Method for selective hydrogenation of reforming generated oil
A technology of reforming to generate oil and selectivity, which is applied in the direction of selective hydrofining, petroleum industry, and hydrocarbon oil treatment. It can solve the problems of reactor overheating, prolonging the start-up time, and processing difficulties, and achieve the reduction of sulfide Effects of pollution, shortened start-up time, and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
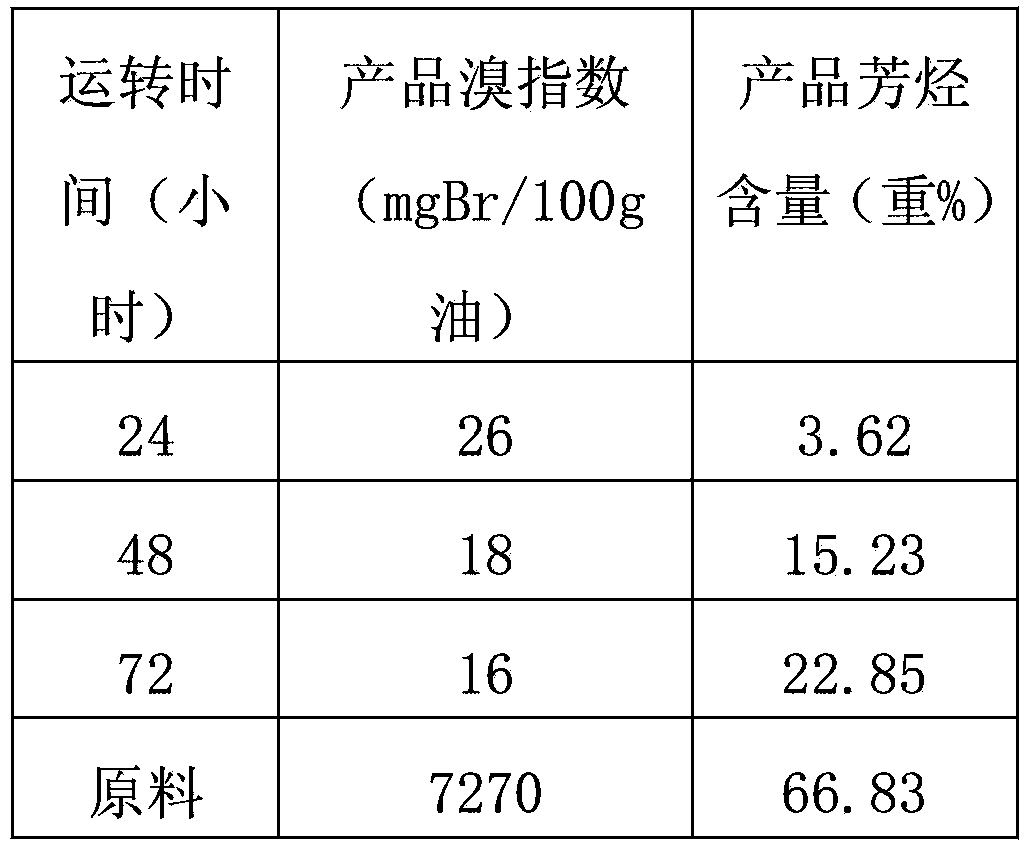
[0018] It can be seen from Table 1 that the unpassivated fresh catalyst has high activity for the hydrogenation of aromatics and olefins, and the loss of aromatics is serious. For the start-up of fresh catalysts, catalyst deactivation must be carried out.
[0019] Table 1. Unpassivated hydrogenation results after fresh catalyst reduction
[0020] Reaction conditions: 170°C, 1.6MPa, 4h -1 , hydrogen / oil (V) 200
[0021]
Embodiment 2
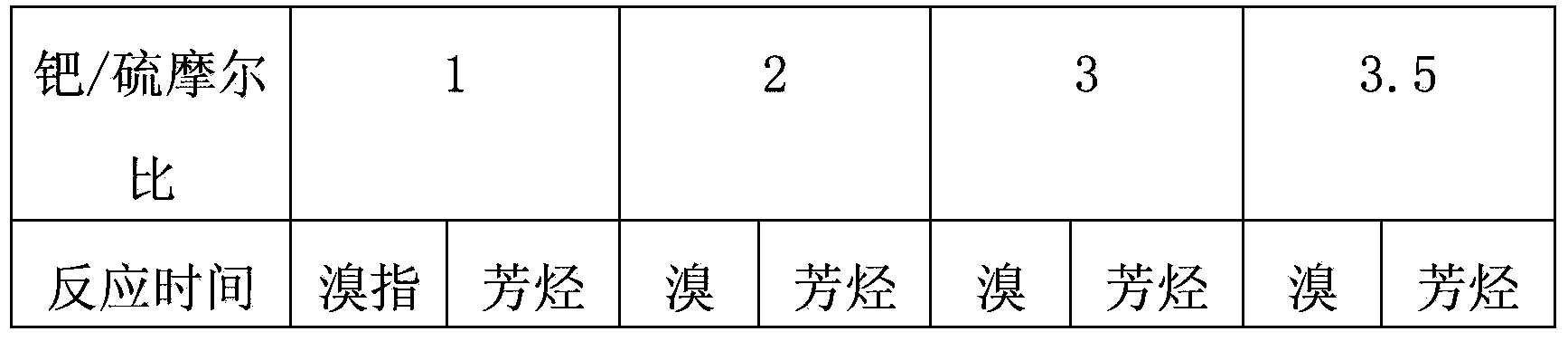
[0023] The amount of dry passivation has a great influence on the passivation effect. Table 2 is a comparison of different dimethyl disulfide additions. The passivation conditions are 170° C., normal pressure, 50 milliliters of catalyst loading, and 20 liters / hour of hydrogen flow.
[0024] Table 2
[0025]
[0026]
[0027] As can be seen from Table 2, when the palladium-sulfur molar ratio is lower than 3, the product aromatics have no loss compared with the raw material, and when the palladium-sulfur molar ratio is 3.5, the aromatics are slightly lost. After the palladium-sulfur molar ratio is operated in this range for 16 hours, the bromine index can reach the requirement below 1000. That is to say, if the molar ratio of palladium to sulfur is lower than 3, the requirement that the loss of aromatics is less than 0.5 (weight) % and the bromine index is lower than 100 mgBr / 100 g oil can be achieved.
Embodiment 3
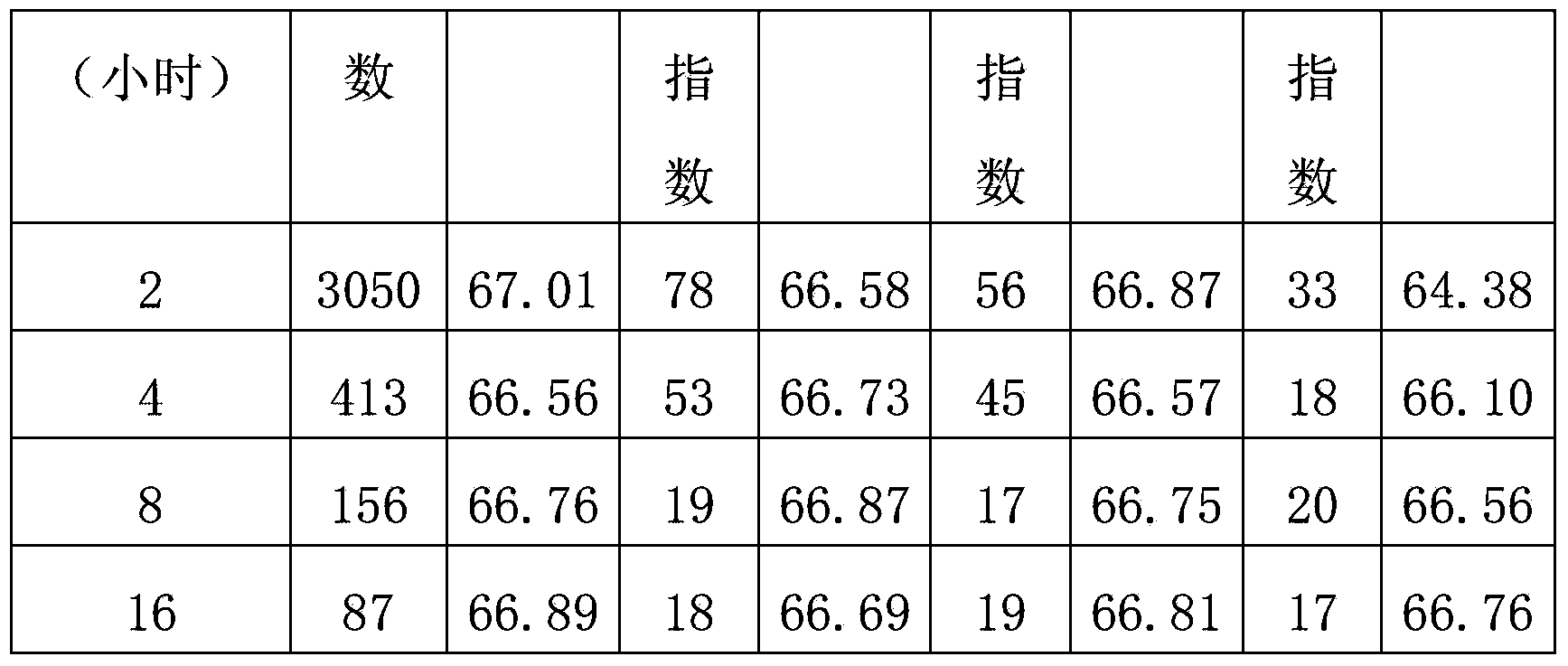
[0029] When the molar ratio of palladium to sulfur is 3, dimethyl disulfide, methyl sulfide, hydrogen sulfide, and butyl mercaptan are used to dry passivate the palladium catalyst respectively. The passivation conditions are 170 ° C, normal pressure, catalyst The filling volume is 50 ml, and the hydrogen flow rate is 20 liters / hour.
[0030] The effect is shown in Table 3.
[0031] table 3
[0032]
[0033]
[0034] Table 3 shows that the passivation of the palladium catalyst using the above sulfides can meet the requirements for the bromine index of the product and the loss of aromatics.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com