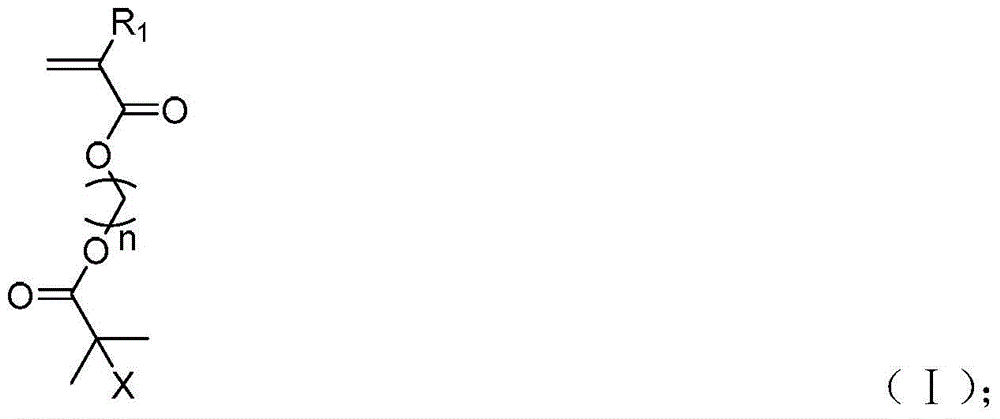Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30results about How to "Huge potential application prospects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Grain boundary diffusion method for improving properties of sintered NdFeB magnets
ActiveCN104388951AIncreased diffusion kinetic energyLow melting pointInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementDiffusion methods
The invention relates to a grain boundary diffusion method for improving properties of sintered NdFeB magnets. The grain boundary diffusion method comprises the following steps of stacking sintered NdFeB magnets and diffusion alloy sheets together and placing in a hot-pressing furnace; vacuumizing the hot-pressing furnace until the vacuum degree reaches a set value, heating the hot-pressing furnace, and when the temperature of the hot-pressing furnace reaches a set value, beginning to exert a pressure and maintaining the pressure and putting the diffused sample into a high-vacuum furnace for annealing, wherein the diffusion alloy sheets are low-melting-point eutectic diffusion alloys and are represented by R-TM, R is one or more of Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr or Nd and TM is one or more of Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn. Compared with the prior art, the sintered NdFeB magnets modified by the pressure diffusion method, which is provided by the invention, have the advantages of large diffusion depth of a diffusion agent, uniform distribution of grain boundary phases, high coercivity and the like, especially, low-melting-point diffusion alloys designed by the invention are free of expensive heavy rare earth element dysprosium and thus the cost of the raw materials is relatively low, the diffusion temperature is low and the energy consumption in the diffusion process is small.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation of non-magnetic high corrosion resistant amorphous steel coating
InactiveCN101323951AImprove mechanical propertiesGood physical propertiesMolten spray coatingHeat inorganic powder coatingSurface engineeringVoid ratio
The invention relates to a ferrous alloy with strong performance of glass formation and a technique method for preparing the coating of the amorphous alloy, in particular to a preparation method of non-magnetic amorphous steel coating with the performance of high anticorrosion and wearing resistance. The method of the invention solves the problem that large brittleness is existed in Fe-based large bulk of amorphous alloy and is a restriction as the structural material to go to engineering application, while the invention causes the application of bulk amorphous alloy to surface engineering field (especially amorphous alloy coating) to be possible. By adopting the Fe-based bulk amorphous alloy to prepare Fe-based amorphous alloy coating, firstly, mater alloy is produced by a method of vacuum induction melting according to needed components; then gas atomization technology is adopted to prepare amorphous alloy powder; supersonic thermal spray technology is adopted to prepare Fe-based amorphous alloy coating. The non-magnetic amorphous steel coating with high anticorrosion performance and wearing resistance produced by the invention is uniform, has low void ratio (less than 0.1 percent), is non-magnetic and has the performance of high anticorrosion and wearing resistance as well as vast application prospect to shell material of ships.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nitrogen-doped carbon aerogel catalyst used for metal-air battery, and preparation method
InactiveCN106129421AMaintain catalytic performanceEasy to prepareCell electrodesPolypyrrolePorous carbon
The invention belongs to the technical field of a catalyst, and discloses a nitrogen-doped carbon aerogel catalyst used for a metal-air battery, and a preparation method. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) adding pyrrole, polyvinylpyrrolidone and sodium chloride into ethyl alcohol, heating and stirring until the ethyl alcohol is fully volatilized to obtain an intermediate product A; (2) adding a ferric salt solution to the intermediate product A obtained in the step (1), and heating and stirring to obtain a polypyrrole nanosheet; and (3) heating the polypyrrole nanosheet obtained in the step (2) to obtain the nitrogen-doped carbon aerogel catalyst. The preparation method is simple without involving the conventional complicated and time-consuming template pore-forming step; instead, a precursor is carbonized directly to obtain the required porous carbon material; the catalytic performance of the material is maintained to the maximum degree; the obtained nitrogen-doped carbon aerogel catalyst is large in specific surface area, high in catalytic property and high in stability; and in addition, the nitrogen-doped carbon aerogel catalyst, used as the negative electrode material of a zinc air battery, has excellent oxygen reduction catalytic activity, so that the nitrogen-doped carbon aerogel catalyst can be applied to the fields of fuel cells.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
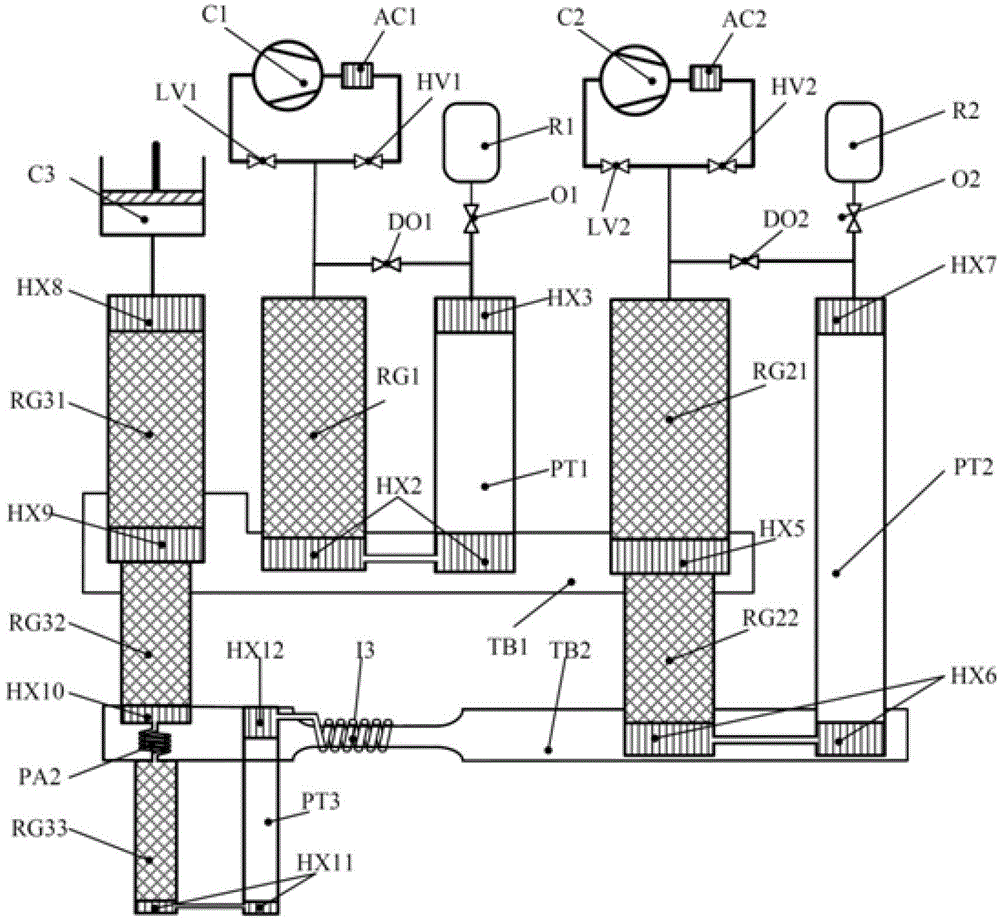
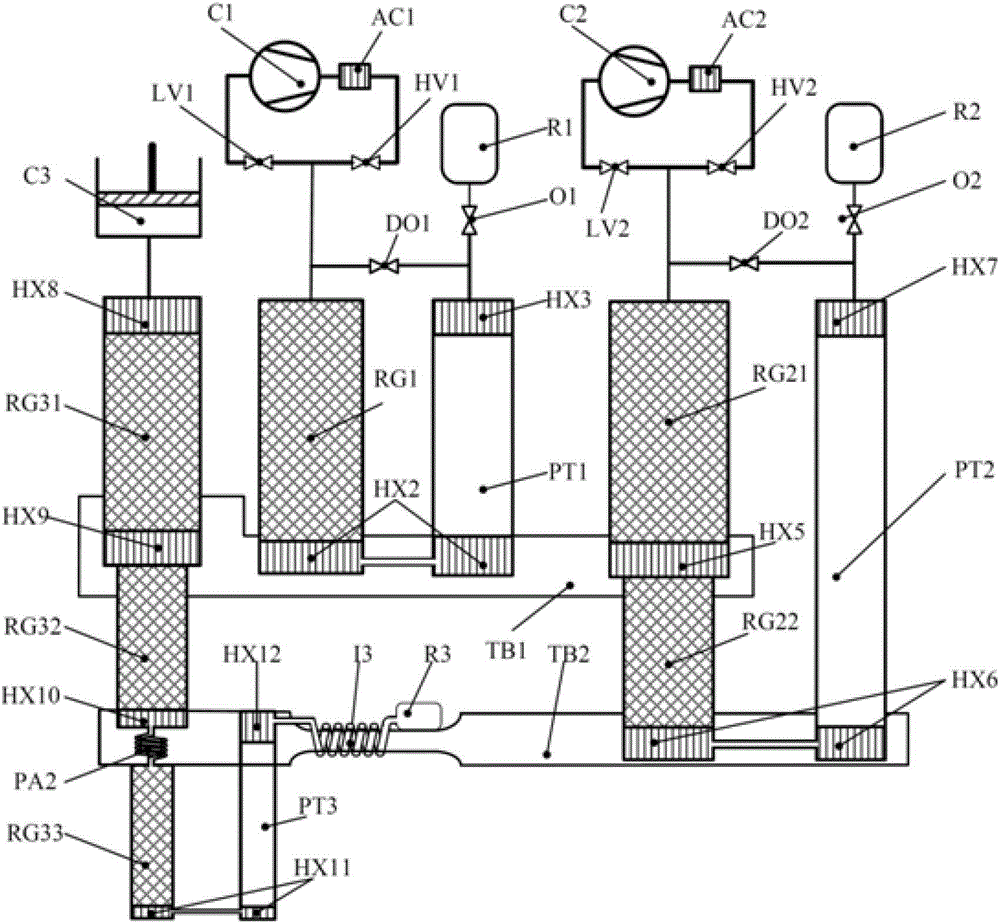
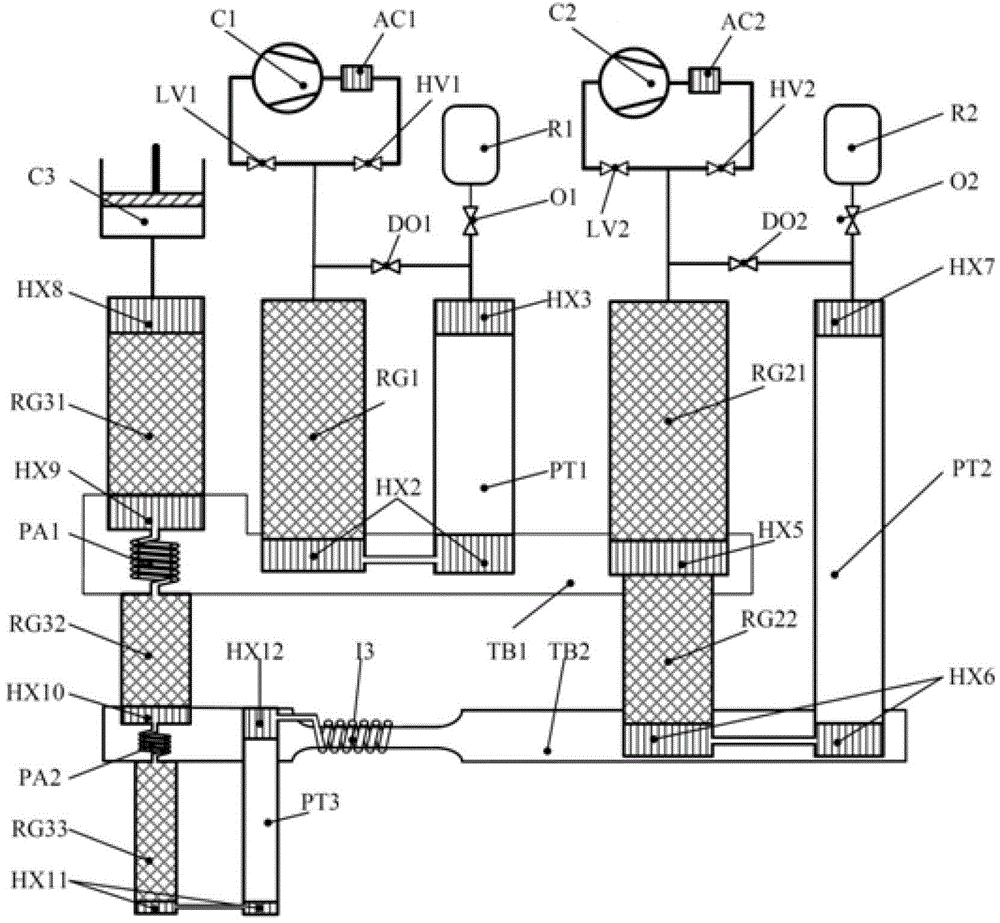
Composite multi-stage pulse tube refrigerator working in 1-2K temperature zone
InactiveCN103017395AReduce volumeReduce dosageCompression machinesPulse tube refrigeratorEngineering
The invention discloses a 1-2K composite multi-stage pulse tube refrigerator which comprises a precooling-stage low-frequency pulse tube refrigerator utilizing a helium-4 working medium and a low-temperature-stage high-frequency pulse tube refrigerator utilizing a helium-3 working medium. The high-frequency pulse tube refrigerator is coupled to the low-frequency pulse refrigerator, so that 1-2K refrigeration temperatures can be obtained under the condition that little helium-3 is used. Compared with the traditional double-stage low-frequency pulse tube refrigerator utilizing helium-3 as a working medium, the 1-2K composite multi-stage pulse tube refrigerator has the advantages that consumption of helium-3 gas can be obviously reduced, and the 1-2K composite multi-stage pulse tube refrigerator is low in cost and convenient to implement and keeps characteristics of compact structure, long service life and high reliability of an existing pulse tube refrigerator.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
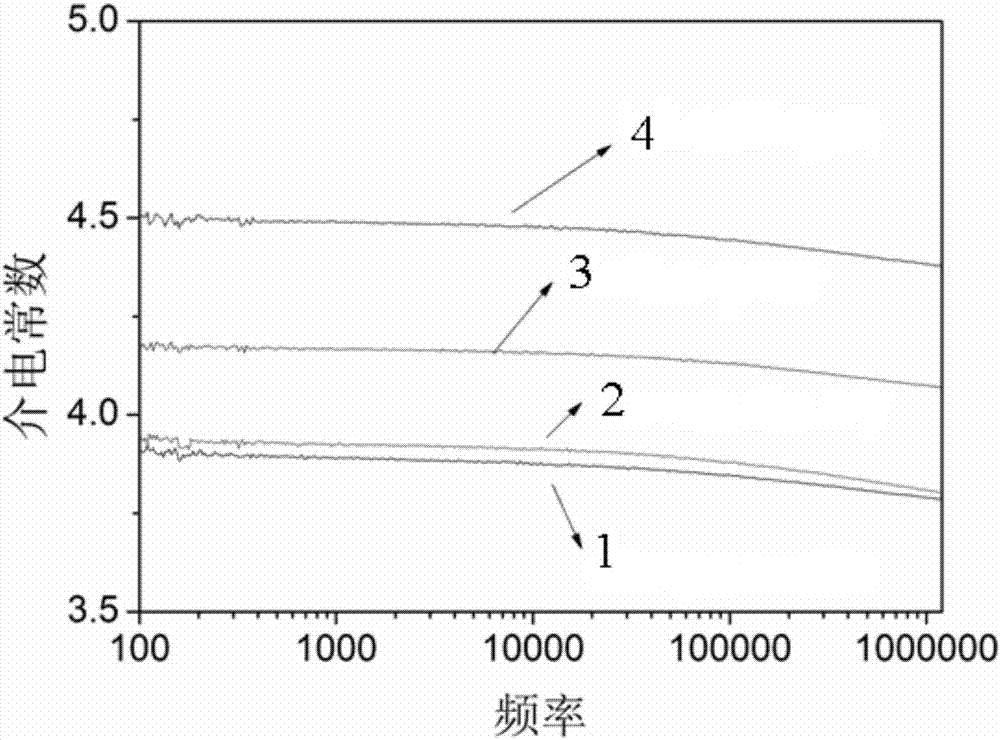
Preparation method of highly hydrophobic carbon fluoride nanotube/polyimide composite material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a highly hydrophobic carbon fluoride nanotube / polyimide composite material, relates to the preparation method of the polyimide composite material, and aims to reduce high dielectric constant of pure polyimide, improve the mechanical properties, reduce the hygroscopicity in engineering application, improve the service life, and solve the problem that special application in electrical insulation and power electronics is limited. The method comprises the steps: firstly, preparing carbon fluoride nanotubes; and secondly, obtaining the highly hydrophobic carbon fluoride nanotube / polyimide composite material through an in-situ polymerization method. The highly hydrophobic carbon fluoride nanotube / polyimide composite material disclosed by the invention can be industrialized in amplification, has great potential application prospects in electrical insulation, power electronics and other fields in future, and has great significance to new application prospects of polyimide. The preparation method of the highly hydrophobic carbon fluoride nanotube / polyimide composite material can be obtained.
Owner:大同共聚西安科技有限公司
Metal/ceramic/metal symmetric gradient structure sealing insulating material and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112170852AAlleviate thermal stressStrong designabilityEngine sealsCorrosive substanceCermet
The invention relates to a metal / ceramic / metal symmetric gradient structure sealing insulating material and a preparation method thereof. The sealing insulating material comprises a high-machinabilitymetal layer (4), a high-melting-point metal layer (3), a gradient middle layer (2), a nitride ceramic layer (1), a gradient middle layer (2), a high-melting-point metal layer (3) and a high-machinability metal layer (4) from top to bottom in the thickness direction, wherein the gradient middle layer (2) is obtained by sintering high-melting-point metal powder and nitride ceramic powder; the content of high-melting-point metal in the gradient middle layer (2) is distributed in a gradient mode, and is gradually reduced in the direction from the high-melting-point metal layer (3) to the nitrideceramic layer (1); and the mass fraction is reduced to 0-10% from 90-100%. The sealing insulating material provided by the invention has very high designability, is suitable for extremely complex working environments such as long-time high temperature and strong corrosion, and has relatively high high-temperature stability, corrosion resistance and insulating sealing performance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Iron-nitrogen-codoped porous carbon catalyst for proton exchange membrane fuel cell and method of iron-nitrogen-codoped porous carbon catalyst
InactiveCN105226298AEasy to prepareMaintain catalytic performanceMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesIonTube furnace
The invention belongs to the technical field of catalysts, and discloses an iron-nitrogen-codoped porous carbon catalyst for a proton exchange membrane fuel cell and a preparation method of the iron-nitrogen-codoped porous carbon catalyst. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding 2-fluoroaniline and a ferric iron salt to deionized water, and stirring the deionized water evenly to obtain a mixed liquid; (2) transferring the mixed liquid obtained in the step (1) to a hydrothermal reaction kettle for a hydrothermal reaction, and cooling, filtering, cleaning and drying the mixed liquid to obtain a 2-fluoroaniline flake; (3) putting the 2-fluoroaniline flake obtained in the step (2) into a quartz tube furnace, introducing nitrogen, warming to 750-850 DEG C, carrying out a thermal reaction for 2-3 hours, and cooling the 2-fluoroaniline flake to obtain the iron-nitrogen-codoped porous carbon catalyst. The prepared catalyst is large in specific surface area, good in catalytic property, high in anti-methanol poisoning capability, good in durability, high in stability and simple in preparation method, and can be applied to the field of the fuel cell.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Carboxylation-modified nanocellulose crystal and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a carboxylation-modified nanocellulose crystal and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding acetic acid buffer solution to microcrystalline cellulose, preparing microcrystalline cellulose dispersion liquid after uniformly mixing, and adding TEMPO-sodium periodate-sodium hypochlorite-sodium chlorite polybasic oxidizing agent, stirring and reacting for 5-48 h in 25-35 DEG C under a dark condition, performing suction filtration, washing, enabling a product to be prepared as dispersion liquid of which a mass fraction is 0.1-4%, and processing for 1-10 times by using a micro-jet high-pressure homogenizer, obtaining the carboxylation-modified nanocellulose crystal. An oxidation system of the preparation method is capableof selectively oxidizing in allusion to different sites of the cellulose, and improving the oxidation efficiency of the natural cellulose with a high crystallinity degree. Surface carboxyl group content, a water retention value, a carboxyl substitution degree, and the crystallinity degree of the nanocellulose crystal are remarkably improved, and the process is stable, the operation is simple and convenient. A raw material is cheap in price and abundant, and pollution-free. The carboxylation-modified nanocellulose crystal can be popularized and produced in large scale, and has the good application prospect in the fields of papermaking, foods, cosmetics, electronic products, medicine and the like.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Lac wax emulsion and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a lac wax nano emulsion and a preparation method thereof. The lac wax emulsion comprises lac wax, Tween-80, Span-80, triethanolamine and water. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) evenly mixing the Tween-80, Span-80 and triethanolamine to obtain a compound emulsifying agent; 2) adding the compound emulsifying agent to the molten lac wax, and evenly stirring; and 3) adding water, and stirring to obtain the lac wax emulsion. The lac wax emulsion provided by the invention has a small particle diameter, and the dispersibility, storage stability, centrifugal stability and freezing and thawing stability are satisfactory and can meet the Level 1 national standards. The preparation method of the emulsion is simple, and is suitable for large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:THE RES INST OF RESOURCES INSECTS RIRI OF THE CHINESE ACADEMY OF FORESTRY
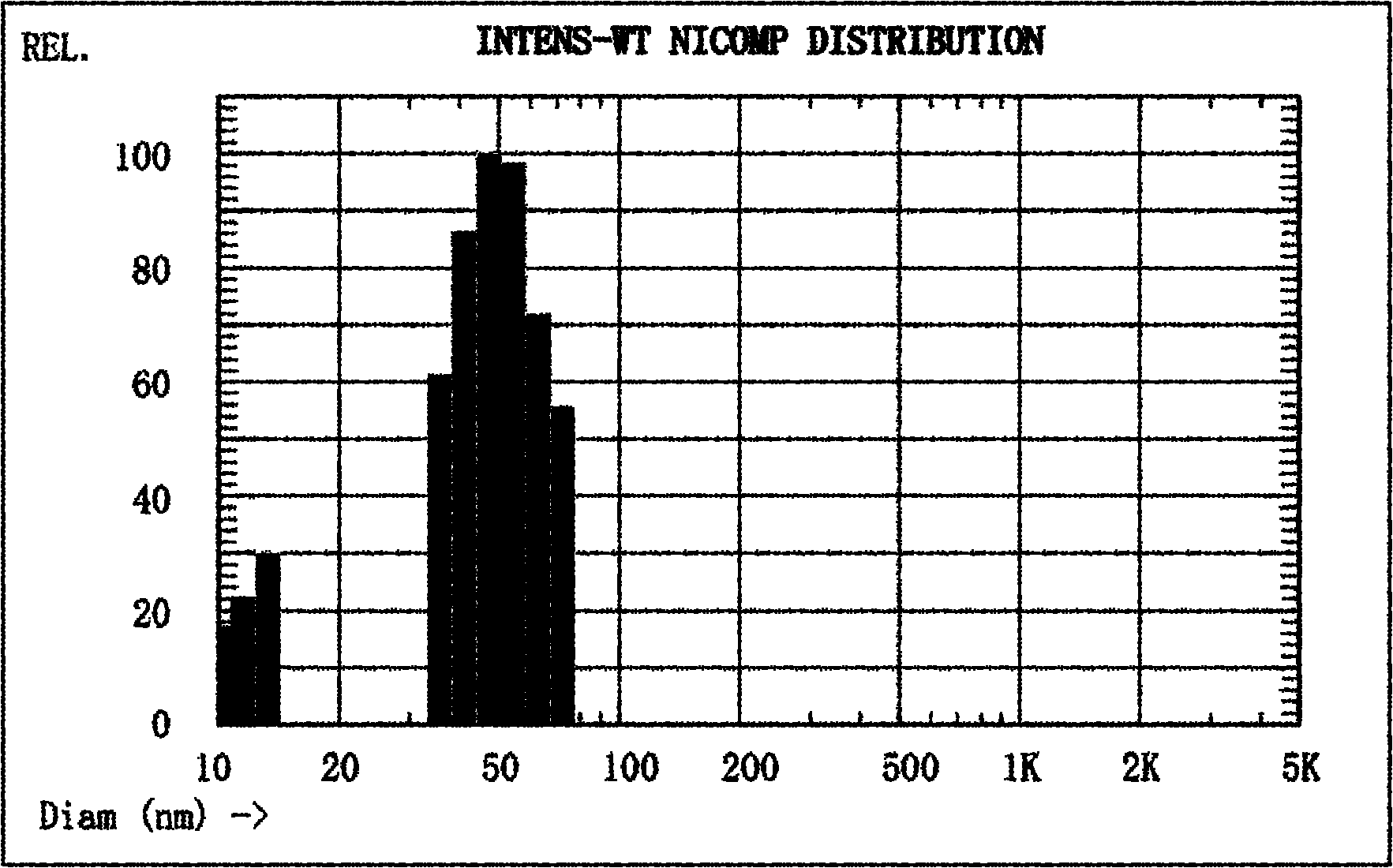
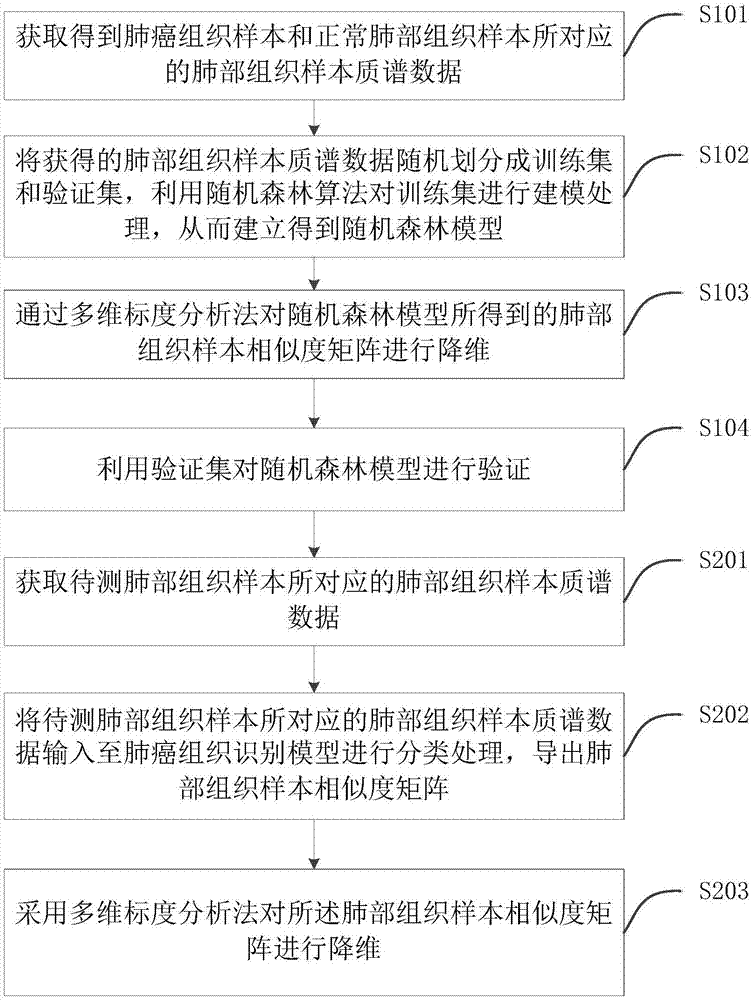
Device and system for processing data for identifying lung cancer tissues
InactiveCN107132268AFast analysisEasy to operateMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCharacter and pattern recognitionDiseaseCritical illness
The invention discloses a device and a system for processing data for identifying lung cancer tissues. The system comprises a sampling module and a classifying module. A processor of the device is used for executing the following steps of obtaining lung tissue sample mass spectrum data corresponding to a to-be-detected lung tissue sample; classifying and processing the obtained lung tissue sample mass spectrum data by a lung cancer tissue identifying model which is established by a random forest algorithm, so as to obtain the classifying result of the to-be-detected lung tissue sample. The system has the advantages that under the conditions of no sample pretreatment, common temperature and common pressure, the tissue samples of lung cancer and health lung cancer can be directly identified; the operation is simple, the analyzing speed is high, the accuracy is high, and the like; the huge potential application prospect is realized in the related technical fields of serious diseases, clinical medicines, life safety and the like; the device and the system for processing the data for identifying the lung cancer tissues can be widely applied to the technical field of identifying of the lung cancer tissue data.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
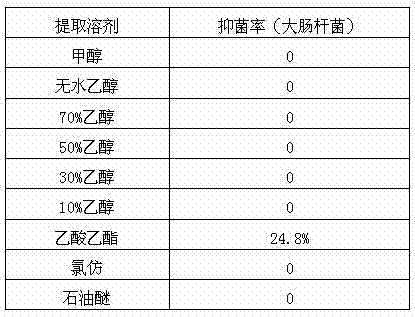
Extraction method and purpose of jute fiber extracts with bacteriostatic activity
InactiveCN102648716AIncrease productionRich sourcesBiocideFibre treatmentBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention provides an extraction method and a purpose of jute fiber extracts with bacteriostatic activity and relates to the extraction method and the purpose of fiber extracts of jute of tiliaceae jute plants. The extraction method provided by the invention overcomes the defects of low raw material yield, low bacteriostatic activyt of extracts and easy activity loss of the existing jute extraction process. The invention provides an extraction process of ester solvents, which adopts the high-yield jute fibers as extraction raw materials, the ester solvents refers to one kind of materials or several kinds of materials from n-butyl acetate, acetic acid isopropyl ester, n-propyl acetate, iso-butyl formate, n-butyl formate, ethyl acetate and methyl acetate with the dielectric constant being 5.0 to 7.5. The extracts obtained by adopting the extraction method have the advantages that the bacteriostatic activity, particularly the escherichia coli inhibiting activity is obviously improved, and the advantage of stable bacteriostatic effect can also be realized when the extracts are used as bacteriostatic agents, particularly as bacteriostatic finishing agents for textiles.
Owner:JIANGSU REDBUD DYEING TECH CO LTD
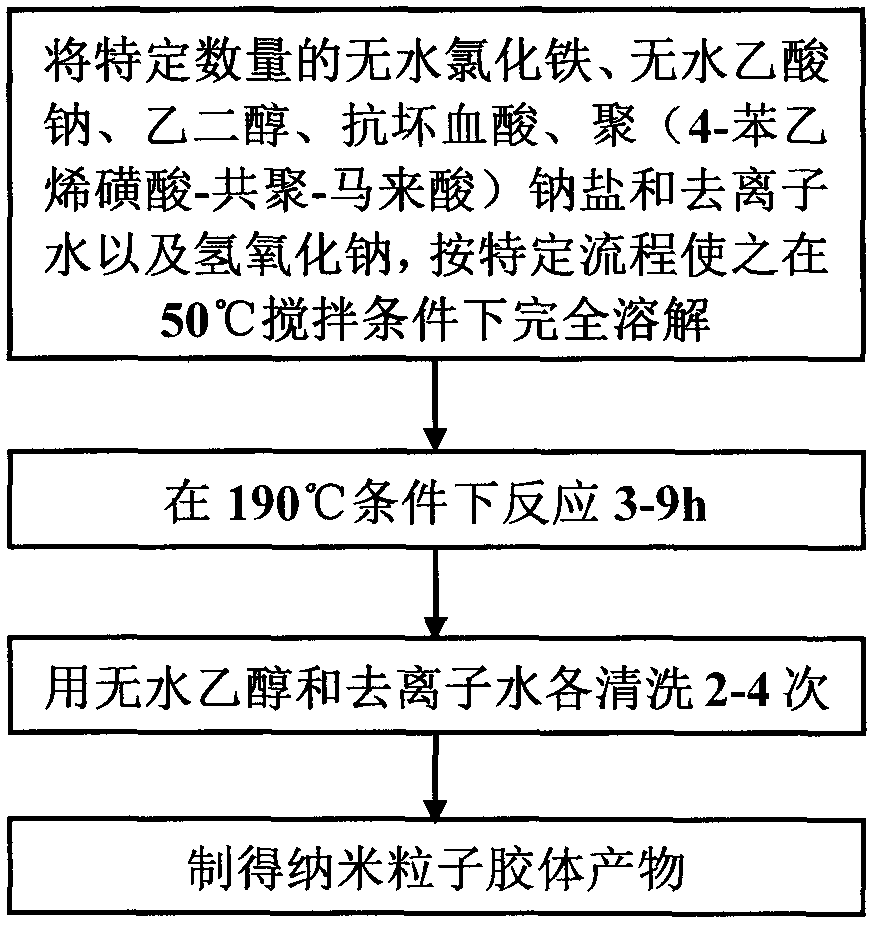
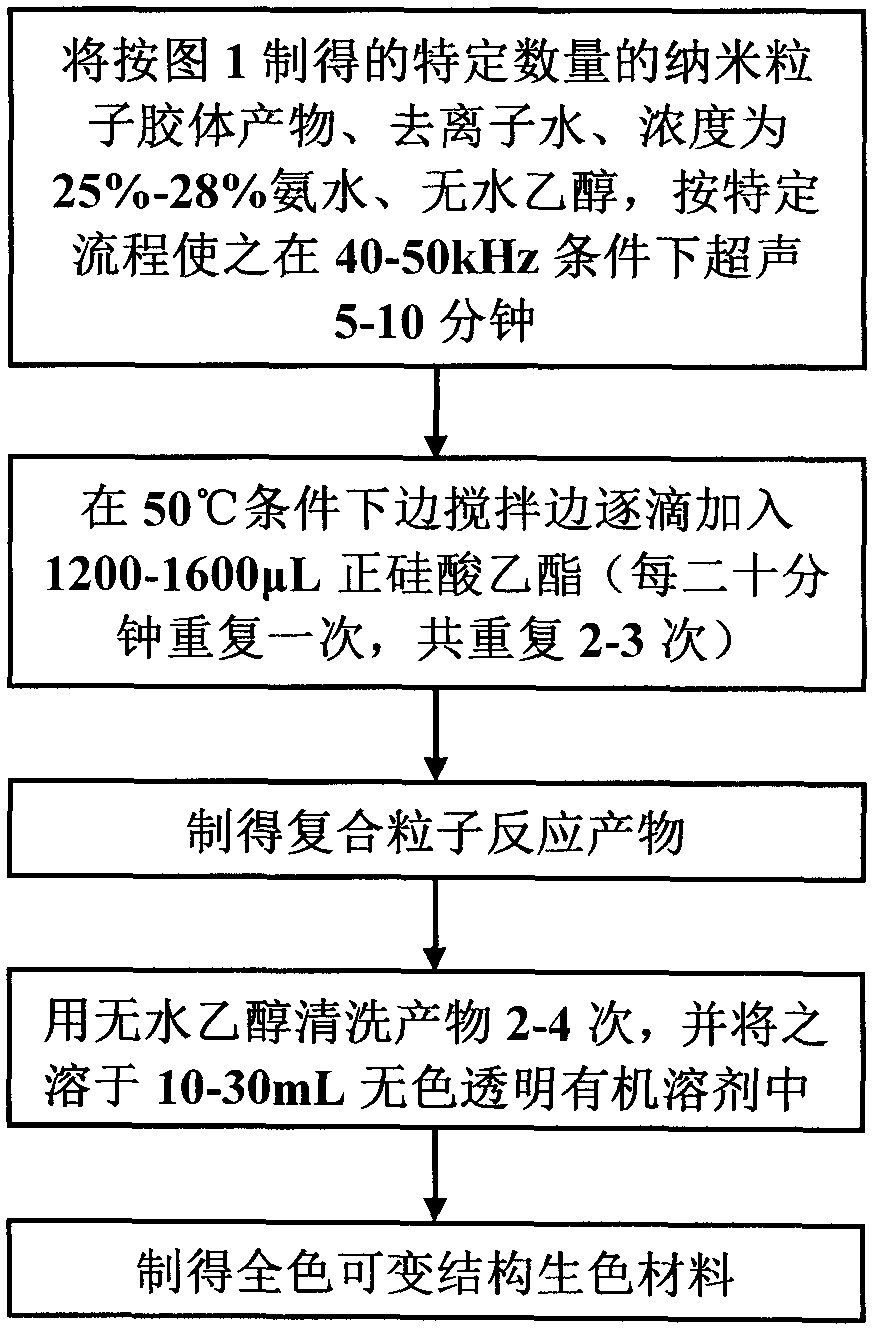
Method for preparing full color variable structural chromogenic material
ActiveCN109370263ALow costEasy to makePigment treatment with macromolecular organic compoundsPigment treatment with organosilicon compoundsColor printingVisible spectral range
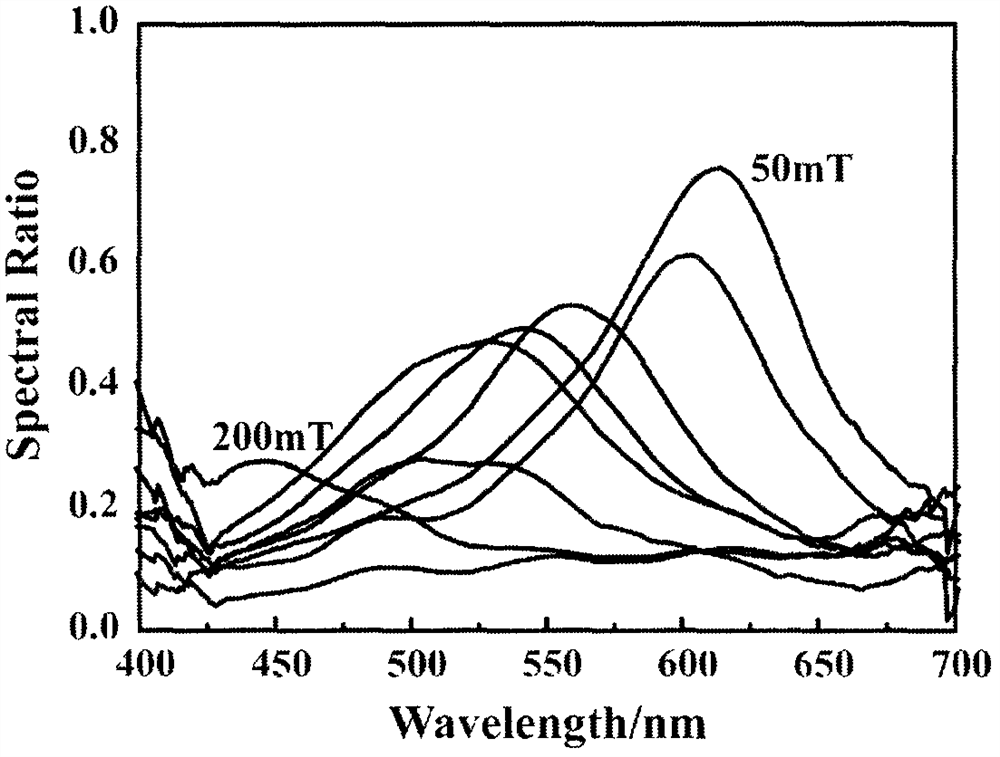
The invention provides a method for preparing a full color variable structure chromogenic material, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of structural color chromogenic materials. The preparation method provides preparation and optimization of visible light band full color variable structural chromogenic materials, and finds specific preparation processes and conditions to promote efficient high-quality growth of chromogenic material nanocrystals. The preparation method adopts a specific strong base as a material crystal growth environment. The preparation method is characterizedin that the strong base environment is utilized for preparation, the prepared chromogenic material composite particles have the particle diameter of 105-280 nm, and the color with the spectral peak inthe visible spectral range of 450-650 nm can be achieved under magnetic field control. The full color variable structural chromogenic material has the advantages of good color rendering effect and fast color reaction, and has great potential application prospects in photonic ink, anti-counterfeiting aspect, structural color printing, biological and chemical sensing and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for forming double-layer orderly-arranged nanoparticles by utilizing polymers as templates
InactiveCN103373703BAchieve overlayFast wayMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufacturePolystyreneSolvent
The invention discloses a method for forming double-layer orderly-arranged nanoparticles by utilizing polymers as templates. The method includes forming high-density metal nanoparticles orderly arranged in nanoscale by utilizing block polymers as the templates, and specifically includes spin-coating multiple layers of polystyrene-block-polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PS-b-PVP) on a substrate for composited forming of a film, inducing microphase separation of the PS-b-PVP to form a micro-area in nanoscale through selective-solvent treatment, and forming an orderly-arranged high-density metal nanoparticle array by a strong synergistic effect, namely prior selectivity to nanoparticles like Au (gold) and Ag (silver), of metal nanoparticles and nitrogen-atoms on pyridine rings of the PS-b-PVP. Currently, orderly-arranged metal nano-arrays are prepared by utilizing monolayer block polymers as the templates; however, according to the method, continuous spin-coating of two layers of the block polymers is utilized to obtain metal nanoparticle arrays in high-density arrangement.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
A Grain Boundary Diffusion Method for Improving the Magnetic Properties of Sintered NdFeB
ActiveCN104388951BIncreased diffusion kinetic energyLow melting pointInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementDiffusion methods
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Lac wax emulsion and preparation method thereof
Owner:THE RES INST OF RESOURCES INSECTS RIRI OF THE CHINESE ACADEMY OF FORESTRY
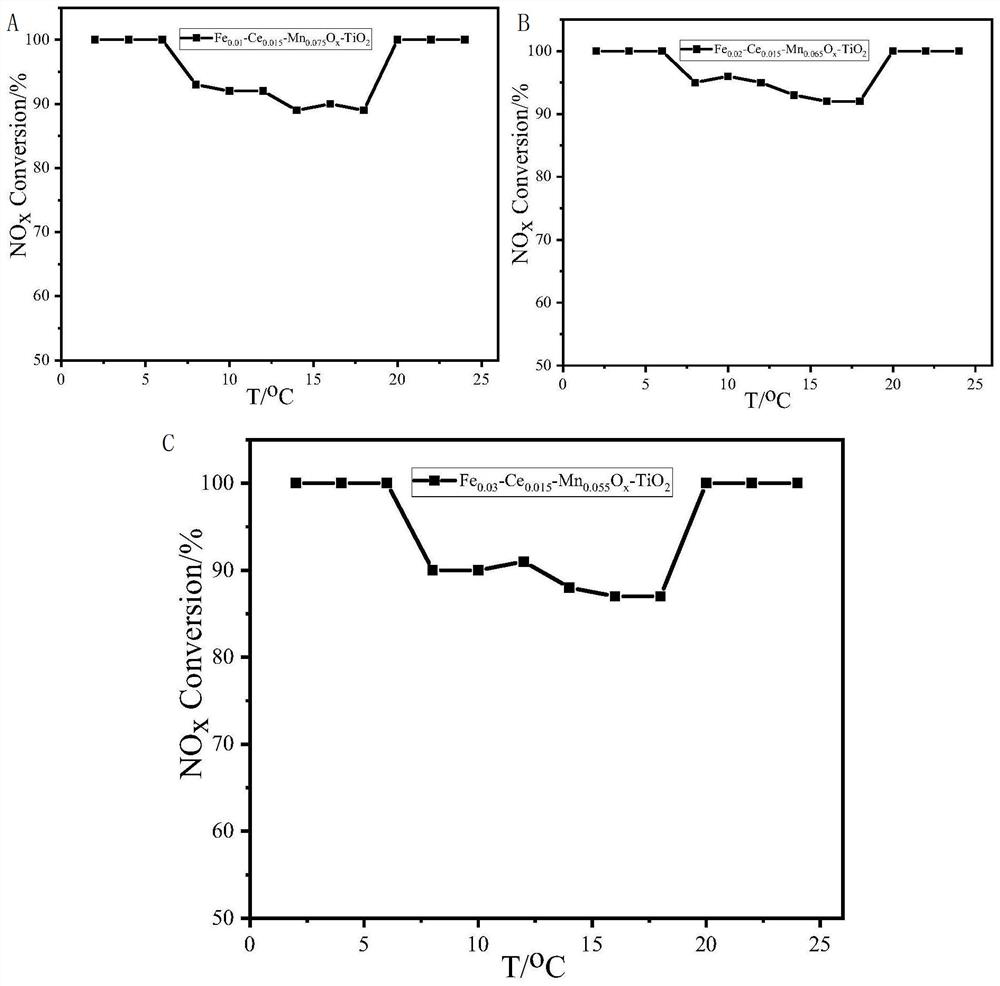
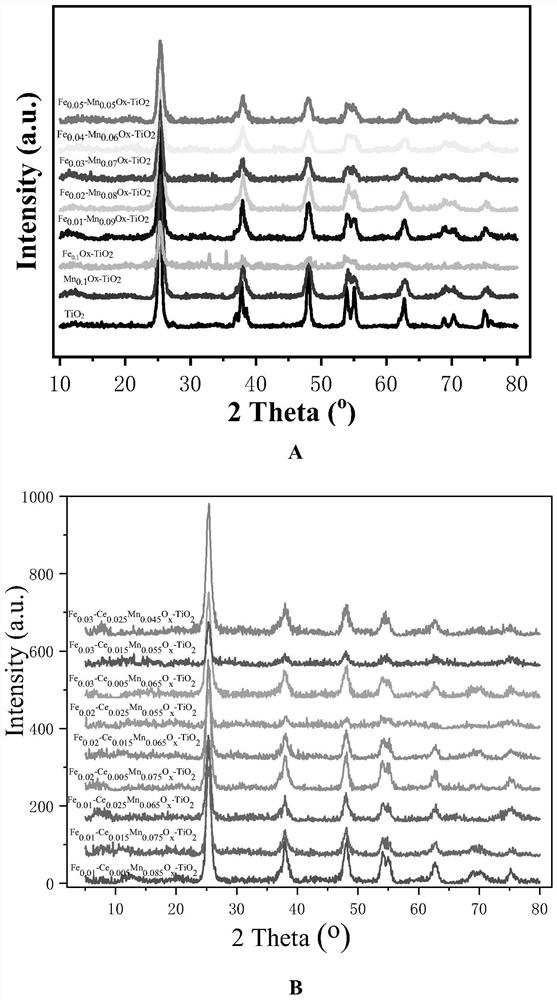
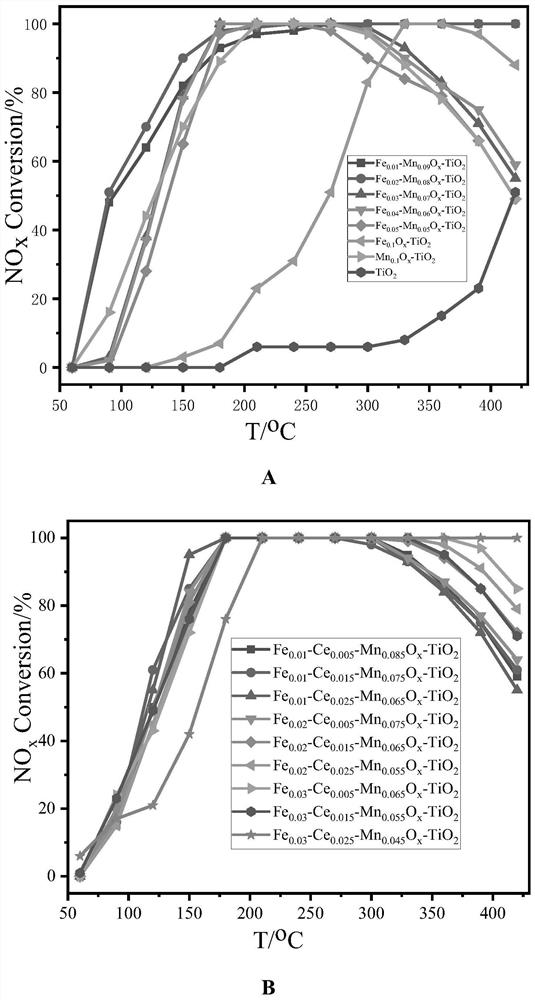
Preparation and application of high-performance Fe, Ce, Mn and Ti four-component catalyst
InactiveCN112337477AWell mixedLarge specific surface areaGas treatmentHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsPtru catalystHigh activity
The invention provides the simple preparation method of a Fem-Cen-Mn0. 1-m-nOx-TiO2 (0 < m < = 0.050, 0 < n < = 0.025) catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides, and the method hasthe advantages of cheap and easily available raw materials, no biotoxicity, simple and fast operation, low energy consumption and no special requirements on equipment, and has huge potential application prospects in the field of flue gas denitrification of coal-fired power plants. The synthesized catalyst combines the advantages of anatase TiO2, trace amounts of Fe, Ce and Mn are added, the advantages of TiO2 and CeO2 are both considered, the disadvantage of poor low-temperature activity of a Ce-Ti oxide catalyst is effectively made up, and the catalyst shows excellent catalytic performance in flue gas denitrification. The catalyst is suitable for being applied under the conditions of large airspeed range and medium and low temperature (180-390 DEG C), can show high activity, has excellent H2O and SO2 resistance and is long in service life.
Owner:HEIHE UNIV
Lac resin hydrosol and preparation method thereof
The invention provides lac resin nanoscale hydrosol and a preparation method thereof. The lac resin hydrosol is composed of lac resin and water. The method comprises the following steps: 1), dissolving lac resin in ethanol so as to obtain a lac resin ethanol solution; and 2), dripping the lac resin ethanol solution in deionized water, and distilling to remove ethanol. The lac resin hydrosol prepared by the method is small in particle size, good in dispersivity, storage stability, centrifugal stability and freeze-thaw stability and can reach national first level standard. The method has the advantages of simplicity and suitability for large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:THE RES INST OF RESOURCES INSECTS RIRI OF THE CHINESE ACADEMY OF FORESTRY
Ionic liquid bis-ammonium acetate and catalytic synthesis process therefor
InactiveCN1569801ASimple processHigh yieldCarboxylic acid salt preparationCatalytic methodOrganic synthesis
The invention discloses an ionic liquid bis-ammonium acetate and catalytic synthesis process, wherein the acetate comprises small cationic inorganic ammonium NH4++ and rather big anion double acetate radical (CH#-[3]COO)#-[2]H#+[-], the catalytic method for synthesizing the ionic liquid consists of mixing acetic acid, mixing the solid acid catalyst and solvent, heating and stirring, reacting, neutralizing with acid and alkali, separating, decompression distilling.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
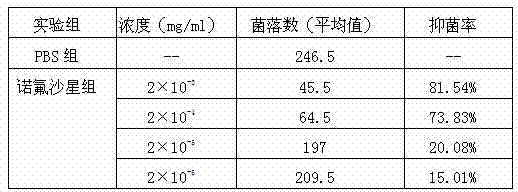
A method for identifying the aroma type of liquor using electronic tongue system
ActiveCN103645182BTargetedLow priceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFlavorAroma
The invention relates to a method for identifying a white spirit flavor type by using an electronic tongue system. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, the electronic tongue system is established, wherein the electronic tongue system comprises an array sensor and a detection system; then white spirit array difference diagrams of known flavor types are obtained by the electronic tongue system, wherein the white spirit array difference diagrams of white spirit with the same flavor type are used as a white spirit standard flavor type database; and finally a detection array difference diagram of a white spirit sample to be detected is obtained by the electronic tongue system and one array difference diagram matched with the array difference diagram of the white spirit sample to be detected is found so that the flavor type of the white spirit sample to be detected is as the same as that of a standard sample corresponding to the matched array difference diagram. According to the method for identifying the white spirit flavor type by using the electronic tongue system, the change of colors of the array sensor can be directly observed; the array difference diagrams only need to be compared in the detection process and the detection is simple, convenient and rapid; furthermore, components of selected sensing substances are common chemical substances and the cost is very low.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
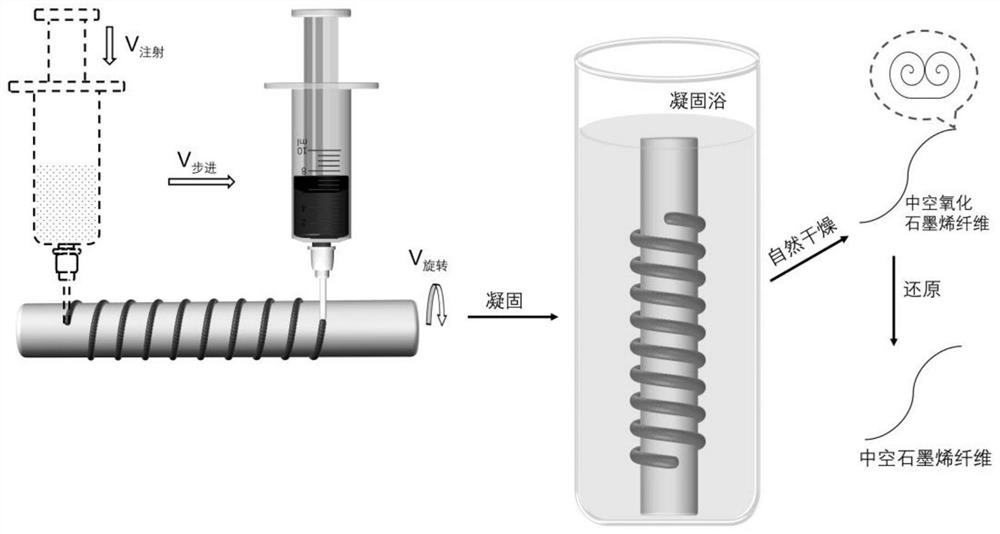
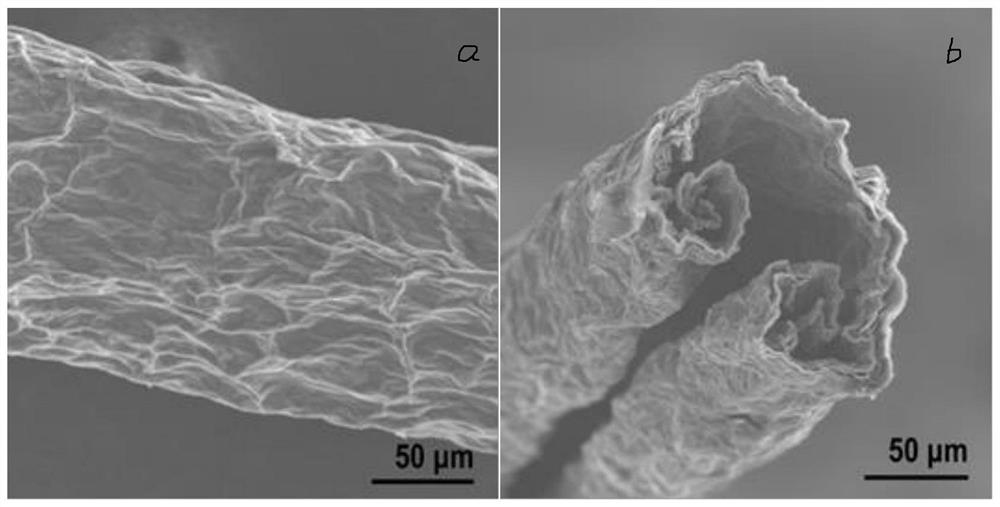
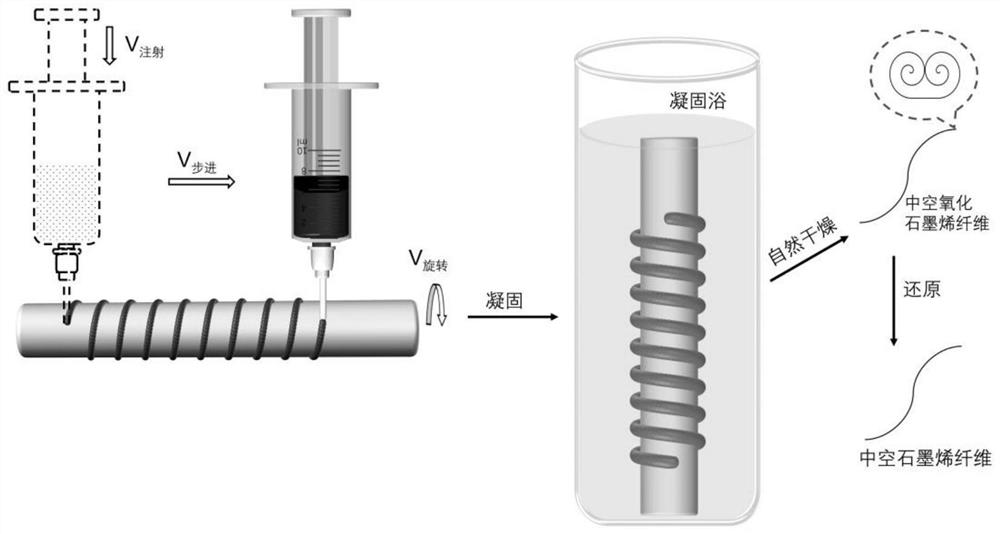
A kind of self-crimping preparation method of hollow graphene fiber and its application
ActiveCN113388905BEasy accessIncrease productivityHollow filament manufactureFilament manufactureFiberSupercapacitor
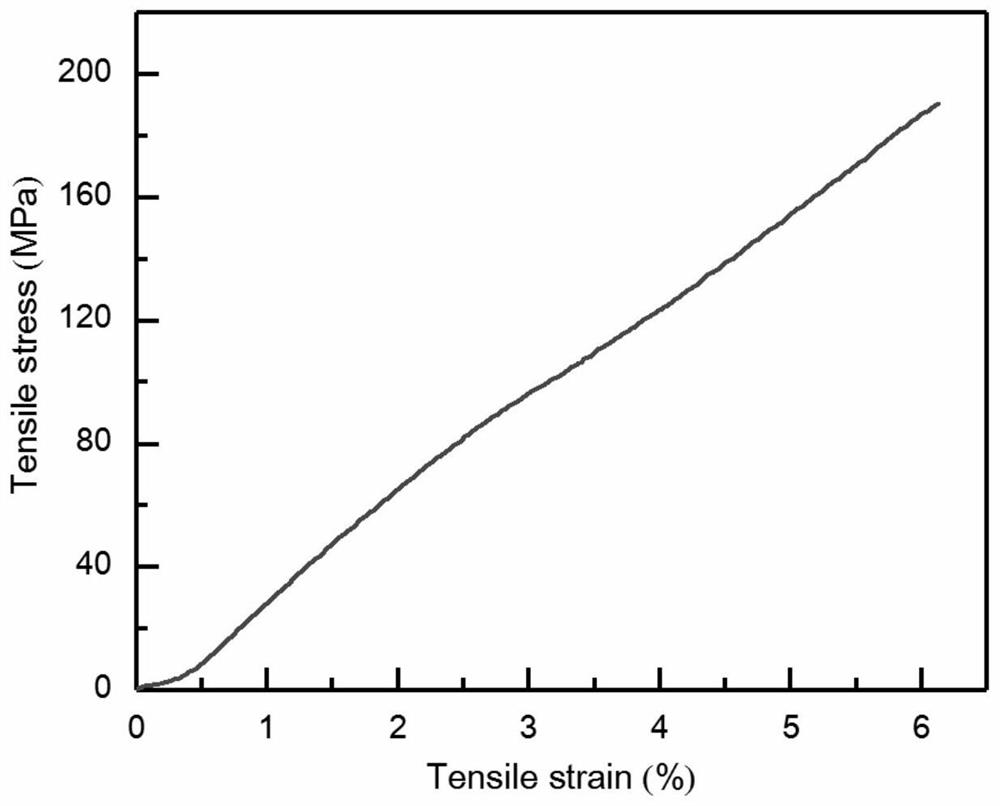
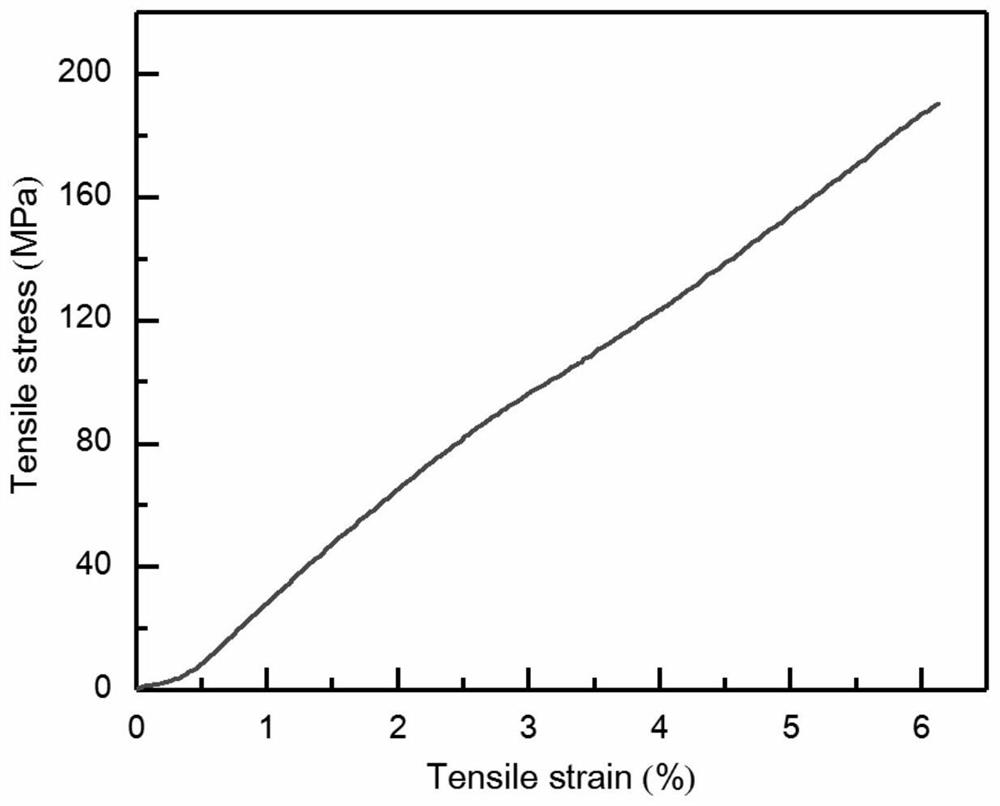
The invention discloses a self-crimping preparation method of hollow graphene fibers, comprising the following operation steps: (1) injecting and printing graphene oxide slurry onto a rotating roller to obtain gelatinous graphene oxide fibers; ( 2) immersing in a coagulation bath to solidify, and taking out to obtain a ribbon-shaped graphene oxide fiber; (3) peeling off the roller and drying to obtain a hollow graphene oxide fiber; (4) reducing to obtain a hollow graphene oxide fiber. The method of the invention obtains fibers of different diameters by adjusting the parameters of the equipment, and adds the unilateral support of the roller during the coagulation process to form a compact microstructure, and the obtained hollow graphene fibers have a tensile strength of 190.5MPa and a tensile strength of 6.1%. Tensile deformation, showing more than 5000 times of bending resistance; the specific capacitance of the prepared supercapacitor reaches 170.6F g ‑1 , which has huge potential application prospects in flexible and wearable energy storage devices.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
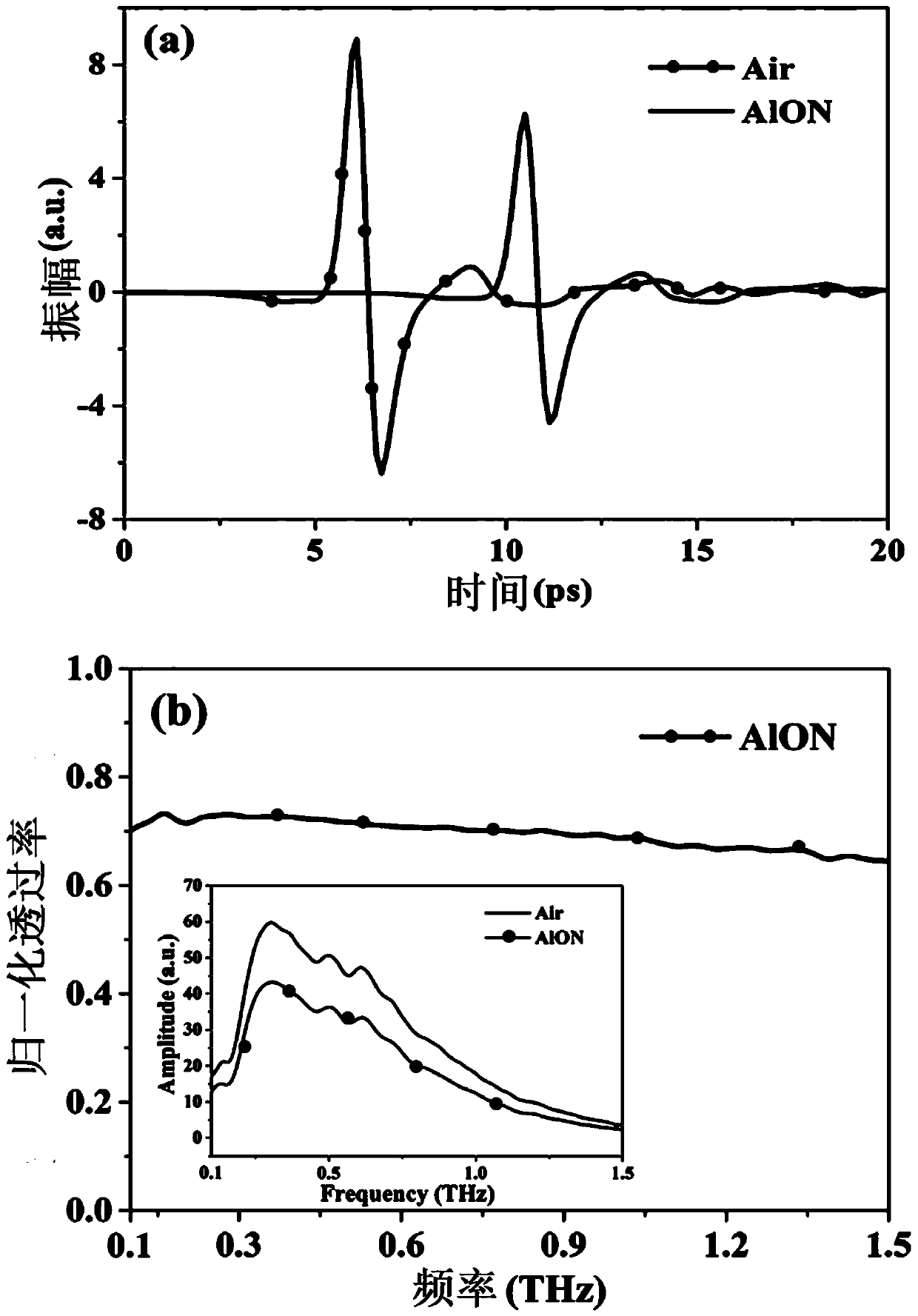
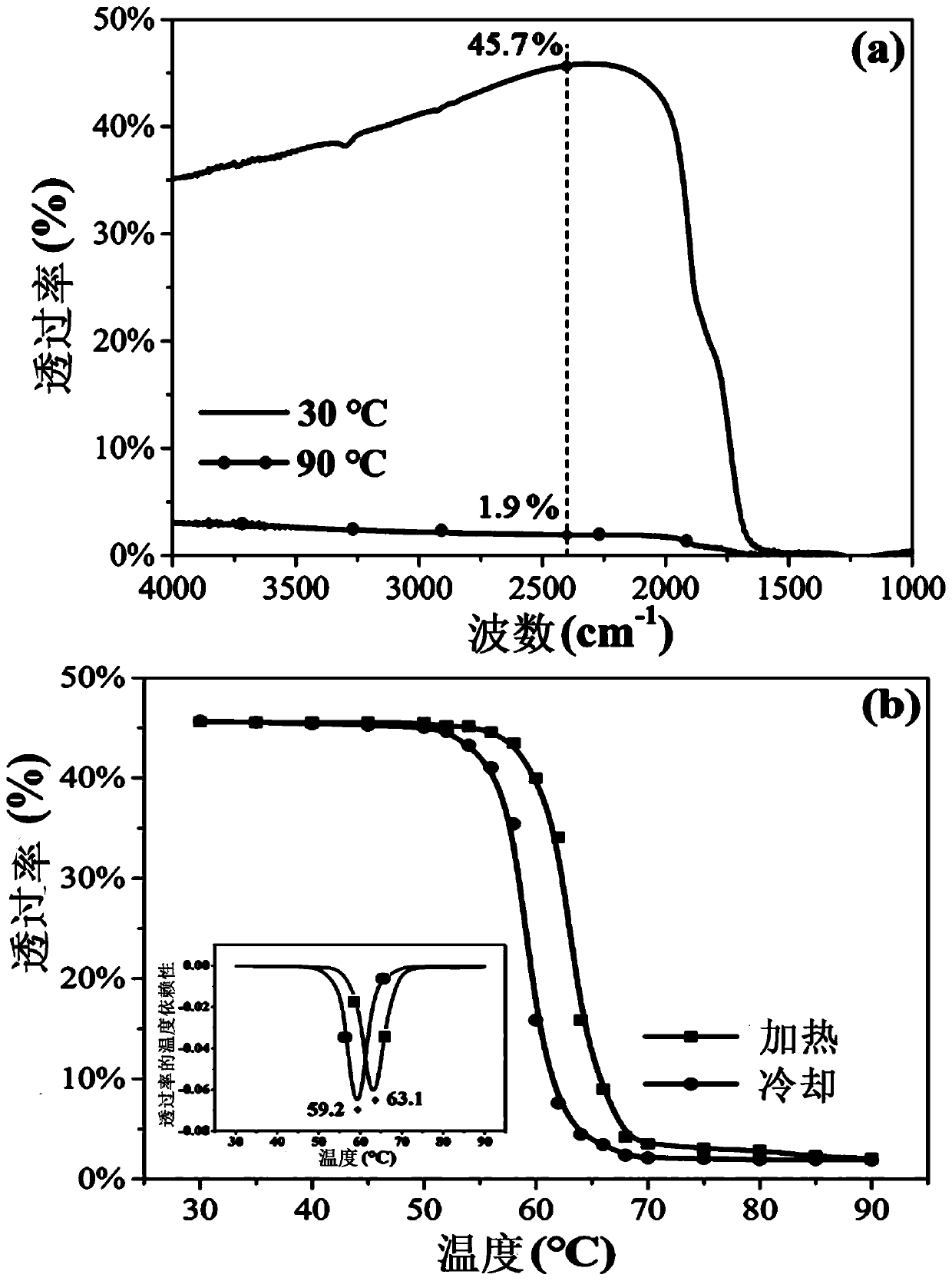
Complex window material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108530072AHigh transparencySignificant terahertz transmittanceVanadium dioxideAluminum oxynitride
The invention provides a complex window material and a preparation method thereof. The method includes the steps: preparing an aluminum oxynitride ceramic; heating vanadium pentoxide to be melted, pouring deionized water, and stirring and filtering the materials to obtain vanadium pentoxide sol; cleaning the aluminum oxynitride ceramic and performing hydrophilic treatment to hydroxylate the surface of the aluminum oxynitride ceramic; depositing the vanadium pentoxide sol on the surface of the aluminum oxynitride ceramic combined with hydroxy or coating the surface of the aluminum oxynitride ceramic combined with hydroxy with the vanadium pentoxide sol, drying the vanadium pentoxide sol, and performing annealing reduction in vacuum to obtain the complex window material with the surface of the aluminum oxynitride ceramic deposited / coated with a vanadium dioxide film. The complex window material comprises the transparent aluminum oxynitride ceramic and the vanadium dioxide film, wherein the transparent aluminum oxynitride ceramic serves as a substrate, and the surface of the transparent aluminum oxynitride ceramic is deposited / coated with the vanadium dioxide film. The preparation method is simple, and the complex window material displays remarkable tunable switching characteristics within infrared and terahertz ranges and has excellent phase transition properties and an effectiveswitch ratio.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
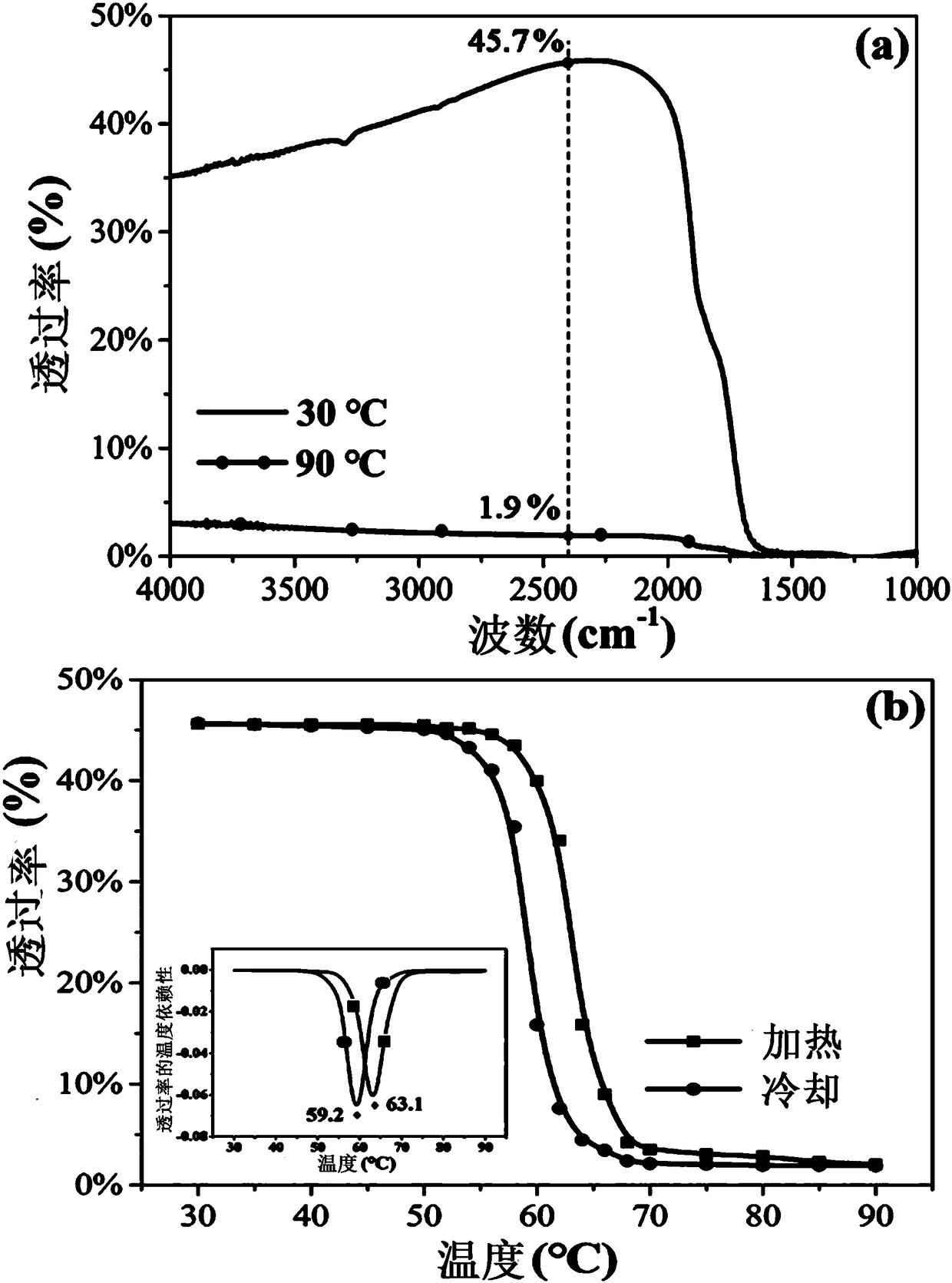
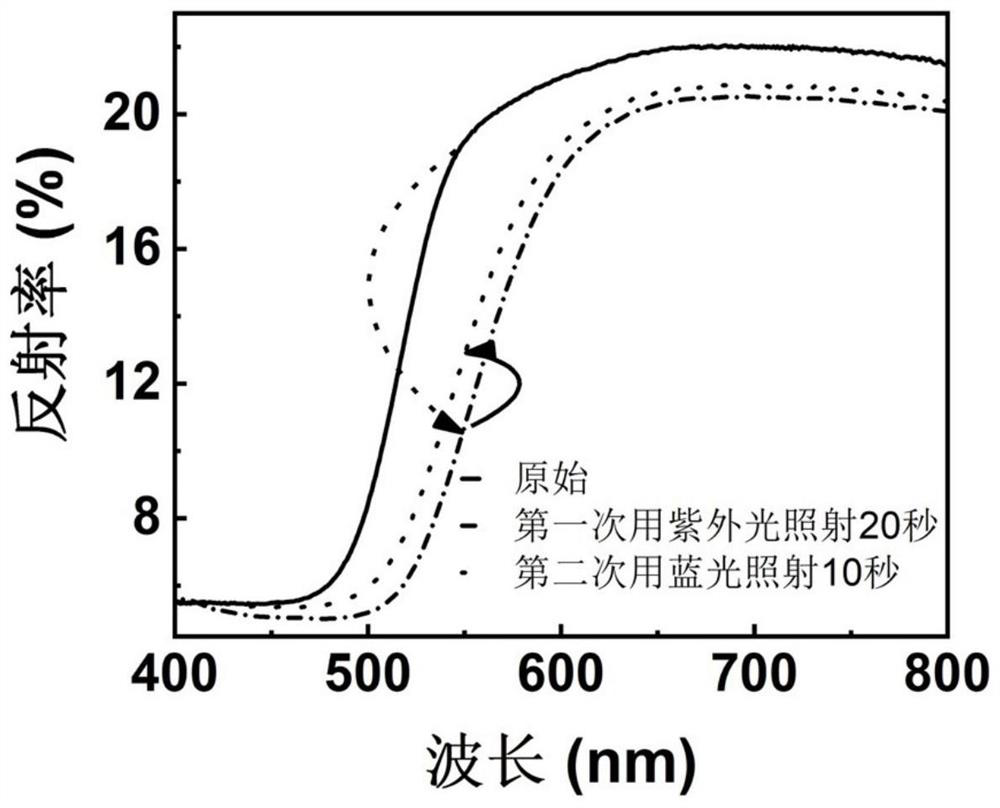
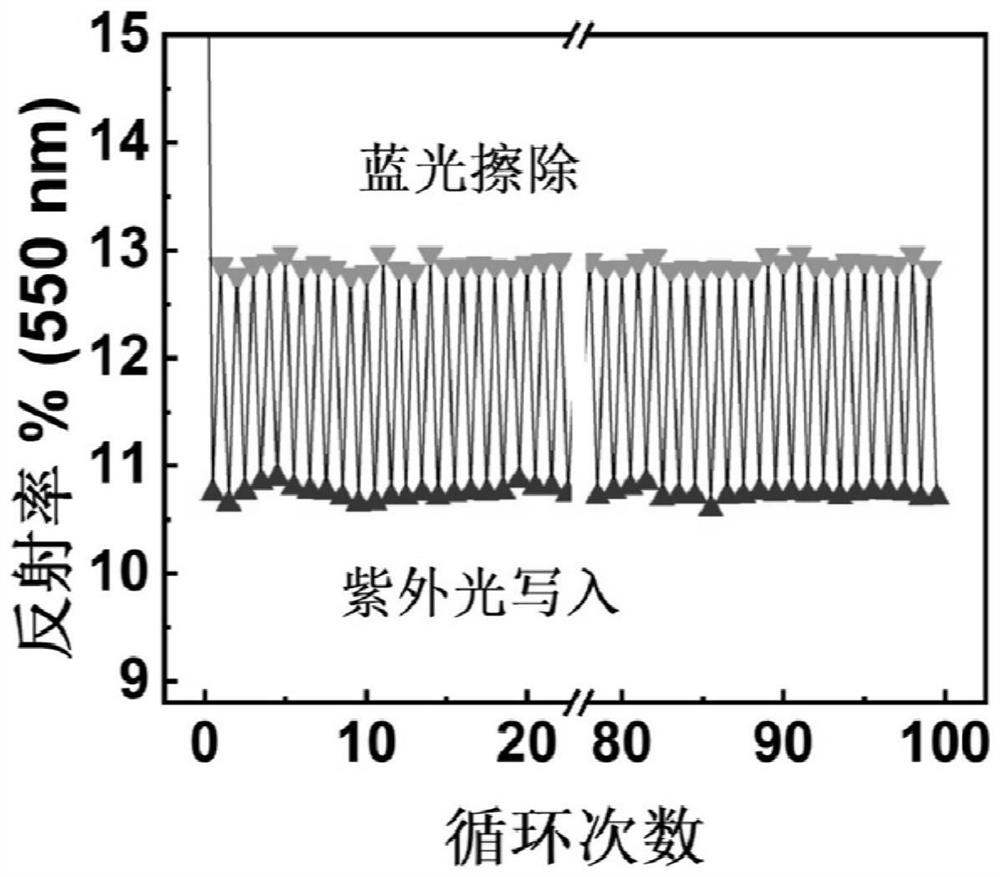
A kind of photochromic ternary copolyester and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111944135BPhotochromic fastImprove mechanical propertiesPhotosensitive materialsTenebresent compositionsPolymer scienceIsopropyl
The invention discloses a photochromic ternary copolyester as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The photochromic ternary copolyester has the following structure: R m and R n Selected from H, F, Cl, Br, I, methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, butyl, isobutyl, nitro, methoxy, etc., m is an integer of 1 to 4, n is An integer from 5 to 8, R a It is a residue of fatty dibasic acid, p is 20-200, q is 20-200, and x is an integer of 2-10. The preparation method comprises: preparing photochromic ternary copolyester through copolymerization of aliphatic dibasic acid compound or its esterified product, azobenzene compound and other diols. The photochromic ternary copolyester of the present invention has a photochromic response speed of less than 20 seconds and has good biodegradability and mechanical properties. The material has potential applications.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Composite multi-stage pulse tube refrigerator working in 1-2K temperature zone
InactiveCN103017395BCompact structureSmall footprintCompression machinesPulse tube refrigeratorEngineering
The invention discloses a 1-2K composite multi-stage pulse tube refrigerator which comprises a precooling-stage low-frequency pulse tube refrigerator utilizing a helium-4 working medium and a low-temperature-stage high-frequency pulse tube refrigerator utilizing a helium-3 working medium. The high-frequency pulse tube refrigerator is coupled to the low-frequency pulse refrigerator, so that 1-2K refrigeration temperatures can be obtained under the condition that little helium-3 is used. Compared with the traditional double-stage low-frequency pulse tube refrigerator utilizing helium-3 as a working medium, the 1-2K composite multi-stage pulse tube refrigerator has the advantages that consumption of helium-3 gas can be obviously reduced, and the 1-2K composite multi-stage pulse tube refrigerator is low in cost and convenient to implement and keeps characteristics of compact structure, long service life and high reliability of an existing pulse tube refrigerator.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A kind of composite window material and preparation method thereof
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
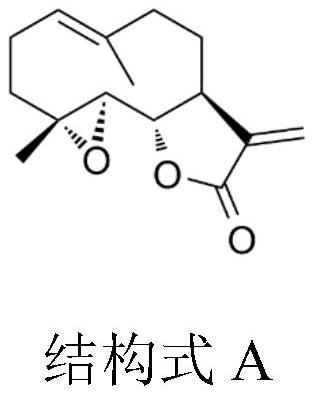
Application of parthenolide medicine in preparation of novel medicine for treating rhabdomyosarcoma
PendingCN114504572AProliferation inhibition rate is highHuge potential application prospectsOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsBiotechnologyMyosarcoma
The invention relates to application of parthenolide in preparation of a novel medicine for treating rhabdomyosarcoma, parthenolide is gemmarane type sesquiterpene lactone extracted and separated from plants such as wild chamomile and the like, and has biological activities such as anti-inflammatory activity, antibacterial activity and anti-tumor activity. According to the application of the medicine, an effective amount of parthenolide is given to rhabdomyosarcoma cells (A204), it is measured that the cell proliferation inhibition rate of the parthenolide reaches up to 97.34%, the parthenolide has huge application prospects in the aspect of rhabdomyosarcoma treatment, and a novel medicine application of parthenolide medicine in rhabdomyoma treatment is provided.
Owner:JIAMUSI UNIVERSITY
Self-curling preparation method and application of hollow graphene fibers
ActiveCN113388905AEasy accessIncrease productivityHollow filament manufactureFilament manufactureFiberSupercapacitor
The invention discloses a self-curling preparation method of hollow graphene fibers. The self-curling preparation method of the hollow graphene fibers comprises the following operation steps of (1) injecting and printing graphene oxide slurry onto a rotating roller to obtain gelatinous graphene oxide fibers; (2) soaking in a coagulating bath for coagulating, and taking out to obtain belt-shaped graphene oxide fibers; (3) stripping from the roller, and drying to obtain the hollow graphene oxide fibers; and (4) reducing to obtain the hollow graphene fibers. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the fibers with different diameters are obtained by adjusting equipment parameters, and a compact microstructure is formed by combining single-side support of the roller in a solidification process, so that the obtained hollow graphene fibers have the tensile strength of 190.5 MPa and the tensile deformation of 6.1 percent, and show the bending resistance of more than 5000 times; and the specific capacitance of a prepared supercapacitor reaches 170.6 F g <-1 >, and the supercapacitor has a huge potential application prospect in flexible and wearable energy storage equipment.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
A kind of preparation method of full-color variable structure chromogenic material
ActiveCN109370263BLow costEasy to makePigment treatment with macromolecular organic compoundsPigment treatment with organosilicon compoundsColor printingVisible spectral range
The invention provides a method for preparing a full color variable structure chromogenic material, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of structural color chromogenic materials. The preparation method provides preparation and optimization of visible light band full color variable structural chromogenic materials, and finds specific preparation processes and conditions to promote efficient high-quality growth of chromogenic material nanocrystals. The preparation method adopts a specific strong base as a material crystal growth environment. The preparation method is characterizedin that the strong base environment is utilized for preparation, the prepared chromogenic material composite particles have the particle diameter of 105-280 nm, and the color with the spectral peak inthe visible spectral range of 450-650 nm can be achieved under magnetic field control. The full color variable structural chromogenic material has the advantages of good color rendering effect and fast color reaction, and has great potential application prospects in photonic ink, anti-counterfeiting aspect, structural color printing, biological and chemical sensing and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of preparation method of highly hydrophobic fluorinated carbon nanotube/polyimide composite material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a highly hydrophobic carbon fluoride nanotube / polyimide composite material, relates to the preparation method of the polyimide composite material, and aims to reduce high dielectric constant of pure polyimide, improve the mechanical properties, reduce the hygroscopicity in engineering application, improve the service life, and solve the problem that special application in electrical insulation and power electronics is limited. The method comprises the steps: firstly, preparing carbon fluoride nanotubes; and secondly, obtaining the highly hydrophobic carbon fluoride nanotube / polyimide composite material through an in-situ polymerization method. The highly hydrophobic carbon fluoride nanotube / polyimide composite material disclosed by the invention can be industrialized in amplification, has great potential application prospects in electrical insulation, power electronics and other fields in future, and has great significance to new application prospects of polyimide. The preparation method of the highly hydrophobic carbon fluoride nanotube / polyimide composite material can be obtained.
Owner:大同共聚西安科技有限公司
Lac resin hydrosol and preparation method thereof
The invention provides lac resin nanoscale hydrosol and a preparation method thereof. The lac resin hydrosol is composed of lac resin and water. The method comprises the following steps: 1), dissolving lac resin in ethanol so as to obtain a lac resin ethanol solution; and 2), dripping the lac resin ethanol solution in deionized water, and distilling to remove ethanol. The lac resin hydrosol prepared by the method is small in particle size, good in dispersivity, storage stability, centrifugal stability and freeze-thaw stability and can reach national first level standard. The method has the advantages of simplicity and suitability for large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:THE RES INST OF RESOURCES INSECTS RIRI OF THE CHINESE ACADEMY OF FORESTRY
Acrylate type polychain transfer agent, its preparation method and its application in the preparation of columnar polymer brushes
The invention discloses an acrylate-type poly-chain transfer agent as well as a preparation method and an application of the poly-chain transfer agent in the preparation of a columnar polymer brush. The acrylate-type poly-chain transfer agent is prepared by synthesizing a main chain containing bromine (or chlorine) functional groups by virtue of RAFT and then introducing disulfide ester functional fragments by virtue of a one-step method. The columnar polymer brush is synthesized from the obtained acrylate-type poly-chain transfer agent by adopting a synthesis strategy of 'grafting from main chain' through the RAFT method, homopolymer and block copolymer containing multifunctional branched monomers can be obtained, namely, a brush-shaped homopolymer and a copolymer are obtained. The main chain of the polymer molecular brush is a (meth) acrylate polymer and the side chain of the polymer molecular brush is polystyrene, poly(meth)acrylate and poly(meth)acrylamide or a copolymer thereof. By the preparation method, the tedious steps used in the synthesis of a complex chain transfer reagent are avoided, the pollution caused by the tedious steps is decreased, the synthesized columnar polymer brush has a controllable structure and the preparation method provides a more simple and efficient method to synthesize the functional columnar polymer brush.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com