Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
364 results about "Gaseous substance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In a solid substance, atoms or molecules, units for macroscopic organization, are bonded through chemical bonds or van der Waals forces. When a solid substance is heated, the thermal motion make the units get rid off the constraint of chemical or physical interactions. In this case, the units in a gaseous substance is dissociative.
Silicon carbide based field effect gas sensor for high temperature applications
InactiveUS20180011052A1Change electrical propertiesLong-term reliable operationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactSemiconductor structure
A field effect gas sensor, for detecting a presence of a gaseous substance in a gas mixture, the field effect gas sensor comprising: a SiC semiconductor structure; an electron insulating layer covering a first portion of the SiC semiconductor structure; a first contact structure at least partly separated from the SiC semiconductor structure by the electron insulating layer; and a second contact structure conductively connected to a second portion of the SiC semiconductor structure, wherein at least one of the electron insulating layer and the first contact structure is configured to interact with the gaseous substance to change an electrical property of the SiC semiconductor structure; and wherein the second contact structure comprises: an ohmic contact layer in direct contact with the second portion of the SiC semiconductor structure; and a barrier layer formed by an electrically conducting mid-transition-metal oxide covering the ohmic contact layer.
Owner:VOLVO CAR CORP
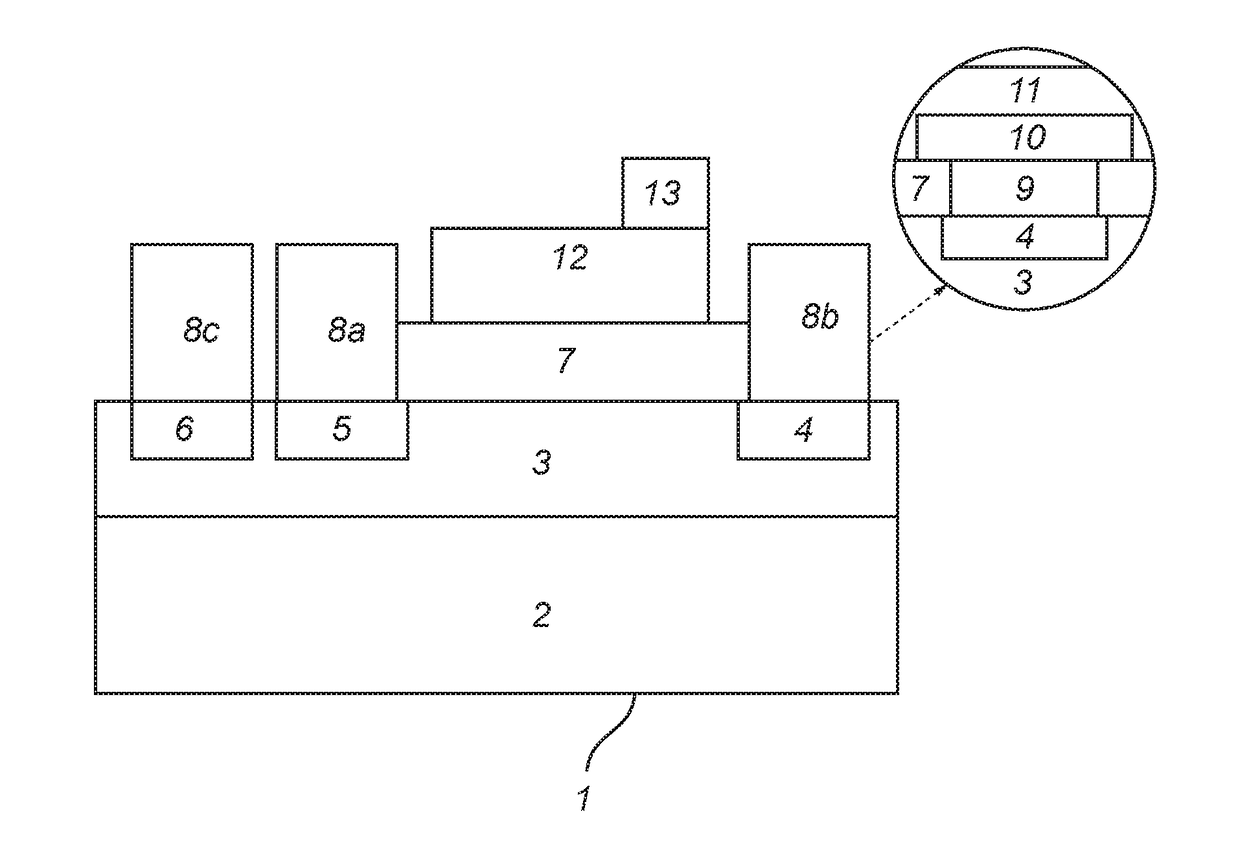
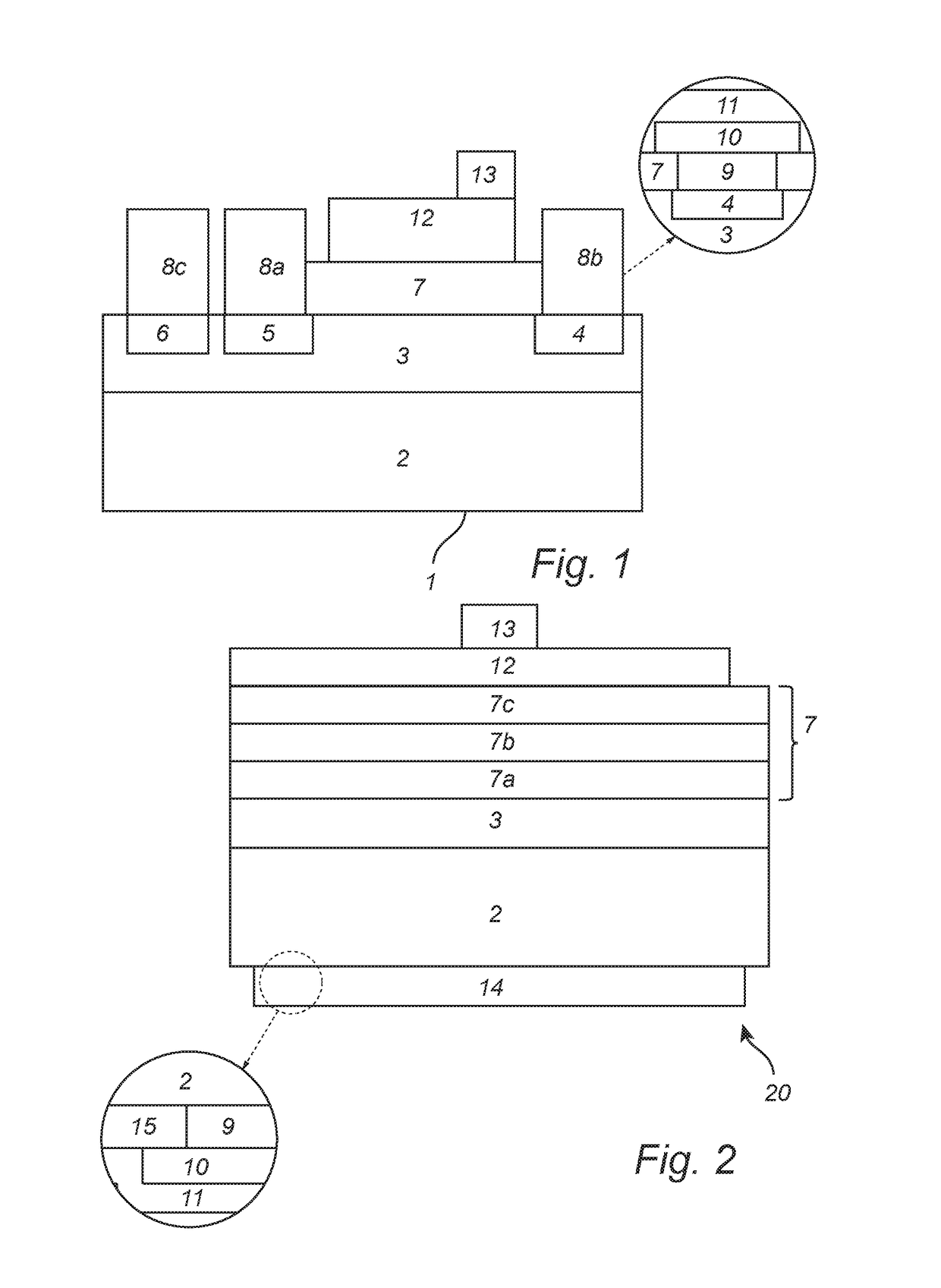
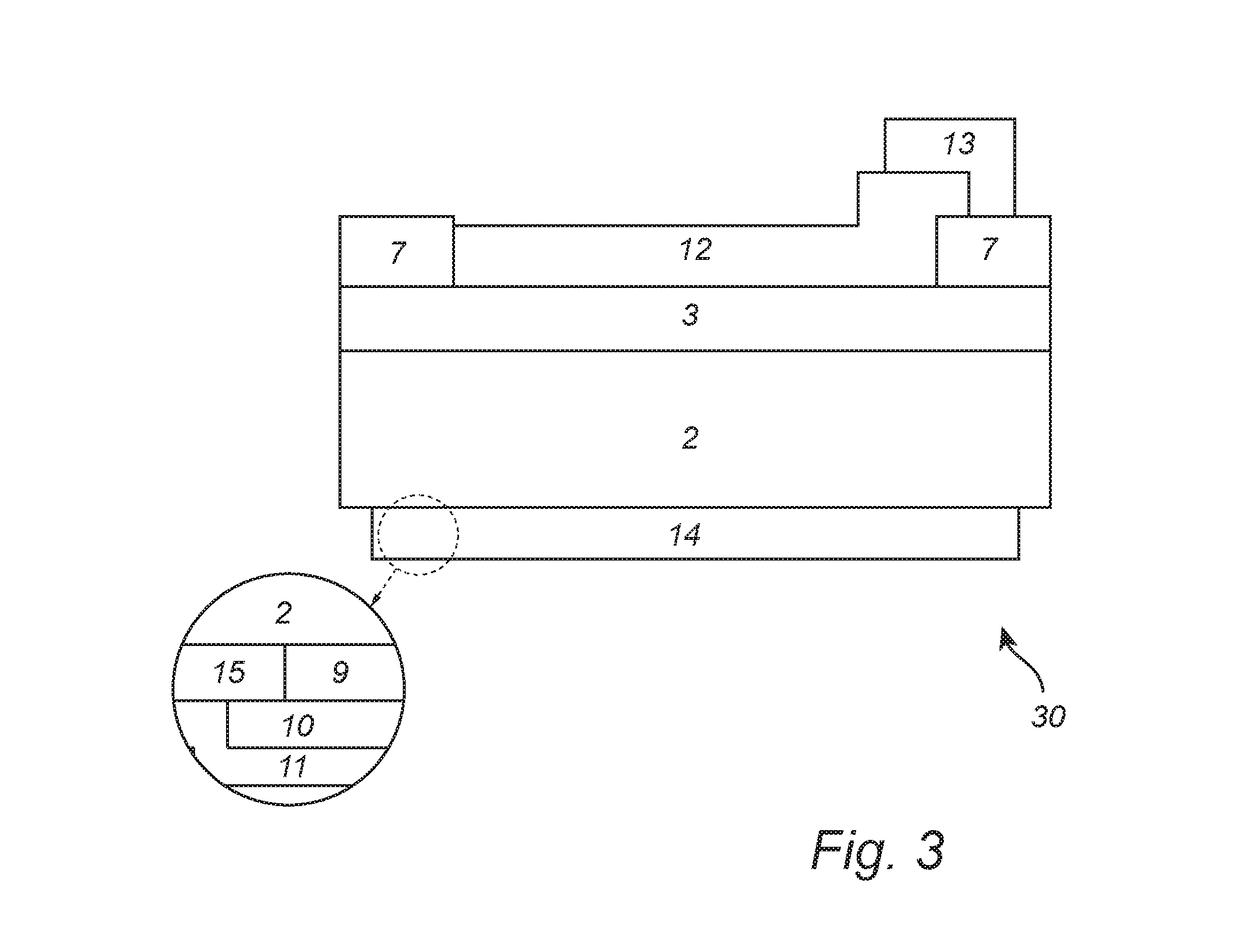
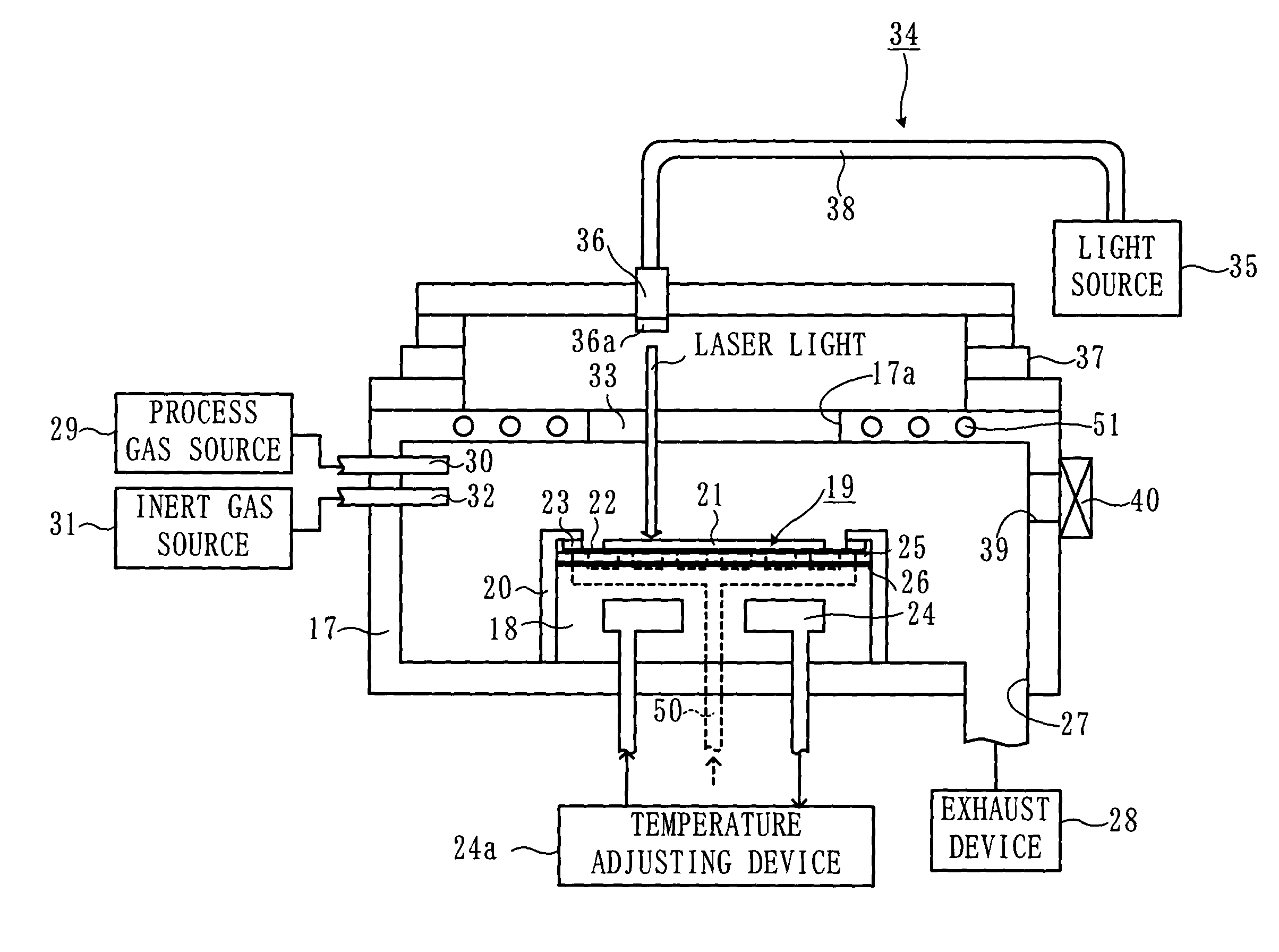
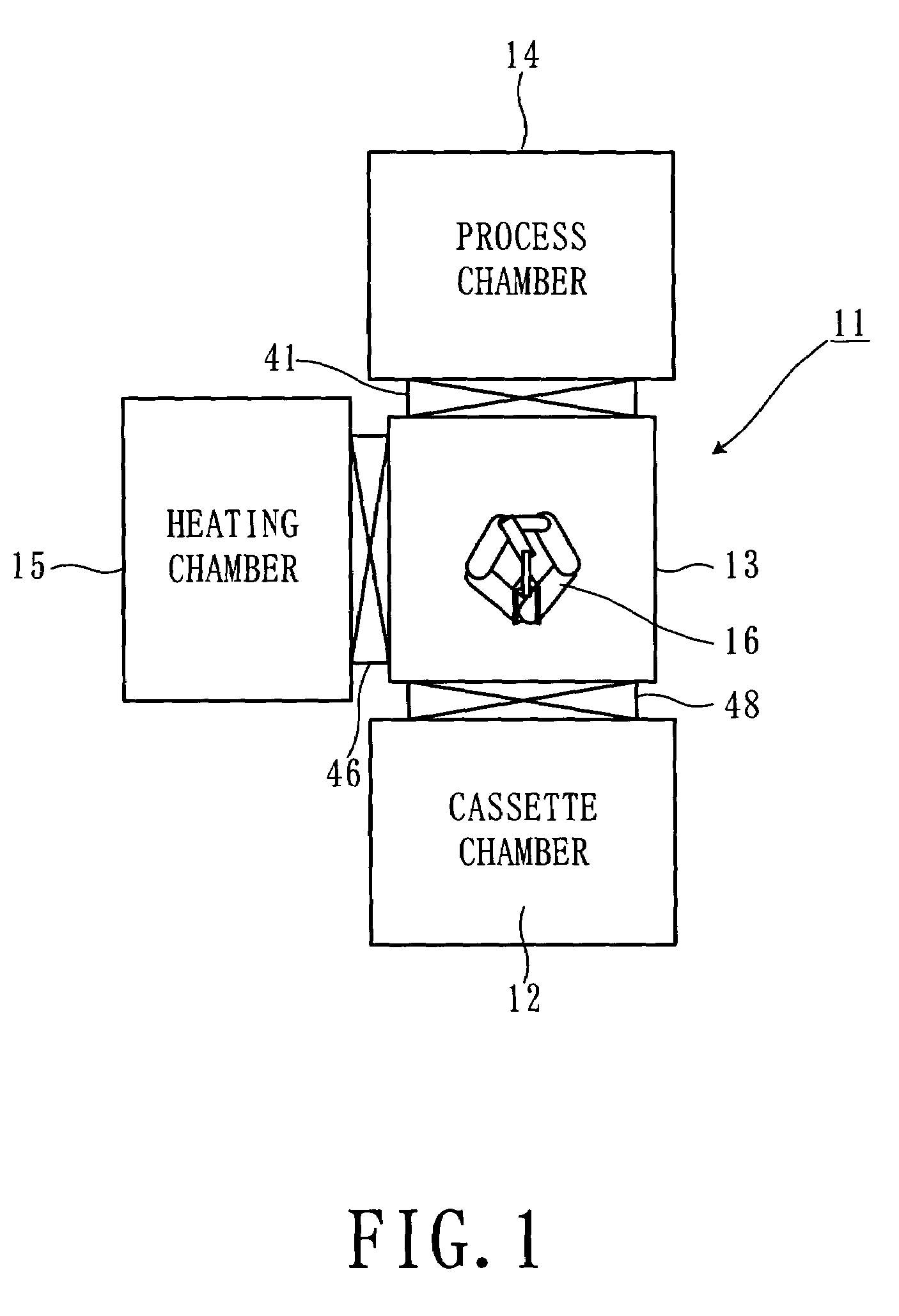
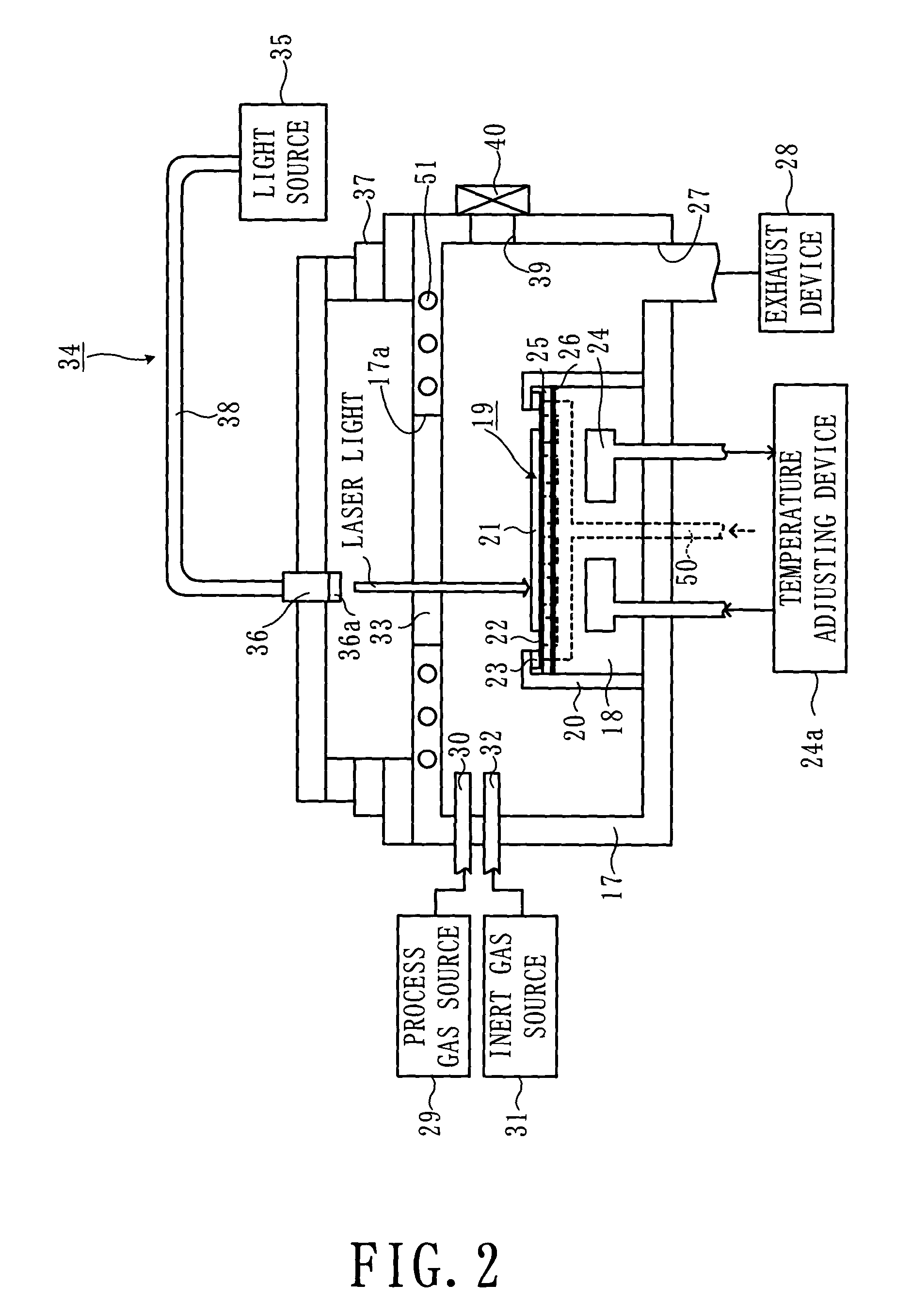
Substrate processing device and processing method
InactiveUS7101797B2Improve reliabilityReduce harmDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoolant flowLaser light
In a state where a process gas including SF.sub. 6 and O.sub. 2 is supplied in a chamber, a laser light irradiator provided outside the chamber irradiates a laser light onto a substrate. At the portion of the substrate onto which the laser light is irradiated, the material that makes up the substrate is excited and converted into a gaseous substance by reacting with the process gas. The temperature of the substrate placed on a stage is kept at a predetermined temperature since a temperature adjuster supplies a chiller to a coolant flow passage provided inside the stage.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Solid state electrochemical gas sensor and method for fabricating same
InactiveUS20070102294A1Small sizeWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementPolymer electrolytesElectrochemical gas sensor
An electrochemical gas sensor, a method for making the sensor and methods for the detection of a gaseous species. The electrochemical gas sensor is a solid-state gas sensor that includes a solid polymer electrolyte. A working electrode is separated from a counter electrode by the solid polymer electrolyte. The sensor can include a multilaminate structure for improved detection properties, where electrode microbands are disposed within the solid polymer electrolyte.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Method of manufacturing GaN ingots
InactiveUS6562124B1Low costSimple growth processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBy pulling from meltSemiconductor materialsIngot
A novel method for growing semiconductor material including GaN is disclosed. The method involves placing a first substance into a growth reactor, supplying a second gaseous substance into the grouth reactor, and applying electrical field to the second gaseous substance to produce the cry stalline compound material.
Owner:OSTENDO TECH INC
Use of Plasma in Formation of Biodegradable Stent Coating
Metallic stents are treated with a gaseous species in a plasma state under conditions causing the species to polymerize and to be deposited in polymerized form on the metallic stent surface prior to the application of a drug-polymer mixture, which is done by conventional non-plasma deposition methods. The drug-polymer mixture once applied forms a coating on the stent surface that releases the drug in a time-release manner and gradually erodes, leaving only the underlying plasma-deposited polymer. In certain cases, the plasma-deposited polymer itself erodes or dissolves into the physiological medium over an extended period of time, leaving only the metallic stent. While the various polymers and drug remain on the stent, the plasma-deposited polymer enhances the adhesion of the drug-polymer anchor coating and maintains the coating intact upon exposure to the mechanical stresses encountered during stent deployment.
Owner:JW MEDICAL SYSTEMS LTD
Apparatus and Method for Purification and Disinfection of Liquid, Solid or Gaseous Substances
ActiveUS20080292497A1Easy to upgradeImprove throughputFrom normal temperature solutionsLiquid separation by electricityProduct gasEngineering
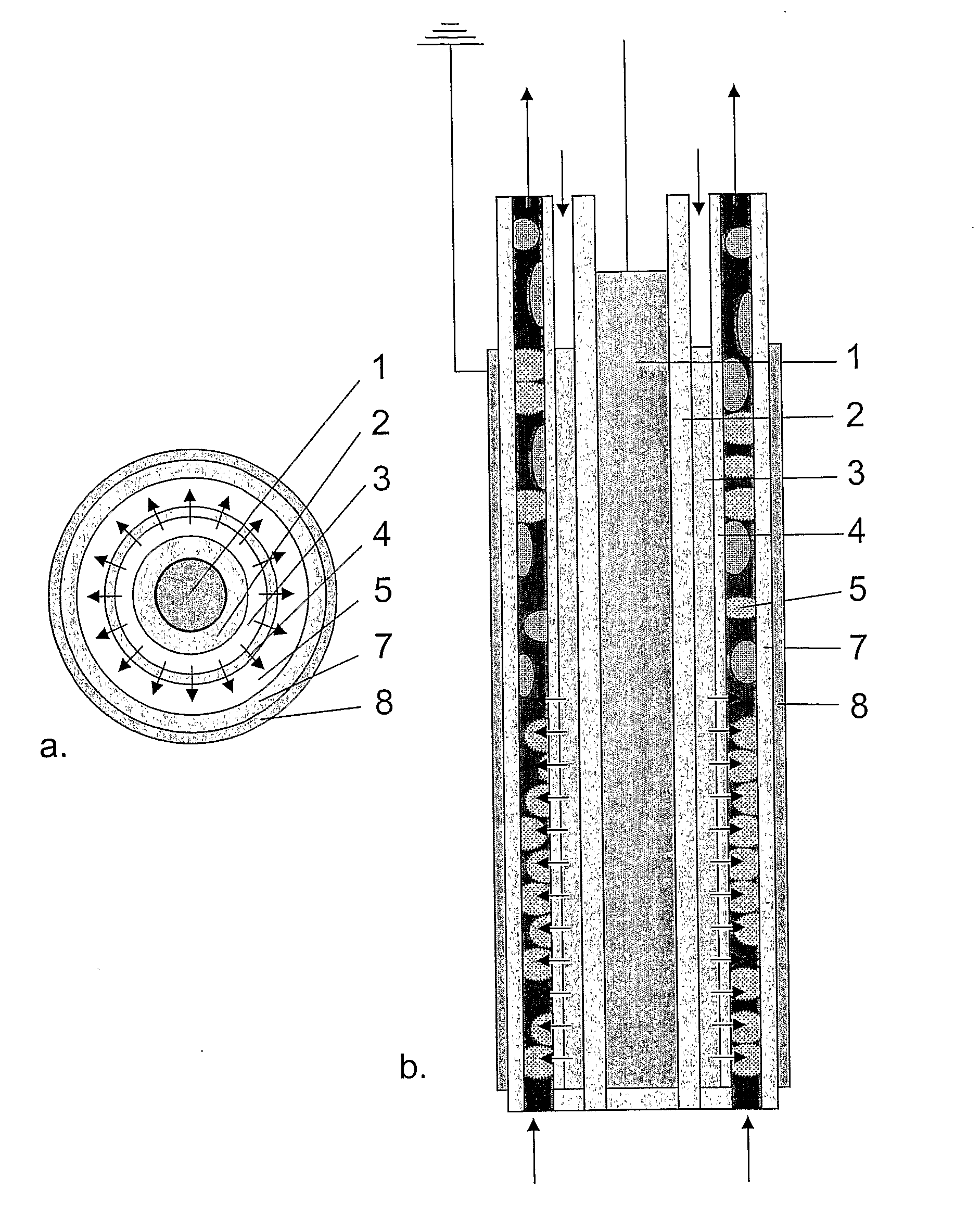
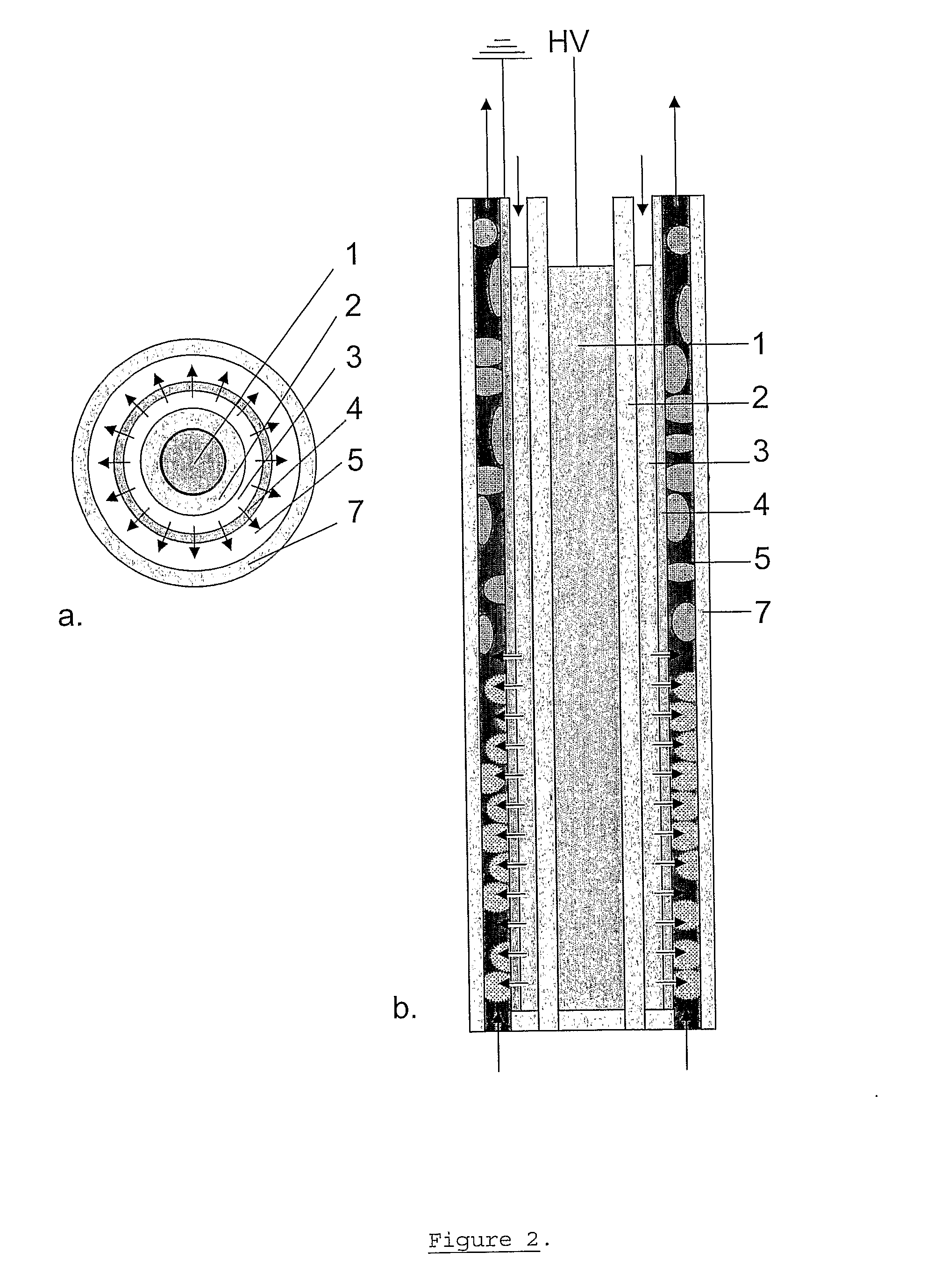
An apparatus and method are for disinfection and purification of a liquid, gaseous or solid phase, or a mixture thereof. The apparatus includes: a central electrode, a dielectric layer adjacent to the electrode, a first area adjacent to the dielectric layer, and is configured to introduce a first medium into the first area, a second area adjacent to the first area. The apparatus is also configured to introduce a second medium into the second area, and for creating a plasma in the first medium, while the first medium is present in the first area, by applying a voltage between the first electrode and a second electrode. An injector injects the plasma into the second area, in order to be mixed with the second medium.
Owner:VLAAMSE INSTELLING VOOR TECHNOLOGISCH ONDERZOEK NV VITO
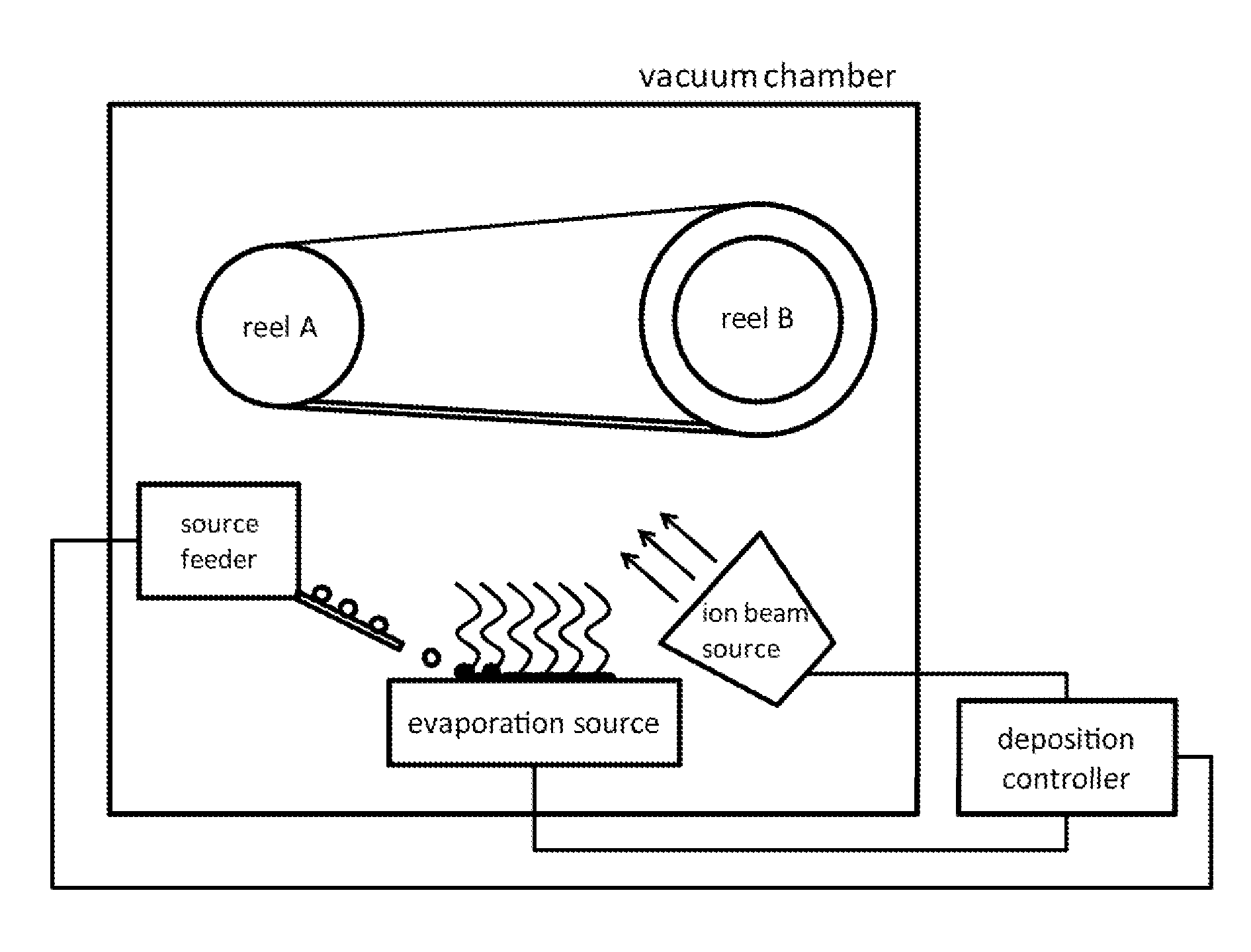
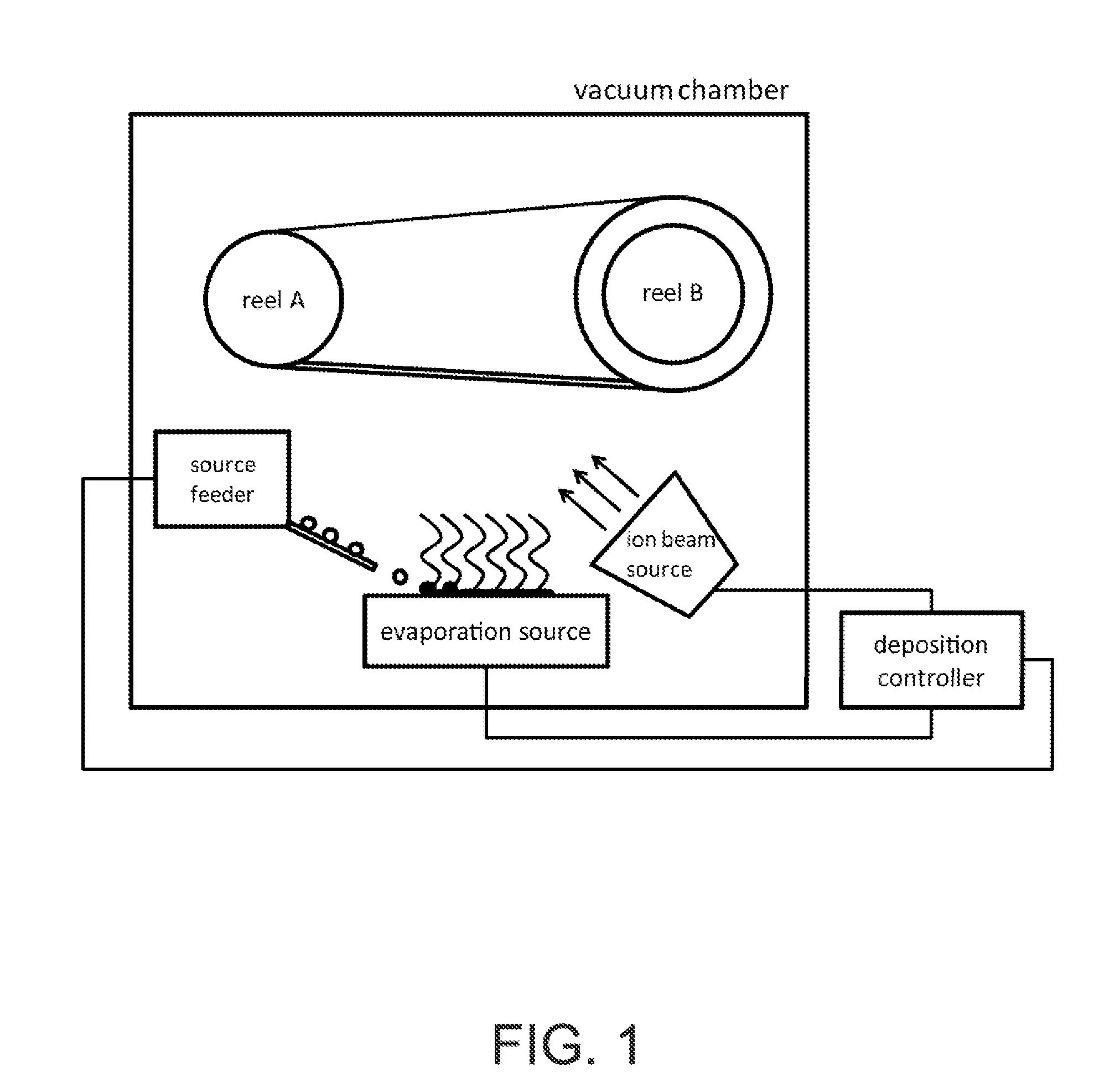
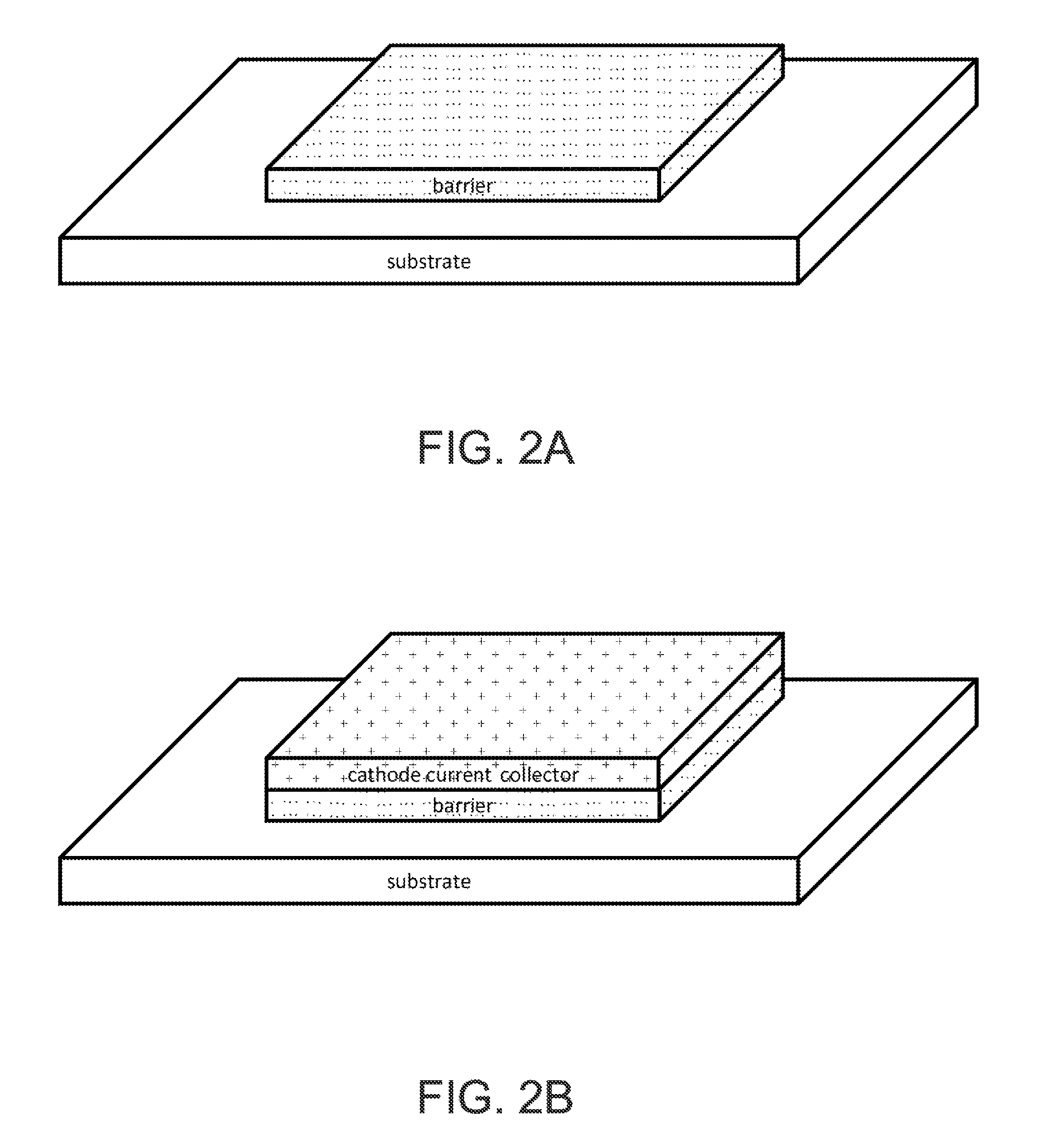
Thermal evaporation process for manufacture of solid state battery devices
ActiveUS20120058280A1Easy to implementEfficient and cost-effectiveFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingThermal energySource material
A method for manufacturing a solid-state battery device. The method can include providing a substrate within a process region of an apparatus. A cathode source and an anode source can be subjected to one or more energy sources to transfer thermal energy into a portion of the source materials to evaporate into a vapor phase. An ionic species from an ion source can be introduced and a thickness of solid-state battery materials can be formed overlying the surface region by interacting the gaseous species derived from the plurality of electrons and the ionic species. During formation of the thickness of the solid-state battery materials, the surface region can be maintained in a vacuum environment from about 10-6 to 10-4 Torr. Active materials comprising cathode, electrolyte, and anode with non-reactive species can be deposited for the formation of modified modulus layers, such a void or voided porous like materials.
Owner:SAKTI3
Strainer/filter unit for an aspirating filtration system and method thereof
ActiveUS20100297577A1Avoid pollutionReduce morbidityTeeth fillingWater/sewage treatmentFiltrationFilter system
A strainer / filter unit for effectively collecting solid, liquid or gaseous substances at the source and the method of using the strainer / filter unit. The strainer / filter unit includes a housing, a one-way valve at one end of the housing, and a filter having a certain depth and thickness within the housing. The filter is formed from a plurality of layers of material with pores such that pores of one layer partially overlap pores of subsequent adjacent layers. Matters entering the strainer / filter unit are collected in the filter while travelling through filter via a tortuous path.
Owner:COHEN HOWARD
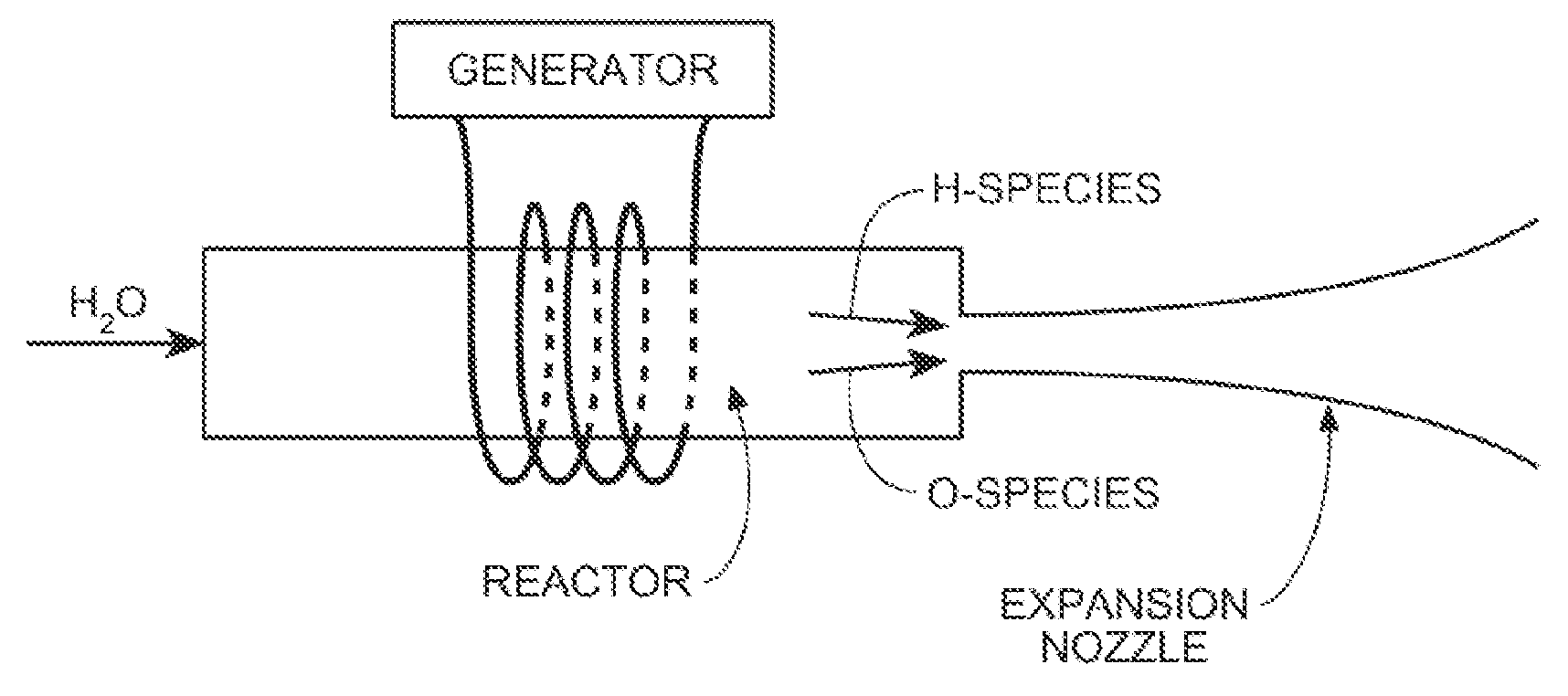
Method for generating hydrogen from water or steam in a plasma
Water molecules, preferably in the form of steam or water vapor, are introduced into a plasma. The plasma causes the water molecules to dissociate into their constituent molecular elements of hydrogen and oxygen. To prevent recombining of the constituent molecular elements, the hydrogen and oxygen are separated from each other. Various devices may be employed to effect this separation. Once separated, the molecular components are prevented from recombining with each other or with other elements by using standard separation techniques normally employed for separating dissimilar gaseous species.
Owner:BAR GADDA
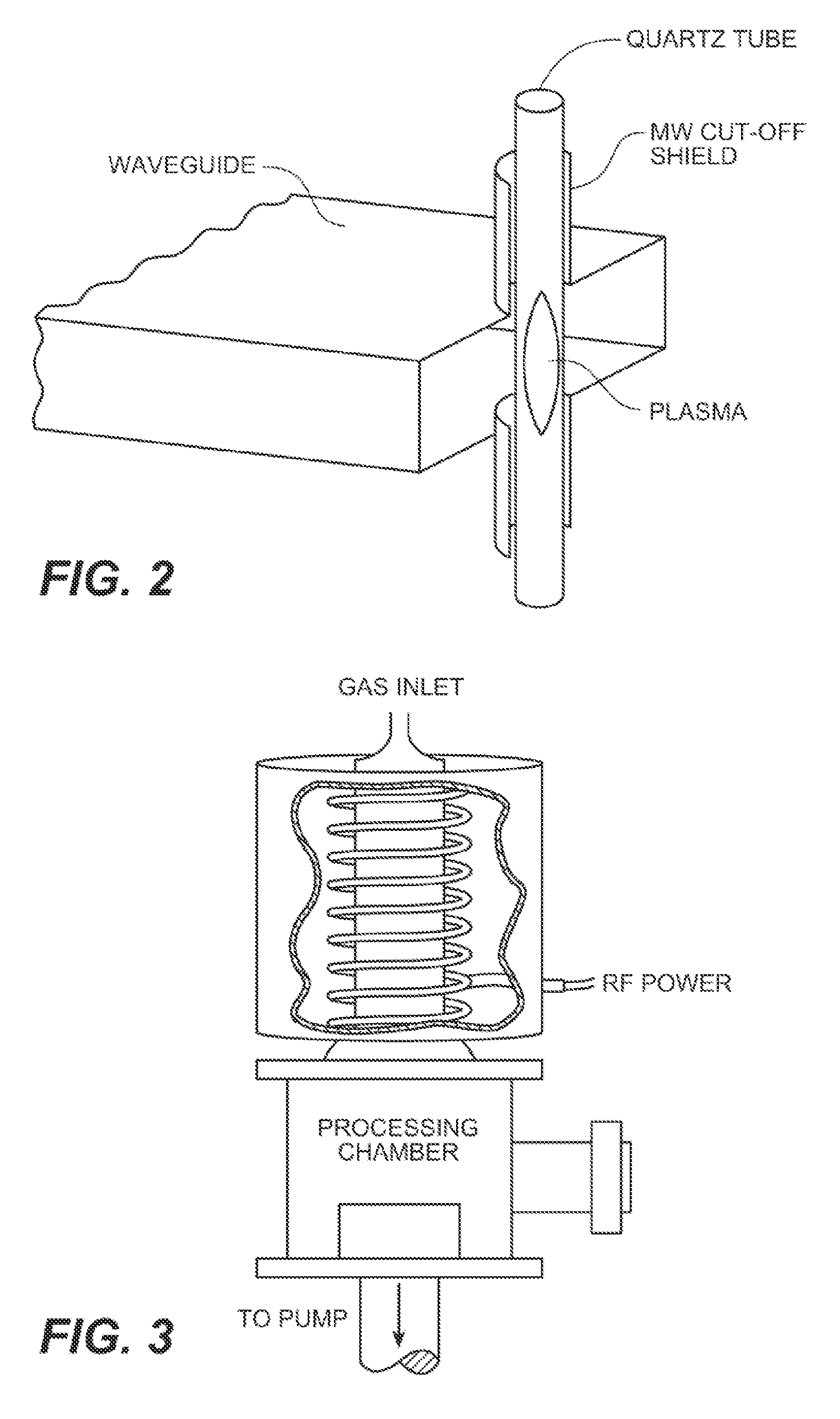
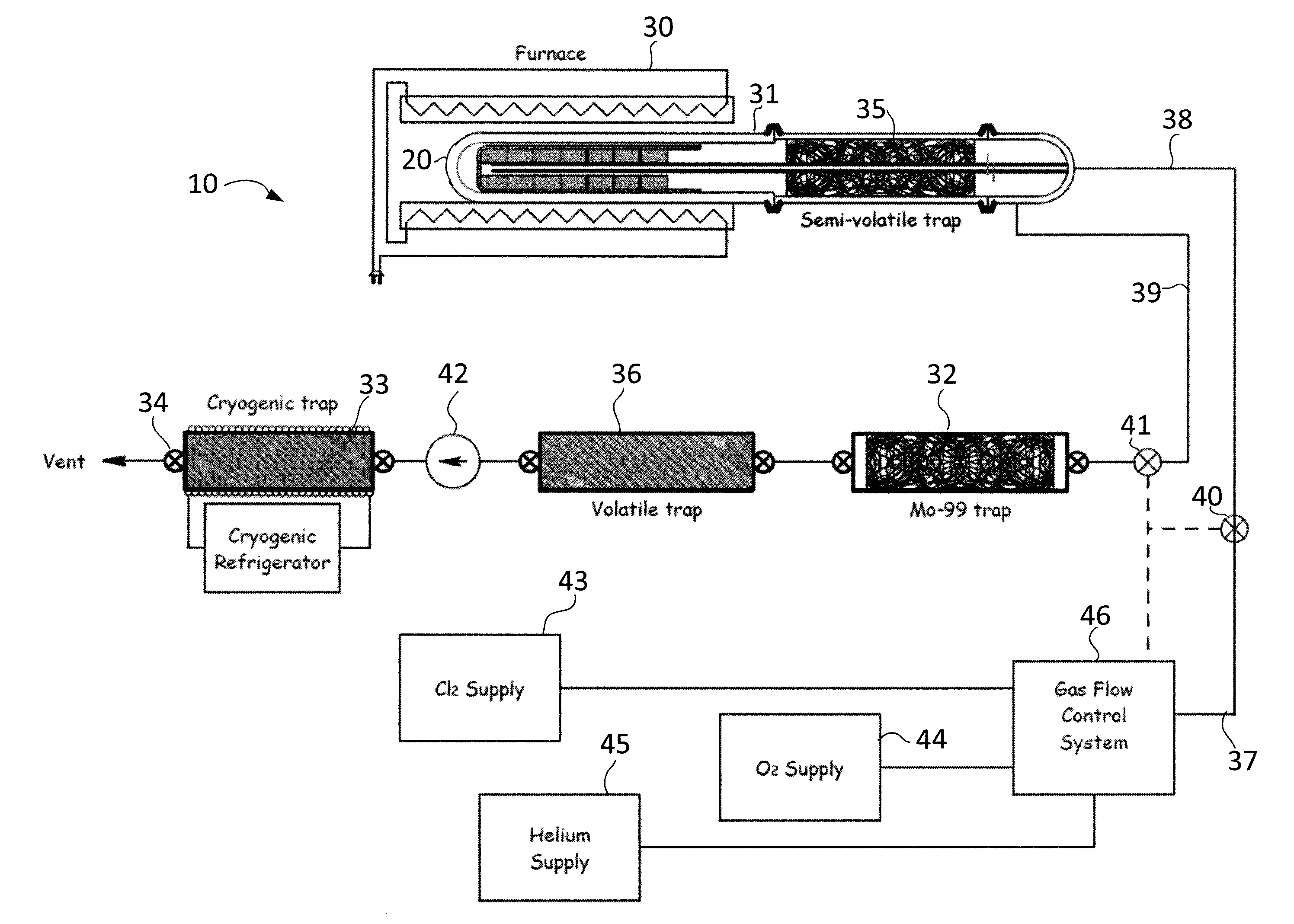
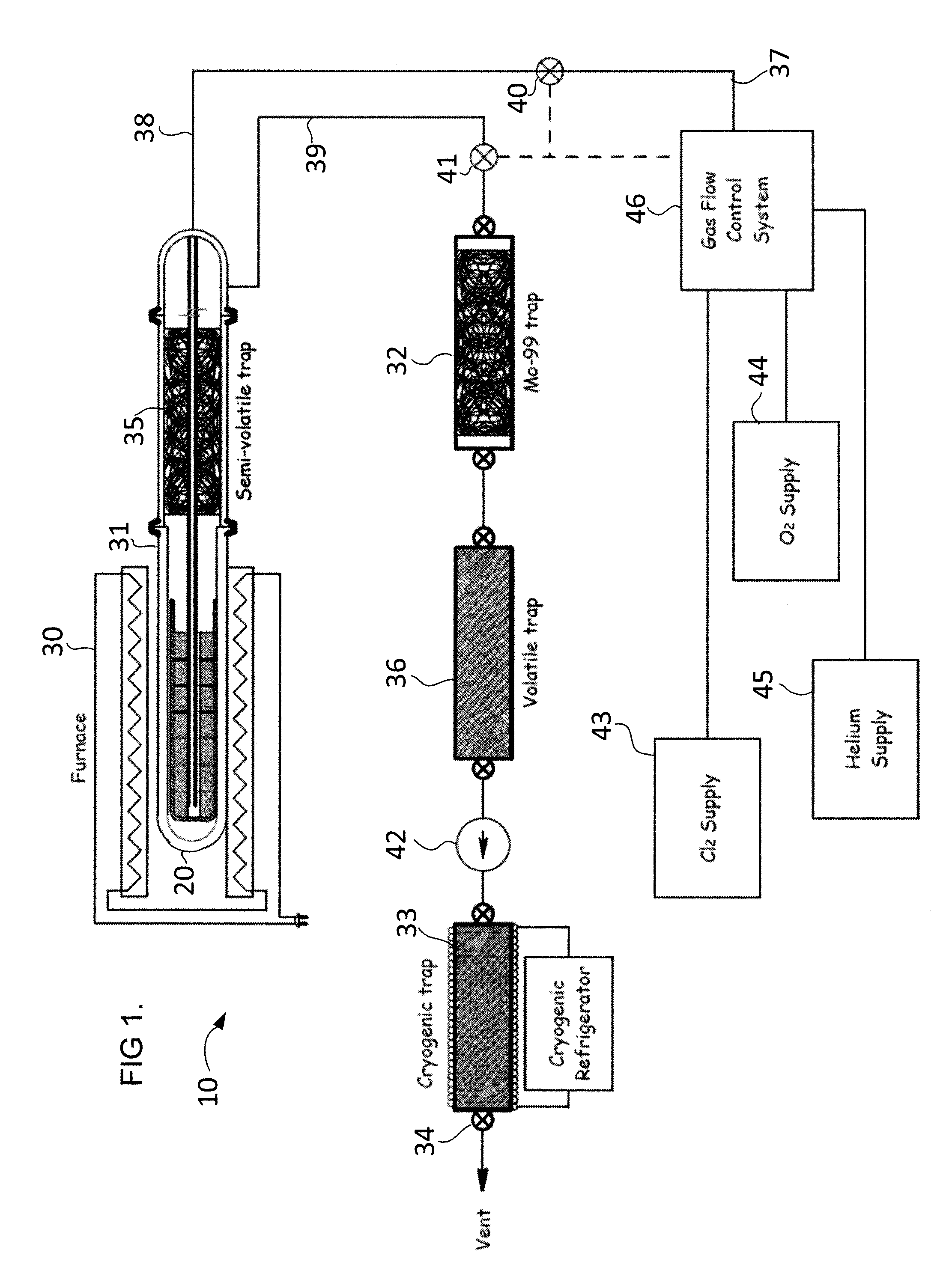
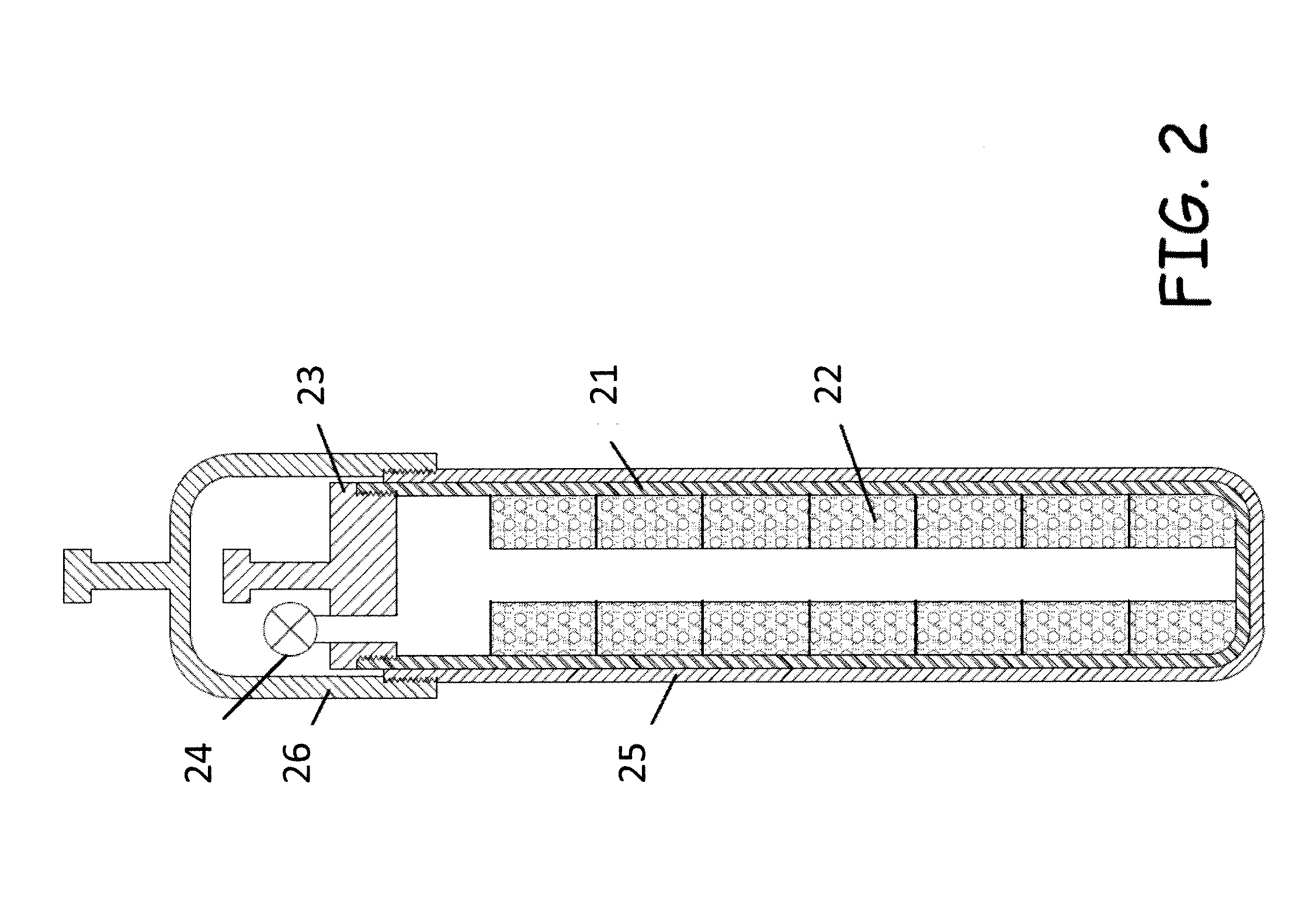
Methods and apparatus for selective gaseous extraction of molybdenum-99 and other fission product radioisotopes
ActiveUS20110305309A1Less capital equipmentRapid productionSpecific isotope recoveryConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsChemistryGaseous substance
Methods and apparatus are provided for producing and extracting Mo-99 and other radioisotopes from fission products that overcome the drawbacks of previously-known systems, especially the excessive generation of radioactive wastes, by providing gas-phase extraction of fission product radioisotopes from a nuclear fuel target using a mixture including halide and an oxygen-containing species with heat to convert the fission product radioisotopes to gas (e.g., Mo-99 to MoO2Cl2 gas). The gaseous species are evacuated to a recovery chamber where the radioisotopes solidify for subsequent processing, while the substantially intact uranium target made available for further irradiation and extraction cycles.
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
Impedance resonance sensor for real time monitoring of different processes and methods of using same
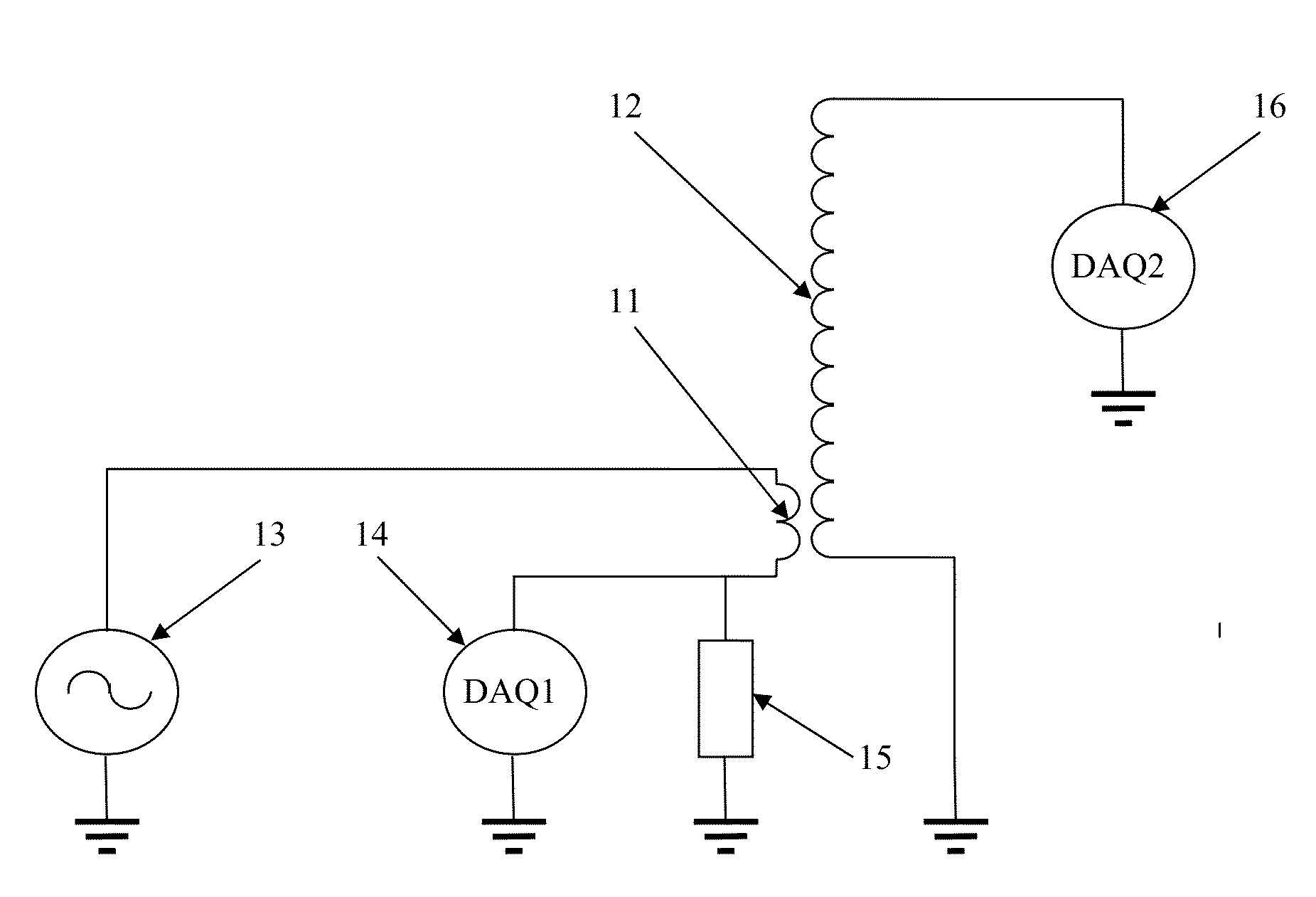
Processes and apparatuses are provided for contactless measuring or monitoring in-situ and in real time composition or other electromagnetic impedance correlated properties of liquid or gaseous substances or bulk materials. One or more apparatus may include a resonance type impedance sensor having at least two coils, at least one coil of the at least two coils being at least one excitation coil connectable to at least one alternating current source with frequency sweep, at least one other coil of the at least two coils being at least one sensing coil connectable to at least one data processing system. The one or more methods may include calculating changes in amplitude and resonant frequency induced by electromagnetic interaction between said sensor and object to determine impedance of said object under test; and matching said impedance with predetermined calibration data to determine said chemical or physical properties of said object under test.
Owner:NEOVISION
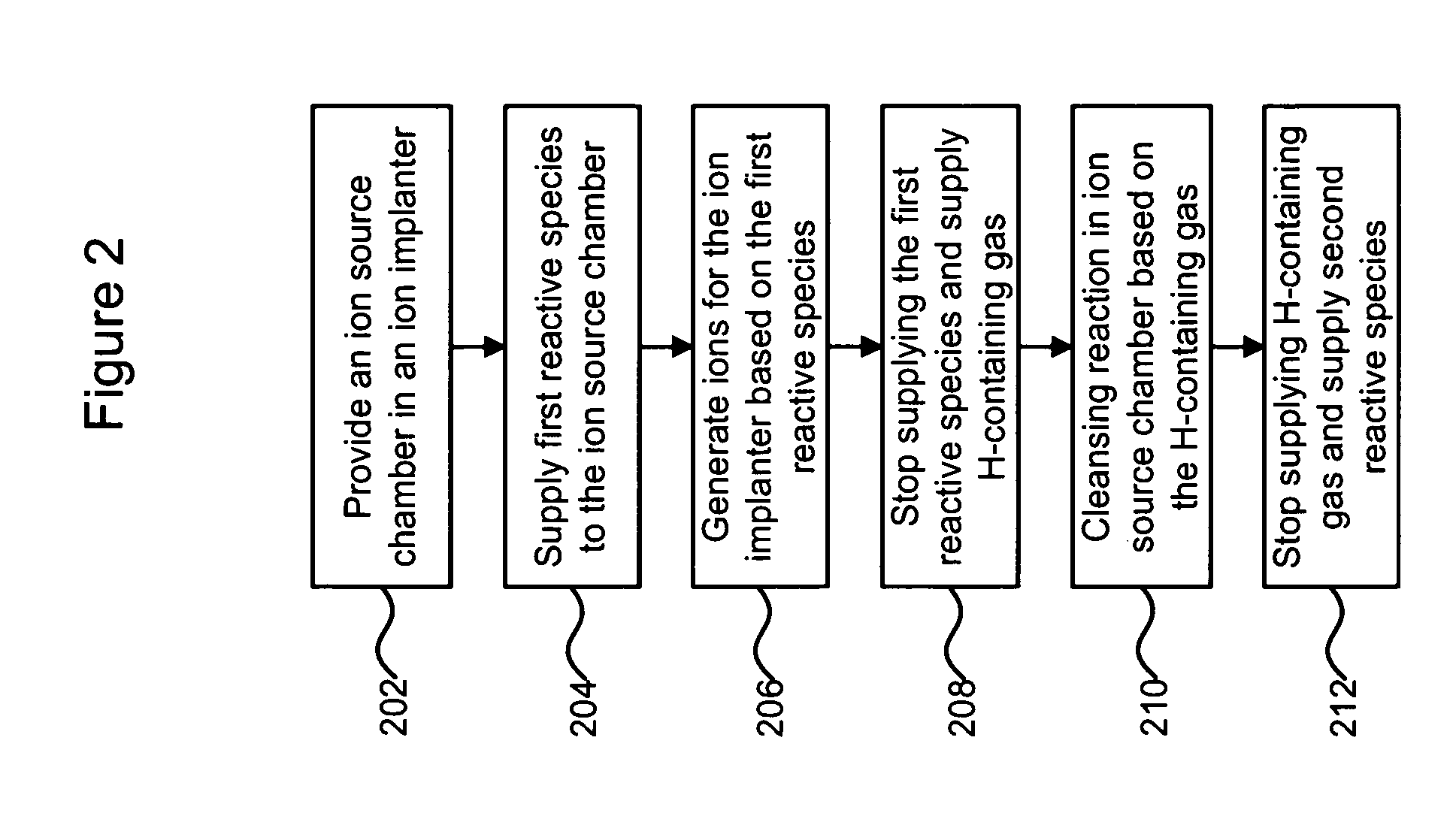
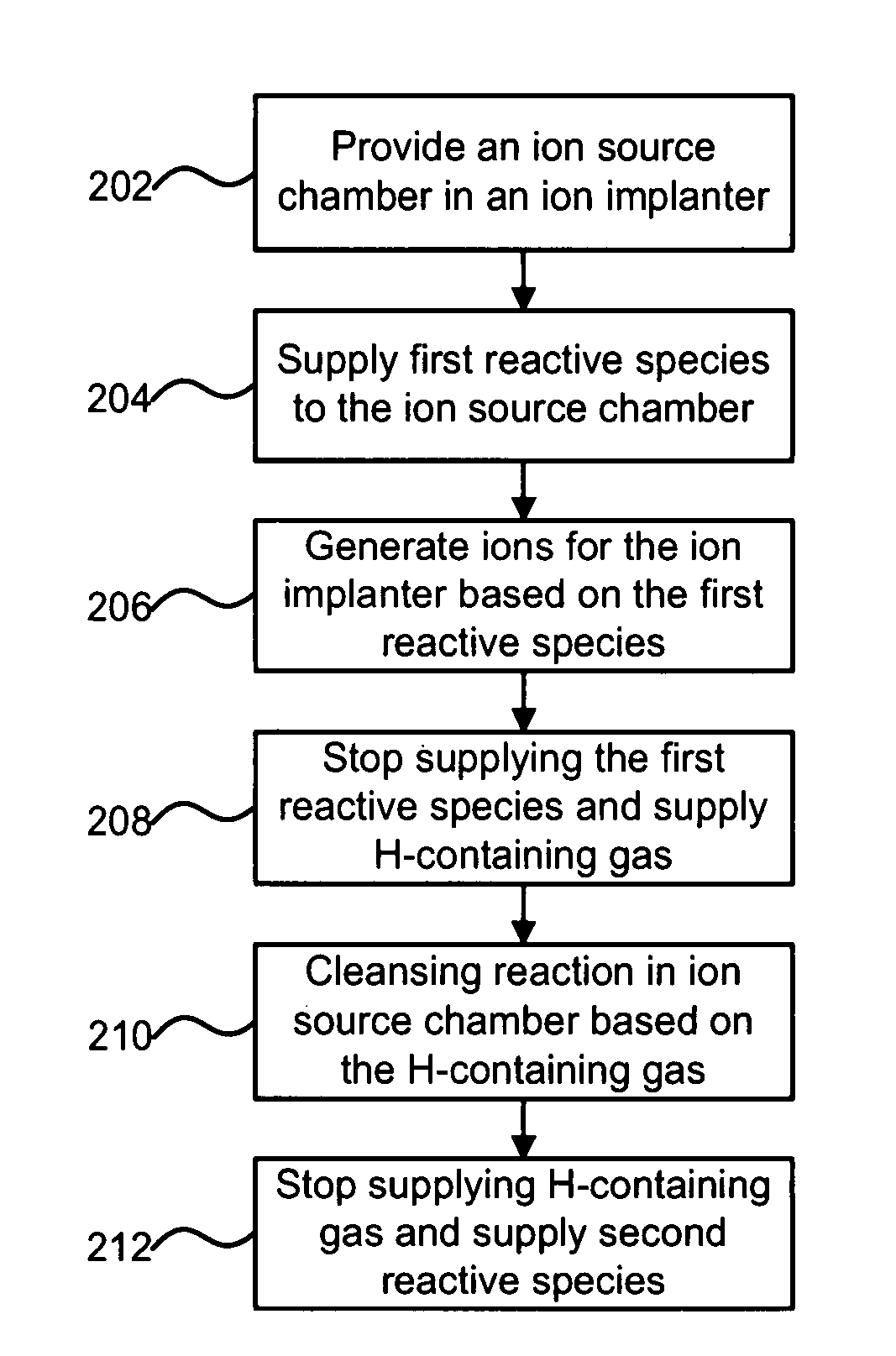
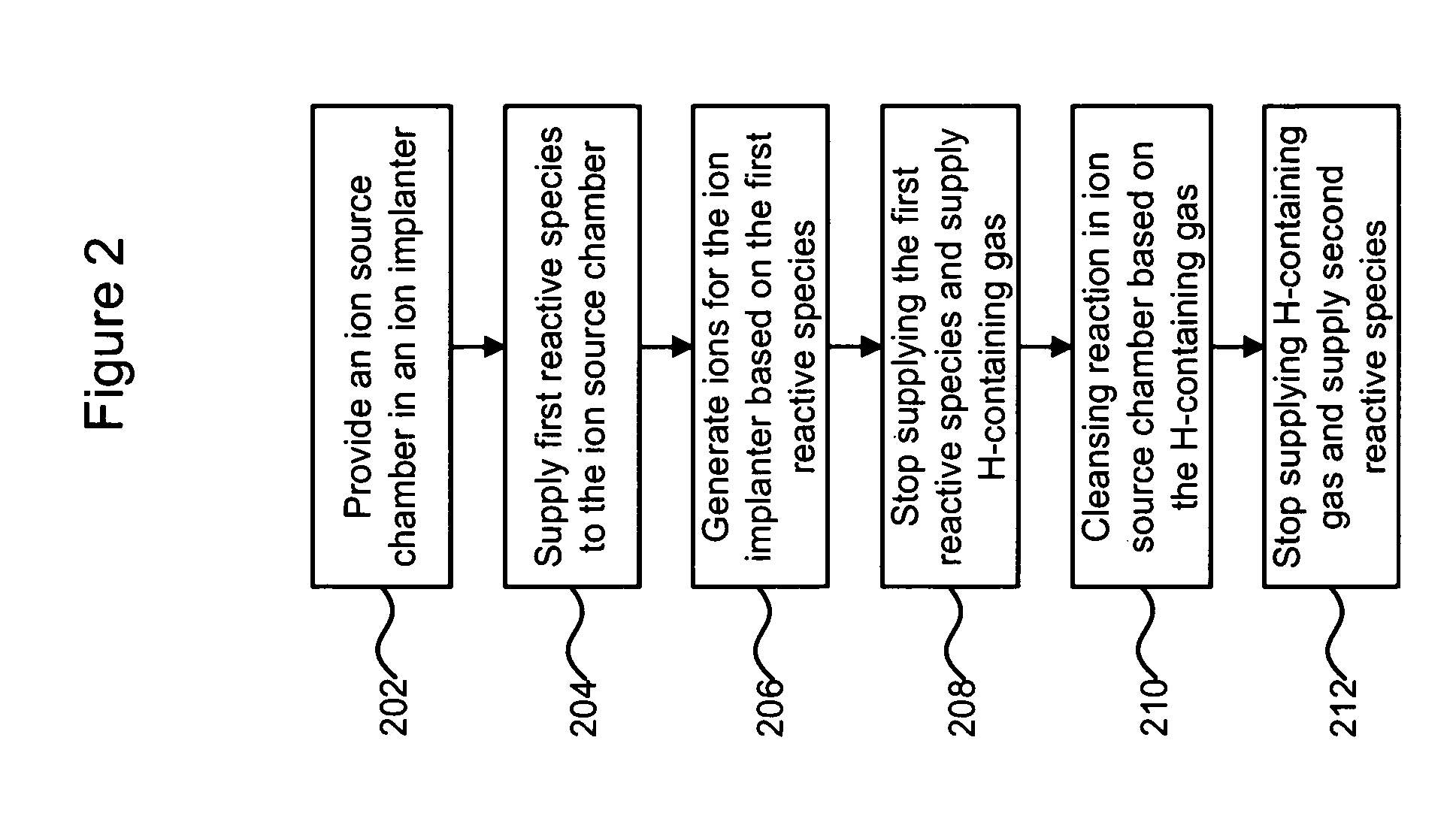
Technique for improving ion implanter productivity
ActiveUS7446326B2Improve productivityElectric discharge tubesRadiation therapyProduction rateHydrogen
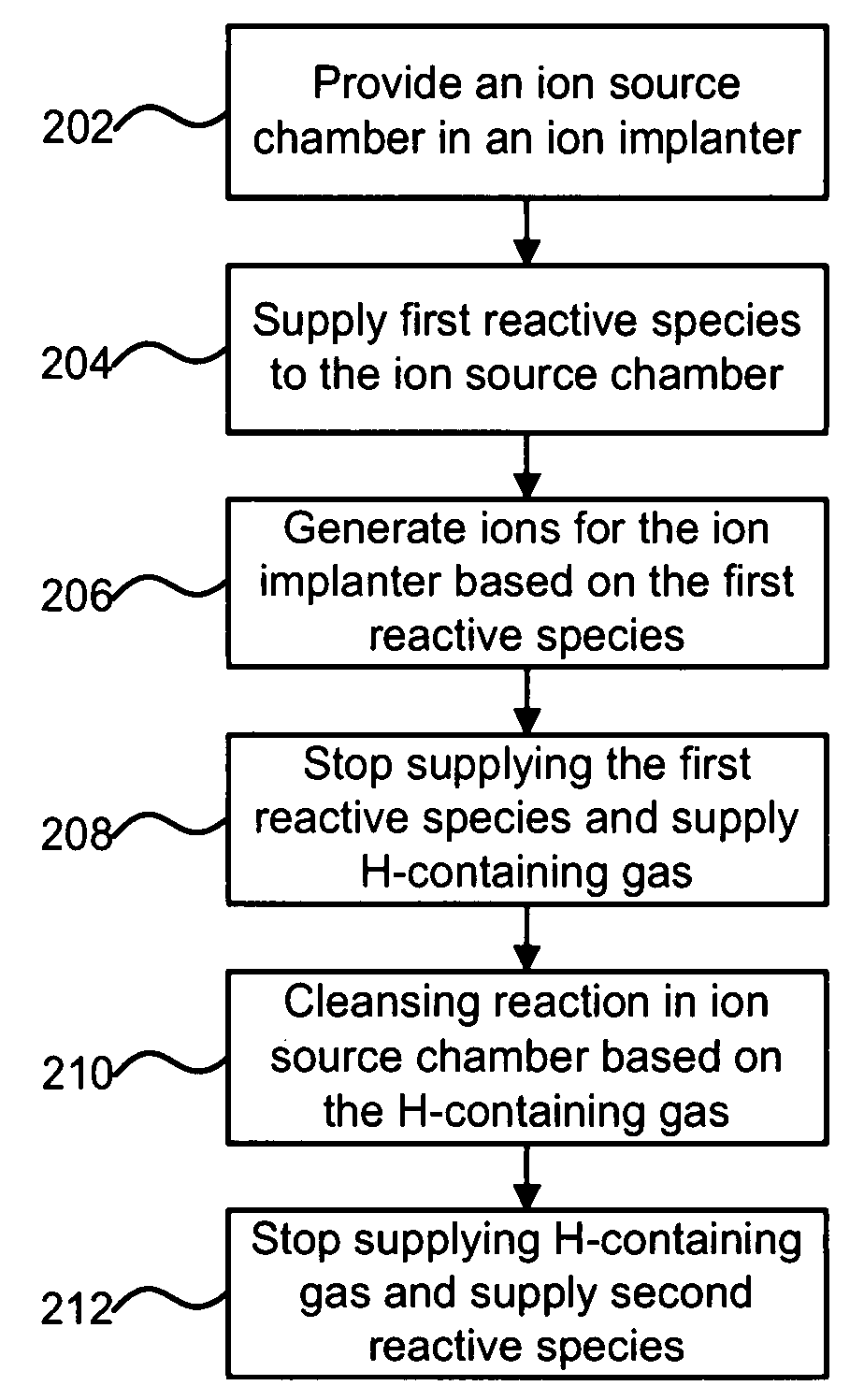
A technique for improving ion implanter productivity is disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the technique may be realized as a method for improving productivity of an ion implanter having an ion source chamber. The method may comprise supplying a gaseous substance to the ion source chamber, the gaseous substance comprising one or more reactive species for generating ions for the ion implanter. The method may also comprise stopping the supply of the gaseous substance to the ion source chamber. The method may further comprise supplying a hydrogen containing gas to the ion source chamber for a period of time after stopping the supply of the gaseous substance.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
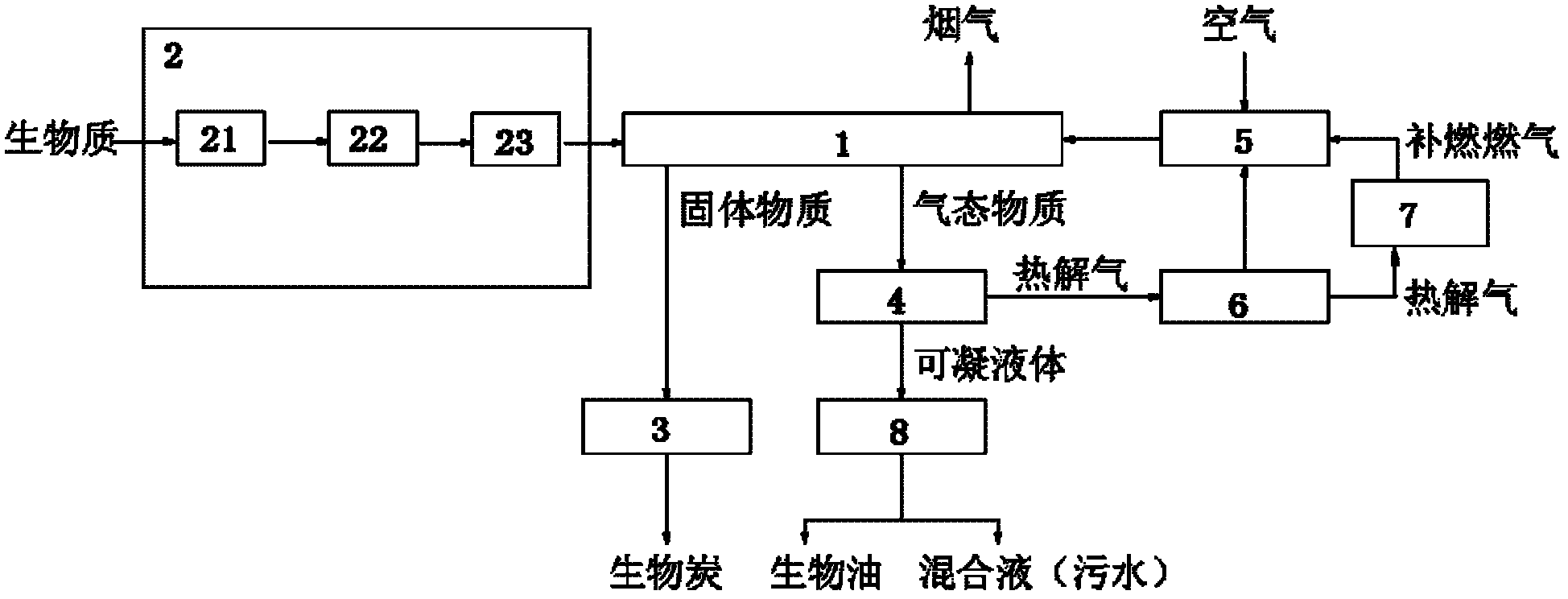
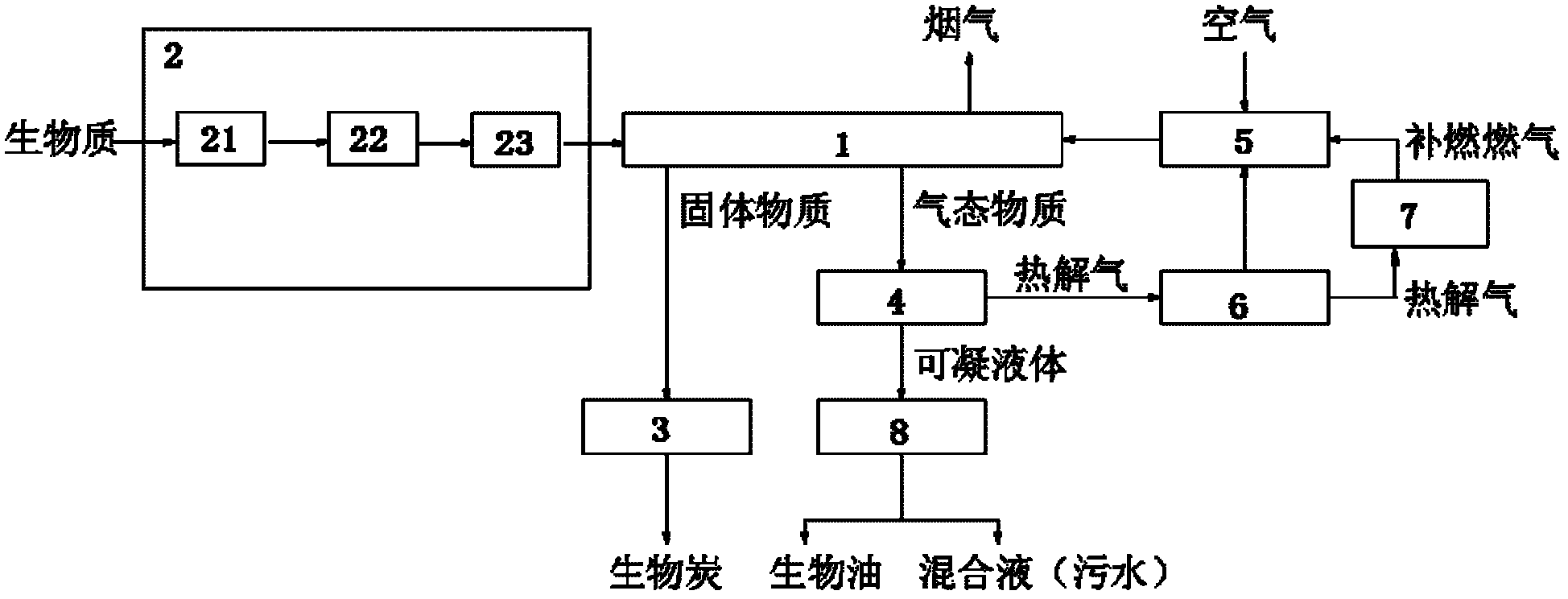
Heat-storage type biomass pyrolysis method and system
InactiveCN102604656AHigh bulk densityEasy to handleDirect heating destructive distillationBiofuelsReaction temperatureProcess engineering
The invention provides a heat-storage type biomass pyrolysis method and system which can realize large-scale production and has low operation cost and low total energy consumption. The heat-storage type biomass pyrolysis method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreating the biomass: pretreating the raw materials of a biomass to obtain the raw materials which can be used for the pyrolysis of the biomass; (2) subjecting the biomass to pyrolysis: spreading the pretreated raw materials of the biomass on the rotating bottom of a heat-storage type gas radiating tube rotating bed uniformly, making the raw materials of the biomass heated gradually in a sealed spaced along with the rotating of the rotating bottom of a heat-storage type gas radiating tube rotating bed, keeping the raw materials of the biomass at the reaction temperature of 200-800 DEG C for 30-120 minutes, subjecting the raw materials of the biomass to reaction to produce the gaseous substance and the solid biological carbon; and (3) collecting and posttreating the products of pyrolysis; collecting the gaseous substance generated in the step (2), condensing, and separating the pyrolysis gas and the condensible liquid. The pyrolysis gas can be totally or partially used as the fuel of a heat-storage type gas radiating tube, and the discharged solid biological carbon is collected after being quenched and cooled.
Owner:SHENWU TECH GRP CO LTD
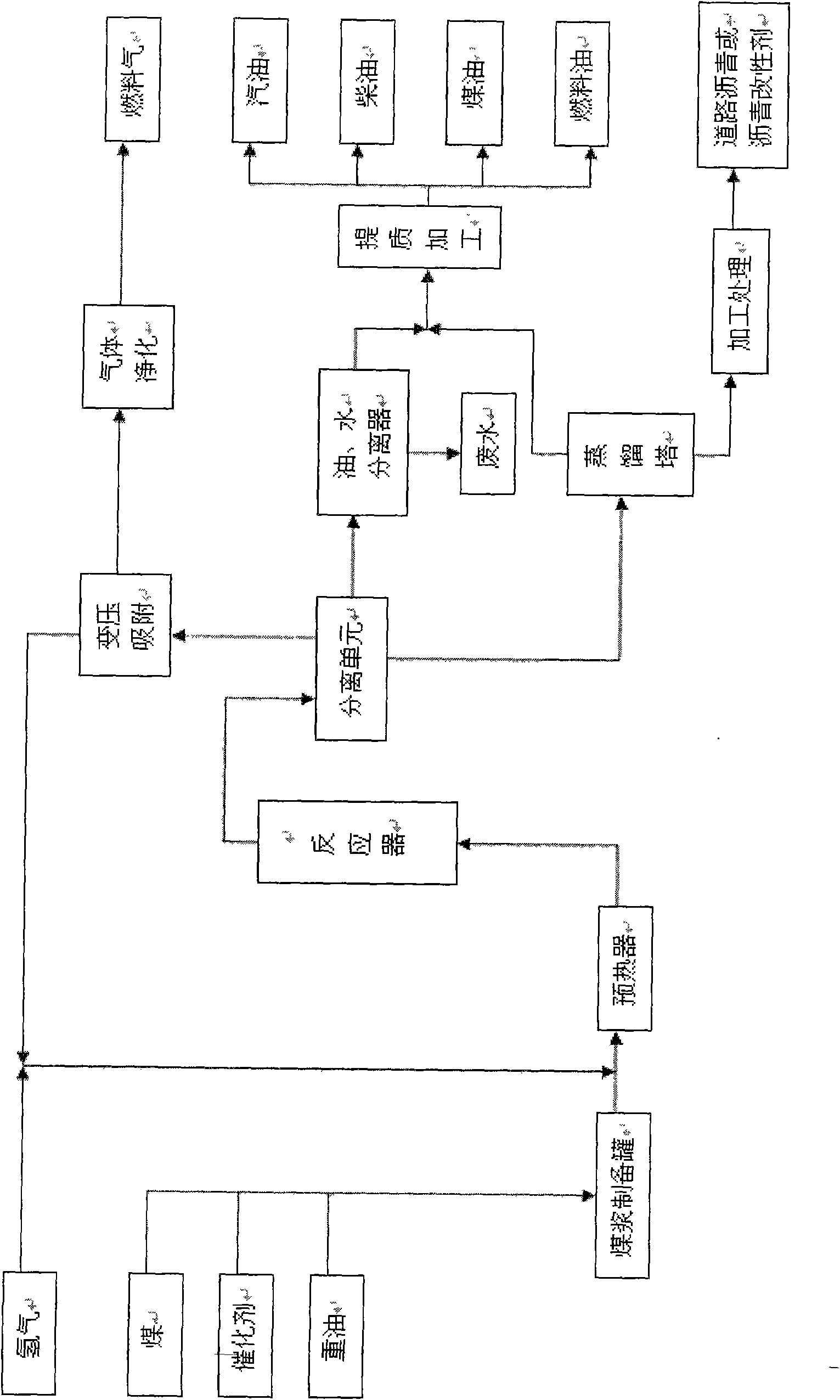
Method for simultaneously producing liquid fuel and asphalt paving materials by coprocessing coal and heavy oil
InactiveCN101649220AReduce investmentLow costHydrocarbon distillationGaseous fuelsKeroseneDistillation
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously producing liquid fuel and asphalt paving materials by coprocessing coal and heavy oil. The method comprises the following steps: mixing coal dust, catalyst and heavy oil to prepare pulp; preheating and entering a reactor to carry out reaction; separating reaction products to separate gaseous substance, light oil, water and heavy mixture; extracting hydrogen from the separated gaseous substance through pressure swing adsorption; returning the purified hydrogen to the reactor to be used circularly, and using the remaining gas as fuel after purification; carrying out oil-water separation on the separated light oil and water to obtain the light oil and the water; leading the heavy mixture into a distilling tower to obtain coarse oil and tower bottom product through distillation separation; mixing the coarse oil and the light oil to obtain liquid fuels of gasoline, kerosene, diesel fuel, fuel oil, and the like through upgrading process; and processing the tower bottom product to get the asphalt paving materials. The invention has the advantage that under the moderate process condition, the liquid fuel and asphalt paving materials canbe produced simultaneously.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus for treating wastes by gasification
InactiveUS6902711B1Low costVarious problemCombustible gas catalytic treatmentCombustible gas thermal treatmentSyngasFluidized bed
An apparatus for treating wastes includes a fluidized bed reactor for partially combusting the wastes at a relatively low temperature, and a separate relatively high temperature reactor for separate gasification of gaseous material and char from the first gasification. This synthesis gas thus formed is cooled, subjected to a conversion operation in a converter to produce hydrogen.
Owner:EBARA CORP +1
Cerium oxide powder
ActiveUS20050036928A1Improve stabilityEasy to mergePigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyHydrogenMetallurgy
Polycrystalline cerium oxide powder in the form of aggregates of primary particles with a specific surface of between 70 and 150 m2 / g, an average primary particle diameter of between 5 and 20 nm and an average, projected aggregate diameter of between 20 and 100 nm. It is produced in that an aerosol is reacted in a flame obtained from a hydrogen-containing combustible gas and primary air and the solid obtained is then separated from the gaseous substances.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Light induced gas sensing at room temprature
InactiveUS20100077840A1Reduces eliminates needReduce power consumptionRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGaseous substanceAmount of substance
A light-assisted sensor and method of light-assisted sensing of gaseous species involves contacting a gaseous medium with a material selected to adsorb on its surface one or more gaseous species of interest and illuminating the surface of the material from a source to induce a change of an electrical property, such as conductivity, of the material in the presence of the one or more gaseous species. The change in the electrical property of the material is measured and can be used to identify and quantify the gaseous species of interest in the gaseous medium.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
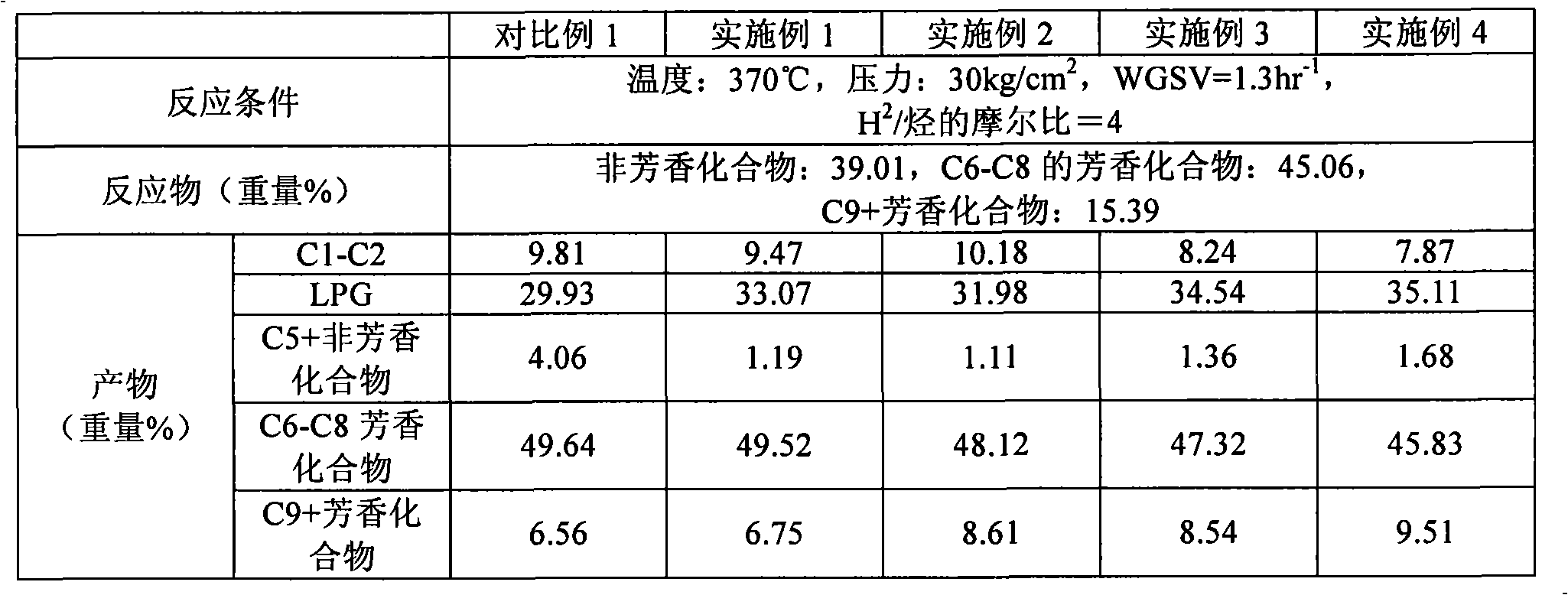
Process of preparing aromatic hydrocarbons and liquefied petroleum gas from hydrocarbon mixture
InactiveCN101305078AHigh purityPromote value-addedCatalytic naphtha reformingHydrocarbon oil crackingLiquid productHydrocarbon mixtures
Disclosed is a process of preparing aromatic hydrocarbons and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) from a hydrocarbon mixture, in which a non-aromatic compound in the hydrocarbon feedstock mixture is converted into a gaseous material having a large amount of LPG through hydrocracking, and an aromatic compound therein is converted into an oil component having large amounts of benzene, toluene, and xylene (BTX) through dealkylation and transalkylation, in the presence of a catalyst obtained by supporting platinum / bismuth onto a mixture support having zeolite and an inorganic binder. The gaseous product is separated into LPG and a mixture of methane and ethane depending on differences in boiling point through distillation, while the liquid product is separated into benzene, toluene, xylene, and C9+ aromatic compounds depending on differences in boiling point through distillation.
Owner:SK ENERGY CO LTD (KR)
Flat-type fluorescent lamp for illumination unit and liquid crystal device
InactiveUS20020063514A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsElectrical conductorEngineering
A flat-type fluorescent lamp for LCD devices is provided, which makes it possible to narrow the picture-frame area and to widen the emission area and which facilitates their wiring, connection and assembly operations. The lamp comprises: (a) a container having a first plate, a second plate, and a frame member; the first and second plates being opposed to each other and fixed together with the frame member in such a way as to have a specific distance between the first and second plates; the first plate forming a flat emission surface; (b) a gaseous substance confined in the container; (c) a fluorescent material layer formed on an inner surface of the container; (d) electrodes formed on an inner surface of the second plate; and (e) a conductor member attached to the second plate in such a way as to extend along the inner surface of the second plate and an outer edge face thereof; a first end of the conductor member being contacted with a terminal part of the electrodes; a second end of the conductor member being located outside the second plate.
Owner:VISTA PEAK VENTURES LLC
Method of inducing porous structures in laser-deposited coatings
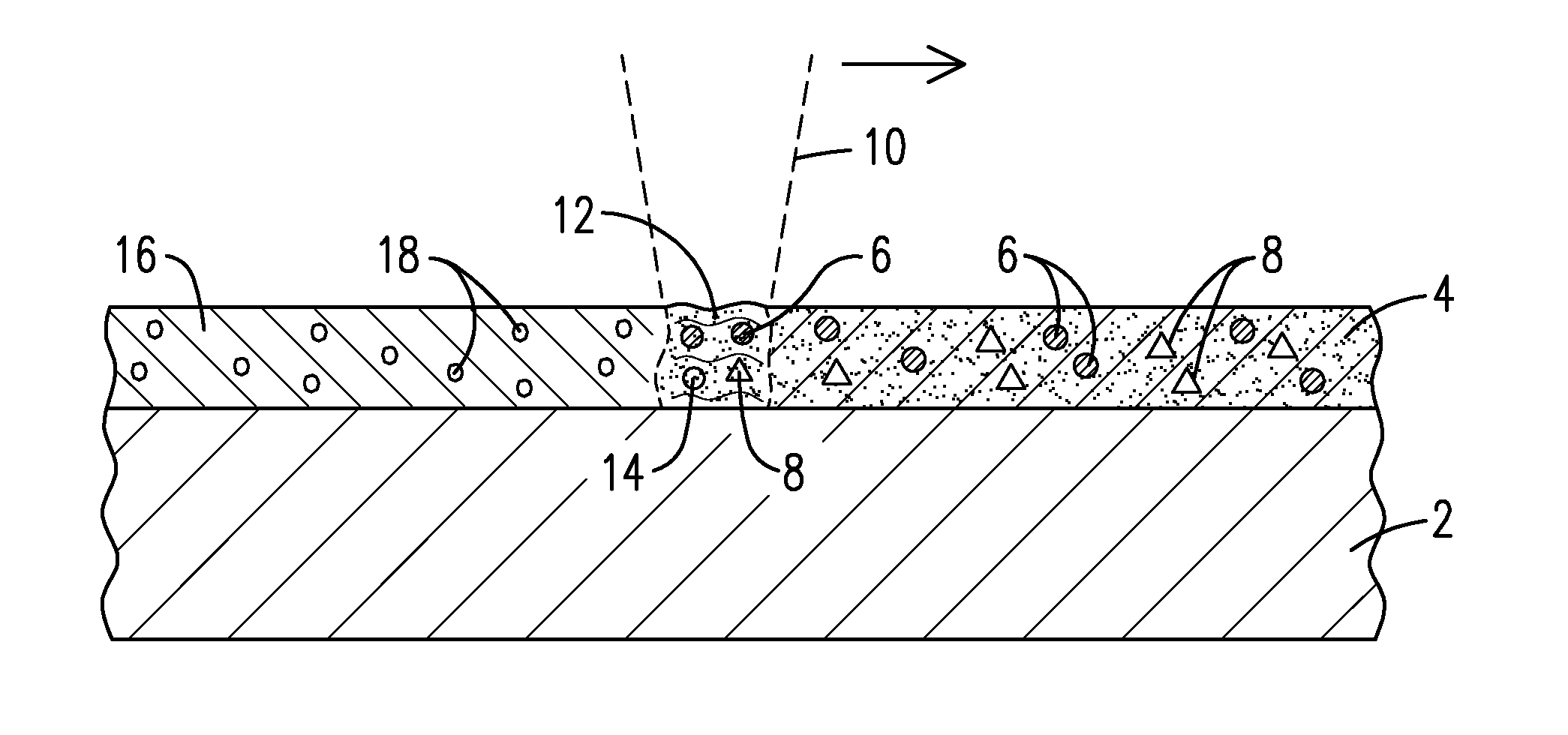
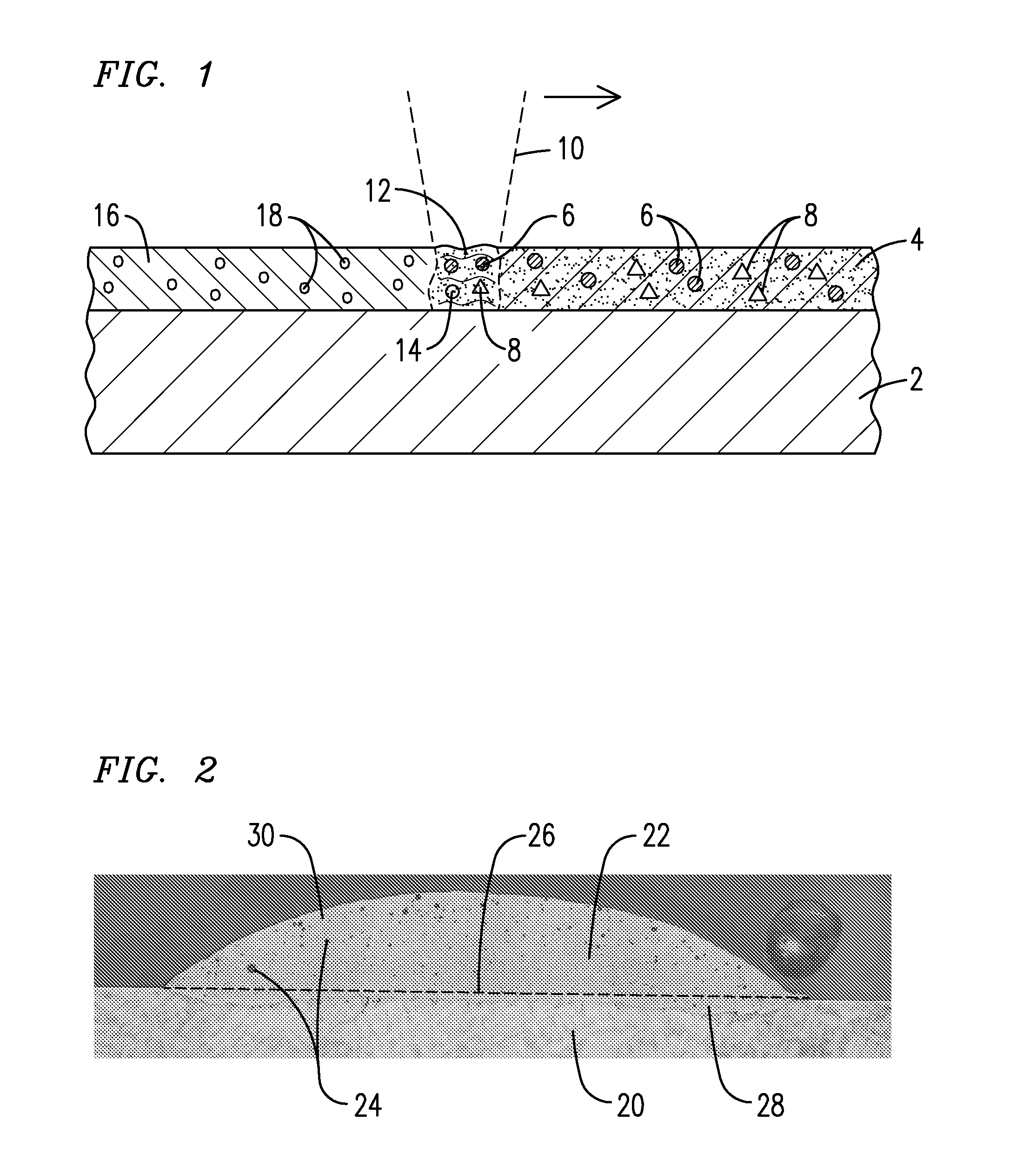
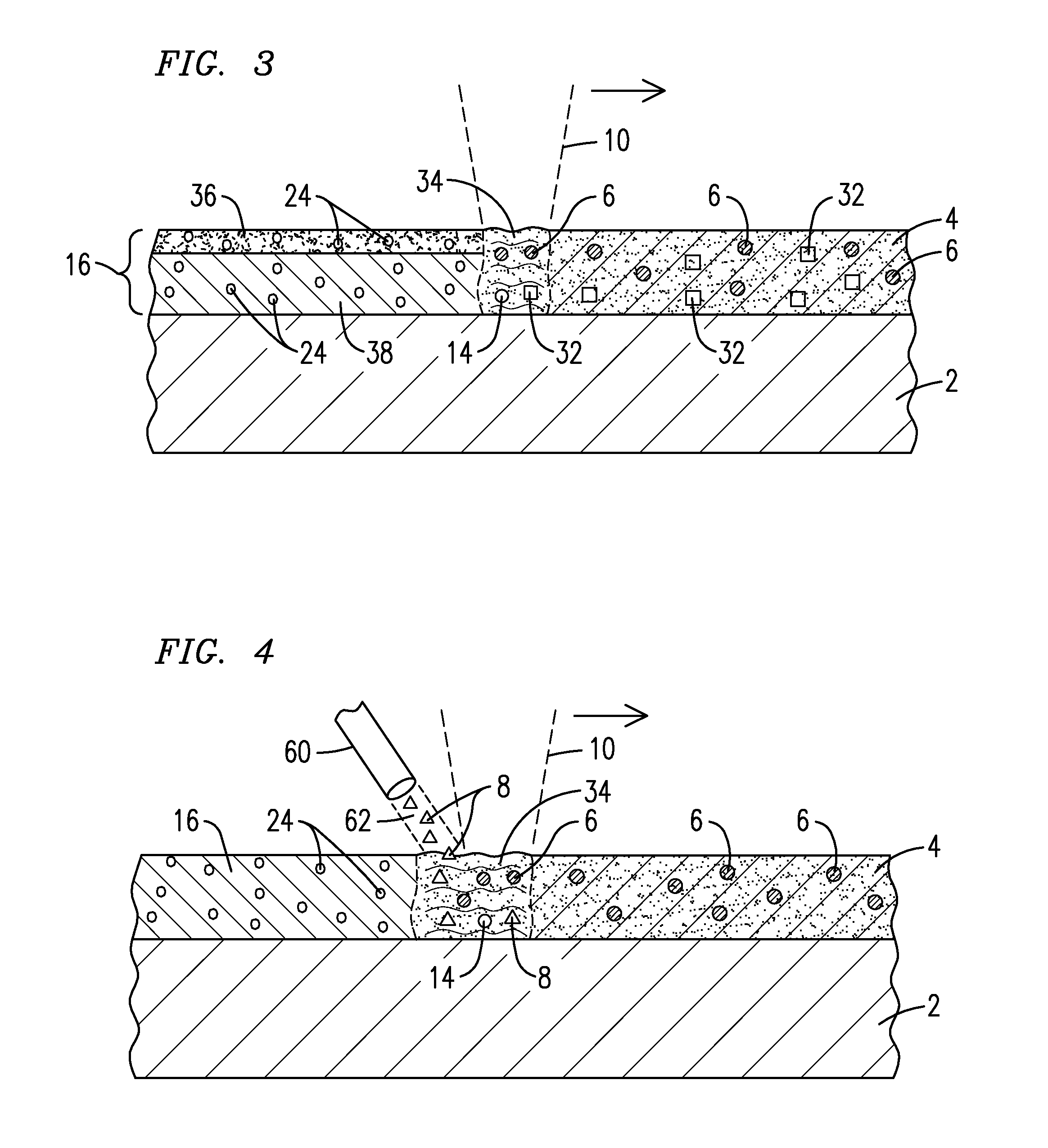
A layer of a powdered material (4) is heated with an energy beam (10) such that at least one gas-generating agent (8) reacts to form at least one gaseous substance (14) to produce a void-containing coating (16) adhered to the surface of a substrate (2).The powdered material may contain a metallic material, a ceramic material, or both, and may also contain at least one of a flux material (32) containing the gas-generating agent and an exothermic agent (64). The heating may occur using a laser beam and may induce a melting or sintering of the powdered material to produce the void-containing coating. A gas turbine engine component exhibiting improved thermal and mechanical properties may be formed to include the void-containing coating, which may take the form of a bond coating, a thermal barrier coating, or both.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
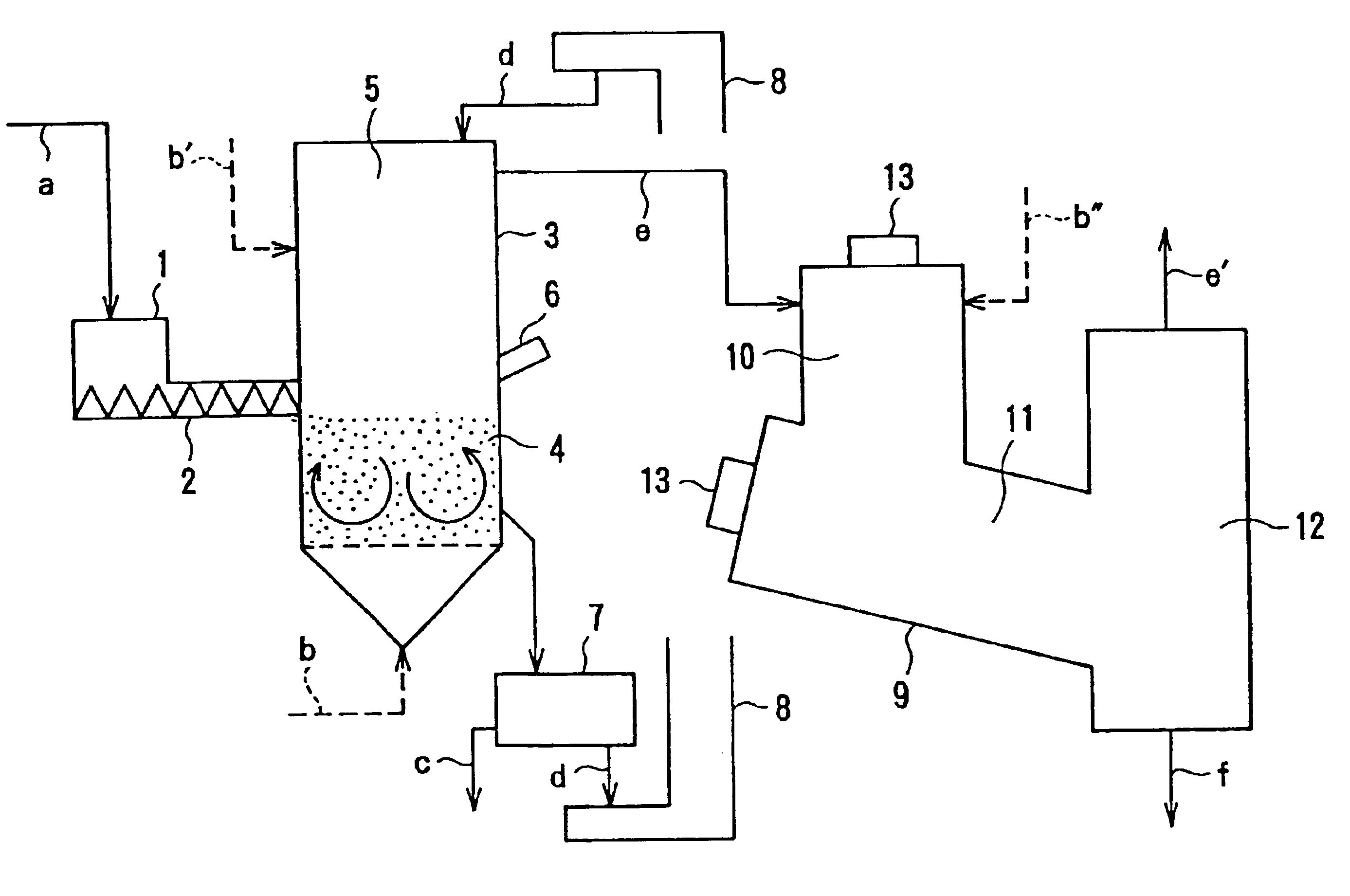
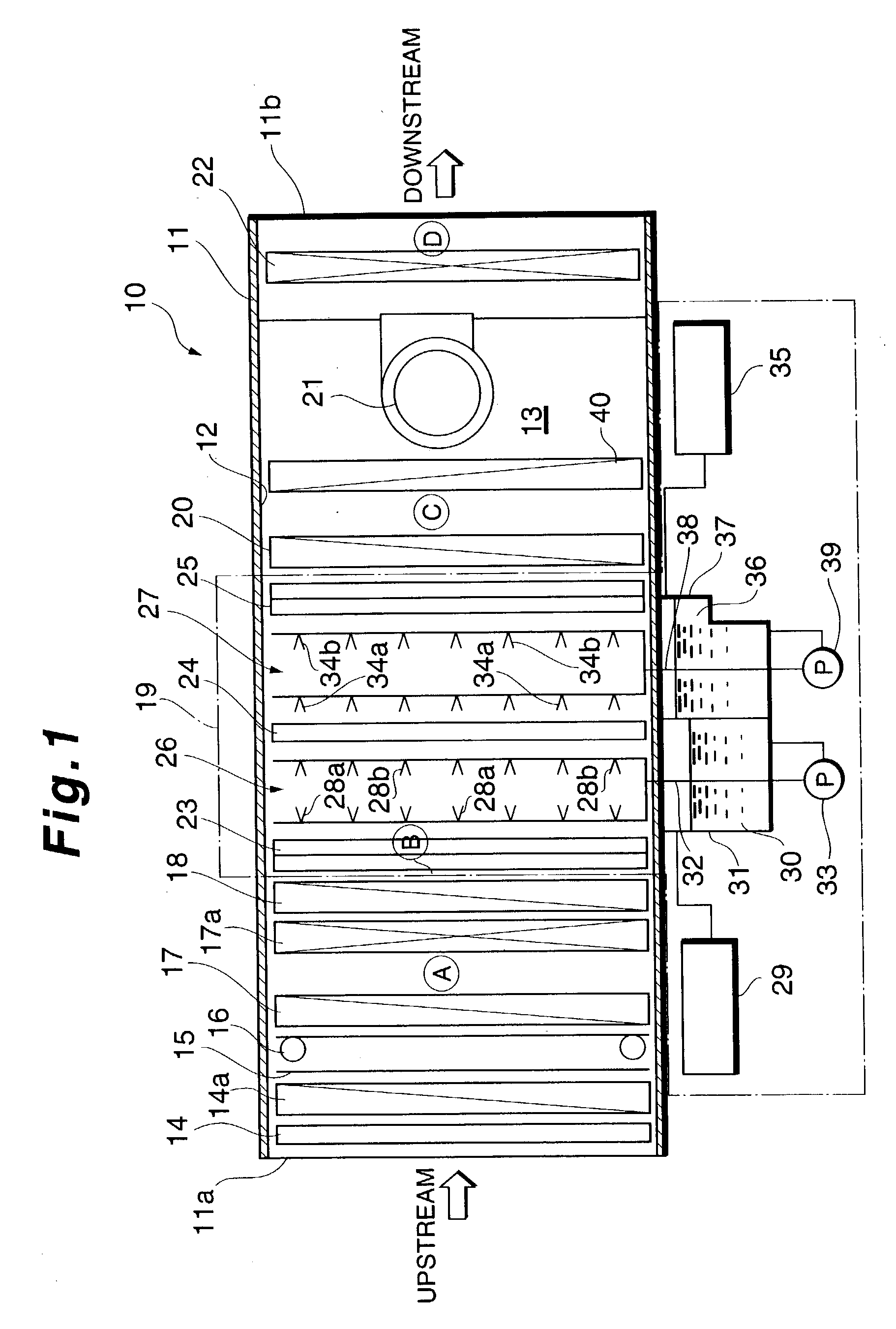
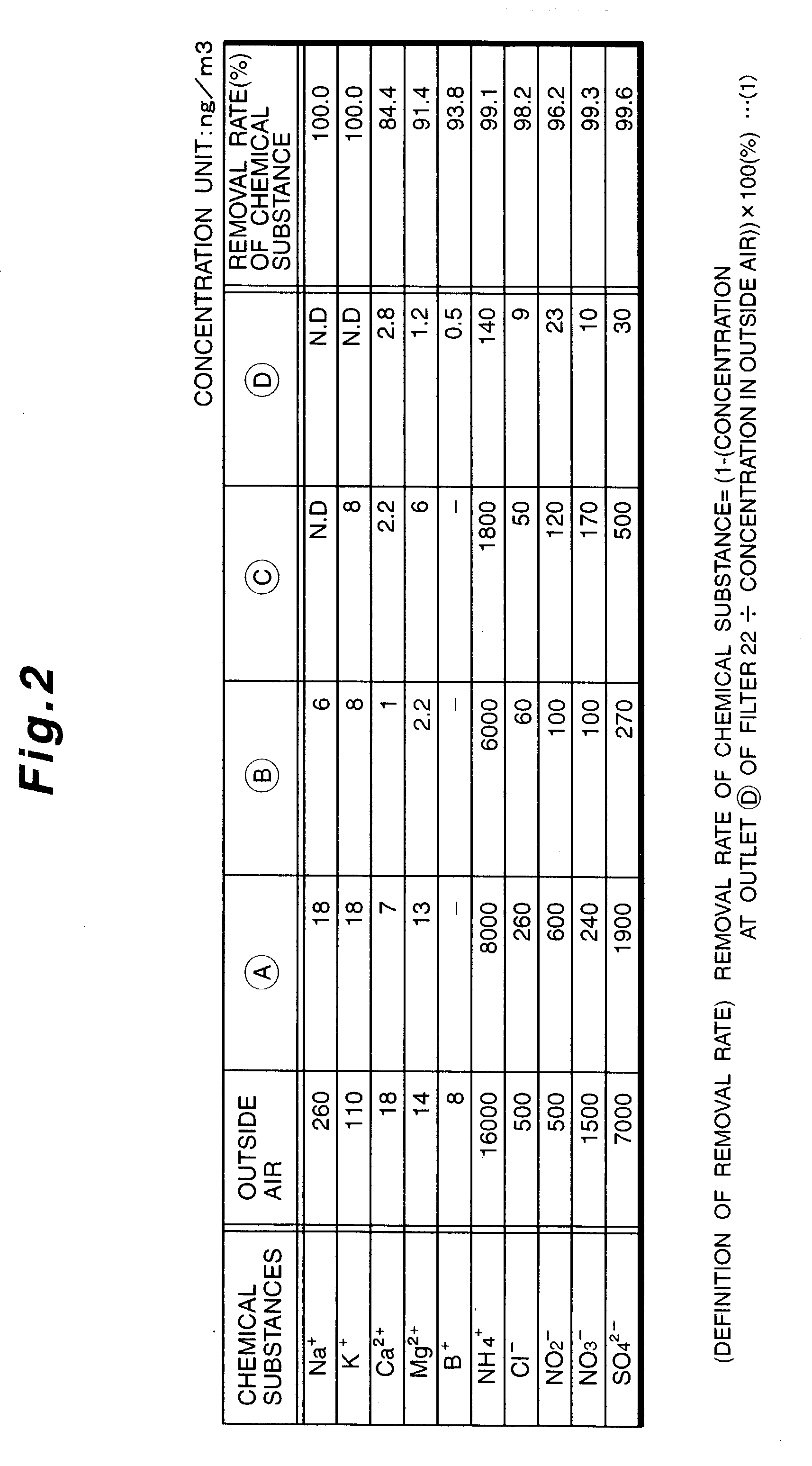
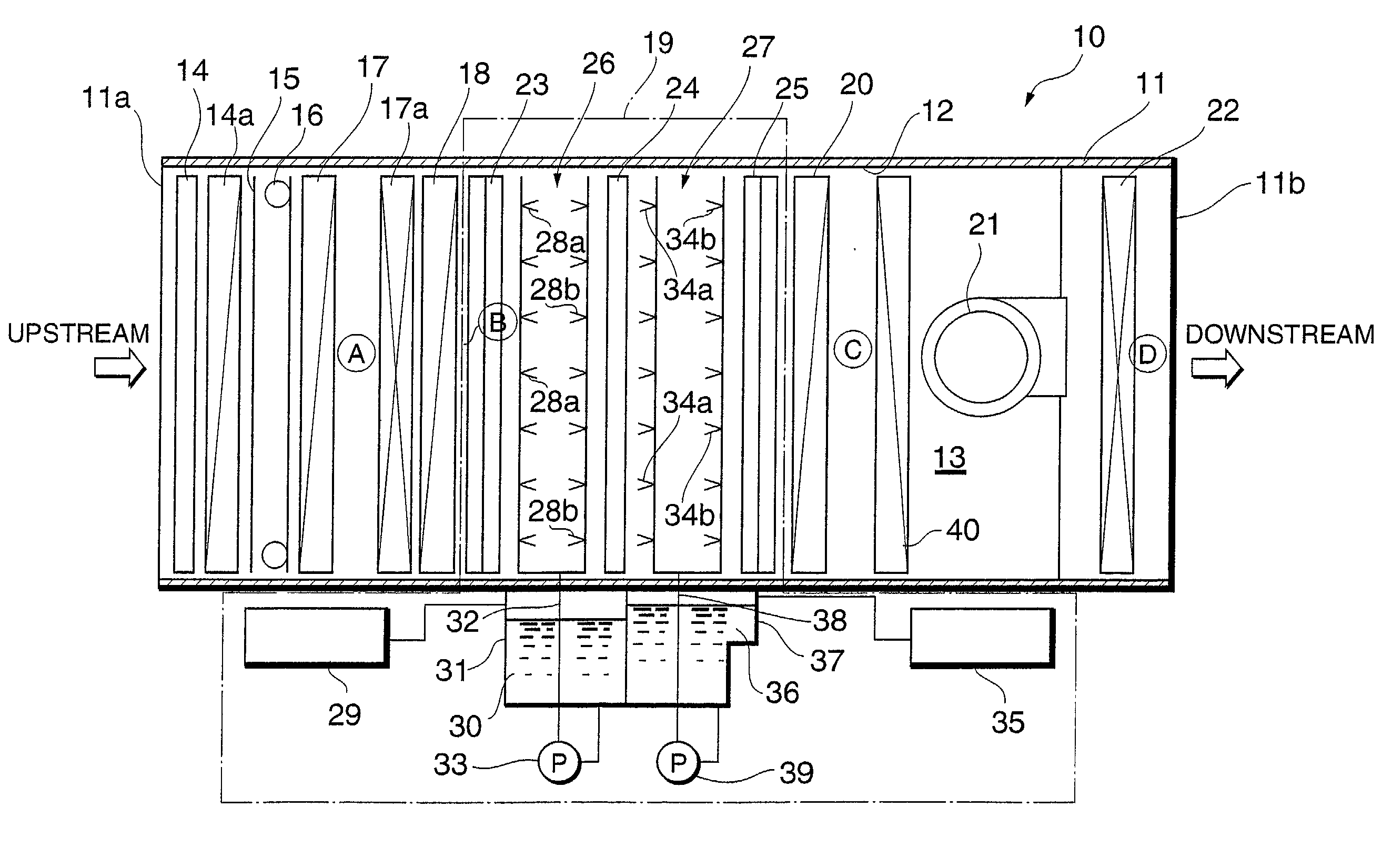
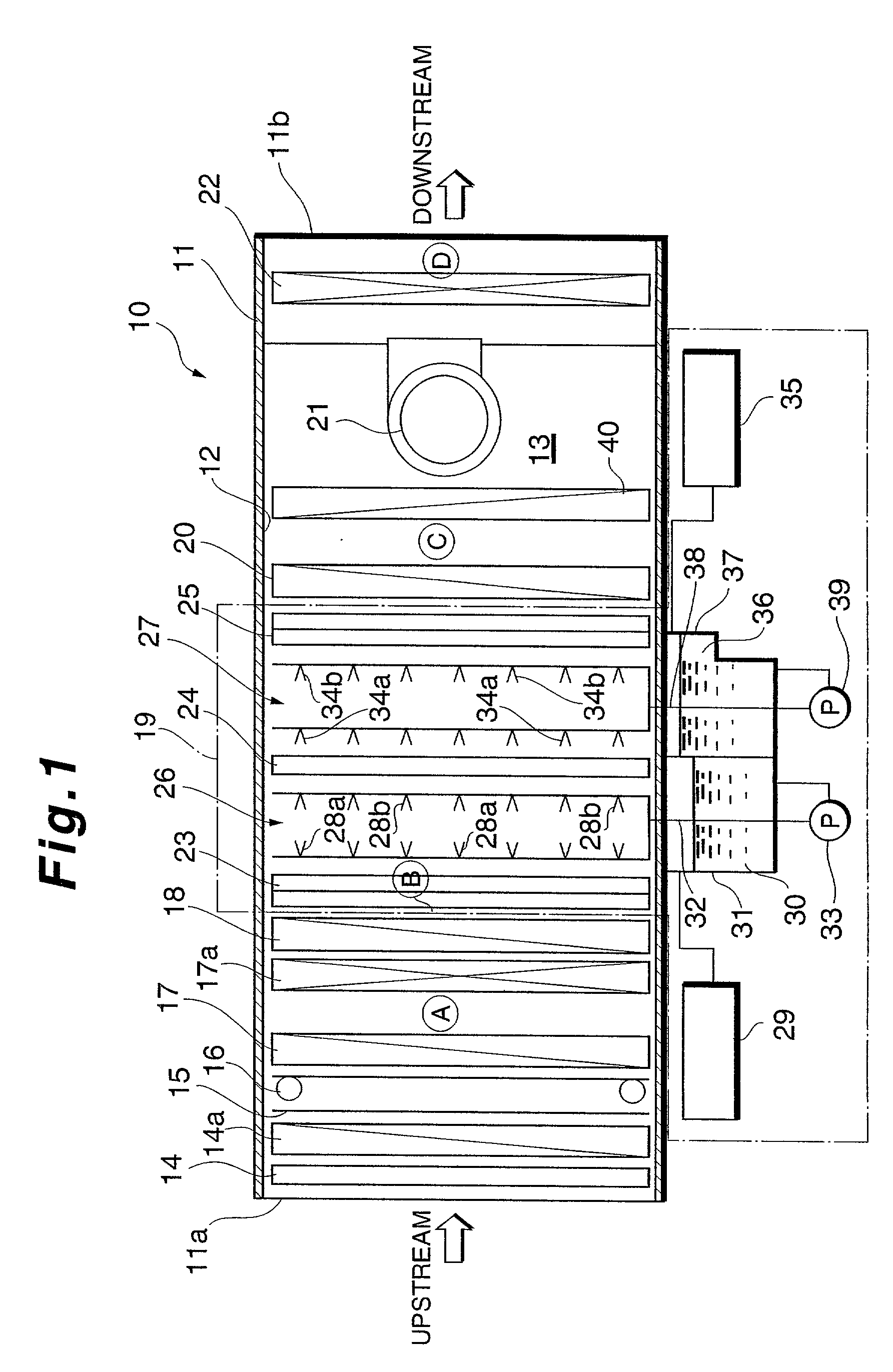
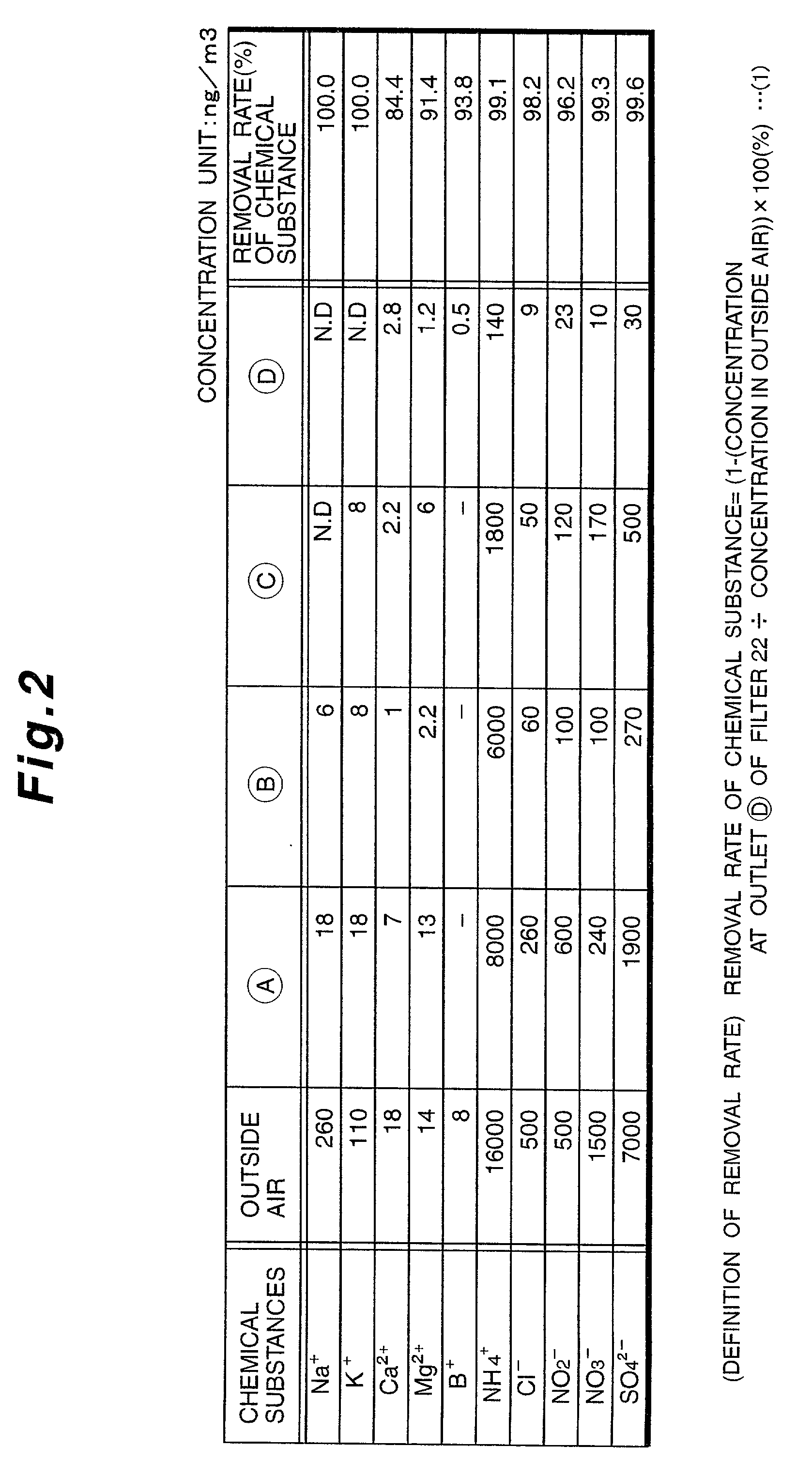
Method for removing impurity contents in the air
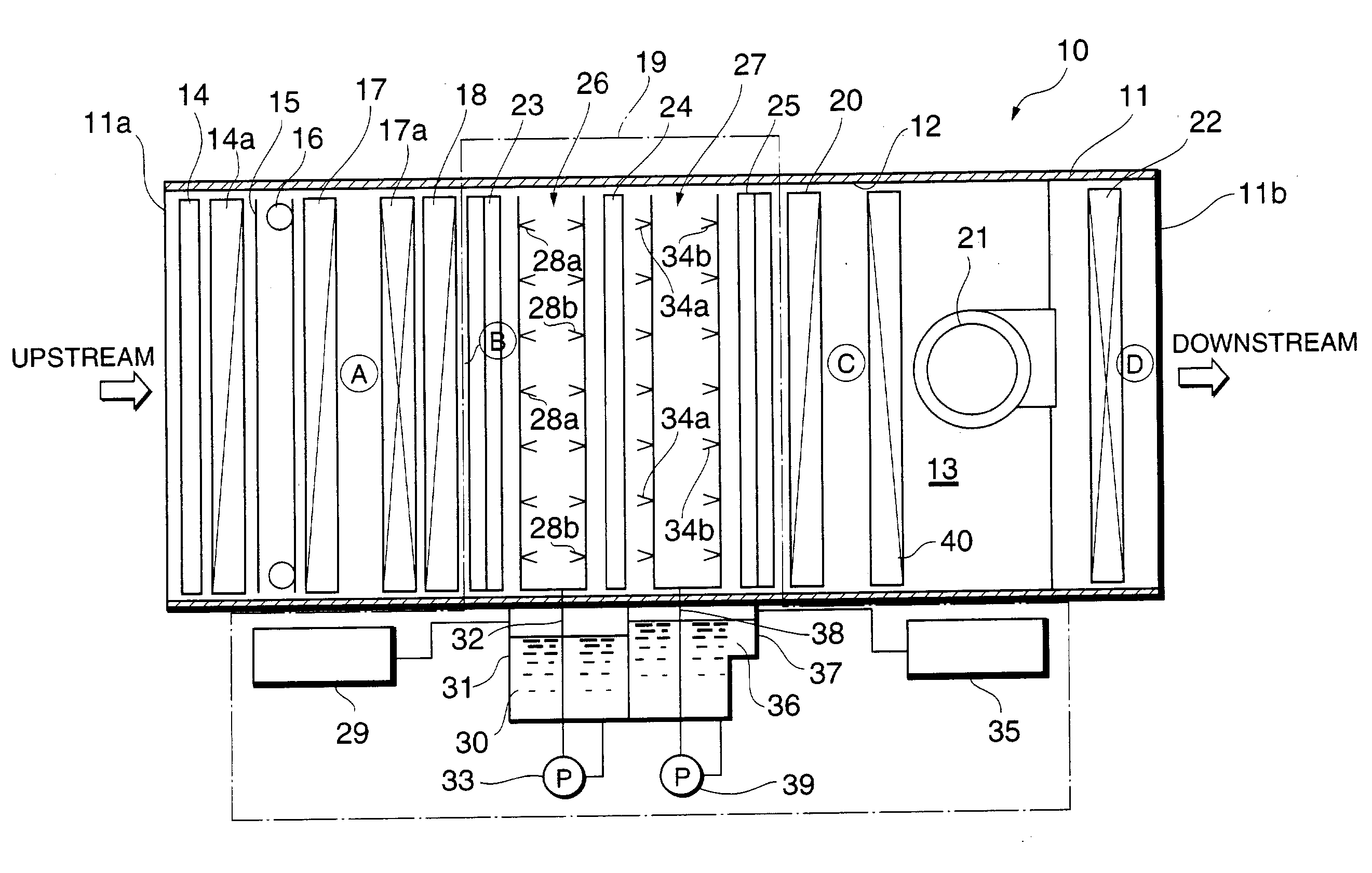
Apparatus for removing impurity substances in the air, comprising a first filter (17) for removing solid substances in the air flowing in a flow passage (13) defined by a housing (11); first cooling means (18) for cooling the air to not higher than its dew-point temperature; a wet-type impurity removing mechanism (19) for capturing gaseous substances in the air; second cooling means (20); and a second filter (22). The wet-type impurity removing mechanism (19) includes first liquid atomizing means (26) having a plurality of nozzle ports (28) for spraying, arranged mutually spaced apart and facing each other in the direction of the air flow passage; first and second condensing and capturing means (23 and 24) located across the first atomizing means 26 and spaced apart from each other, the first capturing means upstream from and the second capturing means downstream from the first atomizing means; second atomizing means for capturing remaining gaseous substances in the air; and third condensing and capturing means (25).
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Technique for improving ion implanter productivity
ActiveUS20070045570A1Improve productivityElectric discharge tubesRadiation therapyProduction rateHydrogen
A technique for improving ion implanter productivity is disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the technique may be realized as a method for improving productivity of an ion implanter having an ion source chamber. The method may comprise supplying a gaseous substance to the ion source chamber, the gaseous substance comprising one or more reactive species for generating ions for the ion implanter. The method may also comprise stopping the supply of the gaseous substance to the ion source chamber. The method may further comprise supplying a hydrogen containing gas to the ion source chamber for a period of time after stopping the supply of the gaseous substance.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Process for using iron oxide and alumina catalyst for slurry hydrocracking
ActiveUS8123933B2Promote conversionSufficient conversionRefining with metalsOther chemical processesSlurryIron oxide
A process and apparatus is disclosed for converting heavy hydrocarbon feed into lighter hydrocarbon products. The heavy hydrocarbon feed is slurried with a catalyst comprising iron oxide and alumina to form a heavy hydrocarbon slurry and hydrocracked to produce lighter hydrocarbons. The iron oxide and alumina catalyst does not require as much iron content relative to non-gaseous material in the reactor to obtain useable products.
Owner:UOP LLC
Continuous thermal process for flavor preparation
InactiveUS20080095906A1Increase temperatureParticipation can be limitedFood preparationFlavorPhase change
A flavor composition is formed by combining a first precursor composition with a second precursor composition to form a precursor flavor composition. The precursor flavor composition is then subjected to a sufficient temperature to cause one or both of the first and second precursor compositions to undergo at least a partial phase change to a gaseous material. Generally, the first and second precursor compositions are immiscible.
Owner:INTERCONTINENTAL GREAT BRANDS LLC
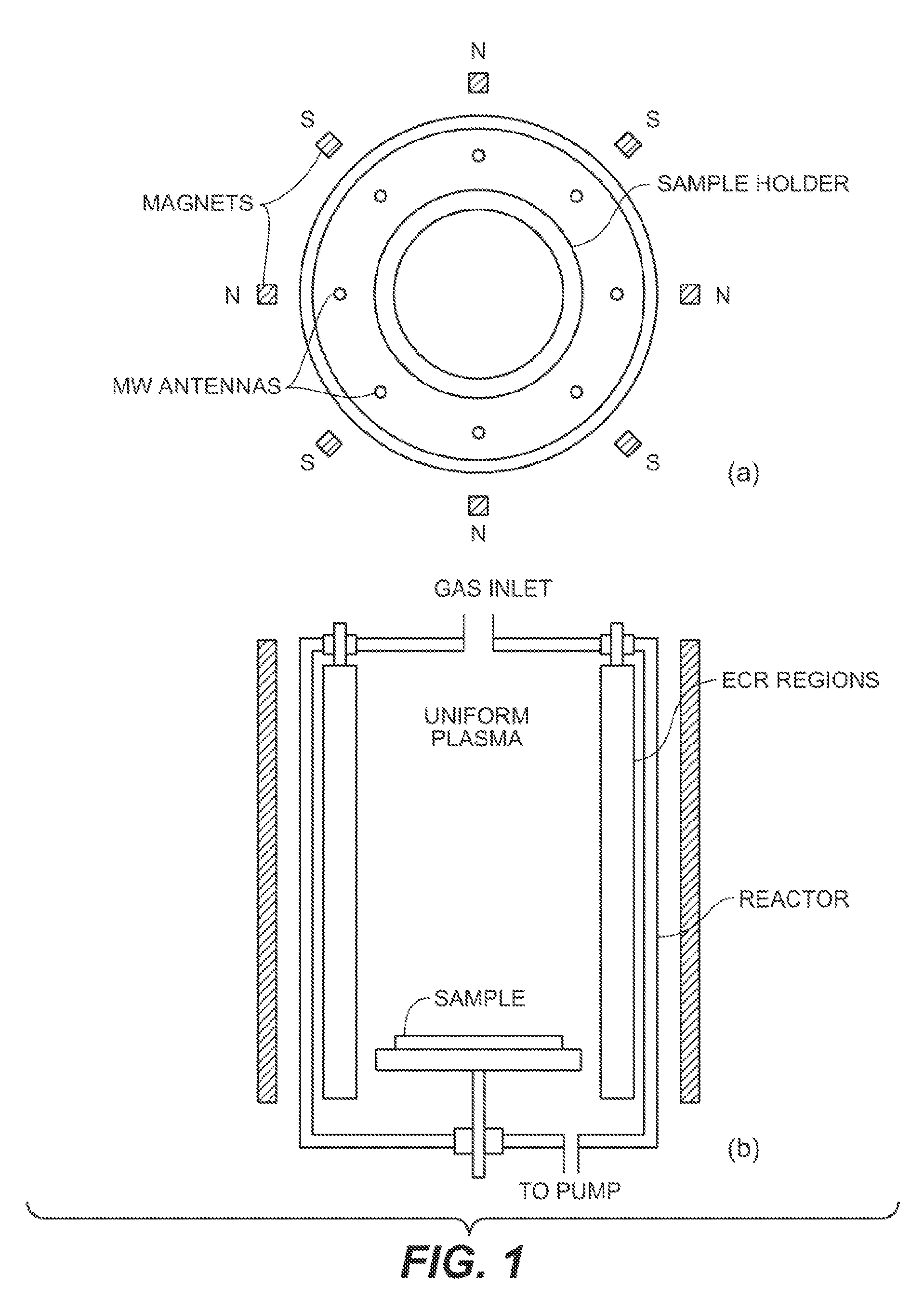
Sensor device and method for qualitative and quantitative analysis of gas phase substances
InactiveUS20080101434A1Shorten the timeAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial thermal conductivityNon destructiveGas phase
New sensors and methods for qualitative and quantitative analysis of multiple gaseous substances simultaneously with both high selectivity and high sensitivity are provided. The new sensors rely on a characteristic difference in energy between the interaction of a particular substance with a catalyst coated heat transfer device (HTD) and a non-catalyst coated (or one coated with a different catalyst) reference HTD. Molecular detection is achieved by an exothermic or endothermic chemical or physical reaction between the catalytic surface of the sensor and the molecule, tending to induce a temperature change of the sensor. Both high temperature and non-destructive low temperature detection are possible. The magnitude and rate of endothermic or exothermic heat transfer from a specific molecule-catalyst interaction is related to molecular concentration.
Owner:SENSOR TECH LLC
Zero excess sludge membrane bioreactor
InactiveUS7311833B2High yieldCost-effectiveTreatment using aerobic processesDialysis systemsChemical oxygen demandMembrane fouling
Owner:YAMAMOTO KAZUO +1
Composite dry vacuum pump having roots rotor and screw rotor
ActiveUS20060083651A1Reduced Power RequirementsIncrease volumeRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsOscillating piston enginesEngineeringVacuum pump
Disclosed is a dry vacuum pump for evacuating a processing chamber in semiconductor or display manufacturing device, or for evacuating the gaseous substance and / or the byproducts generated in process chamber. The dry vacuum pump does not need a partition wall between a roots rotor and a screw rotor. In the dry vacuum pump, a space is formed on the connecting portion to roots rotor among through the under sides of the roots rotor and the screw rotor to stay the object substance thereon.
Owner:LOT VACUUM
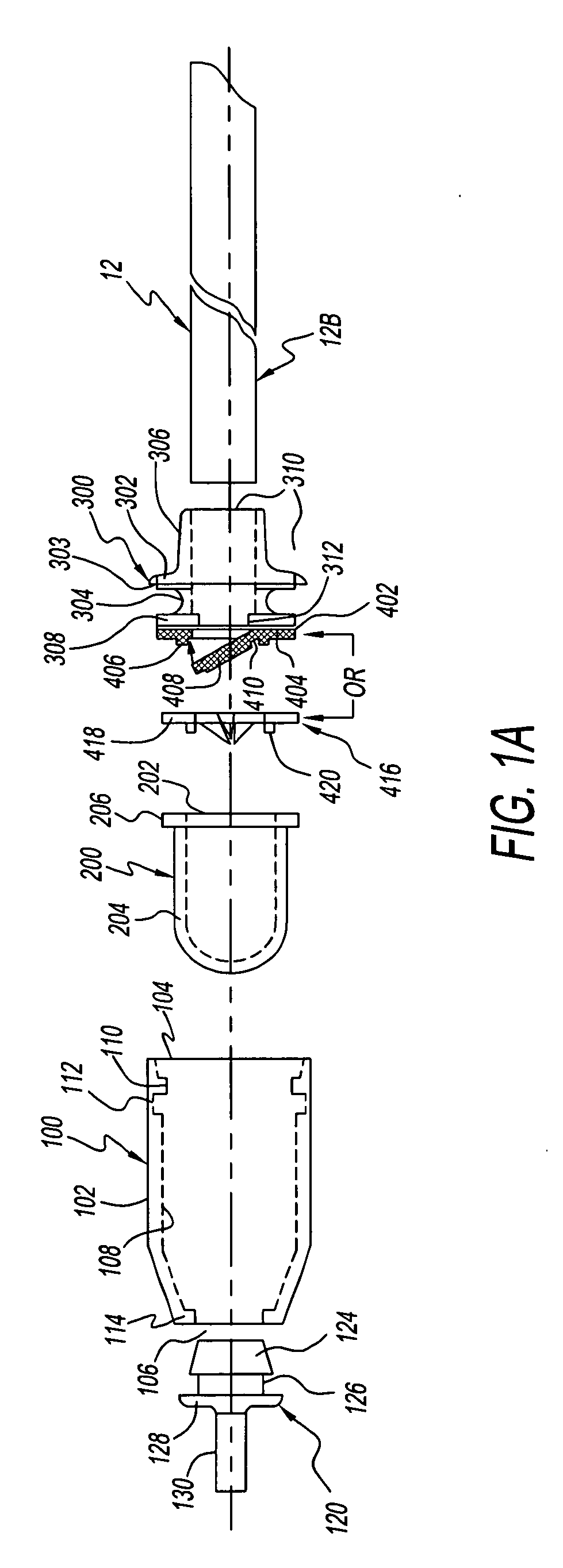
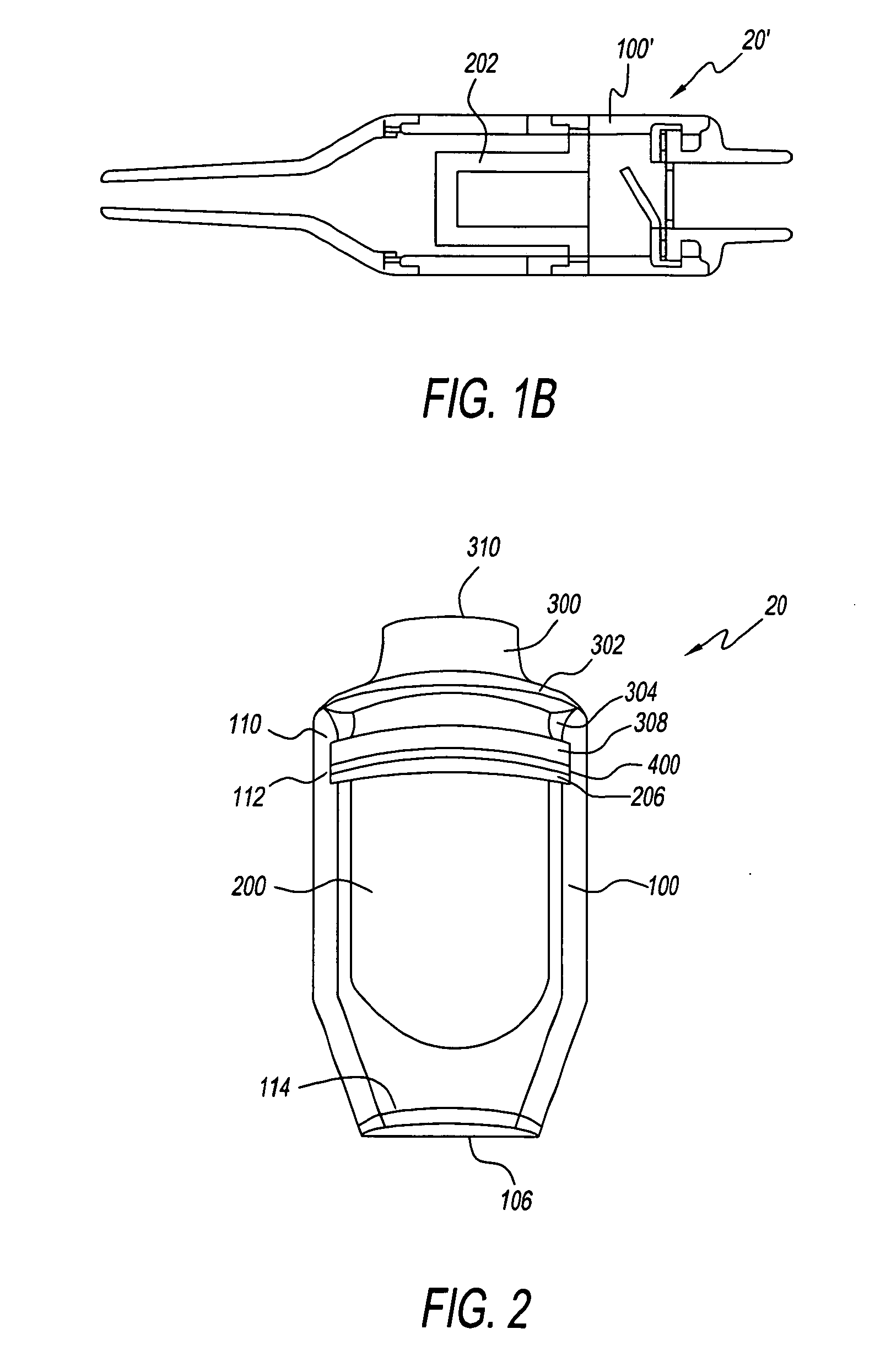
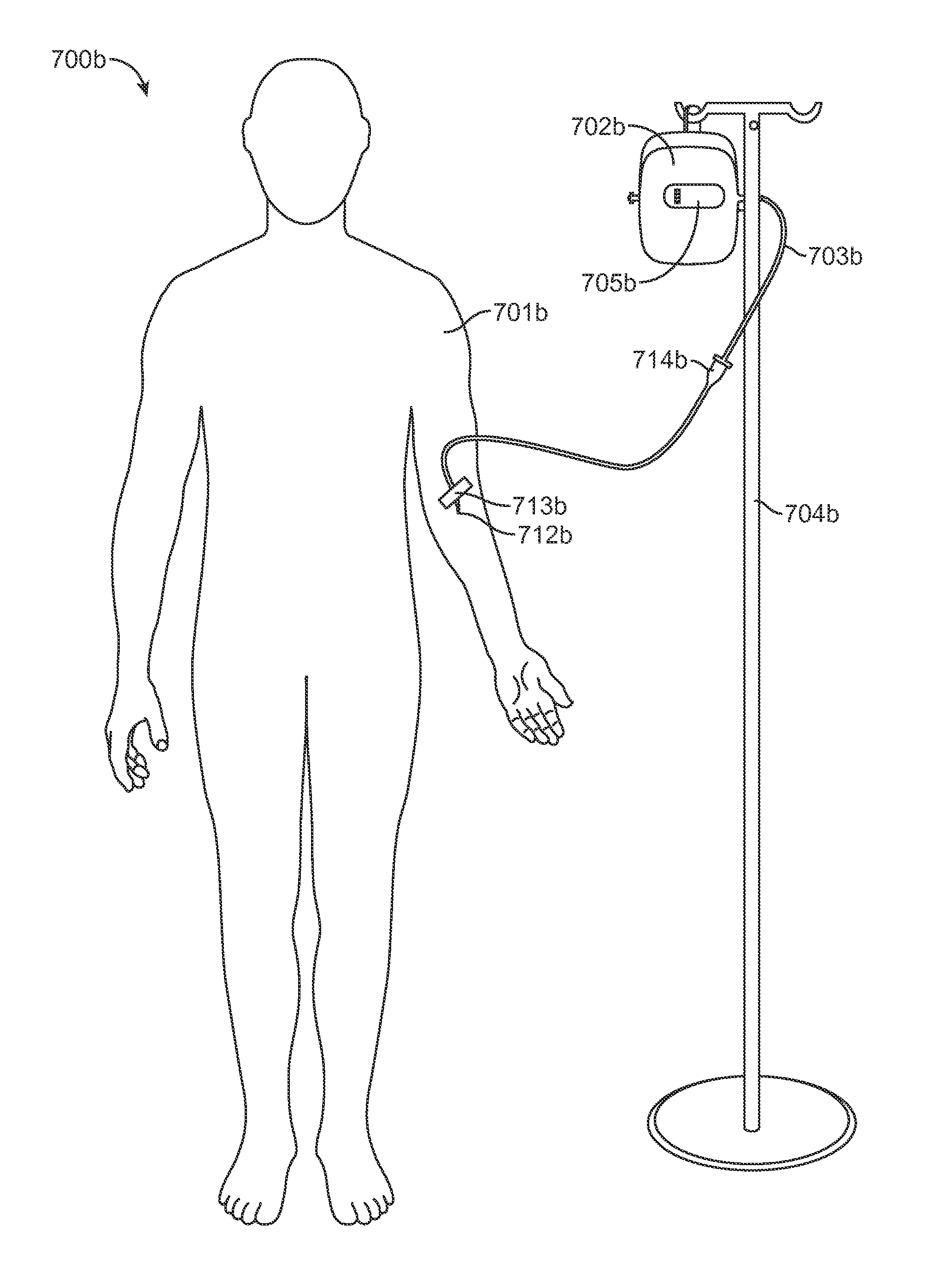
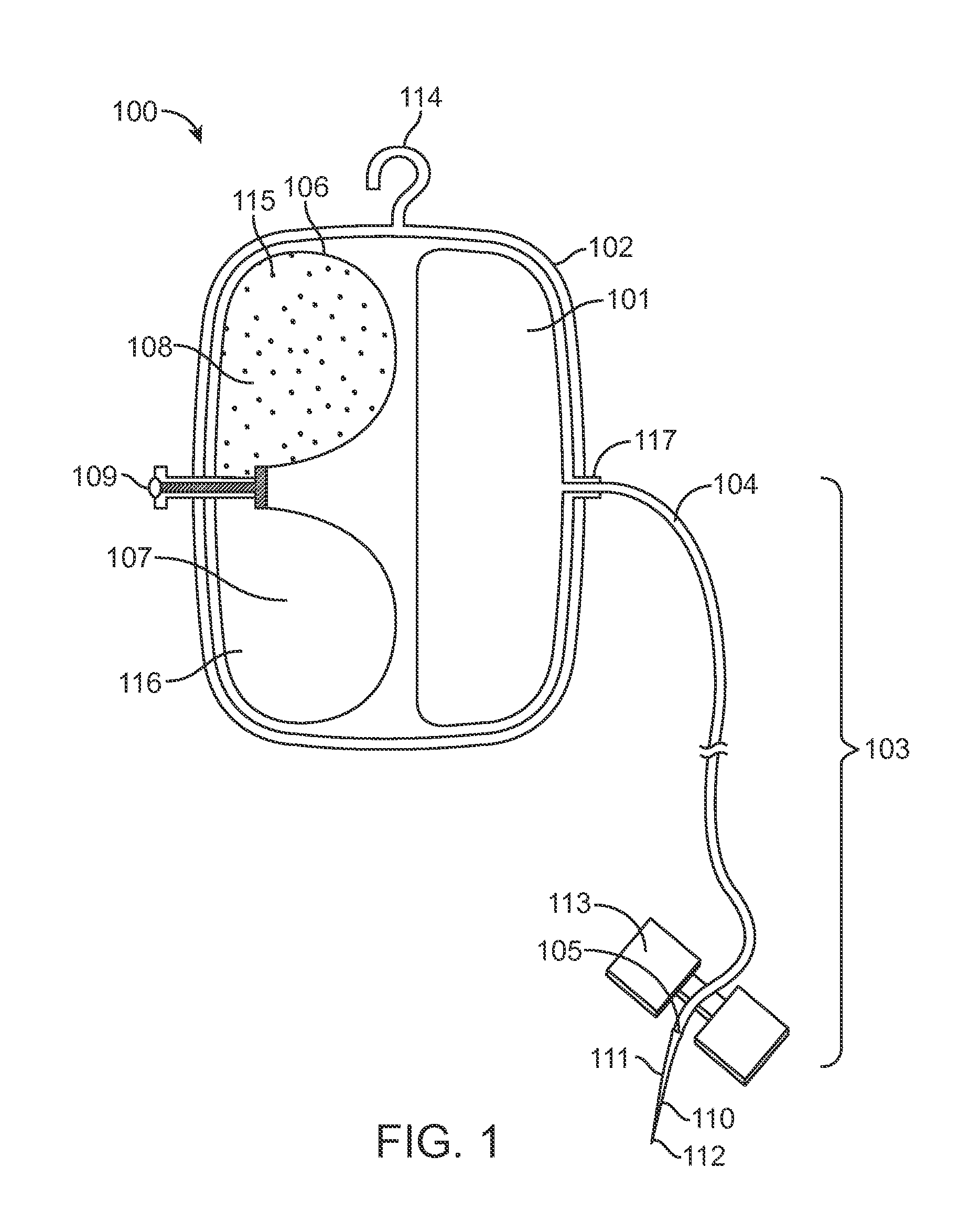
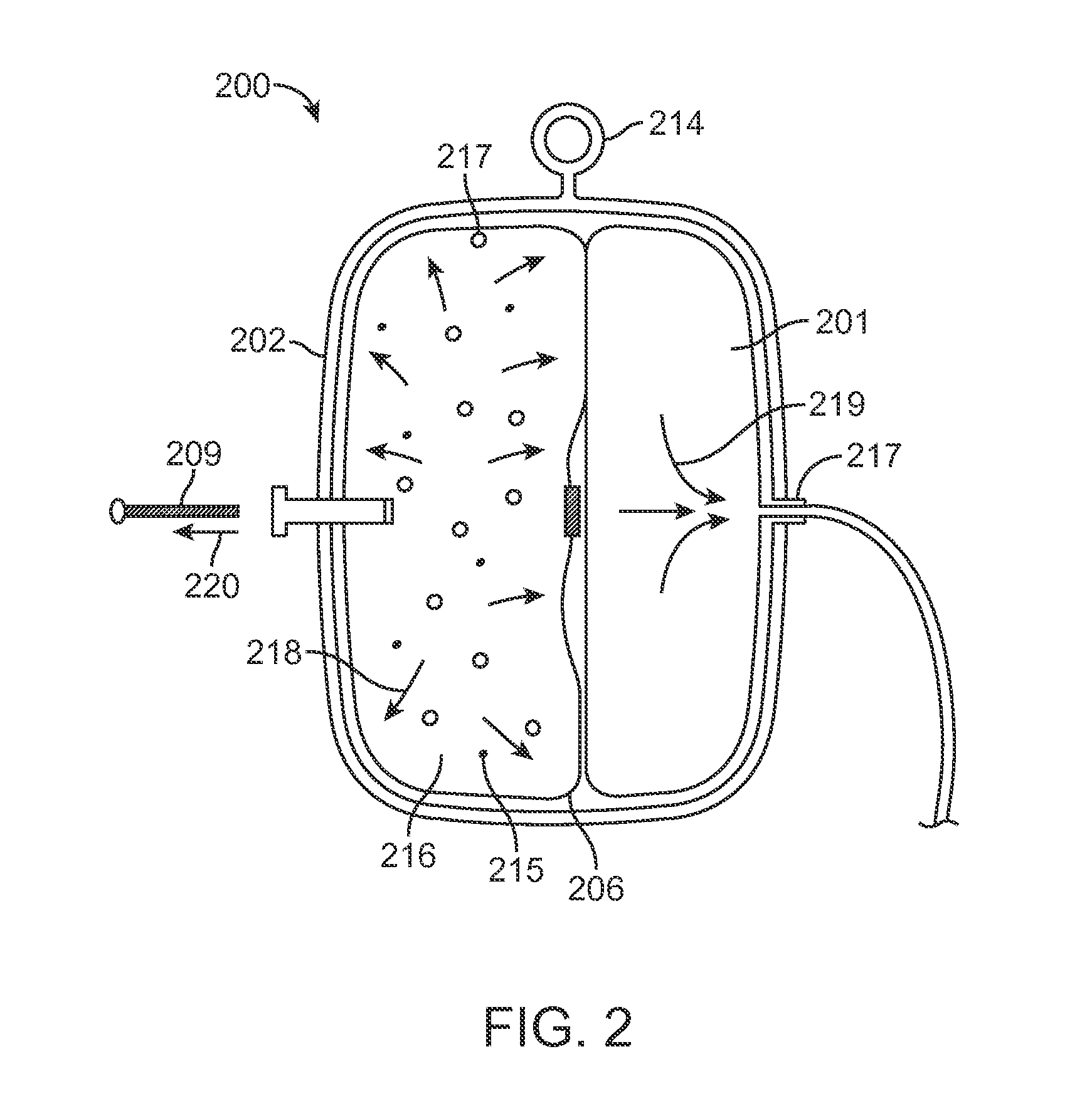
Infusion System for the Controlled Delivery of Therapeutic Agents
ActiveUS20140276587A1Extended shelf lifeKeep sterileMedical devicesPressure infusionDrug reservoirChemical reaction
Embodiments of the invention provide infusion systems for the intravenous or other delivery of drugs and other therapeutic agents to a patient including a human or mammal. The therapeutic agents may be dissolved in solution or comprise the solution itself. Embodiments of the systems can utilize a chemical reaction to predictably drive a flow of drug(s) through a catheter or other flow path and into the patient. More specifically, the reaction may include an acid-base reaction or any other reaction that produces a gaseous substance. The gas is produced and contained in an expandable drive balloon when the acid-base reactants are combined with a liquid. As the gas is produced, the drive balloon expands to exert pressure on a separately-contained drug reservoir which, in turn, pushes drug(s) from the reservoir into the flow path where the drug is ultimately delivered to the patient in a controlled and predetermined manner.
Owner:INCUBE LABS
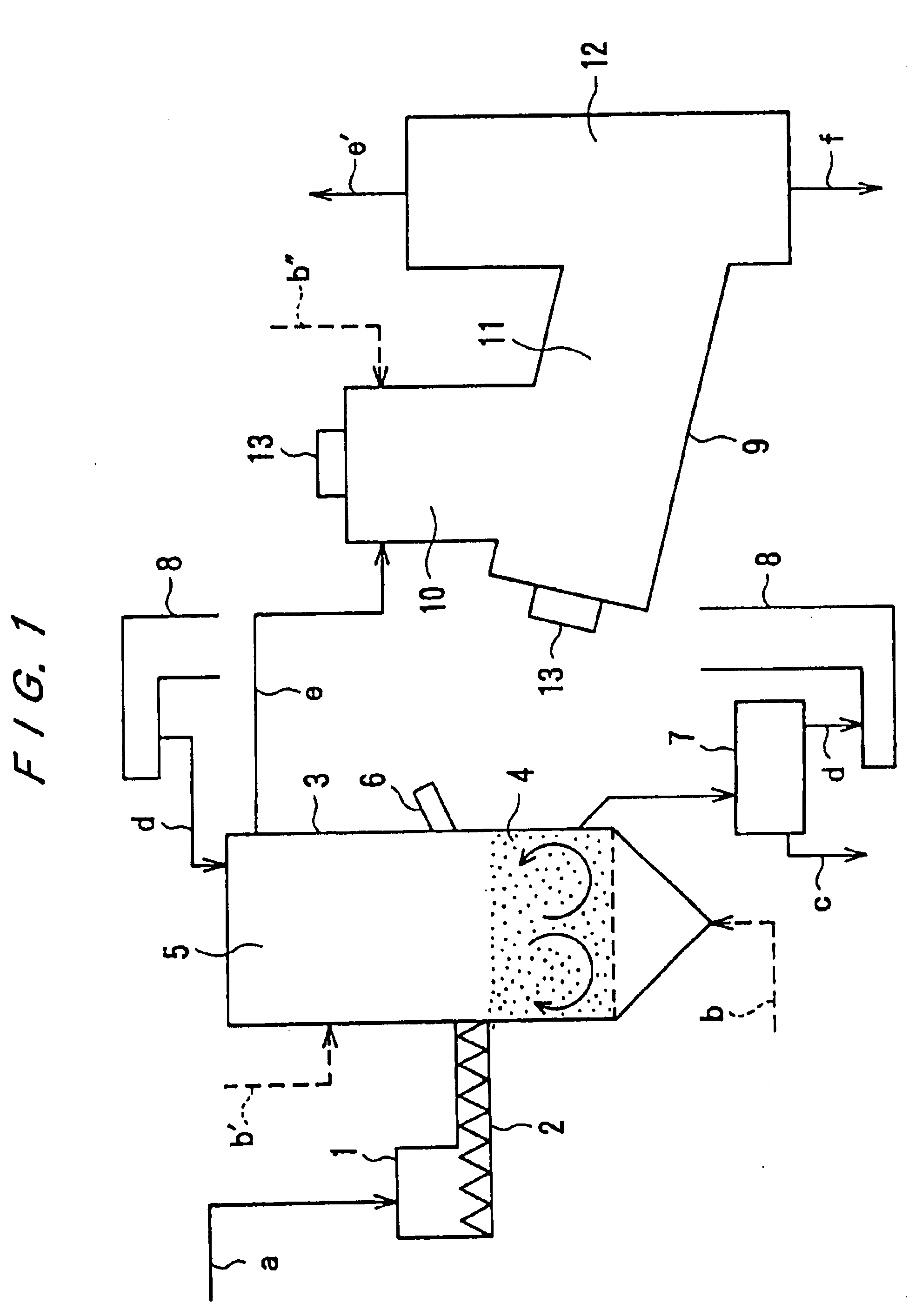
Apparatus for removing impurity contents in the air
Apparatus for removing impurity substances in the air, comprising a first filter (17) for removing solid substances in the air flowing in a flow passage (13) defined by a housing (11); first cooling means (18) for cooling the air to not higher than its dew-point temperature; a wet-type impurity removing mechanism (19) for capturing gaseous substances in the air; second cooling means (20); and a second filter (22). The wet-type impurity removing mechanism (19) includes first liquid atomizing means (26) having a plurality of nozzle ports (28) for spraying, arranged mutually spaced apart and facing each other in the direction of the air flow passage; first and second condensing and capturing means (23 and 24) located across the first atomizing means 26 and spaced apart from each other, the first capturing means upstream from and the second capturing means downstream from the first atomizing means; second atomizing means for capturing remaining gaseous substances in the air; and third condensing and capturing means (25).
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com