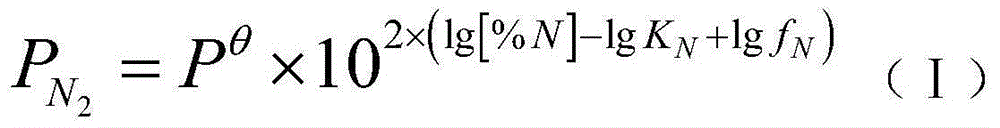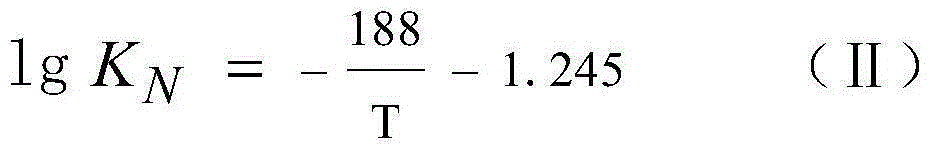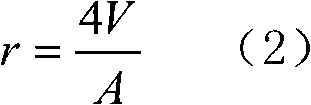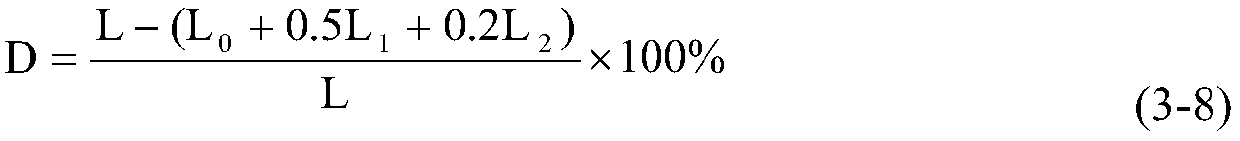Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Nitrogen partial pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
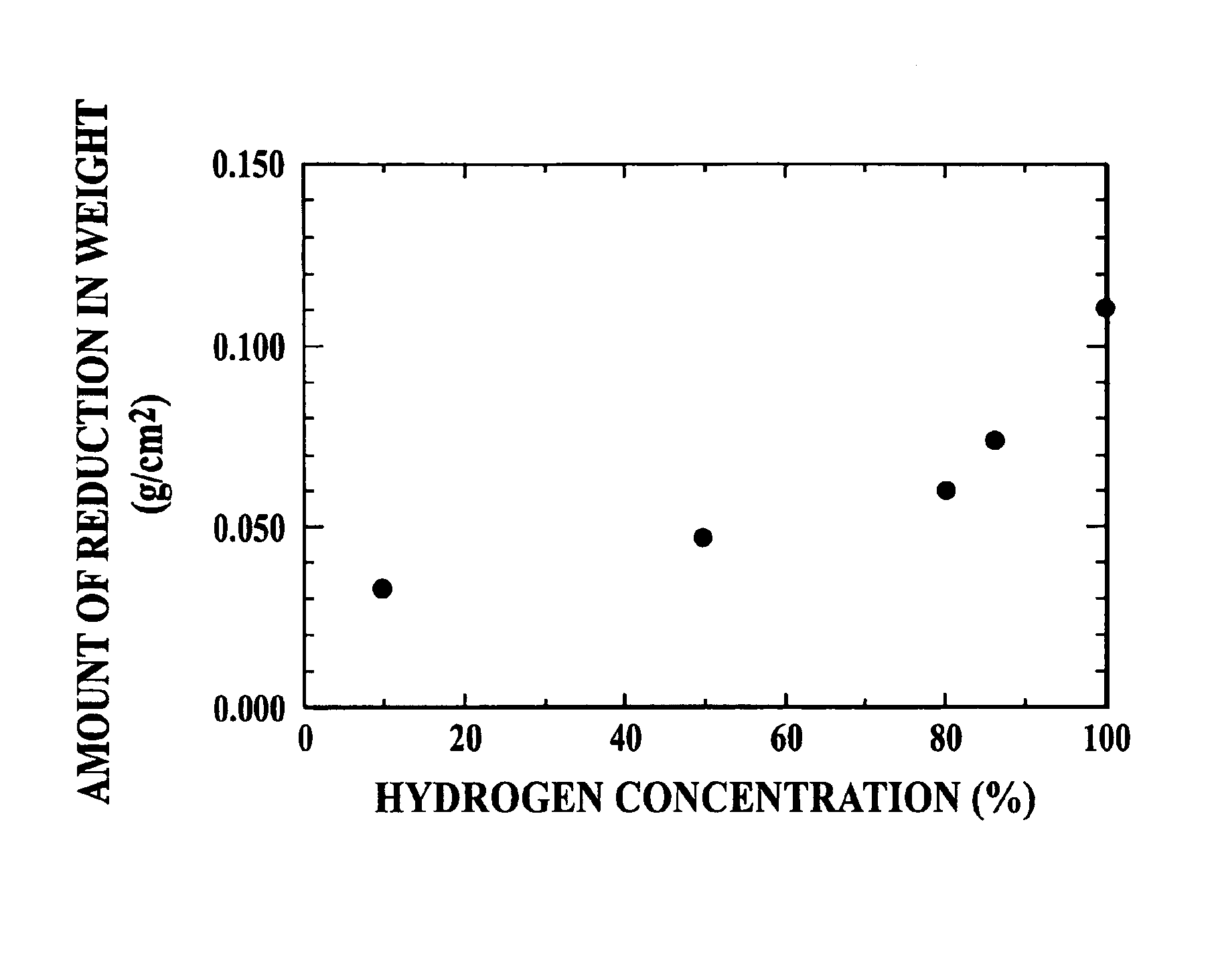
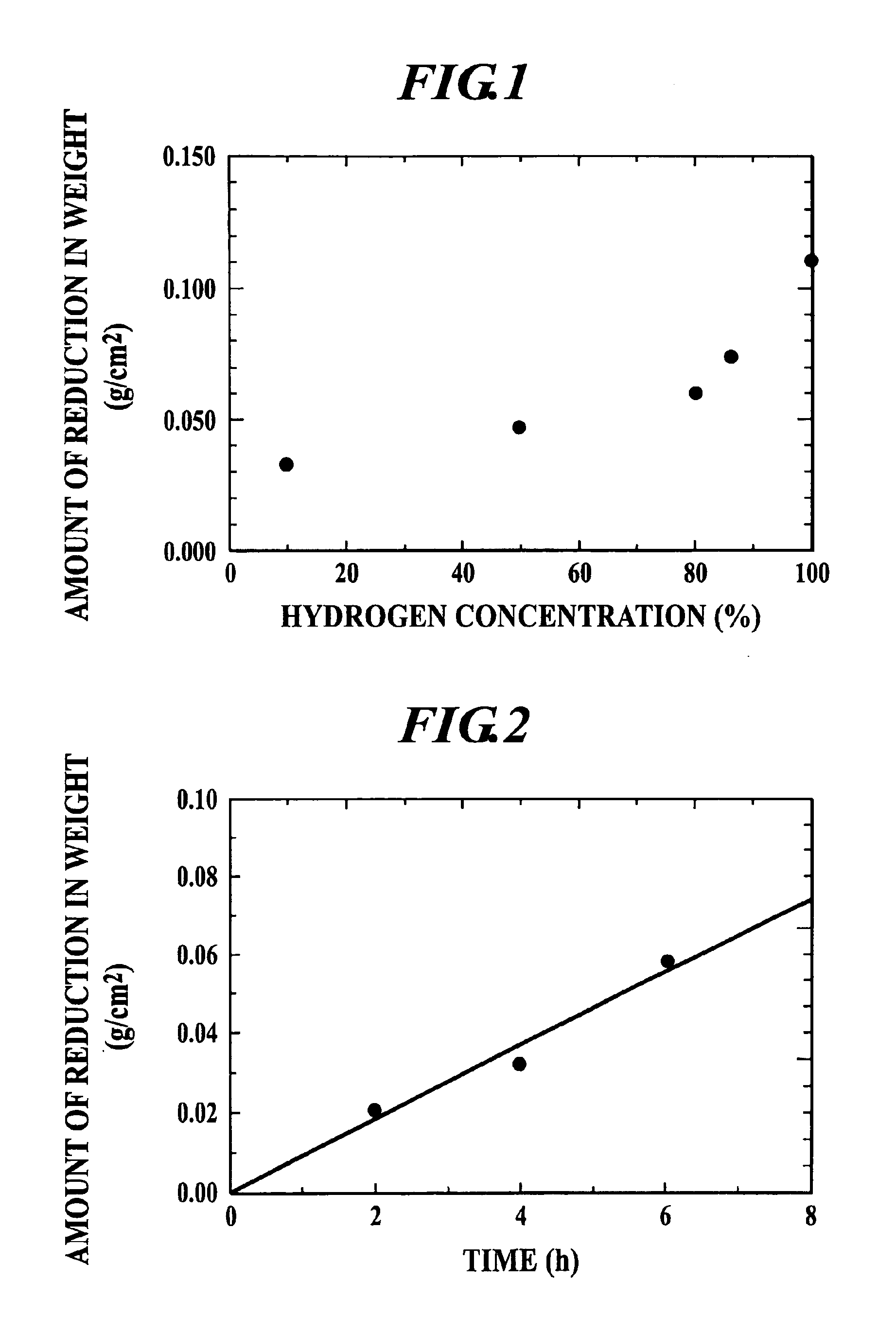
As a result, the total pressure in the container will be equal to the sums of the partial pressures of both components. Using Boyle’s law, the partial pressure of nitrogen is 0.288 atm and the partial pressure of oxygen is 0.769 atm. When you add them together, the total pressure in the apparatus is 1.057 atm.
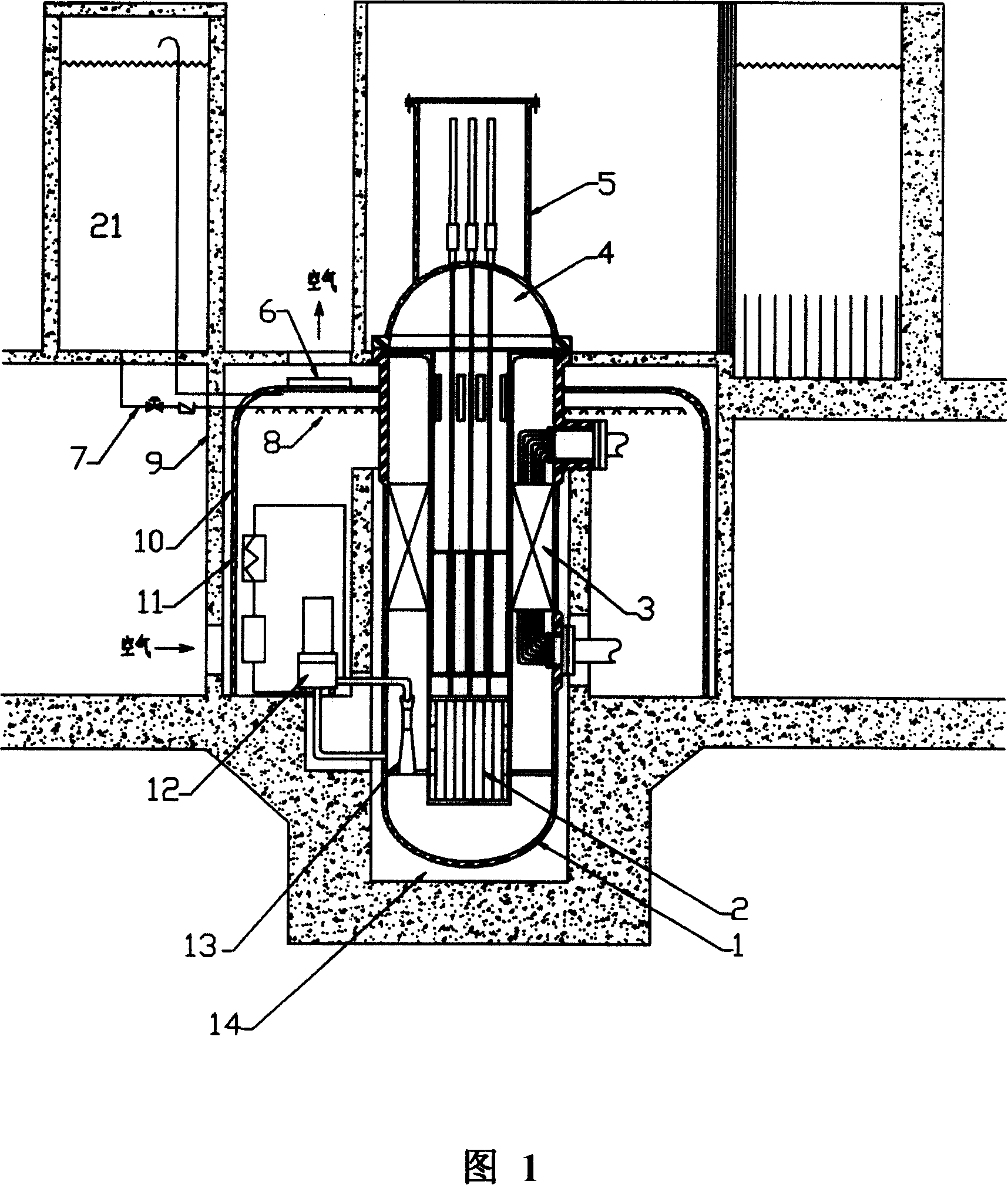
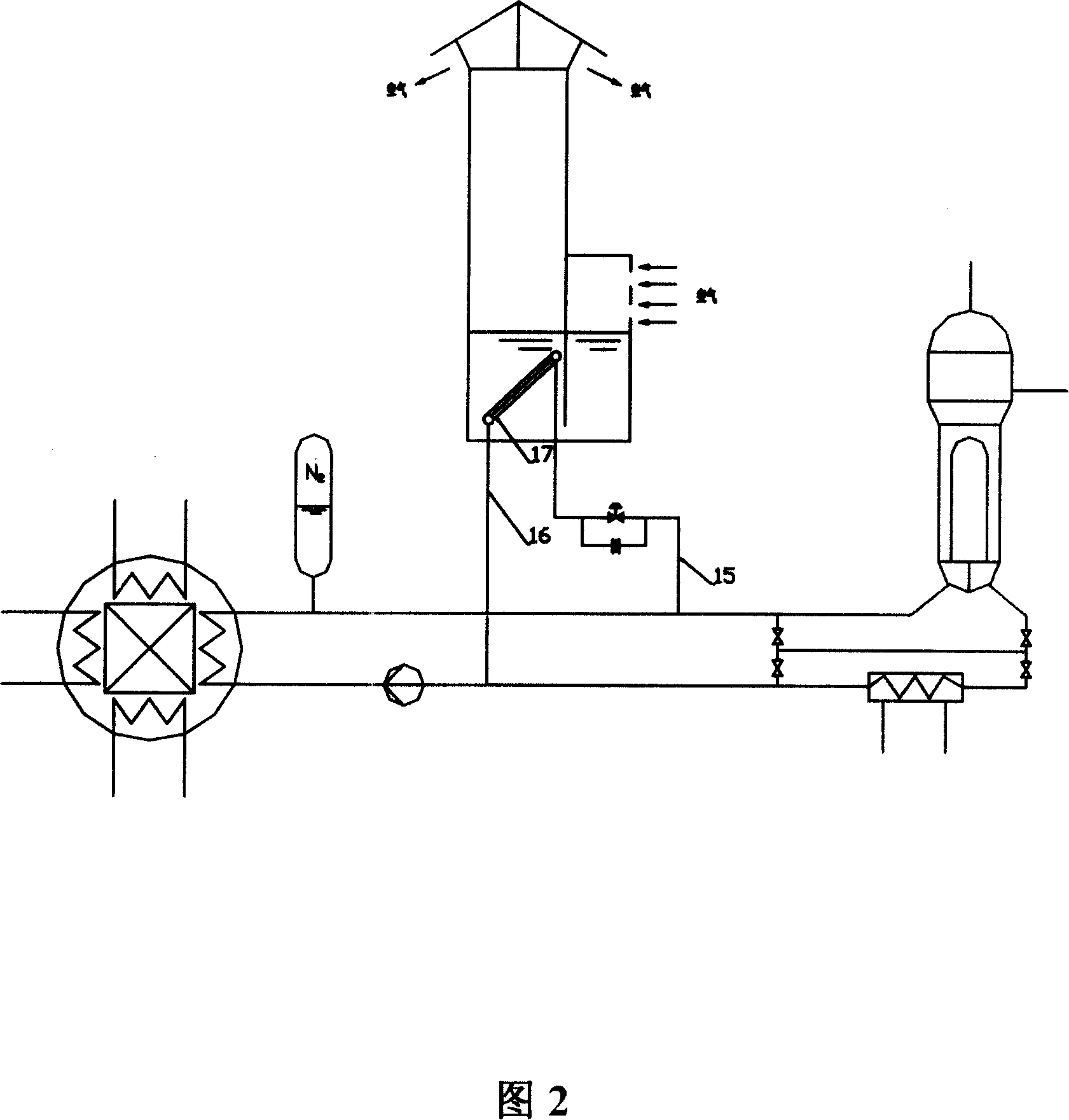
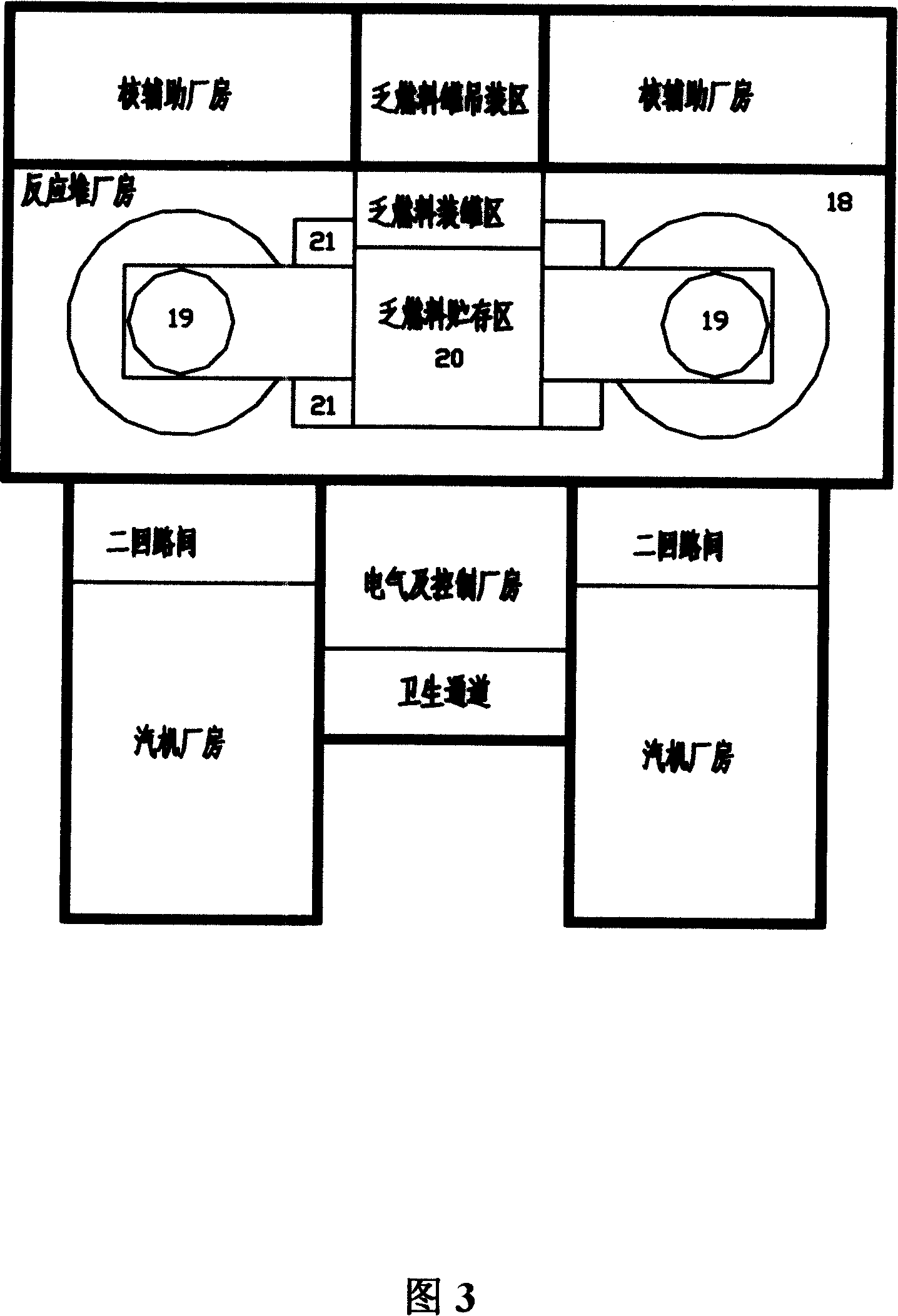
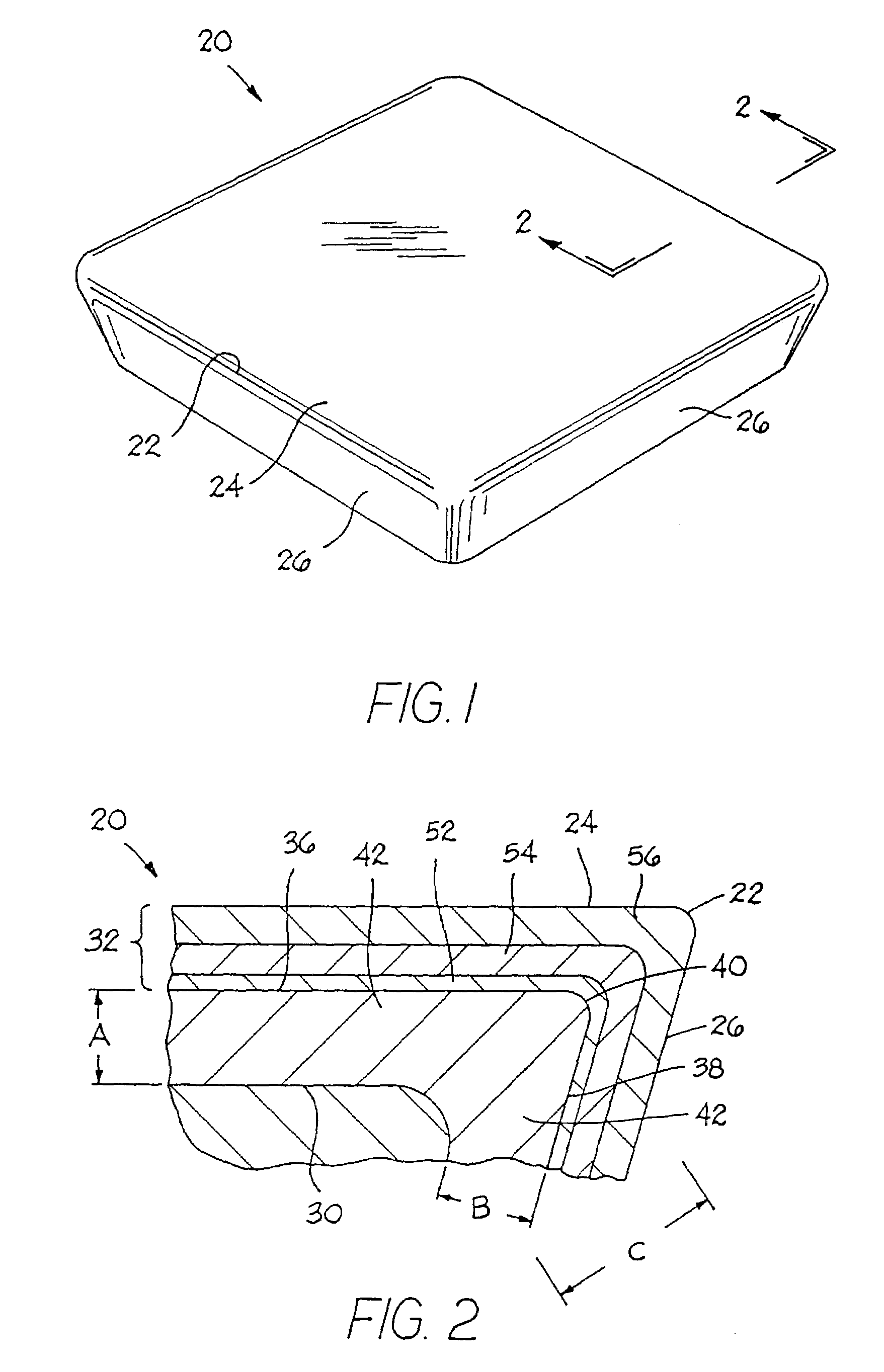
Integrated low-temperature nuclear heat supplying pile
ActiveCN101154472ASmall sizeCompact layoutIntegral reactorsNuclear energy generationReactor pressure vesselPressurized water reactor
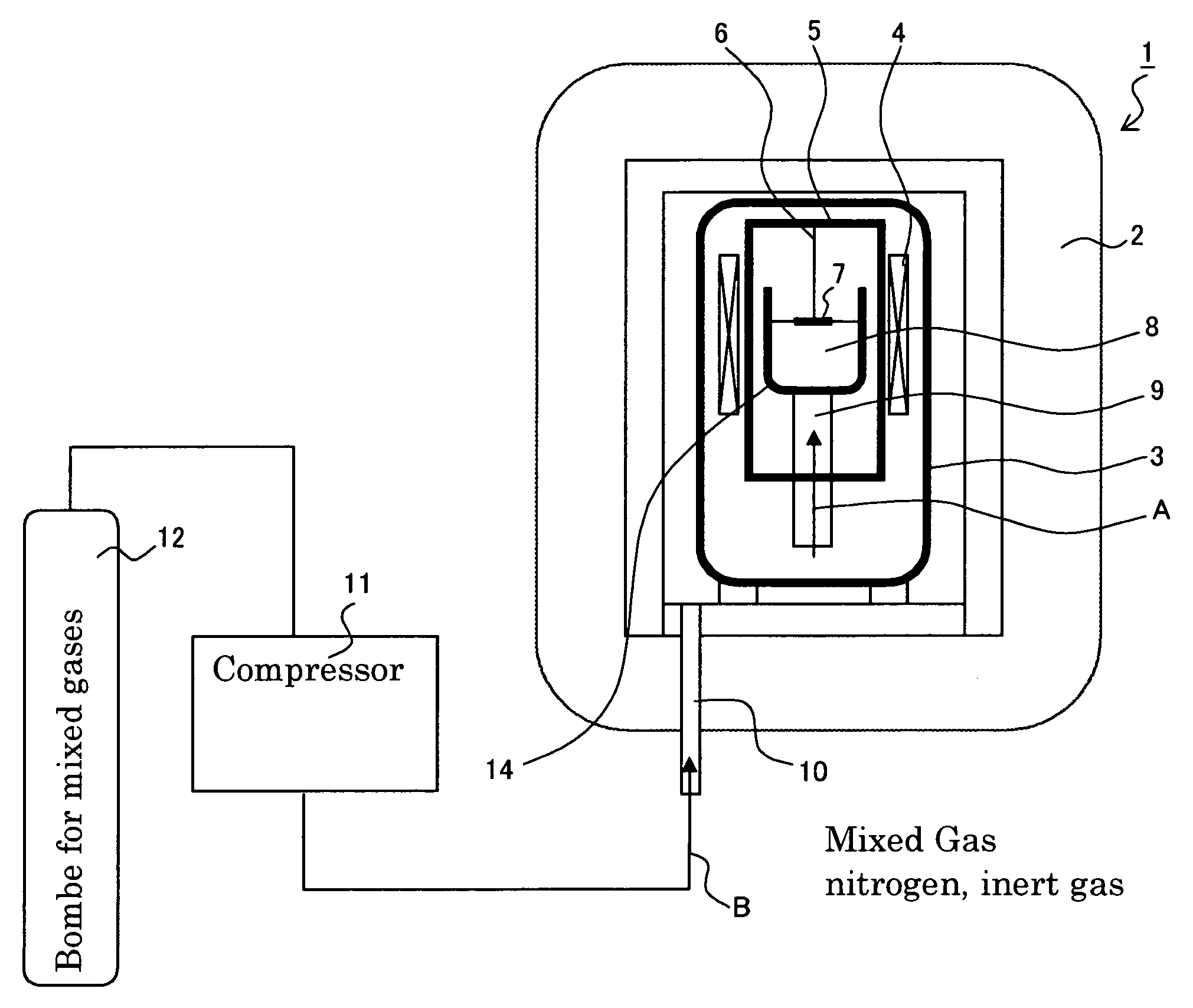
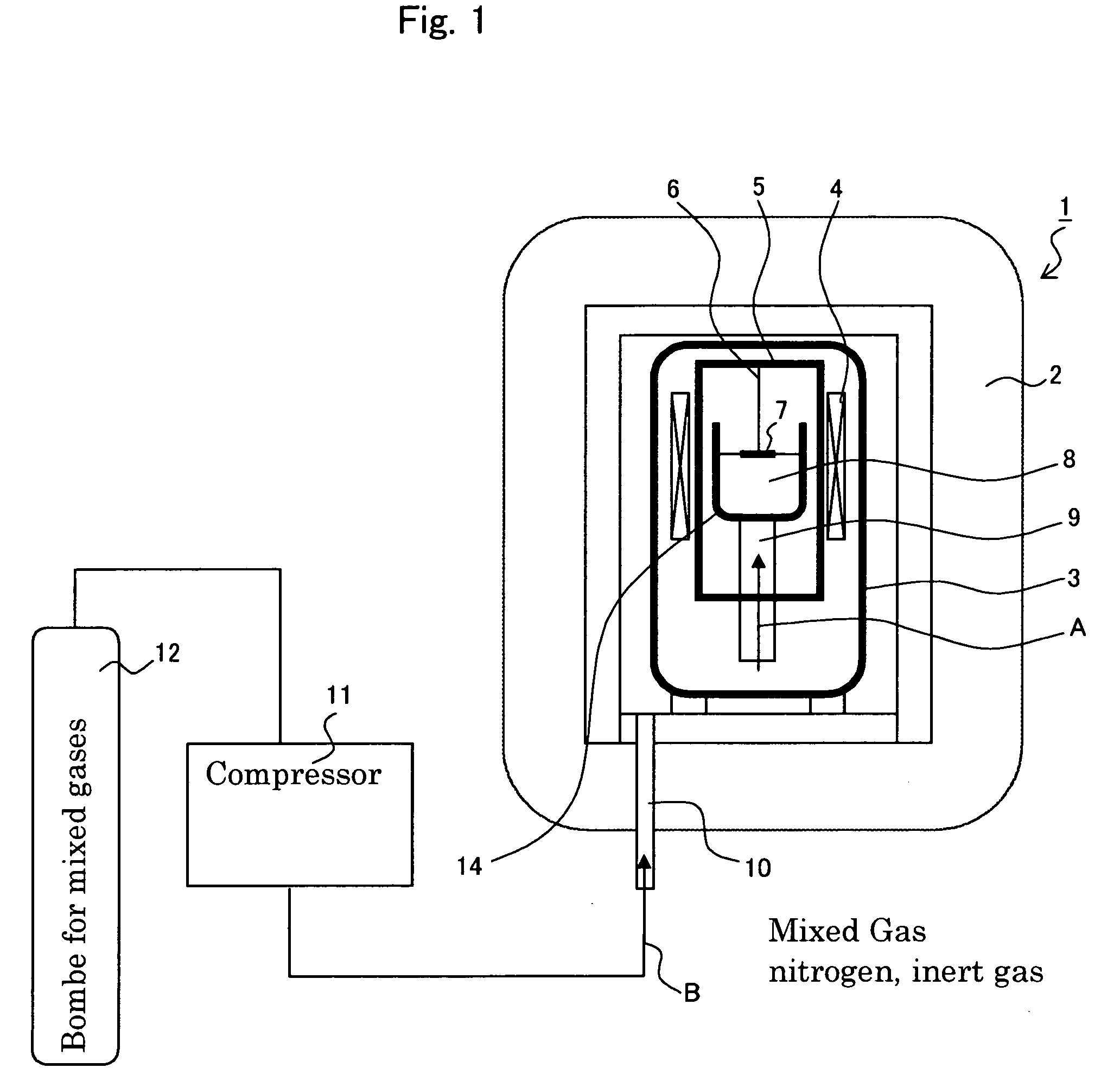
The invention discloses an integral low-temperature nuclear heat reactor with the circuit equipment adopting integral arrangement and belonging to the low- and medium-parameter pressurized-water reactor, wherein, a reactor core adopts the mature nuclear power plant fuel component and control rod component; a main heat exchanger is of integral coil type; a voltage stabilizer is a built-in nitrogen partial pressure control voltage stabilizer; coolant circulation is completed by a built-in jet apparatus and the equipment of an external drive circuit; the drive circuit and the equipment and a main circuit auxiliary system are arranged at the circumference of a reactor pressure vessel; a containment vessel consists of a reactor body containment vessel and a reactor top containment vessel; the reactor body containment vessel which is a structure combined by a reactor vault of reinforced concrete structure and a casing of steel structure is connected with a sealed refueling water storage pool through a pipe and a valve. The thermal power of the reactor can be selected between 50MW and 500MW at will and the outlet temperature of the reactor can be selected between 100 DEG C to 200 DEG C according to application, requirement and power.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Cemented carbide tool and method of making
InactiveUS6998173B2High nitrogen contentPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesNitrogen partial pressureAlloy
A coated cemented carbide tool, and a method for making the same, wherein the as-sintered substrate is formed by sintering in an atmosphere having at least a partial pressure and for a part of the time a nitrogen partial pressure.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
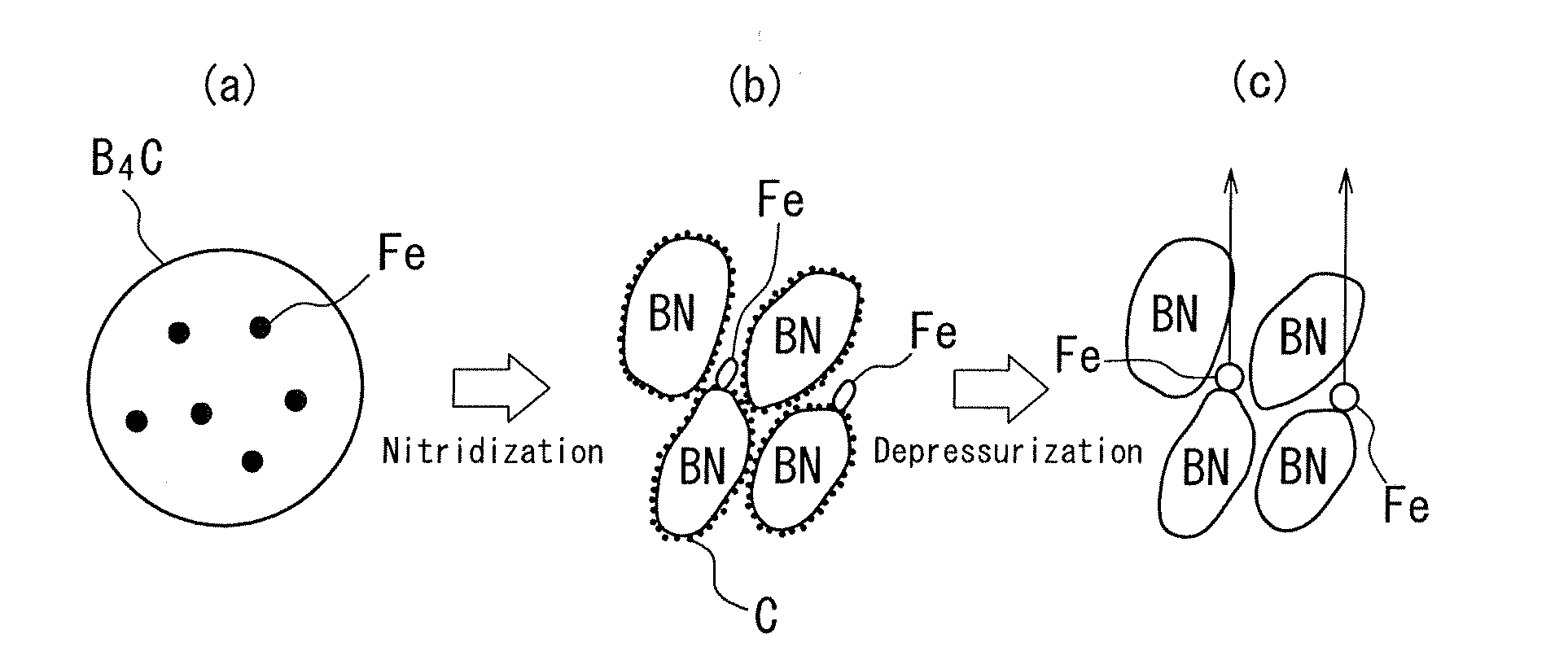
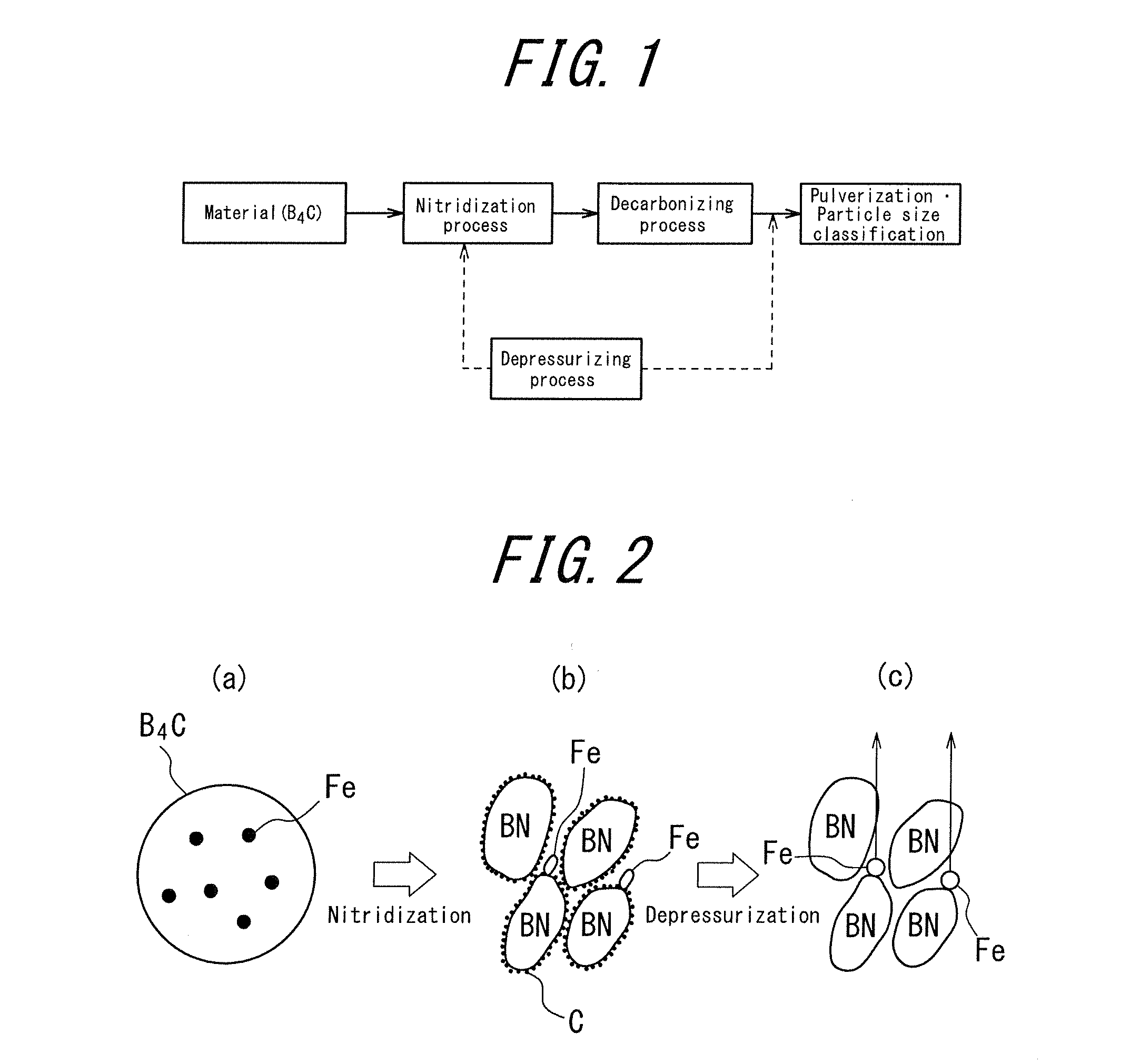
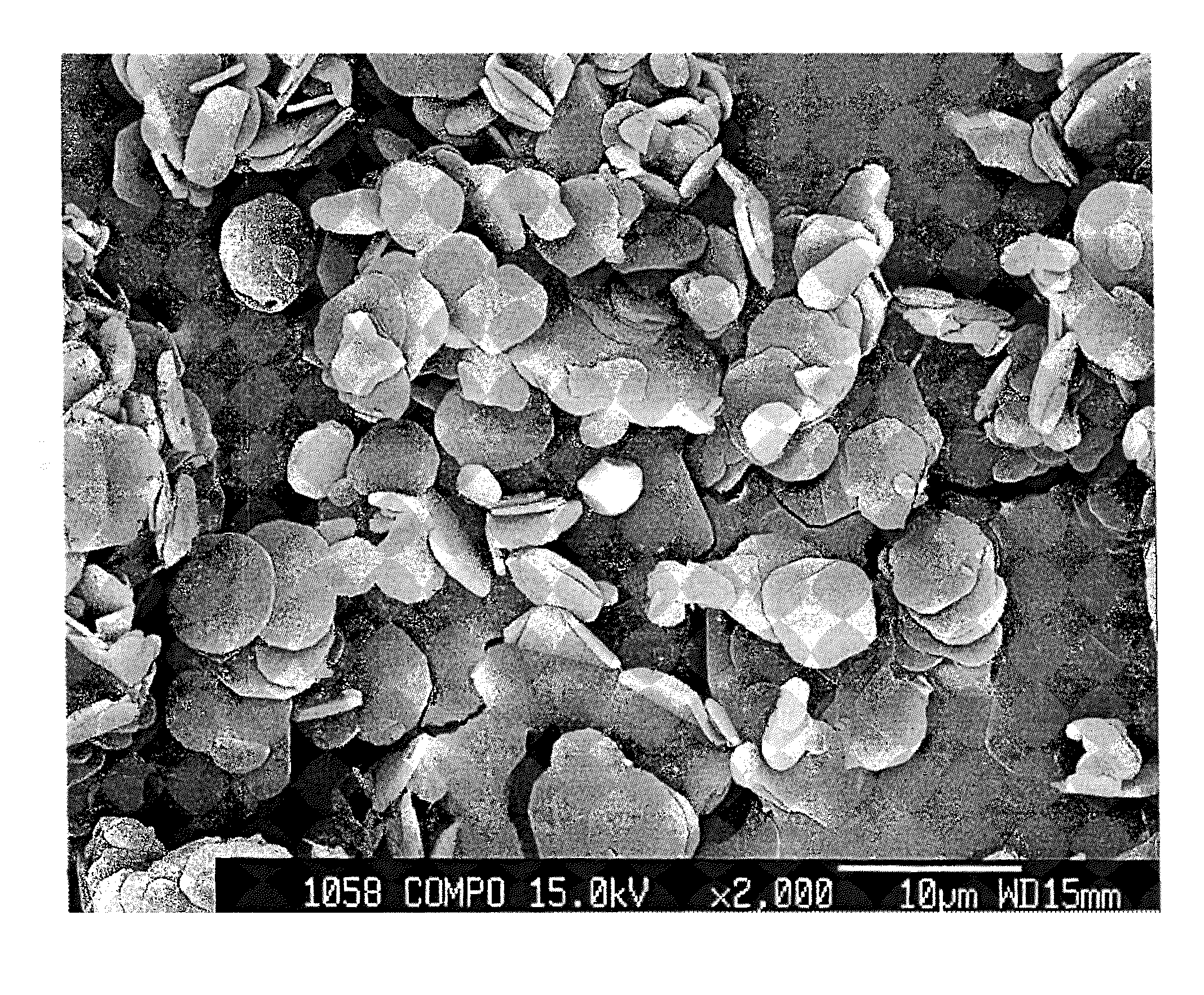
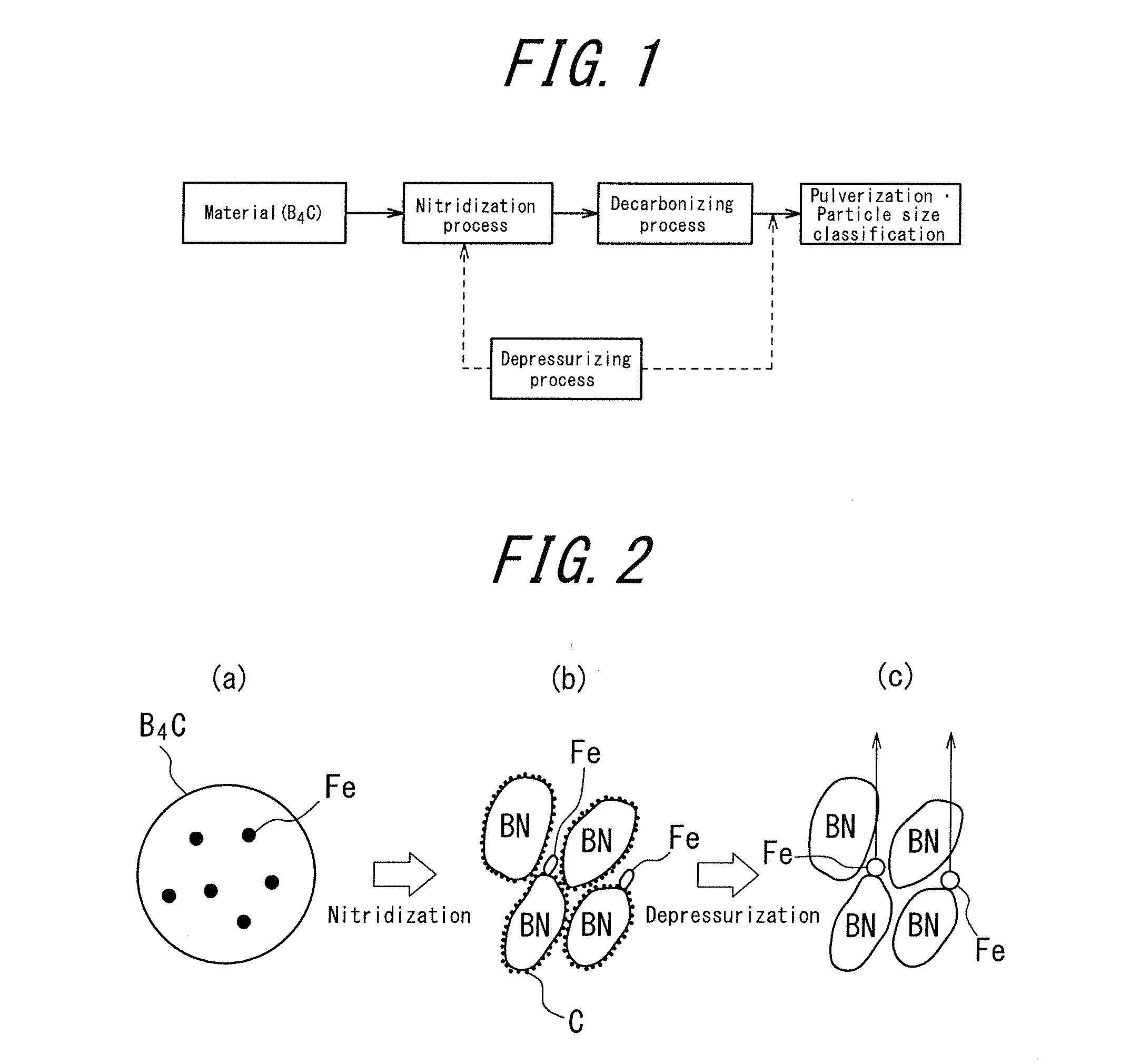
Hexagonal boron nitride powder and method for producing same
ActiveUS20120196128A1Made denserHigh strengthNitrogen compoundsSynthetic resin layered productsLongest DiameterHexagonal boron nitride
A hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) powder is disclosed in which primary particles of the powder exhibit a ratio (D / d) of long diameter (D) to thickness (d) in a range of 5 to 10. Agglomerated particle bodies made of the primary particles have an average particle diameter (D50) in a range of 2 μm to 200 μm, inclusive, and the powder has a bulk density in a range of 0.5 g / cm3 to 1.0 g / cm3. In an exemplary method for producing the h-BN, boron carbide is nitridizated in a nitrogen partial pressure of at least 5 kPa at 1800° C. to 2200° C., inclusive. B2O3 (or precursor thereof) is added to the nitridization product to produce a mixture. The mixture is decarbonized in a non-oxidizing atmosphere at a 1500° C. to 2200° C., inclusive. The decarbonization product is pulverized and subject to particle-size classification, yielding H-BN powder. The method includes a depressurizing step, performed at 100 kPa or less either during nitridization or after decarbonization.
Owner:MIZUSHIMA FERROALLOY
Gallium Nitride Single Crystal Growing Method and Gallium Nitride Single Crystal
InactiveUS20070209575A1Improve productivityQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsProduction rateNitrogen partial pressure
It is provided a method of growing gallium nitride single crystal of good quality with a high productivity, in the growth of gallium nitride single crystal by Na-flux method. Gallium nitride single crystal is grown using flux 8 containing at least sodium metal. Gallium nitride single crystal is grown in atmosphere composed of gases mixture “B” containing nitrogen gas at a pressure of 300 atms or higher and 2000 atms or lower. Preferably, the nitrogen partial pressure in the atmosphere is 100 atms or higher and 2000 atms or lower. Preferably, the growth temperature is 1000° C. or higher and 1500° C. or lower.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Method for preparing nano-structured hard coating on surface of cemented carbide substrate
InactiveCN103898461AHigh hardnessReduce hardnessVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNano structuringNitrogen partial pressure
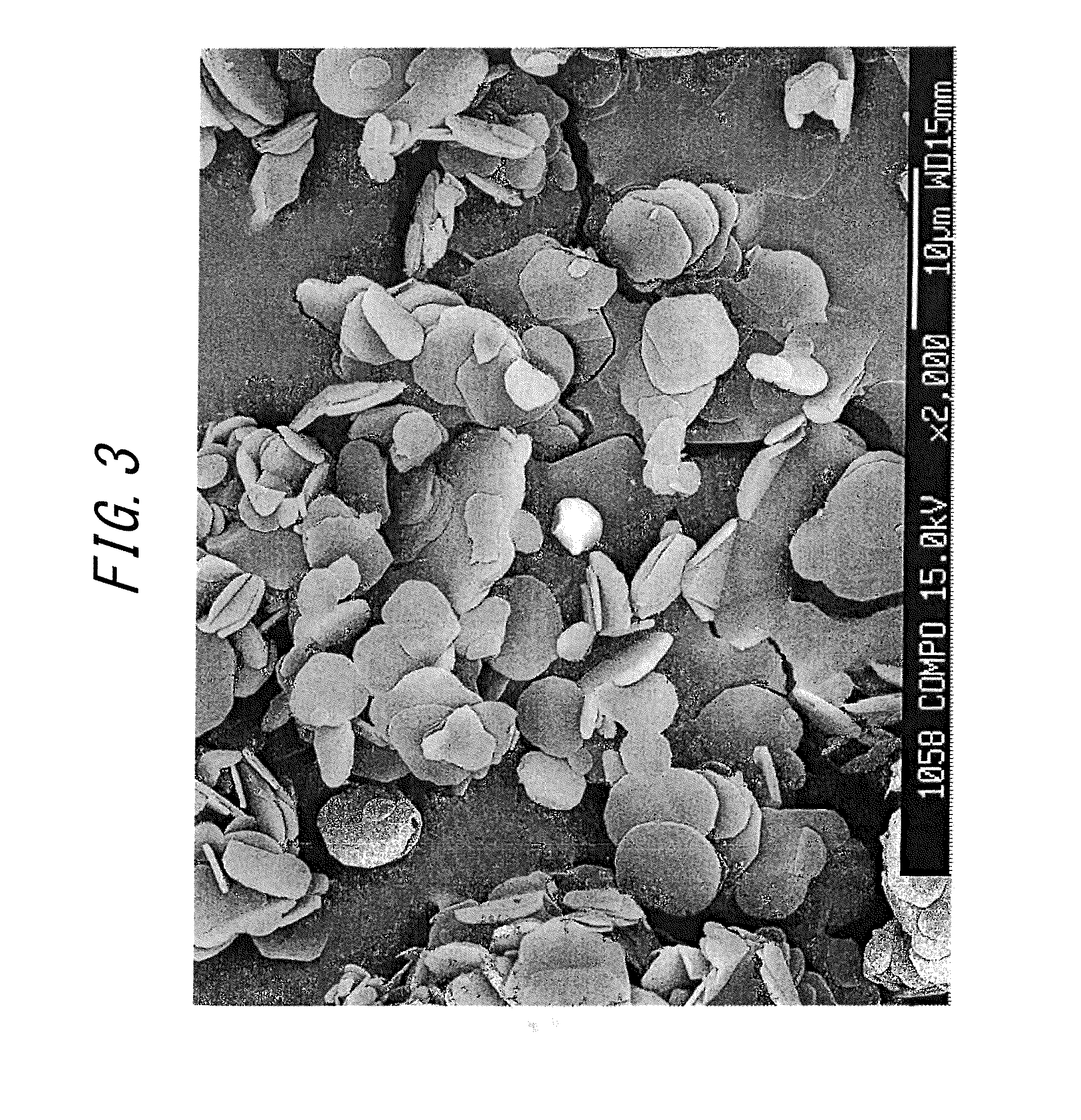
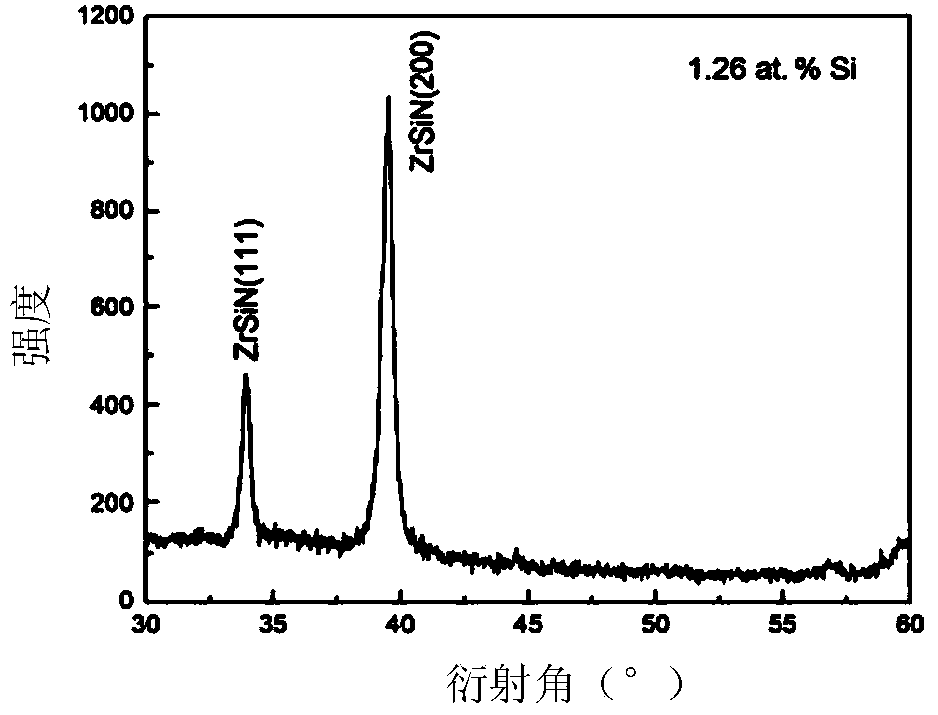
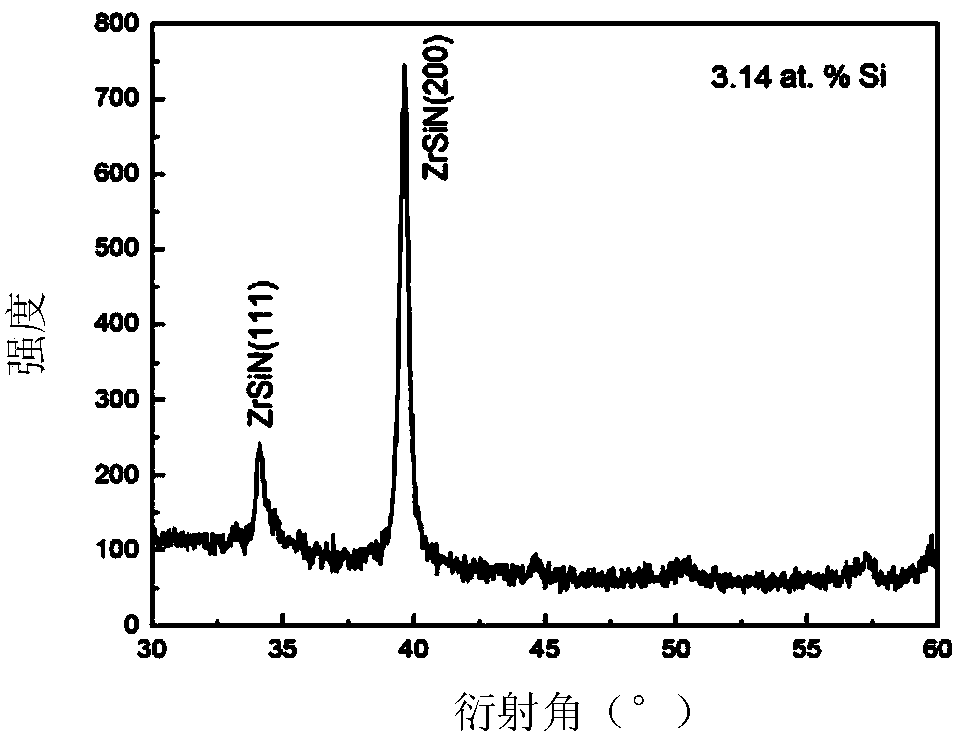
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nano-structured hard coating on the surface of a cemented carbide substrate. The cemented carbide substrate is subjected to grinding, polishing, ultrasonic cleaning, and ion source cleaning; pre-sputtering is performed; and sputtering deposition is implemented. By adopting a direct-current and radio-frequency reactive co-sputtering method, under the conditions of certain deposition pressure, temperature, nitrogen partial pressure and the like, a nano-structured hard coating is prepared on the surface of the substrate through controlling the Si target power. When the Si content of a ZrSiN coating is reduced, Si atoms exist in the coating in a form of substituting Zr atom, therefore, the ZrSiN coating with a low Si content is a solid liquid, and the cross section thereof is of a columnar structure. With the increasing of the Si content, the solid solubility of the ZrSiN coating is increased, so that the hardness of the ZrSiN coating is increased. When the Si content of the coating reaches a certain value, excess Si elements and N elements form amorphous Si3N4 at the grain boundary. With the further increasing of the Si content of the coating, a lot of amorphous Si3N4 is produced, and then the coating becomes an amorphous coating, and is of a non-columnar structure.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
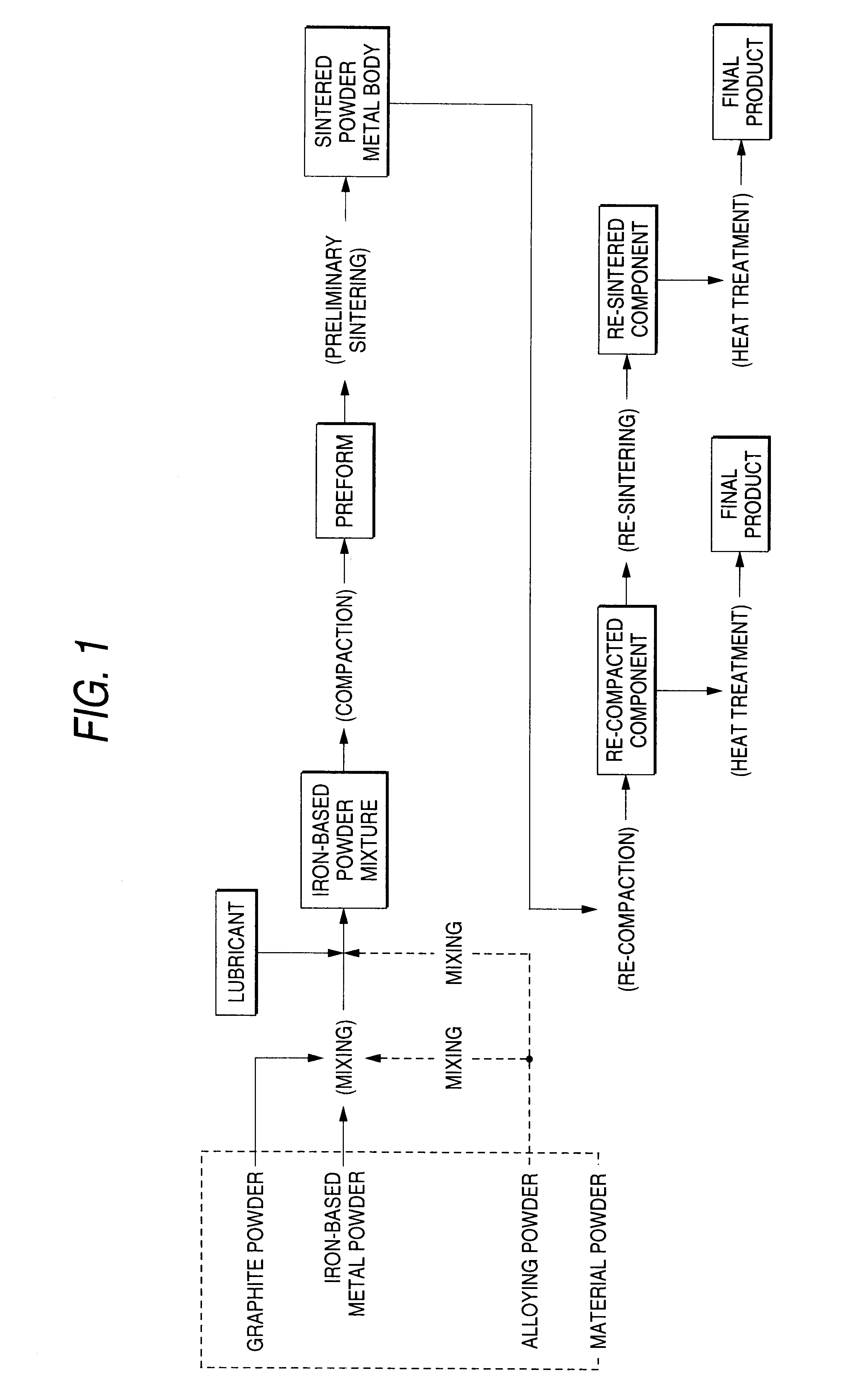
Iron-based sintered powder metal body, manufacturing method thereof and manufacturing method of iron-based sintered component with high strength and high density
InactiveUS6514307B2Transportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusHigh densityNitrogen partial pressure
Owner:KAWASAKI STEEL CORP +1
Method for plating films of multi-arc ion plating
InactiveCN102534514AImprove alloy ionization rateImprove deposition efficiencyVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingVoltage amplitudePlasma electron
The invention relates to a method for plating films of multi-arc ion plating. The method is characterized in that a hollow cathode device is arranged in a vacuum chamber while a multi-arc source launches plasma, a hollow cathode electron gun is used for launching a high-energy plasma electron beam to an anode, and the plasma electron beam and the plasma launched by the multi-arc source carry out a mutual cross motion. The technological parameters of the plasma electron beam launched by the hollow cathode electron gun comprise 70-220 A of hollow cathode current; 10-90 percent of duty ratio; -50 to -1000 V of pulse bias voltage amplitude; 1*10-1 to 5*10-1 Pa of nitrogen partial pressure and 2*10-1 to 8*10-1 Pa of argon partial pressure. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the defect of large particles of coating surfaces can be obviously decreased while the deposition efficiency of the original multi-arc ion plating is not reduced, and therefore the quality and the using performance of coatings are increased.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
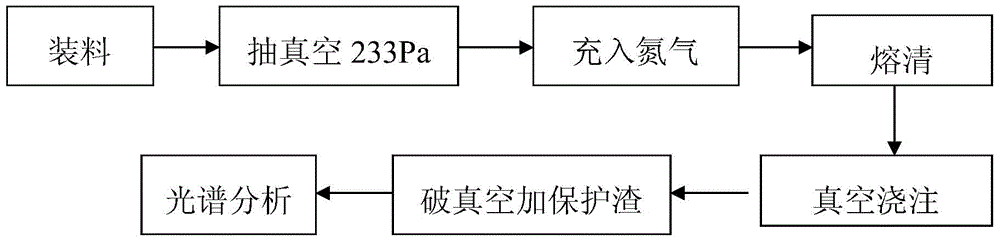
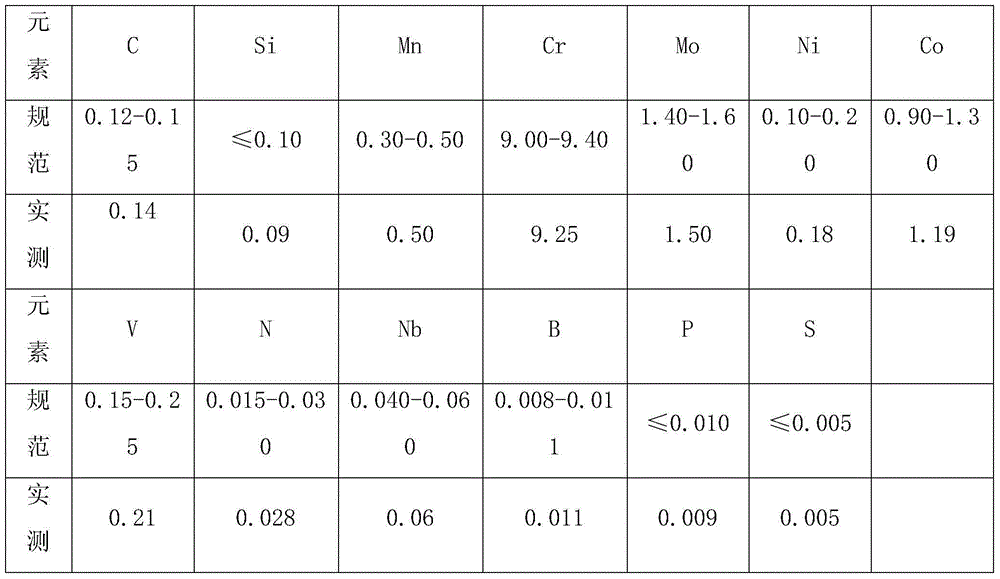
Nitrogen content control method for FB2 steel smelted by vacuum induction furnace
The invention discloses a nitrogen content control method for FB2 steel smelted by a vacuum induction furnace. The nitrogen content in steel is controlled by improving the nitrogen partial pressure, and the method comprises the following steps: step 1, charging; step 2, vacuumizing; step 3, filling with nitrogen; step 4, melting down; step 5, performing vacuum casting; and step 6, destroying the vacuum environment and adding a protective slag. The vacuum induction furnace is employed for smelting FB2 steel, the partial pressure of nitrogen in the vacuum induction furnace is improved by filling with nitrogen, the saturation solubility and the surface adsorption rate of steel in molten steel are improved, and the nitrogen content in molten steel is increased, and thus the target of controlling the nitrogen content is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI HEAVY MACHINERY PLANT
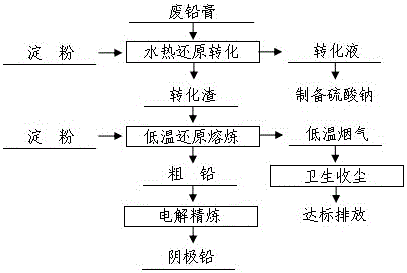
Waste lead-acid battery diachylon hydrothermal reduction dual conversion method
ActiveCN105950872AEasy to operateTechnical indicators are stableWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementLead dioxideSulfate radicals
The invention discloses a waste lead-acid battery diachylon hydrothermal reduction dual conversion method. Waste diachylon and alkali solution are firstly converted under normal pressure to remove most sulfate radicals; normal-pressure conversion liquid is fed to recover sodium sulfate; normal-pressure conversion slag and the alkali solution are pulped to feed into a reducing agent to add in a high-pressure reaction kettle for reaction under requested temperature and nitrogen partial pressure, so that residual lead sulfate in the normal-pressure conversion slag is reacted with alkali to deeply remove the sulfate radicals; meanwhile, lead dioxide is reduced as lead monoxide; after the reaction time is reached, the solid-liquid separation is performed; hydrothermal conversion liquid is returned into the normal-pressure conversion process; and lead is further extracted from the hydrothermal conversion slag. The essence of the method is to realize dual purposes of deep conversion desulfurization and reduction conversion of the waste diachylon by using a water heat and reduction combined mode; the desulfurization rate and the lead dioxide reduction rate both reach above 99.0%; and advantageous conditions are created for subsequent lead extraction from conversion slag.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for preparing nitrogen-enriched functional gradient metal ceramic by low pressure nitriding method
ActiveCN104060143AIncrease costLow costSolid state diffusion coatingFurnace temperatureNitrogen partial pressure
The invention discloses a method for preparing nitrogen-enriched functional gradient metal ceramic by a low pressure nitriding method. The metal ceramic prepared by the method is Ti(C, N)-based metal ceramic which takes Ti(C, N) and / or TiC and TiN as a main hard phase and metals in the iron group such as Co and / or Ni and the like as a bonding phase. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of filling a metal ceramic sintering body in a vacuum integrated furnace; in a vacuum sintering state, heating to a predetermined nitriding temperature at a heating speed being 3-7 DEG C / min, wherein the predetermined nitriding temperature is 1200-1400 DEG C; when the furnace temperature reaches the predetermined nitriding temperature, nitriding by adopting a nitrogen partial pressure sintering process, controlling the partial pressure at 2000-6000Pa, preserving the heat for 2-6 hours, and cooling in a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain the surface nitrogen-enriched functional gradient metal ceramic. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of less investment, low production cost and high efficiency, and is easy to realize industrialized conversion.
Owner:XIAMEN TUNGSTEN
Process for producing optical glass element
InactiveUS7666332B2High light transmittanceGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusTransmittanceNitrogen partial pressure
To provide a production process capable of making the transmittance of an optical glass element obtainable by press-molding a TeO2-containing glass high.A process for producing an optical glass element, which comprises press-molding a TeO2-containing glass, wherein the press-molding is carried out in an atmosphere in which the nitrogen partial pressure is at most 102 Pa. The above process for producing an optical glass element, wherein the face of a mold for the press-molding to be in contact with the glass is made of carbon. The above process for producing an optical glass element, wherein the molded glass obtained by the press-molding is held in an oxygen-containing atmosphere at a temperature within a range of at least a temperature lower by 50° C. than the glass transition point of the TeO2-containing glass and at most the softening point of the glass.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Fe-X-N grain refiner and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses to a Fe-X-N grain refiner and a preparation method thereof in the technical field of metal materials. Components of the Fe-X-N grain refiner by weight percentage are as follows: 35-99.4% of Fe, 0.1-15% of N and 0.5-50% of X; wherein, X is V or Nb or Ti or mixture of V and Nb. The preparation method of the Fe-X-N grain refiner comprises the following steps: mixing iron withthe metal X, melting the mixture in a vacuum intermediate frequency induction furnace to obtain molten mass; charging nitrogen gas when the temperature of the molten mass is 1550-1650 DEG C, adding the nitrogen gas to the molten mass when the nitrogen partial pressure around the molten mass is 0.01-0.1MPa for 10s-3h; stopping adding the nitrogen gas, cutting off the power to obtain the Fe-X-N grain refiner. The preparation method of the grain refiner is simple; the grain refiner is added to steel molten mass to refine steel grain, and proportion of zone of equiaxial crystals such as billet ascast structure is increased to above 60%.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Waste diachylon hydrothermal reduction conversion and low-temperature reduction smelting method
ActiveCN105950871AAchieve depthRealize the dual purpose of reduction and transformationWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementLead dioxideElectrolysis
The invention discloses a waste diachylon hydrothermal reduction conversion and low-temperature reduction smelting method. Waste diachylon and alkali solution are pulped to feed in a reducing agent to add in a high-pressure reaction kettle for reaction under requested temperature and nitrogen partial pressure; after the reaction time is reached, the solid-liquid separation is performed; sodium sulfate is prepared by hydrothermal conversion liquid; hydrothermal conversion slag and starch are fully mixed for low-temperature reduction smelting by an indirect heating mode; and a produced lead bullion is further purified by electrolytic refining. Firstly, the hydrothermal conversion is performed in presence of both alkali and the reducing agent to realize dual purposes of deep conversion desulfurization and reduction conversion of the waste diachylon; and then, the starch serves as the reducing agent under the indirect heating condition to realize the purpose of producing the lead bullion through low-temperature reduction smelting of hydrothermal conversion slag. The desulfurization rate and the lead dioxide reduction rate both reach above 99.0%; the direct yield of lead reaches above 96.0%; the smelting temperature in the low-temperature reduction smelting process is reduced to 800-850 DEG C; and the method has such advantages as simple operation in the technological process, stable technological index, low labor intensity and low production cost.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Steel ladle bottom nitrogen blowing and adding method
The inventiondiscloses a steel ladle bottom nitrogen blowing and adding method. The method process comprises the steps of firstly, calculating nitrogen partial pressure PN2 according to the formula (I); secondly, calculating the bottom blowing gas total pressure P<total> according to the formula (II); thirdly, calculating the argon partial pressure PAr according to the formula (III); and fourthly, setting pressure of the nitrogen and pressure of the argon according to the nitrogen partial pressure PN2 and the argon partial pressure PAr and performing steel ladle bottom blowing at the same time. According to the method, through control over the partial pressure of the nitrogen in the argon and nitrogen mixed gas in the steel ladle bottom nitrogen blowing process, nitrogen adding for nitrogenous steel can be achieved accurately, use of high-cost nitralloy is reduced, and the defect of low control accuracy of sectional bottom nitrogen blowing and adding is prevented; adding of the high-cost nitralloy can be prevented, and high nitrogen mass fraction hit rate can be guaranteed; the steel ladle bottom nitrogen blowing and adding method has the characteristics of being low in cost, high in hit rate and easy to operate.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG IRON & STEEL
Aluminum magnesium oxynitride/boron nitride diphase refractory materials and preparing process thereof
InactiveCN1603278AImprove mechanical propertiesExcellent room temperature flexural strengthNitrogen partial pressureRefractory
The invention belongs to structural ceramics and refractory technology field. It relates to a MgAlON / BN poly-phase refractory material. While compounding MgAlON and BN proportion poly-phase material, if MgAlON is base, the addition quantity of BN is 10% to 40%; if BN is base, the addition quantity is 5% to 25%. The technology request is: sintering temperature is about 1500 degree centigrade to 2000 degree centigrade; sintering pressure is about 0.1Mpa to 50Mpa, nitrogen gas protection while sintering or compounding; the ratio of oxygen partial pressure and nitrogen partial pressure is between 10 negative quintic power to 10 negative fifteen power; temperature keeping span is between 0.5 hour to 10 hour. The compounding of MgAlON / BN can make the most of both features to make the material has good mechanical property, chemical property and high temperature shock stability. The invention may be a new high performance structure ceramics or a new type workable refractory.
Owner:ZHONGYUAN WEIYE NEW MATERIAL
Process for producing optical glass element
InactiveUS20080099937A1High light transmittanceGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusVitrificationTransmittance
To provide a production process capable of making the transmittance of an optical glass element obtainable by press-molding a TeO2-containing glass high. A process for producing an optical glass element, which comprises press-molding a TeO2-containing glass, wherein the press-molding is carried out in an atmosphere in which the nitrogen partial pressure is at most 102 Pa. The above process for producing an optical glass element, wherein the face of a mold for the press-molding to be in contact with the glass is made of carbon. The above process for producing an optical glass element, wherein the molded glass obtained by the press-molding is held in an oxygen-containing atmosphere at a temperature within a range of at least a temperature lower by 50° C. than the glass transition point of the TeO2-containing glass and at most the softening point of the glass.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Method for preparing GaN based compound semiconductor crystal
InactiveUS6875272B2Improve productivityEfficient removalPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsNitrogenNitrogen partial pressure
In a method for growing a GaN based compound semiconductor on a front surface of a substrate to obtain the GaN based compound semiconductor crystal in one body, because the gas for reducing and decomposing the substrate is supplied to the rear surface of the substrate and a heat treatment is carried out in a gas atmosphere in which the nitrogen partial pressure is not less than a predetermined value, in order to remove the substrate, it can be prevented that cracks are caused in the crystal, or fracture or warp is caused by causing strain of the GaN based compound semiconductor crystal in a cooling step.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
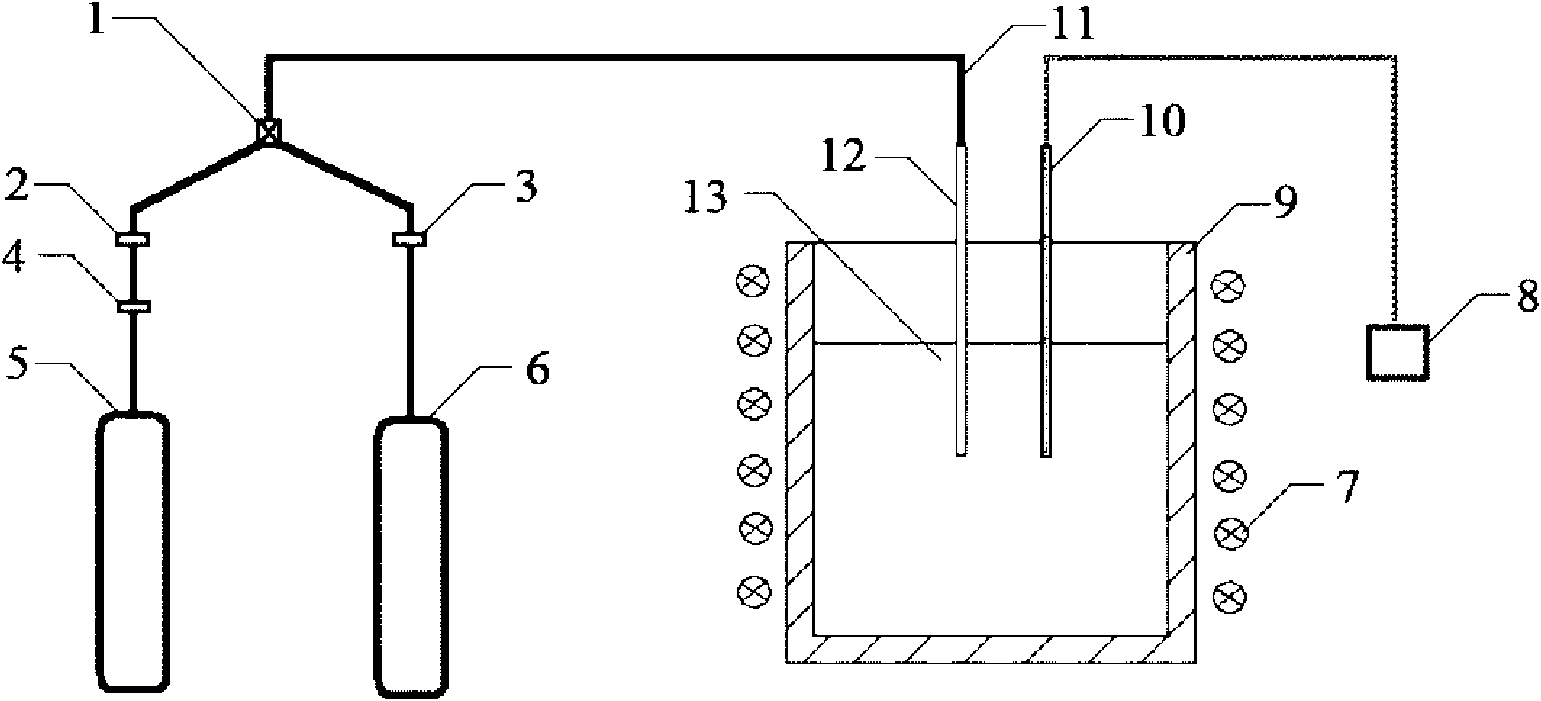
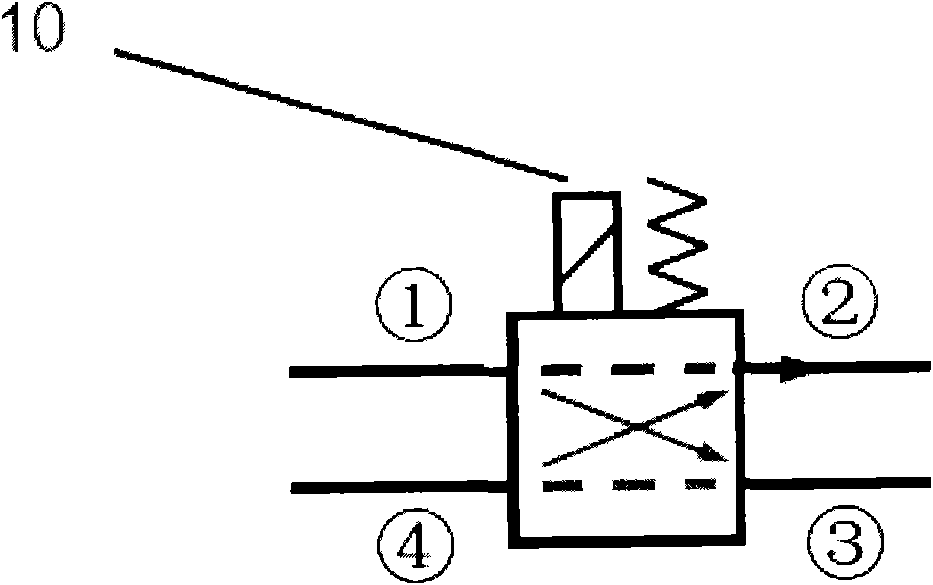
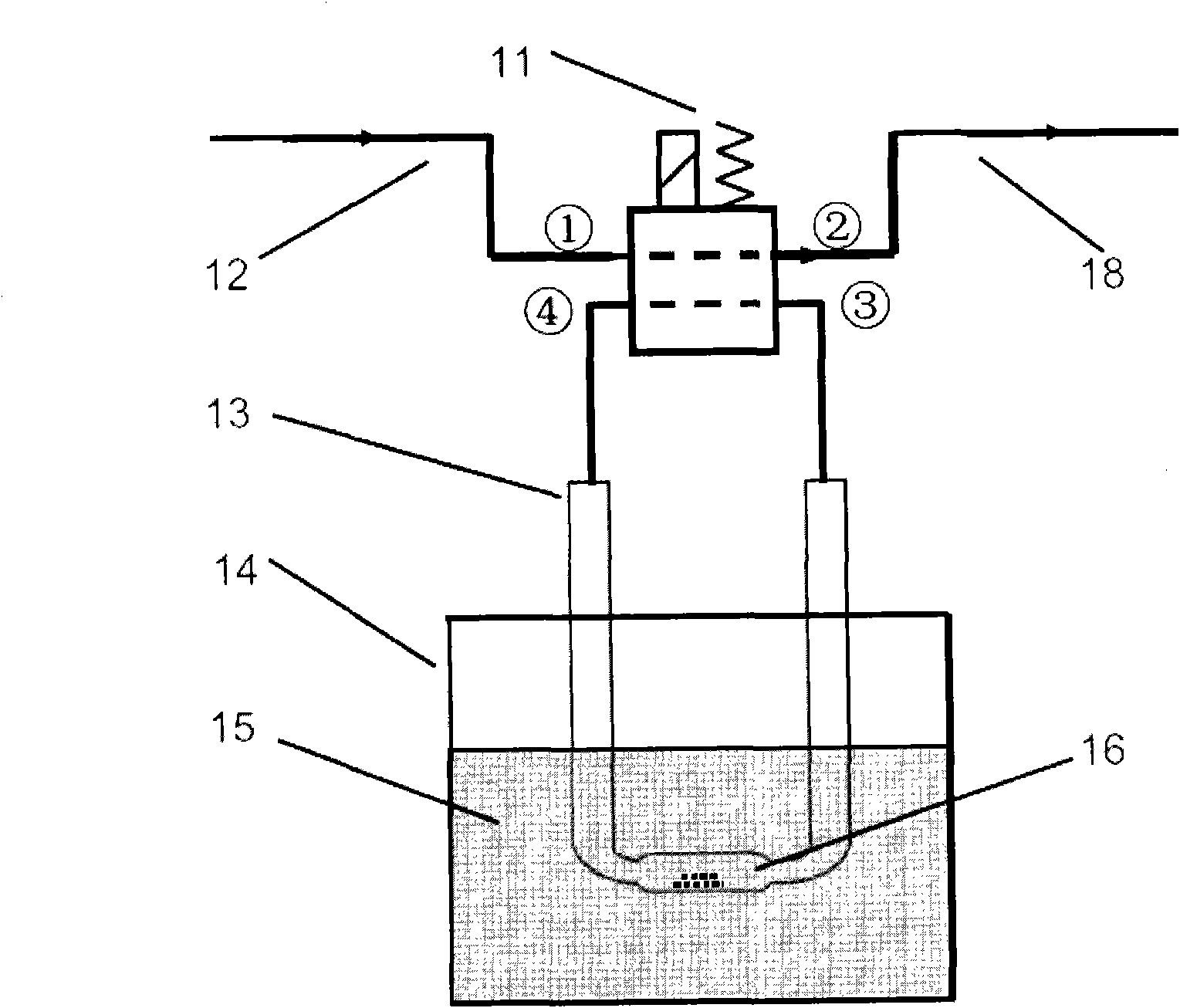
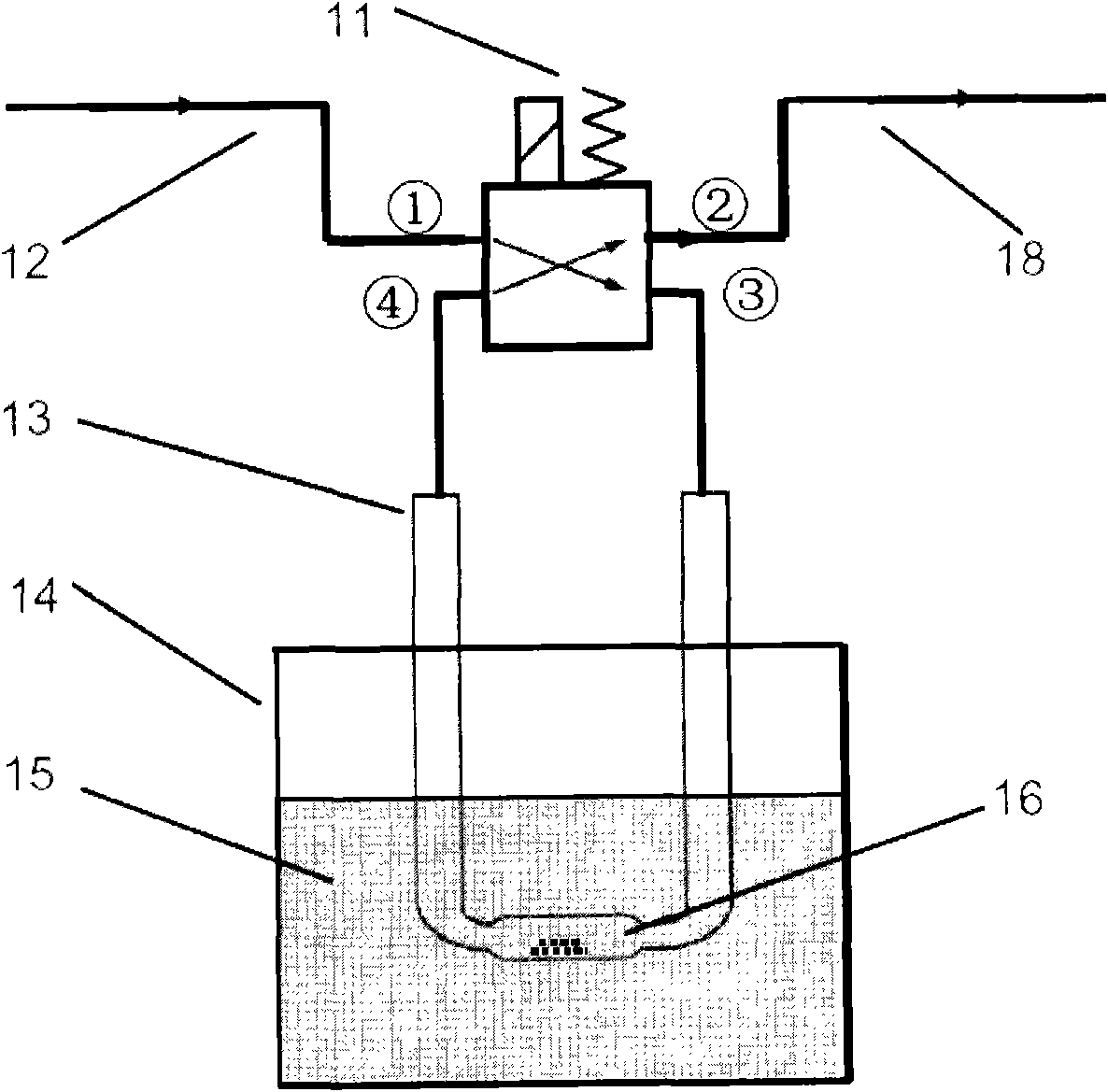
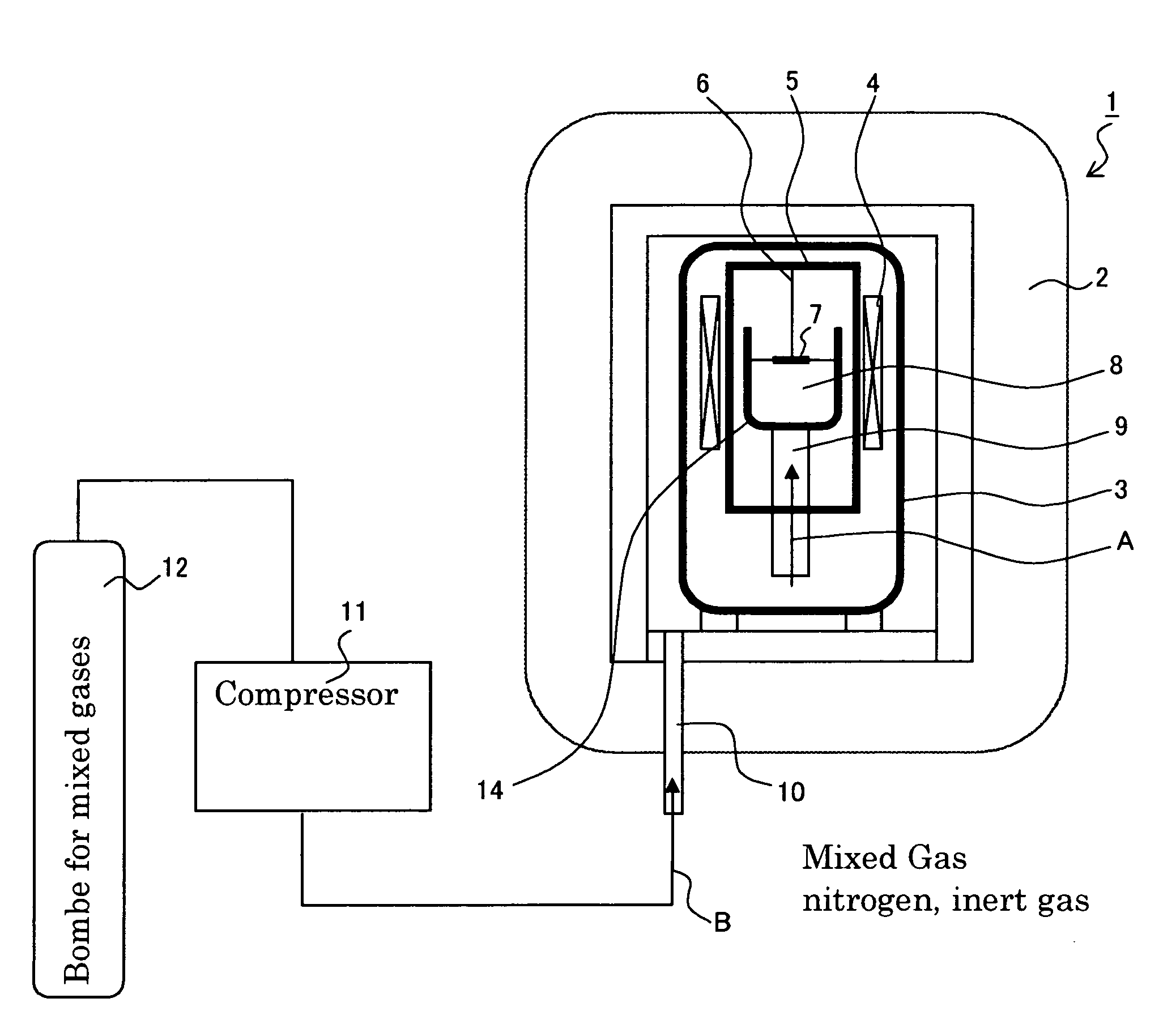
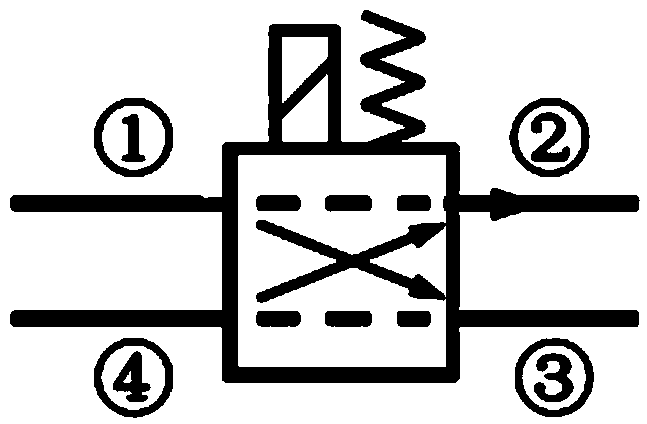
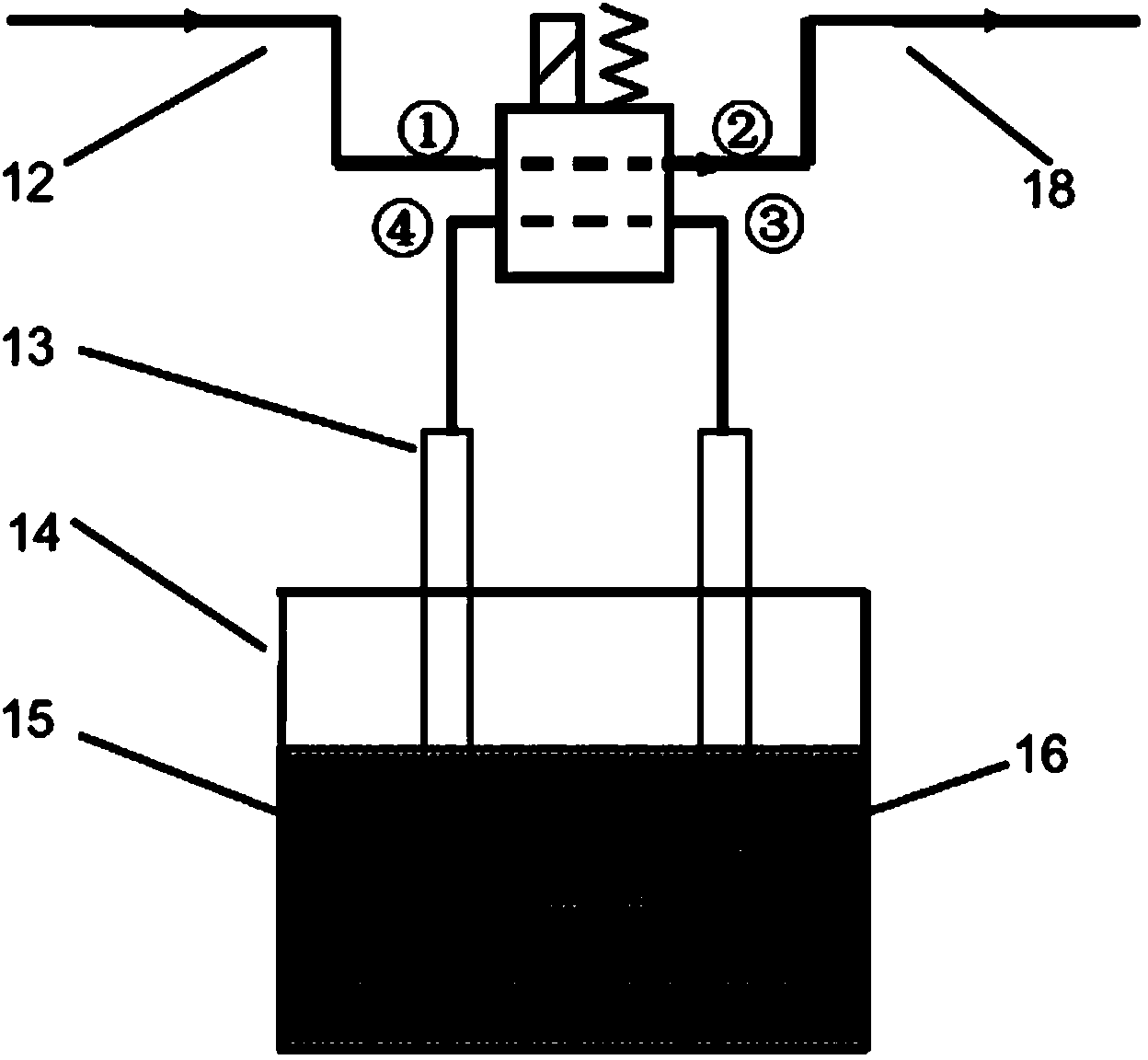
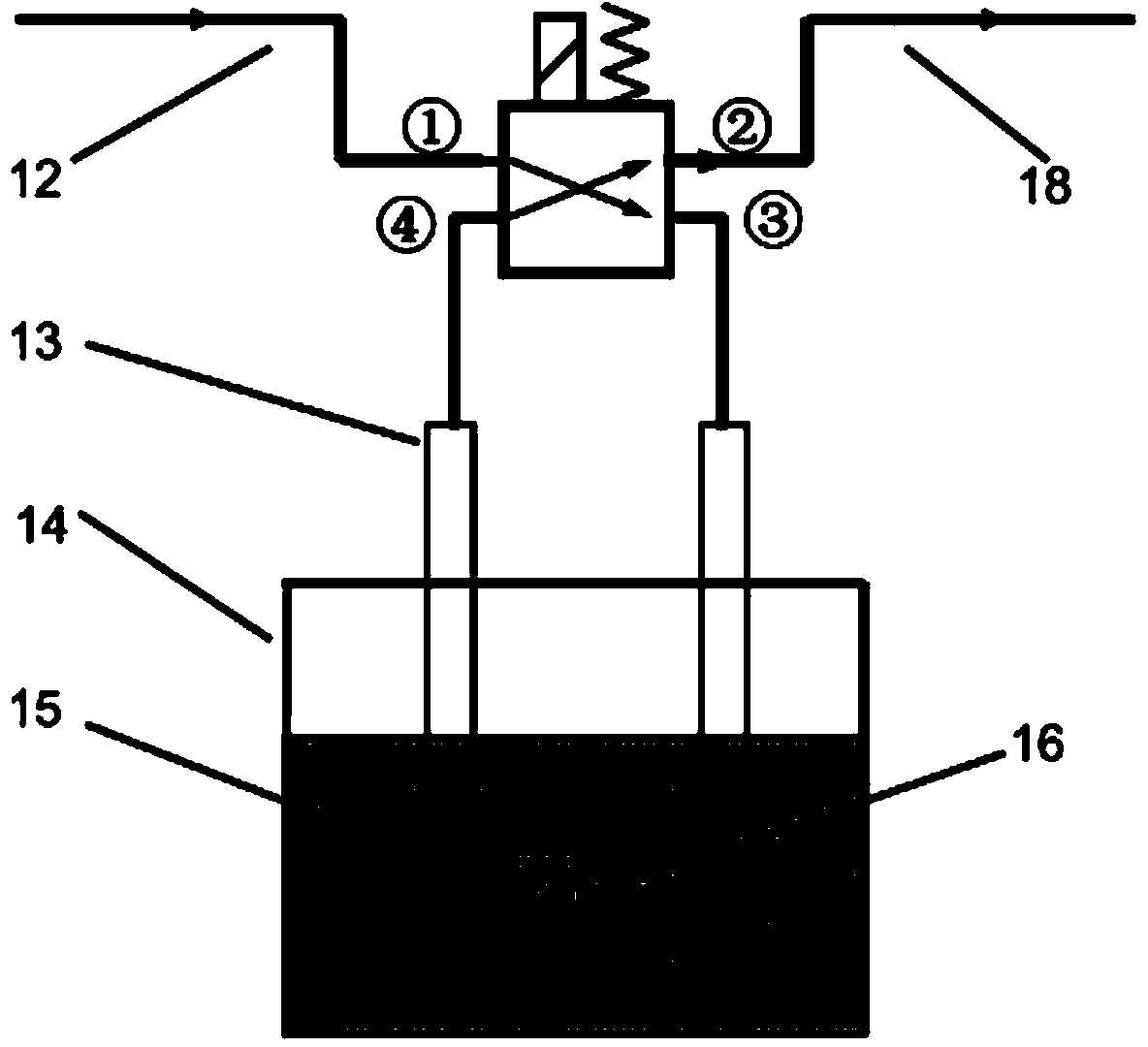
Cascade dynamic nitrogen adsorption instrument
The invention provides a design of a novel dynamic nitrogen adsorption instrument and achieves the purpose of greatly raising test speed and operational reliability of the nitrogen adsorption instrument. By the adoption of a four-way solenoid valve, gas flowing path is subtly controlled. Therefore, rapid and reliable test of sample cell in a liquid nitrogen cup is always maintained only through changing gas flow. Through switch of the solenoid valve, rapid conversion of two working conditions from nitrogen adsorption test to nitrogen partial pressure adjustment and vice verse is realized, and the sample cell is in the liquid nitrogen cup from beginning to end without the need of up-and-down motion of the liquid nitrogen cup. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, accurate control and the like.
Owner:北京精微高博仪器有限公司
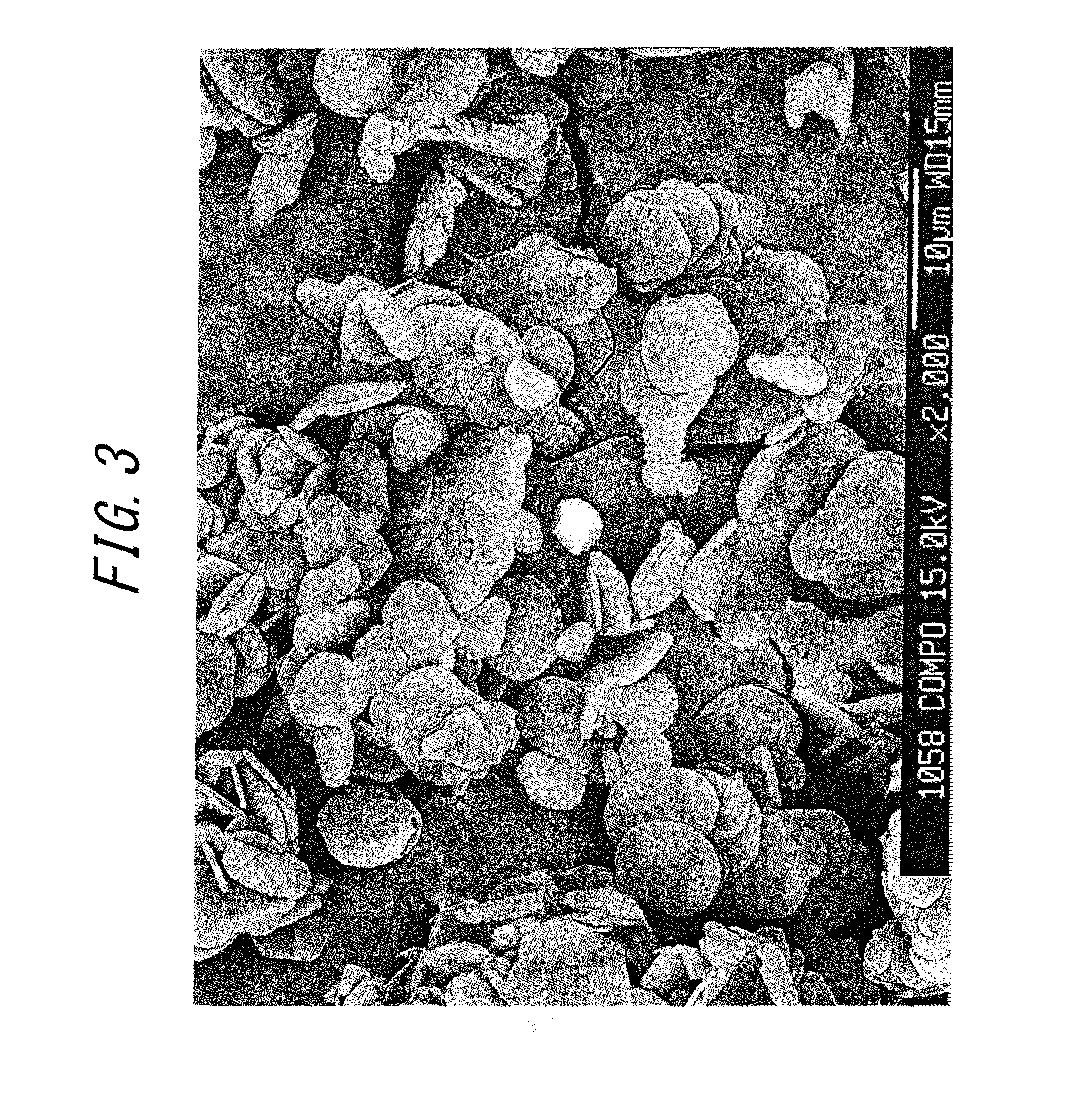
Hexagonal boron nitride powder having specific bulk density and residual Fe particles, and method for producing same
ActiveUS8679429B2Made denserHigh strengthNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsSynthetic resin layered productsLongest DiameterHexagonal boron nitride
A hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) powder is disclosed in which primary particles of the powder exhibit a ratio (D / d) of long diameter (D) to thickness (d) in a range of 5 to 10. Agglomerated particle bodies made of the primary particles have an average particle diameter (D50) in a range of 2 μm to 200 μm, inclusive, and the powder has a bulk density in a range of 0.5 g / cm3 to 1.0 g / cm3. In an exemplary method for producing the h-BN, boron carbide is nitridizated in a nitrogen partial pressure of at least 5 kPa at 1800° C. to 2200° C., inclusive. B2O3 (or precursor thereof) is added to the nitridization product to produce a mixture. The mixture is decarbonized in a non-oxidizing atmosphere at a 1500° C. to 2200° C., inclusive. The decarbonization product is pulverized and subject to particle-size classification, yielding H-BN powder. The method includes a depressurizing step, performed at 100 kPa or less either during nitridization or after decarbonization.
Owner:MIZUSHIMA FERROALLOY
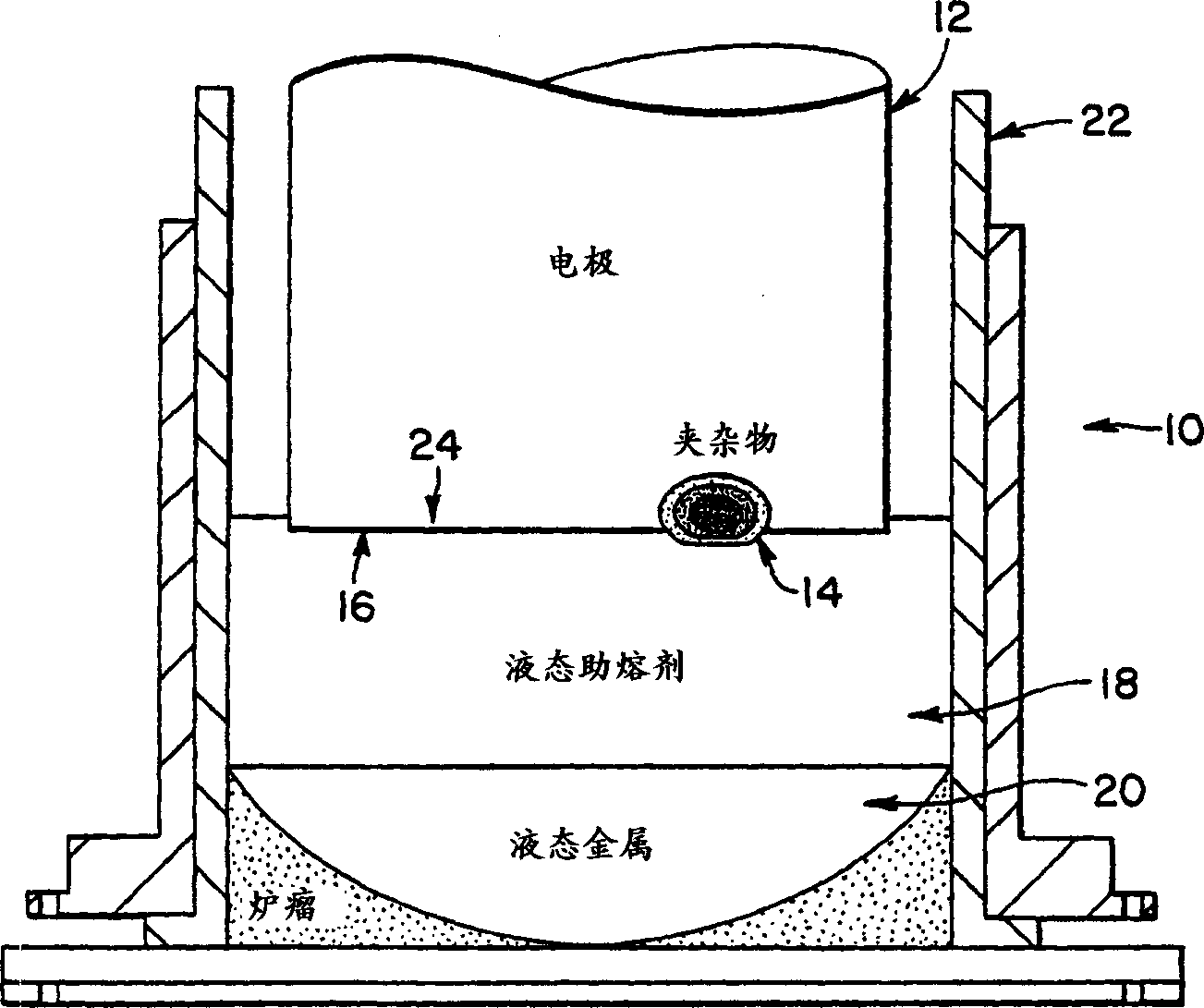
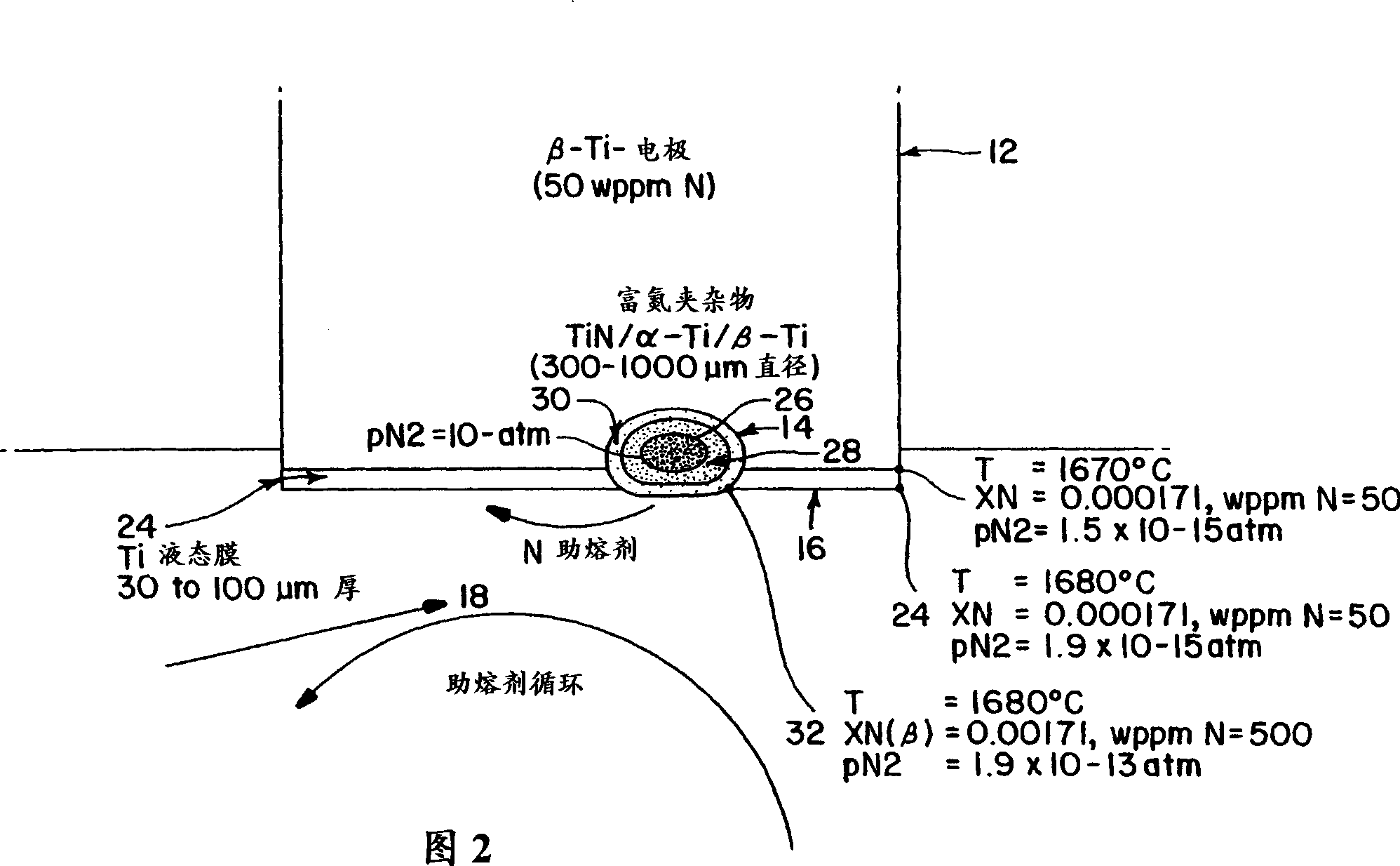
Method for dissolution of nitrogen-rich inclsions in titanium and titanium alloy
It has been discovered that electroslag remelting of titanium metal or alloys under controlled partial pressures of nitrogen, and somewhat oxygen, can dissolve nitrogen-rich inclusions to help eliminate or reduce initiation sites for cracks. The process for the electroslag remelting of titanium and titanium alloys ensures that nitrogen-rich inclusions are dissolved or at least minimized during the melting process.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Gallium nitride single crystal growing method and gallium nitride single crystal
InactiveUS8241422B2Improve productivityQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsProduction rateNitrogen partial pressure
It is provided a method of growing gallium nitride single crystal of good quality with a high productivity, in the growth of gallium nitride single crystal by Na-flux method. Gallium nitride single crystal is grown using flux 8 containing at least sodium metal. Gallium nitride single crystal is grown in atmosphere composed of gases mixture “B” containing nitrogen gas at a pressure of 300 atms or higher and 2000 atms or lower. Preferably, the nitrogen partial pressure in the atmosphere is 100 atms or higher and 2000 atms or lower. Preferably, the growth temperature is 1000° C. or higher and 1500° C. or lower.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Method for smelting COST-FB2 steel through gas-phase nitriding under negative pressure condition
ActiveCN110093582APrecise temperature controlUniform compositionSolid state diffusion coatingGas phaseManganese
The invention relates to a method for smelting COST-FB2 steel through gas-phase nitriding under a negative pressure condition. The method comprises the following steps that firstly carbon deep deoxidation is performed under the condition of high vacuum degree, deoxidation is completed after the surface of molten steel is stable and bubbles do not rush out any longer; then an alloy element for promoting nitrogen dissolution is added and completely molten, and then gas-phase nitriding is started; during gas-phase nitriding, nitriding pressure during gas-phase nitriding is calculated by using thermodynamic calculation software Factsage, the molten steel temperature is accurately controlled, and the nitriding time is calculated and determined through the surface area of the molten steel, the volume of the molten steel and the nitrogen balance content; when gas-phase nitriding is about to be completed, the alloy element boron and the volatile manganese are added, then through argon filling,pressurization is performed until the high pressure is reached, pressurization casting is performed under the condition that the nitrogen partial pressure is kept unchanged, the under-pressure stateis kept in the solidification process, vacuum breaking is performed after complete solidification, and a COST-FB2 steel cast ingot which has the content of N being 0.015%-0.03% and the content of O being less than or equal to 0.0035%, is uniform in component and compact in structure is prepared.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Preparation method of molybdenum alloy plate with hard nitrogen-yttrium-zirconium coating
InactiveCN105887029AImprove and control organizational structureImprove performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNitrogen partial pressureAlloy
The invention discloses a preparation method of a molybdenum alloy plate with a hard nitrogen-yttrium-zirconium coating. When the preparation method is used for preparing the molybdenum alloy plate, the high-hardness nitrogen-yttrium-zirconium coating is prepared on the surface of a base plate according to a direct-current and radio-frequency reactive co-sputtering method by Y-target power control under the conditions of specific deposition pressure intensity, temperature, nitrogen partial pressure and the like, so that material structures can be remarkably improved and controlled, strength and toughness of a prepared molybdenum material can be matched perfectly, and excellent overall performance is achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU SICHUANGYUANBO ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Preparation method of tungsten-nickel alloy provided with nitrogen, yttrium and zirconium hard coating
InactiveCN108239716AImprove and control organizational structureImprove performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNitrogen partial pressureNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a preparation method of a tungsten-nickel alloy provided with a nitrogen, yttrium and zirconium hard coating. The tungsten-nickel alloy prepared by adopting the preparation method can be used for solving the problems of a 'nickel pool' and holes which frequently appear in the traditional fine grain hard alloy preparation process, so as to improve overall performance of thealloy, a direct current and radio frequency reactive co-sputtering method is adopted, and a high-hardness nitrogen, yttrium and zirconium coating is prepared on the surface of a hard alloy matrix by controlling power of a target Y at certain deposition pressure intensity, temperature and nitrogen partial pressure.
Owner:QINGDAO XIANGZHI ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Epitaxial growth technology for nitride semiconductor luminescent device
InactiveCN106206879AImprove the problem of low decomposition efficiencyQuality improvementSemiconductor devicesGas phaseNitrogen partial pressure
The invention discloses an epitaxial growth technology for a nitride semiconductor luminescent device, and belongs to the field of semiconductor photoelectric technologies. When an InGaN trap layer with high In component of an InGaN / GaN multiple-quantum trap active layer with high In component is growing, adopted nitrogen sources comprise nitrogen-containing compounds with high resolution capability under 700 DEG C, so that InGaN alloy can be grown at relatively low temperatures; furthermore, more nitrogen atoms can be provided by the nitrogen-containing compounds compared with NH3 in traditional technologies, and nitrogen partial pressure in gaseous phase can be improved, which all facilitate combination of In, and thus the In component in InGaN alloy is improved, and meanwhile a series of problems brought by InGaN alloy epitaxial growth at high temperatures can also be avoided.
Owner:YANGZHOU ZHONGKE SEMICON LIGHTING
Method for determining tobacco leaf specific surface, pore volume and pore diameter
InactiveCN102095836ACharacterization of adsorptionCharacteristicMaterial analysisTest sampleNitrogen
The invention relates to a method for determining the specific surface, pore volume and pore diameter of a tobacco leaf, belonging to the technical field of research on physical characteristics of the tobacco leaf. The method provided by the invention is carried out according to the BET (Brunauer-Emmett-Teller) test theory and comprises the following steps: a, preparing test samples and testing; b, measuring multilayer adsorption capacities of three groups of test samples under different nitrogen partial pressures according to a BET equation, taking P / P0 within the range of 0.05-0.25 as an X axis, taking a count formula (described in the specification) as a Y axis, drawing according to the BET equation and carrying out linear fitting to obtain the slope and intercept of a straight line, thus the Vm value is solved and the specific surface area of the tested sample is calculated; c, determining the pore volume, wherein single point nitrogen adsorption capacity when the P / P0 is 0.95 is namely the pore volume of material; and d, calculating the pore diameter by the specific surface area and the pore volume according to the formula (described in the specification). The method in the invention has the advantages of safety and simplicity, and the determined indexes of the specific surface, the pore volume and the pore diameter of the tobacco leaf can represent the adsorption capacity and identity of the tobacco leaf.
Owner:YUNNAN RES INST OF TOBACCO SCI
(Ti, Al) N reinforced self-shielded flux-cored wire utilizing air N infiltration
ActiveCN109664046AAvoid adding directlyReduce wire costsWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaNitrogen partial pressurePotassium
The invention discloses a (Ti, Al) N reinforced self-shielded flux-cored wire utilizing air N infiltration. According to the (Ti, Al) N reinforced self-shielded flux-cored wire utilizing air infiltration, a low-carbon steel strip is taken as an outer skin, and a flux core comprises, by mass percentage, 36-55% of micro-carbon ferrochrome, 10-25% of a mechanical mixture of ferrotitanium and aluminumpowder, 10-20% of rutile, 2-6% of marble, 3-8% of lithium fluoride, 1-3% of micro-carbon ferromanganese, 1-3% of potassium fluosilicate, 0.5-1% of sodium alginate and the balance iron powder, whereinferrotitanium: aluminum powder is larger than or equal to 3:2 and smaller than or equal to 4:1, and the flux core powder accounts for 25-30% of the total weight of the welding wire. According to theself-shielded flux-cored wire, no additional shielding gas is required, a certain nitrogen partial pressure is maintained in a welding atmosphere, N in air is used as a raw material, part of N is infiltrated into deposited metal, and a (Ti, Al) N strengthening phase is generated by a reaction with Ti and Al, so that the strength and wear resistance of the wire are increased, and meanwhile the costof the wire is greatly reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method for composite multi-layer thin film coating
InactiveCN105316632AHigh hardnessImprove toughnessVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNitrogen partial pressureFilm coating
The invention discloses a preparation method for a composite multi-layer thin film coating. The preparation method comprises the following preparation steps that an aluminum product is chosen as a substrate, the surface of the substrate is cleaned through ethyl alcohol and ultrasonic waves and is dried after being ground and polished through abrasive paper, a trivalent chromate solution with the mass concentration being 5% is taken, and the content of trivalent chromium of the trivalent chromate solution is 2g / L on a Cr2O3 content basis. The preparation method for the composite multi-layer thin film coating is high in hardness, toughness and bonding strength, resistant to abrasion and resistant to corrosion. Due to the fact that a direct current reaction magnetic control co-sputtering film coating system is adopted, the nitrogen partial pressure does not need to be adjusted frequently, the efficiency is improved and the precision is also improved, so that the production line operation is made to be possible. Due to the fact that a metallic nickel layer is added, the thin film hardness is up to 50 gigapascals, the bonding strength is up to 200 N, and the toughness, the abrasion resistance and the corrosion resistance are all higher than those of a TiN single-layer film.
Owner:芜湖华宇彩晶科技有限公司
Cascade dynamic nitrogen adsorption instrument
ActiveCN102721753BImprove test efficiencySimple designComponent separationSolenoid valvePhysical chemistry
Owner:北京精微高博仪器有限公司
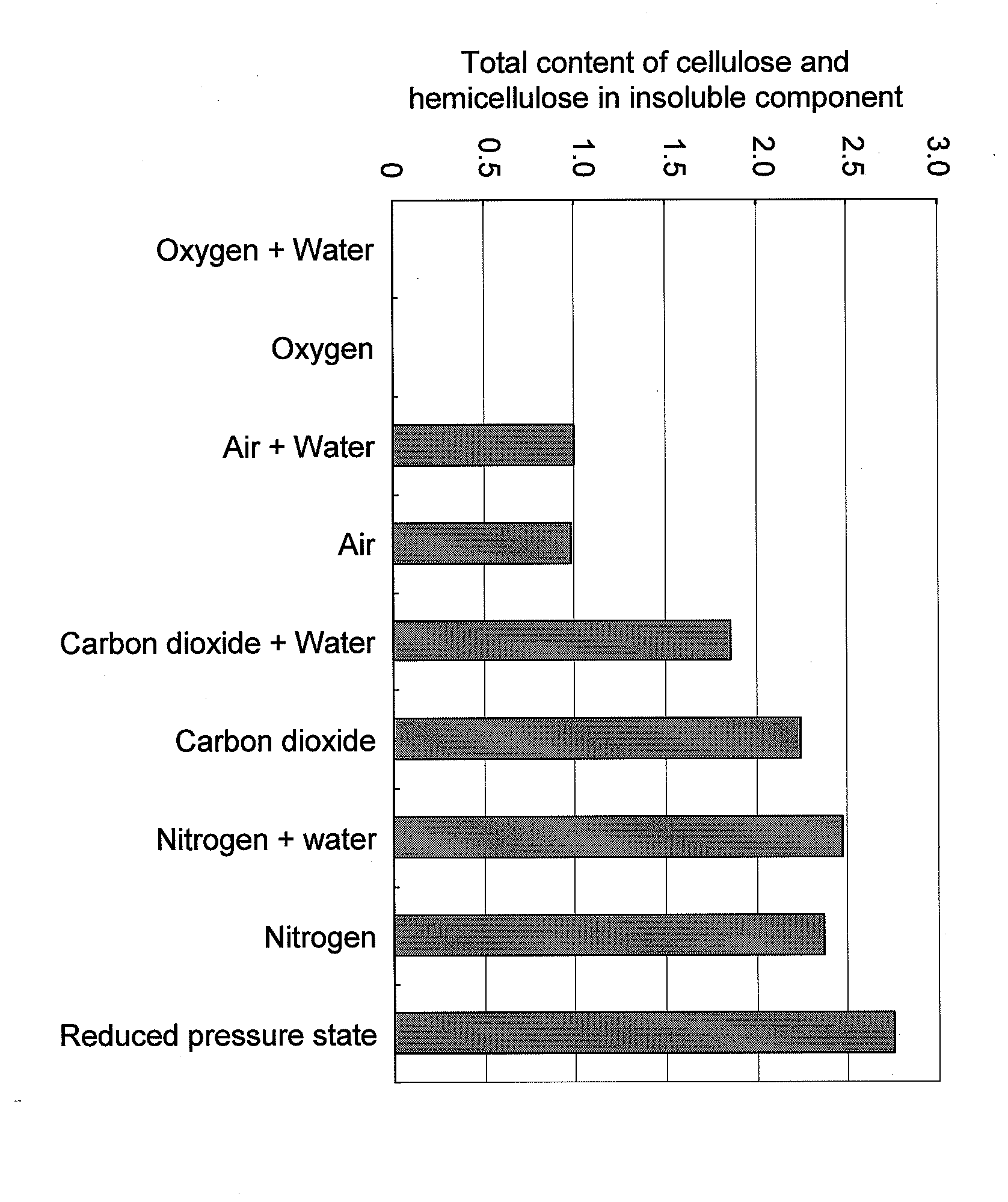
Method for controlling rate of lowering molecular weight of polysaccharides contained in cellulosic biomass, and method for producing sugar, alcohol, or organic acid
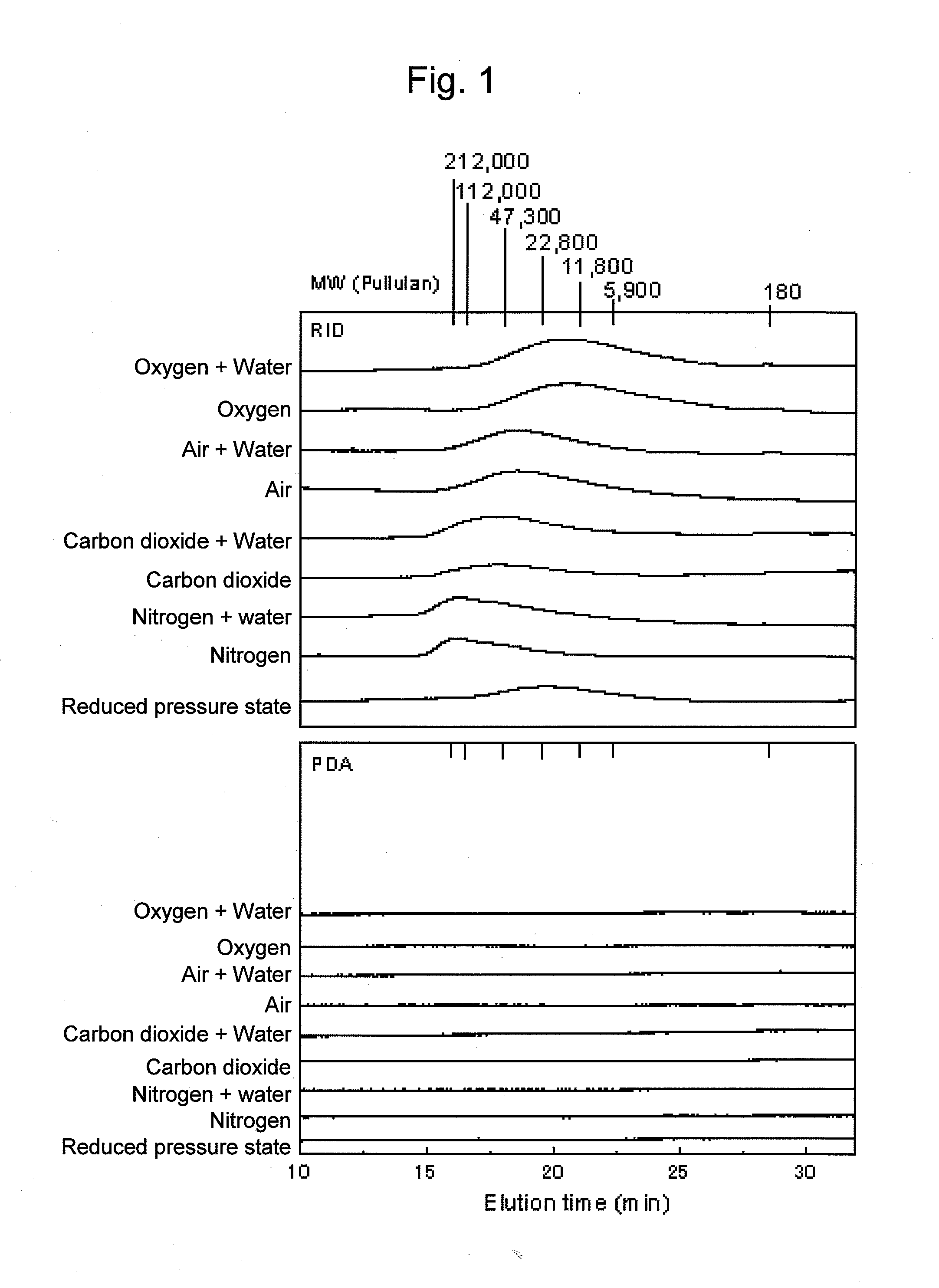
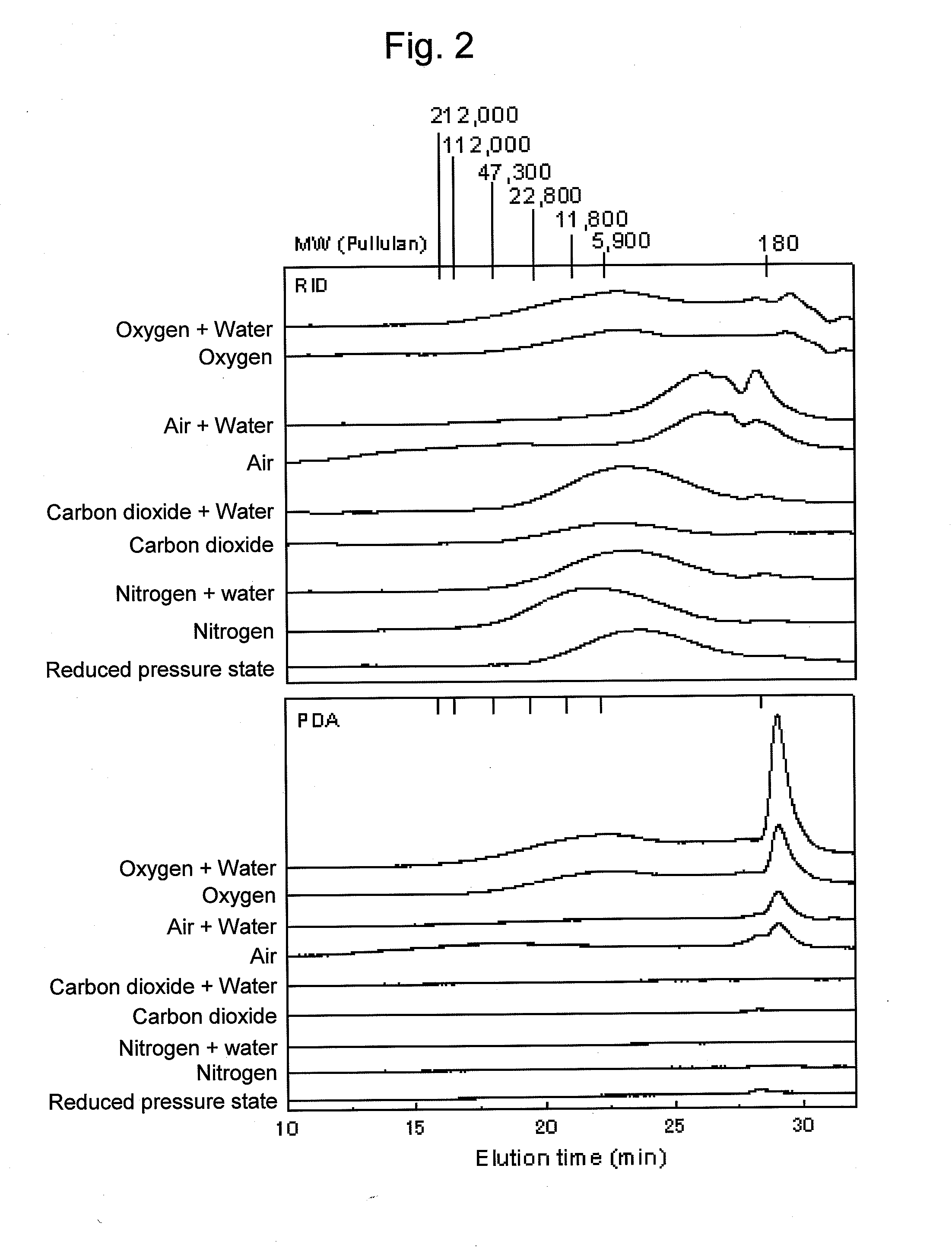
An object of the present invention is to provide, with regard to a method for lowering the molecular weight of polysaccharides contained in a cellulosic biomass by mixing the cellulosic biomass with ionic liquid, a method for controlling such rate of lowering of molecular weight. Also, a method for producing sugar, alcohol, or organic acid using the controlling method is provided. The method comprises mixing a cellulosic biomass with ionic liquid under an atmosphere with a partial pressure ratio differing from that of air. Under such an atmosphere with oxygen partial pressure higher than that of air, the rate of lowering molecular weight can be increased, and under an atmosphere with nitrogen partial pressure or carbon dioxide partial pressure higher than that of air or a reduced-pressure atmosphere, the rate of lowering molecular weight can be decreased.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com