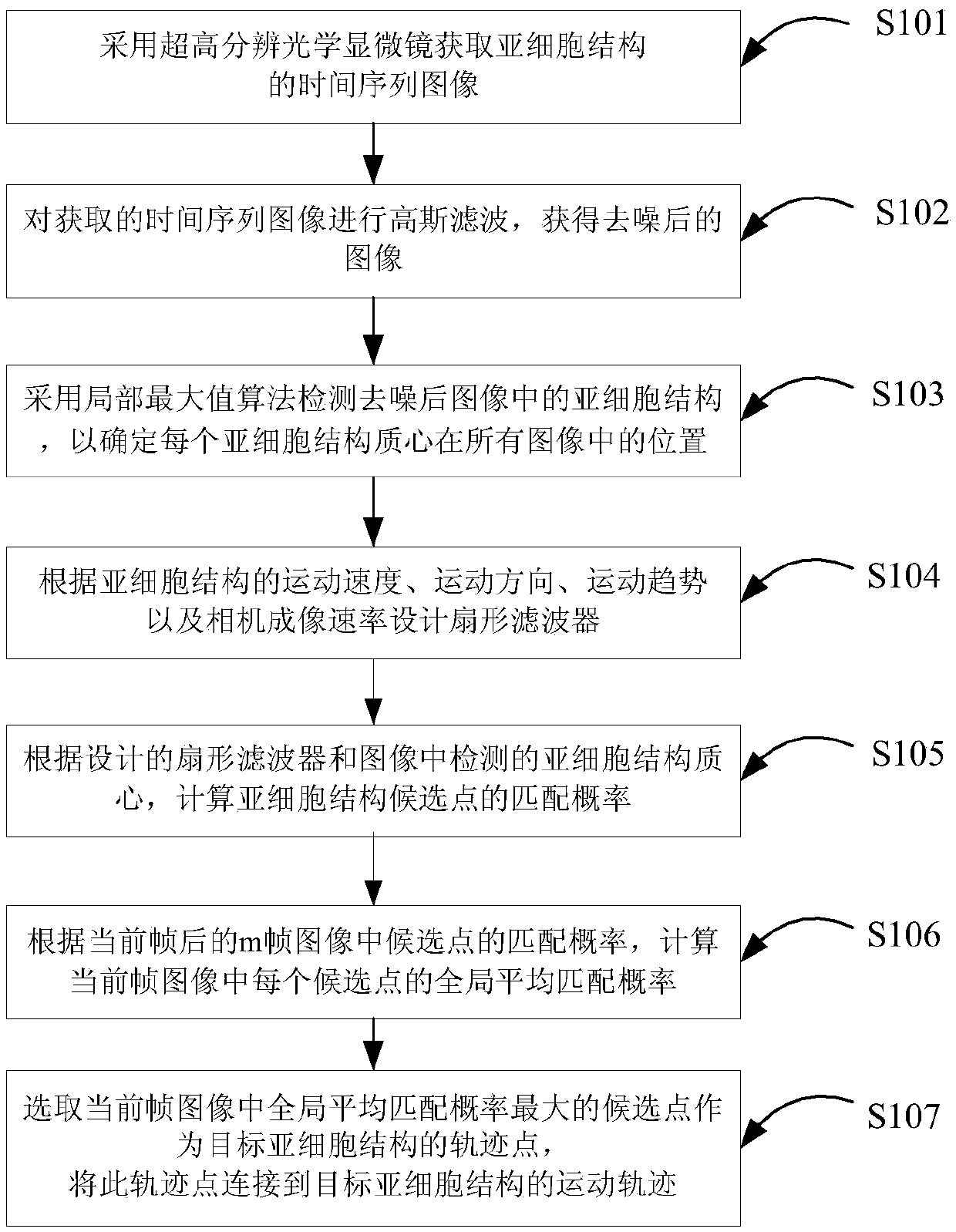
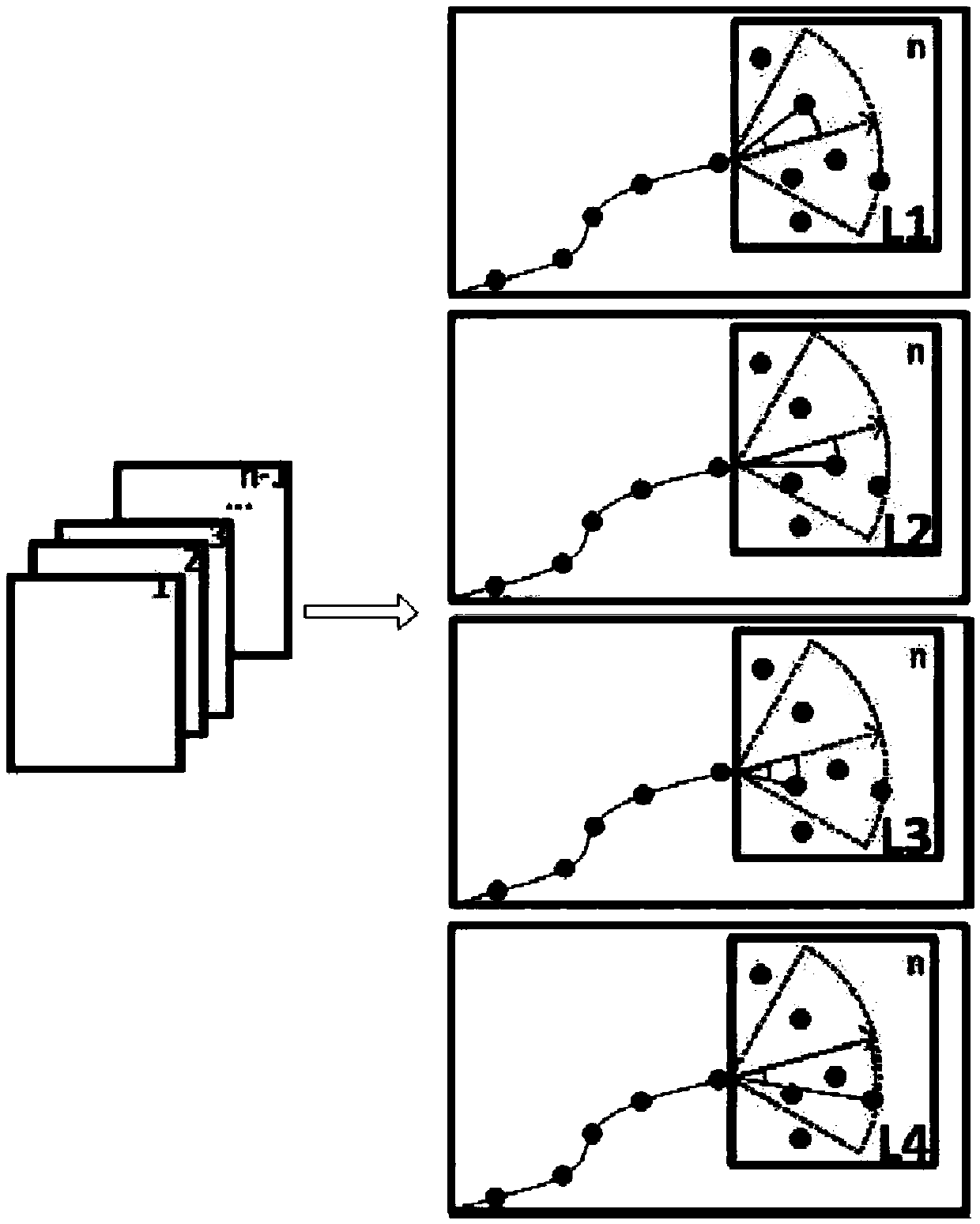
ActiveCN109523577AReduce the numberImprove detection accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageSubcellular structure
The invention discloses a method for determining the motion trajectory of a subcellular structure based on microscopic images, which comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring a time series image ofthe subcellular structure; (2) applying Gaussian filtering to the obtained image to remove noise; (3) detecting the subcellular centroid in the de-noised image by local maximum algorithm; (4) Designing the sector filter according to the velocity, direction, trend of the subcellular structure and the imaging speed of the camera; 5) calculating that matching probability of the candidate point of the subcellular structure according to the sector filter and the centroid of the subcellular structure of the image; (6) for each candidate point in the current frame image, searching for a full connection mode of all possible candidate points in a subsequent m frame image starting from the current frame, and calculating an average matching probability of each m frame continuous trajectory; (7) selecting Candidate points with the highest global average matching probability in the current frame image as the trajectory points, and the trajectory points are connected to the motion trajectory of thetarget subcellular structure.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Analysis method for detecting drug distribution and application thereof
ActiveCN107389776ARealize detectionDetailed distribution informationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMedicineAnalysis method
The present invention provides an analysis method for detecting drug distribution and application thereof, and belongs to the field of drug analysis and detection. The analysis method is as follows: using a fixing treatment method to treat a biological tissue administrated with a to-be-tested drug, and slicing the biological tissue to prepare a sample to be tested; and subsequently analyzing the sample to be tested by using a secondary ion mass spectrometer. Through the analysis method, the distribution of the to-be-tested drug in various tissues, cells and subcellular structures can be known, drug molecules can be detected in cell and subcellular scales, and accumulation of the to-be-tested drug in a target site can be known. The analysis method can be widely used in the study of detection of transport, absorption and metabolism of the drug, or in the study of detection of drug efficacy and drug screening.
Owner:宁波瑞瑧生物科技有限公司
Method for separating and extracting proline in sub-cells of plants
ActiveCN106543064ADetermination of distributionOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorWater bathsCentrifugation
The invention discloses a method for separating and extracting proline in sub-cells of plants. A rice seedling sample is taken and grinded into homogenate in sulfosalicylic acid through ice bath; grinding liquid is centrifuged for 5 minutes; lower-layer precipitate a is put for standby application; supernate a is centrifuged for 30 minutes to obtain supernate b and precipitate b; dissolution and mixing are performed by using a Tris-HCl solution; 600 g of homogenate is centrifuged at the temperature of 4 DEG C, and precipitate c is a cell wall part; supernate c is an organelle part; the supernate c and the precipitate c are respectively centrifuged for 30 minutes, and precipitate d and precipitate e are retained respectively; 3% sulfosalicylic acid is added respectively for dissolution, centrifugation continues, and then precipitate f and precipitate g at the lower portion are retained respectively; 3% sulfosalicylic acid is added respectively for dissolution, ultrasonic treatment is performed, boiling water bath is performed for 30 minutes, centrifugation is performed at the temperature of 4 DEG C for 10 minutes, and obtained supernate d and supernate e are an organelle component and a cell wall component. The proline content in a subcellular structure can be conveniently and directly determined.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
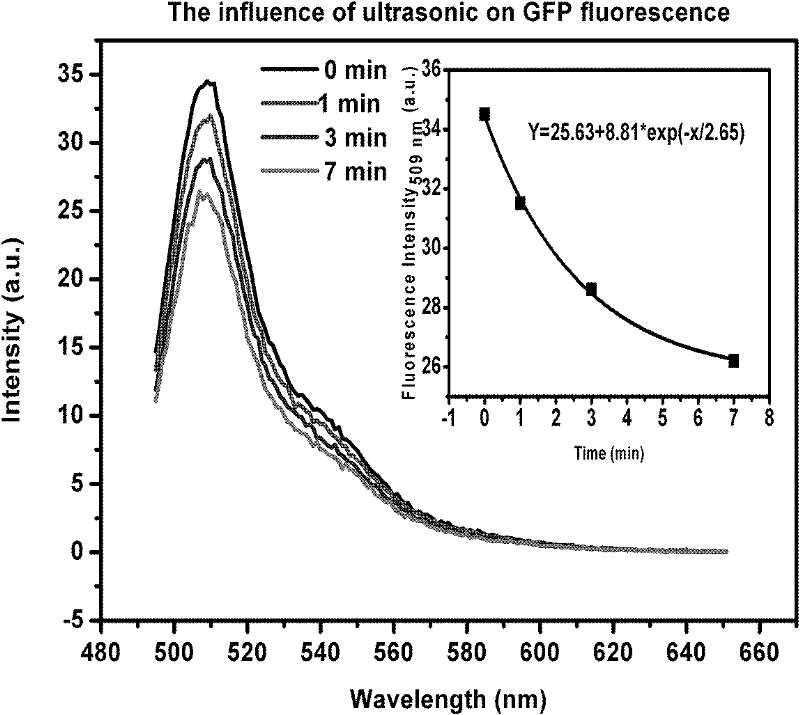
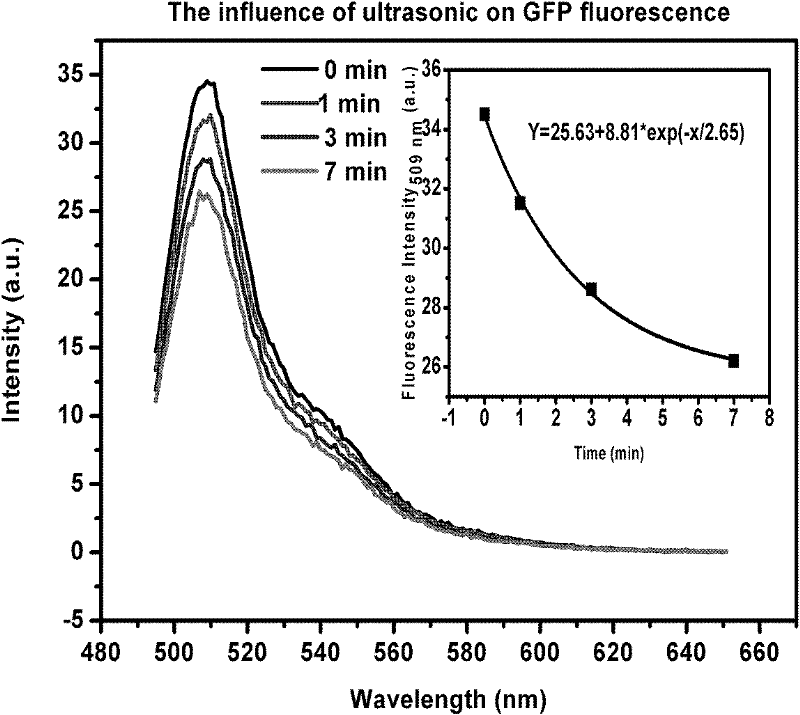
Method for measuring cellular oxidative stress damages under ionizing radiation by using fluorescent protein as fluorescence probe
InactiveCN102230895AEasy to detectNon-toxicFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh resistanceOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a method for measuring cellular oxidative stress damages under ionizing radiation by using fluorescent protein as a fluorescence probe. The content of free radicals generated in ionizing radiation is quantitatively measured by using the fluorescent protein which is selectively positioned and expressed on a subcellular structure sensitive to the ionizing radiation, so that the damages of the ionizing radiation on the specific positions of a cell are speculated by directly observing the fluorescence intensity change of the protein. By the method, the emitted fluorescence is easy to detect, has high sensitivity, stable fluorescence properties, can normally emit light in a wider pH range, has higher resistance to high temperatures, detergents, salt, organic solvents and most ordinary enzymes, is not toxic to the cell, is not interfered by false positive, makes vector construction convenient and is expressed without specificities of species, tissues and positions.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biomarker method
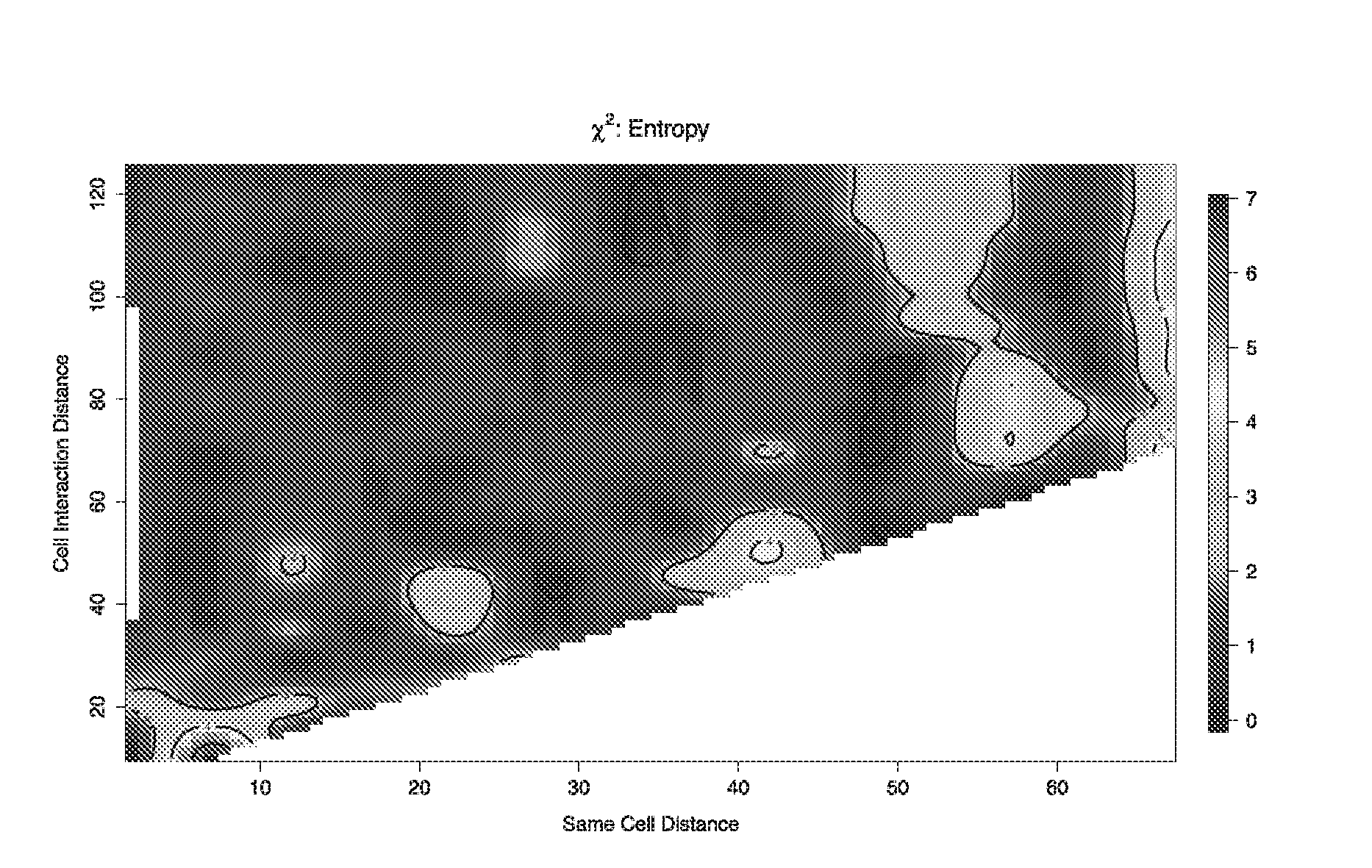
ActiveUS20160239960A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionSymmetric matrixSubcellular structure
Provided herein is a computer-implemented method for quantifying the spatial distribution of cells or sub-cellular structures, the method comprising the following steps performed by a computer: (a) receiving for a subject image data comprising a plurality of biomarkers, N, wherein the data represents a spatial map of the biomarkers; (b) processing the data to obtain a set of coordinates, wherein each coordinate denotes the location of a cell or sub-cellular structure represented by a biomarker or combination of biomarkers; (c) processing the set of coordinates into a two-dimensional symmetric (2N−1)×(2N−1) or 2N×2N matrix (D), wherein each element (i, j) of the matrix indicates the frequency of a cell or sub-cellular structure represented by a first biomarker or combination of biomarkers (i) being observed within an interaction distance, di, of a cell or sub-cellular structure represented by a second biomarker or combination of biomarkers (j), and wherein i and j may be the same or different; and (d) using a classifier to assign the subject to a group or category based on the two-dimensional symmetric matrix (D).
Owner:UNIV OF MANCHESTER
Fluorescent probe for detecting superoxide anion free radicals in peroxisome and application of fluorescent probe
ActiveCN111100184AEasy to synthesizeHigh speedBiological material analysisPeptidesFluoProbesPeroxisome
The invention provides a fluorescent probe for detecting superoxide anion free radicals in peroxisome and application of the fluorescent probe, and belongs to the technical field of detection and analysis. The invention designs the fluorescent probe for detecting the superoxide anion free radicals with caffeic acid as a recognition group and a fluorophore of O2<.-> and a small peptide QSKL as a targeted group of the peroxisome, and the structural formula of the fluorescent probe is shown in the description. The fluorescent probe is particularly applicable to detection of the superoxide anion free radicals at a cellular structure level, particularly at a subcellular structure level (such as the peroxisome) and has good actual application value.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Non-invasive systems and methods for in-situ photobiomodulation
InactiveCN105288619AImprove biological activityBiological activity inhibition or stabilizationAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryDiseaseActive agent
Products, compositions, systems, and methods for modifying a target structure which mediates or is associated with a biological activity, include treatment of conditions, disorders, or diseases mediated by or associated with a target structure, such as a virus, cell, subcellular structure or extracellular structure. The methods may be performed in situ in a non-invasive manner by application of an initiation energy to a subject thus producing an effect on or change to the target structure directly or via a modulation agent. The methods may further be performed by application of an initiation energy to a subject in situ to activate a pharmaceutical agent directly or via an energy modulation agent, optionally in the presence of one or more plasmonics active agents, thus producing an effect on or change to the target structure. The invention provides kits containing products or compositions formulated or configured and systems for use in practicing these methods.
Owner:IMMUNOLIGTHT LLC +1
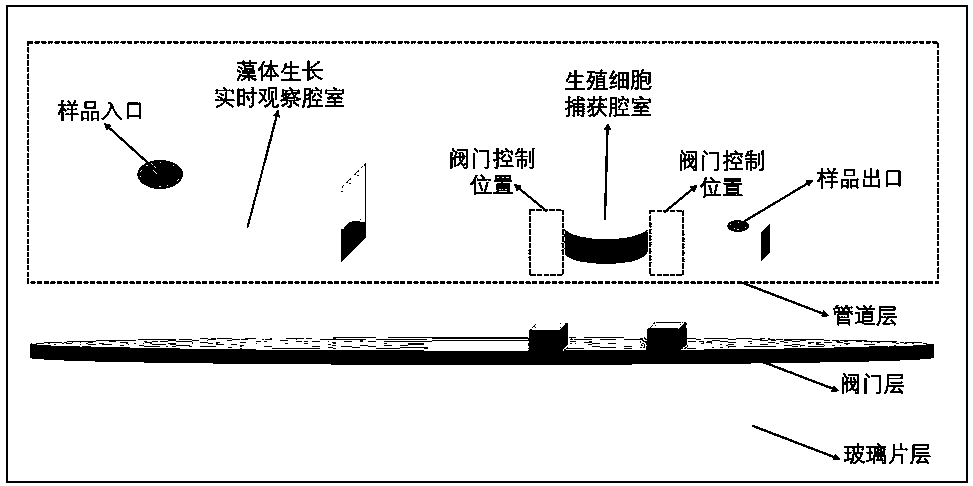
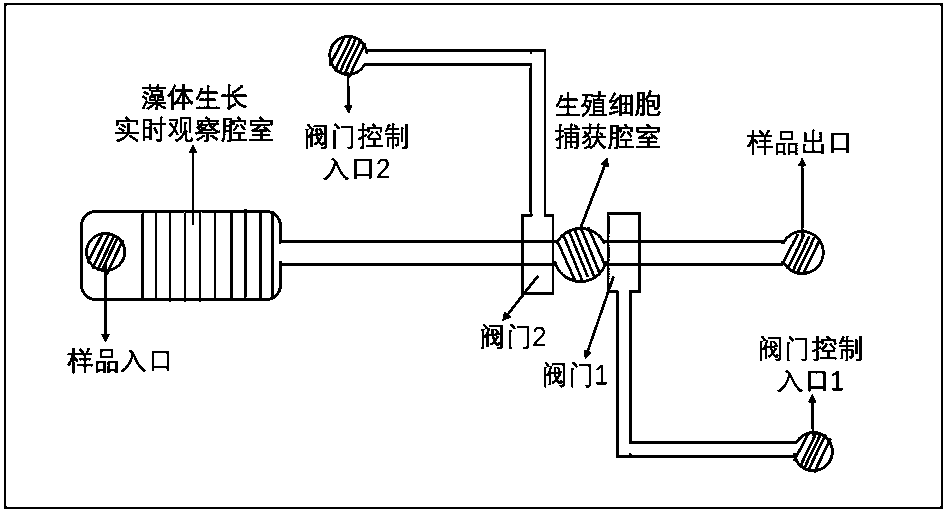
Micro-fluidic chip for researching growth and reproduction of algae
PendingCN108517284ARealize automatic separationMonitor growth in real timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsControl layerMicrobiology
The invention belongs to the technical field of growth and reproduction of algae and in particular relates to a micro-fluidic chip for researching the growth and reproduction of the algae. The micro-fluidic chip provided by the invention is composed of a sample channel layer, a valve control layer and a substrate layer, wherein the sample channel layer comprises four parts which are series connected in sequence: a sample inlet, an alga growth observation chamber, a reproduction cell capturing chamber and a sample outlet; alga culture, reproduction cell releasing and automatic separation functions are realized by adopting a continuous pouring technology, and alga cells and sub-cell structures can be observed and recorded for long time in real time; a culture medium of the algae can be rapidly and accurately replaced, and influences, caused by manual intervention, on a growth state of the algae are avoided; raw cells, which are automatically separated, also can be independently cultured.The chip provided by the invention is especially suitable for reproduction and growth researches of various large-size algae. The chip is low in production cost and a method is simple, easy to operate and convenient to popularize.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
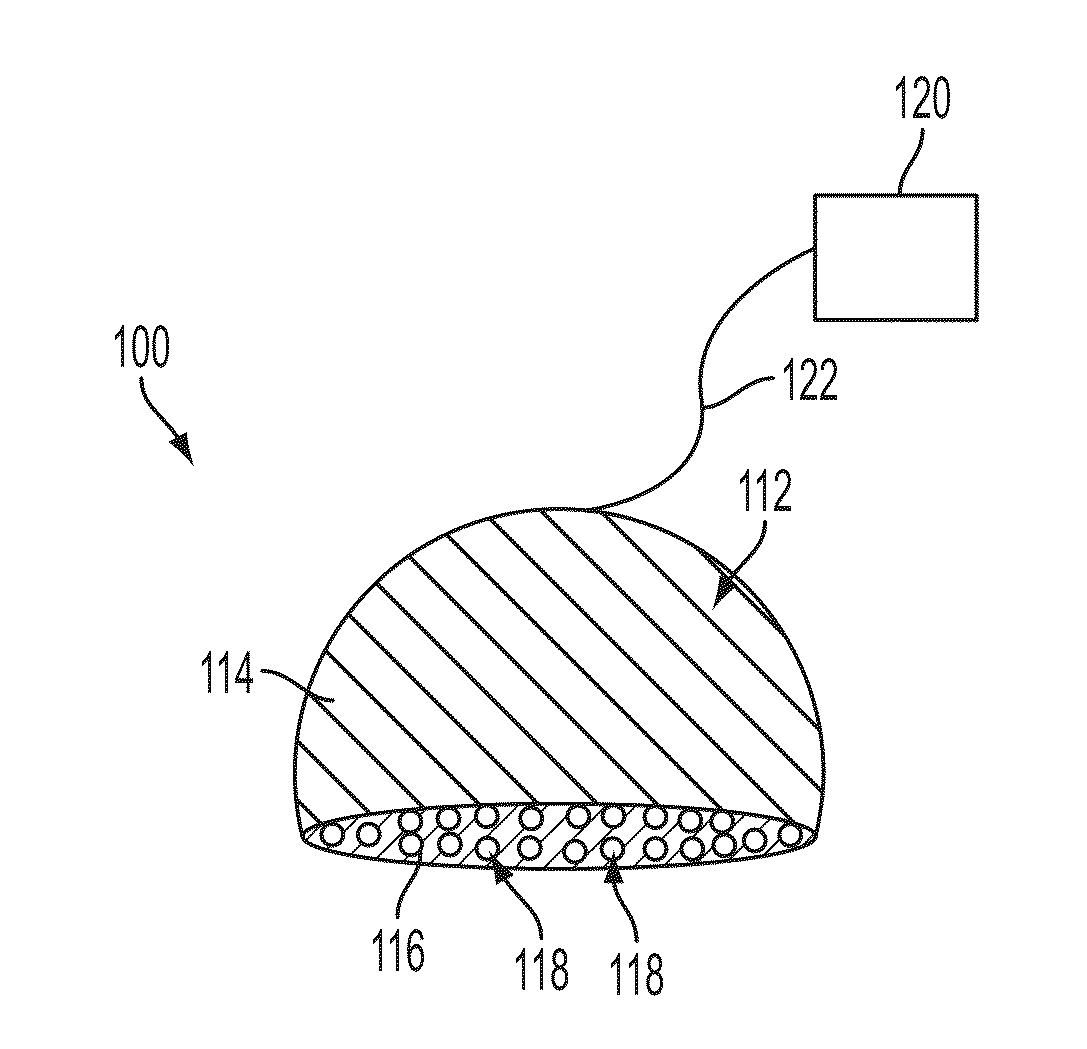
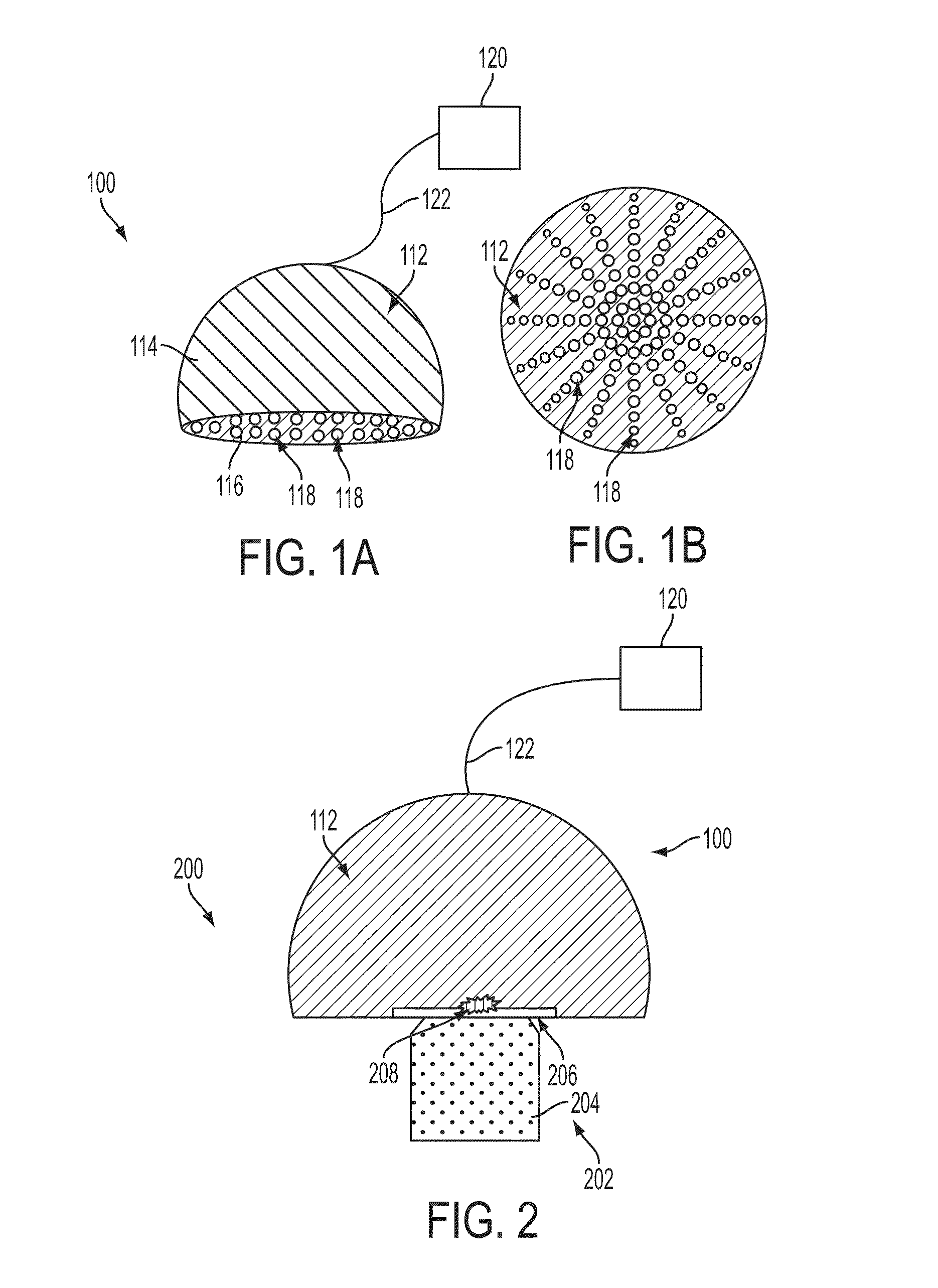
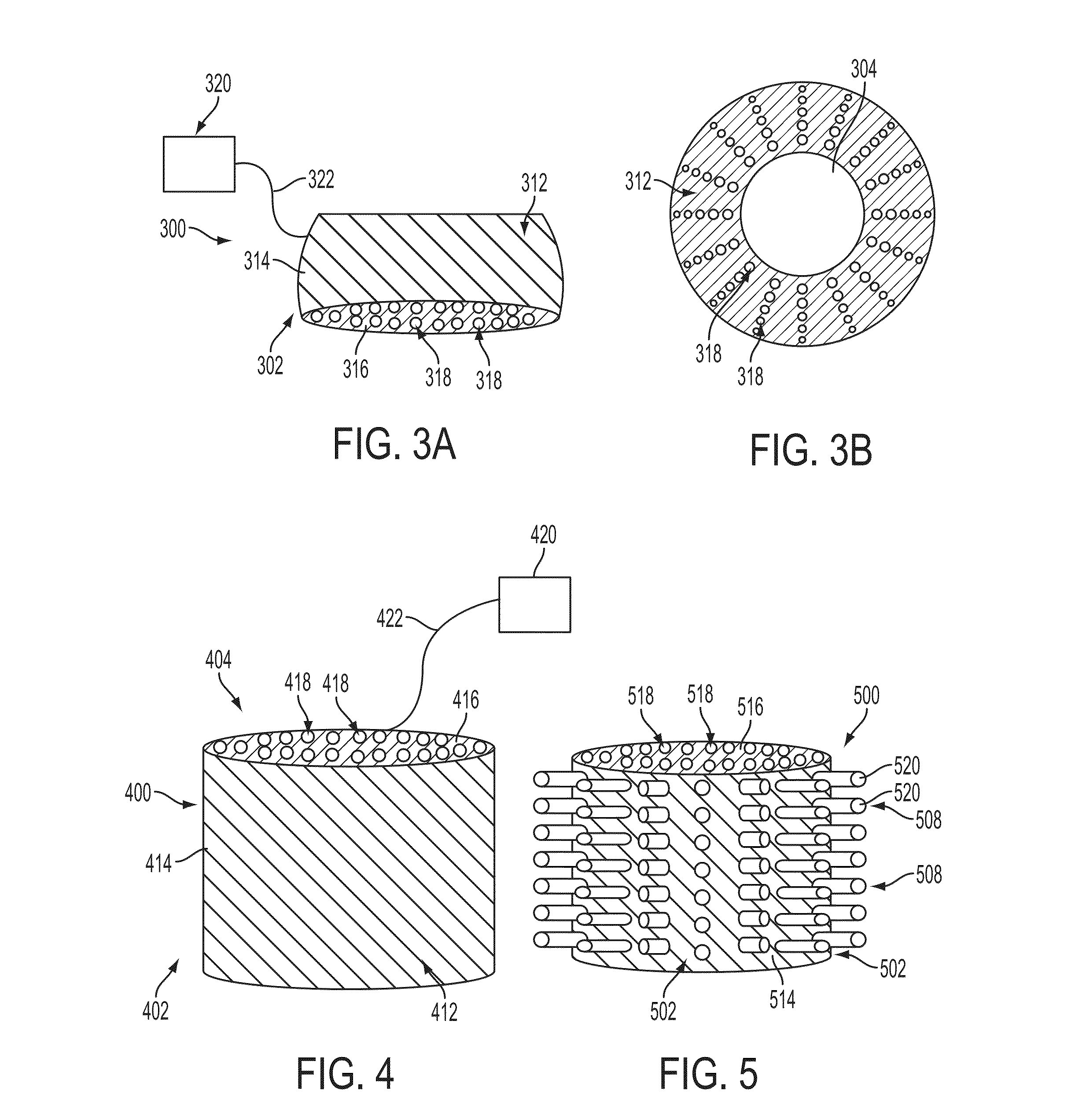
Microscope super-resolution illumination source
An alternative illumination source for traditional optical microscopes is provided. This super-resolution illumination source permits to use a traditional optical microscope for the direct observation of objects smaller than 100 nanometers such as subcellular structures in microorganisms, carbon nanotubes and other nanosize objects, and even nanostructures fabricated on top of a silicon wafer. This invention relies on the integration of two functional elements: a microscope, and the super-resolution illumination source. The super-resolution illumination source is formed by an array of light emitting diodes (LEDs) uniformly distributed in a hemisphere. The object under observation is illuminated by the light emitted in all directions by the array of LEDs. Real, wide-field images of the sample with nano-resolution are direct and analogically formed by the microscope's lenses, without the need of sample tagging, intensive computation or scanning. Depending on the wavelength emission of the LEDs, nano-resolution can be obtained with ultraviolet, infrared, and visible illumination.
Owner:L J TECH
Automatic extraction method of cell components
PendingCN110627864AEvenly brokenImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBatch processingPipette
The present invention belongs to the technical field of biology and discloses an automatic extraction method of cell components. The automatic extraction method comprises the following steps: (1) after mixing a cell sample and a sensitizer, adding the mixture into a sample adding groove for incubation; (2) after incubation for 5-10 min, adding the sample into a filter tube by a pipettor; (3) conducting air injection pressurization and crushing cells under action of shearing force and inertial impact; and (4) if total cellular protein or proteins with a special distribution of a certain subcellular structure need to be collected, pretreating the product obtained in the step (3) and then adding a series of cell component extracts into the filtered product for extraction. The method is different from the traditional method which completely depends on chemical crushing of lysate or grinding and homogenizing method for crushing, so that cell crushing is more uniform, efficiency is high, andprotein damage is small. The method is suitable for processing with small number of samples and batch processing under condition of large total number of the samples, has small requirements on singlesample amount, can effectively save manpower and avoids difference of manual operation.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Imaging method and use thereof
Owner:RIETHMULLER CHRISTOPH
Functional imaging of cells with optical projection tomography
ActiveUS8947510B2Reconstruction from projectionScattering properties measurementsOptical projection tomographyOptical tomography
A method for 3D imaging of a biologic object (1) in an optical tomography system where a subcellular structure of a biological object (1) is labeled by introducing at least one nanoparticle-biomarker. The labeled biological object (1) is moved relatively to a microscope objective (62) to present varying angles of view and the labeled biological object (1) is illuminated with radiation having wavelengths between 150 nm and 900 nm. Radiation transmitted through the labeled biological object (1) and the microscope objective (62) within at least one wavelength bands is sensed with a color camera, or with a set of at least four monochrome cameras. A plurality of cross-sectional images of the biological object (1) from the sensed radiation is formed and reconstructed to make a 3D image of the labeled biological object (1).
Owner:VISIONGATE
Non-invasive systems and methods for in-situ photobiomodulation
Products, compositions, systems, and methods for modifying a target structure which mediates or is associated with a biological activity, including treatment of conditions, disorders, or diseases mediated by or associated with a target structure, such as a virus, cell, subcellular structure or extracellular structure. The methods may be performed in situ in a non-invasive manner by application of an initiation energy to a subject thus producing an effect on or change to the target structure directly or via a modulation agent. The methods may further be performed by application of an initiation energy to a subject in situ to activate a pharmaceutical agent directly or via an energy modulation agent, optionally in the presence of one or more plasmonics active agents, thus producing an effect on or change to the target structure. Kits containing products or compositions formulated or configured and systems for use in practicing these methods.
Owner:IMMUNOLIGTHT LLC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com