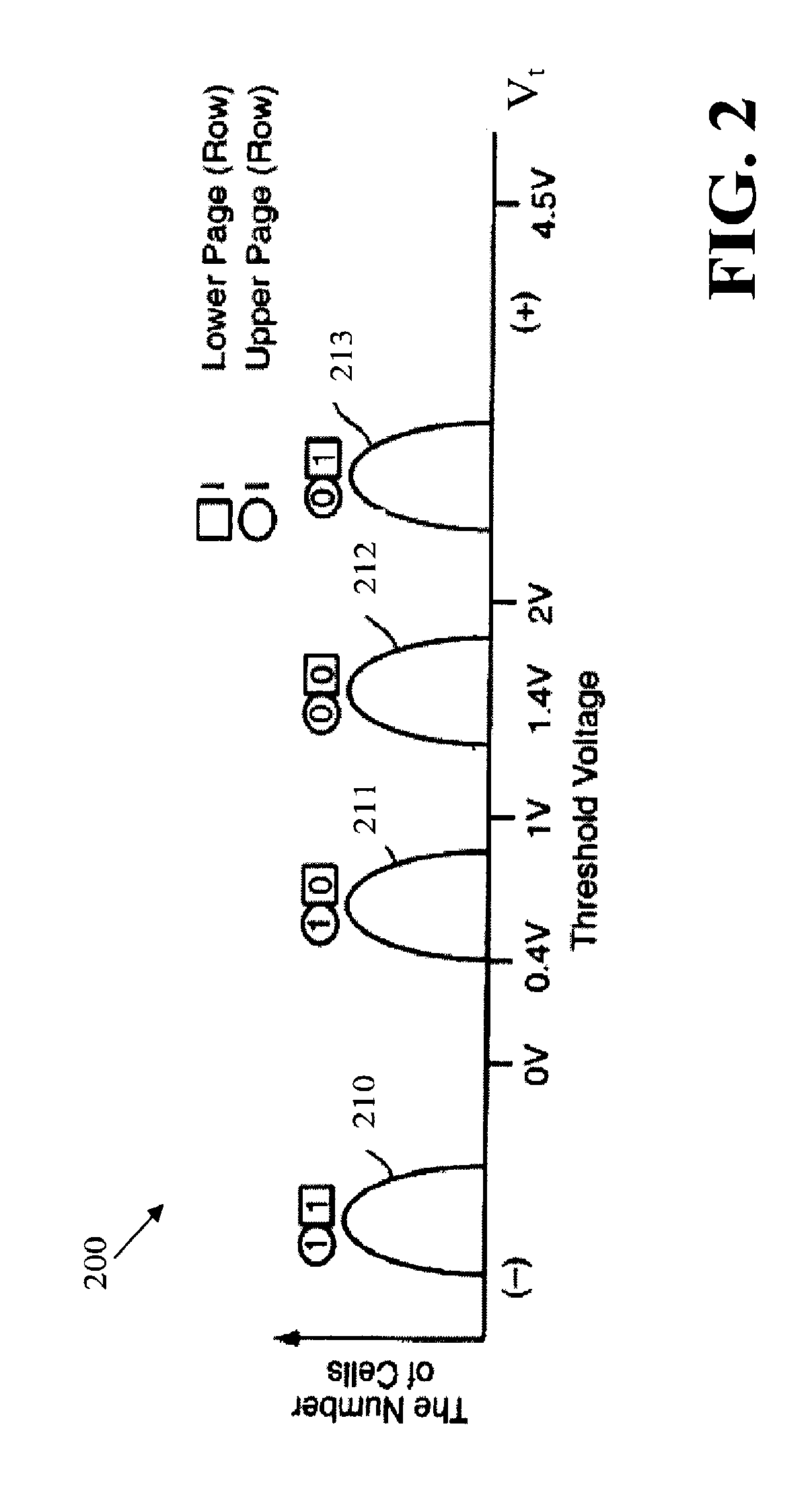
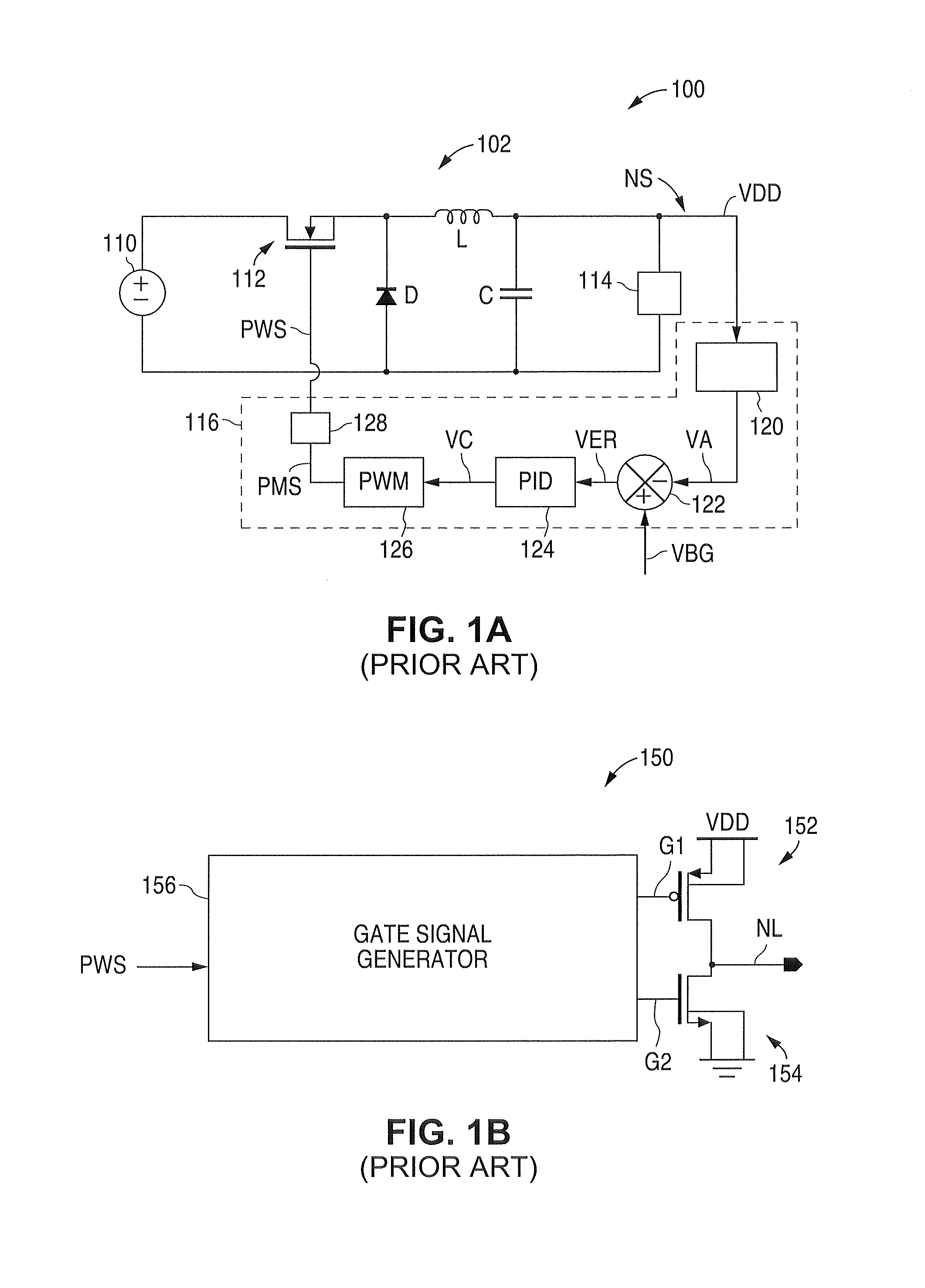
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
225 results about "Process corners" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
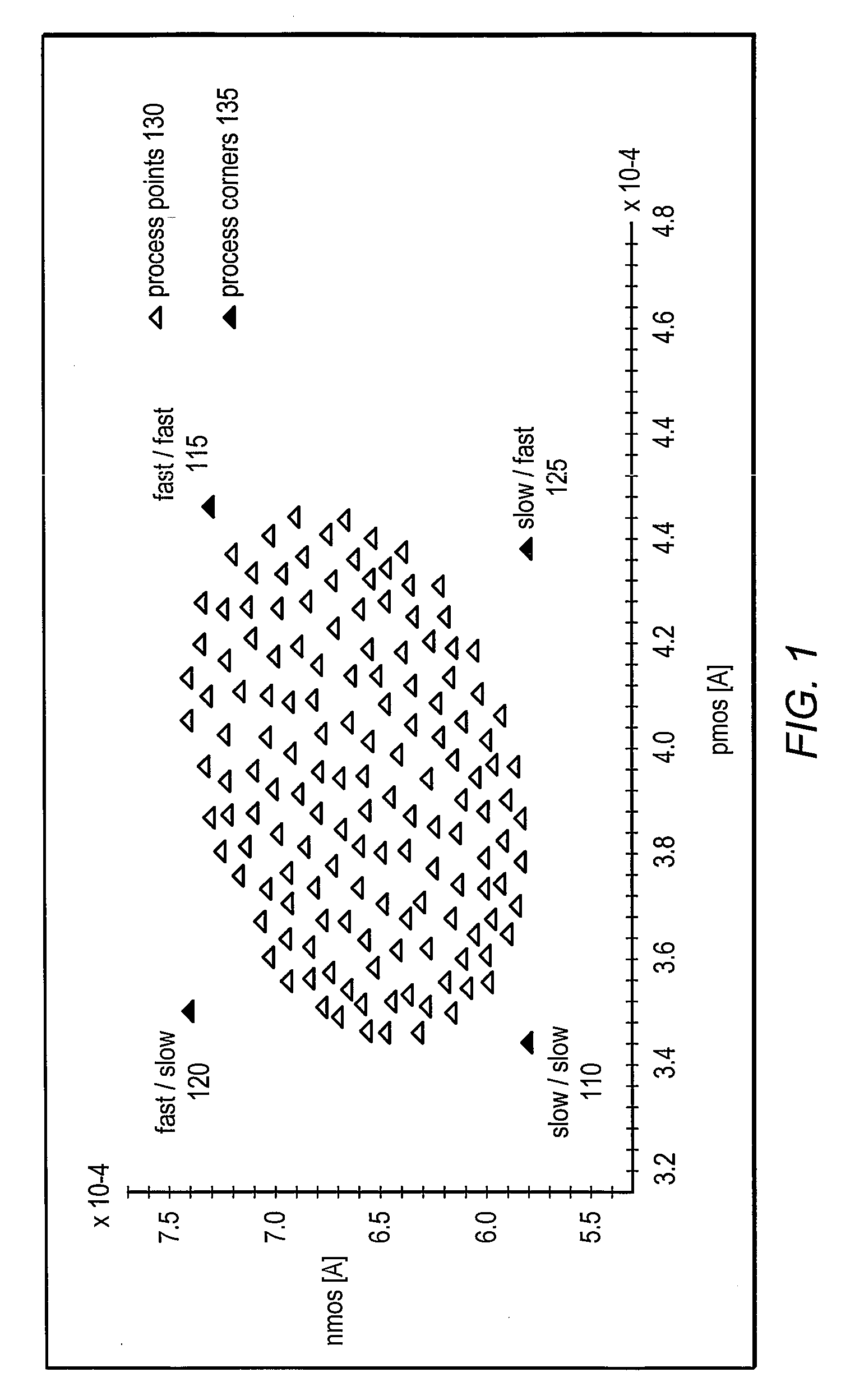
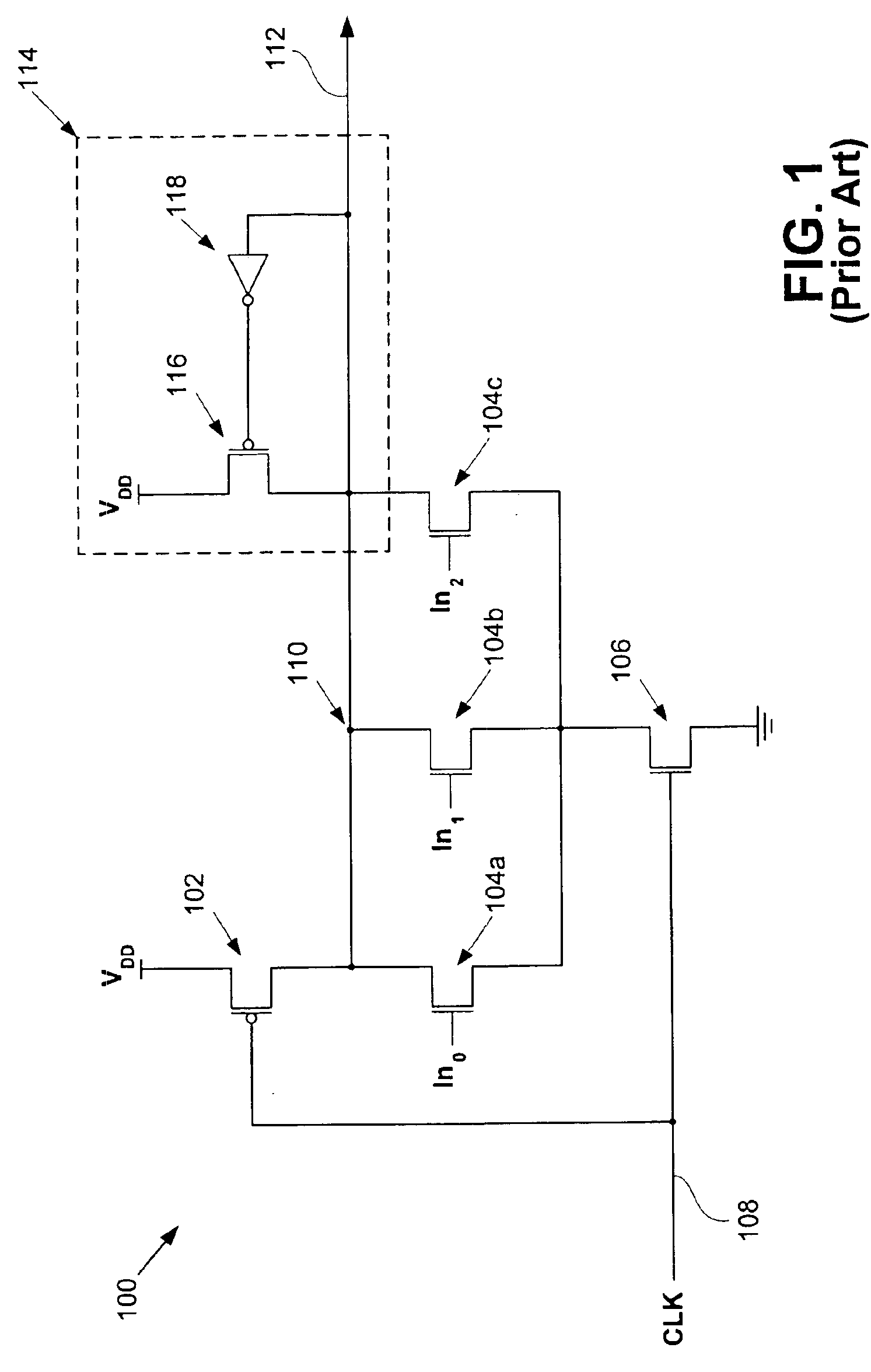
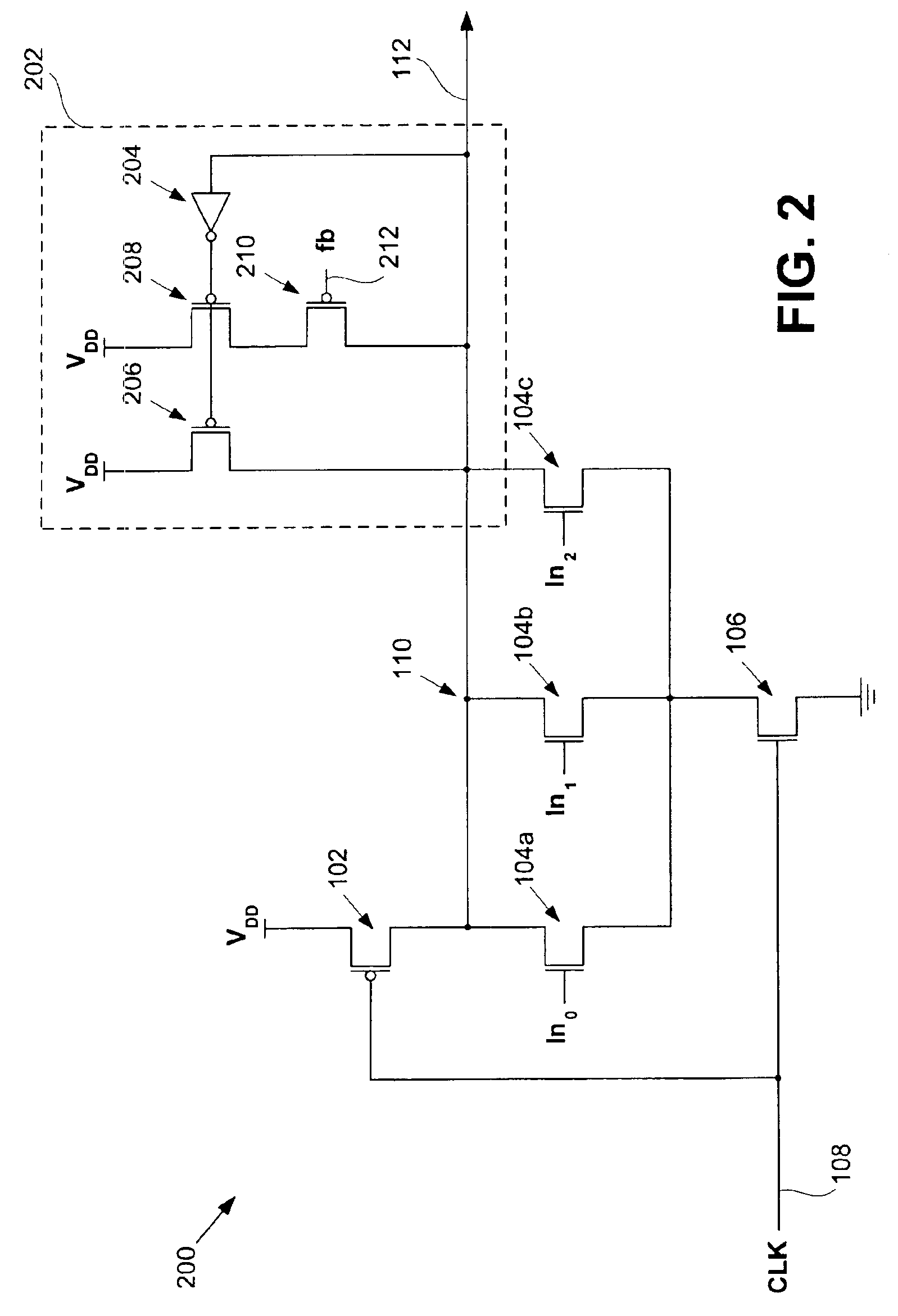
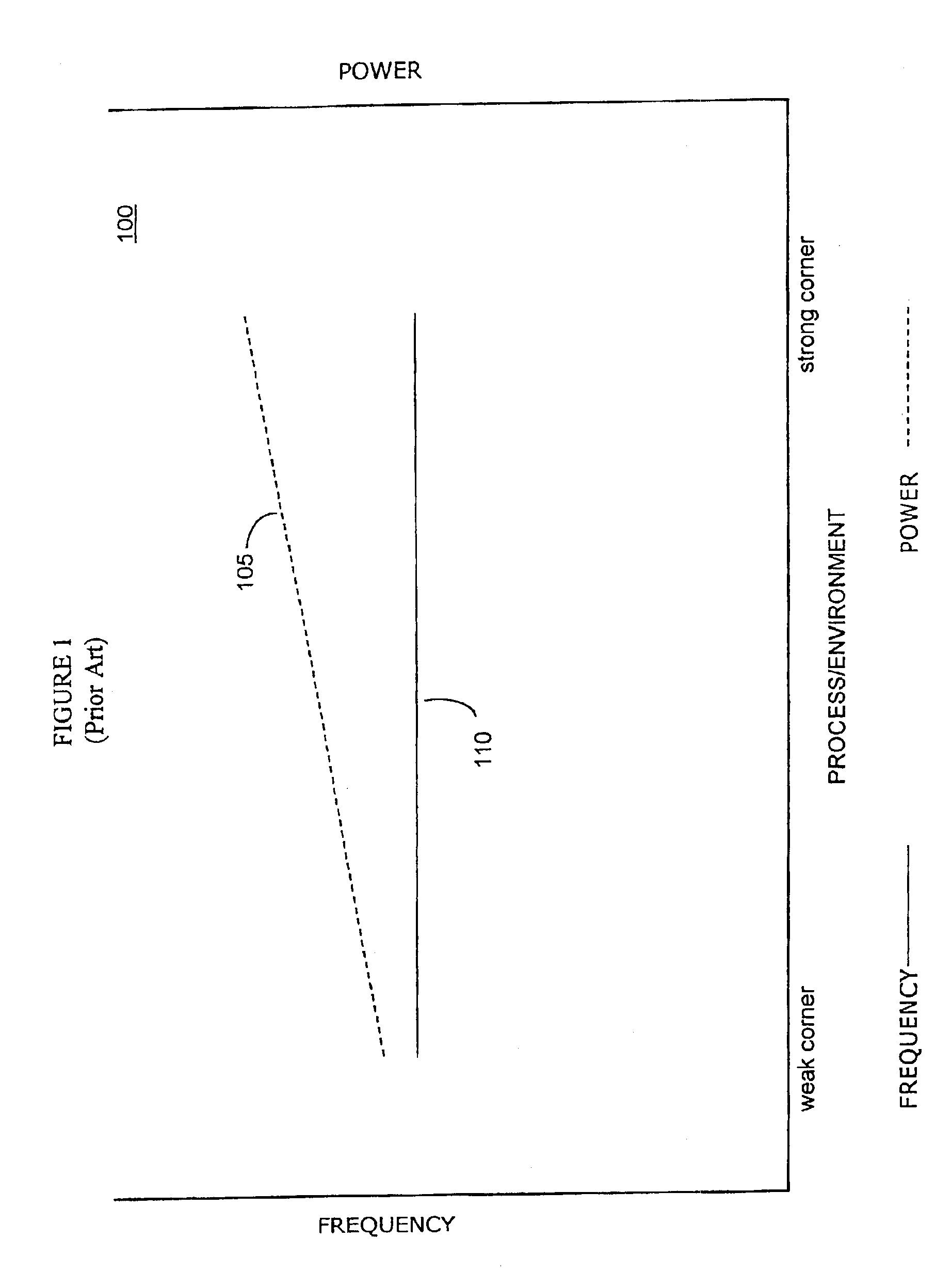
In semiconductor manufacturing, a process corner is an example of a design-of-experiments (DoE) technique that refers to a variation of fabrication parameters used in applying an integrated circuit design to a semiconductor wafer. Process corners represent the extremes of these parameter variations within which a circuit that has been etched onto the wafer must function correctly. A circuit running on devices fabricated at these process corners may run slower or faster than specified and at lower or higher temperatures and voltages, but if the circuit does not function at all at any of these process extremes the design is considered to have inadequate design margin.
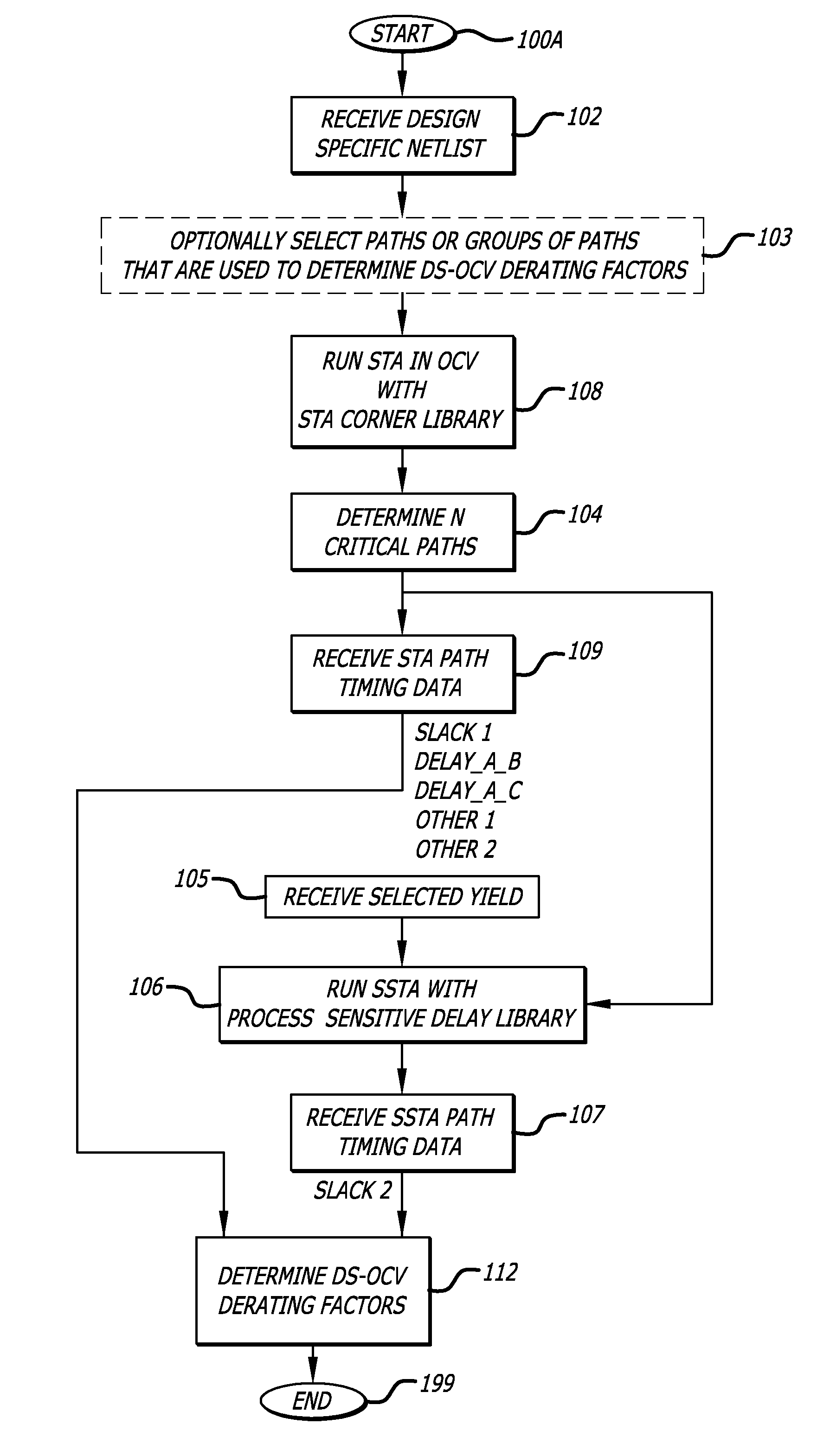
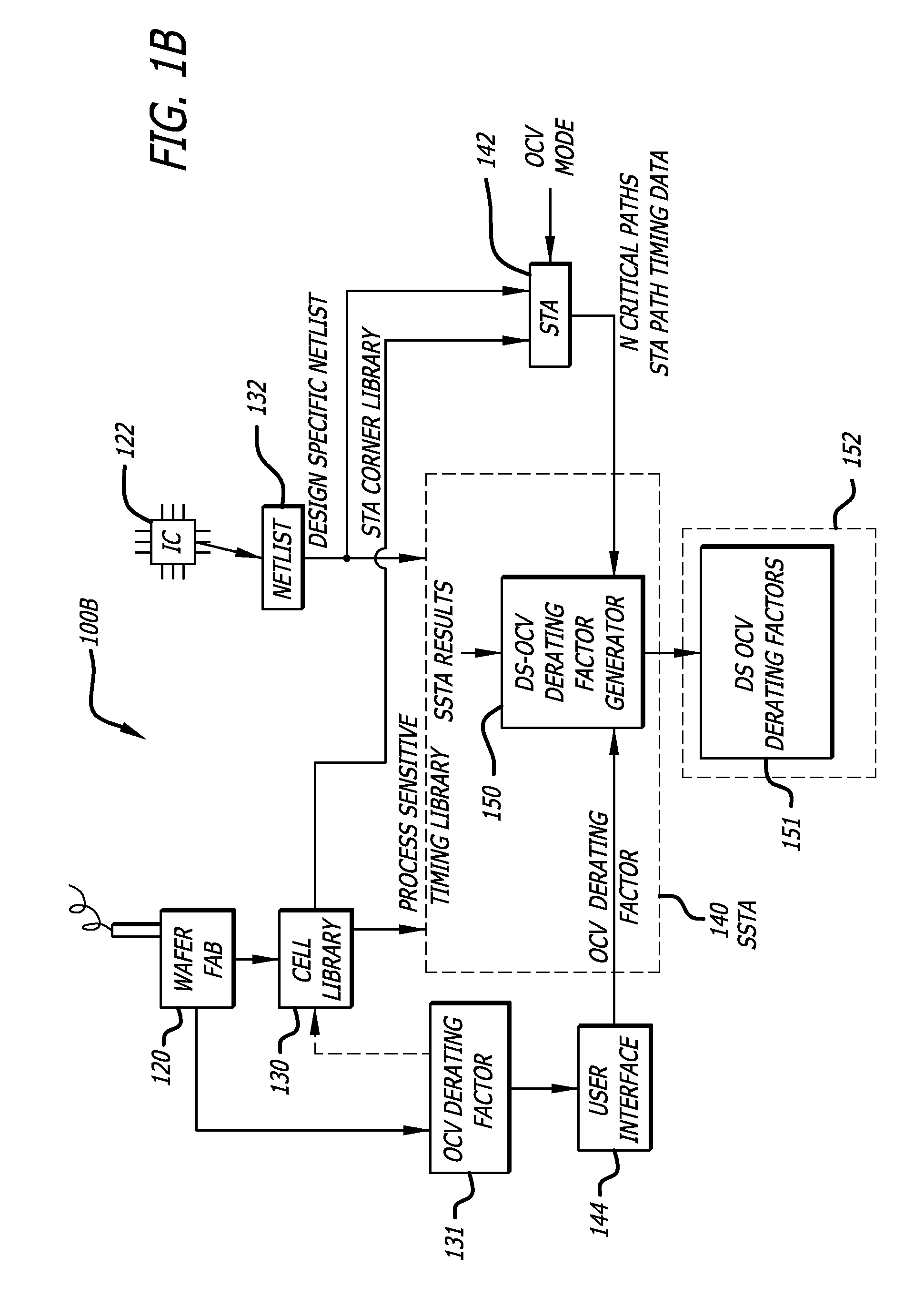
Design-specific on chip variation de-rating factors for static timing analysis of integrated circuits
InactiveUS8336010B1Reduce running timeDesign specificationComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTime informationDying processes
In one embodiment of the invention, a method of analysis of a circuit design with respect to within-die process variation is disclosed to generate a design-specific on chip variation (DS-OCV) de-rating factor. The method includes executing a static timing analysis (STA) in an on-chip variation mode using a process corner library. Collecting timing information of the top N critical timing paths. Executing a statistical static timing analysis (SSTA) on the N critical timing paths using timing models characterized for SSTA with sensitivities of delays to process variables. Compare the two timing results and deriving DS-OCV de-rating factors for the clock / data paths to be used in a STA OCV timing analysis to correctly account for the effects of process variations. A user may select to specify DS-OCV de-rating factors for paths or groups of paths and achieve an accurate timing analysis report in a reduced amount of run-time.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
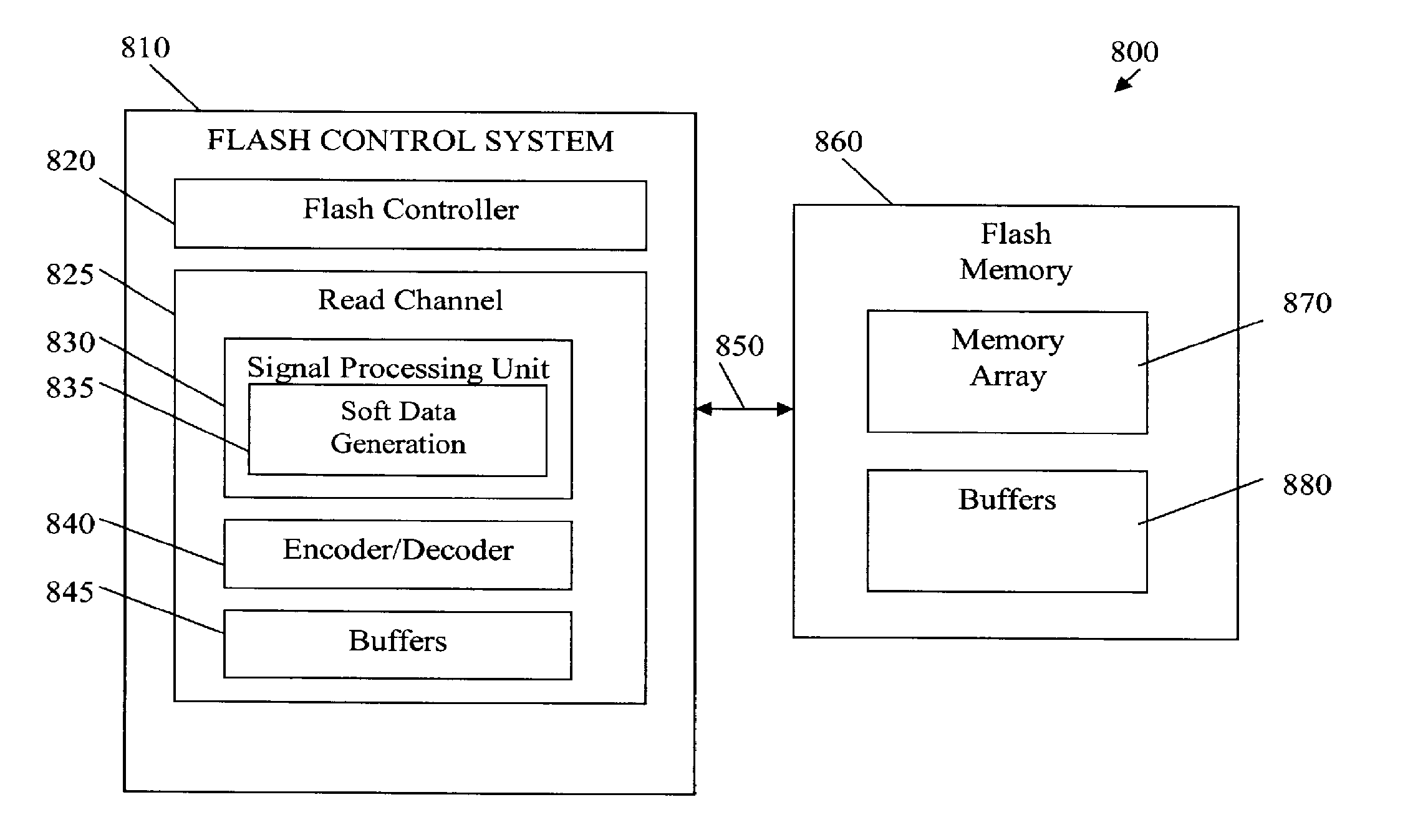
Methods and Apparatus for Soft Data Generation for Memory Devices Based on Performance Factor Adjustment
InactiveUS20110167305A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionElectrical resistance and conductanceRetention time
Methods and apparatus are provided for soft data generation for memory devices based on a performance factor adjustment. At least one soft data value is generated for a memory device, by obtaining at least one read value; and generating the soft data value based on the obtained at least one read value and an adjustment based on one or more performance factors of the memory device. The read values may comprise, for example, data bits, voltage levels, current levels or resistance levels. The read values may be soft data or hard data. The possible performance factors include endurance, number of read cycles, retention time, temperature, process corner, inter-cell interference impact, location within the memory array and a pattern of aggressor cells. One or more pattern-dependent performance factors and / pr location-specific performance factors may also be considered. The generated soft data value may be a soft read value that is used to generate one or more log likelihood ratios, or may be the log likelihood ratios themselves.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
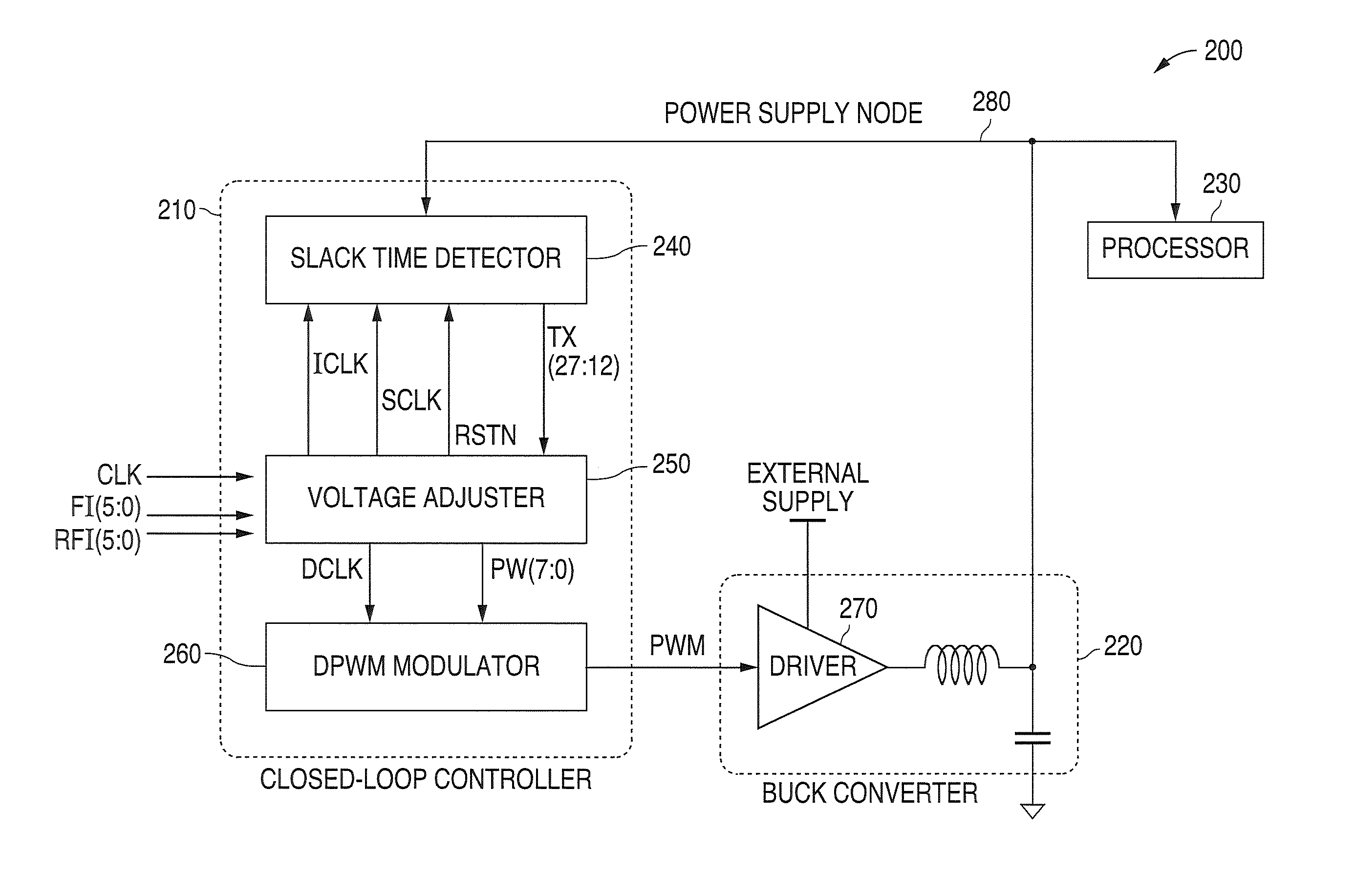
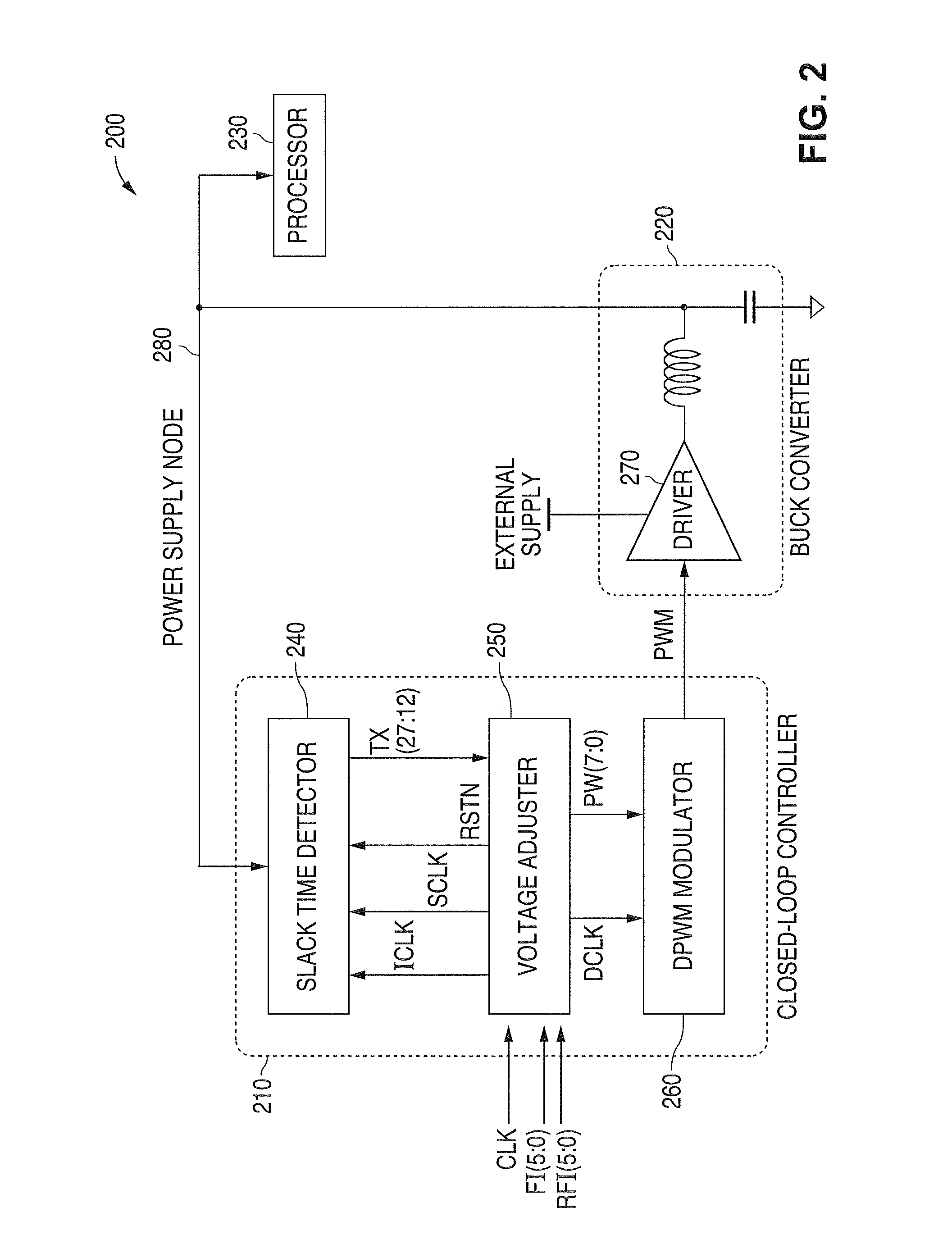
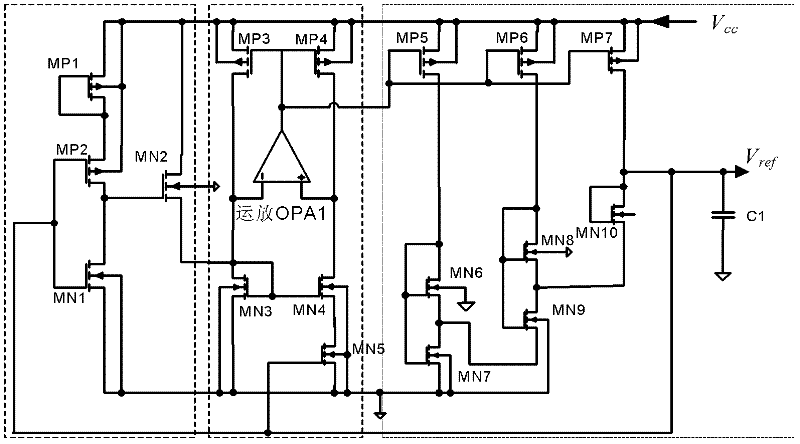
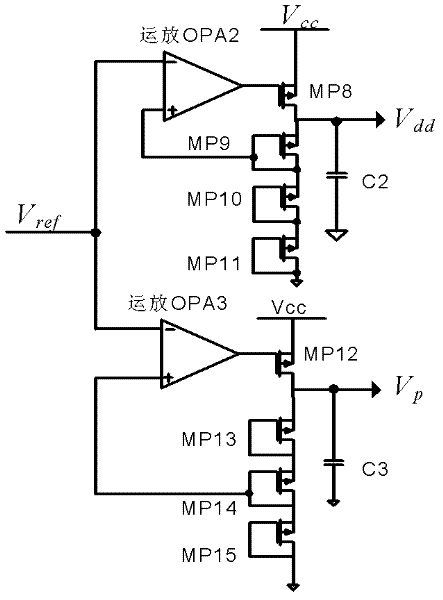
System and method for providing a digital self-adjusting power supply that provides a substantially constant minimum supply voltage with regard to variations of PVT, load, and frequency
A system and method is disclosed that provides a digital self-adjusting power supply for semiconductor digital circuits. The power supply provides a substantially constant minimum supply voltage with regard to process corner, junction temperature, external voltage source, load variation, and operating frequency. The system comprises a slack time detector, a voltage adjuster, and a digital pulse width modulation (PWM) modulator. The system supplies a minimum required voltage without the used of a band gap or reference voltage. A finite state machine is also used to minimize oscillations introduced by start-up, load transients, frequency changes, and the like, thereby eliminating the need for a proportional integrator differentiator (PID) circuit.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
System and method for phase-locked loop (PLL) for high-speed memory interface (HSMI)
ActiveUS7659783B2Optimize allocationMeet the blocking requirementsPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationLoop filterDouble data rate
A phase-locked loop (PLL) to provide clock generation for high-speed memory interface is presented as the innovate PLL (IPLL). The IPLL architecture is able to tolerate external long loop delay without deteriorating jitter performance. The IPLL comprises in part a common mode feedback circuit with a current mode approach, so as to minimize the effects of mismatch in charge-pump circuit, for instance. The voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) of the IPLL is designed using a mutually interpolating technique generating a 50% duty clock output, beneficial to high-speed double data rate applications. The IPLL further comprises loop filter voltages that are directly connected to each VCO cell of the IPLL. Conventional voltage-to-current (V-I) converter between loop filter and VCO is hence not required. A tight distribution of VCO gain curves is therefore obtained for the present invention across process corners and varied temperatures.
Owner:MICREL
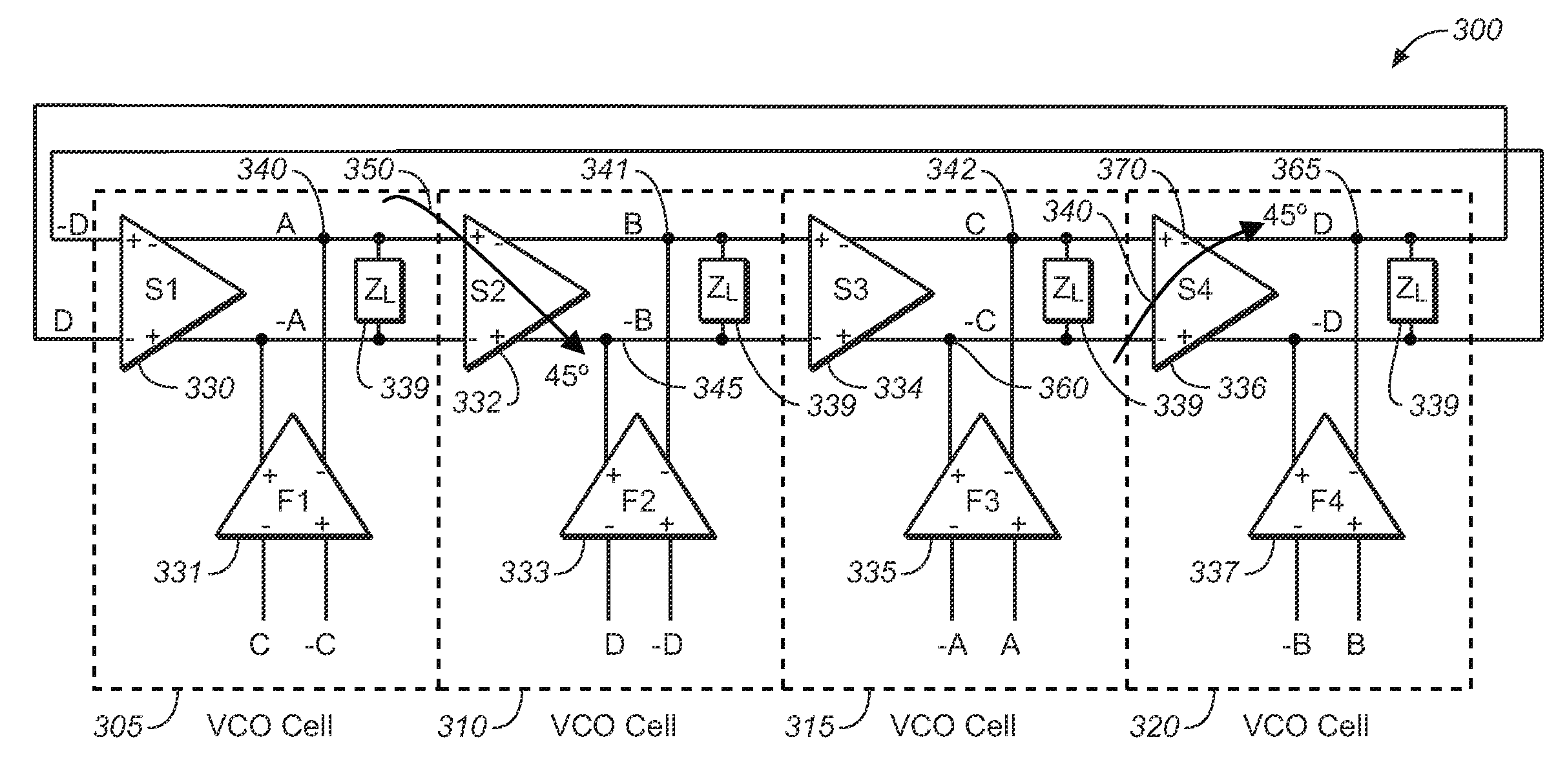
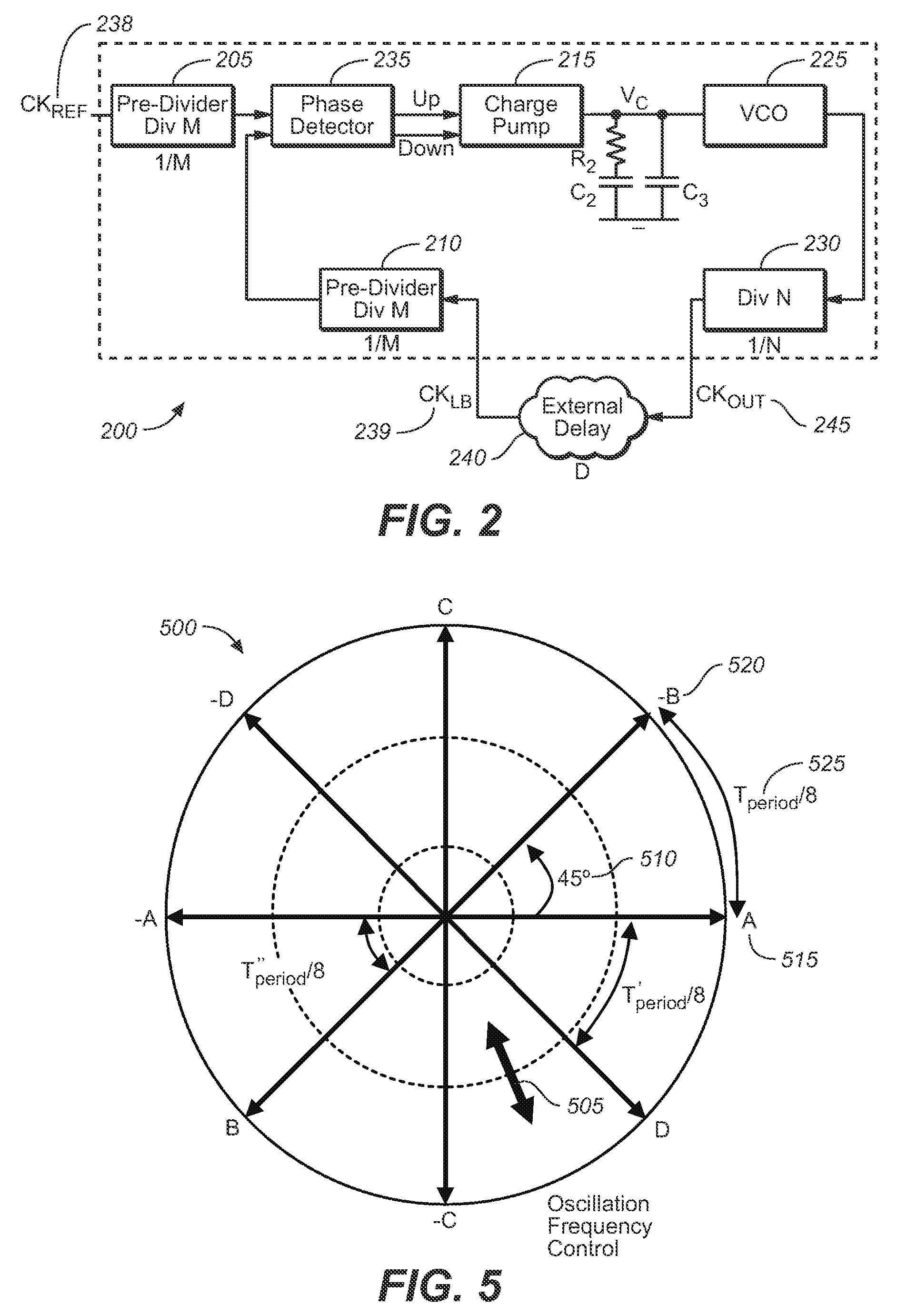
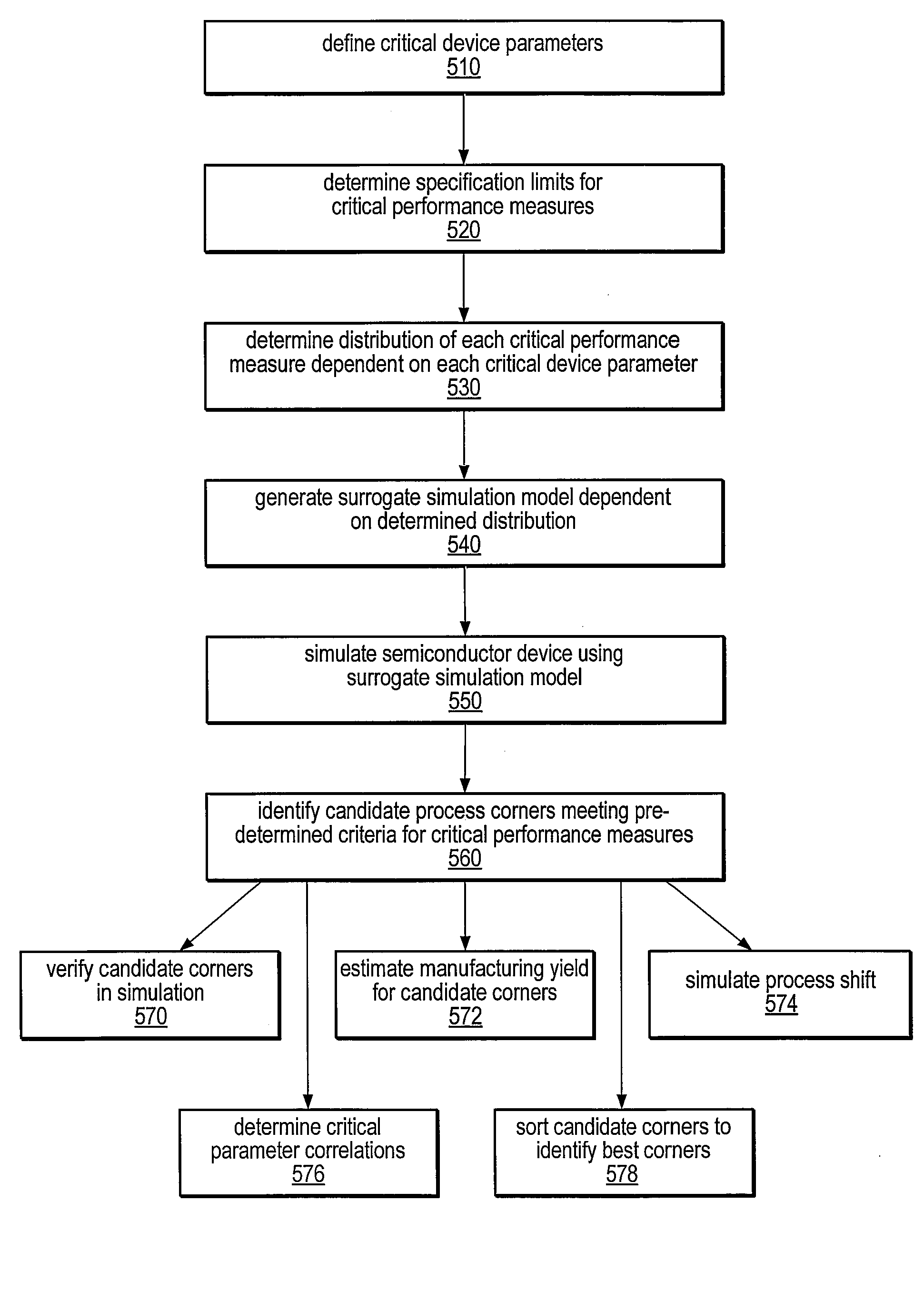
Multidimensional Process Corner Derivation Using Surrogate Based Simultaneous Yield Analysis
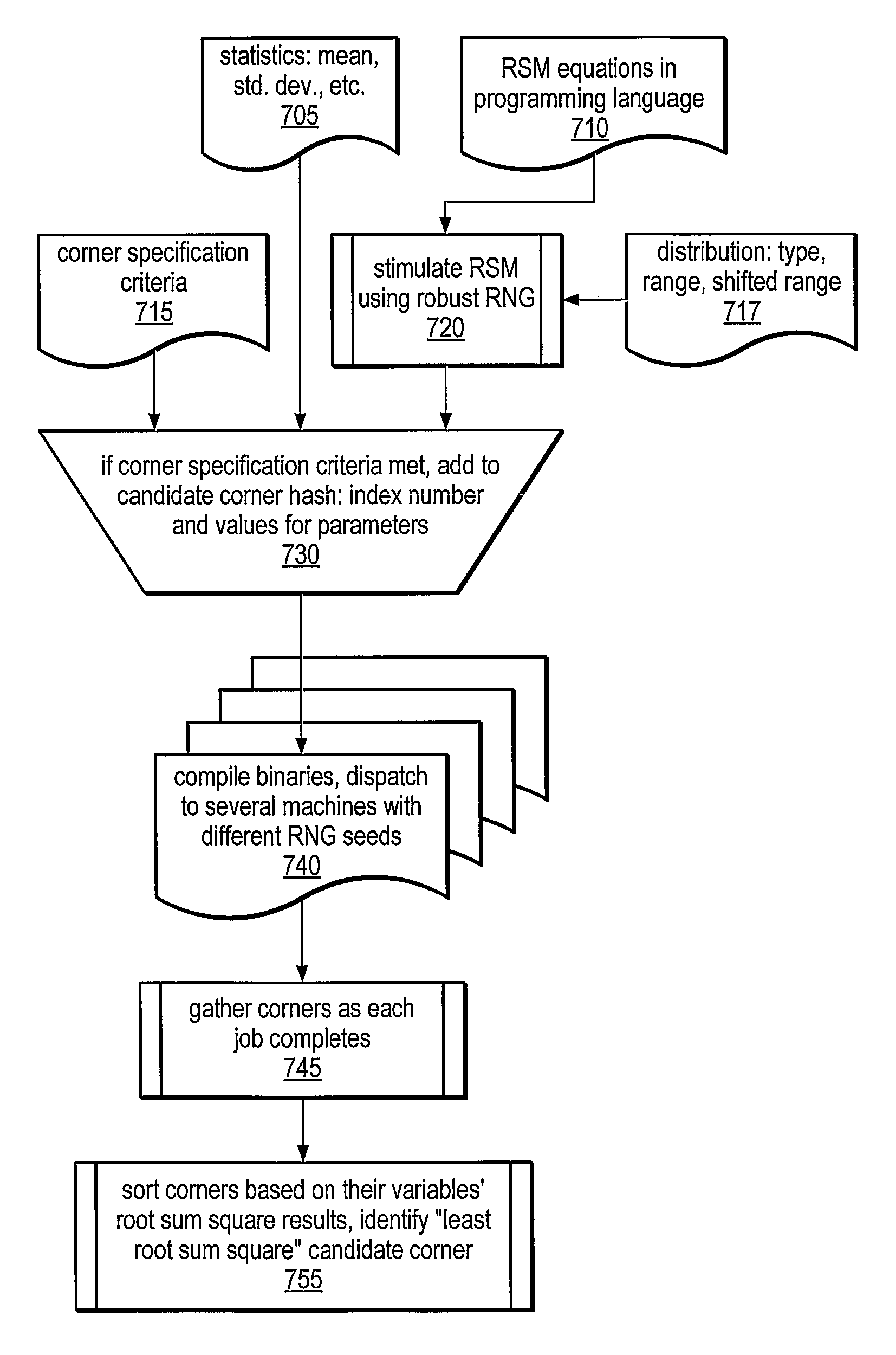
A system and method for deriving semiconductor manufacturing process corners using surrogate simulations is disclosed. The method may be used to determine individual performance metric yields, the number of out-of-specification conditions for a given number of simulation samples, and a total yield prediction for simultaneous multi-variable conditions. A surrogate simulation model, such as a Response Surface Model, may be generated from circuit simulation data or parametric data measurements and may be executed using a large number of multi-variable sample points to determine process corners defining yield limits for a device. The model may also be used to simulate process shifts and exaggerated input ranges for critical device parameters. In some embodiments, the derived process corners may better represent physically possible worst-case process corners than traditional general-purpose process corners, and may address differences in process sensitivities for individual circuits of the device.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Memory cell with built-in process variation tolerance
InactiveUS7672152B1Less sensitive to process variationIncreased process variation toleranceDigital storageSub thresholdStatic random-access memory
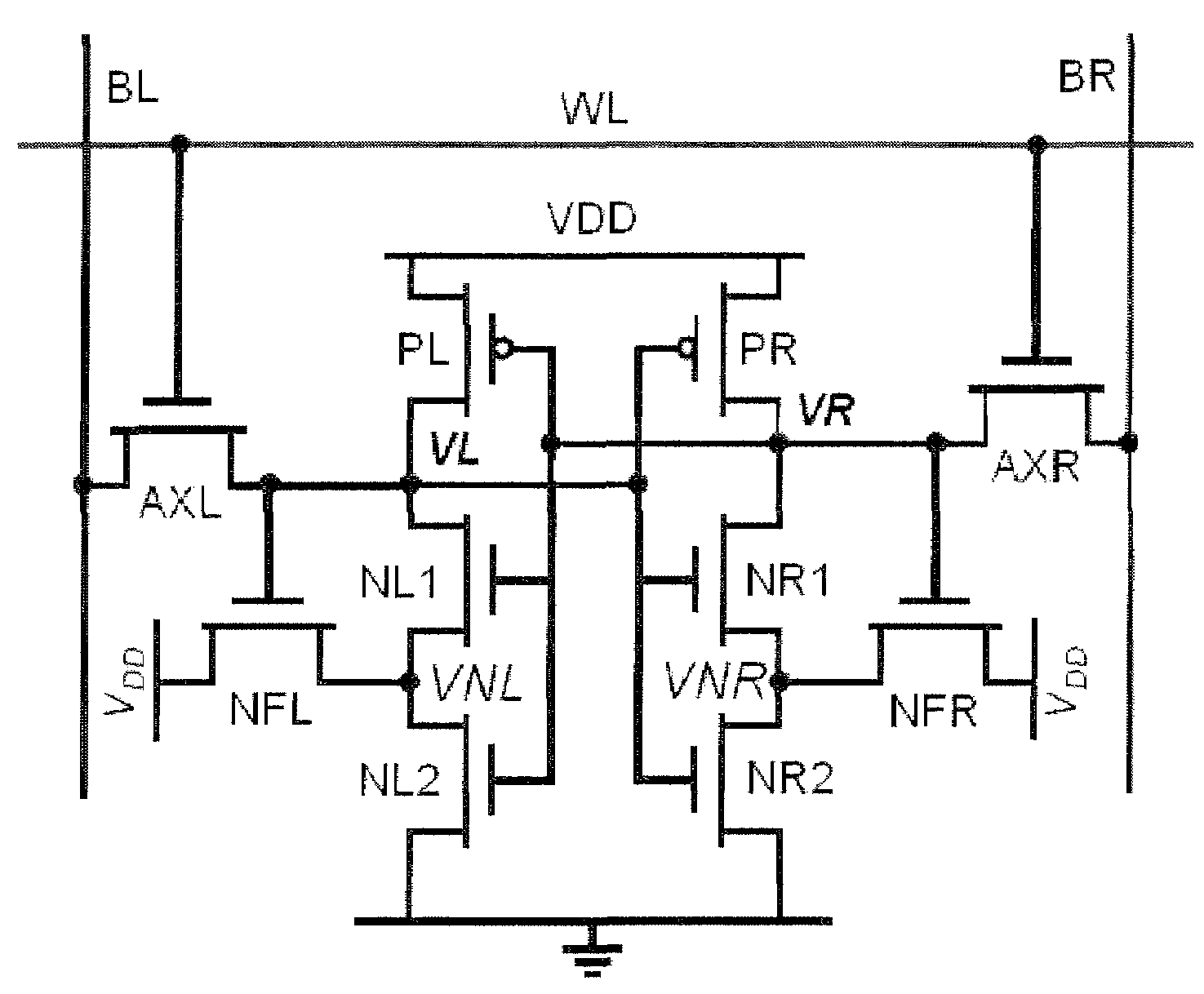
A Schmitt Trigger (ST) based, fully differential, 10-transistor (10T) SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) bitcell suitable for sub-threshold operation. The Schmitt trigger based bitcell achieves 1.56× higher read static noise margin (SNM) (VDD=400 mV) compared to a conventional 6T cell. The robust Schmitt trigger based memory cell exhibits built-in process variation tolerance that gives tight SNM distribution across the process corners. It utilizes fully differential operation and hence does not require any architectural changes from the present 6T architecture. The 10T bitcell has two cross-coupled Schmitt trigger inverters which each consist of four transistors, including a PMOS transistor and two NMOS transistors in series, and an NMOS feedback transistor which is connected between the inverter output and the junction between the series-connected NMOS transistors. Each inverter has one associated NMOS access transistor.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Self-repairing technique in nano-scale SRAM to reduce parametric failures
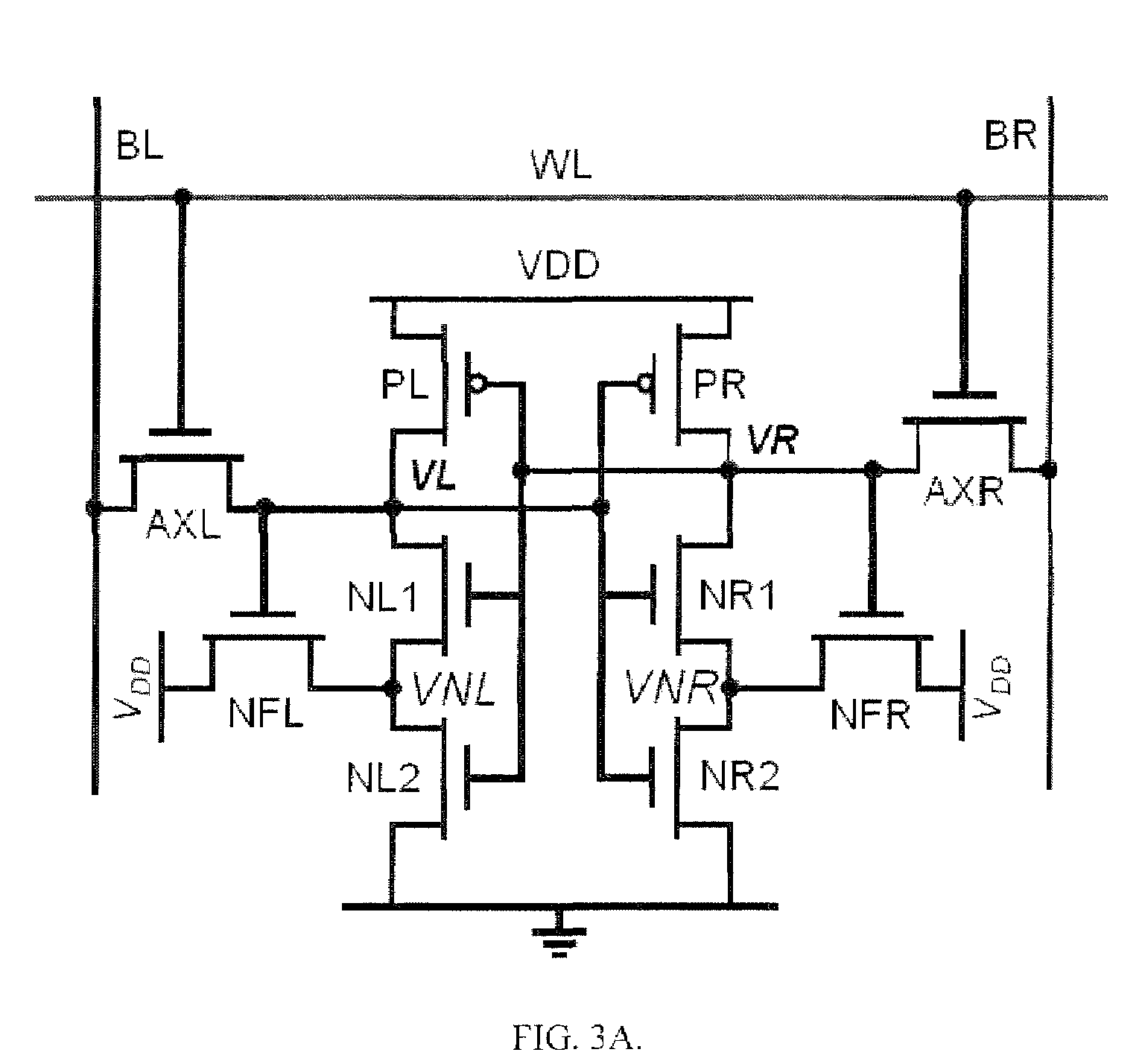
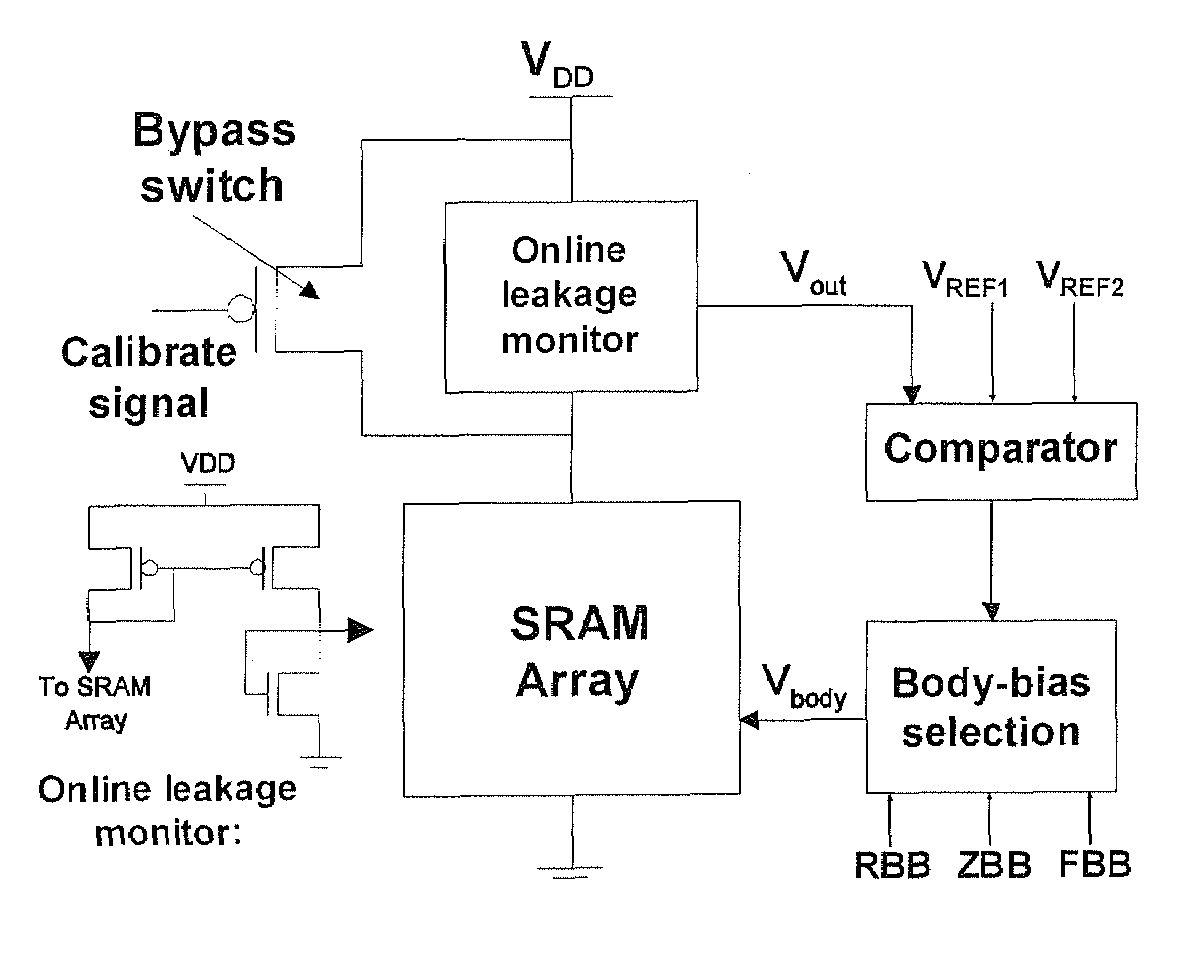
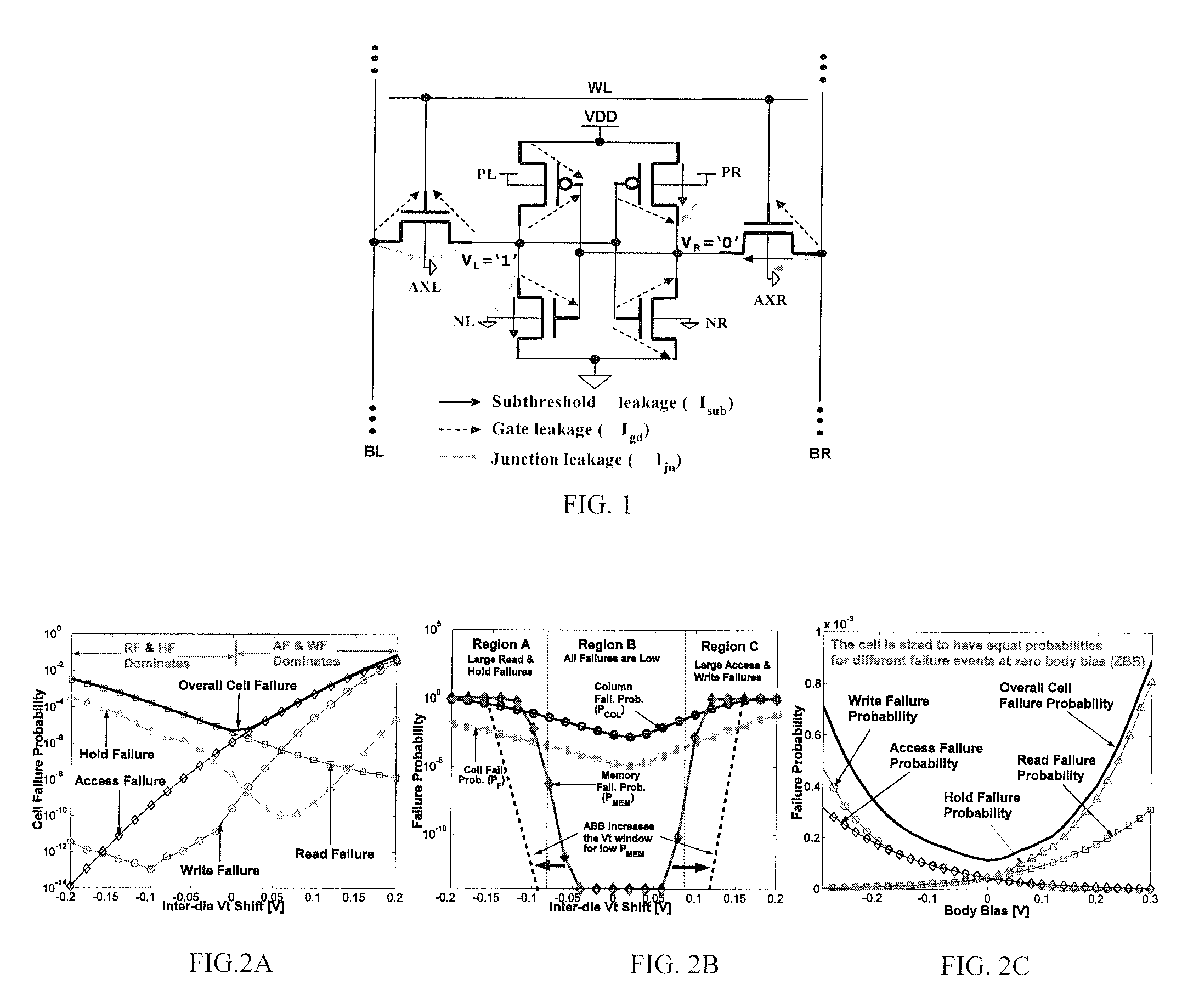
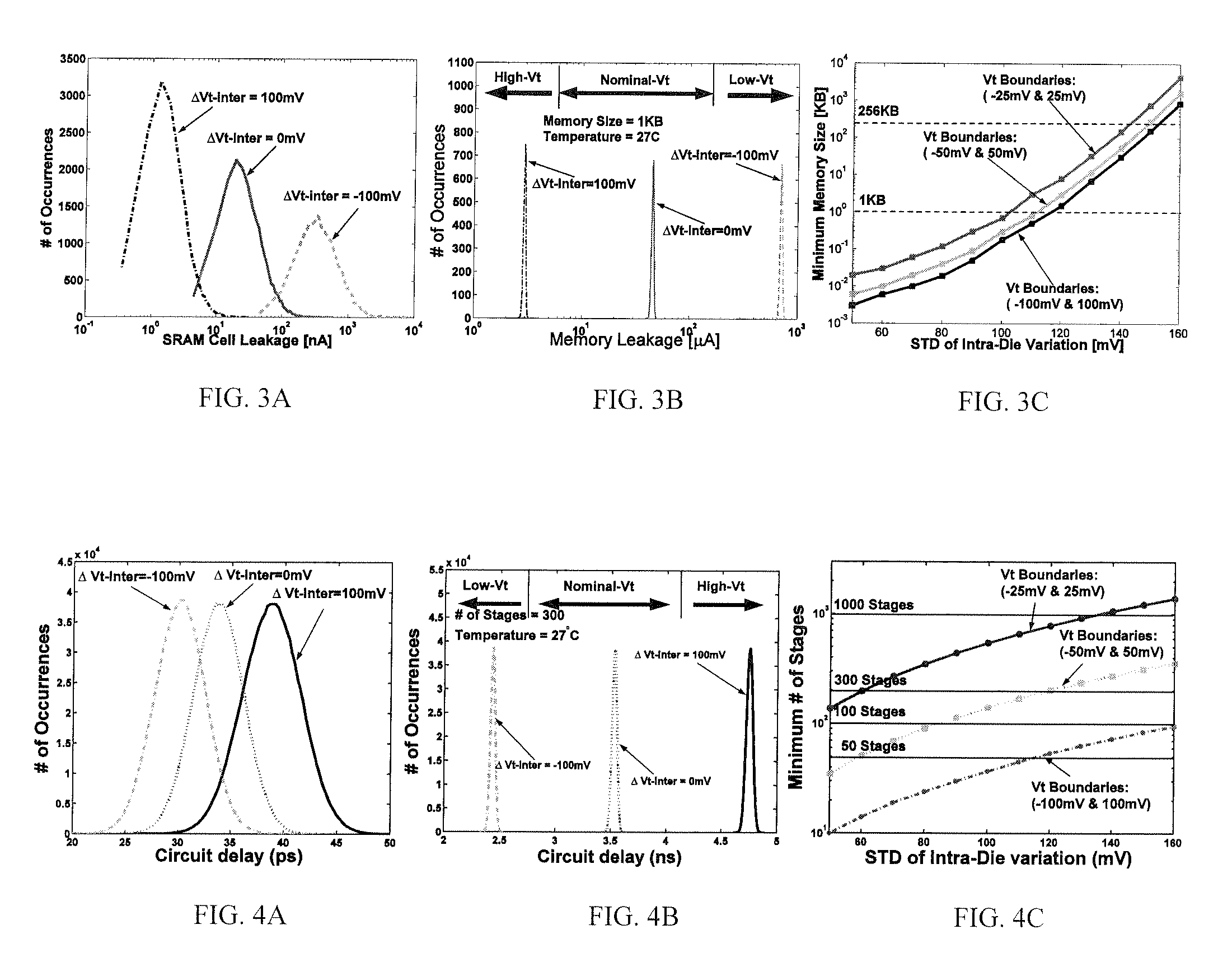
A self-repairing SRAM and a method for reducing parametric failures in SRAM. On-chip leakage or delay monitors are employed to detect inter-die Vt process corners, in response to which the SRAM applies adaptive body bias to reduce the number of parametric failures in a die and improve memory yield. Embodiments include circuitry for applying reverse body bias (RBB) to the SRAM array in the presence of a low inter-die Vt process corner, thereby reducing possible read and hold failures, and applying forward body bias (FBB) to the array in the presence of a high inter-die Vt process corner, thereby reducing possible access and write failures.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
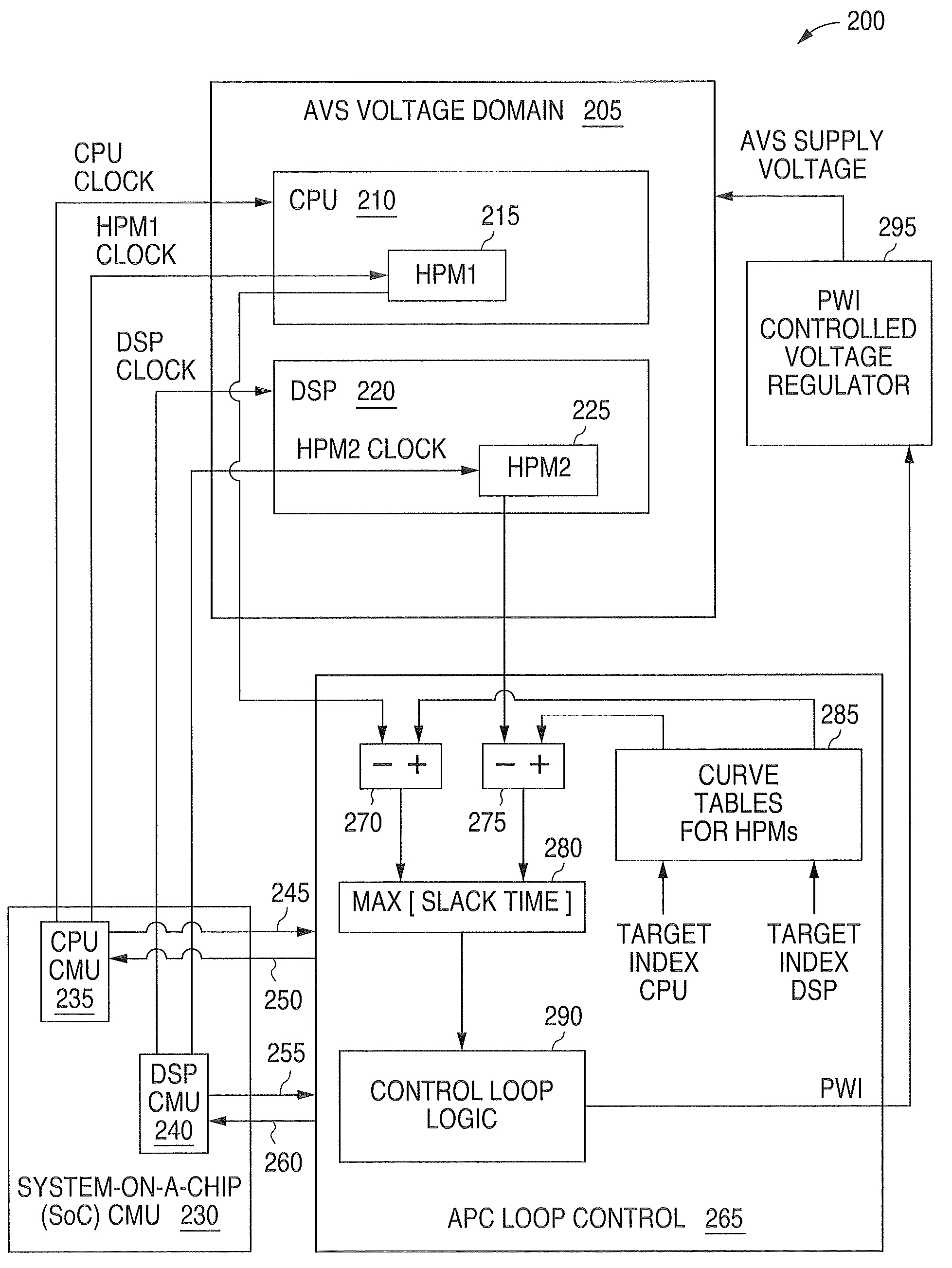
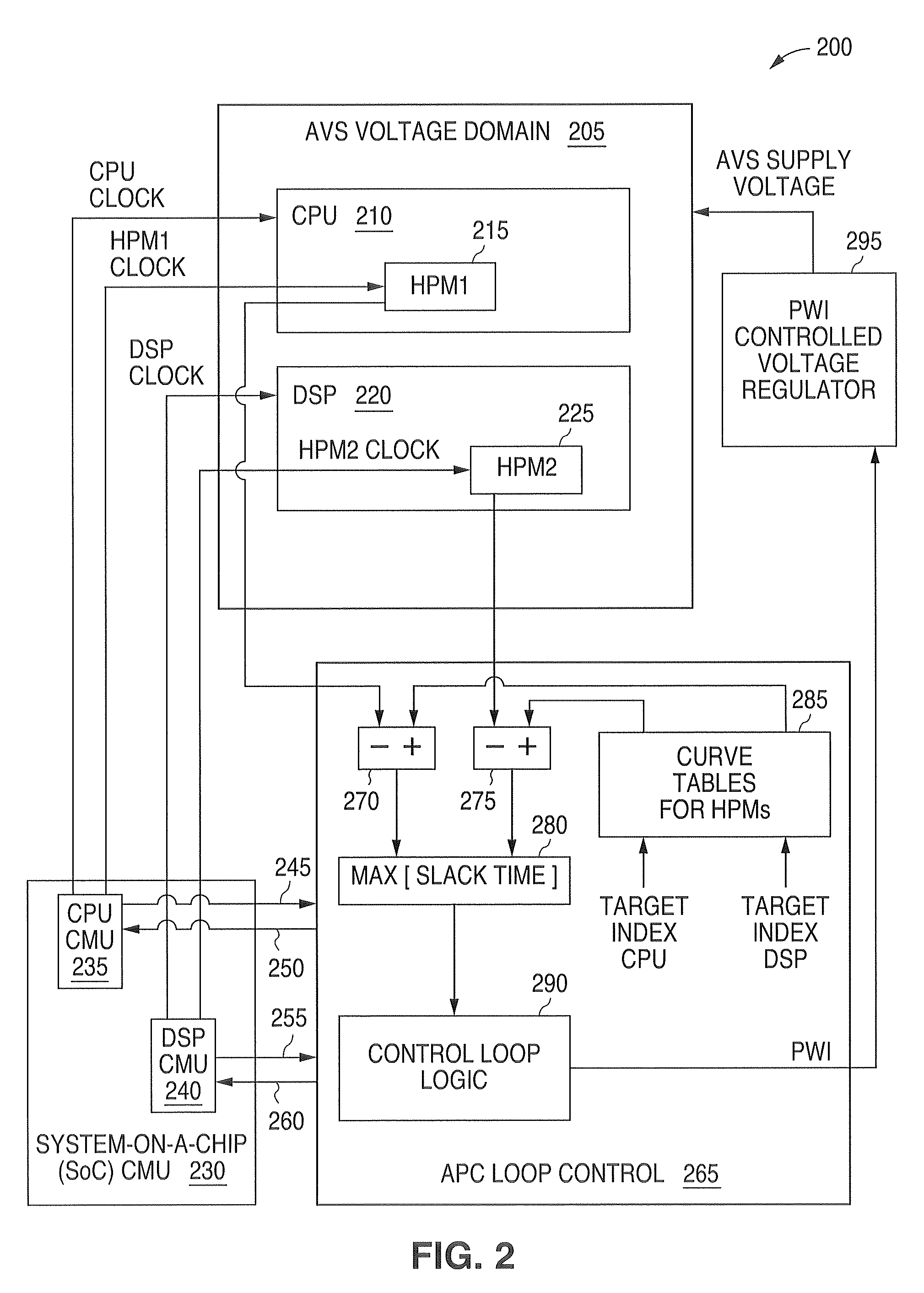
System and method for providing adaptive voltage scaling with multiple clock domains inside a single voltage domain
ActiveUS7921312B1Accurate scaleEnergy efficient ICTImpedence convertorsPower controllerSoftware engineering
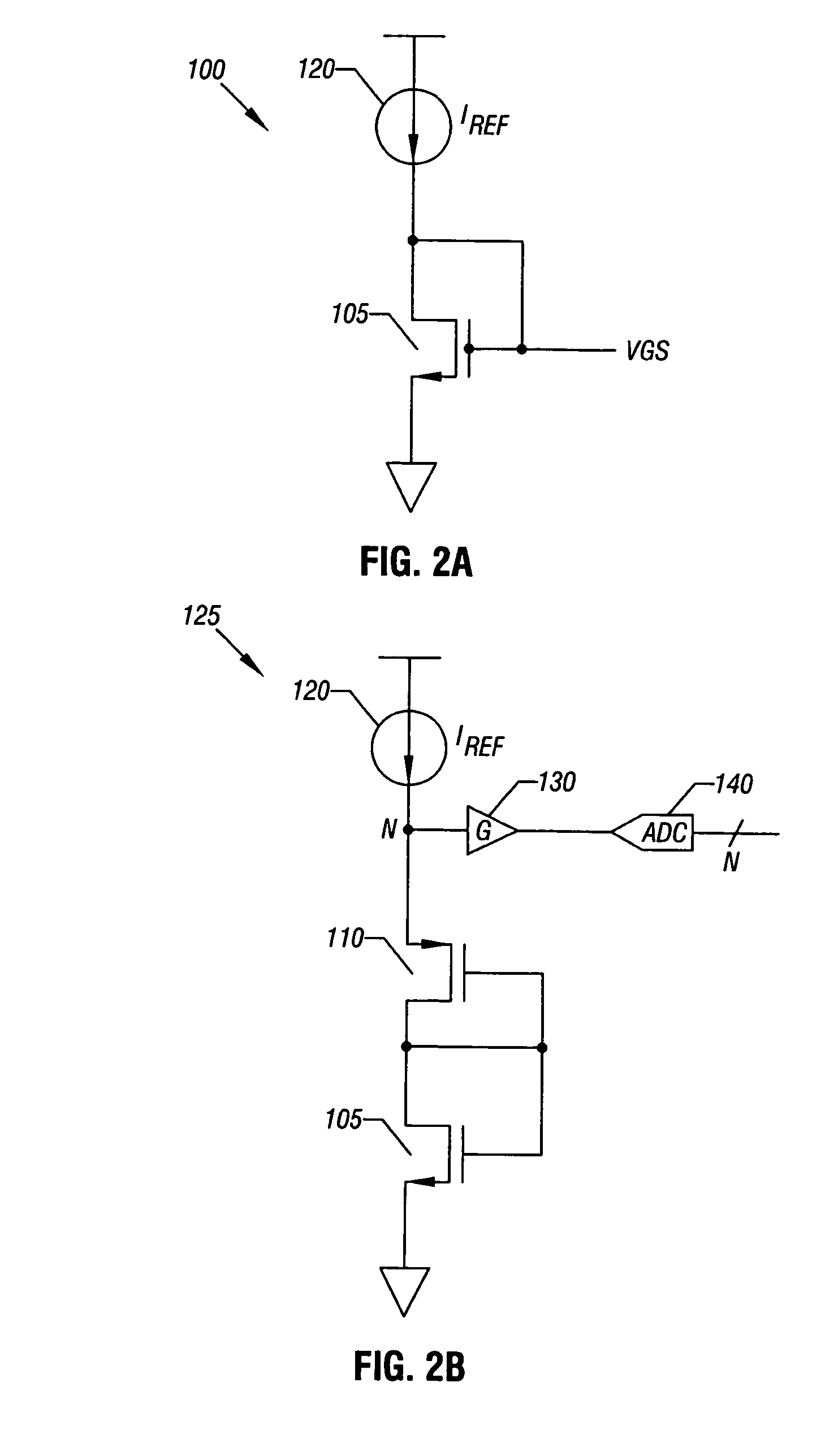
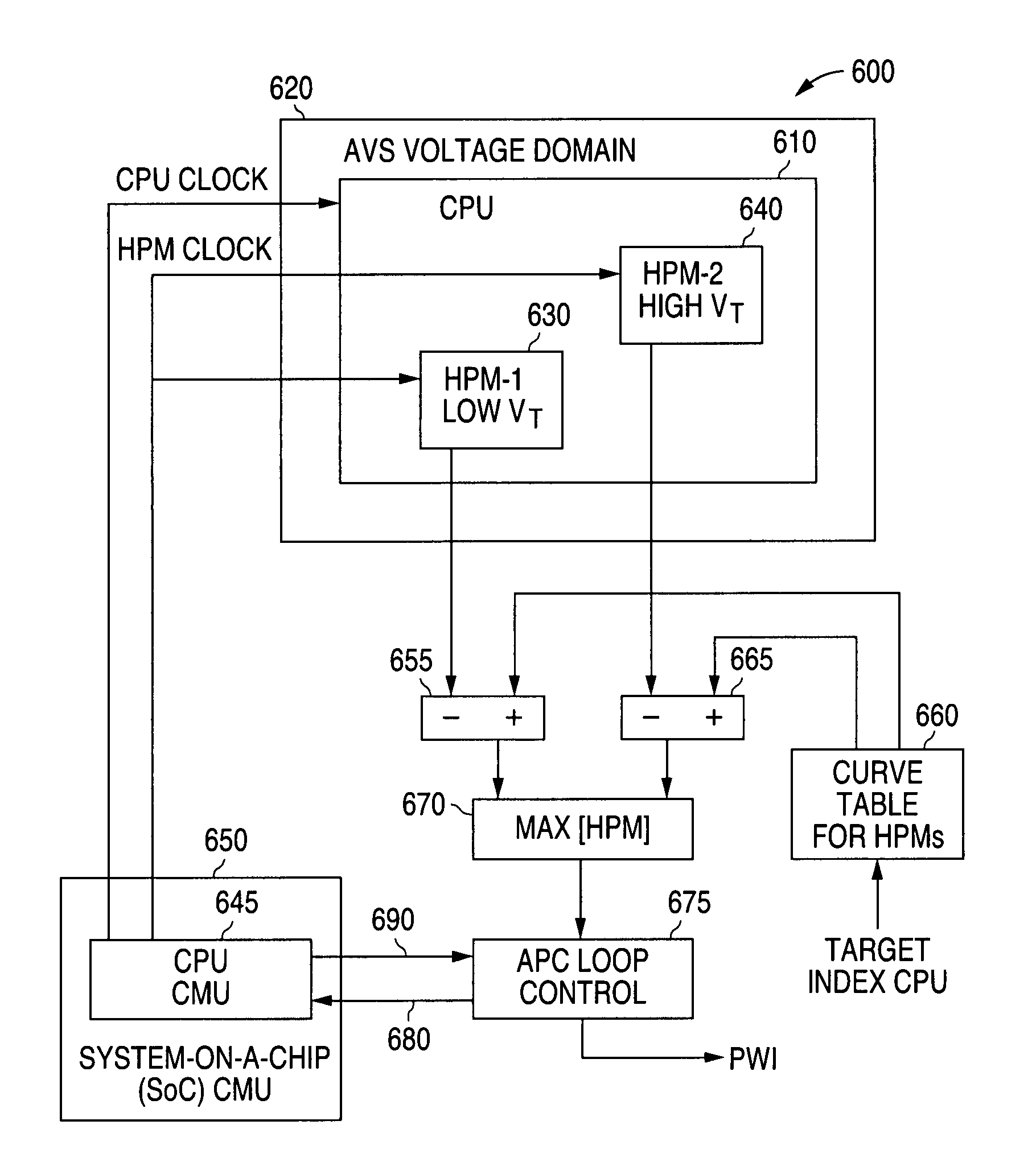
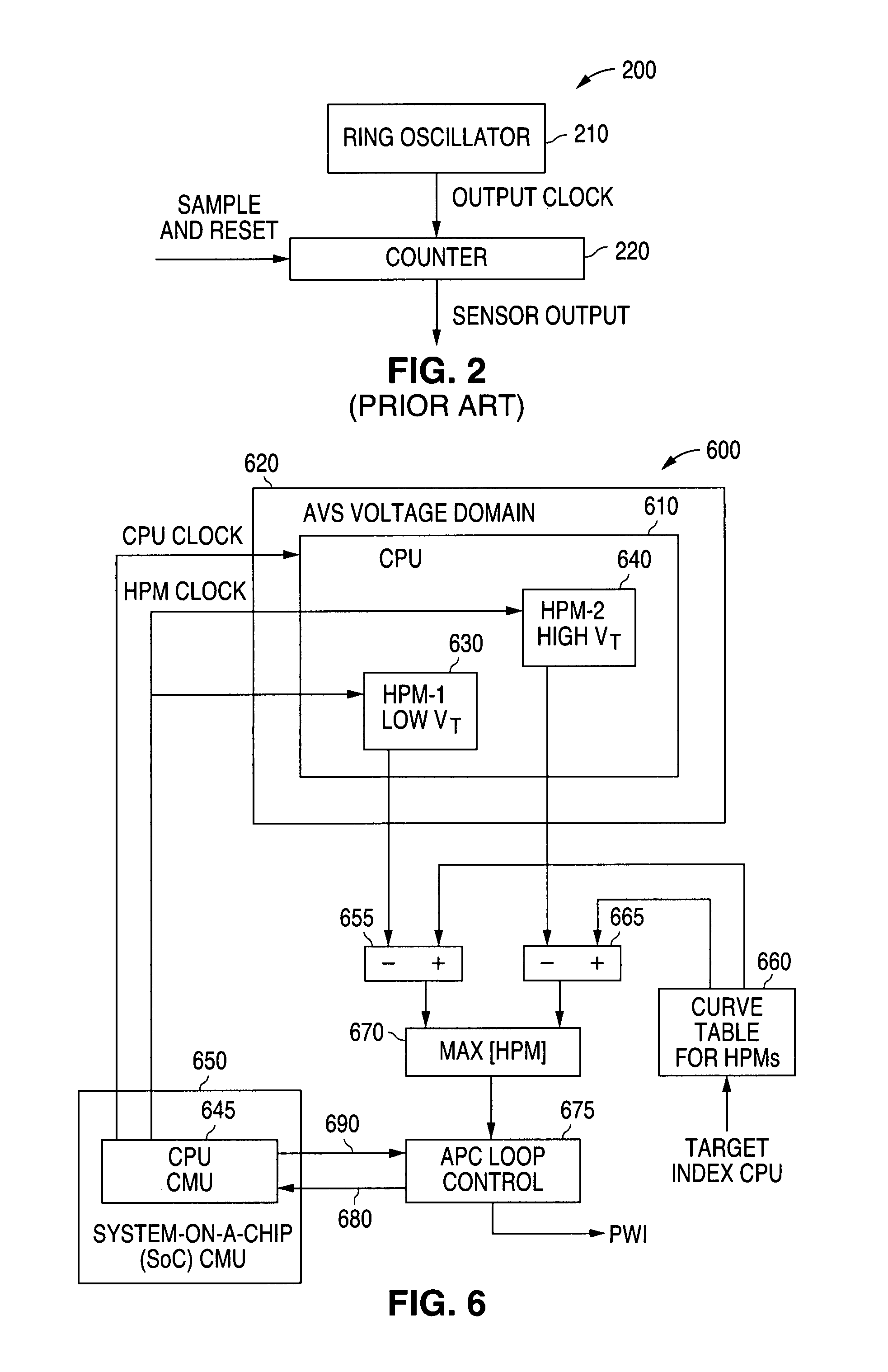
A system and method is disclosed for providing a plurality of hardware performance monitors for adaptive voltage scaling in an integrated circuit system that comprises a plurality of clock domains. Each hardware performance monitor is associated with one of the plurality of clock domains and provides a signal that measures a performance of its respective clock domain temperature, process corner and supply voltage. The difference between the measured performance and a nominal expected performance for each hardware performance monitor is determined. The largest of the plurality of difference signals is selected and used in an advanced power controller to provide adaptive voltage scaling for the integrated circuit system.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Annular voltage-controlled oscillator
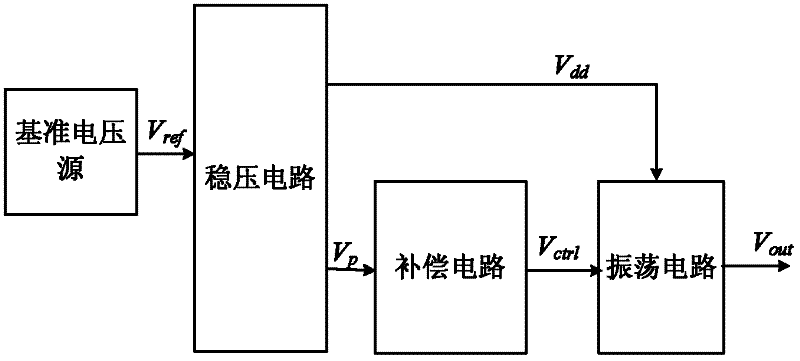
ActiveCN102386848AAchieve output frequency deviationTo achieve the purpose of compensating frequencyOscillations generatorsEngineeringVoltage source
The invention discloses an annular voltage-controlled oscillator, which comprises a reference voltage source, a voltage stabilizing circuit, a compensation circuit and an oscillation circuit; the output of the reference voltage source is connected with the input end of the voltage stabilizing circuit; the voltage stabilizing circuit generates two output voltages, and the first output is used as a working voltage of the oscillation circuit while the second output is input to the compensation circuit as an input voltage of the compensation circuit; and the output of the compensation circuit is used as a bias voltage of the oscillation circuit. The oscillator controls the oscillation frequency of the oscillation circuit by generating a bias voltage changed along the temperature and the technology to realize automatic compensation of output frequency deviation of the oscillator. When temperature rise results in frequency increment of the oscillation circuit, the compensation circuit generates a control voltage reduced along the temperature so as to compensate drop of frequency; and when a process corner is changed from SS (Slow nmos and Slow pmos) to FF (Fast nmos and Fast pmos), the oscillation circuit also has a rise and the compensation circuit generates a control voltage reduced along the technology so as to compensate drop of frequency.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
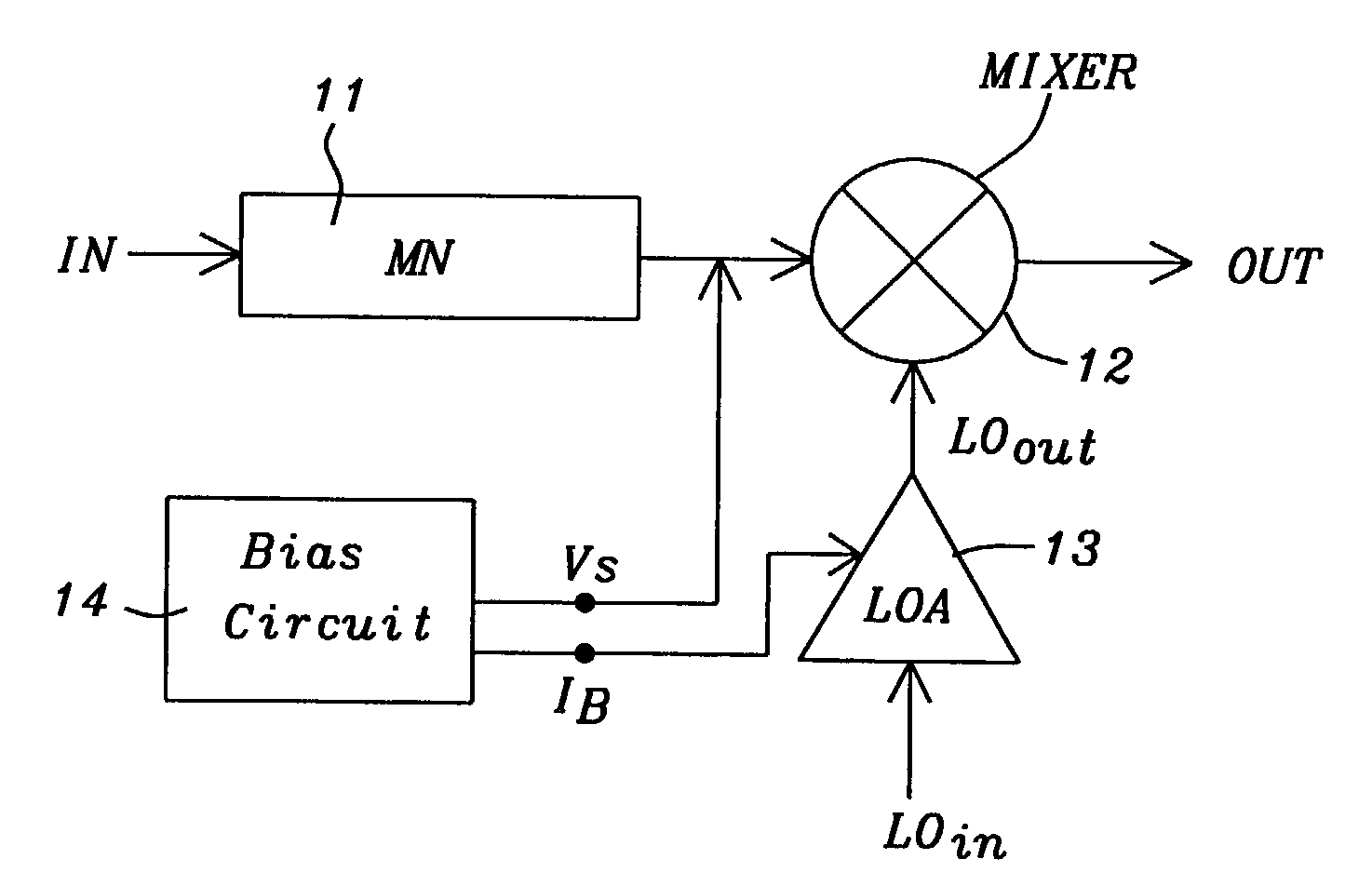
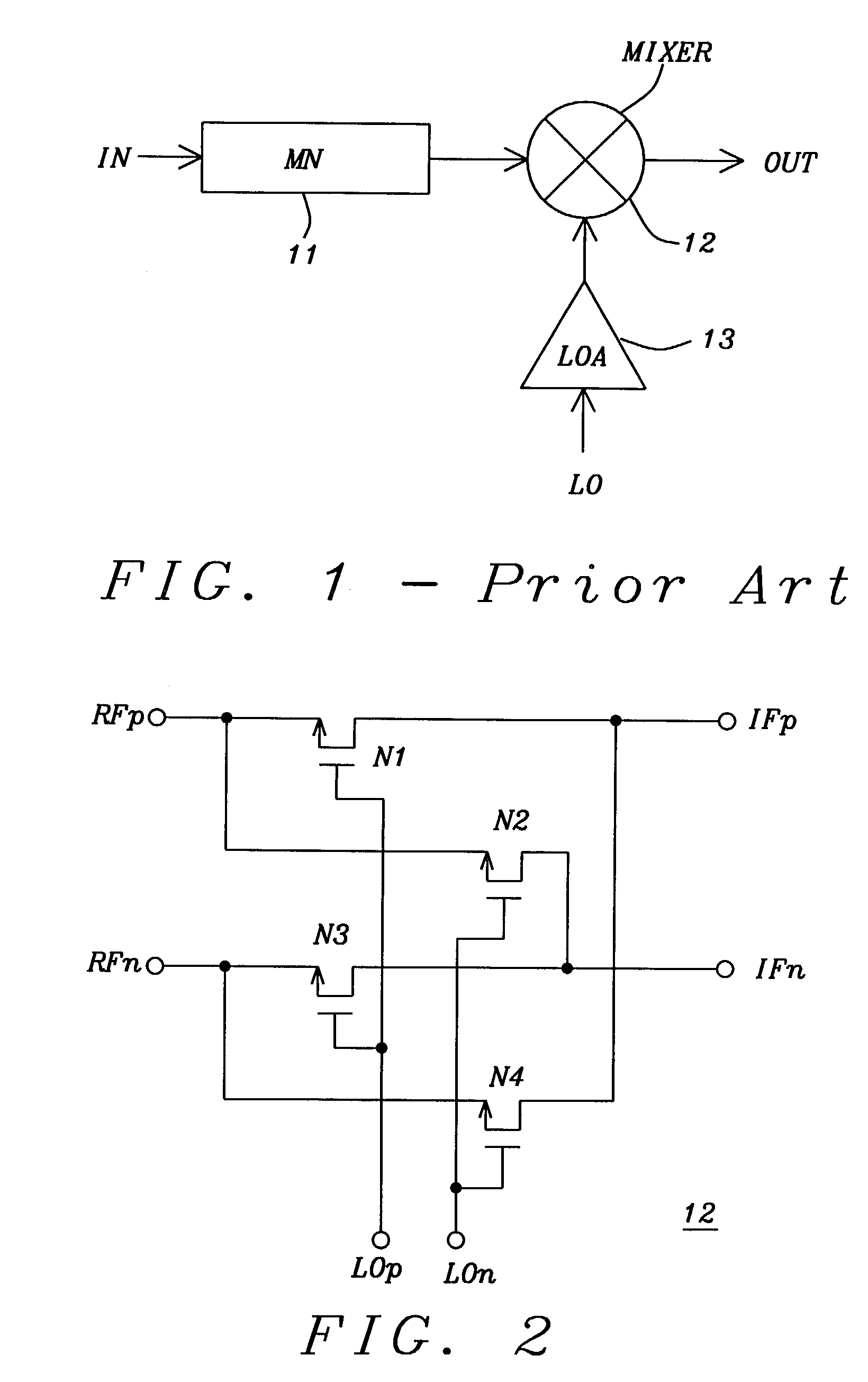
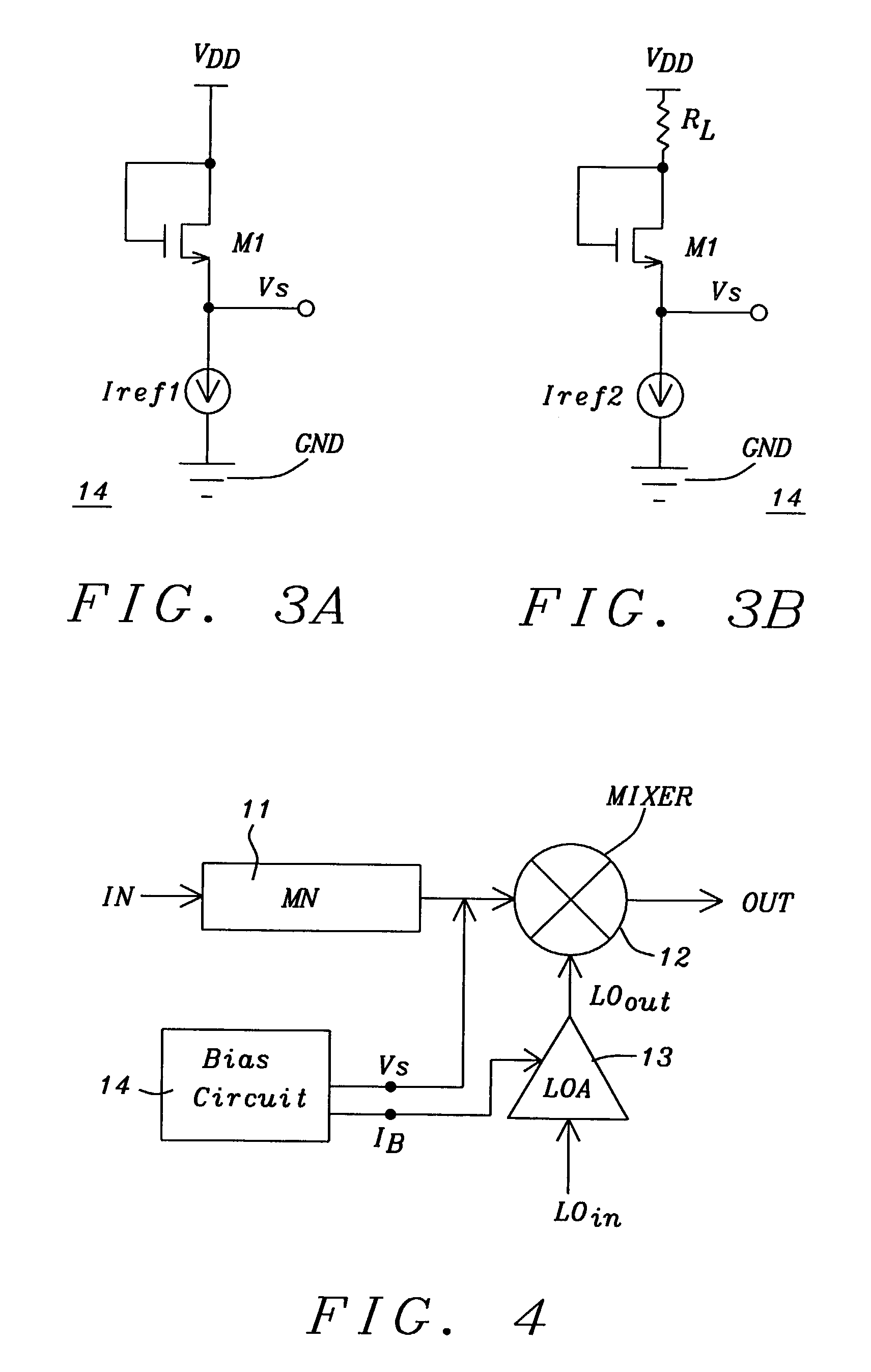
Threshold voltage (Vth), power supply (VDD), and temperature compensation bias circuit for CMOS passive mixer
ActiveUS7092692B2Conversion stabilityLinear stabilityModulation transference balanced arrangementsSolid-state devicesMOSFETReference current
A biasing circuit for a CMOS passive mixer core to stabilize its conversion gain, linearity and noise figure. The RF inputs are fed differentially from the two RF ports, the LO inputs are fed differentially from the two LO ports, and the IF outputs are obtained at the two IF ports. The biasing circuit comprises a reference current derived from the bandgap voltage and a n-channel MOSFET transistor. The conversion gain is stabilized by keeping the Vgs−Vth value of the passive mixer core almost constant at all process corners, temperature and power supply changes. This is achieved by implementing Vs in such a way that it will increase the same amount as VDD decreases, and that Vs will decrease the same amount as Vth increases.
Owner:WIPRO LTD +1
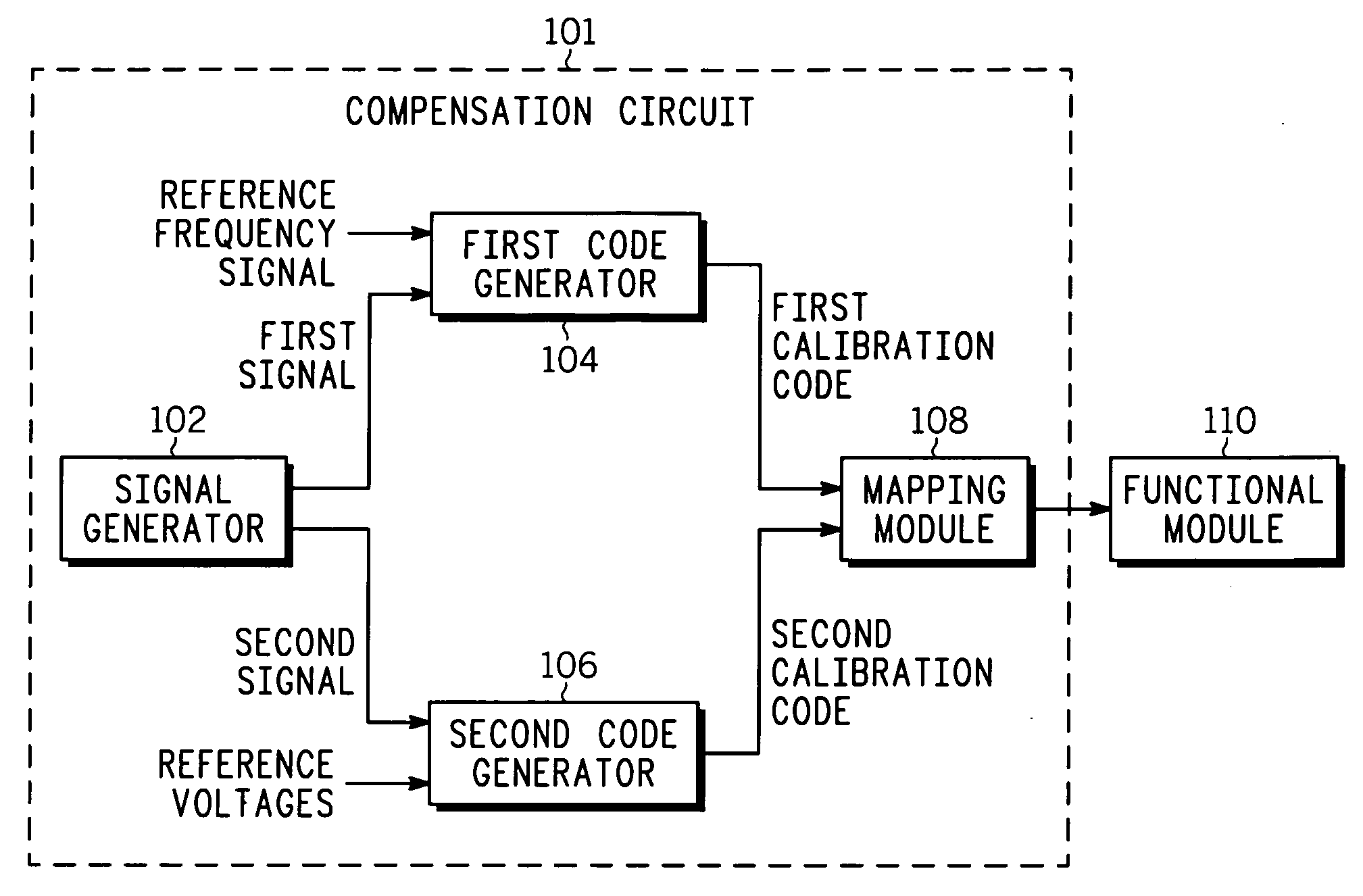
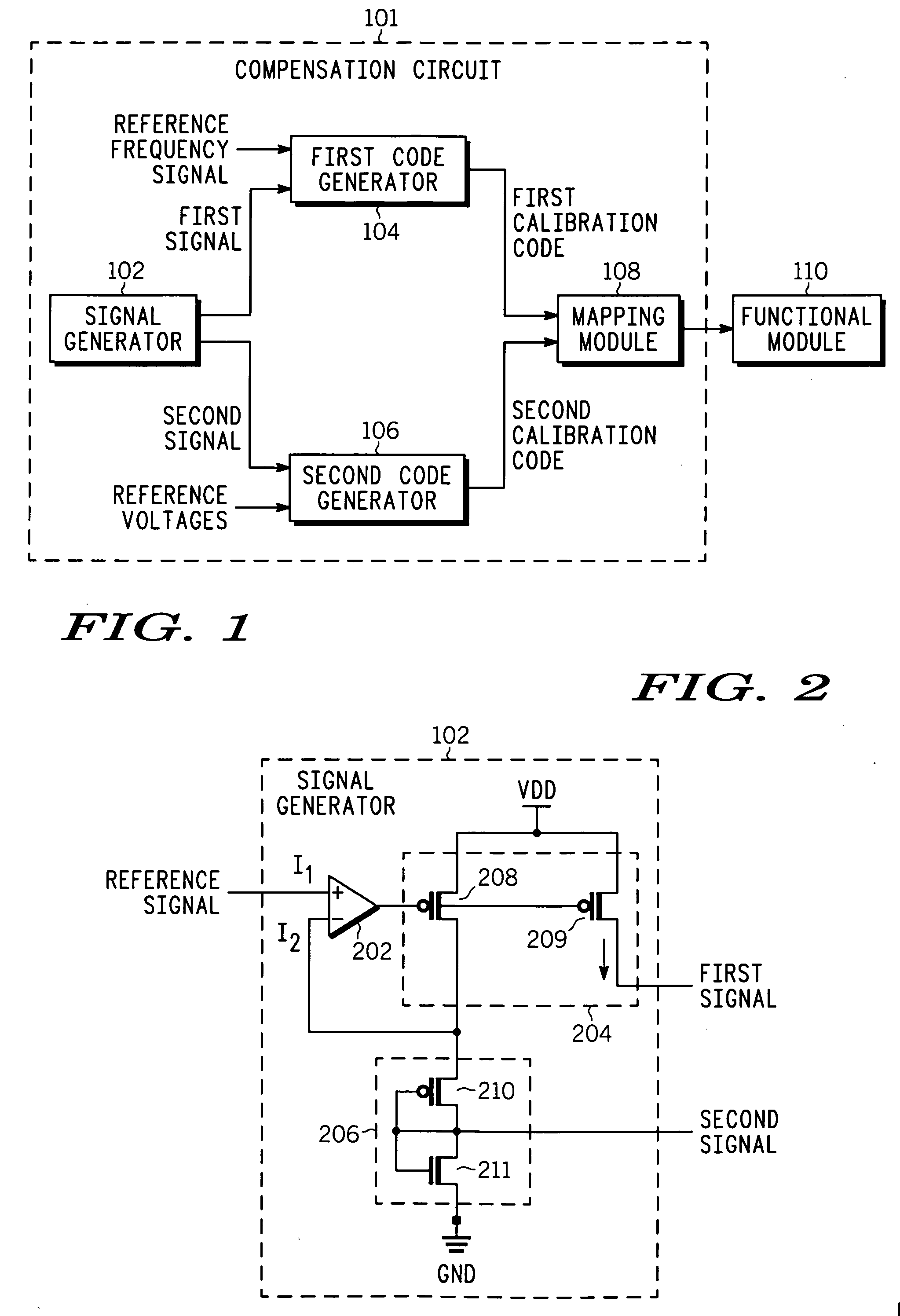
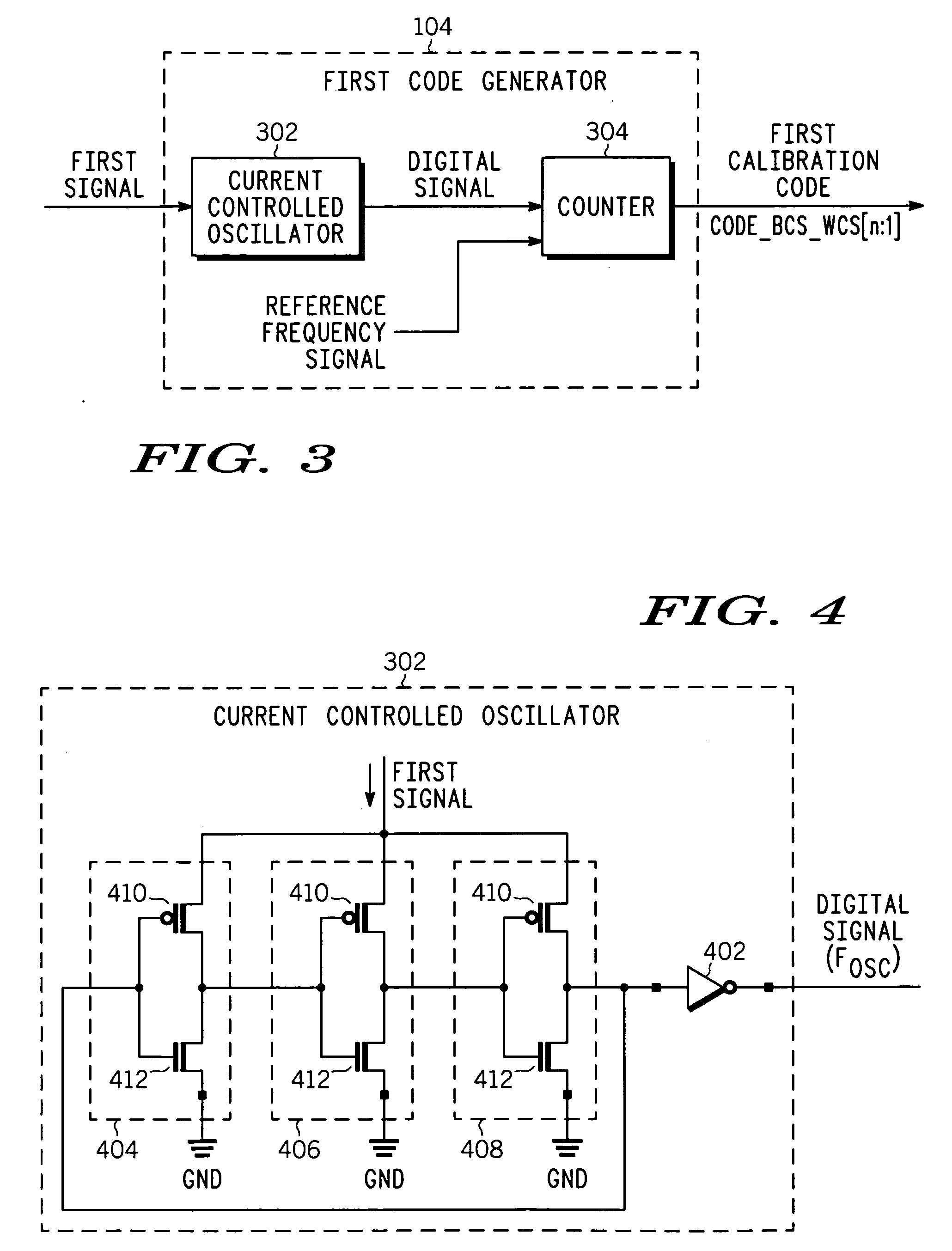
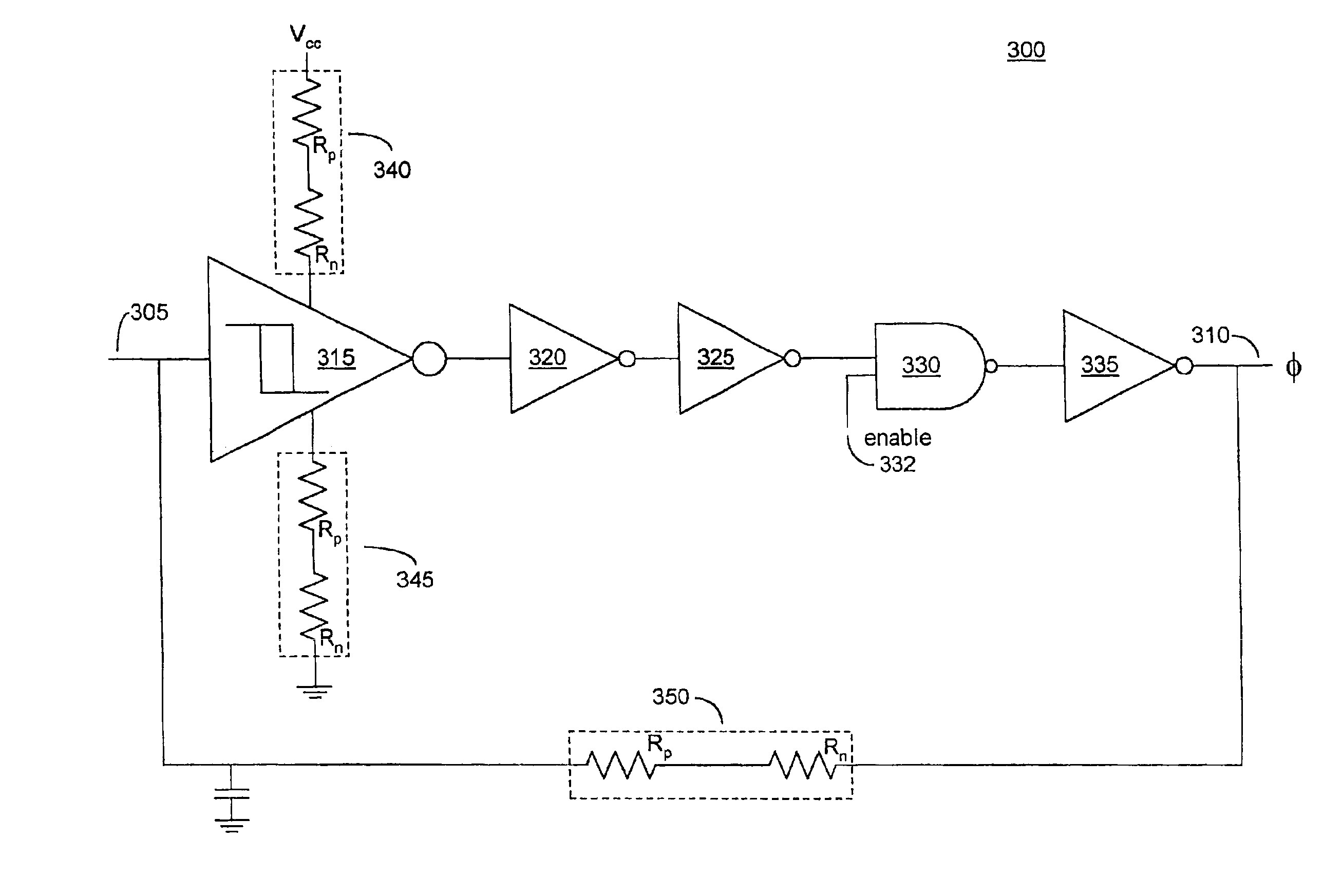
PVT variation detection and compensation circuit
InactiveUS20070018864A1Reliability increasing modificationsElectric signal transmission systemsSignal generatorProcess corners
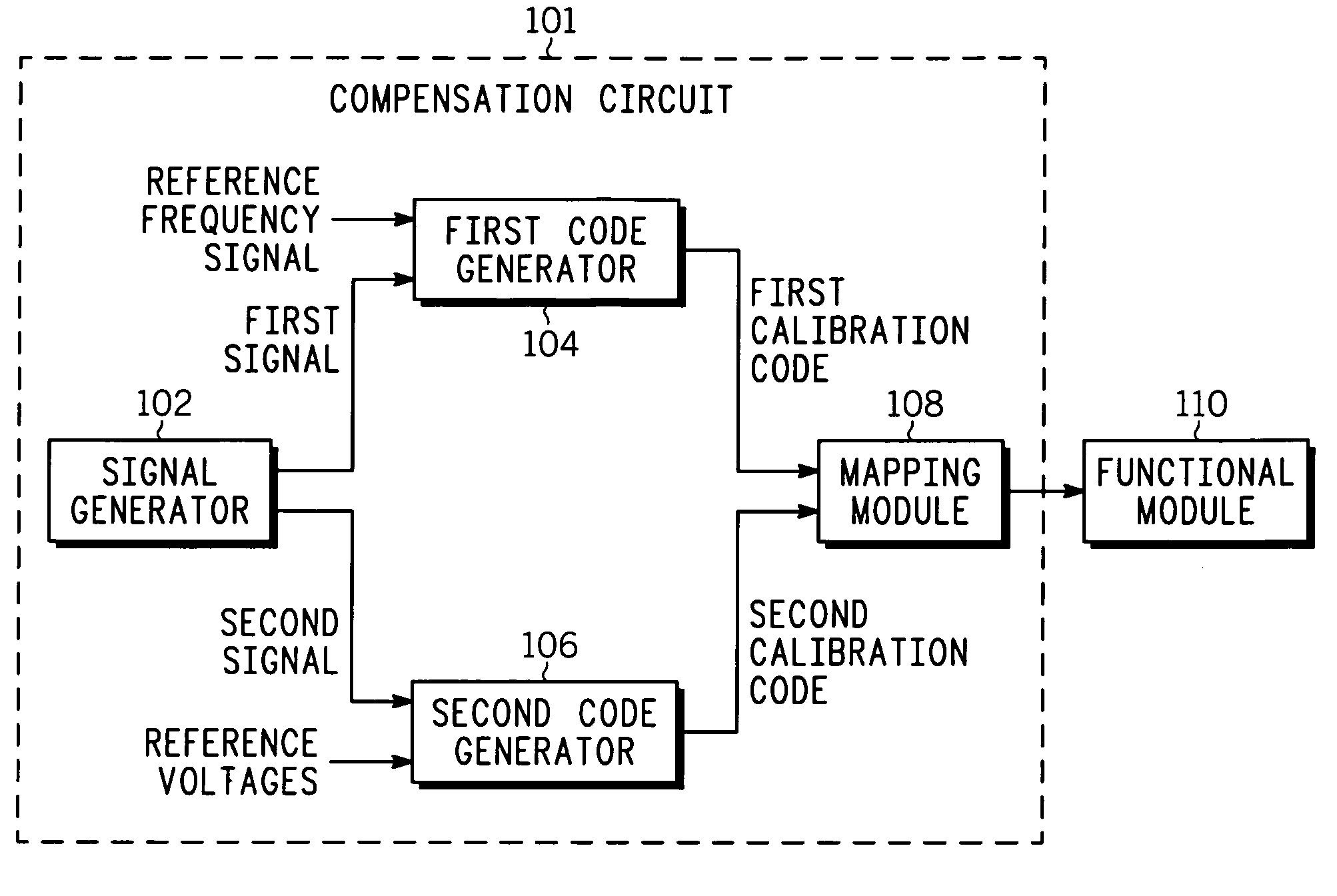
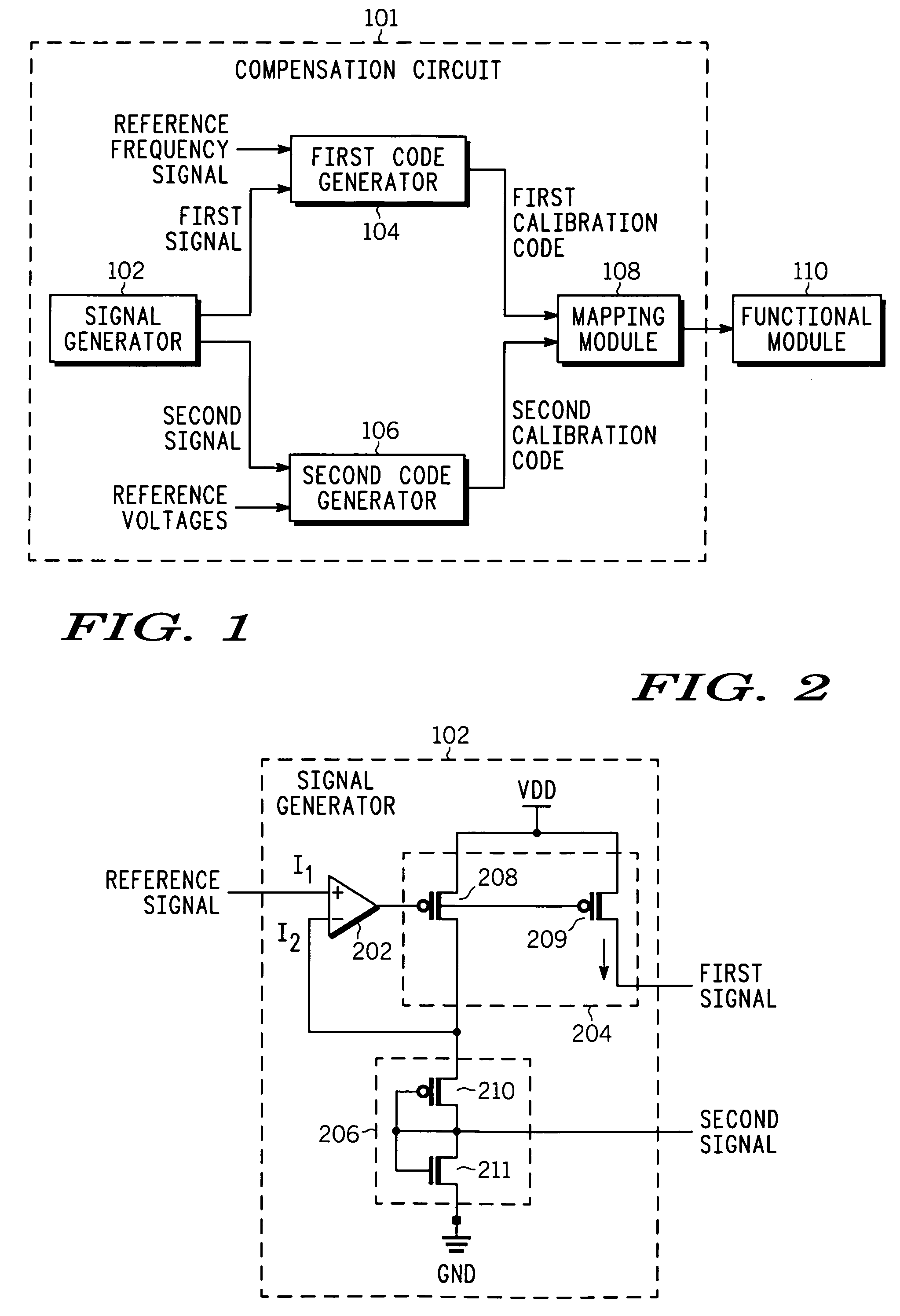
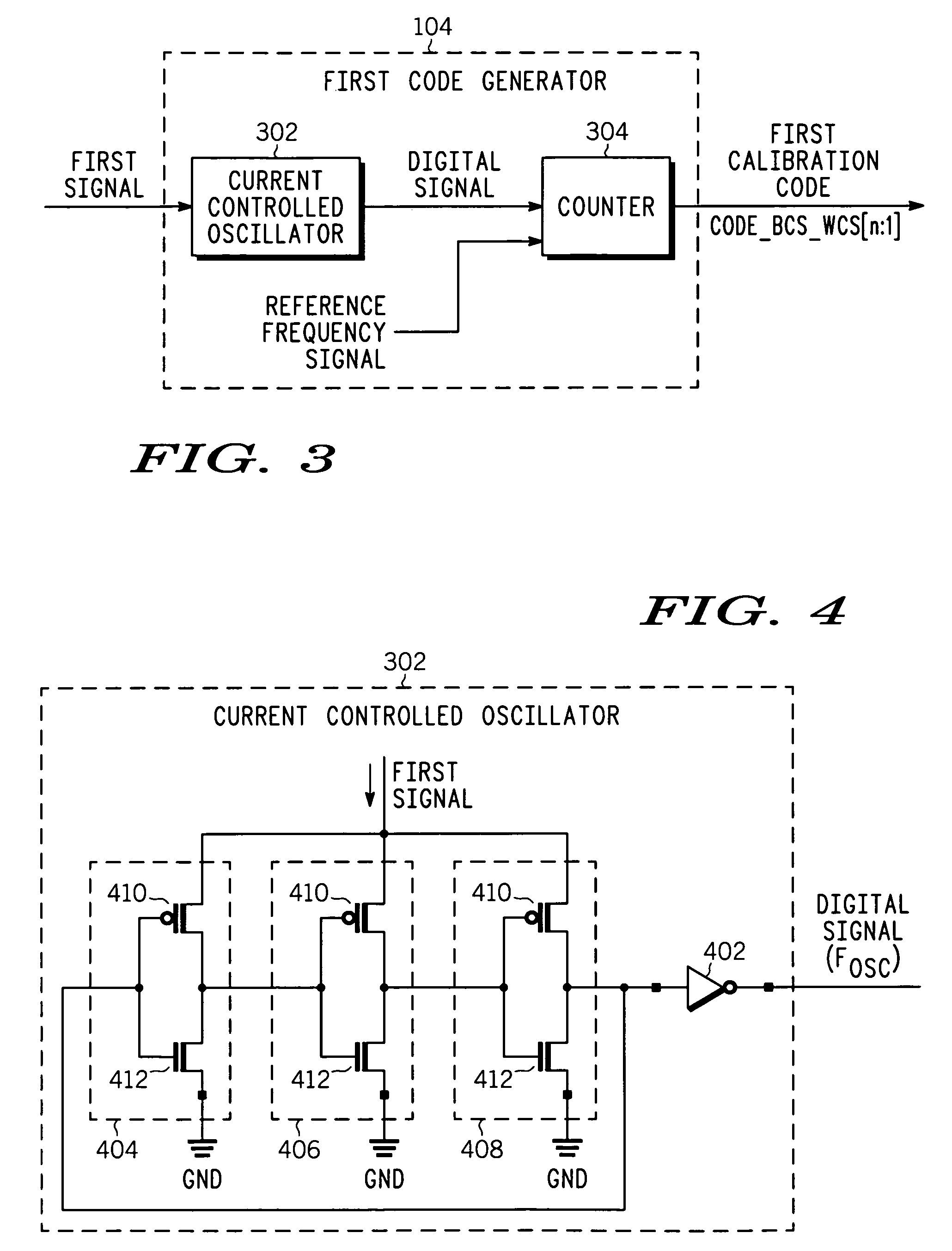
A compensation circuit and a method that compensates for process, voltage and temperature (PVT) variations in an integrated circuit that includes functional modules. The compensation circuit includes a signal generator, a first code generator, a second code generator, and a mapping module. The signal generator generates a first signal and a second signal depending on aligned process corner, voltage and temperature variations and skewed process corner variations respectively. The first code generator receives the first signal, and generates a first calibration code. The second code generator receives the second signal, and generates a second calibration code. The mapping module provides the first and second calibration codes for compensating for the aligned process corner, voltage and temperature variations and the skewed process corner variations associated with the functional modules respectively.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
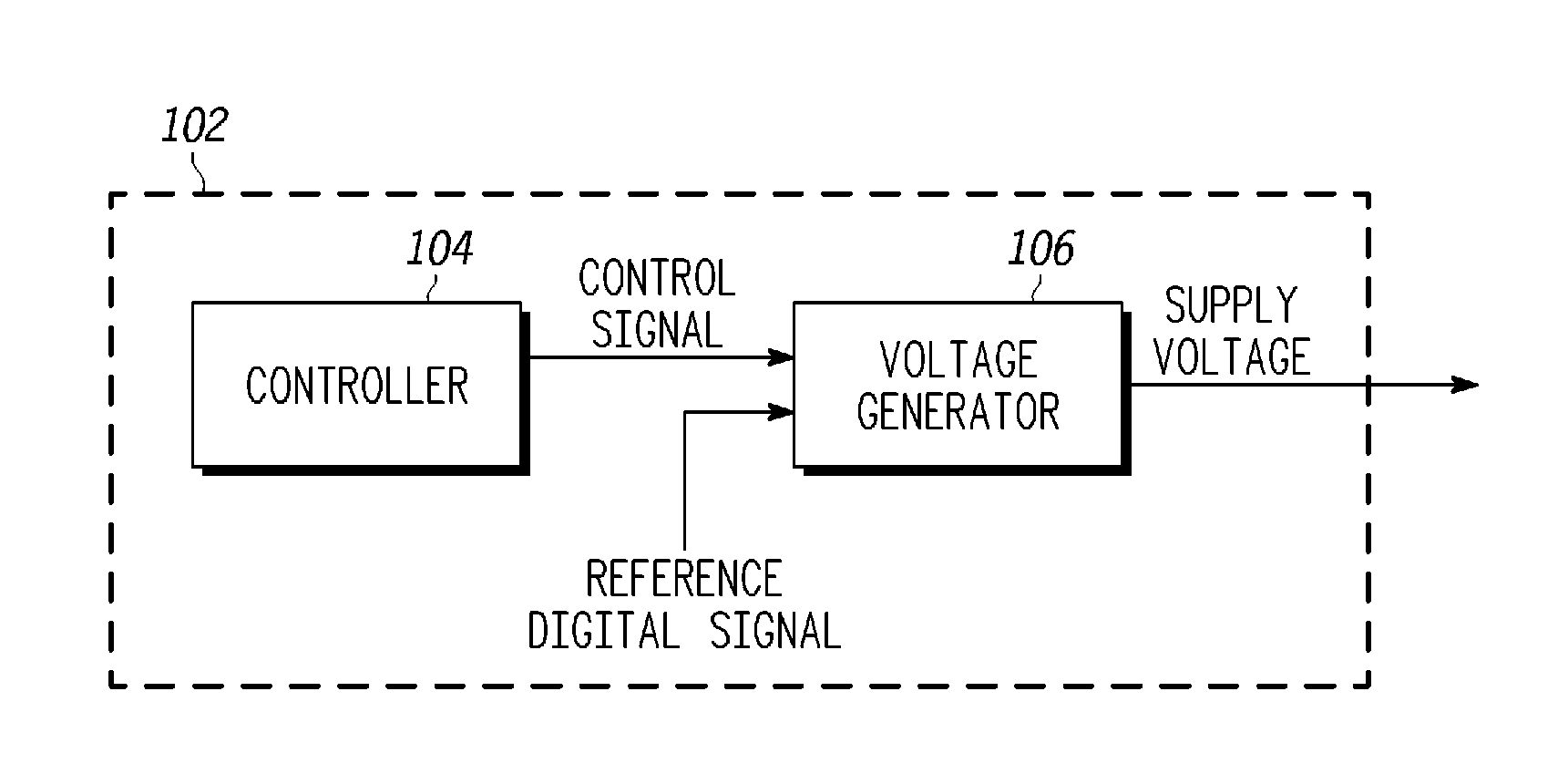
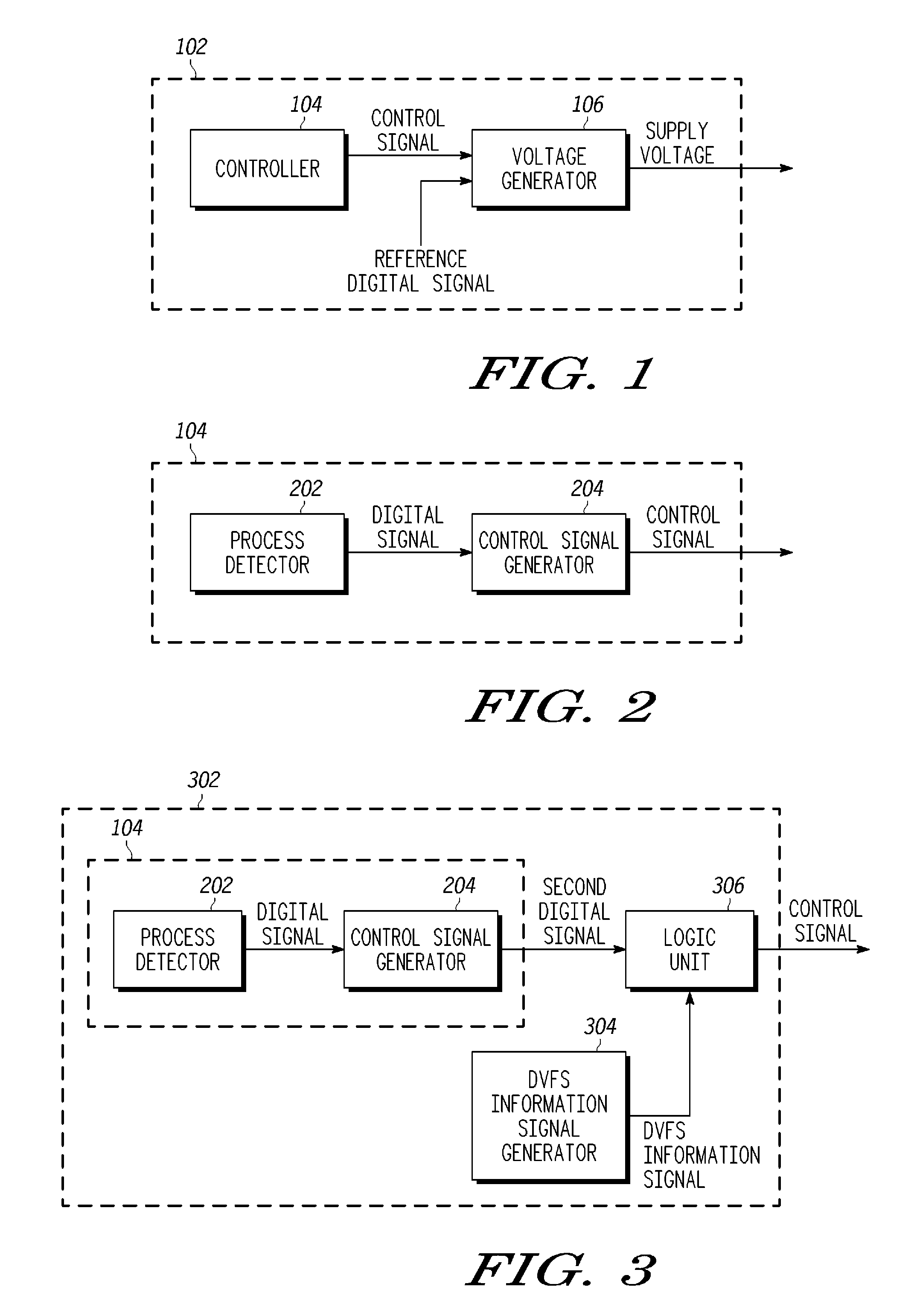
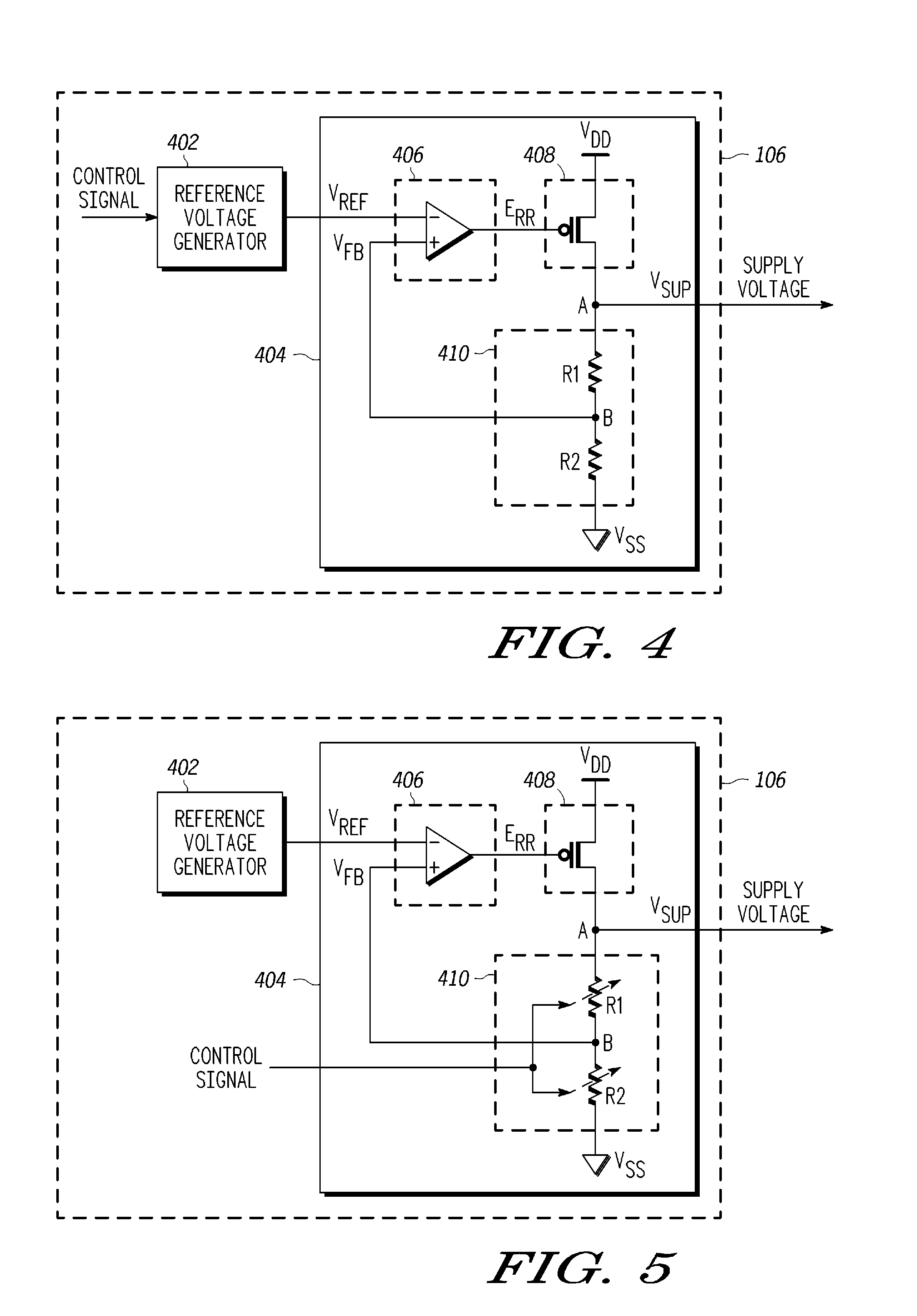
Power management in integrated circuits using process detection
A power management system for managing power in an integrated circuit includes a controller and a voltage generator. The controller generates a control signal based on one or more process corners of the integrated circuit. The voltage generator generates a supply voltage based on the control signal, and provides the supply voltage to the integrated circuit to manage the power within the integrated circuit.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
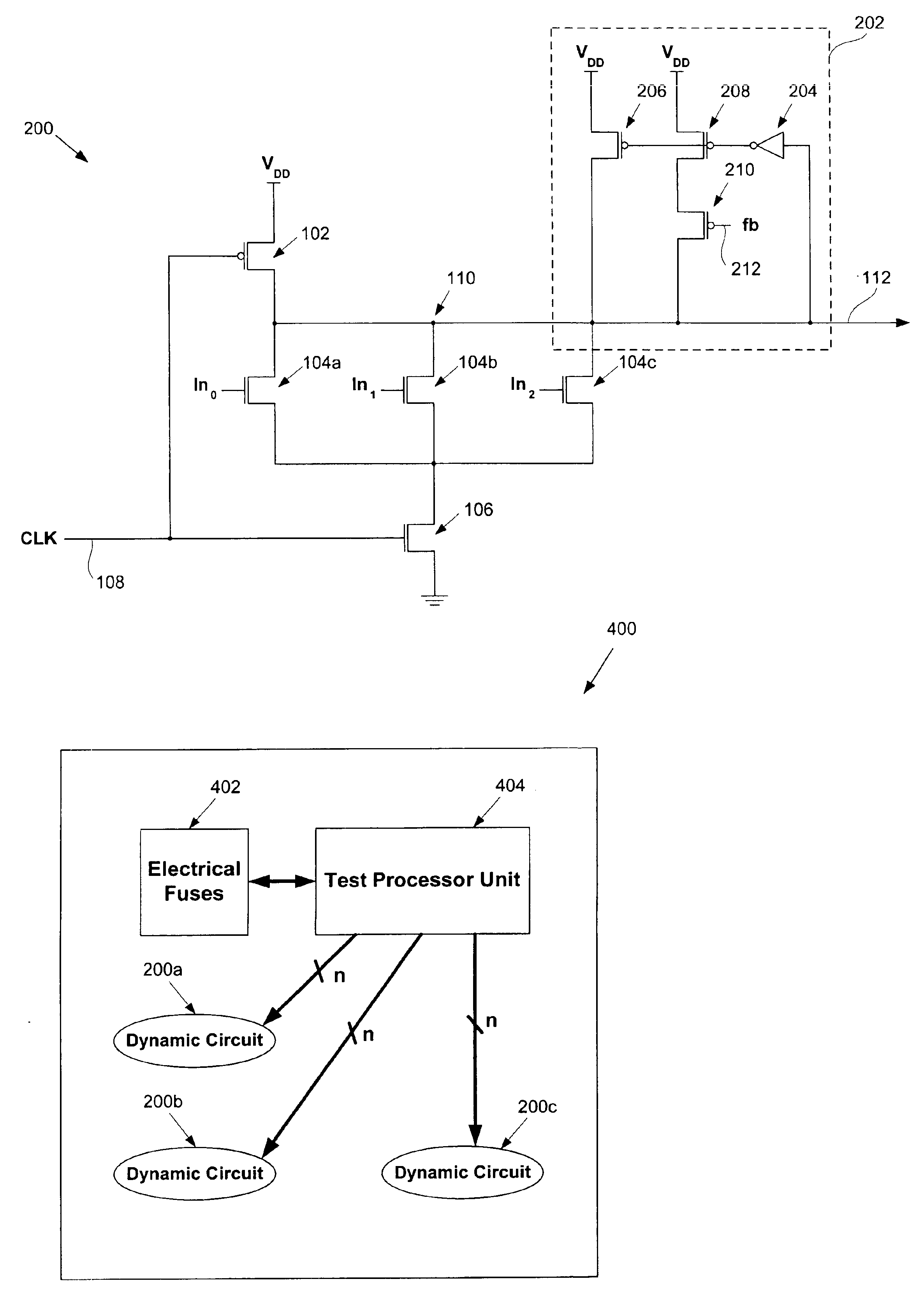
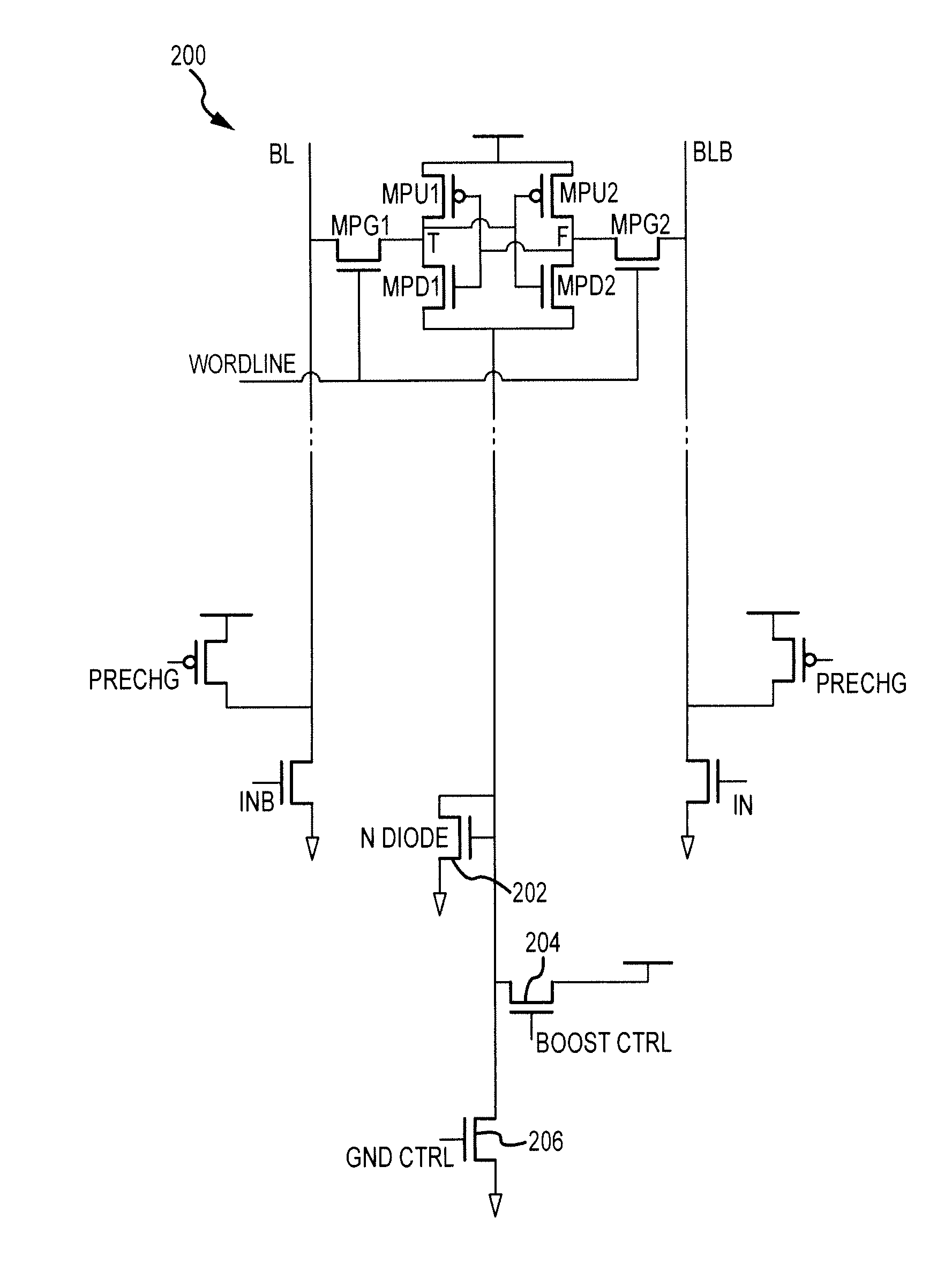
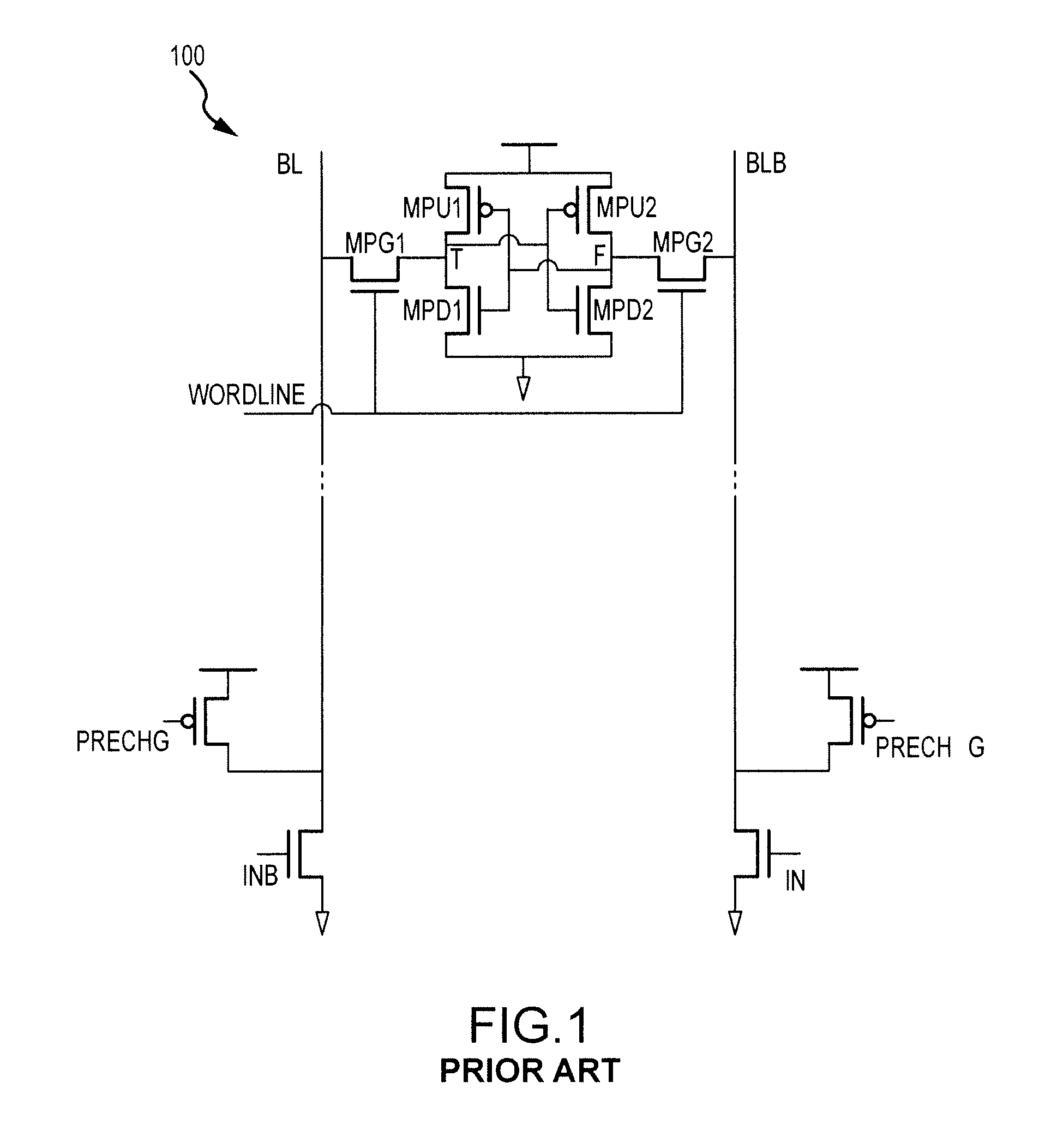
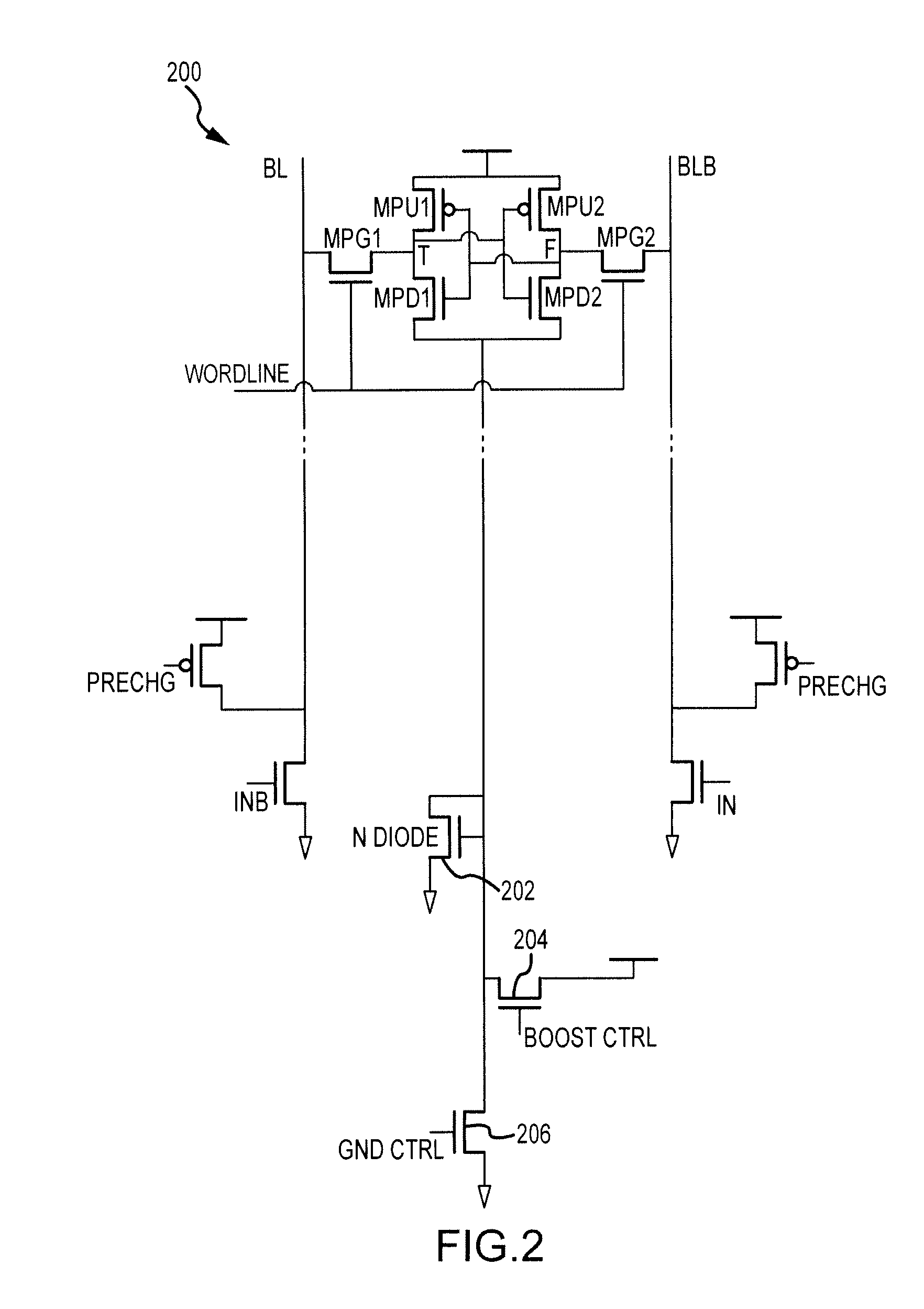
Adaptive keeper sizing for dynamic circuits based on fused process corner data
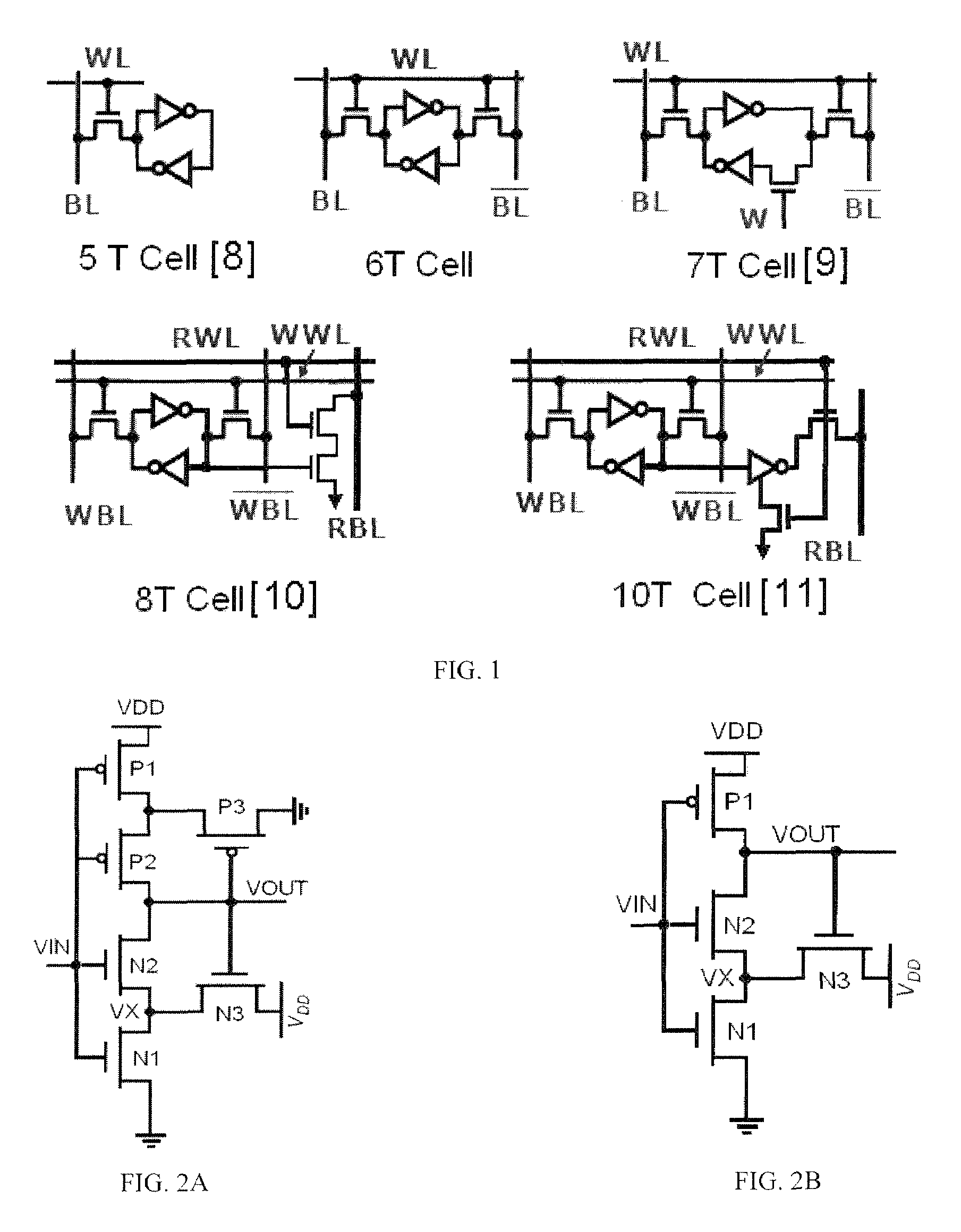
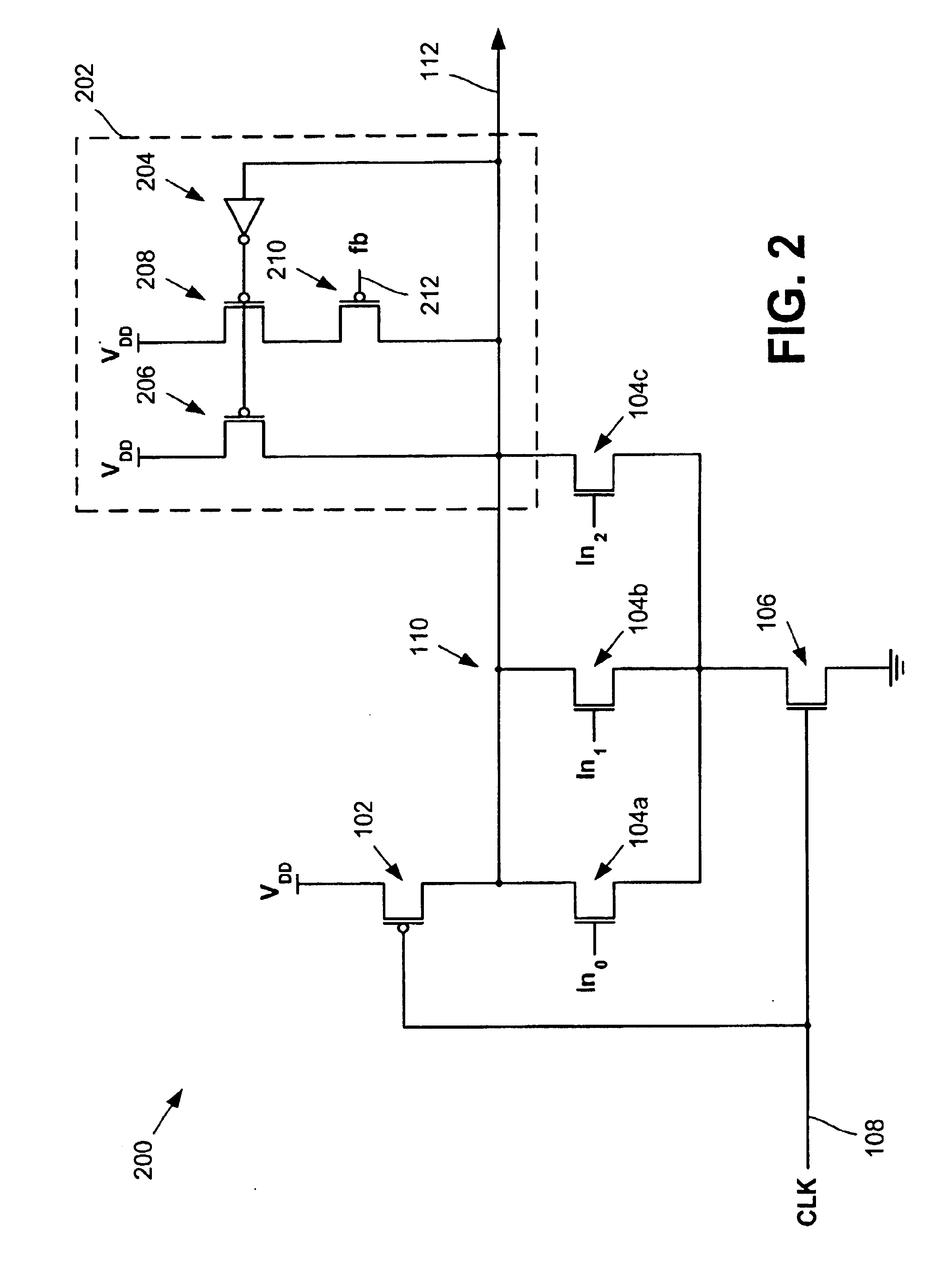
An invention is provided for an adaptive keeper circuit. The adaptive keeper circuit includes a first keeper transistor having a first terminal in electrical communication with a power supply and a second terminal in electrical communication with an internal dynamic node. In addition, a second keeper transistor is included that is configured in parallel to the first keeper transistor. The second keeper transistor also has a first terminal in electrical communication with the power supply. The second keeper transistor can be added to the first keeper transistor using a feedback bit line, which is configured to control current flow between the second keeper transistor and the internal dynamic node based on a state of the feedback bit line. The state of the feedback bit line is based on a process corner characteristic of the die. Additional keeper transistors and corresponding feedback bit lines can be added to the keeper circuit to increase flexibility.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Compensated oscillator circuit for charge pumps
ActiveUS6888763B1More power consumptionConsume moreGenerator stabilizationDigital storageElectrical resistance and conductanceHemt circuits
A charge pump oscillator circuit with compensation for variations in process and operating environment. The charge pump oscillator is designed with a rolloff characteristic that enables operation at both weak and strong process corners without excessive power consumption. Composite resistors in the oscillator circuit are composed of component resistors that are fabricated with different processes, e.g., implant and deposition. The resistance of the composite resistor is thus in order to provide compensation for variations in processing and operating environment. The composite resistor may be used as a feedback loop resistor, or may be used as a source degenerate resistor to control the supply current to the oscillator.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
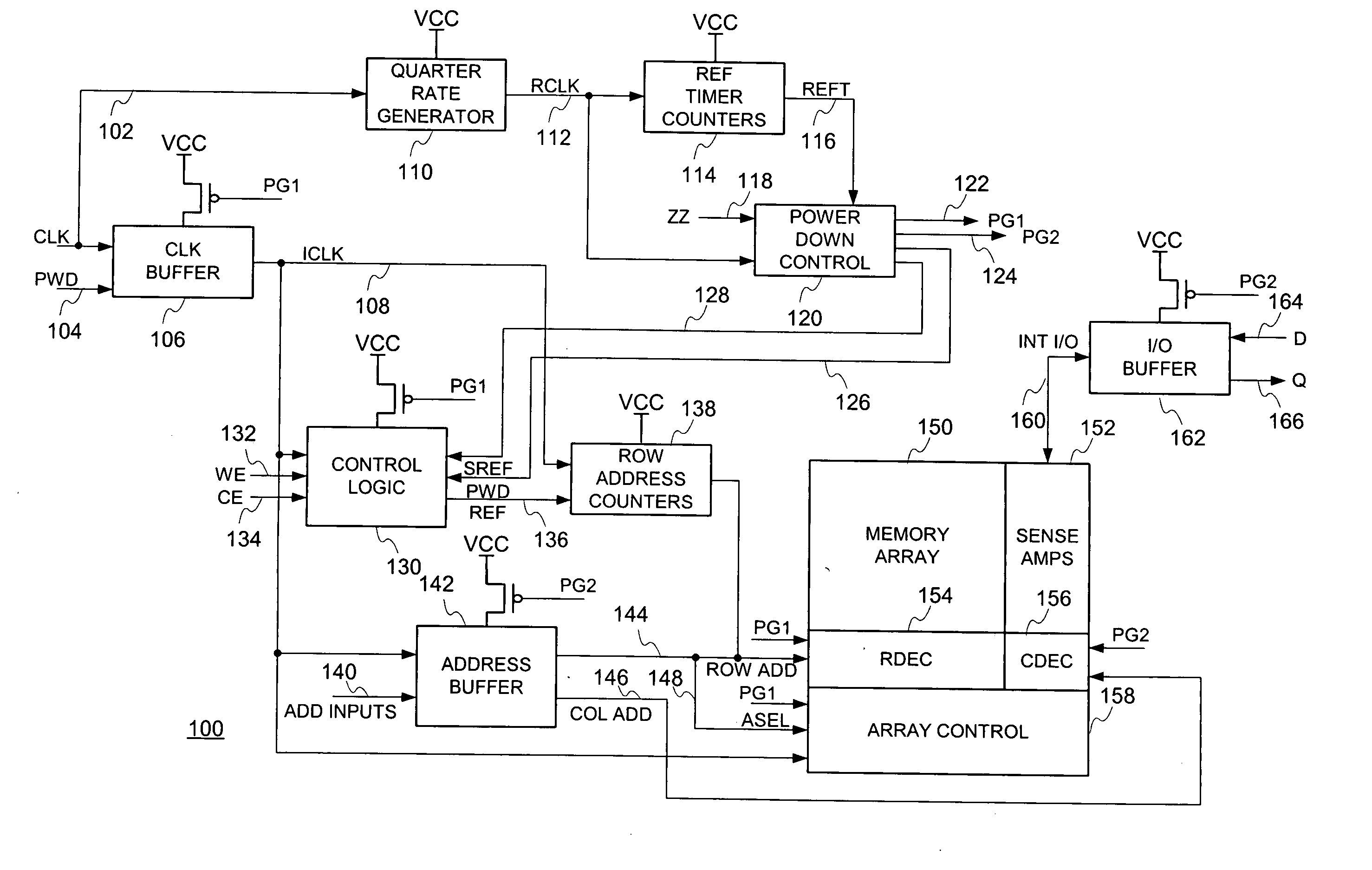
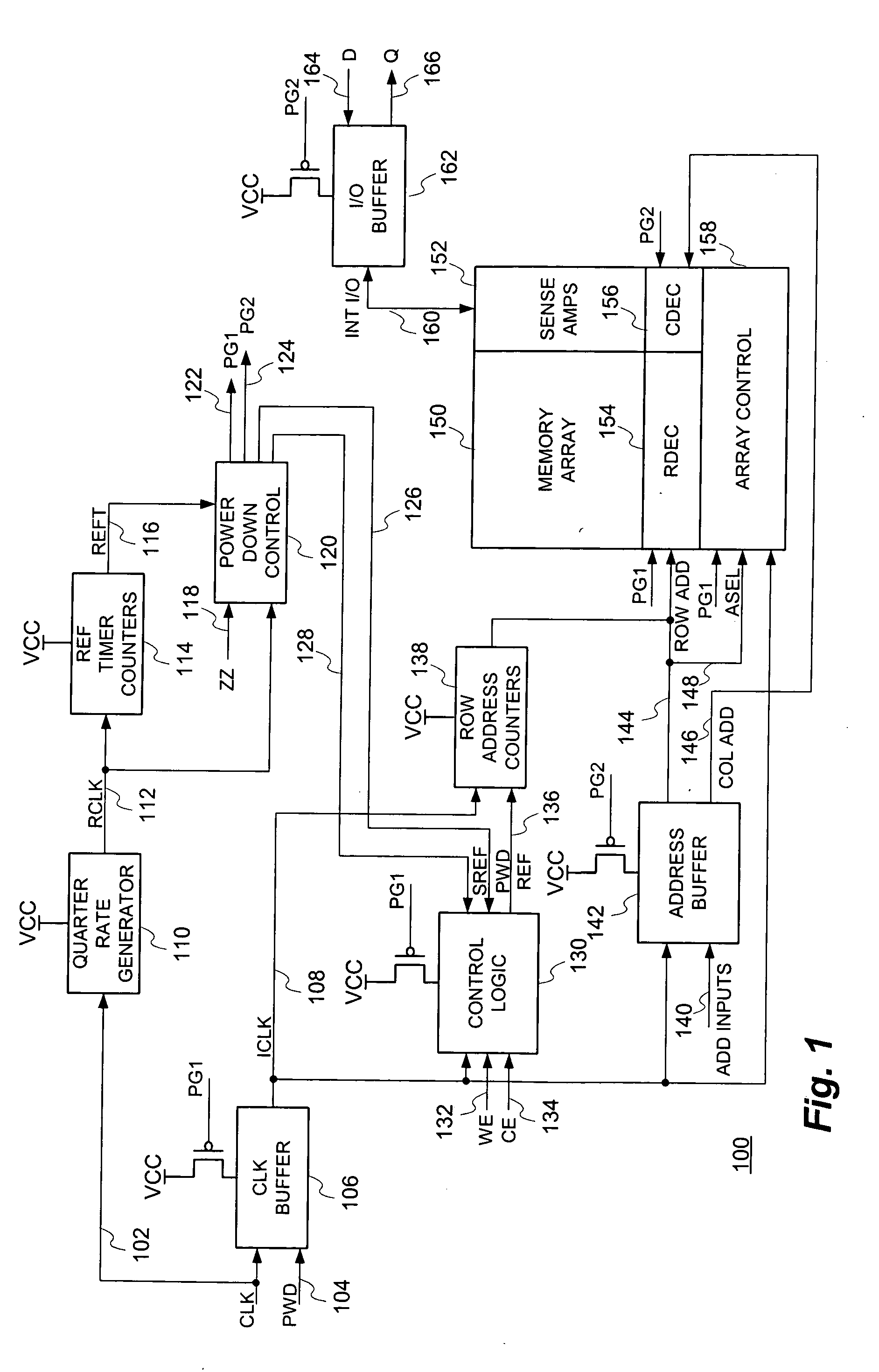
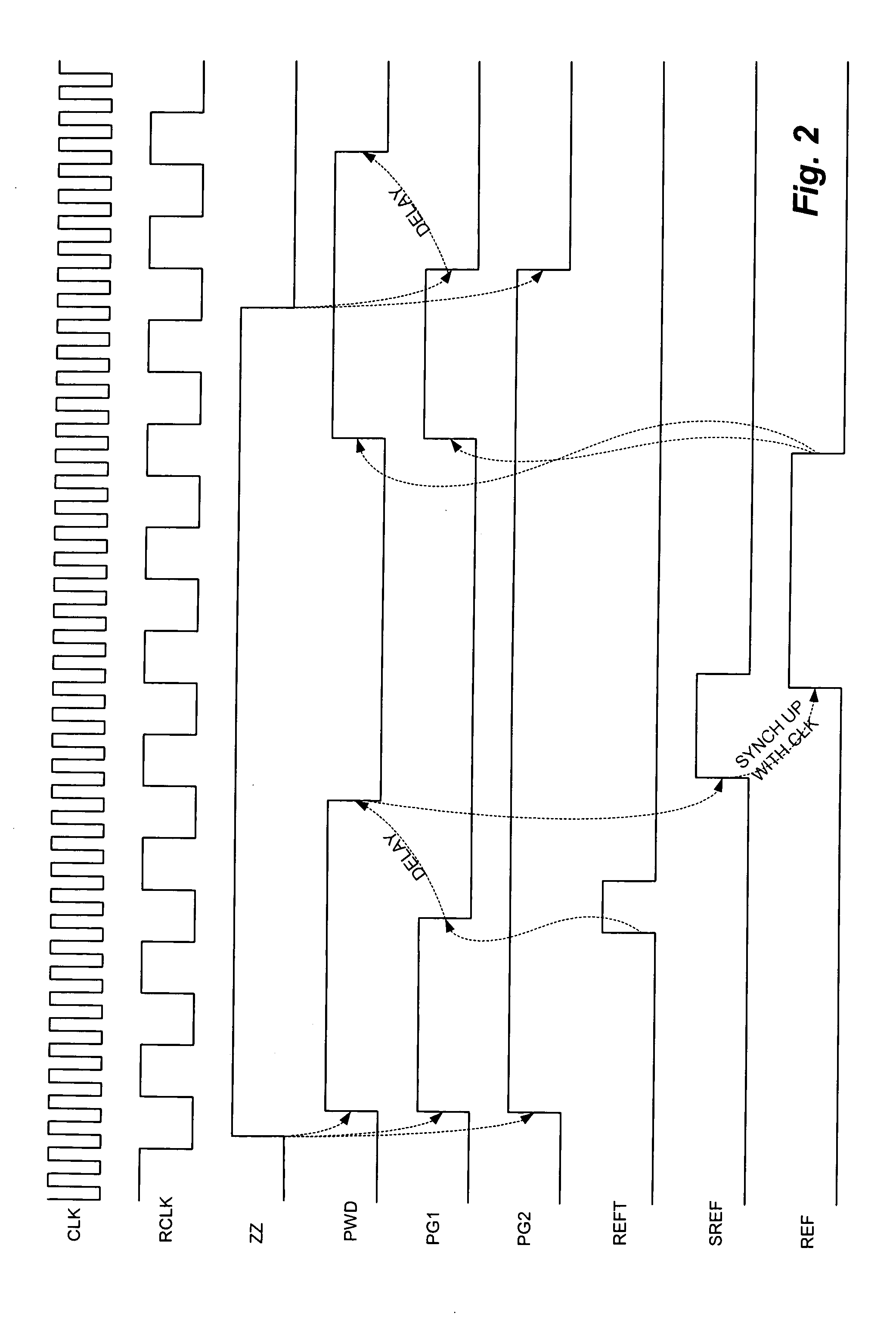
Low power sleep mode operation technique for dynamic random access memory (DRAM) devices and integrated circuit devices incorporating embedded DRAM
ActiveUS20050286339A1Reduces transistor leakageReduce leakageDigital storageHemt circuitsPower gating
A low power Sleep Mode operation technique for dynamic random access (DRAM) devices and integrated circuit devices incorporating embedded DRAM. By counting clock (CLK) cycles in accordance with the technique disclosed, refresh time (tREF) does not vary with all possible process corners, voltages and temperatures (PVT) since the clock signal exhibits a steady frequency over PVT applied to the DRAM and an internal timer placed on chip will vary directly with these parameters. After entering Sleep Mode, the main internal clock signal is inhibited from propagating around the device chip and, at this time, much of the associated circuitry can be power-gated to conserve power, typically with signals that have a boosted level to provide a negative gate-to-source voltage (VGS) on the power-gating transistors.
Owner:SONY CORP
PVT variation detection and compensation circuit
InactiveUS7495465B2Reliability increasing modificationsElectric signal transmission systemsComputer moduleEngineering
A compensation circuit and a method that compensates for process, voltage and temperature (PVT) variations in an integrated circuit that includes functional modules. The compensation circuit includes a signal generator, a first code generator, a second code generator, and a mapping module. The signal generator generates a first signal and a second signal depending on aligned process corner, voltage and temperature variations and skewed process corner variations respectively. The first code generator receives the first signal, and generates a first calibration code. The second code generator receives the second signal, and generates a second calibration code. The mapping module provides the first and second calibration codes for compensating for the aligned process corner, voltage and temperature variations and the skewed process corner variations associated with the functional modules respectively.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Multidimensional process corner derivation using surrogate based simultaneous yield analysis
A system and method for deriving semiconductor manufacturing process corners using surrogate simulations is disclosed. The method may be used to determine individual performance metric yields, the number of out-of-specification conditions for a given number of simulation samples, and a total yield prediction for simultaneous multi-variable conditions. A surrogate simulation model, such as a Response Surface Model, may be generated from circuit simulation data or parametric data measurements and may be executed using a large number of multi-variable sample points to determine process corners defining yield limits for a device. The model may also be used to simulate process shifts and exaggerated input ranges for critical device parameters. In some embodiments, the derived process corners may better represent physically possible worst-case process corners than traditional general-purpose process corners, and may address differences in process sensitivities for individual circuits of the device.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Self-calibrating relaxation oscillator based clock source
ActiveUS8085099B2Pulse automatic controlPulse generation by differential amplifiersClock rateEngineering
A technique and corresponding circuitry are presented for a process independent, self-calibrating relaxation based clock source. The technique and circuitry presented here can reduce the time and cost needed for calibration significantly. The relaxation based clock source produces a clock signal whose frequency is dependent upon a trim value. Starting from an initial trim value, the clock signal is generated, its frequency is compared with a reference clock frequency value, and the trim value is correspondingly adjusted up or down a bit at a time. After this process has continued for a while, min-max logic is used to determine the maximum and minimum trim values and, based on these, the final trim value for the clock is set. This calibration process can also be used to extract whether, and by how much, the implementation on silicon of a particular chip lies in the fast or slow process corners.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Gain bootstrap type C class reverser and application circuit thereof
InactiveCN101692603AChip footprint is smallReduce circuit complexityElectric pulse generator detailsAnalog to digital conversionSetting time
The invention discloses a gain bootstrap type C class reverser and an application circuit thereof. Based on a C class reverser 32 in the prior art, the gain bootstrap type C class reverser is additionally provided with micropower gain bootstrap modules 30 and 31 and bulk potential modulation modules 33 and 34, wherein the gain bootstrap modules 30 and 31 greatly improve the steady-state gain of the C class reverser under the condition of not losing the output swing or increasing the circuit power consumption significantly so as to improve the integral precision of a gain bootstrap type C class reverser-based pseudo-differential structure switched capacitor integrator and the analog-to-digital conversion precision of an analog-to-digital converter, and broaden the application range of the C class reverser; and the bulk potential modulation modules 33 and 34 make the steady-state characteristics (gain, bandwidth, static power consumption and the like) and the dynamic characteristics (slew rate, setting time, dynamic power consumption and the like) of the whole reverser consistent under the condition of different corners, and greatly improve the stability and the robustness of the application circuit of the gain bootstrap type C class reverser under the condition of not increasing the power consumption significantly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
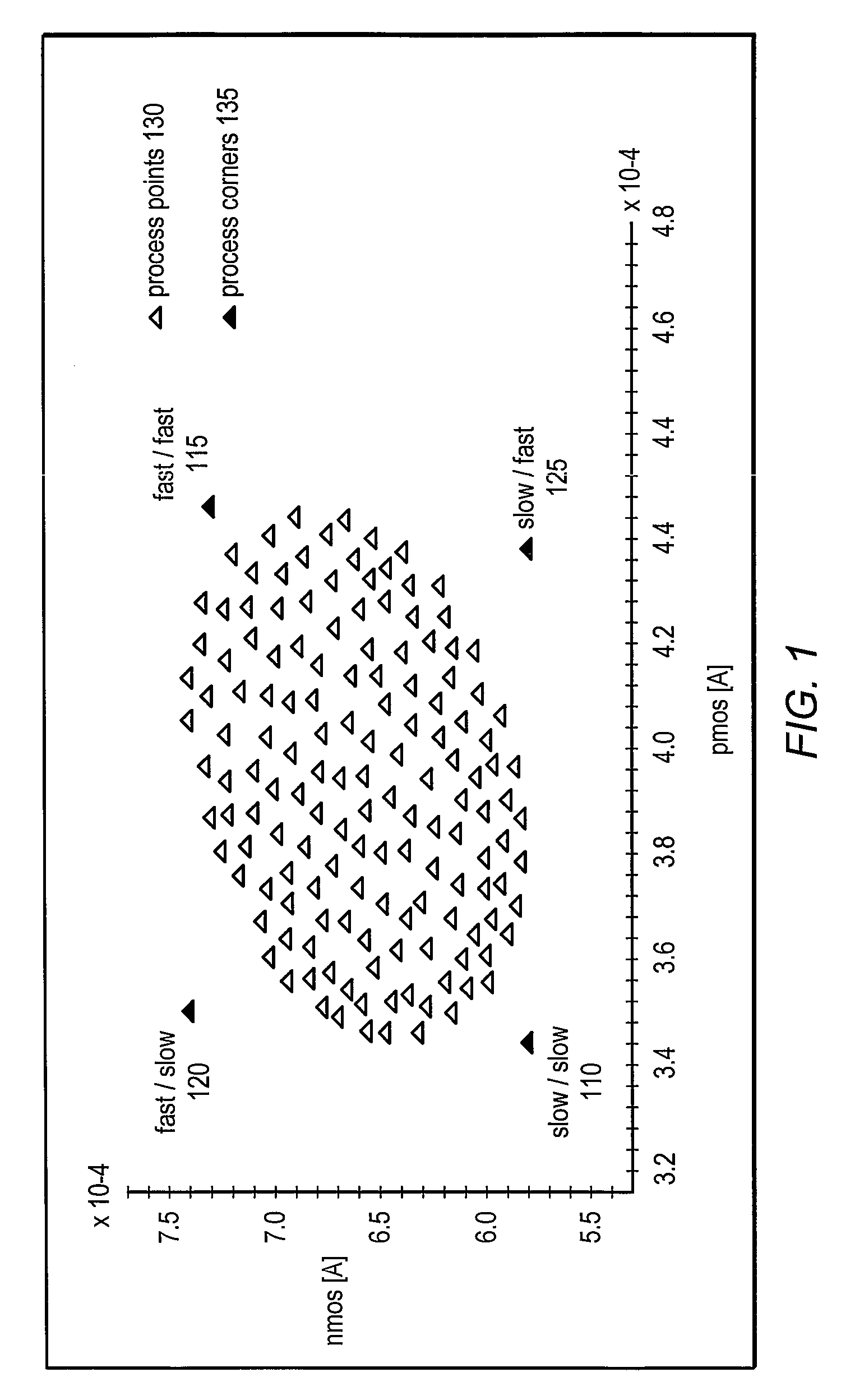
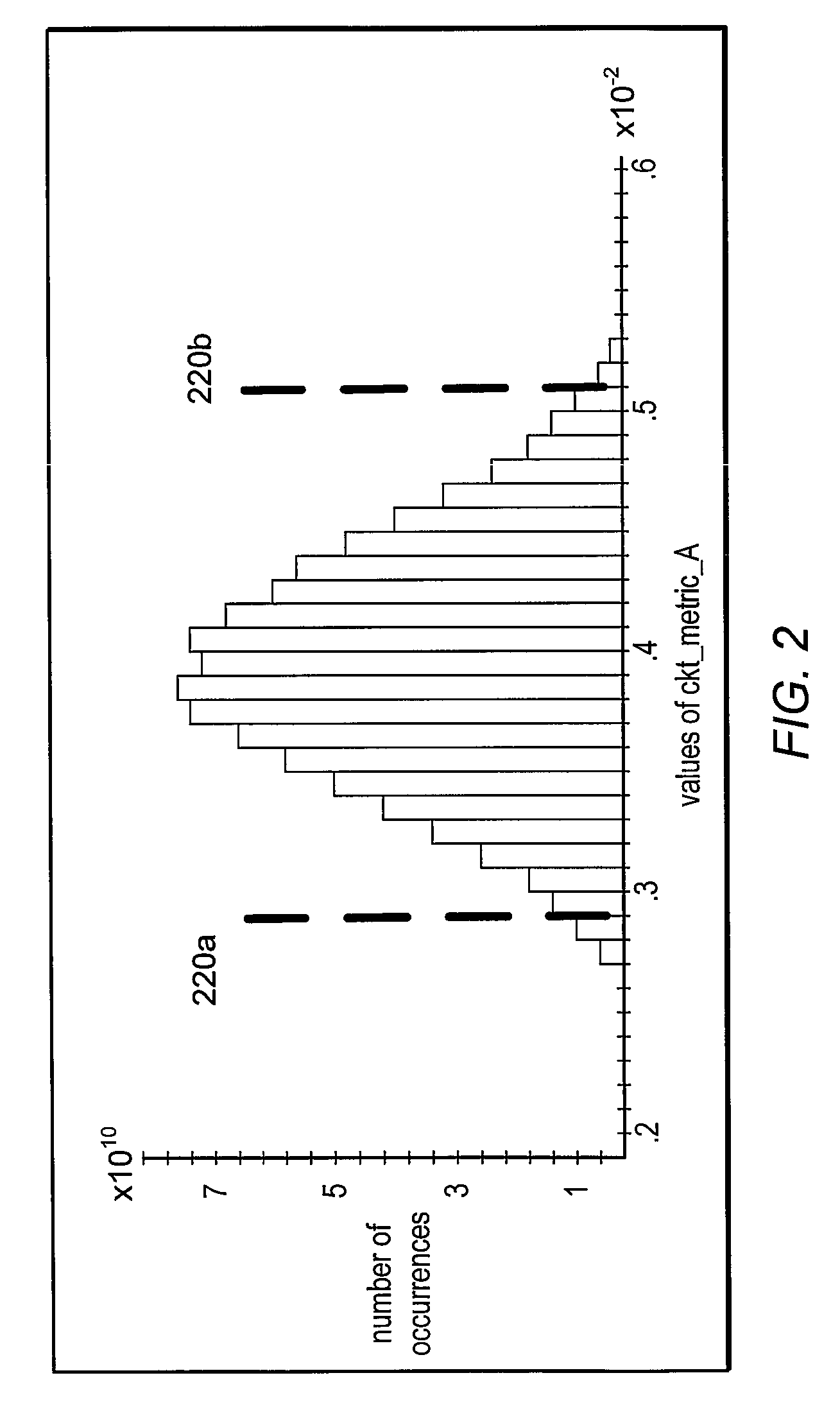
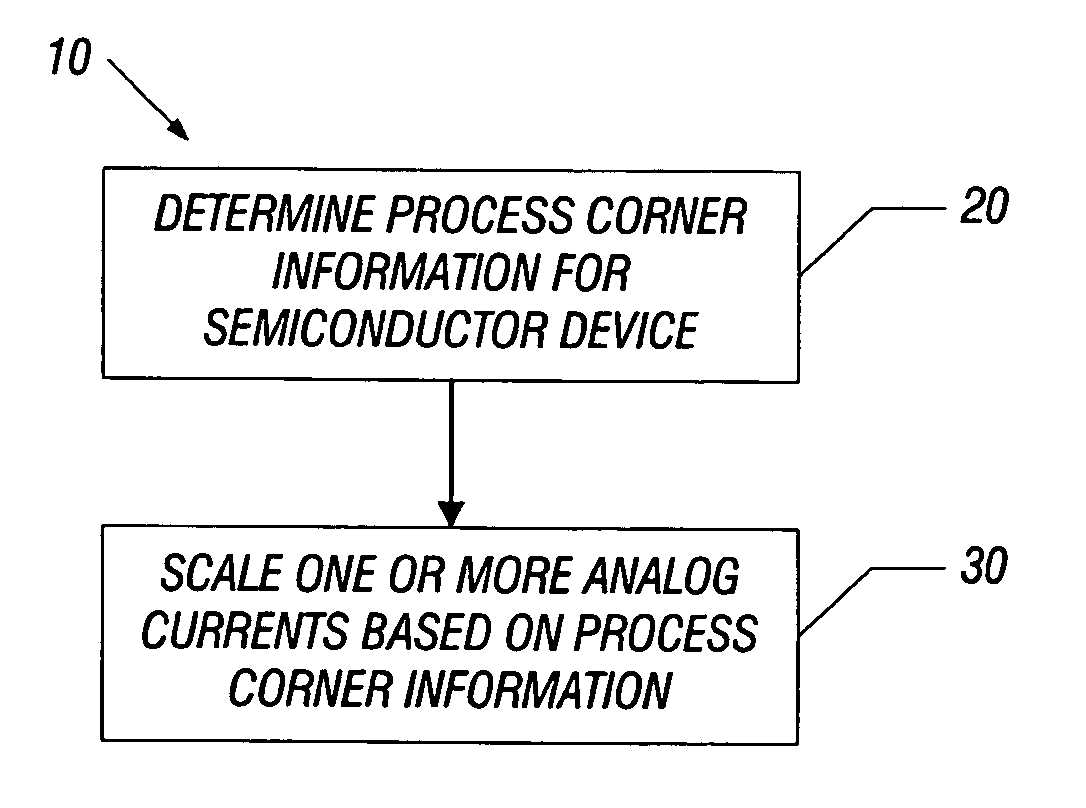
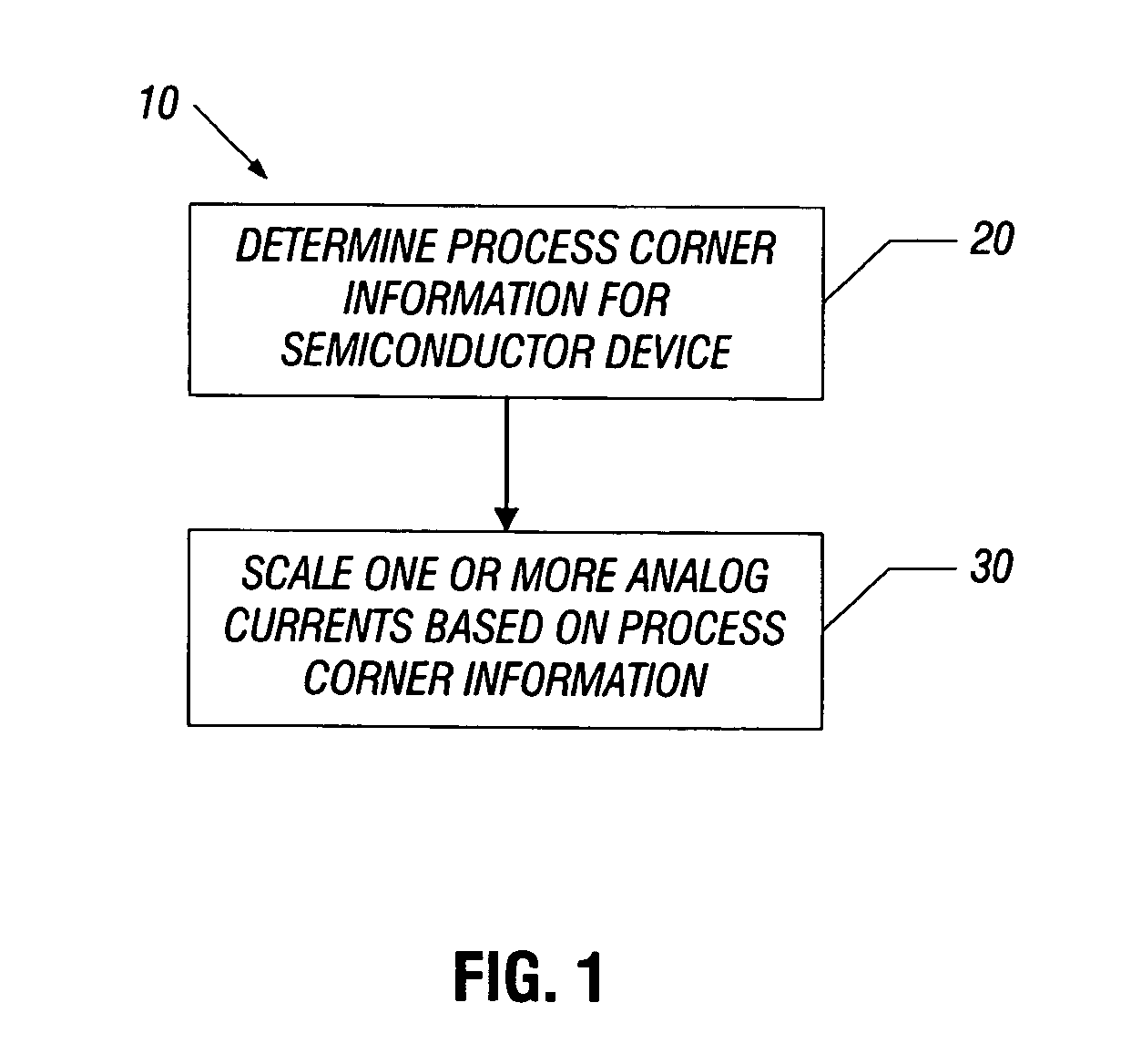
Reducing power dissipation using process corner information
InactiveUS20080076372A1Scale downIncrease currentPower consumption reductionTransmission monitoringCurrent consumptionEngineering
In one embodiment, the present invention includes a method for determining process corner information of an integrated circuit (IC) and controlling at least one analog current for at least one analog circuit of the IC based on the process corner information. More specifically, if the process corner information is indicative of a fast corner IC, the analog current may be scaled down. At the same time that the analog current is scaled down, a current consumption level of digital circuitry of the IC may increase. In this way, overall power consumption of the IC may be reduced to the extent that the analog current(s) are scaled.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Digital pulse width modulator based on digital delayed-locked loop (DLL)
The invention discloses a digital pulse width modulator based on a digital delayed-locked loop (DLL). The digital pulse width modulator comprises: a frequency division circuit, a DLL oscillation loop circuit, a reset signal generation circuit and a PWM output logic circuit. By using inputting a high frequency clock signal fs, the DLL oscillation loop triggers a oscillation loop to perform concussion outputting a 2 channel signal and then the signal is sent to the reset signal generation circuit. The reset signal generation circuit combines the input fs and a duty ratio command signal of mbits so as to generate a pulse signal PWM_clr. Under an effect of post-stage PWM output logic circuit, the PWM signal is generated so as to be taken as the output of the system. The DLL oscillation loop circuit uses a programmable delay unit (PDU) to real-timely track the input signal so that the effect of outputting a good pulse width modulation wave under different process corners and differentworking environments can be achieved. By using the digital pulse width modulator of the invention, areas needed by a chip can be minimized to a larger degree and costs of chip development can be saved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
System and method for providing hardware performance monitors for adaptive voltage scaling with a plurality of VT logic libraries
ActiveUS8010317B1Accurate scaleEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsPower controllerEngineering
A system and method is disclosed for providing a plurality of hardware performance monitors for adaptive voltage scaling in an integrated circuit system that comprises a plurality of threshold voltage VT logic libraries. Each hardware performance monitor is associated with one of the plurality of threshold voltage VT logic libraries and provides a signal that measures a performance of its respective threshold voltage VT logic library die temperature, process corner and supply voltage. The difference between the measured performance and a nominal expected performance for each hardware performance monitor is determined. The largest of the plurality of difference signals is selected and provided to an advanced power controller for use in providing adaptive voltage scaling for the integrated circuit system.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Method and apparatus for slew rate control
InactiveUS20070210832A1Small adjustmentPulse automatic controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFall timeControl signal
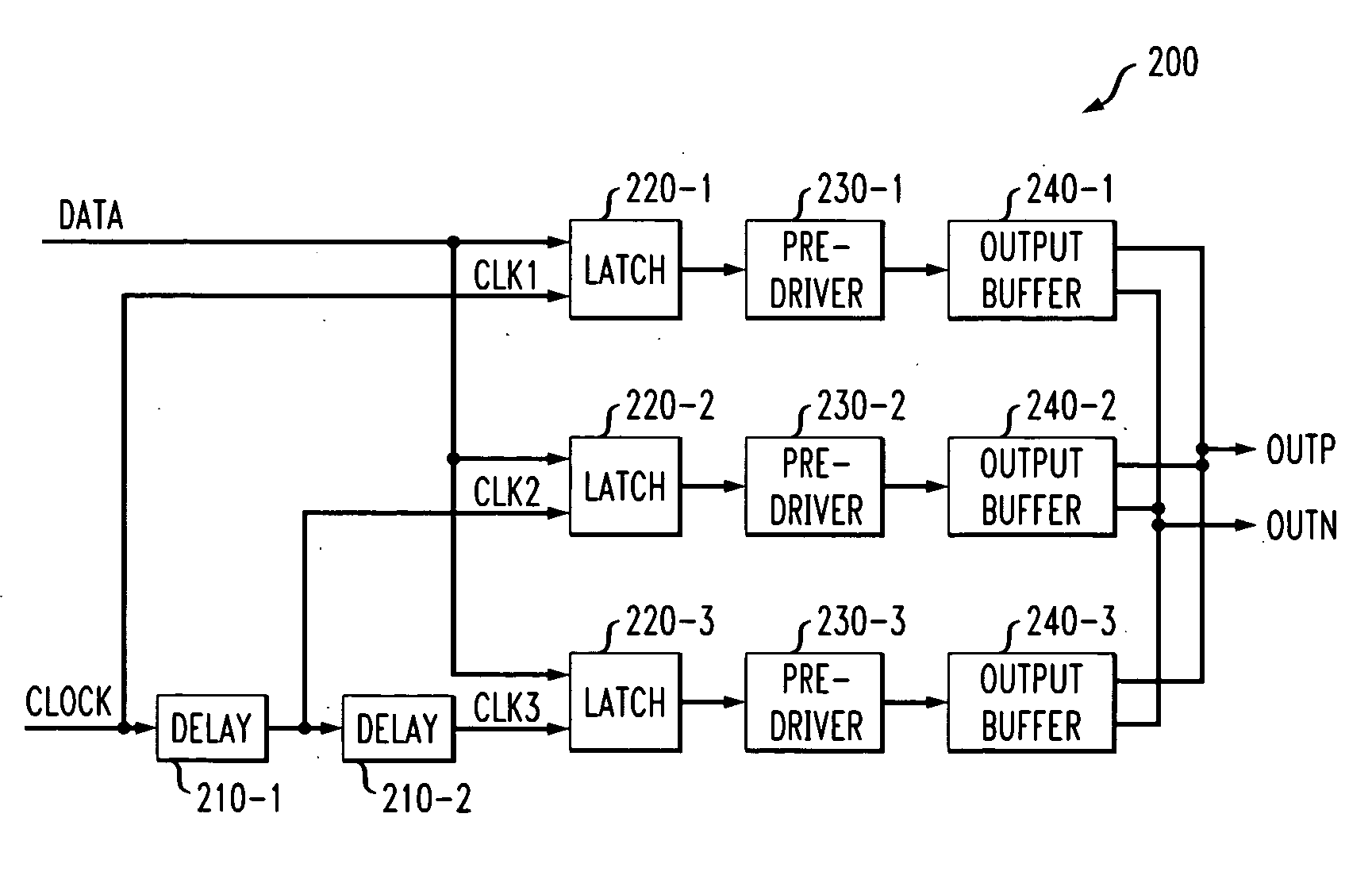
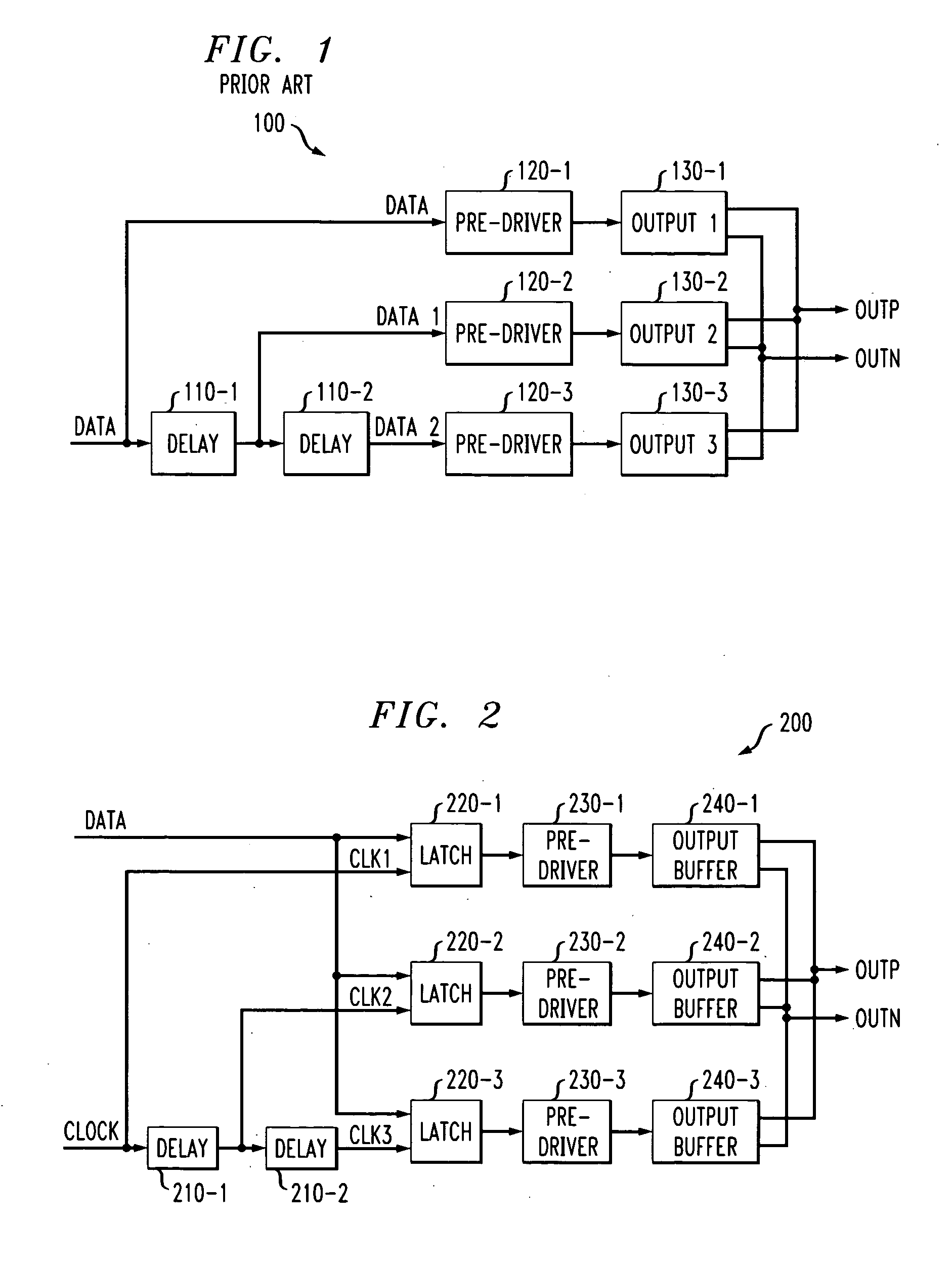
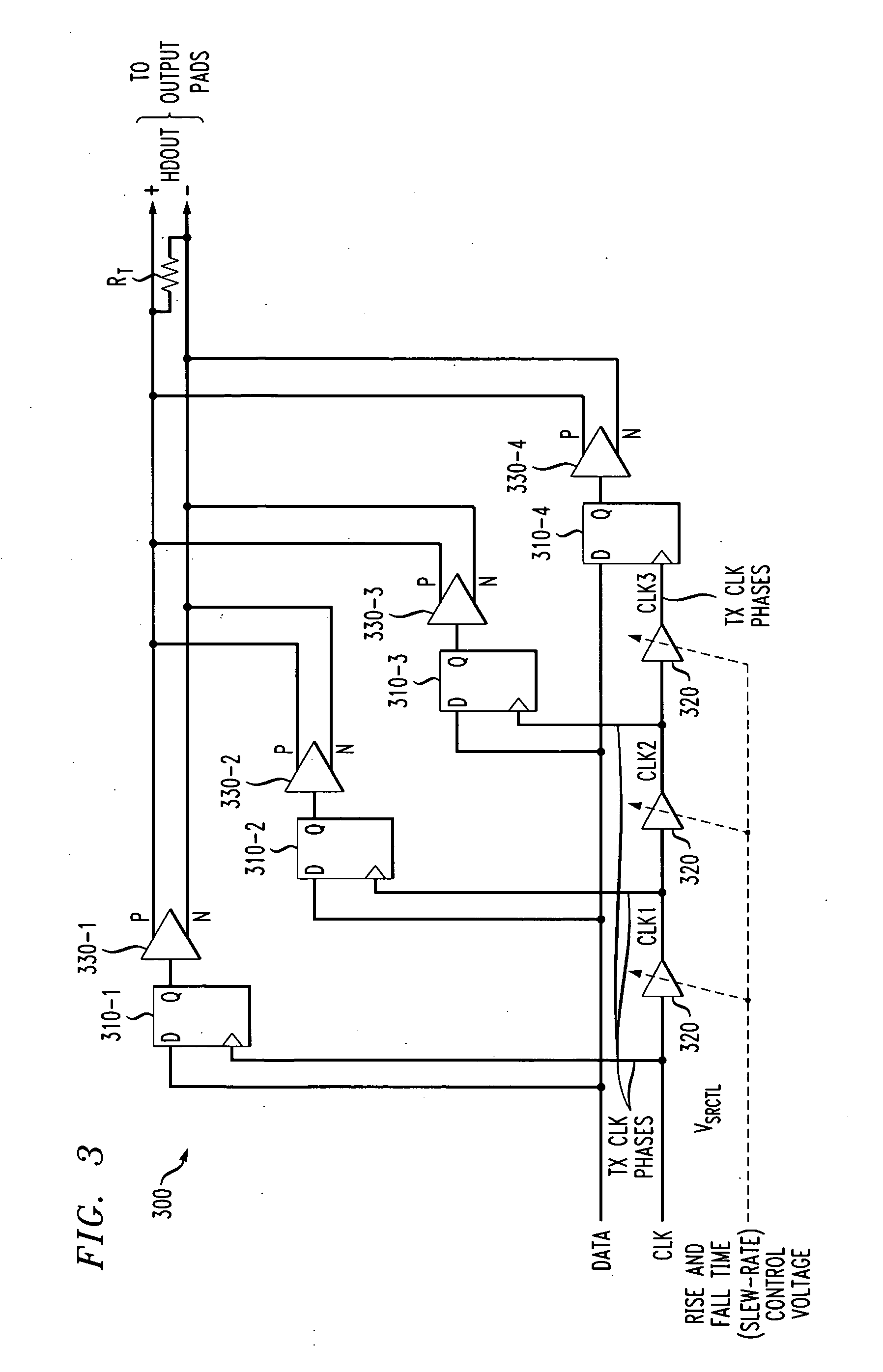
Methods and apparatus are provided for controlling at least one of a rise time and a fall time of a signal. A plurality of time shifted clock signals are generated; and a received data signal is sampled using a plurality of parallel data paths, where each of the data paths are controlled by a corresponding one of the plurality of time shifted clock signals. The plurality of time shifted clock signals can be generated, for example, by at least one delay element. The plurality of parallel data paths can be substantially identical and comprise, for example, at least one latch or at least one flip flop. Compensation can optionally be provided for variations in, for example, process corner, supply voltage, aging and operating temperature.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
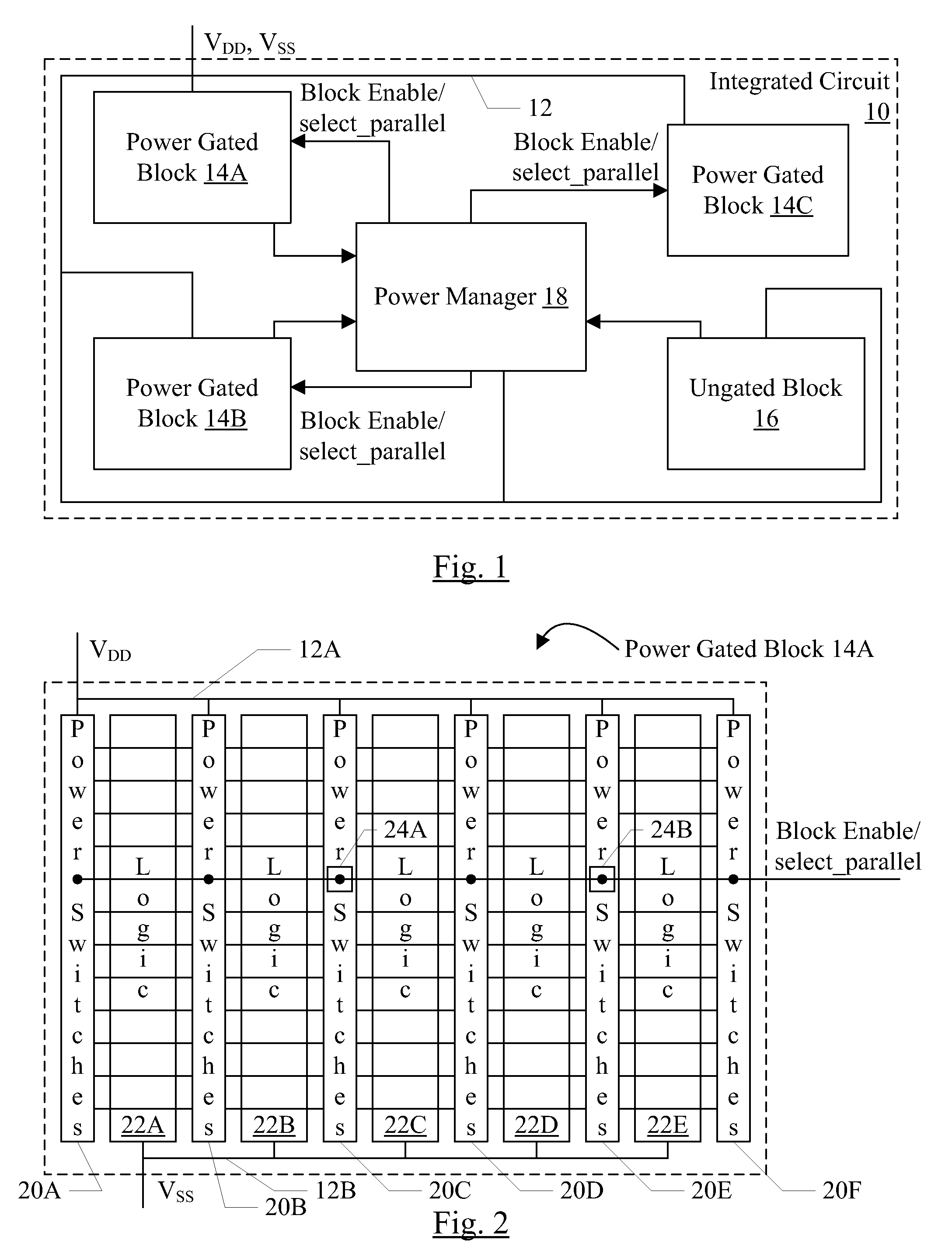
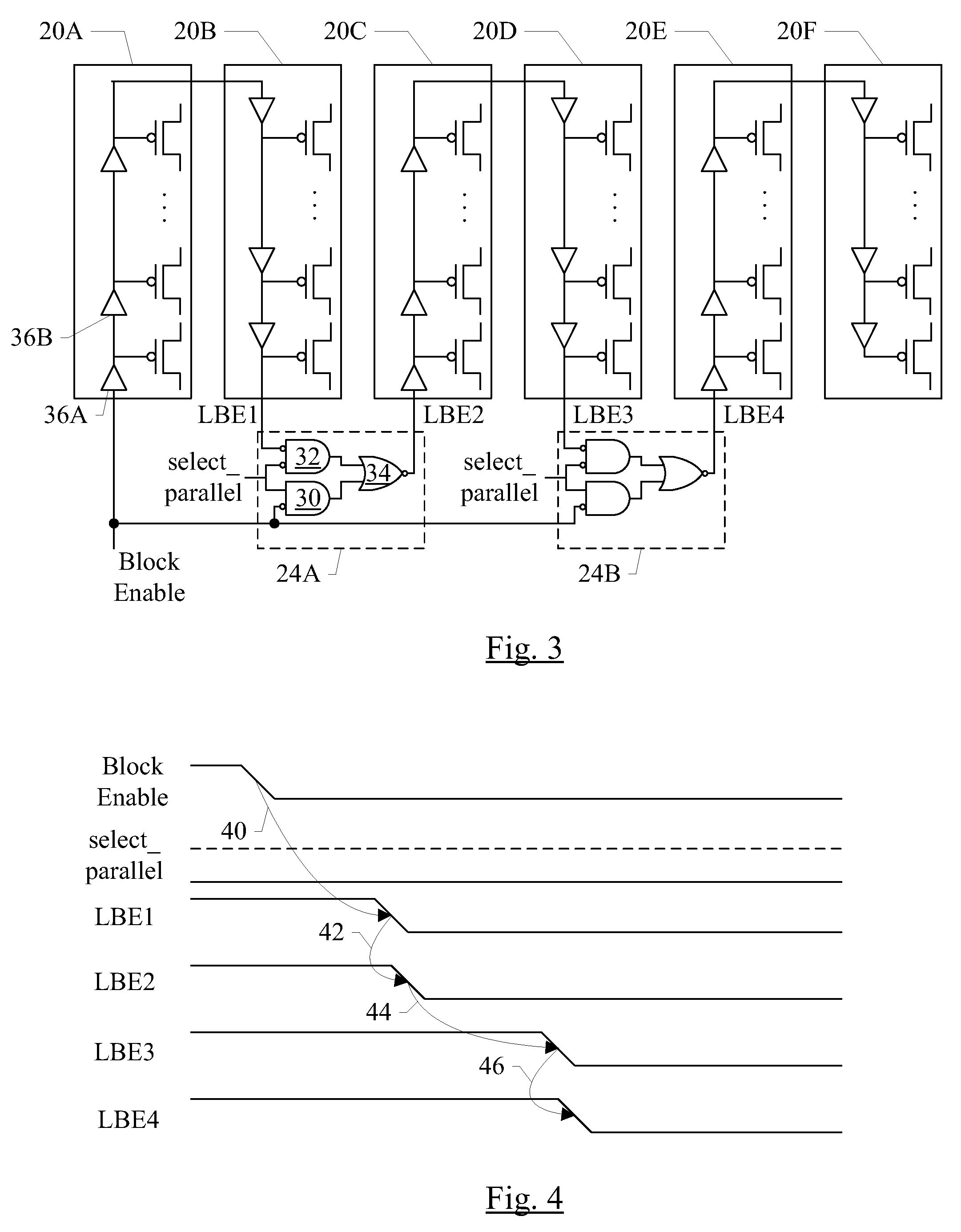
Power switch ramp rate control using programmable connection to switches
ActiveUS8421499B2Reliability increasing modificationsMajority/minority circuitsEngineeringPower gating
In an embodiment, an integrated circuit includes a power gated block and a power manager circuit. The power manager circuit is configured to provide a block enable signal and at least one select signal to the power gated block. The power manager may generate the select signal responsive to various parameters that affect the speed of the integrated circuit, such as power supply voltage magnitude, operating temperature, and / or process corner. The power gated block may control the rate at which power switches are enabled based on the select signal or signals. For example, the power switches may be enabled in a more parallel or more serial fashion and / or the drive strength of block enable buffering to the power switches may be varied. In another embodiment, the power manager circuit may assert multiple block enables to the power gated block (which are connected to separate sets of power switches), and may control the timing of assertion of the enables to control the rate at which power switches are enabled.
Owner:APPLE INC
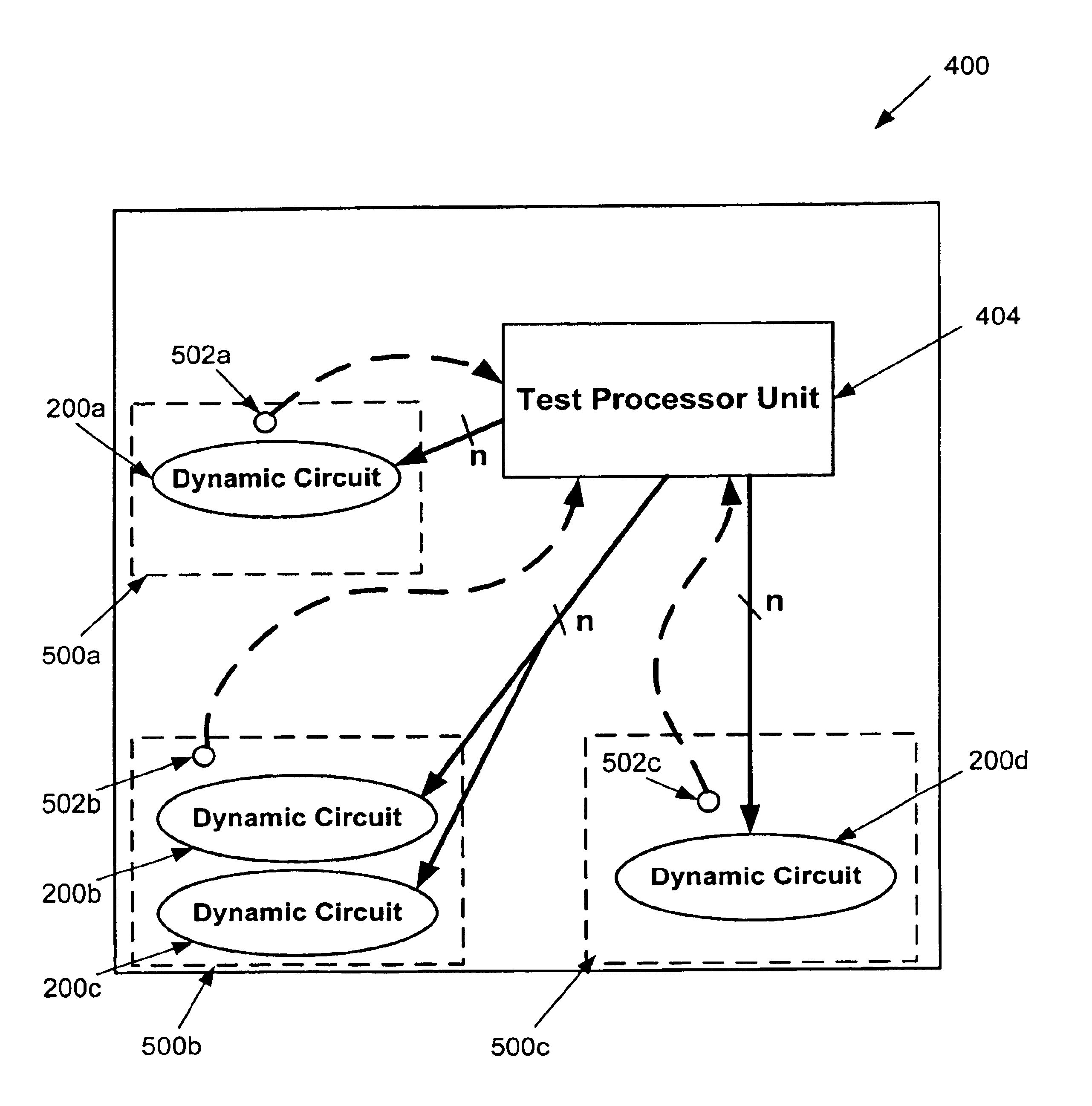
Process monitor based keeper scheme for dynamic circuits
An invention is disclosed for a process monitor based keeper scheme for dynamic circuits. A semiconductor die having a process monitor based keeper scheme of the embodiments of the present invention generally includes a plurality of dynamic circuits, each having an adaptive keeper circuit capable of being adjusted based on a bit code. In addition, a plurality of process monitors is included. Each process monitor is disposed within a corresponding die block, which defines a local area of the die. The process monitors are capable of detecting process corner data for the corresponding die block. In communication with each process monitor and the plurality of dynamic circuits is a test processor unit. The test processor unit obtains process corner data for each die block from the process monitor disposed within the die block, and provides a bit code based on the process corner data to the dynamic circuits disposed within the die block.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Self-timed write boost for SRAM cell with self mode control
A write boost circuit provides an automatic mode control for boost with different modalities with respect to the external supply voltage and also with respect to the extent of boost required at different process corners. The write boost circuit also takes care of the minimum boost provided to process corners with good writability where less boost is required. The boost is realized in terms of ground raising in the particular context and in general applicable to all other methods.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Structure and method for measuring electric property change of MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor) device
ActiveCN102157411ASemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementIndividual semiconductor device testingMOSFETField-effect transistor
The invention provides a structure for measuring electric property change of MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor) device, which comprises an active area, a grid electrode located on the active area, wherein the grid electrode is a resistor in Kelvin structure; two ends of the grid electrode have two polyresistor end points. The structure of the invention has the advantage that the influences of the grid length change, the gate oxide thickness change and the doping change to the MOSFET device are distinguished and determined; and the three process changes are the main factors of electrical fluctuations of device and are the primary parameters for building a monte carlo model and a corner mode of the device; the determination of the three process changes can lead the monte carlo model and the corner model to be more precise, which is quite important under the condition that the requirements on process corner models that is more than 90nm are higher and higher, and in favour of extracting a stress model of the device for placing numbers and distances of different virtual grid electrodes in more than 45nm of process. The invention further provides a method for measuring electric property change of MOSFET device.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT
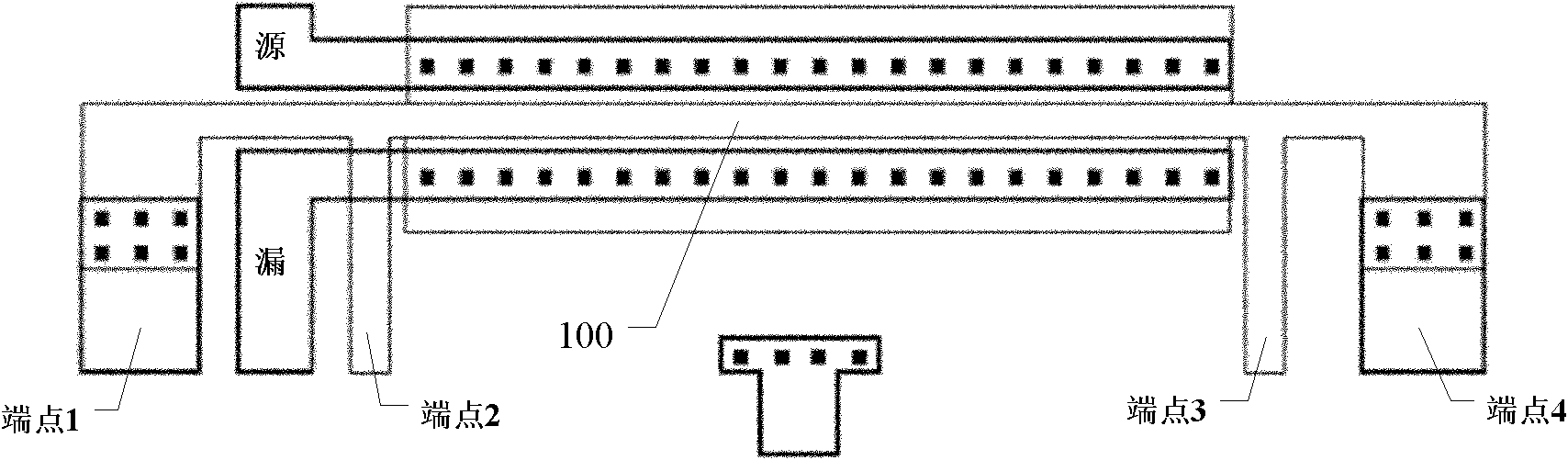
Method and apparatus for an automated input/output buffer information specification model generator
A method for automating input / output buffer information specification (IBIS) model generation. A wrapper utility combines components into an automated generation flow to model multiple input / output (I / O) buffers that conform to single-ended and differential I / O standards. Configuration data files are imported to properly configure the modeled I / O buffers according to a specific set of signal parameters across all process corners. Output and input termination impedance may also be modeled within the I / O buffer. A simulation setup file of the modeled I / O buffer is generated to determine the voltage / current (V / I) and voltage / time (V / T) data for the modeled I / O buffer for each process corner. A raw IBIS model is then created, formatted, and validated to determine the accuracy of the IBIS model. Execution steps of the IBIS model generator are then iterated to automatically generate, correlate, and compile IBIS models for each I / O standard into a single file.
Owner:XILINX INC
Controller for processing corner part in process path
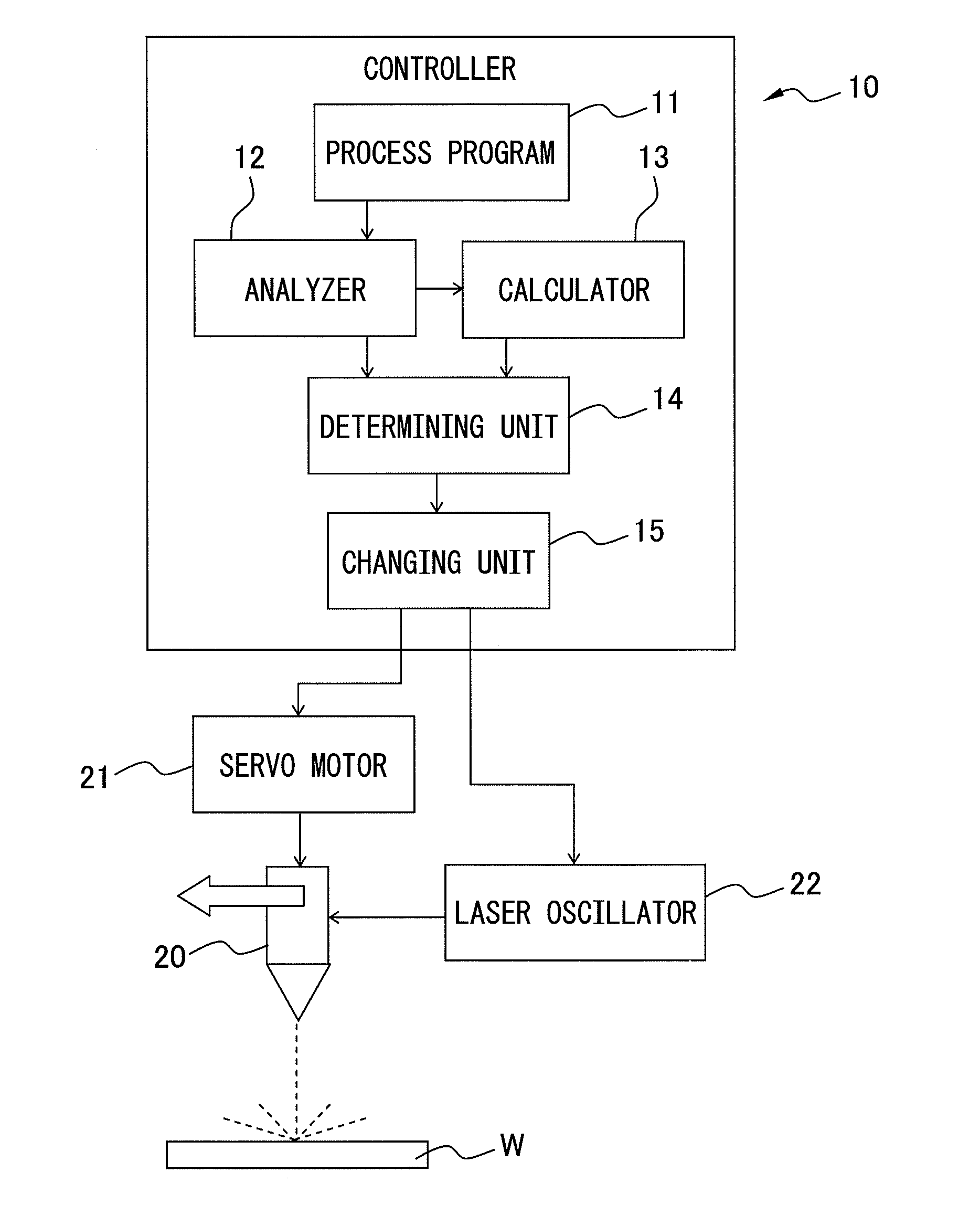
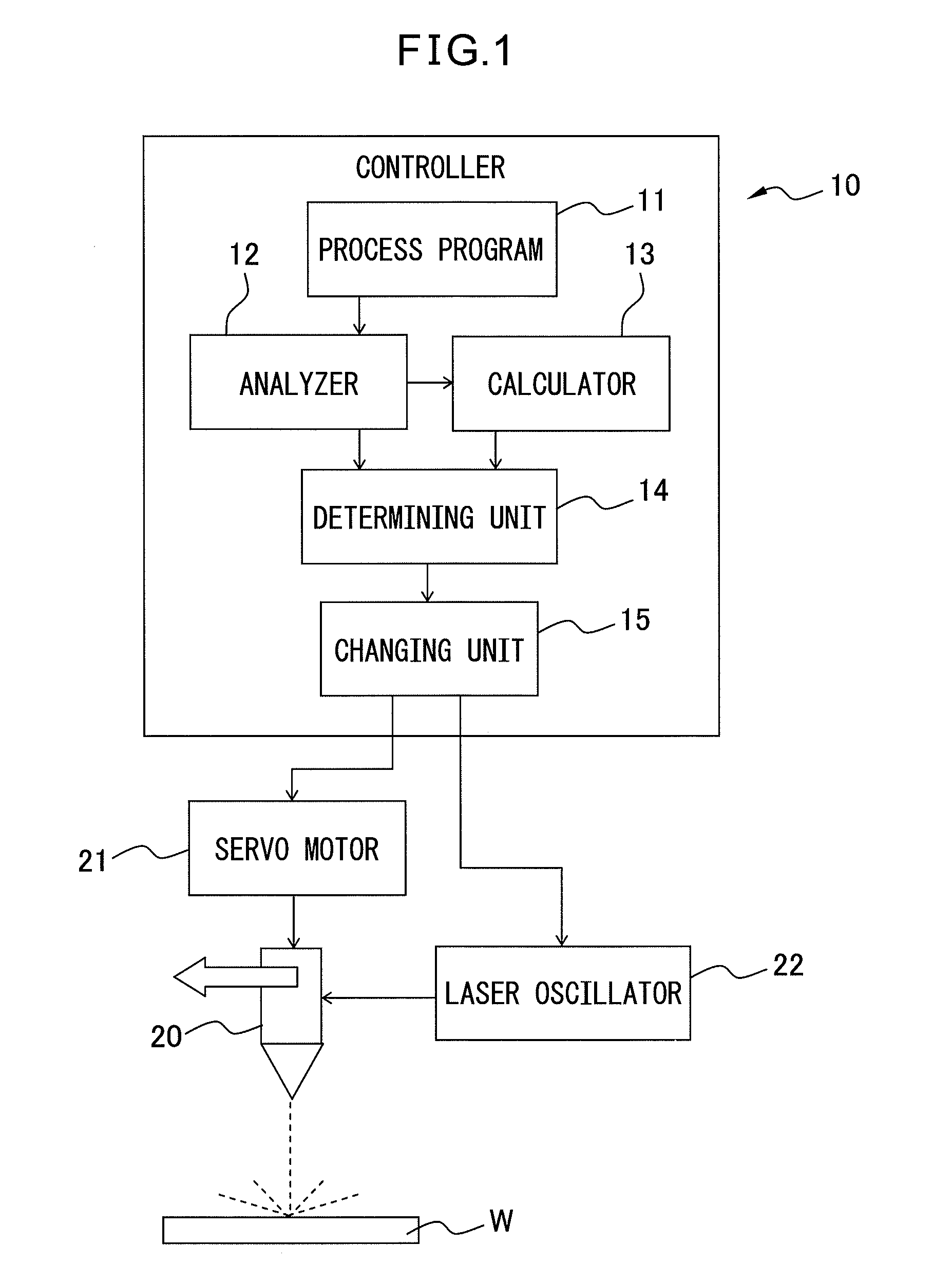
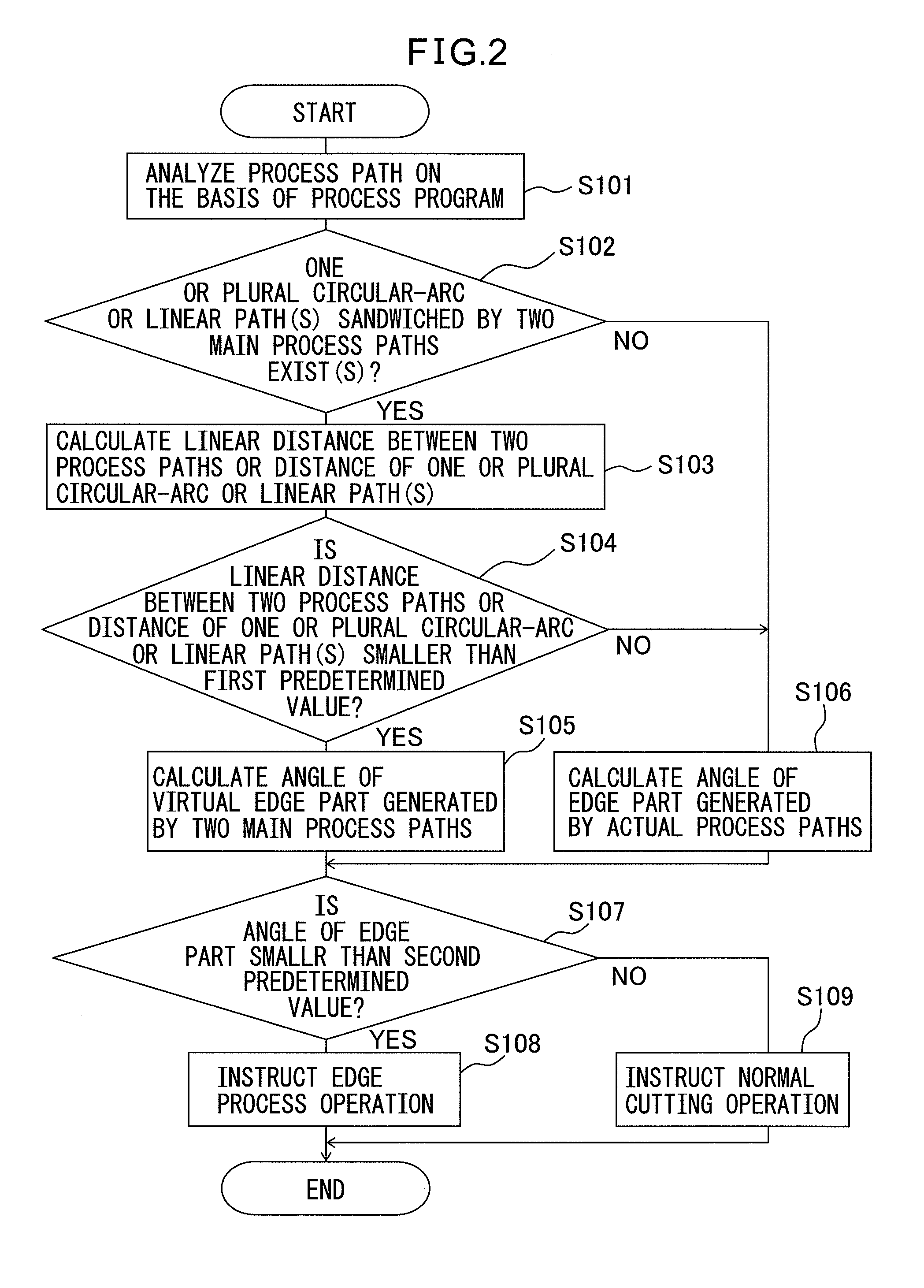
ActiveUS20130087536A1Precise processingAutomatic control devicesArc welding apparatusLaser processingEngineering
A controller (10) for controlling a process nozzle (20) and a laser oscillator (22) includes: an analyzer (12); a calculator (13) for calculating angle of a virtual corner part formed by two main process paths; a determining unit (14) for determining whether distance between the two main process paths corresponding to the circular-arc process path(s) is smaller than a first predetermined value, and determining whether the calculated angle is smaller than a second predetermined value; and a changing unit (15) for changing a laser process condition in the circular-arc process path(s) from a laser process condition in the main process paths when it is determined that the linear distance is smaller than the first predetermined value and the angle is smaller than the second predetermined value.
Owner:FANUC LTD
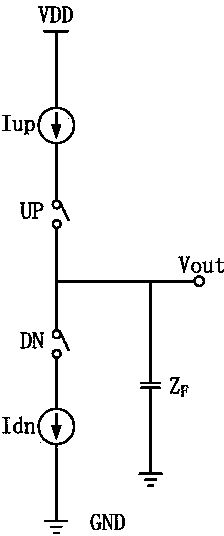
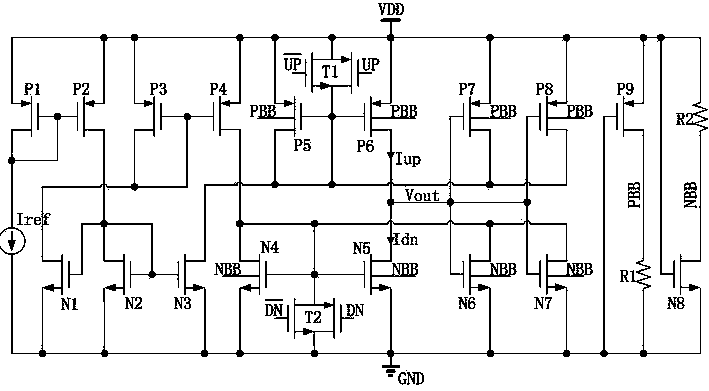
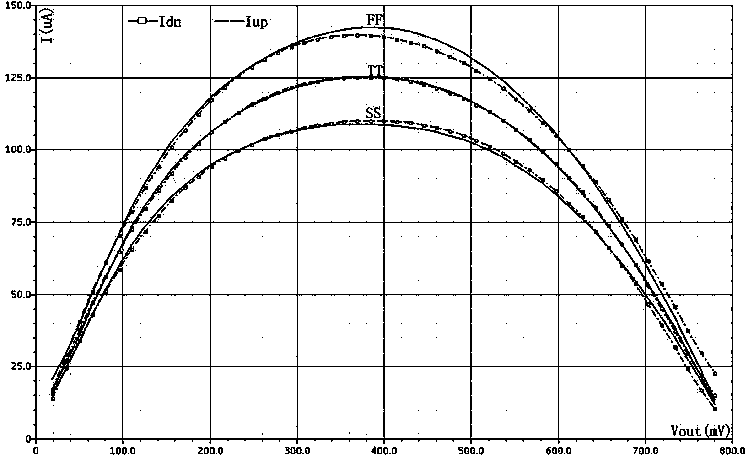
Low current mismatch charge pump circuit for resisting process fluctuation under low voltage of phase lock loop
ActiveCN104201880AAvoid mismatchMeet the output bandwidth requirementsApparatus without intermediate ac conversionLow voltageFeedback circuits
The invention discloses a low current mismatch charge pump circuit for resisting process fluctuation under low voltage of a phase lock loop. The low current mismatch charge pump circuit for resisting the process fluctuation under the low voltage of the phase lock loop comprises a current mirror composed of PMOS devices P1, P2, P3 and P4 and NMOS devices N1, N2 and N3, a charging circuit composed of PMOS devices P5 and P6 and a transmission gate T1, a discharging circuit composed of NMOS devices N4 and N5 and a transmission gate T2, a feedback circuit composed of PMOS devices P7 and P8 and NMOS devices N6 and N7, and a body bias circuit composed of a PMOS device P9, an NMOS device N8 and polycrystalline silicon resistors R1 and R2. The low current mismatch charge pump circuit for resisting the process fluctuation under the low voltage of the phase lock loop can guarantee a voltage output range of a charge pump under low power supply voltage by controlling grid electrodes of charging and discharging current pipes through the transmission gates. The low current mismatch charge pump circuit for resisting the process fluctuation under the low voltage of the phase lock loop performs feedback regulation through MOS pipes different in threshold value, guarantees good match of charging and discharging currents, introduces the body bias circuit, and reduces influences from fluctuation of process corners on performance of the charge pump.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com