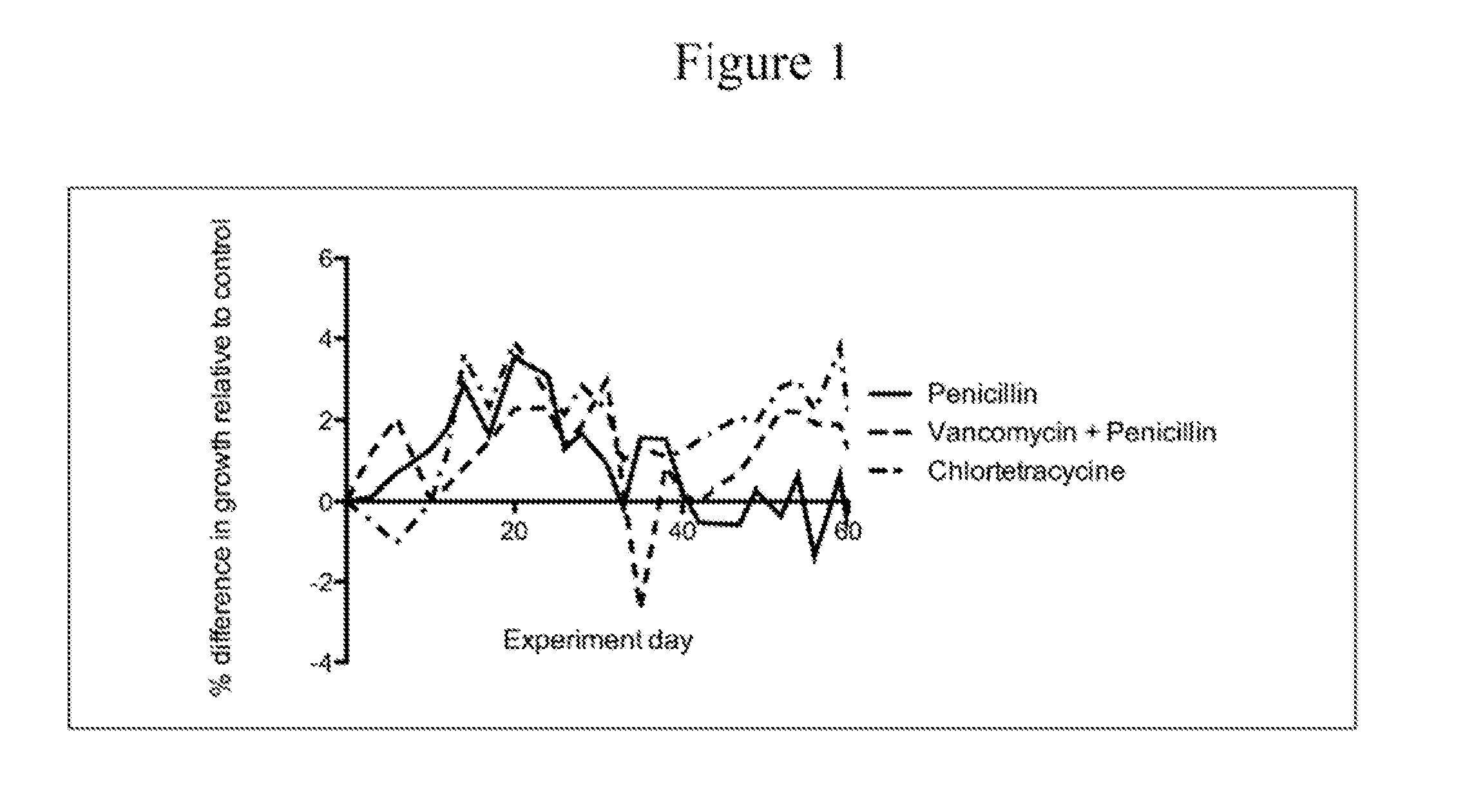
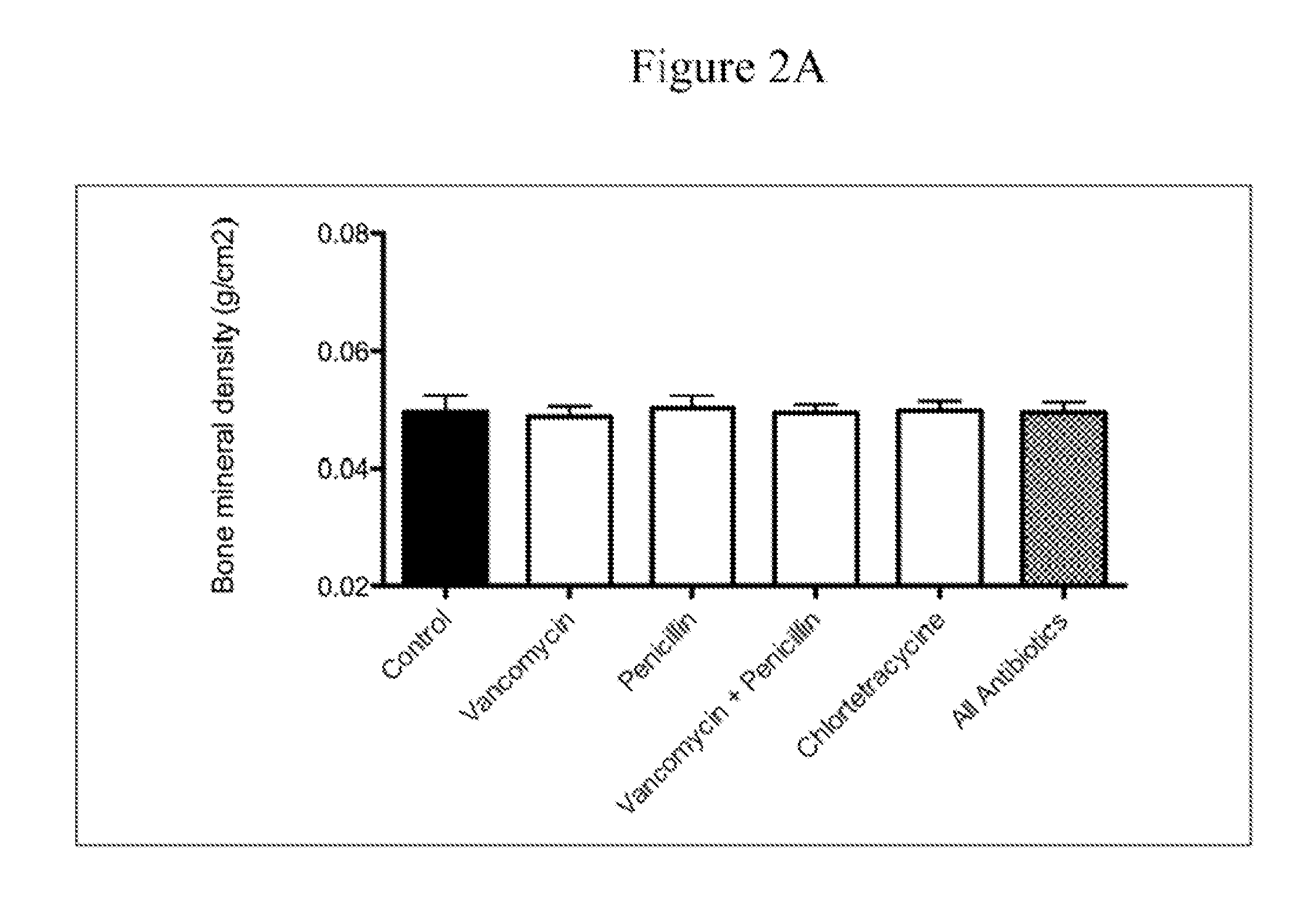
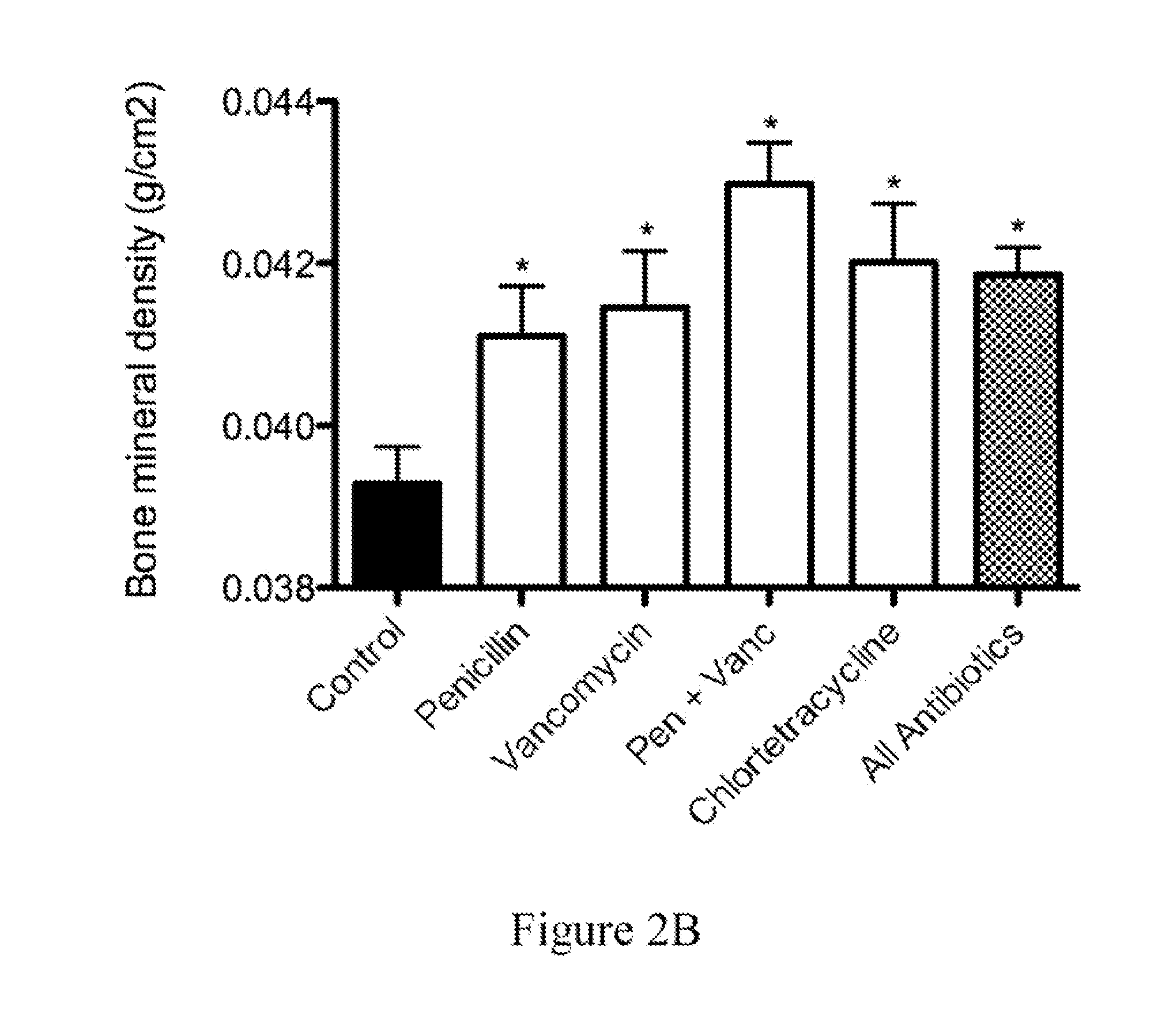
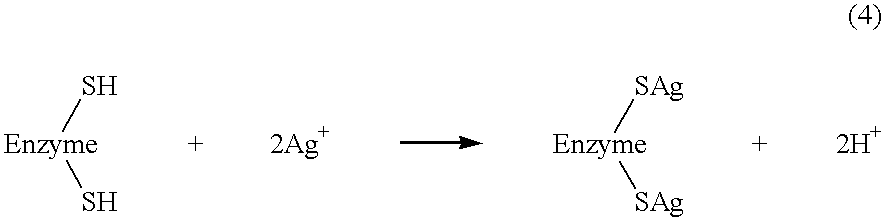
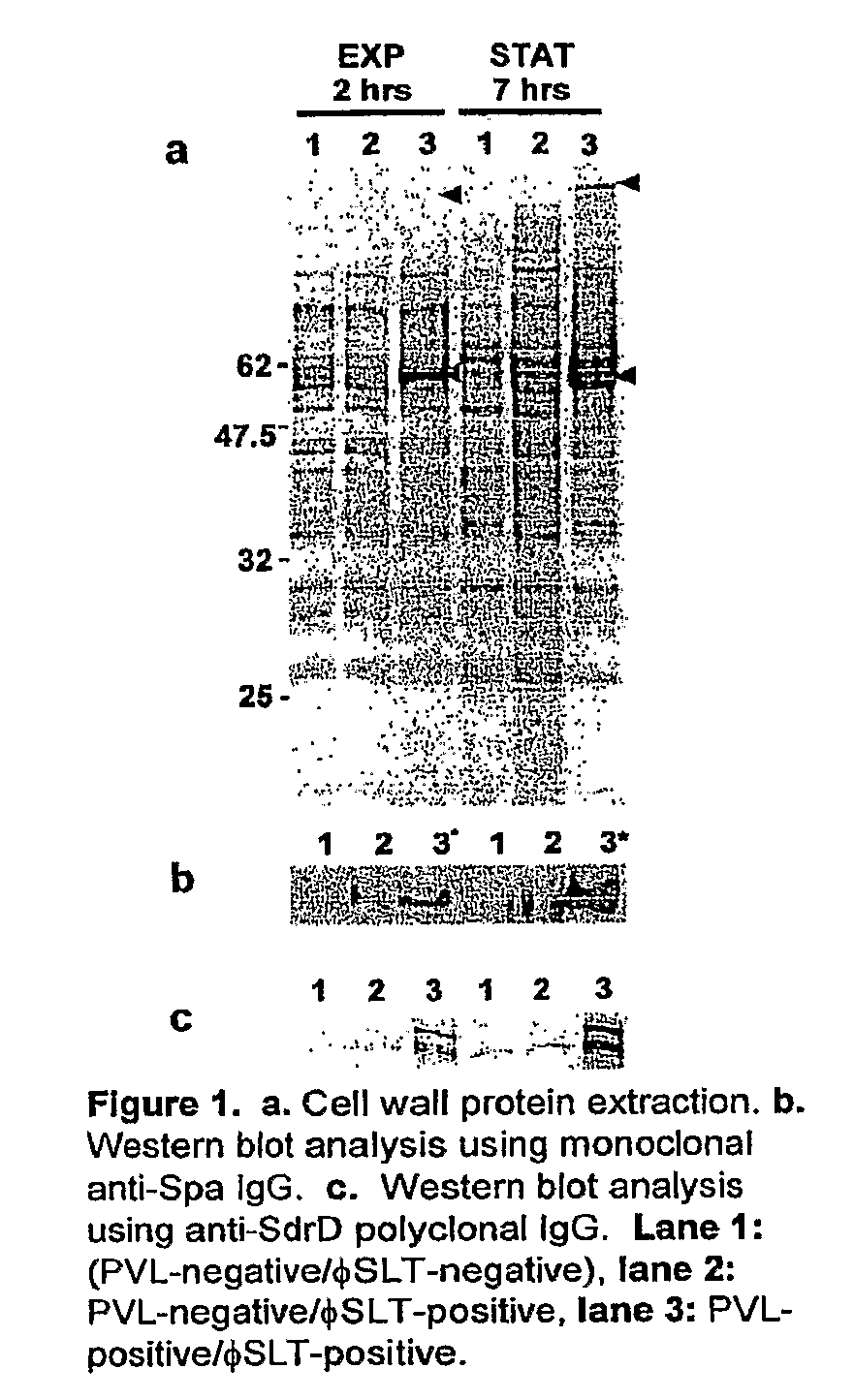
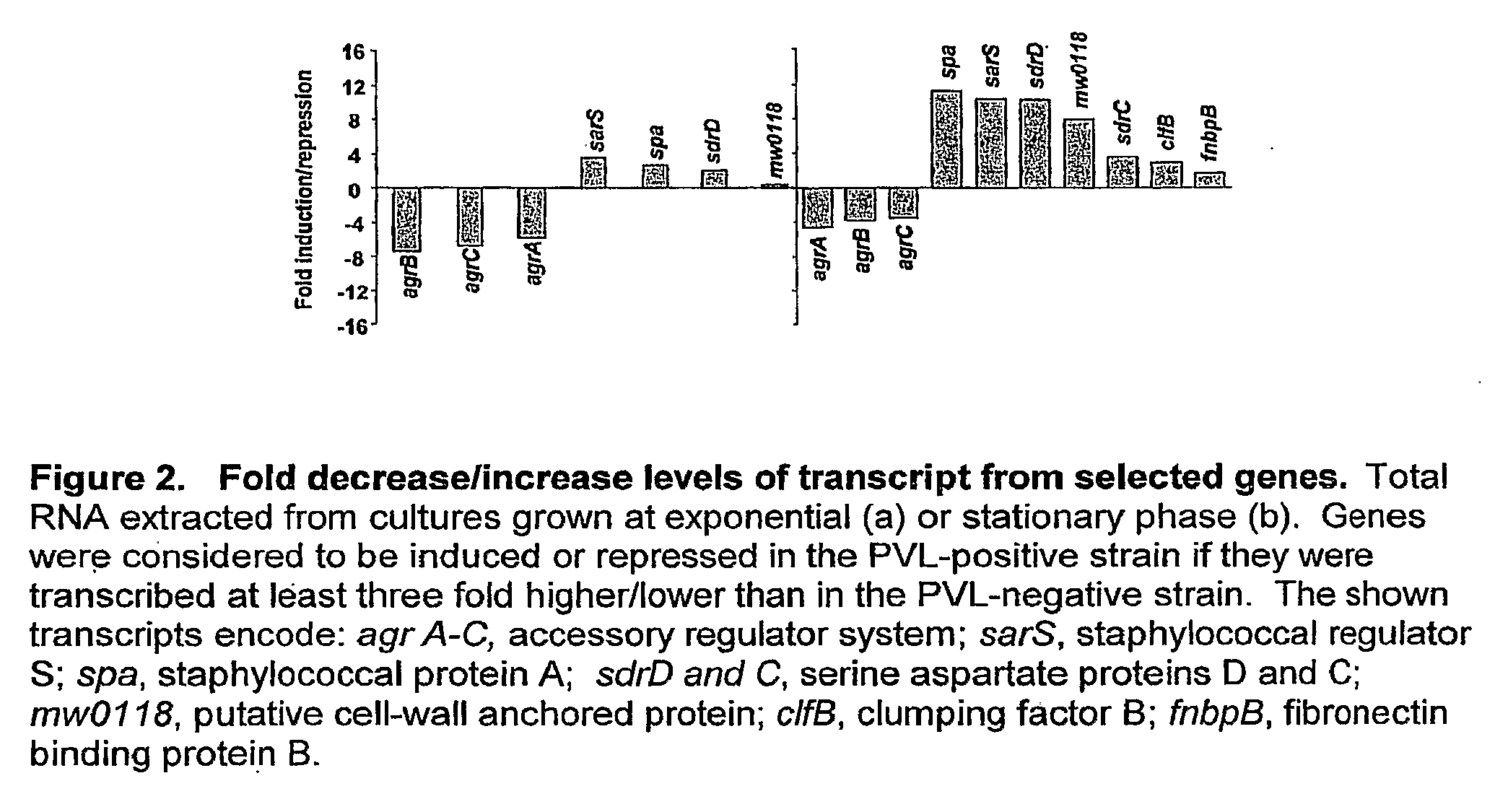
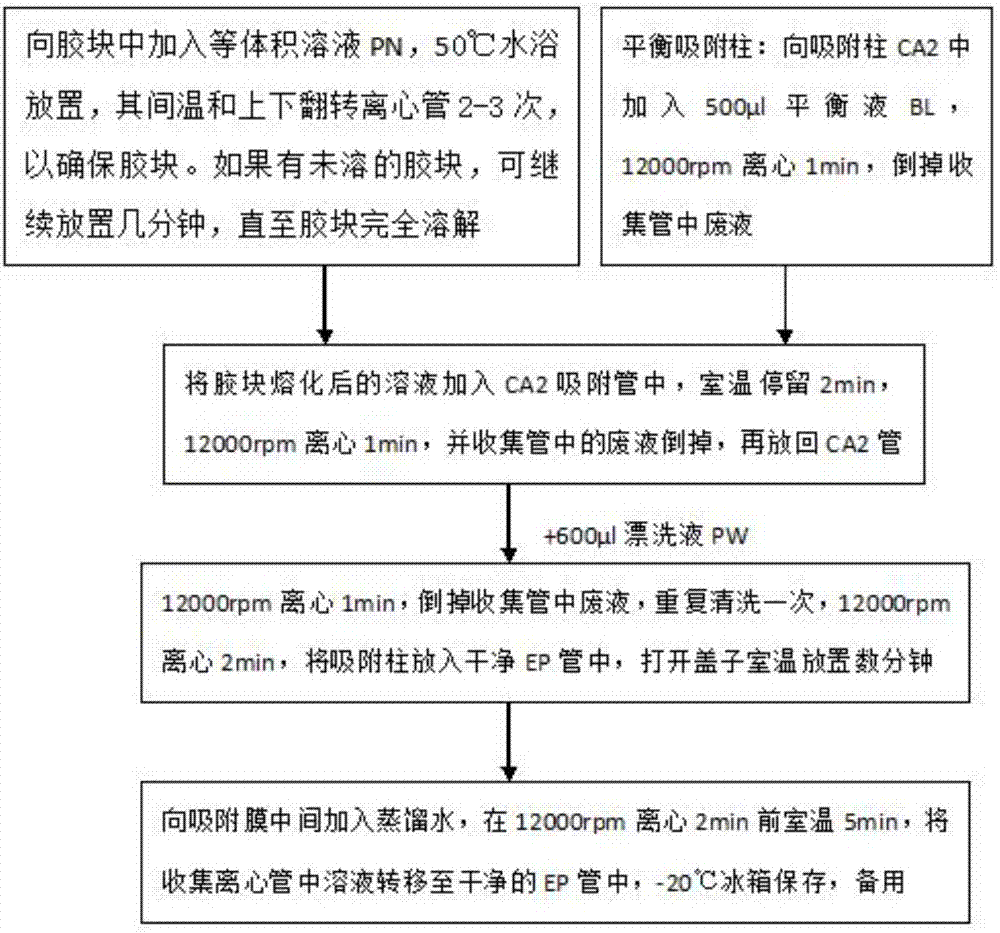
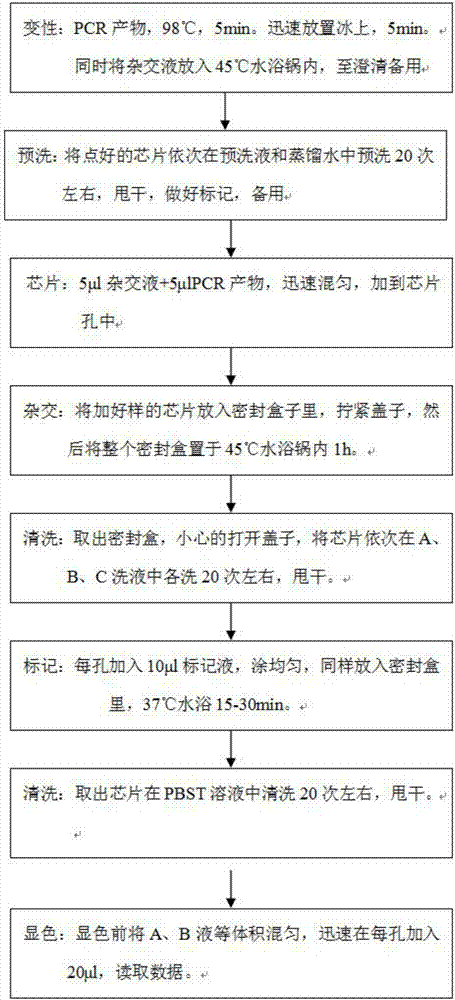
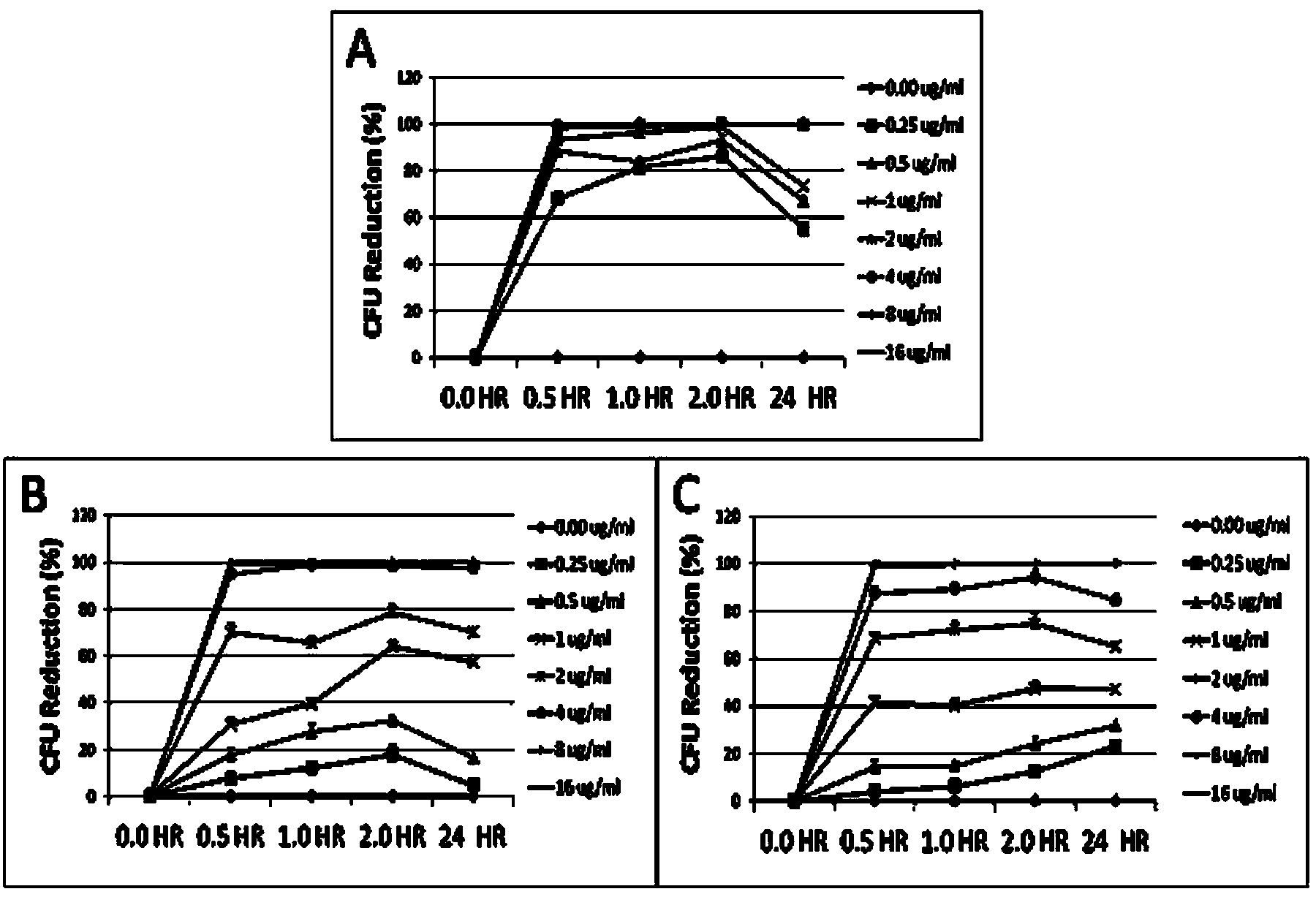
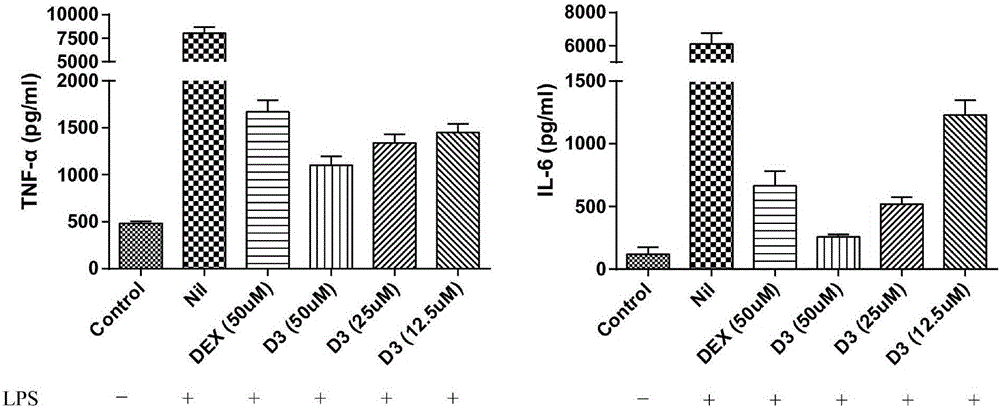
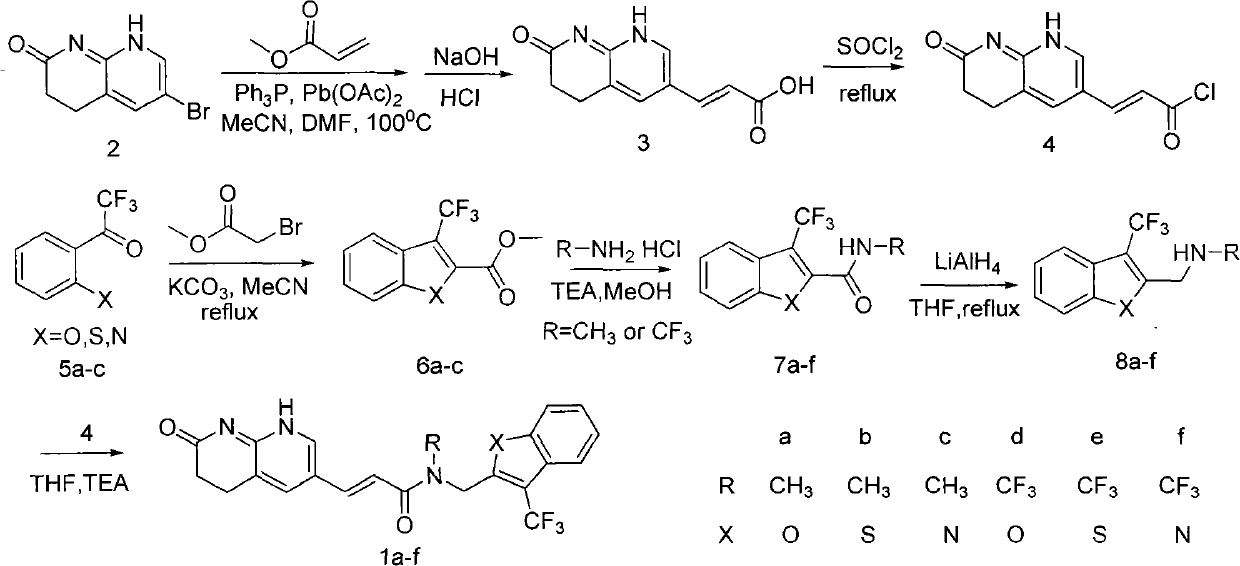
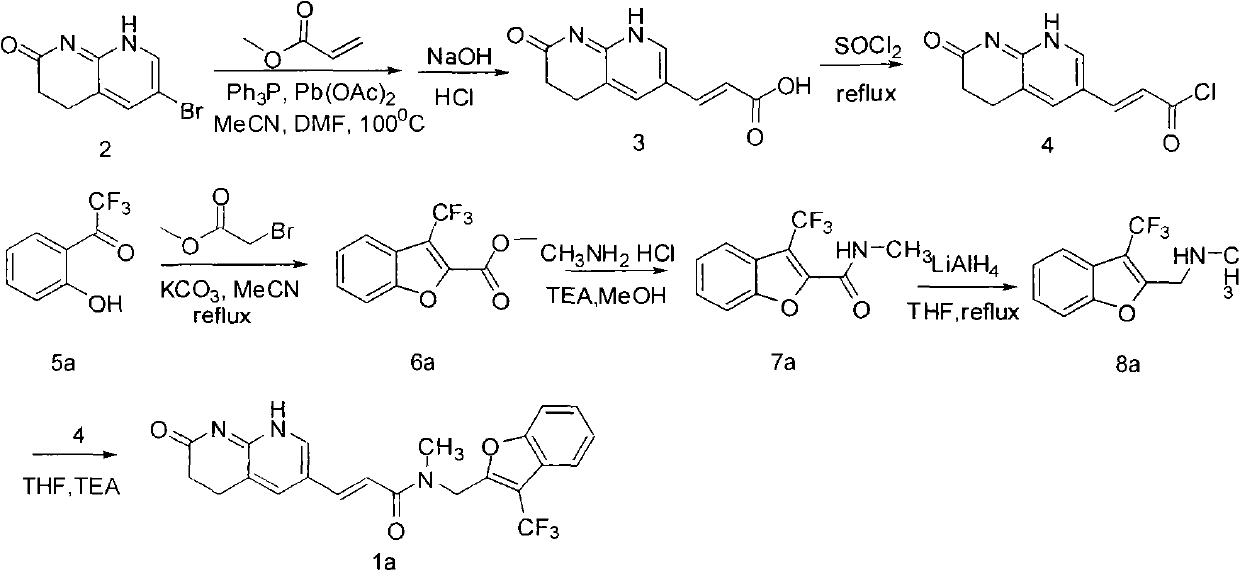
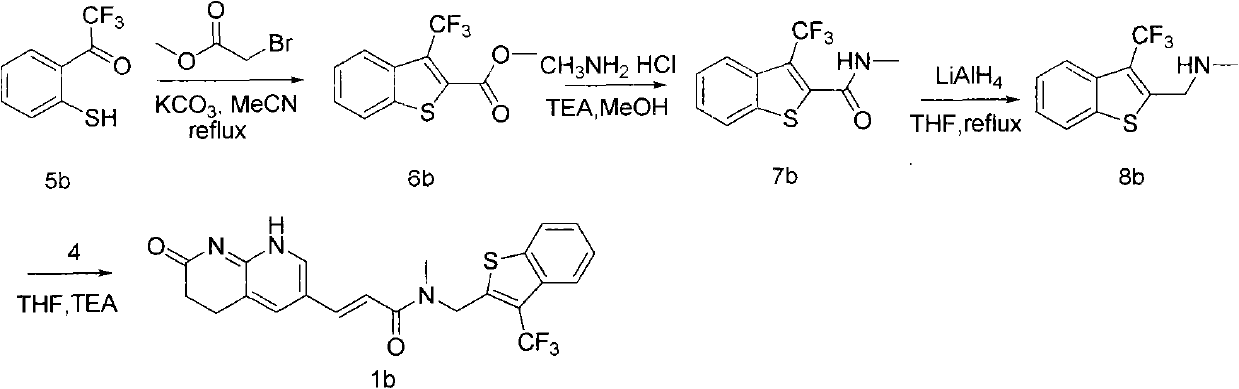
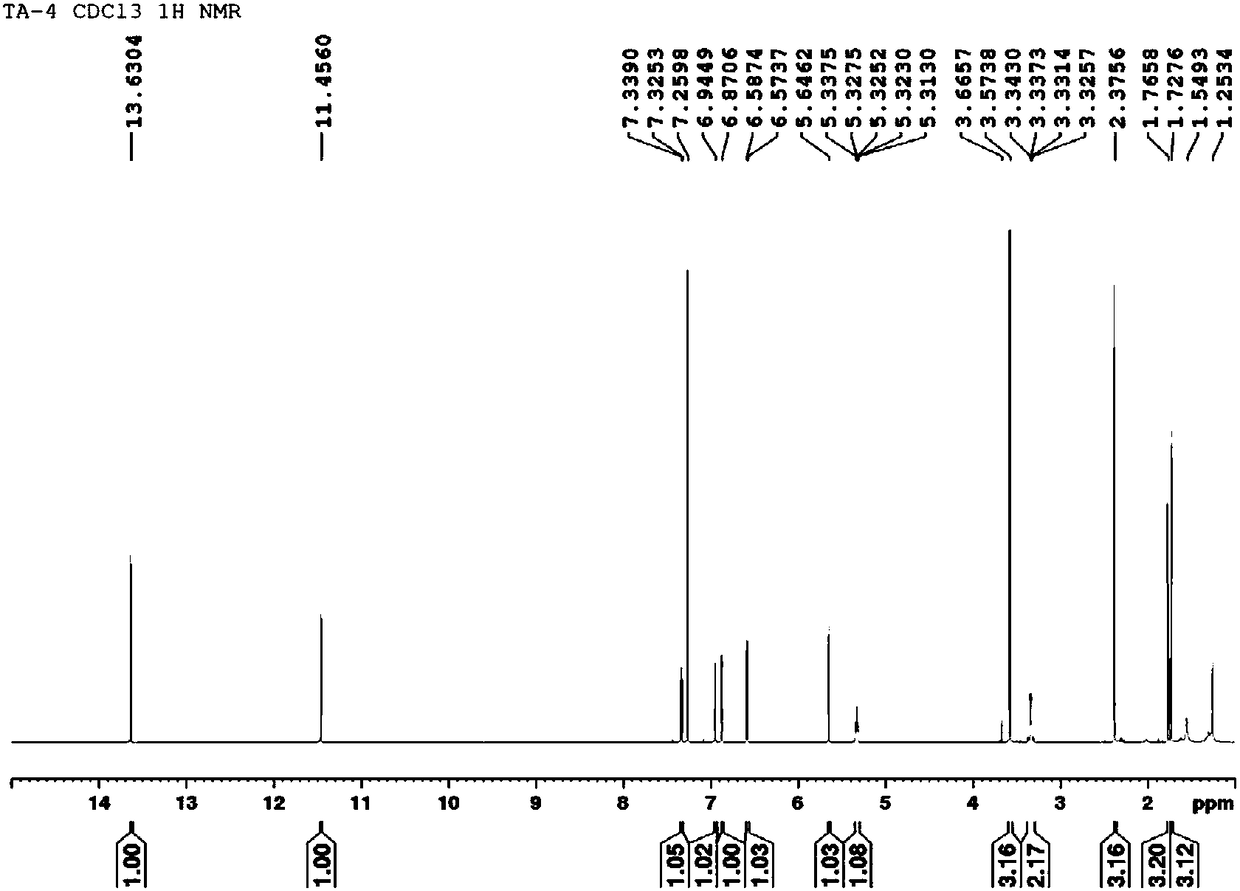
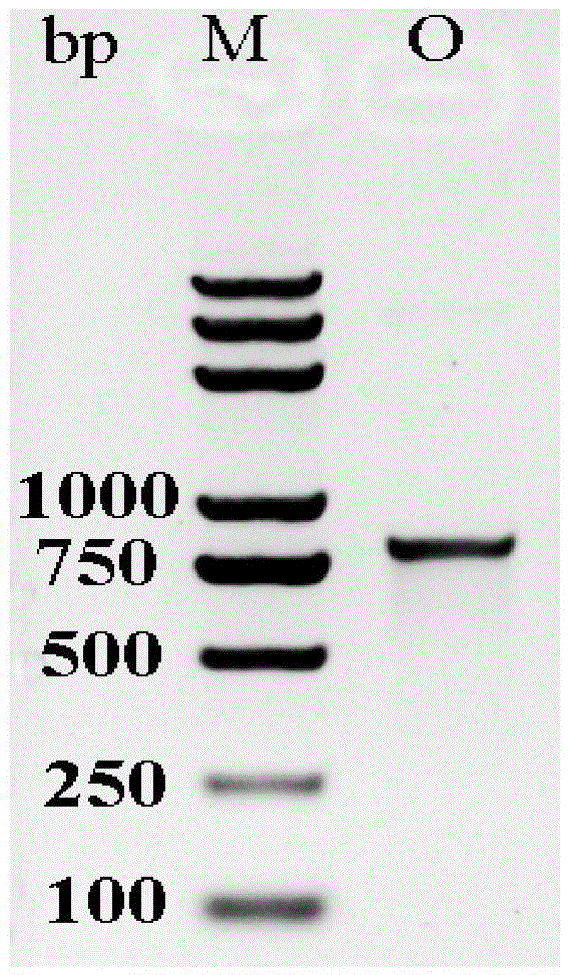Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
108 results about "Meticillin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methicillin, also known as meticillin, is a narrow-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. Meticillin was discovered in 1960.
Compositions and methods for characterizing and restoring gastrointestinal, skin, and nasal microbiota
ActiveUS20100074872A1Growth inhibitionFacilitate calorie uptakeBiocideMetabolism disorderBacteroidesDisease
The present invention relates to characterizing changes in mammalian bacterial gastrointestinal, cutaneous and nasal microbiota associated with antibiotic treatment and various disease conditions (such as asthma, allergy, obesity, metabolic syndrome, gastrointestinal reflux disease (GERD), eosinophilic esophagitis, gastro-esophageal junction adenocarcinomas (GEJAC), infections due to bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics, including Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Clostridium difficile, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, etc.) and related diagnostic and therapeutic methods. Therapeutic methods of the invention involve the use of live bacterial inoculants that are capable of restoring healthy mammalian bacterial gastrointestinal, skin, and nasal microbiota.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Nanosilver-containing antibacterial and antifungal granules and methods for preparing and using the same
The present invention relates to nanosilver-containing antibacterial and antifungal granules ("NAGs"). The NAGs have longlasting inhibitory effect on a broad-spectrum of bacteria and fungi, which include, but are not limited to, Escherichia coli, Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Chlamydia trachomatis, Providencia stuartii, Vibrio vulnificus, Pneumobacillus, Nitrate-negative bacillus, Staphylococcus aureus, Candida albicans, Bacillus cloacae, Bacillus allantoides, Morgan's bacillus (Salmonella morgani), Pseudomonas maltophila, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus foecalis alkaligenes, Streptococcus hemolyticus B, Citrobacter, and Salmonella paratyphi C. The NAGs contain ground stalk marrow of the plant Juncus effuses L. which has been dispersed with nanosilver particles. The nanosilver particles are about 1-100 mn in diameter. Each of the nanosilver particles contain a metallic silver core which is surrounded by silver oxide. The present invention also provides a process for making the NAGs. The NAGs can be used in a variety of healthcare and industrial products. Examples of the healthcare products include, but are not limited to, ointments or lotions to treat skin trauma, soaking solutions or cleansing solutions for dental or women hygiene, medications for treating gastrointestinal bacteria infections, sexual related diseases, and eye diseases. Examples of industrial products include, but are not limited to, food preservatives, water disinfectants, paper disinfectants, construction filling materials (to prevent mold formation).
Owner:LEGEND WIN FINANCE
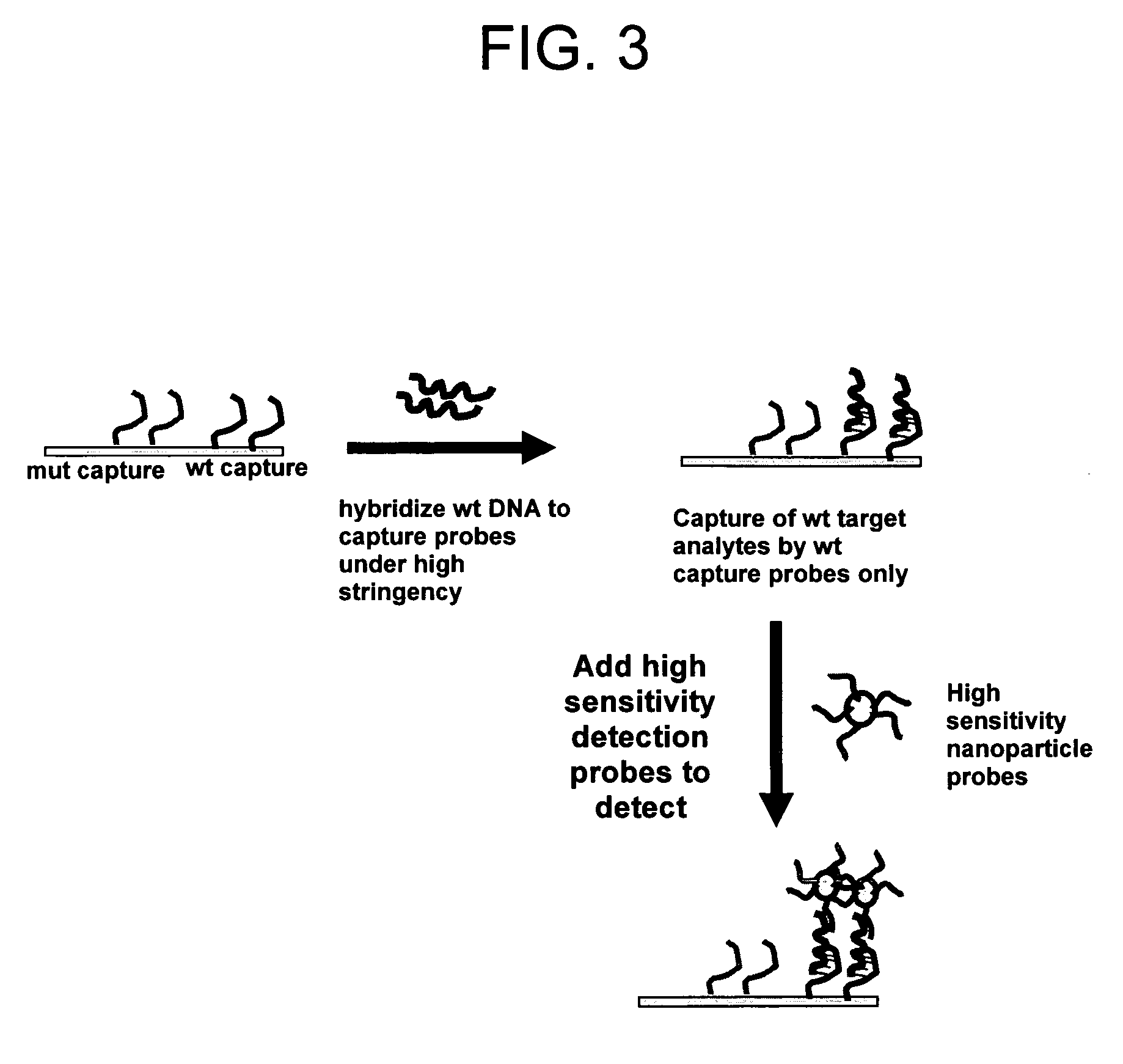
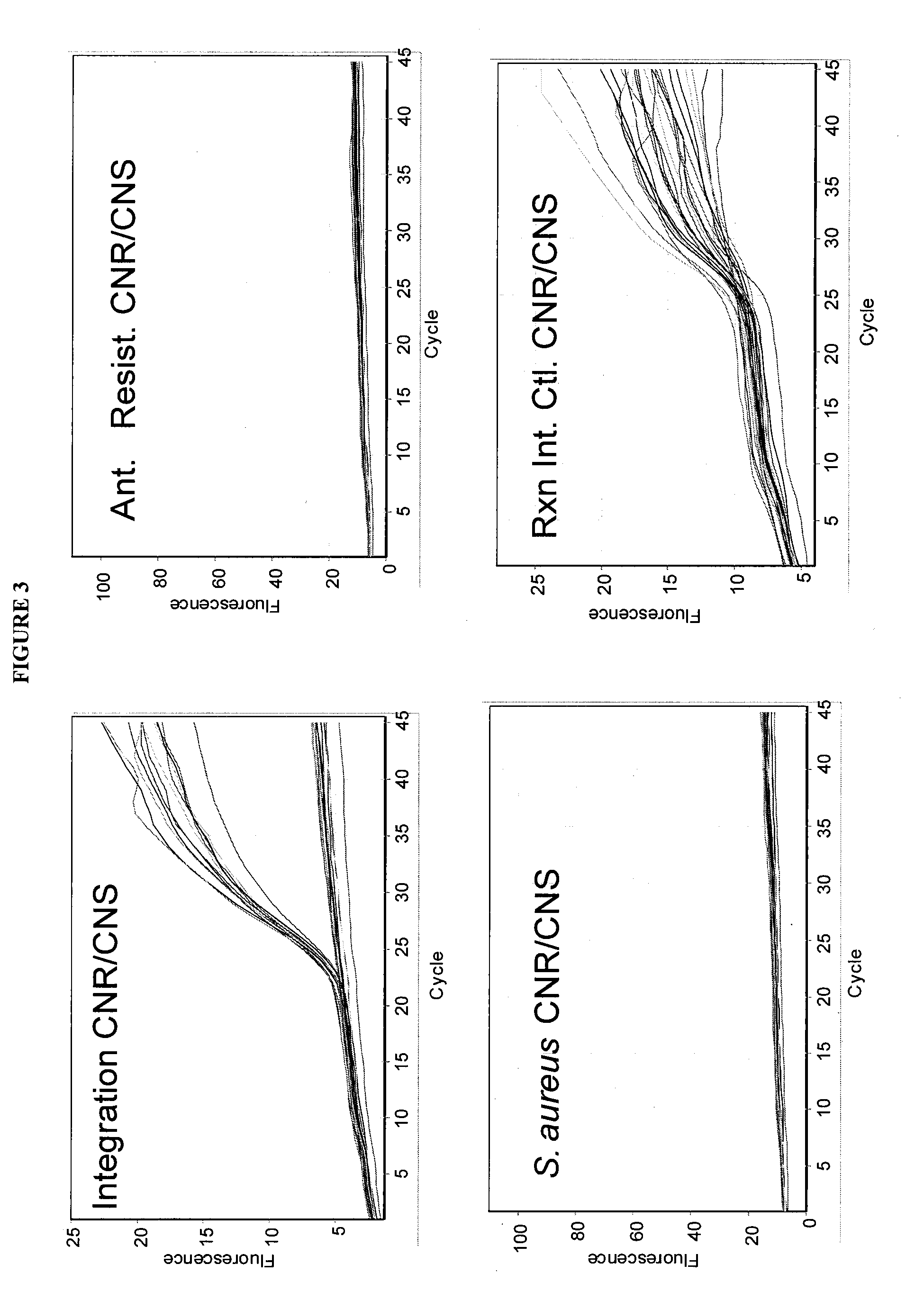
Method for distinguishing methicillin resistant S. aureus from methicillin sensitive S. aureus in a mixed culture
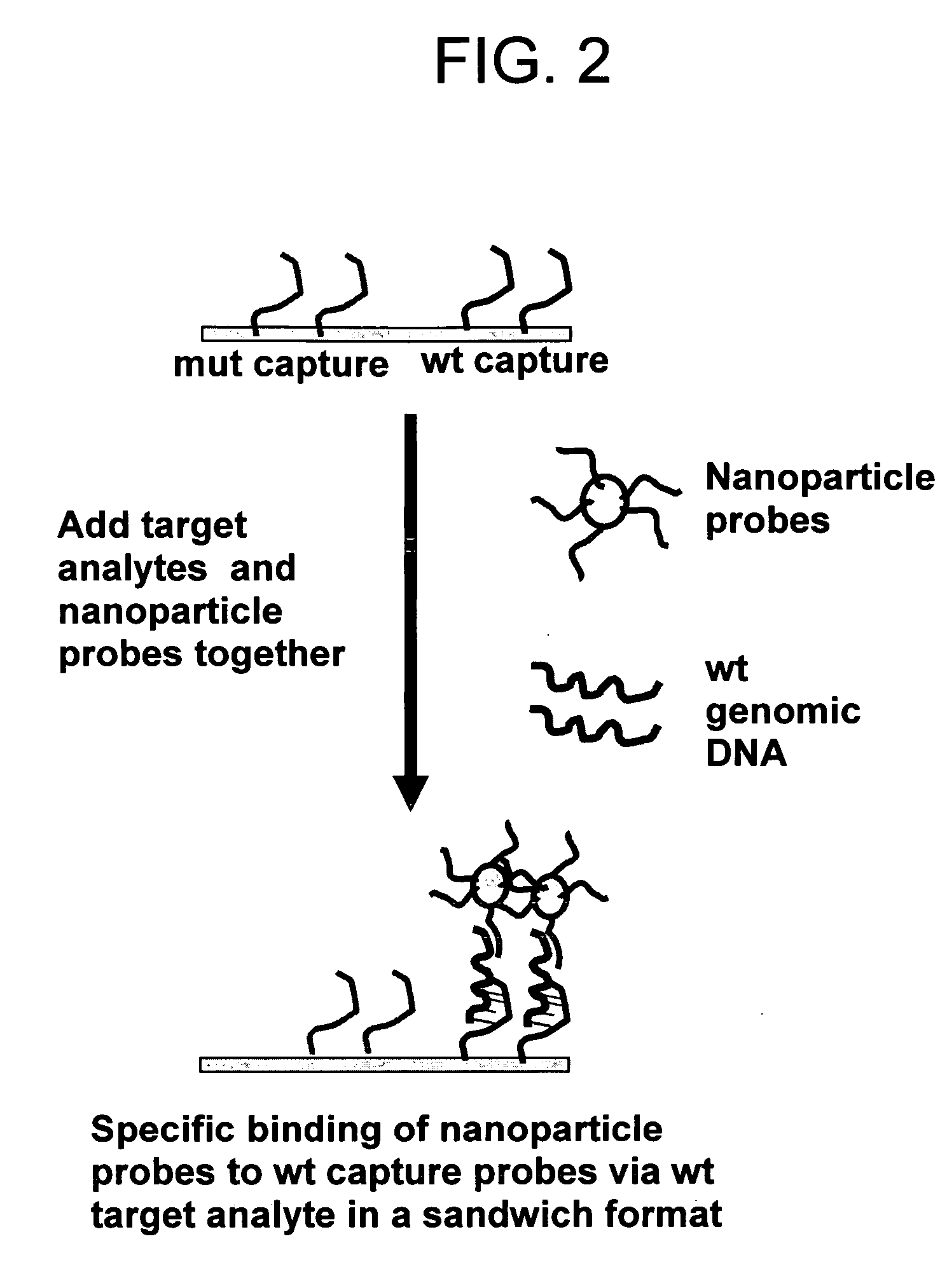
The present invention provides isolated oligonucleotides and methods for detecting a methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a sample, including a sample that comprises nucleic acid molecules of higher biological complexity than that of amplified nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:NANOSPHERE INC
Methods and compounds for antimicrobial intervention
InactiveUS8598342B2Antibacterial agentsBiocideSynthetic analogueMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
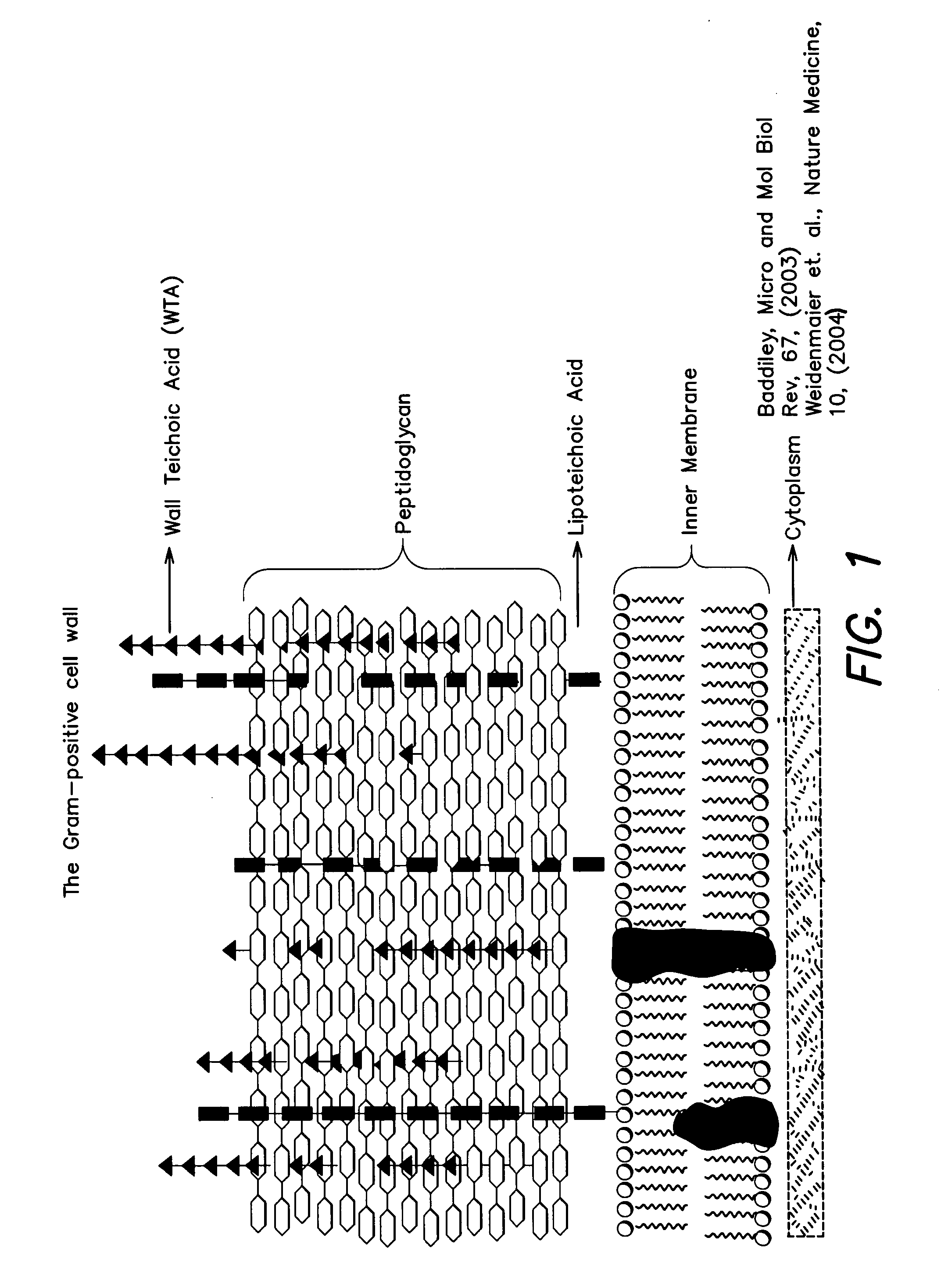
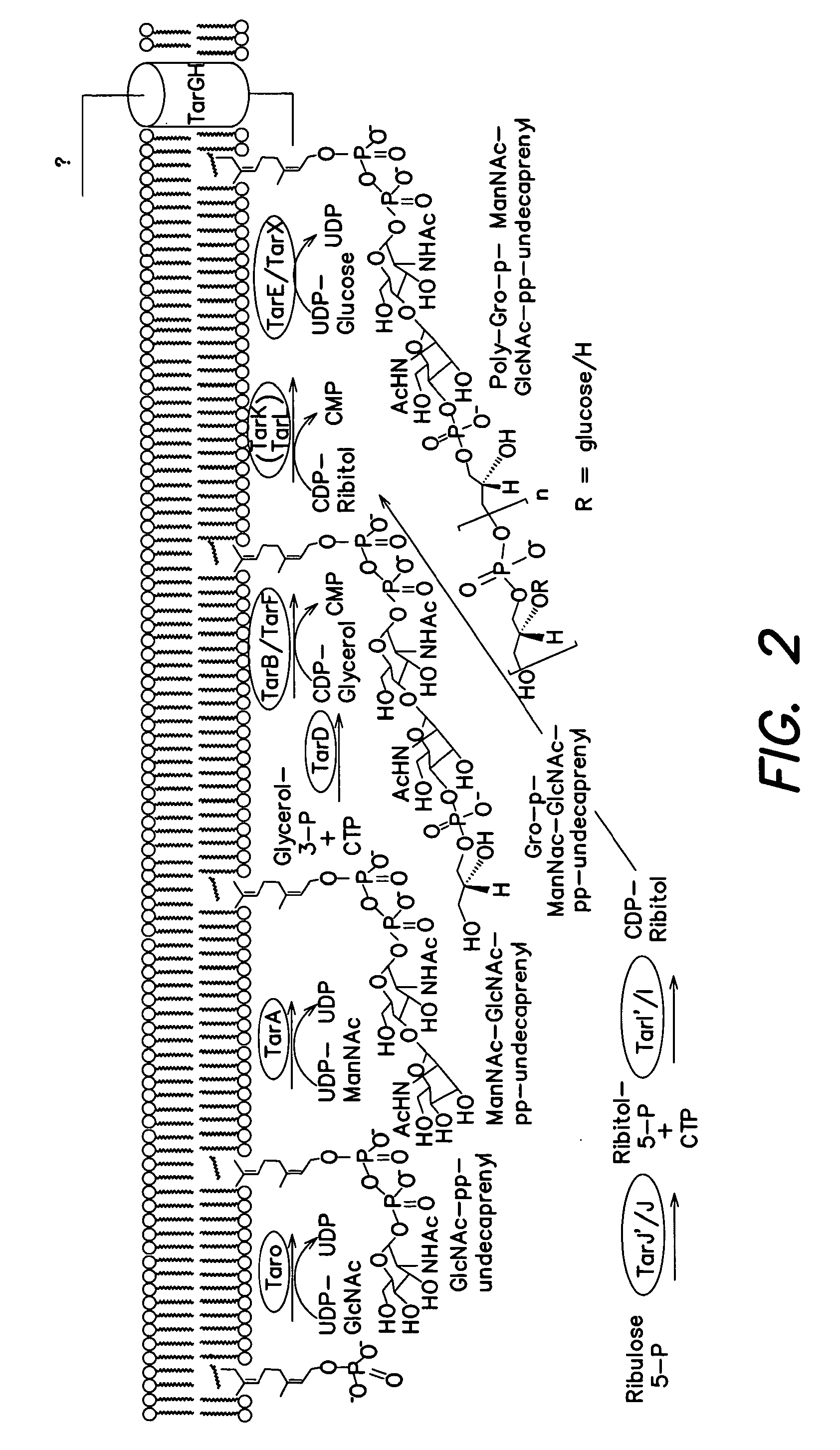
The present invention provides Wall Teichoic Acid biosynthesis inhibitors such as compound 1835F03 (targocil) and related synthetic analogs. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions thereof and methods for treating bacterial infection and the suppression of growth of bacterial cells by administering a Wall Teichoic Acid biosynthesis inhibitor. The invention is particularly useful for the treatment of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The invention further provides procedures for the syntheses of Wall Teichoic Acid biosynthesis inhibitors. The invention also provides methods for the identification of antibacterial therapeutic agents.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
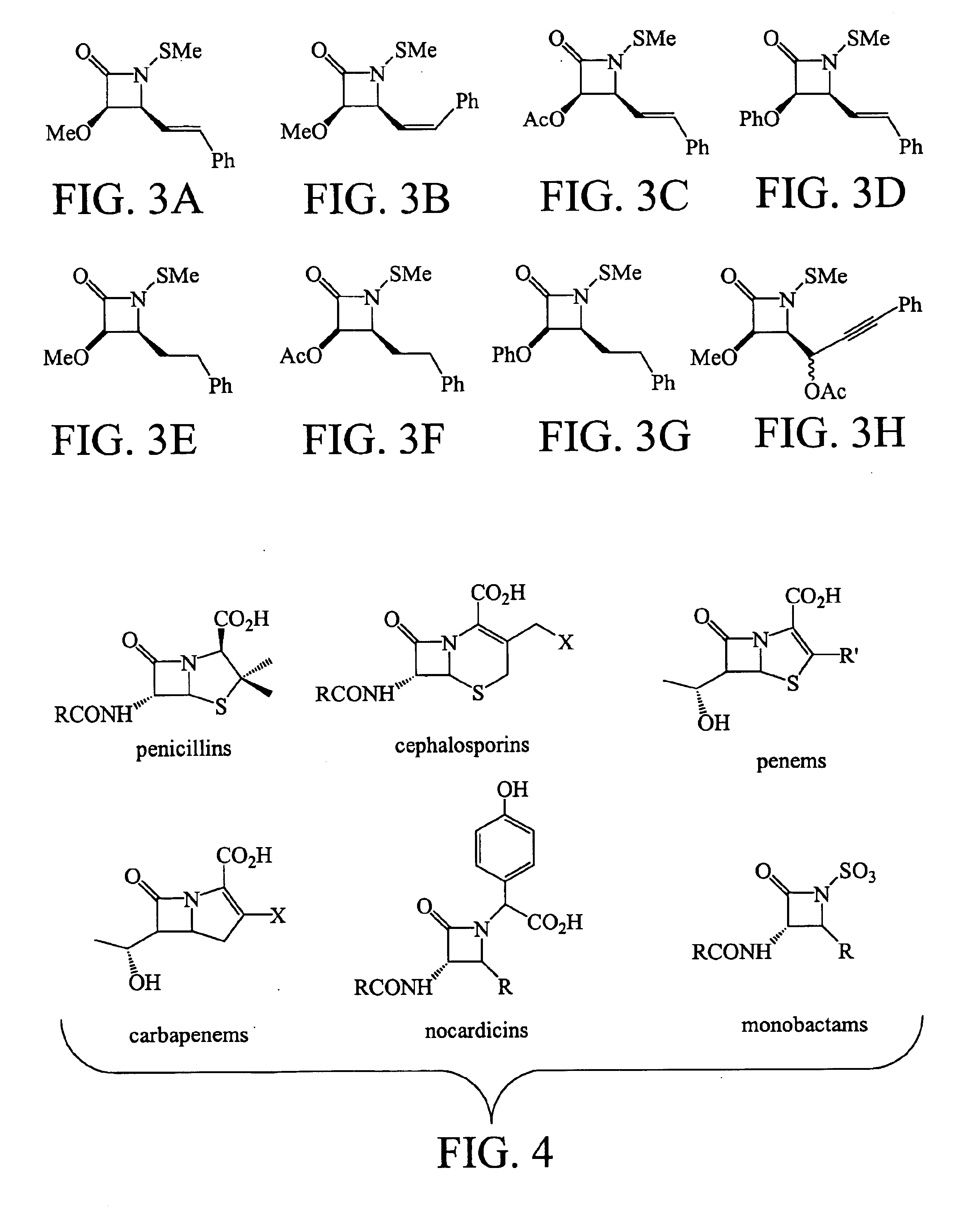
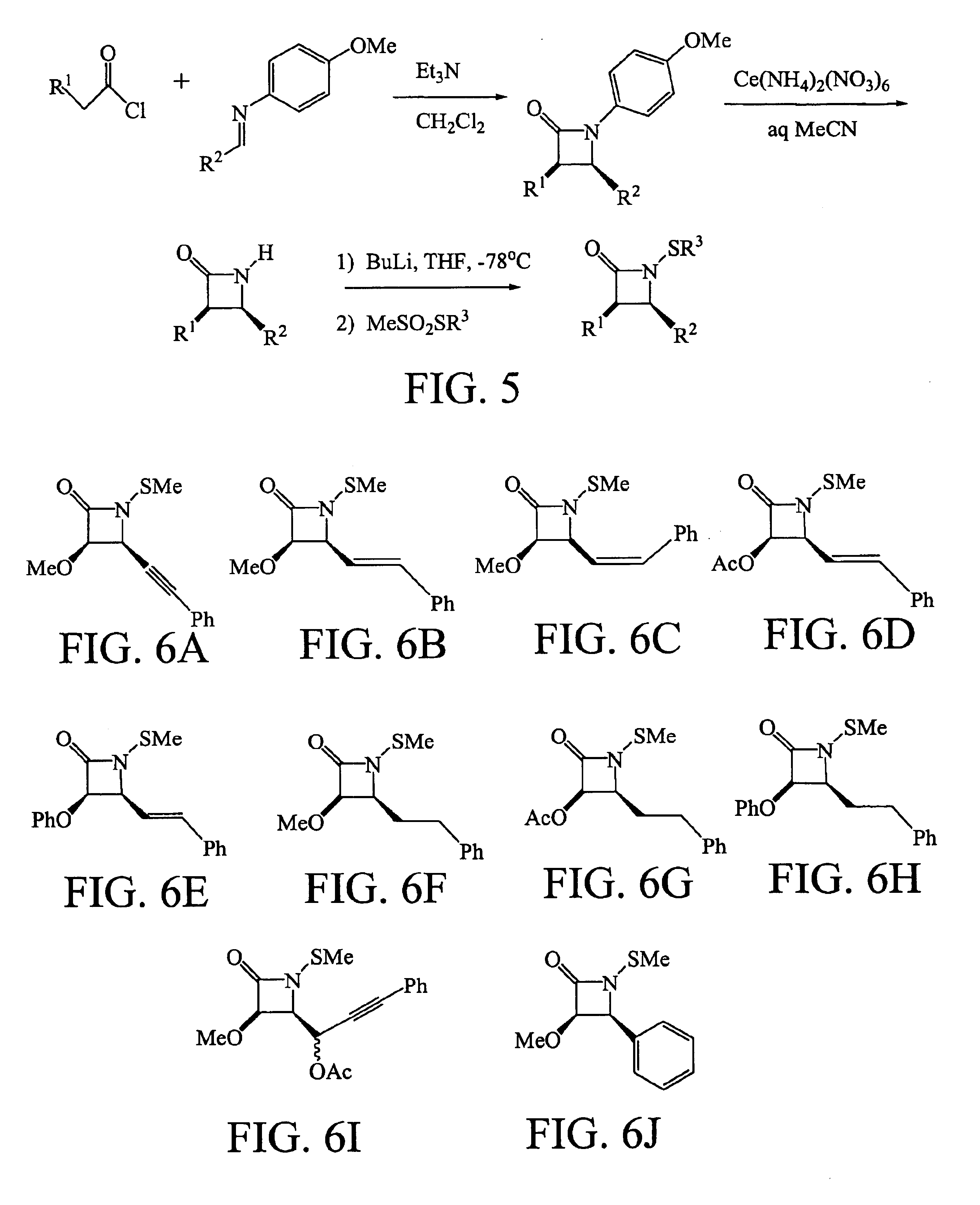
N-thiolated beta-lactams: novel antibacterial agents for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
The invention relates generally to novel N-thiolated β-lactams. More specially, the invention relates to the use of these novel antibacterial agents in the treatment or inhibition of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureaus.
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
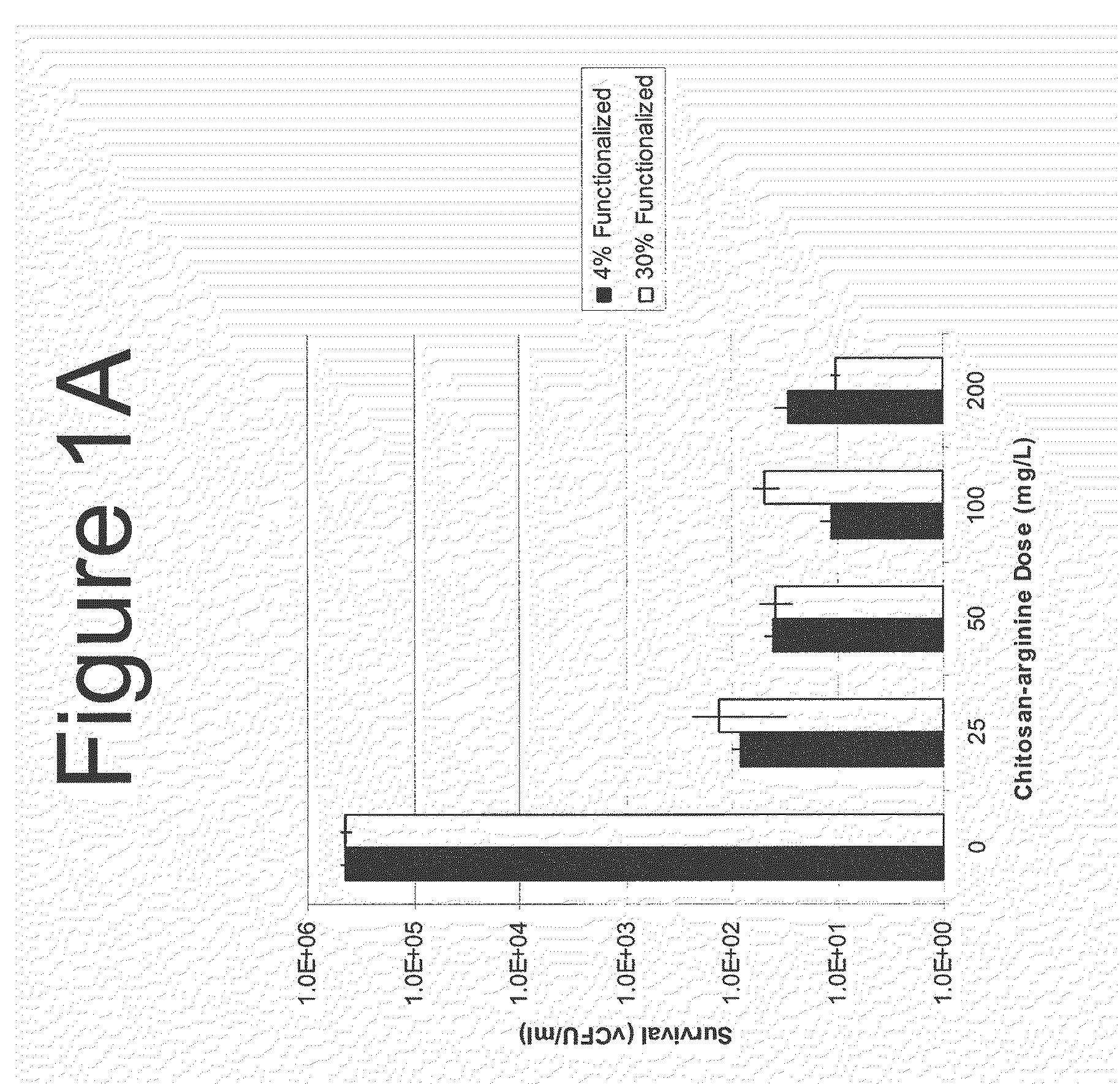
Methods and Compositions for the Prevention of and Treatment of Infections Utilizing Chitosan-Derivative Compounds
The present invention is directed to the treatment and prevention of nosocomial infections or MRSA infections utilizing soluble chitosan or chitosan derivative compounds. These chitosan-derivative compounds, e.g., chitosan-arginine and chitosan-acid amines, exhibit bactericidal activity against bacterial pathogens, e.g., drug resistant bacteria such as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Owner:SYNEDGEN
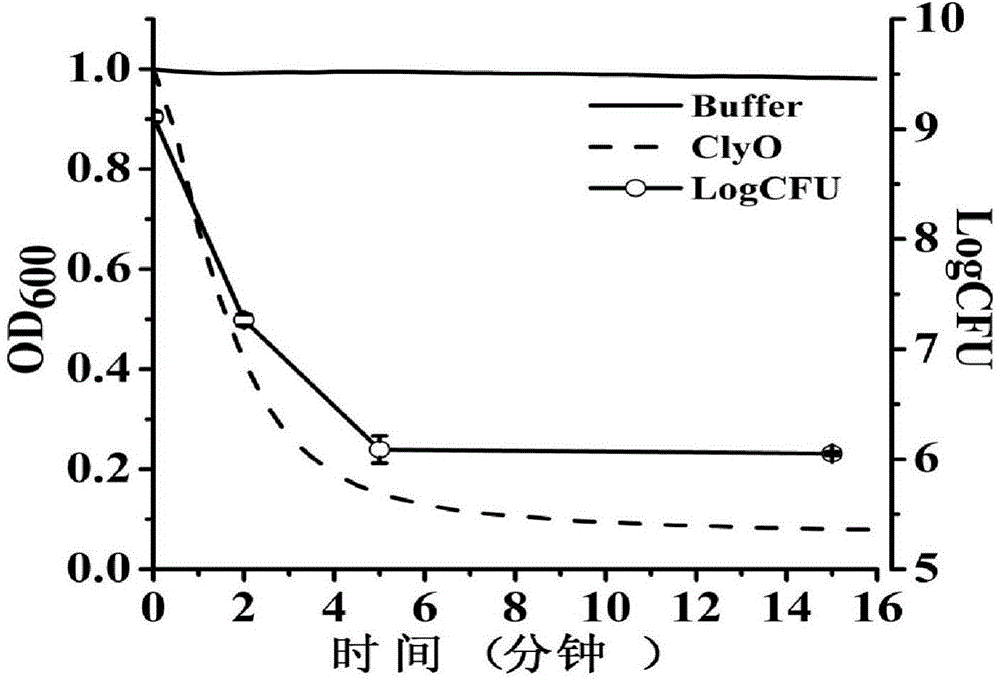
Lyase for killing staphylococcus and application of lyase
ActiveCN103122347ARapid lysisIncrease enzyme activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMethicillin resistanceAdenosine
The invention discloses a lyase for killing staphylococcus and an application of the lyase and also discloses an amino acid sequence and an encoding gene sequence of the lyase. A recombined lyase constructed by using the disclosed encoding gene can realize soluble expression in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3); the lyase can be used for efficiently killing various types of staphylococcus including clinically-separated methicillin-sensitive staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) and methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in vitro and can also be used as an antibiotic for treating staphylococcus infection in vivo; and the disclosed lyase can also be used for rapidly cracking the cell wall of the staphylococcus and releasing substances in cells, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP), DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and the like, and various detections on the staphylococcus can be realized through detecting released substances.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Detection of antibiotic-resistant microorganisms
ActiveUS20090181395A1Easy to separateReduce morbidityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCoagulase testMethicillin sensitive
Method of detecting methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-sensitive S. aureus (MSSA) in a nucleic acid coamplification assay. The invention advantageously reduces the incidence of false-positive MRSA determinations in real-time assays by requiring satisfaction of a threshold criterion that excludes certain co-infections from the MRSA determination. The invention further provides for determination of MSSA, even when the MSSA is present in combination with methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative (MR-CoNS) bacteria at high or low levels.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Antibodies recognizing a highly expressed putative antigen of ca-mrsa and methods of use
ActiveUS20090130115A1Avoid infectionInhibit growthAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenStaphylococcus cohnii
The present invention provides MSCRAMM® proteins from S. aureus which are putative highly-expressed antigens from methicillin-resistant S. aureus, including communit-associated MRSA (CA-MRSA), and these antigens can thus be utilized in methods of generating antibodies capable of binding these antigens which can be useful in methods of treating or preventing infection from MRSA. The present invention is directed to these proteins, antibodies capable of binding these proteins, methods of generating said antibodies, nucleic acids coding for said proteins, and pharmaceutical compositions or vaccines which include the proteins or antibodies of the present invention in combination with a pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle, carrier or excipient.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Kit for quickly detecting drug resistance gene of pneumophila pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN107475422AEasy to operateNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMethicillin resistanceAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to a kit for quickly detecting a drug resistance gene of pneumophila pathogenic bacteria, which comprises a gene chip capable of detecting 24 main drug resistance genes of pneumophila pathogenic bacteria and a reaction system for multiple asymmetric PCR reactions. The 24 drug resistance genes are derived from aminoglycosides, quinolones, extended spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs), cephalosporins (AmpC), carbapenems and drug resistance genes with vancomycin resistance and methicillin resistance causing membrane permeability transition. The kit can be used for directly detecting drug resistance genes of pneumophila pathogenic bacteria in clinical samples, is simple and quick to operate, does not need culture or drug sensitive tests, gains valuable time for reasonable application of antibiotics to a great extent, and is worthy of clinical popularization and application.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA +1
Nosocomial infection multiple causative agent parallel detection gene chip and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103255216AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAerobacter cloacaeEnterococcus faecalis
The invention belongs to the technical fields of molecular biological techniques and clinical tests, and particularly discloses a nosocomial infection multiple causative agent parallel detection gene chip and a preparation method and application thereof. The gene chip can be used for rapidly and sensitively detecting fourteen medical treatment infection typical causative agents such as acinetobacter baumannii, enterobacter cloacae, enterococcus faecalis and the like by using one reaction, and the detection data of coinfection of yeast and bacterium which cannot be provided by a traditional amplification method is offered. Furthermore, the gene chip also comprises a methicillin resistance target spot, thus realizing further detection of staphy lococcus infection, therefore, a clinician can realize which causative agent a patient is infected in one or two hours, and realize whether the patient has drug resistance, so as to decide whether the patient needs antibiotics or which antibiotics is needed, so that the gene chip has a greater clinical guiding significance.
Owner:SHANDONG ACV BIOTECH CO LTD
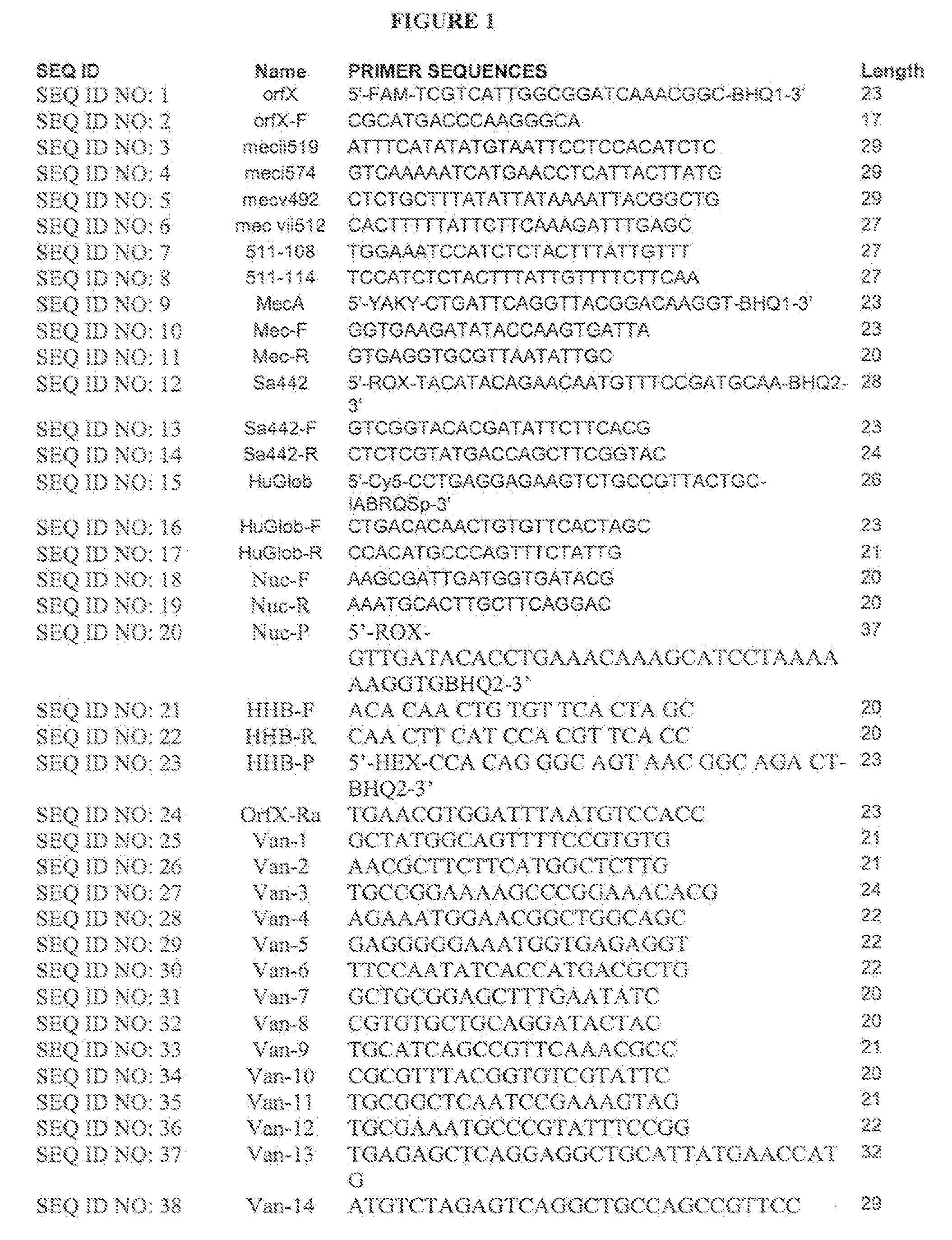
Primer group and kit for rapidly identifying respiratory tract microorganisms based on nanopore sequencing and application of primer group
ActiveCN112501268APrecise positioningImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesPneumonitisEnterococcus
The invention discloses a primer group for detecting respiratory tract microorganisms based on a nanopore sequencing method. The nucleotide sequences of the primer group are as shown in SEQ ID NO:1-20. The microorganisms are streptococcus pneumoniae, staphylococcus aureus (resisting to methicillin), klebsiella pneumoniae, pseudomonas aeruginosa, acinetobacter baumannii, stenotrophomonas maltophilia, candida albicans, haemophilus influenzae, legionella pneumophila, enterococcus faecium, chlamydia psittaci, cryptococcus gattii, aspergillus fumigatus and pneumocystis jiroveci. According to the invention, sequencing optimization is carried out on different types of samples of the respiratory tract microorganisms, so that the detection method, the kit and the like are suitable for various typesof respiratory tract samples; and a targeted amplification method is adopted, so that the detection requirements of sputum, alveolar lavage and other sample types can be met. In addition, parallel sequencing can be performed, so that the flux of the detected samples is increased, the sequencing time is shortened, and the contradiction between the flux of detected pathogenic species and the cost and time is further relieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH
Targeted antimicrobial photodynamic therapy
ActiveUS20190314502A1Fast inactivationAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryBacteroidesTreatment choices
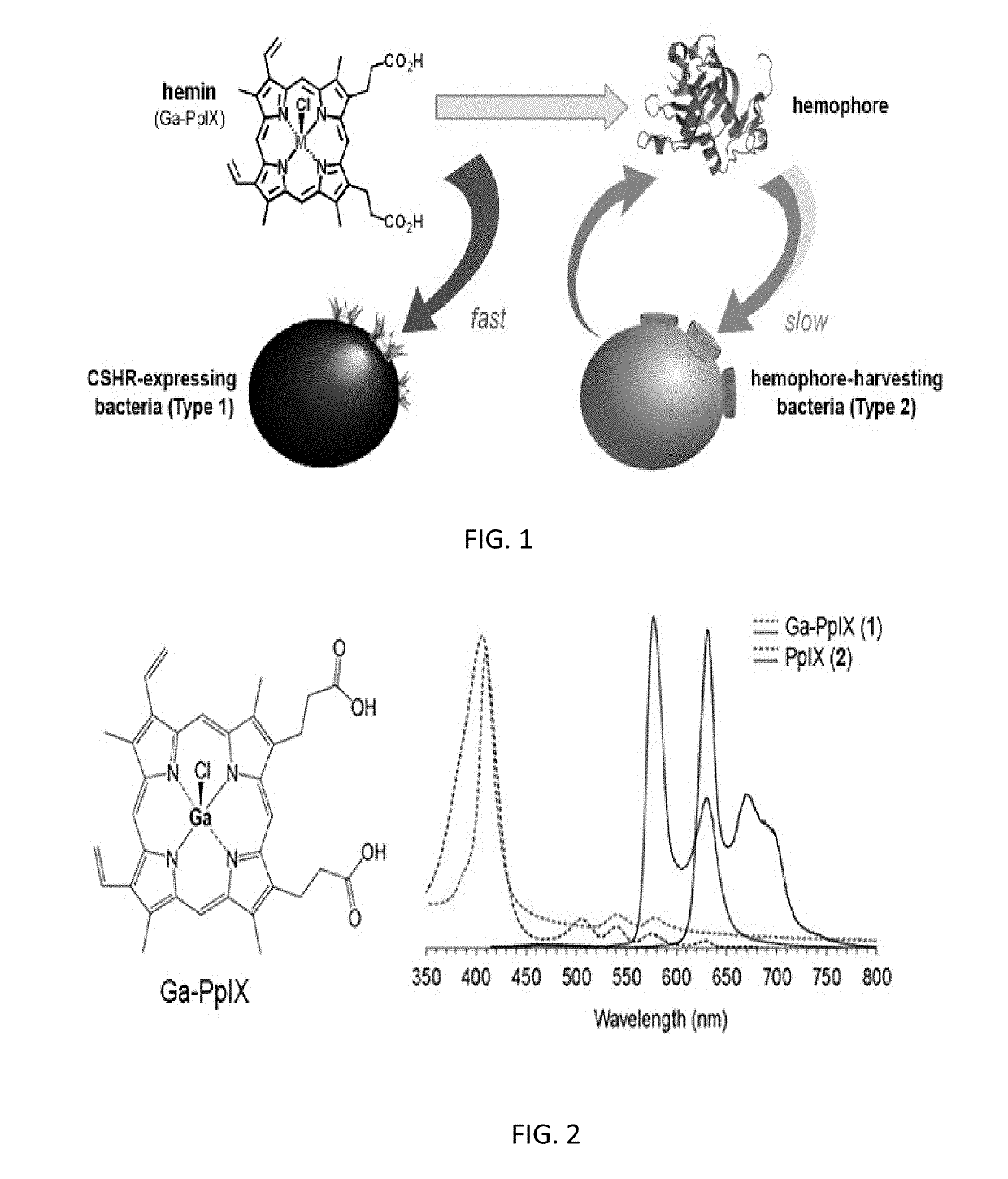
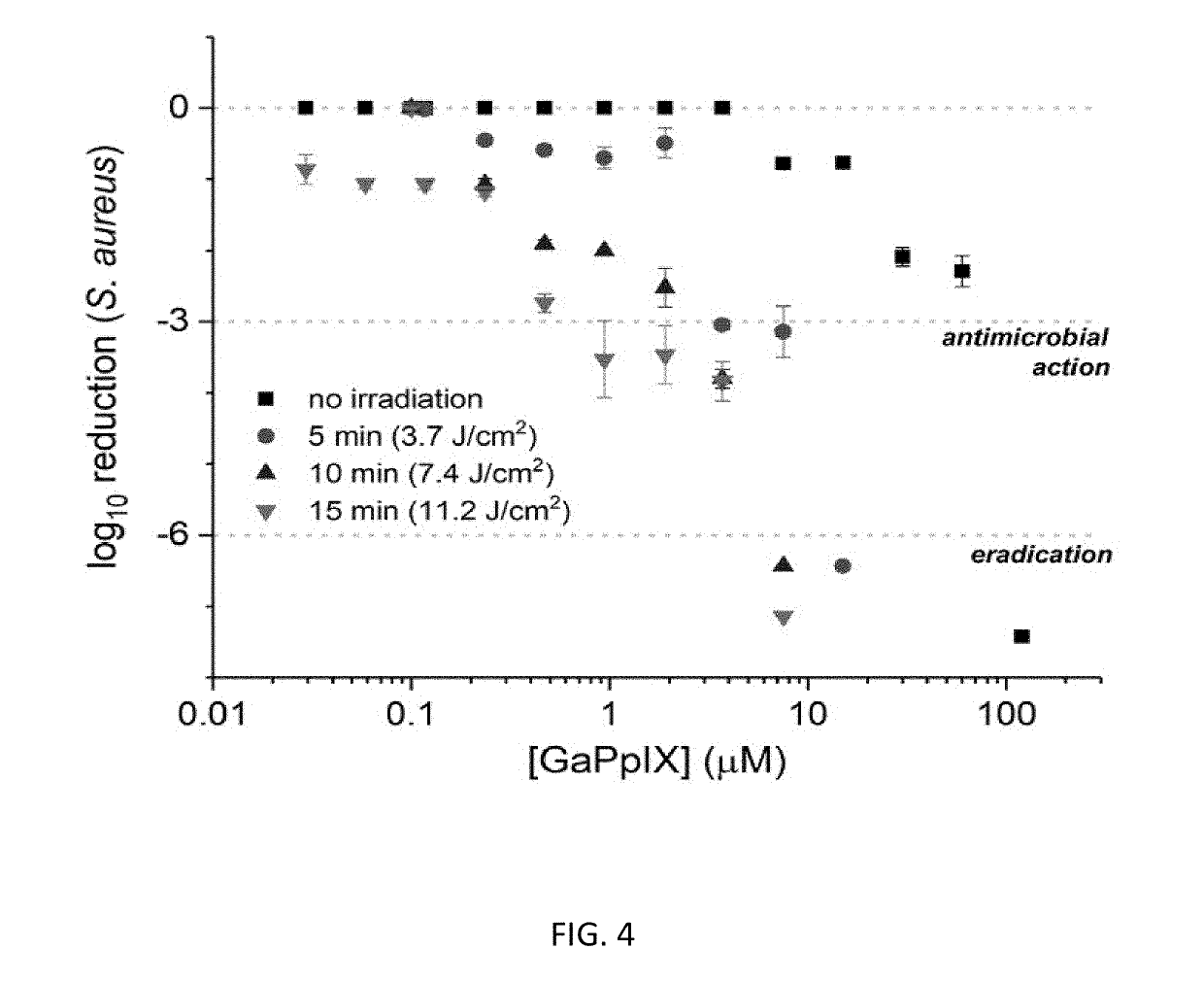
The present application relates generally to a method and a composition matter that provides a rapid and potent antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation (aPDI) of pathogenic bacteria that express high-affinity cell-surface hemin receptors (CSHRs) using Ga(III)-protoporphyrins IX (GaPpIX or Ga-PpIX). The invention provides an effective treatment option for infections of skin or body cavities that are accessible to visible-light irradiation, such as a handheld LED array emitting visible light (405 nm), especially for infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus, Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), pathogenic staphylococci, Streptococcus mutans, S. pneumoniae, S. pyogenes, streptococci, corynebacteria, mycobacteria, and Bacillus anthracis.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
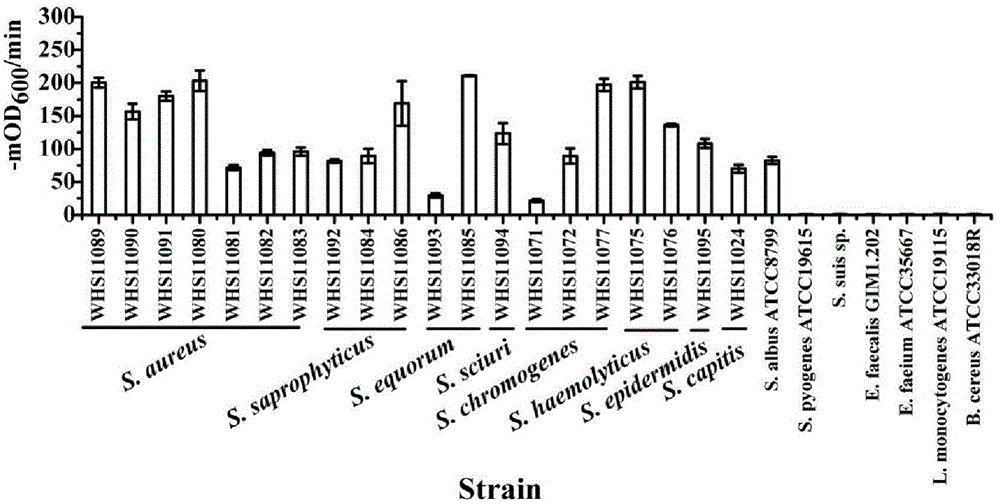
Staphylococcus lyase and application thereof
ActiveCN104805066AIncrease enzyme activityHigh activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsMethicillin sensitiveMethicillin resistance
The invention discloses lyase capable of killing staphylococci and an application of the lyase, which belong to the field of biological agents. The invention discloses an amino acid sequence and a coding gene sequence of the lyase. A pH range of the lyase which plays a role is wide, the activity of cracking the staphylococci is kept within the pH range of 4 to 11, and recombinant protease constructed by adopting coding genes can be solubly expressed in colibacillus BL21(DE3). The lyase can be used for efficiently killing various staphylococci in vitro, including methicillin sensitive staphylococcus aureus and methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus which are clinically separated, and the lyase can be used as antibiotics for treating staphylococcal infection in vivo. The disclosed lyase can be used for quickly cracking staphylococcal cell walls and releasing substances in cells, such as triphosadenine, DNA and the like, and the staphylococci can be detected by utilizing the released substances.
Owner:TARGET ANTI-BIOPHARMACEUTICAL TECH CO LTD
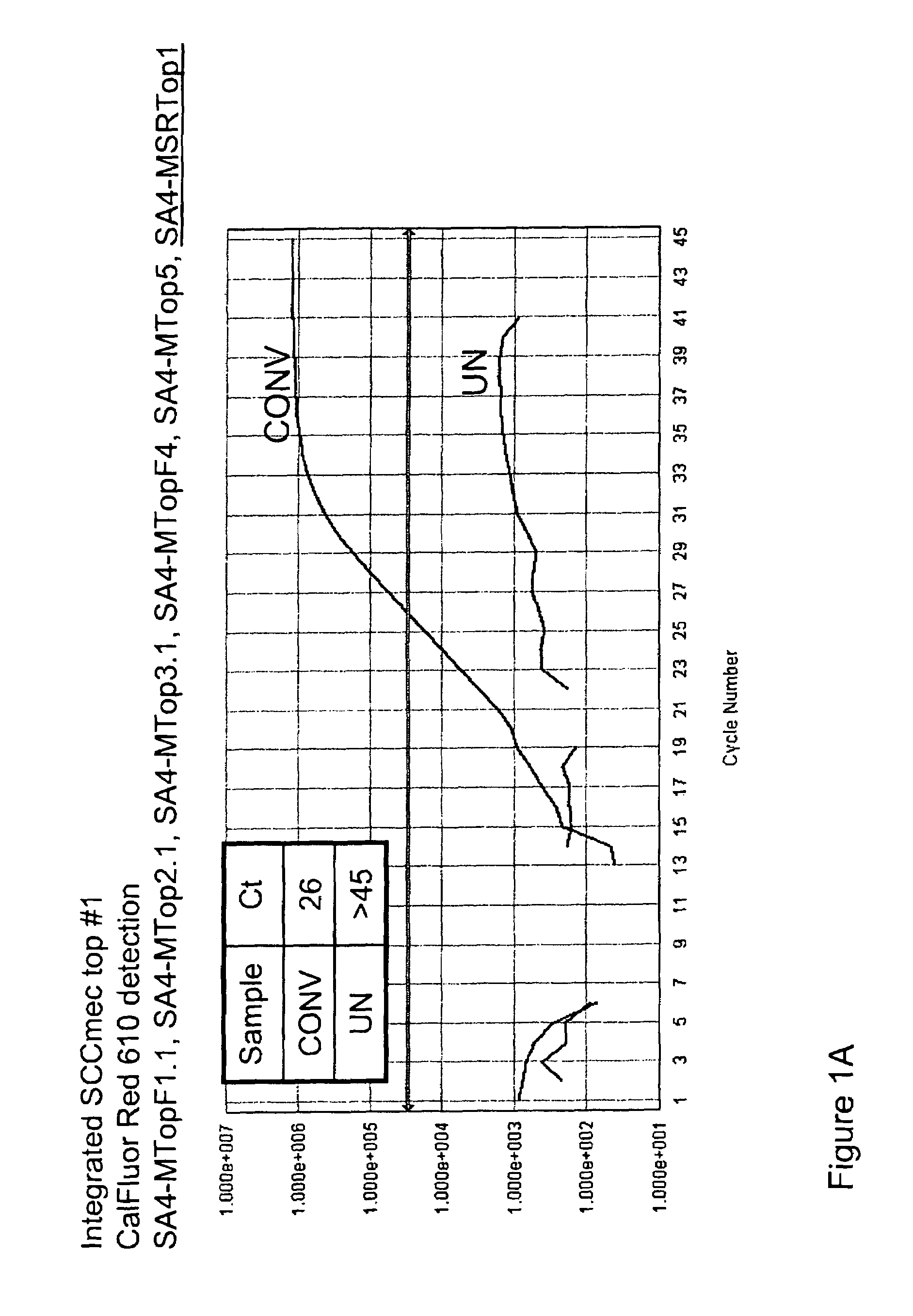
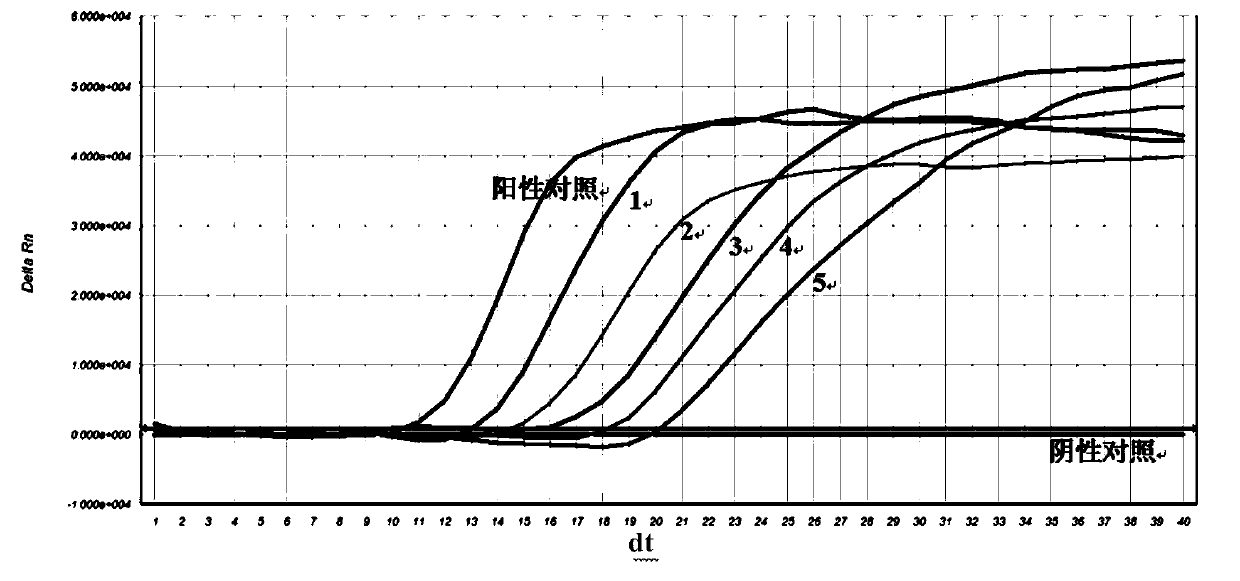
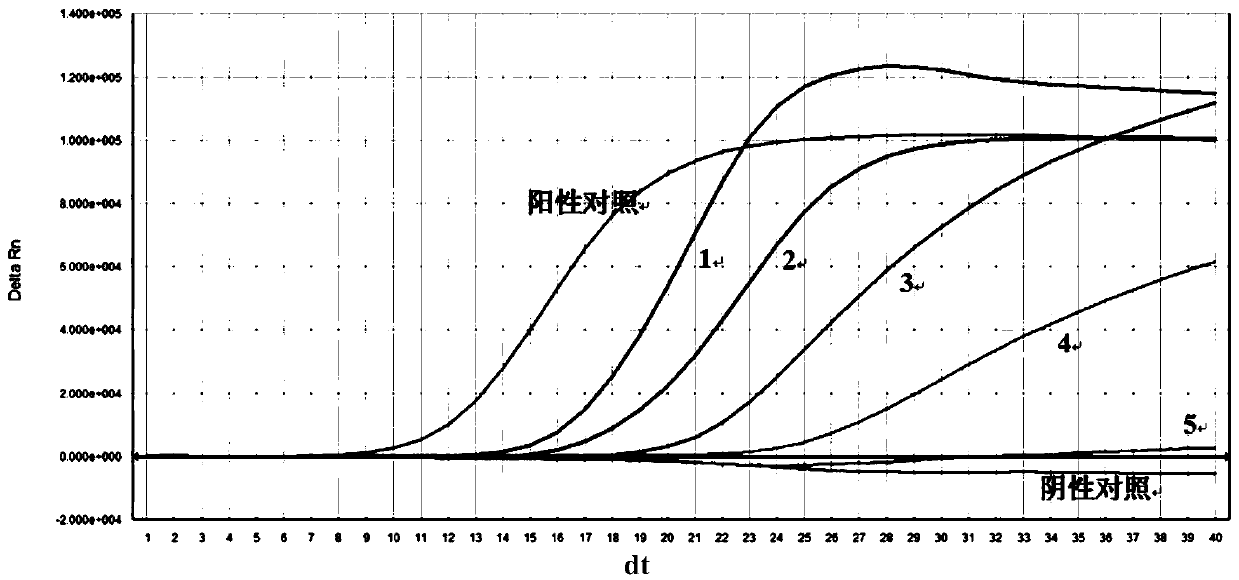
Detection of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus in biological samples
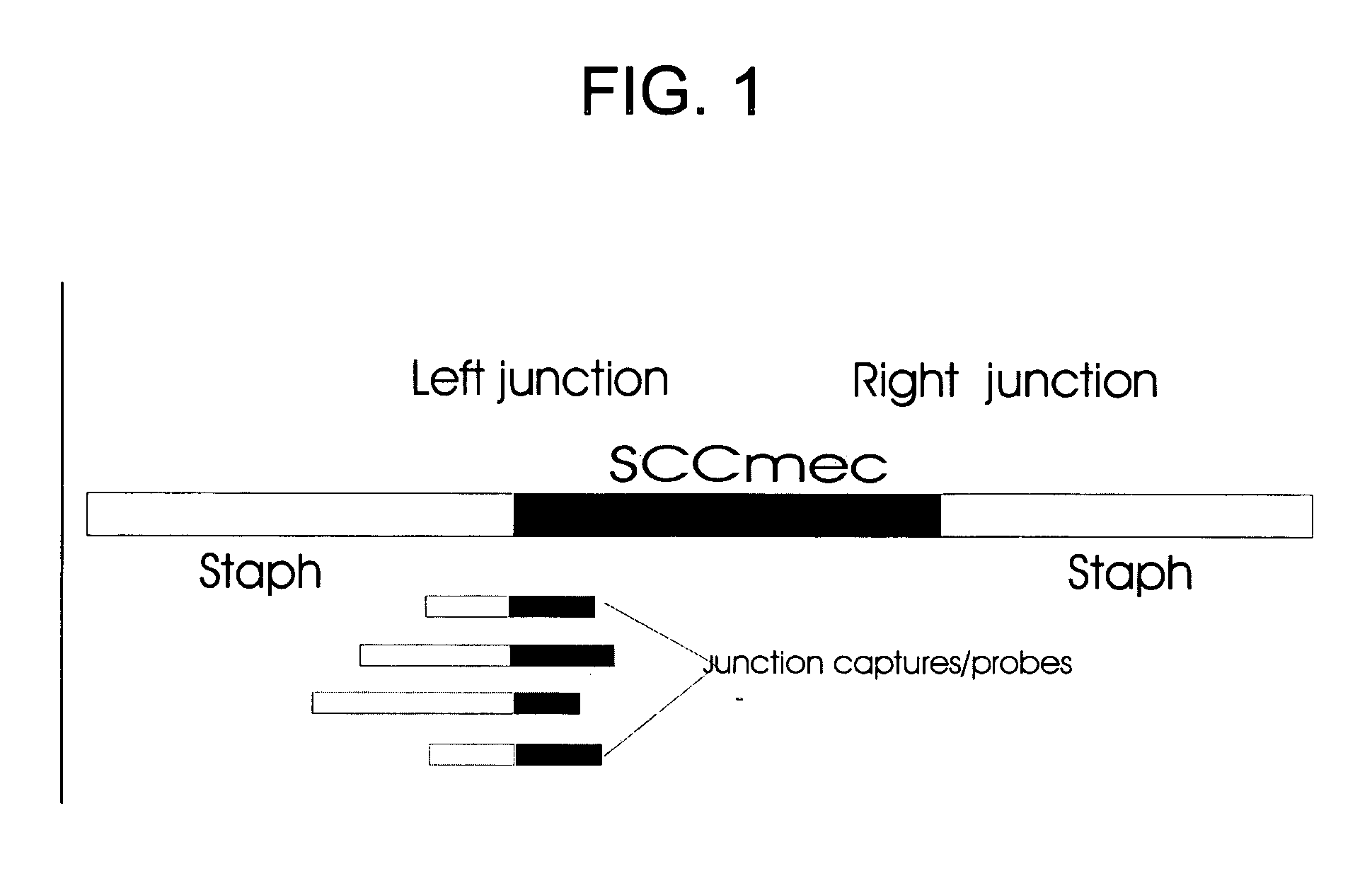
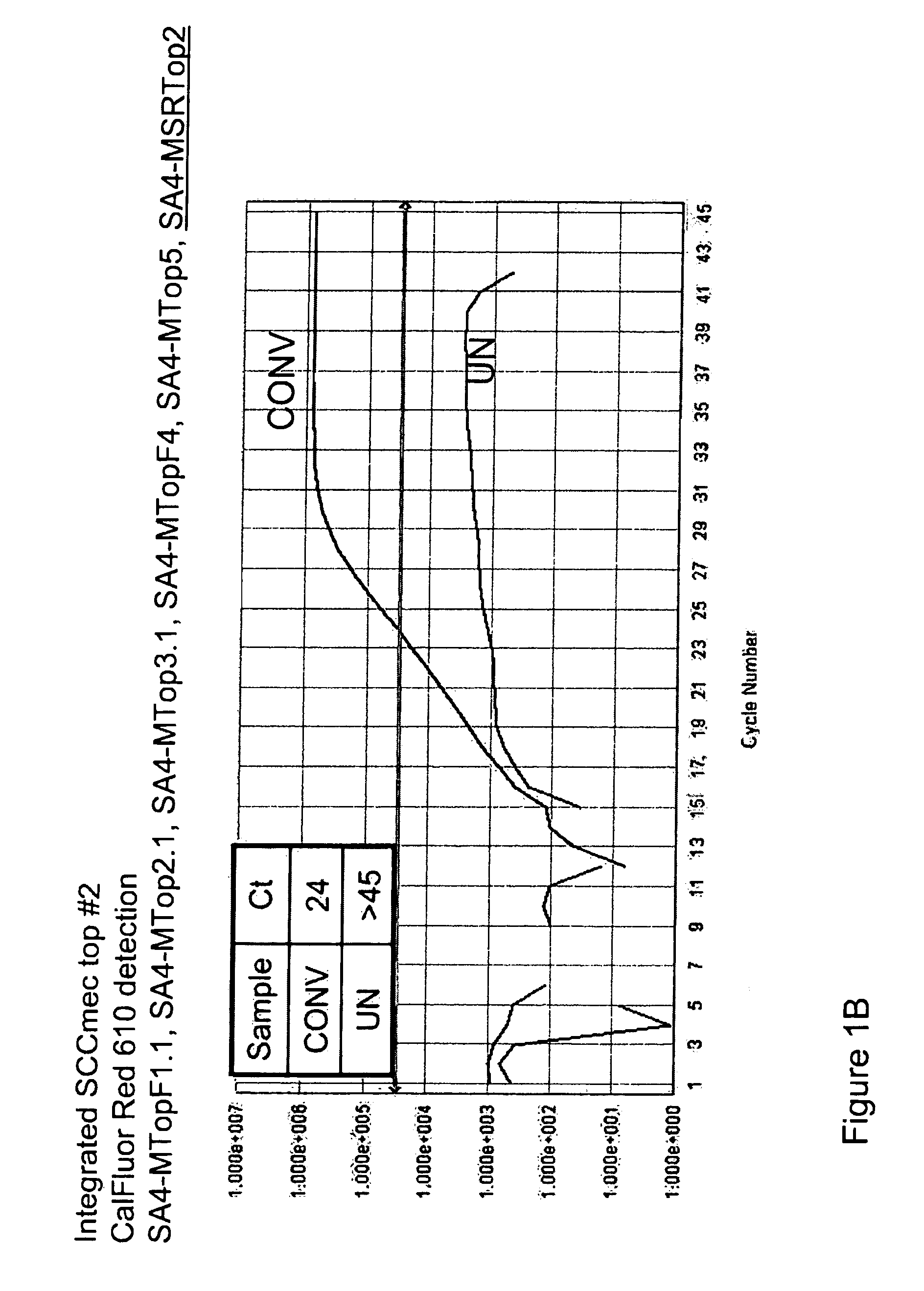
Disclosed are methods of identifying a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) or methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) in a sample. The present invention provides a diagnostic method comprising modification of sequences of S. aureus by converting non-methylated cytosine residues ultimately into thymidine residues in the target nucleic acid. The invention further provides for the detection of modified sequences derived from the spa gene, the mecA gene, and the integrated SCCmec cassette of S. aureus.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Purification method in preparation of methicillin staphylococcus aureus-resistant recombinant genetic engineering vaccine candidate antigen I12C
ActiveCN102898511AHigh feasibilityClear ingredientsMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsAntigenPurification methods
The invention relates to a purification method in preparation of methicillin staphylococcus aureus-resistant recombinant di-subunit genetic engineering vaccine candidate antigen I12C, which comprises the following steps of: collecting prepared antigen; and carrying out high-pressure bacterium breaking and centrifuging, precipitating ammonium sulfate step by step to purify the prepared I12C antigen according to the sequential combination, i.e., the GST (glutathione s transferase) affinity chromatography technology, the PP (propene polymer) digestion technology, the buffer solution replacement technology, the Resource Q chromatography technology and the gel filtration chromatography technology. The purification method provided by the invention is simple and direct, easy to amplify, and good in repeatability, so that the obtained target protein is high in purity; the animal experiment proves that the purified antigen can effectively stimulate the organism to generate higher humoral immune response and have good immune protection function; and the purity of the antigen I12C purified by the method provided by the invention is more than or equal to 99%.
Owner:CHENGDU OLYMVAX BIOPHARM +1
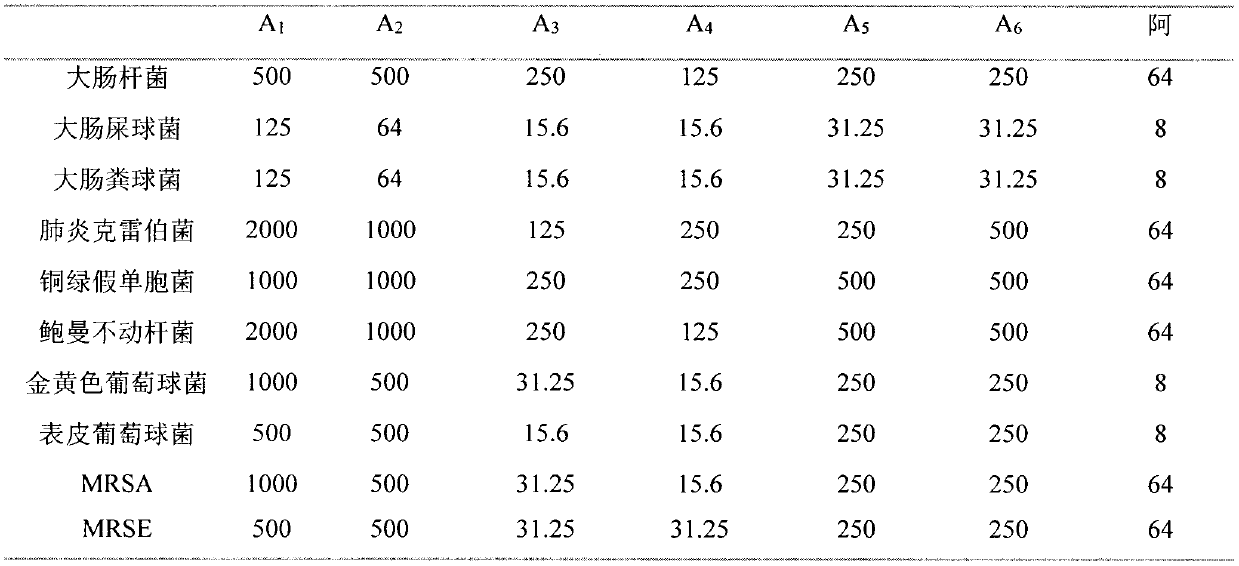
Polypeptide capable of inhibiting and killing multiple medicine-resisting bacteria
ActiveCN104072583AAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis
The invention relates to polypeptide capable of inhibiting and killing bacteria, and in particular relates to multiple medicine-resisting bacteria. The polypeptide is remarkable in effect of killing or inhibiting methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis, klebsiella pneumoniae, baumanii and / or escherichia coli. The invention further relates to a composition with the defined polypeptide, and an application of the defined polypeptide and the composition thereof in preparation of medicines and in killing or inhibiting of multiple in-vitro medicine-resisting bacteria.
Owner:冯小荣 +2
Preparation method and application of VRE/MRSA/KPC/NDM-1 detection gene chip
InactiveCN107130016AImprove throughputStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide chipAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a VRE / MRSA / KPC / NDM-1 detection gene chip. The preparation method includes: preparing specific primers, preparing specific probes, preparing an oligonucleotide chip, and building a multiple PCR system and a hybrid system. By the prepared gene chip, 5 drug-resistant genes and 3 related pathogenic bacteria can be detected at the same time, and the 5 drug-resistant genes and 3 related pathogenic bacteria include Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus VRE drug-resistant genes VanA and VanB, an encoding New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase-1 NDM-1 drug-resistant gene, a methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus MRSA drug-resistant gene mecA, an encoding carbapenemase KPC gene, an enterococcus faecalis specific gene Fddl, an enterococcus faecium specific gene Sddl and a staphylococcus aureus specific gene nuc. The chip which provides a new detection manner for the confirmation of the drug-resistant genes of common antibiotics resistance phenotypes has advantages of quickness, accuracy, high flux and the like.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA +1
DNA-based methods for clone-specific identification of staphylococcus aureus
InactiveUS20120208714A1Rapid and reliable identificationHigh variationNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesTest performance
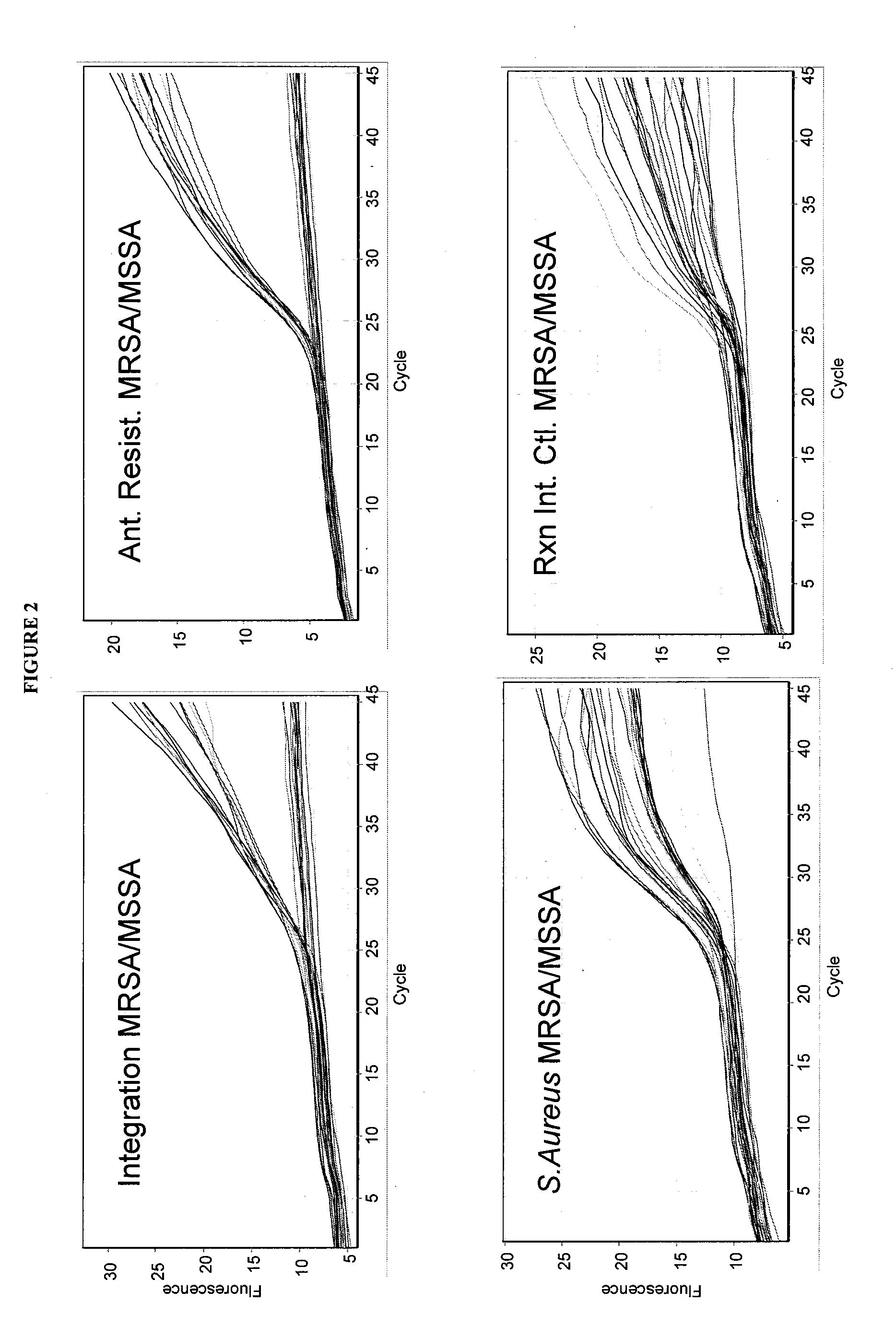
MRSA CC398 is a clone of S. aureus that has recently emerged in pigs and other domestic animals worldwide. As any other MRSA, the clone displays high levels of antibiotic resistance and poses a serious threat to human health because of the risk of antibiotic treatment failure in human patients. We developed a new diagnostic test for identification of MRSA CC398 using a single one-step PCR that is very easily performed within a few hours. The test is based on the principle that clonal differences within S. aureus are reflected in the sequence of a gene (sau1hsdS1) located on the chromosome of this bacterial species. Accordingly, such a gene represents an optimal target for S. aureus and MRSA identification at the clone level. The test includes detection of the gene conferring methicillin resistance (mecA), therefore allowing rapid discrimination between methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant variants of the clone. A preliminary validation of the test was performed on a collection of CC398 and non-CC398 strains, resulting in 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity. The test can be combined to real-time PCR technology to further reduce simplify the test performance as well as to allow quantification of the target MRSA clone in biological specimens. The invention has important applications related to surveillance and control of MRSA CC398 in humans, animals and food products.
Owner:ST GEORGES HOSPITAL MEDICAL SCHOOL +2
Nitric oxide donor type hexadecadrol as well as preparation method and purpose thereof
ActiveCN105001296AIncreased anti-inflammatory activityLittle side effectsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsNitric oxideChemistry
The invention relates to nitric oxide donor type hexadecadrol as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The nitric oxide donor type hexadecadrol as a compound is obtained by enabling nitrous acid ester to be connected with hexadecadrol through ethyl cyclohexanecarboxylate; the in-vitro antiinflammatory activity of the nitric oxide donor type hexadecadrol is better than that of the hexadecadrol; besides, the nitric oxide donor type hexadecadrol can restrain the growth of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in vitro, restrain the formation of MRSA biomembrane, and lead to the death of bacteria in the MRSA biomembrane. In addition, the compound can notably increase the survival rate of mice in MRSA sepsis lethal models, reduces the inflammation pathology damage of the mice in sub-sepsis models, decreases the constant value number of bacteria, and has notable advantages in the respect of preventing and treating MRSA sepsis.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Fluoro-acrylamide derivative
InactiveCN102675311AAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsStaphylococcus cohniiMethicillin sensitive
The invention relates to a new compound with remarkable antibacterial and antineoplastic activity, which has the following structure (shown in formula I), and has good antibacterial function for methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and methicillin sensitive staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) as well as good antineoplastic function for human cervical cancer Hela cells, human liver cancer BEL-7402 cells, human mucinous epidermoid lung cancer A549 cells, human breast cancer MCF-7 / s cells and human glioma U251 cells. (In the formula I,) R=-CH3 or CF3, X=O, S or N, and R1=-Cl, -F, -CH3, -CF3, -OCH3 and -OCF3.
Owner:苏春华 +1
Dibenzoanthracene oxepanone compound and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108485987APotent anti-Vibrio parahaemolyticus activityIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyTalaromyces stipitatus
The present invention relates to a dibenzoanthracene oxepanone compound from a marine fungus WH4-2 and a preparation method and application thereof. The marine fungus talaromyces stipitatus has the efficient V.parahemolyticus activity, the yield of an active substance, namely the dibenzoanthracene oxepanone compound containing an isoprene group is large, the dibenzoanthracene oxepanone compound isexpected to be applied to medicinal development of novel V.parahemolyticus, it is found that the compound further has Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC29213 and Enterococcus faecium ATCC35667 resistance activity in further activity analysis, and the dibenzoanthracene oxepanone compound is expected to be developed into a broad-spectrum antibacterial medicine.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus combined drug and application
ActiveCN104274454ANo growth inhibitory effectGrowth inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical medicineReserpine
Belonging to the field of pharmacy, the invention relates to a drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus combined drug and application. The drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus combined drug involved in the invention is composed of isoflavone and norfloxacin, wherein the natural compound isoflavone can be separated from plants, is especially high in content in leguminous plants, and has no obvious toxic or side effect. The result of bacteriostatic experiments shows that for norA gene containing fluoroquinolone resistant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus SA1199B, the isoflavone itself has no bacterial growth inhibiting effect, but after compatibility of the isoflavone and the antibiotic norfloxacin in a ratio of 1:1, the formed combined drug can reduce the minimum bacteriostatic concentration value of norfloxacin by 4 times, and has the same synergistic ability to that of the positive reference substance reserpine. The combined drug provided by the invention can lower the minimum bacteriostatic concentration of norfloxacin, generate an drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus synergistic effect for norfloxacin, and can be further prepared into drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus drugs or pharmaceutical preparations for external use.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Broad spectrum type antimicrobial peptide (AMP) and application thereof
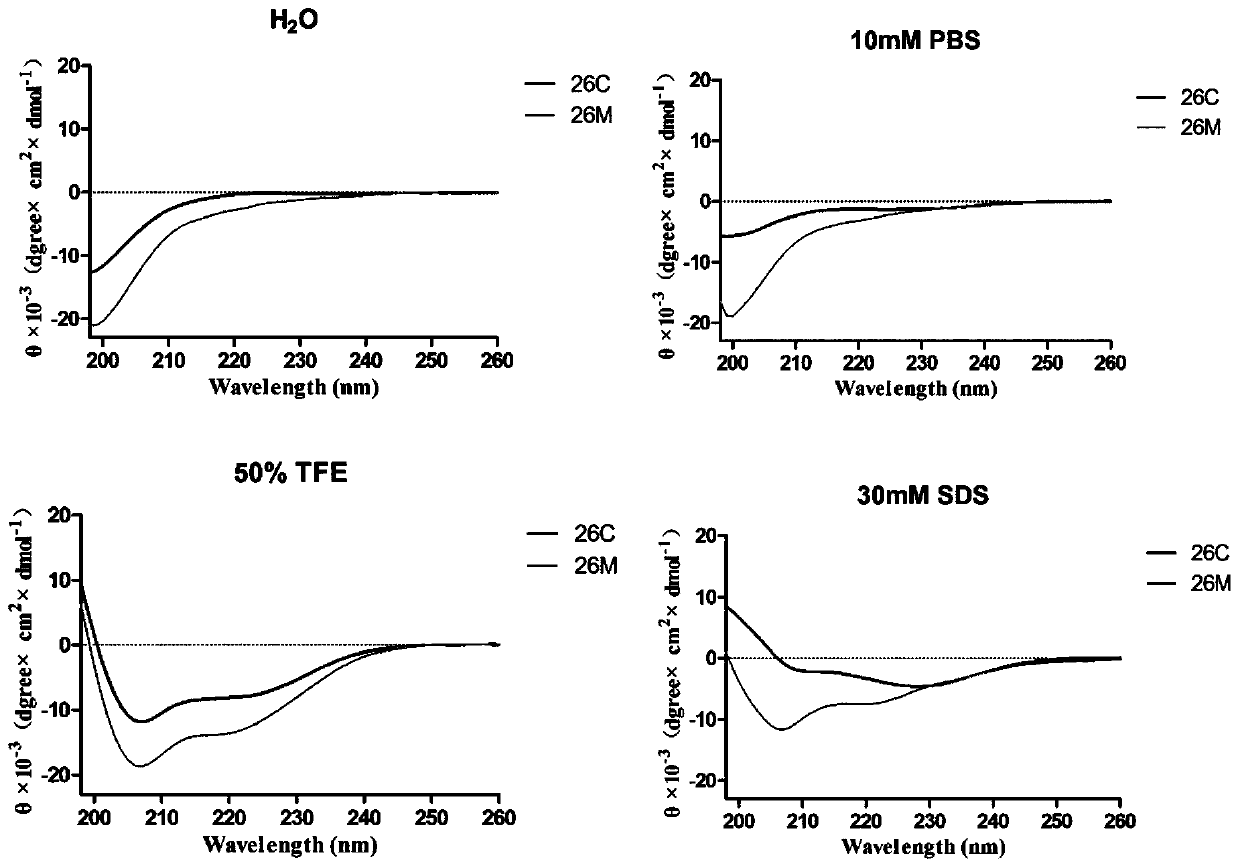
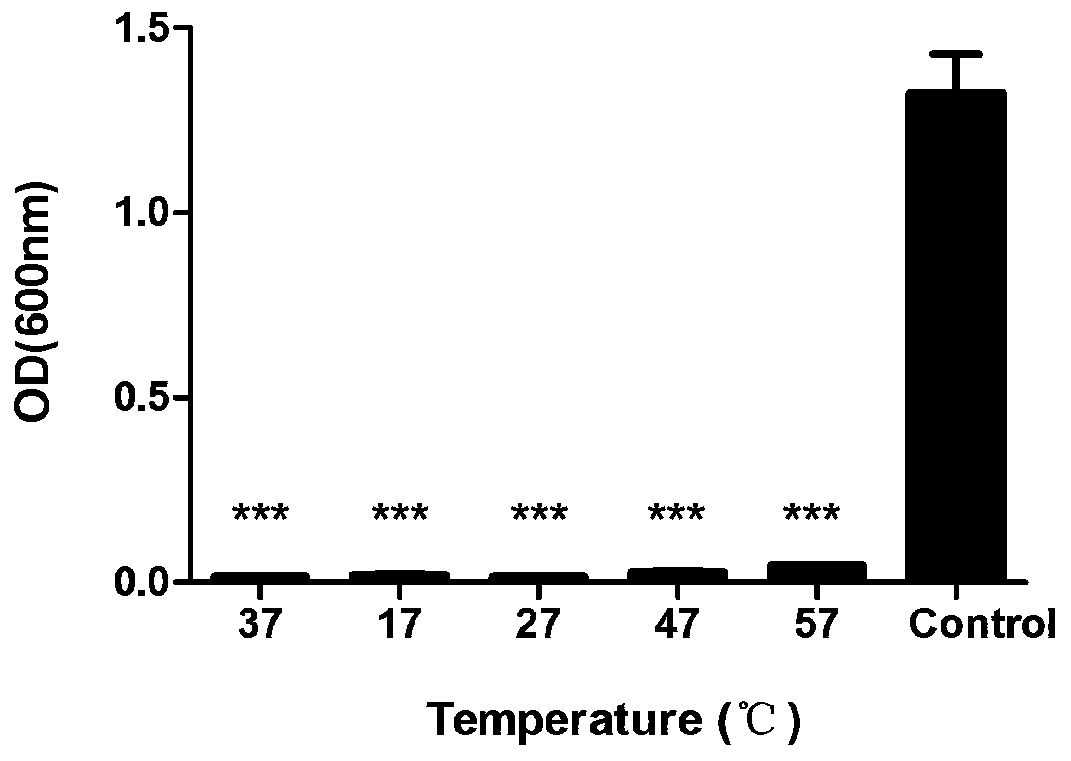
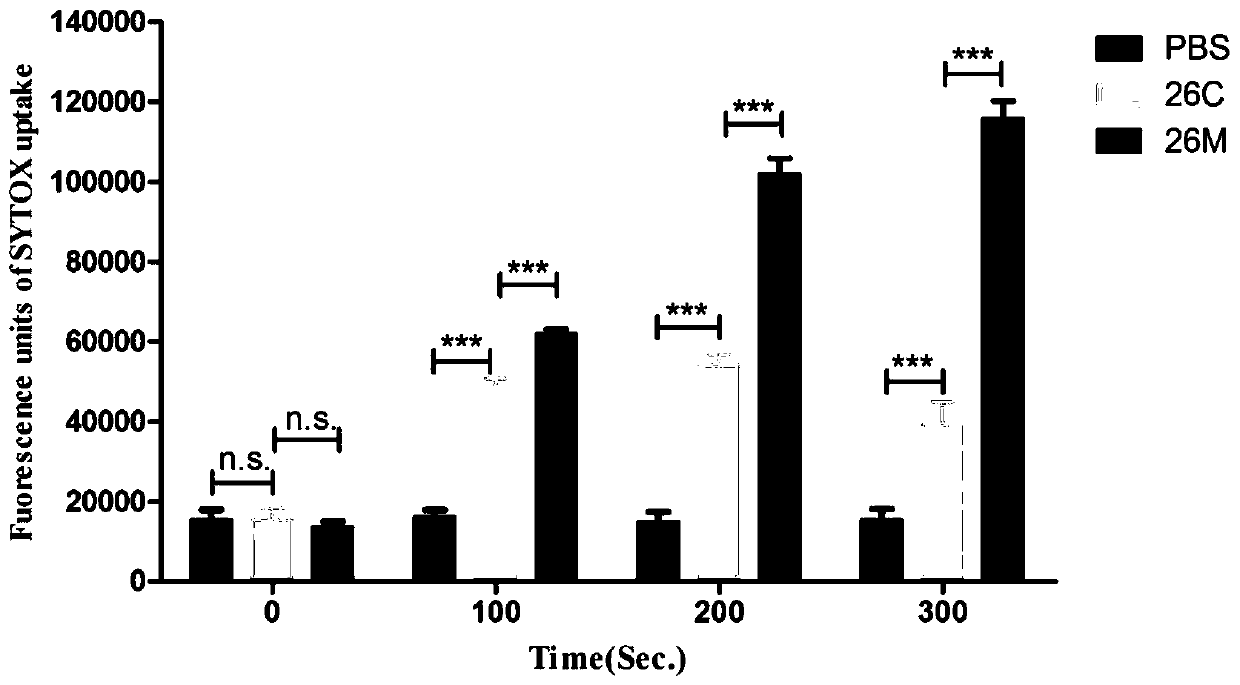
The invention discloses a broad spectrum type antimicrobial peptide (AMP) and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of medicine. The AMP is named 26 M, contains 18 amino acid residues, has a molecular weight of 2475.16 Daltons, has an isoelectric point of 12.03, and has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. Experiments show that the AMP has the effect of significantly inhibiting the growth and reproduction of various pathogenic bacteria including Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Streptococcus suis, Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium. The invention provides the novel AMP with a broad-spectrum antimicrobial effect,and the AMP can replace traditional antibiotics and cannot produce drug resistance easily, and has good application prospects in resisting infectious diseases caused by pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
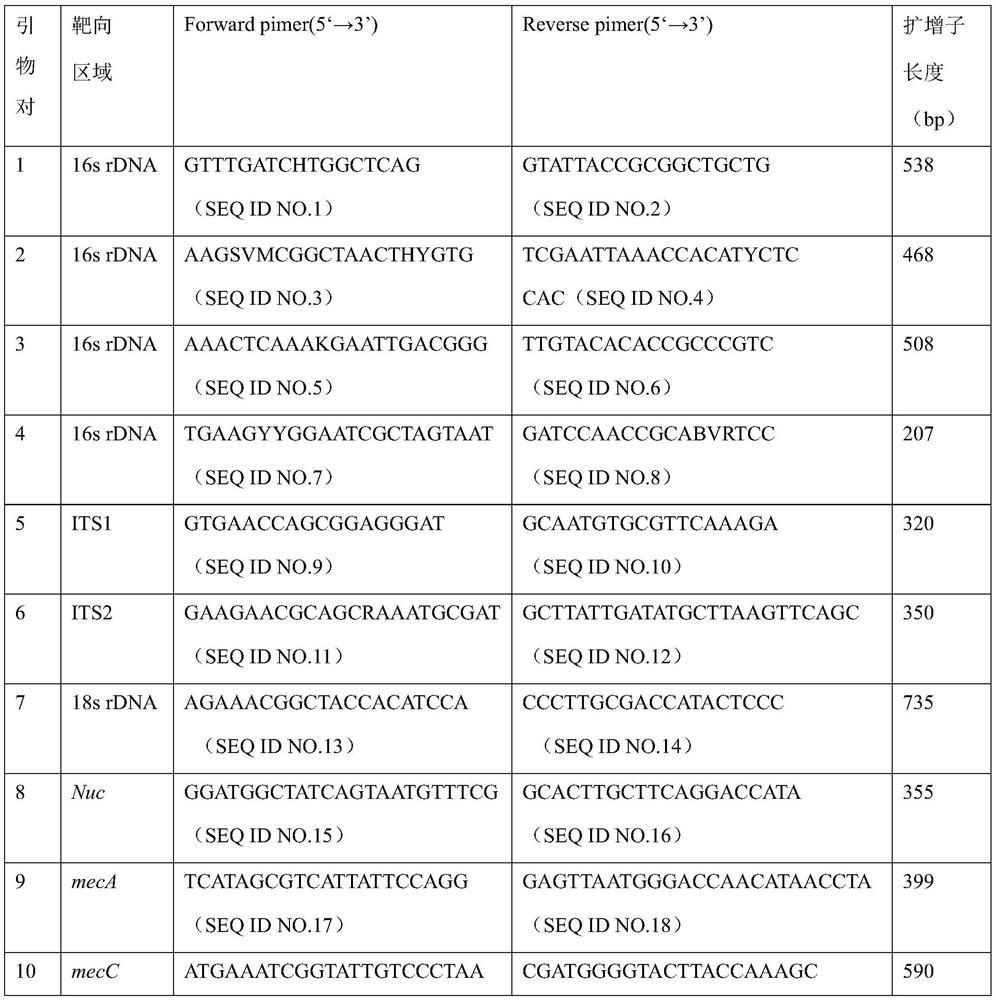
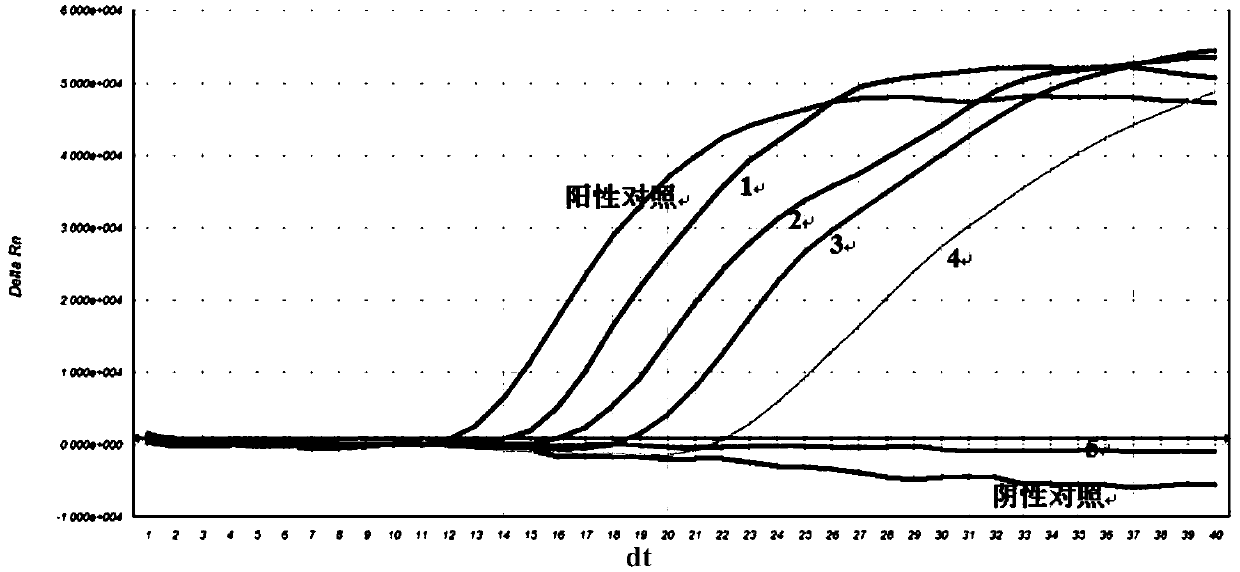
Nucleic acid constant-temperature amplification method of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
PendingCN110734988AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMeticillinStaphylococcus aureus bacteria
The invention discloses a nucleic acid constant-temperature amplification method of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Specifically, the method disclosed by the invention comprises the following step: performing amplification in a reaction system, wherein the reaction system comprises two specific primer pairs of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA); and the primersare capable of amplifying amplification products corresponding to two characteristic sequences (SA 23s rRNA and mecA RNA) of the Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from a detection sample with a very low MRSA copy number. The method disclosed by the invention is capable of amplifying a to-be-detected sample with MRSA (SA 23s rRNA and mecA RNA) with high specificity, high sensitivity, low pollution and high rapidness, has the characteristics of high detection efficiency and high accuracy and has wide application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI RENDU BIOTECH
Methods, compositions and kits for detection and analysis of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
InactiveUS20100255490A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementResistant bacteriaStaphylococcus
The present invention relates generally to detection of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in a sample. In particular, the invention provides methods, compositions and kits for detecting and analyzing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and other methicillin-resistant bacteria in a sample.
Owner:MOLECULAR DETECTION
New lactic acid bacterium, natural immunostimulant having new lactic acid bacterium as active ingredient, and food or drink containing new lactic acid bacterium
ActiveCN105637084AHigh innate immune activation capacityImprove the immunityMilk preparationBacteriaBacteroidesGenus Lactococcus
The present invention pertains to a lactic acid bacterium belonging to the genus Lactococcus and having a receipt number NITE ABP-01694 with the Patent Microorganisms Depositary (NPMD) of the National Institute of Technology and Evaluation (NITE), a natural immunostimulant having this lactic acid bacterium as an active ingredient, a food or drink containing this lactic acid bacterium or this natural immunostimulant, and yogurt containing lactic acid bacteria, wherein the yogurt has resistance to at least one bacterium selected from the group comprising methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterococcus mundtii.
Owner:GENOME PHARMA INST +2
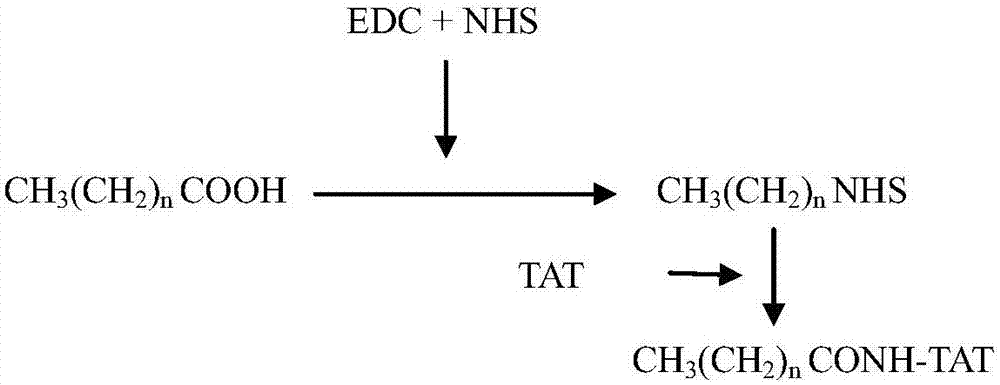
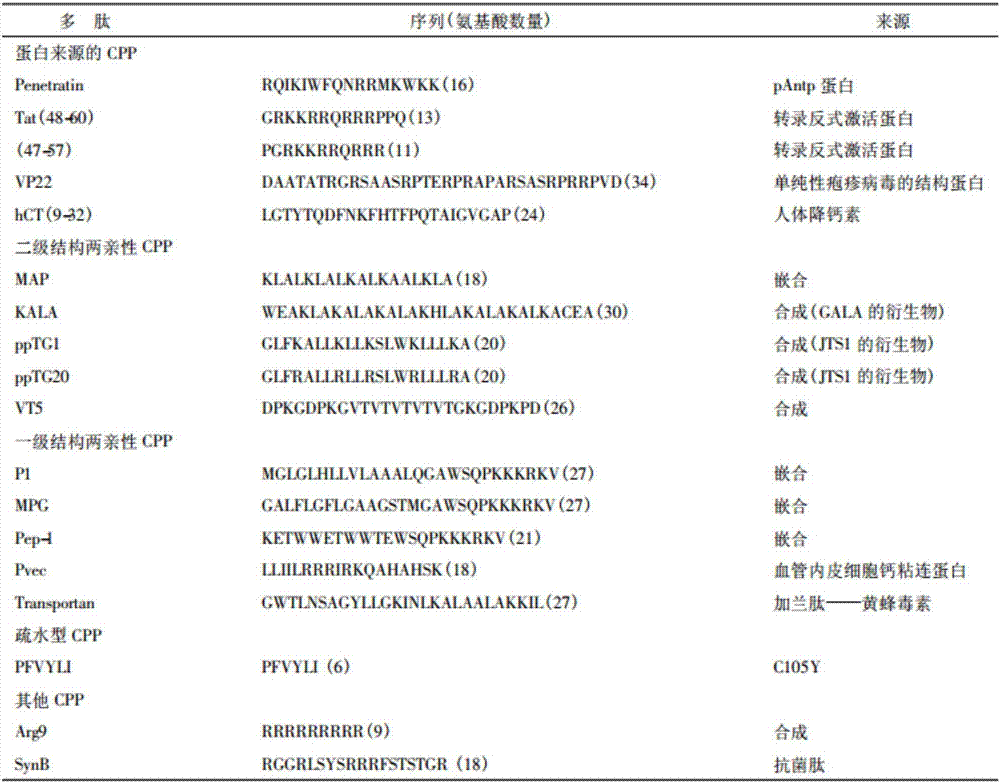
Lipophilic compound conjugate of cell penetrating peptide and its application in antibiosis
ActiveCN107236022AGood in vivo antibacterial activityEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntimicrobial peptidesClarithromycin
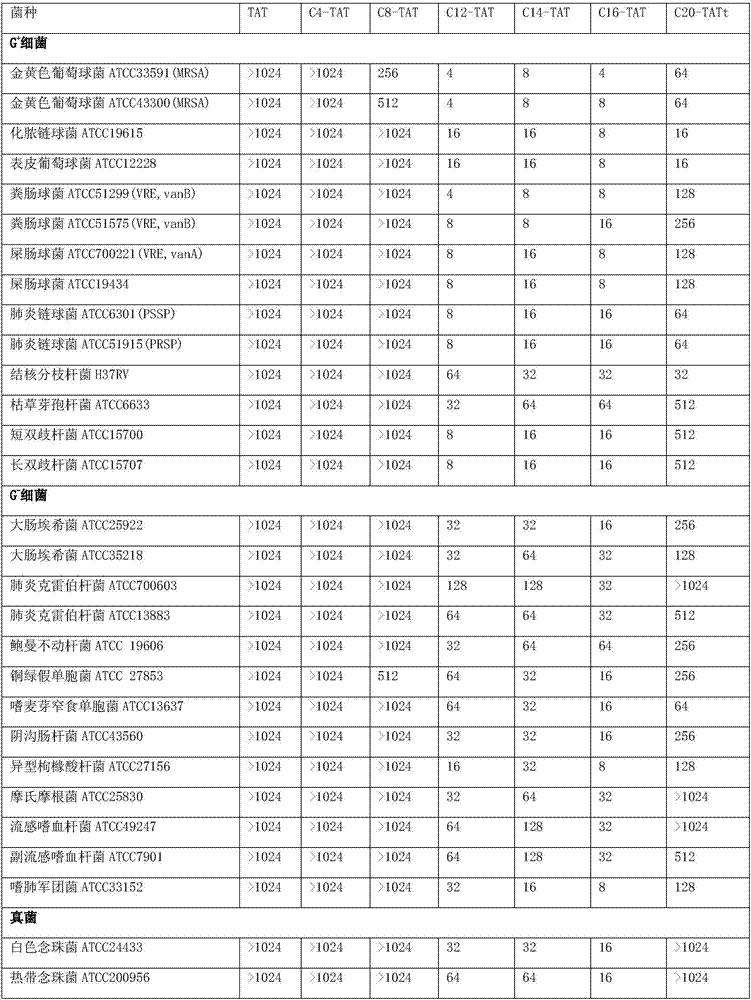
The invention discloses a lipophilic compound conjugate of cell penetrating peptide and its application in antibiosis. The lipophilic compound conjugate is formed by connecting cell penetrating peptide, and a lipophilic compound connected with an amino terminal or a carboxyl terminal of the cell penetrating peptide. The lipophilic compound conjugate of antimicrobial peptide has good inhibiting and killing effects on gram positive bacteria, gram negative bacteria and fungus, so the conjugate has broad-spectrum antibacterial effect,. On inhibition of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus, C12-TAT united clarithromycin has additive effect; C12-TAT united imipenem has obvious synergistic effect. On inhibition of pseudomonas aeruginosa, C16-TAT united clarithromycin has additive effect; C16-TAT united imipenem has obvious synergistic effect.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Effective humulus scandens part with antibacterial activity and application thereof
InactiveCN104000881AHigh antibacterial activityRich sourcesAntibacterial agentsDigestive systemBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses an effective humulus scandens part, the antibacterial activity of the effective humulus scandens part and the application of the effective humulus scandens part to preparation of antibacterial drugs. The whole plants of humulus scandens are used as the raw material, extraction is performed through water or 5% to 100% alcohol, after the primary treatment, the effective humulus scandens part is obtained through the macroporous resin-polyamide resin combination technology or the silica-gel column chromatography and mainly contains flavonoids compounds, the total flavonoid content ranges from 20 percent to 90 percent, and the effective humulus scandens part mainly contains apigenin, luteolin, luteolin-7-O-beta-D-glucoside, cosmosiin and the like. The effective part has the remarkable antibacterial activity and shows high antibacterial activity to clinically methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis, enterococcus faecium and enterococcus faecalis. The effective humulus scandens part can be used as the raw material of medicines and made into antibacterial drug tablets and capsules and the like and particularly can be used for preparing drugs for treating diseases of the urinary system such as diarrhea, enterogastritis, pyelonephritis and acute nephritis caused by bacterial infection and foods with the digestion aid, prevention and health care functions.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Monoclonal antibodies against the pbp2-a protein and homologous sequences for the treatment of infections by and immunodiagnostics of bacteria of the firmicutes phylum
ActiveCN102741281AImmunoglobulins against bacteriaAntibody ingredientsStaphyloccocus aureusHomomeric
The present invention relates to monoclonal antibodies capable of recognising and binding to the PBP2-a protein and to other proteins having sequences homologous to PBP2-a, including pathogenic species such as the methyciline-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA), coagulase-negative Staphilococcus, Staphylococcus sciuri and Enterococcus, and any other bacteria containing the PBP2-a protein or homologous sequences. The invention also relates to the use of the monoclonal antibodies capable of recognising and binding to the PBP2-a protein and to other proteins having sequenceshomologous to PBP2-a in a complementary immunodiagnostic test for detecting resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics.
Owner:FUNDACAO OSWALDO CRUZ FIOCRUZ
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com