Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
449 results about "Hydrogen partial pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hydrogen partial pressures are recommended when processing some alloys (like copper) and vacuum brazing with some filler metals (ie. silver or copper). A hydrogen partial pressure also improves the cleaning action during a vacuum furnace bake-out cycle. When properly design and constructed, a hydrogen partial pressure system is perfectly safe.
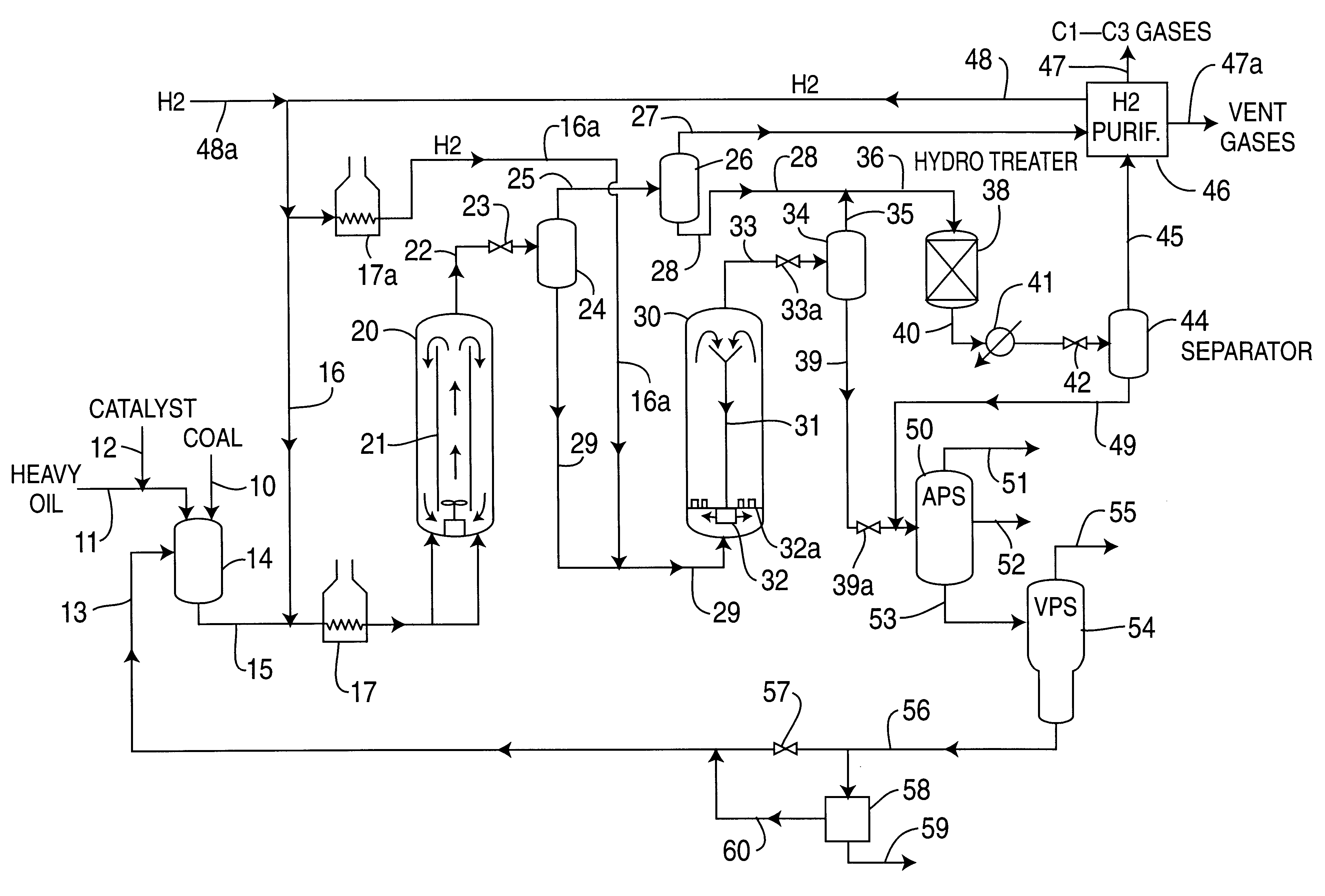
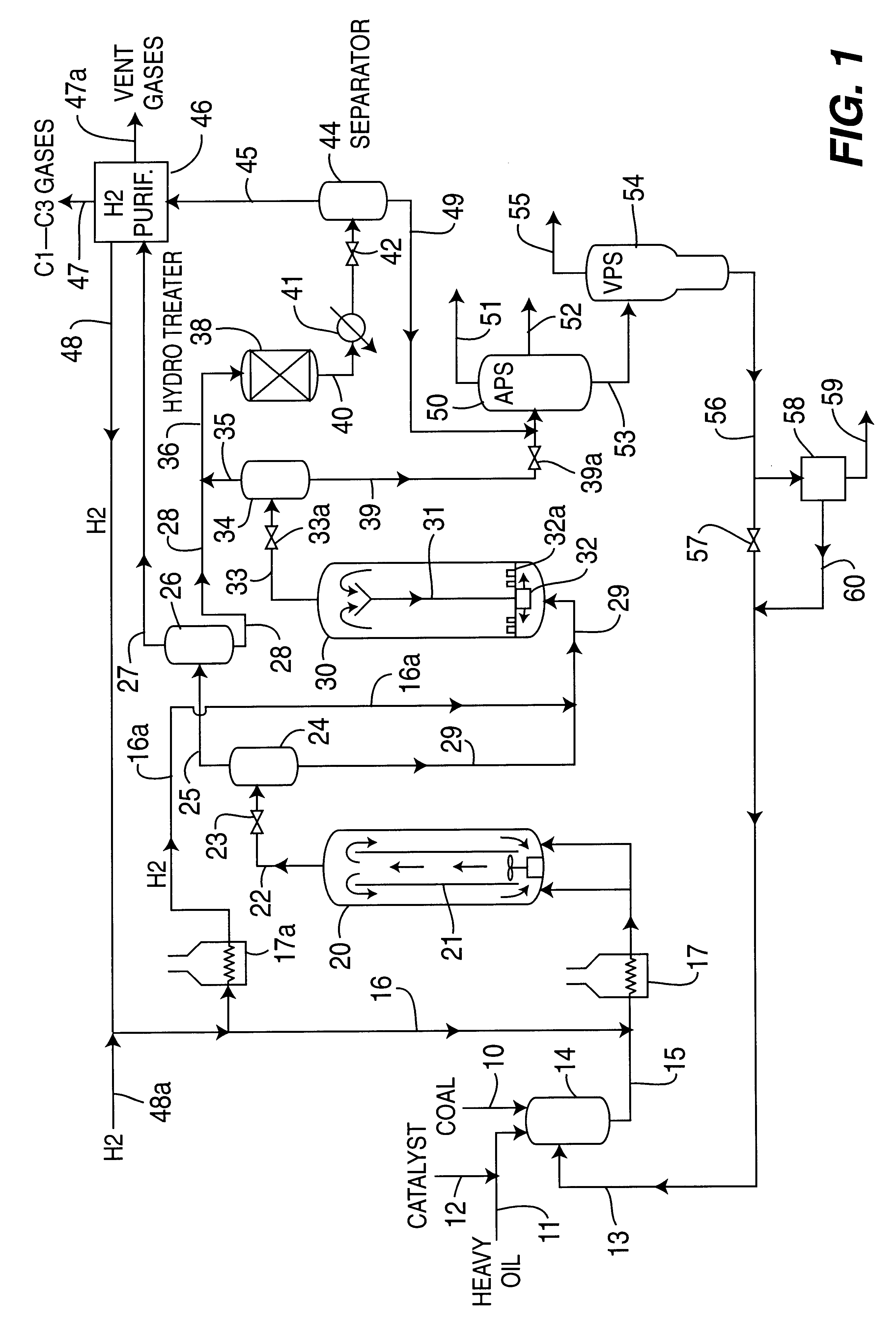
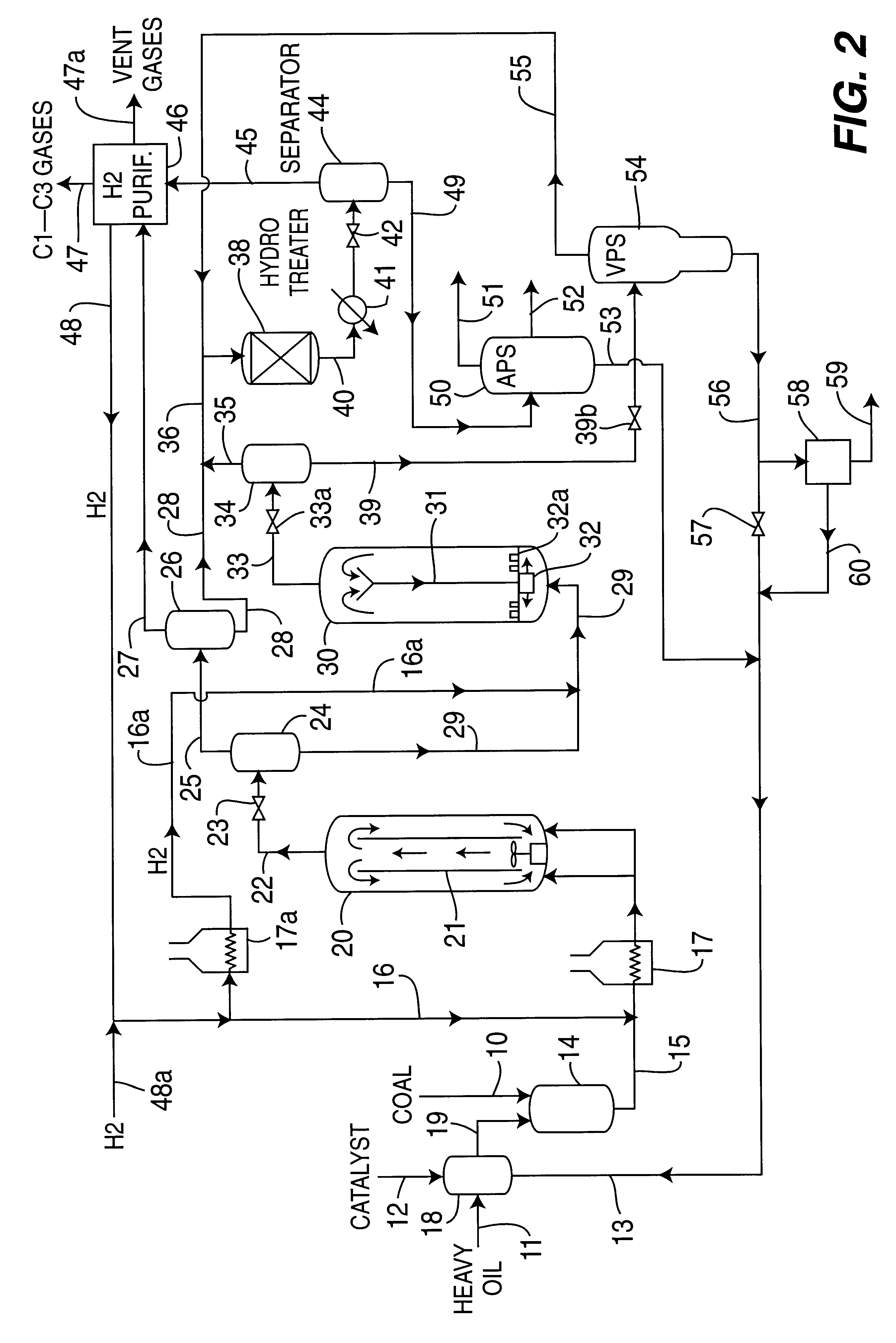
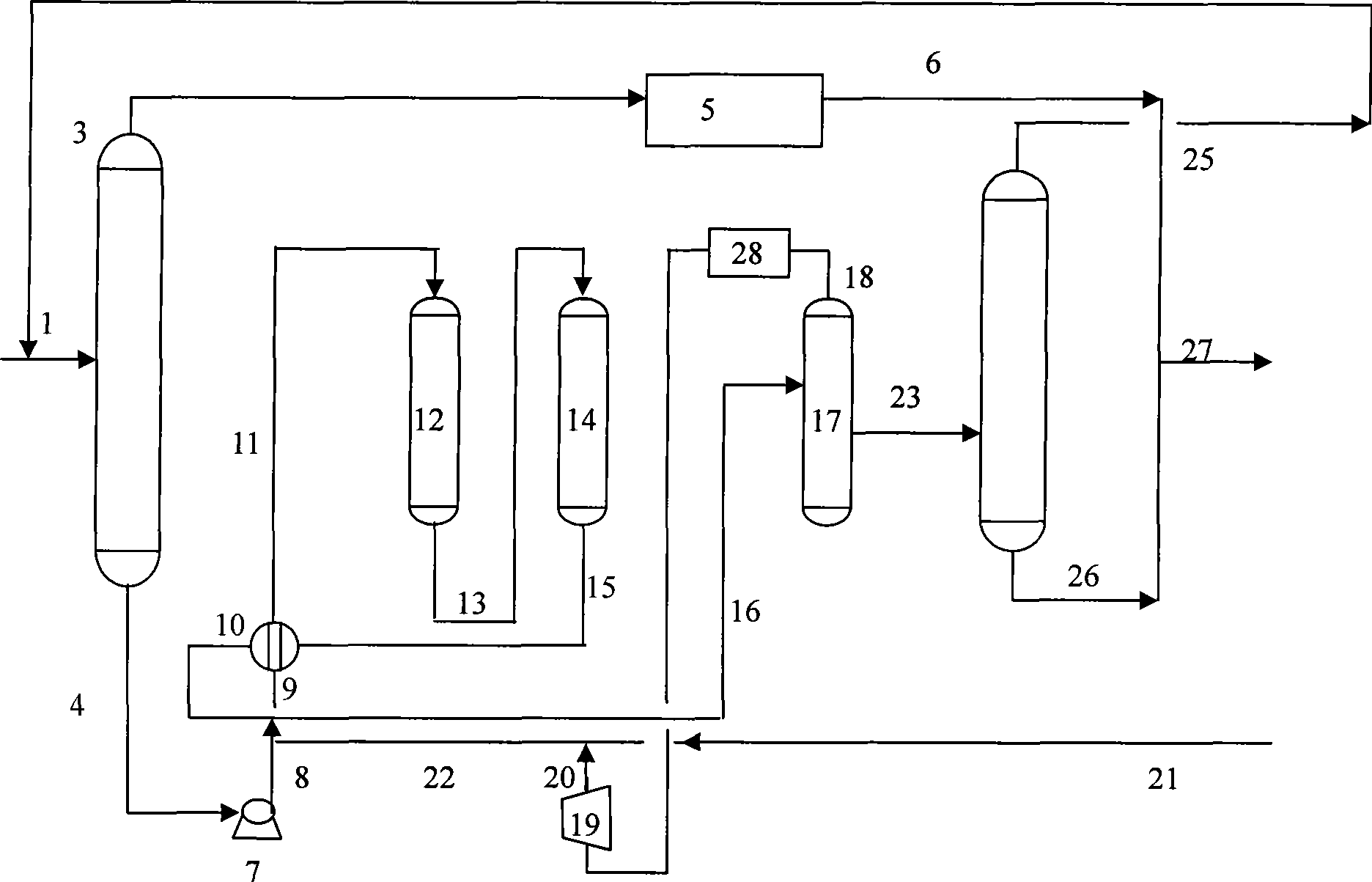
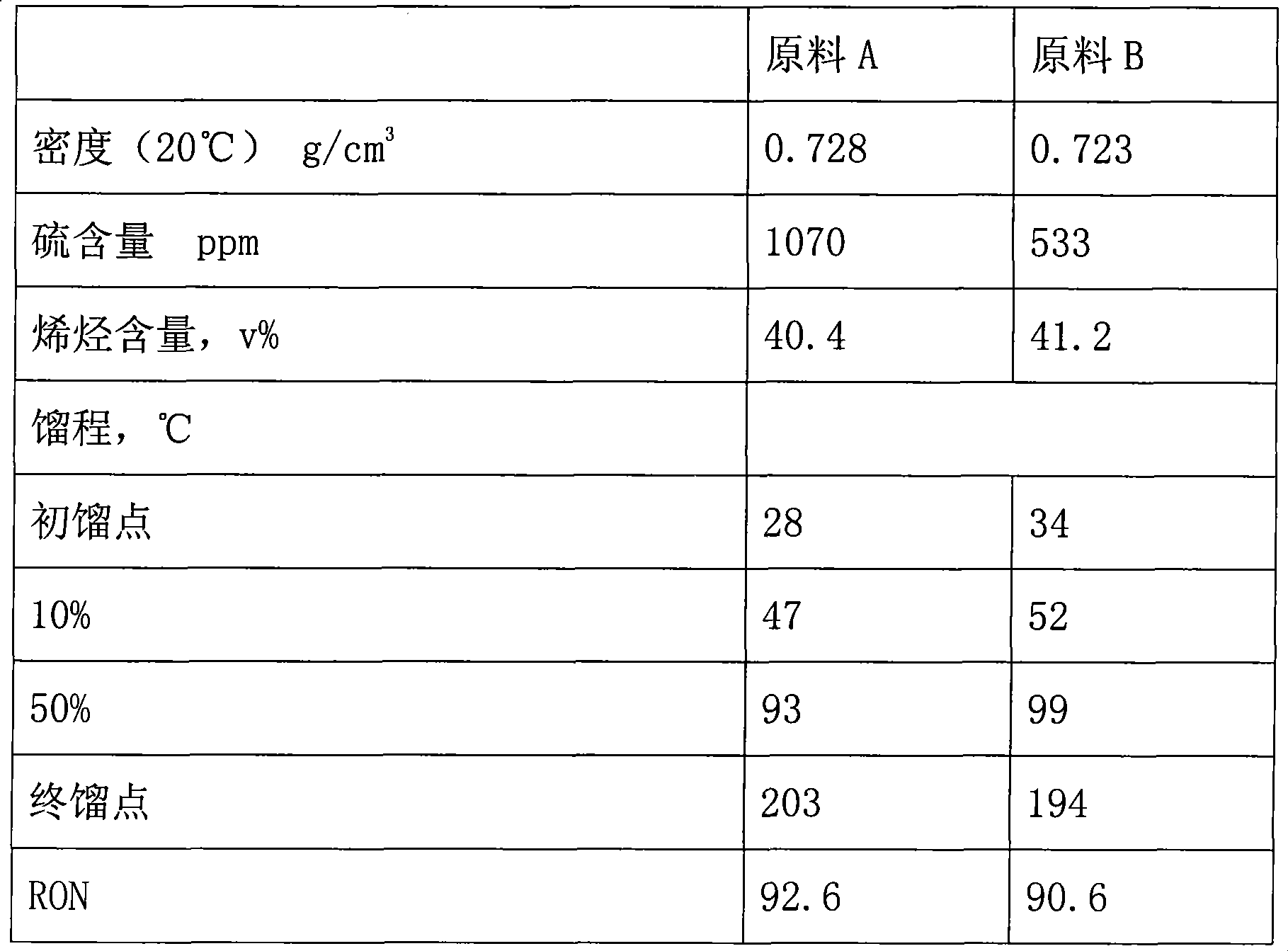
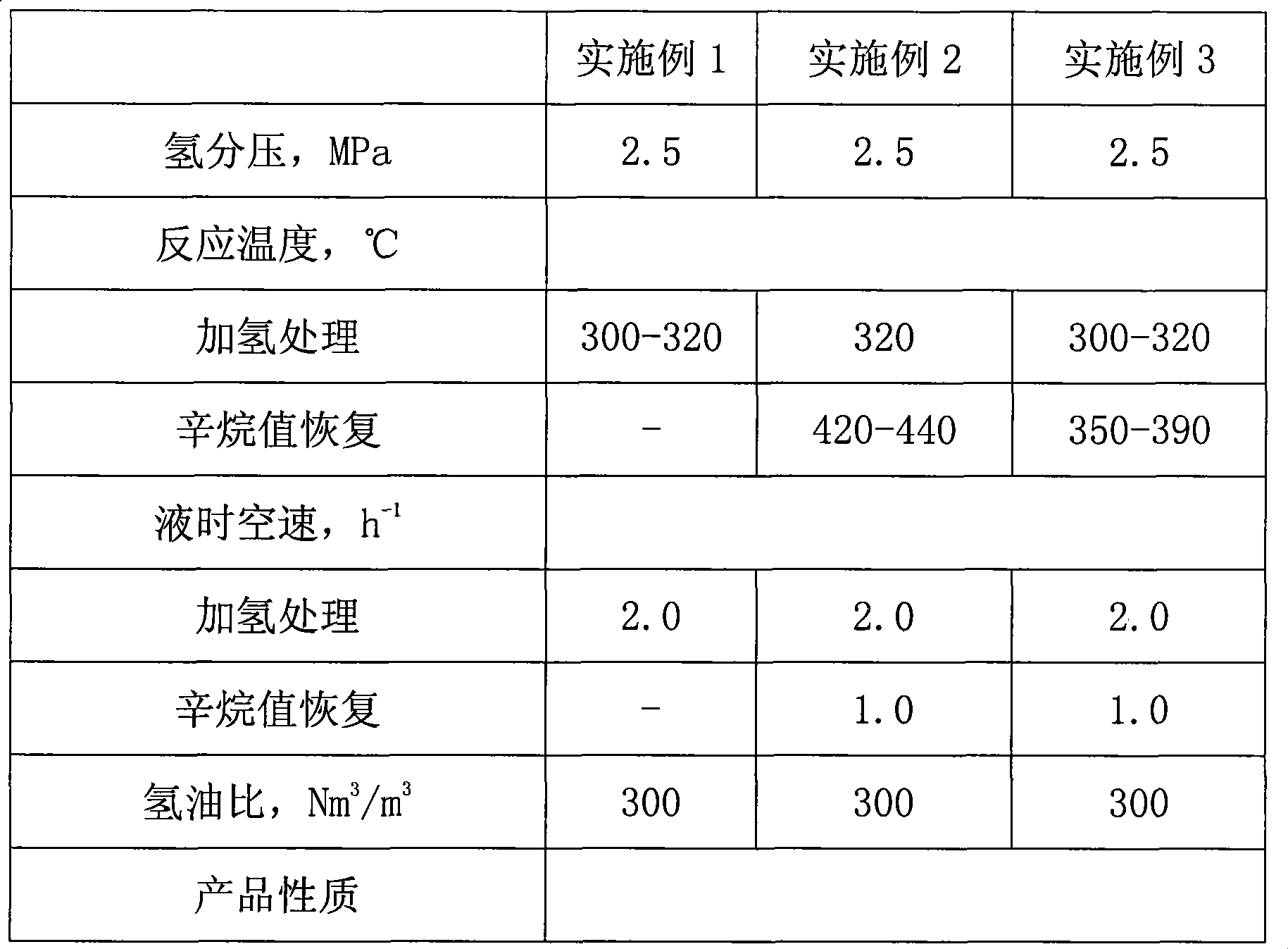
Catalytic multi-stage process for hydroconversion and refining hydrocarbon feeds
InactiveUS6190542B1Improve distillation yieldQuality improvementCatalyst activation/preparationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionLiquid productDistillates petroleum
A multi-stage catalytic hydrogenation and hydroconversion process for heavy hydrocarbon feed materials such as coal, heavy petroleum fractions, and plastic waste materials. In the process, the feedstock is reacted in a first-stage, back-mixed catalytic reactor with a highly dispersed iron-based catalyst having a powder, gel or liquid form. The reactor effluent is pressure-reduced, vapors and light distillate fractions are removed overhead, and the heavier liquid fraction is fed to a second stage back-mixed catalytic reactor. The first and second stage catalytic reactors are operated at 700-850.degree. F. temperature, 1000-3500 psig hydrogen partial pressure and 20-80 lb. / hr per ft.sup.3 reactor space velocity. The vapor and light distillates liquid fractions removed from both the first and second stage reactor effluent streams are combined and passed to an in-line, fixed-bed catalytic hydrotreater for heteroatom removal and for producing high quality naphtha and mid-distillate or a full-range distillate product. The remaining separator bottoms liquid fractions are distilled at successive atmospheric and vacuum pressures, low and intermediate-boiling hydrocarbon liquid products are withdrawn, and heavier distillate fractions are recycled and further upgraded to provide additional low-boiling hydrocarbon liquid products. This catalytic multistage hydrogenation process provides improved flexibility for hydroprocessing the various carbonaceous feedstocks and adjusting to desired product structures and for improved economy of operations.
Owner:HEADWATERS CTL
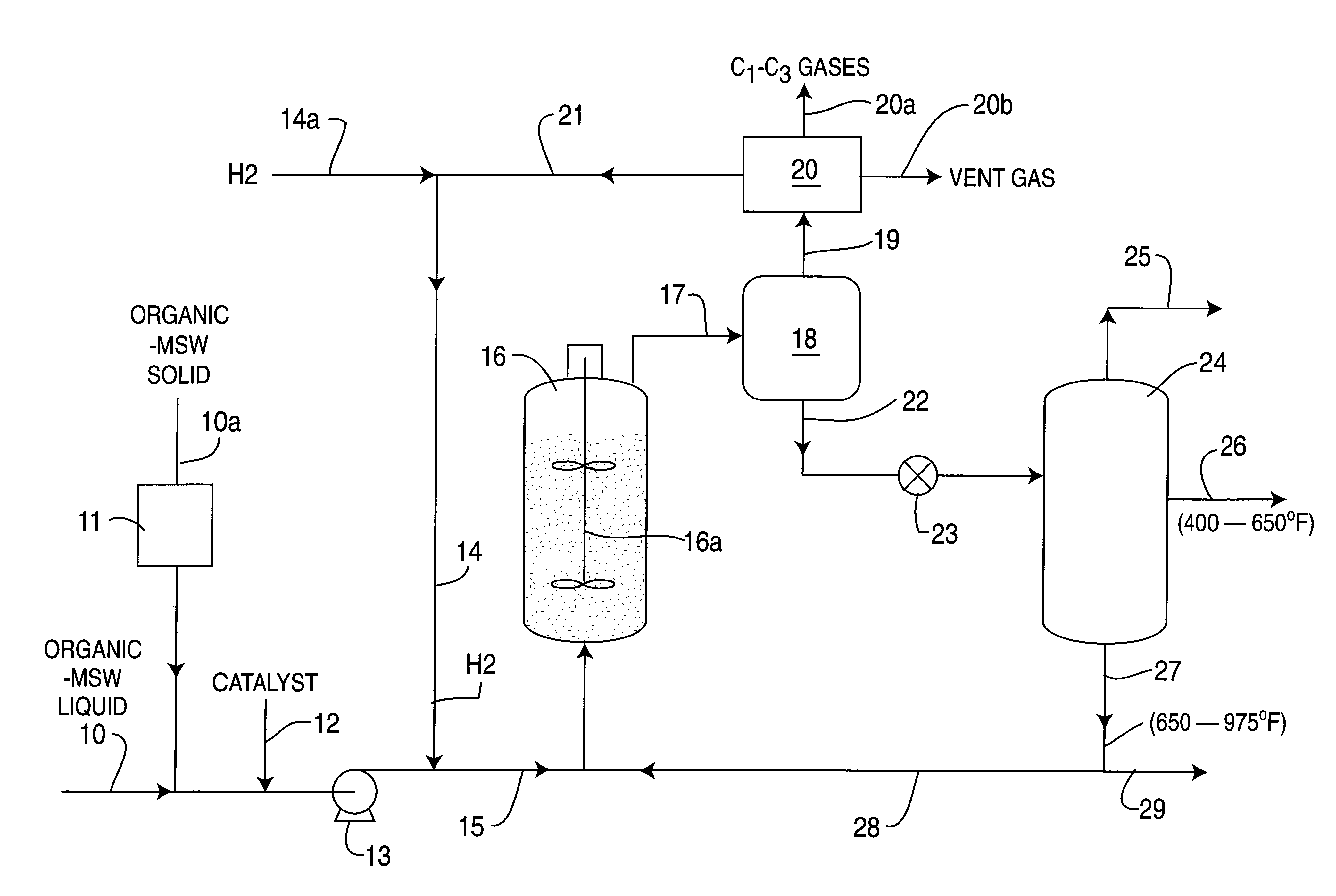
Catalytic hydroconversion of chemically digested organic municipal solid waste materials
InactiveUS6270655B1Increase surface areaReduce total nitrogenLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionHydrocarbon oil crackingParticulatesLiquid product
A hydrocarbon liquid feedstock containing at least 50 wt. % chemically digested organic-MSW material is catalytically hydroconverted utilizing either a single stage or two-stage catalytic reaction process to produce desirable lower-boiling hydrocarbon liquid products. The catalyst can be either a particulate supported type catalyst such as containing cobalt and / or molybdenum and / or nickel on alumina support, or a dispersed slurry type catalyst containing mainly iron oxide with anions of molybdate, phosphate, sulfate or tungstate, and combinations thereof. Broad useful reaction conditions are 600-860° F. (315-460° C.) temperature, 1000-3000 psi hydrogen partial pressure, and fresh feed rate of 20-60 pounds / hr / ft3 reactor volume. Effluent material from the final stage catalytic reactor is phase separated and the resulting liquid portion is fractionated to produce the desired low-boiling hydrocarbon liquid products particularly useful as transportation fuels. If desired, the chemically digested organic-MSW feedstock can be blended with petroleum residua and / or particulate coal and / or mixed waste plastics and the blended feed material processed in catalytic two-stage reactors to produce similar desirable low-boiling hydrocarbon liquid products.
Owner:HYDROCARBON TECH
Process for catalytic dewaxing and catalytic cracking of hydrocarbon streams
InactiveUS7261805B2Reducing pour point pointReducing point cloud pointTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyCoke ovensWaxIsomerization
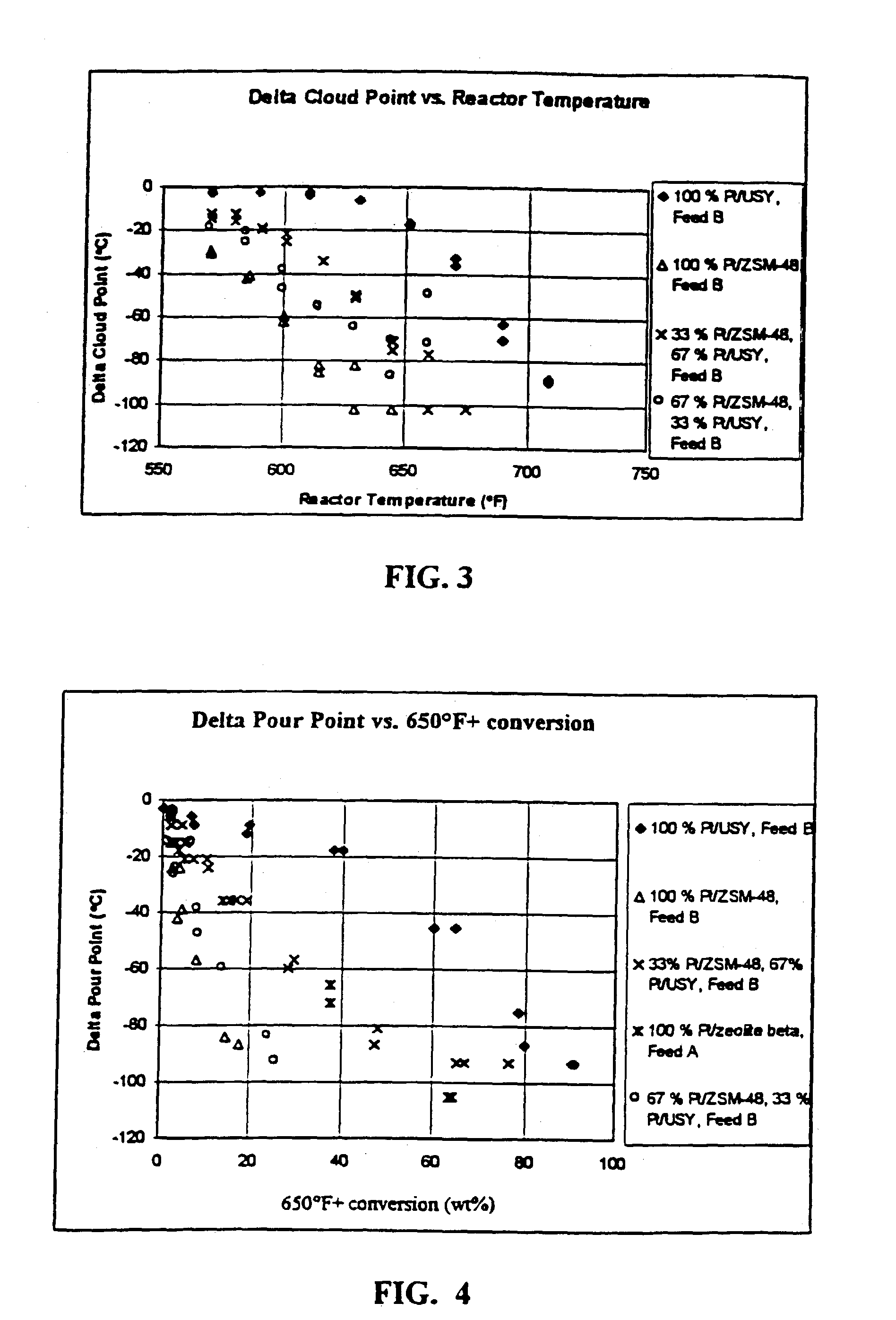
A process for upgrading a hydrocarbon feedstock containing waxy components and having an end boiling point exceeding 650° F., which includes contacting the feedstock at superatmospheric hydrogen partial pressure with an isomerization dewaxing catalyst that includes ZSM-48 and contacting the feedstock with a hydrocracking catalyst to produce an upgraded product with a reduced wax content. Each catalyst is present in an amount sufficient to reduce the cloud point and the pour point of the feedstock at a conversion of greater than about 10%, and an overall distillate yield of greater than about 10% results from the process.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Catalyst combination for the hydroisomerization of waxy feeds at low pressure
ActiveUS20060091043A1Low pour pointReduce pointsMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationMolecular sieveWax
A process for the hydroisomerization of a waxy feed having a major portion boiling above 650° F. to produce a lubricating base oil having a lower pour point, said process comprising (a) passing the waxy feed along with hydrogen gas through a hydroisomerization zone maintained at a hydrogen partial pressure of between about 100 psia and about 400 psia, said hydroisomerization zone comprising a catalyst bed containing at least two active wax hydroisomerization catalysts, said catalysts comprising at least (i) a first catalyst comprising an active hydrogenation component and a 1-D, 10-ring molecular sieve having a maximum crystallographic free diameter of the channels equal to 6.2 Å units or greater and (ii) a second catalyst comprising an active hydrogenation component and a 1-D, 10-ring molecular sieve having a maximum crystallographic free diameter of the channels equal to 5.8 Å units or less, wherein the weight ratio of molecular sieve contained in the first catalyst to the molecular sieve contained in second catalyst in the hydroisomerization zone falls within the range between about 2 to 1 and about 12 to 1; and (b) recovering from the hydroisomerization zone a lubricating base oil having a lower pour point as compared to the waxy feed.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
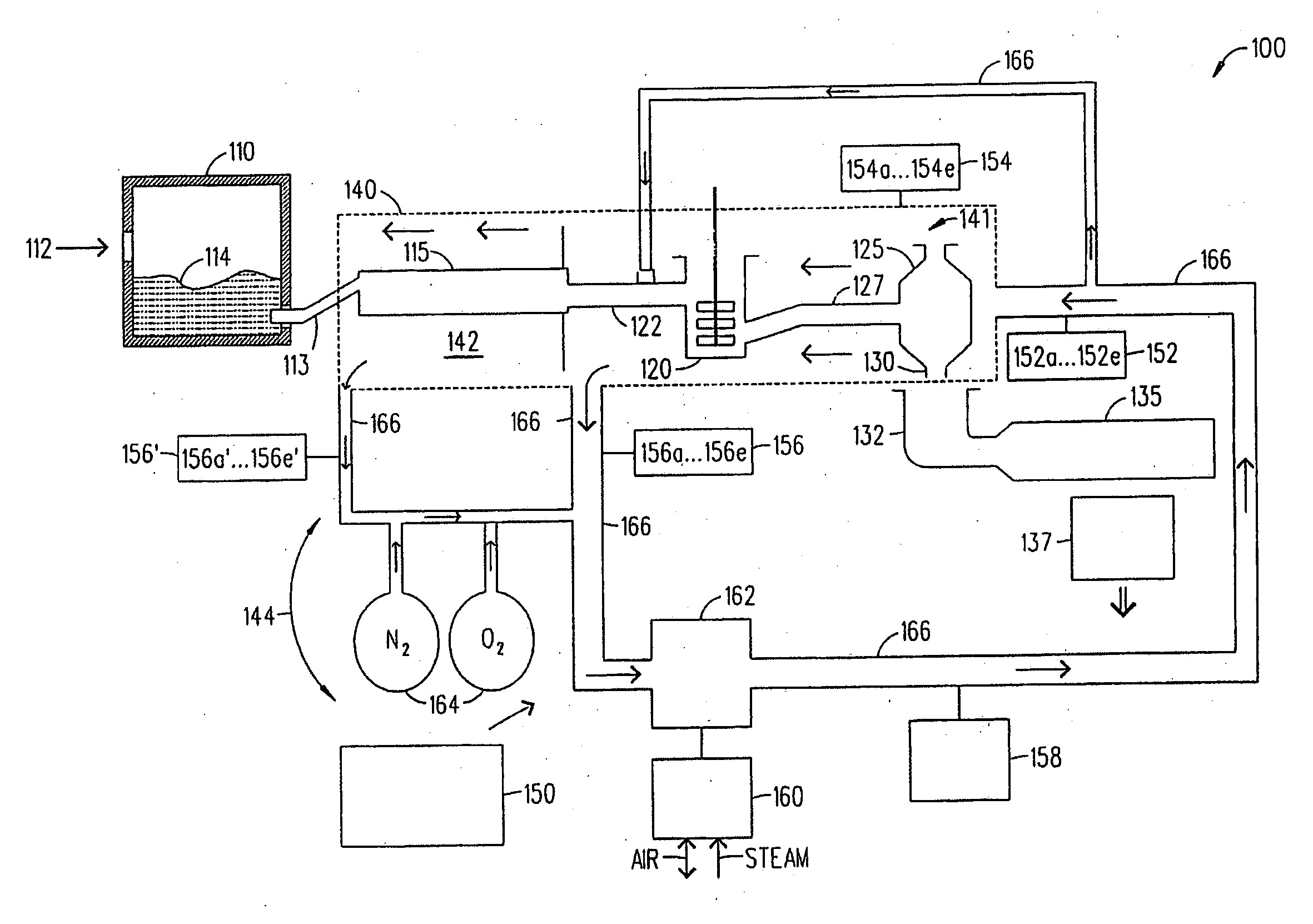
Method of fining glass
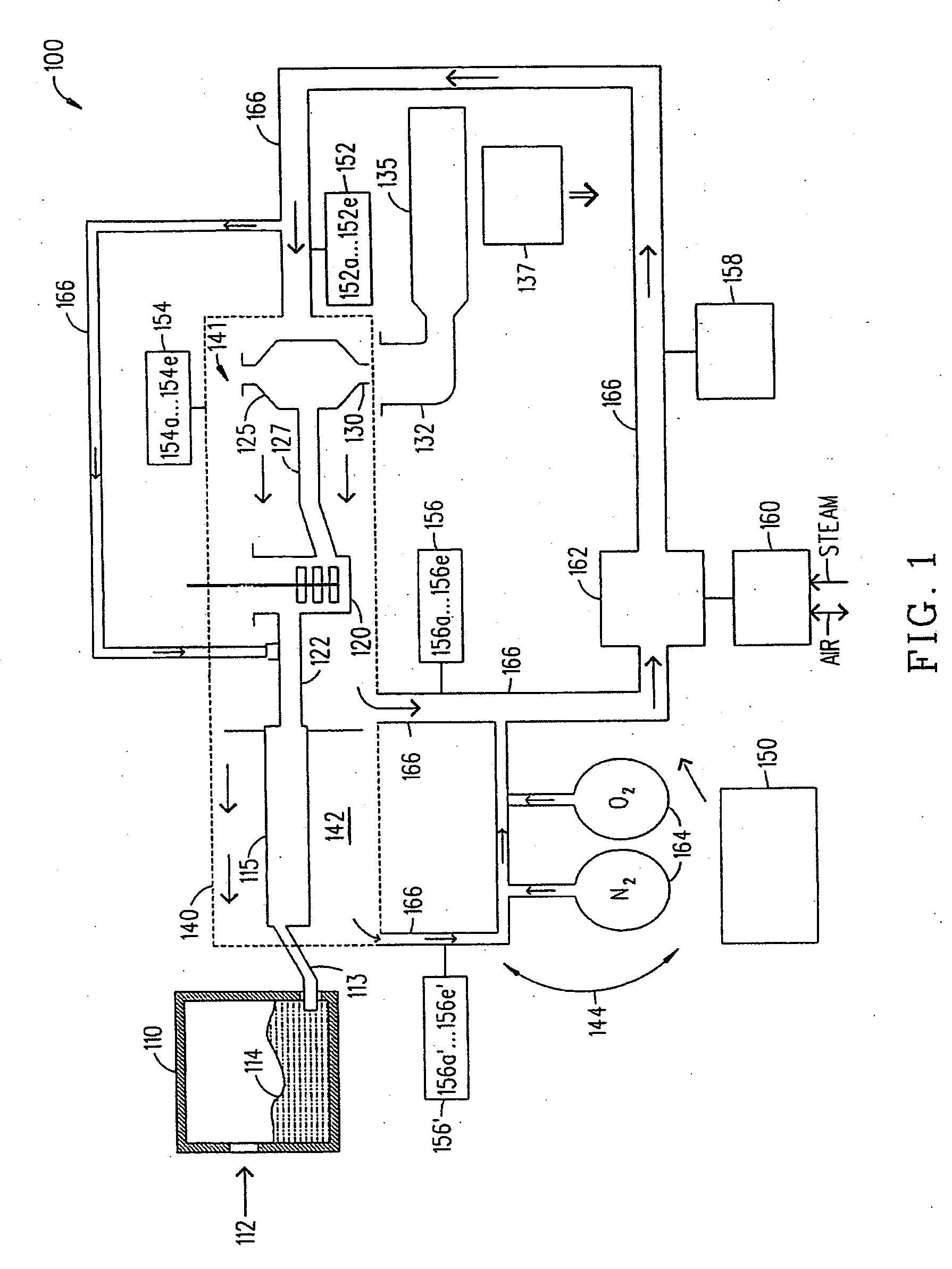
InactiveUS20060242995A1Increased hydrogen permeationAvoid formingGlass furnace apparatusGlass vesselAlloy
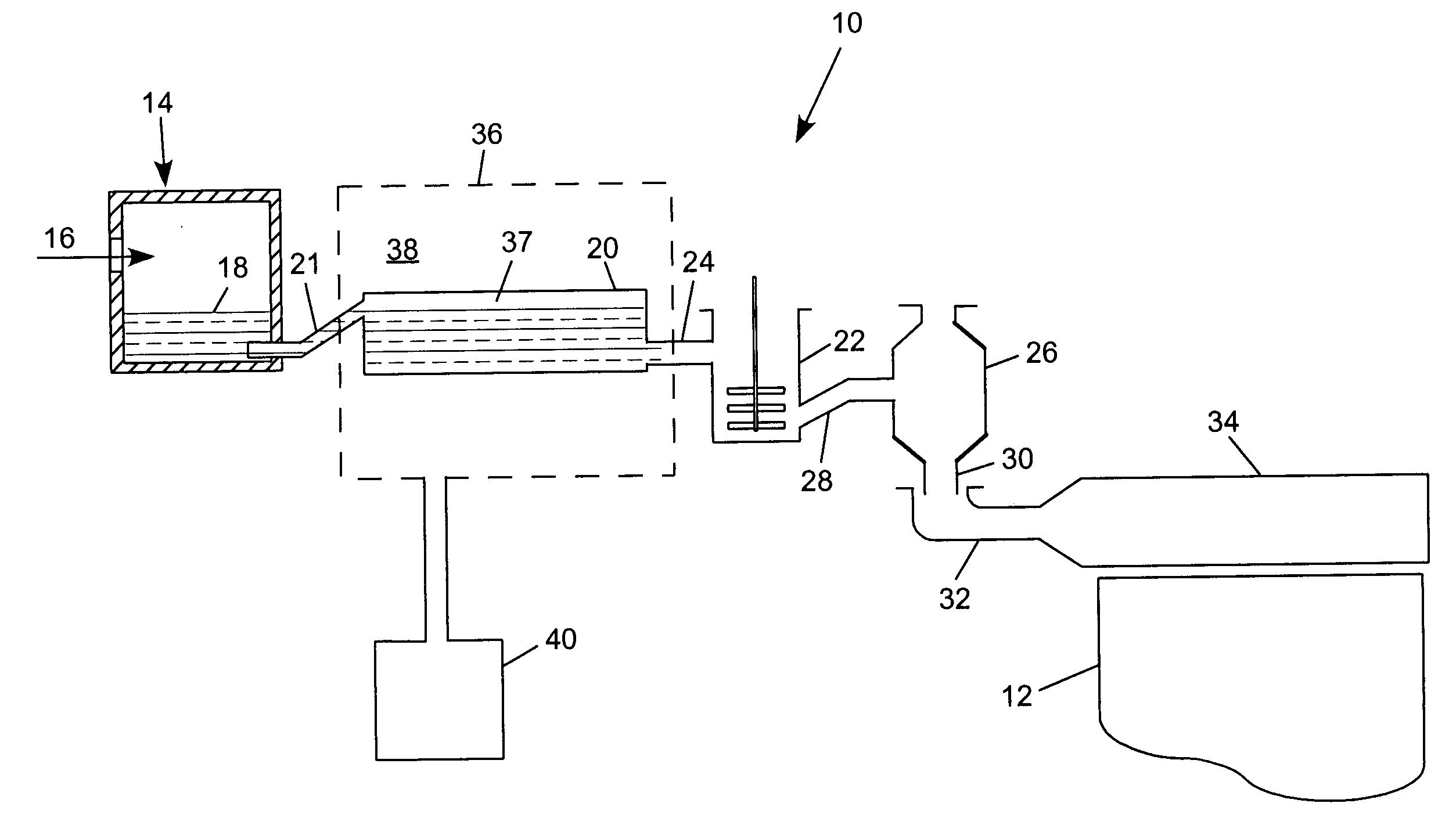
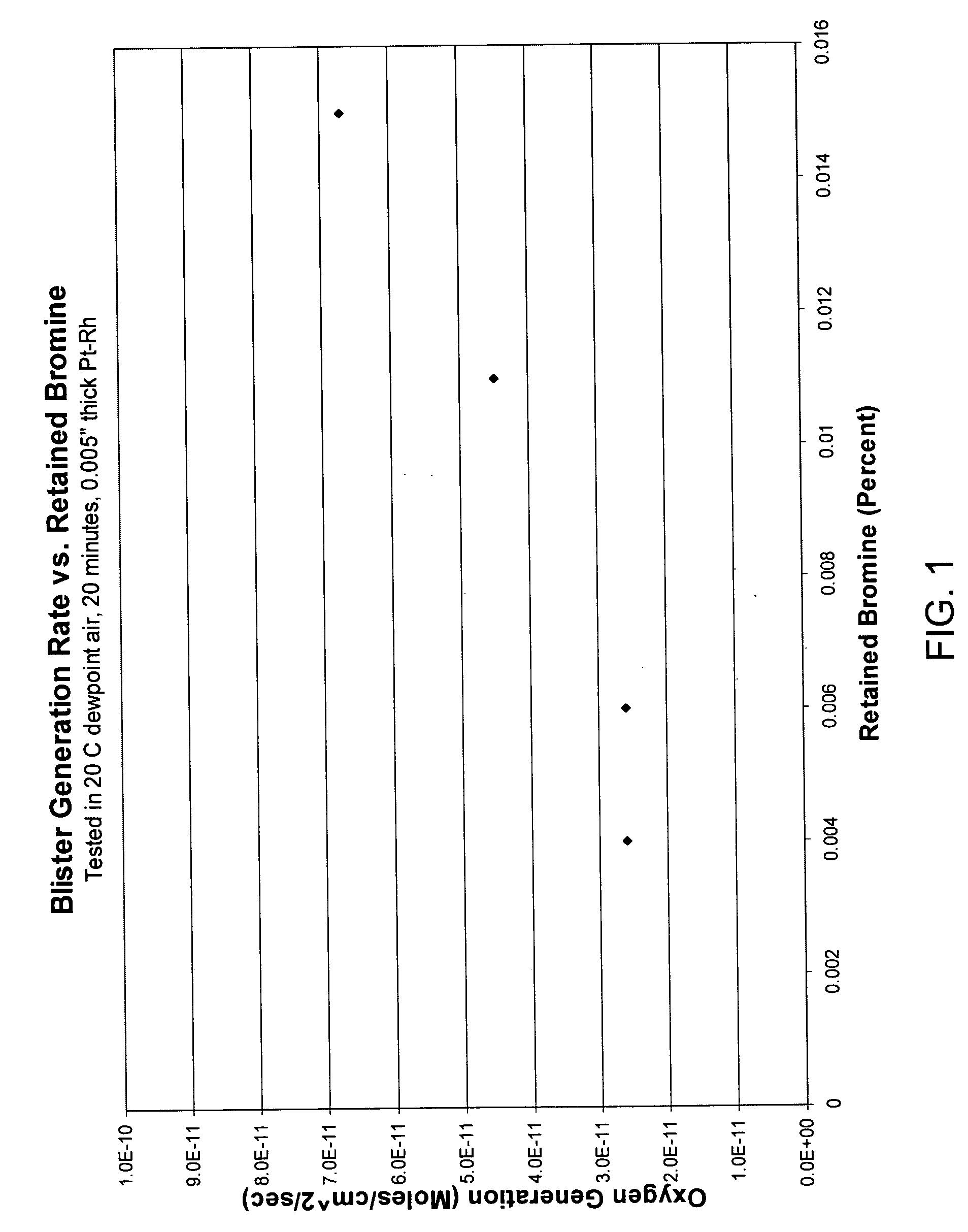
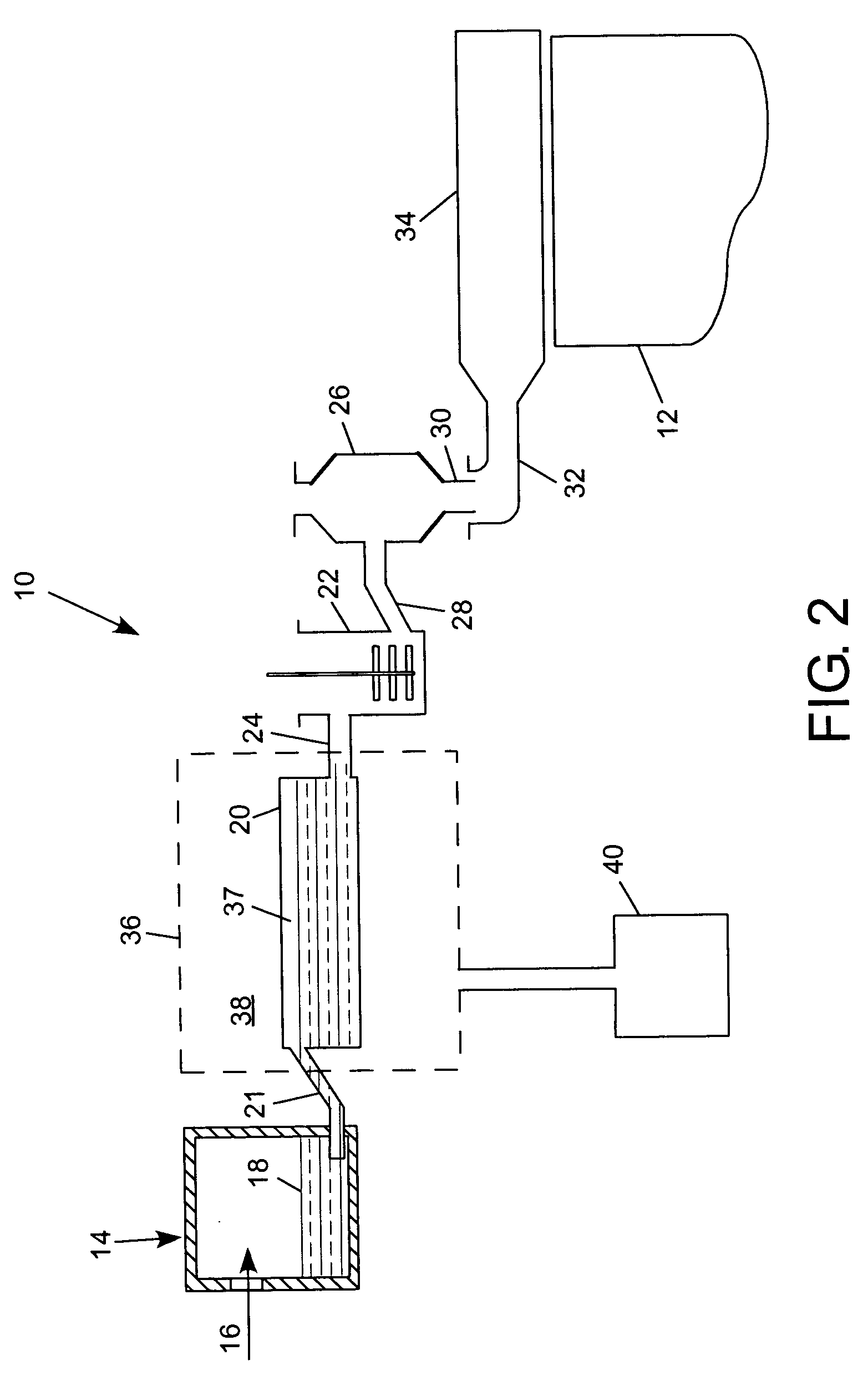
A method of forming an oxide glass including heating a glass melt having a β—OH concentration of at least about 0.35 in a vessel comprising a metal selected from the group consisting of platinum, molybdenum, palladium, rhodium, and alloys thereof, there being an interface present between the vessel and the glass, and controlling a partial pressure of hydrogen in an atmosphere in contact with an outside surface of the vessel in an amount such that hydrogen permeation blisters form in a region of the glass adjacent the glass-vessel interface.
Owner:CORNING INC
Hydrogenation modification method for catalytically cracked gasoline
ActiveCN101368111ANo change in octaneReduce hydrogen sulfide contentGasoline stabilisationRefining to eliminate hetero atomsIsomerizationHydrodesulfurization
The invention relates to a hydro-upgrading method for catalytic cracking gasoline; the method comprises the following steps: gasoline whole fraction is cut into light fraction and heavy fraction; the cutting point is 60 DEG C to 80 DEG C; mercaptan in the light gasoline fraction is removed through mercaptan removal alkali washing; the heavy gasoline fraction and hydrogen gas have catalytic hydrodesulfurization, denitrogenation and olefin saturated reaction; reactor effluent or the reactor effluent after removing hydrogen sulfide is contacted with octane value restore catalyzer, and isomerization, aromatizatian and building up reaction are implemented, hydrogenated oil is separated and lighter hydrocarbon gasoline fraction is obtained, hydrogen-rich gas at the top of a high partial tank is circularly used through hydrogen sulfide removal, and lighter hydrocarbon at the top of a stabilizer tower is feedback to a fractionation tank to be fractionated again; the condition of the hydrotreating reaction is that hydrogen partial pressure is 1.5 to 3.0 MPa; the reaction temperature is 250 to 320 DEG C; the liquid hourly space velocity is 3.0 to 5.0 h<-1>, and the hydrogen-oil ratio is 200 to 500 Nm<3> / m<3>; the sulfur content of the gasoline product is smaller than 100 ppm, the octane value is unchanged, and the yield of gasoline reaches 98.5 weight percent.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
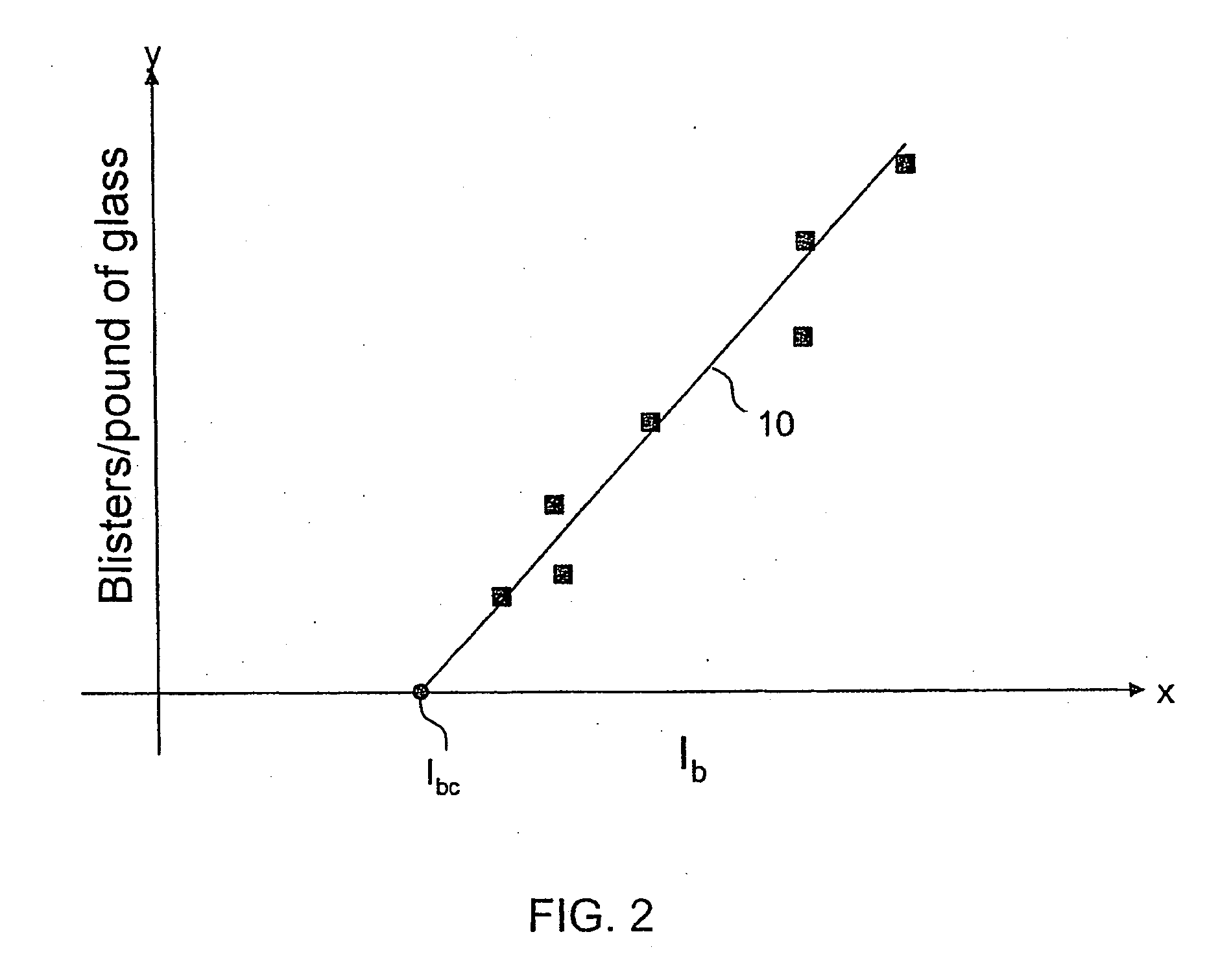
Method of eliminating blisters in a glass making process
InactiveUS20070149380A1Easy to understandGlass furnace apparatusGlass drawing apparatusBlistersHydrogen partial pressure
A method of controlling blister formation in a glass melt flowing through a system comprising one ore more refractory metal vessels by developing a blister index and determining the critical blister index value. The critical value of the blister index may be used to control the principal variables responsible for blister formation, including the water content of the melt, the concentration of reduced multivalent oxide compounds in the melt, and the hydrogen partial pressure of an atmosphere in contact with the outside surface of the refractory metal vessel. Also disclosed is a minimum partial pressure of hydrogen necessary to produce an essentially blister-free glass article in a glass essentially free of arsenic and antimony.
Owner:CORNING INC
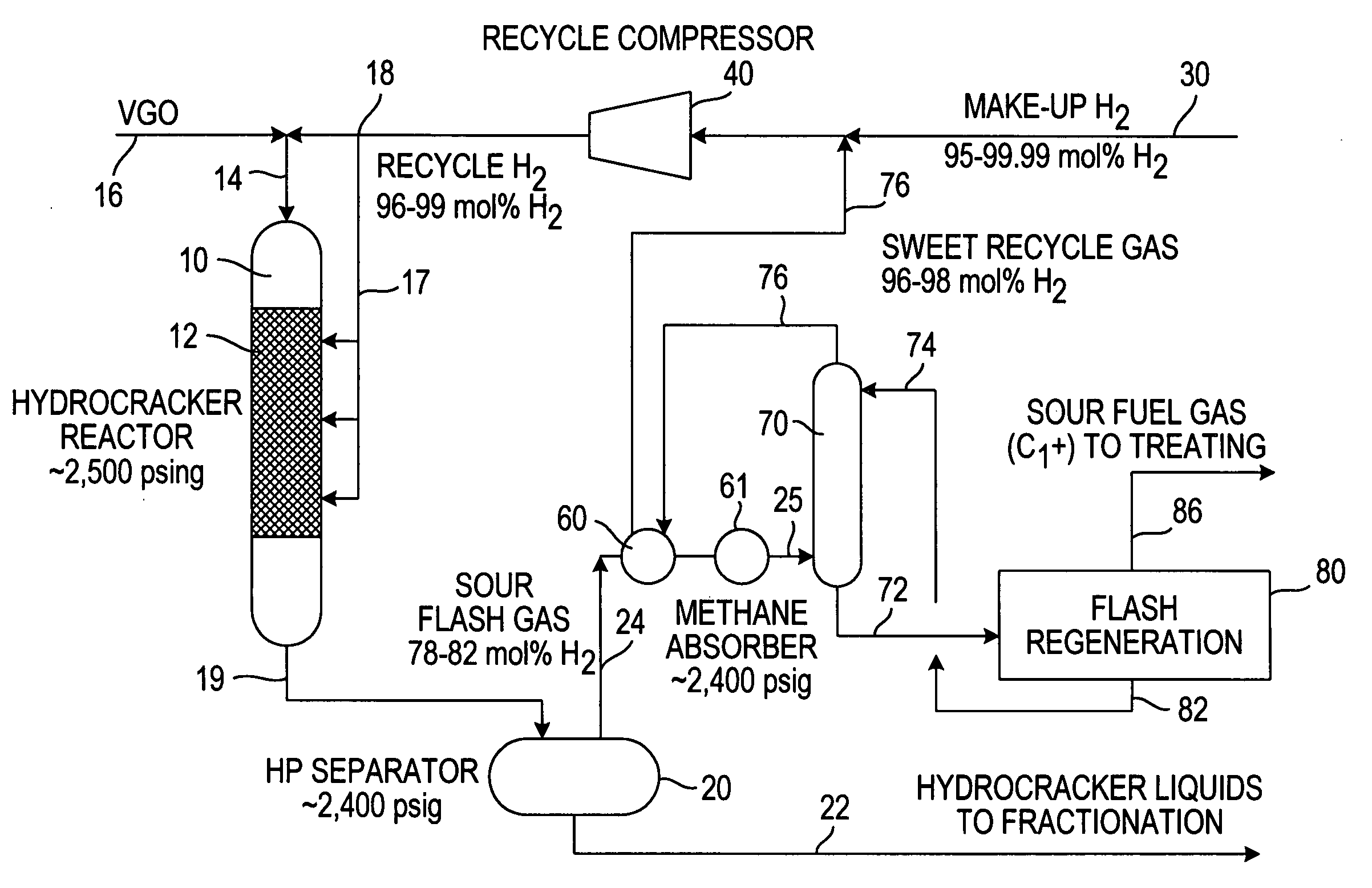
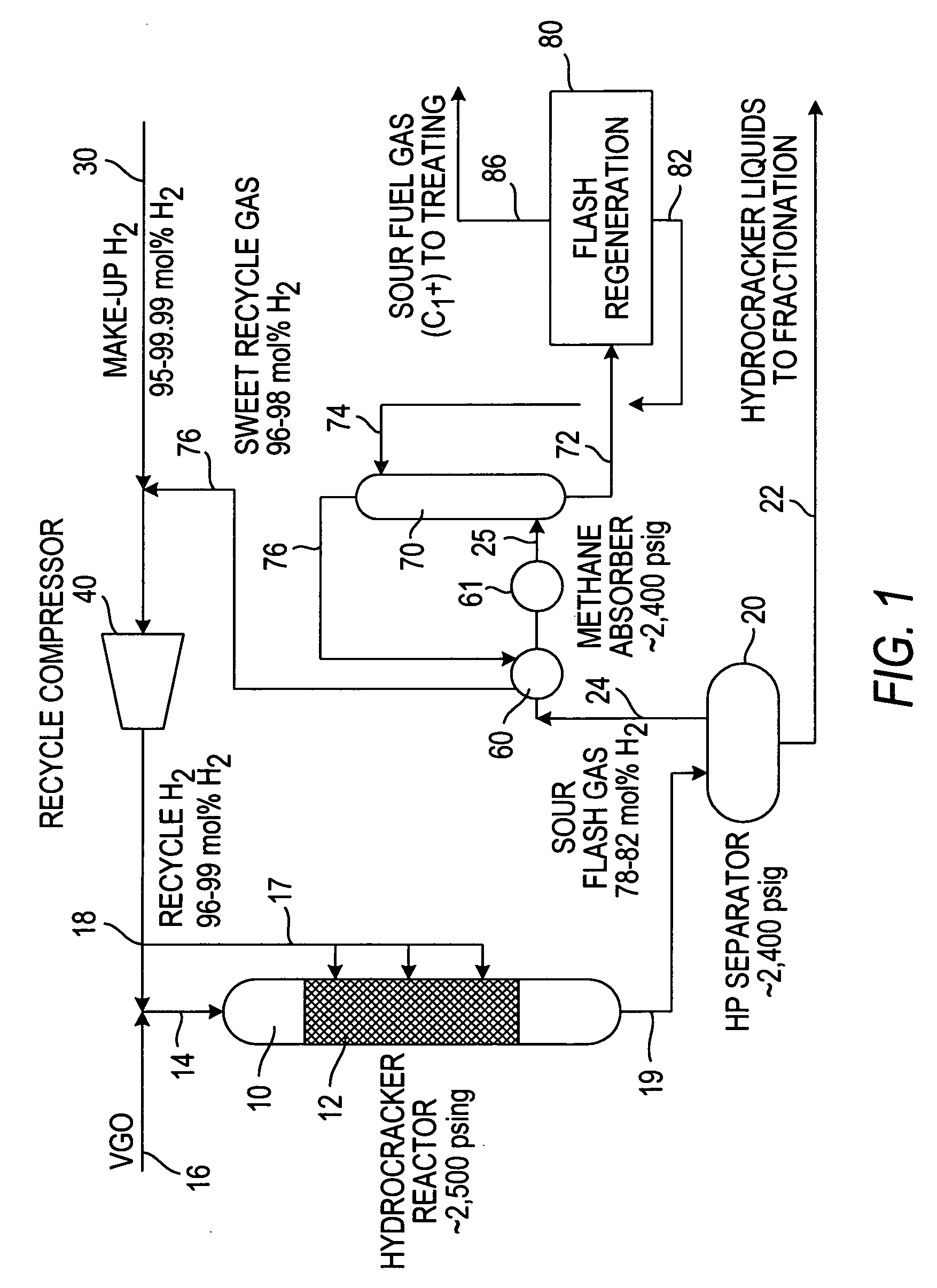
Hydrogen purification for make-up gas in hydroprocessing processes
InactiveUS20070017851A1Minimize changesHigh levelHydrocarbon oil crackingTreatment with hydrotreatment processesGas compressorFlash-gas
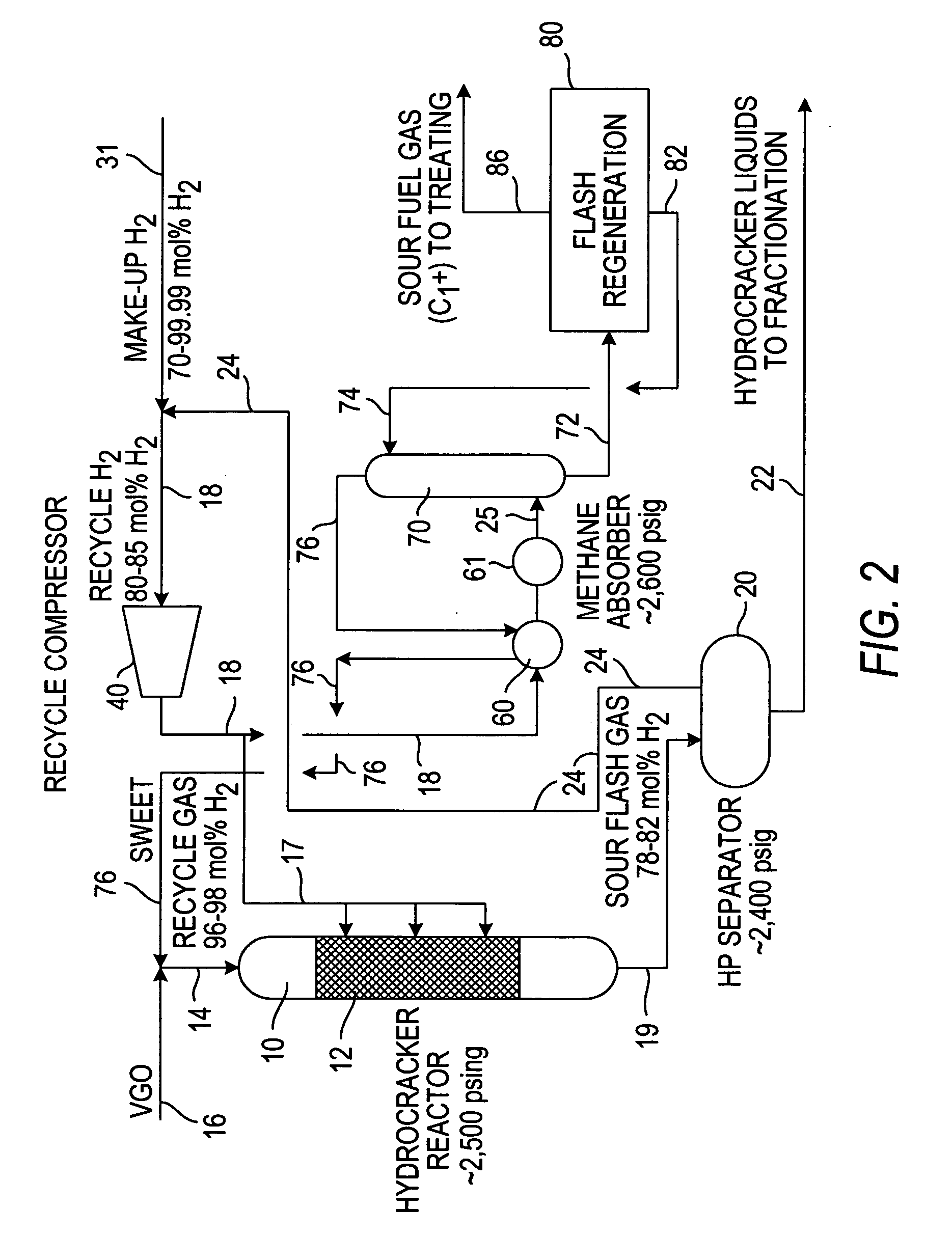
The recycle gas stream containing hydrogen that is part of the feedstream to a hydroprocessing reactor is mixed with the low purity make-up hydrogen and the sour flash gases upstream of the recycle gas compressor and compressed by the recycle gas compressor. The compressed gases pass through a methane and higher (C1+) absorber to produce a sweet hydrogen recycle gas stream that is delivered to the hydroprocessing reactor at 96-98 mol % hydrogen. The process can be used to advantage in existing process facilities to increase the hydrogen partial pressure in the feedstream to the hydroprocessor where the existing recycle gas compressor is not designed for compressing the high purity hydrogen.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Hydrocracking method of midbarrel oil circulation
ActiveCN1955261AHigh hydrogen contentReduce hydrogen contentTreatment with hydrotreatment processesForeign matterNaphtha
This invention discloses a poor quality catalytic cracking diesel hydrocracking method. After mixing poor quality catalytic cracking diesel and heavy hydrocracking material, hydrocracking is conducted at first, then its intermediate fraction is conducted the second hydrocraking. High aromatic hydrocarbon heavy naphtha and low BMCI value end oil. The catalyst activity will play sufficiently because some intermediate fraction oil has removed foreign matters, such as sulphur, nitrogen and so on, so it can be operated under higher space speed and lower temperature, and even operated under lower hydrogen partial pressure to take on a new look of economical. Further more; lower hydrogen partial pressure will be helpfulin intermediate fraction oil changing into High aromatic hydrocarbon heavy naphtha and lower temperature will reduce further cracking of heavy naphtha, so it will improve the yeild of heavy naphtha greatly.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +2
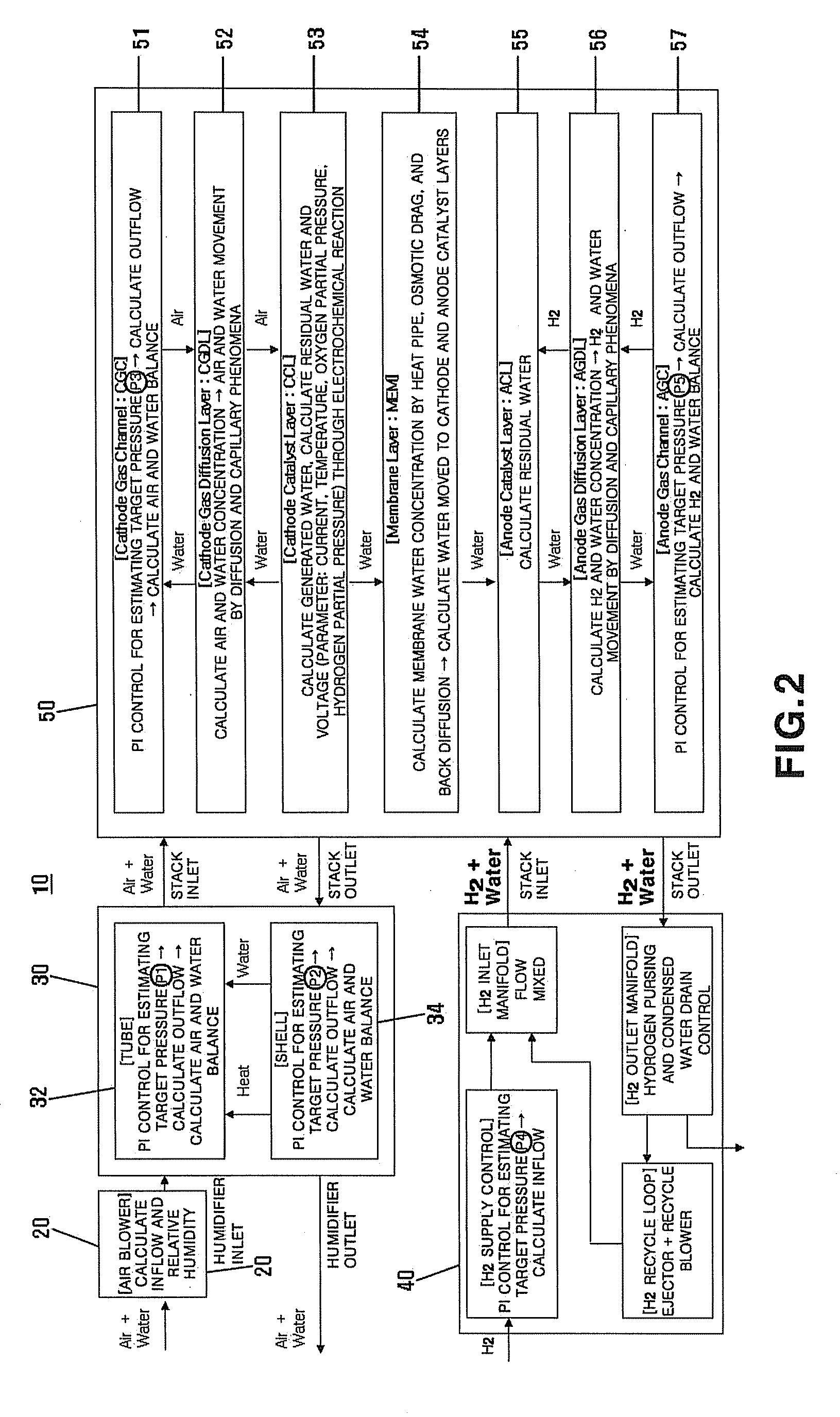
Controller for estimating relative humidity and condensed water, and method for controlling condensed water drain using the same
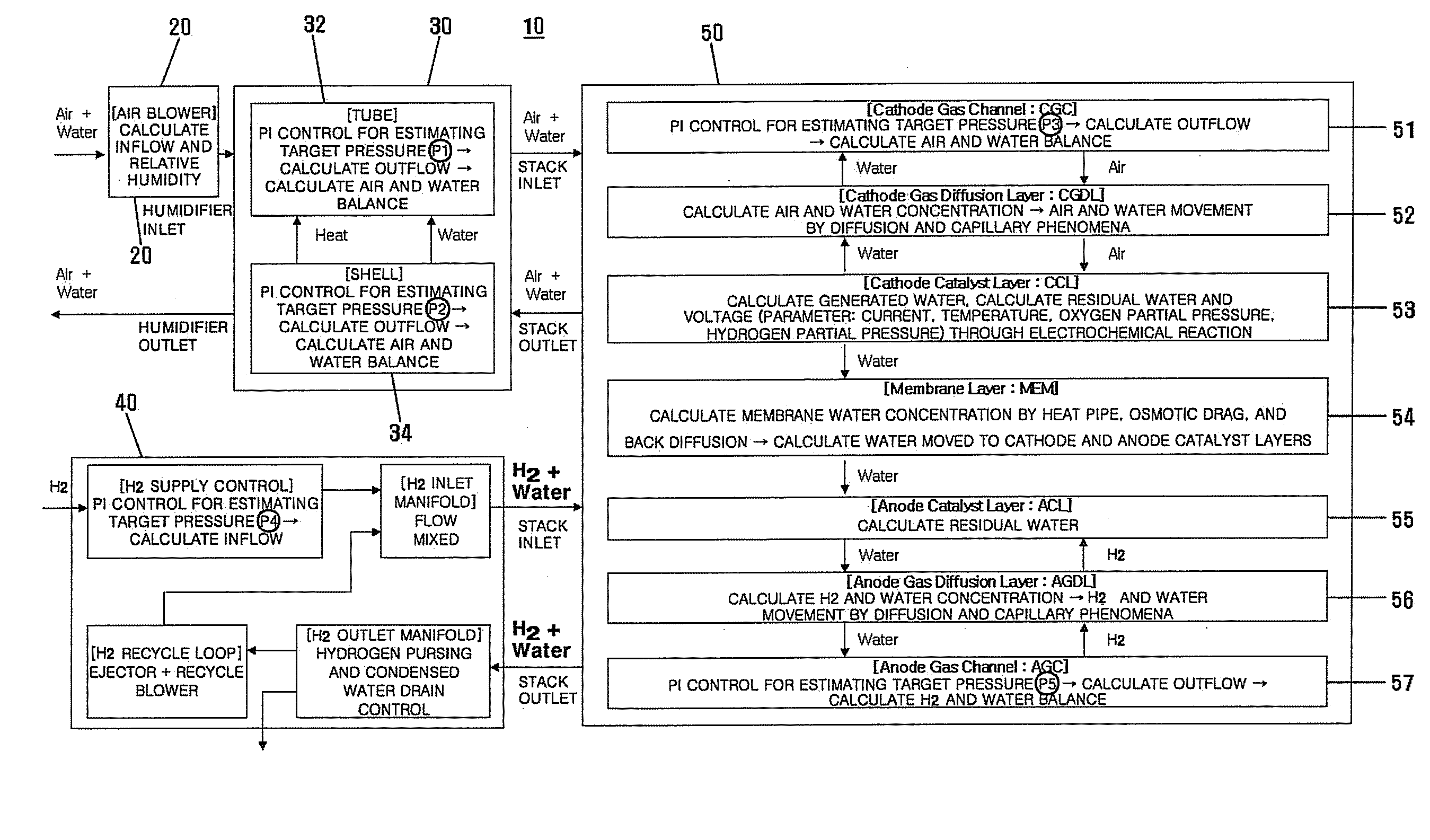
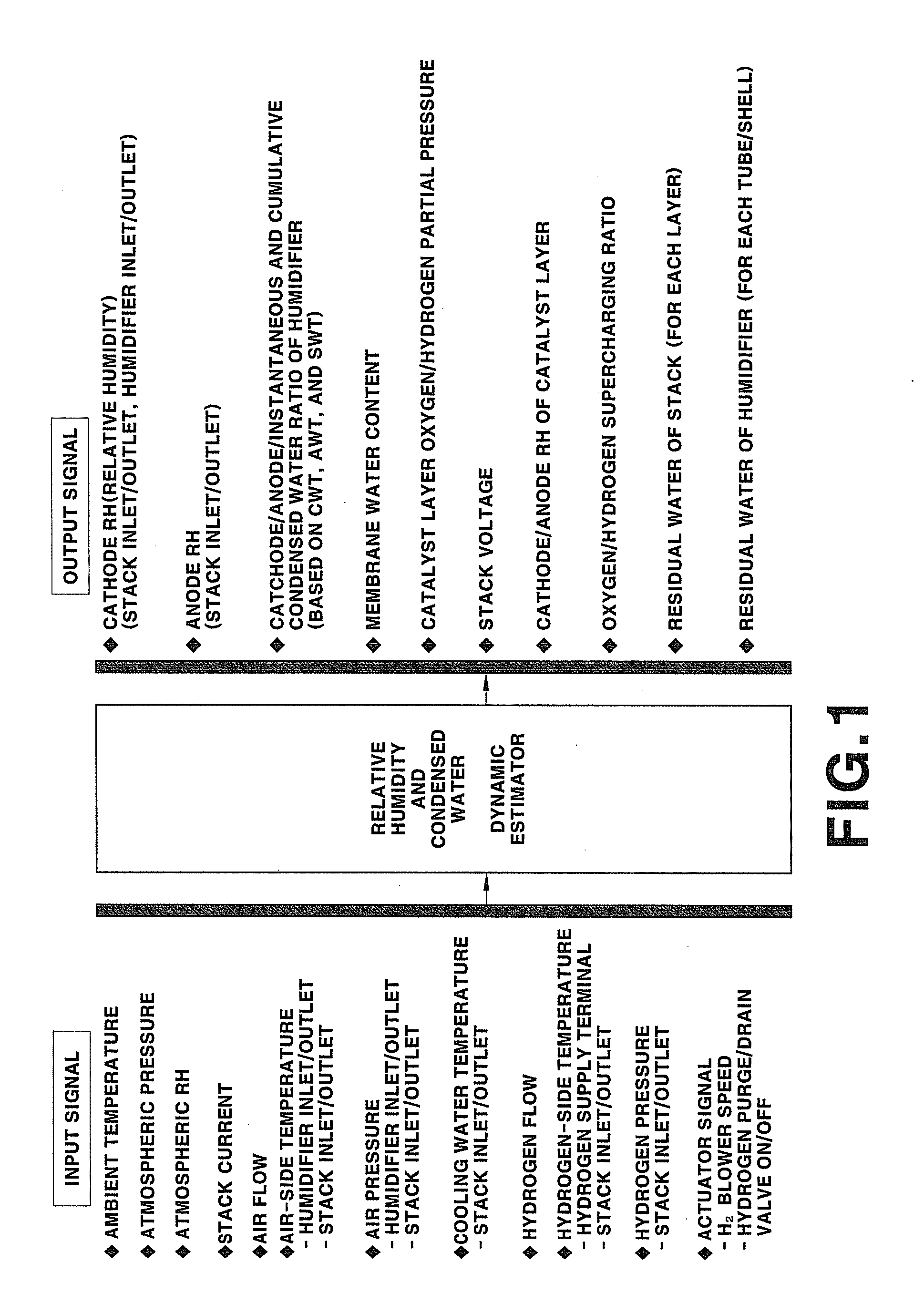
The present invention provides a relative humidity and condensed water estimator for a fuel cell and a method for controlling condensed water drain using the same. Here, the relative humidity and condensed water estimator is utilized in control of the fuel cell system involving control of anode condensed water drain by outputting at least two of signals comprising air-side relative humidity, hydrogen-side relative humidity, air-side instantaneous or cumulative condensed water, hydrogen-side instantaneous or cumulative condensed water, instantaneous and cumulative condensed water of the humidifier, membrane water contents, catalyst layer oxygen partial pressure, catalyst layer hydrogen partial pressure, stack or cell voltage, air-side catalyst layer relative humidity, hydrogen-side catalyst layer relative humidity, oxygen supercharging ratio, hydrogen supercharging ratio, residual water in a stack, and residual water in a humidifier.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Methods for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS7683212B2Efficient productionReduce formationHydrogenOrganic compound preparationGas phaseReaction rate
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
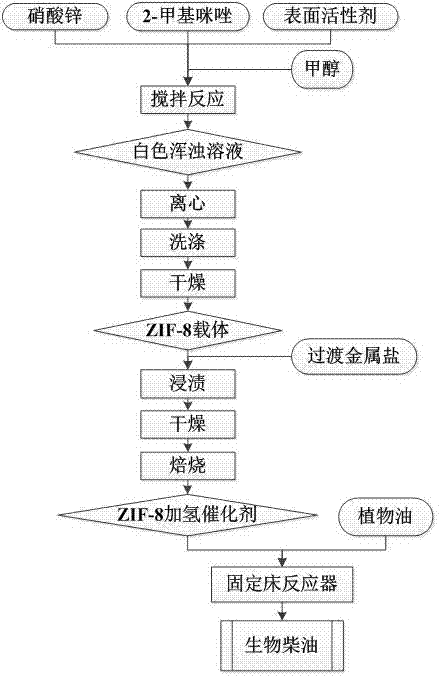
ZIF-8 material-based hydrogenation catalyst and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN104772165ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getEfficient preparation processOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionBiodieselPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a ZIF-8 material-based hydrogenation catalyst and a synthetic method thereof. The synthetic method particularly comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving zinc nitrate, 2-methylimidazole and a surface active agent with methanol, carrying out stirring reaction for 1-6h at 20-60 DEG C, and standing for 10-18h to obtain a turbid solution; (2) carrying out centrifugal treatment on the turbid solution, placing sediments in a drying oven to be dried to obtain a ZIF-8 carrier after washing with methanol; and (3) dissolving transition metal salt with water, dipping the ZIF-8 carrier into the dissolved transition metal salt, and roasting in a muffle furnace to obtain the ZIF-8 material based hydrogenation catalyst. The hydrogenation catalyst can be used for preparing biodiesel; the biodiesel preparation method comprises the steps of placing the ZIF-8 material based hydrogenation catalyst into a fixed bed reactor to be reduced, and introducing vegetable oil into the reactor for hydrocracking reaction at 300-400 DEG C under the conditions that the hydrogen partial pressure is 2-4MPa, the air speed is 0.9-3.6h<-1> so as to obtain the biodiesel finally. The catalytic efficiency of the synthesized ZIF-8 material based hydrogenation catalyst is improved by dozens of times compared with the catalytic efficiency of a traditional aluminum oxide catalyst.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS7476761B2Decrease in reaction rate can be inhibitedIncrease hydrogen partial pressurePreparation from carboxylic acid saltsOrganic compound preparationCarbon numberReaction rate
A process for producing a carboxylic acid comprises allowing an alcohol having a carbon number of “n” to continuously react with carbon monoxide in the presence of a carbonylation catalyst system, and a limited amount of water, continuously withdrawing the reaction mixture from the reaction system 1, introducing the withdrawn reaction mixture into a distillation step (distillation columns 3a and 3b), and separating a higher-boiling component and a lower-boiling component containing a carboxylic acid having a carbon number of “n+1”, respectively. In the process, the amount of carbon monoxide and / or hydrogen contained in a liquid phase of the reaction system is adjusted to at least one of the following conditions (i) and (ii): (i) the amount of carbon monoxide relative to 1 kilogram of the liquid phase by weight is at least 2 mmol per 1 MPa of carbon monoxide partial pressure of the reaction system, and (ii) the amount of hydrogen relative to 1 kilogram of the liquid phase by weight is at least 50 mmol per 1 MPa of hydrogen partial pressure of the reaction system. Such a process inhibits deactivation of a metal catalyst and deterioration in a reaction rate, and decreases formation of by-products in producing a carboxylic acid under a low water content.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
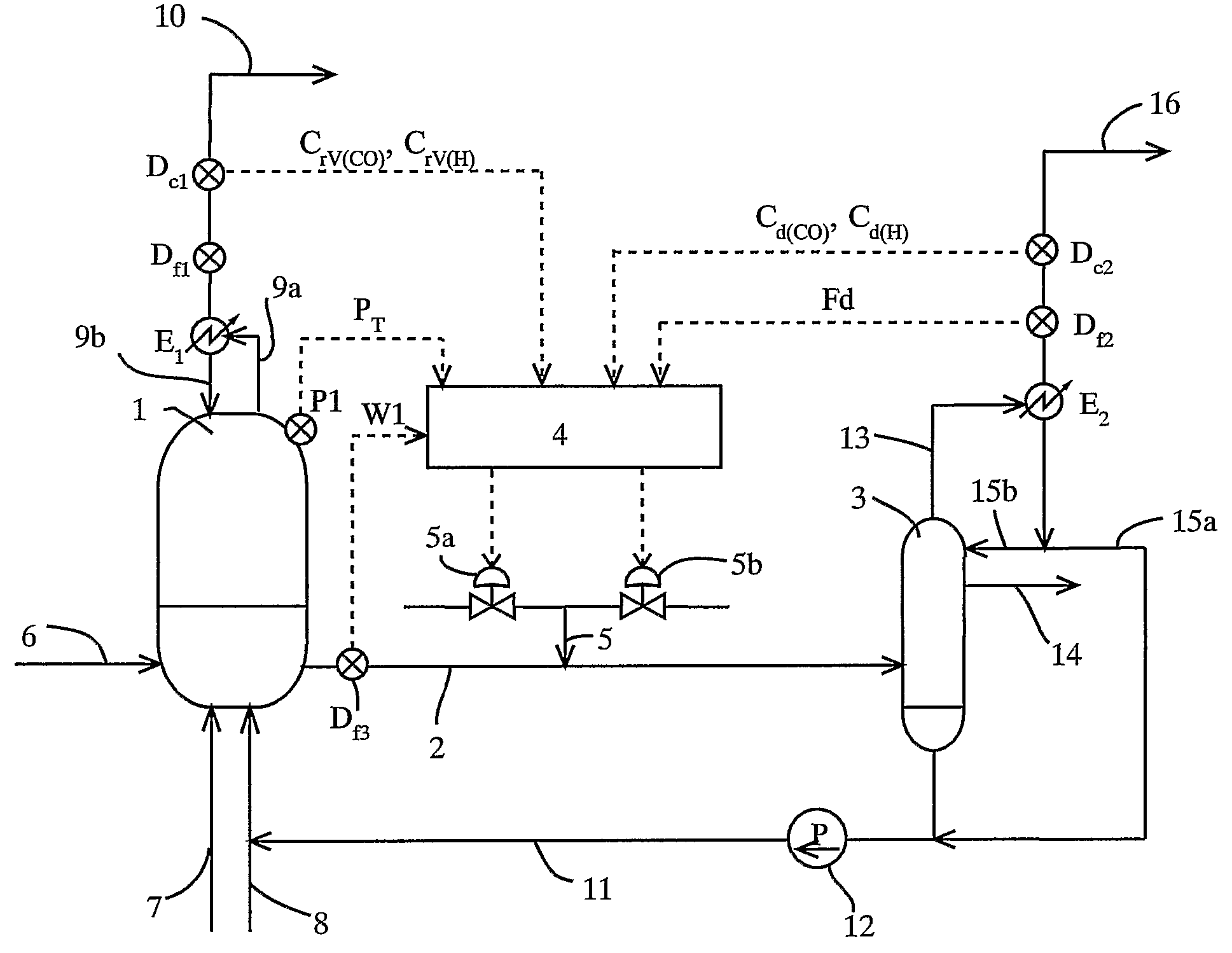
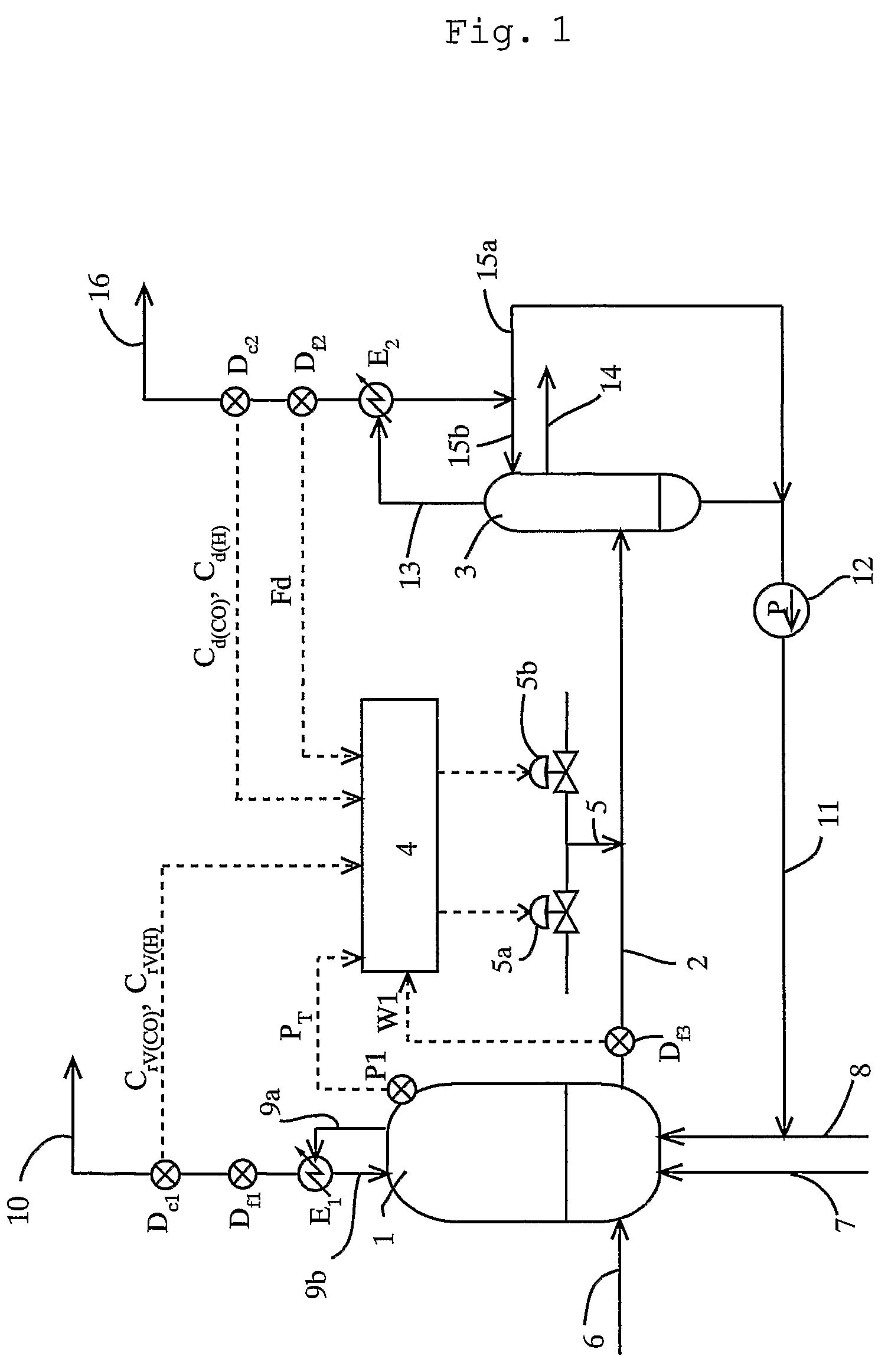
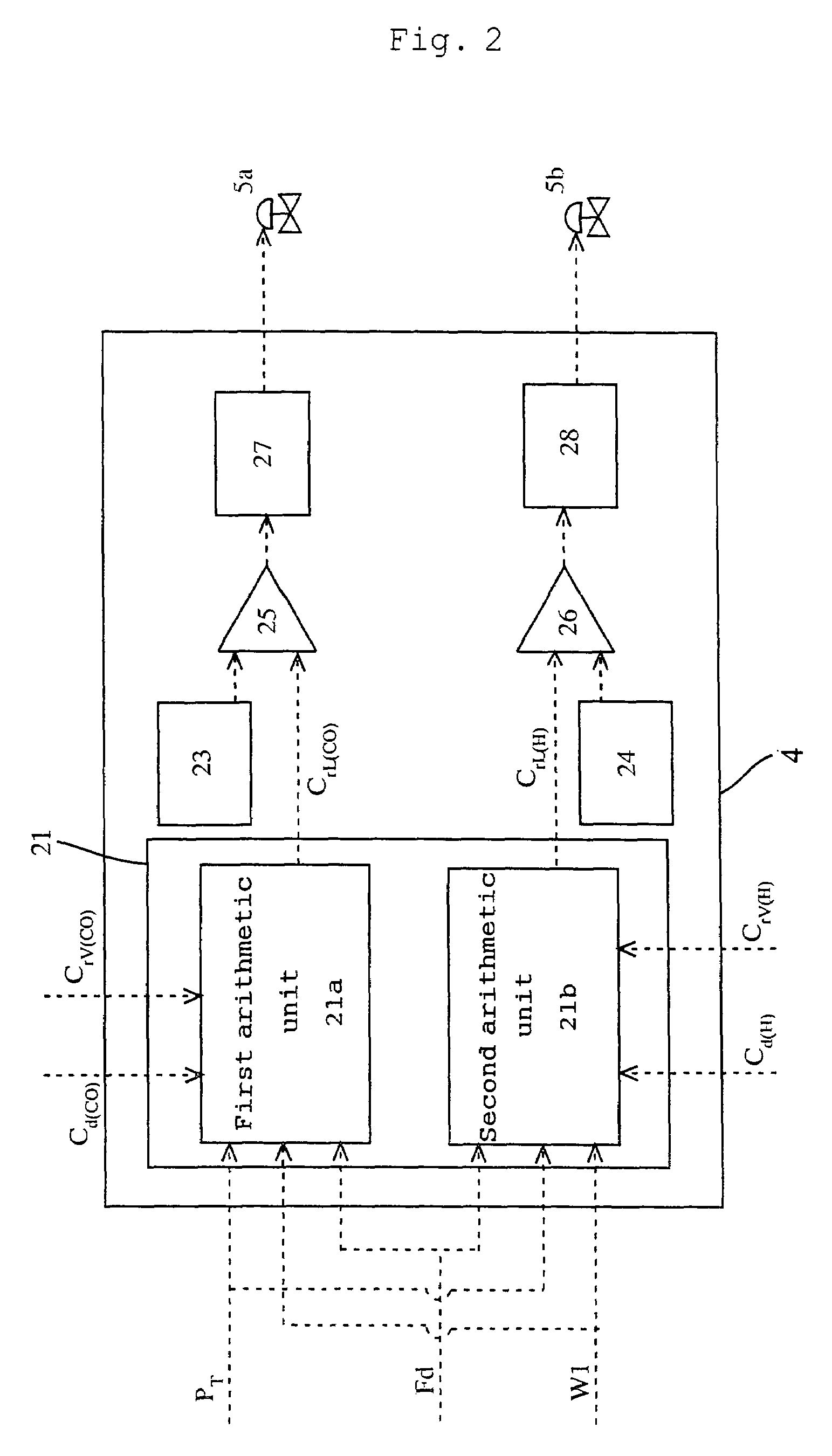
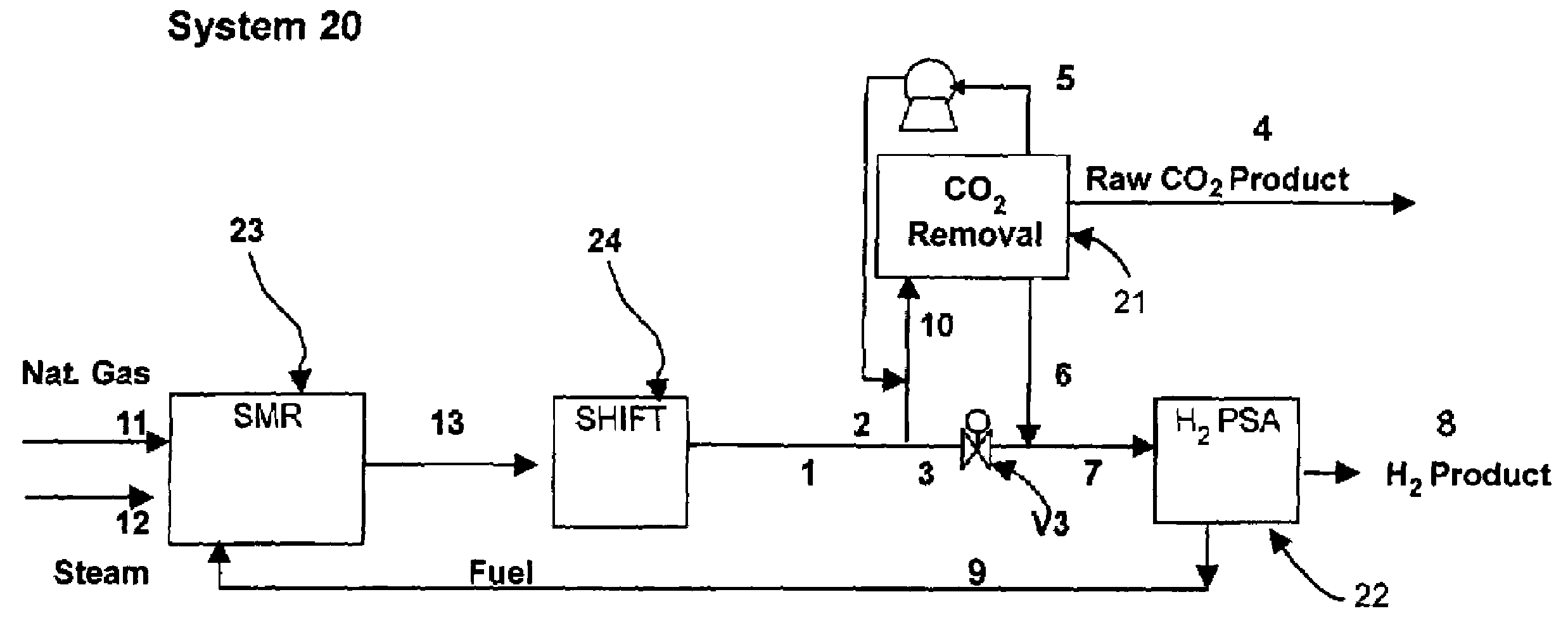
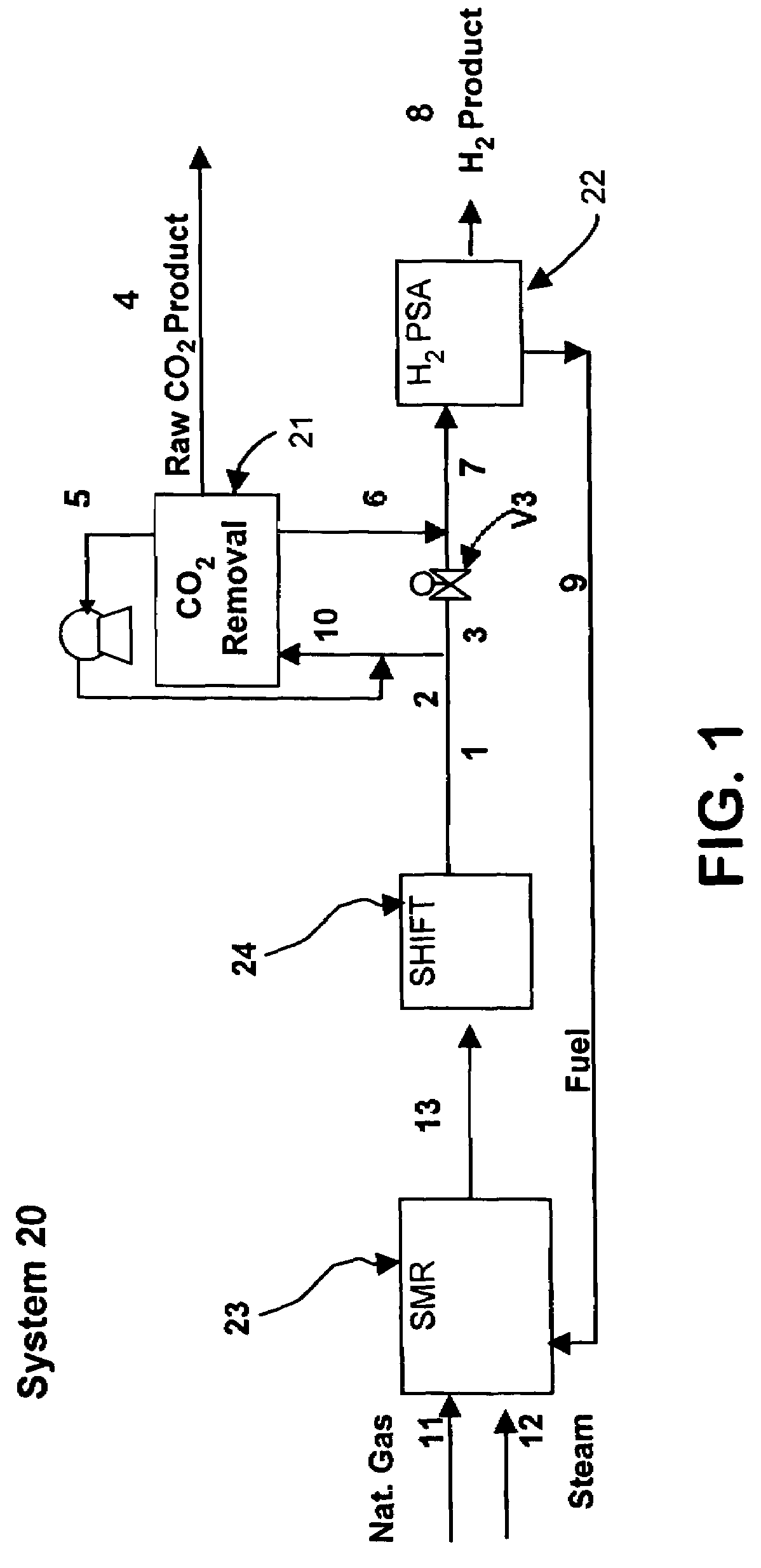
Process and apparatus for carbon dioxide recovery
InactiveUS20080072752A1Simplifies process flow sheetReduce processing costsProductsGas treatmentSyngasVacuum pressure
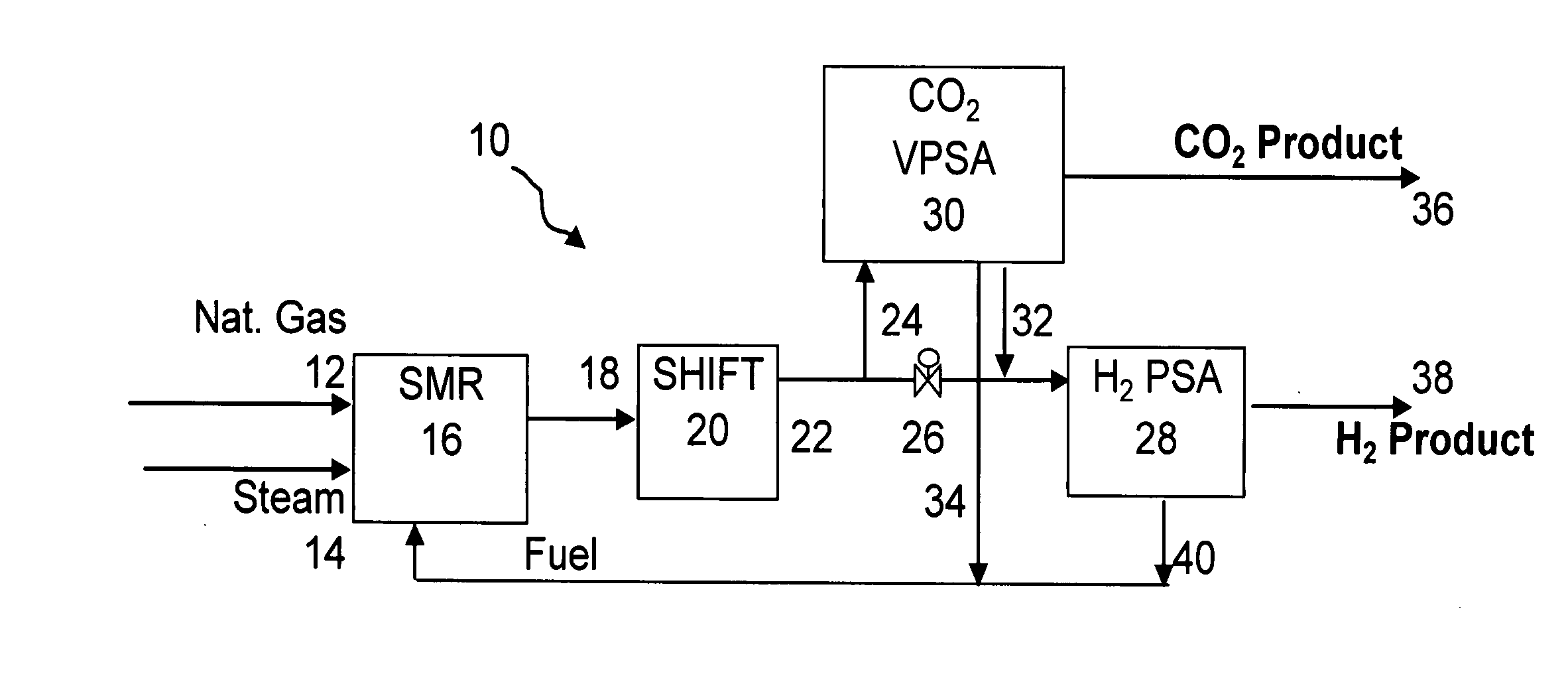
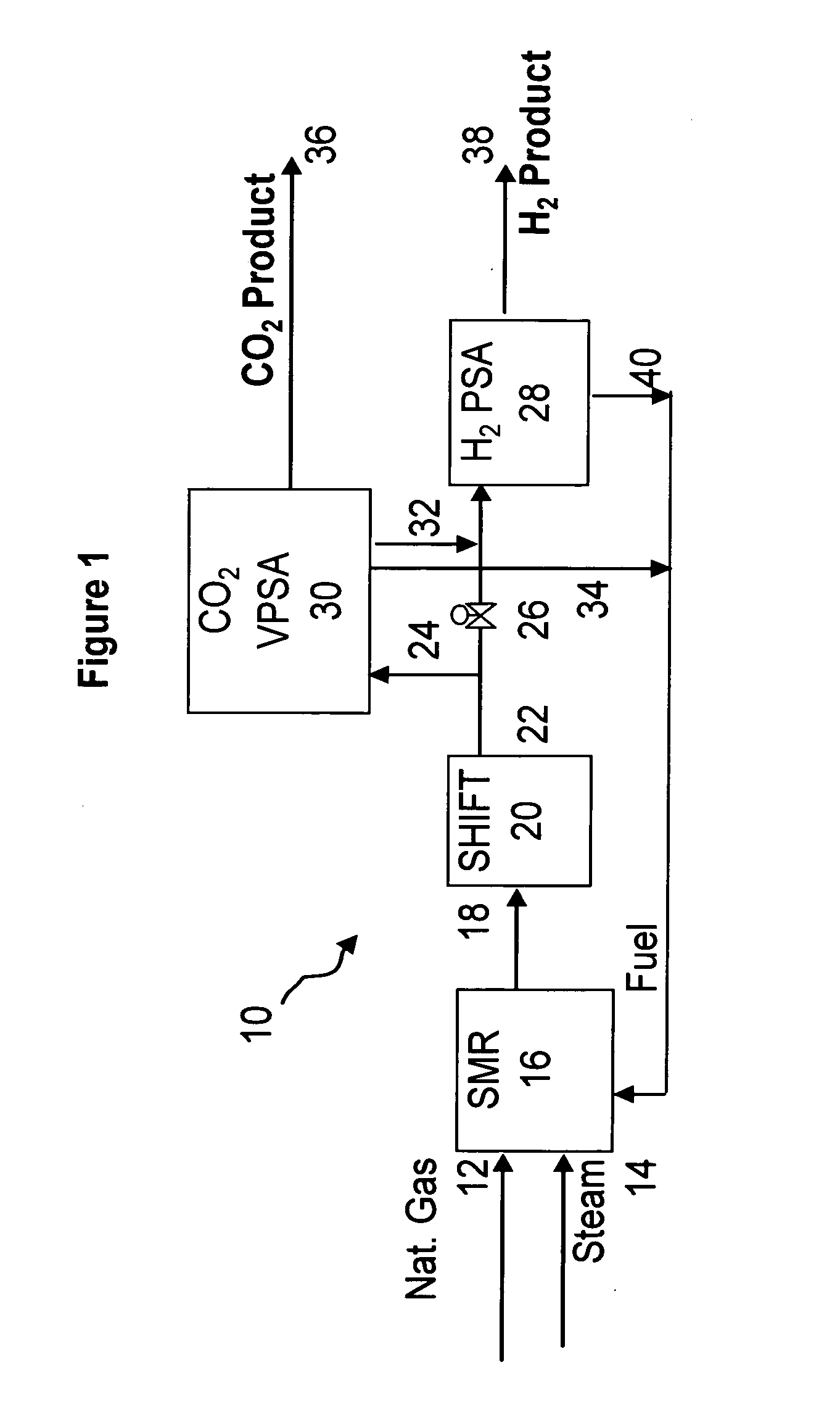
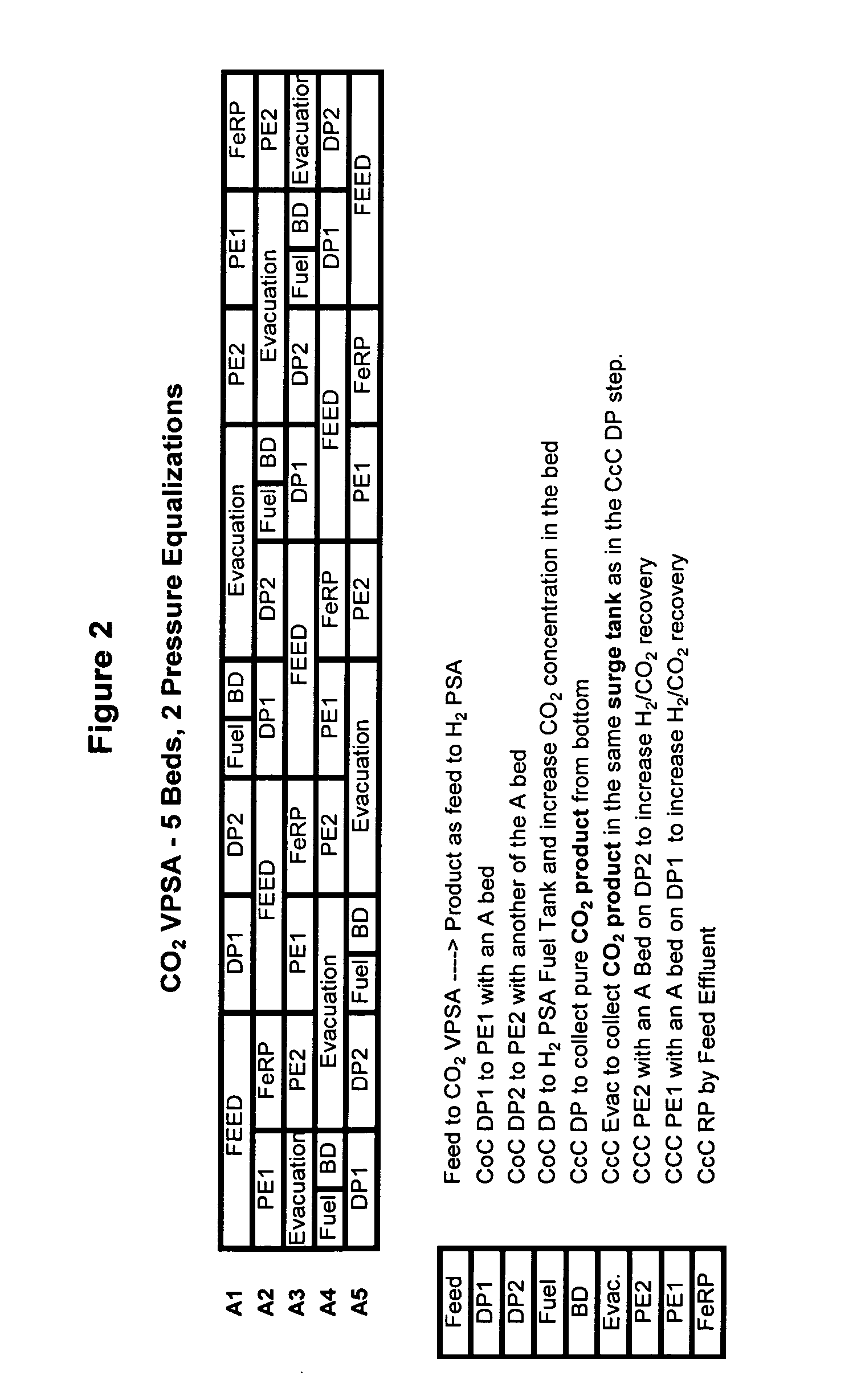
The present invention generally relates to vacuum pressure swing adsorption (VPSA) processes and apparatus to recover carbon dioxide having a purity of approximately ≧90 mole % from streams containing at least carbon dioxide and hydrogen (e.g., syngas). The feed to the CO2 VPSA unit can be at super ambient pressure. The CO2 VPSA unit produces three streams, a H2-enriched stream, a H2-depleted stream and a CO2 product stream. When the CO2 VPSA unit is installed between an SMR / shift reactor and a H2 PSA unit, hydrogen recovery is expected to be increased by extracting CO2, thereby increasing hydrogen partial pressure in the H2 PSA feed. The stream from the CO2 VPSA unit, normally used as fuel, is recycled as feed to increase CO2 recovery. The recovered CO2 can be further upgraded, sequestered or used in applications such as enhanced oil recovery (EOR).
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
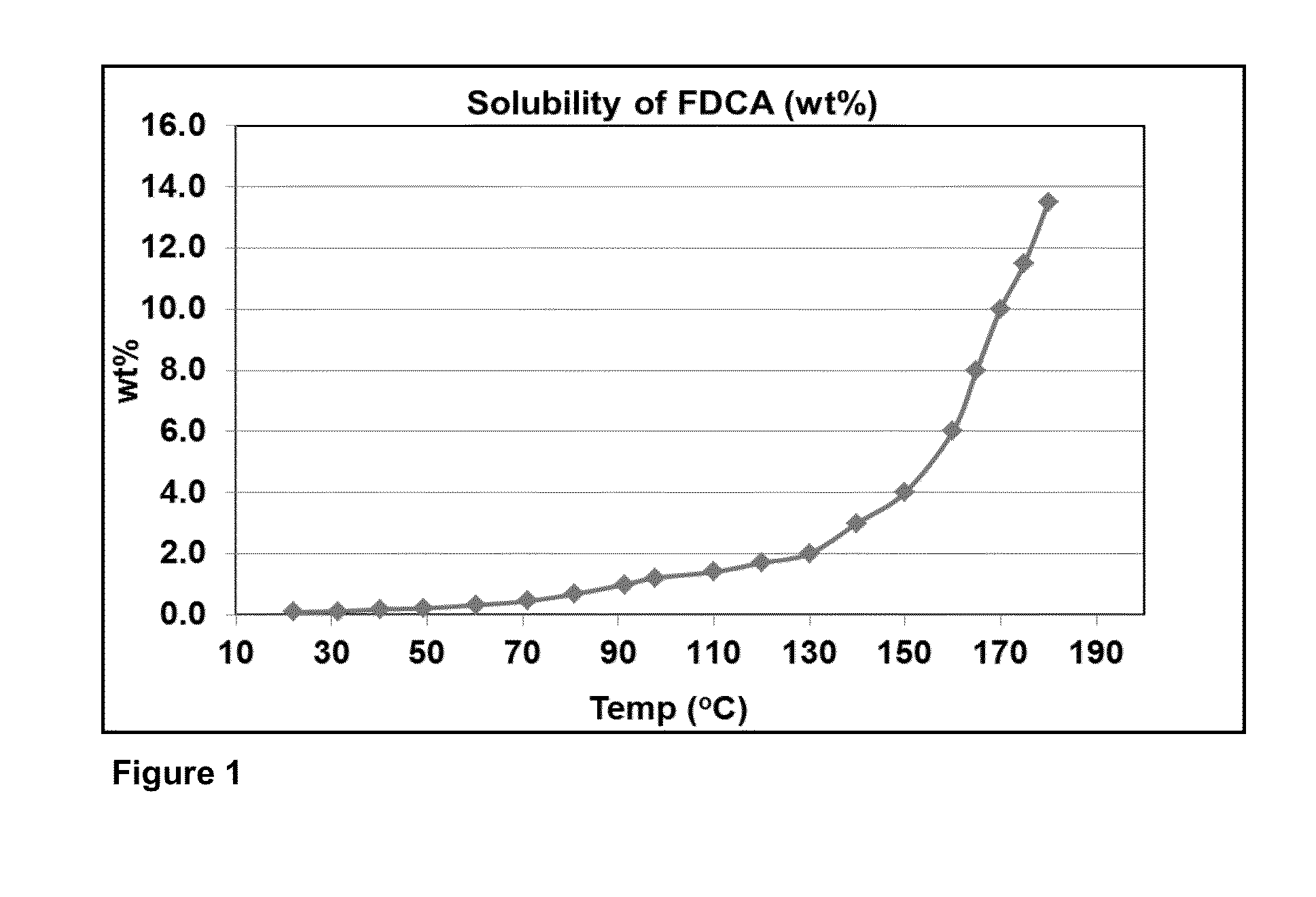
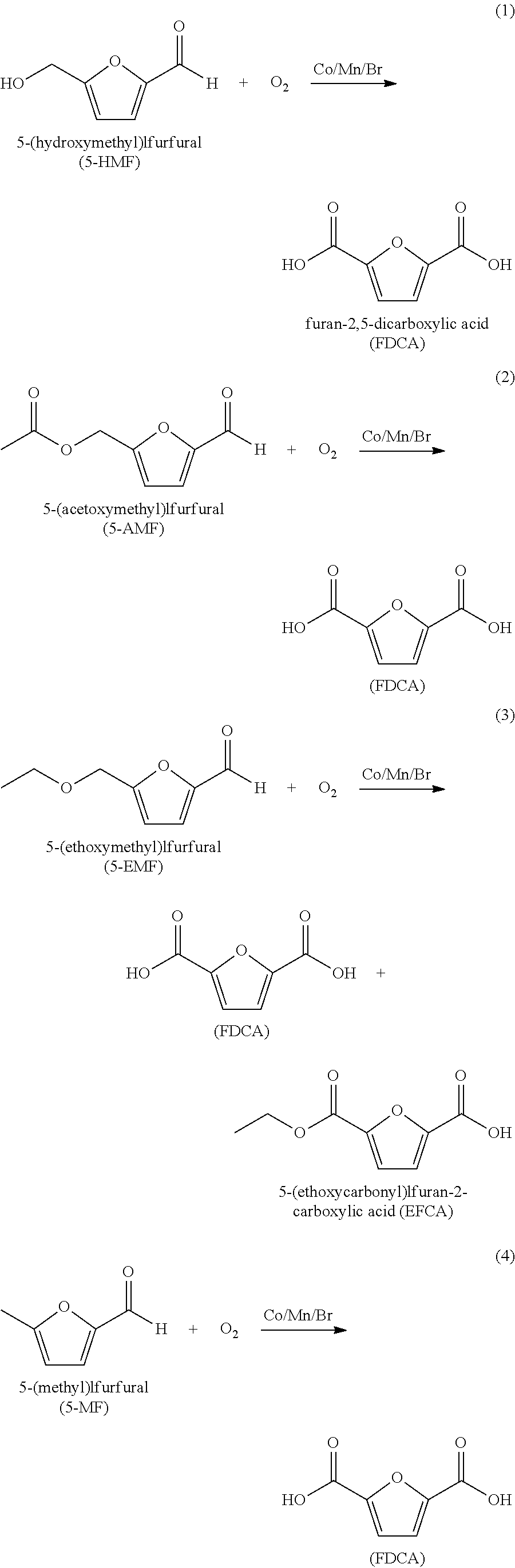
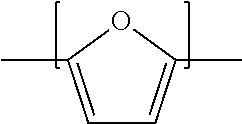
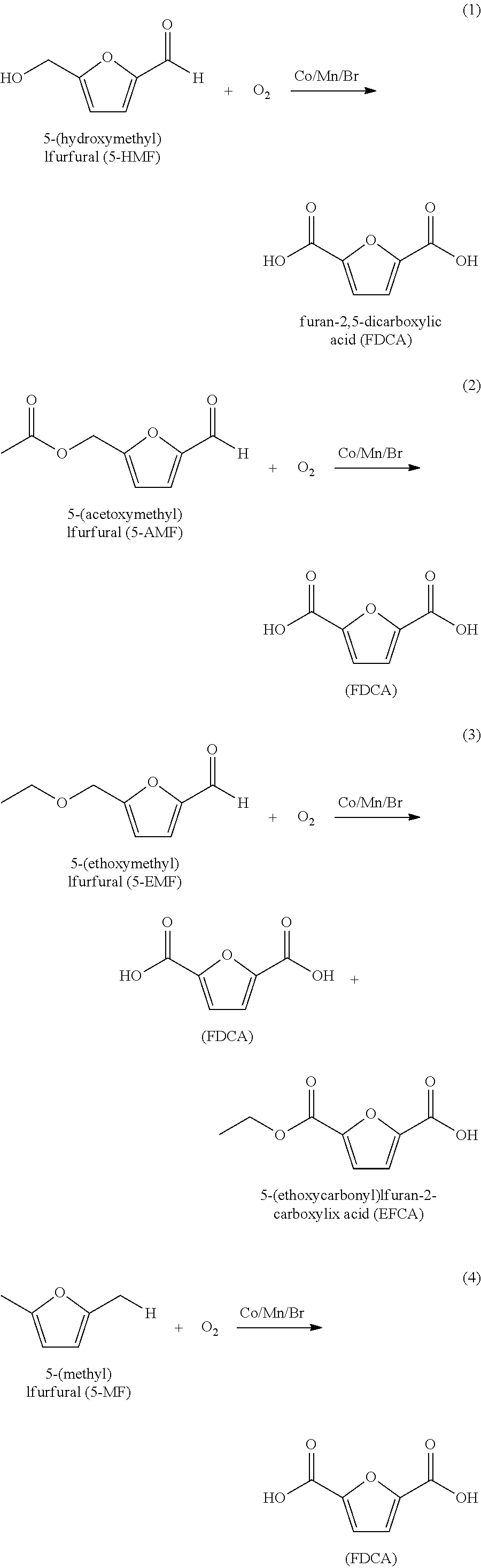
Purifying crude furan 2,5-dicarboxylic acid by hydrogenation
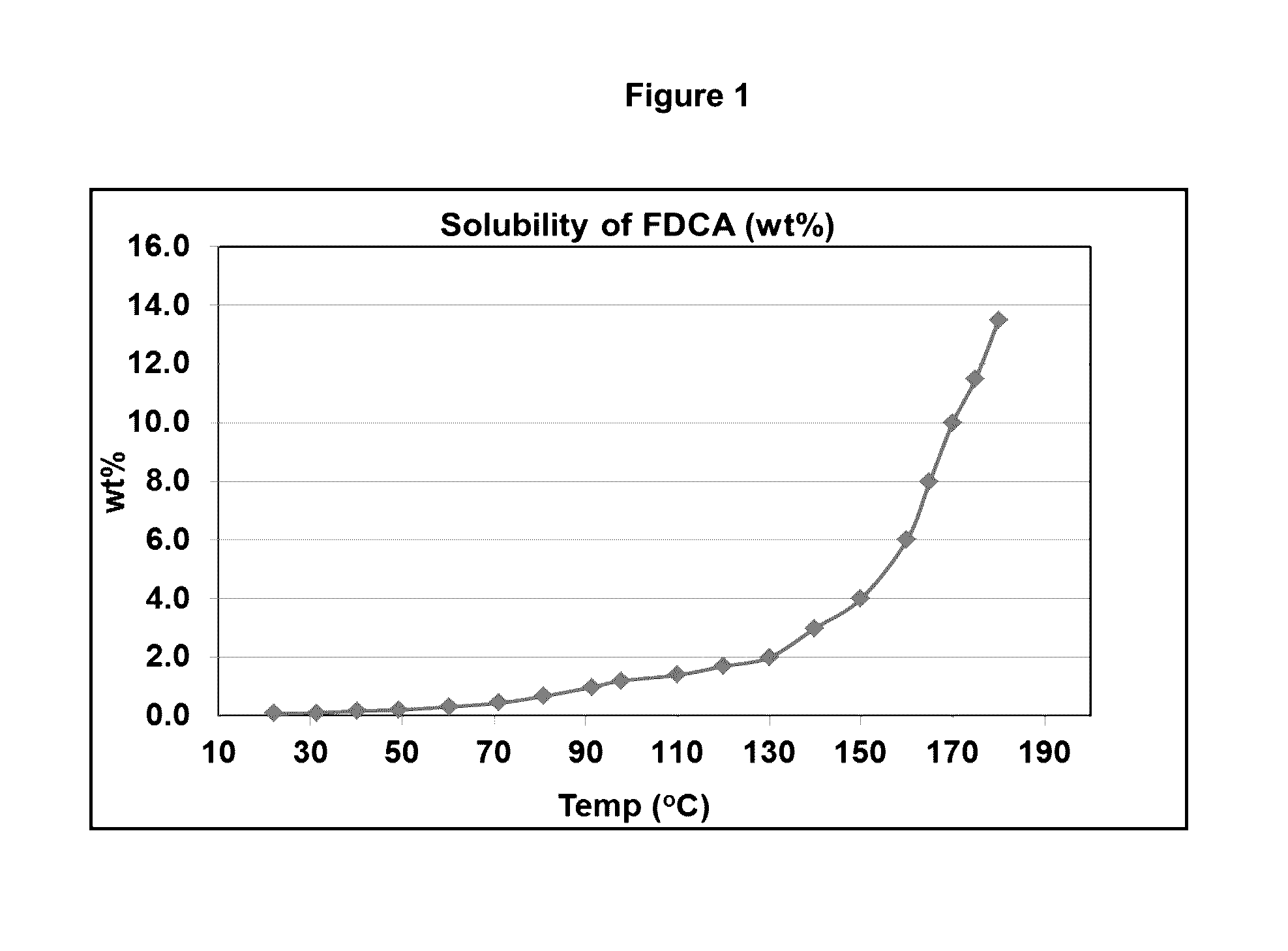
ActiveUS20130345452A1Lower energy requirementsImprove solubilityOrganic chemistryFuranDicarboxylic acid
A process for purifying a crude furan 2,5-dicarboxylic acid composition (cFDCA) by hydrogenation of a FDCA composition dissolved in a hydrogenation solvent such as water, and hydrogenating under mild conditions, such as at a temperature within a range of 130° C. to 225° C. by contacting the solvated FDCA composition with hydrogen in the presence of a hydrogenation catalyst under a hydrogen partial pressure within a range of 10 psi to 900 psi. A product FDCA composition is produced having a low amount of tetrahydrofuran dicarboxylic acid, a low b*, and a low amount of 5-formyl furan-2-carboxylic acid (FFCA).
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Selective hydrodesulfurization method for high-sulfur high-olefin catalytic gasoline
InactiveCN102041086AReduce lossesHigh total sulfur contentTreatment with hydrotreatment processesHydrodesulfurizationReaction temperature
The invention relates to a clean production method for high-sulfur high-olefin catalytic gasoline, which comprises the following steps of: performing selective hydrogenation on full fraction catalytically cracked gasoline in the presence of a gasoline hydrogenation pretreatment catalyst to remove active sulfide such as micro-molecular mercaptan, thioether, disulfide and the like, wherein the process conditions of the selective hydrogenation are that: hydrogen partial pressure is 1.5 to 3.0MPa, the reaction temperature is between 200 and 260 DEG C, liquid hourly space velocity is 6.0 to 12.5h<-1>, and the volume ratio of hydrogen to the gasoline is 150:1-500:1; performing fractionation segmentation on the gasoline subjected to the selective hydrogenation to form a light gasoline fraction and a heavy gasoline fraction, mixing the heavy gasoline fraction and the hydrogen, adding into a deep hydrodesulfurization unit and performing hydrofining in the presence of a gasoline hydrofining catalyst to obtain heavy fraction hydrogenated gasoline with low sulfur content, wherein the process conditions of the hydrofining are that: the hydrogen partial pressure is 1.5 to 2.5MPa, the reaction temperature is between 220 and 350 DEG C, the liquid hourly space velocity is 3.0 to 6.0h<-1>, and the volume ratio of the hydrogen to the gasoline is 200:1-500:1; and blending light fraction gasoline with the heavy fraction hydrogenated gasoline to obtain China IV clean gasoline.
Owner:江苏佳誉信实业有限公司
Purifying crude furan 2,5-dicarboxylic acid by hydrogenation and a purge zone
ActiveUS20160311790A1Lower energy requirementsImprove solubilityOrganic chemistrySolvent extractionFuranCarboxylic acid
A process for purifying a crude furan 2,5-dicarboxylic acid composition (cFDCA) by hydrogenation of a FDCA composition dissolved in a hydrogenation solvent such as water, and hydrogenating under mild conditions, such as at a temperature within a range of 130° C. to 225° C. by contacting the solvated FDCA composition with hydrogen in the presence of a hydrogenation catalyst under a hydrogen partial pressure within a range of 10 psi to 900 psi. A product FDCA composition is produced having a low amount of tetrahydrofuran dicarboxylic acid, a low b*, and a low amount of 5-formyl furan-2-carboxylic acid (FFCA).
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
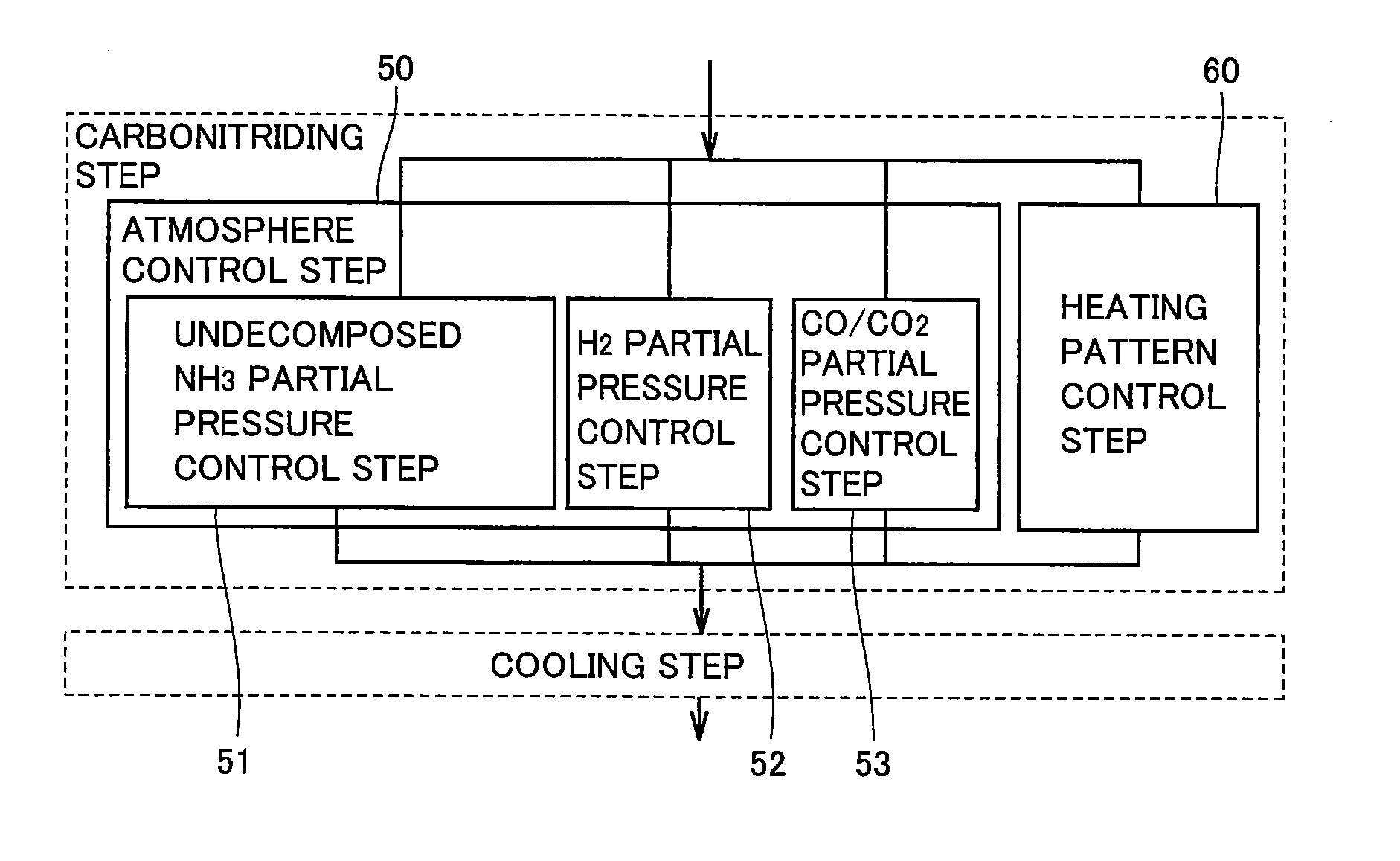
Carbonitriding method, machinery component fabrication method, and machinery component
ActiveUS20100154937A1Improves nitrogen permeating rateReduce manufacturing costBearing componentsSolid state diffusion coatingNitrogenEngineering
A carbonitriding method that can improve the nitrogen permeating rate to render the carbonitriding process effective includes an atmosphere control step (50), and a heating pattern control step (60). The atmosphere control step (50) includes an undecomposed NH3 partial pressure control step (51), and a CO / CO2 partial pressure control step (53). The undecomposed NH3 partial pressure control step (51) and the CO / CO2 partial pressure control step (53) are carried out in the atmosphere control step (50) such that ac* defined by the following equation (1) is at least 0.88 and not more than 1.27, and α defined by equation (2) is at least 0.012 and not more than 0.020, where PN is the undecomposed ammonia partial pressure and PH is the hydrogen partial pressure in the heat treatment furnace, whereinac*=(Pco)2K×Pco2(1)PCO: partial pressure of carbon dioxide (atm), PCO<sub2>2< / sub2>: partial pressure of carbon dioxide (atm)K: equlibrium constant at <C>+CO22COα=PN0.006×(PH)32×(1.877-1.055×ac*)100(2)
Owner:NTN CORP
Method for selective hydrogenation of reforming generated oil
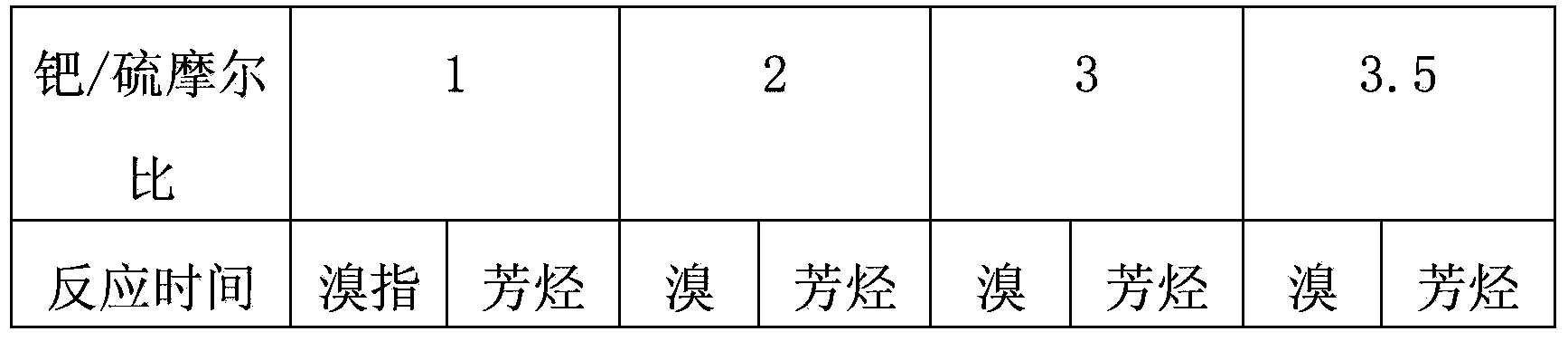
ActiveCN104342200AReduce pollutionLow costRefining by selective hydrogenationHydrocarbon oils treatment productsReaction temperaturePalladium catalyst
The invention relates to a method for selective hydrogenation of reforming generated oil. According to the reforming generated oil, the bromine index is 7270mgBr / 100g oil, and the weight of arene is 66.83%; the reaction conditions are as follows: the reaction temperature is 170 DEG C, the hydrogen partial pressure is 1.6MPa, the speed of liquid is 4h<-1> and the volume ratio between hydrogen and oil is 200. The method is characterized in that the used catalyst is Pd / gamma-Al2O3 containing 0.3wt% of palladium, and is passivated by a dry method with sulfur-containing compounds such as dimethyl disulfide, methyl thioether, butyl mercaptan or hydrogen sulfide before being filled; the added amount of the sulfide for passivation is as follows: the molar ratio of the palladium and the sulfur is 1-3.5; and the passivation temperature ranges from normal temperature to 230 DEG C. The method has the advantages that the pollution can be reduced, the investment can be reduced, convenience is brought for starting operation; after the palladium catalyst is passivated by the sulfide, the loss of arene of a hydrorefined product is lower than 0.5% (weight); after short-time reaction, the bromine index of the product is lower than 100 and the requirement of arene extraction for the raw materials can be met.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
Process of production and production system of high strength galvannealed steel sheet
ActiveUS20070051438A1High strengthHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesHigh intensityEquipment use
A process of production for producing a high strength galvannealed steel sheet by a hot-dip galvanized steel sheet production equipment using an all radiant tube type annealing furnace and a production equipment for the same are provided, comprising continuously hot-dip galvanizing a high strength steel sheet having a content of Si of 0.4 to 2.0 wt % during which making the atmosphere of the reducing zone an atmosphere containing H2 to 1 to 60 wt % and comprised of the balance of N2, H2O, O2, CO2, CO, and unavoidable impurities, controlling the log(PCO2 / PH2) of the carbon dioxide partial pressure and hydrogen partial pressure in the atmosphere to log(PCO2 / PH2)≦−0.5 and the log(PCO2 / PH2) of the water partial pressure and hydrogen partial pressure to log(PH2O / PH2)≦−0.5, and controlling the log(PT / PH2) of the total partial pressure PT of the carbon dioxide partial pressure PCO2 and water partial pressure PH2O and the hydrogen partial pressure to −3≦log(PT / PH2)≦−0.5.
Owner:USINOR SA +1
Catalyst for hydrogenation treatmet of gas oil and method for prepn. thereof and process for hydrogenation treatment of gas oil
InactiveCN1463204AMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPore diameterSpace velocity
A catalyst for hydrotreating gas oil, which comprises an inorganic oxide support having provided thereon: at least one selected from metals in the Group 6 of the periodic table at from 10 to 30% by weight, at least one selected from metals in the Group 8 of the periodic table at from 1 to 15% by weight, phosphorus at from 1.5 to 6% by weight, and carbon at from 2 to 14% by weight, each in terms of a respective oxide amount based on the catalyst, wherein the catalyst has a specific surface area of from 220 to 300 m2 / g, a pore volume of from 0.35 to 0.6 ml / g, and an average pore diameter of about from 65 to 95 Å; a process for producing the catalyst; and a method for hydrotreating gas oil, which comprises subjecting a gas oil fraction to a catalytic reaction in the presence of the catalyst under conditions at a hydrogen partial pressure of from 3 to 8 MPa, a temperature of from 300 to 420° C., and a liquid hourly space velocity of from 0.3 to 5 hr-1.
Owner:COSMO OIL CO LTD
Hydroconversion Processes Employing Multi-Metallic Catalysts and Method for Making Thereof
ActiveUS20090107886A1Catalytic crackingOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCelluloseOxidation state
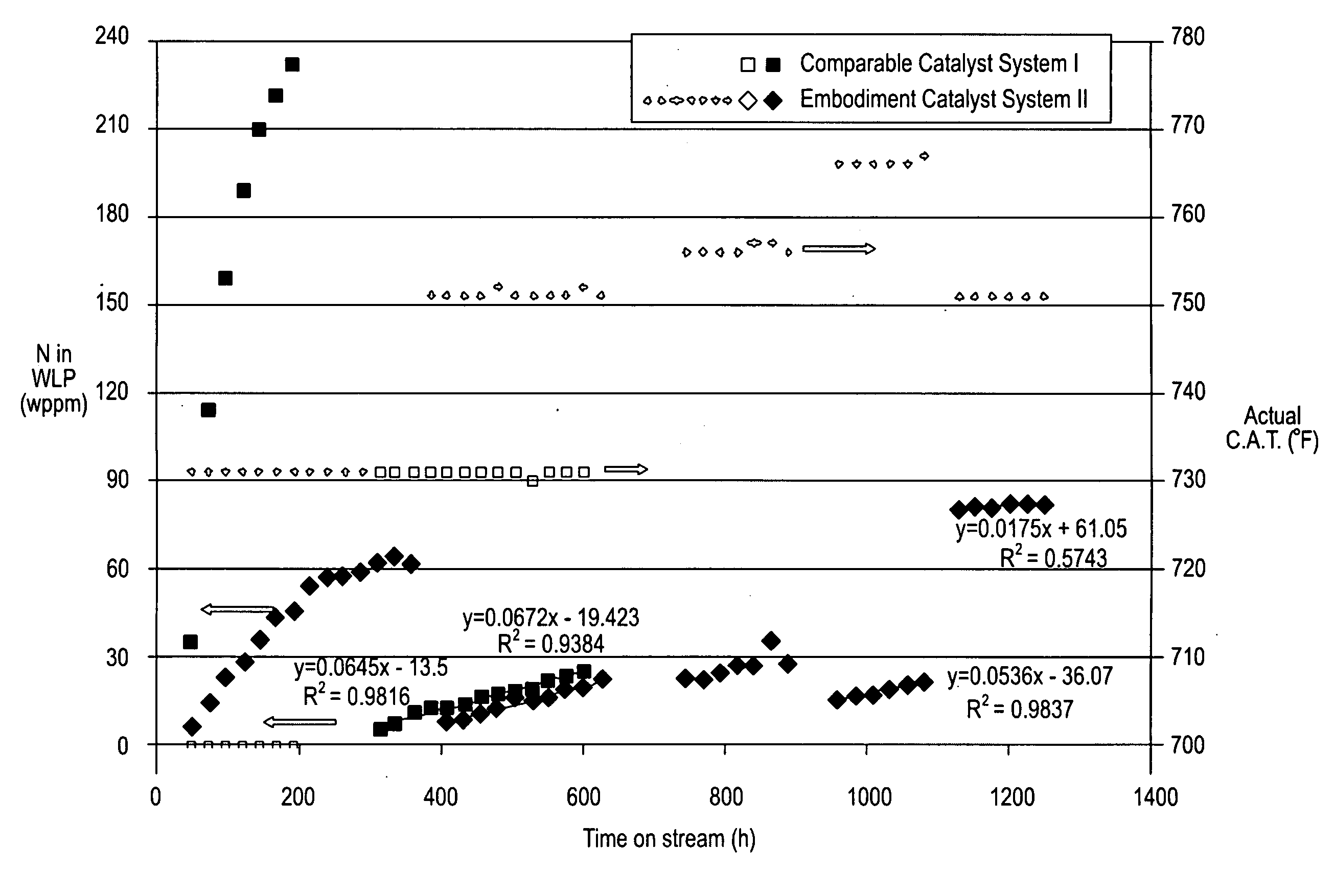
A catalyst precursor composition and methods for making such a catalyst precursor are disclosed. The catalyst precursor comprises at least a promoter metal selected from Group VIII, Group IIB, Group IIA, Group IVA and combinations thereof, having an oxidation state of +2 or +4, at least one Group VIB metal, at least one organic, oxygen-containing ligand, and a cellulose-containing material. In one embodiment, the catalyst precursor is of the formula Av[(MP) (OH)x (L)ny]z (MVIBO4), wherein A is one or more monovalent cationic species, MP is selected from Group VIII, Group IIB, Group IIA, Group IVA and combinations thereof, L is one or more oxygen-containing ligands, MVIB is at least a Group VIB metal, MP:MVIB has an atomic ratio between 100:1 and 1:100. In one embodiment, catalysts prepared from the sulfidation of such catalyst precursors are used in the hydroprocessing of hydrocarbon feeds. In a hydroconversion process at a hydrogen partial pressure of ˜450 psig, the catalyst a 700° F.+ conversion rate of at least 50% of the 700° F.+ conversion results gives obtained under comparable conditions and with a hydrogen partial pressure of 600 psig.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
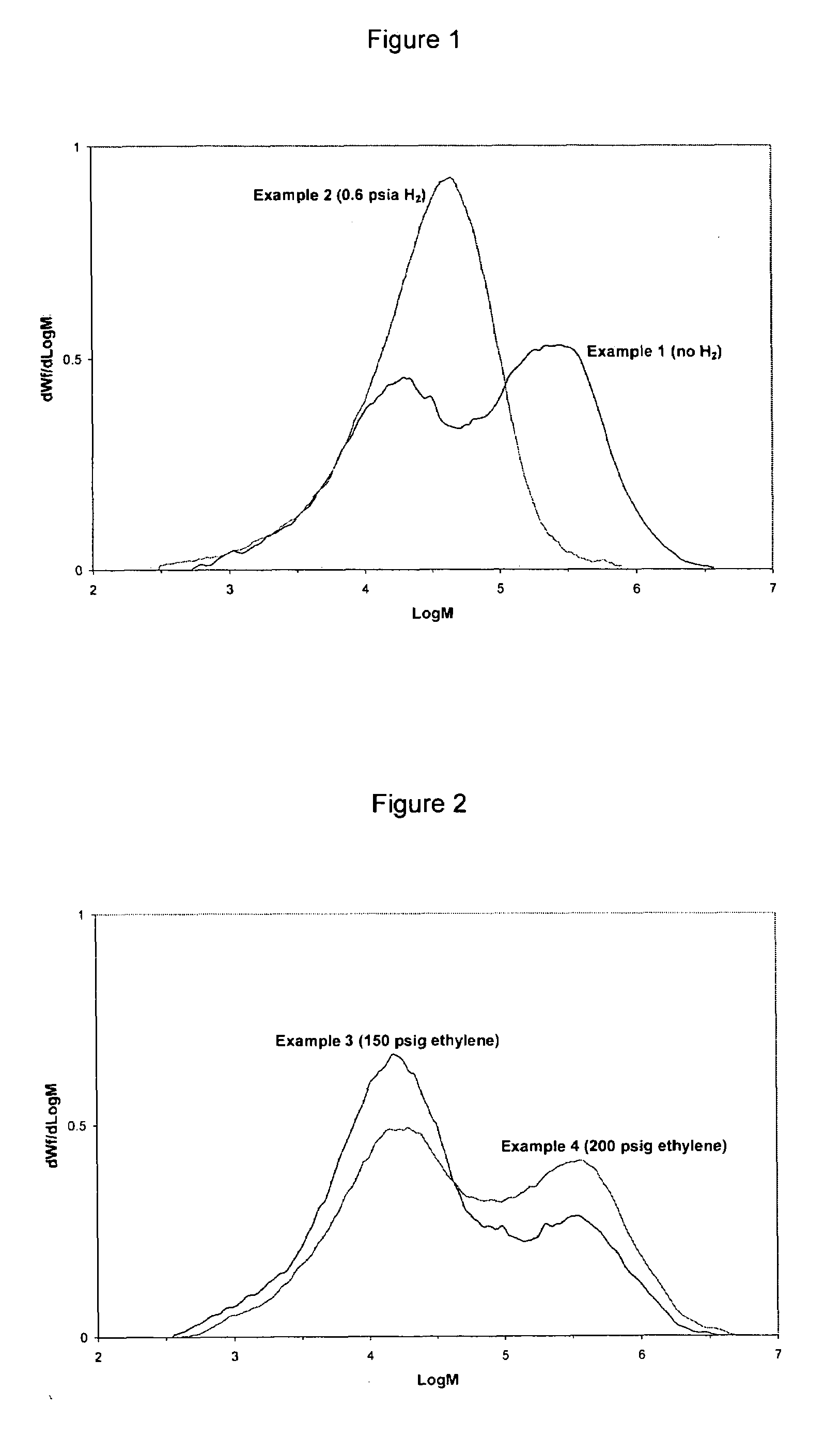
Adjusting polymer characteristics through process control
Properties of a polymer produced using a dual catalyst on the same support, such as polydispersity and comonomer incorporation, may be controlled by controlling reaction parameters such as temperature, monomer pressure, hydrogen partial pressure and the presence of non-polymerizable hydrocarbon. This provides an easy method to control the bimodality of a polymer as well as comonomer incorporation.
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
Method for operating catalytic reformers
ActiveUS20060213811A1Lower overall pressure dropReduce stepsCatalytic naphtha reformingTreatment with hydrotreatment processesCatalytic reformingHydrogen pressure
A reforming process in which a hydrocarbon feed containing aliphatic hydrocarbons is converted to a hydrocarbon product comprising an increased proportion of aromatics by passage over a reforming catalyst in a sequence of moving bed reactors operating under reforming conditions including moderate hydrogen pressure. The process is applicable when a former fixed moving bed reformer has been converted to moving bed reactor operation with the recycle and other ancillary equipment retained so that moderate pressure (hydrogen partial pressure at least 11 barg) is required, usually with a catalysts such as Pt / Re which tend to exhibit excessive hydrogenolysis activity in moving bed service. The recycle hydrogen stream is split with a portion going to at least one reactor subsequent to the first reactor.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Dual catalyst on a single support
ActiveUS20060122054A1Group 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolyolefinSingle support
Bimodal polyolefins having a reverse or partial reversed comonomer incorporation may be prepared in the presence of a dual catalyst on the same support wherein each catalyst has a different response to temperature, ethylene partial pressures, partial pressure of non-polymerizable hydrocarbons present in the reaction mixture and hydrogen partial pressure.
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
Process and apparatus to recover high purity carbon dioxide
The present invention generally relates to vacuum pressure swing adsorption (VPSA) processes and apparatus to recover carbon dioxide having a purity of approximately ≧90 mole % from streams containing at least carbon dioxide and hydrogen (e.g., syngas). The feed to the CO2 VPSA unit can be at super ambient pressure. The CO2 VPSA unit produces three streams, a H2-enriched stream, a H2-depleted stream and a CO2 product stream. When the CO2 VPSA unit is installed between an SMR / shift reactor and a H2 PSA unit, hydrogen recovery is expected to be increased by extracting CO2, thereby increasing hydrogen partial pressure in the H2 PSA feed. The recovered CO2 can be further upgraded, sequestered or used in applications such as enhanced oil recovery (EOR).
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Process for producing anisotropic magnet powder
ActiveUS20060048855A1Fast feverFast heat absorptionInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRare-earth elementMetallurgy
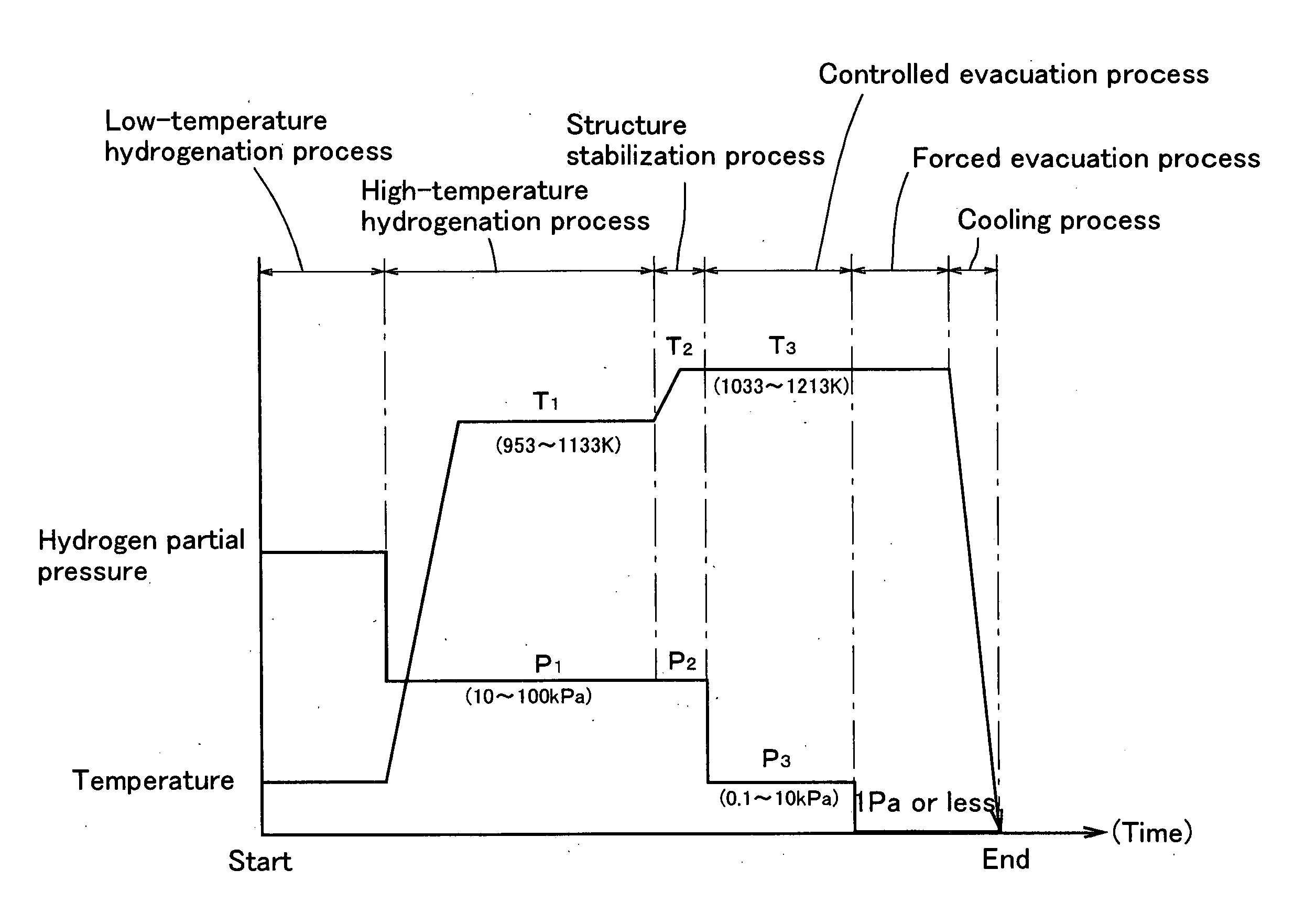
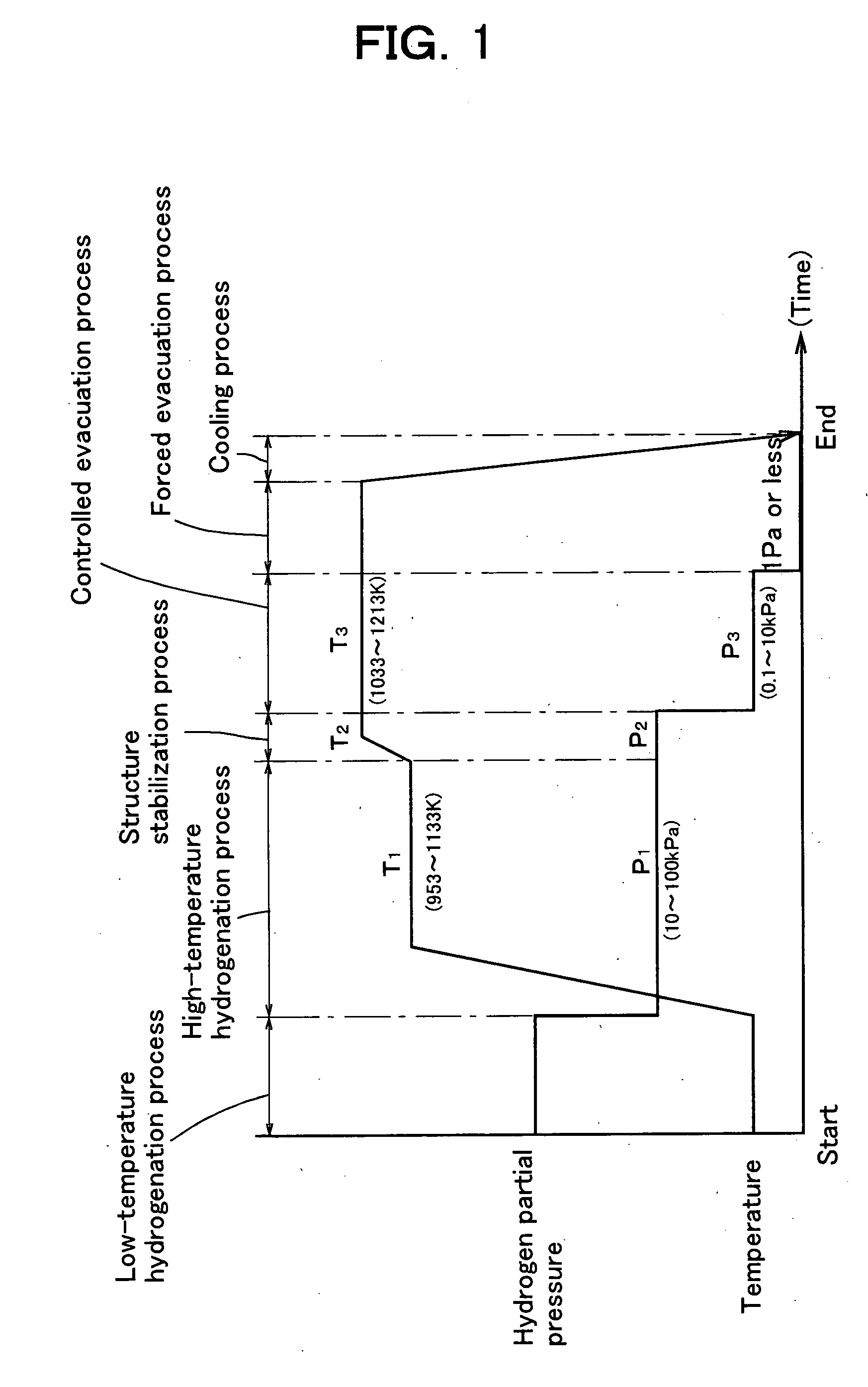
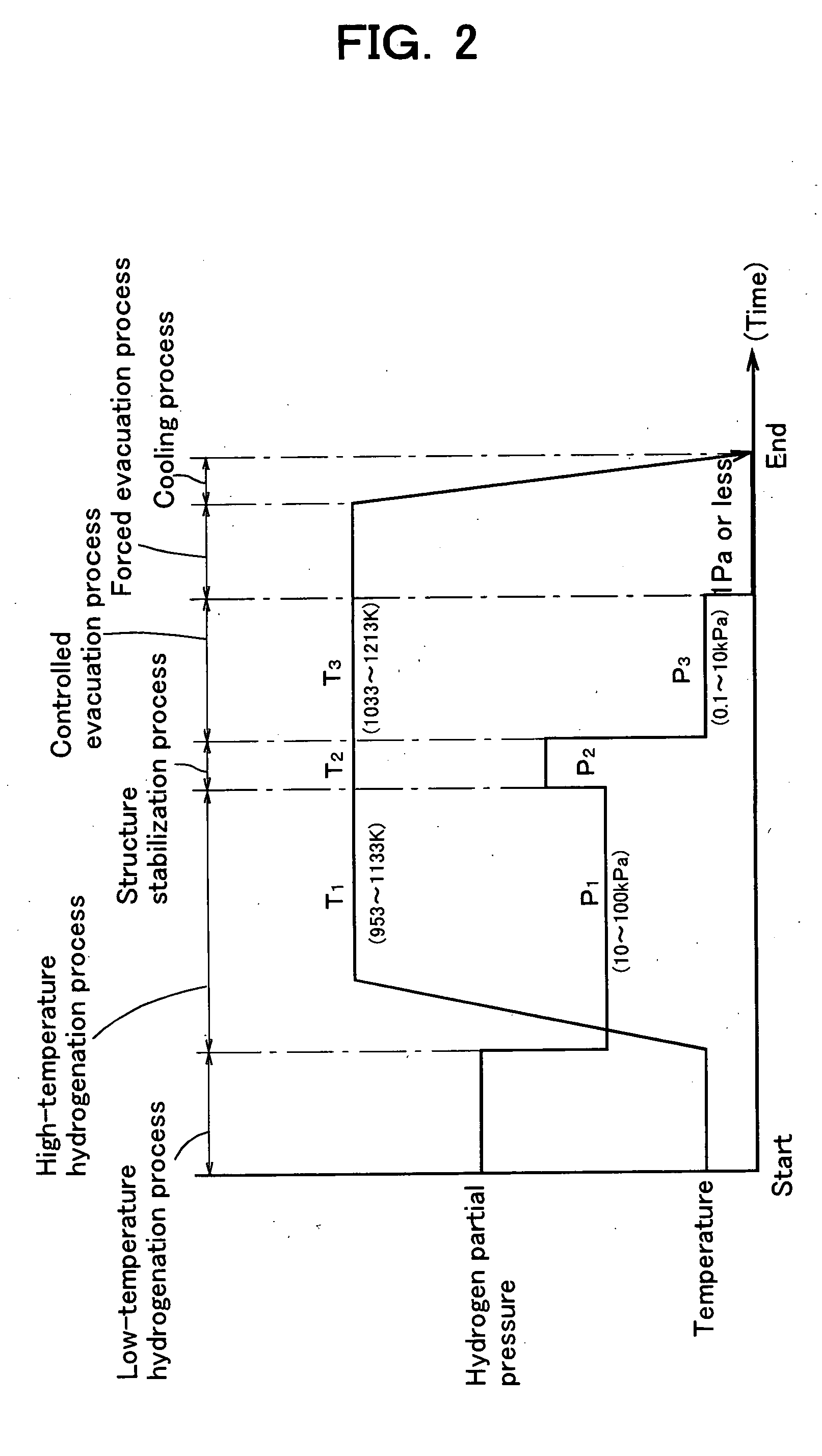
A method for manufacturing an anisotropic magnet powder includes a high-temperature hydrogenation process of holding an RFeB-based alloy containing rare earth elements (R), B and Fe as main ingredients in a treating atmosphere under a first treating pressure (P1) of which a hydrogen partial pressure ranges from 10 to 100 kPa and at a first treating temperature (T1) which ranges from 953 to 1133 K, a structure stabilization process of holding the RFeB-based alloy after the high-temperature hydrogenation process under a second treating pressure (P2) of which a hydrogen partial pressure is 10 or more and at a second treating temperature (T2) which ranges from 1033 to 1213 K such that the condition T2>T1 or P2>P1 is satisfied, a controlled evacuation process of holding the RFeB-based alloy after the structure stabilization process in a treating atmosphere under a third treating pressure (P3) of which a hydrogen partial pressure ranges from 0.1 to 10 kPa and at a third treating temperature (T3) which ranges from 1033 to 1213 K, and a forced evacuation process of removing residual hydrogen (H) from the RFeB-based alloy after the controlled evacuation process. With this method, the magnetic properties of the anisotropic magnet powder can be improved.
Owner:AICHI STEEL
Catalyst combination for the hydroisomerization of waxy feeds at low pressure
A process for the hydroisomerization of a waxy feed having a major portion boiling above 650° F. to produce a lubricating base oil having a lower pour point, said process comprising (a) passing the waxy feed along with hydrogen gas through a hydroisomerization zone maintained at a hydrogen partial pressure of between about 100 psia and about 400 psia, said hydroisomerization zone comprising a catalyst bed containing at least two active wax hydroisomerization catalysts, said catalysts comprising at least (i) a first catalyst comprising an active hydrogenation component and a 1-D, 10-ring molecular sieve having a maximum crystallographic free diameter of the channels equal to 6.2 Å units or greater and (ii) a second catalyst comprising an active hydrogenation component and a 1-D, 10-ring molecular sieve having a maximum crystallographic free diameter of the channels equal to 5.8 Å units or less, wherein the weight ratio of molecular sieve contained in the first catalyst to the molecular sieve contained in second catalyst in the hydroisomerization zone falls within the range between about 2 to 1 and about 12 to 1; and (b) recovering from the hydroisomerization zone a lubricating base oil having a lower pour point as compared to the waxy feed.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip and grain-oriented electrical steel strip obtained according to said process
InactiveUS20170283903A1Simple stepsReduce oxidationInorganic material magnetismSolid state diffusion coatingThin slabWater vapor
A process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip by means of thin slab continuous casting, comprising the following process steps: a) smelting a steel, b) continuously casting the smelt by thin slab continuous casting, c) heating up the thin slabs and subjecting the slabs to homogenization annealing at a maximum temperature of 1250° C., d) heating to a temperature between 1250° C. and 1350° C., e) continuously hot rolling the thin slabs to form a hot-rolled strip, f) cooling and reeling the hot-rolled strip to form a coil, g) annealing the hot-rolled strip after reeling and prior to a subsequent cold rolling step, h) cold rolling the hot-rolled strip to the nominal usable thickness, i) subjecting the cold-rolled strip to recrystallization, decarburization and nitridation annealing, j) applying an annealing separator (non-stick layer) to the strip surface of the cold-rolled strip, k) subjecting the cold-rolled strip to secondary recrystallization annealing, forming a finished steel strip having a pronounced Goss texture, and l) stress-free annealing the finished steel strip, which has been coated with an insulating layer, provides an improved process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip by means of thin slab continuous casting. This is achieved in that the recrystallization, decarburization and nitridation annealing of the cold-rolled strip in process step h) comprises a decarburization annealing phase and a subsequent nitridation annealing phase, with an intermediate reduction annealing phase being interposed between the decarburization annealing phase and the nitridation annealing phase, and carried out at a temperature ranging from 820° C.-890° C., for a maximum period of 40 seconds, with a dry, gaseous annealing atmosphere, which contains nitrogen (N2) and hydrogen (H2) and acts on the cold-rolled strip, and which has a water vapor / hydrogen partial pressure ratio pH2O / pH2 of less than 0.10.
Owner:SMS GRP GMBH
Method of producing jet fuel from coking distillate
A process for preparing the jet fuel from coking distillate features that the coking distillate and hydrocatalyst take part in reaction in the conditions of 3-12 MPa for hydrogen pressure, 300-400 deg.c, 400-1000 Ncu.m / cu.m for H2 / oil ratio, and 0.5-5 / hr for space speed. Said hydrocatalyst is composed of the active component chosen from the metals in VIII or VIB family and the carrier (the mixture of alumina and zeolite).
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com