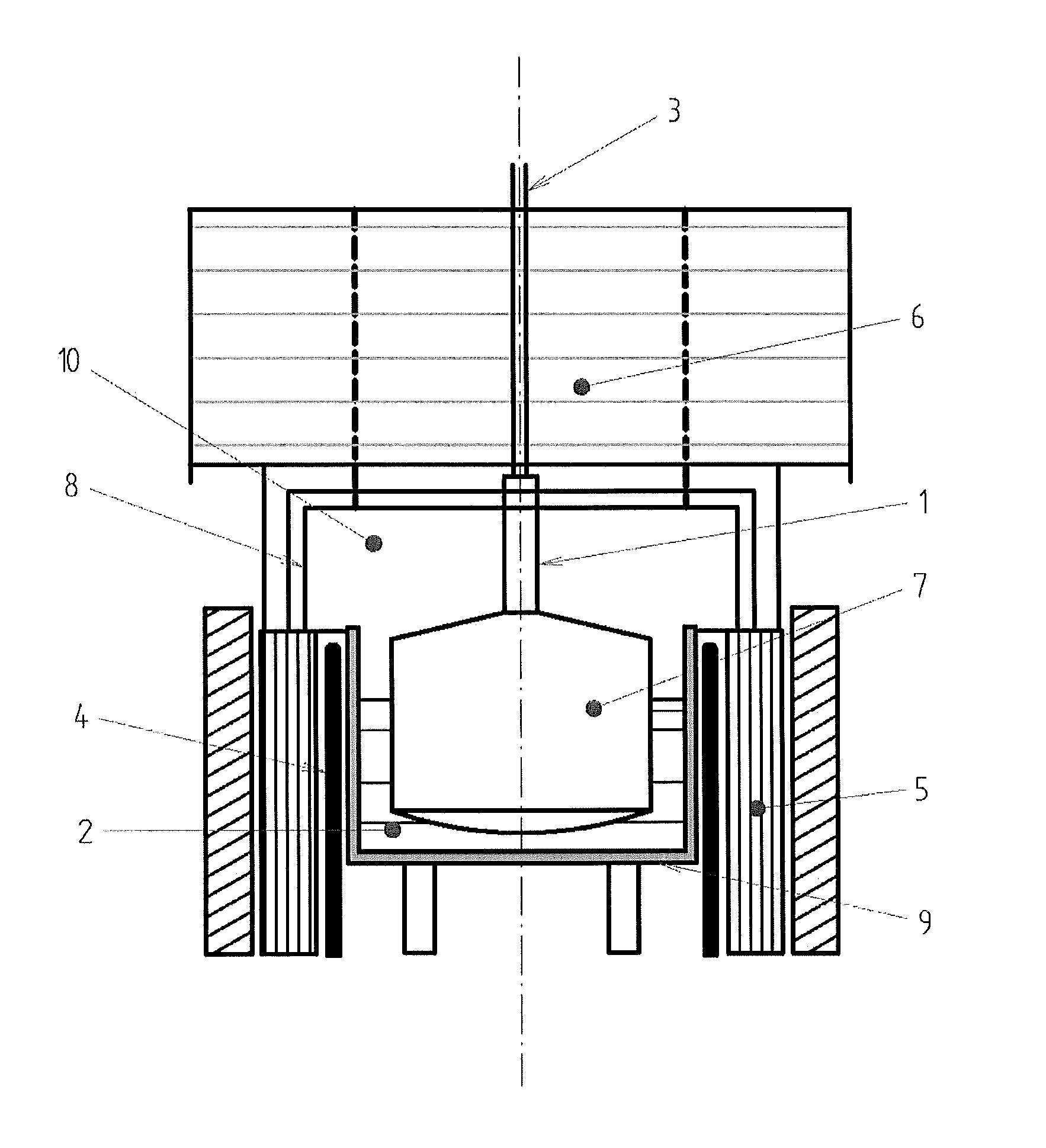
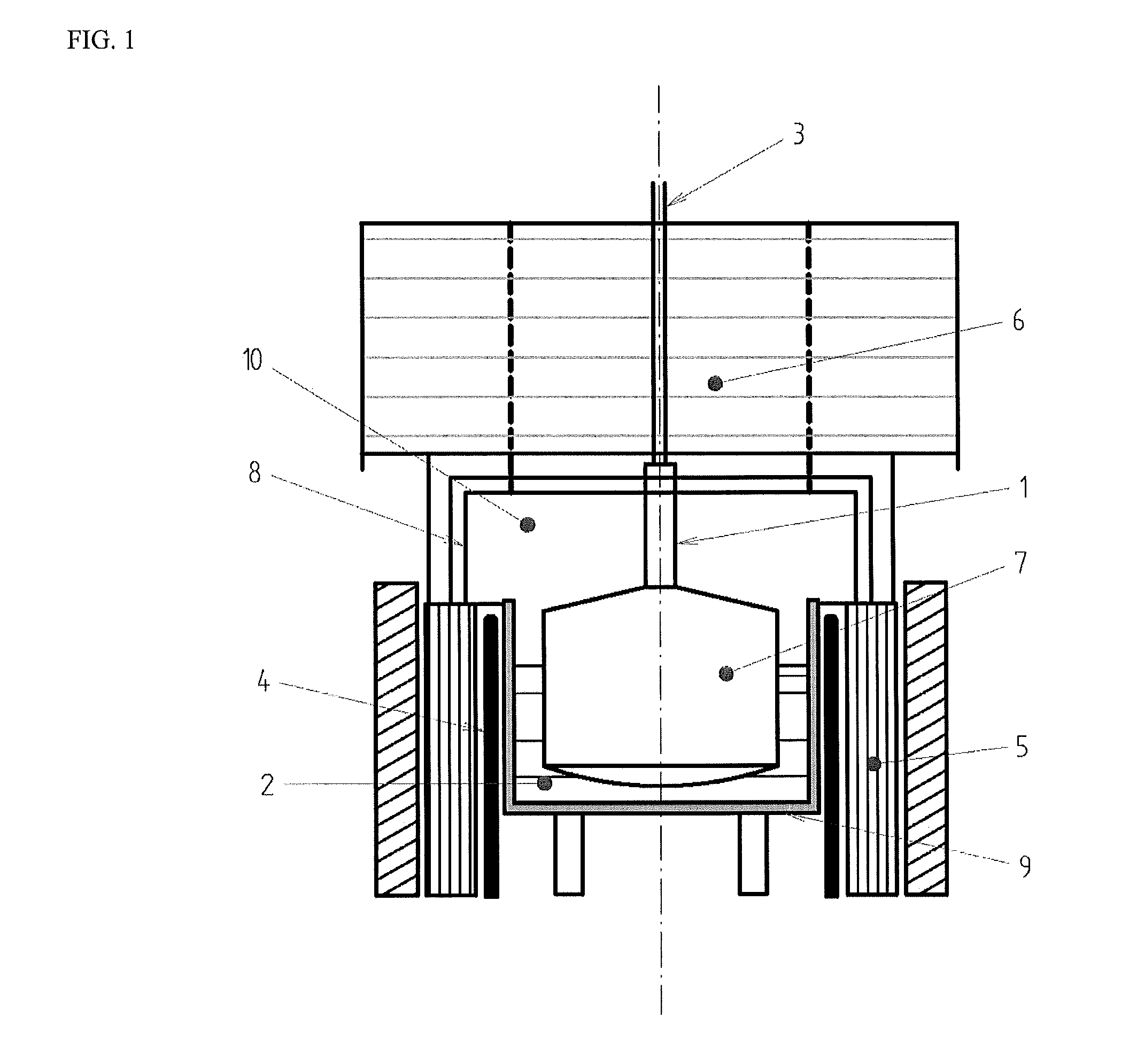
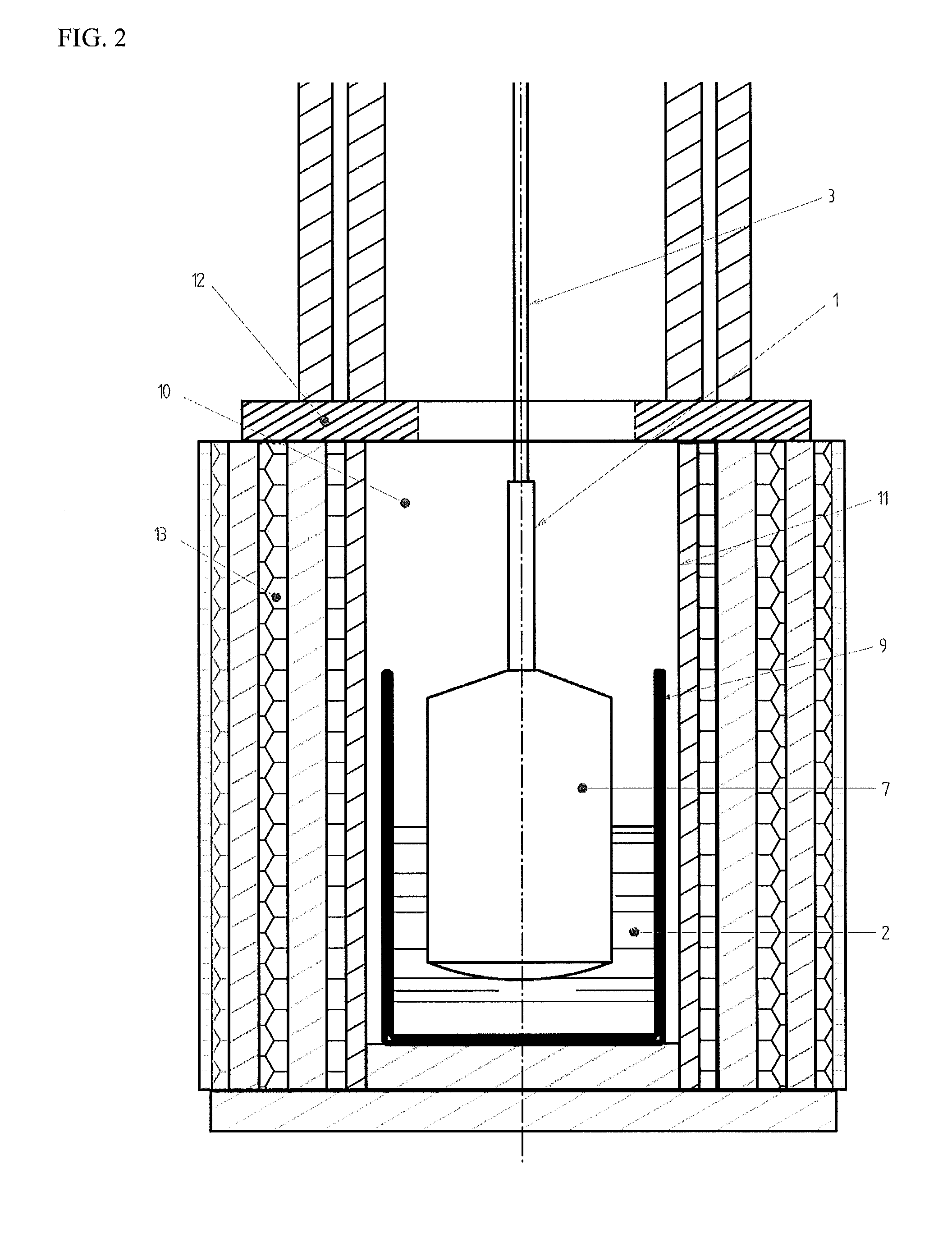
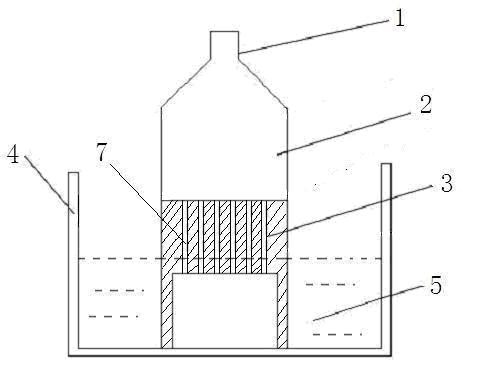
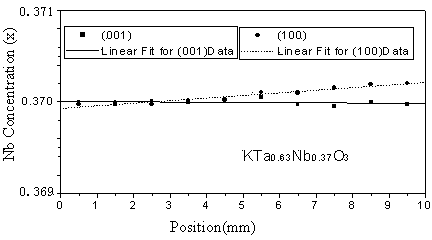
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
175 results about "Crystal growth rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
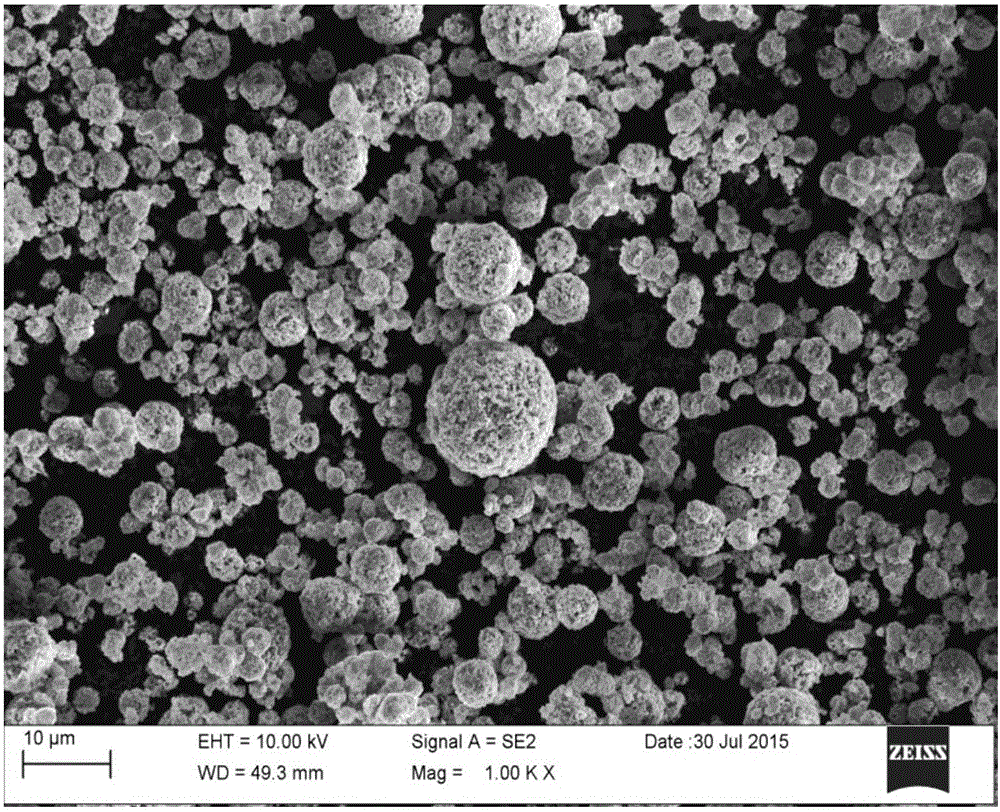
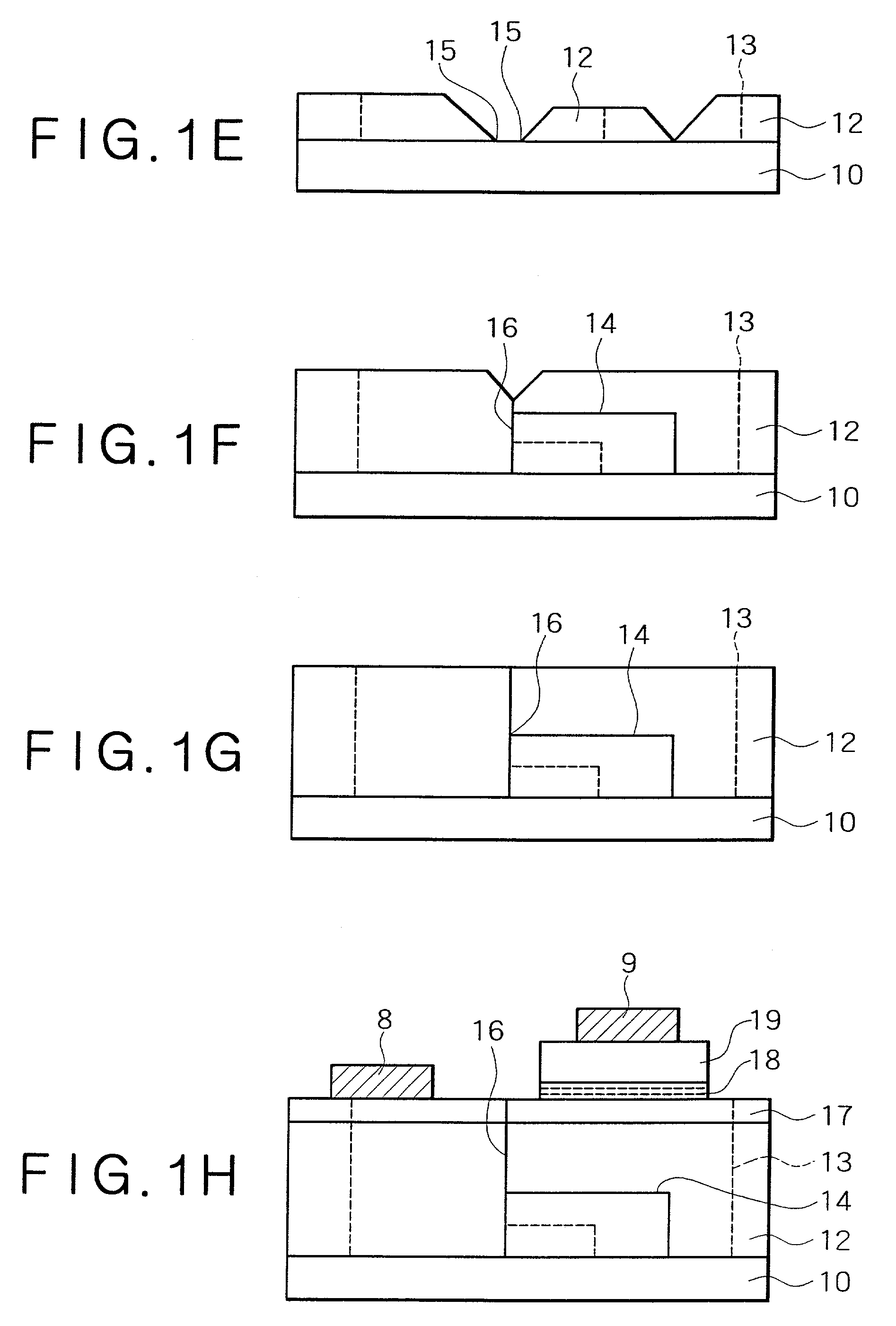
Method for producing nitride semiconductor, crystal growth rate increasing agent, single crystal nitride, wafer and device
InactiveUS20100104495A1Improve performanceIncrease probabilityPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsNitrogenCrystal structure
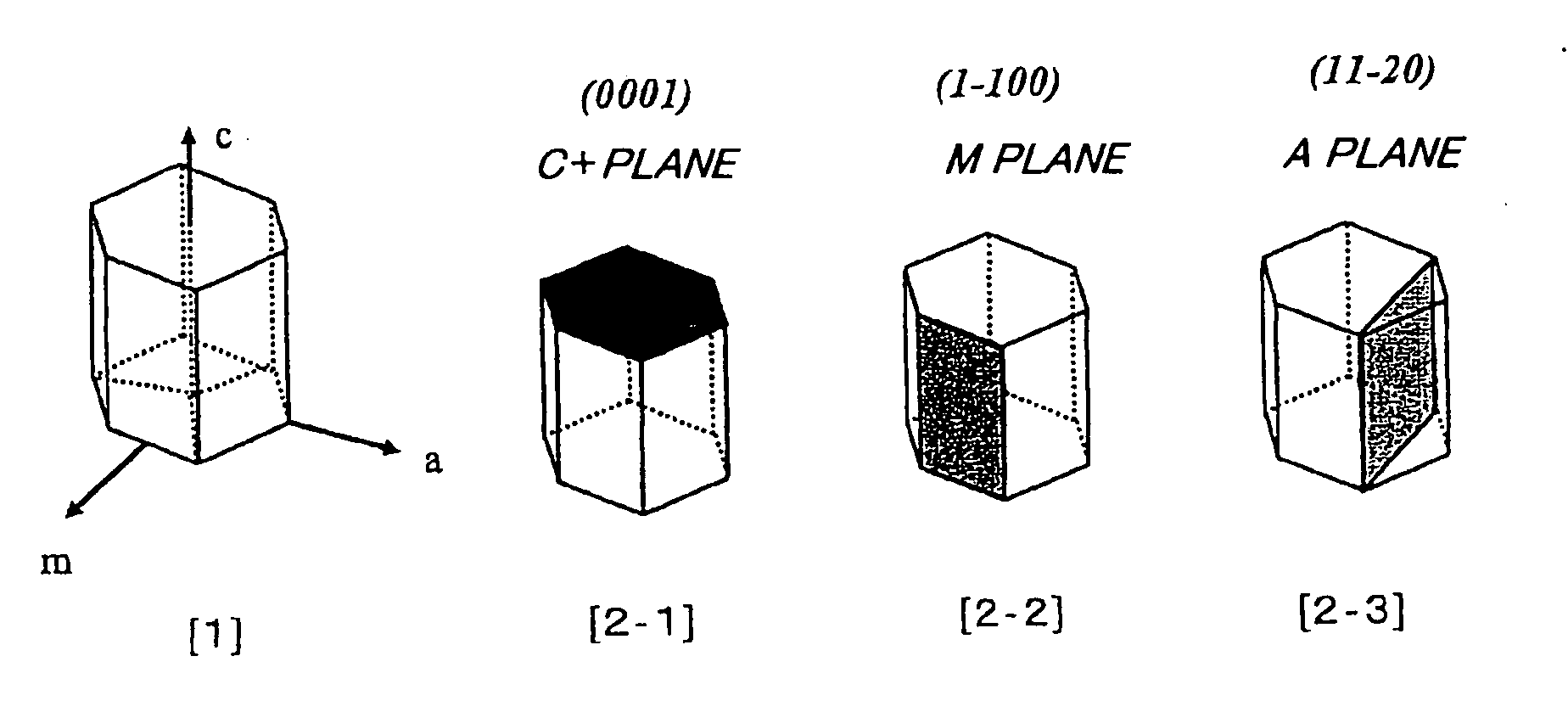
A method for producing a nitride semiconductor, comprising controlling temperature and pressure in a autoclave containing a seed having a hexagonal crystal structure, a nitrogen element-containing solvent, a raw material substance containing a metal element of Group 13 of the Periodic Table, and a mineralizer so as to put said solvent into a supercritical state and / or a subcritical state and thereby ammonothermally grow a nitride semiconductor crystal on the surface of said seed, wherein the crystal growth rate in the m-axis direction on said seed is 1.5 times or more the crystal growth rate in the c-axis direction on said seed. By the method, a nitride semiconductor having a large-diameter C plane or a nitride semiconductor thick in the m-axis direction can be efficiently and simply produced.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP +1
Crystal growth method for nitride semiconductor and formation method for semiconductor device
InactiveUS7033436B2Improving performance lifeExtended service lifePolycrystalline material growthLaser detailsSemiconductor materialsCrystal growth rate
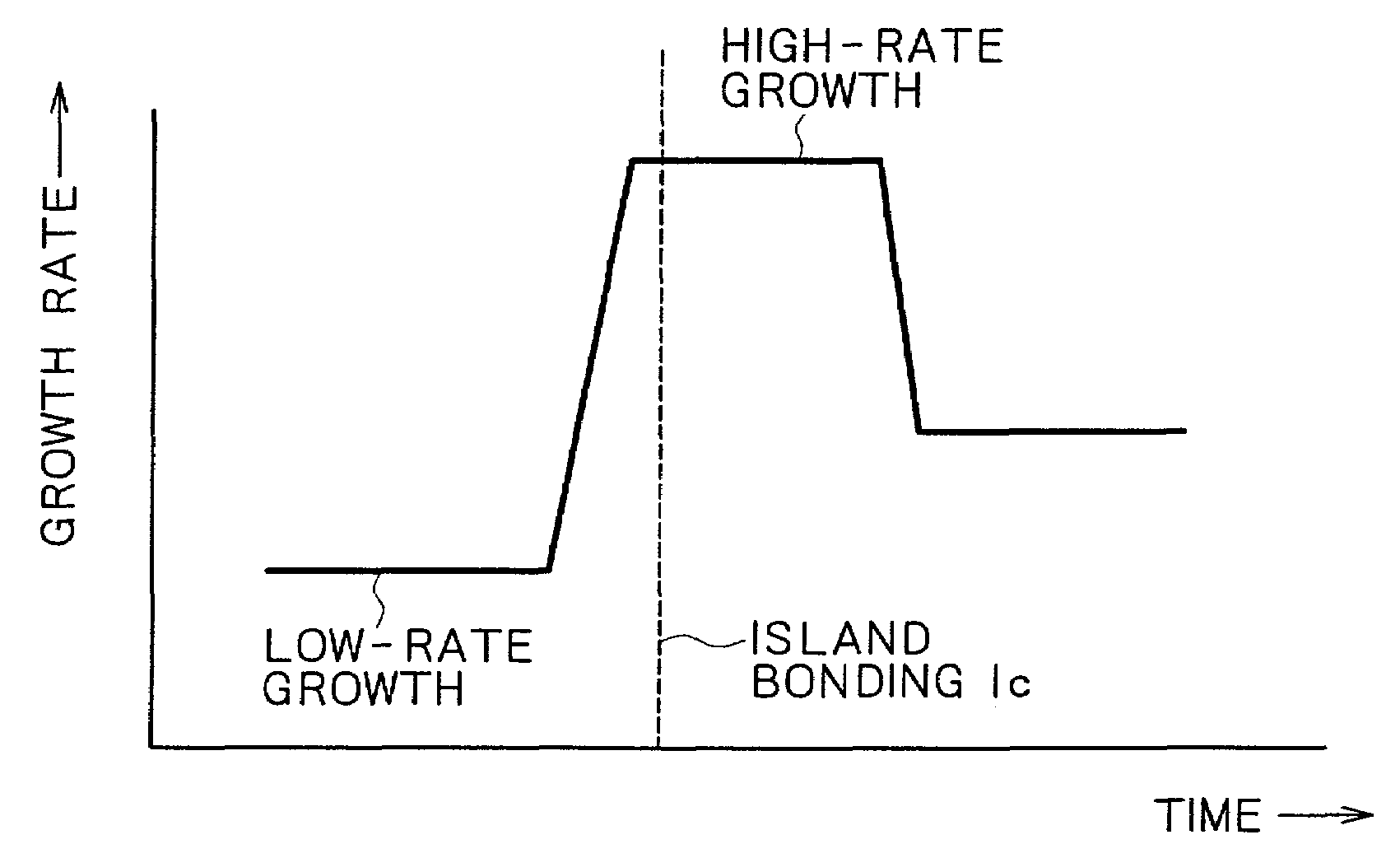
Methods of crystal growth for semiconductor materials, such as nitride semiconductors, and methods of manufacturing semiconductor devices are provided. The method of crystal growth includes forming a number of island crystal regions during a first crystal growth phase and continuing growth of the island crystal regions during a second crystal growth phase while bonding of boundaries of the island crystal regions occurs. The second crystal growth phase can include a crystal growth rate that is higher than the crystal growth rate of the first crystal growth phase and / or a temperature that is lower than the first crystal growth phase. This can reduce the density of dislocations, thereby improving the performance and service life of a semiconductor device which is formed on a nitride semiconductor made in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method of fabricating an implantable medical device by controlling crystalline structure
A method of fabricating an implantable medical device that includes deforming and heating setting a polymer construct, for use in fabricating the device, in a temperature range in which the crystal nucleation rate is greater than the crystal growth rate is disclosed.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
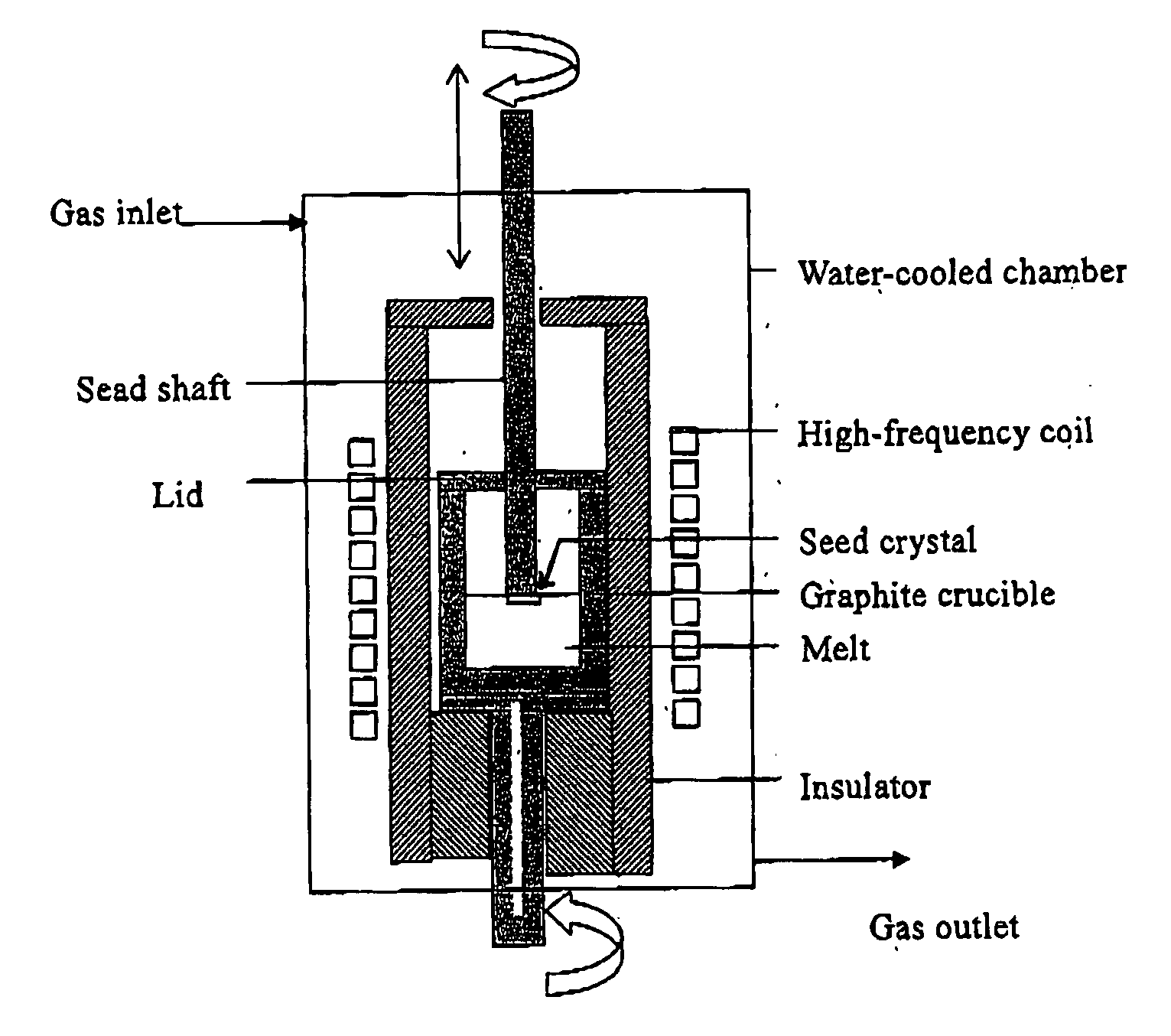
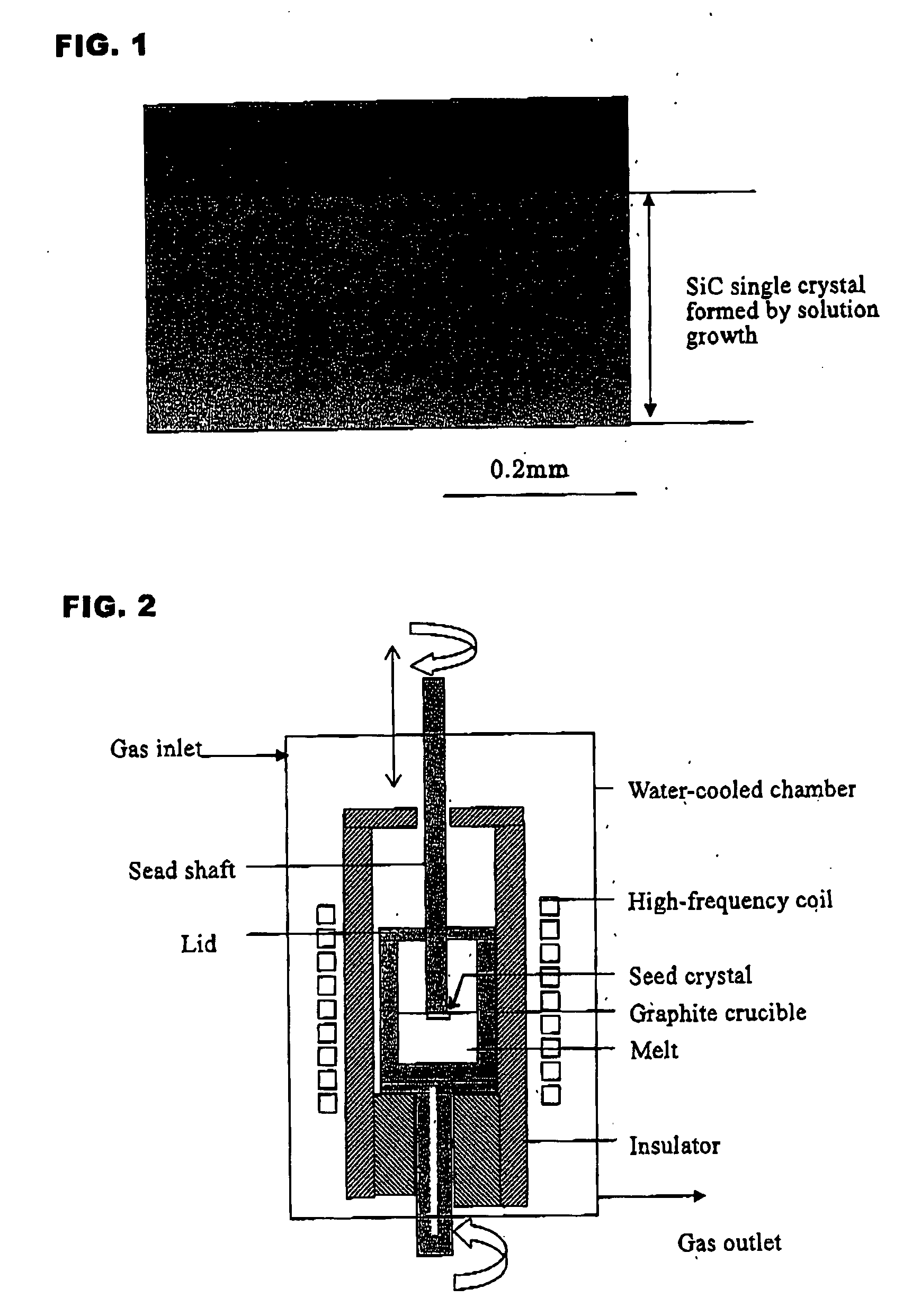
Method for preparing silicon carbide single crystal
InactiveUS20070209573A1Quality improvementIncrease speedAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthCrucibleAlloy
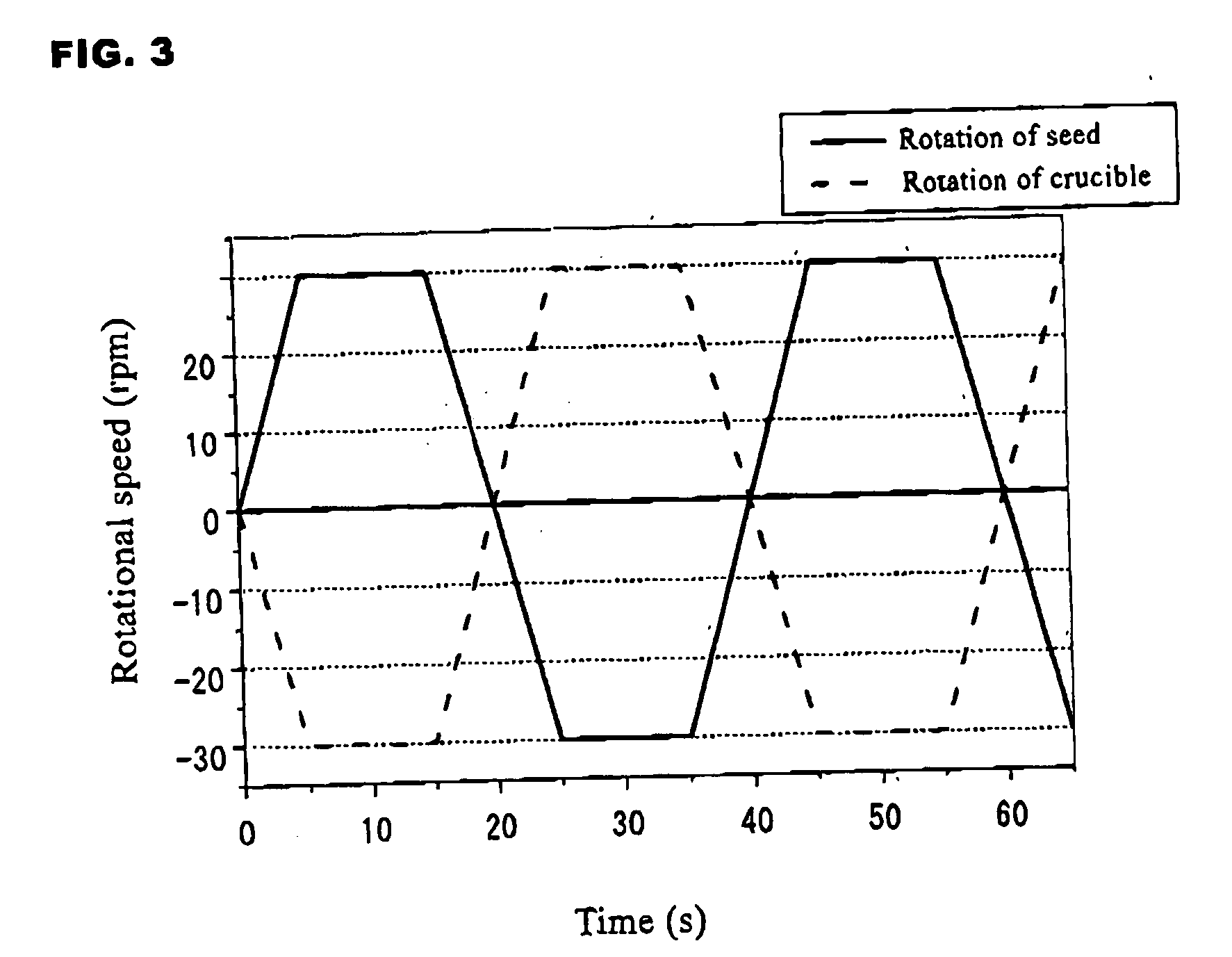
A SiC single crystal is produced by the solution growth method in which a seed crystal attached to a seed shaft is immersed in a solution of SiC dissolved in a melt of Si or a Si alloy and a SiC single crystal is allowed to grow on the seed crystal by gradually cooling the solution or by providing a temperature gradient therein. To this method, accelerated rotation of a crucible is applied by repeatedly accelerating to a prescribed rotational speed and holding at that speed and decelerating to a lower rotational speed or a 0 rotational speed. The rotational direction of the crucible may be reversed each acceleration. The seed shaft may also be rotated synchronously with the rotation of the crucible in the same or opposite rotational as the crucible. A large, good quality single crystal having no inclusions are produced with a high crystal growth rate.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Microwave synthesis process for ZSM-11 molecular sieve
InactiveCN101531376AIncrease growth rateHigh crystallinityPentasil aluminosilicate zeoliteCrystallinityCrystal growth rate
The invention relates to a microwave synthesis process for a ZSM-11 molecular sieve. The process uses aluminum source, alkali source, silicon source, tetrabutylammonium bromide and de-ionized water as the raw materials and adopts the heating mode of microwave radiation. The reaction mixture is crystallized for 1 to 8 hours under microwave radiation and self-generated pressure at 130 to 180 DEG C, solid is separated from the mother liquid, and then the product is washed by the de-ionized water until the pH value is 8 to 9, thus obtaining the raw powder of the ZSM-11 molecular sieve. The microwave synthesis process for the ZSM-11 molecular sieve has the advantages of replacing traditional water heating by microwave radiation heating and obtaining the ZSM-11 molecular sieve with the advantages of high crystallinity, pure crystal phase and controllable and wide range of grain size, and the process accelerates the nucleation rate and crystal growth speed obviously and shortens the crystallization time greatly by pre-placing crystal seeds.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Group III Nitride Crystal, Method of Its Manufacture, and Equipment for Manufacturing Group III Nitride Crystal
Affords Group III nitride crystals whose crystal growth rate is extensive, methods of their manufacture, and equipment for manufacturing such Group III nitride crystals. The manufacturing methods include: a melt-formation step, within a reaction vessel (21), of forming around a seed crystal (2) a melt (1) containing at least a Group III element and a catalyst; and a crystal-growth step of supplying a nitrogen-containing substance (3) to the melt (1) to grow a Group III nitride crystal (4) onto the seed crystal (2); characterized in controlling temperature so that in the crystal-growth step, the temperature of the melt (1) lowers from the interface (13) between the melt (1) and the nitrogen-containing substance (3), through to the interface (12) between the melt (1) and the seed crystal (2) or to the interface (14) between the melt (1) and the Group III nitride crystal (4) having grown onto the seed crystal (2).
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
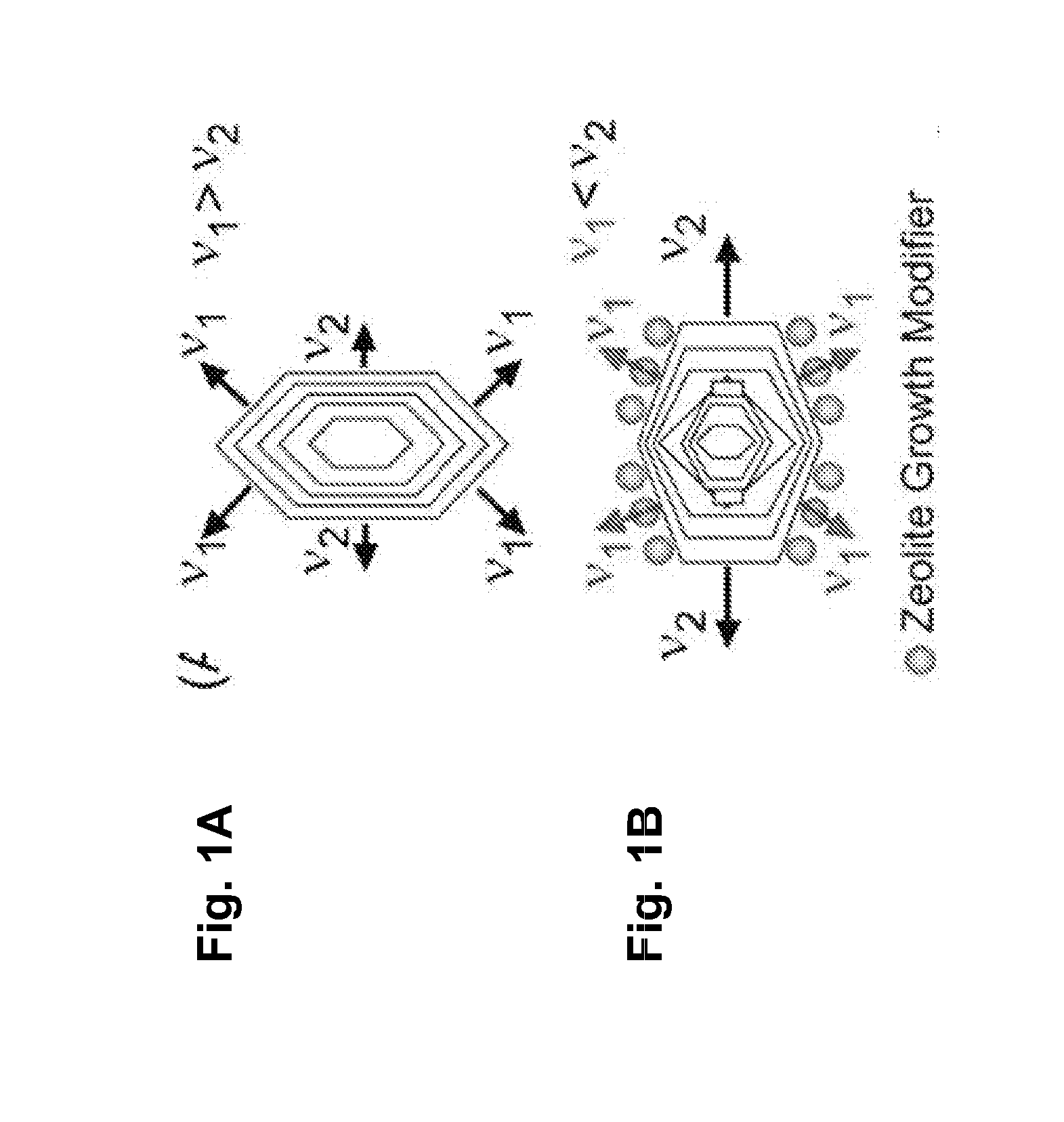
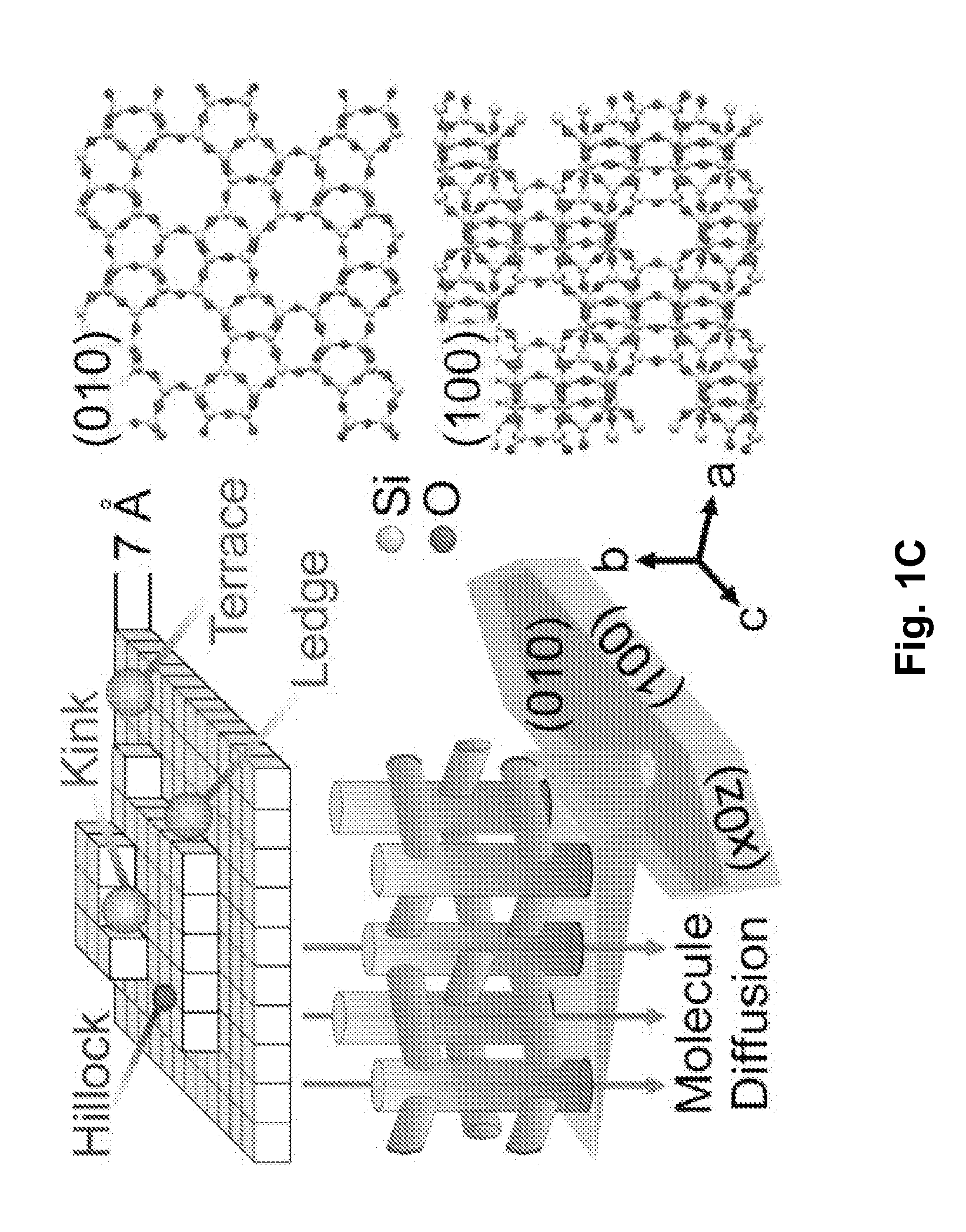
Zeolite compositions and methods for tailoring zeolite crystal habits with growth modifiers
InactiveUS20120202006A1Minimized crystal thicknessShortened internal diffusion pathlengthPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsCrystal habitCrystal growth rate
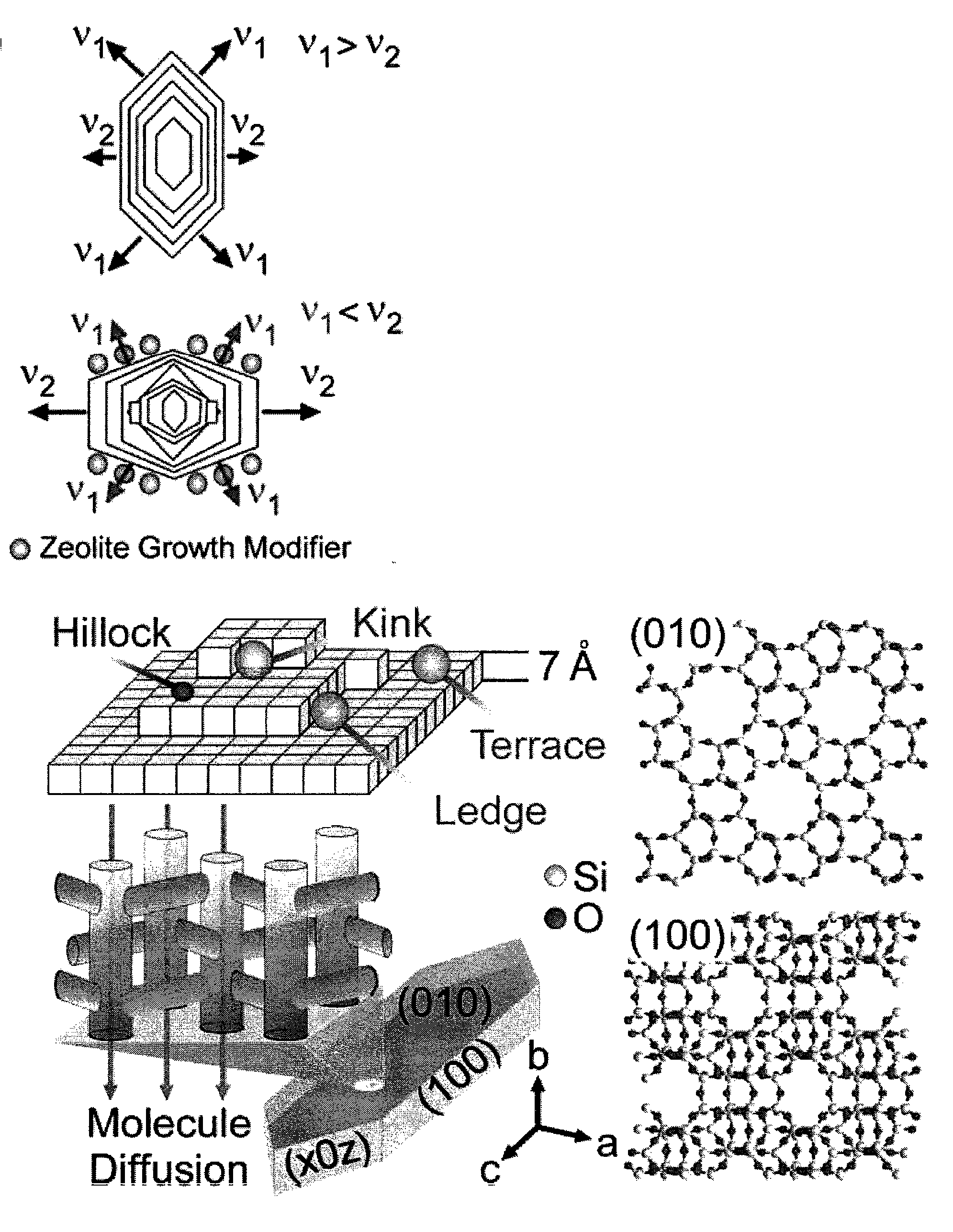
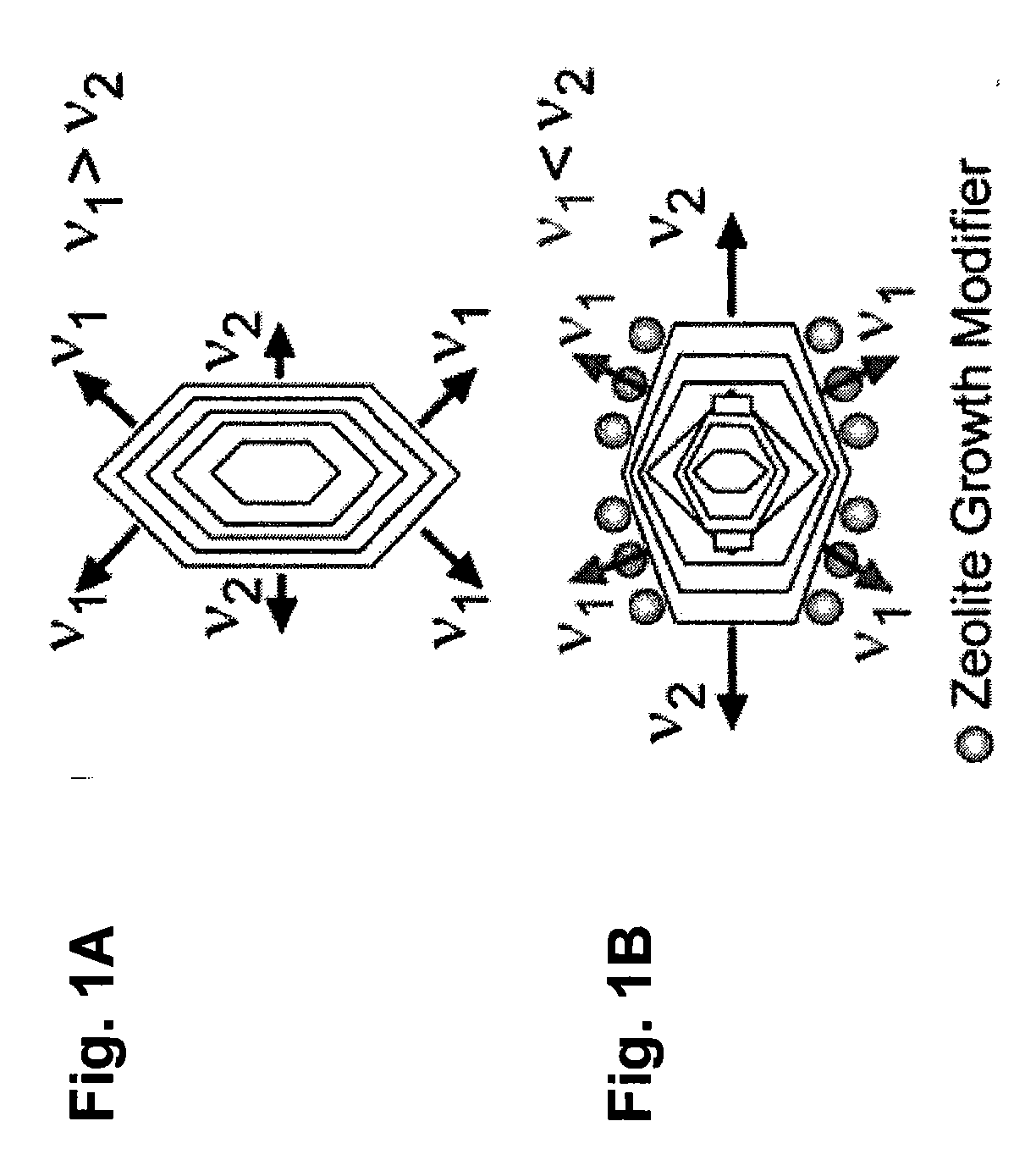
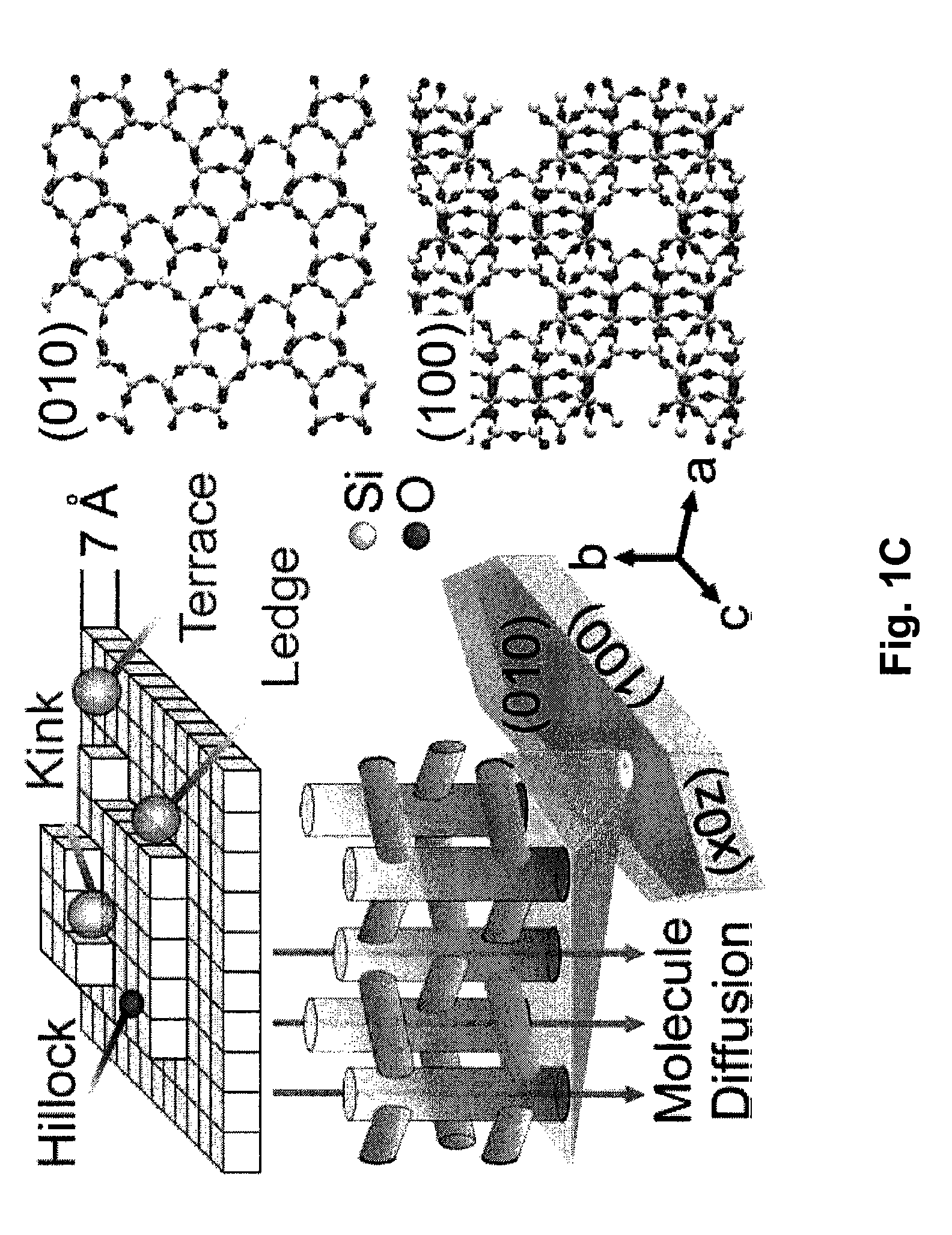
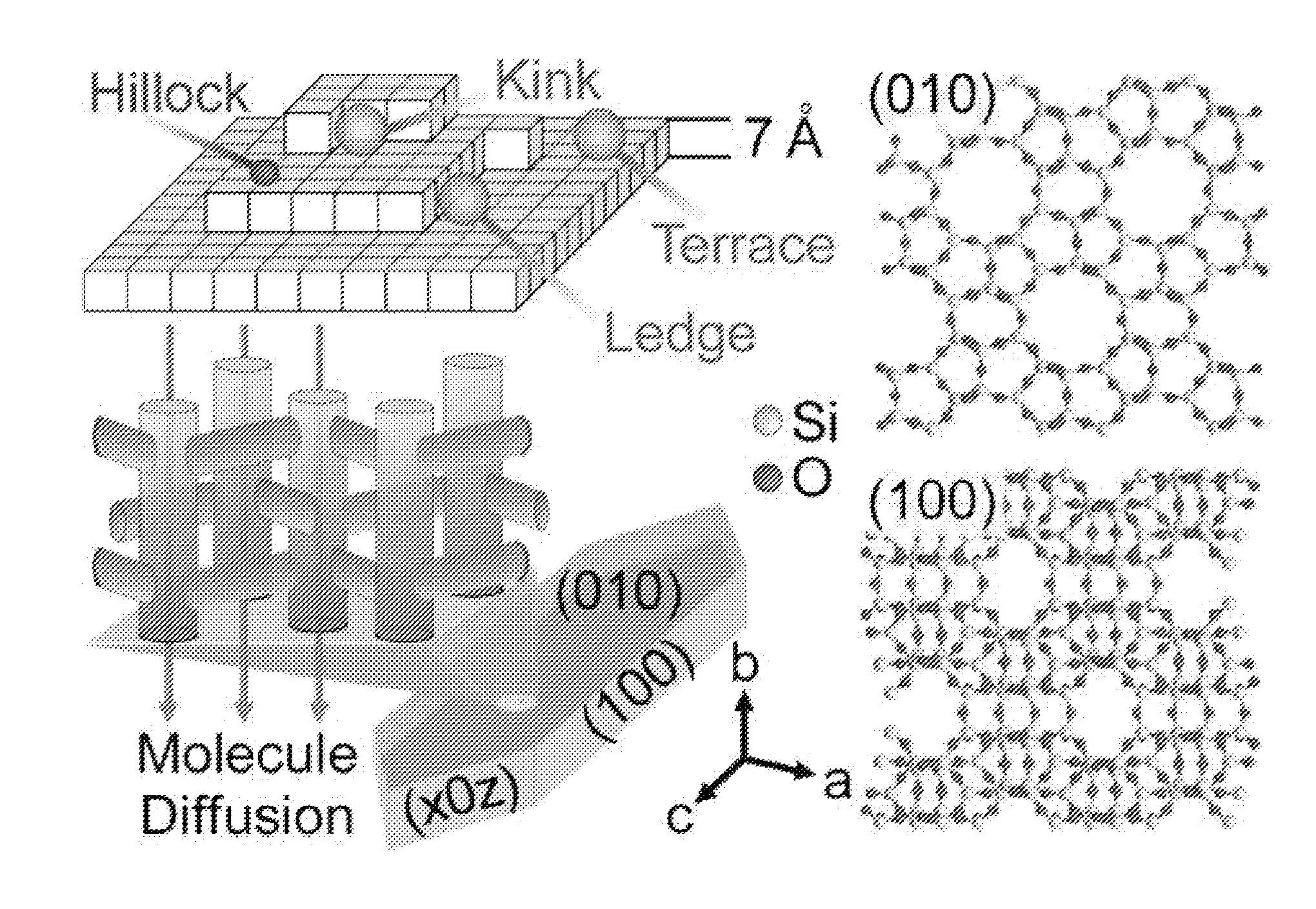
Embodiments of the invention generally provide compositions of crystalline zeolite materials with tailored crystal habits and the methods for forming such crystalline zeolite materials. The methods for forming the crystalline zeolite materials include binding one or more zeolite growth modifiers (ZGMs) to the surface of a zeolite crystal, which results in the modification of crystal growth rates along different crystallographic directions, leading to the formation of zeolites having a tailored crystal habit. The improved properties enabled by the tailored crystal habit include a minimized crystal thickness, a shortened internal diffusion pathlength, and a greater step density as compared to a zeolite having the native crystal habit prepared by traditional processes. The tailored crystal habit provides the crystalline zeolite materials with an aspect ratio of about 4 or greater and crystal surfaces having a step density of about 25 steps / μm2 or greater.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Control method of crystal growth by crystal pulling method
InactiveCN101392404AQuick responseGood isometric controlBy pulling from meltCzochralski methodEngineering
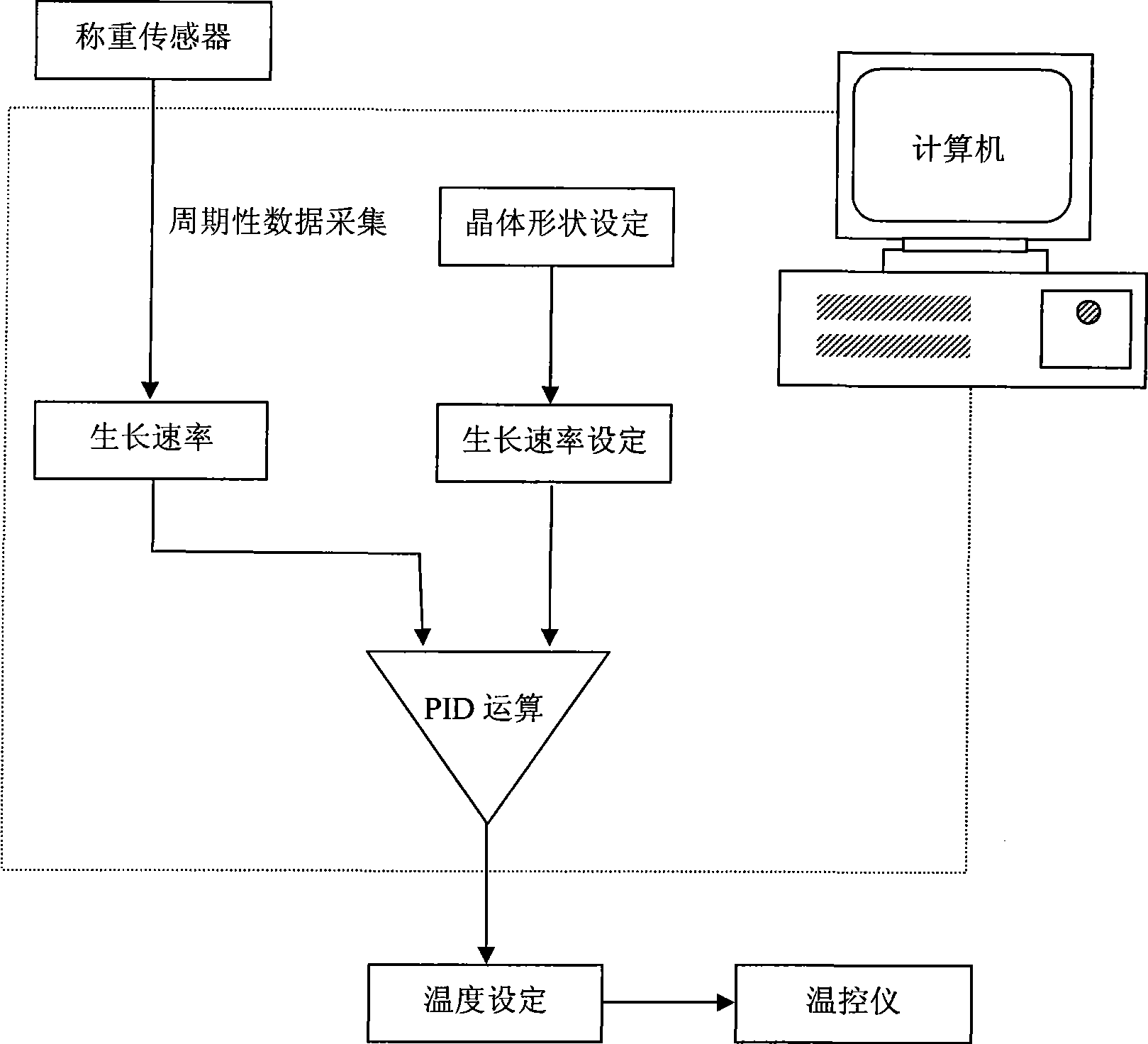
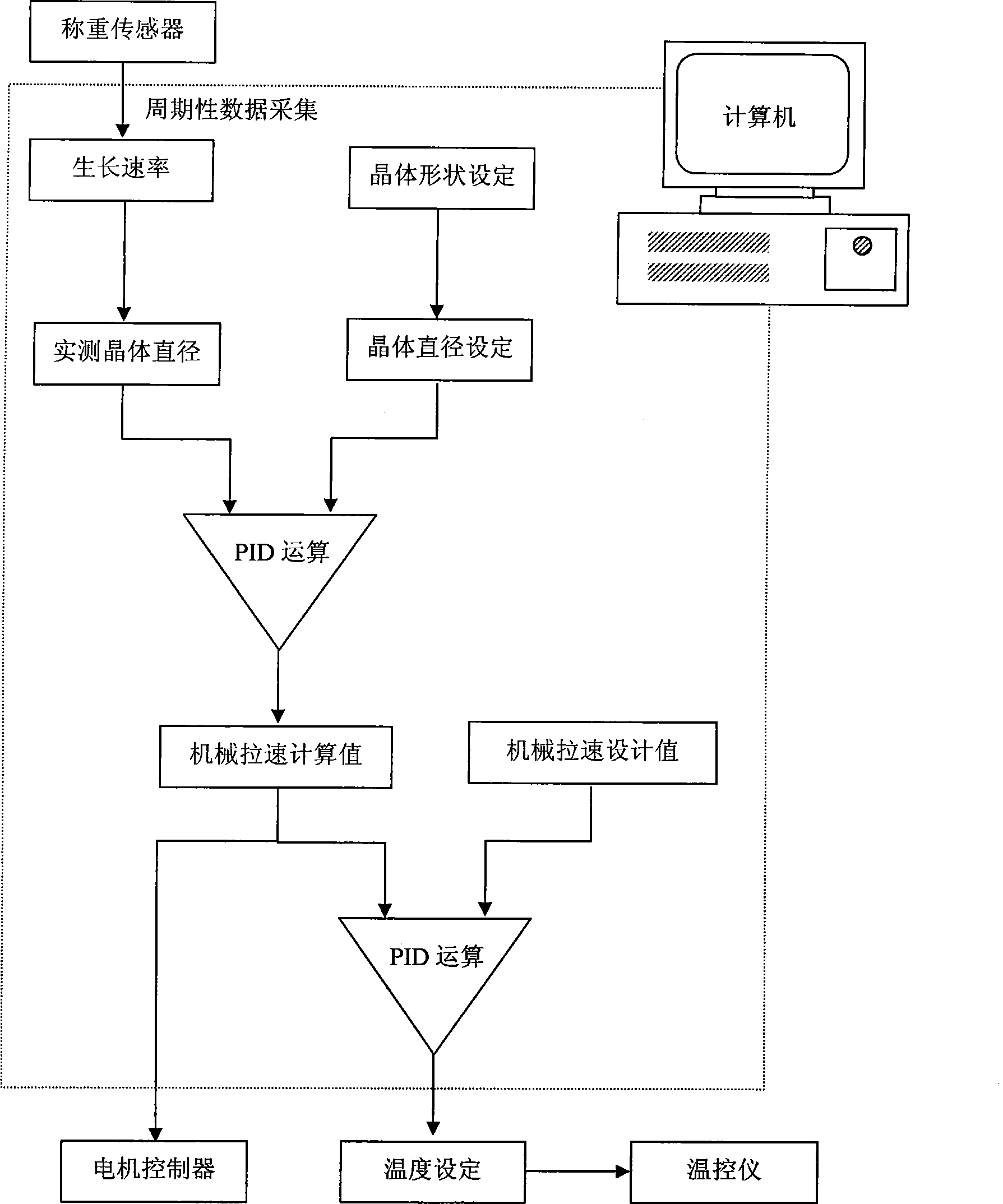
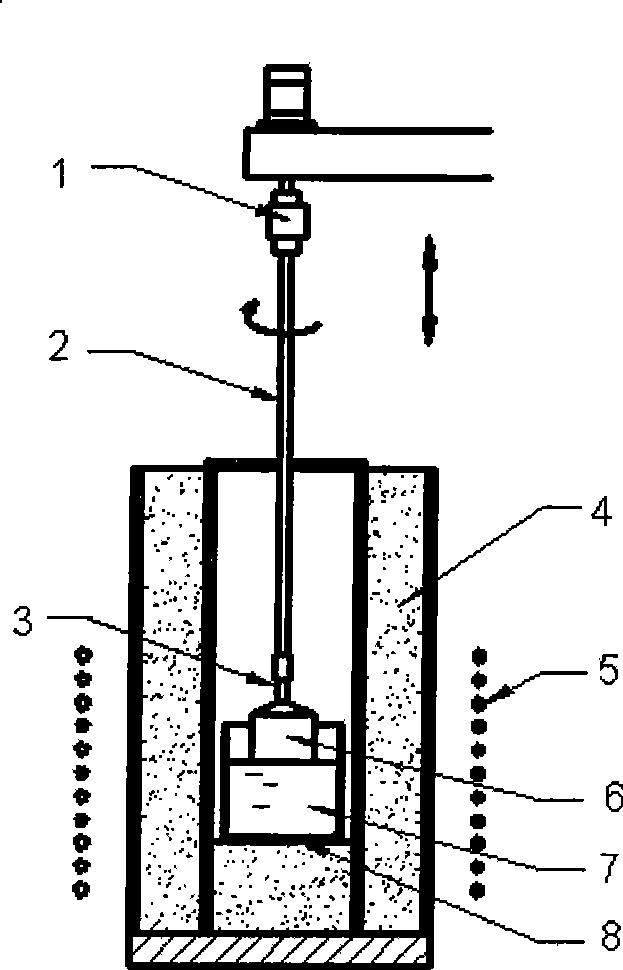
The invention relates to a control method for crystal growth by Czochralski method. A weight signal of a growing crystal is obtained by the sampling of a computer and is converted, according to a signal processing method, to a crystal diameter feedback signal independent of the growth rate; the crystal diameter feedback signal is compared with the preset crystal diameter value to acquire a signal error, and then the calculated value of a mechanical pulling speed for the control of a seed crystal is gained by the PID calculation of the signal error; the calculated value of the mechanical pulling speed is compared with the preset mechanical pulling speed value to get a new signal error, and the temperature (or power) is controlled through the PID calculation of the new signal error. The pulling speed is controlled by a primary control circuit while the temperature is controlled by a secondary control circuit; the constant diameter control of the growing crystal is realized by the synergism of the pulling speed circuit and the temperature circuit. The control method has the advantages of rapid response speed, good constant diameter control effect, smoother crystal surface, higher crystal growth rate and production efficiency, and the using of the control method is not affected by the material of the crystal and can be applied to most growing processes of Czochralski method.
Owner:惠梦君
Zeolite compositions and methods for tailoring zeolite crystal habits with growth modifiers
ActiveUS20150360964A1Minimized crystal thicknessShortened internal diffusion pathlengthIon-exchange process apparatusPolycrystalline material growthVolumetric Mass DensityCrystal habit
Embodiments of the invention generally provide compositions of crystalline zeolite materials with tailored crystal habits and the methods for forming such crystalline zeolite materials. The methods for forming the crystalline zeolite materials include binding one or more zeolite growth modifiers (ZGMs) to the surface of a zeolite crystal, which results in the modification of crystal growth rates along different crystallographic directions, leading to the formation of zeolites having a tailored crystal habit. The improved properties enabled by the tailored crystal habit include a minimized crystal thickness, a shortened internal diffusion pathlength, and a greater step density as compared to a zeolite having the native crystal habit prepared by traditional processes. The tailored crystal habit provides the crystalline zeolite materials with an aspect ratio of about 4 or greater and crystal surfaces having a step density of about 25 steps / μm2 or greater.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Method for purifying dodecanedioic acid
ActiveCN102329224ALow local supersaturationReduced nucleation rateCarboxylic compound separation/purificationCrystal growth rateMoisture
The invention discloses a method for purifying dodecanedioic acid, which comprises the following steps of: carrying out demulsification, filtration and decoloration on stop fermentation liquor of dibasic acid and adding pure water to dilute; adding purified water into a crystallization kettle, pumping diluted fermented clear liquid into a crystallizer, simultaneously filling dilute sulphuric acid with the mass concentration of 30 percent into a discharge hole of an external circulating pump and adding the dilute sulphuric acid into the crystallizer, and controlling the PH of reaction materials; ensuring crystal mush to flow to the lower part of a crystallization chamber through a central downcomer and then flow upwards, so that crystals with large granularities are enriched on the bottom layer of the crystallization chamber; and cooling the crystals outflowing from a discharge hole of the crystallizer by a cooler and carrying out filter pressing, washing and drying to obtain the dodecanedioic acid. Due to the adoption of the purifying method, the micro mixing effect is achieved by diluting local concentration of the reaction mass through the material circulating pump, the solution nucleation rate, the crystal growth rate and the aggregation rate are reduced, the moisture percentage and the impurity content of a filter cake are obviously reduced, the dried dibasic acid product has large and uniform particles, good glossy and high purify, and the continuity of the crystallizing process is realized.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for preparing SiC crystal and SiC crystal
InactiveUS7081420B2Reduce in quantityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle crystal substrateSingle crystal
A process for closing hollow-core defects, called micropipes, during growth by CVD of a SiC crystal on a SiC single crystal substrate having hollow-core defects, and a crystal obtained according to the process, by contacting the SiC crystal with a source gas adjusted to a C / Si atom ratio range in which the crystal growth rate is determined by the carbon atom supply limitation, then epitaxially growing and laminating a plurality of SiC crystal layers, wherein hollow-core defects in the SiC single crystal substrate dissociate into a plurality of dislocations given by small Burghers vector in order not to propagate to the crystal surface. In addition, the present invention provides a fabrication process of a SiC crystal, wherein a first SiC crystal is made as a buffer layer, and a further SiC crystal is layered thereon using a source gas adjusted to be higher than that of the C / Si ratio when forming the buffer layer, whereby a desired film property is conferred.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Growth early-stage control method of automatic photoelectric crystal furnace
InactiveCN101824649AFully automatedAvoid interferencePolycrystalline material growthTemperature controlControl system
The invention relates to a growth early-stage control method of an automatic photoelectric crystal furnace. The automatic photoelectric crystal furnace comprises a furnace body, a lifting rod, a heating module, a temperature measuring module, a temperature control module, a lifting module, a rotating module, a monitoring module and a control system. The method comprises the following steps: heating and smelting furnace body crystal materials; using the lifting rod for feeding crystals so that seed crystals on the lifting rod can go under the liquid level of the furnace body; entering a next step when the liquid absorbs the seed crystals; lifting and rotating the lifting rod to enter the neck reduction process; using the monitoring module for reading the weight of the rest seed crystals in the furnace body; lowering the heating temperature when the monitored crystal growth speed rate is a negative value; raising the heating temperature when the monitored crystal growth speed rate is a great positive value; completing the neck reduction process when a neck reduction part reaches the preset length; improving the growth speed rate of the crystals so that the diameter of the crystals becomes larger from a small value until the preset crystal diameter is reached; and completing the growth early stage.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Process for preparing molecular sieves via continuous addition of nutrients
A process for synthesizing a variety of molecular sieves has been developed. The process involves forming a reaction mixture comprising reactive sources of the framework elements plus at least one templating agent, reacting the mixture to at least partially crystallize the molecular sieve and provide a slurry of seed crystals and adding to it nutrients (sources) of the framework elements, e.g. aluminum and silicon in order to grow the seed crystals. The rate of addition of the nutrients is controlled such that it is substantially the same as the crystal growth rate and such that there is substantially no nucleation of new crystals. The seed crystals may be the same or different than the nutrients being added, thus allowing for a layered molecular sieve. When the crystals have reached a desired size, they are isolated by conventional techniques.
Owner:UOP LLC
Method for preparing sic crystal and sic crystal
InactiveUS20050181627A1Number of defectReduce in quantityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle crystal substrateSingle crystal
A process for closing hollow-core defects, called micropipes, during growth by CVD of a SiC crystal on a SiC single crystal substrate having hollow-core defects, and a crystal obtained according to the process, by contacting the SiC crystal with a source gas adjusted to a C / Si atom ratio range in which the crystal growth rate is determined by the carbon atom supply limitation, then epitaxially growing and laminating a plurality of SiC crystal layers, wherein hollow-core defects in the SiC single crystal substrate dissociate into a plurality of dislocations given by small Burgers vector in order not to propagate to the crystal surface. In addition, the present invention provides a fabrication process of a SiC crystal, wherein a first SiC crystal is made as a buffer layer, and a further SiC crystal is layered thereon using a source gas adjusted to be higher than that of the C / Si ratio when forming the buffer layer, whereby a desired film property is conferred.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Method and apparatus for growing single crystal
InactiveUS6899758B2High crystal growth rateHigh ratePolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCzochralski methodSingle crystal
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for growing a single crystal by the Czochralski method, wherein a single crystal is grown with forced cooling of neighborhood of a crystal growth interface by disposing a cooling cylinder formed of copper or a metal having a heat conductivity larger than that of copper at least in the vicinity of the crystal growth interface so as to surround the single crystal under pulling and circulating a cooling medium in the cooling cylinder. Thus, there are provided a method and apparatus for growing a single crystal, which can exert cooling effect on a growing single crystal to the maximum extent so as to realize higher crystal growth rate, even when a silicon single crystal having a diameter of 300 mm or more is grown.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Method for Forming Zno Nano-Array and Zno Nanowall for Uv Laser On Silicon Substrate
InactiveUS20070220713A1Excellent laser characteristicSuperior laser characteristicMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthHexamethylenetetramineZno nanoparticles
Provided are low-temperature formation methods of a perfectly oriented ZnO nanorod array and a new-type ZnO nanowall array having a new crystal growth rate, morphology, and orientation, from ZnO nanoparticles coated on a substrate. The method of forming the ZnO nanorod array includes synthesizing ZnO nanoparticles, coating on a substrate the ZnO nanoparticles serving both as a buffer layer and a seed layer, and growing the ZnO nanoparticles into crystals in a nutrient solution containing Zn nitrate, Zn acetate, or a derivative thereof, and hexamethylenetetramine. The method of forming the ZnO nanowall array includes synthesizing ZnO nanoparticles, coating on a substrate the ZnO nanoparticles serving both as a buffer layer and a seed layer, and growing the ZnO nanoparticles into crystals in a nutrient solution containing Zn acetate or its derivative and sodium citrate.
Owner:NANOHYBRID CO LTD
Preparation method and device for doping semi-insulating gallium arsenide polycrystal with carbon
PendingCN107268085AEvenly distributedHigh electron mobilityPolycrystalline material growthDiffusion/dopingChemical reactionGas phase
The invention discloses a preparation method and device for doping a semi-insulating gallium arsenide polycrystal with carbon. Physicochemical vapor transportation is realized by controlling the temperature distribution in a source area and a growth area, that is, a raw material undergoes a chemical reaction in the source are to form a gaseous substance, and the gaseous substance is physically transported into the gallium arsenide polycrystals under the action of an axial temperature gradient. The high resistance semi-insulating gallium arsenide polycrystal synthesized by the method is used for drawing a semi-insulating gallium arsenide monocrystal, and the drawn semi-insulating gallium arsenide monocrystal has the advantages of high resistivity, uniform carbon distribution and high electron mobility; the method has the advantages of avoiding the direct doping during the gallium arsenide monocrystal drawing process, and effective reduction of the crystal growth rate and the control difficulty of the C concentration and the C concentration distribution uniformity; and the device has the advantages of simplicity and low cost.
Owner:JIANGXI DEYI SEMICON TECH
Process for producing nitride semiconductor, crystal growth rate enhancement agent, nitride single crystal, wafer and device
InactiveCN101522962AImprove performanceEfficient and easy to manufacturePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsWaferingCrystal structure
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP +1
Flow guide cylinder for monocrystal silicon growth furnace and application thereof
InactiveCN105239150AIncrease growth rateReduce oxygen contentPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltInsulation layerCarbon felt
The invention provides a flow guide cylinder for a monocrystal silicon growth furnace, which includes a tapered flow guide inner cylinder and a tapered flow guide outer cylinder, a heat preservation layer filled with heat preservation carbon felt is disposed therebetween. A heat insulation layer made from metal molybdenum or tungsten is disposed between the outer cylinder and the heat preservation layer. The tapered inner cylinder is used for absorbing radiation heat from a crystal ingot and then cooling the crystal ingot by means of gas rectifying to increase axial temperature gradient of the crystal ingot. Meanwhile, by means of the flow guide cylinder to rectify the gas, the flow speed of the gas is increased to reduce the partial pressure of SiO at liquid level of the melt, thereby reducing oxygen content in the melt. The flow guide cylinder can improve the quality of the crystal ingot, can accelerate growth of the crystal and can reduce production cost. The invention also provides an application method of eliminating polycrystal particles in quartz crucible walls by means of the flow guide cylinder.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED SILICON TECH CO LTD
Al2O3-coated modified lithium nickel manganese oxide positive electrode material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106129348AControllable growth rateImprove securityCell electrodesSecondary cellsCharge dischargeCrystal growth rate
The invention discloses an Al2O3-coated modified lithium nickel manganese oxide positive electrode material. A preparation method of the Al2O3-coated modified lithium nickel manganese oxide positive electrode material comprises the following steps of (1) preparing a solution; (2) dispersing lithium nickel manganese oxide into deionized water to form a turbid liquid and adding an anionic surfactant for ultrasonic dispersion for 15-30 minutes; (3) adding an Al(NO3)3 solution to an ultrasonic dispersed solution, carrying out ultrasonic dispersion for 15-30 minutes and then adding an NaAlO2 solution while stirring; (4) adding a citric acid solution of which the concentration is 0.5mol / L to the mixed solution obtained in the step (3) while stirring; (5) carrying out ageing, cleaning and drying; and (6) carrying out high-temperature pyrolysis. The crystal growth rate is consistent with the nucleation rate in the preparation process; coating is uniform; the prepared material is high in safety and low in cost; the energy density and the charge-discharge capacity at high voltage are obviously improved; and the capacity retention ratio reaches 86.3% after 500 charge-discharge cycles at a room temperature under the condition of 1C.
Owner:四川省有色冶金研究院有限公司
Silicon carbide crystal growth method for increasing crystal growth rate
ActiveCN102899718AReduce crystallizationReduce the degree of densificationFrom condensed vaporsCrucibleGraphite
The invention discloses a silicon carbide crystal growth method for increasing a crystal growth rate. The silicon carbide crystal growth method specifically comprises the following steps: manufacturing a graphite column; filling silicon carbide powder resource into a crucible, and then inserting the graphite column into the silicon carbide powder resource, and placing the crucible assembly into a growth device; firing the silicon carbide powder resource and removing the impurities; taking the graphite column out of the crucible; and performing crystal growth operation. According to the silicon carbide crystal growth method, the problems of the prior art that the use ratio of the silicon carbide powder resource is not high and the average growth rate of the crystal is low are solved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
System and control method for drawing crystal bar
PendingCN111020691AAchieve growthPrecise control of temperature gradientPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltThermodynamicsCrucible
The invention provides a system and a control method for drawing a crystal bar. The system comprises: a first control unit which is used for controlling the drawing speed of the drawn crystal bar to be constant; an obtaining unit which is used for obtaining a distance between a solid-liquid interface and a reference surface, wherein the solid-liquid interface is an interface between a crystal liquid and the current crystal bar; a crucible used for containing the crystal liquid; a heating device used for heating the crucible; a second control unit used for adjusting the crucible lifting ratio under the condition that the distance is different from the preset distance in order to make the distance reach the preset distance, wherein the crucible lifting ratio is the ratio of the crystal growth rate to the crucible lifting rate; and a third control unit connected with the heating device and used for controlling the heating power of the heating device to make the diameter of the crystal barat each position is within a preset range. The system makes the ratio v / G of the drawing speed of the drawn crystal bar to the temperature gradient of the solid-liquid interface kept unchanged, so that the defect concentration of the drawn crystal bar is reduced.
Owner:XUZHOU XINJING SEMICON TECH CO LTD +1
Halide perovskite single crystal, preparation method and application of halogenated perovskite single crystal in preparation of X-ray detector
ActiveCN111647944AReduce the density of defect statesQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsCharge carrier mobilityMetallic materials
The invention discloses a halide perovskite single crystal, a preparation method and application of the single crystal in preparation of an X-ray detector, and belongs to the technical field of X-raydetectors. The invention develops a method for controlling the growth of halide perovskite single crystals through solvent evaporation, the growth rate of the crystals is constant mainly by regulatingand controlling the growth temperature, the opening area of a solution and other factors, and the perovskite single crystals with lower crystal defect state density and higher carrier mobility-carrier lifetime deposition are grown. Polyoxyethylene is used for passivating surface defects of the perovskite single crystal, so that the crystal surface defects and surface leakage current are remarkably reduced, and the crystal has higher resistivity and lower noise current signals. The sensitivity of the prepared X-ray detector under 120 keV hard rays reaches 1274 [mu] C.Gyair.cm <2>, the lowest detection amount is as low as 0.56 [mu] Gyair.s <-1>, the requirements of medical imaging application are met, and the X-ray detector can be applied to metal material component analysis and flaw detection.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for growing large size Ta2O5 single crystal by using floating zone method
ActiveCN102312293AProcess advantagesNo macro defectsPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsRoom temperatureCrystal growth rate
The invention relates to a method for growing a large size Ta2O5 single crystal by using a floating zone method, and belongs to the field of crystal growth. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out ball milling and drying for a Ta2O5 powder material; placing the treated Ta2O5 powder material in a rubber tube, and carrying out isostatic pressing for the material to prepare a biscuit rod; carrying out sintering for the biscuit rod to obtain a polycrystalline rod; adopting the biscuit rod or the polycrystalline rod as the material rod, and adopting the polycrystalline or the Ta2O5 single crystal as the seed crystal, wherein the seed crystal and the material rod form a straight line in a vertical direction, and the contact point and a halogen lamp are at the same horizontal line; heating the material rod and the seed crystal until the material rod and the seed crystal are molten, wherein the heating rate is 30-60 DEG C per minute; adjusting the rotation speeds and the rotation directions of the material rod and the seed crystal, then carrying out inoculation; adopting the movement of a focusing lens or the up and down movement of the rod to enable the molten zone to be far away from the focusing point, enable the temperature of the molten zone to be decreased to realize the crystallization, wherein the crystal growth rate is 10-60 mm / h; cooling the grown crystal to the room temperature. With the method provided by the present invention, the growth period is short; the preparation efficiency is high; the Ta2O5 single crystal can be rapidly grown, wherein the grownTa2O5 single crystal has characteristics of size in centimeter magnitude, no macroscopic defect and high quality.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Group III nitride crystal, method of its manufacture, and equipment for manufacturing group III nitride crystal
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Method for the preparation of doped garnet structure single crystals with diameters of up to 500 mm
ActiveUS20130291788A1Remove heatImprove controllabilityPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltLutetiumCrucible
Preparation of lutetium and yttrium aluminate single crystals doped with rare earth oxides and transition elements consists in the preparation of oxide mixture sinter which is melted throughout and homogenized for a period of at least one hour. The crystal growth rate and broadening of the crystal cone are maintained uniform at an angle of at least 60° from the crystal axis up to a diameter of at least 80% of the crucible diameter which is at least 100 mm. The completion of the process occurs by separating the crystal from the melt while the crystal continues to be positioned inside the crucible in the zone wherein it was grown, and wherein final tempering of the crystal also takes place.
Owner:CRYTUR SPOL SRO
Method for growing yttrium ferrite crystal by guided mold pulling method
InactiveCN101942694AFast growthImprove optical qualityPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltCrucibleCrystal growth rate
The invention relates to a method for growing an yttrium ferrite crystal by a guided mold pulling method, which comprises the following steps: placing a guided mold with internal longitudinal gaps in a crucible, adding polycrystal materials into the crucible, heating the crucible to melt the polycrystal materials, enabling the molten polycrystal materials to rise over the gaps at the bottom of the guided mold so as to enable the molten polycrystal materials to be raised to the top surface of the guided mold along the longitudinal gaps in the guided mold under the capillary effect, then dropping seed crystals, and finally pulling to obtain the yttrium ferrite single crystal. The invention can prepare large-size yttrium ferrite single crystals, simplify the post processing procedure of the crystal and lower the preparation cost of the crystal, and has the advantages of high crystal growing speed and good optical uniformity of the prepared crystal, thereby solving the problem that the pulling method can not be used for preparing large-size single crystals.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for improving homogeneity of potassium tantalate niobate crystal through double-crucible real-time material-feeding technology
InactiveCN104294353ALow costGood repeatabilityPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltCrucibleCzochralski method
The invention discloses a method for improving homogeneity of a potassium tantalate niobate crystal through a double-crucible real-time material-feeding technology. In the method, high-purity K2CO3, Ta2O5, Nb2O5 are employed as raw materials. A KTN polycrystal basic material and a KTN polycrystal supplying material are respectively weighted and prepared according to required crystal components. The polycrystal materials are prepared through a grinding process, a uniformly blending process, a pressing moulding process and a sintering process. According to requirements of the double-crucible real-time material-feeding technology, an internal-external double-crucible temperature field system is designed and corresponding transformation of a lifting furnace is carried out for satisfying a real-time material-supplying requirement. A crystal growing process includes following steps: a seed adding process, a necking process, a shoulder-releasing process, an equal-neck turning process and an equal-neck growing process. During the crystal growing process, a crystal growing speed and a material-supplying speed are maintained to be equal for ensuring melt components to be stable. When the crystal growth is finished, the crystal is lifted from a liquid surface and is cooled slowly to room temperature to obtain a KTN monocrystal. By means of the technical scheme, crystal component fluctuation caused by fluctuations of the melt components and a growth temperature during the KTN monocrystal growing process through a conventional melt lifting method is greatly reduced, thereby greatly improving the homogeneity of the KTN crystal. The method has an important significance on practical application of the KTN crystal.
Owner:NEW MATERIAL INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for growing terbium-aluminum garnet crystal by using guide die pulling method
ActiveCN101792926AFast growthImprove optical qualityPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltCrucibleGarnet crystals
The invention relates to a method for growing a terbium-aluminum garnet crystal by using a guide die pulling method, comprising the following steps of: placing a guide die internally provided with a longitudinal gap into a crucible; adding a polycrystal raw material into the crucible; heating the crucible to melt the polycrystal raw material; immersing a molten mass of the polycrystal raw material into a gap at the lower part of the guide die so as to raise the molten mass of the polycrystal raw material to an upper surface of the guide die under the action of capillary effect along the longitudinal gap of the guide die; and then pulling a lower seed crystal into a single crystal consistent with the shape of the guide die. By the invention, a large-size terbium-aluminum garnet single crystal can be prepared, post processing procedures can be simultaneously simplified and the cost for preparing the crystal can be reduced; in addition, the growth speed of the crystal is high, the optical homogeneity of the prepared crystal is favorable and the problem that a large-size body single crystal is not difficult to prepare by adopting a pulling method can be solved.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for growing CaxBa1-xNb2O6 series crystals
InactiveCN102358954AImprove crystal qualityGood dielectricPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsCooking & bakingRoom temperature
The invention relates to a method for growing CaxBa1-xNb2O6 series crystals, belonging to the field of crystal growth. The method comprises the following steps: mixing powder CaCO3, BaCO3 and Nb2O5 according to the stoichiometric proportion of CaxBa1-xNb2O6, carrying out ball milling, baking, and passing through a 200-mesh screen, wherein x=0.22, 0.25, 0.28, 0.32 or 0.35; presintering, carrying out ball milling again, baking, and passing through a 80-mesh screen; putting the powder in an elongated rubber balloon, compacting, sealing, and vacuumizing to prepare a biscuit rod with uniform thickness and density under isopressing conditions; sintering the biscuit rod in a dip-coating rotary sintering furnace to obtain a compact and uniform polycrystal rod; putting the polycrystal rod in a floating region furnace, and heating at 60-100 DEG C / minute until the rod and seed crystals are molten, and abutting; and after setting the crystal growth rate at 2-5mm / hour, starting growth, and coolingto room temperature. The invention grows a CaxBa1-xNb2O6 crystal, which is 6-8mm in diameter 50-115mm long and does not have macroscopic defects, by an optical floating region process, has the advantages of high crystallization quality and high efficiency, and simplifies the technique.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com