Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
125 results about "Spherical pore" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Porous nanosheath networks, method of making and uses thereof
A method for making a porous material, includes melt-blending two or more non-miscible polymers to obtain a co-continuous melt, solidifying the melt to obtain a solid mass consisting of two co-continuous polymer phases, and selectively extracting one of the co-continuous phases thereby creating within the solid mass an essentially continuous pore network having an internal surface. The method further includes replicating the internal surface of the pore network within the solid mass by coating the internal surface with successive layers of materials, and selectively extracting the solid mass without extracting the layers of materials, to thereby yield the product porous material, formed of the layers of materials. The material has a void fraction higher than about 75%, and mainly having essentially fully interconnected sheath-like non-spherical pores and essentially non-fibrous walls.
Owner:POLYVALOR LP
Proton-conductive composite electrolyte membrane and producing method thereof
InactiveUS20060083962A1High ion conductivityImprove heat resistanceSolid electrolytesSemi-permeable membranesComposite electrolyteHeat resistance
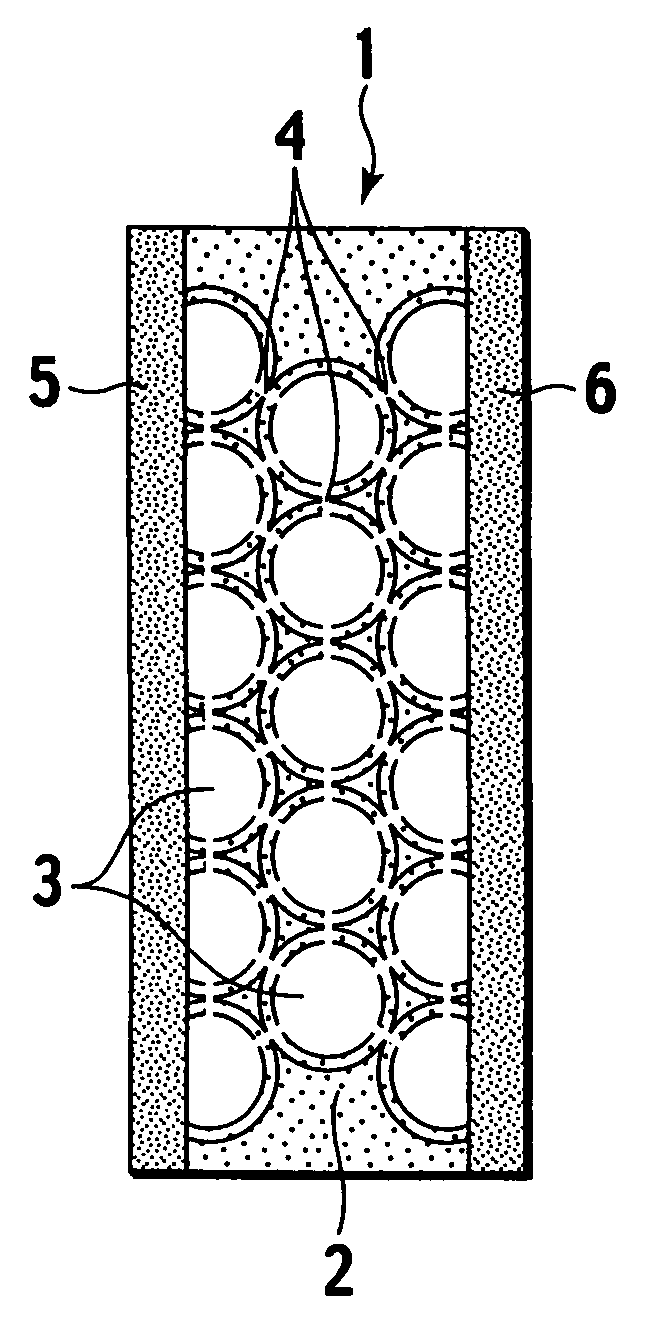
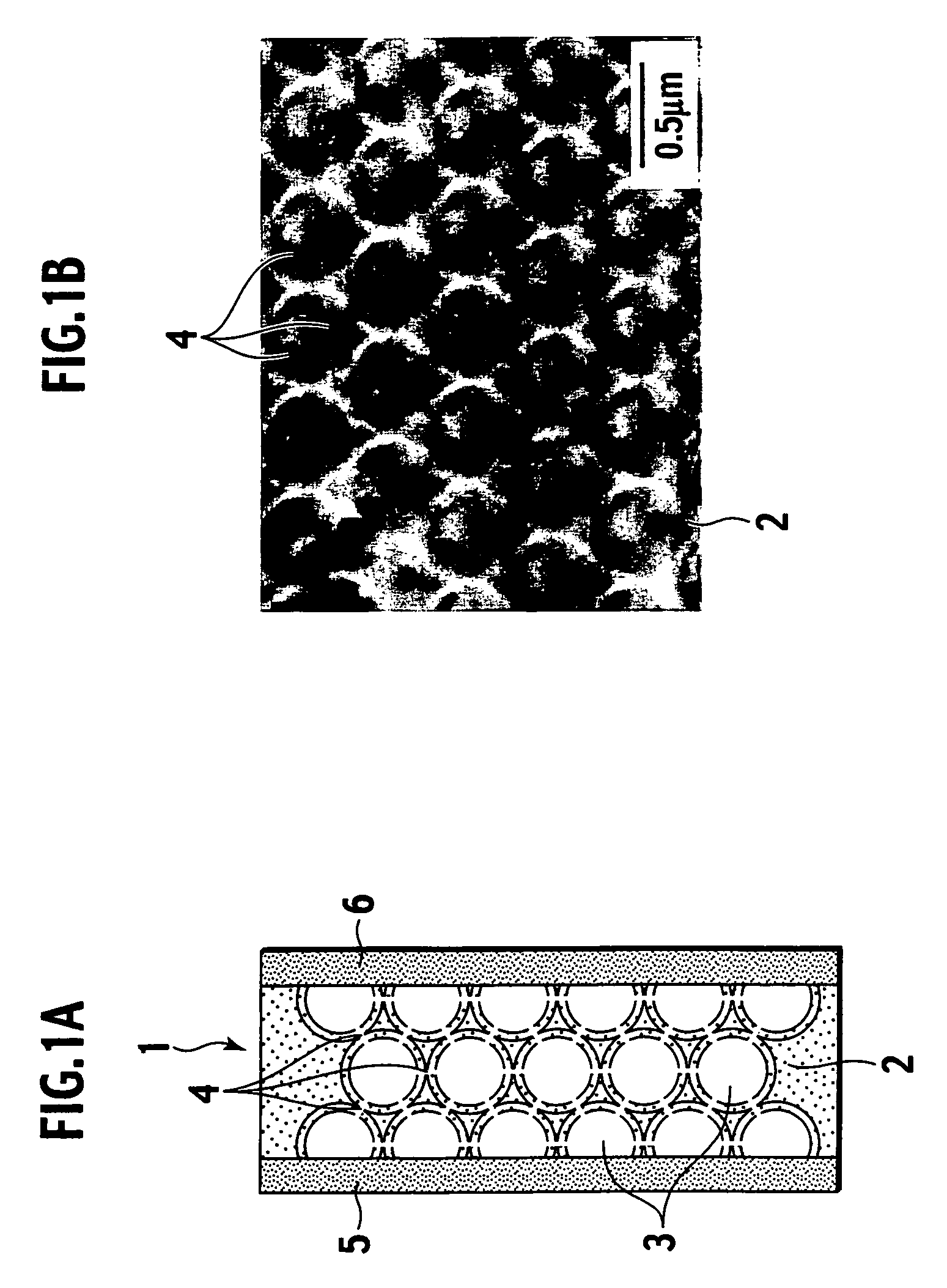
A composite electrolyte membrane of the present invention includes a porous body composed of an inorganic substance and an electrolyte material. The porous body includes therein plural spherical pores in which a diameter is substantially equal, and communicating ports each allowing the spherical pores adjacent to each other to communicate with each other. The electrolyte material is provided on the spherical pores and the communicating ports, has proton conductivity, and is composed of a hydrocarbon polymer. The proton-conductive composite electrolyte membrane has excellent ion conductivity, high heat resistance, and restricted swelling when being hydrous, and is capable of being produced at low cost.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD +1
Drug eluting medical devices having porous layers
InactiveUS20090029077A1Reduce retentionImprove cell adhesionEnvelopes/bags making machineryLayered productsPorous layerMicrosphere
In accordance with an aspect of the invention, implantable or insertable medical devices are provided that comprise (a) a substrate and (b) a porous layer comprising close packed spherical pores disposed over the substrate. The porous layer may also comprise a therapeutic agent. In another aspect, the present invention provides methods of forming implantable or insertable medical devices. These methods comprise forming a predecessor structure that comprises (i) a substrate over which is disposed (ii) an assembly of microspheres. This assembly of microspheres is then used as a template for the formation of a porous layer, which may be subsequently loaded with a therapeutic agent.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Ceramic cores for casting superalloys and refractory metal composites, and related processes
A rare earth-based core for use in the casting of a reactive metal is described. The core contains a ceramic composition which includes at least about 10% by weight of monoclinic rare earth aluminate (RE4Al2O9), wherein RE represents at least one rare earth element; and at least about 10% by weight of at least one free rare earth oxide. The ceramic phase of the composition may include a microstructure which comprises a multitude of substantially spherical pores which are formed as a result of the removal of aluminum metal from the core composition during a heat treatment step. Additional embodiments relate to a method for the fabrication of a ceramic core, employing a rare earth oxide, aluminum metal, and a binder. Methods for removing cores from a cast part are also described.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
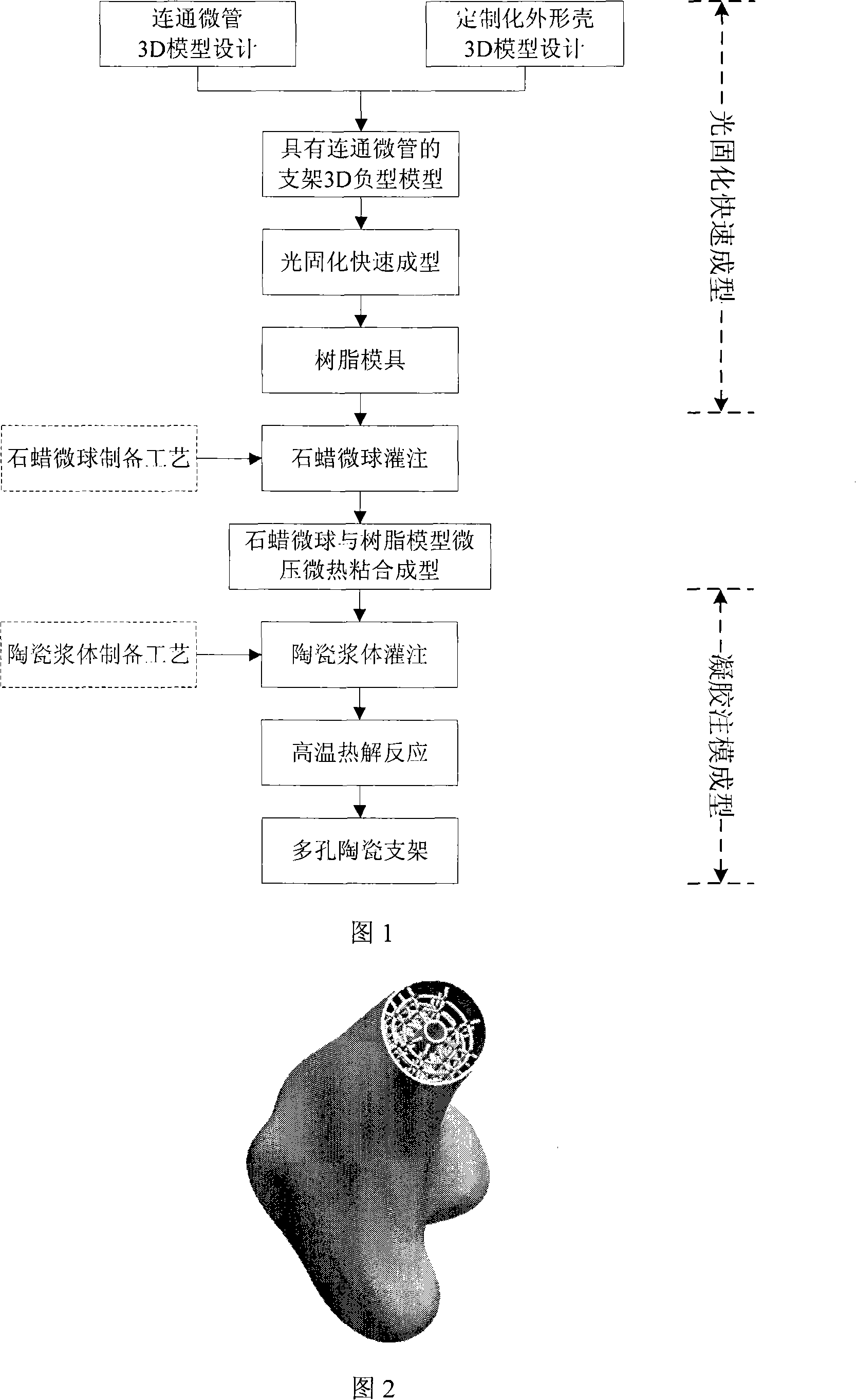
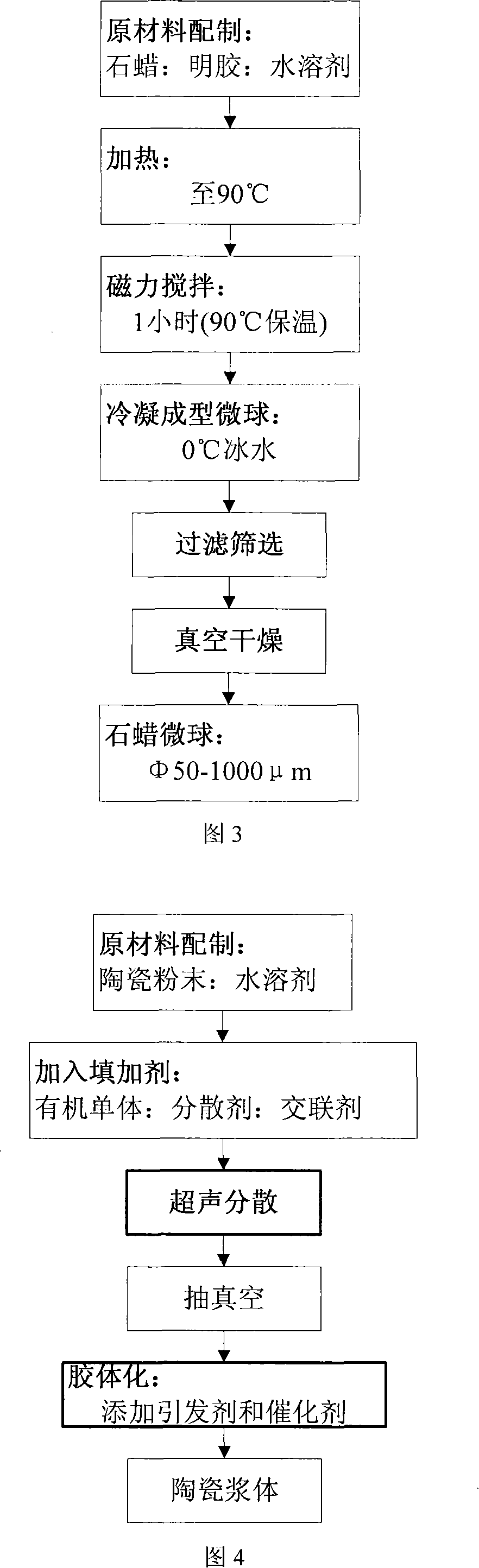
Customized forming method for gradient porous structure ceramic
InactiveCN101148360ALow costHigh precisionCeramic shaping apparatusCeramicwareSpherical porePorous ceramics
The present invention discloses the customized forming process of gradient porous structural ceramic. By means of the combined fast light solidifying and gel molding formation technology, porous ceramic product in spherical pore and micro tube combining structure and complicated profile may be obtained. The technological process of the present invention is simple and has low cost, high precision and high forming efficiency.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for fixing an implant, fixing member for the implant and implant composite
InactiveUS20050079469A1Fix tightOperational savingDental implantsImpression capsHydroxyapatite ceramicsApatite
A fixing member for an implant which comprises a tube or a pillar made of an hydroxyapatite ceramics at least one part of which is a ceramics porous article consisting essentially of a hydroxyapatite formed by agitation foaming, in which a number of approximately spherical pores mutually contact having pore structures communicated three-dimensionally opened at the contact area and having an averaged porosity of from 65% to 85%. A method for fixing an implant comprising a step of inserting an implant whose at least one part of the periphery is integrated with a hydroxyapatite ceramics into an implant insertion site of an alveolar bone or a gnathic bone. A method for fixing an implant, a fixing member for the implant and an implant composite in order to reinforce an implant insertion site by compensating or regenerating an alveolar bone or a gnathic bone on an implant treatment in dentistry or in oral surgery is obtained.
Owner:AKAGAWA YASUMASA +2
Proton-conductive composite electrolyte membrane and producing method thereof
InactiveUS20080213646A1Improve ionic conductivityImprove battery performanceSemi-permeable membranesSolid electrolytesComposite electrolyteProton
A composite electrolyte membrane of the present invention includes a porous body composed of an inorganic substance and an electrolyte material. The porous body includes therein plural spherical pores in which a diameter is substantially equal, and communicating ports each allowing the spherical pores adjacent to each other to communicate with each other. The electrolyte material is provided on the spherical pores and the communicating ports, has proton conductivity, and is composed of a hydrocarbon polymer. The proton-conductive composite electrolyte membrane has excellent ion conductivity, high heat resistance, and restricted swelling when being hydrous, and is capable of being produced at low cost.
Owner:KANAMURA KIYOSHI +1
Cobalt-base catalyst adopting silicon oxide mesoporous foam as carrier, and application thereof
ActiveCN102728359AAvoid easy cloggingLarge specific surface areaLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsDispersityAdjuvant
The invention belongs to the technical field of novel Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst preparation, and specifically discloses a preparation method for a cobalt-base catalyst adopting silicon oxide mesoporous foam MCF as a carrier, and an application of the cobalt-base catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. According to the present invention, the carrier of the present invention has a three-dimensional ordered pore structure; the specific surface area of the carrier can be up to 1000 cm<2> / g; the pore size of the carrier can be adjusted in a range of 20-50 nm; the pore volume of the carrier is 1.5-3.0 cm<3> / g; the pore presents a spherical structure; the spherical pores are communicated through windows; the diffusion effect is good; the prepared catalyst has a high surface area; the active metal loading is high; and the active metal particles are uniformly dispersed, and the dispersity is good. Compared with the activity of the conventional silicon oxide carrier loaded cobalt-base catalyst, the activity of the cobalt-base catalyst of the present invention is increased by more than two times. In addition, the activity and the heavy hydrocarbon selectivity of the cobalt-base catalyst of the present invention are significantly increased compared with SBA-15 loaded cobalt-base catalysts having the same structured ordered structure, and the catalyst shows excellent performances after adjuvant element impregnating or doping.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Ceramic cores for casting superalloys and refractory metal composites, and related processes
A rare earth-based core for use in the casting of a reactive metal is described. The core contains a ceramic composition which includes at least about 10% by weight of monoclinic rare earth aluminate (RE4Al2O9), wherein RE represents at least one rare earth element; and at least about 10% by weight of at least one free rare earth oxide. The ceramic phase of the composition may include a microstructure which comprises a multitude of substantially spherical pores which are formed as a result of the removal of aluminum metal from the core composition during a heat treatment step. Additional embodiments relate to a method for the fabrication of a ceramic core, employing a rare earth oxide, aluminum metal, and a binder. Methods for removing cores from a cast part are also described.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Preparation method of porous silicon nitride ceramic material with spherical pore structure
The invention relates to a preparation method of a porous silicon nitride ceramic material with a spherical pore structure. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing silicon nitride powder with a mono-dispersed polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) spherical pore forming agent to prepare a stable slurry, preparing microsphere powder (the silicon nitride powder and / the spherical pore forming agent are uniformly dispersed in the above microspheres) with good fluidity and regular shape through a spray drying process, carrying out a direct cold isostatic pressing technology on the microsphere powder to prepare a blank with uniform density, carrying out an optimized batching technology to completely remove the pore forming agent and other organic matters, and sintering in nitrogen pressure atmosphere to obtain the complete non-crack porous silicon nitride ceramic material. The porous silicon nitride ceramic material prepared through the method has the advantages of uniform space distribution, uniform size spherical pores, high bending strength and small discreteness.
Owner:AEROSPACE RES INST OF MATERIAL & PROCESSING TECH +1
Porous rack with spherical pores and its molding prepn process
InactiveCN1486754ALiquidGood shape retentionPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingSpherical poreBiological materials
The present invention belongs to the field of polymer material and biological material technology, and is especially one porous rack with spherical pores and its molding preparation process. The 3D porous rack is prepared with polymer material as base material and through molding at normal temperature. The simple process may be used in preparing both rack with simple and regular outer appearance and rack with complicated and irregular outer appearance. The prepared porous rack may be relatively thick and has regular spherical pore structure of porosity over 90%, and the pores are communicated mutually and homogeneously distributed. The rack has high mechanical strength, and is suitable as 3D porous cell rack in tissue engineering and in other application fields.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Water absorbent swelling resin aggregate concrete and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a water absorbent swelling resin aggregate concrete and a preparation method thereof. The water absorbent swelling resin aggregate concrete is prepared by blending the following raw materials by weight through a certain preparation process: 300-420 portions of cement, 186-306 portions of an admixture, 0-624 portions of a water absorbent swelling aggregate, 0-954 portions of a fine aggregates, 87-131 portions of mixing water, 11-14 portions of a water reducing agent and 1.8-2.2 portions of a fiber. The invention employs spherical polymer water absorbent resin particles as the water absorbent swelling resin aggregate; a type of concrete with controllable internal pore structure is prepared by controlling the size of the water absorbent swelling aggregate; the inside of the concrete comprises closed spherical pores with regular shape and in uniform distribution, and has the advantages of low density, strength high, good performance and saving of concrete solid material; besides, the water absorbent swelling aggregate before absorption has small volume, light weight, and is convenient for transportation.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Resol-assisted synthetic large aperture ordered mesopore metallic oxide material and preparation method of material
InactiveCN105129856AEffective control of wall thicknessEffective control of mesopore diameterTungsten oxides/hydroxidesNanotechnologySolvent evaporationMesoporous material
The invention belongs to the technical field of nano porous materials, in particular to a resol-assisted synthetic large aperture ordered mesopore metallic oxide material and a preparation method of the material. According to the material and the preparation method thereof, an amphiphilic block copolymer (PEO-b-PS and PEO-b-PMMA) with large molecular weight hydrophobic segments is taken as a template agent, the principle of assisted self-assembly of resol is utilized, and in a solvent evaporation process, the resol fixes a metal precursor to a hydrophilic end of the template agent, the self-assembly is induced through solvent evaporation, so as to enable the template agent and a mesoporous material precursor to react to form microphase separation, and obtain an ordered mesostructure; after using large molecular weight hydrophobic block to form a large hydrophobic area, and removing the template agent, the large aperture ordered mesopore metallic oxide material is obtained. The synthetic mesoporous material has a super large aperture, the shape of the pore channel of the material is spherical, the mesoporous of the material is orderly arranged, and the material has a bimodal mesoporous structure and a super high specific surface area; the method is simple, the raw material is easy to obtain and the material is suitable for enlarged production.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Porous humidity-control tile and method for manufacturing the same
Provided is a porous humidity-control tile including about 40% to about 95% by weight of diatomite, and one or more of ochre, red clay, kaolin, zeolite, illite, vermiculite, feldspar, pottery stone, and pyrophyllite. The porous humidity-control tile has about 10 vol % to 80 vol % of cellular spherical pores having a size corresponding to a size of hollow pore forming material that is removable by heat treatment. The porous humidity-control tile has a rate of moisture adsorption / desorption per unit weight in a range from about 20 g / kg to about 60 g / kg and a rate of moisture adsorption / adsorption per unit area in a range from about 150 g / m2 to about 450 g / m2. Therefore, the porous humidity-control tile can be light, and the amount of adsorption / desorption per unit weight of the porous humidity-control tile can be improved.
Owner:KOREA INST OF MATERIALS SCI
Surface activation method of dental implant
InactiveCN101773412AEvenly distributedPromote ingrowthDental implantsArtificial teethActivation methodTitanium alloy
A surface activation method of a dental implant comprises: putting a titanium implant in 1-3M of H2SO4 liquid, using the titanium or titanium alloy of the titanium implant as an anode and using a Pt material as a cathode to carry out anode oxidation by using an anode oxidation method, preparing an oxidation film with a three-dimensional spherical pore microstructure on a surface, and existing round pits in different sizes and with apertures of 100-200nm in local areas; and putting the titanium implant with the oxidized anode in 3-5M of NaOH alkali solution for processing and forming a titanium gel on the surface, wherein the enriched Ti-OH groups induce the generation of calcium phosphate crystal nucleuses to form a bone-like apatite layer. The invention uses the combination of the anode oxidation method and an alkali process method for preparing an active TiO2 coating layer on the surface of the titanium alloy, the implant processed by the anode oxidation method has good compatibility with bone, and bonding strength and bone sediment yield are both obviously higher than that of the unprocessed titanium, thereby greatly improving the clinic success ratio of the dental implant.
Owner:沈阳天贺新材料开发有限公司
Drug sustained release agent, adsorbent, functional food, mask, and adsorptive sheet
Provided is a drug sustained release agent comprising a carbon material (porous carbon material) having an inverted opal structure. The drug sustained release agent comprises a porous carbon material having a surface area of 3 x 102 m2 / gram or greater wherein spherical pores having an average diameter of 1 x 10-9 m to 1 x 10-5 m are three-dimensionally arranged; a porous carbon material wherein pores are visibly arranged in a pattern corresponding to a crystal structure; or a porous carbon material wherein pores are visibly arranged at the surface of a pattern corresponding to the (111) face orientation of a face-centered cubic structure.
Owner:SONY CORP
Foam metal with hierarchical pore structure, preparation method of foam metal and sound absorption and noise reduction material
ActiveCN111515395AHigh porosityMake full use of Helmholtz resonanceTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusPolyvinyl alcoholMetallic materials
The invention belongs to the technical field of foam metal, and particularly relates to foam metal with a hierarchical pore structure, a preparation method of the foam metal and a sound absorption andnoise reduction material containing the foam metal. The method comprises the steps that a spherical pore forming agent is screened through a screen, and pore forming agent particles are obtained; thepore forming agent particles are placed in a disc granulator, metal powder is added, and a polyvinyl alcohol water solution is sprayed to the surface of a mixture of the pore forming agent particlesand the metal powder; and the pore forming agent particles with the metal powder adhering to the surfaces are placed in a metal mold, a prefabricated product is manufactured through a blank pressing process, then vacuum pre-sintering is conducted, desolventizing treatment is conducted, finally vacuum sintering treatment is conducted, and the foam metal material with the hierarchical pore structureis obtained. According to the foam metal with the hierarchical pore structure, the preparation method of the foam metal and the sound absorption and noise reduction material containing the foam metal, on the basis of inheriting the related process thought of a traditional powder metallurgy method, a spherical pore forming agent aggregation technology is creatively introduced, core-shell structureprefabricated particles evenly coated with the metal powder are obtained, and a foundation is laid for subsequent construction of the hierarchical pore structure.
Owner:ANHUI NEOFOUND TECH
Drug eluting medical devices having porous layers
In accordance with an aspect of the invention, implantable or insertable medical devices are provided that comprise (a) a substrate and (b) a porous layer comprising close packed spherical pores disposed over the substrate. The porous layer may also comprise a therapeutic agent. In another aspect, the present invention provides methods of forming implantable or insertable medical devices. These methods comprise forming a predecessor structure that comprises (i) a substrate over which is disposed (ii) an assembly of microspheres. This assembly of microspheres is then used as a template for the formation of a porous layer, which may be subsequently loaded with a therapeutic agent.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method for welding foamed aluminium and aluminium alloy using solder capable of foaming
InactiveCN101347853AEvenly dispersedPrevent sinkingSoldering apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesSpherical pore5052 aluminium alloy
The invention discloses a welding method for welding foamed aluminium and aluminium alloy by using foaming solder, which belongs to the welding field of foamed metal. The steps are that 1. spherical pore foamed aluminium alloy blank is prepared as foaming welding solder by the melt foaming process; 2. the foamed aluminium and the aluminium alloy to be weld are selected and manufactured into the material with suitable size, then purified and dried; 3 a steel sealed mould is designed according to the outline dimension of the foamed aluminium and the aluminium alloy to be weld; 4. the solder with the thickness of 3 to 10mm is cut, as well as put and fixed in the solder together with the foamed aluminium and aluminium alloy joint into the sealed mould, and 0.5 to 4 Mpa of pressure is applied on both ends; 5. the solder in the foaming solder layer between the foamed aluminium and the aluminium alloy in the sealed mould is heated, and the second foaming procedure is started, the solder and base metal are infiltrated and diffused, and connected with each other by occlusal holes; 6. the steel mould is demolished and the overflow foaming solder is cleaned, and a welded framing member of the foamed aluminium and the aluminium alloy is obtained.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Paper craft model with articulating element
A paper craft model with articulating elements includes a paper craft model sheet that includes a paper substrate including a cut out with a multiplicity of scored lines adapted to facilitate a folding of the cut out into a first atomic three-dimensional object. The sheet also includes a spherical orifice defined on one surface of the first atomic three-dimensional object. Finally, the sheet includes an additional cut out disposed within the paper substrate, and including a multiplicity of scored lines adapted to facilitate a folding of the additional cut out into a second atomic three-dimensional object. The additional cut out defines an articulation tab including a neck extending from the additional cut out and a head disposed at a distal end of the neck. The neck has a width not exceeding a diameter of the orifice, and the head has a width that exceeds the diameter.
Owner:JAZWARES
Ceramic Cores for Casting Superalloys and Refractory Metal Composites, and Related Processes
A rare earth-based core for use in the casting of a reactive metal is described. The core contains a ceramic composition which includes at least about 10% by weight of monoclinic rare earth aluminate (RE4Al2O9), wherein RE represents at least one rare earth element; and at least about 10% by weight of at least one free rare earth oxide. The ceramic phase of the composition may include a microstructure which comprises a multitude of substantially spherical pores which are formed as a result of the removal of aluminum metal from the core composition during a heat treatment step. Additional embodiments relate to a method for the fabrication of a ceramic core, employing a rare earth oxide, aluminum metal, and a binder. Methods for removing cores from a cast part are also described.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for producing light ceramic materials
The present invention relates to a novel process for producing ceramic materials, in particular refractory materials having a reduced relative density. In particular, the invention relates to a process for producing light, refractory materials having non-contiguous pores based on shaped and unshaped materials. These materials can be used as working lining in high-temperature applications. The process is based on the production of spherical, closed and isolated pores in the microstructure of the material. The pores having a pore diameter which can be set in a targeted manner are generated by use of polymer particles, in particular polymethacrylates, in particular polymers or copolymers prepared by means of suspension polymerization, as pore formers which can be burnt out. The polymers or copolymers are present in the form of small spheres having a defined diameter. The introduction of isolated spherical pores allows the production of ceramic materials having a sometimes significantly reduced relative density and improved corrosion resistance and better mechanical strength compared to the prior art. The specific, closed pore system at the same time contributes to reducing the thermal conductivity of the ceramic materials. In addition, the novel process has the advantage that there is no risk of formation of undesirable black cores, even in the production of thick-walled ceramic products.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
High specific area composite foam and an associated method of fabrication
ActiveUS20160146556A1Decorative surface effectsLayered productsSurface-area-to-volume ratioMetallurgy
Composite foams are provided including a metal template and a conformal atomic-scale film disposed over such metal template to form a 3-dimensional interconnected structure. The metal template includes a plurality of sintered interconnects, having a plurality of first non-spherical pores, a first non-spherical porosity, and a first surface-area-to-volume ratio. The conformal atomic-scale film has a plurality of second non-spherical pores, a second non-spherical porosity, and a second surface-area-to-volume ratio approximately equal to the first surface-area-to-volume ratio. The plurality of sintered interconnects has a plurality of dendritic particles and the conformal atomic-scale film includes at least one of a layer of graphene and a layer of hexagonal boron nitride.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Polyimide-based porous single-ion polymer electrolyte PI-FPAS diaphragm as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111081946AImprove thermal stabilityHigh porosityCell component detailsSecondary cells servicing/maintenancePolyethylene glycolLithium-ion battery
The invention discloses a polyimide-based porous single-ion polymer electrolyte PI-FPAS diaphragm as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The diaphragm disclosed by the invention hasuniformly distributed spherical pore structures, the pore structures are communicated with each other, the porosity of the diaphragm is 65-67%, and the liquid absorption rate is 265-275wt.%. Accordingto the invention, polyimide is adopted as a framework supporting material to be blended with a single-ion polymer electrolyte, the single-ion polymer electrolyte membrane with excellent thermal stability and high porosity is obtained by using polyethylene glycol 6000 as a pore-foaming agent according to a template leaching technique, polyethylene glycol is a non-toxic environment-friendly material, and the removal of polyethylene glycol is much easier than the removal of common organic solvents from a solution mixture, so that the pore-forming technology disclosed by the invention is greener,more environment-friendly and easier to operate. In addition, the diaphragm prepared by the invention is applied to the lithium ion battery, so that the cycling stability and the safety performance of the battery can be improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Zirconium oxide-containing micro-nano pore heat insulation refractory material and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of refractory materials, and particularly relates to a zirconia-containing micro-nano pore heat insulation refractory material and a preparation method thereof. The zirconia-containing micro-nano pore heat insulation refractory material is prepared from a basic raw material, an additive and water, the mass content of ZrO2 in the refractory material is 5-98%. The zirconia-containing micro-nano pore heat insulation refractory material is white, light yellow or light pink in appearance, in the refractory material, the pore size of spherical pores is distributed between 0.006-250 microns, the average pore size is 0.1-20 microns, and the existence of the micro-nano pore structure ensures that the product has better heat insulation performance under the conditions of low volume density and high strength. The preparation method is green, environment-friendly and pollution-free, the structure and performance of the product are easily and accurately controlled, and the finally prepared refractory material can meet the requirements of ultralow heat conductivity and light weight and also has relatively high strength by regulating and controlling the dosage of each raw material and a process.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
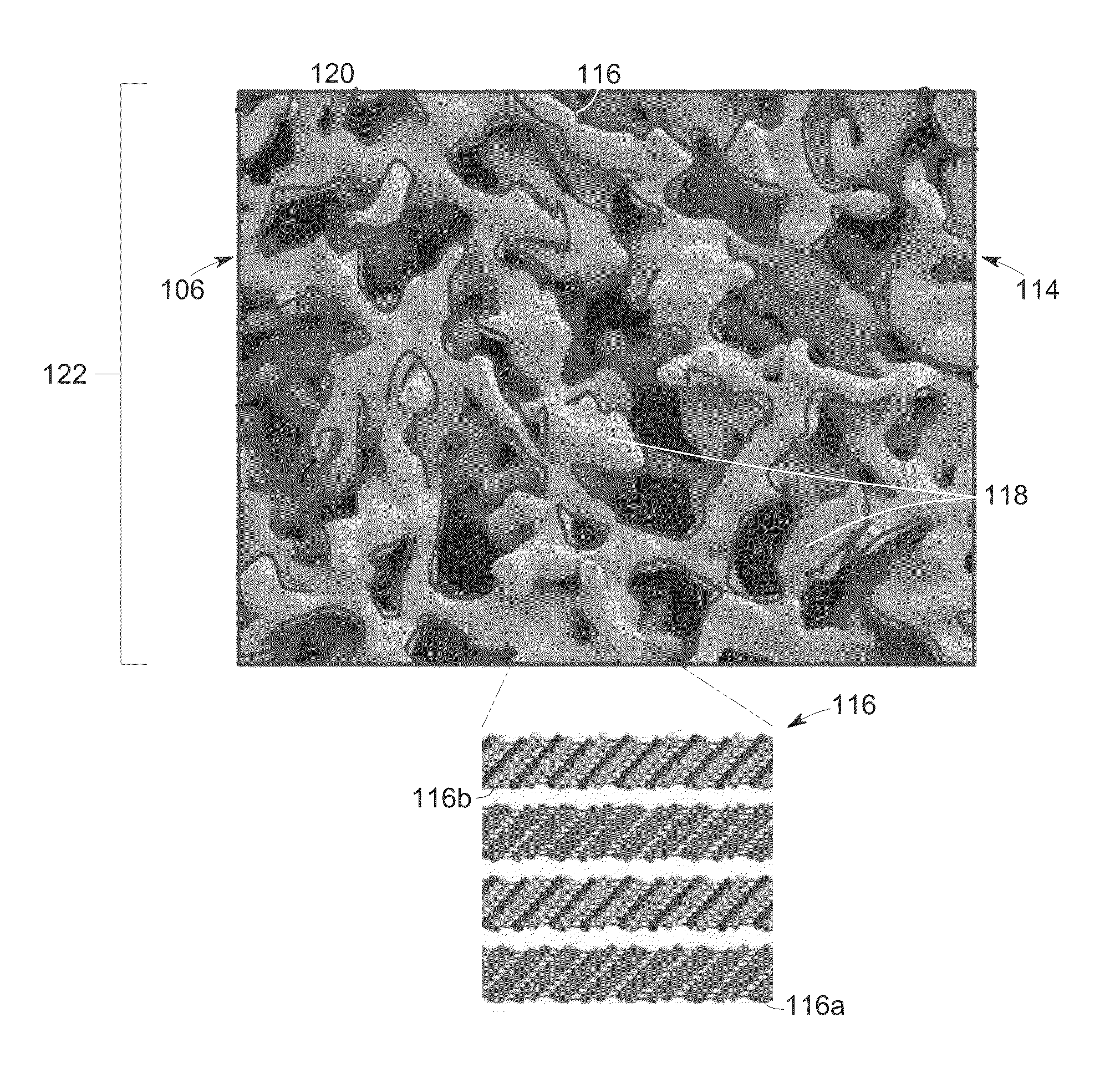
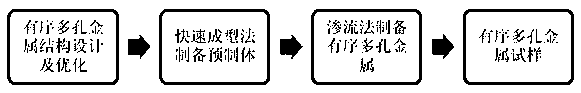
Design optimization and preparation method for ordered porous metal
ActiveCN105506337AGuaranteed Design PerformanceImprove recycling ratesAdditive manufacturing apparatusIngotDimensional modeling
The invention discloses a design optimization and preparation method for ordered porous metal, belonging to the technical field of metal preparation. The design optimization and preparation method comprises the steps of designing an ordered porous structure by using three-dimensional modeling software; simulating a seepage process and optimizing a prefabricated structure by using a numerical simulation method; preparing a precoated sand perform by using a laser sintering method; seeping by using a seepage method to obtain an original ingot of the porous metal; and finally, scattering the perform by heating to finally obtain the ordered porous metal. By using the method, the designability and reliability of ordered porous aluminum holes are achieved, and the aim of designing the sizes, shapes and orders of the holes is achieved; the minimum apertures of the holes obtained by using the method are 2mm, and the design and preparation of ordered porous aluminum such as spherical holes, square holes, cylindrical holes and various combined holes with simple hole forms are realized. The perform required by the seepage method is prepared by using a rapid molding technology, so that the production efficiency is increased, and the production cost is reduced. The method has the advantages of designability, controllability, low cost, high efficiency, recyclable raw materials and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing hollow alumina sphere bricks by utilizing pore forming substance
ActiveCN108947568AImprove high temperature creep resistanceImprove thermal shock resistanceCeramicwareBrickRefractory
The invention relates to the technical field of refractory matters and relates to a method for preparing hollow alumina sphere bricks by utilizing a pore forming substance. The method for preparing the hollow alumina sphere bricks by utilizing the pore forming substance comprises the following steps: premixing Al2O3 micro powder, clay fine powder and silica powder to serve as a matrix part; fullystirring a spherical pore forming substance of 50-150 microns with a silica sol solution, fully wetting the silica sol solution, and attaching onto the surface of the spherical pore forming substance;performing mixing granulation on the mixed powder of three kinds of micro powder serving as the matrix and the spherical pore forming substance attached with the silica sol solution so as to obtain coating particles obtained by coating the mixed powder with the spherical pore forming substance; and fully mixing the hollow alumina spheres and a binding agent, adding the coating particles for mixing again, and finally adopting a vibration pressurization manner to prepare various set products of needed sizes, drying, maintaining the heat, and firing, thereby obtaining the hollow alumina sphere bricks. The hollow alumina sphere brick disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of being excellent in high temperature creep resistance and excellent in thermal shock resistance.
Owner:SINOSTEEL LUOYANG INST OF REFRACTORIES RES
Preparation method of MXene aerogel with spherical pore structure
InactiveCN112850711ARich in microporesSolve the self-stacking problemMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsEmulsionCapacitive deionization
The invention belongs to the field of synthesis of environmental nanomaterials, and provides a preparation method of MXene aerogel with a spherical pore structure. The MXene aerogel with the three-dimensional spherical pore structure is constructed through a template induction method and an emulsion method, and the preparation method comprises the steps of preparation of polystyrene (PS) microspheres, preparation of a Ti3C2Tx MXene dispersion liquid, preparation of PS (at) MXene, preparation of Jauns MXene and preparation of the MXene aerogel. The process is simple and convenient to operate and simple in flow, and the prepared MXene aerogel with the spherical pore structure is light in density, rich in micropores, adjustable in pore structure and wide in application value, and can be applied to the fields of electromagnetic shielding, capacitive deionization, electro-adsorption and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
A kind of cobalt-based catalyst with silicon oxide mesoporous foam as carrier and its application
ActiveCN102728359BLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsDispersityAdjuvant
The invention belongs to the technical field of novel Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalyst preparation, and specifically discloses a preparation method for a cobalt-base catalyst adopting silicon oxide mesoporous foam MCF as a carrier, and an application of the cobalt-base catalyst in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. According to the present invention, the carrier of the present invention has a three-dimensional ordered pore structure; the specific surface area of the carrier can be up to 1000 cm<2> / g; the pore size of the carrier can be adjusted in a range of 20-50 nm; the pore volume of the carrier is 1.5-3.0 cm<3> / g; the pore presents a spherical structure; the spherical pores are communicated through windows; the diffusion effect is good; the prepared catalyst has a high surface area; the active metal loading is high; and the active metal particles are uniformly dispersed, and the dispersity is good. Compared with the activity of the conventional silicon oxide carrier loaded cobalt-base catalyst, the activity of the cobalt-base catalyst of the present invention is increased by more than two times. In addition, the activity and the heavy hydrocarbon selectivity of the cobalt-base catalyst of the present invention are significantly increased compared with SBA-15 loaded cobalt-base catalysts having the same structured ordered structure, and the catalyst shows excellent performances after adjuvant element impregnating or doping.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Method for preparing porous aluminum alloy by using hollow microspheres
The invention relates to a method for preparing porous aluminum alloy by using hollow microspheres. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of adopting the aluminum oxide (Al 2O3) hollow microspheres as pore-forming agents, putting the aluminum oxide hollow microspheres and aluminum alloy powder into a closed container according to a certain volume ratio in a glove box undera protective atmosphere, and fully mixing the materials to obtain uniformly mixed aluminum oxide hollow microspheres and aluminum alloy precursor powder; and adopting vacuum hot pressing sintering, uniformly placing the aluminum oxide hollow microspheres and aluminum alloy precursor powder into a mold, controlling sintering parameters and pressure, and obtaining the porous aluminum alloy providedwith uniform spherical pores with certain porosity. The method for preparing the porous aluminum alloy by using the hollow microspheres solves the problems that the pore-forming agents are difficultto remove and the size and shape of the pores are difficult to control accurately, and the prepared porous aluminum alloy is uniform in pore distribution, the pores are spherical and the aperture is in micron size. The process is simple, the operation is flexible, and the cost is low.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com