Optical clearing agent for bone tissue
A technology of optical clearing agent and bone tissue, applied in the field of biomedical optical imaging, can solve problems such as restricting the development and application of cortical optical imaging in transcranial in vivo imaging, transparency of hard bone tissue, etc., so as to reduce the internal scattering of the tissue and improve the imaging depth. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
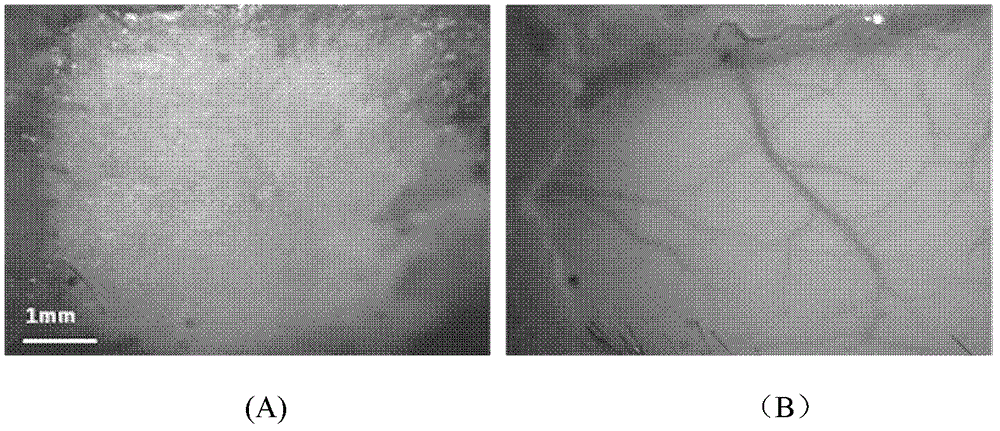
[0015] The scalp of a C57 mouse (20 weeks old) was cut open to expose the skull of about 1cm×1cm square. The optical transparency agent is prepared into a mixed solution according to the proportions of the components of the solution in Example 1 in Table 1, and is directly dripped onto the skull of a living mouse, smeared evenly (0.5-0.8ml / cm 2 ). figure 1 The CCD images taken before and after treatment with the transparent agent of the live mouse skull are given. among them figure 1 (A) is the case of a normal C57 mouse with bare skull. Due to the turbidity of the skull, it is impossible to see the intracranial cortical blood vessels; figure 1 (B) is the situation 5 minutes after the application of the transparent agent. At this time, the skull becomes transparent to light, the cortical blood vessels below the skull become clearly visible, and some small branches can also be distinguished in the visual field.
Embodiment 2
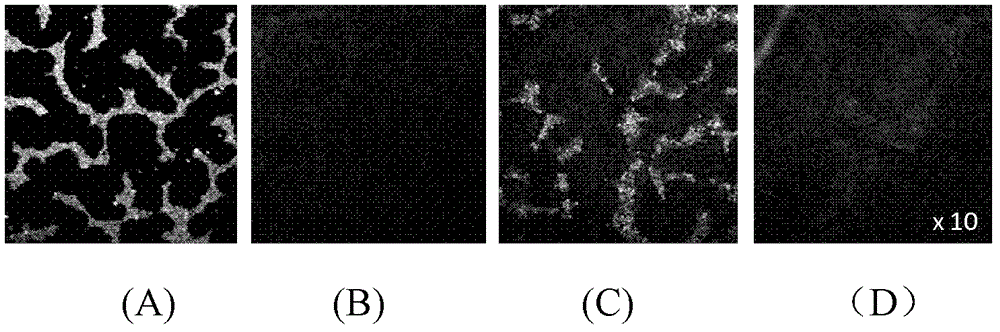
[0017] The isolated skull was taken from a 4-week-old SD rat, covered it on the encapsulated fluorescent bead solution, and observed with a fluorescence microscope. The transparent agent is prepared according to the ratio of the components of the solution in Example 2 in Table 1. The rat skull is immersed in vitro (1.5-2ml / cm 2 ) In a light transparent agent, 5 minutes later, cover the encapsulated fluorescent bead solution for imaging. Rinse the skull on which the optical transparency has been acted with saline to reverse the optical transparency effect, and then image under a fluorescent microscope. figure 2 The fluorescence signals observed without skull, with skull, phototransparency on the skull and after the phototransparency effect of normal saline is reversed are respectively given. figure 2 (A) gives the fluorescence signal observed without skull, the fluorescence information at this time is very strong; figure 2 It can be seen in (B) that the skull almost completely ...
Embodiment 3
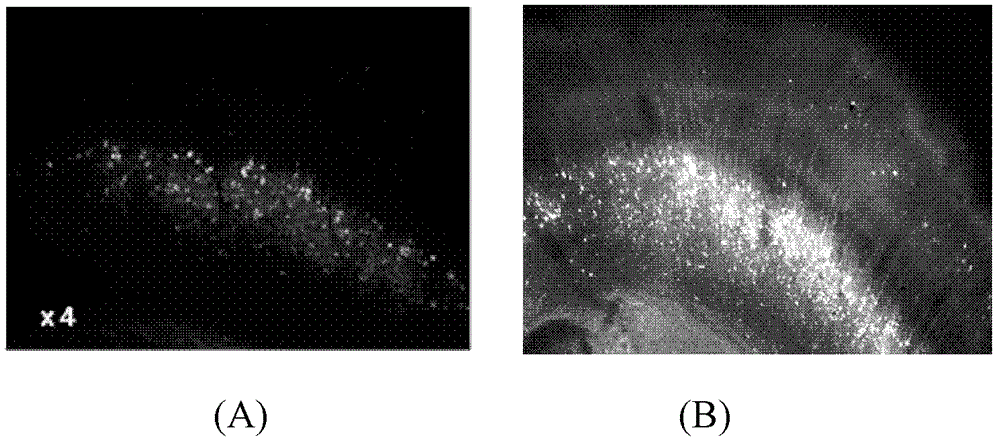
[0019] Cut the GFP-labeled transgenic mouse brain slices to a thickness of 100 μm. One group was not treated with a transparent agent and observed directly under a fluorescent microscope; the other group, the transparent agent was mixed according to the proportions of the components of the solution in Example 3 in Table 1. Solution, directly apply to mouse brain slices (0.2-0.4ml / cm 2 ), observe with a fluorescence microscope after 1 minute. image 3 Respectively given is the 4x objective lens before the optical transparency agent ( image 3 (A)) after ( image 3 (B)) Fluorescence signal of mouse brain slice. Only a small amount of neurocytes can be observed in the mouse brain slices that have not been treated with a transparent agent; but after a short period of treatment with a transparent agent, the cell bodies of the nerve cells are significantly brighter and the dendritic structure is now clearly distinguishable.
[0020] The different transparent agent formulations shown in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com