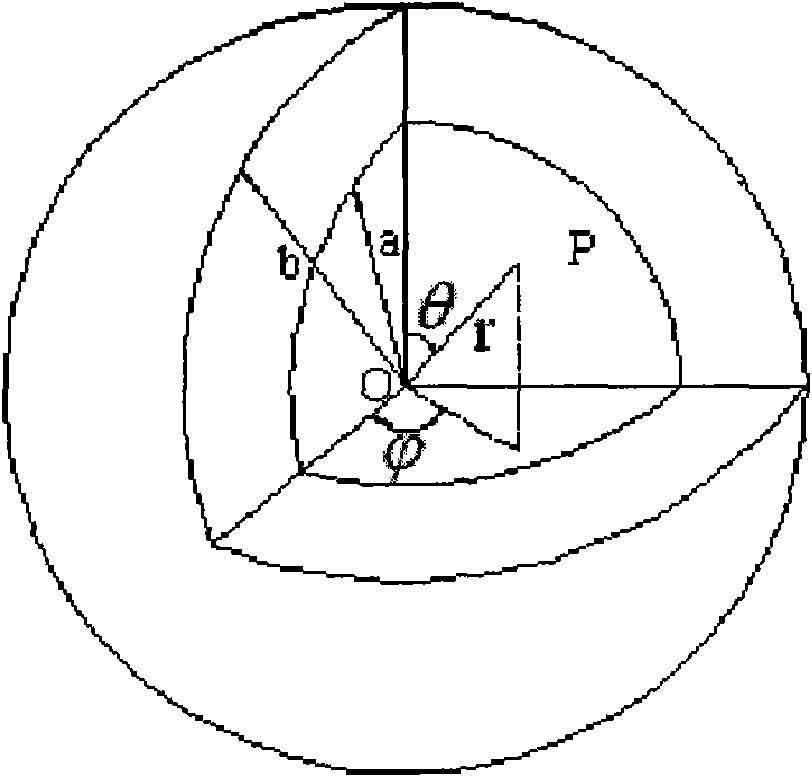Method for evaluating cracking of brazing diamond abrasive grain alloy layer
A technology of brazing alloy and evaluation method is applied in the field of evaluation of cracking of brazed diamond abrasive grain alloy layer, which can solve the problems of micro-crack diamond, reducing the service life of brazed diamond tools, and transgranular cracking.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] Introduce the content of the present invention in detail below by example.
[0027] 1. Use Ni-Cr alloy as the solder to make brazed diamond abrasive grains, ignoring the transition layer.
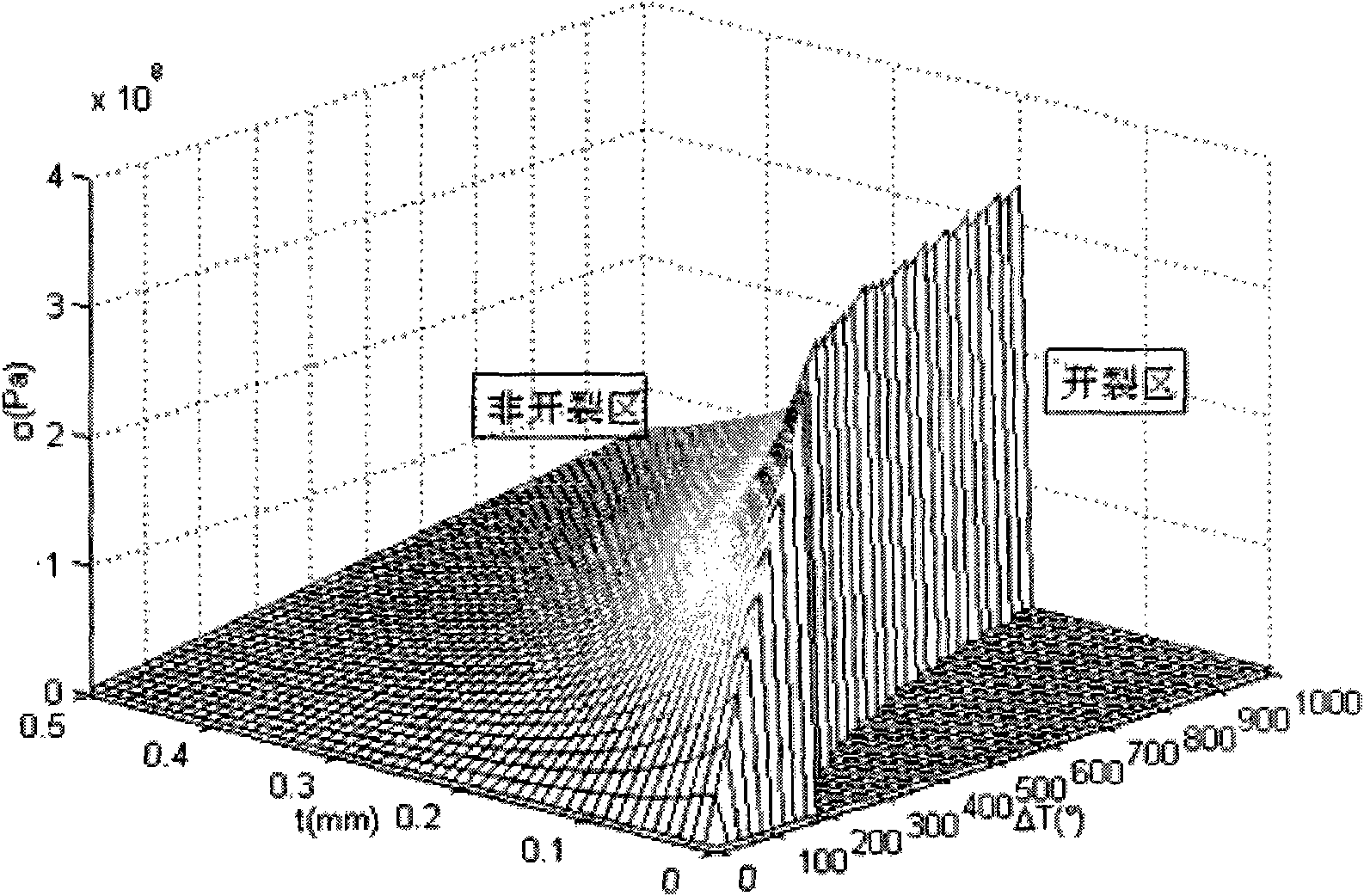
[0028] 2. Among them, the tensile strength of the brazing alloy layer Ni-Cr alloy σ (Ni-Cr)max =280-330Mpa.
[0029] 3. Establish the thermoelastic model of brazing diamond, based on the fact that the radius of diamond particles is very small (generally less than 0.4mm), although the shape of the particles is relatively complex, it is approximately considered as a sphere, and the temperature field of the brazing diamond particles is uniform during the heating process of the brazing furnace , and according to a certain cooling rate cooling, cooling temperature difference is ΔT, diamond and nickel-chromium alloys are in line with the continuous, uniform and isotropic elastic mechanics of materials. A simplified schematic diagram of brazed diamond abrasive grains is attached figure 1...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com