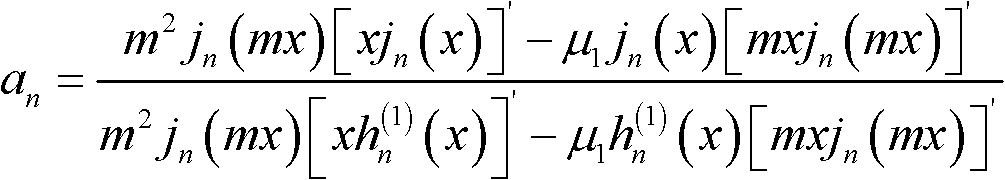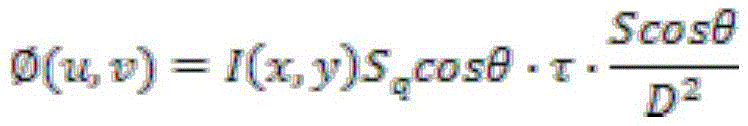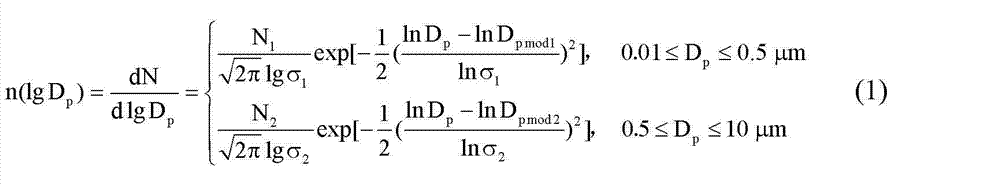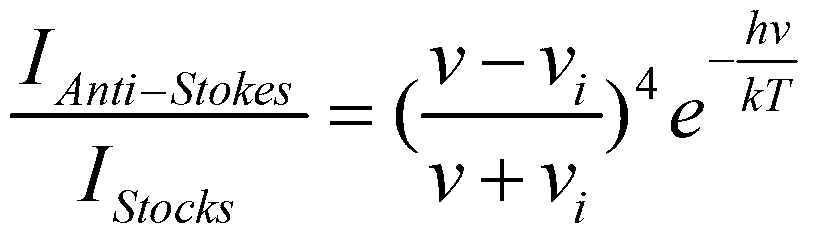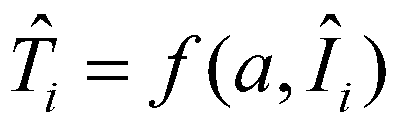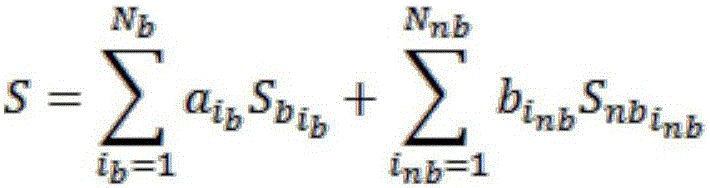Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
86 results about "Scattering theory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
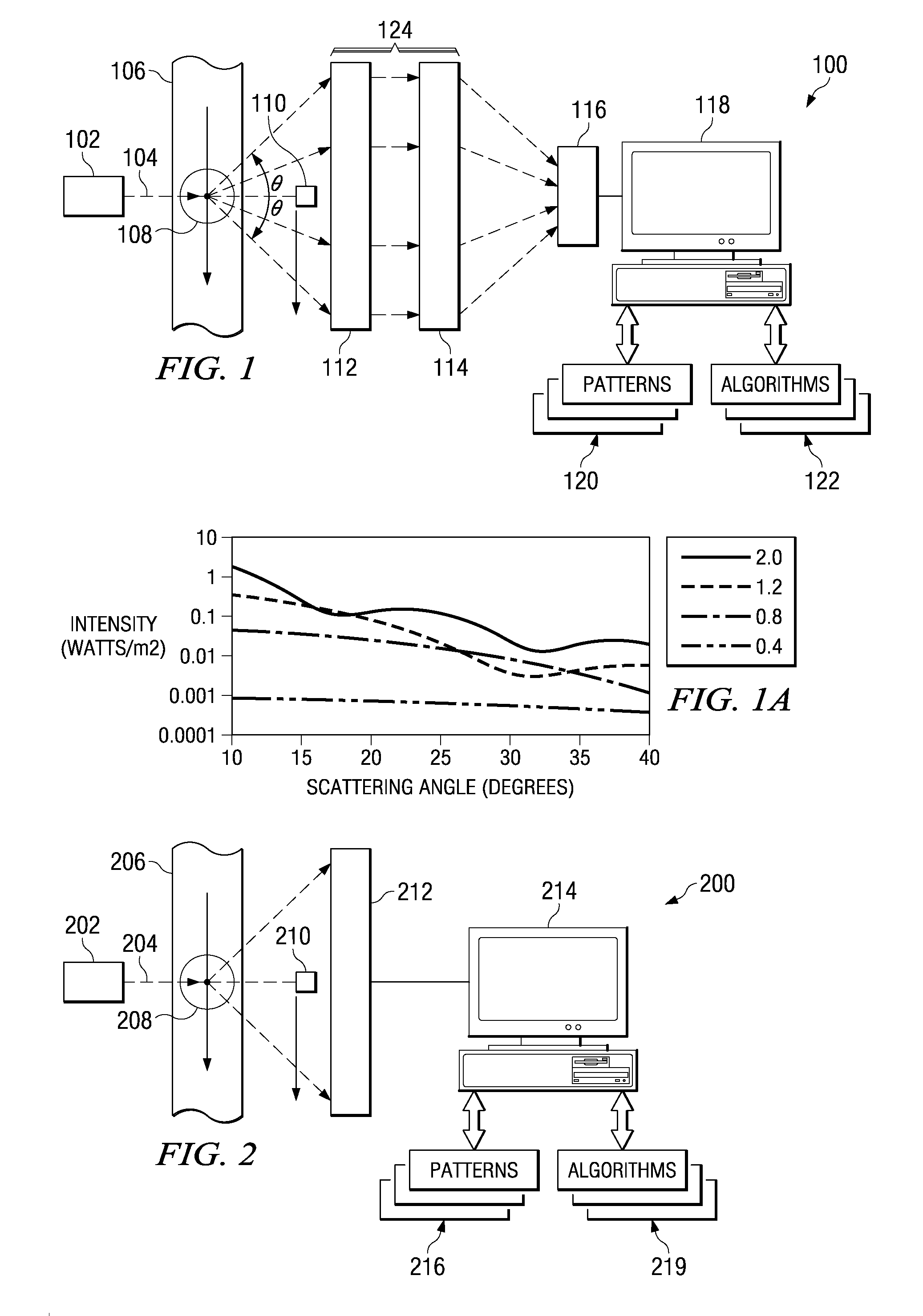
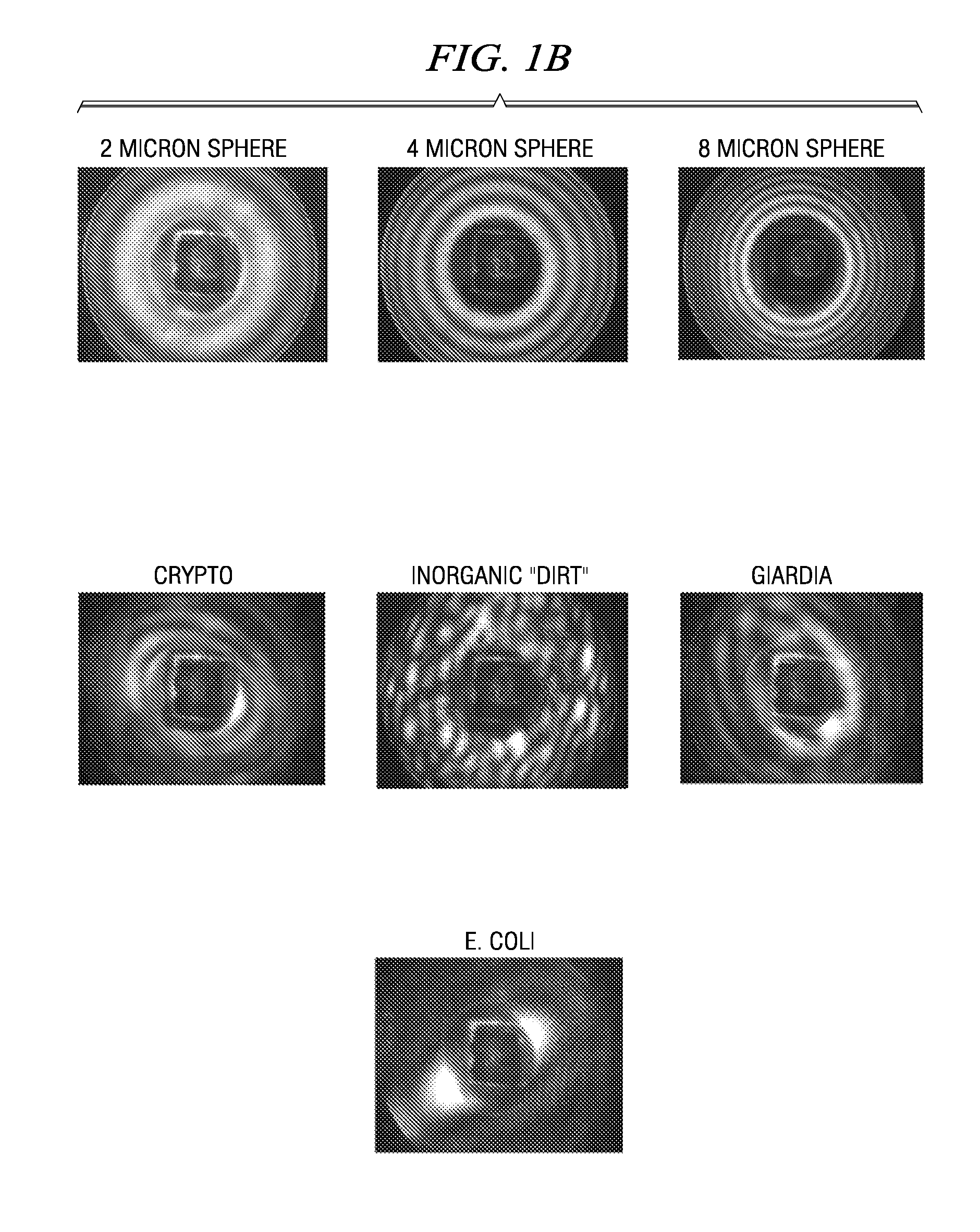
In mathematics and physics, scattering theory is a framework for studying and understanding the scattering of waves and particles. Wave scattering corresponds to the collision and scattering of a wave with some material object, for instance sunlight scattered by rain drops to form a rainbow. Scattering also includes the interaction of billiard balls on a table, the Rutherford scattering (or angle change) of alpha particles by gold nuclei, the Bragg scattering (or diffraction) of electrons and X-rays by a cluster of atoms, and the inelastic scattering of a fission fragment as it traverses a thin foil. More precisely, scattering consists of the study of how solutions of partial differential equations, propagating freely "in the distant past", come together and interact with one another or with a boundary condition, and then propagate away "to the distant future". The direct scattering problem is the problem of determining the distribution of scattered radiation/particle flux basing on the characteristics of the scatterer. The inverse scattering problem is the problem of determining the characteristics of an object (e.g., its shape, internal constitution) from measurement data of radiation or particles scattered from the object.
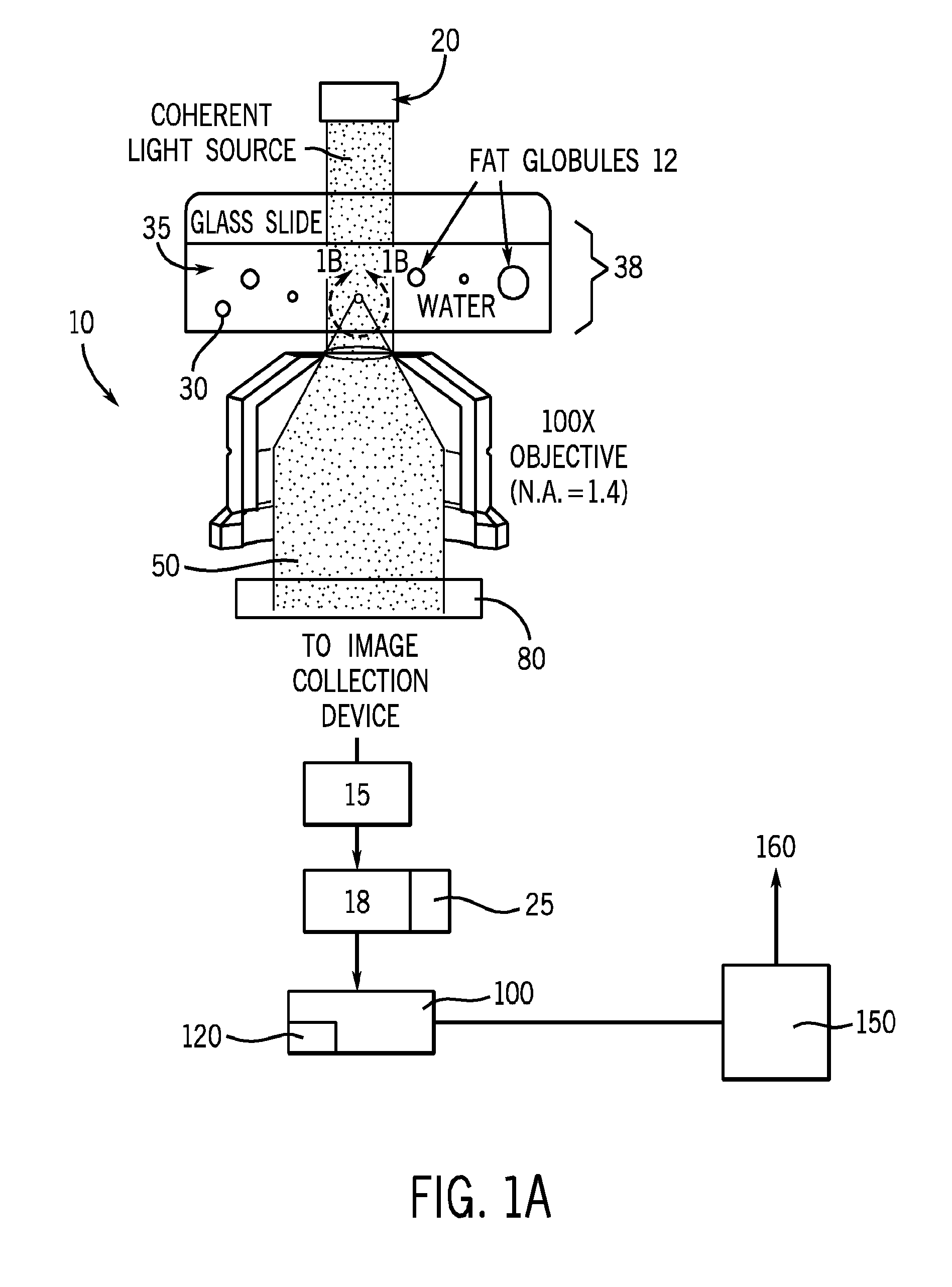
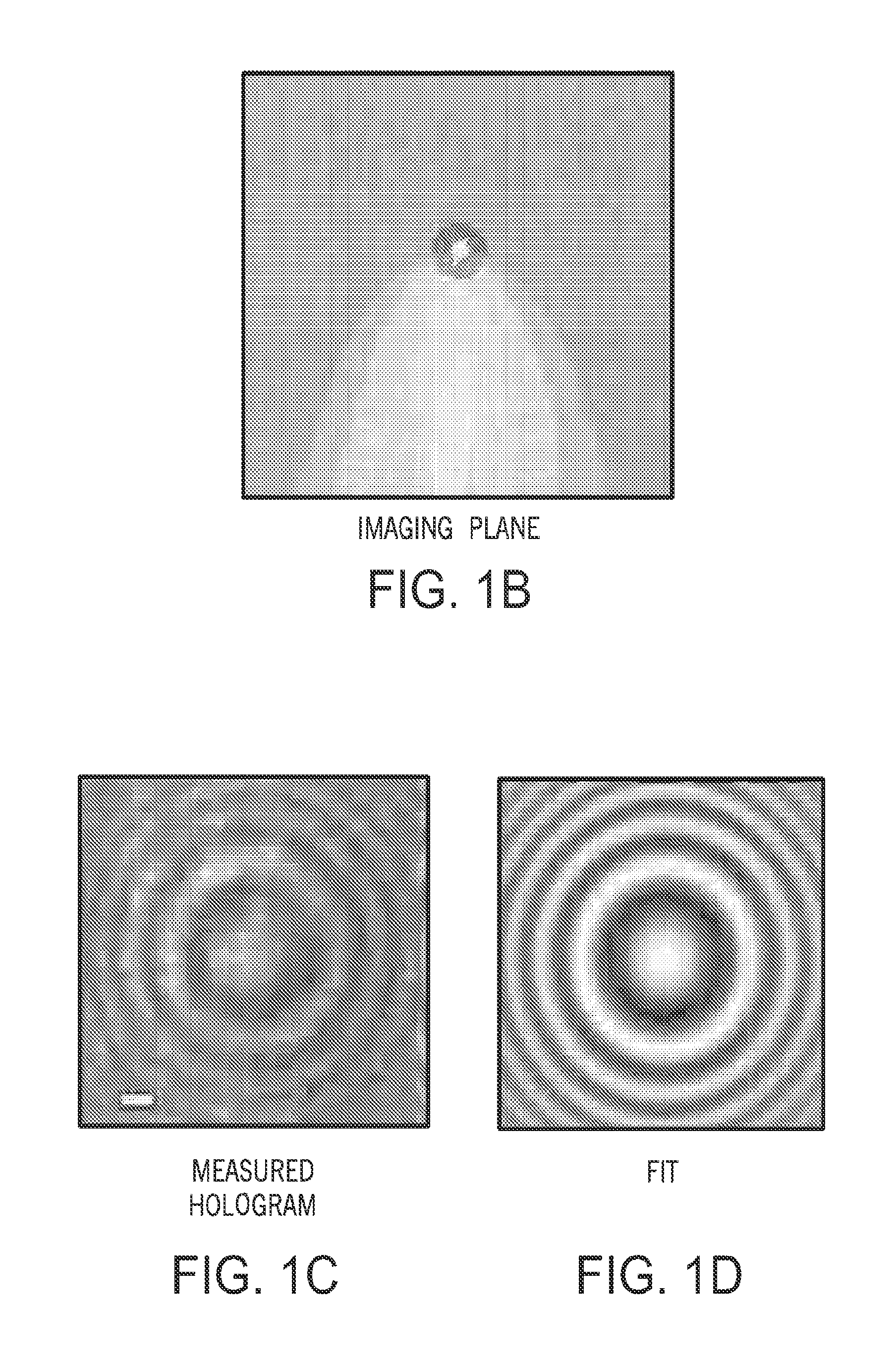
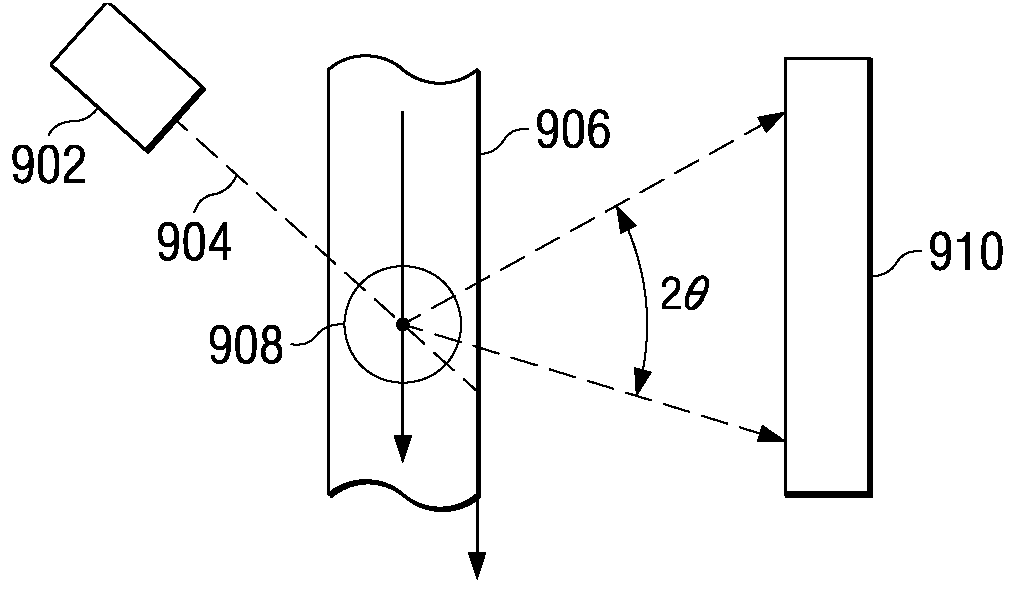
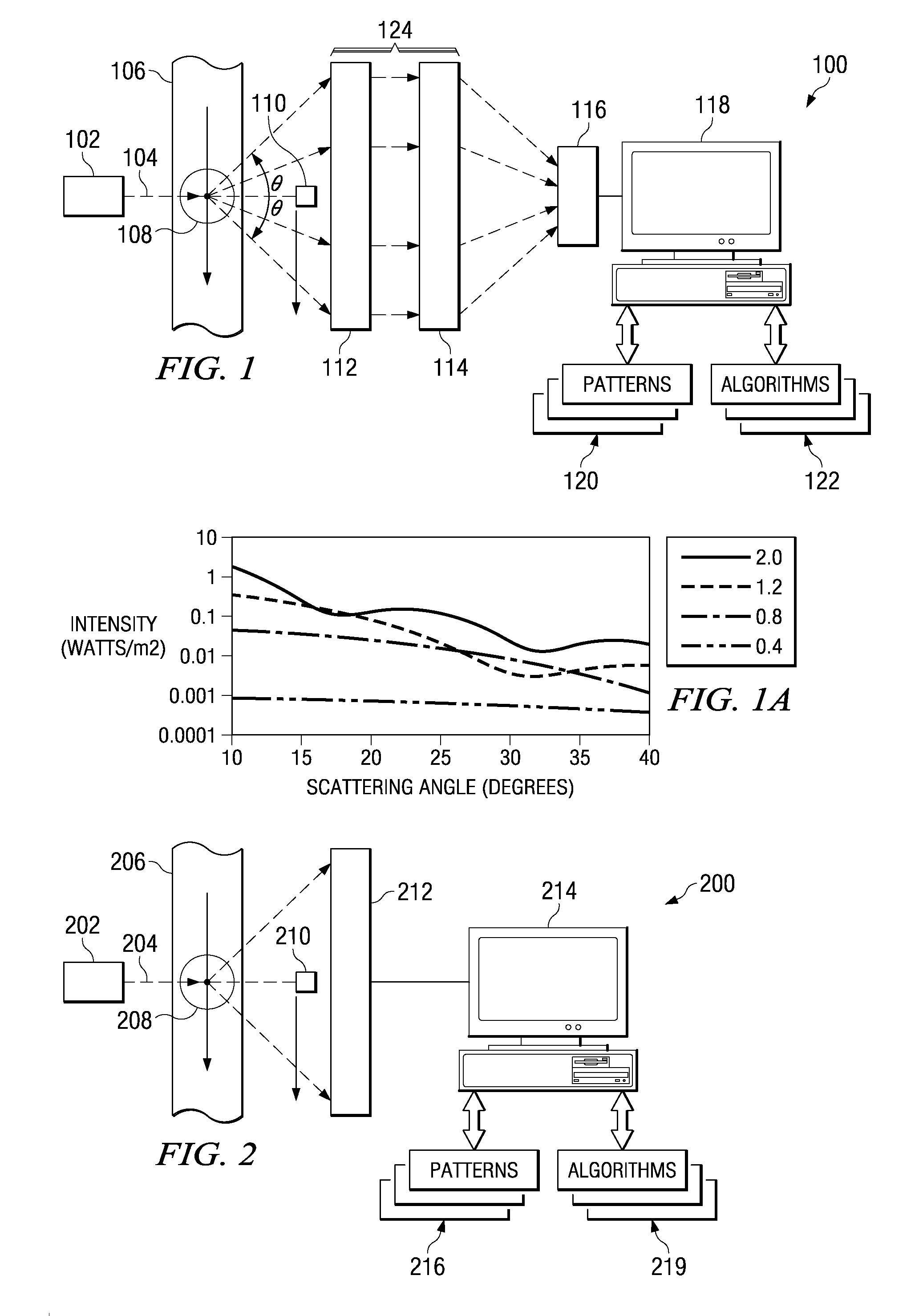
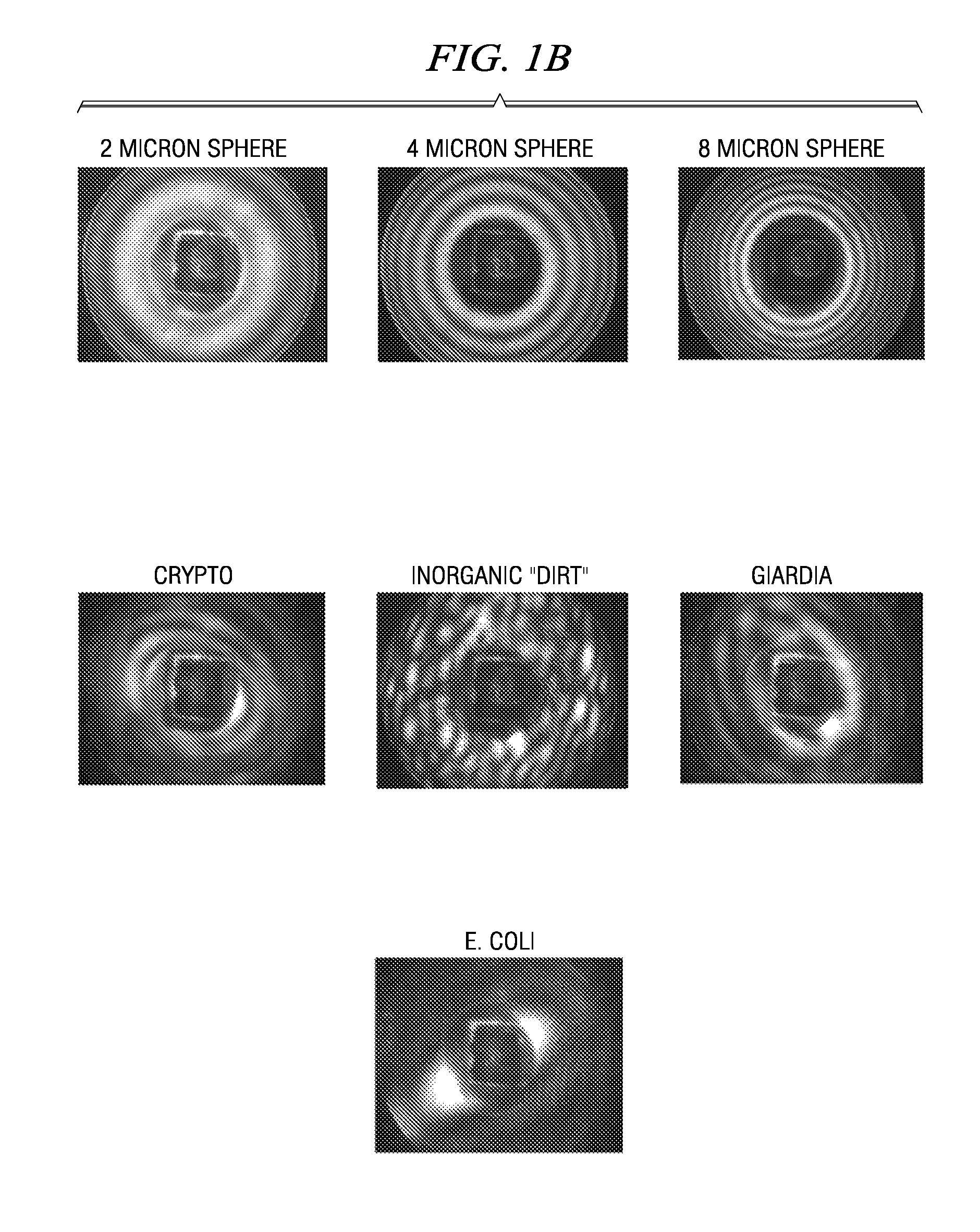
Tracking and characterizing particles with holographic video microscopy
ActiveUS20110043607A1Accurate representationTelevision system detailsNanoparticle analysisImage resolutionRefractive index
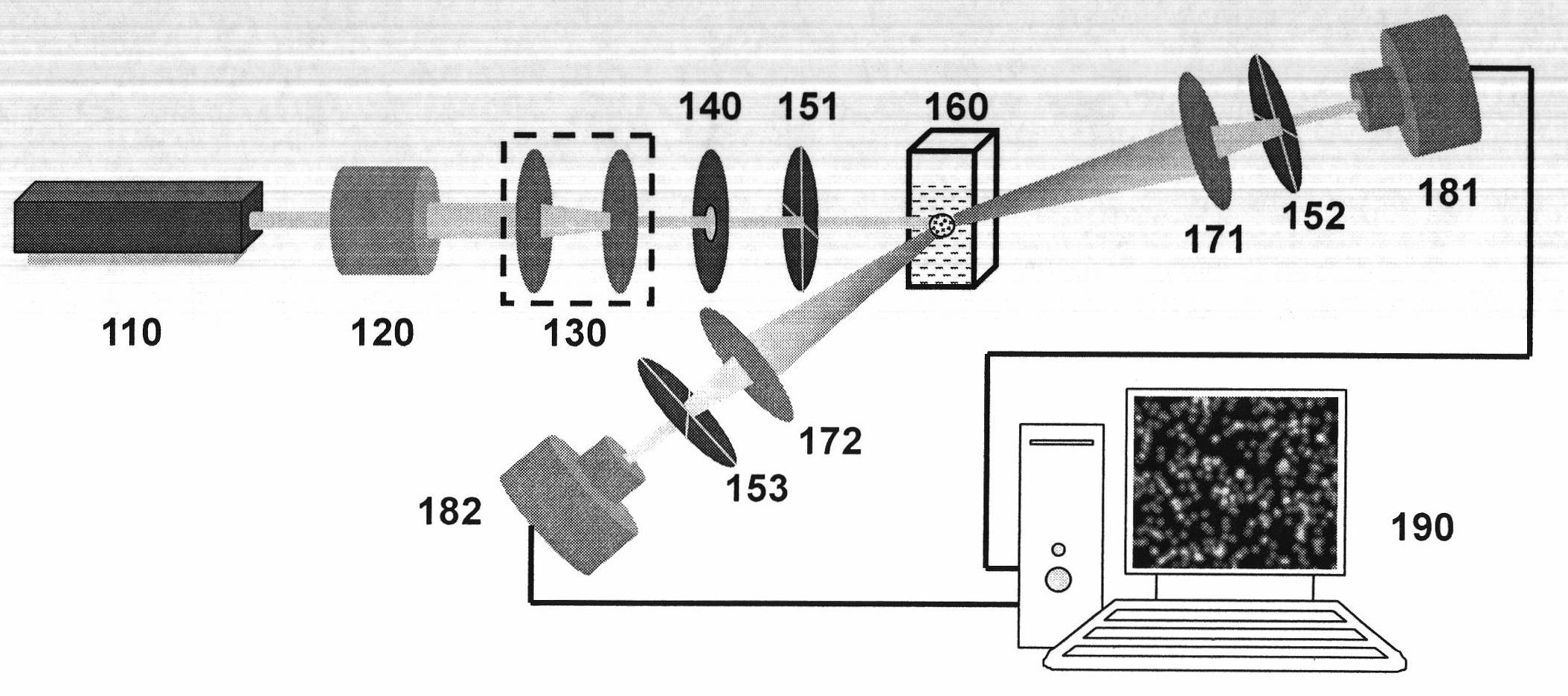
In-line holography to create images of a specimen, such as one or more particles dispersed in a transparent medium. Analyzing these images with results from light scattering theory yields the particles' sizes with nanometer resolution, their refractive indexes to within one part in a thousand, and their three dimensional positions with nanometer resolution. This procedure can rapidly and directly characterize mechanical, optical and chemical properties of the specimen and its medium.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
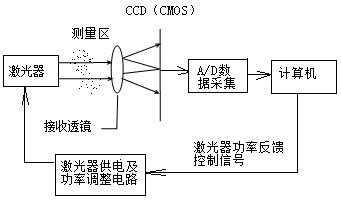
Granularity centering measuring method utilizing CCD (charge coupled device) or CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) as photoelectric detector
InactiveCN102053050AOvercome satietyDefects overcome or damagedParticle size analysisCMOSPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses a granularity centering measuring method utilizing a CCD (charge coupled device) or CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) as a photoelectric detector. The method comprises the following steps: 1, adopting a CCD or CMOS as a multielement photoelectric detector, utilizing a power adjustable laser, and lowering the power of the laser before granularity of granules ismeasured, thus a low power laser beam is not saturated when being focused on the CCD or CMOS; and recording the pixel position of the laser spot on the CCD or CMOS, and taking the measured pixel of the spot as a scattering center position during granularity measurement; 2, adjusting the power of the laser to the limit power at which the pixel with a peak signal is not saturated, carrying out measurement, and recording the distribution of lights scattered by the granules; and 3, calculating according to the light scattering theory to obtain granularity distribution of the granules on the basisof the initially determined scattering center position. According to the invention, the defects that the traditional laser granularity instrument is complex in centering and the pixel is easily saturated or damaged when the CCD or CMOS is adopted as the photoelectric detector are solved, a hardware centering device is omitted, no concentric adjusting is required, and the granularity measurement of the granules can be realized.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Device for monitoring micro-particles shapes and dispersion based on image
InactiveCN101082562AQuick Statistical ClassificationInversion theory revisionScattering properties measurementsIndividual particle analysisFiberScattering theory
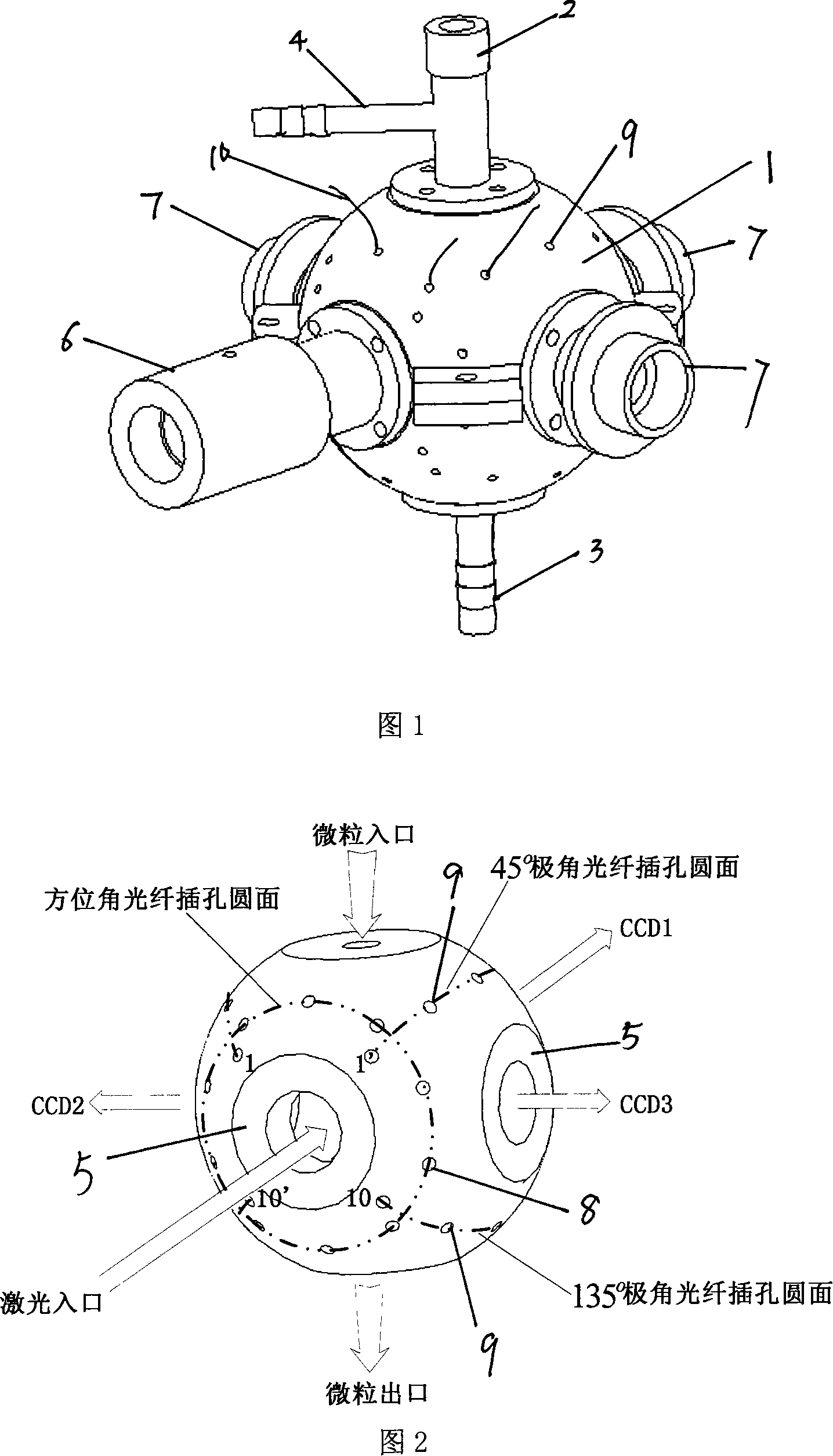
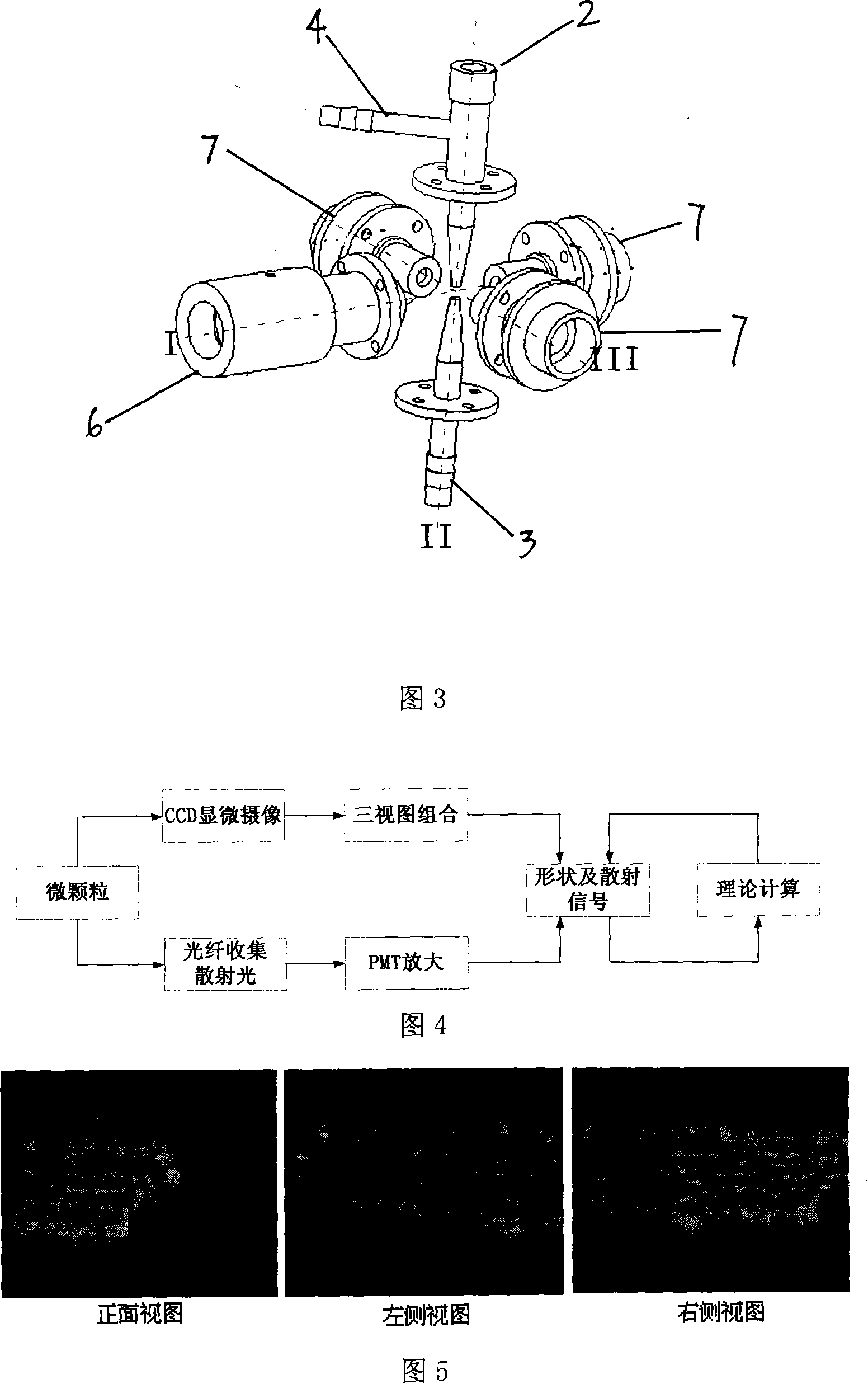
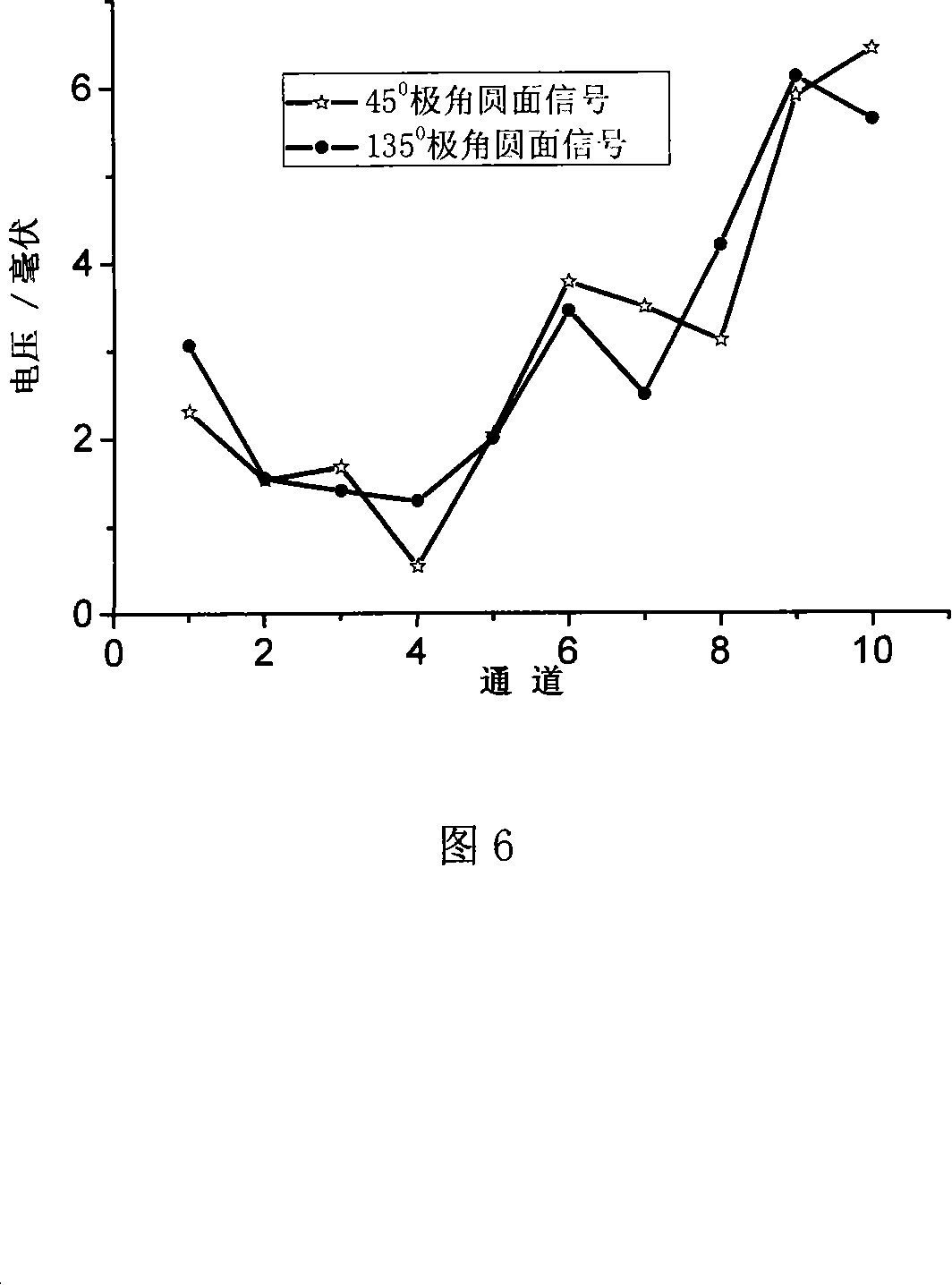
The invention discloses a kind of instrument bases on the graphic monitoring micro-particle shape and scatter. On the scatter cavity the inner surface is roughed and black finish and the bottom side and the top side sets up the micro-particle flowing sample pipe and escape pipe. On the horizontal direction radial face of the scatter cavity installs one semiconductor laser interval 90degree and three adjustable microscope. The scatter cavity distributes forty azimuth angles directing to the cavity center and the polar angles fiber jack in regular and in the polar fiber jack installs sample fiber and it can over-all detect the micro-particle scatter signal from the forty azimuth angles and screens the single particle through the light beam by the microscope enlarge CCD imagery technology and make the shape of particle statistical and classified and general the relevance condition of the presented scatter theory meanwhile make the inversion theory modified.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device and method for measuring particulate motion of turbid media by using dynamic speckle method
InactiveCN102175580AEliminate the effects of measurement accuracyMeasuring DynamicsMaterial analysisParticulatesForward scatter
The invention relates to a device and a method for measuring particulate motion of turbid media by using a dynamic speckle method. The device comprises a laser beam shaping contracting part, a forward scattering speckle field measuring part, a backward scattering speckle field measuring part, and a computer control and processing system. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing the device to record a forward scattering speckle field and a backward scattering speckle field generated by the particulate motion of turbid media and store the fields into the computer; according to the particle light scattering theory, choosing the forward scattering speckle field or backward scattering speckle field data; and analyzing the motion characteristic of the particulate, by utilizing a speckle chart characteristic value. The method is characterized by real time, dynamic and accuracy and can be widely applied to the fields such as medicaments, biology, life science, and the like.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Complete and high-resolution test method for motion characteristics of particles in turbid media
InactiveCN101980000AReal-time detectionContinuous detectionScattering properties measurementsApplicability domainTemporal resolution
The invention discloses a complete and high-resolution test method for the motion characteristics of particles in turbid media. The method comprises the following steps of: performing continuous, complete and real-time detection on the motion characteristics of the particles in the process of 'solution-colloid-sediment' of the turbid media by combining the resolution relation between the characteristic value of a speckle pattern and particle motion and utilizing a dynamic speckle test light path according to the particle light scattering theory; simultaneously, performing transient study on different critical points of the particle motion in the process by using a femtosecond laser test light path to perform the analysis of high spatial and temporal resolution on transient dynamics of the particles in the turbid media; and combining the two steps to realize the complete test with high spatial and temporal resolution characteristic on motion images of the particles in the process of 'solution-colloid-sediment' of the turbid media finally. The method is a non-contact, high-accuracy and real-time online detection method, has the characteristics that the operation is simple and the application range is wide, and can be widely used in the fields of medical science, pharmacy, chemical production and the like.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Systems and methods for a high capture angle, multiple angle light scattering (MALS) instrument
InactiveUS20060256333A1Material analysis by optical meansParticle size analysisRayleigh scatteringLiquid medium
A particle detection system uses a reflective optic comprising a curved surface to detect high angle scattered light generated by a particle in a liquid medium, when a laser beam is incident on the particle. When the particles transit the laser beam, light is scattered in all directions and is described by MIE scattering theory for particles about the size of the wavelength of light and larger or Rayleigh Scattering when the particles are smaller than the wavelength of light. By using the reflective optic, the scattered light can be detected over angles that are greater than normally obtainable.
Owner:JMAR LLC A DELAWARE LLC
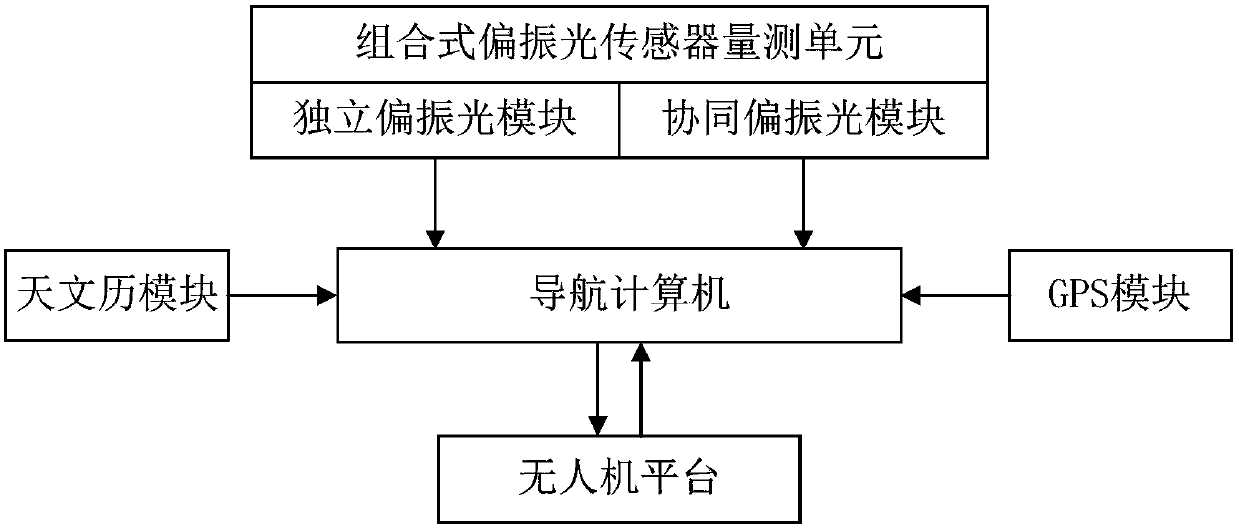
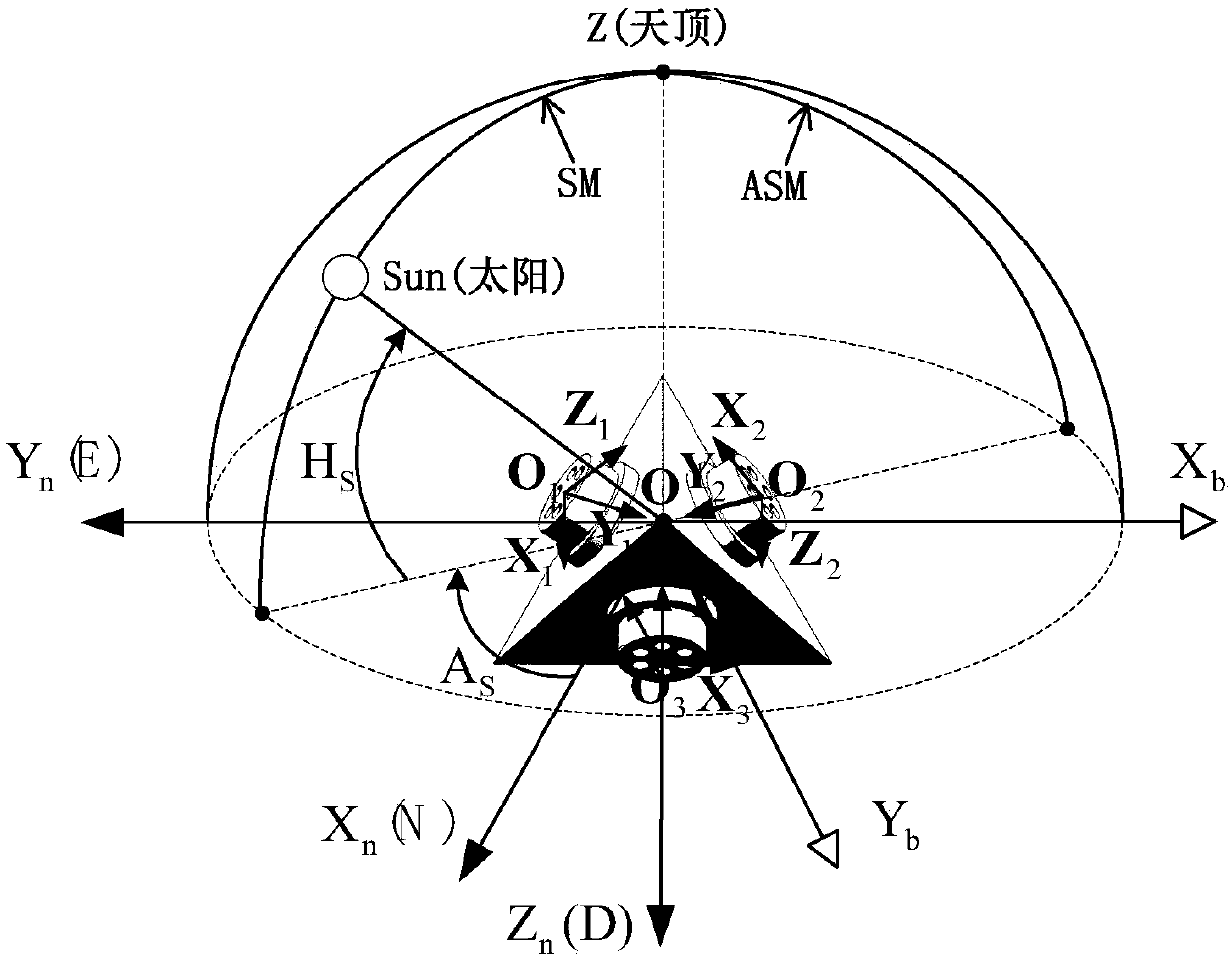
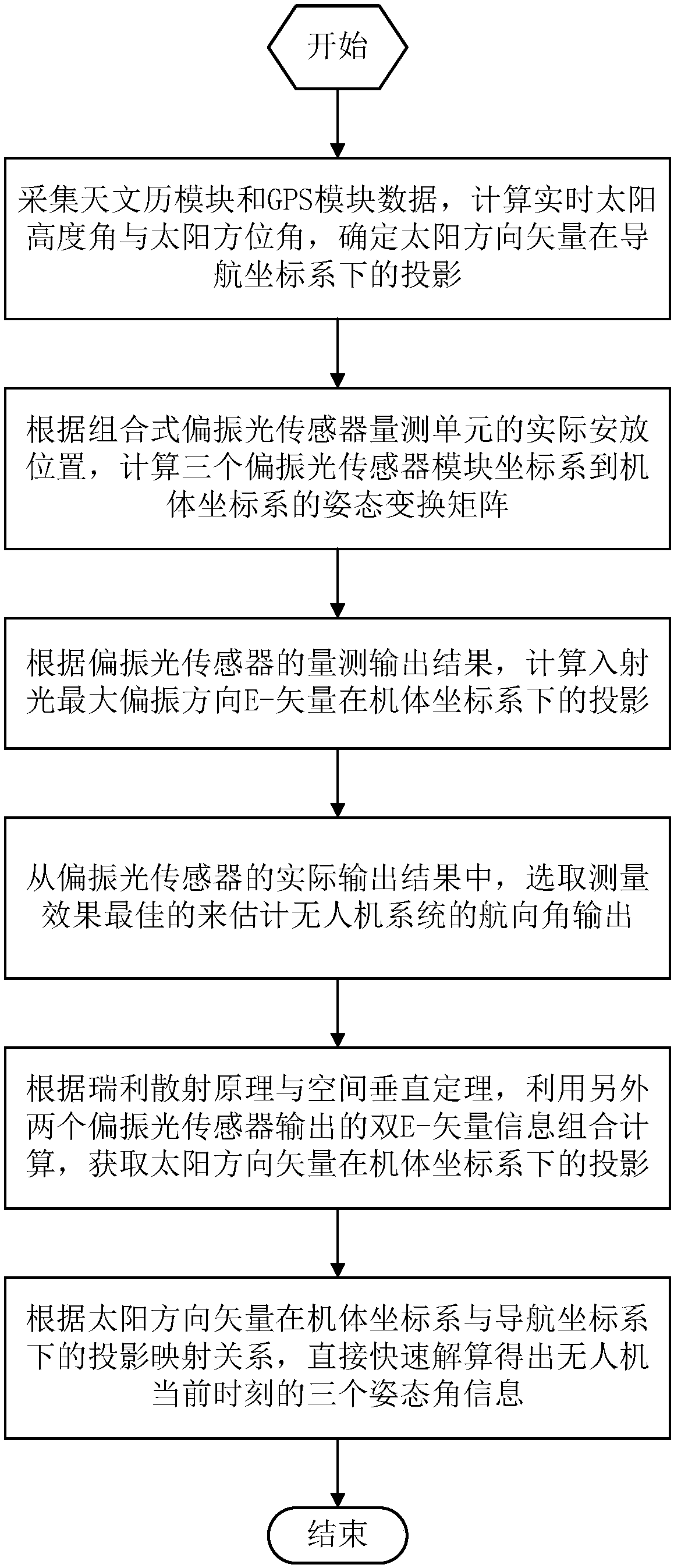
Quick three-dimensional attitude information resolving method based on dual polarized light vectors
ActiveCN107727101AGet rid of dependenceAvoid defects that are susceptible to external interferenceNavigational calculation instrumentsAttitude controlMarine navigationTransfer phenomenon
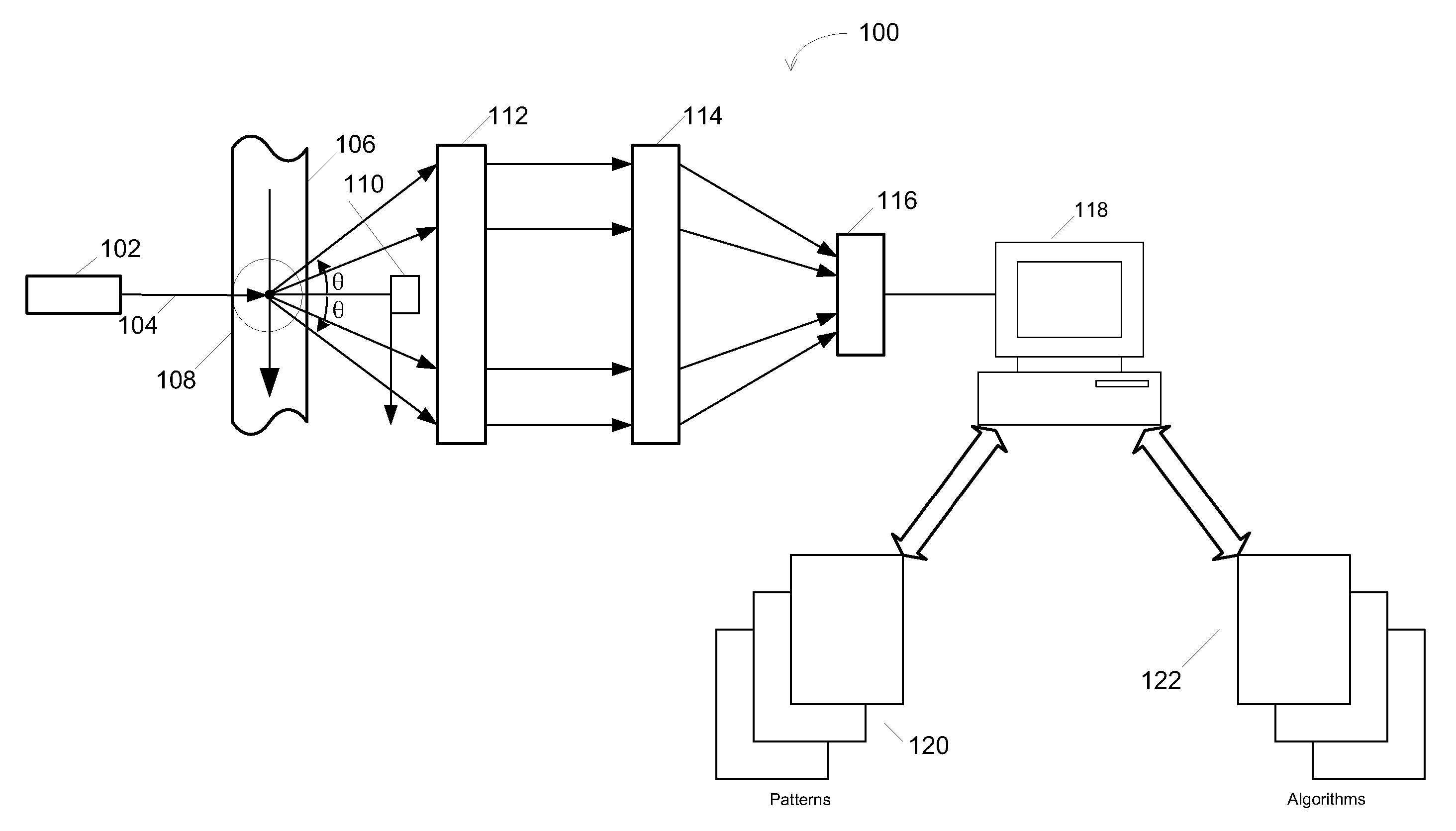
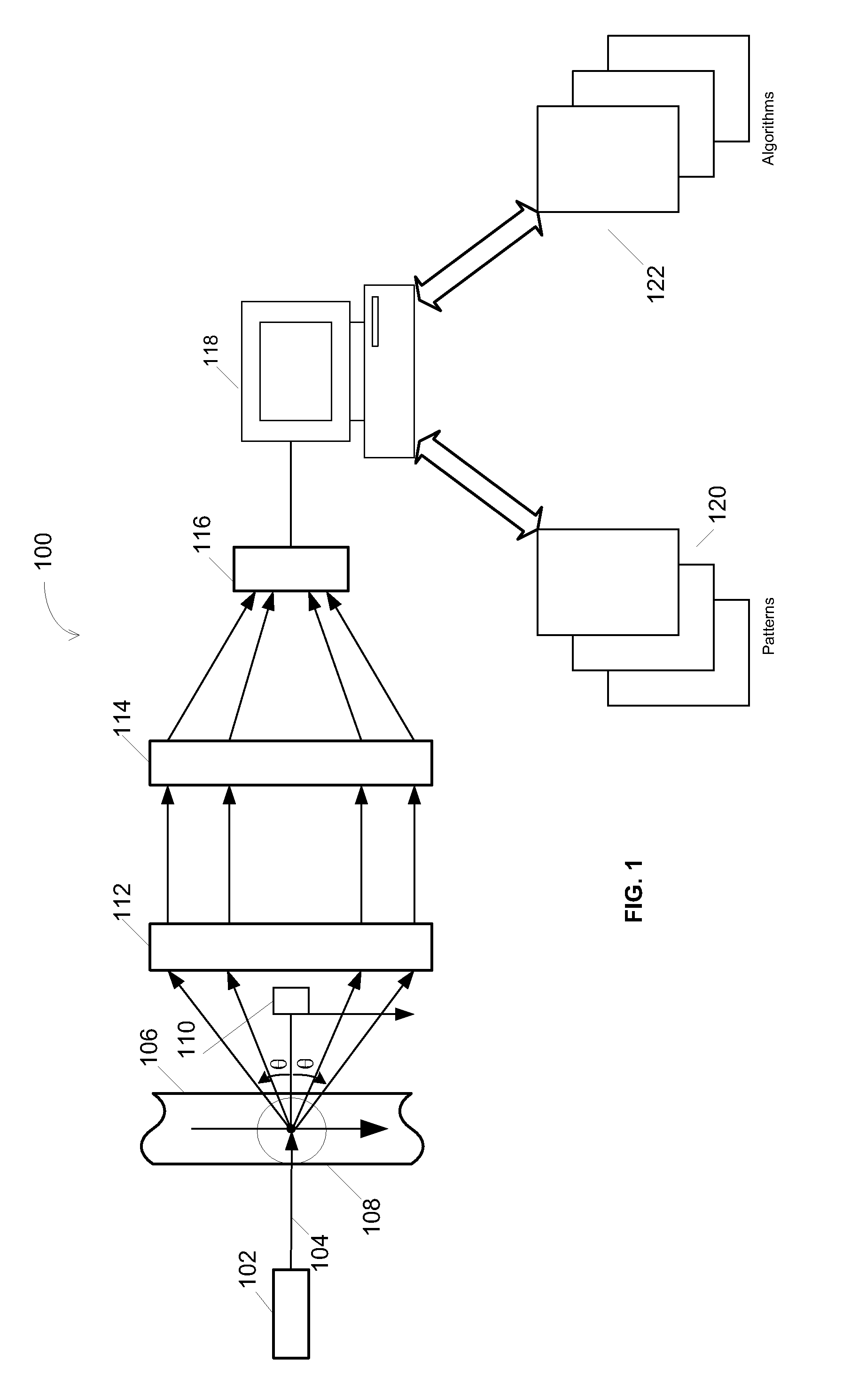
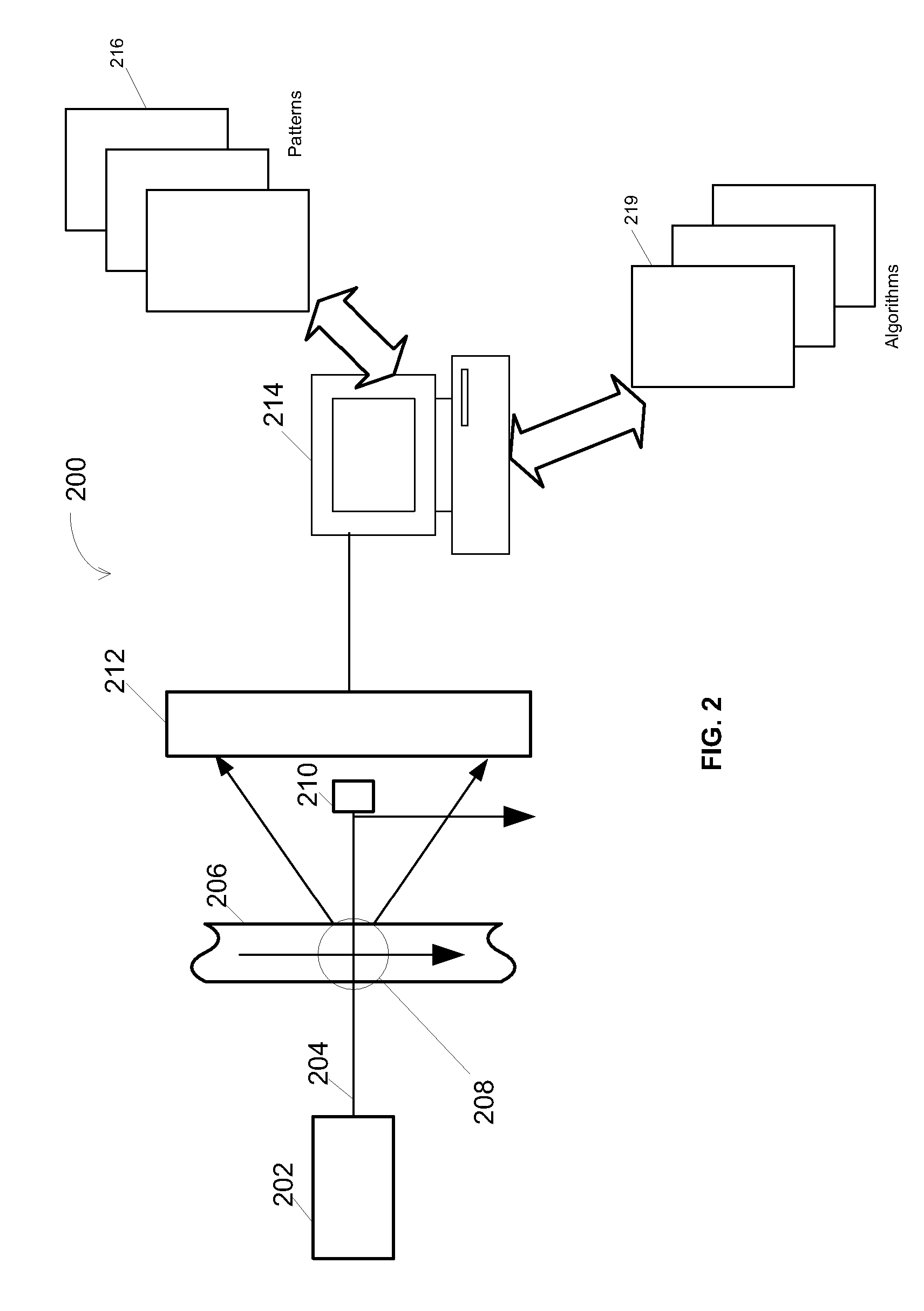
The invention belongs to the technical field of resolving three-dimensional attitude information of an unmanned aerial vehicle and provides a quick three-dimensional attitude information resolving method based on dual polarized light vectors. According to the quick three-dimensional attitude information resolving method, an output characteristic of a polarized light sensor is analyzed, a Rayleighscattering theory is combined, and local time and location information are further combined to calculate out the solar feature point spatial position under a navigation coordination system based on that an output dual polarized light E-vectors are utilized and measured to determine the solar spatial position under a vehicle body coordination system; thus, the purpose of directly resolving a three-dimensional attitude angle in the current moment is achieved, the error transfer phenomenon in an existing resolving method is avoided, and real timeliness and quickness requirements in an unmanned aerial vehicle attitude resolving process are guaranteed. The quick navigation vehicle body three-dimensional attitude resolving method disclosed by the invention can be applied to three-dimensional heading and attitude measurement of polarized light.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of solid simulation body for optical breast imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical engineering and relates to a preparation method of a solid simulation body for optical breast imaging. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving near infrared absorption dye in epoxy resin to prepare absorption mother solution; obtaining the spectral absorption curve of the mother solution, calculating the dosage of the absorption mother solution; calculating the dosage of titanium dioxide required by the simulation body according to the Mie scattering theory; weighting the absorption mother solution, weighting titanium dioxide according to the volume of the required titanium dioxide, mixing titanium dioxide, the absorption mother solution and epoxy resin to fully stir; placing the mixed solution in a vacuum pump, pumping out bubbles; preparing a mould according to the shape and volume of the required simulation body; adding the mixed solution and curing agent in the mould; stirring in a constant speed along one directly to mix evenly; and pumping out bubbles again; and performing low temperature solidification. By adopting the method of the invention, the solid simulation body for optical breast imaging which has stable physical properties and can be stored for long time, can be prepared.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Systems and methods for a multiple angle light scattering (MALS) instrument having two-dimensional detector array
A particle detection system uses a reflective optic comprising a curved surface to detect high angle scattered light generated by a particle in a liquid medium, when a laser beam is incident on the particle. When the particles transit the laser beam, light is scattered in all directions and is described by MIE scattering theory for particles about the size of the wavelength of light and larger or Rayleigh Scattering when the particles are smaller than the wavelength of light. By using the reflective optic, the scattered light can be detected over angles that are greater than normally obtainable.
Owner:JMAR LLC A DELAWARE LLC
Two-dimensional smoke concentration field measuring device based on sheet light source
ActiveCN105588792AReduce distractionsStable supportParticle suspension analysisMeasurement deviceImaging processing
The invention discloses a two-dimensional smoke concentration field measuring device based on a sheet light source. The device comprises a smoke generation device, a laser emission device and a photographing and processing device, wherein the smoke generation device comprises a smoke generation box, a disturbance draught fan, a porous rectification layer, a glass smoke cavity and an optical smoke densimeter; the laser emission device comprises a laser device, a sheet light source lens set, a cylindrical lens, a plurality of upright columns and a guide rail A; the photographing and processing system comprises a CCD camera, an upright column, a guide rail B and a computer, the CCD camera receives scattered light of the sheet light source in the lateral vertical direction, intensities of the scattered light in different positions in a two-dimensional plane are obtained through image processing, a relative two-dimensional smoke concentration field is calculated according to a light scattering theory, and finally obtained data can be calibrated through linear average concentration measured by the linear optical smoke densimeter. Interference to a smoke field is small, smoke with uniform concentration distribution can be generated by means of disturbance and rectifying design, and theoretical research is well supported.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Particulate matter concentration monitoring system on basis of mie scattering theories and method for applying particulate matter concentration monitoring system
InactiveCN106290093AReal-time monitoring of concentration changesHigh measurement accuracyParticle suspension analysisMicrocontrollerSignal processing circuits
Owner:TIANJIN TONGYANG TECH DEV
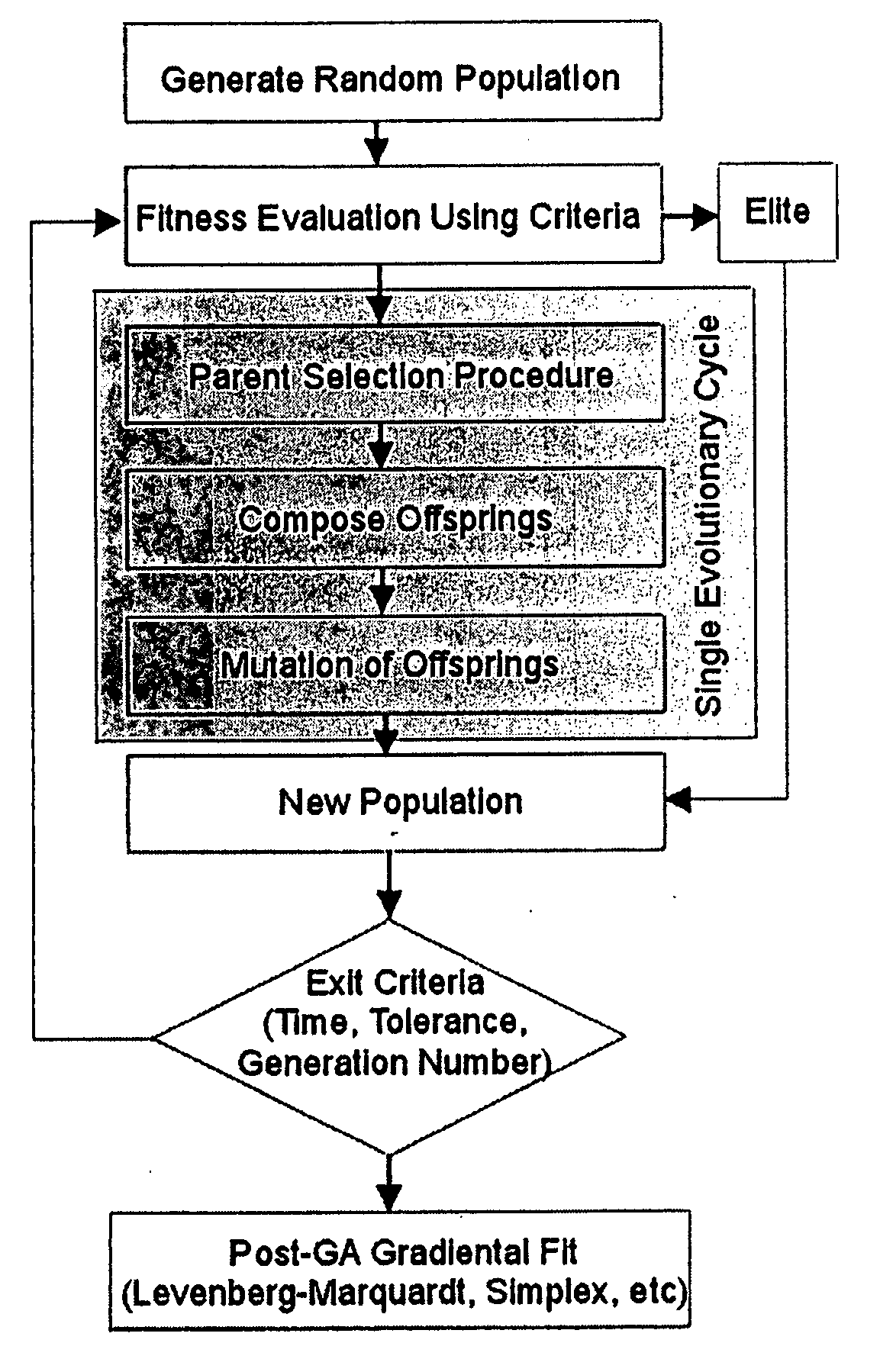
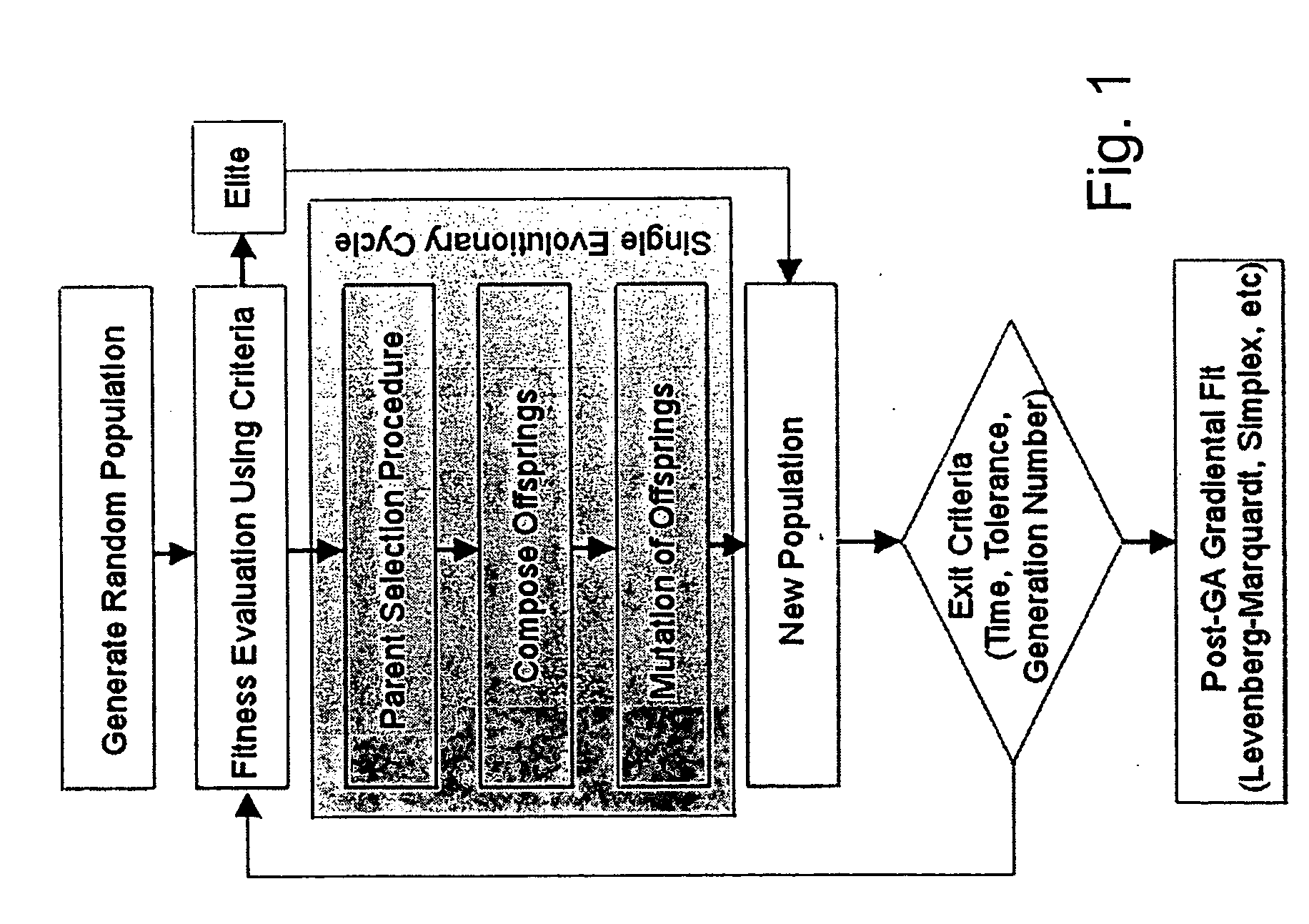
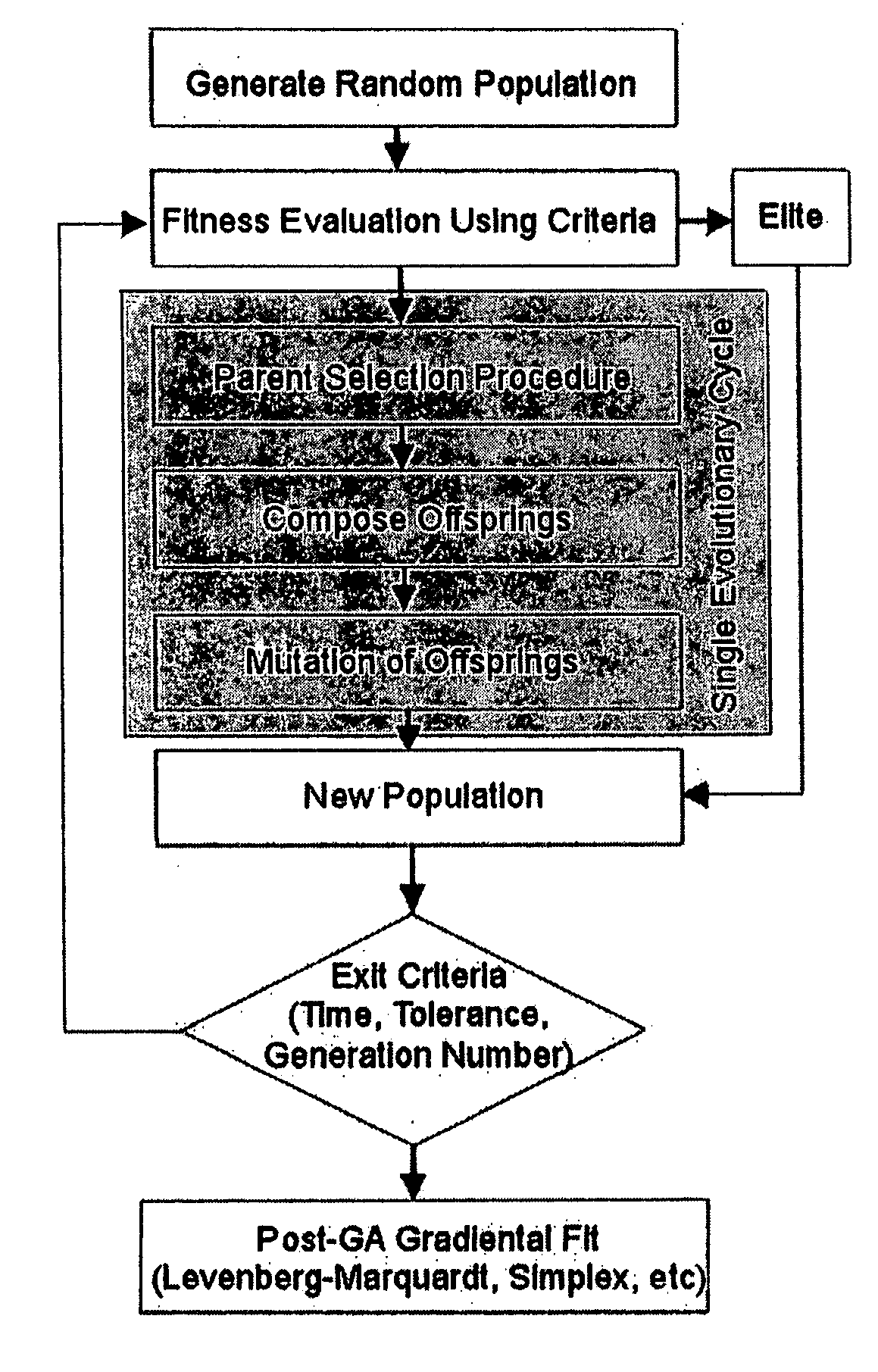
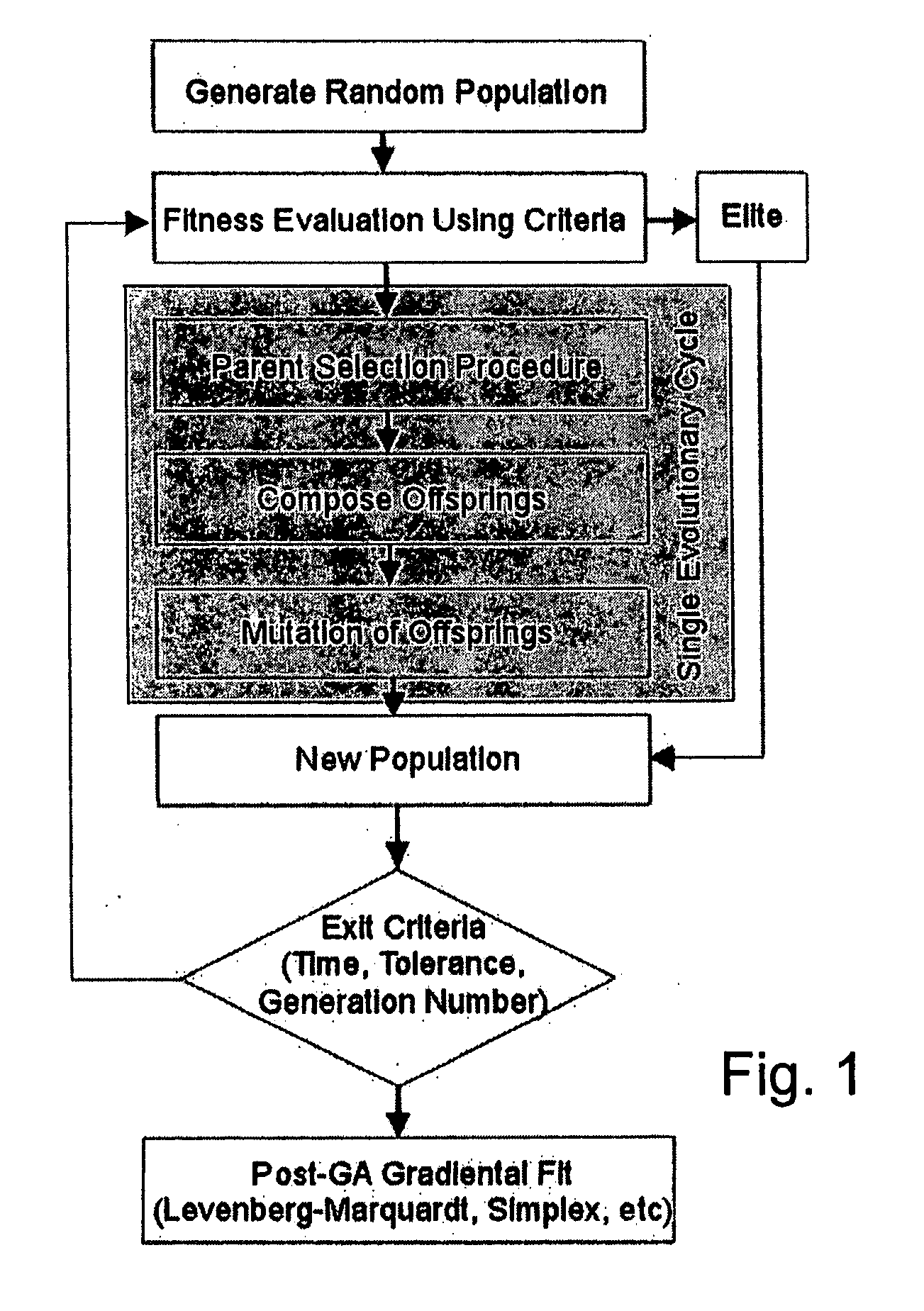
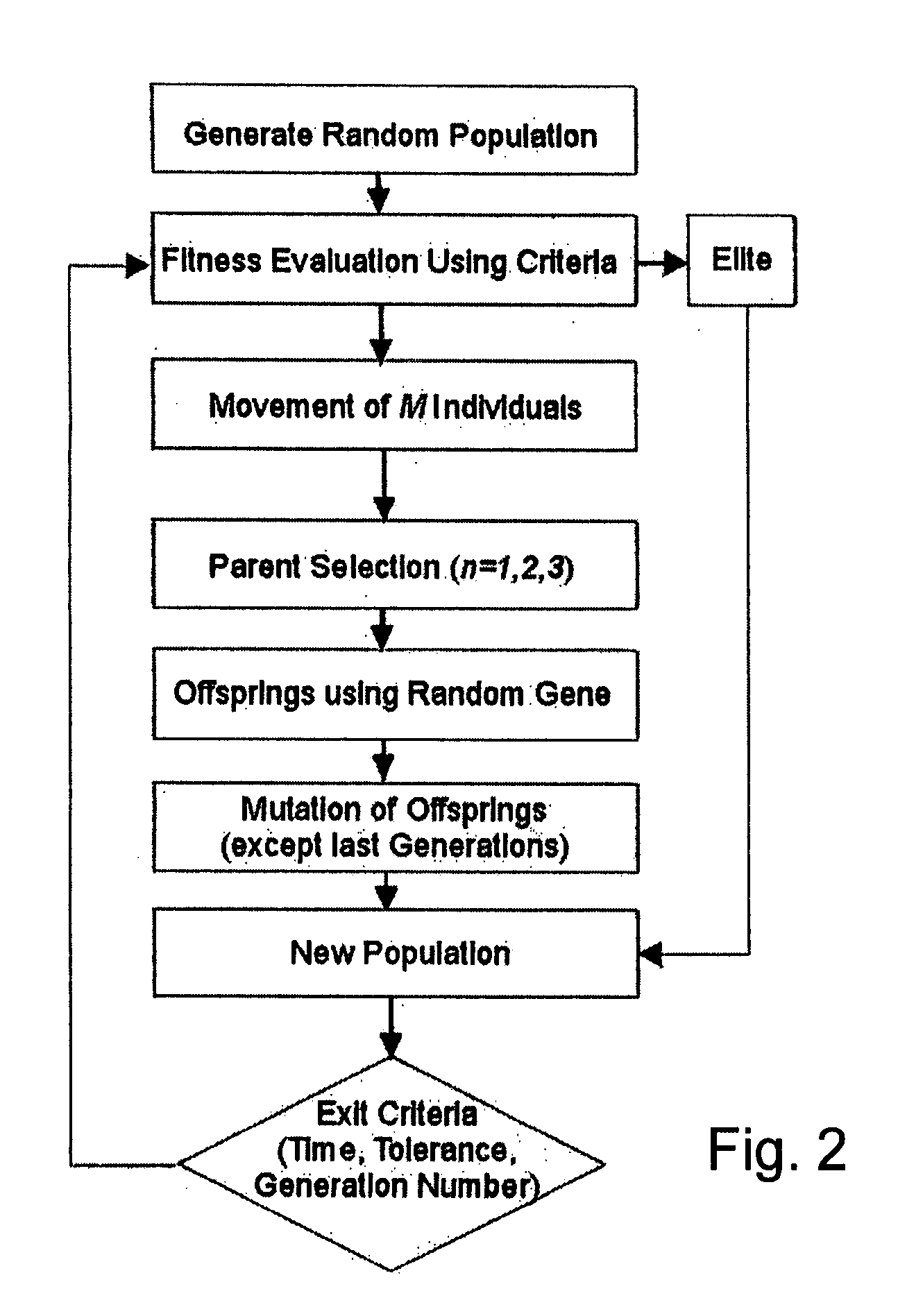
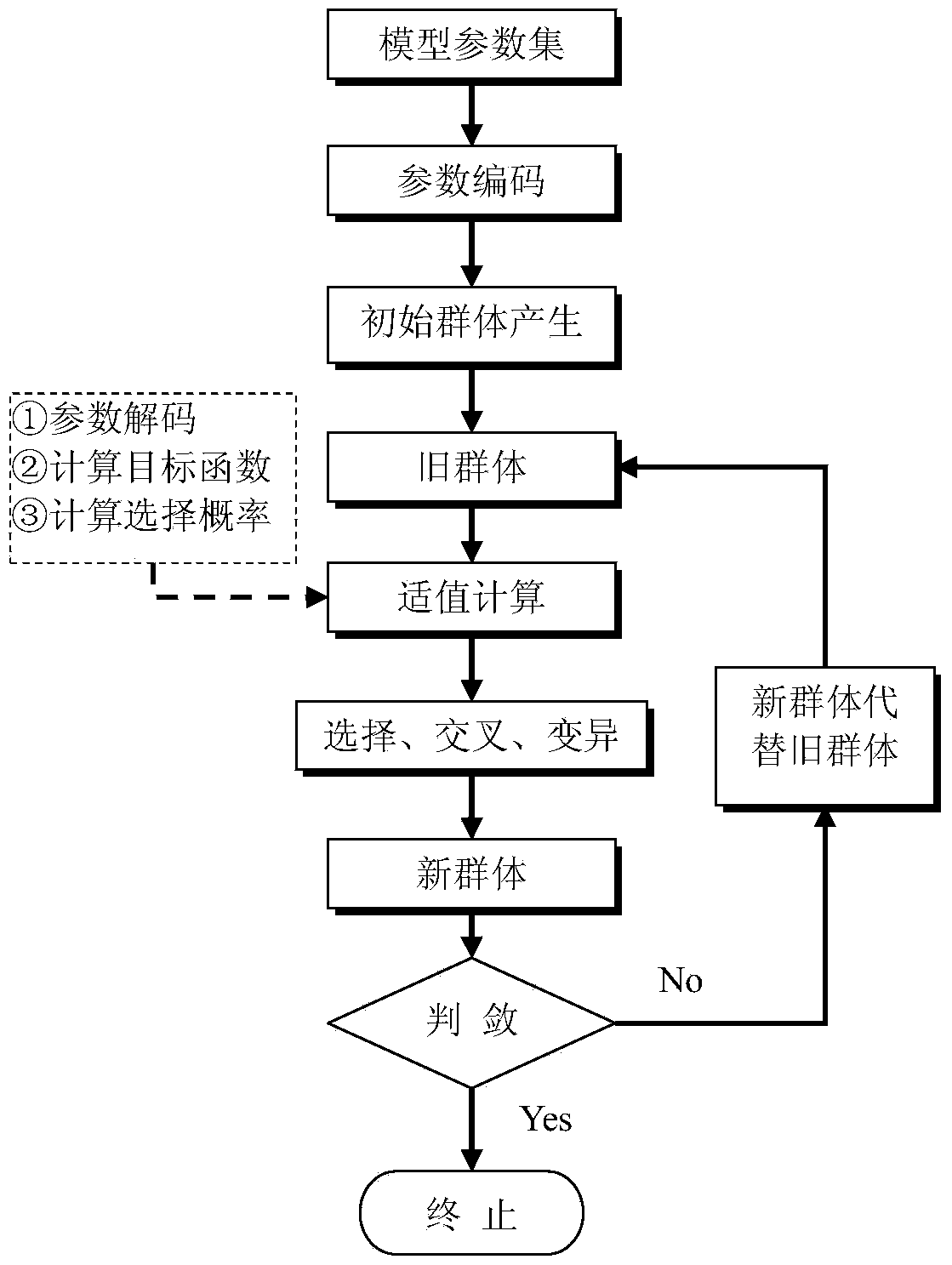
Method of determining parameters of a sample by X-ray scattering applying an extended genetic algorithm including a movement operator
InactiveUS20050074090A1Random changes in the genesQuality improvementMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionGenetic algorithmsGenetic algorithmX-ray
A method of determining parameters of a sample by X-ray scattering comprising the steps of exposing the sample to X-rays and measuring scattered X-ray intensity, generating a parameterized model of the sample which is used for numerical simulation of scattered X-ray intensity on the basis of a physical scattering theory, comparing the experimental and simulated X-ray scattering data to generate an error value, and modifying the parameters of the model by means of a genetic algorithm involving an amount of individuals each with an equal number N of encoded parameters forming a generation and applying the genetic operators of “selection”, “crossover” and “mutation” used for composing successive generations of evolving individuals, is characterized in that from one generation to the next a “movement” genetic operator is applied which moves at least some of the encoded parameters of at least some of the individuals towards the respective encoded parameters of the individual with the smallest error value. The inventive method improves the genetic algorithm such that it can approximate the true sample parameters faster and with better reliability.
Owner:BRUKER AXS
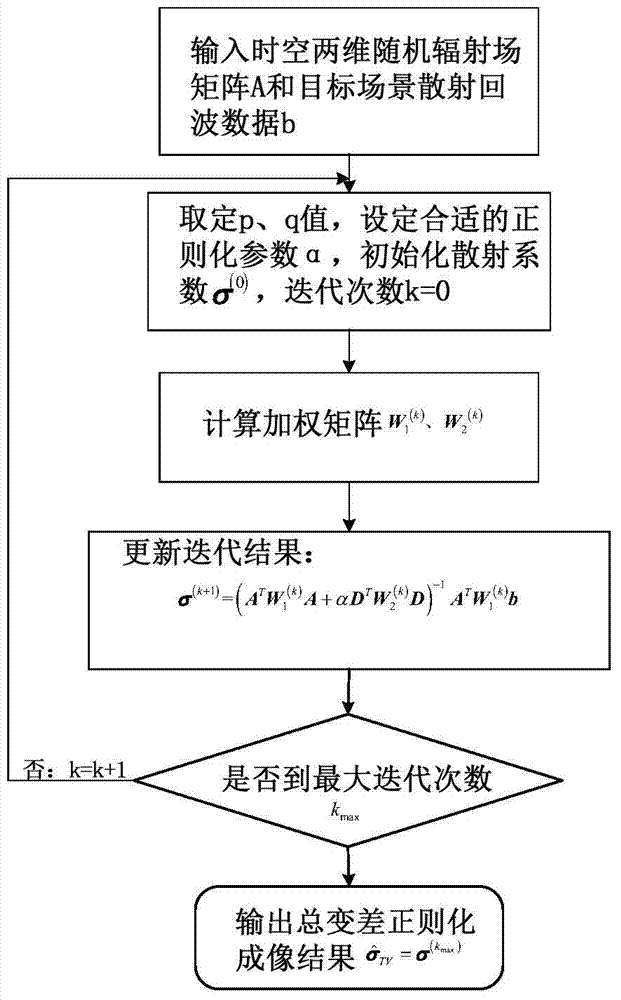
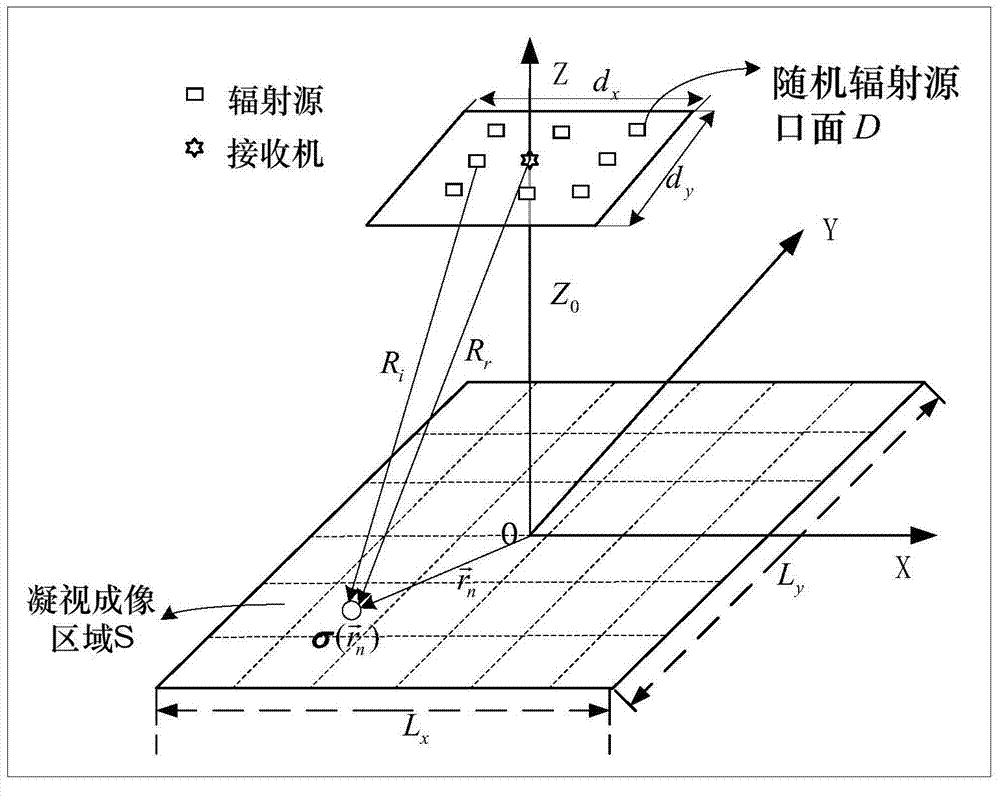
Microwave gazing correlated imaging treatment method convenient in extracting of object contour
The invention discloses a microwave gazing correlated imaging treatment method convenient in extracting of an object contour. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a microwave gazing correlated imaging linear model on the basis of an electromagnetic scattering theory and radar parameters; reconstructing a microwave gazing correlated imaging linear model by virtue of a total variation regularizing method so as to obtain a reconstructed target model of microwave gazing correlated imaging; and setting regularizing parameters and carrying out iterative inversion imaging so as to obtain a microwave gazing correlated inversed image which is stable and is high in definition. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively solving the ill-posed problems of a random radiation field matrix; and the method is conducive to maintaining the edge characteristics of a target, and is especially suitable for an imaging scene which is clear in target outline and keeps a high contrast ratio with the surrounding environment.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
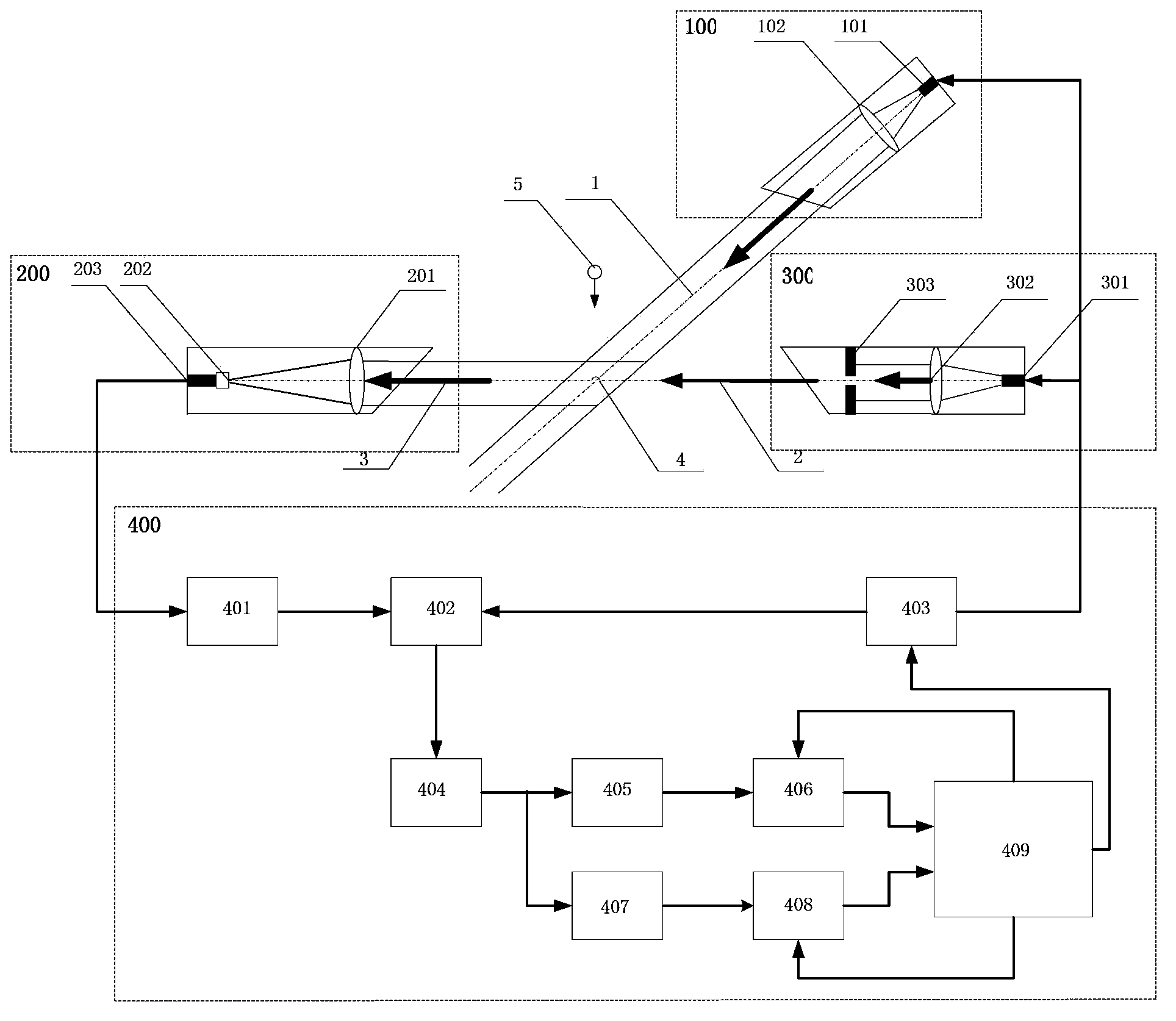
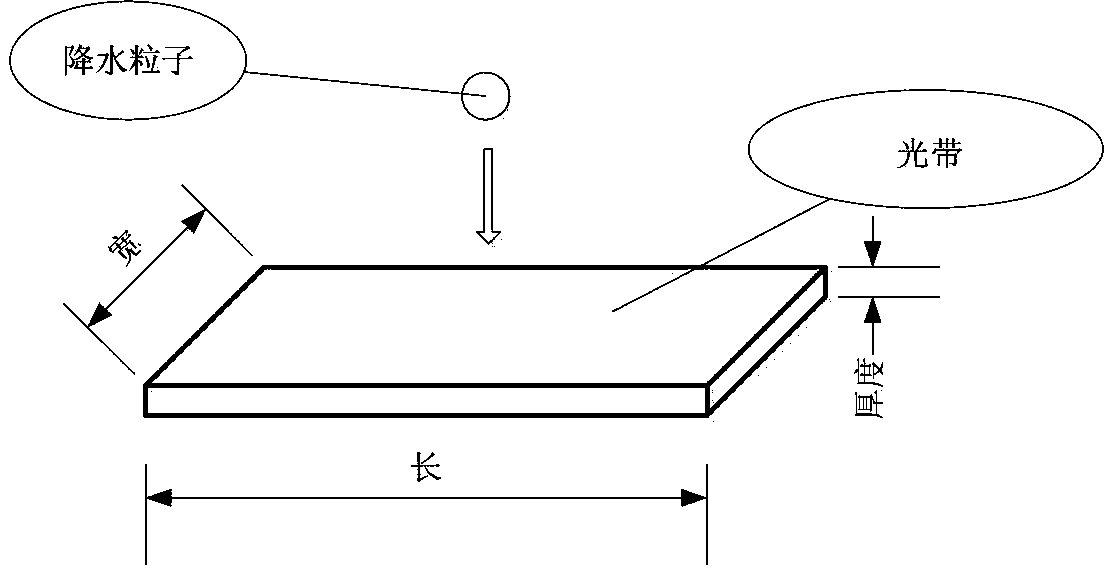
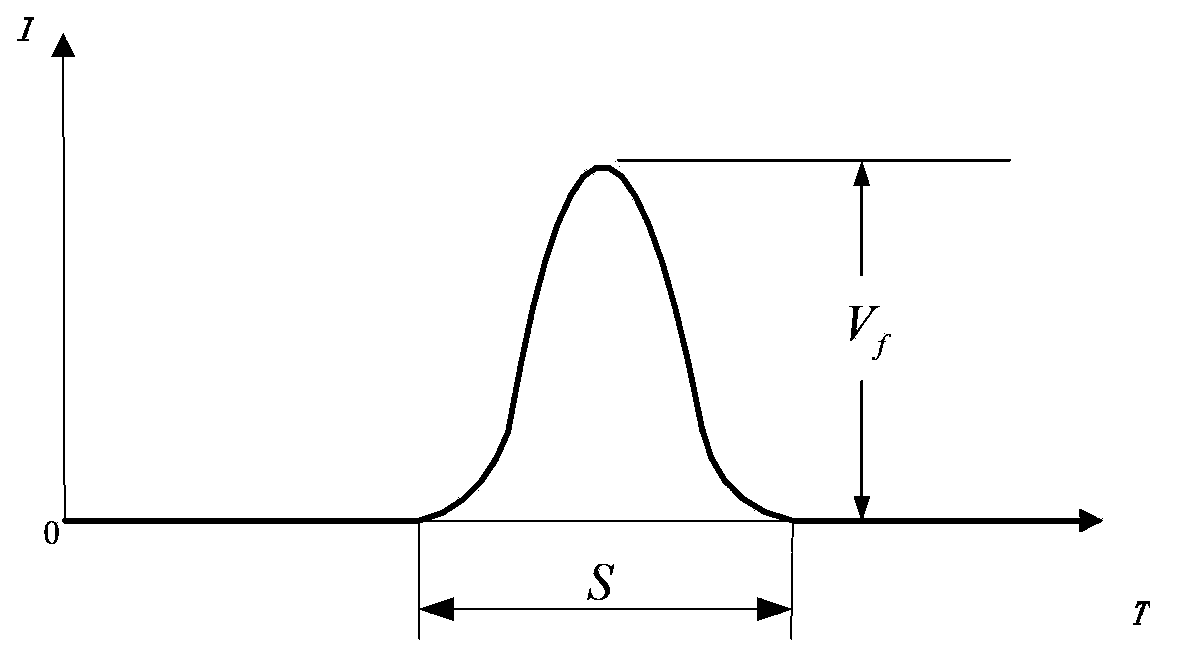
Online observation device and method for weather phenomena based on light attenuation and scattering theory
ActiveCN103399363ARealize automatic online observationEnsure objectivityInstrumentsEngineering researchPrecipitation particle
The invention relates to an online observation device and method for weather phenomena based on a light attenuation and scattering theory. The online observation device adopts an optical-mechanical structure with double light-source transmitting terminals and a single receiving end, and the optical-mechanical structure is as follows: a light source 1 transmits a precise parallel measuring light band; when falling precipitation particles pass through the measuring light band, the falling precipitation particles play a role of blocking and attenuating the light band; a photoelectric conversion signal is analyzed, so that the falling speed of the precipitation particles and the information of particle sizes can be obtained, the judgment to a precipitation weather phenomenon is realized, and the information such as precipitation intensity and raindrop spectrum can be provided; a light source 2 transmits a collimated measuring light beam; the scattering light intensity in an angle of horizontal 45 degrees of atmospheric particles in a sampling area on the light beam is detected, so that atmospheric visibility is reflected, and the identification of a visible weather phenomenon is realized. The device and the method realize the online automatic observation of a variety of weather phenomena, avoid adverse factors such as subjectivity in manual observation to cause observed results to be more accurate, timely, complete and integrated, have real significances on corresponding sciences such as meteorology, agriculture and environmental protection and engineering researches, and are widely applied to the fields of meteorological service observation, traffic safety scheduling, prevention and reduction of agricultural disasters, air quality monitoring and the like.
Owner:合肥中科环境监测技术国家工程实验室有限公司
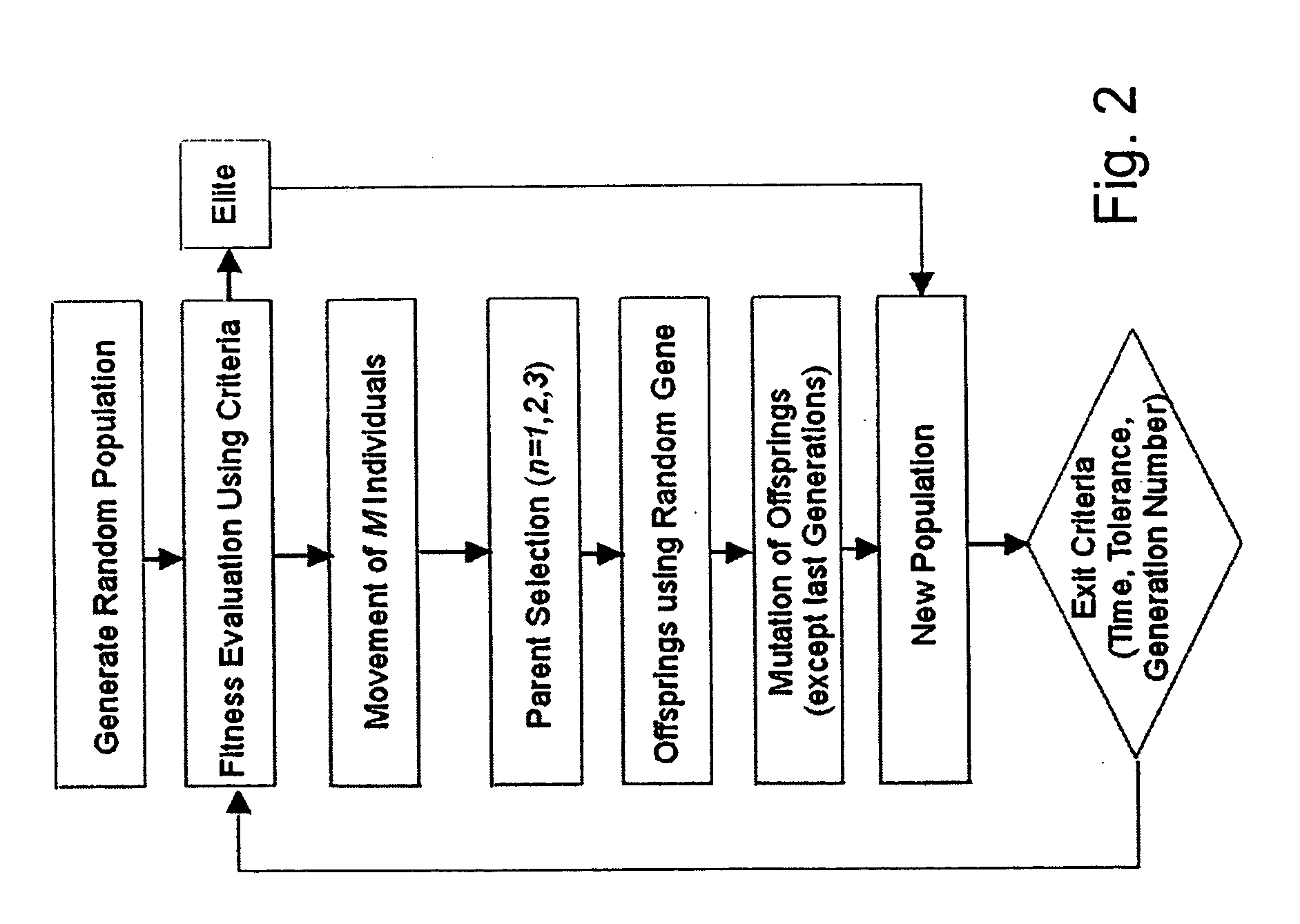
Method of determining parameters of a sample by X-ray scattering applying an extended genetic algorithm with truncated use of the mutation operator
InactiveUS20050074097A1Improve accuracyRandom changes in the genesX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionMutation operatorGenetic algorithm
A method of determining parameters of a sample by X-ray scattering comprising the steps of exposing the sample to X-rays and measuring scattered X-ray intensity, generating a parameterized model of the sample which is used for numerical simulation of scattered X-ray intensity on the basis of a physical scattering theory, comparing the experimental and simulated X-ray scattering data to generate an error value and modifying the parameters of the model by means of a genetic algorithm involving an amount of individuals each with an equal number N of encoded parameters forming a generation and applying the genetic operators of “selection”, “crossover” and “mutation” used for composing successive generations of evolving individuals, is characterized in that after a given number k of successive generations the genetic operator of “mutation” is no longer applied in evolution of further generations. The inventive method improves the genetic algorithm such that it can approximate the true sample parameters faster and with a higher accuracy.
Owner:BRUKER AXS
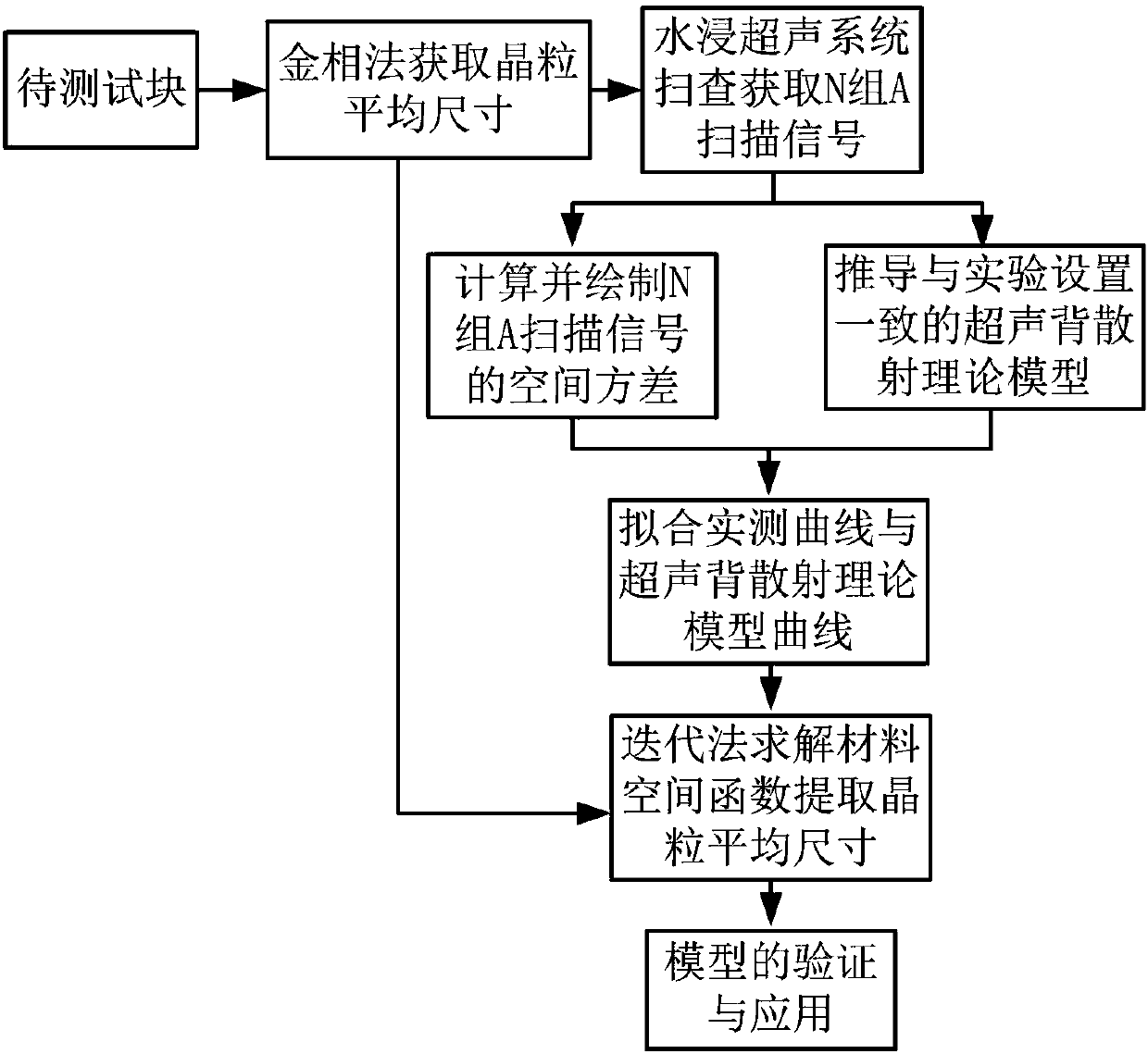
Crystal grain size averaging method based on polycrystalline material extraction by effective ultrasonic backscatter signal
ActiveCN107941907AImprove accuracyIncreased sensitivityAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationCorrelation function
The invention provides a crystal grain size averaging method based on polycrystalline material extraction by an effective ultrasonic backscatter signal, which belongs to the field of ultrasonic nondestructive characterization. The method comprises the following steps: a water immersion ultrasonic scanning system having a full-waveform storage function and a water immersion ultrasonic focusing probe are employed for collecting an A scanning signal of a reference test block; then a space variance of the A scanning signal is calculated through MATLAB, and an actual measurement experiment curve isobtained; a ultrasonic backscatter theoretical model coupled with a practical detection system; finally, the actual measurement experiment curve and a ultrasonic backscatter theoretical model curve are subjected to fitting, a material space correlation function corresponding to a reference test block is solved by an iterative method is employed, and an average size of the crystal grain can be extracted, a solution scheme is provided for the average crystal grain size of the ultrasonic nondestructive characterization of a polycrystalline material, and the method has good application prospect and popularization value.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method of obtaining spectrum distribution of aerosol particles based on integrating nephelometer
ActiveCN103196872AEasy to implementReasonable theoretical analysisScattering properties measurementsSuperimpositionTurbidity
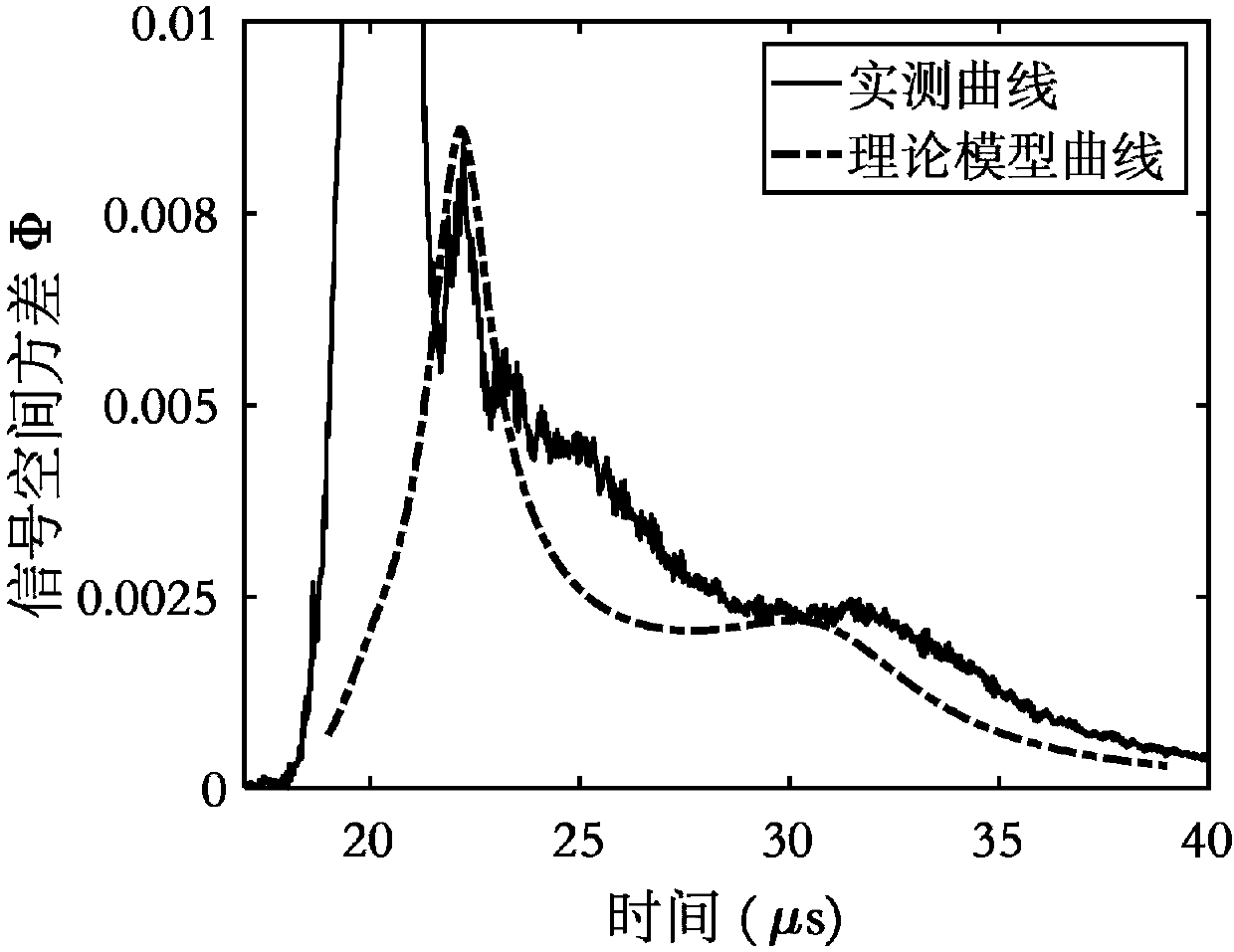
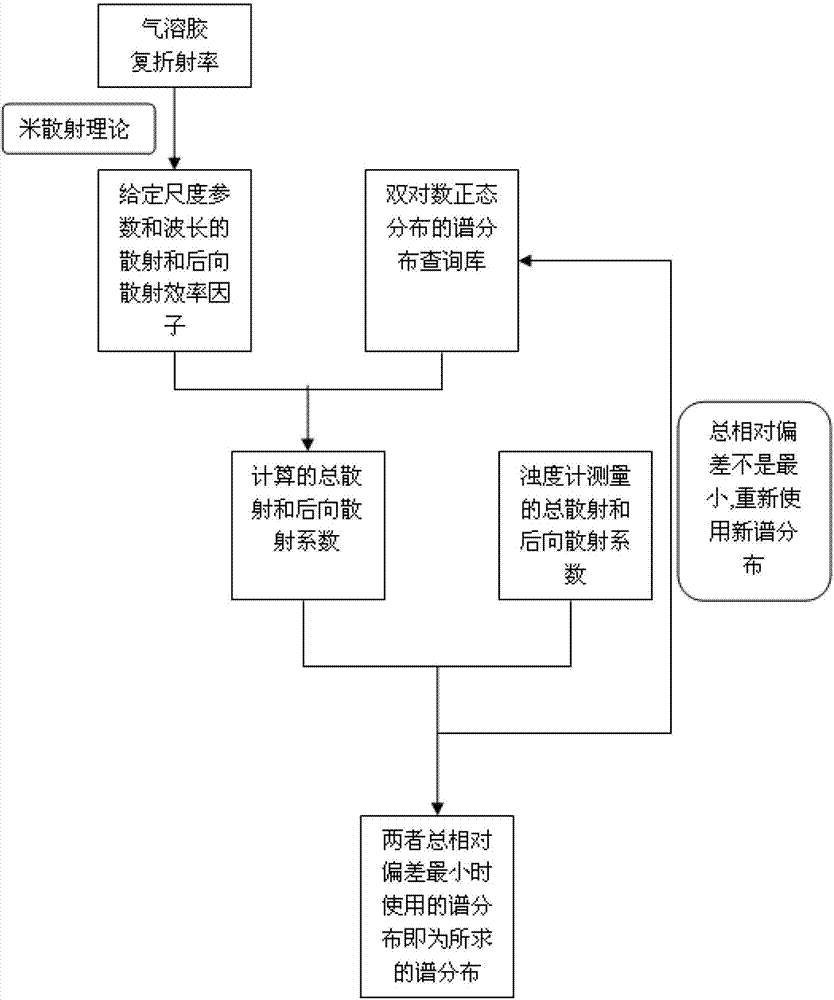
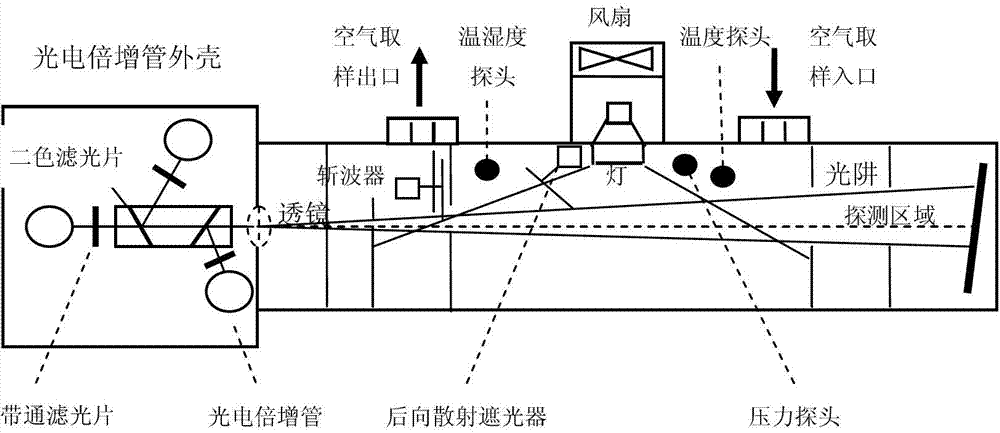
The invention discloses a method of obtaining a spectrum distribution of aerosol particles based on an integrating nephelometer. The method comprises measuring a total scattering coefficient of the aerosol at 7-170 DEG and a backscattering coefficient of the aerosol at 90-170 DEG through the integrating nephelometer, obtaining calculated values of the total scattering coefficient and the backscattering coefficient of corresponding angle ranges based on an assumption that the spectrum distribution of aerosol particles is two lognormal distribution superimpositions and a Mie scattering theory, and analyzing relative deviations of the measured values and the calculated values. A spectrum distribution with a minimum relative deviation is the spectrum distribution of the aerosol particles.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Systems and methods for a multiple angle light scattering (MALS) instrument having two-dimensional detector array
InactiveUS7616311B2Material analysis by optical meansParticle size analysisRayleigh scatteringLiquid medium
A particle detection system uses a reflective optic comprising a curved surface to detect high angle scattered light generated by a particle in a liquid medium, when a laser beam is incident on the particle. When the particles transit the laser beam, light is scattered in all directions and is described by MIE scattering theory for particles about the size of the wavelength of light and larger or Rayleigh Scattering when the particles are smaller than the wavelength of light. By using the reflective optic, the scattered light can be detected over angles that are greater than normally obtainable.
Owner:JMAR LLC A DELAWARE LLC
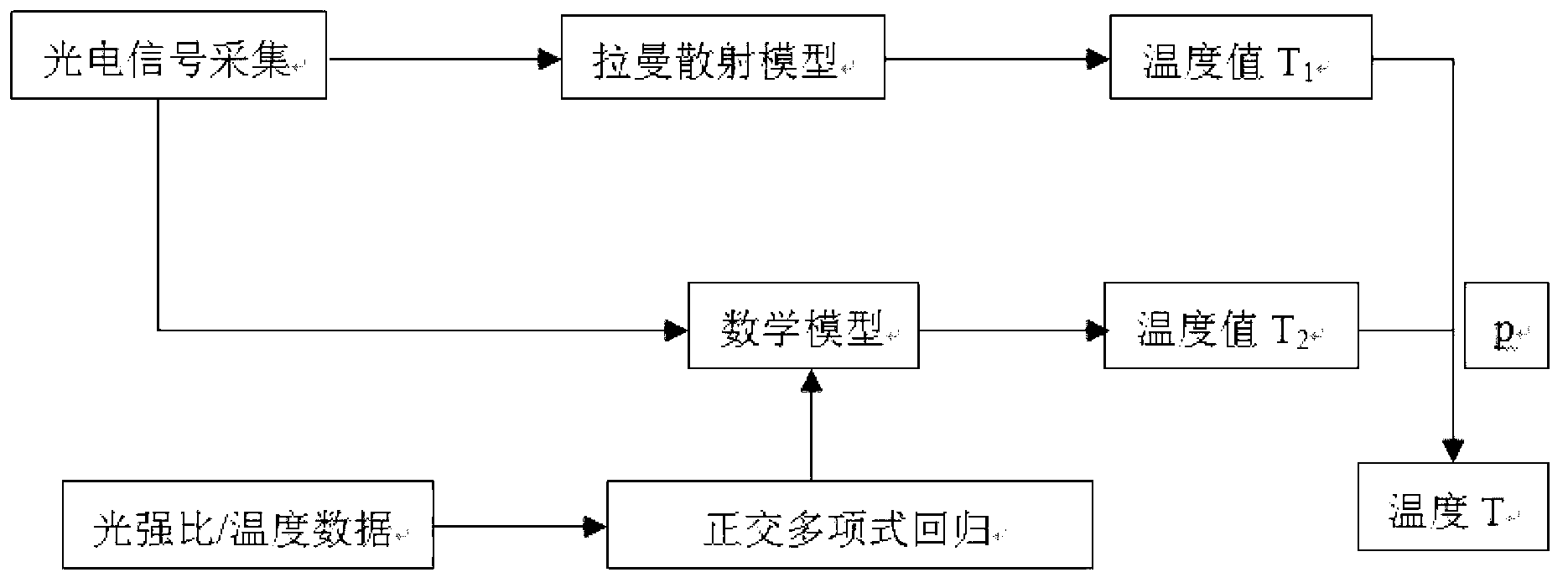
Distributed type optical fiber temperature measuring method
ActiveCN103256999AHigh precisionIncrease flexibilityThermometers using physical/chemical changesComputational physicsRaman scattering
The invention discloses a distributed type optical fiber temperature measuring method which comprises the following steps: a, adopting a plurality of pre-measured light intensity ratios of an optical fiber and a plurality of pre-measured temperature data of the optical fiber, carrying out fitting through an orthogonal polynomial regression method, obtaining a fitting curve, establishing an orthogonal polynomial model, b, measuring light intensity data at a measured position of the optical fiber, calculating first temperature through the light intensity data based on the Raman scattering theoretical model, calculating second temperature through the orthogonal polynomial model, and confirming temperature of the measured position based on the first temperature and the second temperature. Compared with a regular optical fiber temperature measuring method, the distributed type optical fiber temperature measuring method can effectively improve accuracy of temperature measuring results.
Owner:SHENZHEN YINGTANG SOFTWARE TECH
Systems and methods for a multiple angle light scattering (MALS) instrument having two-dimensional detector array
InactiveUS20070046938A1Material analysis by optical meansParticle size analysisRayleigh scatteringLiquid medium
A particle detection system uses a reflective optic comprising a curved surface to detect high angle scattered light generated by a particle in a liquid medium, when a laser beam is incident on the particle. When the particles transit the laser beam, light is scattered in all directions and is described by MIE scattering theory for particles about the size of the wavelength of light and larger or Rayleigh Scattering when the particles are smaller than the wavelength of light. By using the reflective optic, the scattered light can be detected over angles that are greater than normally obtainable.
Owner:JMAR LLC A DELAWARE LLC
Method and device for monitoring flight speeds of air vehicle and environmental parameters thereof
ActiveCN109990843AReduce the impactAvoid influenceElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationLow speedLine width
The invention discloses a method and a device for monitoring flight speeds of an air vehicle and environmental parameters thereof. The emitted laser of a single-longitudinal mode narrowband laser interacts with the air to generate Rayleigh-Brillouin scattering, a Rayleigh-Brillouin scattering spectral line is measured by using a heterodyne method of a multi-longitudinal mode laser with a wide radiation line width, the atmospheric molecular density and the temperature information of the environment where the air vehicle is located are obtained by combining the gas scattering theory with a model, meanwhile different flight speeds of the air vehicle are measured according to the Doppler effect, and finally, multiple parameters are simultaneously measured accurately. The method and the devicedisclosed by the invention have the advantages of simultaneously and accurately monitoring multiple parameters from ow speed to high speed and from low altitude to high altitude in real time in all weathers, high sensitivity and high temporal-spatial resolution.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
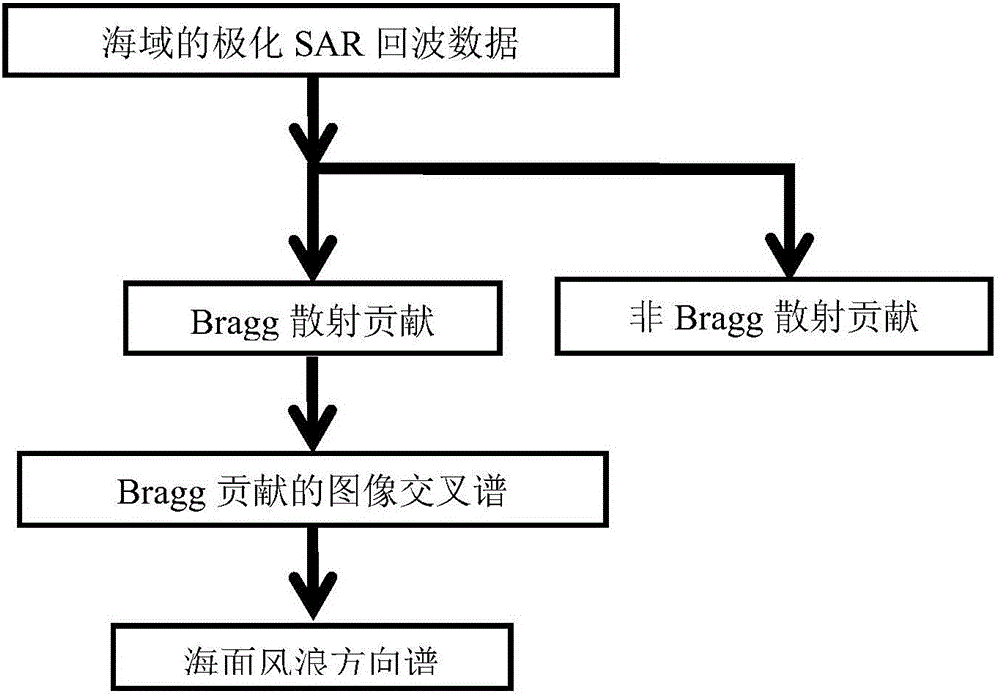
Method for resolving sea level stormy wave spectrum by means of full-polarized SAR echo data
InactiveCN106501804ASolve nonlinear problemsResolution directionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSea wavesDecomposition
The invention provides a method for resolving a sea level stormy wave spectrum by means of full-polarized SAR echo data. The method is based on decomposition of a sea level scattering mechanism of polarized SAR measured data. The method comprises the steps of performing polarization decomposition on the full-polarized SAR echo data; according to a coherent polarization decomposition theory and a sea level scattering theory, by means of a Bragg scattering theory model, separating simple Bragg scattering contribution from the full-polarized SAR echo data; and using the echo component which is concentrated by Bragg scattering into calculation of an image cross spectrum, thereby analyzing a directional spectrum of sea level stormy wave frequency band which corresponds with Bragg scattering except for a stormy wave cut-off frequency. The method for resolving the sea level stormy wave spectrum by means of the full-polarized SAR echo data is characterized by comprising the technical processes of (1), a polarization decomposition method of full-polarized SAR sea level echo data; and (2), a spectrum characteristic analysis method of Bragg scattering contribution.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
SPAMS actual measurement-based non-linear inversion method of optical parameters of uniform spherical particles of aerosol based on
InactiveCN104266943AEasy to convergeAvoid the situationParticle size analysisIndividual particle analysisOptical propertyComputational physics
The invention discloses a SPAMS actual measurement-based non-linear inversion method of optical parameters of uniform spherical particles of aerosol. The non-linear inversion method comprises the following steps: detecting PSL balls with different particle diameters and known optical property parameters by adopting an SPAMS, and obtaining the scattering intensity of the actually-measured PSL balls by averaging; simultaneously, combining geometrical parameters of an ellipsoidal reflector of the SPAMS and a single-particle uniform spherical model according to a Mie scattering theory to obtain the optical scattering theory response of the PSL balls; carrying out the linear combination on the optical scattering theory response and the scattering intensity obtained by the actual measurement so as to obtain a linear relation of actually-measured scattering data and theory scattering data; applying the obtained linear relation in atmospherical single-particle scattering data in the SPAMS actual measurement, so as to obtain corresponding the Mie theory scattering intensity; and carrying out the non-linear inversion fitting on the Mie theory scattering intensity so as to obtain the optical property parameters. The non-linear inversion method disclosed by the invention is high in efficiency and accurate, is applied in the SPAMS, and can be widely applied in the field of the atmospheric environment science.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
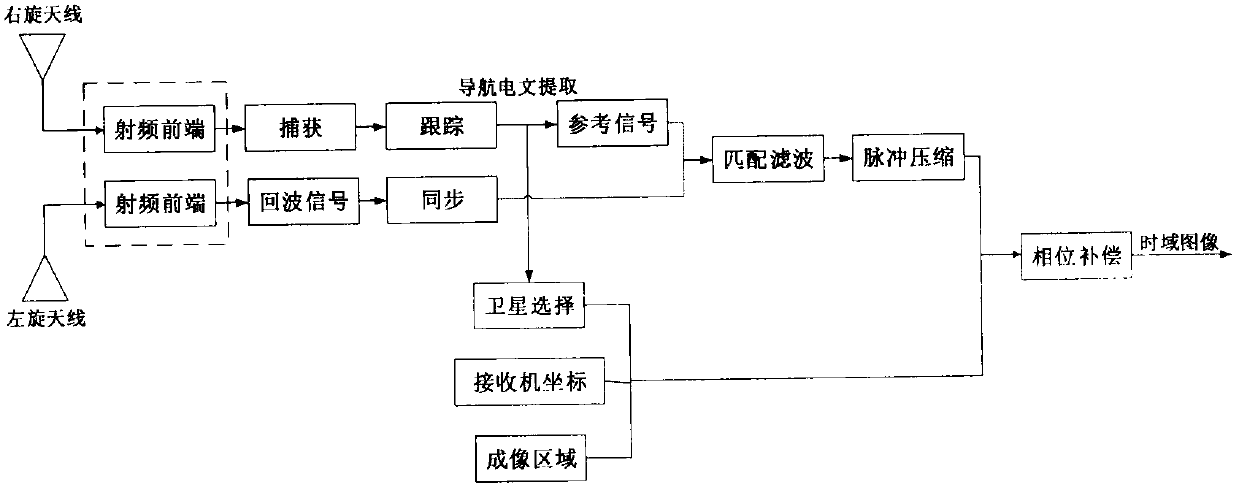
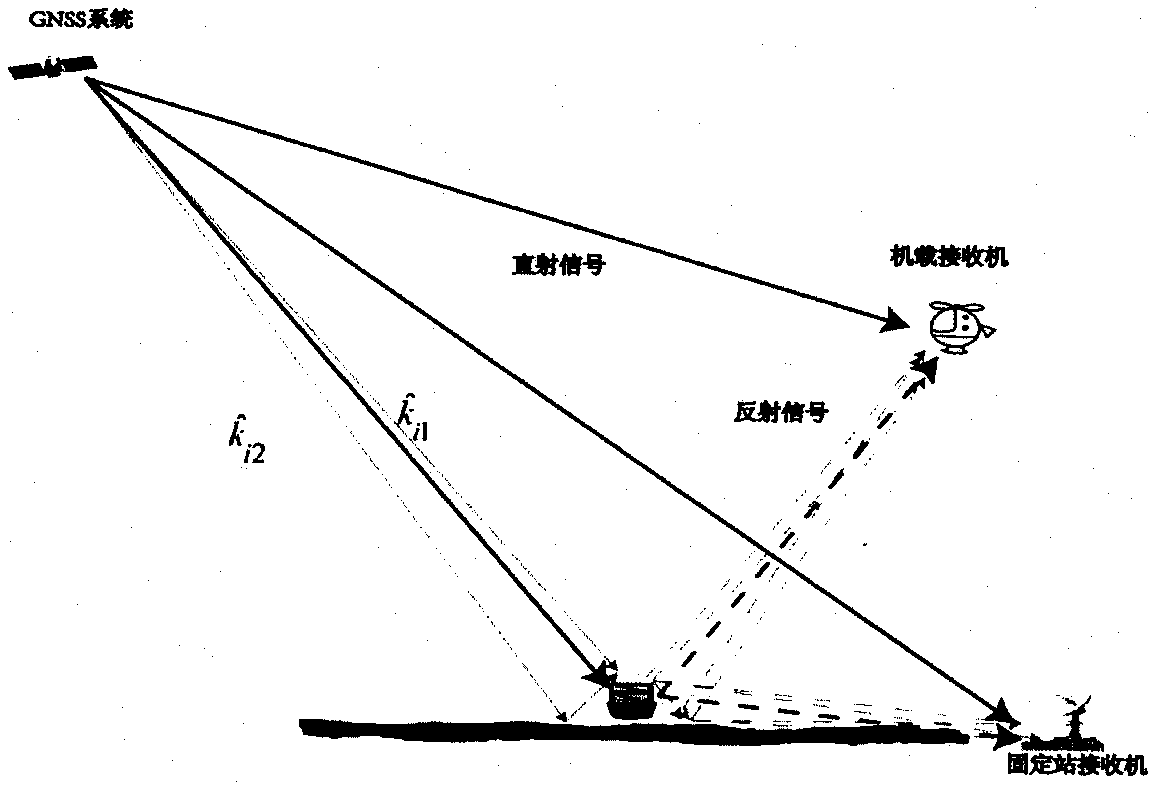
GNSS-SAR imaging simulation model based on traditional high-frequency electromagnetic scattering theory
PendingCN109917377AAccurate calculationIncrease authenticitySatellite radio beaconingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSignal sourceScattering theory
The invention discloses a GNSS-SAR imaging simulation model based on traditional high-frequency electromagnetic scattering theory with very high applicability. The model is combined with a physical optical method and a four-path method in a traditional composite electromagnetic scattering calculation model, GNSS signals are used as a signal source, and electromagnetic scattering data of an imagingscene are calculated. On the basis of electromagnetic scattering data calculation, imaging simulation is carried out on a sea surface scene by utilizing a backward projection algorithm in a syntheticaperture radar imaging algorithm.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
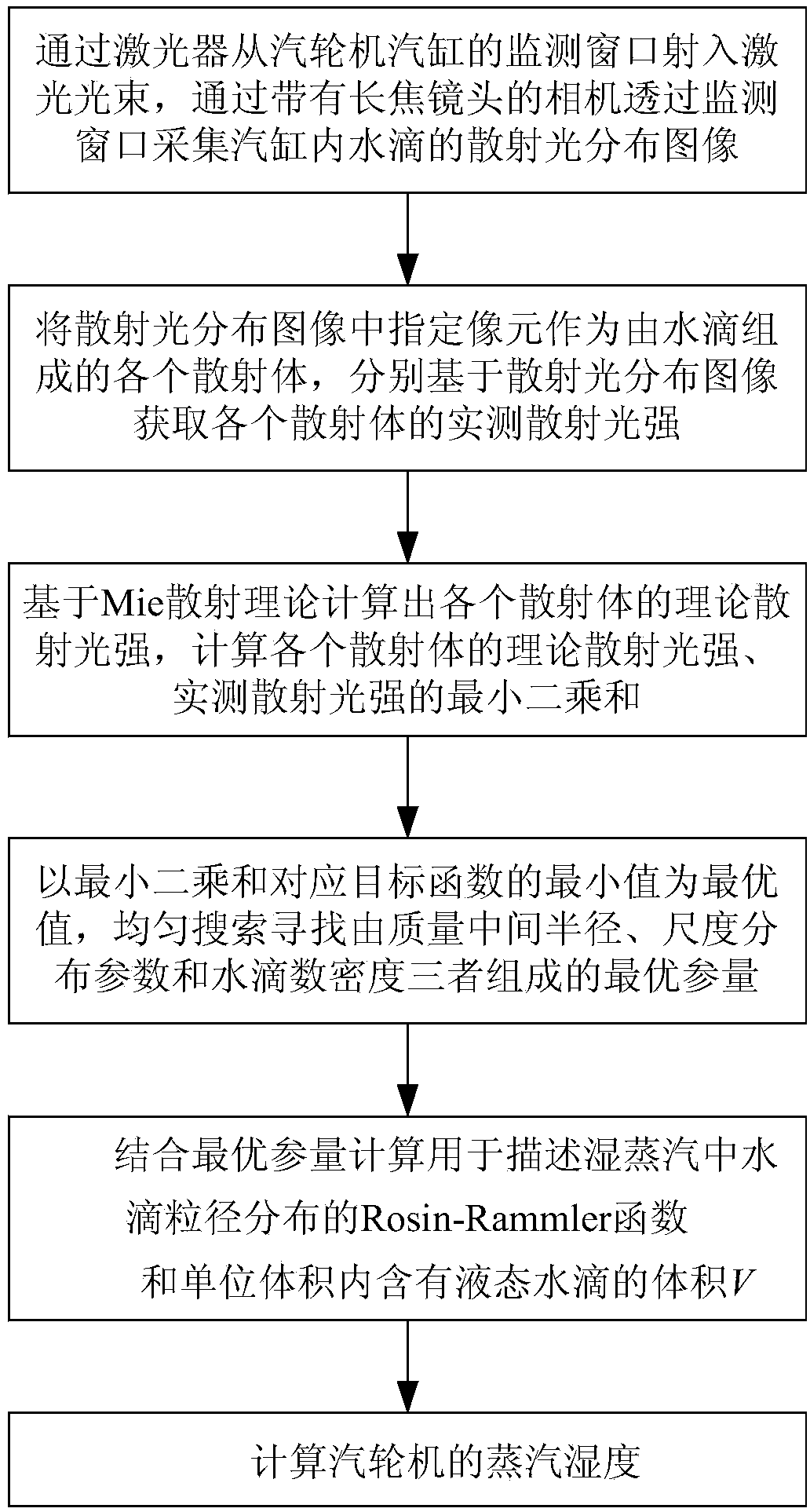
Method for measuring steam humidity of steam turbine based on Mie scattering theory
InactiveCN104089929ADoes not affect normal operationReal-time monitoring of particle size changesScattering properties measurementsLiquid waterNumber density
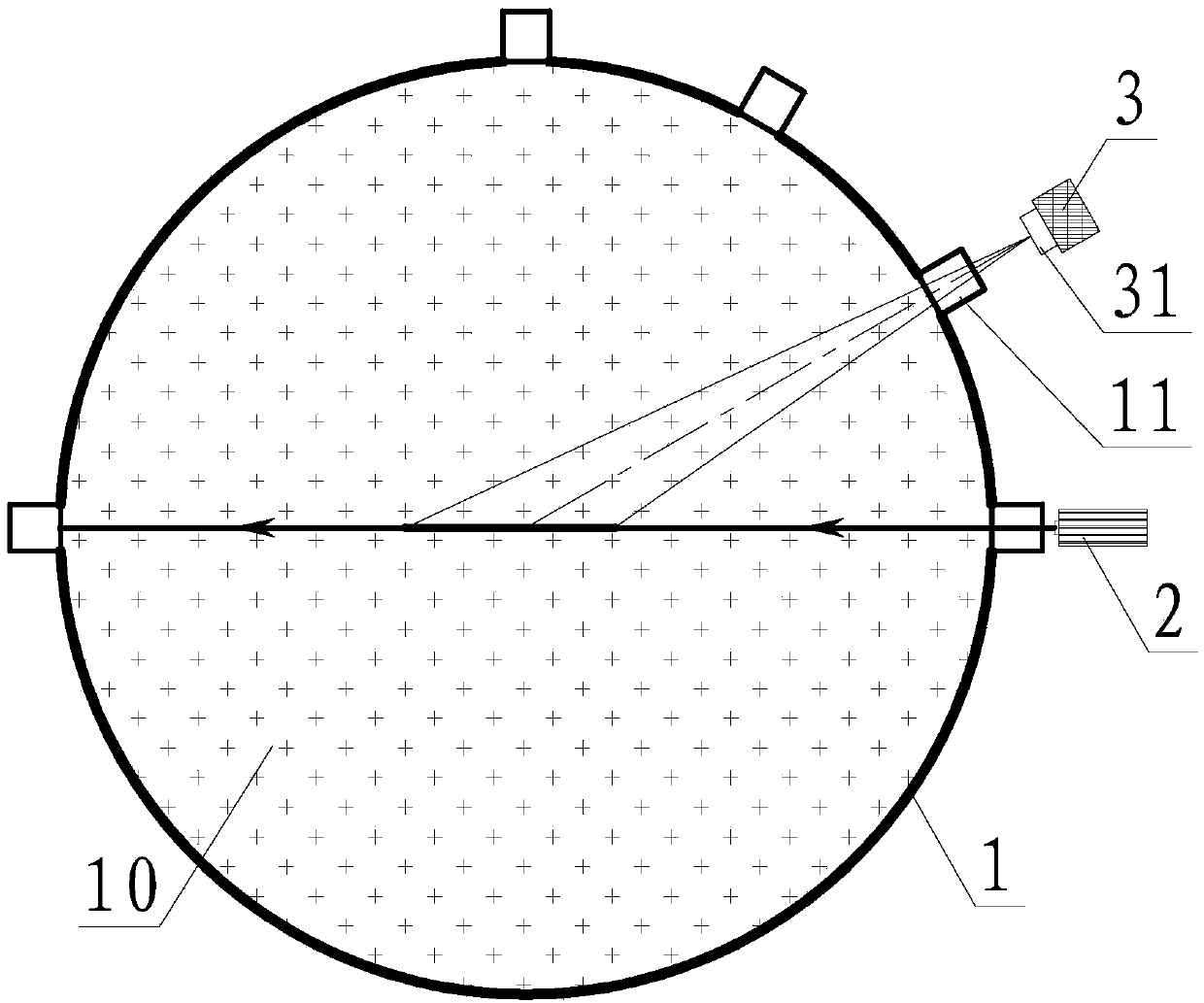
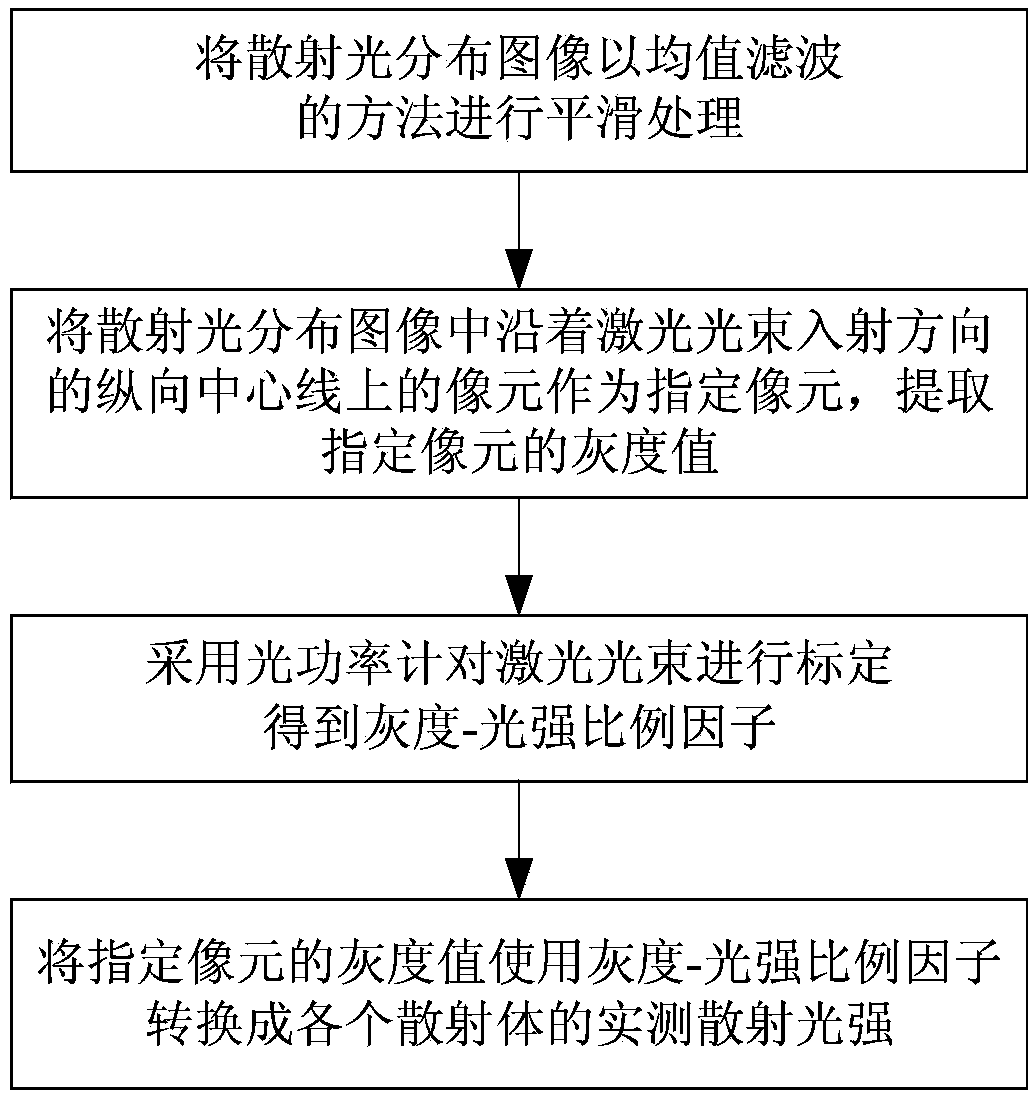
The invention discloses a method for measuring steam humidity of a steam turbine based on a Mie scattering theory. The method comprises the following steps: (1) allowing laser beams to come into a monitoring window of a steam turbine cylinder through a laser, acquiring a distribution image of scattered light, and acquiring the actual measured scattered light intensity of each scattering body based on the distribution image of the scattered light; (2) calculating theoretical scattered light intensity of each scattering body based on the Mie scattering theory, calculating least squares of the theoretical scattered light intensity and the actual measured scattered light intensity of each scattering body, and uniformly searching and finding the optimal parameters consisting of mass median radius, size distribution parameter and water droplet number density; (3) combining the optimal parameters to calculate a Rosin-Rammler function and the volume of liquid water droplets contained in unit volume; (4) calculating the steam humidity of the steam turbine. The method has the advantages of non-contact, wide range, accuracy, real-time property, high safety, high reliability and simplicity and convenience in use.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Rapid microorganism detection equipment based on Mie scattering and spatial light modulator
ActiveCN105259143ARealize the collectionImprove general performanceScattering properties measurementsCuvetteSpatial light modulator
The invention discloses rapid microorganism detection equipment based on Mie scattering and a spatial light modulator. The equipment comprises a laser, an optical system, a detector spherical array frame, a cuvette and photoelectric detectors, wherein laser beam emitted by the laser forms parallel light after being collimated and is converged by the optical system and irradiated to a microorganism sample in the cuvette, a microorganism emits scattered light to the space after irradiated by the laser light, the scattered light is received by photoelectric detectors surrounding the sample pool, a computer performs analysis and calculation on received optoelectronic signals on the basis of the Mie scattering theory, and the form of the current microorganism can be detected in real time. Microorganisms are rapidly detected in real time by the device, the detection speed and accuracy are improved by means of the optical scattering principle, and signals are acquired, processed and analyzed in real time in the acquisition process.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Method for preparing prefabricated rod of gradation type plastic optical fiber
This invention relates to a process method of a graded plastic fiber prebar which is to process polymer core bar with pretty high refractive index to be swelled and infiltrated in monomer solution. According to scatter theory, small molecules will form concentration gradient on the polymer bar radius then turn to refractive index gradient after polymerization. Monomer mixed proportion is to be altered in solution and prepare serial monomer solution to increase refractive index components steadily then the polymer bar will be swelled and infiltrated in monomer solution and solidified after polymerization. After finishing the above steps and polymerization, plastic fiber prebar is to be processed with refractive index similar to parabola distributed along radius.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
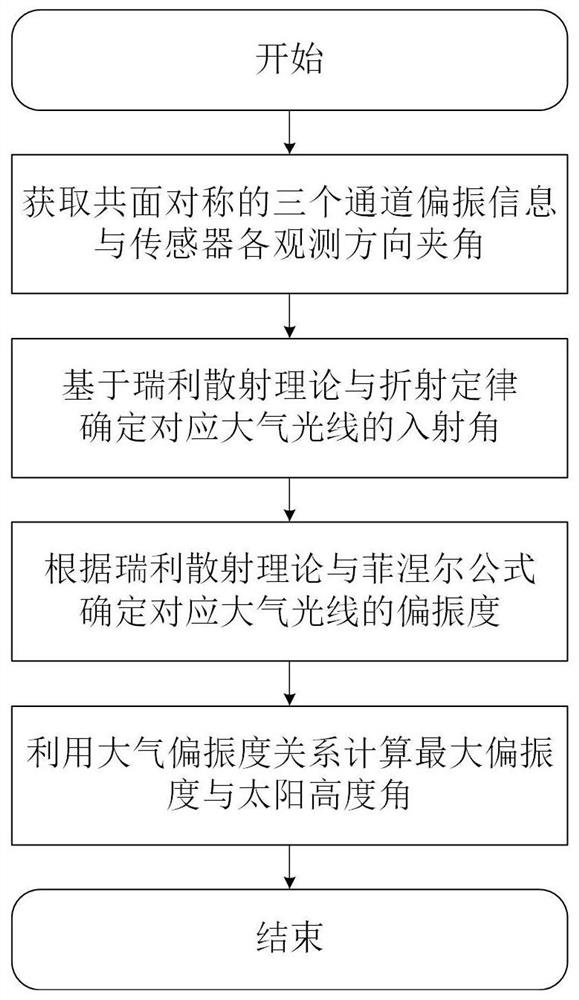
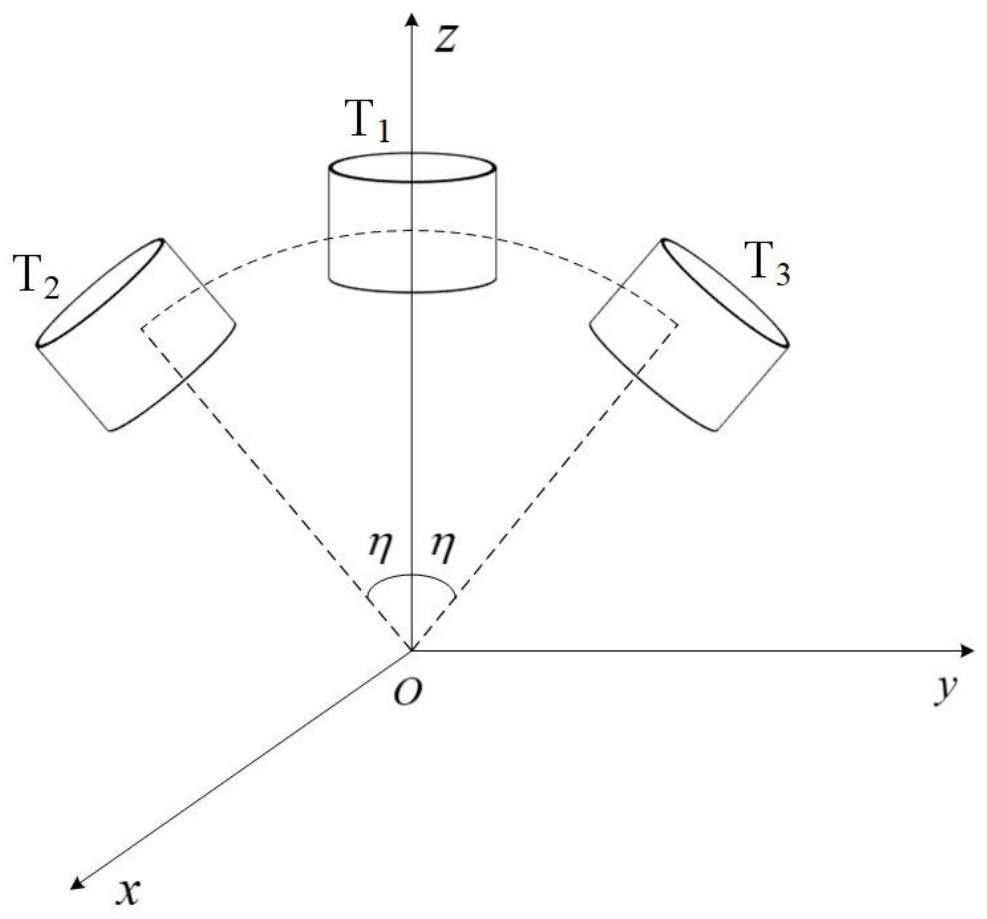
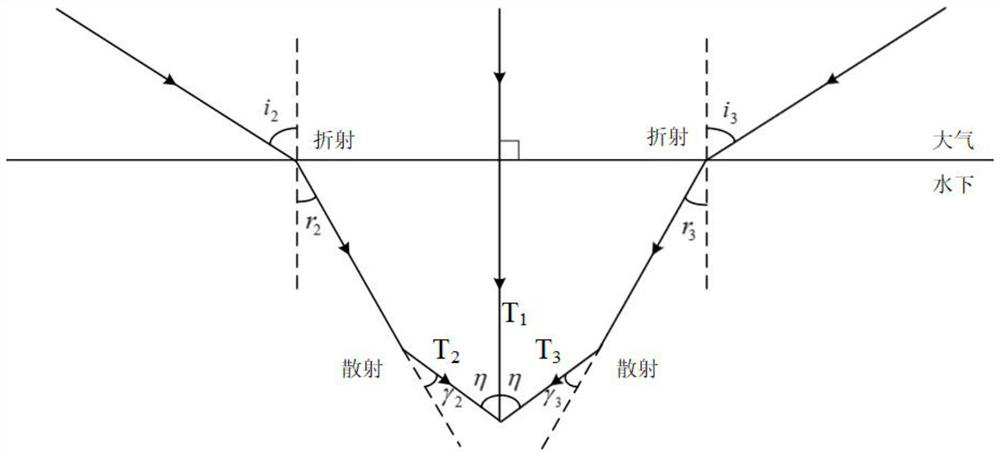
Sun height resolving method based on underwater refraction and scattering coupling polarization degree
ActiveCN112461191AImprove environmental adaptabilityAngle measurementComplex mathematical operationsRayleigh scatteringAngle of incidence
The invention relates to a sun height resolving method based on underwater refraction and scattering coupling polarization degree. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, designing a compound-eye-imitating multi-directional underwater polarization sensor, defining an included angle of observation directions of the sensor, and acquiring underwater polarization degree and underwater polarization azimuth angle information of the polarization sensor in three observation directions; then determining an incident angle of atmospheric light entering the sensor based on a Rayleigh scatteringtheory and a refraction law, analyzing light propagation direction changes in scattering and refraction processes; determining the atmospheric polarization degree of light incident to each observation direction of the sensor by utilizing a Rayleigh scattering theory and a Fresnel theorem; and finally, calculating the maximum polarization degree according to the polarization degree constraint relationship in the atmosphere, and determining the solar altitude angle. According to the invention, the sun height angle resolving method based on the underwater refraction and scattering coupling polarization degree mode under the horizontal attitude is established, and can be used for navigation and positioning of an underwater carrier.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for controlling optical force which radial isotropic nanowire is subjected to
The invention discloses a method for controlling optical force which a radial isotropic nanowire is subjected to. Researches show that optical force which the radial isotropic nanowire is subjected to meets the Rayleigh's law, but the optical force which the radial isotropic nanowire is subjected to has abnormal behaviors under the conditions of non-Rayleigh disappearance and non-Rayleigh divergence. According to the method, according to the full-wave electromagnetic scattering theory and Maxwell stress tensor integral method, by utilizing changes of incident wave vectors, the optical force which the radial isotropic nanowire is subjected to is controlled. The optical force which the radial isotropic nanowire is subjected to can be enhanced or weakened by adjusting nanowire isotropic parameters. The method for controlling the optical force which the radial isotropic nanowire is subjected to can be used for capturing nano particles, and is favorable for practical application of a radial isotropic nanowire material.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Anode active material and battery
InactiveCN1797819AIncrease capacityExcellent cycle characteristicsNegative electrodesLi-accumulatorsIndiumNiobium
A battery with a high capacity and superior cycle characteristics and an anode active material used for it are provided. An anode contains an anode active material capable of reacting with lithium. The anode active material contains tin, cobalt, and carbon, and further contains at least one from the group consisting of indium, niobium, germanium, titanium, molybdenum, aluminum, phosphorus, and bismuth. Further, in the anode active material, the carbon content is from 9.9 wt % to 29.7 wt %, and the ratio of cobalt to the total of tin and cobalt is from 30 wt % to 70 wt %. Further, coordination number of cobalt as a first neighboring atom around tin obtained by the radial structure function calculated based on one scattering theory of X-ray absorption spectroscopy is 4 or less.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com