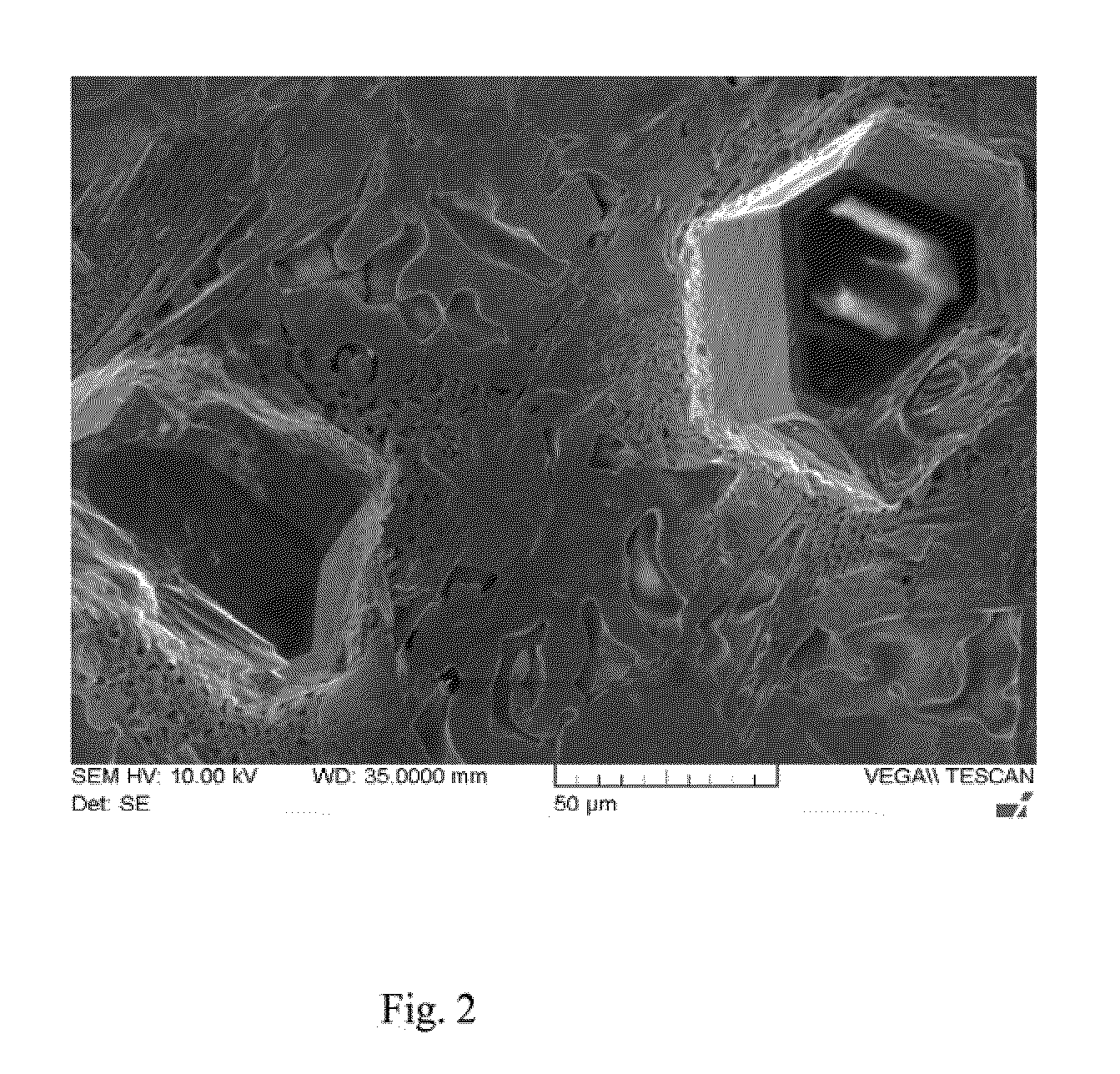
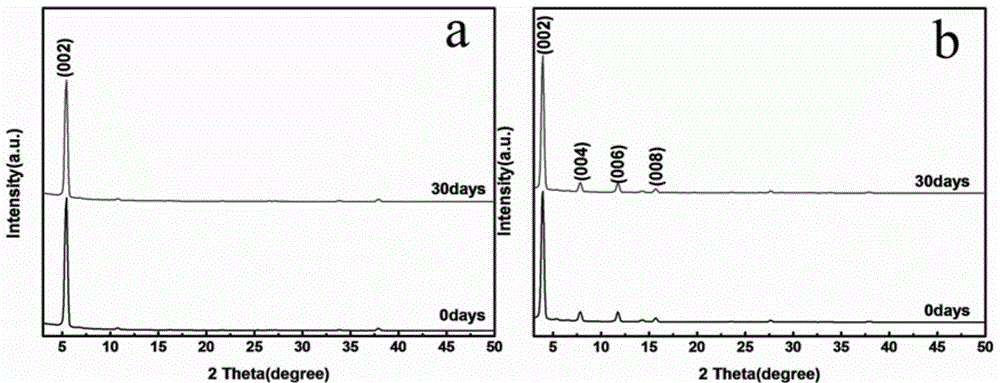
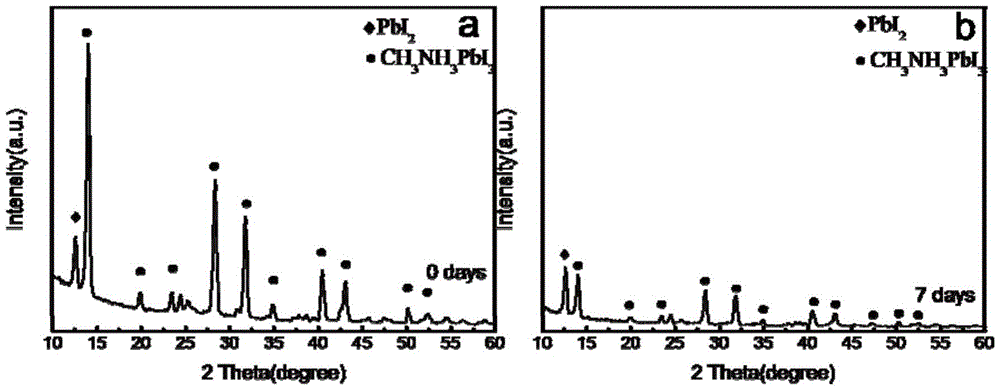
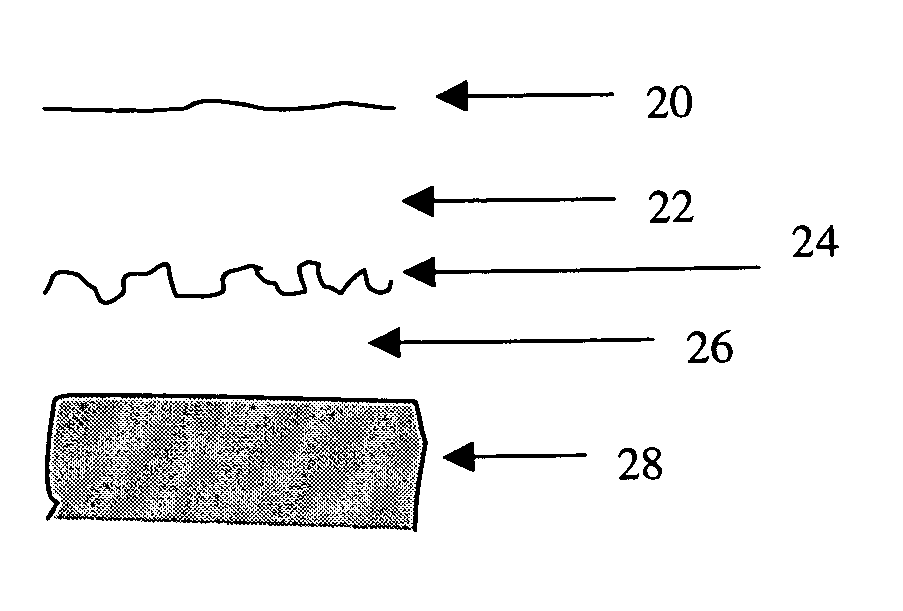
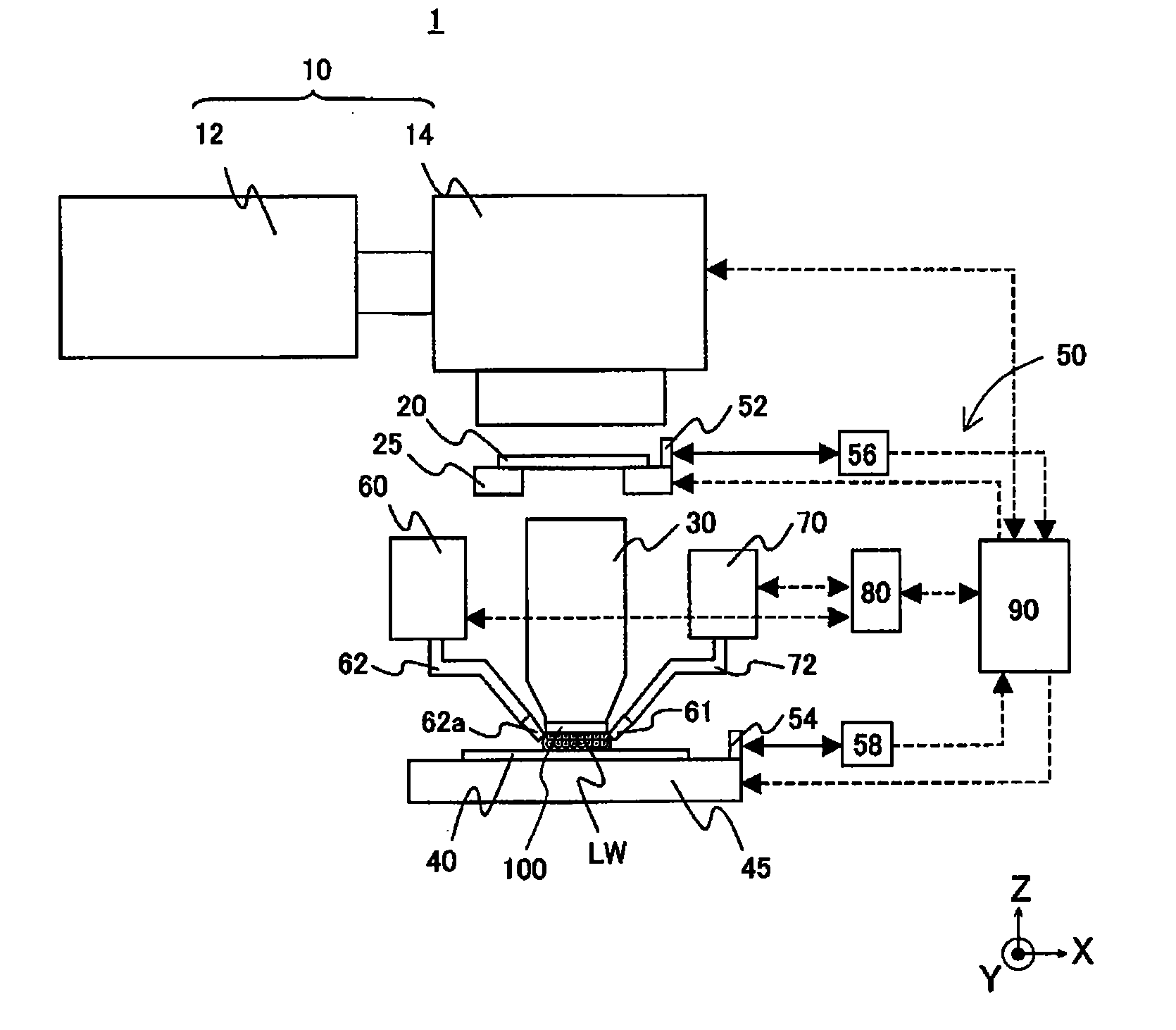
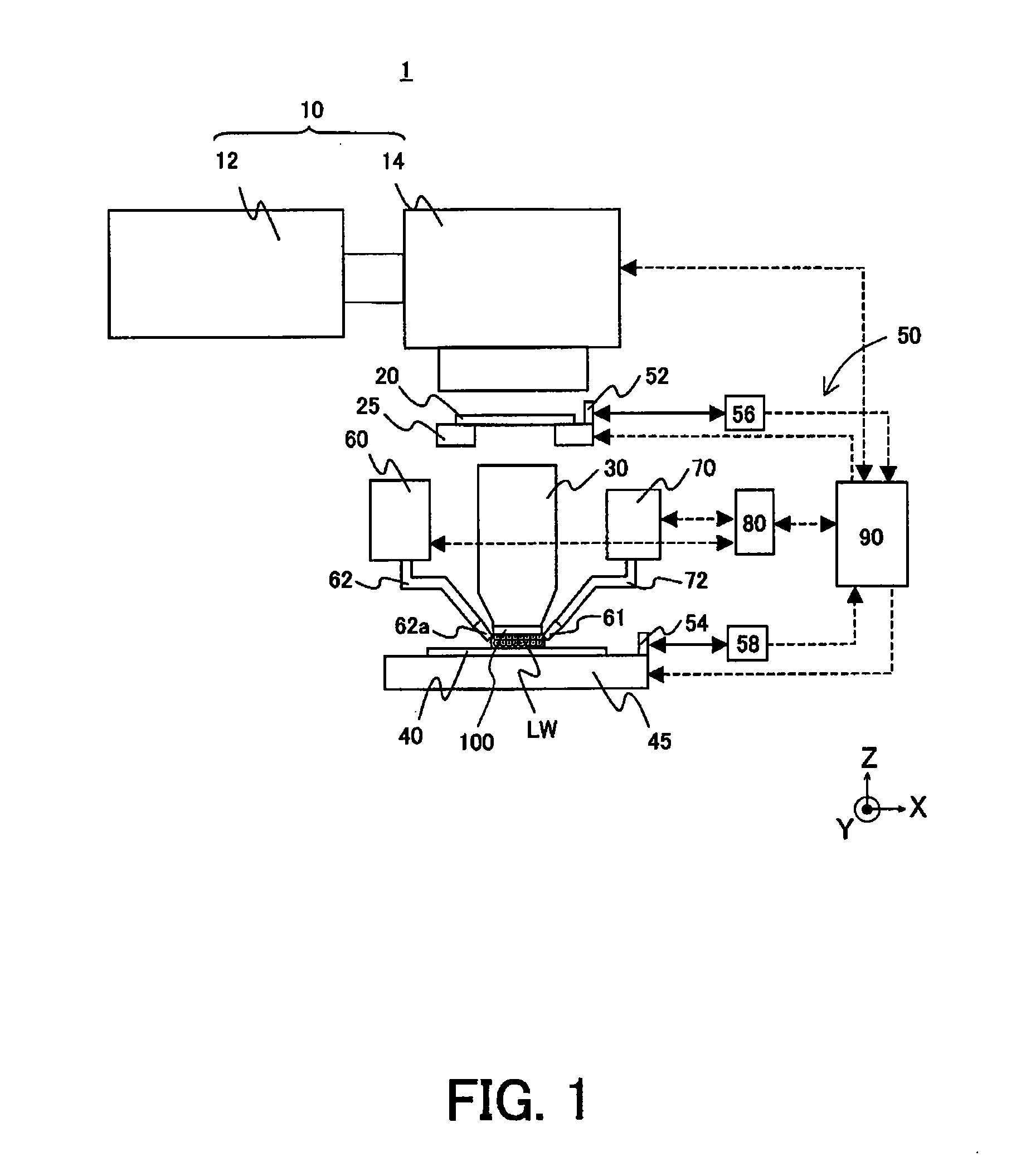
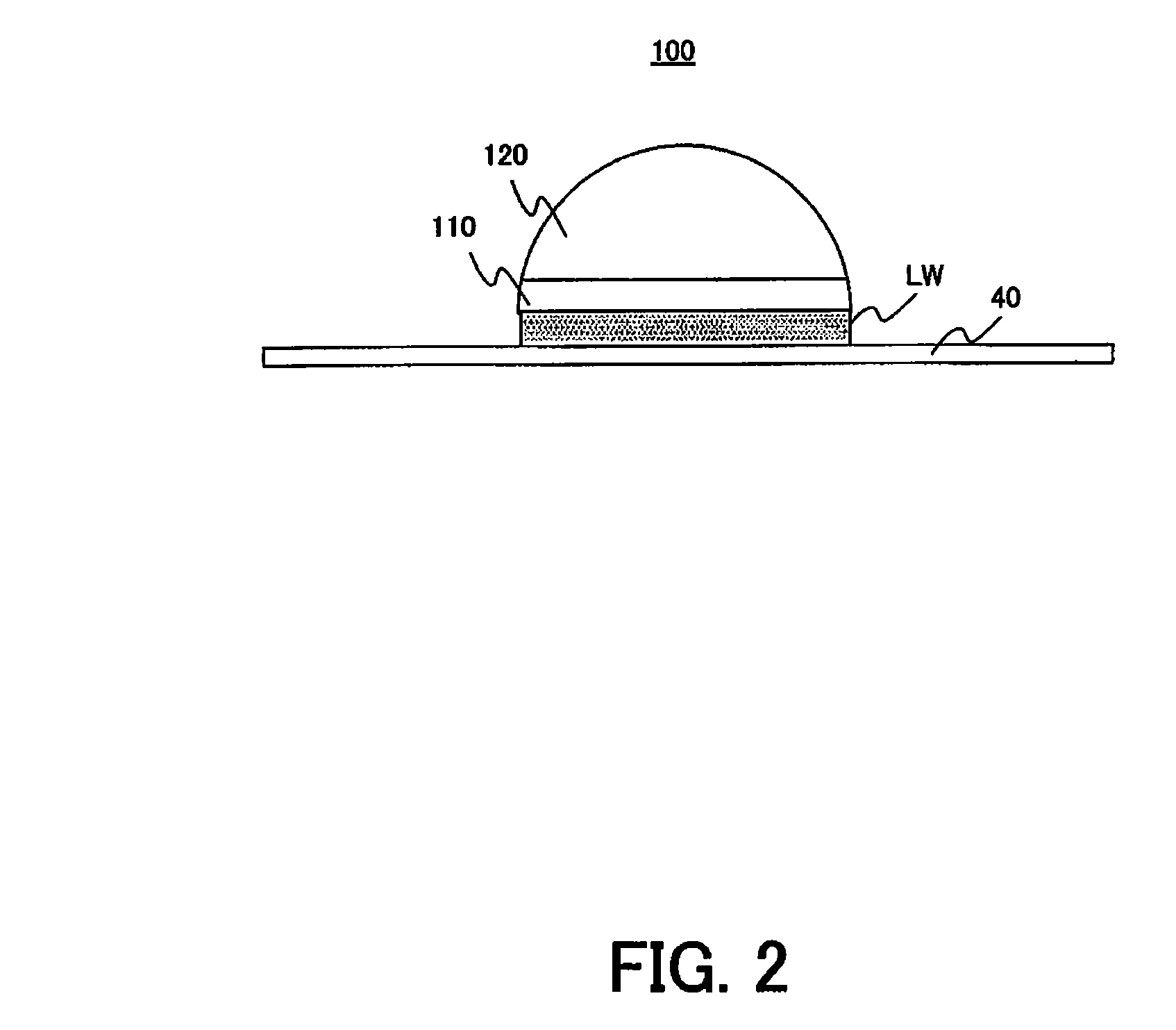
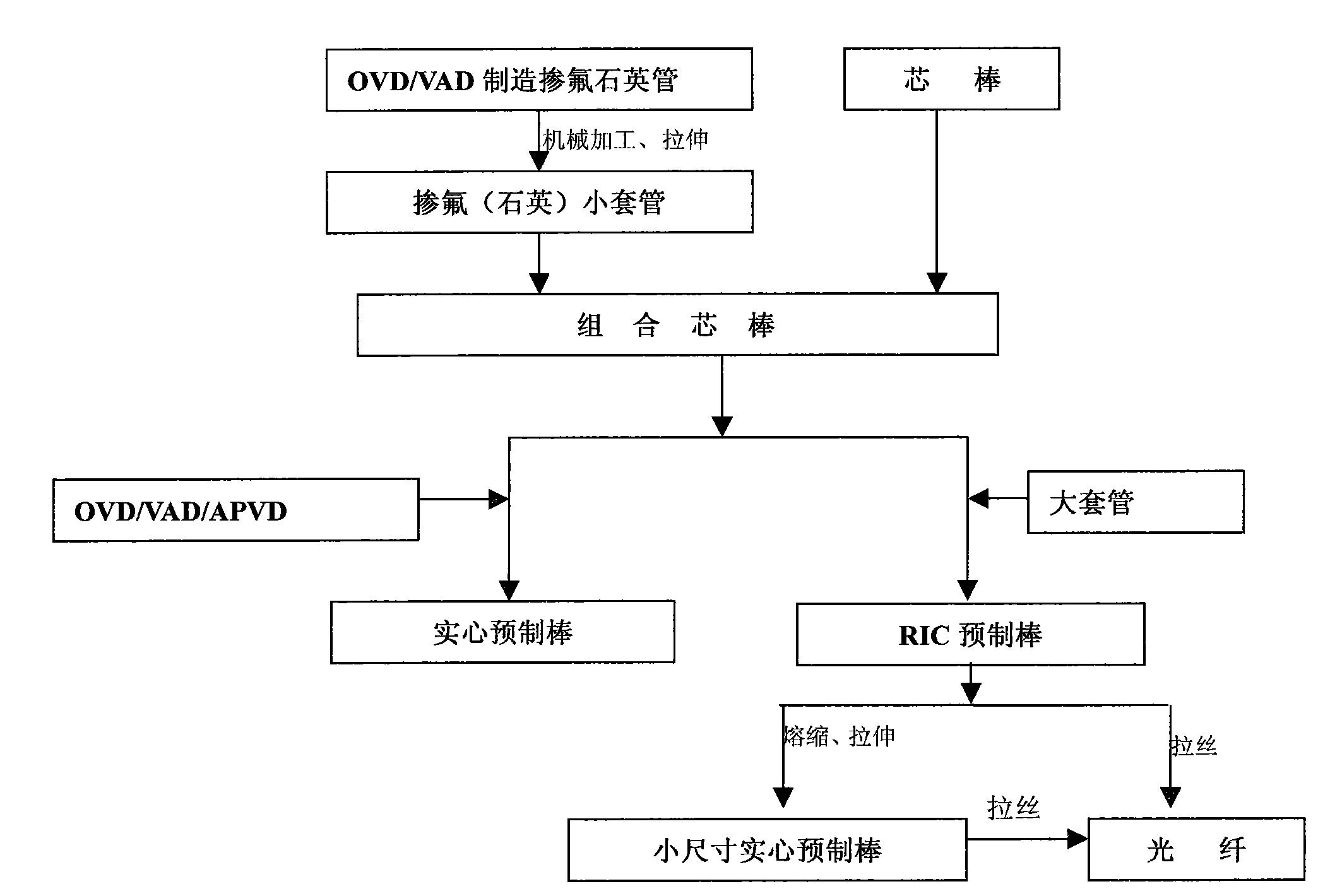
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
820 results about "Fluorine doping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
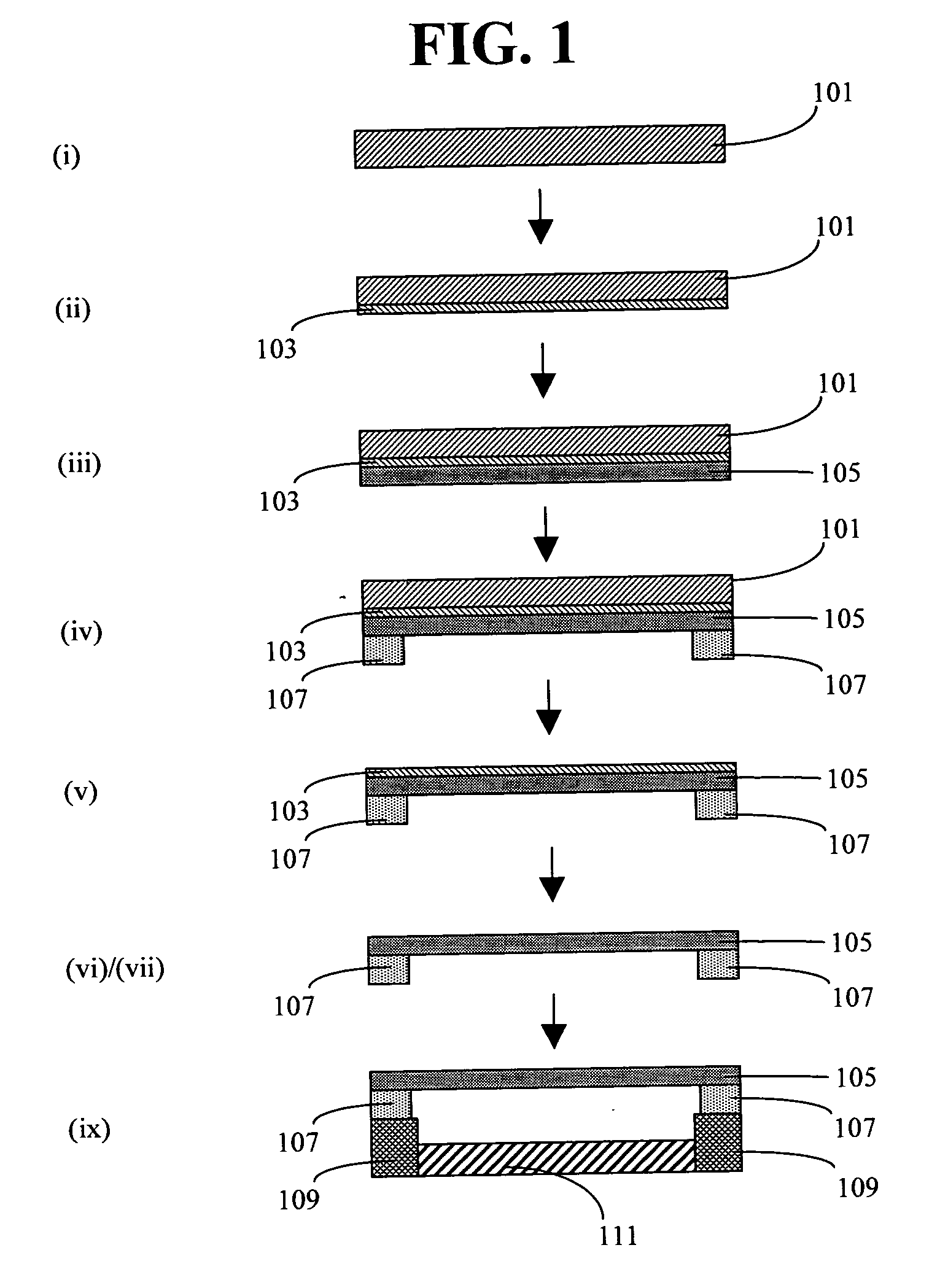
Fluorine doped lithium rich metal oxide positive electrode battery materials with high specific capacity and corresponding batteries
ActiveUS20100086854A1Desirable battery performanceElectrode manufacturing processesFinal product manufactureLithiumDopant
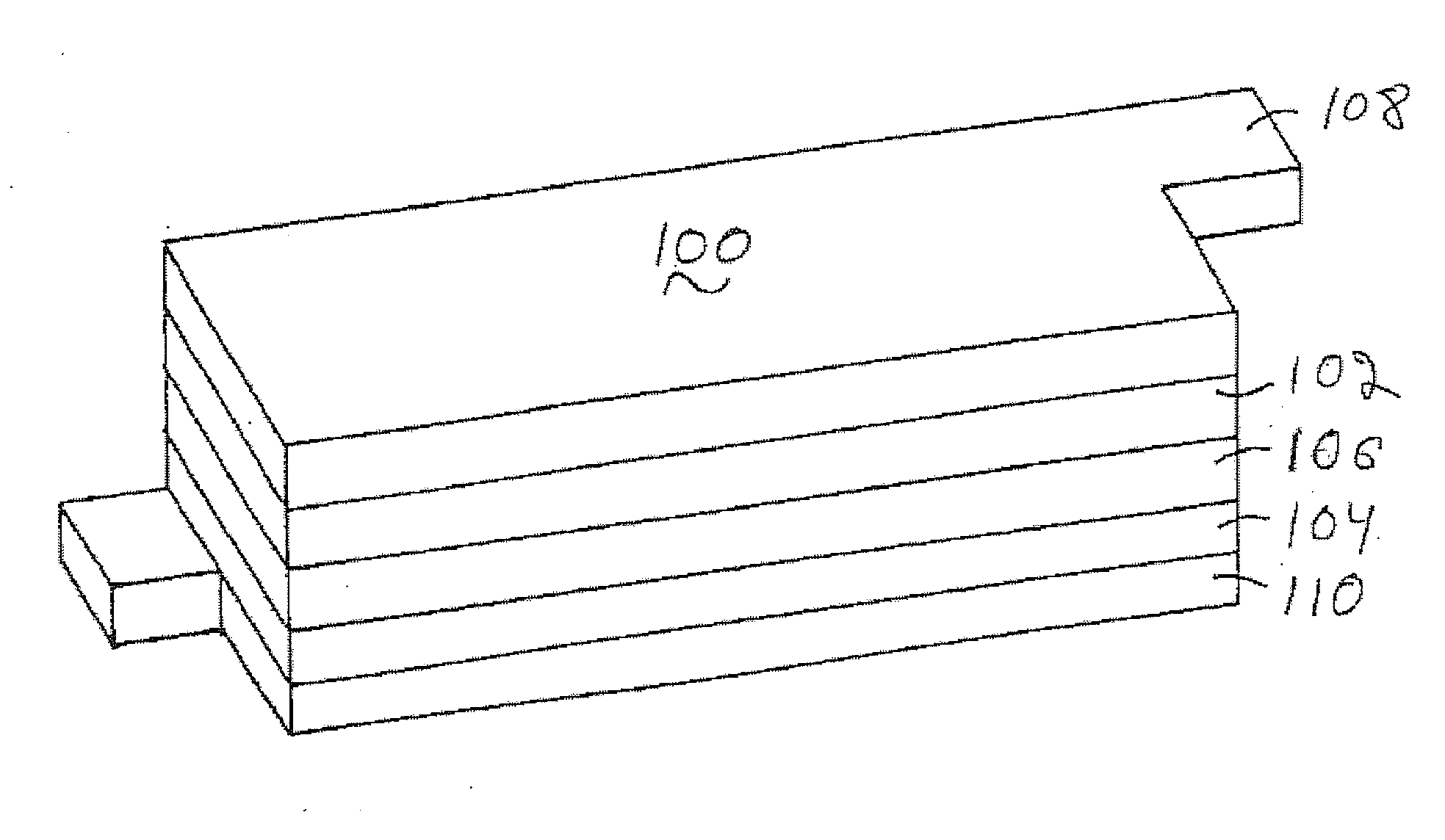
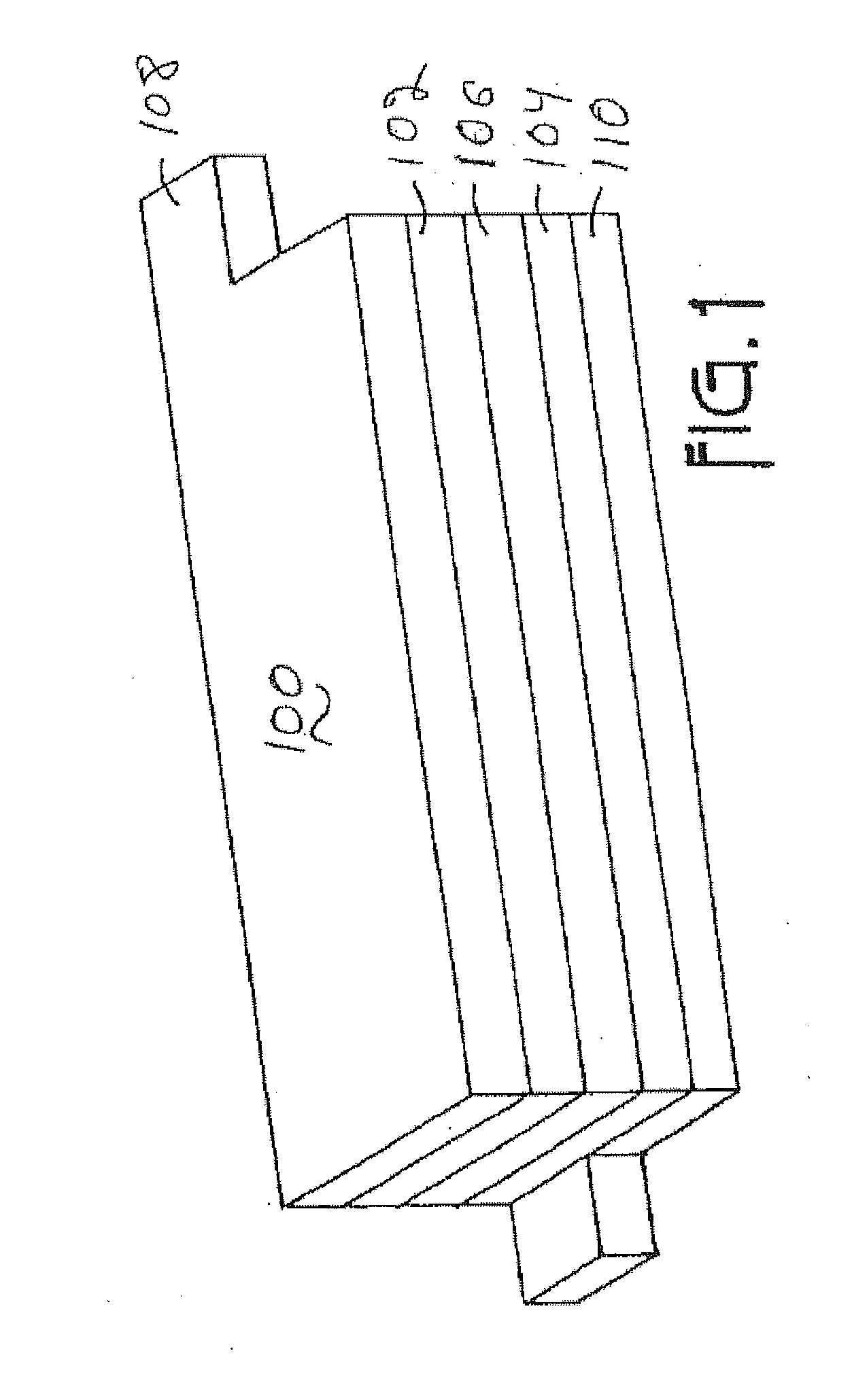
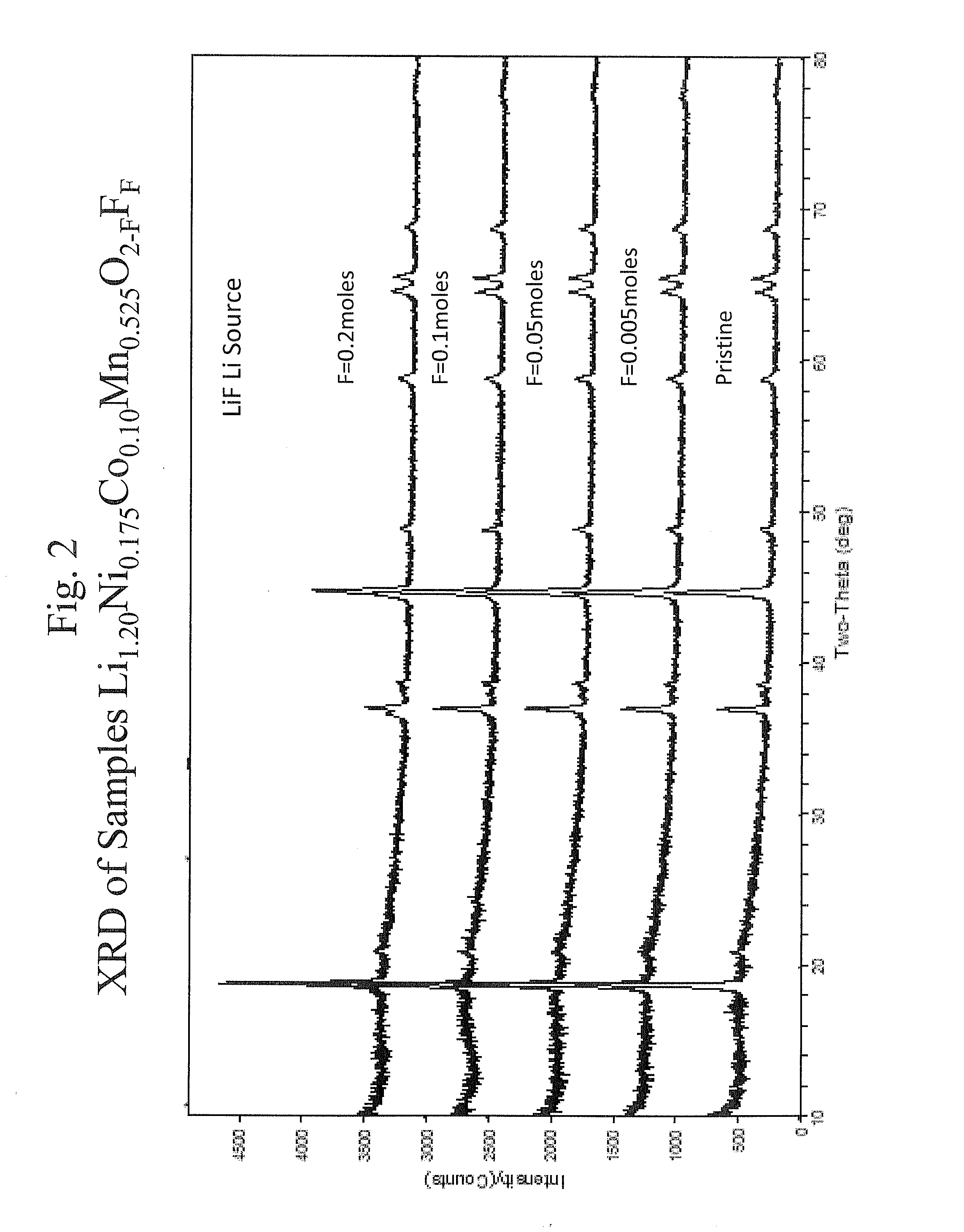
Lithium rich metal oxyfluorides are described with high specific capacity and, good cycling properties. The materials have particularly good high rate capabilities. The fluorine dopant can be introduced in a low temperature process to yield the materials with desirable cycling properties. In some embodiments, the positive electrode active materials have a composition represented approximately by the formula Li1+xNiαMnβCoγAδO2−zFz where:x is from about 0.02 to about 0.19,α is from about 0.1 to about 0.4,β is from about 0.35 to about 0.869,γ is from about 0.01 to about 0.2,δ is from 0.0 to about 0.1 andz is from about 0.01 to about 0.2,where A is Mg, Zn, Al, Ga, B, Zr, Ti, Ca, Ce, Y, Nb or combinations thereof.
Owner:IONBLOX INC
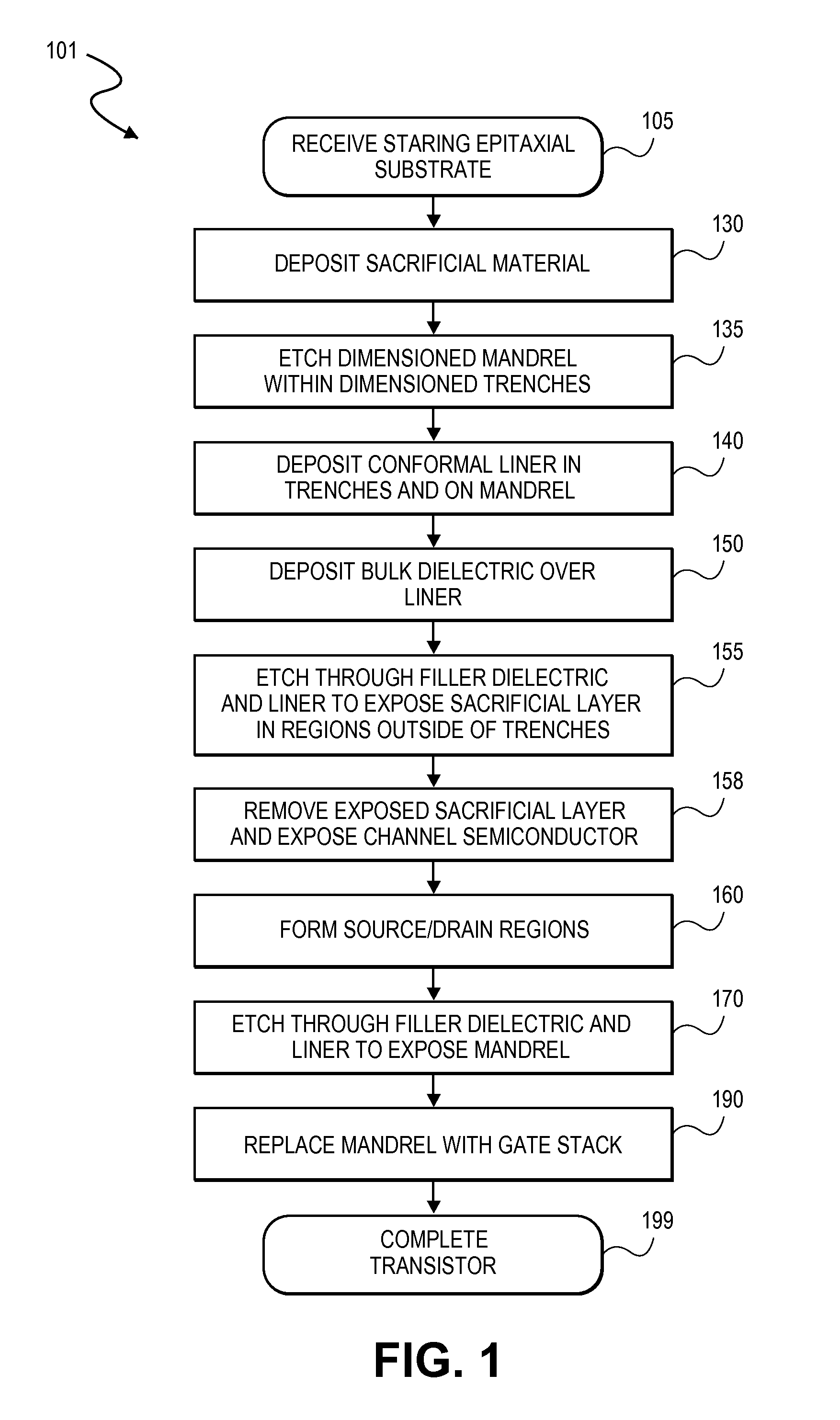
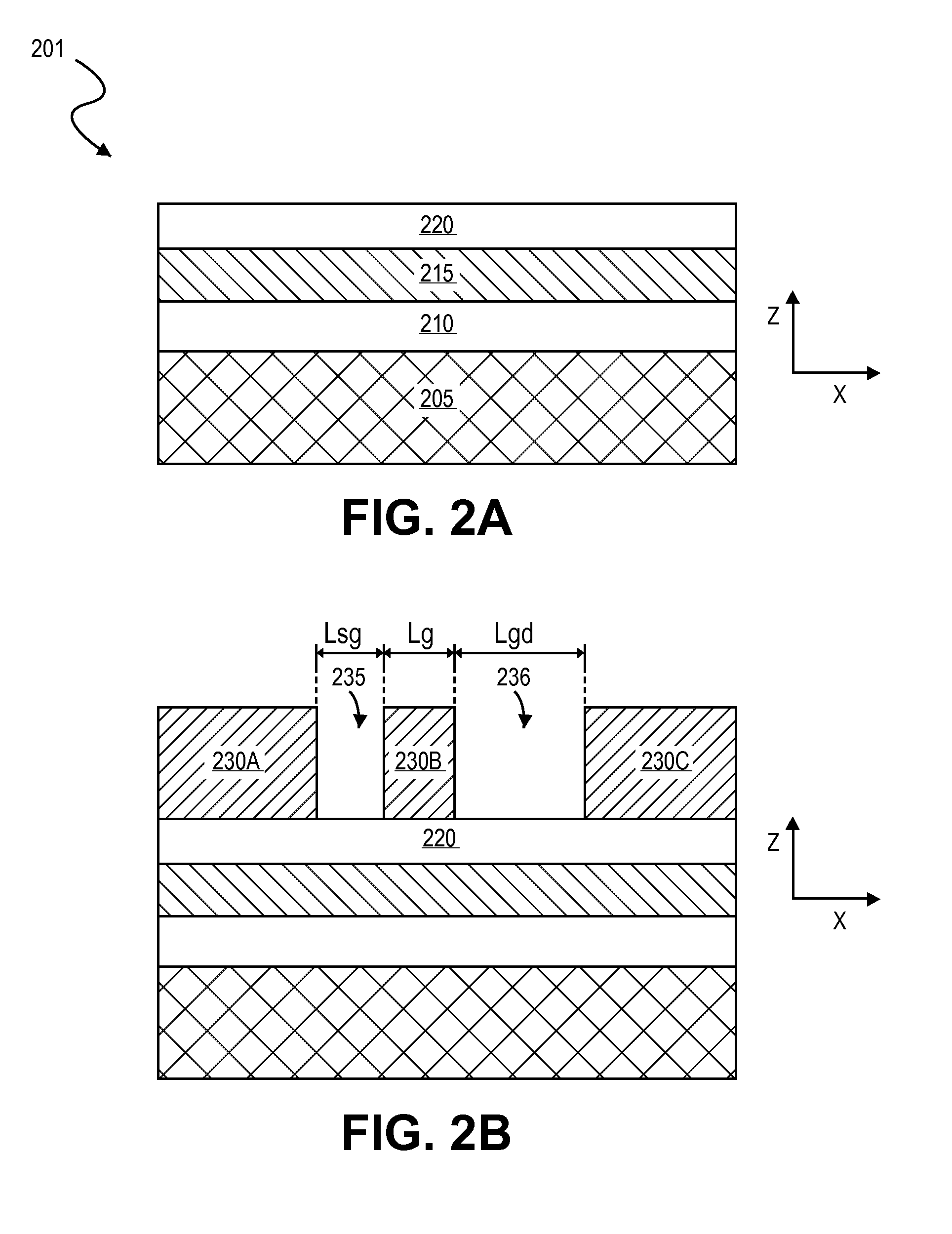
Self-aligned structures and methods for asymmetric GAN transistors & enhancement mode operation
ActiveUS20140091308A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesNon symmetricEngineering
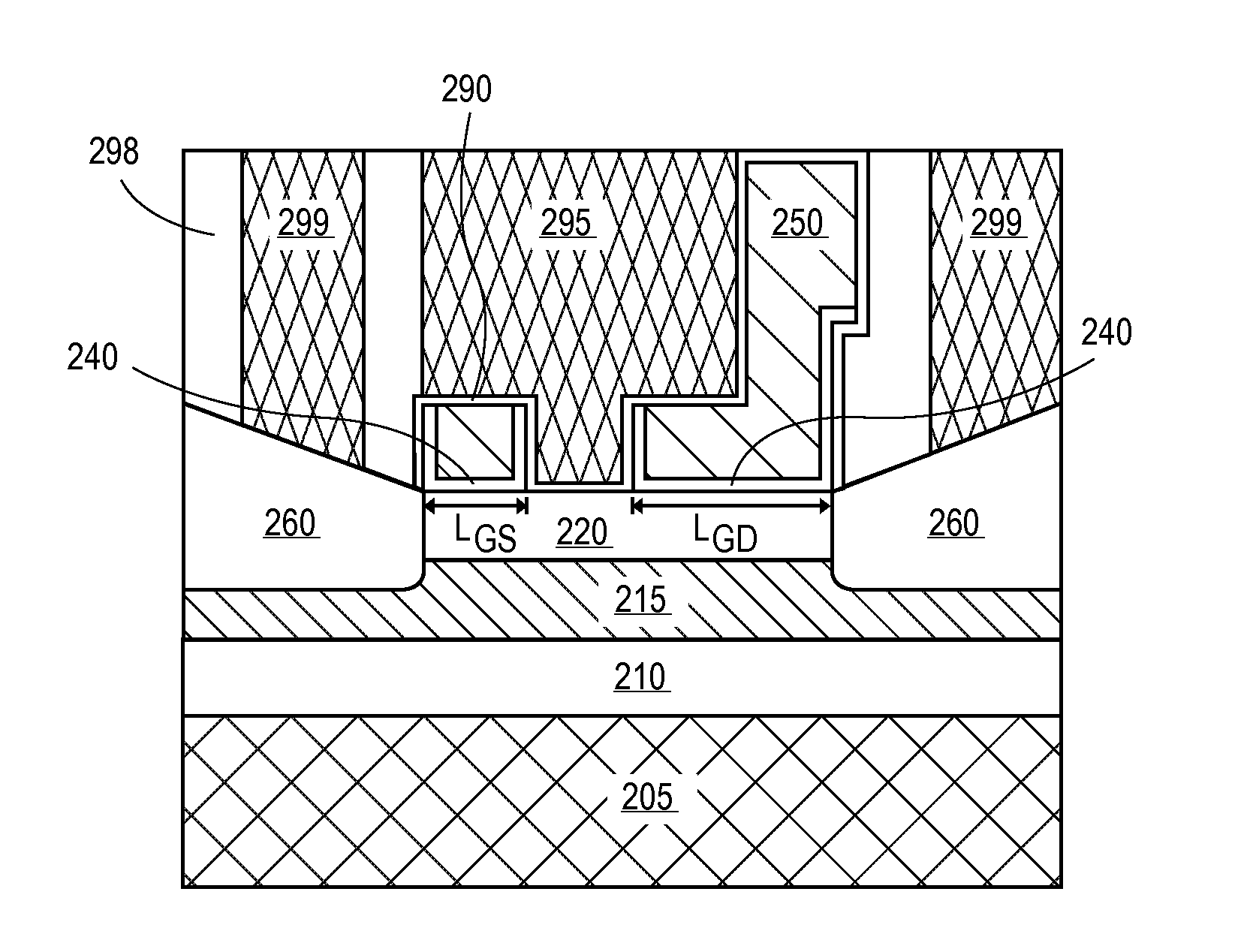
Embodiments include high electron mobility transistors (HEMT). In embodiments, a gate electrode is spaced apart by different distances from a source and drain semiconductor region to provide high breakdown voltage and low on-state resistance. In embodiments, self-alignment techniques are applied to form a dielectric liner in trenches and over an intervening mandrel to independently define a gate length, gate-source length, and gate-drain length with a single masking operation. In embodiments, III-N HEMTs include fluorine doped semiconductor barrier layers for threshold voltage tuning and / or enhancement mode operation.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Alkali and fluorine doped optical fiber
ActiveUS7088900B1Reduce decreaseOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDopantSilica measurement
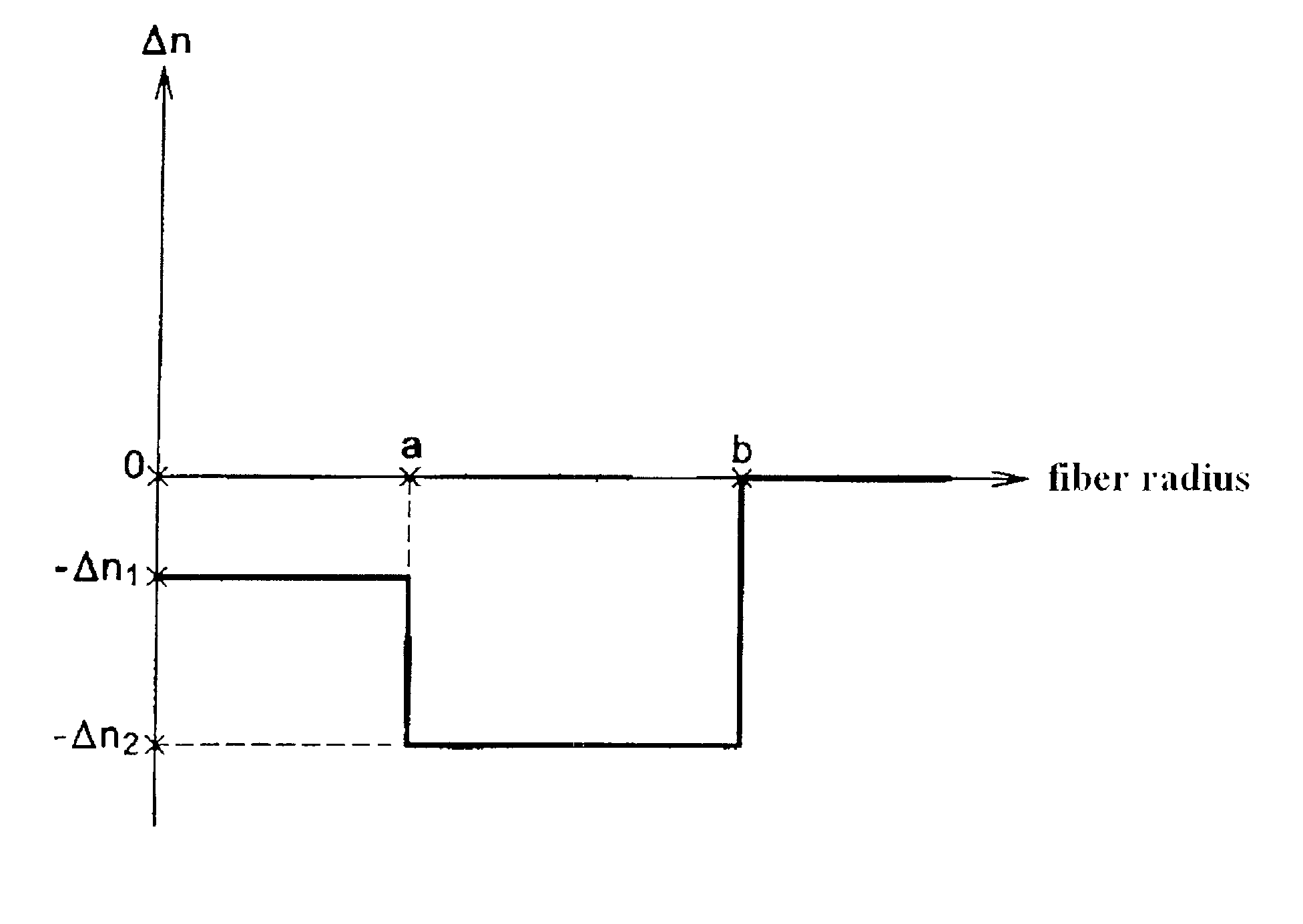
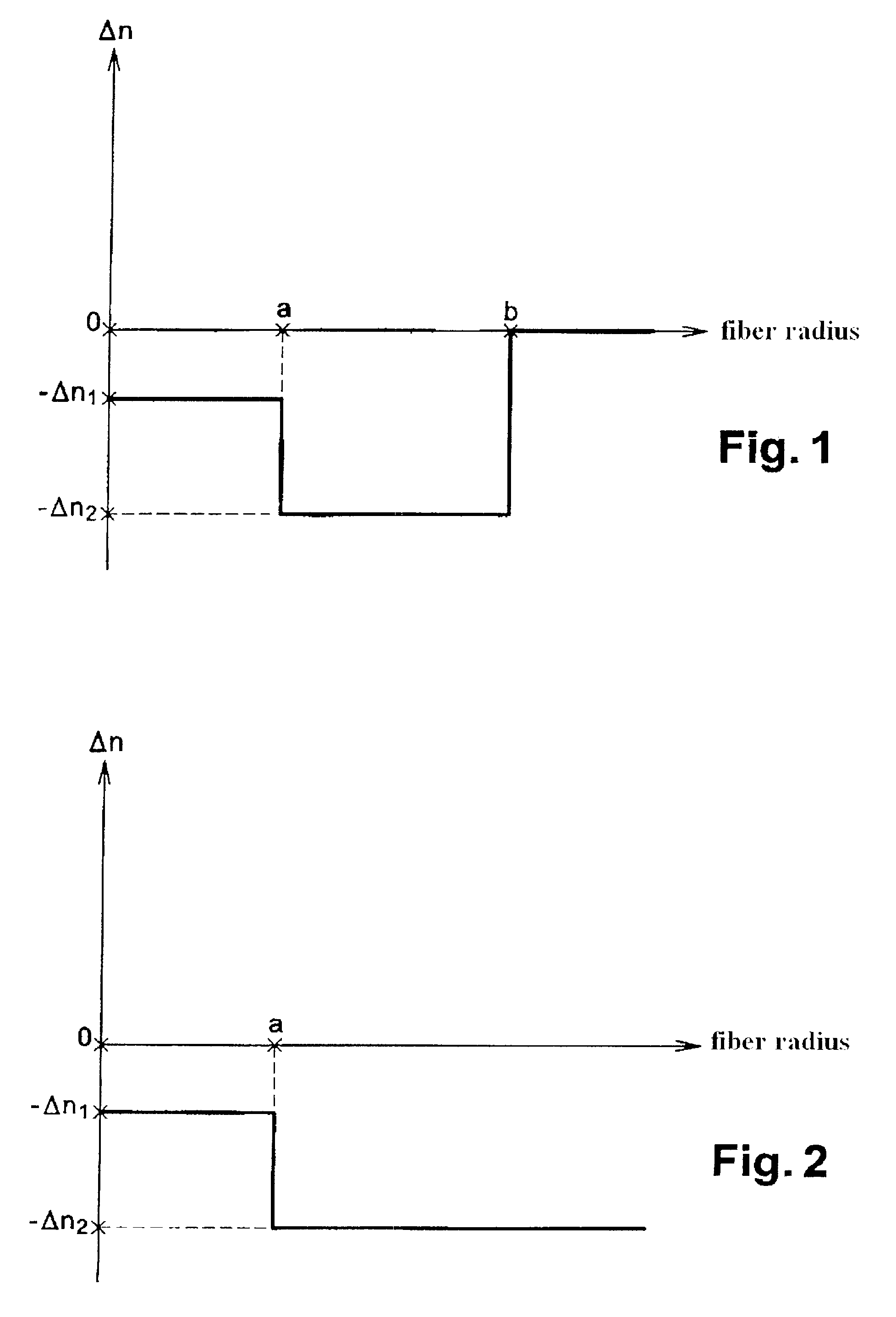
Disclosed is an optical fiber having a core of SiO2 doped with fluorine and an alkali metal oxide dopant. The alkali metal oxide is selected from the group consisting of K, Na, Li, Cs and Rb and is provided in amount of at least 20 ppm wt. %. The fiber has an inner cladding surrounding the core, which also includes fluorine. A relative refractive index of the inner cladding (Δ2%), measured relative to pure silica, is preferably between −0.39% and −0.7%. The fiber preferably exhibits attenuation at 1550 nm of less than or equal to 0.178 dB / km.
Owner:CORNING INC
Fluorine-doped optical fiber
ActiveUS7526177B2Improve the immunityReduce transmission lossOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexSingle mode fiber transmission
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Method for manufacturing an optical fiber preform
ActiveUS7702204B2Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingTransmission lossSilicon dioxide
A method for manufacturing a final optical fiber preform via overcladding of a primary preform having a cross section area is disclosed. The method includes at least one manufacturing step of the primary preform by deposit of an inner cladding and of a central core inside a tube of fluorine-doped silica, the tube being chosen such that it has a cross section area that is maximally about 15% less than the cross section area of the primary preform. With the method of the invention it is possible to manufacture a preform of large capacity at reduced cost which allows the drawing of an optical fiber having reduced transmission losses.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
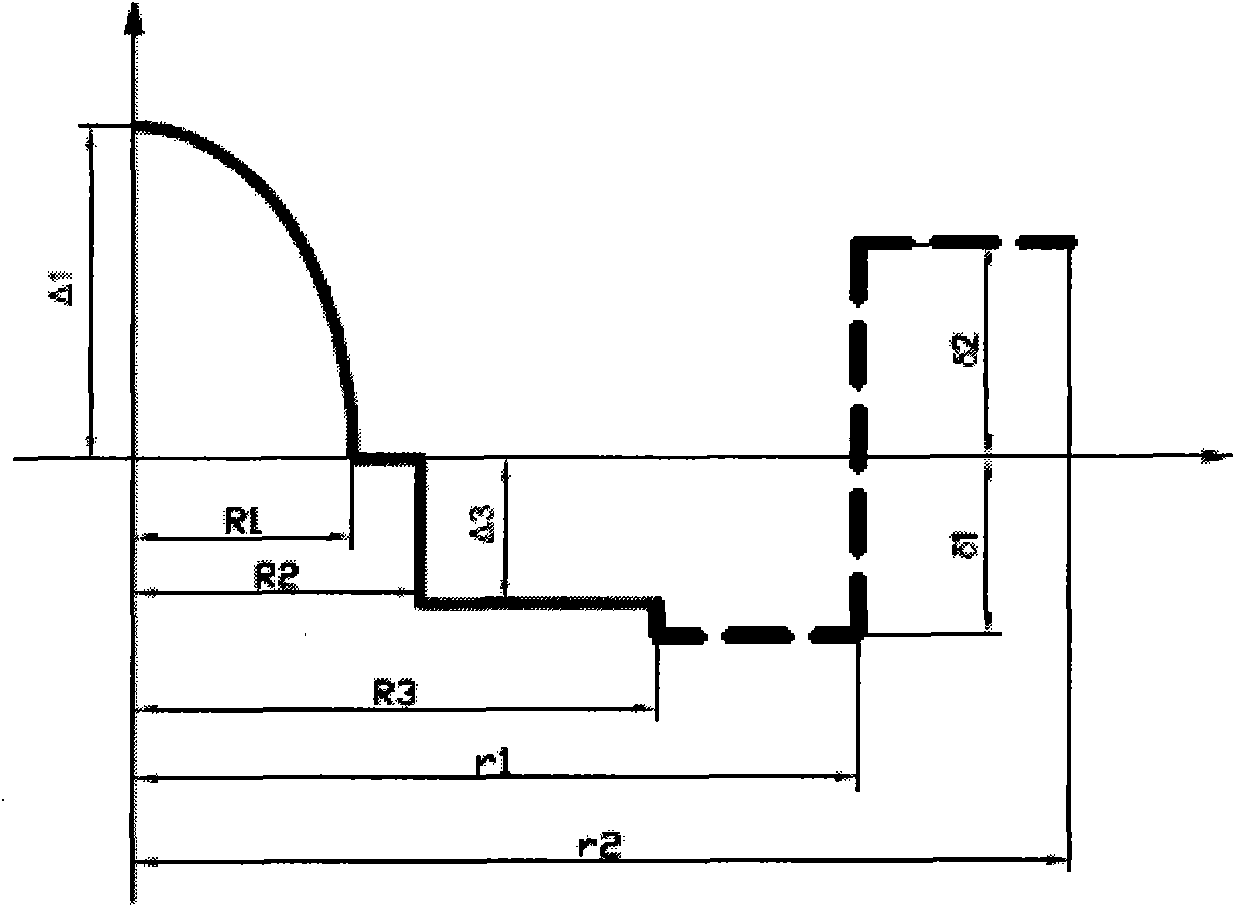
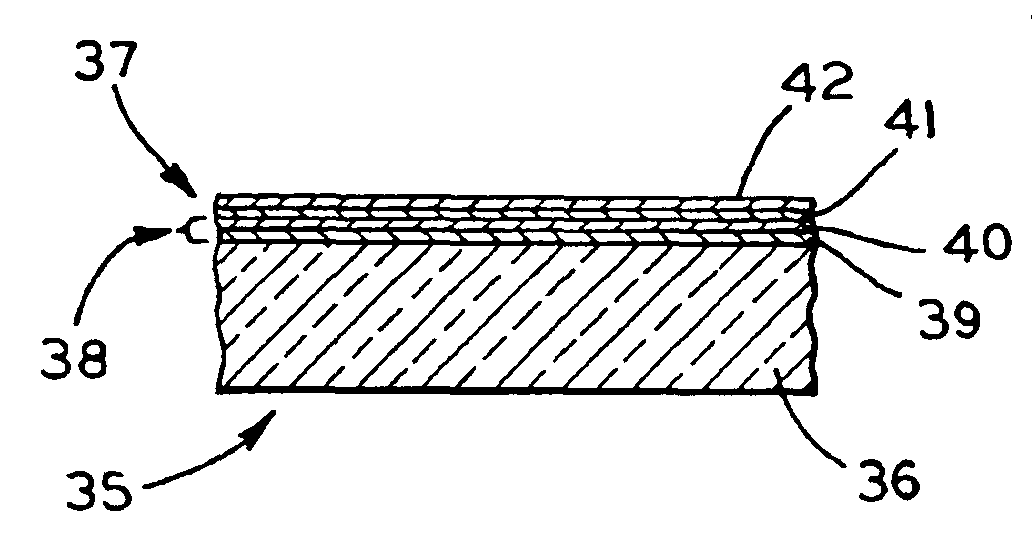
Large effective area fiber with graded index GE-free core
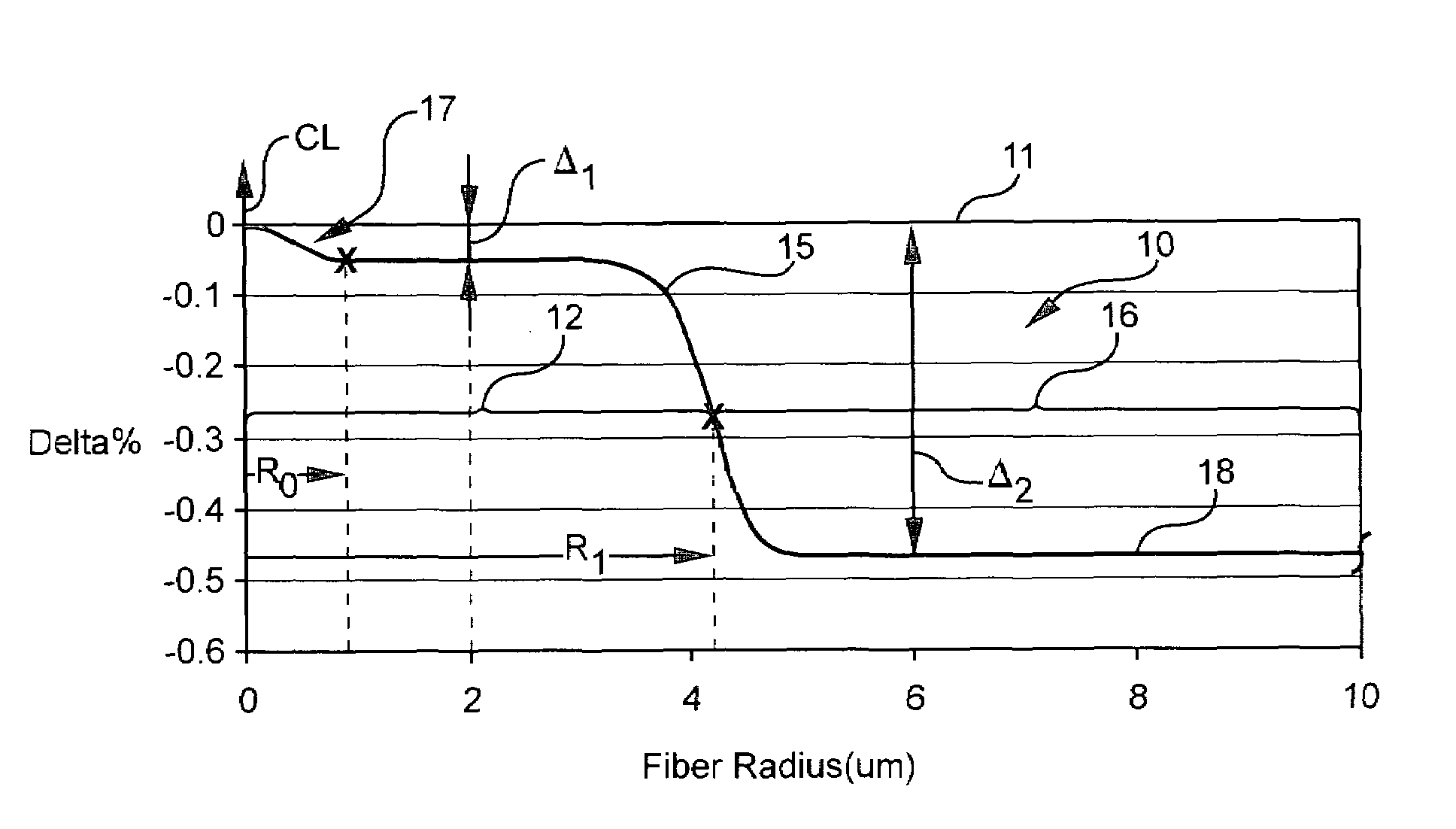
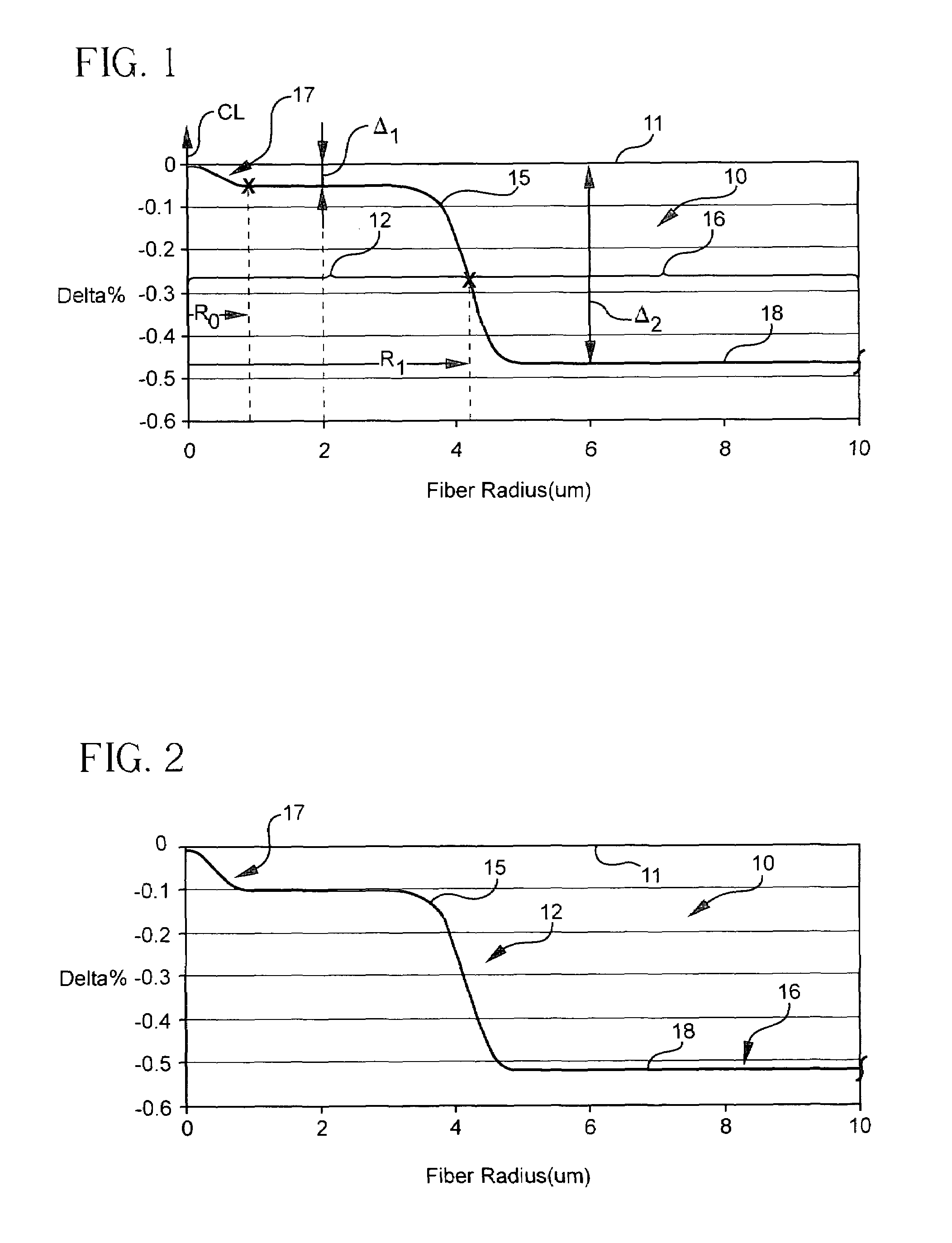
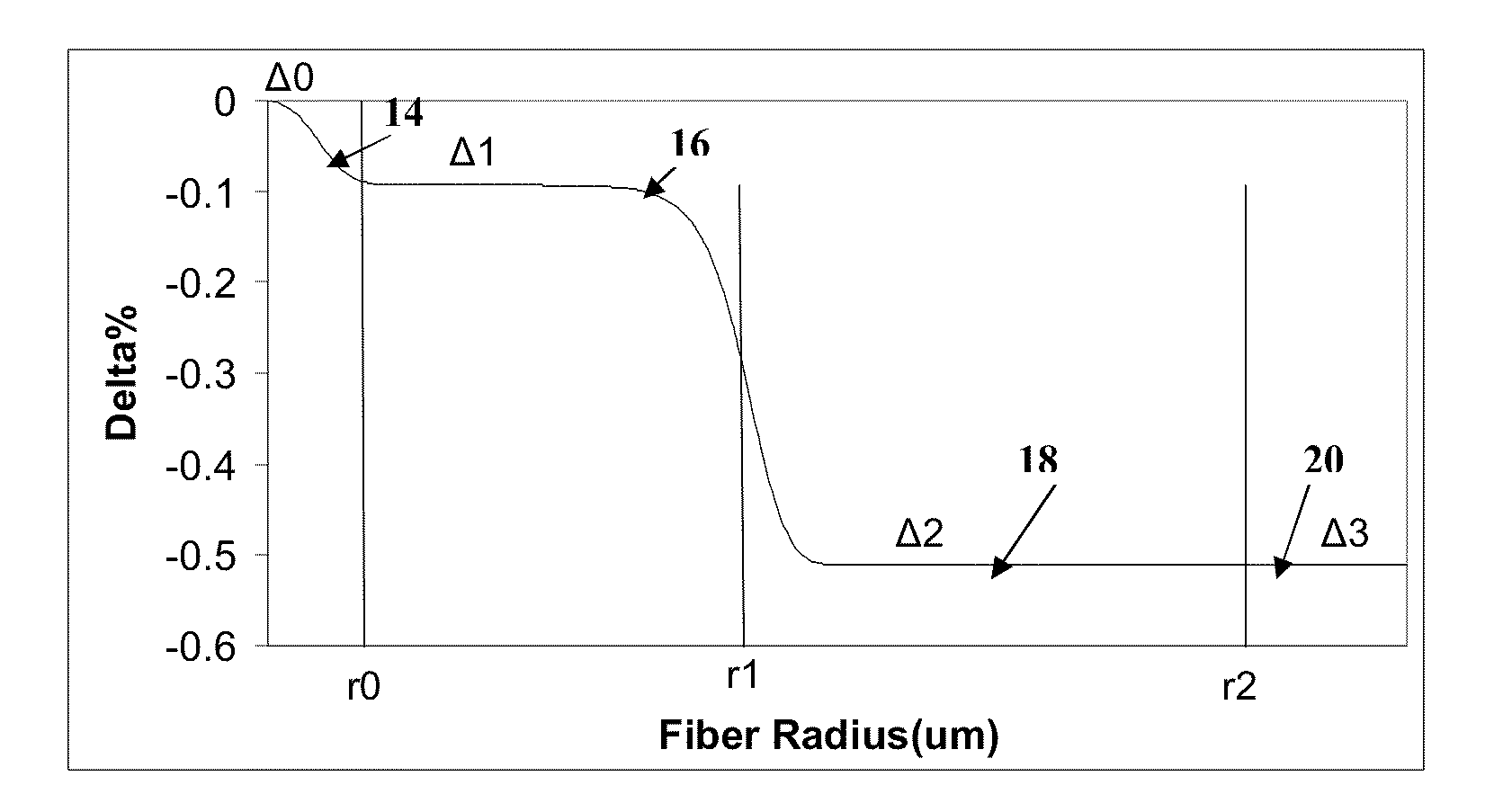
ActiveUS7929818B1Glass optical fibreOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingUltrasound attenuationSilica measurement
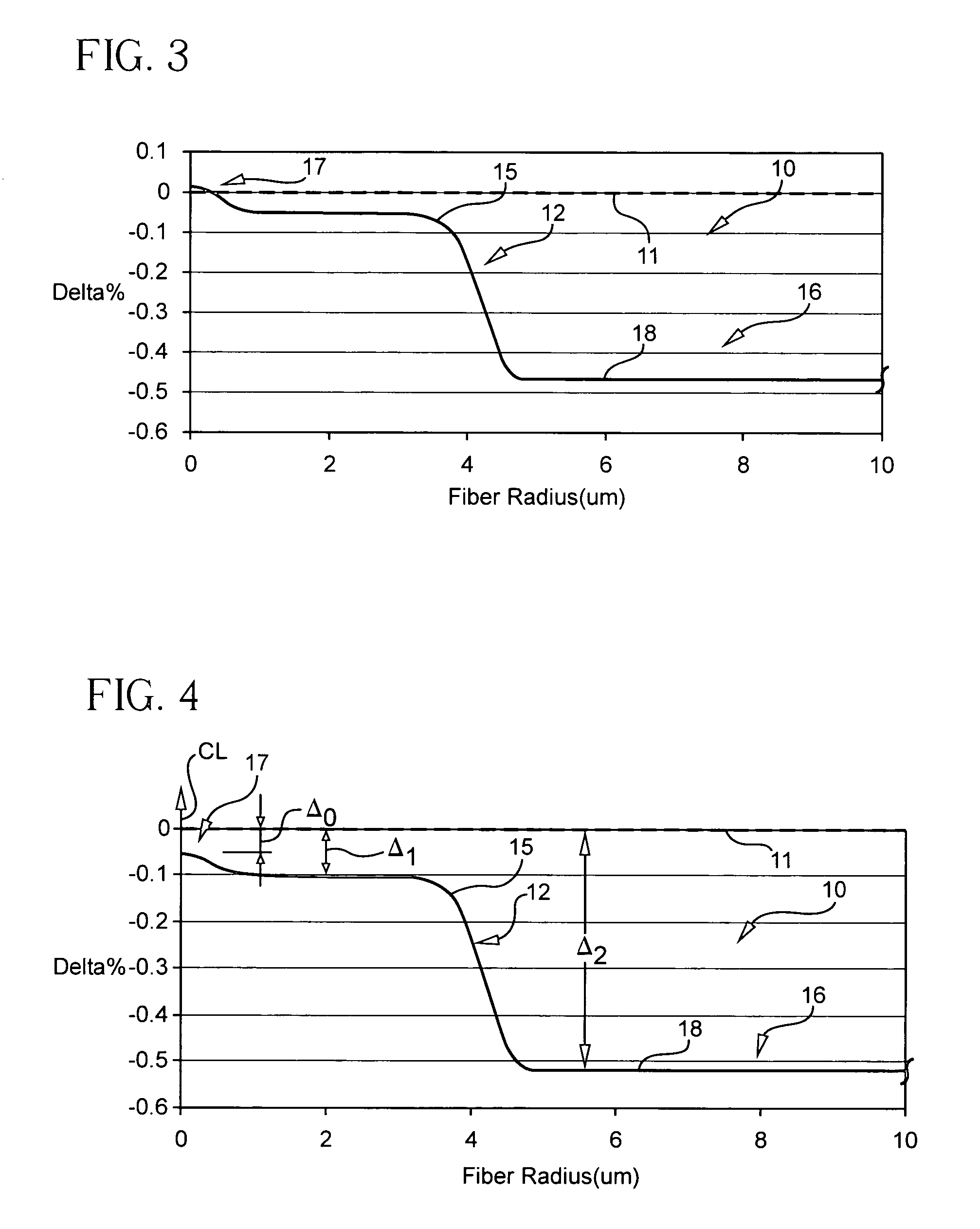
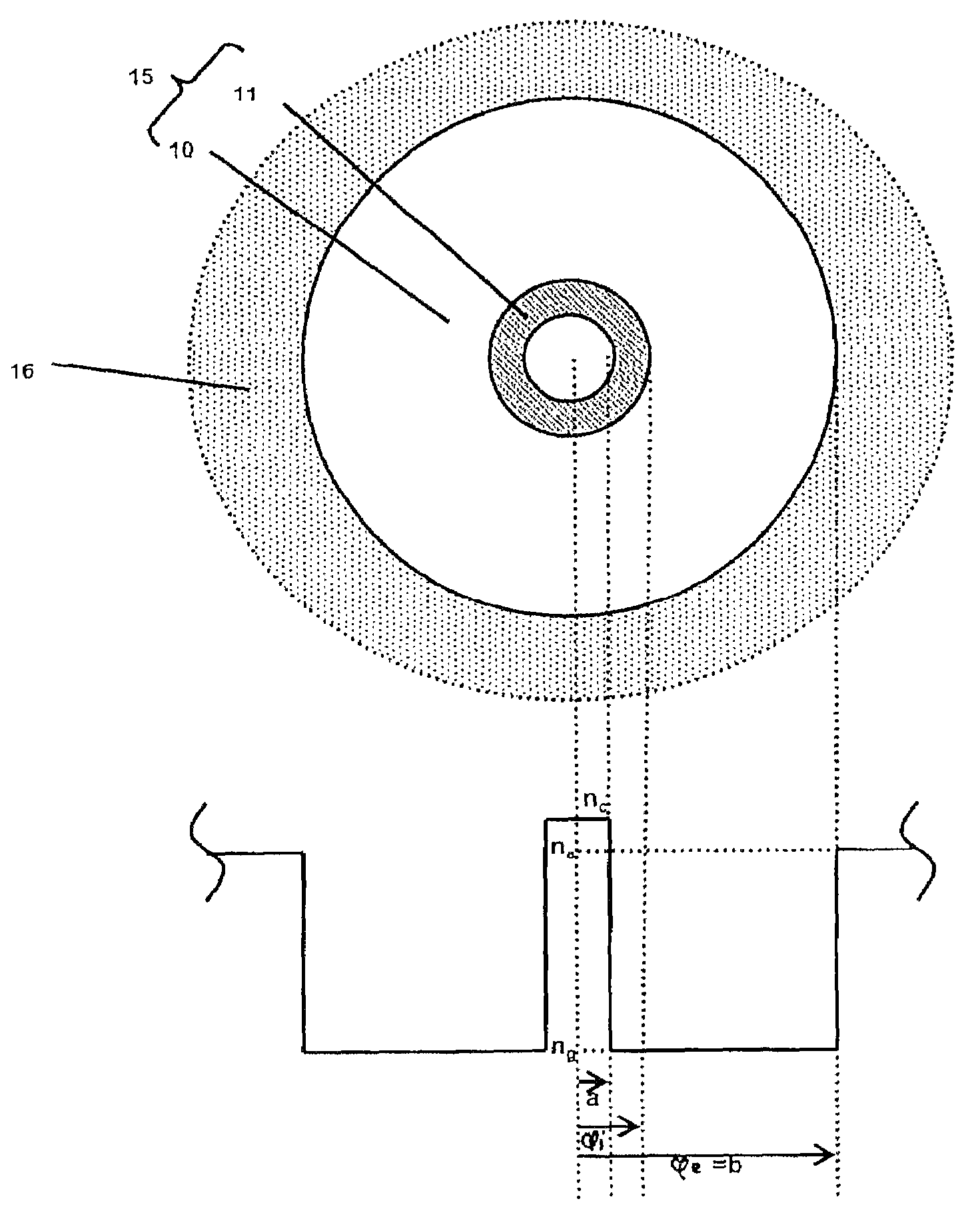
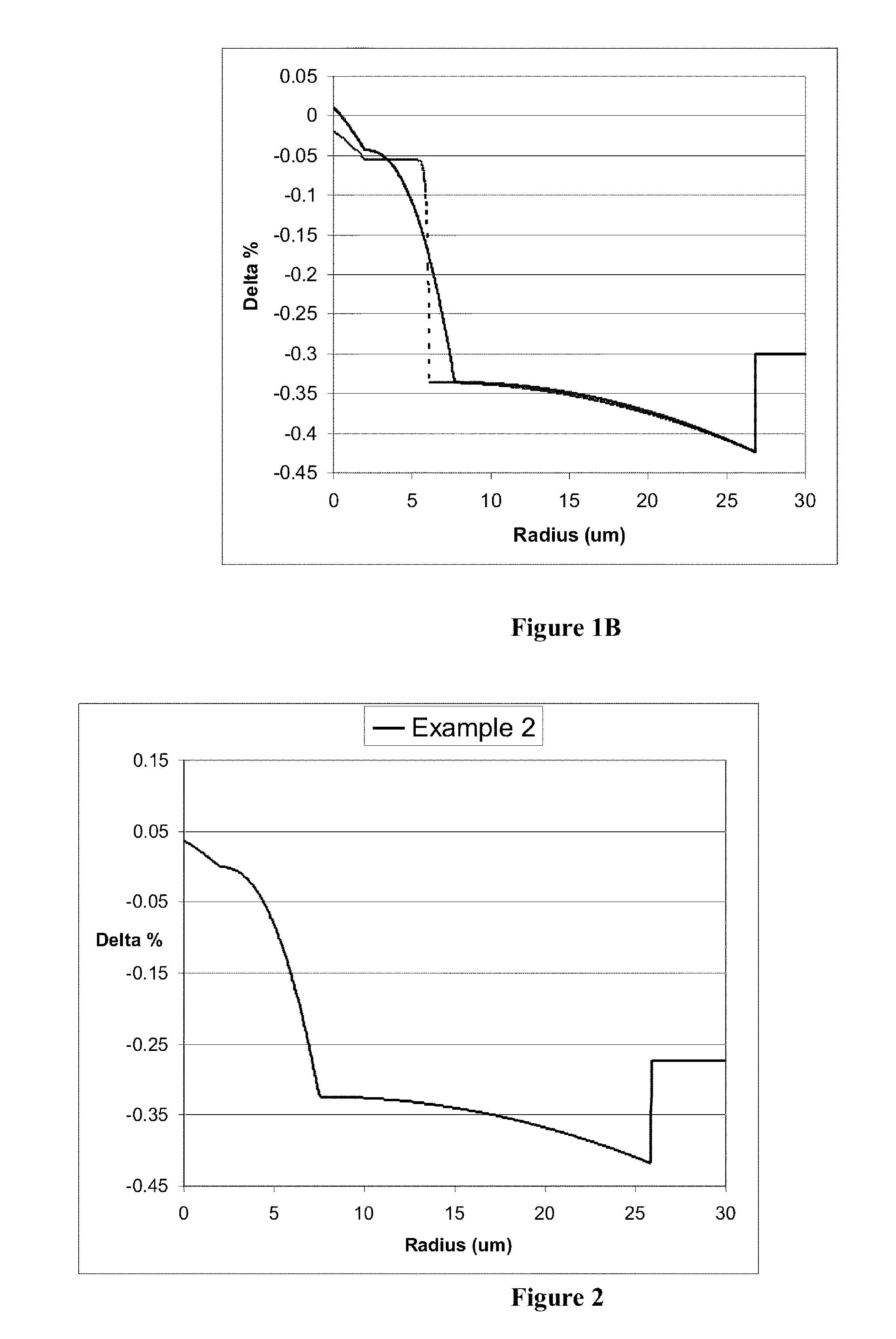
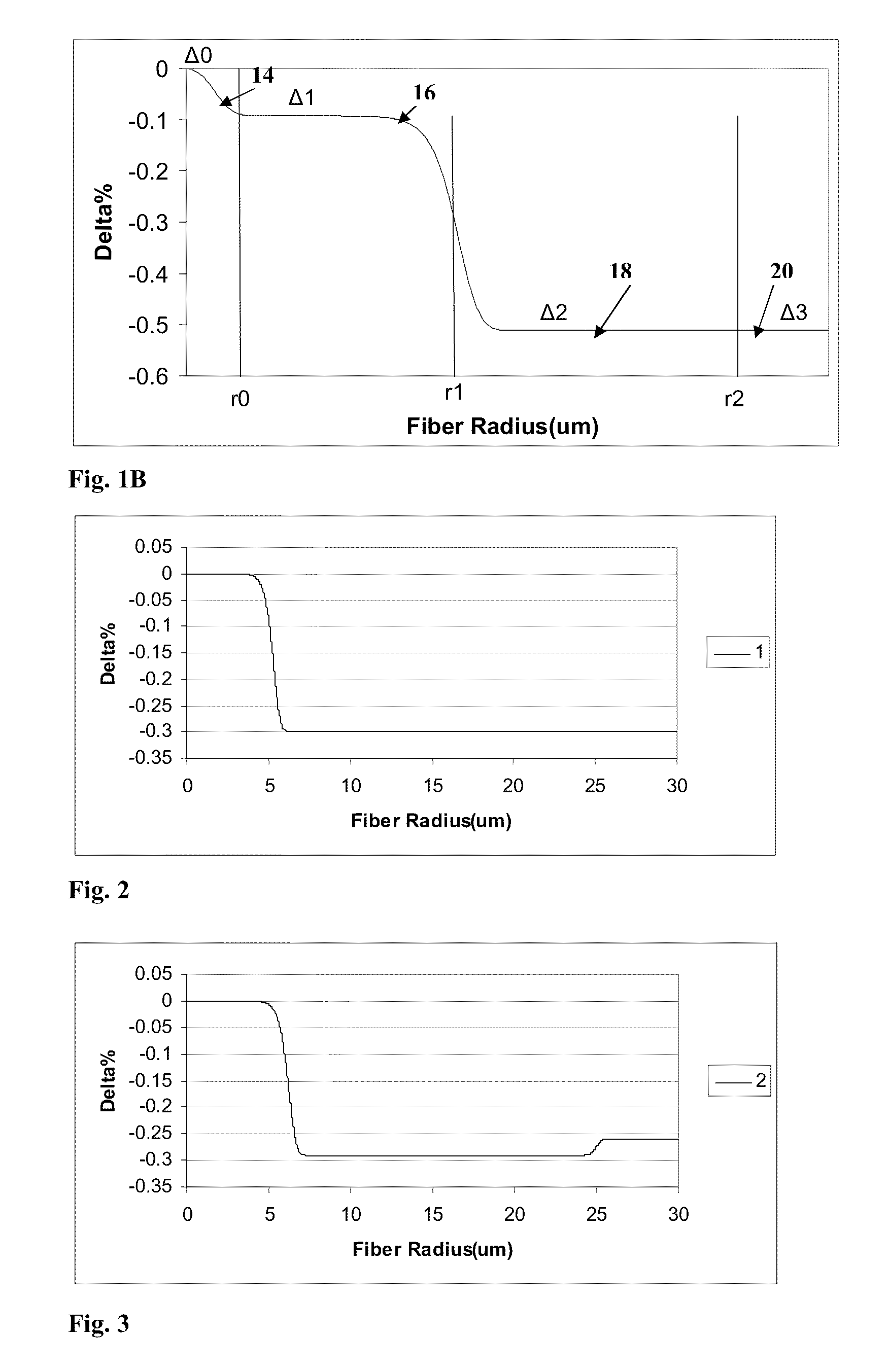
According to some embodiments an optical waveguide fiber comprises (i) a Ge free core having an effective area of 100 μm2to 150 μm2, at 1550 nm wavelength, said core comprising: a) a central core region extending radially outwardly from a centerline to a radius r1, and having a relative refractive index percent profile Δ1(r) in % measured relative to pure silica, wherein −0.1%≦Δ1(r)≦0.12%, wherein the central core region has a maximum relative refractive index percent, Δ1MAX; (b) a first annular core region surrounding and directly adjacent to the central core region, having an α value 1.5≦α≦10, and extending to an outer radius r2, wherein 6 μm≦r2≦10 μm, and having a relative refractive index percent profile, Δ2(r) in % measured relative to pure silica, a minimum relative refractive index Δ2MIN, a maximum relative refractive index Δ2MAX and the relative refractive index measured at a radius r=2 μm, wherein 0.45≦Δ2≦0; −0.25≧Δ2MIN≧−0.45 and Δ1MAX≧Δ2(r=2 μm); (c) a fluorine doped second annular region surrounding and directly adjacent to the first annular core region and extending to a radius 20 μm≦r3≦30 μm and having a negative relative refractive index percent profile, Δ3(r) in %, measured relative to pure silica, with a minimum relative refractive index percent Δ3MIN and −0.5%<Δ3MIN<−0.25%; and Δ3MIN≦Δ2MIN; (ii) a cladding surrounding the core and having a relative refractive index percent Δ4(r) in % measured relative to pure silica and a minimum refractive index delta Δ4MIN, and −0.4%<Δ4<−0.2%; wherein the relative refractive index profile of the optical fiber is selected to provide attenuation of no more than 0.17 dB / km at the 1550 nm wavelength.
Owner:CORNING INC
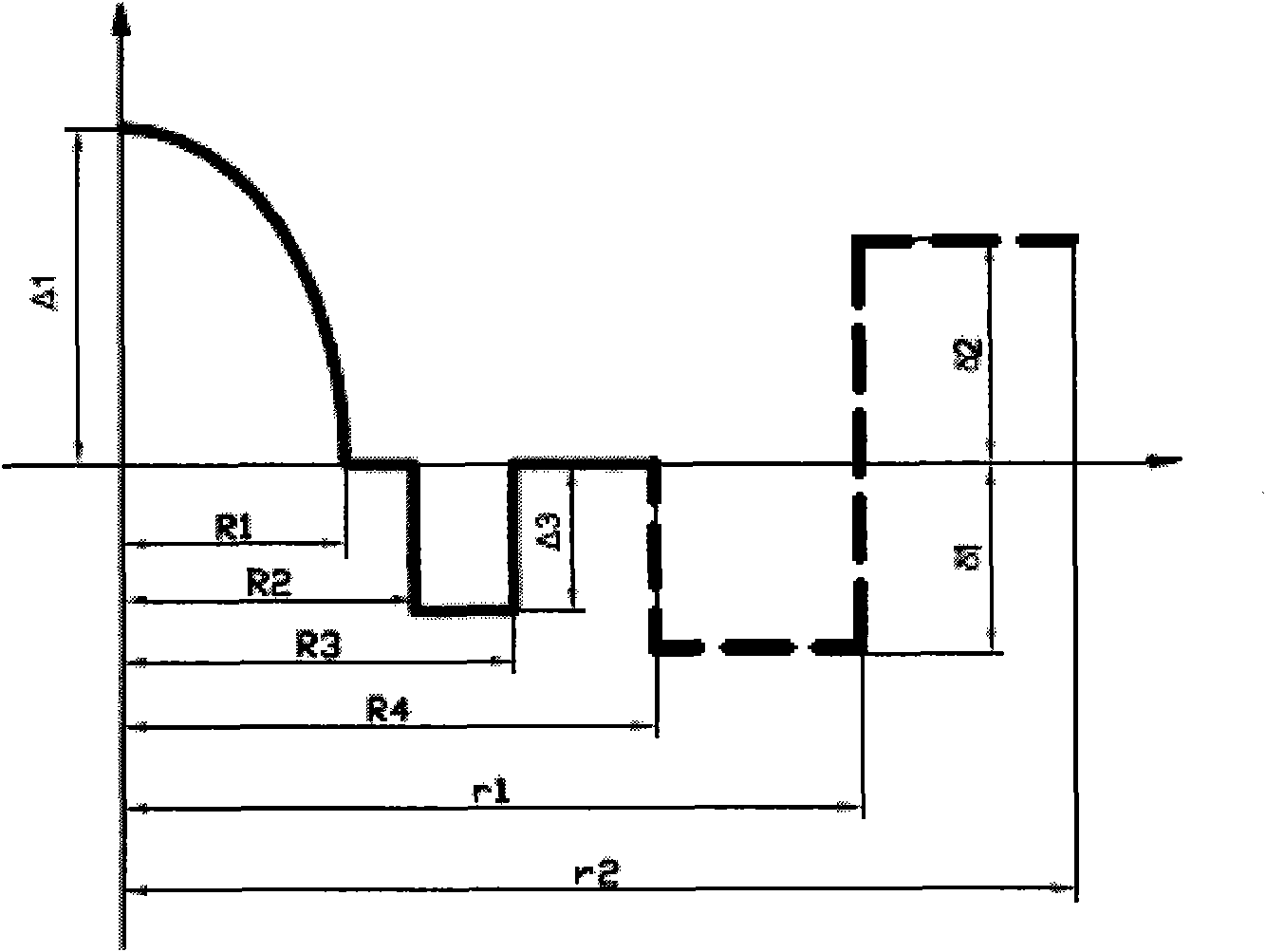
Large Effective Area Fiber With GE-Free Core
ActiveUS20100195966A1Glass optical fibreOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingUltrasound attenuationSilica measurement
According to some embodiments an optical waveguide fiber comprises:(i) a Ge free core having an effective area of 90 μm2 to 160 μm2, at a 1550 nm wavelength, and α value 12≦α≦25, said core comprising:(a) a central core region extending radially outwardly from a centerline to a radius 0 μm≦r0≦2 μm, and having a relative refractive index percent profile Δ0(r) in % measured relative to pure silica, wherein −0.1%≦Δ0(r)≦0.1%, wherein the central core region has a maximum relative refractive index percent, Δ0MAX,(b) a first annular core region surrounding and directly adjacent to the central core region and extending to an outer radius r1, wherein 4.8 μm≦r1≦10 μm, and having a relative refractive index percent profile, Δ1(r) in % measured relative to pure silica, and a minimum relative refractive index, Δ2MIN, and the relative refractive index measured at a radius r=2.5 μm being:−0.15≦Δ1(r=2.5 μm)≦0, and Δ0MAX≧Δ1(r=2.5 μm);(c) a fluorine doped second annular region surrounding and directly adjacent to the first annular core region and extending to a radius 13 μm≦r2≦30 μm and having a negative relative refractive index percent profile, Δ2(r) in %, measured relative to pure silica,with a minimum relative refractive index percent Δ2MIN being:Δ2MIN≦Δ1(r=2.5 μm), and −0.7%≦Δ2MIN≦−0.28%;(ii) a cladding surrounding the core and having a relative refractive index percent Δc(r) in % measured relative to pure silica, and Δc(r)=Δ2MIN±0.3%;wherein the relative refractive index profile of the optical fiber is selected to provide attenuation of no more than 0.175 dB / km at the wavelength of 1550 nm.
Owner:CORNING INC
Corrosion-Resistant CMP Conditioning Tools and Methods for Making and Using Same
ActiveUS20100330886A1Reduce and minimize corrosive effectReducing minimizing and formationPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesNanocomposite coatingMetal
An abrasive tool for conditioning CMP pads includes abrasive grains coupled to a substrate through a metal bond and a coating, e.g., a fluorine-doped nanocomposite coating. The abrasive grains can be arranged in a self-avoiding random distribution. In one implementation, an abrasive tool includes a coated plate and a coated abrasive article that has two abrading surfaces. Other implementations related to a process for producing an abrasive tool that includes a coating at one or more of its surfaces. Also described are methods for dressing a CMP pad.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN ABRASIVES INC +1
Perovskite solar cell and method for manufacturing same
InactiveCN104795501ASimple and fast operationLow costFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesHole transport layerMetal electrodes
The invention relates to a perovskite solar cell and a method for manufacturing the same. The perovskite solar cell comprises an FTO (fluorine-doped tin oxide) transparent conducting glass substrate, an electron transport layer, a light absorption layer, a hole transport layer and a metal electrode. The light absorption layer is made of (C<6>H<5>CH<2>CH<2>NH<3>)<2>(CH<3>NH<3>)<n-1>Pb<n>I<3*n+1> (the n is equal to 1 or 2) materials which are of two-dimensional layered structures. The perovskite solar cell and the method have the advantages that the layered perovskite light absorption layer is manufactured by the aid of a spin coating process, the method is simple and is excellent in film-forming property, the materials of the light absorption layer can be changed along with the layer number n, gaps of the materials can be adjusted, and the materials are excellent in chemical stability and still can keep the excellent layered structures without chemical decomposition after being exposed at high air humidity (50-80%) for 30 days, solar cell prototype devices with excellent and stable performance can be obtained, and the perovskite solar cell and the method are favorable for promoting perovskite solar cell commercialization progress.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Surfacing of metal fluoride excimer optics
ActiveUS20060046099A1High purityEnhanced vapor depositionNatural mineral layered productsWater-setting substance layered productSingle crystalPrism
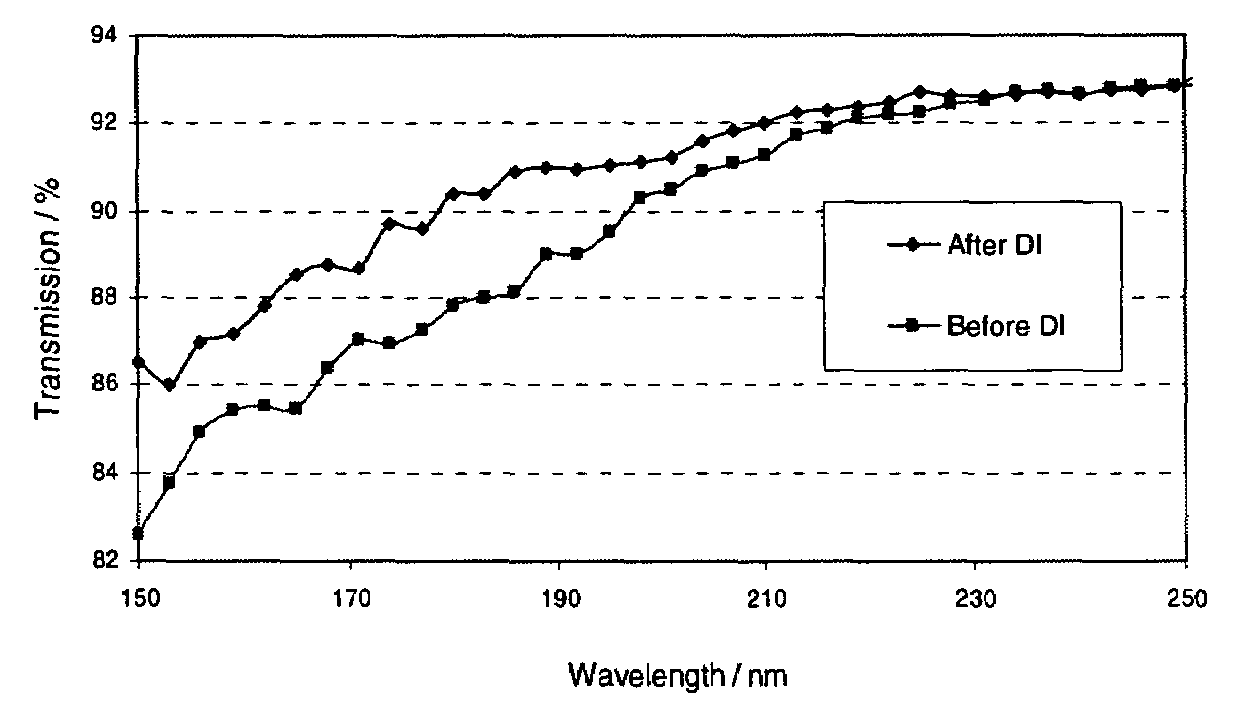
The invention is directed to improved coated metal fluoride single crystal optical elements suitable for use in below 250 nm optical lithography, and particularly below 200 nm lithography. The coated elements of the invention can be lenses, windows, prisms and other elements used in lithographic methods, including the laser sources used therein. The invention is also directed to a method of removing the quasi-Bielby layer formed when a shaped optical element is polished. Removal of the quasi-Bielby layer prior to coating results in improved durability and optical transmission characteristics of the coated lenses. The coating material can be any material that does not impede the transmission of below 250 nm electromagnetic radiation. Fluorine doped silicon dioxide is the preferred coating material.
Owner:CORNING INC
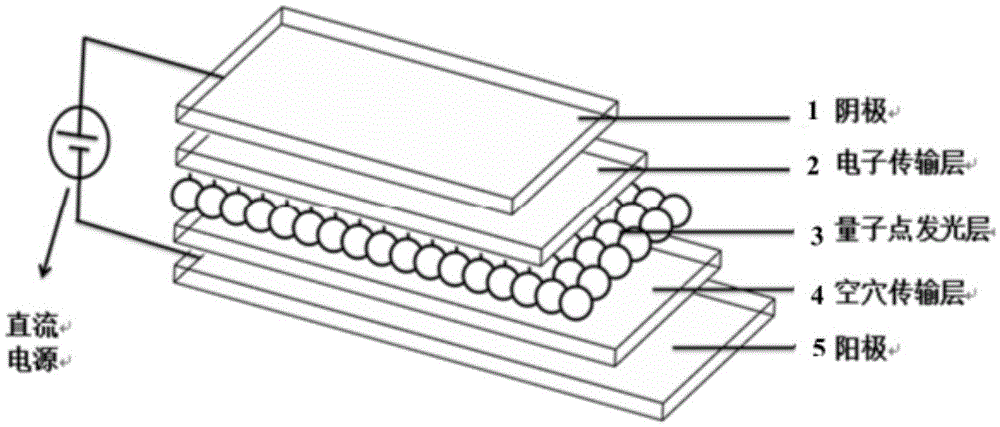
High-efficiency quantum dot light emitting diode with self-assembly polymer hole transmission layer structure
InactiveCN105609651AIncrease transfer rateImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZinc selenidePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
The invention discloses and proposes a high-efficiency quantum dot light emitting diode with a self-assembly polymer hole transmission layer structure. Except a positive electrode and a negative electrode, the high-efficiency quantum dot light emitting diode comprises a three-layer structure: a hole transmission layer, a quantum dot light emitting layer and an electron transmission layer, wherein one end of the quantum dot light emitting layer is connected with the hole transmission layer, the other end of the quantum dot light emitting layer is connected with the electron transmission layer, the electron transmission layer is organic nanoparticles after doped, the hole transmission layer is formed by doping a monomer, a polymer, small-molecule, inorganic oxidized metal nanoparticles or a two-dimensional nanometer material into poly(3,4- ethylenedioxythiophene monomer), a quantum dot is quantum dots of zinc sulfide, zinc selenide, cadmium sulfide, cadmium selenide, cadmium telluride, mercury sulfide, mercury selenide, mercury telluride or core-shell nanometer structured cadmium selenide-zinc sulfide, cadmium sulfide-zinc sulfide, cadmium sulfide-zinc selenide and graphene thereof and the like, and the negative electrode is glass or polyethylene terephthalate (PET) with a layer of indium tin oxide (ITO) or fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) or graphene.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
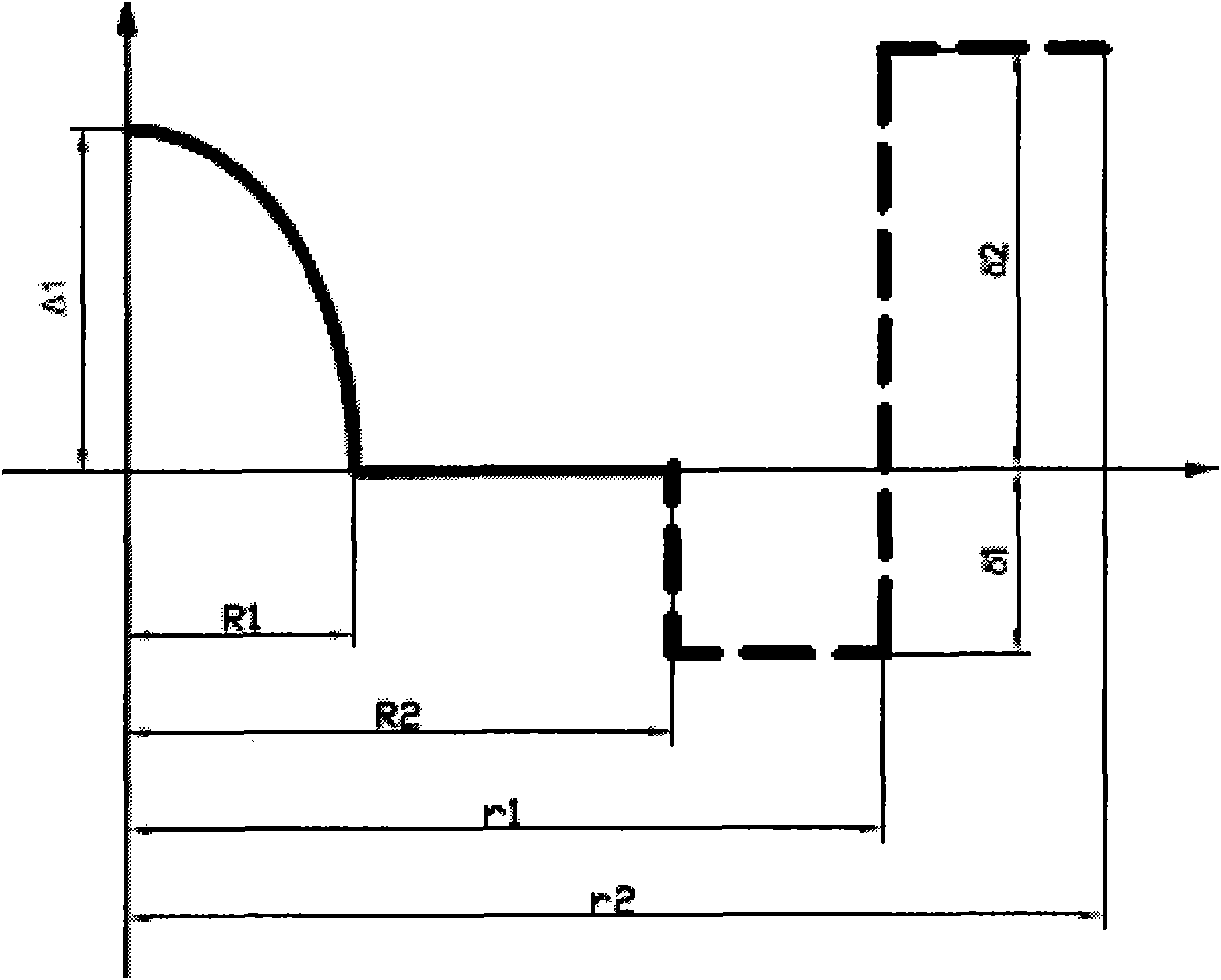
Large effective area fiber with GE-free core
ActiveUS7689085B1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingMedicineRelative refractive index
An optical waveguide fiber comprising:(i) a Ge free core having an effective area of 90 μm2 to 160 μm2, at a 1550 nm wavelength, and α value 12≦α≦25, said core comprising:(a) a central core region extending radially outwardly from a centerline to a radius r0≦2 μm, and having a relative refractive index percent profile Δ0(r) wherein −0.1% ≦Δ0(r) ≦0.1%, and wherein the central core region has a maximum relative refractive index, Δ0MAX,(b) a first annular core region surrounding and directly adjacent to the central core region and extending to an outer radius r1, wherein 4.8 μm ≦r1≦10 μm, and having a relative refractive index percent profile, Δ1(r), and a minimum relative refractive index, Δ2MIN, and the relative refractive index measured at a radius r=2.5 μm being −0.15≦Δ1(r=2.5 μm) ≦0, and Δ0MAX ≧Δ1(r=2.5 μm);(c) a fluorine doped second annular region surrounding and directly adjacent to the first annular core region and extending to a radius 13 μm ≦r2≦30 μm and having a negative relative refractive index percent profile, Δ2(r), with a minimum relative refractive index Δ2MIN being:Δ2MIN<Δ1(r=2.5 μm), and −0.7% ≦Δ2MIN≦−0.28%; and(ii) a cladding surrounding the core and having a relative refractive index percent Δc (r) in % measured relative to pure silica, and Δc (r)=Δ2MIN±0.3%;wherein the relative refractive index profile of the optical fiber is selected to provide attenuation of no more than 0.175 dB / km at the wavelength of 1550 nm.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for preparing positive material fluorine-doped sodium vanadium phosphate of sodium-containing lithium ion battery
The invention relates to a method for preparing positive material fluorine-doped sodium vanadium phosphate of a sodium-containing lithium ion battery, and particularly relates to a method for preparing Na3V2(PO4)3-x / 3Fx (x is not smaller than 0 and not less than 6) by mechanical activation-assisted one-step high-temperature solid state reaction. The method comprises the following steps: dispersing sodium (Na) source, vanadium (V) source, phosphorus (P) source, fluorine (F) source, and carbon (C) source with reducing and conductive effect in a certain amount of liquid dispersion medium; high-speed ball milling the blended materials for mechanical activation; calcining the activated material at 450 to 1000 DEG C for 1 to 72 hours in an inert or reducing atmosphere; and cooling to obtain the final product. The positive material Na3V2(PO4)3-x / 3Fx prepared by the method has good electrochemical property. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple and convenient process, easy control, low cost, and friendly environment, and the synthesis process is simplified so as to facilitate large-scale production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Optical fiber preform cladding fluorine doping method
ActiveCN103224325AReduce OH
<sup>-</sup>
contentSuitable for large-scale productionGlass making apparatusGlass fibre productsGlass transitionCore (optical fiber)
The present invention discloses an optical fiber preform cladding fluorine doping method, which comprises the following steps: depositing a core layer loose body on a target rod; heating the outer surface of the core layer loose body to form a dense layer, such that density of the dense layer is higher than density in the core layer loose body; depositing an inner cladding loose body outside the dense layer to form a core rod loose body comprising the core layer loose body and the inner cladding loose body; taking the target rod out to form a center hole in the center of the core rod loose body; placing the core rod loose body into a glass transition furnace, carrying out heating dewatering in a dewatering atmosphere, and introducing dewatering gas into the center hole during heating; heating the core rod loose body in a fluoride atmosphere, such that fluorine is selectively doped into the inner cladding loose body to form step refraction index distribution; and carrying out glass transition on the core rod loose body, such that the center hole is shrunk, the core layer loose body forms a core layer, and the inner cladding loose body forms an inner cladding so as to form a core rod. With the method, OH<-> content in the core layer can be effectively reduced, attenuation of optical fiber 1383 nm can be reduced, and fluorine distribution in a radial direction of the cladding is uniform.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FUTONG OPTICAL FIBER TECH +1
Method for manufacturing an optical fiber preform
ActiveUS20080031582A1Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingTransmission lossSilicon dioxide
A method for manufacturing a final optical fiber preform via overcladding of a primary preform having a cross section area is disclosed. The method includes at least one manufacturing step of the primary preform by deposit of an inner cladding and of a central core inside a tube of fluorine-doped silica, the tube being chosen such that it has a cross section area that is maximally about 15% less than the cross section area of the primary preform. With the method of the invention it is possible to manufacture a preform of large capacity at reduced cost which allows the drawing of an optical fiber having reduced transmission losses.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Exposure Apparatus, Manufacturing Method of Optical Element, and Device Manufacturing Method
InactiveUS20060170889A1Improve reliabilityImprove imaging effectPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingReticleQuartz
An exposure apparatus includes a projection optical system for projecting an image of a pattern of a reticle onto a substrate via liquid, the liquid being filled in a space between an optical element of the projection optical system and the substrate, the optical element being closest to the substrate in the projection optical system, wherein the optical element includes quartz glass that contacts the liquid and is arranged at a side of the substrate, and fluorine-doped quartz glass adhered to the quartz glass.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical fiber perform and manufacture method thereof
InactiveCN101585658AIncrease productivityGood effectGlass making apparatusThin material handlingQuartzSingle-mode optical fiber
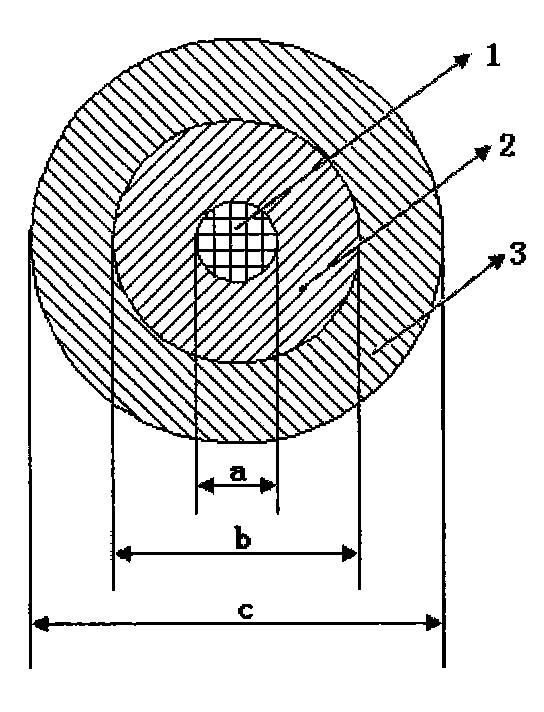
The invention relates to an optical fiber perform and manufacture method thereof, characterized in that: the ratio of the diameter of the optical fiber core rod to the core layer diameter b / a is 2.1-2.8; the optical fiber core rod is sleeved in the fluorine-doped quartz glass small casing and the optical fiber core rod and the fluorine-doped quartz glass small casing are fused together to form a combination core rod and the ratio of the diameter difference between the combination core rod and the optical fiber perform to the core layer diameter (c-b) / a is 0.5-2.2; the fluorine-doped amount of the fluorine-doped quartz glass small casing Delta F is -0.20% to -0.35% and the hydroxyl group content is smaller than or equal to 500 ppb; a pure quartz glass big casing is arranged on the combination core rod according the to RIC technology or a SiC2 glass surrounding layer directly deposits on the combination core rod and the ratio of the effective diameter of the optical fiber perform to the diameter of the combination core rod d / c IS 2.0-5.6. The bending-countering lower water peak monomode fiber is prepared and the optical fiber capable of satisfying TIU-T G.652.D and G.657 is prepared.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
Method for preparing BiVO4 film with photocatalysis performance by using sol-gel method
ActiveCN102949991ASolve the fixed loadSolve the problem of secondary useWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAmmonium metavanadateSolvent
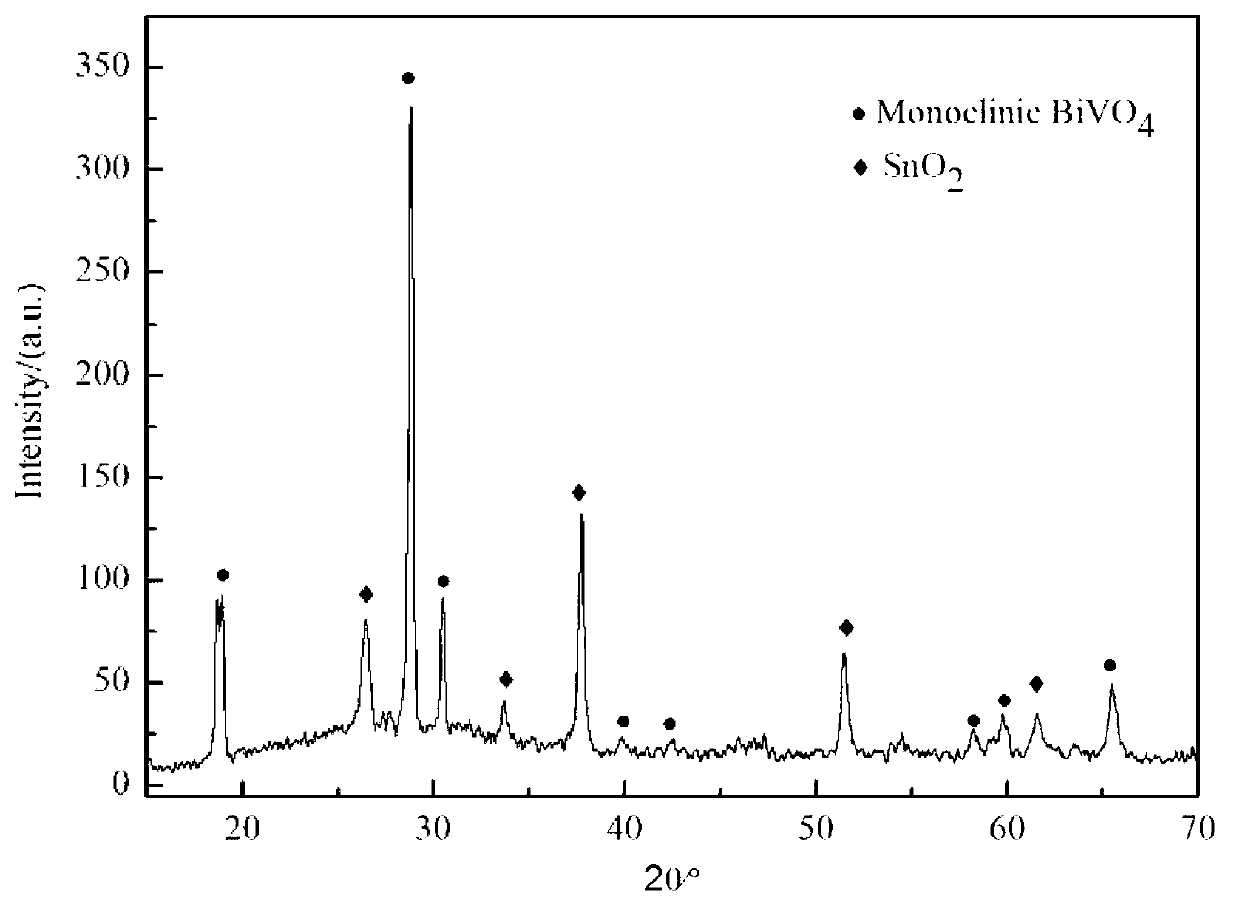
The invention discloses a method for preparing a BiVO4 film with photocatalysis performance by using a sol-gel method. The method comprises the following steps of: respectively preparing a precursor solution A and a precursor solution B by taking bismuth nitrate pentahydrate (Bi(NO3)3.5H2O) and ammonium metavanadate (NH4VO3) as raw materials and taking citric acid as a solvent, preparing BiVO4 sol by mixing the precursor solution A with the precursor solution B; and coating the BiVO4 sol to a treated FTO (Fluorine-doped Tin Oxide) glass substrate surface in a spinning manner by adopting a spin coating method so as to form a film, and carrying out pre-annealing and annealing treatment on the film formed after spin coating, thereby obtaining the BiVO4 film fixed on the FTO glass substrate surface. According to the method for preparing the BiVO4 film with the photocatalysis performance by using the sol-gel method, the pure-monoclinic-phase BiVO4 film is prepared by combing the sol-gel method with the spin coating method, the prepared BiVO4 film has certain photocatalysis activity under visible light irradiation, meanwhile, the problem of immobilization of a BiVO4 photocatalyst is solved, and then, the separation, recovery and reuse of the BiVO4 photocatalyst are realized.
Owner:盐城市鹤业实业投资有限公司
Hard pellicle and fabrication thereof
InactiveUS20050025959A1Improve transmittanceHigh laser stabilityPicture framesVacuum evaporation coatingEngineeringSilicon oxide
Disclosed are thin hard pellicle for projection photolithography and process for making the same. The thin hard pellicle comprises a pellicle layer having a thickness in the range of about 5 to 120 μm and a mount frame attached to the peripheral area of a surface of the pellicle layer. The pellicle layer can consist essentially of a material selected from silica, fluorine doped silica, aluminum doped silica, methylated silica, fluorinated and methylated silica, fluorinated aluminum doped silica, CaF2, MgF2, BaF2 and SiC. The mount frame is preferred to have substantially the same CTE of the pellicle layer to minimize stress caused by temperature change. The process for making the hard pellicle involves ion implantation of a silicon wafer, deposition of the pellicle layer on the silicon wafer, mounting the frame to the pellicle layer and the separation of the pellicle from the wafer by heat treatment.
Owner:CORNING INC
Bending-resistant multi-mode fiber
ActiveCN101840023AImprove mechanical propertiesFree from mechanical damageGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberRefractive index
The invention relates to a bending-resistant multi-mode fiber used in an access network or a miniature optical device. The bending-resistant multi-mode fiber comprises an optical fiber and a coating coated on the outer surface of the optical fiber, wherein the fiber consists of a quartz glass core layer which has a section structure with a parabolic shape or step-type refraction index and a quartz glass cladding which surrounds the core layer. The optical fiber is characterized in that: the core layer has a diameter of between 20 and 200 mu m and consists of a germanium-and-fluorine-doped quartz glass material; and double solidified polymer coatings are coated out of the cladding, wherein an inner coating coated on the outer surface of the cladding is a low-refraction index flexible polymer coating while an outer coating is a high-Young's modulus polymer coating. Because of the design of the low-refraction index inner coating, an internal stress of the optical fiber is avoided, the mechanical performance of the optical fiber is greatly improved, and the use performance and the service life of the optical fiber working in a small-radius bending state are ensured. The bending-resistant multi-mode fiber has high bending-resistant performance; and at a wavelength of 850 nm, the additional attenuation of the bending caused by winding 1 circle with a bending radius of 10 mm is less than or equal to 0.15 dB. The bending-resistant multi-mode fiber has the characteristic of simple, convenient and effective manufacturing method, and is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:EVERPRO TECH COMPANY
Glass article having a solar control coating
InactiveUS6858306B1High degreeReduce the amount requiredMirrorsOptical filtersLow emittanceEmissivity
A glass article having a solar control coating is disclosed for use in producing heat reducing glass especially for use in architectural windows. The coated article includes a glass substrate, a coating of an antimony doped tin oxide deposited on and adhering to the glass substrate and a coating of fluorine doped tin oxide deposited on and adhering to the surface of the coating of antimony doped tin oxide. The low emittance of the coated glass article, when combined with the surprisingly selective solar absorption of the multilayer stack provides improved heat rejection in summer and heat retention in winter, while permitting the transmittance of a relatively high degree of visible light.
Owner:PILKINGTON NORTH AMERICA INC +1
Anode active substance for lithium ion battery and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103928672AStable structureImprove electrochemical performanceCell electrodesSecondary cellsPower flowPhysical chemistry
The invention provides an anode active substance for a lithium ion battery and a preparation method thereof. The anode active substance is fluorine-doped Li2MnO3; the composition formula is Li2MnO3-xFx and x is more than or equal to 0.03 and less than or equal to 0.12. The preparation method is simple; according to the battery produced by the preparation method, the first-time specific discharge capacity is 172.4-209.1mAh / g when the current density is 5mA / g, and keeps 112.7-139.9mAh / g after 20 times of cycles; the retention rate is 58.6-66.9%.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
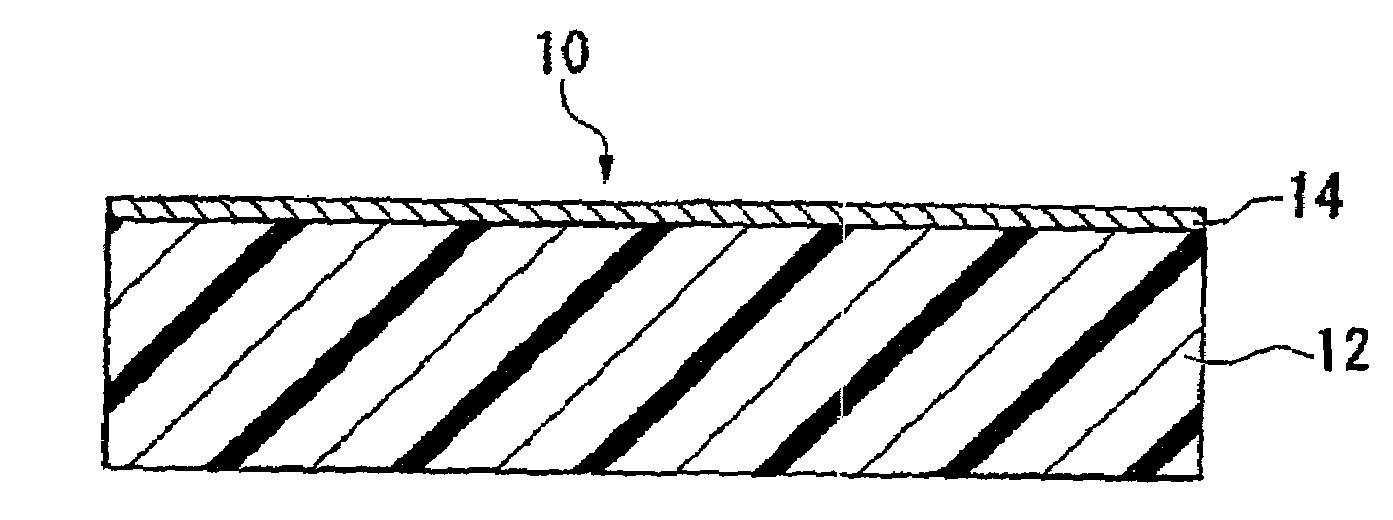
Ethylene/tetrafluoroethylene copolymer molded product and method for its production
ActiveUS20090214801A1Highly hydrophilic surfaceGood light transmissionLiquid surface applicatorsChemical vapor deposition coatingSilicon tetrafluorideSilicon oxide
To provide an ethylene / tetrafluoroethylene (ETFE) copolymer molded product of which the surface has a high hydrophilicity and which is excellent in the light transmission property; and a method for producing the molded product.A method for producing an ETFE copolymer molded product comprising a substrate 12 made of a material containing at least 50 mass % of an ETFE copolymer, and a fluorine-doped silicon oxide film 14 formed on the surface of the substrate 12, characterized by supplying electric power between electrodes so that the electrical power density between the electrodes becomes from 0.5 to 1.1 W / cm3 to cause discharge and thus to plasmatize the following mixed gas so as to form the silicon oxide film 14 on the substrate 12: Mixed gas comprising silicon tetrafluoride, oxygen and a hydrocarbon, wherein the atomic ratio of oxygen atoms to carbon atoms (O / C) is from 1 to 10, and the atomic ratio of oxygen atoms to silicon atoms (O / Si) is from 1.7 to 25.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Dual work function metal gate structure and related method of manufacture
A semiconductor device and related methods of manufacture are disclosed in which dual work function metal gate electrodes are formed from a single metal layer by doping the metal layer with carbon and / or fluorine.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Tungsten trioxide nano-film with photocatalytic performance, and preparation method thereof
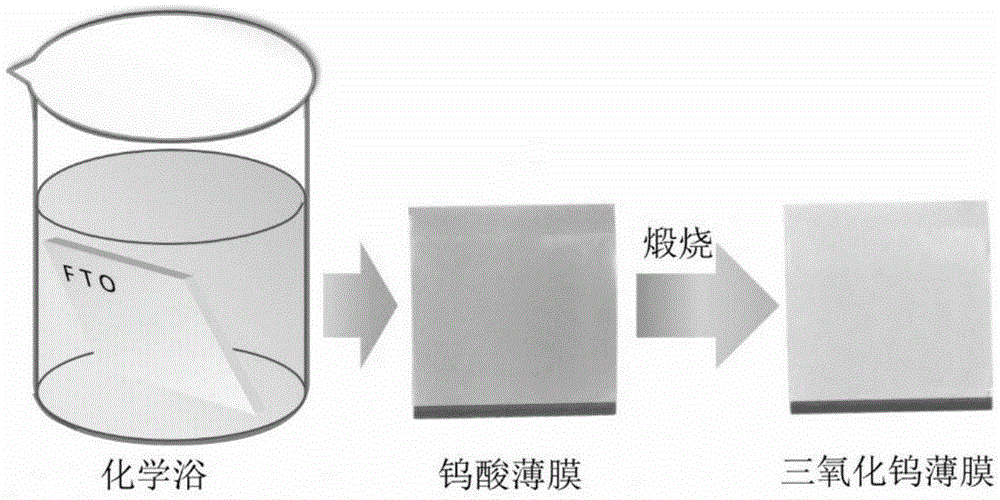
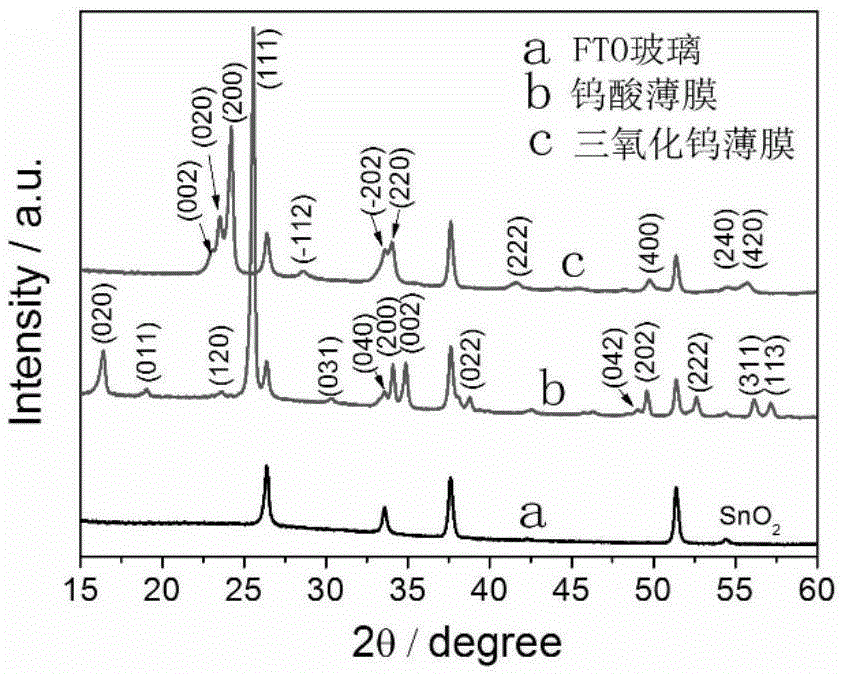
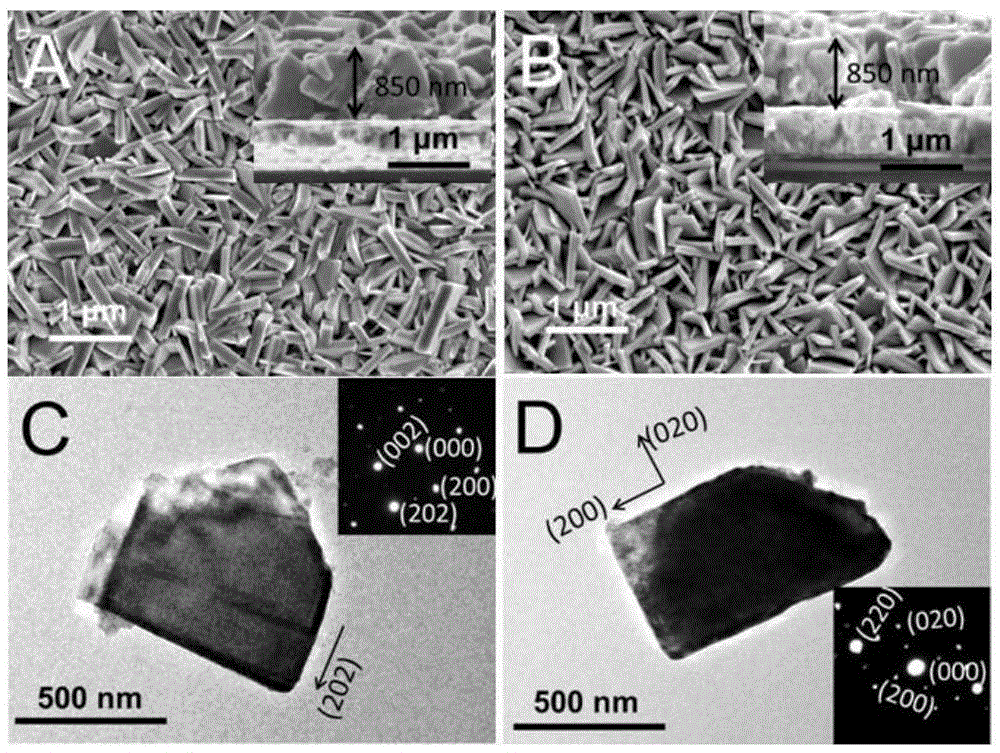
ActiveCN103708559ALarge specific surface areaIncrease profitMaterial nanotechnologyTungsten oxides/hydroxidesNanopillarPhotocatalytic water splitting
The invention discloses a tungsten trioxide nano-film with photocatalytic performance, and a preparation method thereof. The tungsten trioxide nano-film is characterized in that a WO3 nano layer with a WO3 nano structure is grown on a WO3 crystal seed layer, and the WO3 nano structure is shaped like a two-dimensional flying saucer including a middle main sheet and a nano-column. The preparation method of the tungsten trioxide nano-film comprises the steps of preparing a tungsten acid crystal seed layer precursor solution, preparing FTO (Fluorine-doped Tin Oxide) conductive glass with the crystal seed layer, preparing thermal tungsten acid solvent precursor solution, and finally performing hydrothermal synthesis to obtain the tungsten trioxide nano-film. According to the tungsten trioxide nano-film with photocatalytic performance, and the preparation method thereof, the specific surface area of the WO3 nano layer can be effectively enlarged; the efficiency of photocatalytic water splitting can be improved, the performance of photocatalytic water splitting in a photoelectric chemical pool is excellent, and excellent chemical stability can be achieved, the preparation method is simple, and the low-cost and large-scale application can be realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Water-based transparent heat-insulating paint used for energy-saving doors and windows and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103351757AReduce usageRich varietyPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsWater basedAluminum doped zinc oxide
The invention discloses a water-based transparent heat-insulating paint used for energy-saving doors and windows. The paint comprises the following components by weight: 50 to 60% of an aqueous base latex, 20 to 30% of aqueous nanometer heat-insulating slurry, 0.5 to 1% of a defoaming agents, 1 to 5% of a thickening agent, 0.5 to 1% of a film forming auxiliary agent and 0.5 to 1% of a leveling agent, with the balance being deionized water, wherein the aqueous base latex is an aqueous acrylic resin emulsion with solid content of 30 to 60 wt% or an aqueous polyurethane resin emulsion with solid content of 30 to 60 wt%, and the aqueous nanometer heat-insulating slurry contains the two functional particles consisting of fluorine-doped tin oxide and aluminum-doped zinc oxide. The invention further discloses a preparation method for the paint. The paint prepared in the invention can be coated on the surface of door and window glass to form a transparent film; and the film can absorb the vast majority of ultraviolet light and obstruct more than 60% of infrared light and has average transmittance of more than 70% in a visible light area.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method and application research of WO3 nanosheet array film
InactiveCN105384358AThe preparation process is simpleThe preparation process is mildCoatingsWater bathsLight response
The invention discloses a preparation technology of a visible-light response WO3 nanosheet array film electrode. The preparation technology comprises the following steps that Na2WO4.2H2O and ammonium oxalate are dissolved in deionized water to react with hydrochloric acid to obtain tungstic acid precipitates, and the tungstic acid precipitates react with H2O2 to obtain a clear peroxotungstic acid solution; an ethyl alcohol reducing agent is added into the peroxotungstic acid solution, fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) conducting glass serves as a substrate to be placed in the solution, under the water bath condition, the peroxotungstic acid is slowly reduced into tungstic acid, the tungstic acid is slowly separated out on an FTO film, and then a tungstic acid film is obtained; after being cleaned and dried, the tungstic acid film is calcined to obtain the WO3 nanosheet array film electrode. The preparation technology has the advantages of being simple, convenient, mild, efficient and suitable for large-scale preparation. The prepared WO3 nanosheet array film electrode has the good visible-light absorption property and good stability and is high in photoelectric efficiency, good in photoelectrocatalytic degradation effect on organic matter and capable of being applied to the fields of photoelectrocatalysis hydrogen production and organic matter degradation, and the better effect is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Polarization maintaining optical fiber with small bending radius and manufacture method of polarization maintaining optical fiber
ActiveCN103018821AImprove bending resistanceReduce disturbanceGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with polarisationInformation transmissionPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
The invention discloses a polarization maintaining optical fiber with a small bending radius and a manufacture method of the polarization maintaining optical fiber and relates to the field of optical fiber manufacture. The polarization maintaining optical fiber comprises a silica cladding, a core layer, a second silica cladding ring, a third fluorine-doped silica cladding ring and two stress cat eyes are sequentially arranged in the silica cladding from inside to outside, and the two stress cat eyes are in central symmetry with the core layer. By means of the manufacture method, the bending radius of the manufactured polarization maintaining optical fiber is smaller than 5mm, operating wavelength of the polarization maintaining optical fiber is 1550nm, and supplementary deterioration of the polarization maintaining optical fiber is under 0.4dB / km. According to the polarization maintaining optical fiber, under the condition that the bending radius is small, low-loss information transmission of the polarization maintaining optical fiber is achieved, low supplementary deterioration and good crosstalk characteristics of the polarization maintaining optical fiber are guaranteed, fiber optic sensors with small sizes can be manufactured by means of the polarization maintaining optical fiber, and requirements of users are satisfied.
Owner:RUIGUANG TELECOMM TECH CO LTD
Surfacing of metal fluoride excimer optics
ActiveUS7128984B2Natural mineral layered productsWater-setting substance layered productSingle crystalPrism
The invention is directed to improved coated metal fluoride single crystal optical elements suitable for use in below 250 nm optical lithography, and particularly below 200 nm lithography. The coated elements of the invention can be lenses, windows, prisms and other elements used in lithographic methods, including the laser sources used therein. The invention is also directed to a method of removing the quasi-Bielby layer formed when a shaped optical element is polished. Removal of the quasi-Bielby layer prior to coating results in improved durability and optical transmission characteristics of the coated lenses. The coating material can be any material that does not impede the transmission of below 250 nm electromagnetic radiation. Fluorine doped silicon dioxide is the preferred coating material.
Owner:CORNING INC
Nanoparticle Electrodes and Methods of Preparation
The present invention provides an electrode which comprises (a) a supporting substrate, and (b) nanoparticle composition comprising optically transparent conductive nanoparticles. In one embodiment, the nanoparticles are selected from tin-doped indium oxide (ITO), fluorine doped tin oxide (FTO), antimony tin oxide (ATO), gallium zinc oxide (GZO), indium zinc oxide (IZO), copper aluminum oxide, fluorine-doped zinc oxide and aluminum zinc oxide (AZO) nanoparticles and combinations thereof. In one embodiment, the electrode further comprises a transition metal catalyst, and the catalyst is absorbed to the surface of the nanoparticles. Another aspect of the invention relates to methods for preparing the electrode described herein which comprises the step of (1) preparing a suspension of nanoparticles; (2) applying the suspension of the nanoparticles to a support substrate; and (3) annealing the supporting substrate with the nanoparticle for a period of time and at a temperature sufficient to produce nanoparticle film on the electrode.
Owner:CORBEA JAVIER JESUS CONCEPCION +3
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com