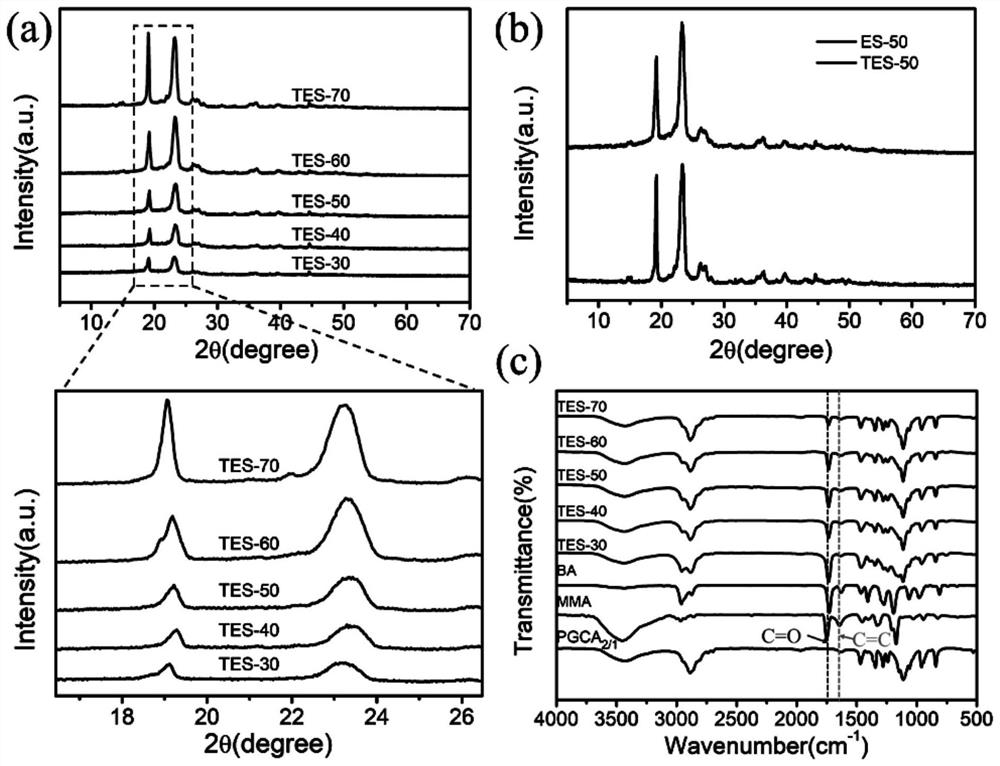
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Thermo elastic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
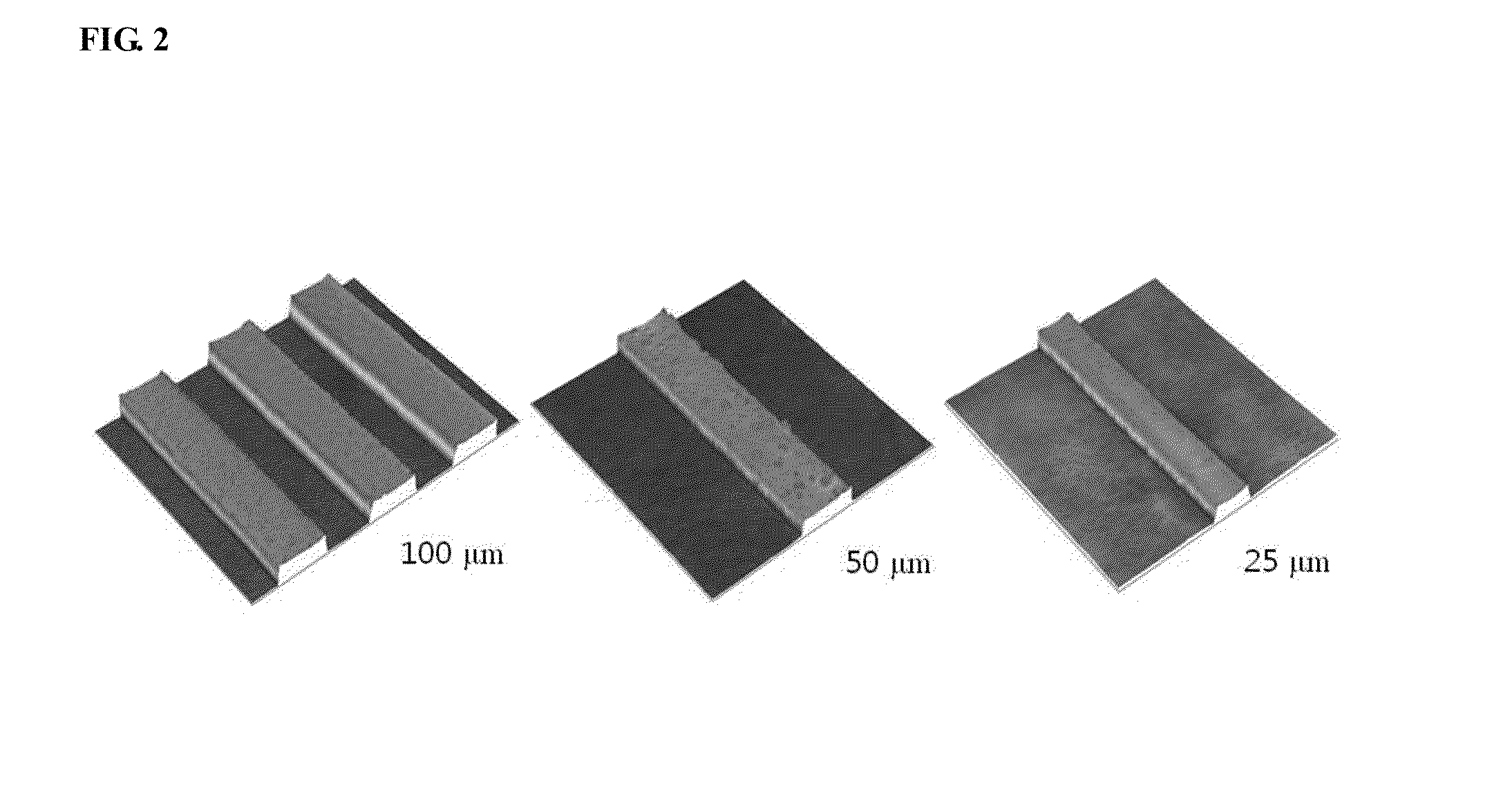
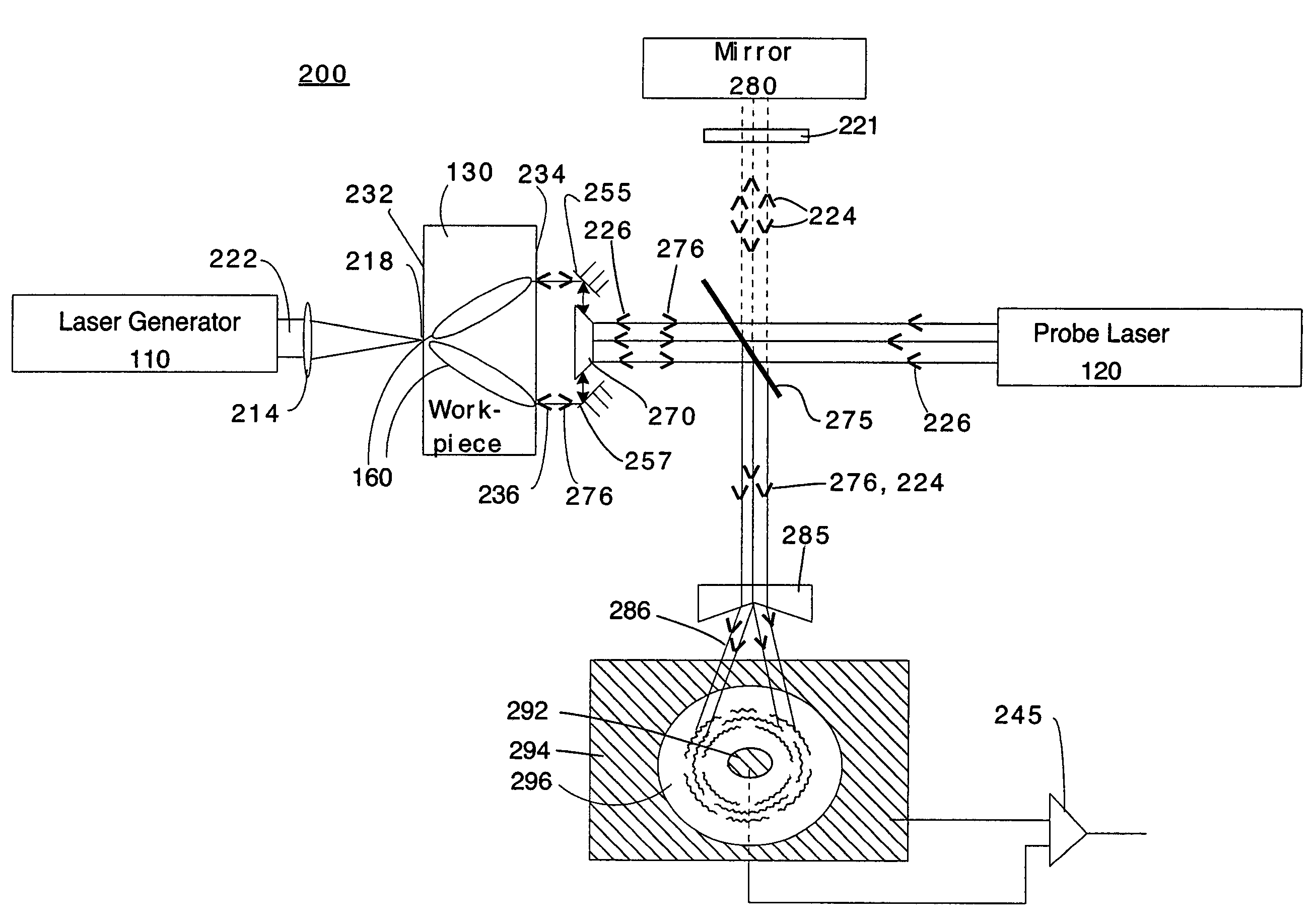
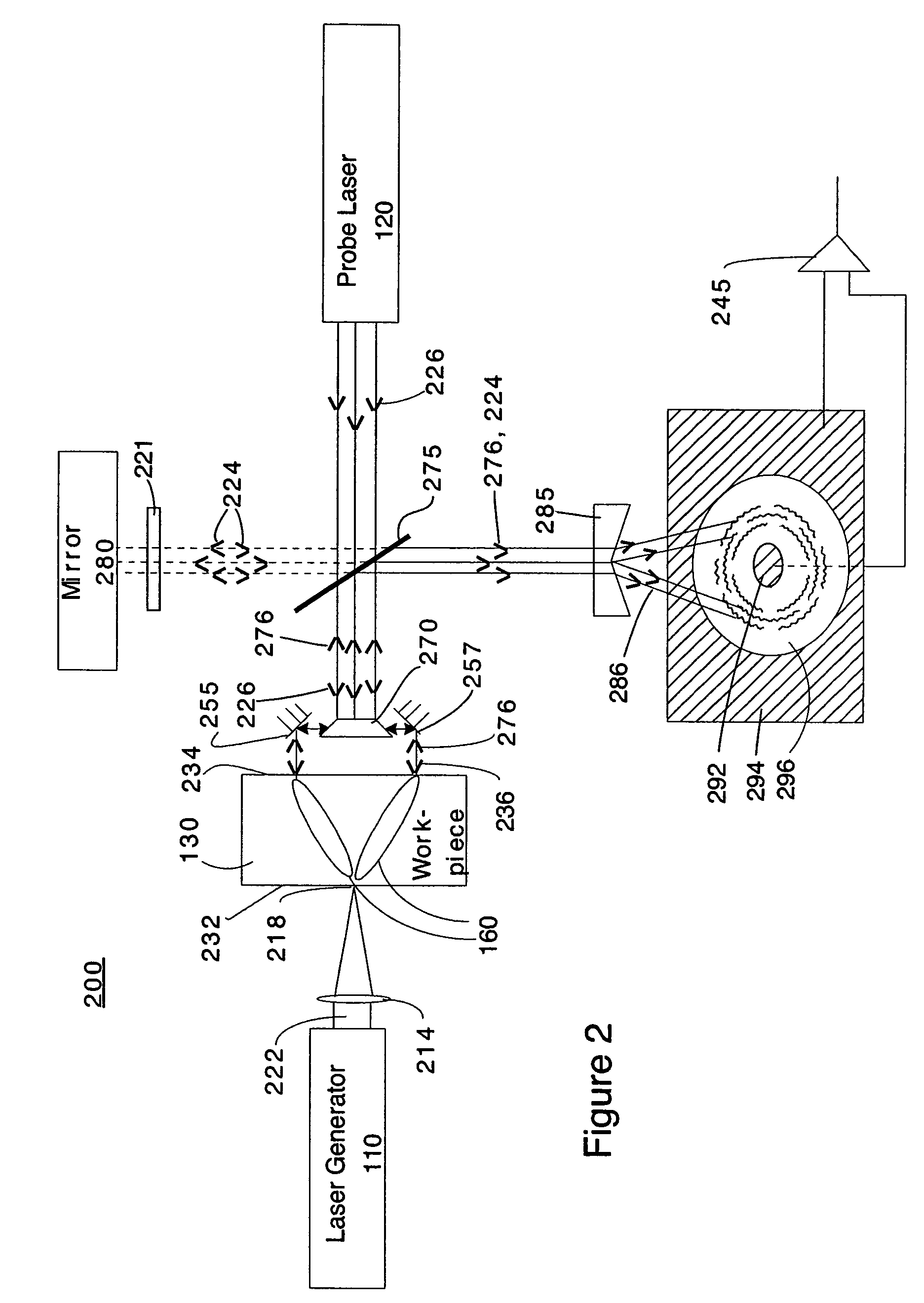
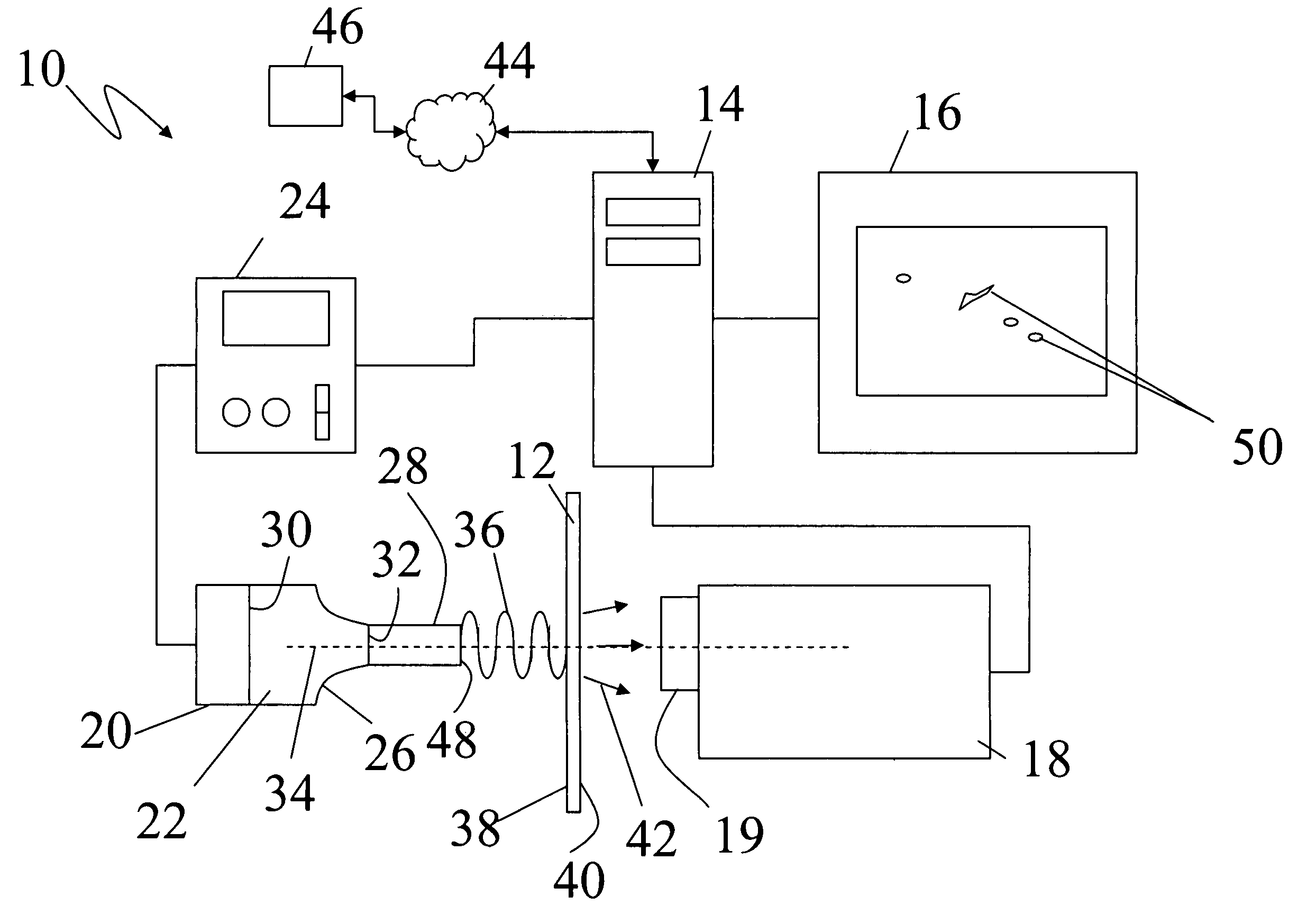
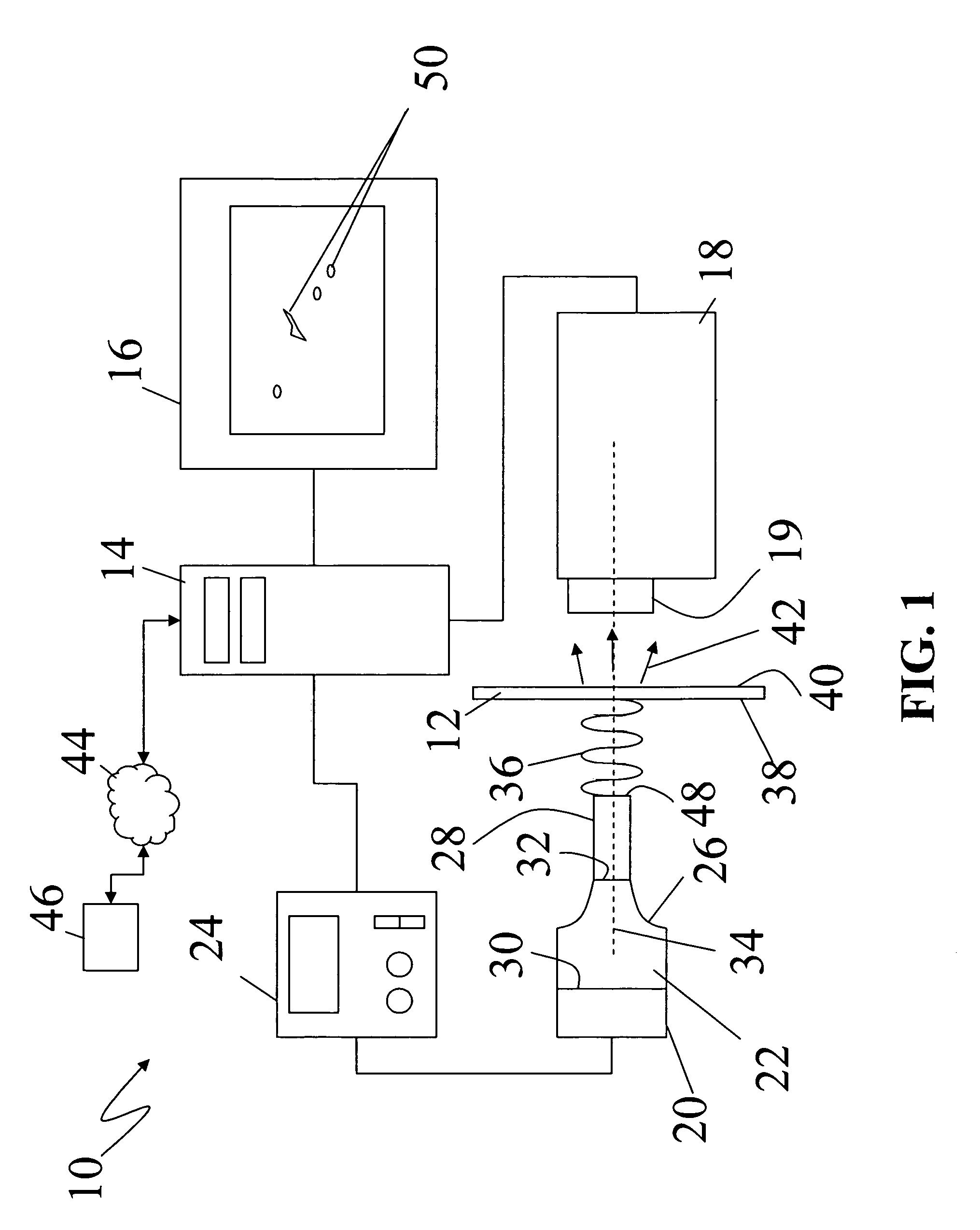
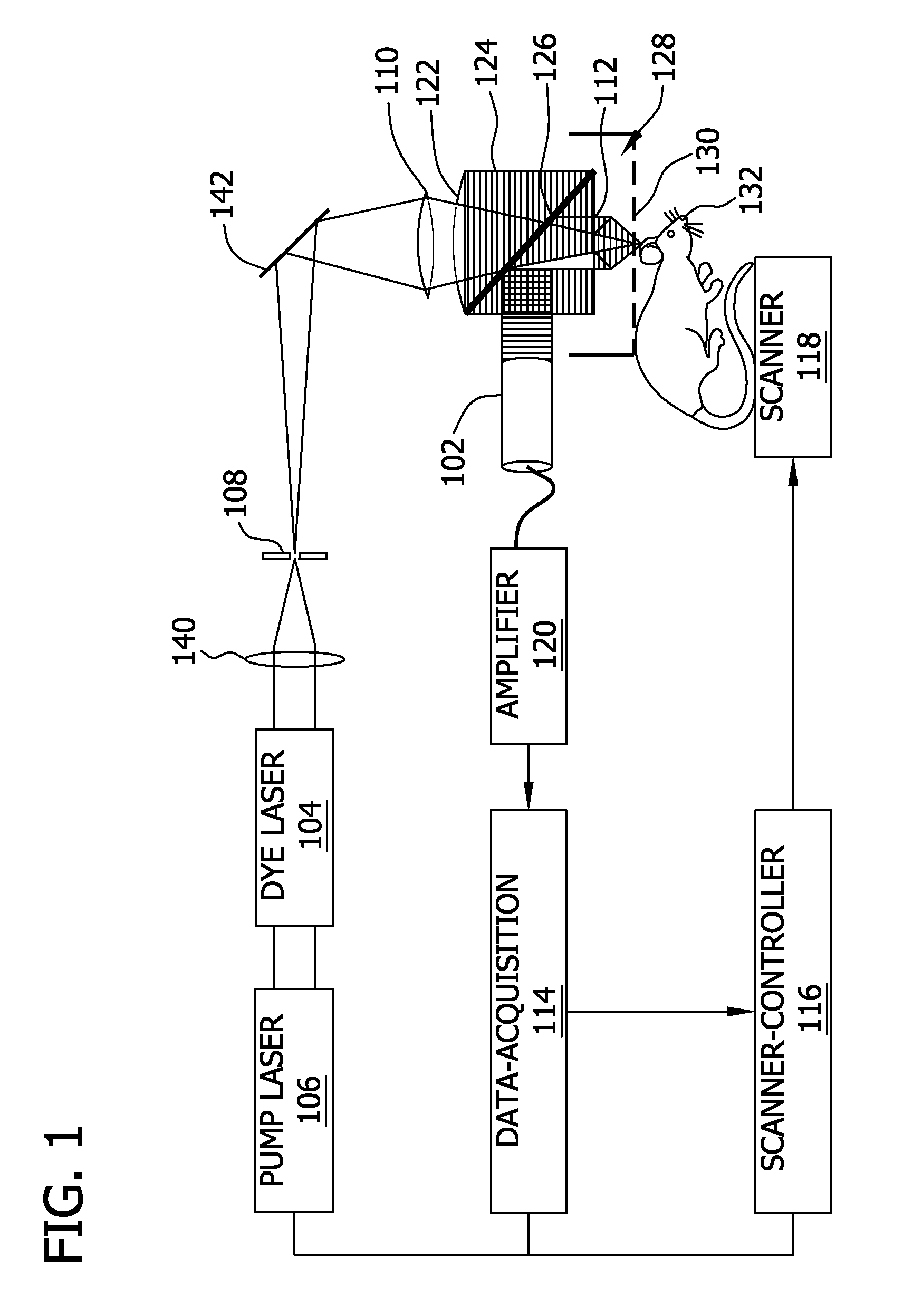
Ultrasound single-element non-contacting inspection system
InactiveUS7262861B1Low costReduce complexityVibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A laser ultrasonic inspection apparatus and method which enables remote sensing of thickness, hardness, temperature and / or internal defect detection is disclosed. A laser generator impinges a workpiece with light for generating a thermo-elastic acoustic reaction in a workpiece. A probe laser impinges the workpiece with an annularly-shaped probe light for interaction with the acoustic signal in the workpiece resulting in a modulated return beam. A photodetector having a sensitive region for detecting an annularly-shaped fringe pattern generated by an interaction of a reference signal and with the modulated return beam at said sensitive region.
Owner:HRL LAB
Quantification of optical absorption coefficients using acoustic spectra in photoacoustic tomography
ActiveUS20130199299A1Vibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsFluorescenceOptical absorption coefficient
Accurately quantifying optical absorption coefficient using acoustic spectra of photoacoustic signals. Optical absorption is closely associated with many physiological parameters, such as the concentration and oxygen saturation of hemoglobin, and it can be used to quantify the concentrations of non-fluorescent molecules. A sample is illuminated by, for example, a pulsed laser and following the absorption of optical energy, a photoacoustic pressure is generated via thermo-elastic expansion. The acoustic waves then propagate and are detected by a transducer. The optical absorption coefficient of the sample is quantified from spectra of the measured photoacoustic signals. Factors, such as system bandwidth and acoustic attenuation, may affect the quantification but are canceled by dividing the acoustic spectra measured at multiple optical wavelengths.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Nested annular MEMS oscillation gyro with period distribution type concentrated mass blocks
ActiveCN104976996AQuality improvementAchieve stiffnessSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesCapacitanceResonance oscillation
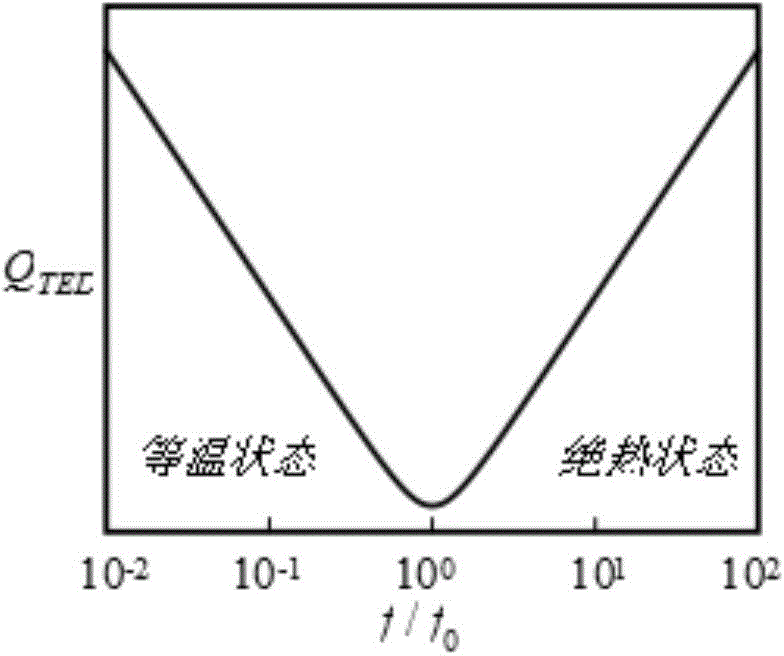
The invention provides a nested annular MEMS oscillation gyro with period distribution type concentrated mass blocks. The gyro comprises a nested annular harmonic oscillator with the period distribution type concentrated mass blocks, and an electrode which is arranged inside / outside the nested annular harmonic oscillator; the nested annular harmonic oscillator comprises a nested annular flexible frame, the mass blocks arranged on the nested annular flexible frame, and anchors for fixing the oscillator; the whole harmonic oscillator is fixedly anchored with a base by the anchor on the center of the harmonic oscillator; the nested annular flexible frame comprises nested rings and spoke-shaped supporting beams; the mass blocks can be additionally arranged on the nested annular flexible frame in a plurality of kinds of manners; and the electrode can be arranged inside / outside the harmonic oscillator, or the electrodes are arranged inside and outside the harmonic oscillator. The gyro has the relatively high thermo-elastic property Q value, relatively large resonance oscillation mass, and relatively large driving amplitude; and as the design of the internal electrode is adopted or the design of the internal and external electrodes is adopted, the gyro also has the advantages that the capacitance detection area is large, the number of detection and control electrodes is large and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Non-contact thermo-elastic property measurement and imaging system for quantitative nondestructive evaluation of materials
ActiveUS20080022775A1Boost energy levelsRadiation pyrometryAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcoustic energyNondestructive testing
A non-contact thermo-elastic property measurement and imaging system and method thereof are described. Acoustic energy is incident on a first surface of a specimen under test. The acoustic energy is converted partially into heat by the specimen, causing a slight increase in the temperature in a region of interaction. The temperature increase is imaged using a high sensitivity infrared camera. Presence of defects (surface and subsurface) in the material modifies the distribution of temperature. An image of temperature distribution can be used for nondestructive testing and evaluation of materials. The temperature change in the specimen caused by acoustic excitation is related to thermal and elastic properties of the material. A measurement of the change in the temperature as a function of the amplitude of incident excitation can be used for direct measurement of thermo-elastic property of the specimen.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON
Non-contact thermo-elastic property measurement and imaging system for quantitative nondestructive evaluation of materials
ActiveUS7716987B2Boost energy levelsRadiation pyrometryAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveAcoustic energy
A non-contact thermo-elastic property measurement and imaging system and method thereof are described. Acoustic energy is incident on a first surface of a specimen under test. The acoustic energy is converted partially into heat by the specimen, causing a slight increase in the temperature in a region of interaction. The temperature increase is imaged using a high sensitivity infrared camera. Presence of defects (surface and subsurface) in the material modifies the distribution of temperature. An image of temperature distribution can be used for nondestructive testing and evaluation of materials. The temperature change in the specimen caused by acoustic excitation is related to thermal and elastic properties of the material. A measurement of the change in the temperature as a function of the amplitude of incident excitation can be used for direct measurement of thermo-elastic property of the specimen.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON
Method for simulation of welding distortion
InactiveCN102152016AImprove calculation accuracyReduce computing timeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElastic analysisComputer science
It is an object of the present invention to accomplish both improvement of a calculation precision and reduction of a calculation time in prediction of a welding distortion of a large welded structure. A method of modeling a welded structure subjected to analysis by generating a mesh and performing thermo-elastic-plastic analysis thereon constructs a global model of the welded structure, and extracts a local model including a welded part from the global model. Next, the method constrains a boundary part of the extracted local model with the remaining portion of the global model, performs thermo-elastic-plastic analysis, and pastes the local model including the analysis result of the thermo-elastic-plastic analysis on the remaining portion of the global model, thereby reconstructing the global model. Thereafter, the method releases the constraint on the boundary part, and performs elastic analysis on the global model, thereby calculating a distortion of the welded structure.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for simulation of welding distortion
InactiveUS20110213594A1Calculation precision can be improvedReduce computing timeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDistortionThermo elastic
It is an object of the present invention to accomplish both improvement of a calculation precision and reduction of a calculation time in prediction of a welding distortion of a large welded structure. A method of modeling a welded structure subjected to analysis by generating a mesh and performing thermo-elastic-plastic analysis thereon constructs a global model of the welded structure, and extracts a local model including a welded part from the global model. Next, the method constrains a boundary part of the extracted local model with the remaining portion of the global model, performs thermo-elastic-plastic analysis, and pastes the local model including the analysis result of the thermo-elastic-plastic analysis on the remaining portion of the global model, thereby reconstructing the global model. Thereafter, the method releases the constraint on the boundary part, and performs elastic analysis on the global model, thereby calculating a distortion of the welded structure.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
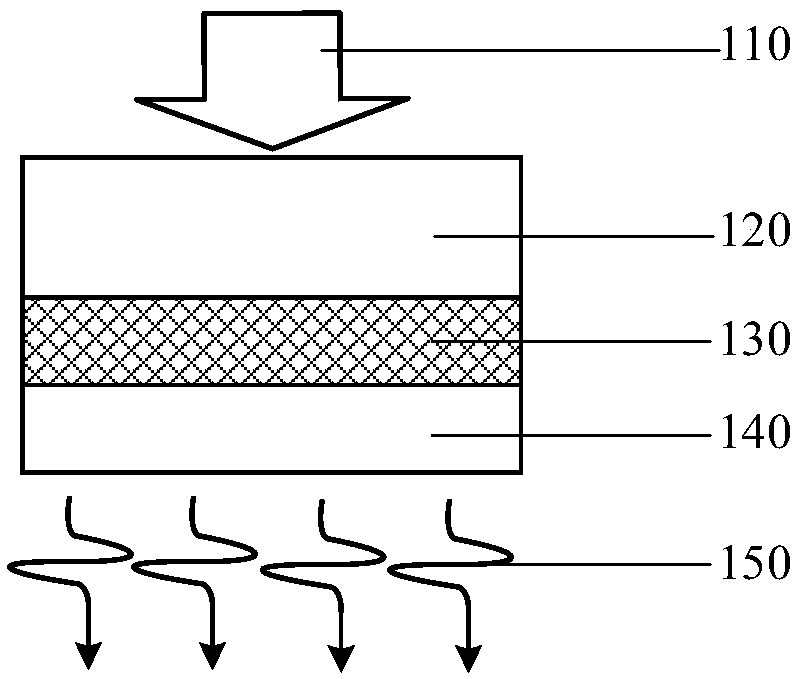
Flexible photoinduced ultrasonic thin film transducer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109433571AHigh photoacoustic conversion efficiencyHigh-resolutionMechanical vibrations separationPolymer substrateCarbon nanotube
The invention discloses a flexible photoinduced ultrasonic thin film transducer and a preparation method thereof. The ultrasonic thin film transducer comprises a flexible transparent substrate (120),a light absorbing layer (130) and a thermos-elastic layer (140) from top to bottom in sequence. The flexible transparent substrate (120) is transparent polydimethylsiloxanepolymers; the light absorbing layer (130) is carbon nanotubes; and the thermo-elastic layer (140) is polydimethylsiloxane polymers. The preparation method of the flexible photoinduced ultrasonic thin film transducer comprises the steps that a glass substrate is spin-coated with a polydimethylsiloxane agent, and the flexible transparent substrate is prepared; an aluminum oxide inorganic screening film deposited with a carbonnanotube filter cake is pressed onto the transparent polymer thin film prepared in the second step, the aluminum oxide inorganic screening film is peeled off, and a carbon nanotube thin film transferred with the light absorbing layer is obtained on a transparent polymer substrate; and a carbon nanotube thin film layer is spin-coated with the polydimethylsiloxane polymers, and the thermos-elastic layer is formed after solidification. After the thermo-elastic layer is solidified, the glass substrate is peeled off.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quantification of optical absorption coefficients using acoustic spectra in photoacoustic tomography
ActiveUS9086365B2Vibration measurement in solidsMedical imagingFluorescenceOptical absorption coefficient
Accurately quantifying optical absorption coefficient using acoustic spectra of photoacoustic signals. Optical absorption is closely associated with many physiological parameters, such as the concentration and oxygen saturation of hemoglobin, and it can be used to quantify the concentrations of non-fluorescent molecules. A sample is illuminated by, for example, a pulsed laser and following the absorption of optical energy, a photoacoustic pressure is generated via thermo-elastic expansion. The acoustic waves then propagate and are detected by a transducer. The optical absorption coefficient of the sample is quantified from spectra of the measured photoacoustic signals. Factors, such as system bandwidth and acoustic attenuation, may affect the quantification but are canceled by dividing the acoustic spectra measured at multiple optical wavelengths.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
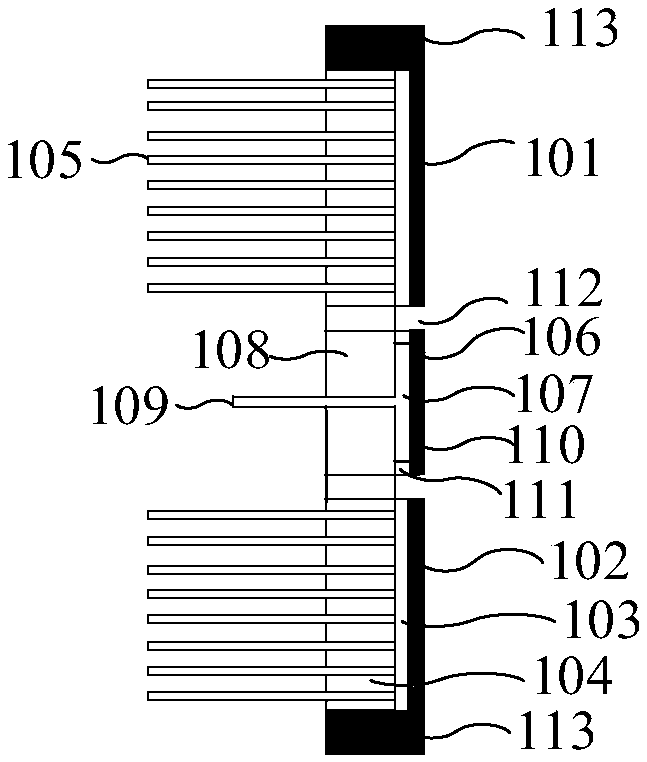
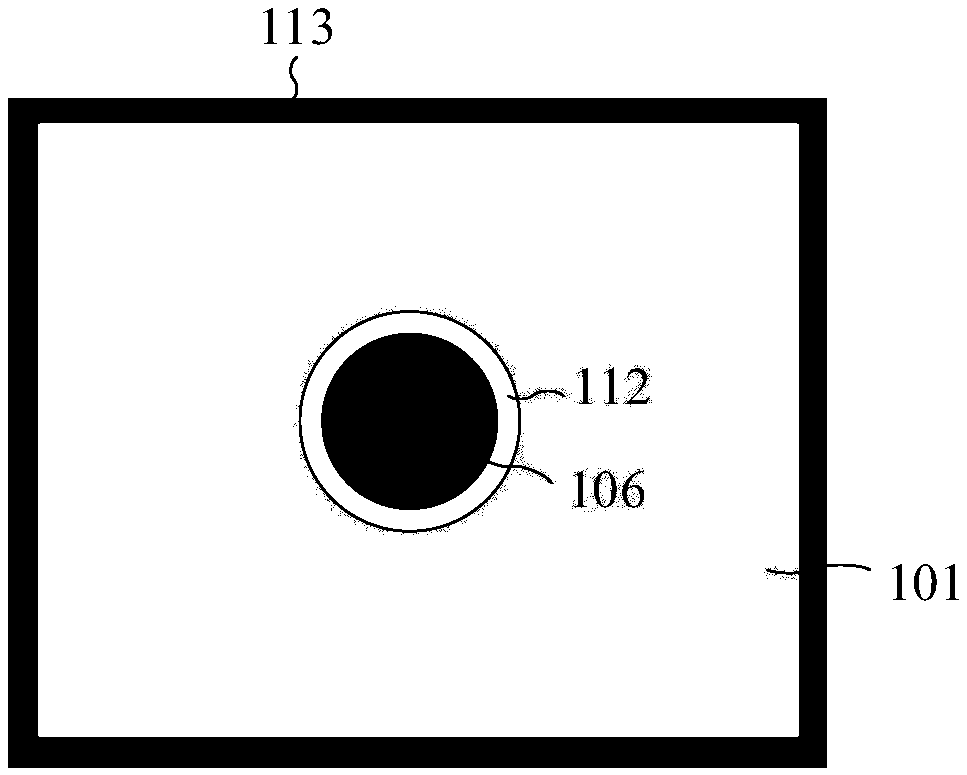
Light driven ultrasonic probe and ultrasonic imaging system thereof
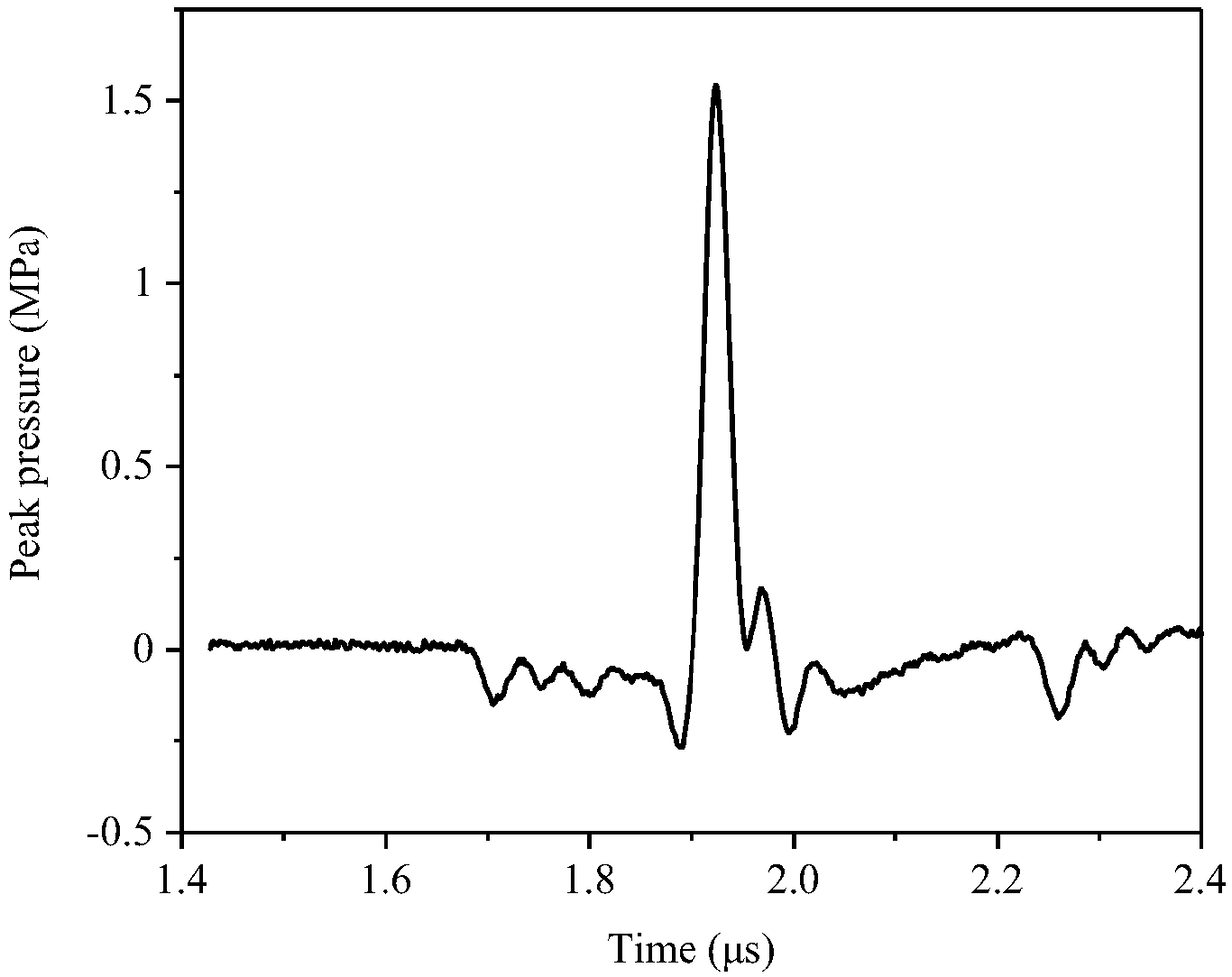
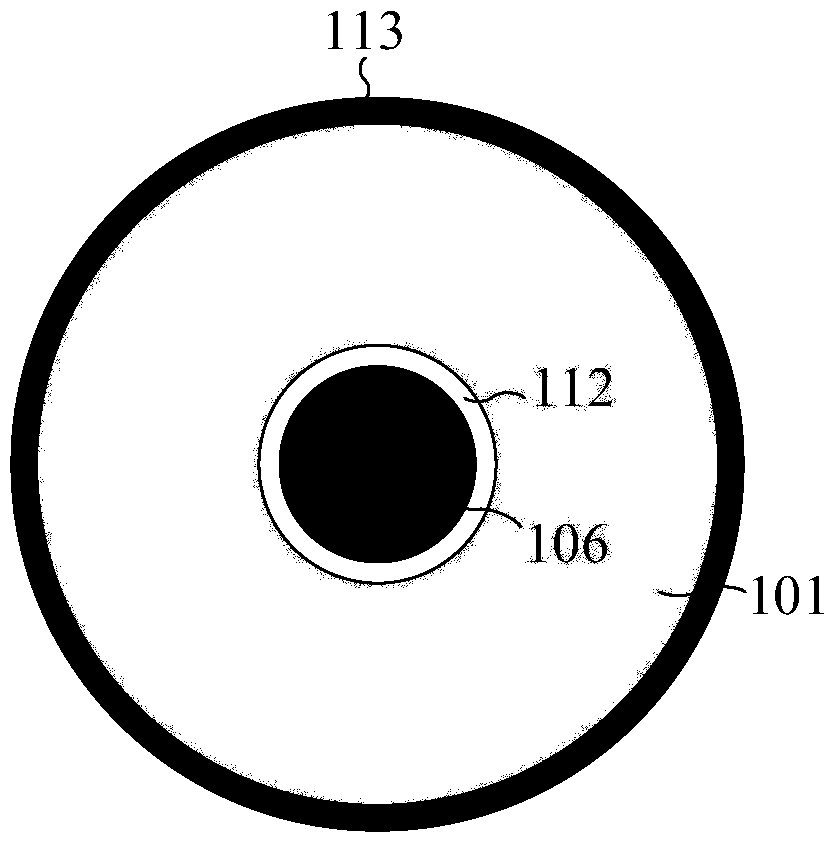
ActiveCN109141493AControl phase delayControl curvatureConverting sensor ouput using wave/particle radiationUltrasonic imagingLight driven
The invention relates to a light driven ultrasonic probe and an ultrasonic imaging system thereof. A Fabry-Perot (F-P) cavity (106) which receives ultrasonic signals is positioned in the center of anphoto-acoustic emitter (101). The photo-acoustic emitter (101) comprises a photo-acoustic conversion film (102) generating ultrasound, a transparent substrate (103), and a support pedestal (104) whichsupporting the photo-acoustic conversion film (102) and the transparent substrate (103). The upper surface of the transparent substrate (103) is coated with the photo-acoustic conversion film (102),and the lower surface of the transparent substrate (103) is welded to the front surface of the support pedestal (104). A light absorption layer and a thermo-elastic layer are deposited successively inthe upper surface of the transparent substrate. The ultrasonic imaging system of the light driven ultrasonic probe is used to convert an array pulse laser beam into pulse ultrasound, and radiate theultrasound on a target. Ultrasonic echoes reflected from the target reaches the F-P cavity of the light driven ultrasonic probe, detection laser enters the head of the F-P cavity, and cavity length change caused by ultrasonic pressure of the F-P cavity is detected.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Non-contact laser ultrasonic nondestructive testing system and method applicable to any curved surface
InactiveCN109799192ALower requirementIncrease flexibilityMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansBeam splitterData treatment
The invention discloses a non-contact laser ultrasonic nondestructive testing system and method applicable to any curved surface. The system comprises a light source, a first reflector, a second reflector, an optical medium, a continuous laser device, a beam splitter, a photoelectric detector, a mechanical arm, a controller, a signal modulating device, a data collecting card and a computer. The method comprises that the light source emits pulse laser onto the surface of an object to be detected, ultrasonic waves produced based on the thermo-elastic mechanism penetrate through the optical medium between the two reflectors to cause change in the intensity of transmitted and reflected laser, the photoelectric detector measures the intensity of the laser and outputs signals, with assistance ofa mechanical scanning unit, scanning over of a region of interest is completed, during scanning, the output signals and scanning position data are synchronously collected, and through data treatment,three-dimensional distribution information of defects can be acquired. The non-contact laser ultrasonic nondestructive testing system and method applicable to any curved surface achieves ultrasonic wave excitation and detection with laser, thereby adapting to complex detecting conditions and achieving rapid, accurate and automatic non-destructive detection of defects of any curved surface part.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
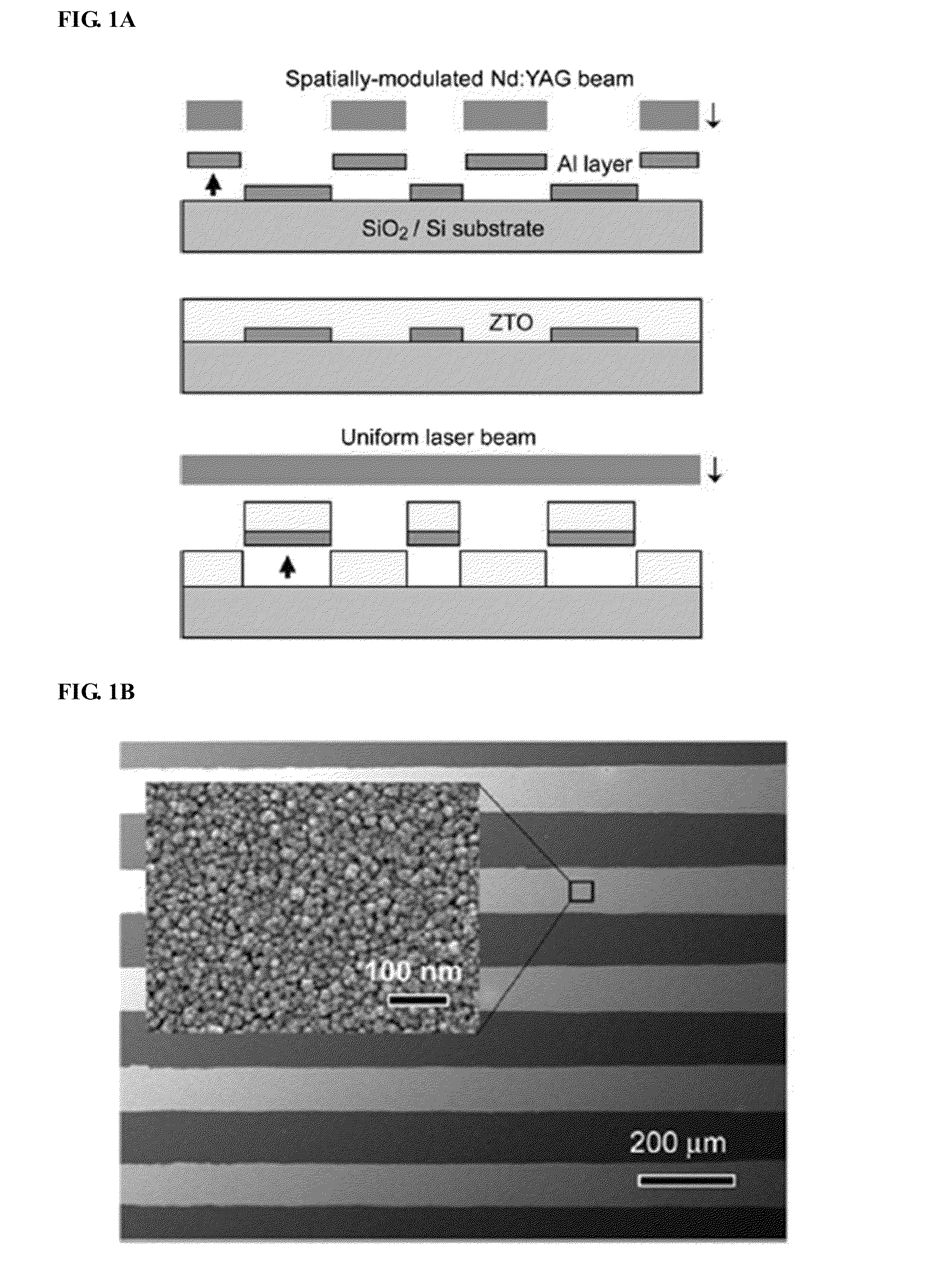
Method of patterning thin film solution-deposited
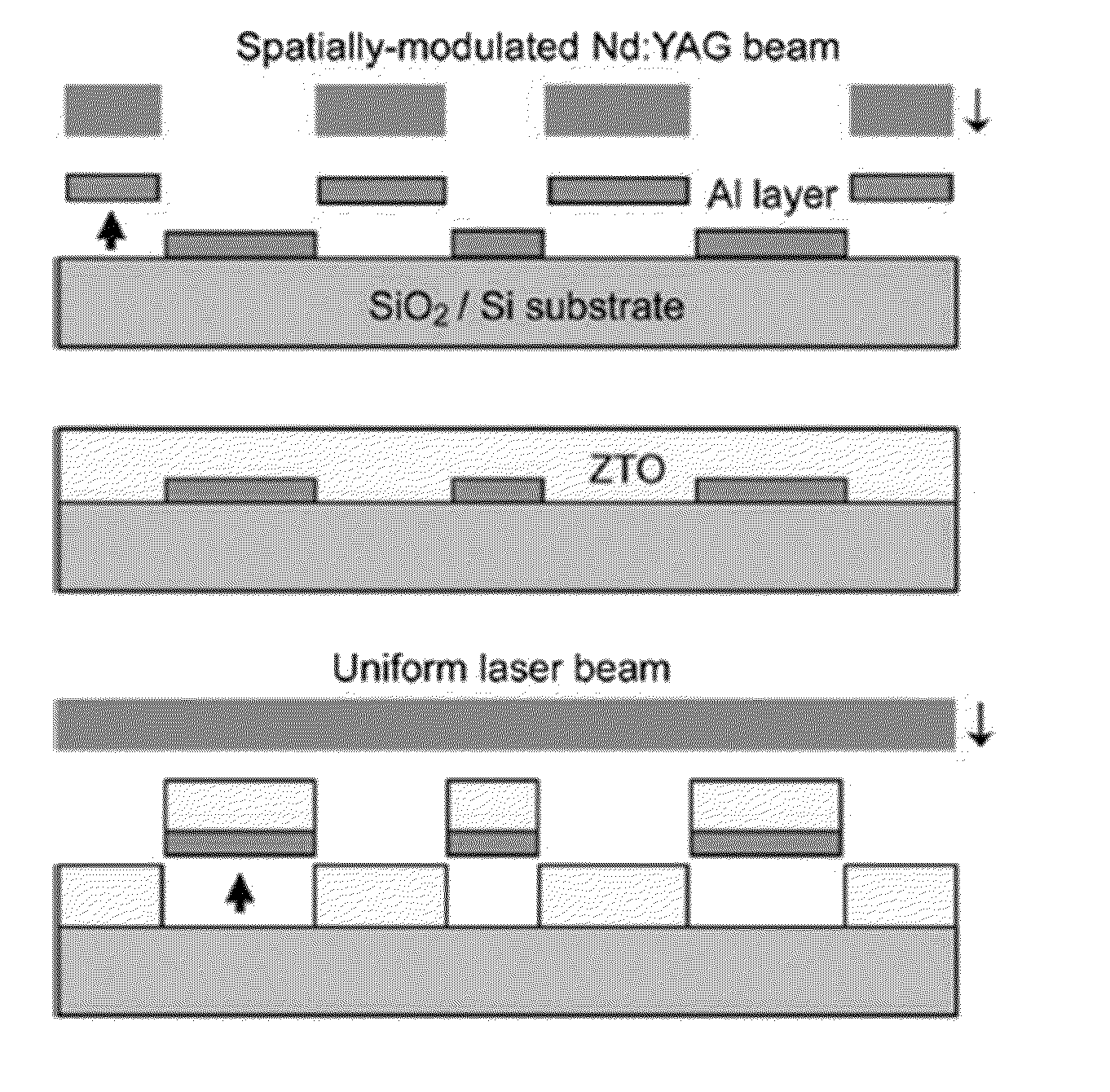
InactiveUS20110278566A1Complex shapeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOptoelectronicsPulsed laser beam
A method of patterning a solution-deposited thin film is provided. The method includes photoetching a pattern in a laser absorption metal layer by allowing a pulsed laser beam to pass through a spatial optical modulator so that the laser beam is radiated on the metal layer, the pattern corresponding to the spatial optical modulator; solution-depositing an oxide layer over a surface of the substrate that is exposed to an outside and a surface of the patterned metal layer; patterning the solution-deposited oxide layer by radiating a pulsed laser beam directly on the solution-deposited oxide layer without passing through the spatial optical modulator, and heating the metal layer underlying the oxide layer to induce thermo-elastic force, so that the metal layer is detached along with the overlying oxide layer from the substrate.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
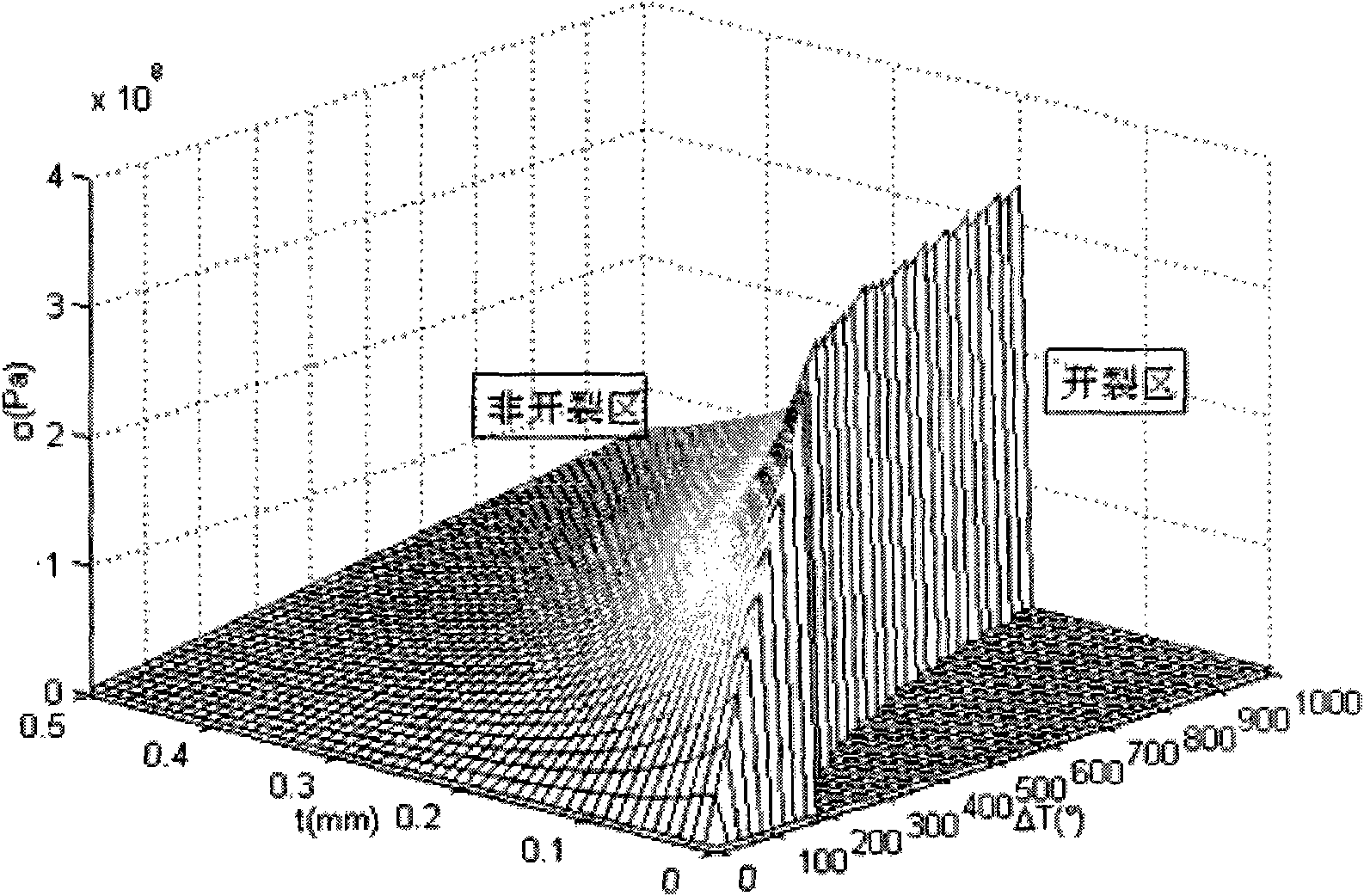
Method for evaluating cracking of brazing diamond abrasive grain alloy layer
InactiveCN101859337AReduce the chance of crackingQuality improvementSpecial data processing applicationsGranularityMathematical model
The invention relates to a method for evaluating cracking of a brazing diamond abrasive grain alloy layer. The method comprises the following three basic steps of: 1) determining an evaluation index of brazing diamond heat damage; 2) establishing a brazing diamond abrasive grain thermo-elastic mathematical model; and 3) processing data by adopting specific software, and analyzing a brazing diamond cracking range. The method can effectively and theoretically evaluate the quality of brazing diamond, and predict the brazing diamond cracking possibility of different diamond granularities, brazingalloys and brazing temperatures to obtain good consistency with a practical evaluation result. The method can improve the brazing diamond quality and improve a brazing diamond process.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Shoe press belt, method for manufacturing the same, and use in shoe press
InactiveUS20130269895A1High operating temperatureImprove efficiencyCalendersPaper/cardboardElastomerYarn
A shoe press belt, and a method for manufacturing and using it. The press belt comprises a base formed of heat-resistant elastomer, inside which base there is a support structure comprising a plurality of support yarns. At least some of the support yarns are heat-resistant polymer yarns, the polymer structure of the material of which comprises a naphthalene group.
Owner:VALMET TECH INC
Method for eliminating thermal buckling of lattice sandwich panel structure and restraining nonlinear flutter
InactiveCN111723438AEliminates thermal bucklingEliminate Structural EffectsGeometric CADSustainable transportationDot matrixThermal buckling
The invention discloses a method for eliminating thermal buckling of a lattice sandwich panel structure and restraining nonlinear flutter. The invention aims to solve the problems that an existing piezoelectric material is often used for controlling flutter and thermal buckling of a structure, the influence caused by temperature change cannot be completely compensated by active rigidity, and the change of the inherent frequency of the structure is also caused. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a strain-displacement relationship and a constitutive relationship of a latticesandwich panel structure; establishing expressions of work done by supersonic aerodynamic force and in-plane thermal load and a mathematical model of the elastic foundation structure, obtaining expressions of kinetic energy, deformation energy and elastic foundation potential energy of the dot matrix sandwich panel, and establishing an aerodynamic thermal elastic motion equation of the dot matrixsandwich panel structure; based on a four-order Runge-Kutta method, solving an aerodynamic thermoelastic motion equation of the lattice sandwich panel structure, and performing analyzing to obtain aninfluence rule of an elastic foundation on aerodynamic thermoelastic characteristics of the lattice sandwich panel structure. The invention belongs to the field of aerospace.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Optimization method of cooling curve in vacuum brazing process of flat cracked antenna
InactiveCN106650289AImprove welding residual deformationGuaranteed electrical performanceInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsThermal expansionEngineering
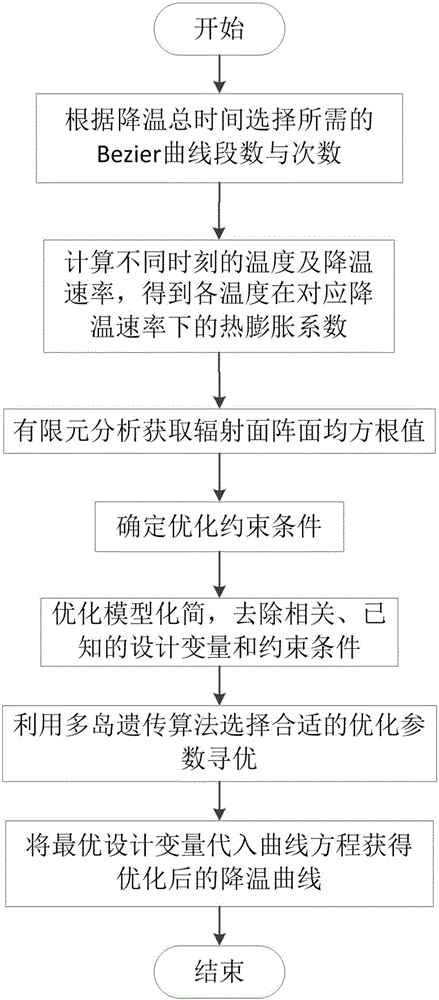
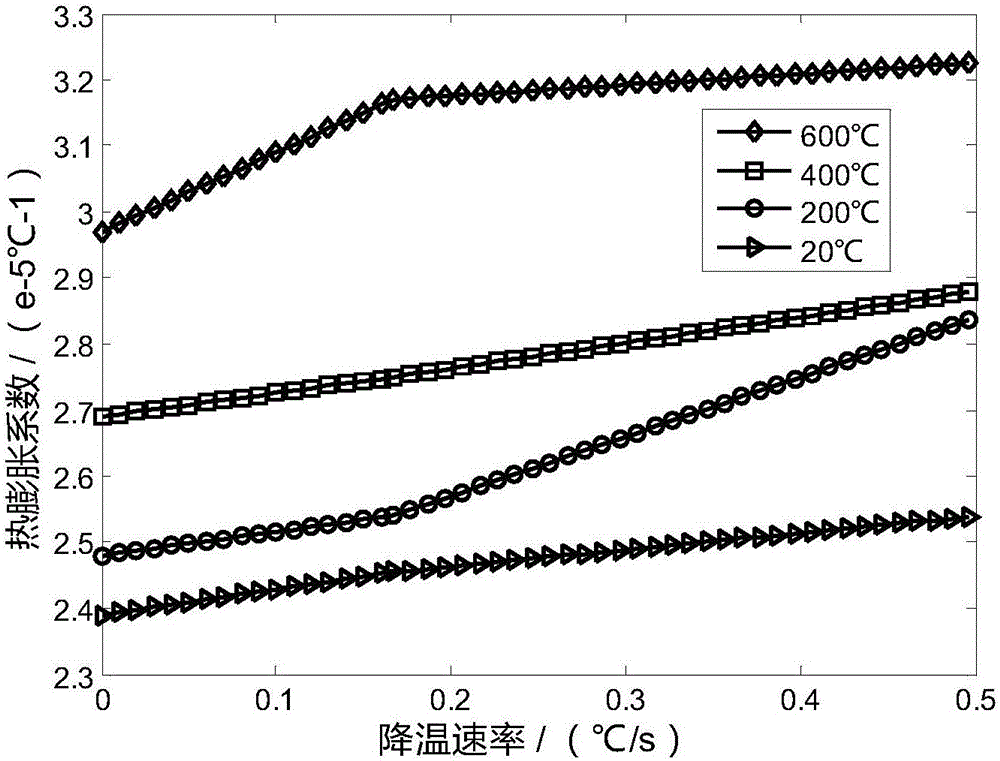
The invention relates to an optimization method of a cooling curve in the vacuum brazing process of a flat cracked antenna. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting appropriate Bezier curve segment number m and the number of times n according to the total cooling time TIME, and determining the number of the points requiring control m*(n+1); (2) calculating the temperature and cooling rate at different times according to the cooling curve, and determining the thermal expansion coefficients of the base metal and the brazing filler metal at different times; (3) calculating the radiation array mean square root value RMS of the antenna under the cooling curve by using the thermo-elastic-plastic finite element method; (4) giving the optimal constraint conditions; (5) on the premise that the position and slope of the Bezier curve are continuous, simplifying the constraint conditions obtained for the steps; (6) calculating an optimization model by a multi-island genetic algorithm, and extracting the optimal objective function value and the corresponding optimal design variable after the optimization stop condition is satisfied; and (7) obtaining a cooling curve form according to the optimal design variable.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Non-flow lines crack high twice processing thermo-elastic resin composition applied in PVC transparent sheet
InactiveCN101381434AAddressing Insufficient Thermal ElasticityPolymer scienceEmulsion polymerization
The invention provides a flow liner free high secondary processing thermoelastic resin composite applied to PVC transparent sheets. The composite is characterized in that a polymerization monomer is subjected to three-stage emulsion polymerization reaction to obtain a graft polymer; in the reaction, a first-stage polymerization monomer is one of methyl methacrylate and ethyl acrylate, a second-stage polymerization monomer is one of the methyl methacrylate and ethyl methacrylate, a third-stage polymerization monomer is one of the methyl methacrylate, butyl methacrylate and butyl acrylate, and the consumption of the polymerization monomer in each of the three-stage reaction is one-third of the total consumption. When the thermoelastic resin composite is added in the PVC transparent sheets, the problems of flow liner appeared during the PVC transparent sheet processing and poor thermoelasticity in the secondary processing are solved.
Owner:SHANDONG RUIFENG CHEM
Photovoltaic cell array with mechanical uncoupling of the cells from the carrier thereof
The present invention proposes a solution for reducing the mechanical coupling of the photovoltaic array of a solar generator relative to the bearing substrate thereof. A photovoltaic cell is very thin (some tens of microns) and very fragile. When the photovoltaic cell is bonded to a substrate, the cell is subjected to all the geometrical deformations caused by vibrations, and in particular to thermo-elastic effects that can lead to the breakage of the cell. The invention comprises securing the cell via a flexible system (8) that enables the uncoupling of the cell (6) from the substrate (7) deformations while maintaining a sufficient radiating coupling of the cell to the substrate in order to avoid the heating thereof in an aerial condition and any loss of efficiency. The solution comprises using photovoltaic cells with a back surface having a high emissivity (using, at the rear, a metallisation or kapton application on the Ge or Ag substrate) that is placed on the substrate using Velcro.
Owner:THALES TOUR CARPE DIEM PLACE DES COROLLES ESPLANADE NORD COURBEVOIE
Low-temperature plasma-induced thermo-acoustic imaging method
PendingCN106821334AHigh resolutionIncrease contrastDiagnostics using spectroscopyInfrasonic diagnosticsMicron scaleSound sources
The invention discloses a low-temperature plasma-induced thermo-acoustic imaging method and particularly relates to a pulse low-temperature plasma-induced thermo-acoustic coupling functional imaging method in the field of biomedical imaging. A nanosecond pulse-excited 'low-temperature plasma jet' acts on a biological tissue, and low-temperature plasma induces pulse energy to the inside of the tissue; and electrical impedance of a normal tissue and a pathological tissue and absorption coefficients on a jet spectrum are different, so that absorption on energy of the plasma jet is also different. The biological tissue absorbs the energy of the plasma jet to generate a heat effect, transient thermal expansion is caused, and a thermo-elastic high-frequency ultrasonic signal is excited. The signal carries the information of the electrical impedance in the tissue and the absorption strength on the jet spectrum; a heat sound source image related to the electrical impedance and the spectrum absorption coefficient can be obtained in micron scale by adopting a sound source reconstruction algorithm; and thus, high-resolution and high-contrast biological tissue medical imaging is provided for early diagnosis of a disease.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Using method for heat preserving and thermal insulating elastic joint mixture
The invention discloses a using method for heat preserving and thermal insulating elastic joint mixture. The using method for the heat preserving and thermal insulating elastic joint mixture comprises weighting the follow raw materials which comprise 10 to 15 parts of polypropylene short fibers, 10 to 30 parts of phenolic resin, 60 to 80 parts of quartz powder, 5 to 8 parts of tackifier, 1 to 3 parts of surface active agent, 15 to 25 parts of polrvinyl benzene, 3 to 7 parts of silane coupling agent and 12 to 18 parts of white cement; stirring the polypropylene short fibers, the phenolic resin, the quartz powder, the surface active agent, the polrvinyl benzene, the silane coupling agent and the white cement in a stirrer for 20 to 30 minutes, adding the tackifier and stirring for 10 to 15 minutes and obtaining the heat preserving and thermal insulating elastic joint mixture; mixing the joint mixture and water, mixing into sticky material to be filled between ceramic tiles and spraying water for one time after the sticky material is dried. According to the using method for the heat preserving and thermal insulating elastic joint mixture, operation is simple and convenient, the joint mixture can be mixed when being used, water spraying can consolidate the joint mixture when the joint mixture is used, and the wall surface generates no cracks caused by ceramic file replacement.
Owner:NANJING HENGAN RESIN CHEM
Novel trans-1,4-polyisoprene synthesis method with high monomer conversion rate
InactiveCN108690156AExcellent flex fatigue resistanceImprove distributionPolymer scienceSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a preparation method of trans-1,4-polyisoprene (TPI). A supported titanium catalyst is used to catalyze polyisoprene polymerization, and a solution-slurry method is adopted tosynthesize powdery or block shaped trans-1,4-polyisoprene (TPI). The catalysis efficiency and monomer conversion rate are high, and the method has reached the industrialization standards. The synthesized TPI has the advantages of high hardness and excellent dynamic properties and can be easily crystallized at a room temperature. TPI has a wide application range. In a zero crosslinking phase, TPIis a thermoplastic material and is used as a medical material; in a low crosslinking phase, TPI is a thermo-elastic material and is used as a shape memory material; and when the crosslinking density exceeds a certain value, TPI becomes a rubber type high elasticity material. At present, TPI has great advantages in fields of green tires and medium-high temperature damping materials, and has a greatapplication value.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Remote sensing satellite star sensor thermo-elastic error estimation method
ActiveCN109696179AHigh measurement accuracyGood application effectMeasurement devicesStar sensorThermo elastic
The invention discloses a remote sensing satellite star sensor thermo-elastic error estimation method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a star sensor measurement model including star sensor thermo-elastic errors; 2) converting the unit direction vector from the center of mass of a satellite to a landmark under a satellite body coordinate system and obtained through load observation to an inertial coordinate system through the star sensor measurement model established in the step 1); and 3)obtaining unit direction vector from the center of mass of the satellite to the landmark in the inertial coordinate system by utilizing the satellite GPS data and geographic data of the landmark and combining coordinate system conversion, and establishing equality relationship with the unit direction vector from the center of mass of the satellite to the landmark under the inertial system comprising the star sensor measurement model, obtaining a star sensor measurement model through multiple measurement of load and estimating star sensor thermo-elastic errors.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Balance spring for timepiece movements and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS11137721B2Help shapeEasy to processFrequency stabilisation mechanismVacuum evaporation coatingTitaniumTitanium alloy
A balance spring for a balance with a blank containing: niobium: the remainder to 100 wt %, titanium: between 40 and 60 wt %, traces of elements selected from the group formed of O, H, C, Fe, Ta, N, Ni, Si, Cu, Al, between 0 and 1600 ppm by weight individually, and less than 0.3 wt % combined, a step of β-quenching the blank with a given diameter, such that the titanium of the alloy is essentially in solid solution form with β-phase niobium, the α-phase titanium content being less than or equal to 5% by volume, at least one deformation step of the alloy alternated with at least one heat treatment step such that the niobium and titanium alloy obtained has an elastic limit higher than or equal to 600 MPa and a modulus of elasticity lower than or equal to 100 GPa, a winding step to form the balance spring being performed prior to the final heat treatment step, prior to the deformation step, a step of depositing, on the alloy blank, a surface layer of a ductile material such as copper, the surface layer of ductile material being retained on the balance spring, the thermoelastic coefficient of the niobium and titanium alloy being adapted accordingly.
Owner:NIVAROX FAR
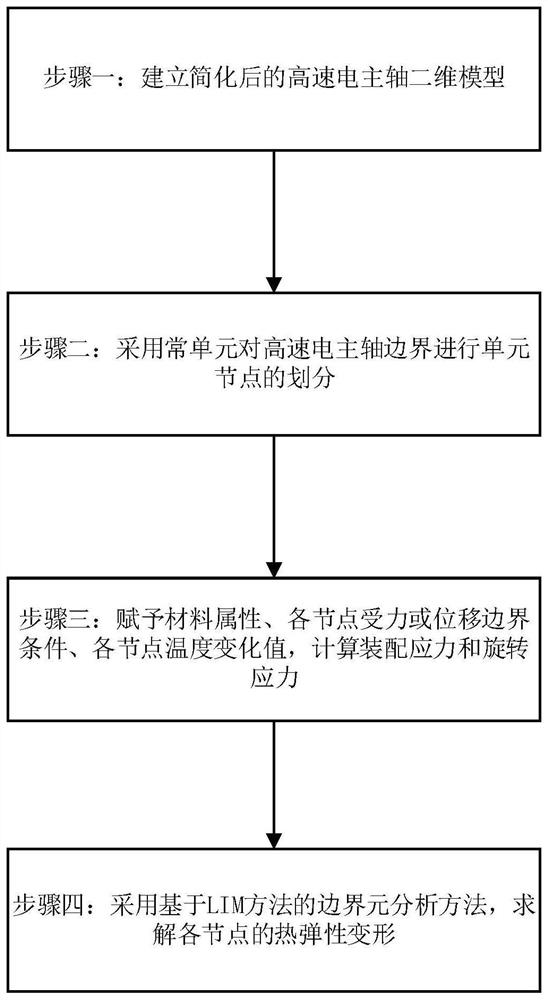
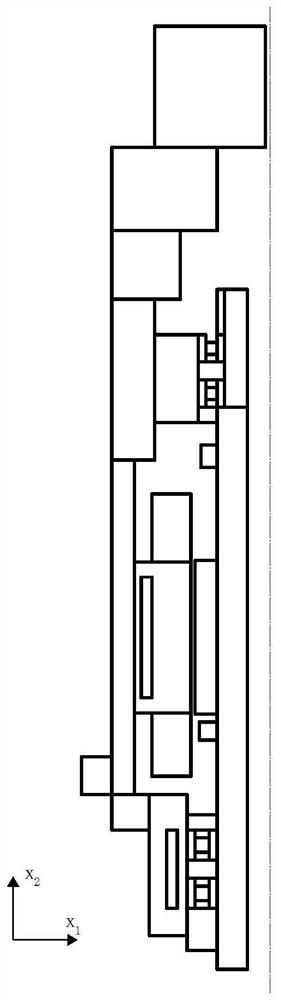
High-speed motorized spindle thermoelastic deformation simulation method and system based on boundary element model
PendingCN114818197ARich design toolsEasy to operateGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a high-speed motorized spindle thermoelastic deformation simulation method and system based on a boundary element model, and the method comprises the steps: intercepting a 1 / 4 plane of a motorized spindle as a two-dimensional plane model of the high-speed motorized spindle, removing parts and features which can neglect the influence on thermoelastic deformation calculation according to the features of a shaft system, simplifying the model, and calculating the thermoelastic deformation of the motorized spindle. In the simplified two-dimensional plane model, carrying out node division on the boundary of the motorized spindle by adopting a constant unit, constructing a unit model of a motorized spindle boundary element, endowing each part of the motorized spindle with material attributes and boundary conditions, and according to the unit model of the motorized spindle boundary element and the boundary conditions, adopting a boundary element method based on an LIM method, the boundary element method is applied to the modeling and solving process of the thermoelastic deformation of the high-speed motorized spindle, the model universality is improved while the solving precision is guaranteed, and the method is suitable for solving the thermoelastic deformation of various high-speed motorized spindles.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Intelligent Anti-icing material and preparation method and use thereof
PendingUS20220213367A1Easy to useGood anti-icing effectOther chemical processesCrazingTitanium alloy
An intelligent anti-icing material and a preparation method and use thereof are disclosed. The intelligent anti-icing material includes a hydrophobic resin and a nickel-titanium alloy wire embedded in the hydrophobic resin. When the surrounding temperature decreases, the hydrophobic resin in the intelligent anti-icing material shrinks, and the nickel-titanium alloy wire featured by thermoelastic martensitic transformation undergoes phase transformation and expands, which changes the direction of the expansion force inside the ice layer, and thus tiny cracks occur at the interface between the ice layer and the surface of the material, thereby reducing the adhesion of the ice layer to the surface of the material, accelerating the spontaneous shedding of the ice layer, without heating, and achieving an excellent anti-icing effect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Finite element solution optimization method for structural thermal response induced by re-entry aerodynamic environment
ActiveCN112364544BHigh simulationGeometric CADSustainable transportationPartial differential equationEngineering
The invention discloses a finite element solution optimization method for structural thermal response caused by re-entry aerodynamic environment, which includes: discretizing the coupled control equation based on heat conduction and material thermoelastic dynamics through the finite element method and providing a corresponding algorithm flow; wherein, In the algorithm process, for time-dependent partial differential equations, the finite element method discretizes the spatial region first, and obtains the grid division of the solution region, and then differentially discretizes the time item. According to the iterative coupling relaxation calculation principle, step by step Advance to capture the vibration of structural materials in space and the nonlinear behavior of thermal response deformation of large spacecraft after de-orbiting and re-entry into a strong aerodynamic thermal environment. The present invention provides an optimization method based on the finite element method for solving thermal-mechanical coupling response, which is beneficial for analyzing and researching the thermal-mechanical coupling response of material structures under strong aerodynamic / thermal environments, and is conducive to carrying out the performance prediction of aircraft and spacecraft structures with simulation.
Owner:中国空气动力研究与发展中心超高速空气动力研究所 +2
Preparation method of a thermally conductive elastic shape-setting phase change energy storage material
ActiveCN111647116BHigh enthalpy changeHigh thermal decomposition temperatureHeat-exchange elementsPolymer sciencePolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a preparation method of a thermally conductive elastic shape-setting phase-change energy storage material, comprising: preparing graphene oxide / carbon nanotube hybrid airgel; heating polyethylene glycol to 60-70°C to obtain molten polyethylene glycol Diol: Mix methyl methacrylate and butyl acrylate, stir for 25-45 minutes, heat to 60-70°C, add the initiator, continue stirring for 25-45 minutes, then add molten polyethylene glycol, continue Stir for 60 minutes to obtain a mixed solution; add the graphene oxide / carbon nanotube hybrid airgel to the mixed solution, place in a vacuum oven, heat to 65°C, and evacuate to 0.02Mpa, so that the mixed solution enters the airgel and reacts After 24 hours, the thermally conductive elastic shape-setting phase change energy storage material was obtained. The thermally conductive elastic shape-setting phase change energy storage material prepared by the present invention has a high enthalpy change value, and the error between the actual latent heat value and the theoretical value is as low as -0.8%. The introduction of graphene oxide / carbon nanotube hybrid airgel can further improve the material The thermal decomposition temperature of the material is better.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Elastic heat-conducting structure, manufacturing method thereof and electronic device
ActiveCN111918519ATo meet the needs of thinningImprove thermal conductivityCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsThermodynamicsEngineering
An elastic heat conduction structure is matched with an electronic device for application, and the elastic heat conduction structure is arranged between a heat source of the electronic device and a bearing piece, and comprises a substrate, a patterned heat conduction supporting piece and a heat conduction elastic piece. The substrate is provided with a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first surface, the patterned heat conduction supporting piece is arranged on the first surface, the heat conduction elastic piece is arranged on the substrate and covers the patterned heat-conduction supporting piece, and the heat conduction elastic piece is provided with a third surface far away from the patterned heat conduction supporting piece, wherein when the distance between the heatsource and the bearing piece is a constant value, the compression amount X of the heat conduction elastic piece and the temperature difference Y between the third surface of the heat conduction elastic piece and the second surface of the substrate meet the formula that Y =-0.0004X2 + 0.0973X+ 19.039. The invention further discloses a manufacturing method of the elastic heat conduction structure and the electronic device.
Owner:CTRON ADVANCED MATERIAL CO LTD
Nested-ring mems vibrating gyroscope with periodically distributed lumped masses
ActiveCN104976996BQuality improvementAchieve stiffnessSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesResonance oscillationCapacitance
The invention provides a nested annular MEMS oscillation gyro with period distribution type concentrated mass blocks. The gyro comprises a nested annular harmonic oscillator with the period distribution type concentrated mass blocks, and an electrode which is arranged inside / outside the nested annular harmonic oscillator; the nested annular harmonic oscillator comprises a nested annular flexible frame, the mass blocks arranged on the nested annular flexible frame, and anchors for fixing the oscillator; the whole harmonic oscillator is fixedly anchored with a base by the anchor on the center of the harmonic oscillator; the nested annular flexible frame comprises nested rings and spoke-shaped supporting beams; the mass blocks can be additionally arranged on the nested annular flexible frame in a plurality of kinds of manners; and the electrode can be arranged inside / outside the harmonic oscillator, or the electrodes are arranged inside and outside the harmonic oscillator. The gyro has the relatively high thermo-elastic property Q value, relatively large resonance oscillation mass, and relatively large driving amplitude; and as the design of the internal electrode is adopted or the design of the internal and external electrodes is adopted, the gyro also has the advantages that the capacitance detection area is large, the number of detection and control electrodes is large and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Deformation prediction method and system for laser thermoforming of hull skins
ActiveCN112906136BQuick solution to deformation resultsRealize fully automatic laser heating forming processingGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationNerve networkElastic plastic
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com