Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
348results about How to "Good deoxidation effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Wearable tubular welding rod made from tungsten carbide
InactiveCN1562550AGood welding performanceReduce burning lossWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaAdhesiveCarbide
An antiwear tubular welding tungsten carbide electrode for strengthening the surface of steel members, such as the surface of steel roller in roller bit, is composed of the welding tube and the filler consisting of sintered tungsten carbide particles, cast tngsten carbide particles, organic adhesive and powdered alloy containing Cr, Si, B, Mn and Ni.
Owner:SINOPEC OILFIELD EQUIP CORP
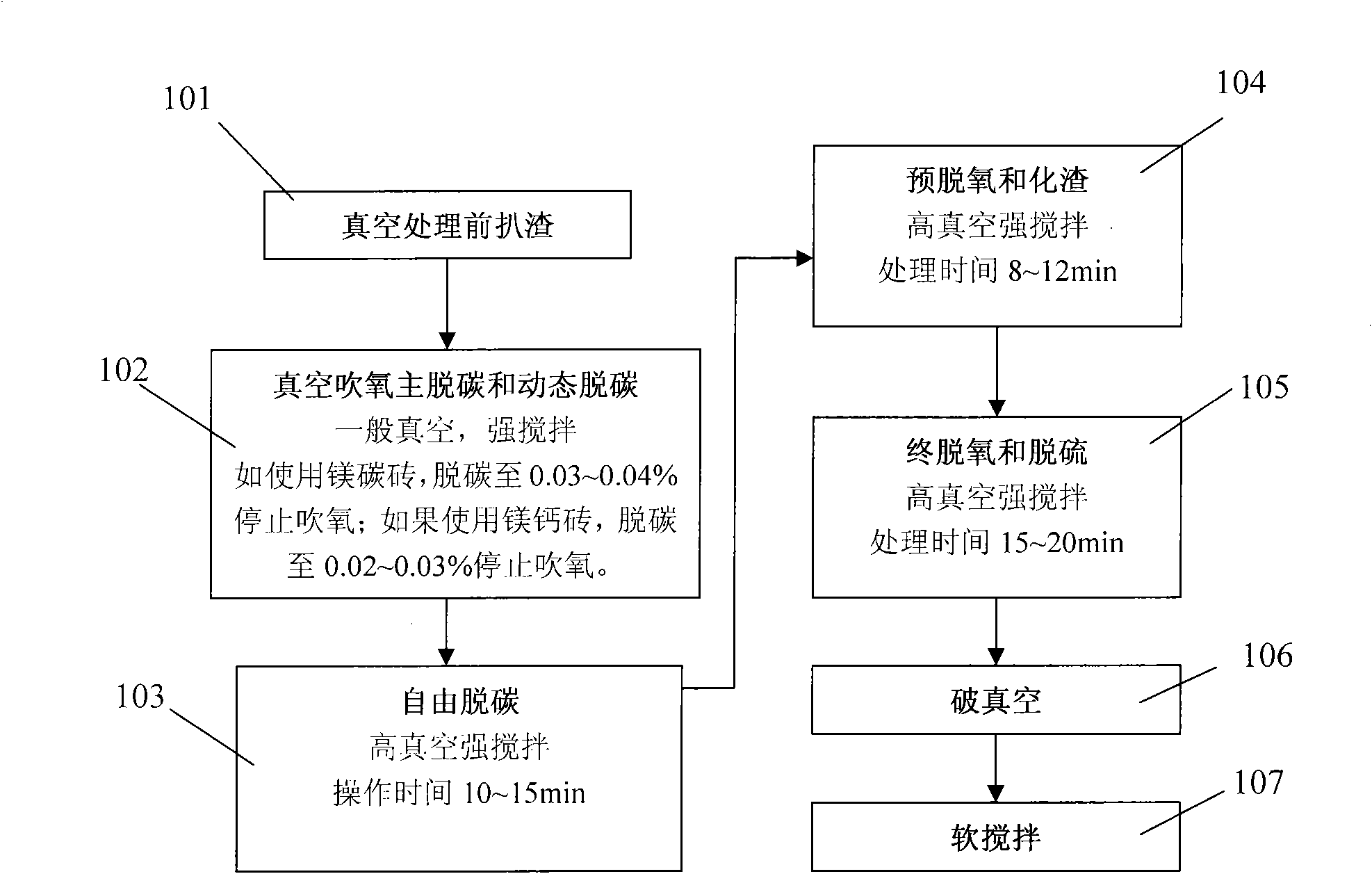
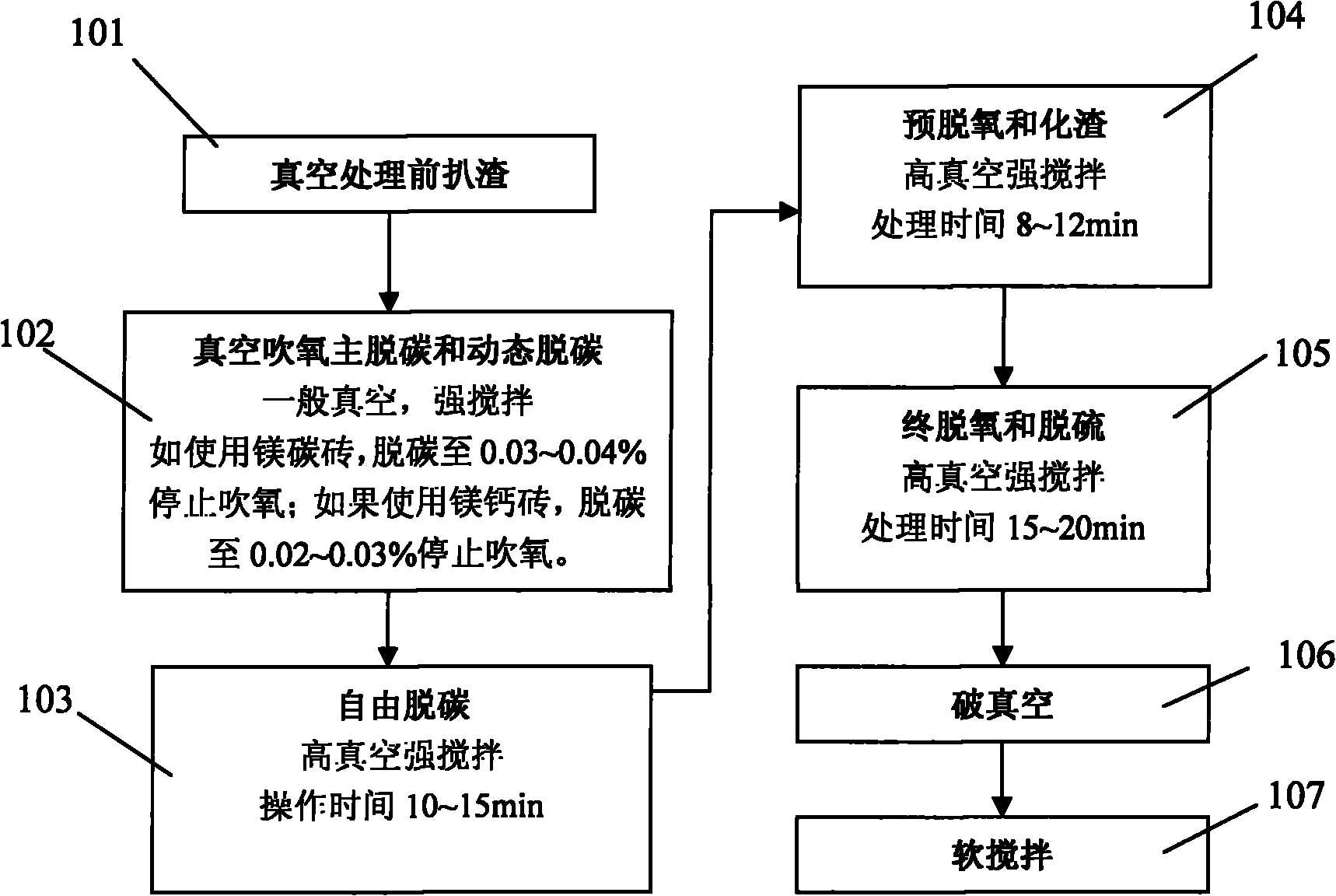
Method for refining ultra-low carbon ferritic stainless steel under vacuum
The invention discloses a method for refining ultra-low carbon ferritic stainless steel under vacuum, comprising the following steps: 1) steel ladle enters a vacuum oxygen-blowing decarburization furnace, the pressure in a vacuum is less than 100 Pa, initial chromium content of the molten steel is 10%-25%, the carbon content is 0.25%-0.60%, and the initial temperature of the molten steel is less than 1600 degrees C.; 2) oxygen-blowing decarburization processing, then main decarburization stage followed by dynamic decarburization stage; 3) free decarburization processing under high vacuum condition; 4) reducing, pre-deoxidizing, and adding active lime, ferrosilicon for pre-deoxidation and slag formation after free decarburization processing; deoxidizing, adding aluminum block, ferrosilicon, realizing final oxygen, silicon alloying, and desulphurizing strongly; 5) reducing argon-gas-blowing flow to small flow, conducting vacuum-breaking treatment, and then stirring to promote inclusion behavior to float up. The invention further reduces end-point carbon content during the ferritic stainless steel vacuum refining, meets requirements on strong desulphurization of molten steel, in order to increase the success rate of ultra-low carbon ferritic stainless steel smelting, thereby increasing the product quality and reducing the smelting cost.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High-strength corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy profile and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-strength corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy profile and a preparation method thereof. The aluminum alloy profile comprises an aluminum alloy base body and a ceramic coating. The aluminum alloy base body is prepared from Cu, Si, Fe, Cr, Mg, Mn, Zn, Ti, Li, Ni, Zr, Y, W, V and the balance Al. The ceramic coating is prepared from SiC, Cr2O3, NiO, Cr3C2, Al2O3 and Si3N4. According to the high-strength corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy profile, ceramic powder is arranged on the surface of the aluminum alloy base body through plasma cladding, and then laser remelting is conducted, so that the obtained aluminum alloy profile has good mechanical performance such as strength, hardness and impact toughness; and meanwhile, the high-strength corrosion-resistant aluminum alloy profile has the beneficial effects of being resistant to corrosion, good in abrasion resistance, long in service life and the like.
Owner:安徽省煜灿新型材料科技有限公司
Molten steel deoxygenating agent and its prepn
The molten steel deoxygenating agent is Fe-base alloy containing Al, Mg and RE, and comprises Mg 8-12 wt%, RE alloy 0.03-1 wt%, Al 48-58 wt% and Fe for the rest, with metal Mg being added while the Al-containing molten steel at the temperature of 900-1100 deg.c. The molten steel deoxygenating agent has great density, Al and Mg yield, high S and O eliminating capacity, and other advantages.
Owner:邹杰
Deoxidation method for converter tapping molten steel
The invention discloses a deoxidation method for converter tapping molten steel. The deoxidation method comprises the steps of: firstly adding a deoxidizer into a ladle before the converter tapping, wherein the addition amount of the deoxidizer is 1.75-4.0kg per ton of tapping molten steel; then tapping at 1660-1700 DEG C and blowing argon to the bottom of ladle at the same time; adding a deep deoxidizer when the tapping molten steel accounts for 30%-40% of the total molten steel, and carrying out deep deoxidation, wherein the addition amount of the deep deoxidizer is 0.5-2.5kg per ton of tapping molten steel, and the addition of the deep deoxidizer is finished before that the tapping molten steel accounts for 75% of the total molten steel. The deoxidation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the pre-deoxidation is finished by mainly adopting relatively cheap deoxidizer such as carbon powder, SiC and CaC2 and final deoxidation is finished by cooperating with the deep deoxidizer; and the deoxidizer can effectively reduce the oxidation property of the slag on the surface of the molten steel, is beneficial to reducing the oxidation loss of alloying element and reducing the oxidation erosion of the slag to the refractory, and significantly improves the yield of the alloying element.
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL (GROUP) CORP
Composite deoxidizing agent aluminum-calcium-iron alloy for smelting steel
The invention provides steel-smelting complex deoxidizing agent- calcium-aluminium- ferrum alloy. It is to solve problems of great loss of aluminium during deoxidation process, low effective component content, bad utilization rate and large consumption, easy secondary oxidation and Al2O3 generation. The alloy comprises aluminium 20- 70%, calcium 1- 10% and left is ferrum and inevitable foreign substance. The manganese 1- 20%, silicon 1- 20% and titanium 1- 5% can be added into said alloy to prevent alloy efflorescence and increase steel alloy element. The invention is characterized by high deoxidation efficiency, lowered foreign substance content in steel, smooth steel smelting process, improved steel quality and reduced cost.
Owner:谢应凯
Production device and method of high-purity oxygen-free copper ingot billet
The invention provides a production device of a high-purity oxygen-free copper ingot billet. The device comprises a melting furnace, a partition bin and a heat preservation furnace which are sequentially communicated, the partition bin is further provided with a deoxygenator, the deoxygenator comprises a gas conveying pipe used for conveying deoxygenation gas and an air exhaust cover which is located in the partition bin and connected with the outlet end of the gas conveying pipe, and a plurality of air exhaust holes with the diameter of 0.5 mm to 1 mm are formed in the air exhaust cover; the melting furnace and the partition bin are connected through a liquid inlet hole, the air exhaust cover right faces the liquid inlet hole, and the distance between the air exhaust cover and the liquid inlet hole ranges from 10 mm to 40 mm; in the flowing direction of molten copper, the projection of the air exhaust cover is larger than the projection of the liquid inlet hole; the invention further provides a method capable of adopting the device for producing the oxygen-free copper ingot billet. By the adoption of the method, the oxygen-free copper ingot billet which is good in production compactness and low in oxygen content can be produced.
Owner:JIANGXI GUANGXIN COPPER IND
Electric furnace highly effective metallurgy complexing agent
The invention relates to a kind of efficient metallurgical complex reagent for electrical furnace, which is particularly relates to an additives for the production of a special slag. The complex reagent contains by percentage of quality as follow: 35~50% of MgO, 20~30% of C, 4~15% of SiC, 5~9% of CaSi, 8~15% of CaO, and a remaining amount of impurities and binder. The complex reagent is added into the electrical furnace at the middle and late oxidation period of electric furnace for significant effect.
Owner:马鞍山中冶钢铁冶金高新技术有限公司
Method for preparing high-purity oxygen-free copper rod by upper leading method
The invention discloses a method for preparing a high-purity oxygen-free copper rod by a upper leading method. The method comprises the following steps: (S1) electrolytic copper is molten to obtain molten copper; molten salt is added, and consists of 60-65% of sodium borate, 10-15% of sodium fluosilicate, 10-15% of cryolite, 5-10% of calcium fluoride, 1-5% of titanium dioxide and 5-10% of sodium chloride; and high-purity nitrogen is introduced in the molten copper; (S2) a deoxidizer consisting of a Cu-Re alloy and lithium oxide is added in the molten copper for stirring to reach uniform distribution; (S3) the molten copper is leaded to an insulation furnace; and a layer of flake graphite covers the surface of the molten copper; and (S4) a hollow crystallizer extends in the molten copper; a solid is condensed in the hollow crystallizer; and the upper end of the solid is pulled by a stretching mechanism to prepare the high-purity oxygen-free copper rod. The method for preparing the high-purity oxygen-free copper rod by the upper leading method is simple, high in impurity removing and oxygen removing efficiency and lower in pollution, and can obtain the high-purity oxygen-free copper rod with an oxygen content of not higher than 20 PPM.
Owner:安徽晋源铜业有限公司
Efficient utilization process of aluminum ash in electrolytic aluminum plant
ActiveCN107245549AAvoid pollutionReduce steelmaking costsProcess efficiency improvementSlagAluminium
The invention discloses an efficient utilization process of aluminum ash in an electrolytic aluminum plant. Limestone powder and graphite carbon are added into white aluminum ash in the electrolytic aluminum plant and pressed to form spheres for the LF refining process; the weight percentage contents of three components are respectively aluminum ash of 60%, limestone powder of 30% and graphite carbon of 10%; limestone and graphite are crushed, are finely grinded in a Raymond mill to reach the particle size below 1 mm, are mixed with the aluminum ash for uniform mixing, and are added in a high-pressure ball press to be pressed to form slag balls; the slag balls are transferred to a converter tapping station for future use; a deoxidizing agent is replaced during LF smelting; 0.8-3 kg of slag balls are added in each ton of steel; and a traditional steel refining process is operated.
Owner:王强
Gas shield welding wire with high strength and tenacity
ActiveCN101722386AHigh strengthImprove toughnessWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaImpurityREL
The invention relates to a gas shield welding wire with high strength and tenacity, which is suitable for the welding of 800MPa-grade high-strength steel. The gas shield welding wire comprises the following ingredients in percentage by weight: 0.02-0.05 percent of C, 0.30-0.80 percent of SiO, 2.0-2.50 percent of Mn, less than 0.010 percent of P, less than 0.010 percent of S, 0.70-1.2 percent of Cr, 0.70-1.2 percent of Mo, 0.02-0.12 percent of Ti, 0.003-0.005 percent of B, 2.0-3.2 percent of Ni, 0.05-0.1 percent of RE, 0-0.06 percent of Nb, and the balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities. The welding wire has the advantages of simple ingredient design, low cost, good manufacturability, and the like; in addition, and weld metal has high tenacity and is suitable for the welding at the position with higher low-temperature tenacity requirement. Experiments show that the Rm of the weld metal welded by the welding wire is not less than 800MPa, and the ReL is more than 760MPa; and the impact energy at -50 DEG C of the weld metal is not less than 37J.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Al-Ca matter converter slag deacidizing modifier
The invention relates to a deoxidization modifier of Al-Ca converter slag, which is a mixture compounded by or is a complex slag ball pressed by 15 percent to 35 percent of active lime, 35 percent to 50 percent of calcium carbide, 35 percent to 50 percent of aluminum powder (or aluminum grain, aluminum scrap and aluminum line segment) according to the weight ratio. Since the aluminum powder and active CaO are mixed with CaC2, no adhesives or additives are used, so additional pollution to molten steel does not exist, which is in favor of improving the quality of excellent and special steel and being no damage for ladle lining refractory materials; the aluminum has high comprehensive utilization rate, the deoxidation effect of the converter slag is good, the slag amount is low and the slag forming is fast. Because no moisture contains in raw materials, the active CaO and CaC2 can not be hydrated and the reaction ability thereof can not be decreased, thus ensuring the functions and effect thereof; the molten steel has high cleanliness and no water gap nodulation after 5 continuous casting heats.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Steel-smelting alterant for molten steel refining
InactiveCN1807657AImprove performanceQuality improvementBlast furnace componentsBlast furnace detailsNon-metallic inclusionsSmelting
The invention discloses a composition alloy smelling method in mining heater in carbothermic method, which is characterized by the following: using alkaline earth alloy and rare earth alloy as raw material; adopting purified alterant of steel-smelting molten steel to deoxidize, sulfur removal and dispel harmful substance; making shape of non-metallic inclusion of steel balling, size smaller and adequate distribution. The method improves the mass of steel, which reduces steel-smelting cost by using the invention.
Owner:谢廷声
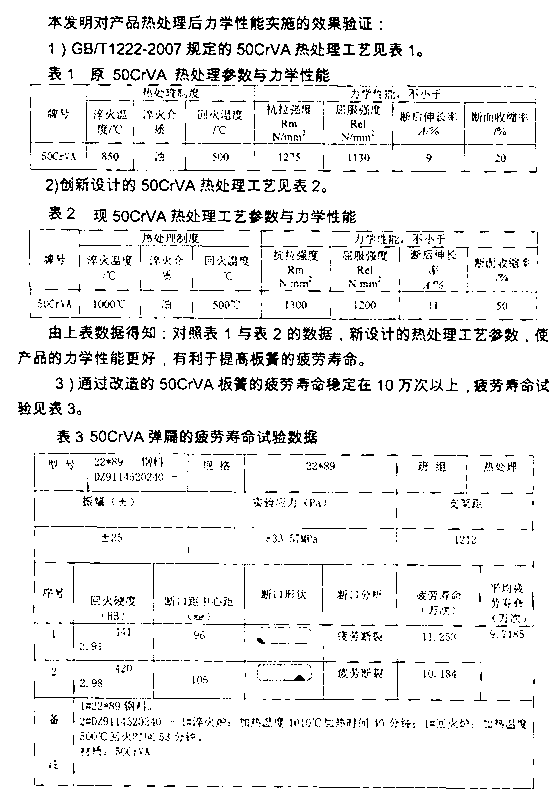
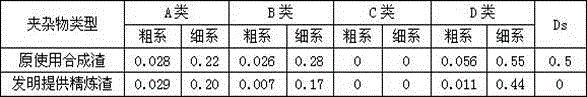
Technique for prolonging fatigue life of 50CrVA plate spring
ActiveCN103014533AGood deoxidation effectAvoid formingFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesChemical compositionSlag
The invention provides a technique for prolonging the fatigue life of a 50CrVA plate spring. The technique includes the optimal design for the following chemical components of a 50CrVA flat spring steel: 0.49 to 0.53% of C, 0.20 to 0.30% of Si, 0.65 to 0.75% of Mn, 0.90 to 1.05% of Cr, 0.11 to 0.15% of V, 0.006 to 0.009% of Al, 0.018 to 0.020% of P, 0.016 to 0.020% of S, not greater than 0.25% of Ni, and not greater than 0.25% of Cu. The method for controlling and denaturating treatment on nonmetallic inclusion in steel comprises the following steps: (1) sealing a connector between a long nozzle of a large steel ladle and an intermediate submersed nozzle through an argon seal ring; controlling the amount of slag in tapping to 0 to 5kg / t; controlling the weight of the molten steel of the steel ladle to be not less than 7t; and controlling the molten steel level of a crystallizer to fluctuate within the scope of + / -2mm; and (2) carrying out denaturating treatment on inclusion; and adding SiCa wires at 2.1m / t through a wire feeder under a white slag condition, wherein the molten steel is at temperature of 1550 to 1580 DEG C; the parameters in heat treatment of the plate spring include quenching temperature of 1000 DEG C, tempering temperature of 500 DEG C, tensile strength of not less than 1300N / mm<2>, yield strength of not less than 1200N / mm<2>, percentage elongation after fracture of not less than 11%, and percentage reduction of area of not less than 50%.
Owner:XINJIANG BAYI IRON & STEEL
Method for deoxidizing copper solution
The invention discloses a method for deoxidizing a copper solution, comprising the following steps of: firstly, preparing a deoxidizing agent mixture, wherein the deoxidizing agent mixture comprises Mn, Mg and a Cu-P alloy, the weight ratio of the Mn relative to the copper solution is 0.300-0.600 percent, the weight ratio of the Mg relative to the copper solution is 0.005-0.015 percent and the weight ratio of the Cu-P alloy relative to the copper solution is 0.010-0.050 percent; secondly, wrapping the prepared deoxidizing agent mixture with a copper belt to form deoxidizing agent bags; and finally, placing the deoxidizing agent bags into the copper solution, pressing the deoxidizing agent bags into the bottom and stirring. The deoxidizing agent adopted by the invention is a precipitation deoxidizing agent; the precipitation and deoxidization processes can be carried out in the full copper solution; remarkable deoxidizing effect can be achieved; a gaseous or solid state product is formed to facilitate the separation from the copper solution; the components of the deoxidizing agent have little influence on the copper solution so as to ensure the purity; and the deoxidizing agent hashigh deoxidizing effect and is suitable for being popularized and applied.
Owner:江苏富威科技股份有限公司
Efficient composite desulfurizer
The invention discloses a high-efficiency compound desulfurizing agent, relating to the ladle desulphurization accessory field. In the existing ladle desulphurization, the uniserial desulfurizing agent is uniformly adopted, with narrower function, and non-agreeable desulphurization effect. Aiming at the condition that small and medium-sized steel mills do not have liquid iron pretreatment systems or desulphurization stations, and do not have powder spraying desulphurization devices, the desulfurizing agent of the invention adopts ingredient with multi-components, namely, the compound desulfurizing agent consisting of limestone, calcined soda, fluorite, calcium carbide, magnesium powder and caustic-calcined magnesite, with the weight proportion of 40 to 50, 10 to 20, 5 to 15, 10 to 20, 4 to 6 and 5 to 15 sequentially. The desulfurizing agent has the following advantages that: 1. the integral desulphurization capability is strong, and the sulfur content can be reduced to 20ppm; 2. sulfur substance can be contained, and resulfurization phenomenon can not be generated; 3. the desulfurizing agent can be directly poured, and equipment and investment are not needed to be increased; and 4. the desulphurization speed is high.
Owner:西峡县福盈冶金材料有限公司
High-carbon high-chromium stainless bearing steel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103014536AImprove cleanlinessReduce oxygen contentRecovering materialsElectric furnaceHigh carbonNiobium
The invention relates to a high-carbon high-chromium stainless bearing steel and a preparation method thereof. The high-carbon high-chromium stainless bearing steel comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.9-0.95% of carbon, 0.80-0.85% of silicon, 0.3-0.35% of manganese, less than 0.025% of sulfur, less than 0.02% of phosphorus, 0.15-0.3% of molybdenum, 3.5-4.0% of chromium, 0.01-0.02% of nitrogen, 0.1-0.2% of nickel, 0.02-0.03% of niobium, 0.02-0.03% of vanadium and the balance of iron. The technical scheme provided by the invention is beneficial to deoxidation effect, enhances the cleanliness of the bearing steel, and lowers the oxygen content in the bearing steel.
Owner:LIXING JINYAN STEEL BALL (NINGBO) CO LTD
Refining slag for bearing steel production and smelting process of refining slag
The invention discloses refining slag for bearing steel production and a smelting process of the refining slag, wherein the refining slag comprises the following components in percentage by weight: less than or equal to 6% of SiO2, 40-50% of Al2O3, 45-55% of CaO, less than or equal to 8% of MgO, less than or equal to 0.05% of TiO2 and less than or equal to 2% of Fe2O3, the particle size is controlled at 3-45mm, and the alkalinity is controlled at about 10; and the smelting process comprises the main steps of predeoxidizing after converter tapping, starting to alloy at 80s after starting to tap (the tapping quantity is about 35t), adding one of aluminum iron, carbon powder, alloy and lime in sequence, impacting and smelting by using a steel flow, and then, adding the other material; adding 600Kg of the refining slag at one step after a refining furnace is seated; and adding a deoxidizer by strictly executing the principles of multiple batches and small quantity. By using the refining slag, the problem for controlling the O content as well as B, D and TiN inclusions in a bearing steel production process is simultaneously solved; and the refining slag plays a critical role in improving the quality of bearing steel.
Owner:SGIS SONGSHAN CO LTD
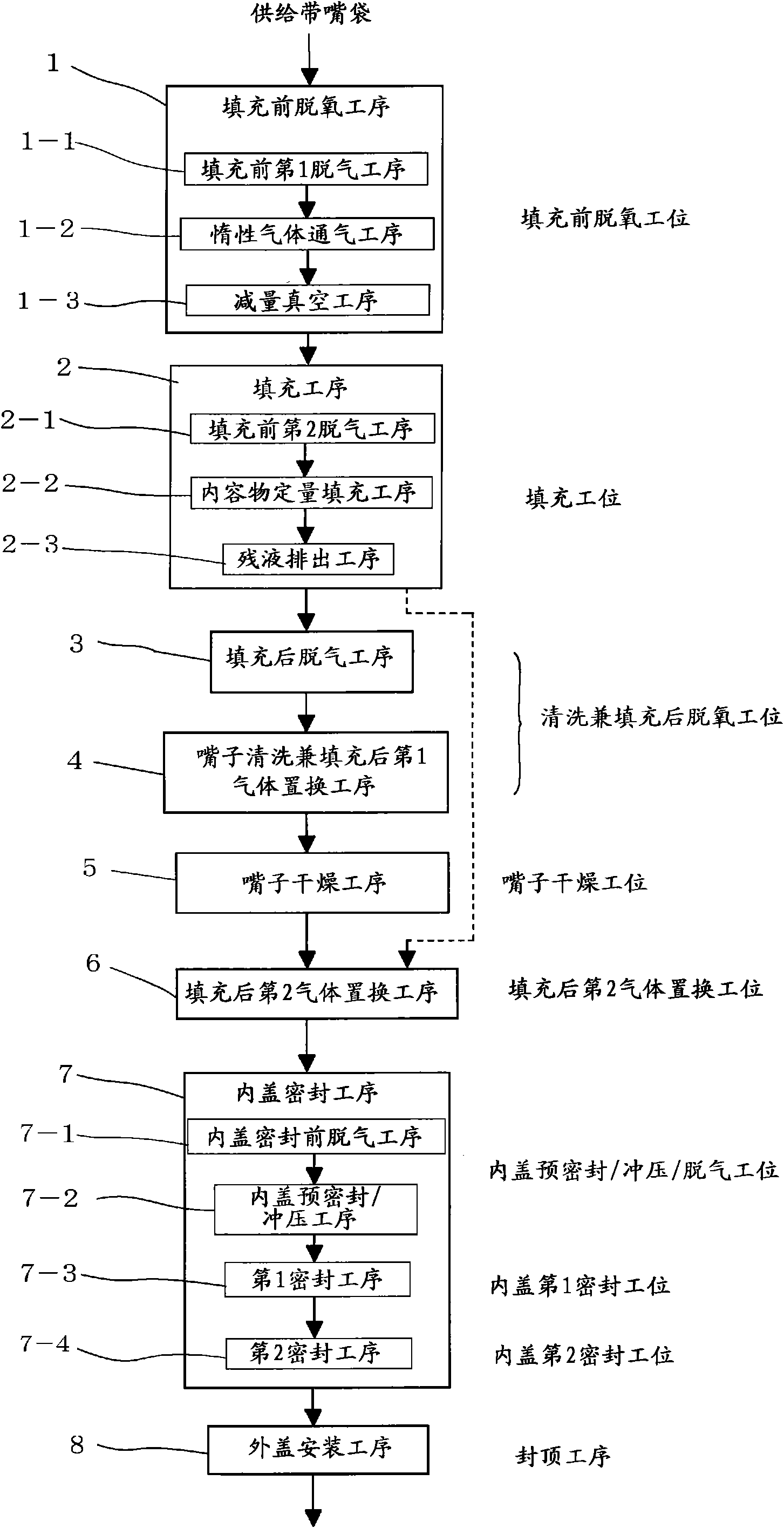
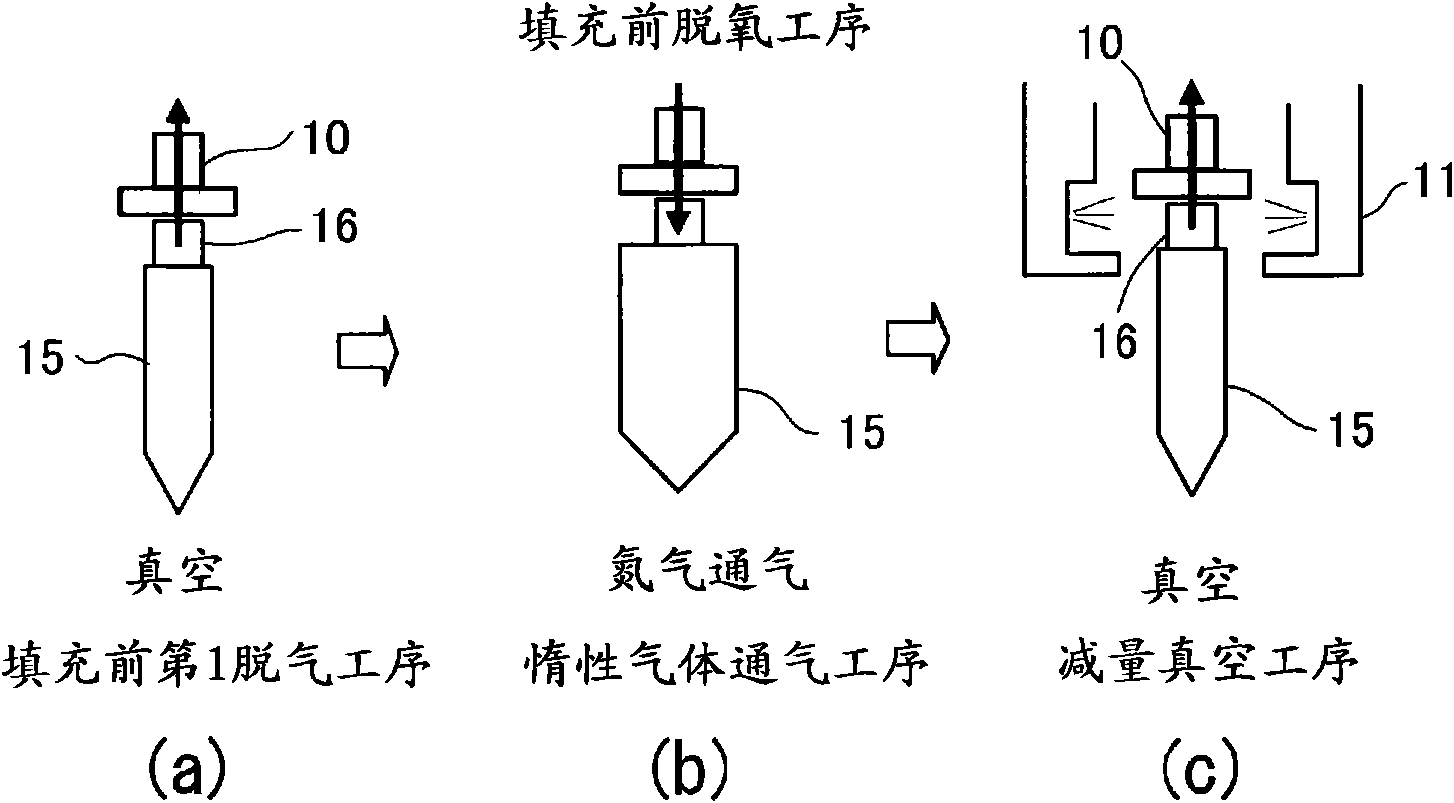
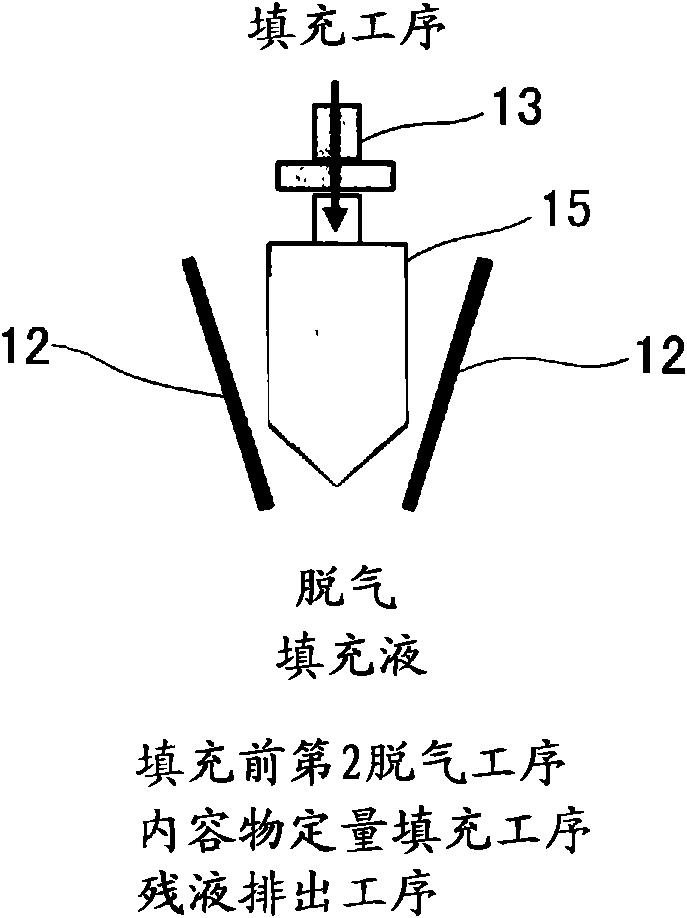
Method of packing liquid filling into spouted pouch and sealing the pouch and apparatus therefor
InactiveCN101588968AImprove qualityHigh deoxygenation ratePackaging by pressurising/gasifyingPackaging protectionLiquid stateProduct gas
To obtain a spouted-pouch package having a high degree of deoxidation by a method in which even a liquid filling which readily lathers can be packed while being inhibited from lathering. [MEANS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMS] A before-packing deoxidation step (1) is performed before a liquid filling is packed into a pouch. The step (1) comprises: a vacuum step (1-1) in which the pouch is evacuated under vacuum; an inert-gas blow step (1-2) in which an inert gas is blown into the pouch after the vacuum step; and a gas-diminishing vacuum step (1-3) in which the gas in the pouch after the inert-gas blow step is discharged under vacuum to diminish the gas in the pouch to a given amount. Thereafter, the pouch is evacuated in a second before-packing evacuation step (2-1) and then packed with the filling. After the packing, gas replacement is conducted.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN KAISHA LTD
High Ca, silicon-free aluminum calcium iron alloy for deoxidising of molten steel and its preparation method
The invention discloses calcium-aluminium- ferrum alloy for steel- melting and deoxidizing, the weight proportion of them is as follows: 15% C21C 7 / 06 C22C 33 / 04 C22C 33 / 06 0 6 1 2007 / 7 / 16 101086029 2007 / 12 / 12 100475980 2009 / 4 / 8 2009 / 4 / 8 2009 / 4 / 8 Guo Qingcheng Liaoning 117100 Guo Qingcheng Fan Songtao
Owner:本溪铸新冶炼有限公司
High-calcium non-silicon aluminium calcium magnesium ferrous alloy for steel-smelting deoxidization and method for preparing the same
The invention discloses a high-calcium no-silicon aluminum-calcium-magnesium-ferric alloy used for steelmaking deoxidization. According to the weight proportion of the components, Ca is more than 15 percent but less than or equal to 28 percent, the proportion of Al to Ca is 1-2:1, 2-6 percent of Mg, the rest is Fe. The optimization scope is 18-25 percent of Ca, the proportion of Al to Ca is 1-1.3:1, 2-4 percent of Mg, the rest is Fe. A preparation method is that: aluminum, calcium, magnesium, low-carbon steel scrap are chosen as raw materials; the materials are smelted into aluminum-magnesium and aluminum-calcium master alloys in a low-frequency furnace; the materials continue being smelted in a high-frequency furnace and aluminum-iron metal liquid is obtained; the master alloy is pressed into the deep of the aluminum-iron metal liquid under a meshed high-temperature resistance container to be melted and at last the master alloy is cast under the protection of argon gas. The obtained alloy can be used for the final deoxidation in smelting low-carbon low-silicon al-killed steel, and can lower the harmful effect of the deoxidation product Al2O3 with good effect in integral deoxidation.
Owner:郭庆成
Ultra-low aluminum steel and smelting method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of ferrous metallurgy and particularly relates to ultra-low aluminum steel and a smelting method thereof. The smelting method provided by the invention adopts a production route with the steps of deep removal of S and P by molten iron pretreatment, decarbonization by a converter, deoxidization and alloying of silicon manganese during tapping, deslagging by argon blowing, deep removal of O, S and P by ladle refining, micro-alloying of Ti, Ni, Mo, V and other elements, RH (Ruhstahl-Hausen) vacuum circulation degassing, soft argon blowing and full-protection casting; the prepared ultra-low aluminum steel has low content of harmful elements, particularly has low content of O and Al, can prevent the inclusion of brittle aluminum oxide and realize high impact-resistant and fatigue-resistant performances of the steel, and is suitable for application fields with relatively high requirements for fatigue and impact performances, such as high-speed track traffic and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Large-diameter high-purity oxygen-free copper cast blank horizontal continuous casting process and connected furnace
The invention relates to a large-diameter high-purity oxygen-free copper cast blank horizontal continuous casting process. An oxide layer and particles are removed from the standby cathode copper surface, in addition, preheating treatment is carried out, and the preheating temperature is controlled to be 280 DEG C to 300 DEG C; pretreated cathode copper is placed into a smelting furnace to be smelted, the smelting temperature is controlled to be 1180 to 1230 DEG C, inert gas is introduced into the bottom of the smelting furnace, a calcined charcoal layer floats above molten copper to be used as the coverage, and the molten copper is stirred through electromagnetic stirring; then, the smelted molten copper flows into a heat insulation furnace, inert gas is introduced into the bottom of the heat insulation furnace, the calcined charcoal layer floats above molten copper to be used as the coverage, and the temperature inside the heat insulation furnace is controlled to be 1180 to 1230 DEG C; the molten copper in the heat insulation furnace is guided out, a graphite crystallizer is subjected to water cooling, and high-purity oxygen-free copper cast blanks are obtained. The process has the advantages that the oxygen content of the cast blanks can be effectively controlled, the production cost is reduced, products can completely reach TU1 standards, and the yield can reach more than 90 percent.
Owner:JIANGSU XINGRONG MEILE COPPER IND
Corrosion-resistant steel plate for ocean platform and production method of steel plate
The invention belongs to the technical field of ferrous metallurgy, and discloses a corrosion-resistant steel plate for an ocean platform and a production method of the steel plate. The corrosion-resistant steel plate is prepared firstly from the combination of proper components in percentage by weight and then by carrying out KR molten iron pretreatment, converter smelting, argon-blowing station fed with aluminum wire, LF furnace refining, VD vacuum refining, continuous casting, heating, controlled rolling and controlled cooling, heap cooling, quenching, tempering and the like. According to the corrosion-resistant steel plate for the ocean platform and the production method of the steel plate, compared with the prior art, the produced steel plate has the advantages of excellent corrosion resistance, good low-temperature impact toughness and excellent comprehensive performance, and is especially suitable for being used under cold weather and seawater corrosion conditions.
Owner:NANYANG HANYE SPECIAL STEEL CO LTD
Oxygen-free copper rod production method
InactiveCN108517419ACompact structureBright surfaceProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisGraphite
The invention discloses an oxygen-free copper rod production method, which comprises the following steps of adding baked electrolytic copper and dried deoxidants into a melting furnace in batches formelting; after the melting, performing stirring through a graphite stirrer arranged in the melting furnace; then, introducing copper liquid deoxidized by a deoxidant into a heat insulation furnace; introducing nitrogen gas containing 1-percent natural gas into the heat insulation furnace; using an upper guiding method traction pulling casting machine to perform pulling casting on copper liquid toobtain the oxygen-free copper rod. The oxygen-free copper rod production method has the advantages that the process is simple; the production cost is low; the multiplex deoxygenation is performed on the raw materials; the deoxygenation effect is improved; meanwhile, the safety coefficient is high; the conditions are not harsh; wide market prospects are realized; the oxygen-free copper rod preparedby the method has a compact structure and bright surface; the oxygen content can be lower than 3ppm.
Owner:中海宏祥铜业江苏有限公司
Process for producing steel-making deoxidizer by use of overhaul slag of aluminium cell in aluminum electrolytic plant
The invention discloses a process for producing a steelmaking deoxidizer by utilizing the overhaul slag of an aluminum electrolytic cell in an electrolytic aluminum plant. The overhaul slag of an aluminum electrolytic cell is first crushed to about 5 cm by using a jaw crusher, and then ground to a fineness of 0.5 to 3 mm by a ball mill. , purchase local raw dolomite, in which the magnesium oxide content in the middle of the dolomite is greater than 18%, and the calcium oxide content is greater than 20%. After the raw dolomite is crushed and ground to 0.075-0.5mm, the aluminum electrolytic cell of the above two raw materials is overhauled The slag powder and raw dolomite powder are mixed evenly according to the weight ratio of 7:3, put into a high-pressure ball briquetting machine and pressed into balls as a deoxidizer, and then transported to the converter tapping station for use; when the converter is tapping, it is no longer used Calcium carbide, add 0.8-3kg of deoxidizer per ton of steel, and use it according to the traditional steelmaking process.
Owner:王强
Seamless steel tube and preparation method of seamless steel tube
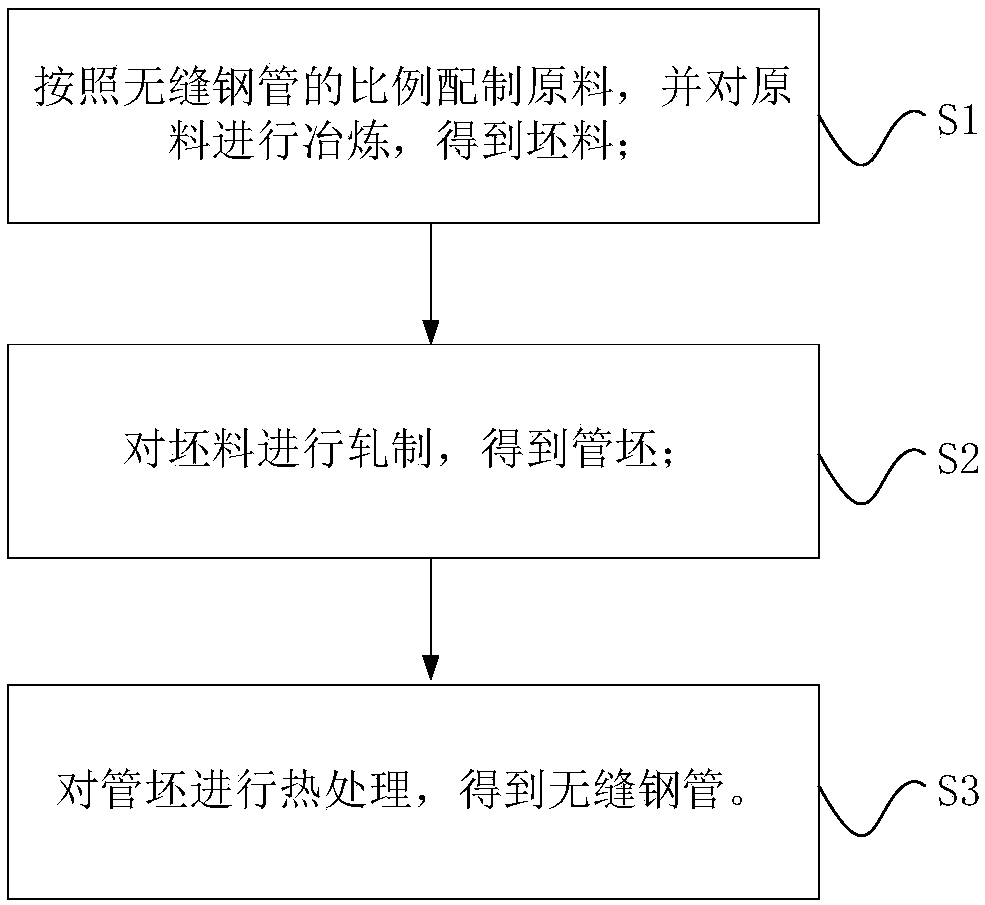
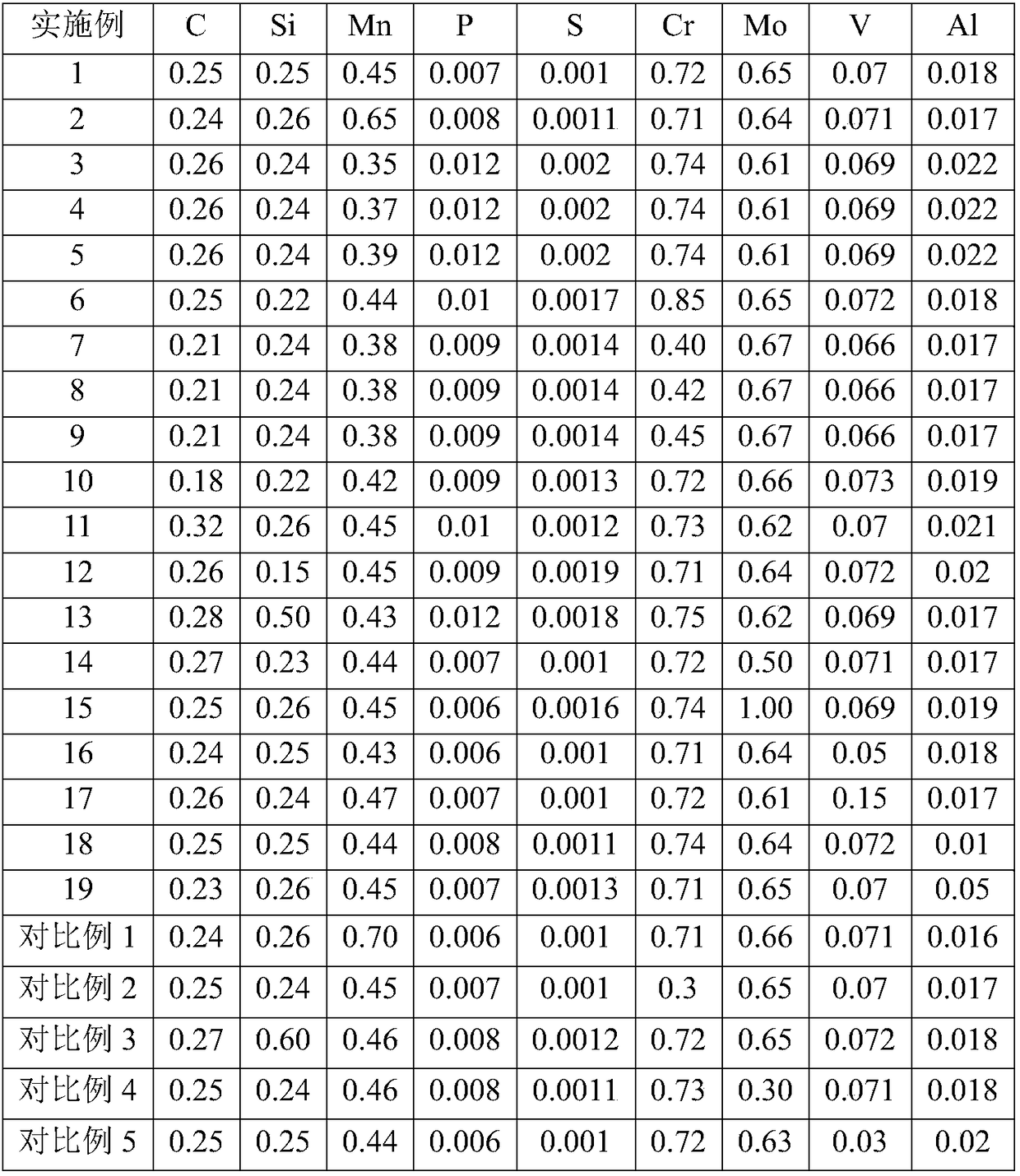
InactiveCN108660377AImprove toughnessHigh strengthProcess efficiency improvementRigid pipesHigh pressureUltimate tensile strength
The invention provides a seamless steel tube and a preparation method of the seamless steel tube. Relative to the total weight of the seamless steel tube, the seamless steel tube is prepared from thefollowing components in percent by weight: 0.18-0.32% of C, 0.15-0.50% of Si, 0.35-0.65% of Mn, 0.40-0.85% of Cr, 0.50-1.00% of Mo, 0.05-0.15% of V, 0.01-0.05% of Al, less than 0.015% of P, less than0.003% of S and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. By strictly controlling the chemical constituent contents of raw materials, the chemical components are reasonably proportioned, so that the strength, toughness and hydrogen sulfide stress corrosion resistance of the obtained seamless steel tube can meet the exploiting demands on high-pressure and high-temperature oil and gas fields in severe corrosive environments.
Owner:HENGYANG VALIN STEEL TUBE
Process for preparing ferrotitanium alloy
The invention discloses a process for preparing a ferrotitanium alloy. The process comprises the following steps: (1) smelting the titanium concentrate into the titanium slag in an electric furnace, adding the alkali carbonate into the electric furnace, and introducing the oxygen and stirring; (2) electrolyzing by taking the graphite as an anode and the molten iron at bottom part of the electric furnace as a cathode, and putting the metallic titanium to melted iron to form a liquid phase ferrotitanium alloy; (3) discharging the molten iron and the liquid phase ferrotitanium alloy under an inert gas, and cooling to obtain the crude ferrotitanium alloy; and (4) deoxidizing and refining: electrolyzing by taking the alkali chloride and the titaniferous villiaumite as the electrolytes, taking the crude ferrotitanium alloy as the cathode and taking the carbon steel as the anode at the temperature of 600-800 DEG C, controlling the cathode current density to 1.0-1.5 A / cm<2. while electrolyzing, taking the cathode product out under normal temperature after finishing electrolyzing, and washing by deionized water to obtain the ferrotitanium alloy. The process for preparing the ferro titanium alloy provided by the invention is low in production cost, short in process flow, complete in de-oxygenation, low in process energy consumption and high in current efficiency and the application of the ferrotitanium alloy in the steelmaking can be improved.
Owner:铜陵百荣木业有限公司
High-tenacity gas shielded welding wire for welding low-temperature steel and using method thereof
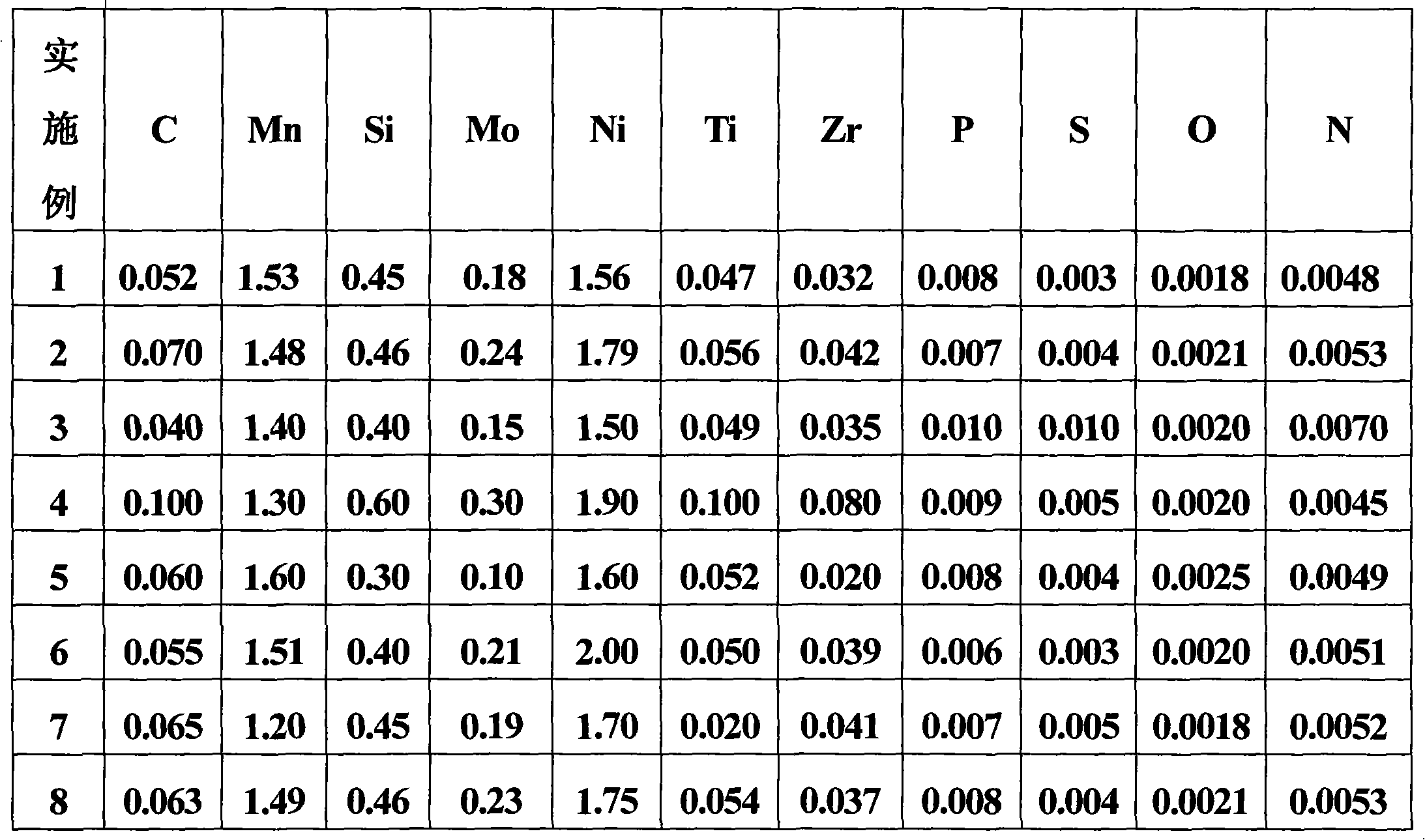
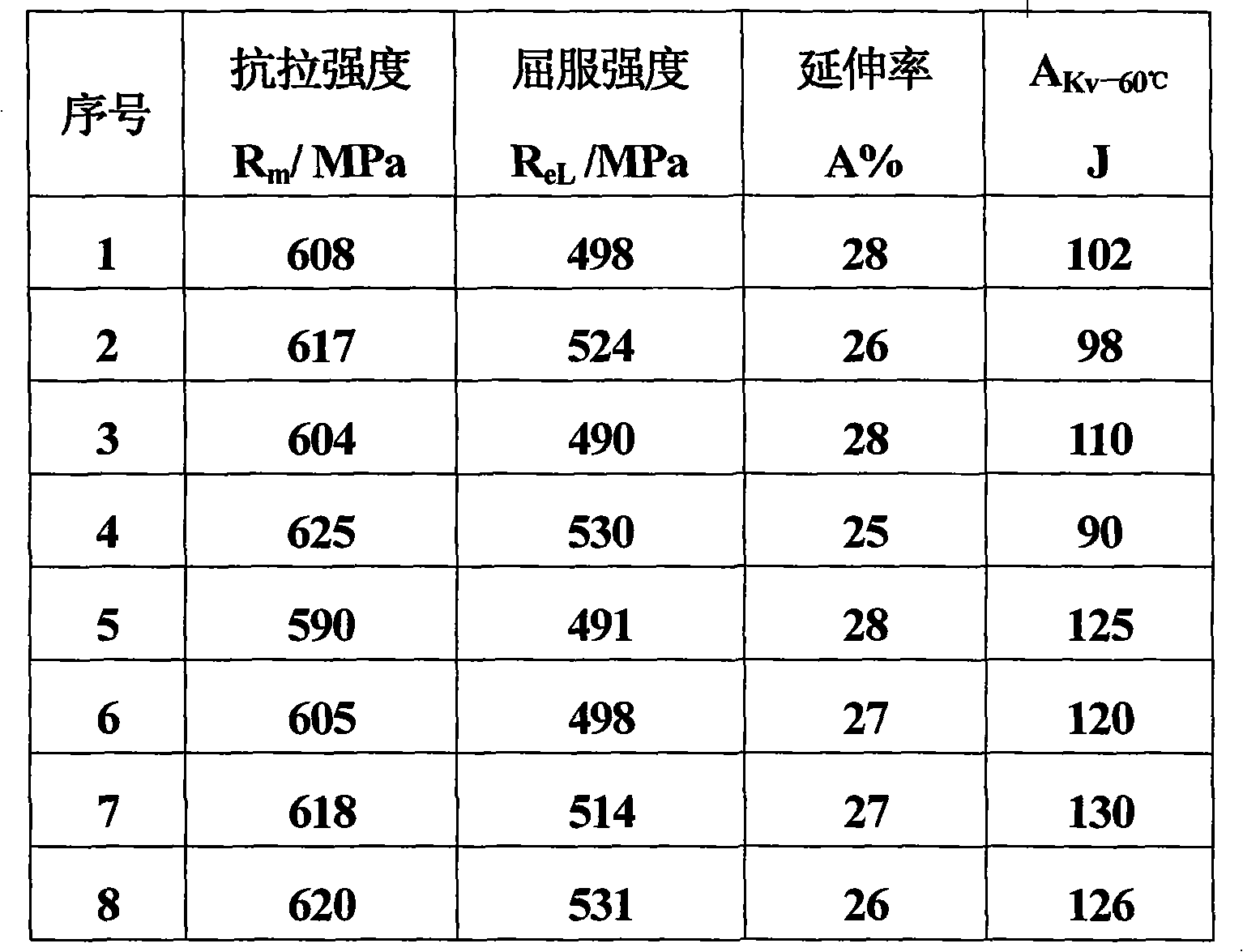
ActiveCN101913035AReduce the ductile-brittle transition temperatureReduce contentArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsImpurityArgon gas
The invention provides a high-tenacity gas shielded welding wire for welding low-temperature steel, which is suitable for welding the low-temperature steel subjected to service in the environment of over minus 60 DEG C. The gas shielded welding wire comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.04 to 0.10 percent of C, 0.20 to 0.60 percent of Si, 1.20 to 1.60 percent of Mn, 1.5 to 2.0 percent of Ni, 0.10 to 0.30 percent of Mo, 0.02 to 0.10 percent of Ti, 0.02 to 0.08 percent of Zr, less than or equal to 0.010 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.010 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.0025 percent of O, less than or equal to 0.0070 percent of N, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The welding wire welds by adopting Ar + 20%CO2 full-argon gas shielding so a weld metal has high low-temperature tenacity in a welding state and under a heat treatment condition after welding.
Owner:山东索力得焊材股份有限公司
700MPa low-alloy high-strength welding wire for heavy machinery and use method thereof
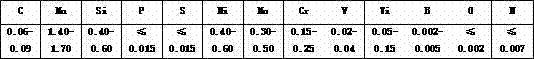
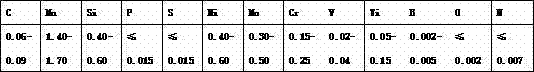
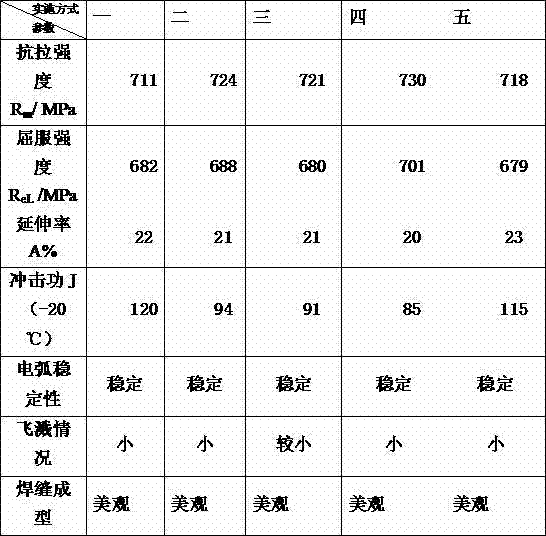
ActiveCN102873465AGuaranteed welding effectAvoid crackingArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsGas metal arc weldingAlloy
The invention provides a low-alloy high-strength welding wire suitable for heavy machinery. The low-alloy high-strength welding wire is characterized in that the strength of a deposited metal is more than 700MPa, the elongation is greater than 16% and the impact energy is more than 47J at minus 20 DEG C.; the welding wire has the advantages of stable electric arc, relatively small spatter and beautiful welding seam forming during use. Chemical components (by mass percent, %) of the welding wire with gas metal arc welding are as follows: 0.06-0.09% of C, 0.40-0.60% of Si, 1.40-1.70% of Mn, 0.4-0.6% of Ni, 0.30-0.50% of Mo, 0.15-0.25% of Cr, 0.02-0.04% of V, 0.05-0.15% of Ti, 0.002-0.005% of B, less than or equal to 0.015% of S, less than or equal to 0.015% of P, less than or equal to 0.0025% of O, less than or equal to 0.0070% of N, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. Ar +20% CO2 argon-rich gas protection is adopted by the welding wire for welding, so that the deposited metal has high low-temperature toughness under the conditions of as-welded and post-welding heat treatment.
Owner:山东索力得焊材股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com