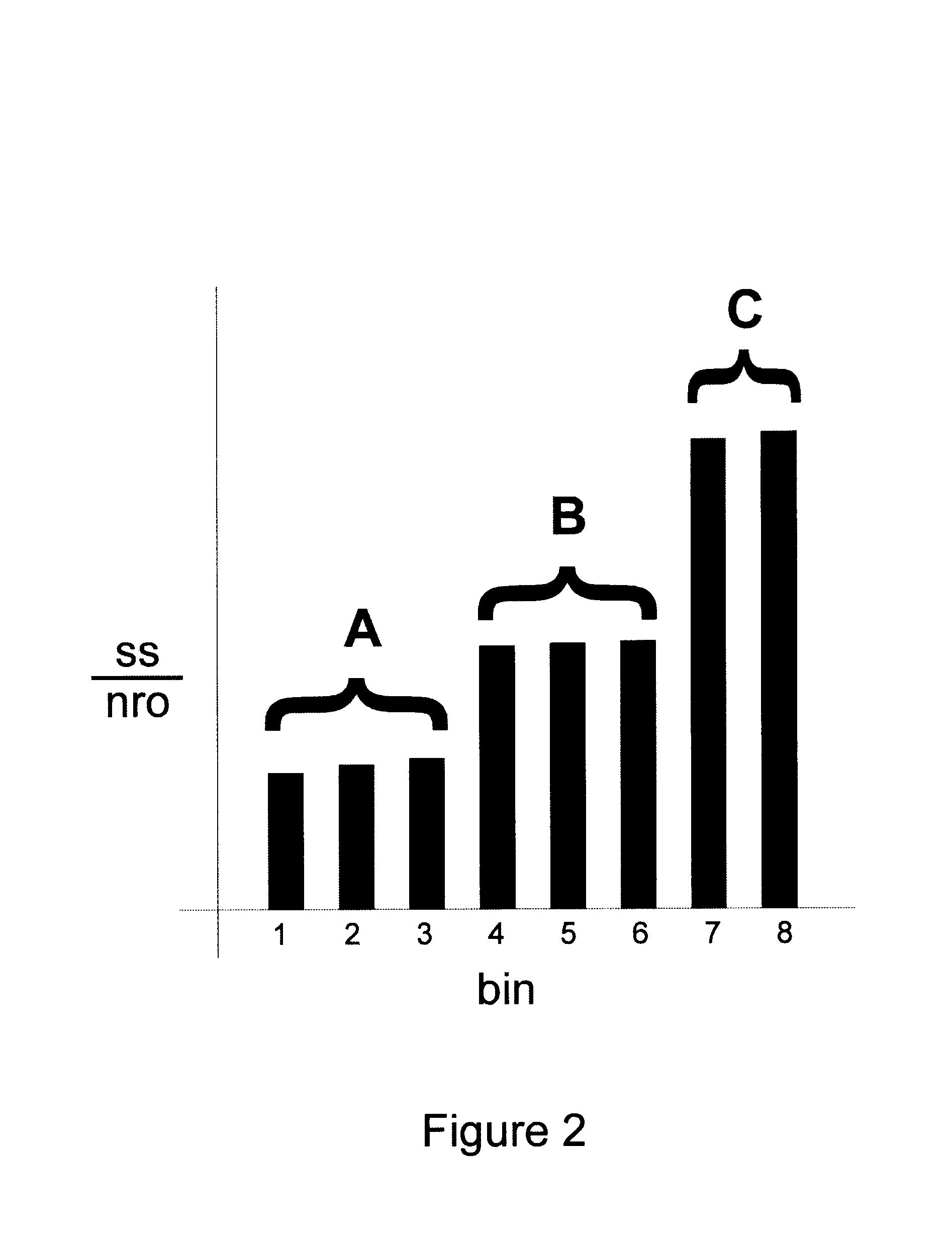
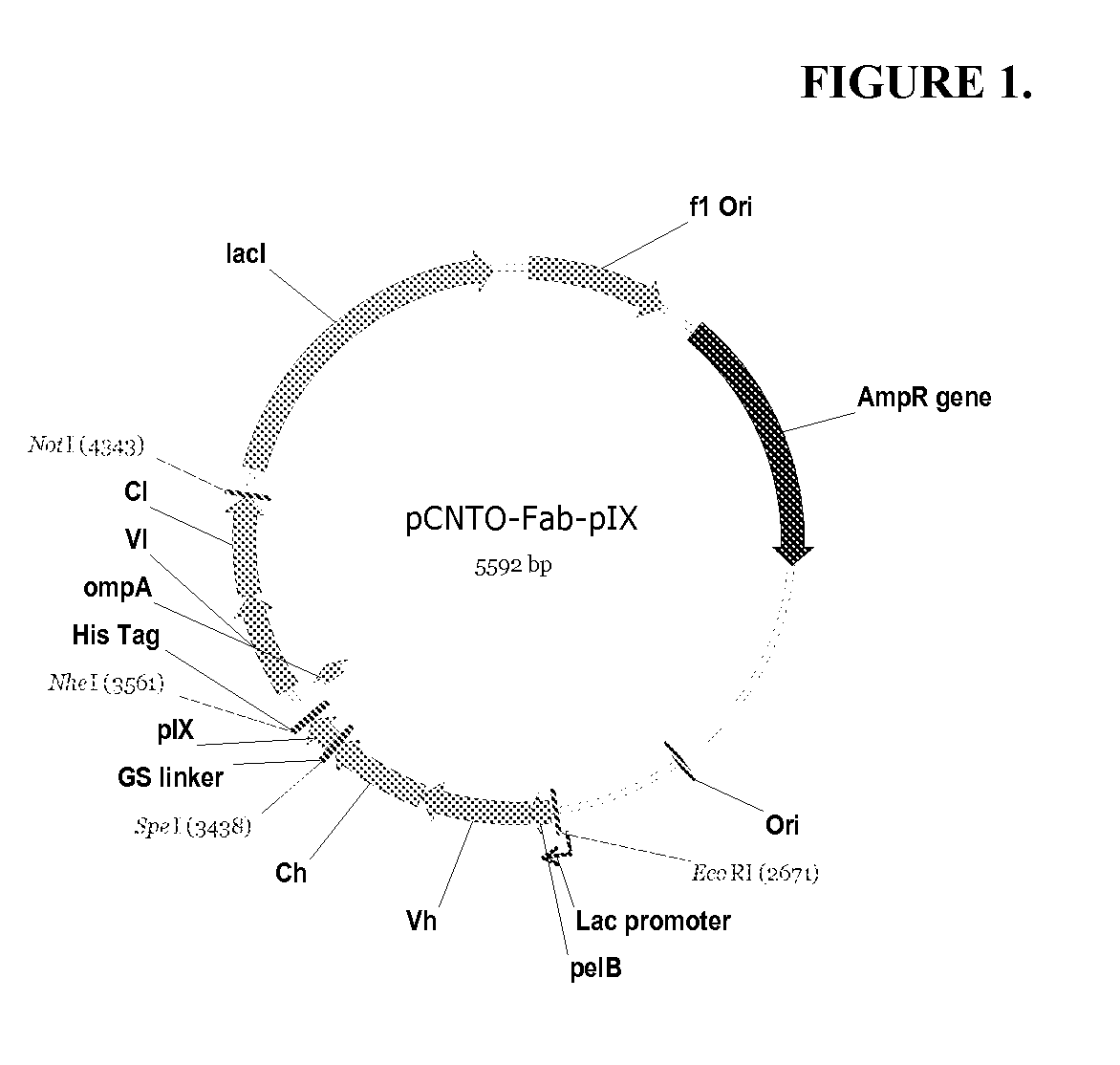
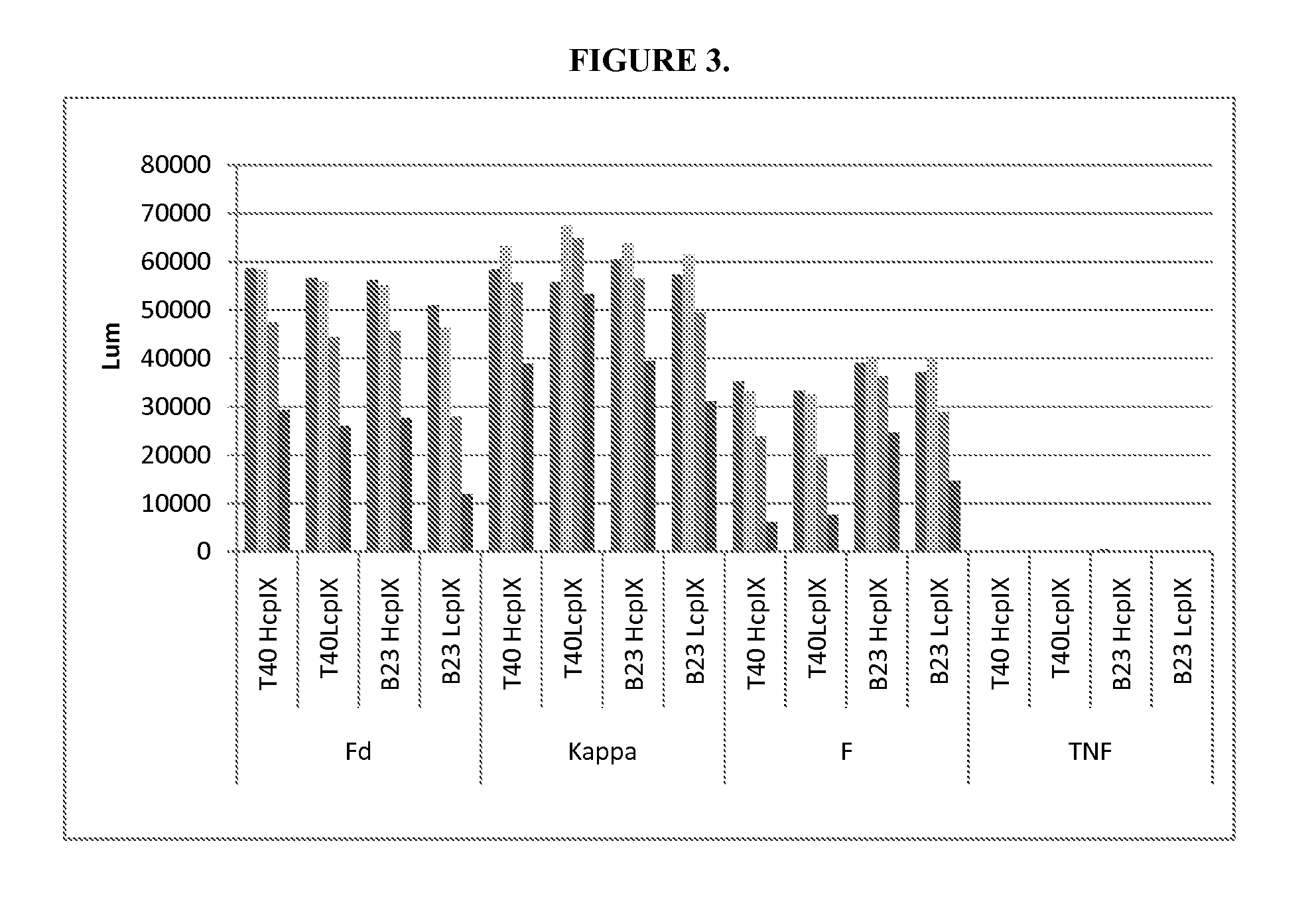
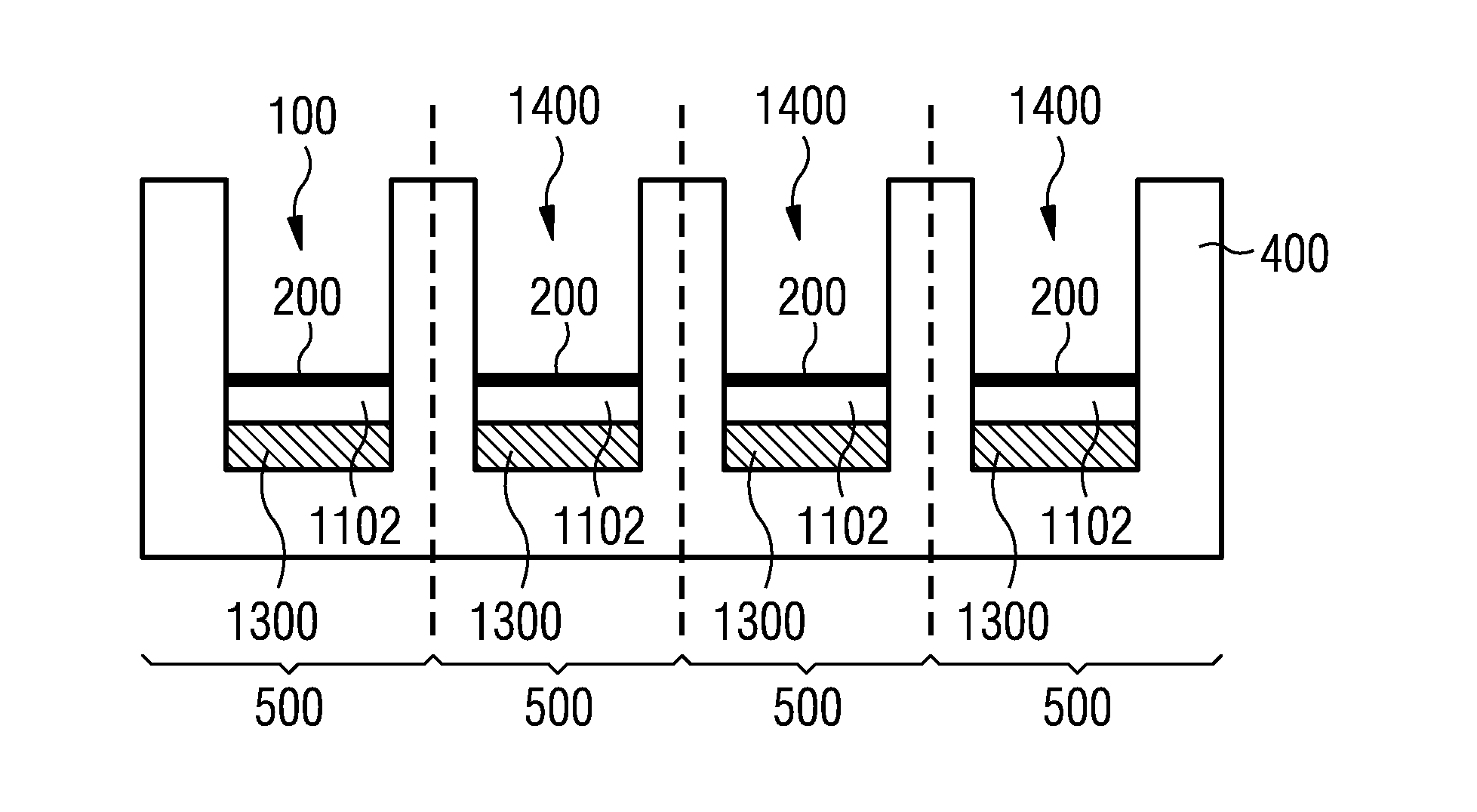
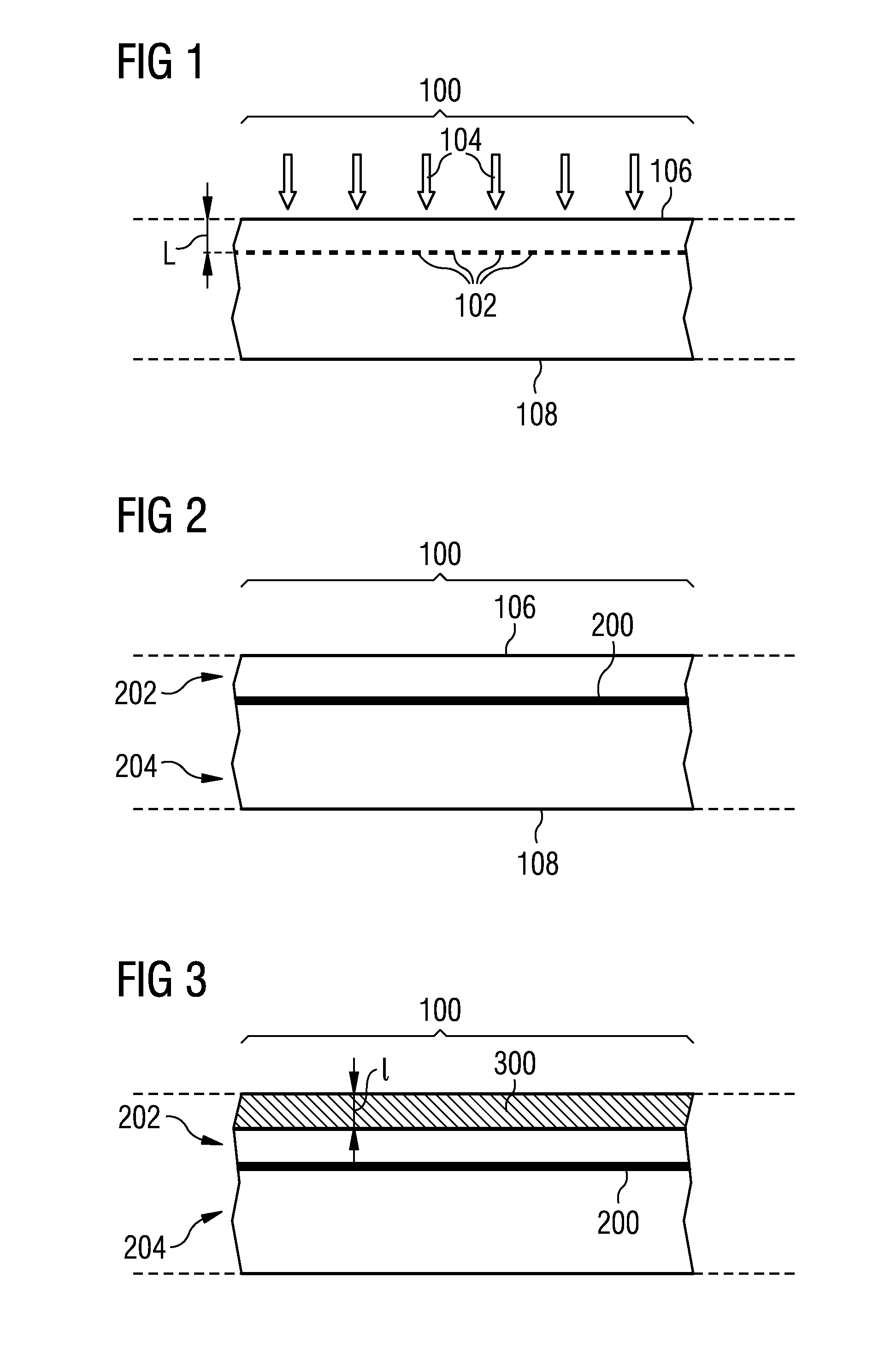
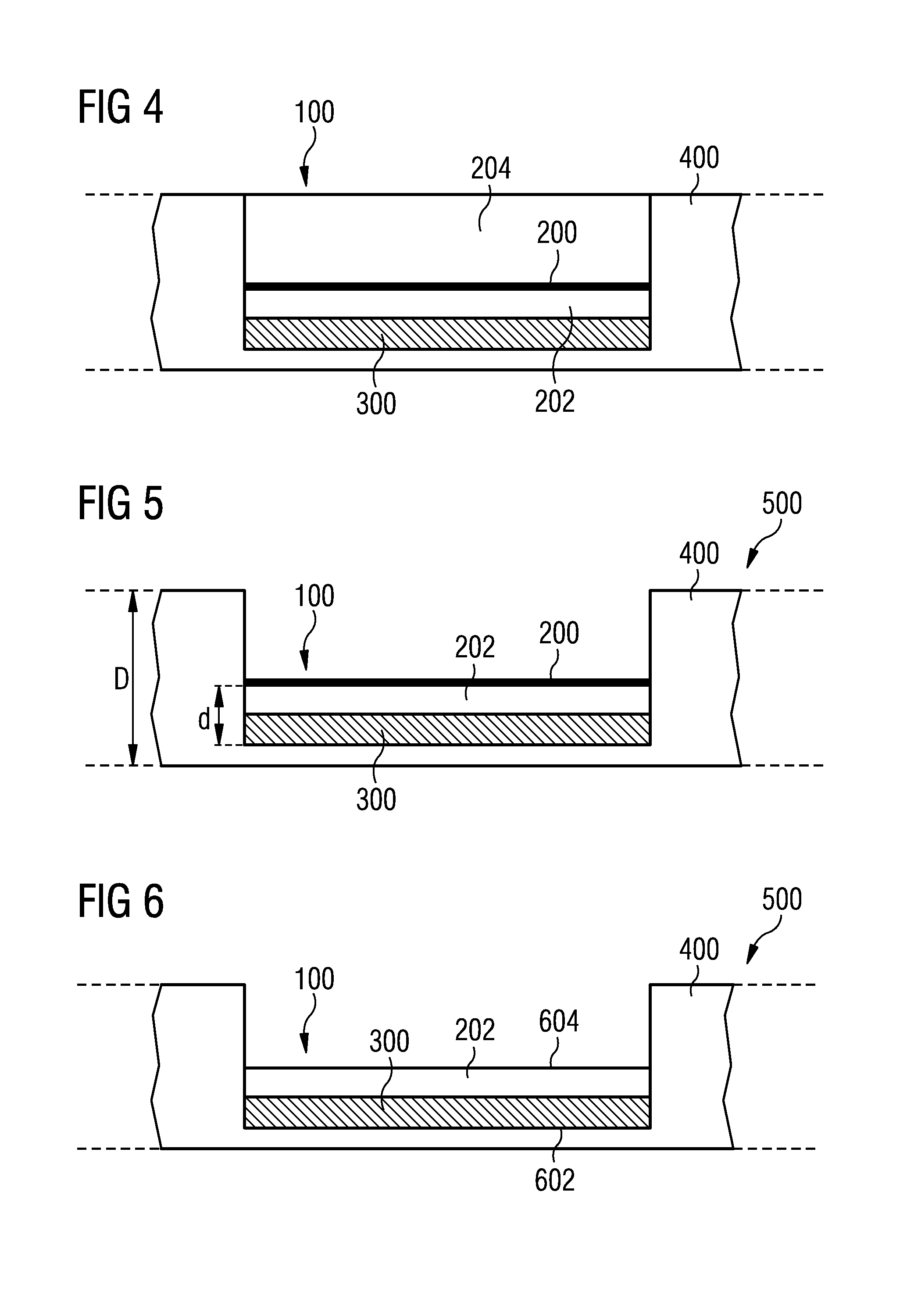
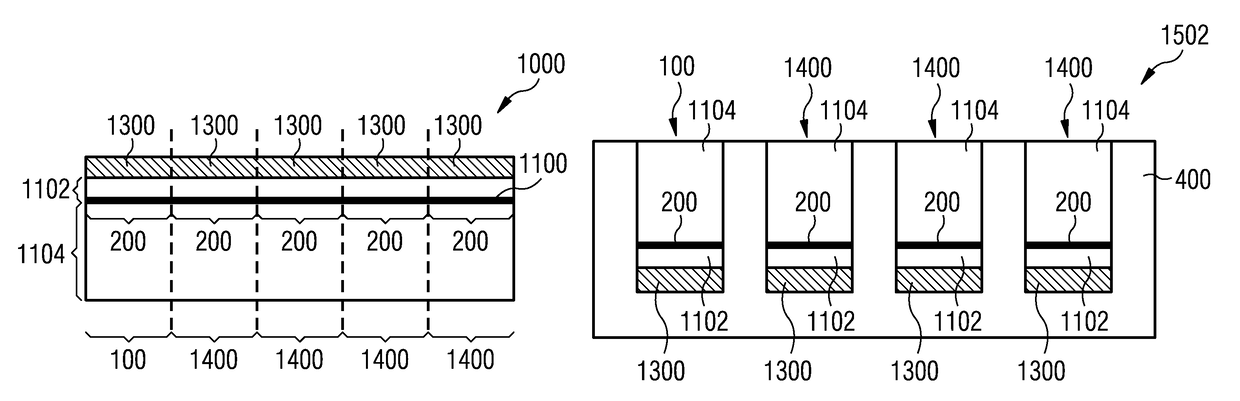
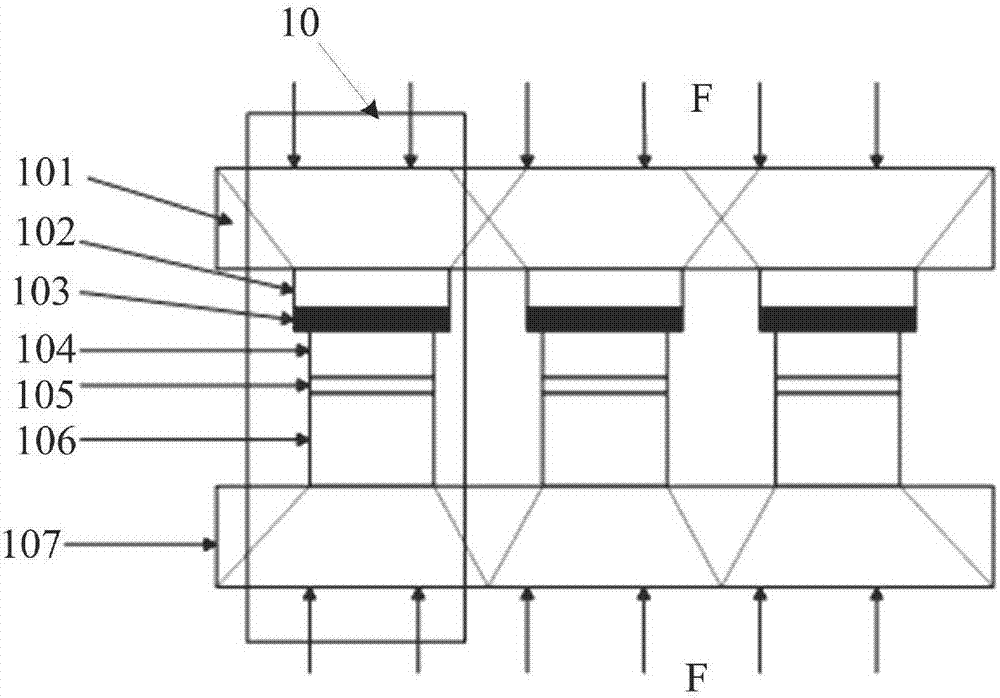
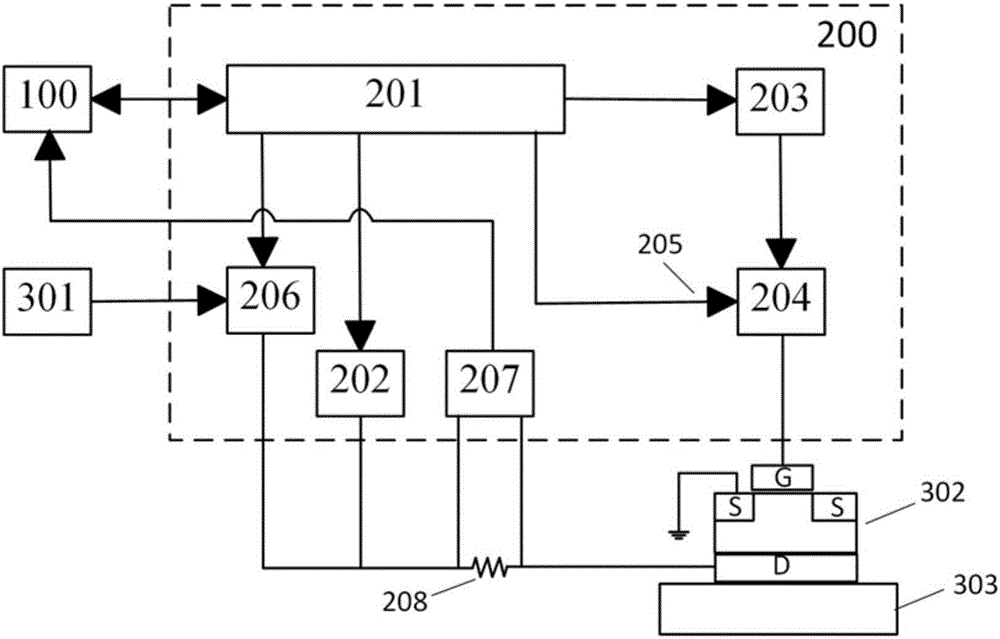
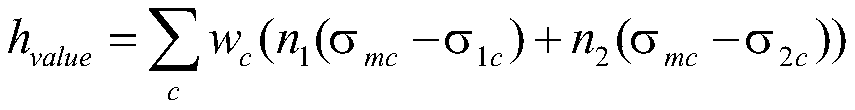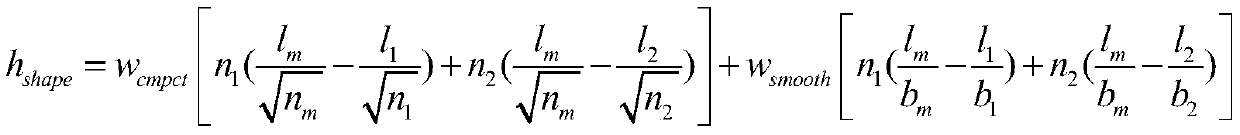Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
395 results about "Structure function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
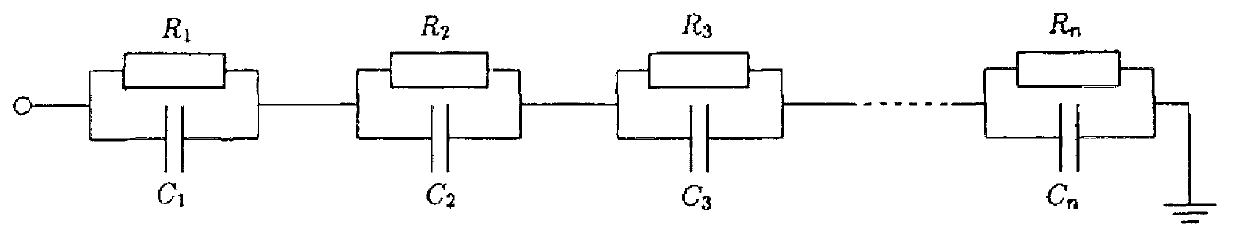
The structure function (also known as the proton structure function), like the fragmentation function, is a probability density function. It is somewhat analogous to the structure factor in solid-state physics, and the form factor (quantum field theory).
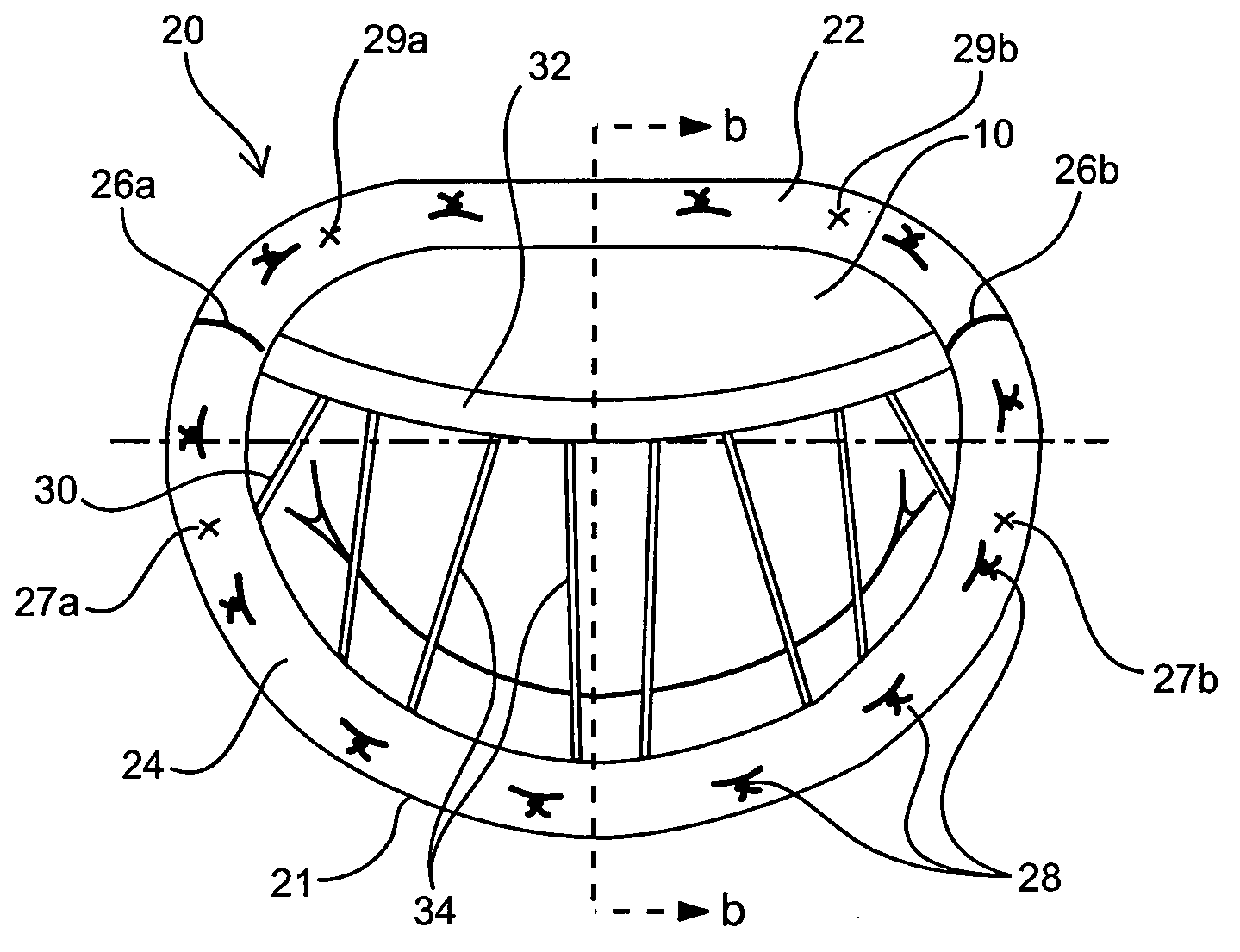
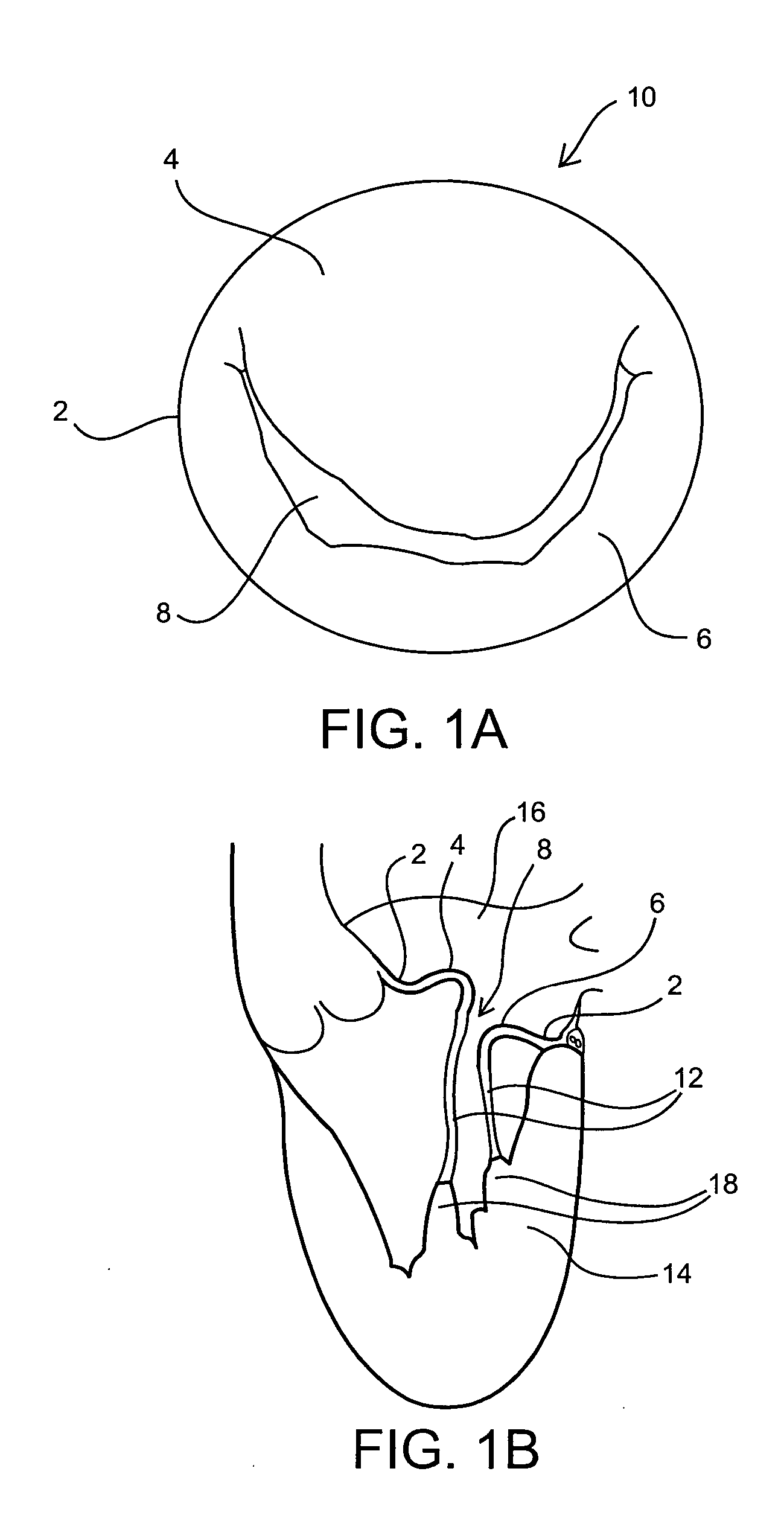
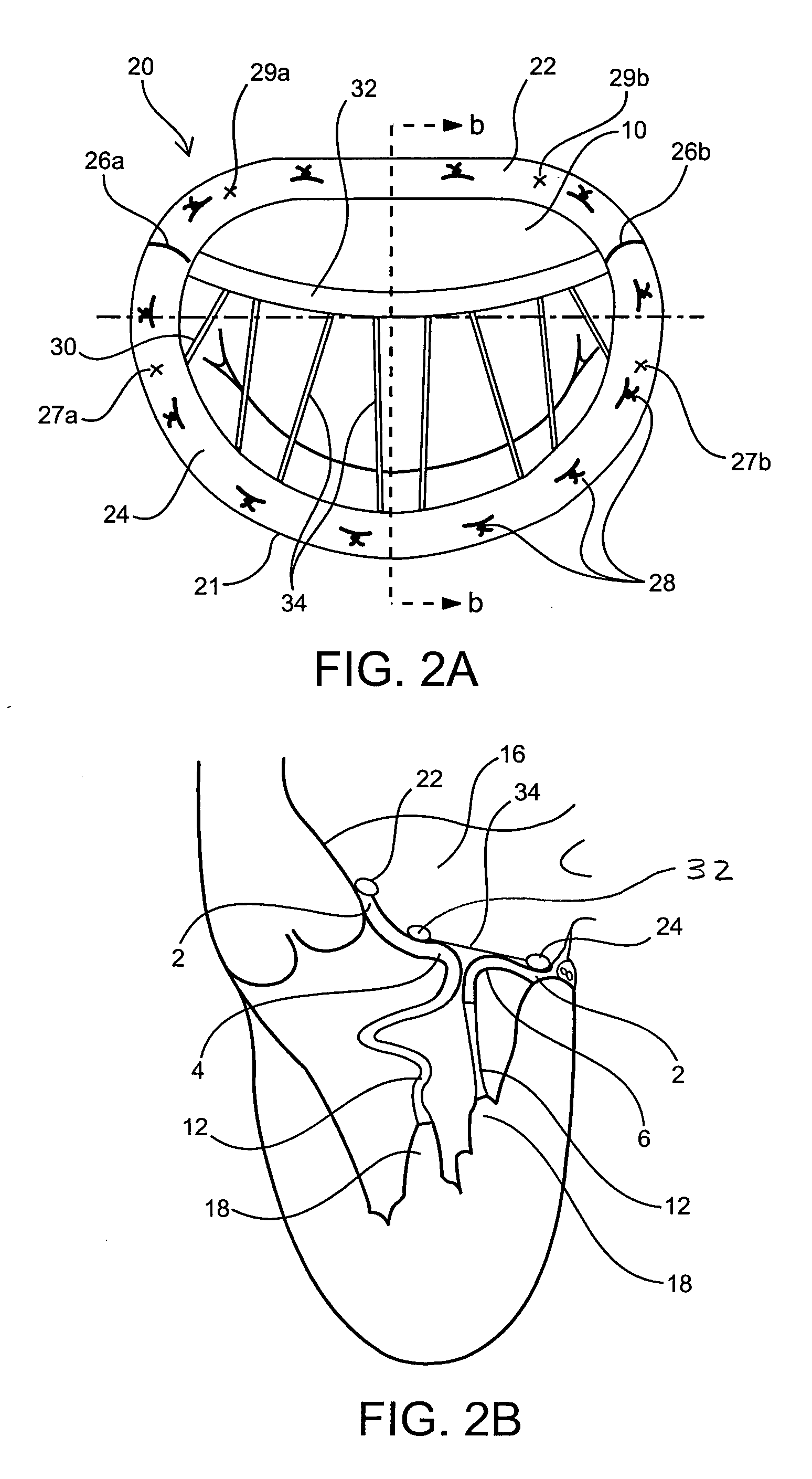
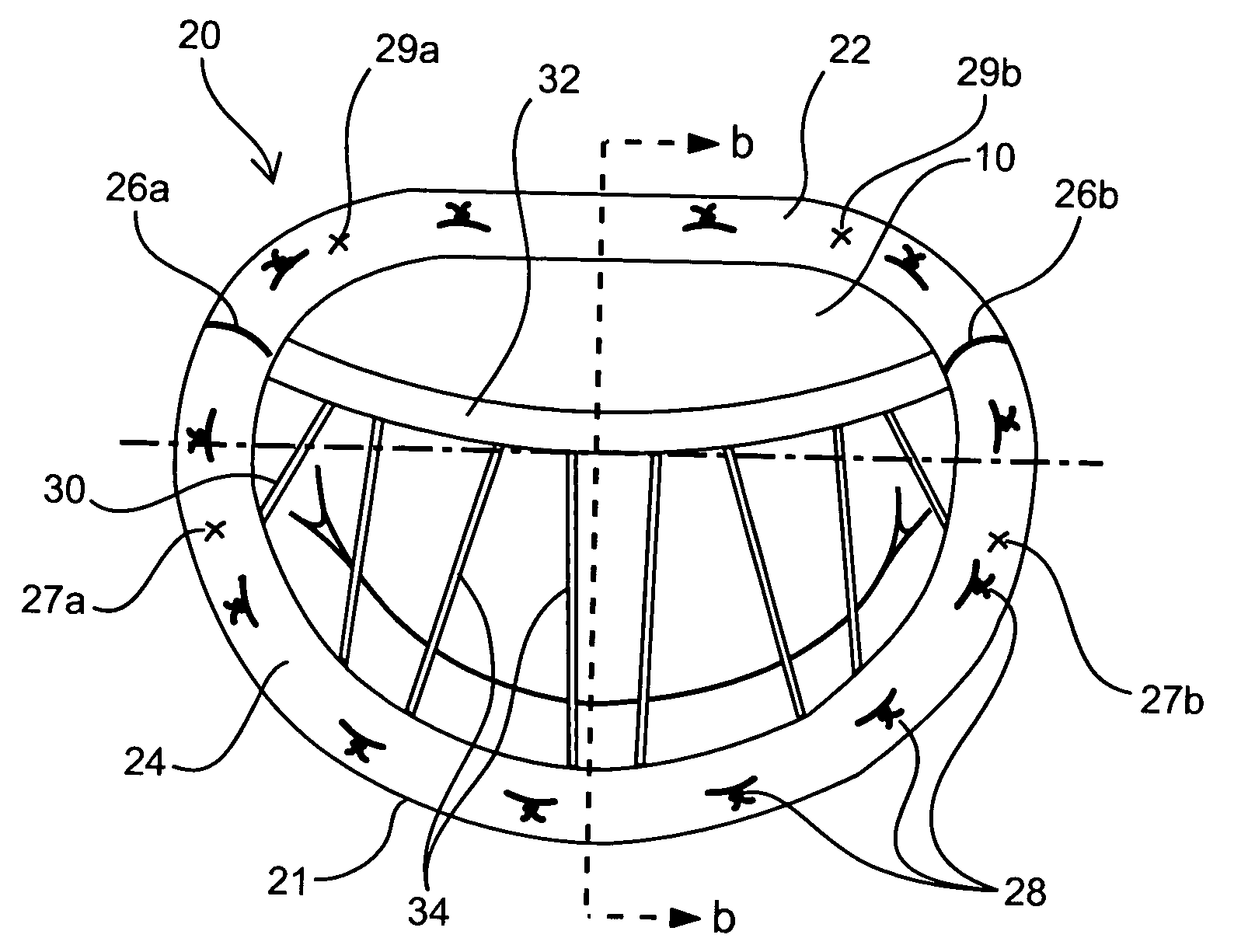
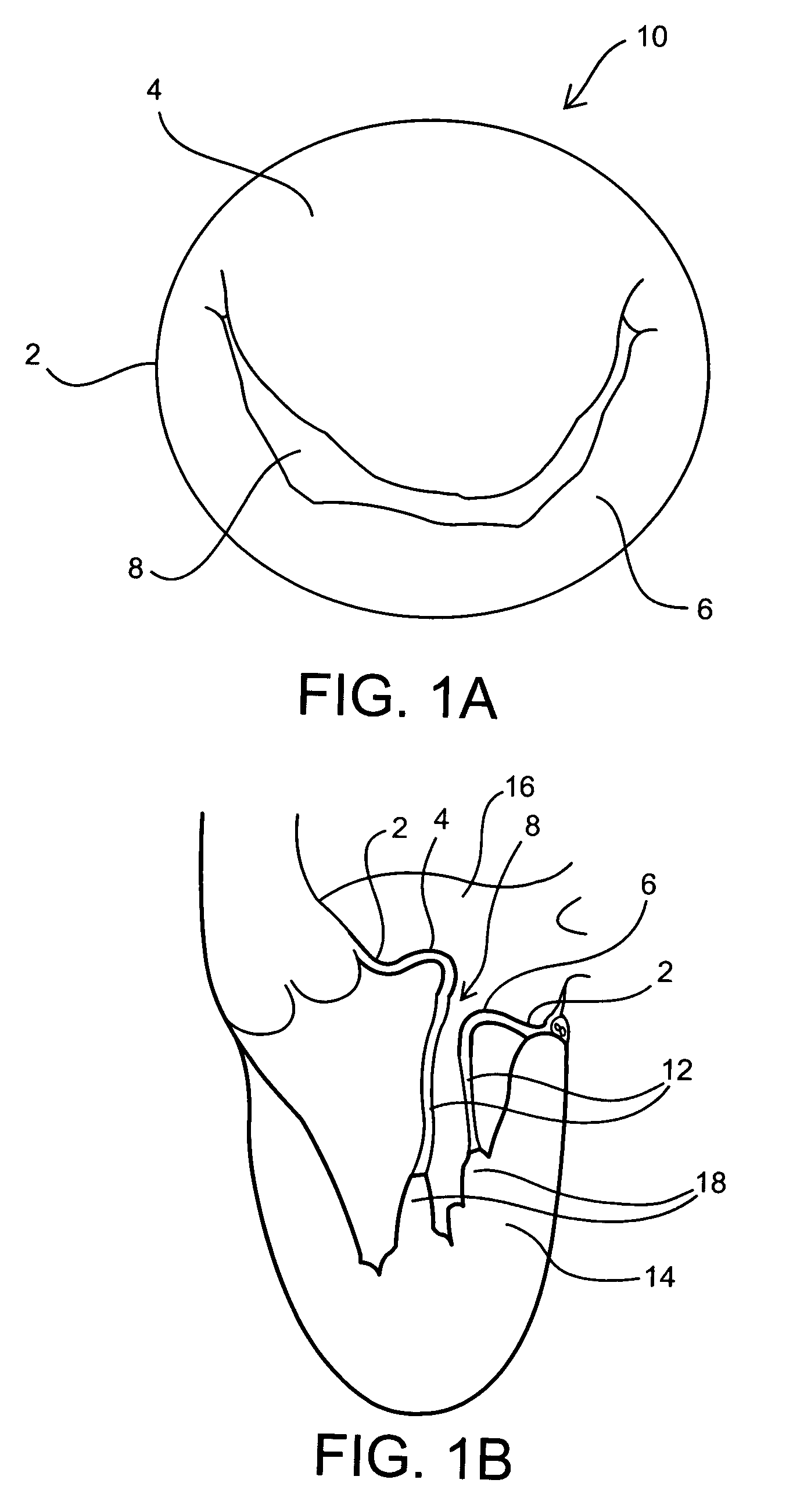
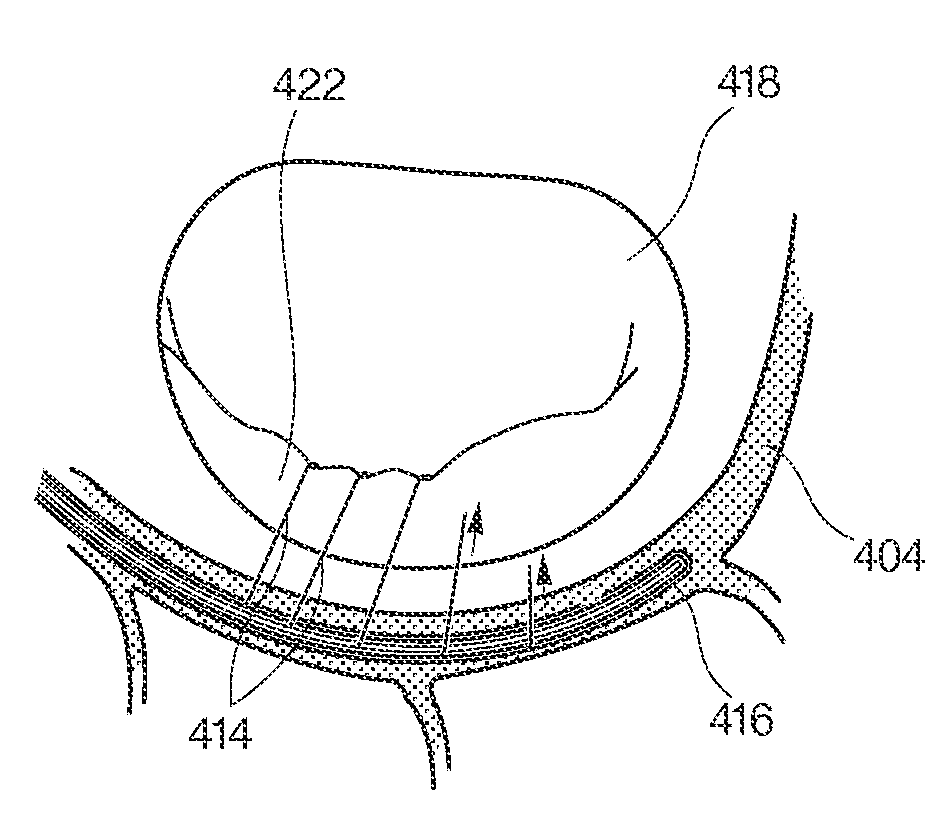
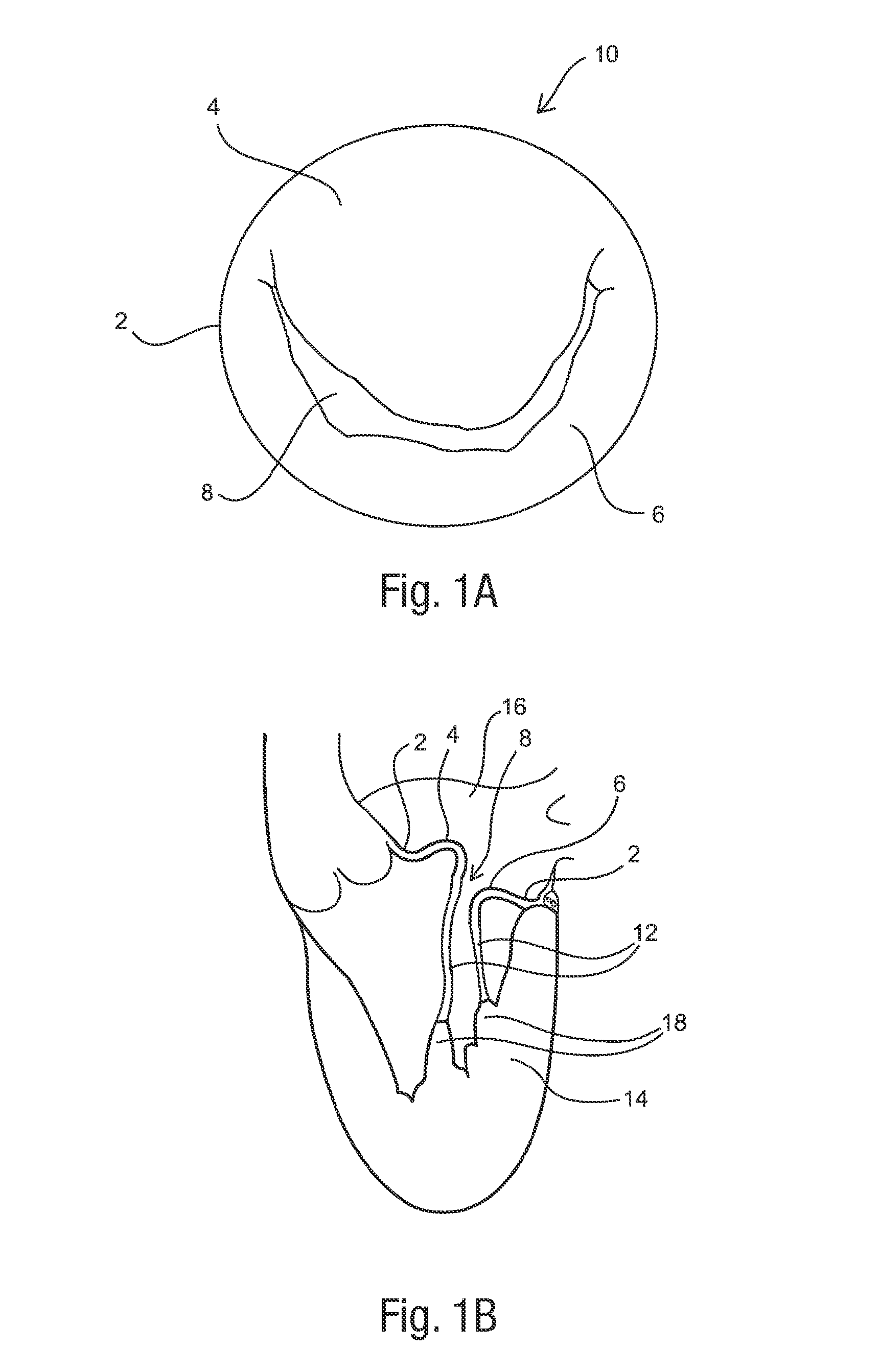
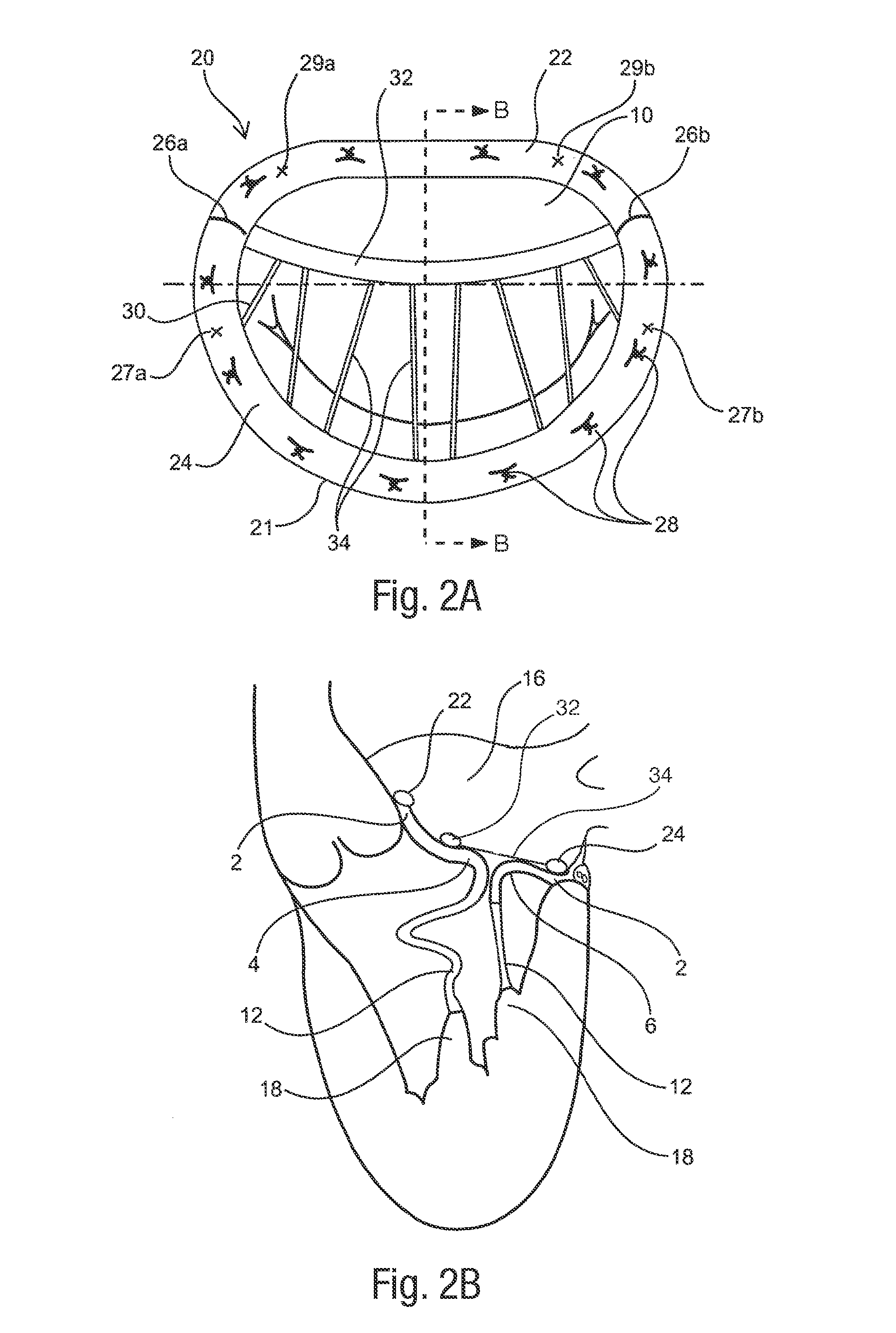
Annuloplasty rings and methods for repairing cardiac valves
InactiveUS20050004668A1Facilitate customized remodelingAccurate shapeBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsStructure functionImplanted device
Owner:FLEXCOR
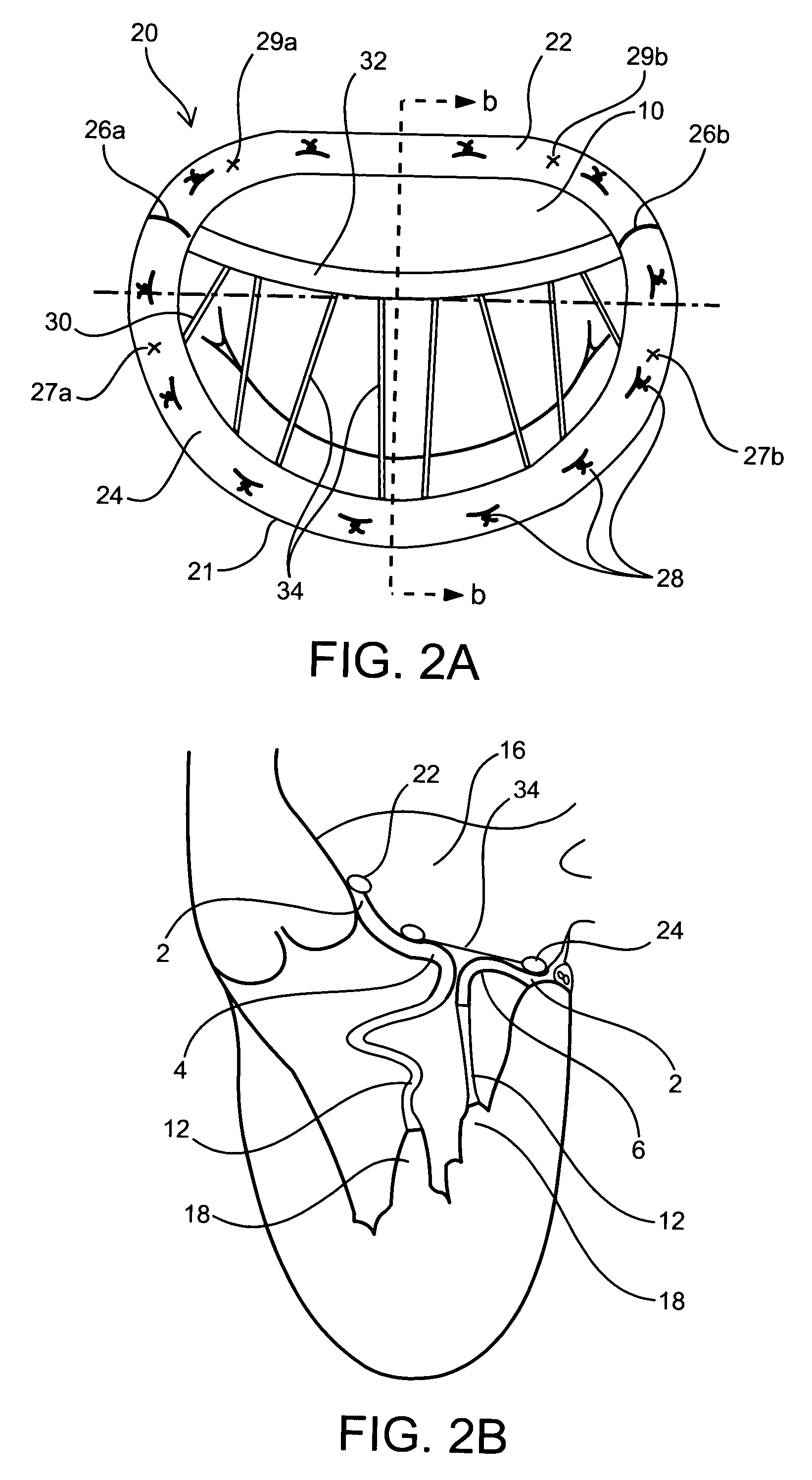
Annuloplasty rings and methods for repairing cardiac valves
InactiveUS20050004665A1Simple procedureCorrect dysfunctionBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsStructure functionAnnuloplasty rings
Implantable devices and methods for the repair of a defective cardiac valve are provided. The implantable devices include an annuloplasty ring and a restraining or support structure or mechanism. The annuloplasty ring functions to reestablish the normal size and shape of the annulus bringing the leaflet in proximity to each other. The restraining structure functions to restrain the abnormal motion of at least a portion of the valve being repaired. The restraining structure may include at least one restraining member across the interior of the circumference of the ring in a configuration consisting of a primary member to which secondary members are attached or one where all members traverse the ring. Kits for using the devices and practicing the methods of the invention are also provided.
Owner:FLEXCOR
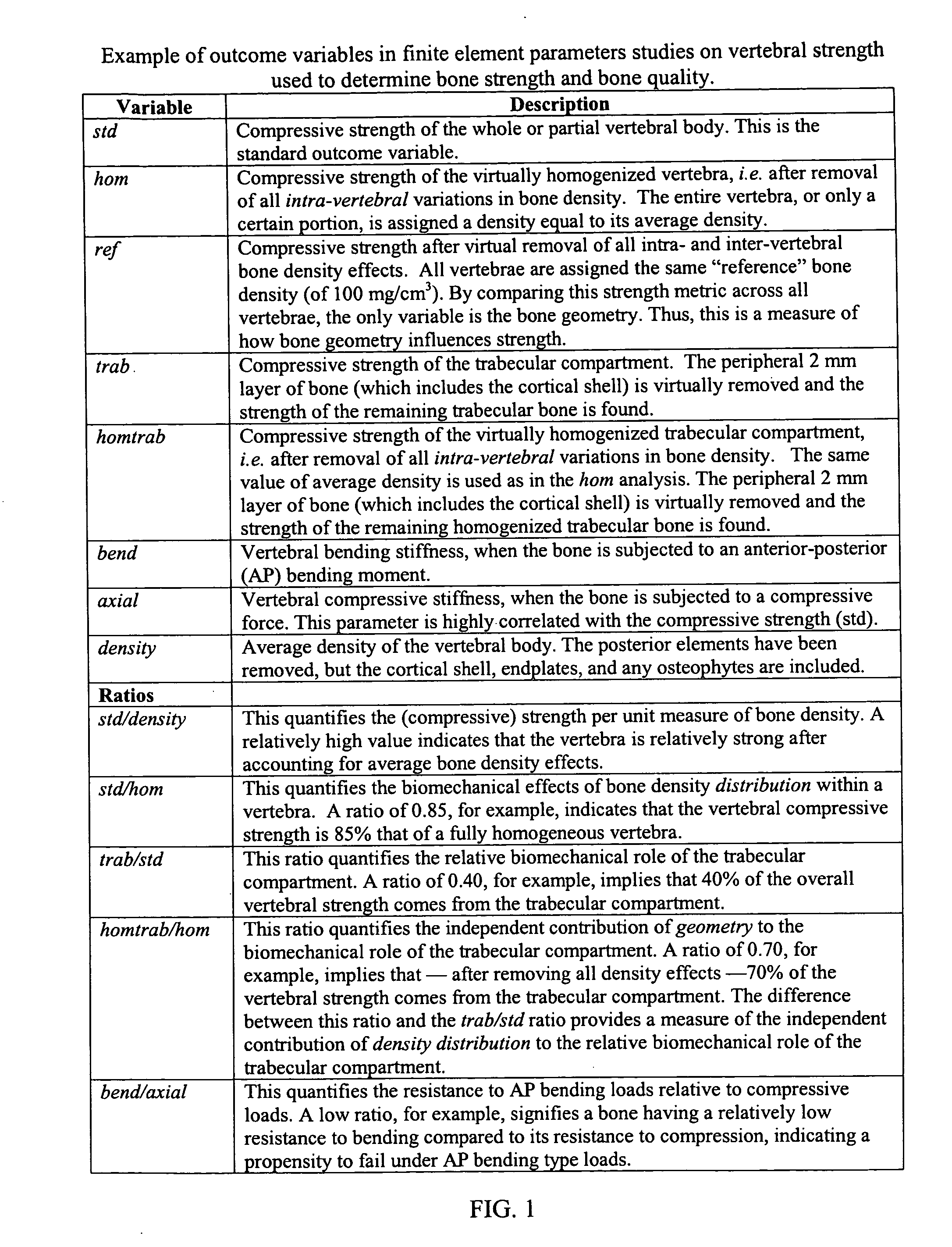
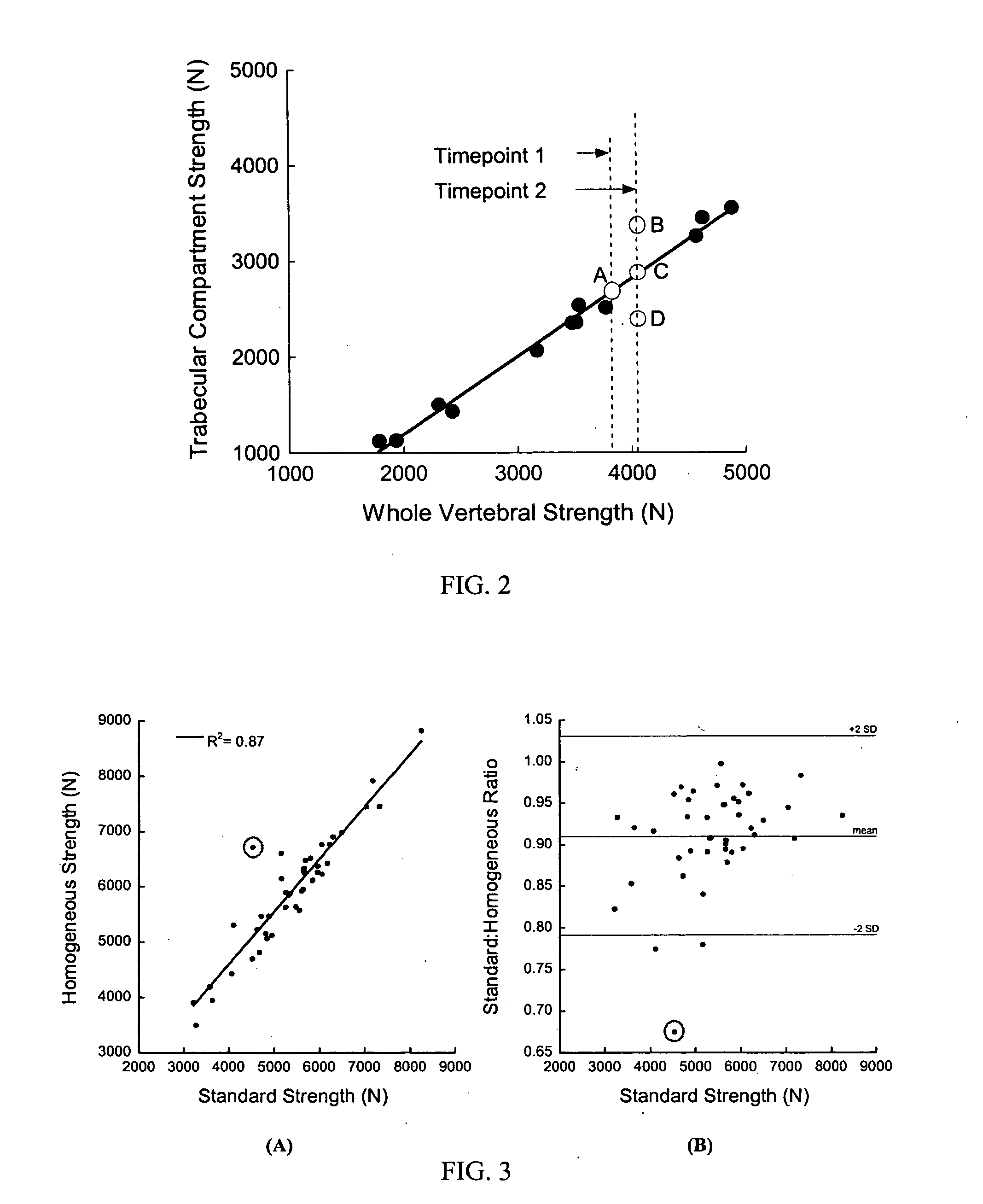
Method for assessment of the structure-function characteristics of structures in a human or animal body
A method for determining one or more structure-function characteristics of a structure in a human or animal body from an image of the structure includes generating a structural model of a structure based on an image of the structure. A first biomechanical quantity is computed based on the structural model. The structural model is varied to create a variant model. A second biomechanical quantity is computed based on the variant model. The first and second biomechanical quantities are compared, in order to assess a structure-function characteristic of the structure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and device for measuring heart rate, and method for manufacturing the device
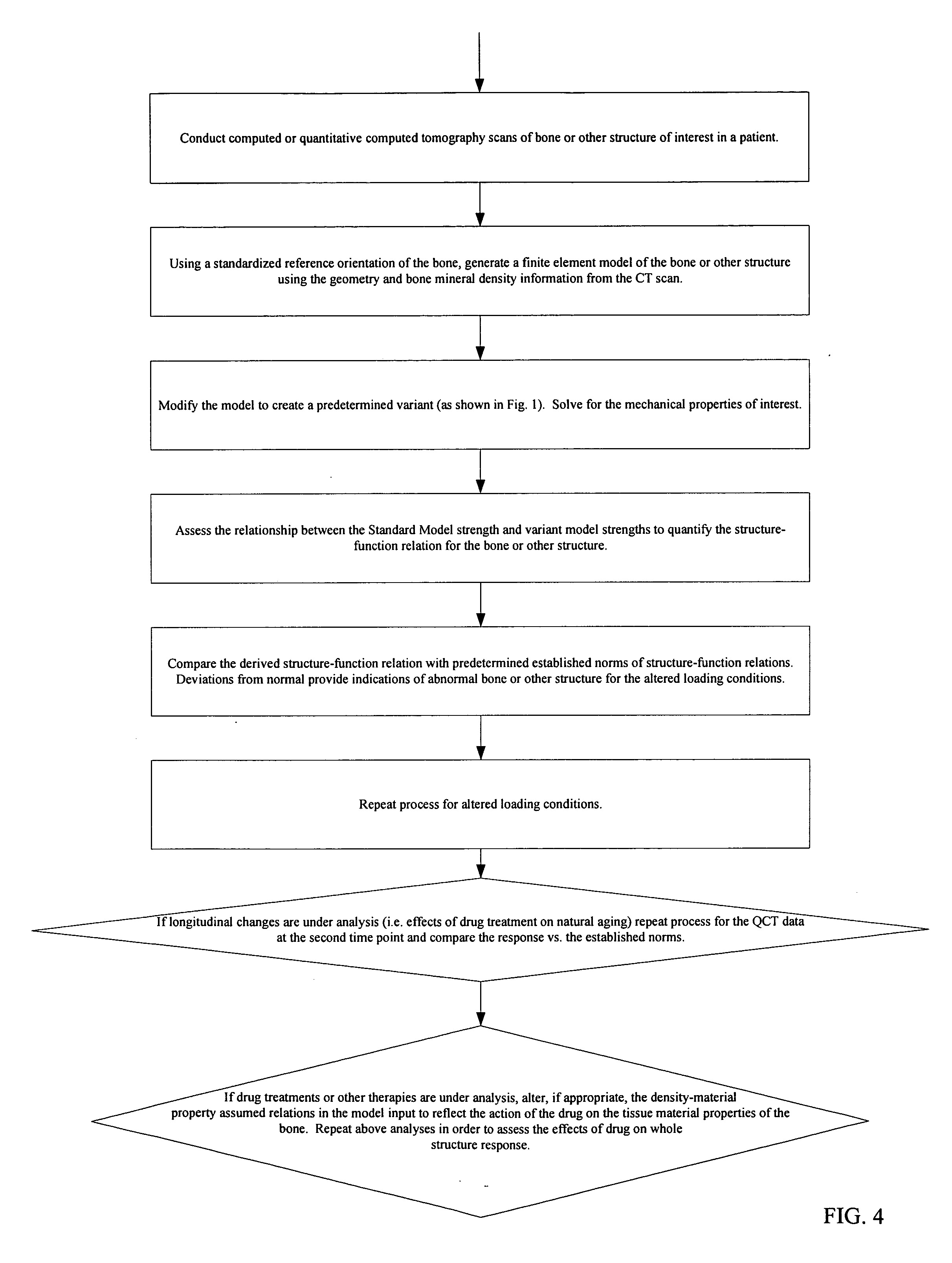
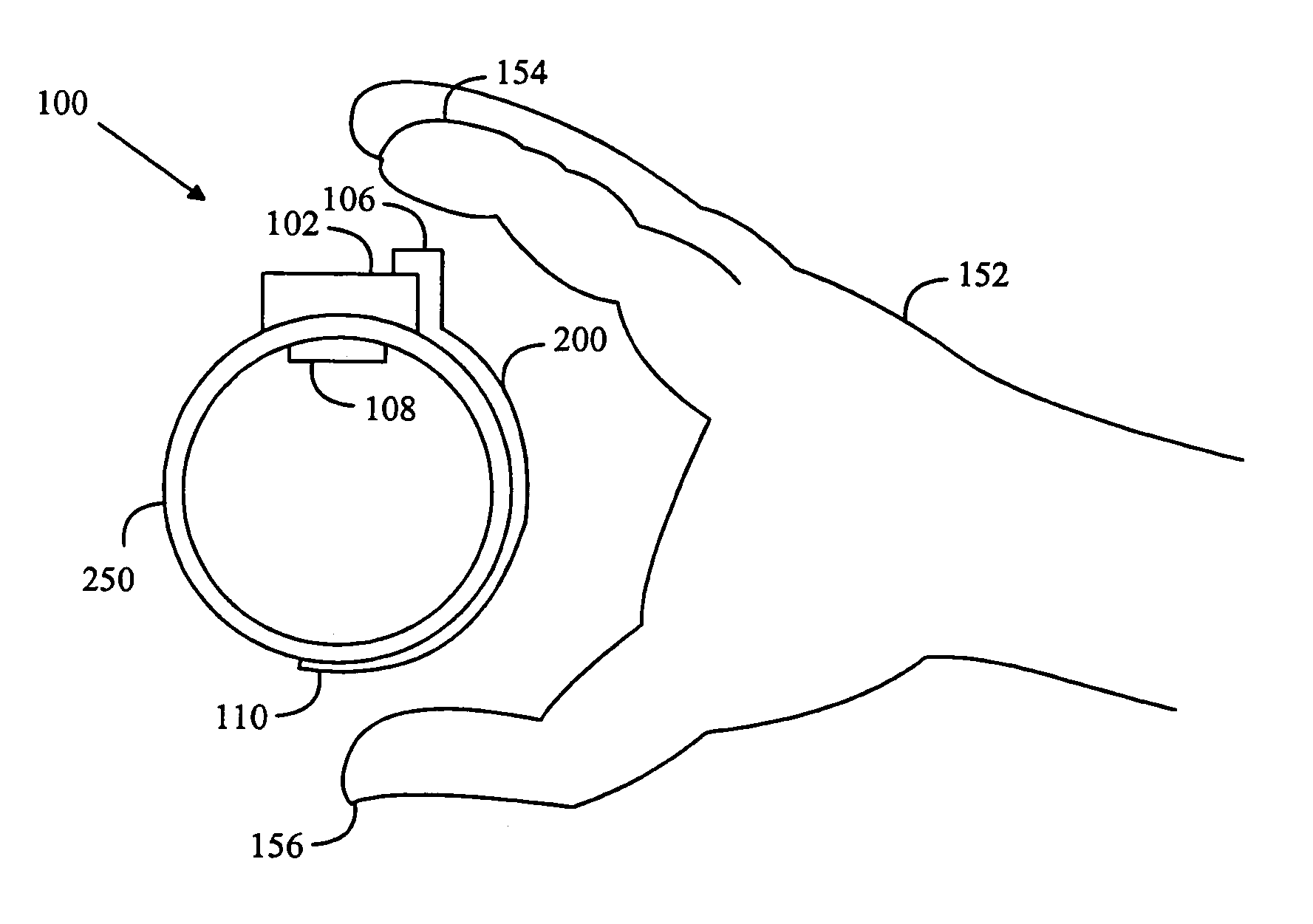
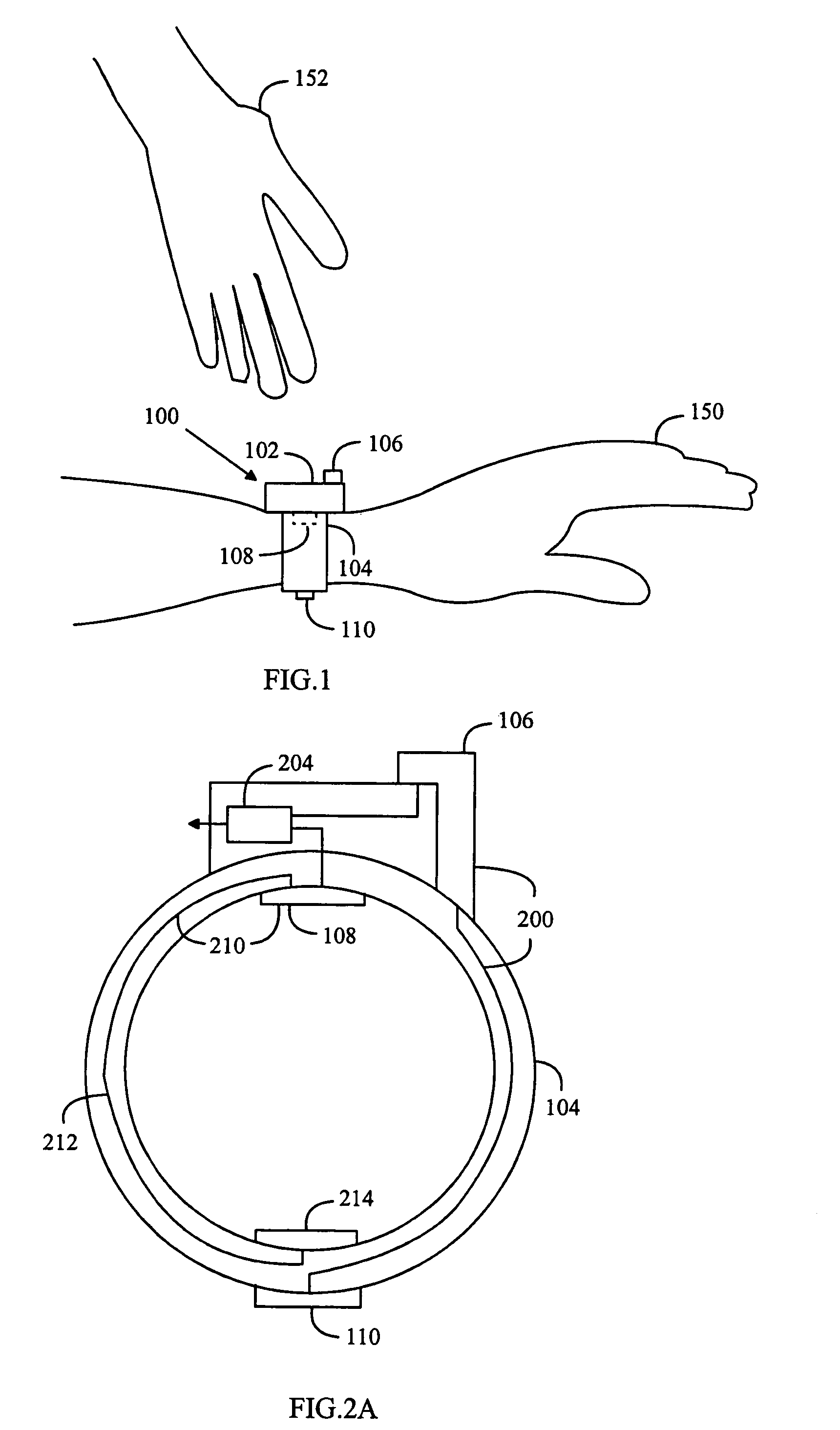
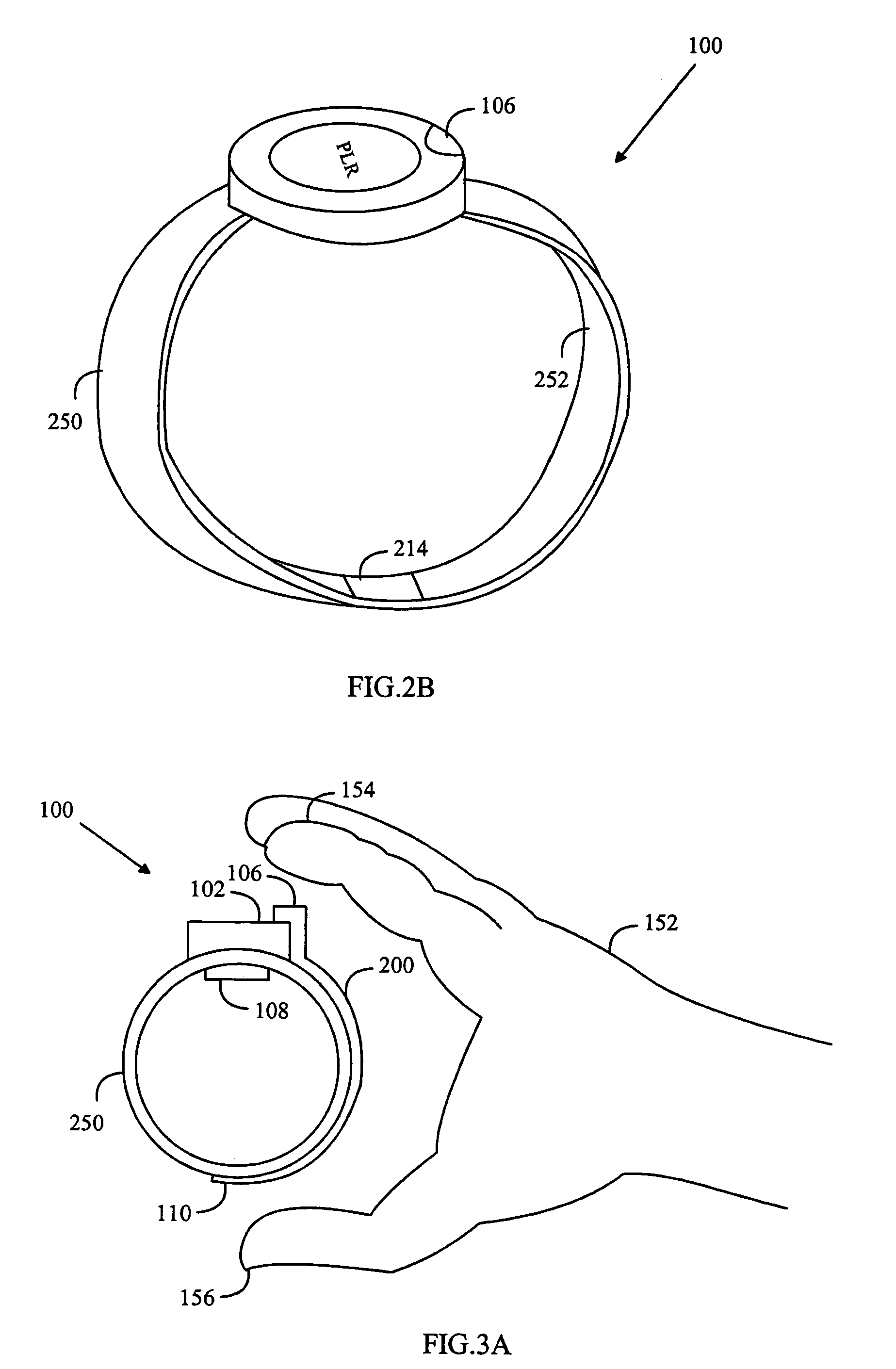
ActiveUS7171259B2Firm and convenient gripLower impedanceElectrocardiographySensorsMeasurement deviceStructure function
A heart rate measuring device is attached around a user's hand, the device having an inner surface, which is in contact with the skin on the hand to which it is attached, and an outer surface, which is other than the inner surface. The inner surface of the measuring device is provided with an electrically conductive inner structure, which functions as an electrode for a contact with the skin of the hand to which the device is attached. An electrically conductive outer structure functions as an electrode for a contact with the user's other hand and it is electrically isolated from the electrically conductive inner structure. The electrically conductive outer structure on the measuring device extends at least to opposite sides of the hand to which the device is attached, and at least part of the electrically conductive outer surface is on the outer surface of the measuring device, on opposite sides of the hand to which the device is attached. The electrically conductive outer structure and inner structure are connected to a measuring unit for heart rate measurement.
Owner:POLAR ELECTRO
Annuloplasty rings for repairing cardiac valves
InactiveUS8052751B2Simple procedureCorrect dysfunctionBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsStructure functionAnnuloplasty rings
Owner:FLEXCOR
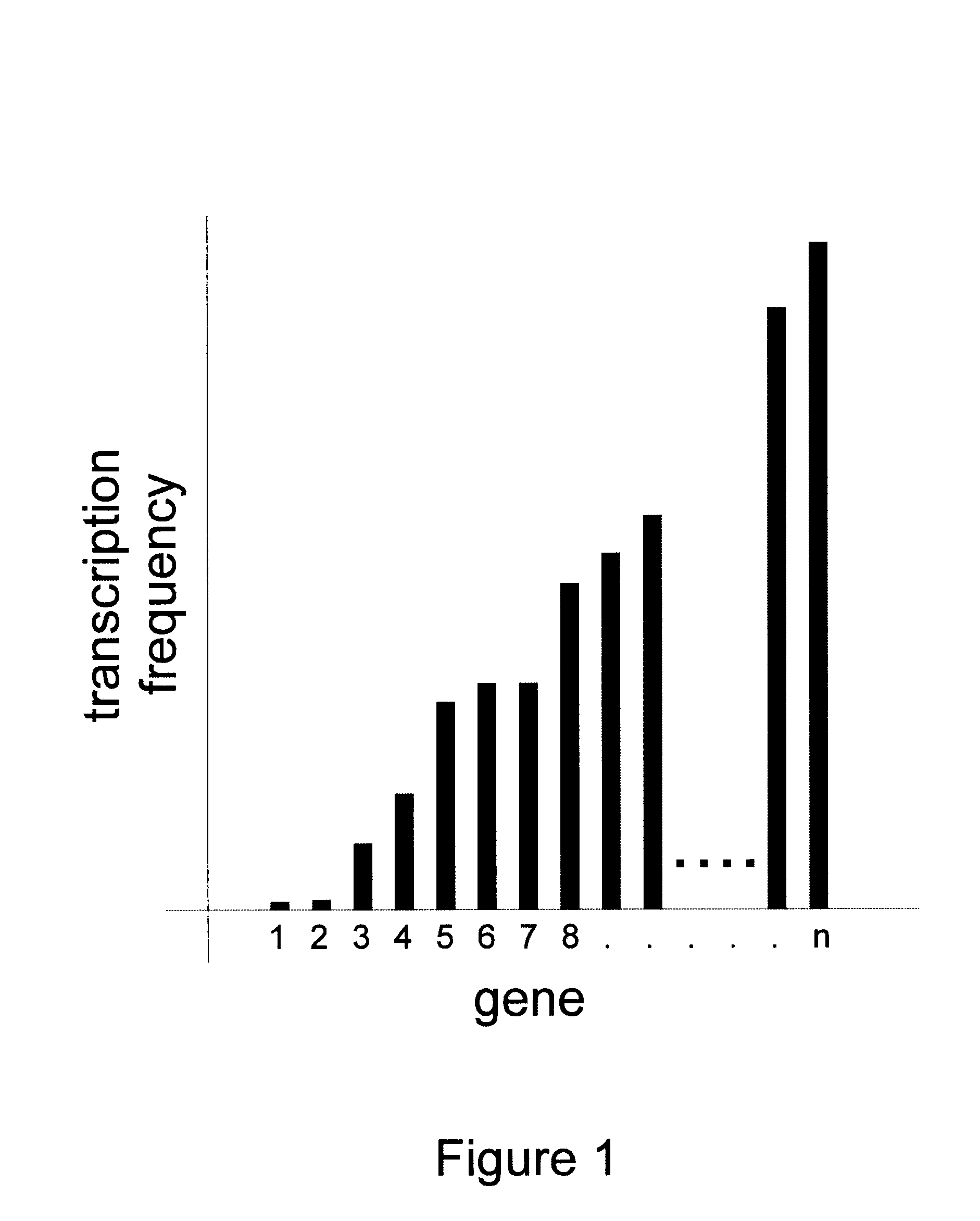
Methods for gene array analysis of nuclear runoff transcripts
InactiveUS6617112B2Rapid and efficient and extensive analysisAccurate predictionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementStructure functionOrganism
Methods for determining transcription rate of mRNA in eukaryotic cells using nuclear runoff transcription where labeled RNA molecules are hybridized against an array of at least 500 nucleic acid molecule probes representing at least part of the genome of the native eukaryotic organism to identify the quantity of nascent mRNA transcripts in said cells. The method can be used to simultaneously identify the quantity of a large number of mRNA transcripts. A rate of degradation for distinct mRNA in a eukaryotic cell rate is determined by comparing a steady state mRNA with nuclear runoff mRNA. Steady state to nuclear runoff ratios are used to determine gene and mRNA structure function relations that leads to gene expression and mRNA stability, predict structural determinants for mRNA stability and predict regulatory motifs for transcription rates. Methods of constructing recombinant organisms with enhanced stability for mRNA expressed from a gene of interest comprise introducing into the genome of an organism a gene containing one or more sequence elements that confer structural stability on mRNA transcribed from said gene.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
DESIGN AND GENERATION OF HUMAN DE NOVO pIX PHAGE DISPLAY LIBRARIES
InactiveUS20100021477A1Easy to understandIncrease diversityBacteriaLibrary screeningNatural antibodyStructure function
Described and claimed herein are combinatorial synthetic Fab libraries displayed on a phage pIX protein. The libraries were built on scaffolds representing the most frequently used genes in human antibodies, which were diversified to mirror the variability of natural antibodies. After selection using a diverse panel of proteins, numerous specific and high-affinity Fabs were isolated. By a process called in-line maturation the affinity of some antibodies was improved up to one hundred-fold yielding low pM binders suitable for in vivo use. This work thus demonstrates the feasibility of displaying complex Fab libraries as pIX-fusion proteins for antibody discovery and lays the foundations for studies on the structure-function relationship of antibodies.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Thinning in package using separation structure as stop
ActiveUS20150108666A1Without risk of quality deteriorationImprove accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesStructure functionEngineering
A method of forming a thinned encapsulated chip structure, wherein the method comprises providing a separation structure arranged within an electronic chip, encapsulating part of the electronic chip by an encapsulating structure, and thinning selectively the electronic chip partially encapsulated by the encapsulating structure so that the encapsulating structure remains with a larger thickness than the thinned electronic chip, wherein the separation structure functions as a thinning stop.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Thinning in package using separation structure as stop
ActiveUS9627287B2Without risk of quality deteriorationImprove accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesStructure functionElectronic chip
A method of forming a thinned encapsulated chip structure, wherein the method comprises providing a separation structure arranged within an electronic chip, encapsulating part of the electronic chip by an encapsulating structure, and thinning selectively the electronic chip partially encapsulated by the encapsulating structure so that the encapsulating structure remains with a larger thickness than the thinned electronic chip, wherein the separation structure functions as a thinning stop.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Vertical field effect transistor and method for fabricating the same
A vertical field effect transistor includes: an active region with a bundle of linear structures functioning as a channel region where electric carriers are transported; a lower electrode, connected to the bottom of the active region and functioning as one of source and drain regions; an upper electrode, connected to the top of the active region and functioning as the other of the source and drain regions; a gate electrode for controlling the electric conductivity of at least a portion of the bundle of linear structures included in the active region; and a gate insulating film arranged between the active region and the gate electrode to electrically isolate the gate electrode from the bundle of linear structures. The transistor further includes a dielectric portion between the upper and lower electrodes. The upper electrode is located over the lower electrode with the dielectric portion interposed and includes an overhanging portion that sticks out laterally from over the dielectric portion. The active region is located right under the overhanging portion of the upper electrode.
Owner:JOLED INC
Methods and Apparatus for Jammable HCI Interfaces
In exemplary implementations of this invention, a jammable structure functions as an HCI interface. A user provides input by changing the shape of a flexible layer of the jammable structure (e.g., by pressing against it or stretching, twisting or bending it) and receives haptic feedback (e.g., varying stiffness). Sensors are used to determine the shape of the flexible layer. The sensors output data that is indicative of electromagnetic waves that have traveled through the jammable media or of electrical or magnetic phenomena that are produced by the waves. For example, visible or infrared light may be shone through a transparent jammable media to the flexible layer and reflect back to a camera. The media may comprise granular particles (e.g., glass beads) and a liquid (e.g., oil) with matching indices of refraction. Or capacitive sensing may be used to detect the shape of the flexible layer.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for predicating surface roughness and surface topography simulation of car milling compound machining
A method for predicating surface roughness and surface topography simulation of a car milling compound machining comprises the following six steps: step one, a modeling of a unified cutter position coordinate model of a whole cutter and an inserted blade cutter; step two, a modeling of the geometrical movement trace of a milling cutter cutting edge; step three, a consideration of influences of the vibration of the cutters to a workpiece surface morphology; step four, a microscopic surface morphology representation method; step five, a car milling compound machining basic structure function; step six, a simulation algorithm example and an orthogonal test method. The method combines the geometrical simulation and the physical simulation together, static and dynamic deformations which are produced when cutters cut under stress are fully considered, models for general car milling compound machining method of any angle are theoretically built, and a surface method of the roughness calculation of the car milling compound machining is deduced. The method for predicating surface roughness and surface topography simulation of the car milling compound machining has good practical values and broad application prospects in the technical field of machinery manufacturing processing.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Chip Guard Ring Including a Through-Substrate Via
ActiveUS20100237472A1Fully groundedArea minimizationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipStructure function
At least one through-substrate via is formed around the periphery of a semiconductor chip or a semiconductor chiplet included in a semiconductor chip. The at least one through-substrate via may be a single through-substrate via that laterally surrounds the semiconductor chip or the semiconductor chiplet, or may comprise a plurality of through-substrate vias that surrounds the periphery with at least one gap among the through-substrate vias. A stack of back-end-of-line (BEOL) metal structures that laterally surrounds the semiconductor chip or the semiconductor chiplet are formed directly on the substrate contact vias and electrically connected to the at least one through-substrate via. A metallic layer is formed on the backside of the semiconductor substrate including the at least one through-substrate via. The conductive structure including the metallic layer, the at least one through-substrate via, and the stack of the BEOL metal structures function as an electrical ground built into the semiconductor chip.
Owner:TESSERA INC
Anterior Segment Drug Delivery
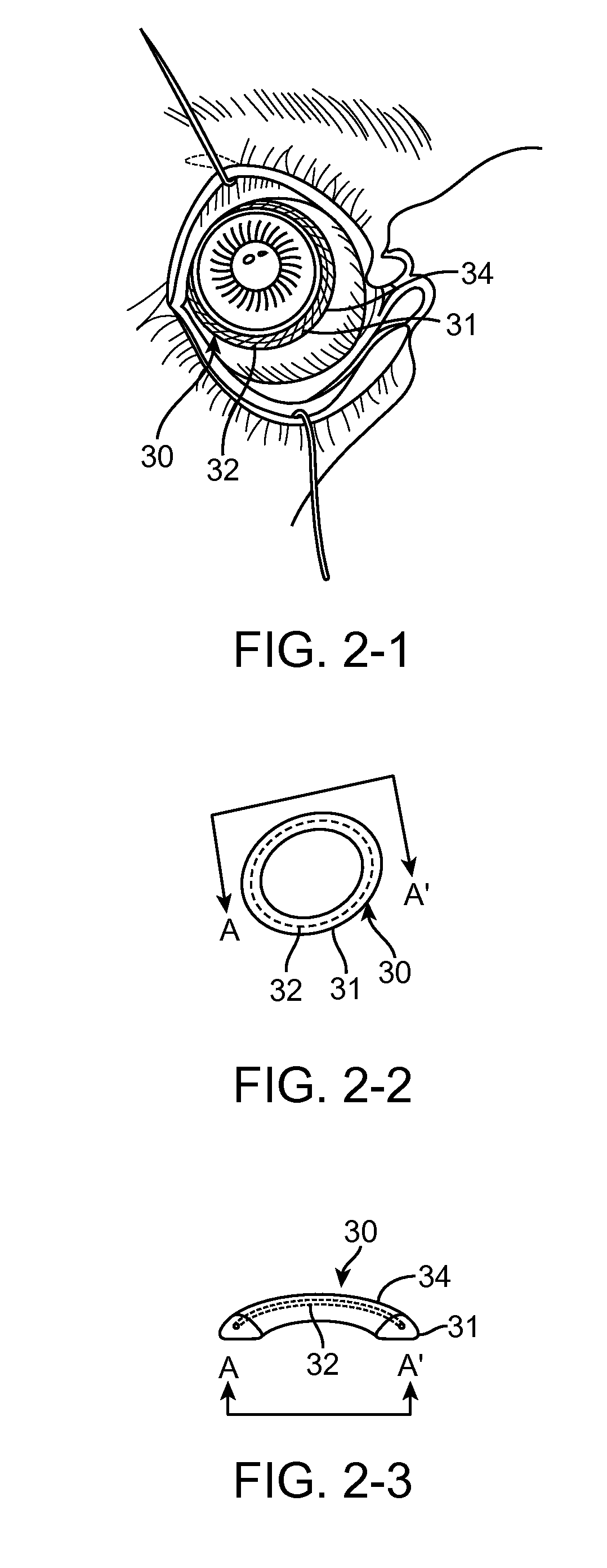
ActiveUS20120136322A1Maintain positionProvide supportSenses disorderElcosanoid active ingredientsCushioningConjunctiva
A therapeutic system comprises an ocular insert placed on a region outside an optical zone of an eye. The ocular insert comprises two structures: a first skeletal structure and a second cushioning structure. The first structure functions as a skeletal frame which maintains positioning of the implant along the anterior portion of the eye and provides support to the second, cushioning structure. This first structure maintains the attachment of the therapeutic system to the anterior portion of the eye for at least thirty days. In some embodiments the first structure remains a constant size and shape, e.g. a ring shape, a ring with haptics, or a curvilinear ring that is confined to and restrainingly engages the inferior and superior conjunctival fornices so as to retain the implant within the tear fluid and / or against the tissues of the eye.
Owner:FORSIGHT VISION5 INC
Method and device for regulation of limbic system of the brain by means of neuro-electrical coded signals
A method and device for limbic system control to provide medical treatment for emotions and instinct. The method comprises selecting neuro-electrical coded signals from a storage area that are representative of limbic brain structure function. The selected neuro-electrical coded signals are then transmitted to a treatment member, which is in direct contact with the body, and which then broadcasts the neuro-electrical coded signals to a specific nerve or organ to modulate the limbic system functioning. A control module is provided for transmission to the treatment member. The control module contains the neuro-electrical coded signals which are selected and transmitted to the treatment member, and computer storage can be provided for greater storage capacity and manipulation of the neuro-electrical coded signals.
Owner:NEUROSIGNAL TECH
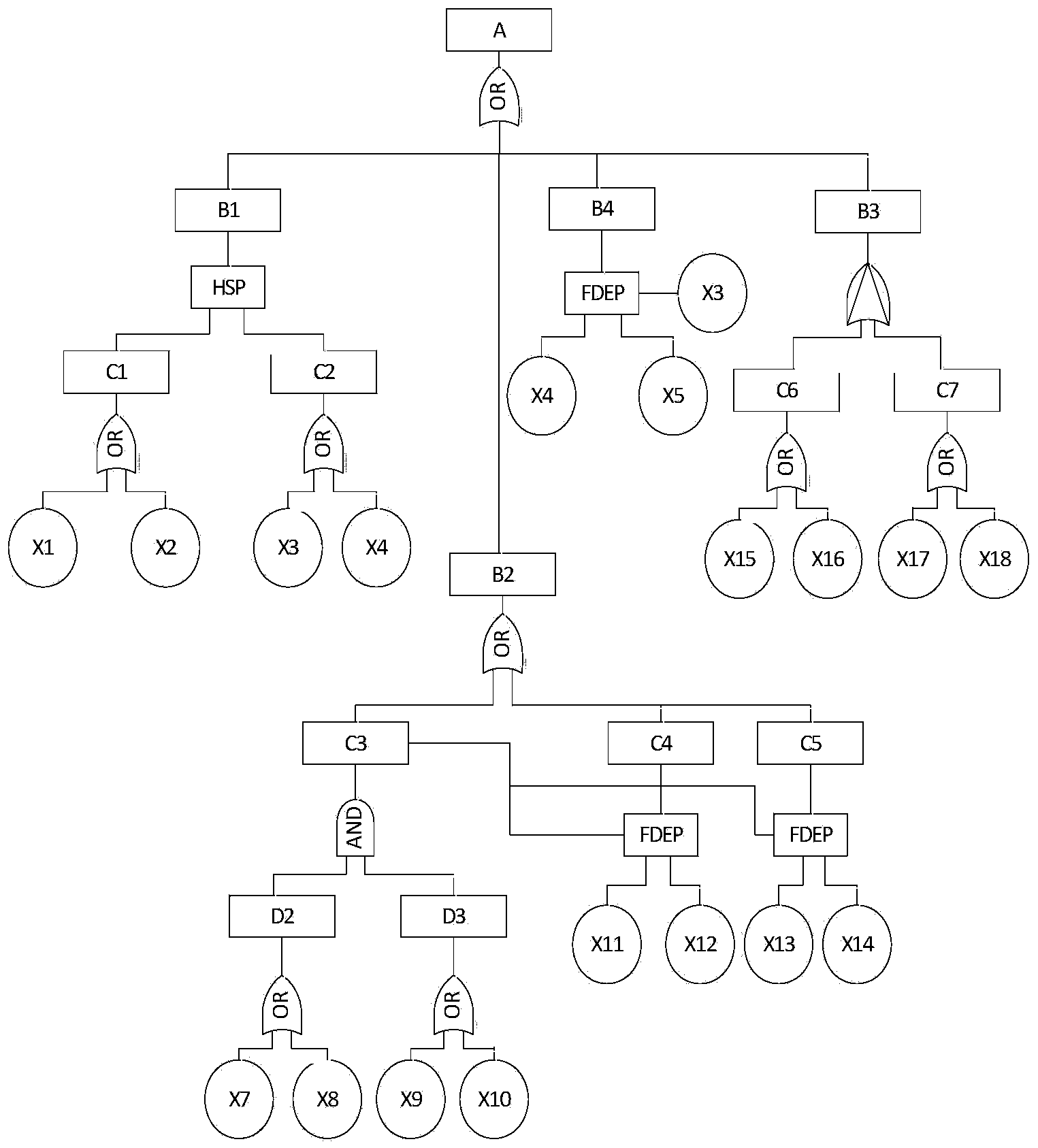
Equipment integration system reliability analysis method based on dynamic fault tree
InactiveCN104392072AImprove efficiencyImprove analysis efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsMarkov chainStructure function
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
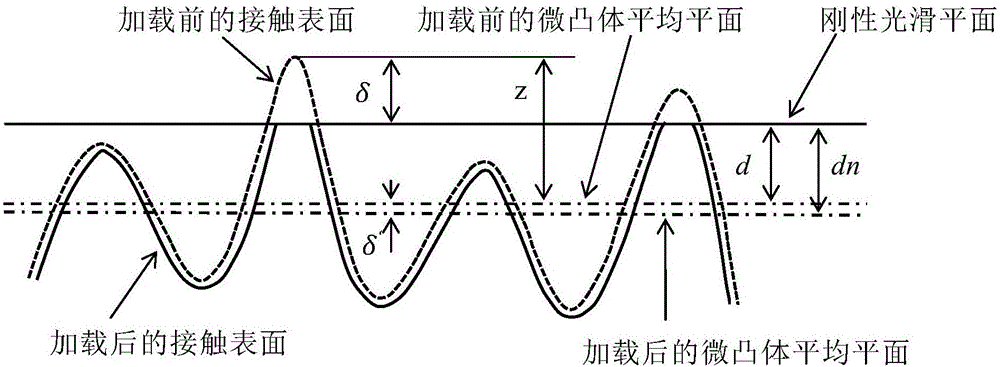
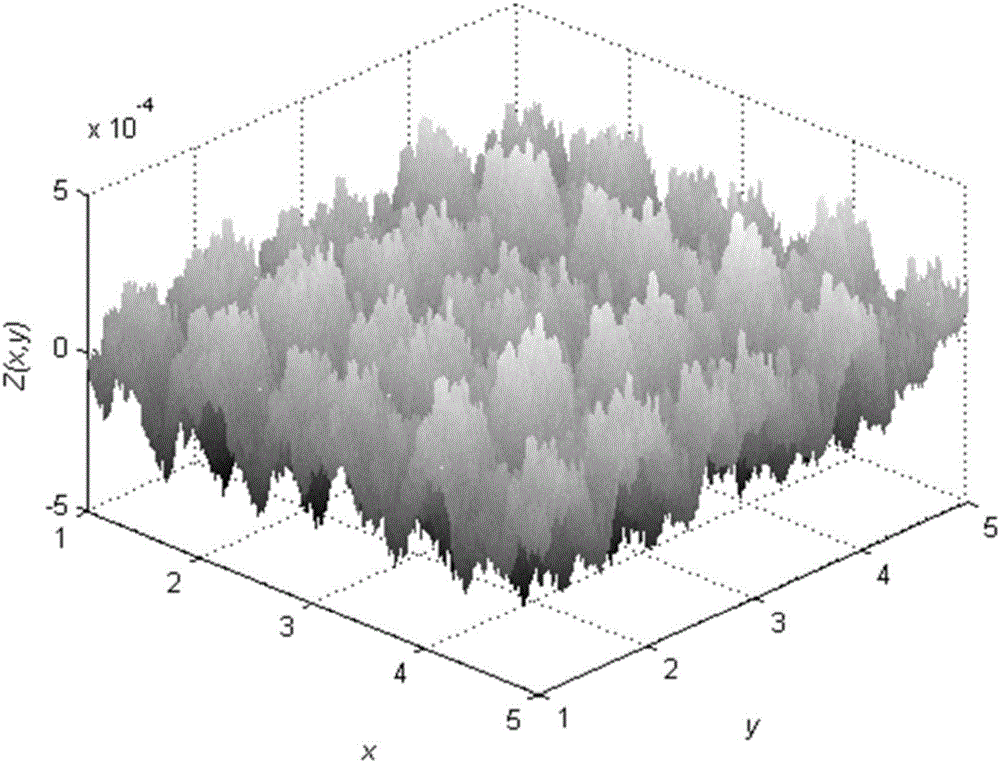
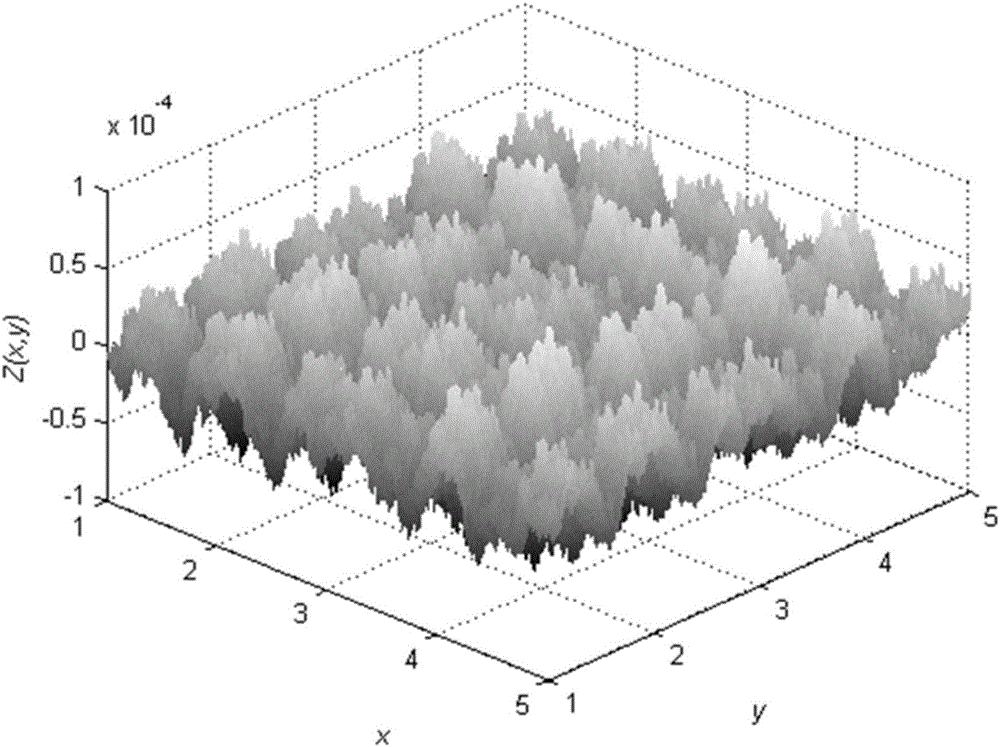
Method for determining normal contact rigidity of loaded joint part by considering interaction effect of micro-bulges on rough surfaces
ActiveCN106709207AOvercome the shortcomings of inaccurate calculation resultsScale-independentDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsRough surfaceNormal load
The invention provides a method for determining normal contact rigidity of a loaded joint part by considering the interaction effect of micro-bulges on rough surfaces. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring microstructure data of contact surfaces, acquiring micro-profile data of contact surfaces of the joint part by using a three-dimensional profile measuring instrument, extracting the position coordinate of each micro-bulge peal in the length direction, and simulating micro-bulge forms of the rough surfaces; building a relation between a normal load and the contact rigidity; computing fractal parameters of the contact surfaces, theoretically computing the extracted data by using a structure function method, and acquiring fractal dimensions and scale coefficients of the surfaces; and according to the above steps, putting each parameter value of the material to finally compute the normal contact rigidity of the joint part. The new method for determining the normal contact rigidity of the joint surfaces provided by the invention overcomes the defect that the traditional method based on a fractal theory is inaccurate in computation result in the case of heavy load, and has the advantages of strong reliability, being close to actual situation, small computation amount and improved computation efficiency.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Vertical field effect transistor using linear structure as a channel region and method for fabricating the same
A vertical field effect transistor includes: an active region with a bundle of linear structures functioning as a channel region; a lower electrode, functioning as one of source and drain regions; an upper electrode, functioning as the other of the source and drain regions; a gate electrode for controlling the electric conductivity of at least a portion of the bundle of linear structures included in the active region; and a gate insulating film arranged between the active region and the gate electrode to electrically isolate the gate electrode from the bundle of linear structures. The transistor further includes a dielectric portion between the upper and lower electrodes. The upper electrode is located over the lower electrode with the dielectric portion interposed and includes an overhanging portion sticking out laterally from over the dielectric portion. The active region is located right under the overhanging portion of the upper electrode.
Owner:JOLED INC
Bi-stable hinge and systems using same
ActiveUS7251323B2Simplifies hinge assemblyCost-effectiveInterconnection arrangementsSynthetic resin layered productsCost effectivenessStructure function
The present invention provides an improved hinge design for a mobile station or other electronic device that simplifies hinge assembly and thus, provides a more cost-effective manufactured product. Moreover, the improved hinge assembly complements the aesthetic appeal of the foldable mobile station and provides less stress on various internal elements. In particular, the present invention includes a foldable mobile station or other foldable electronic device having a first functional component that is coupled to a second functional component via a bi-stable structure. The bi-stable structure functions to bias the first and second functional components in either an open or closed position.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Electrostatic discharge mitigation structure and methods thereof using a dissipative capacitor with voltage dependent resistive material
InactiveUS20050275070A1Mitigating ESD damageReduce EMI/RFISemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal energyParallel plate
The present invention relates to structures and methods that reduce ESD damage to electronic devices. In an embodiment, the structure is a parallel plate dissipative capacitor formed by sandwiching a dissipative dielectric layer between two conductive layers in series to the electronic device. The dissipative dielectric layer includes a nonconductive dielectric doped with a voltage dependent resistive material that defines a conductive threshold voltage. The structure functions as a voltage dependent resistor in response to an applied voltage such as an ESD surge voltage exceeding the defined conductive threshold voltage and dissipates the applied voltage into thermal energy before it can reach the electronic device and cause damage. The dissipative dielectric layer restores to a dielectric and the structure functions as a capacitor when the excess voltage is depleted that is drops below the defined conductive threshold voltage. In another embodiment, the structure is a parallel plate dissipative capacitors in series that enhances ESD mitigation through a capacitive voltage divider structure. The structures can be used in EMI / RFI shielding applications.
Owner:SOLECTRON
Napthoquinone derivatives as inhibitors of tau aggregation for the treatment of alzheimer's and related neurodegenerative disorders
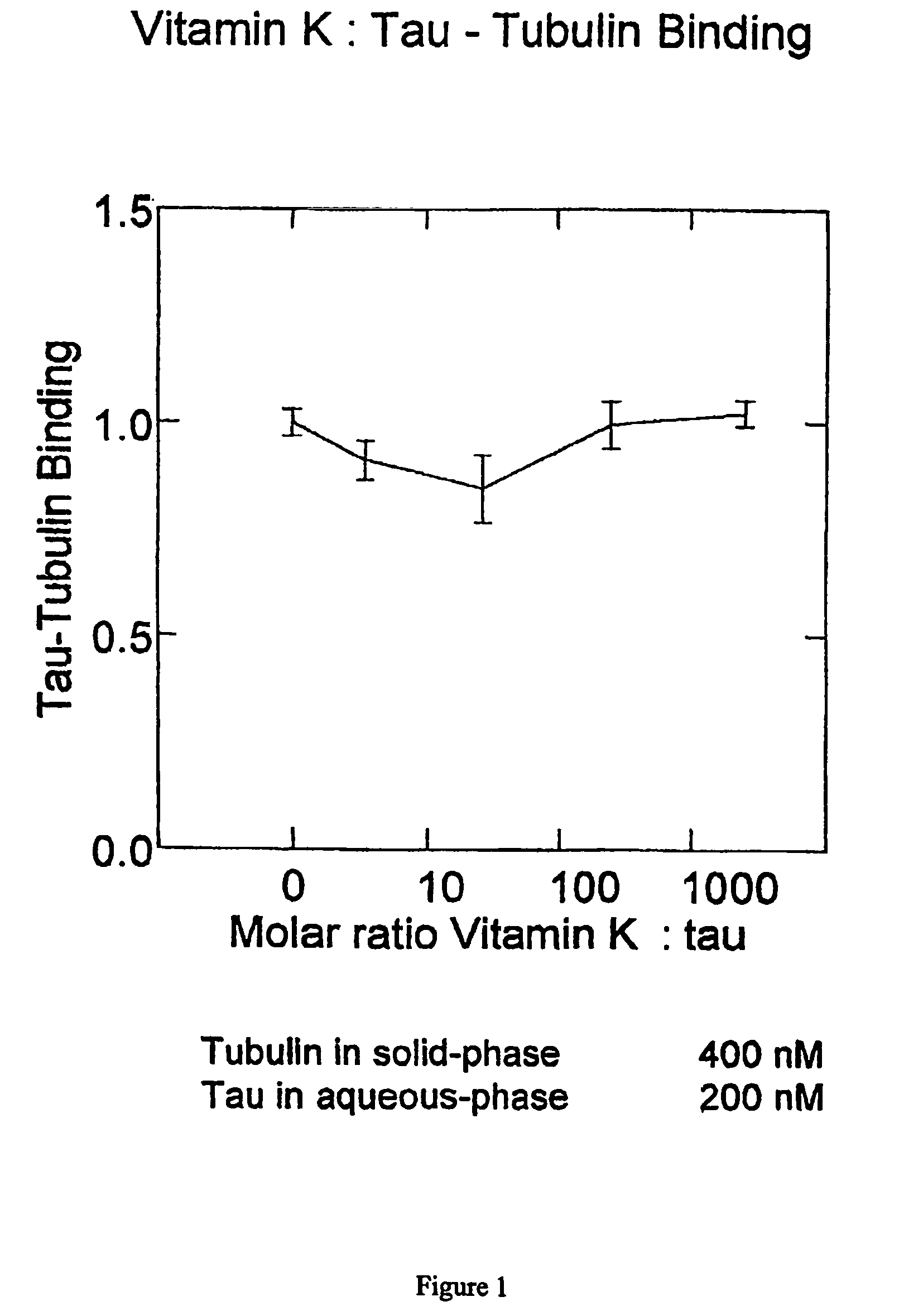
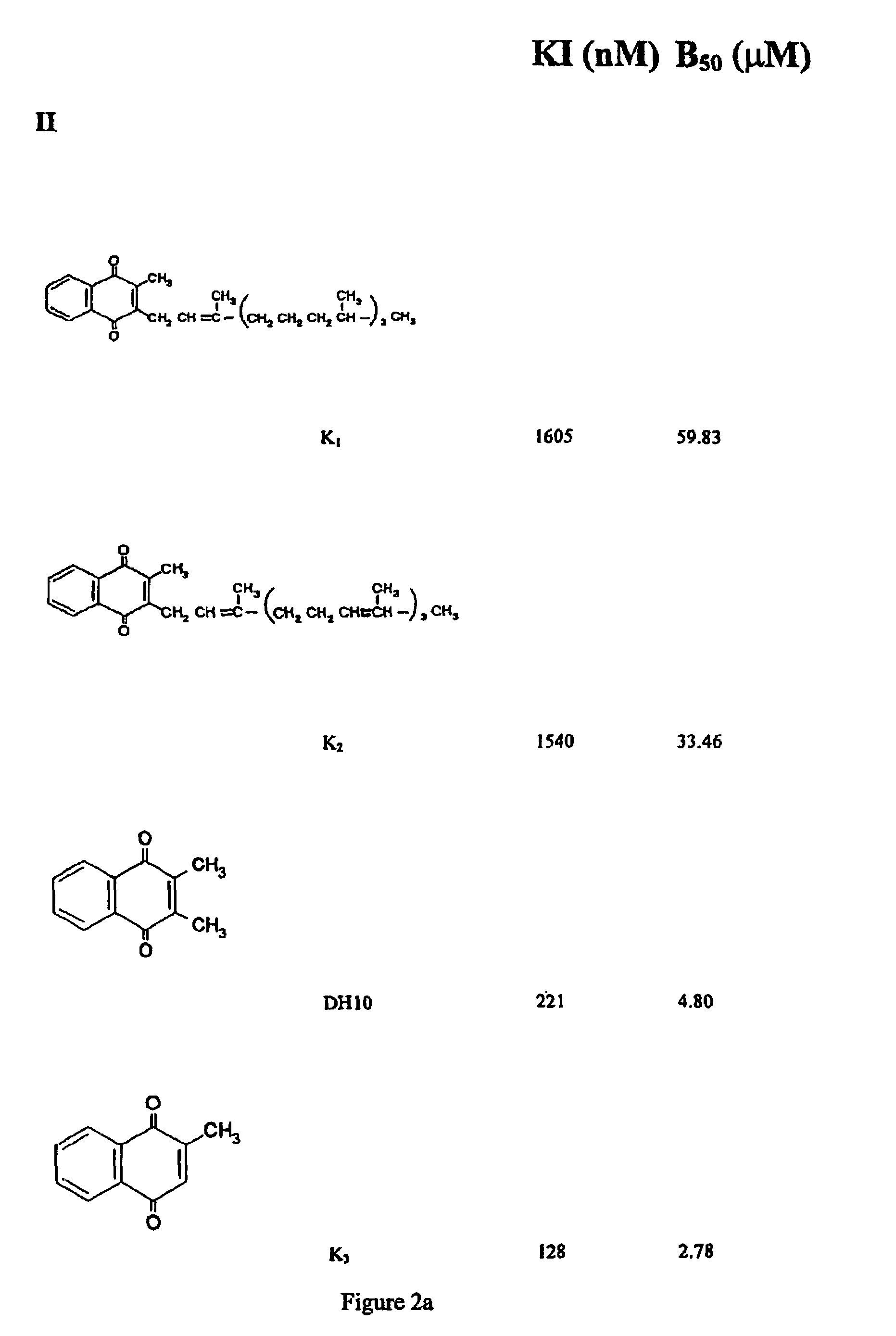
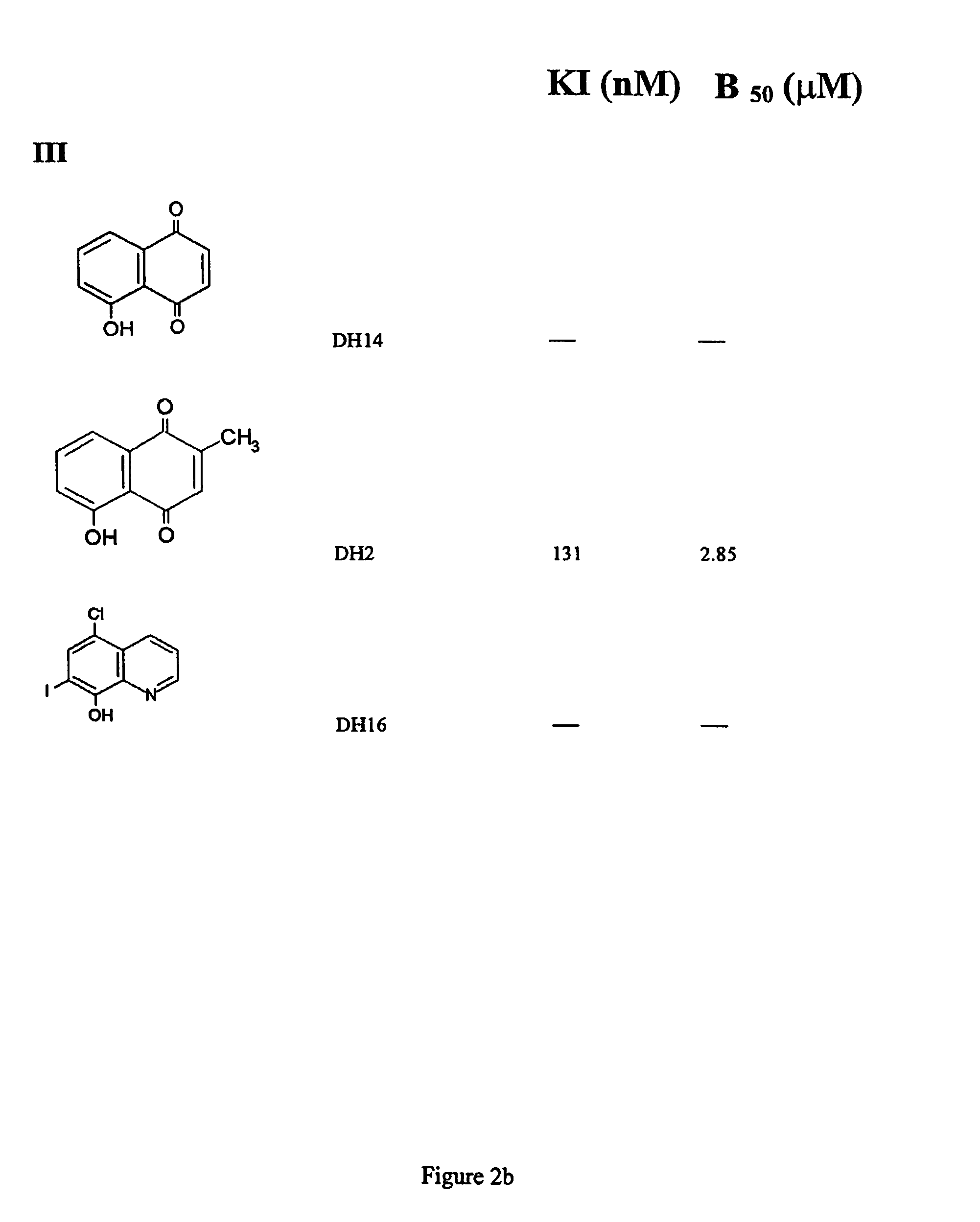
Provided are napthoquinone-type compounds which can be used to modulate the aggregation of protein (e.g. tau) associated with neurodegenerative disease (e.g. Alzheimer's disease). Structure-function characteristics for oxidised and reduced napthoquinone-type compounds, such as menadione-related compounds, are disclosed. The invention further provides methods of treatment or prophylaxis of neurodegenerative diseases and / or clinical dementias based on the compounds.
Owner:WISTA LAB LTD
Satellite structure for platform and load integration
InactiveCN104648693ACompact structureReduce volumeArtificial satellitesSystem qualityResource utilization
The invention discloses a satellite structure for platform and load integration, which relates to the technical field of aerospace and solves the problems of large system mass, large size and the like caused by low resource utilization rate and high structure redundancy of an existing satellite structure system adopting a method that a platform and a load are separately designed. The satellite structure comprises an upper plate, a center bearing cylinder, side plates, a docking ring and a bottom plate, wherein the docking ring is used as an assembling reference, the bottom plate is installed on the docking ring, the center bearing cylinder is installed on the bottom plate, the upper plate is installed on the center bearing cylinder, the side plates are fixed on the side surfaces of the upper plate and the bottom plate, a plurality of upper plate brackets are uniformly arranged in the circumferential direction of the center bearing cylinder, and the upper plate is installed on the center bearing cylinder through the plurality of upper plate brackets. The satellite structure has the advantages of compactness, small size, light weight, high structure function density, high rigidity, large structure safety margin and high reliability.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
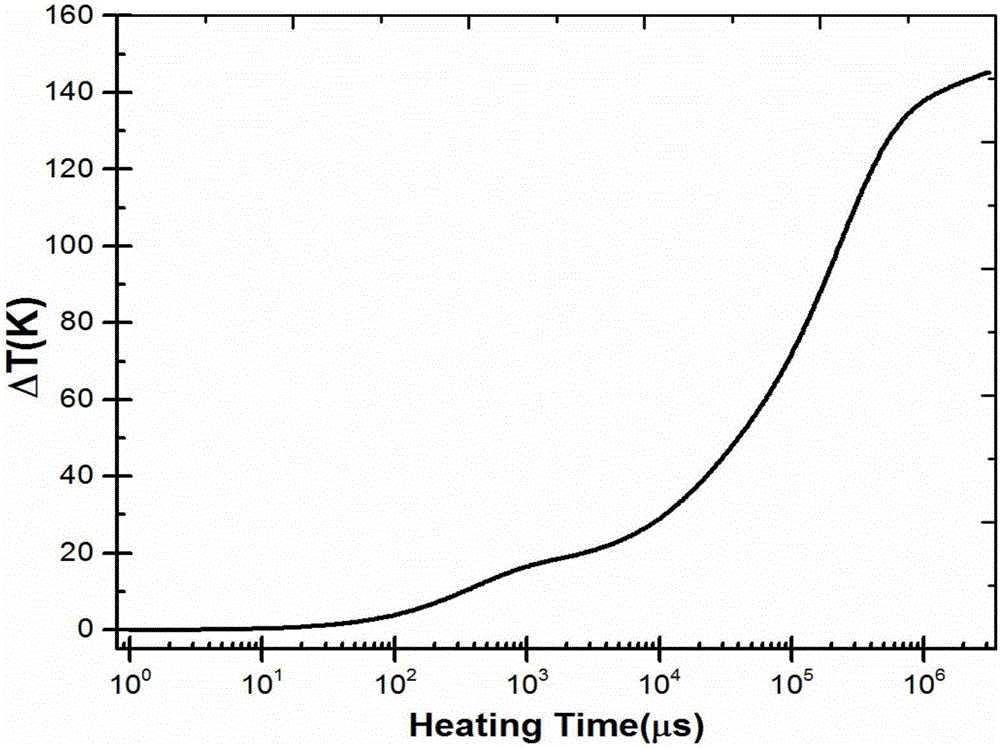
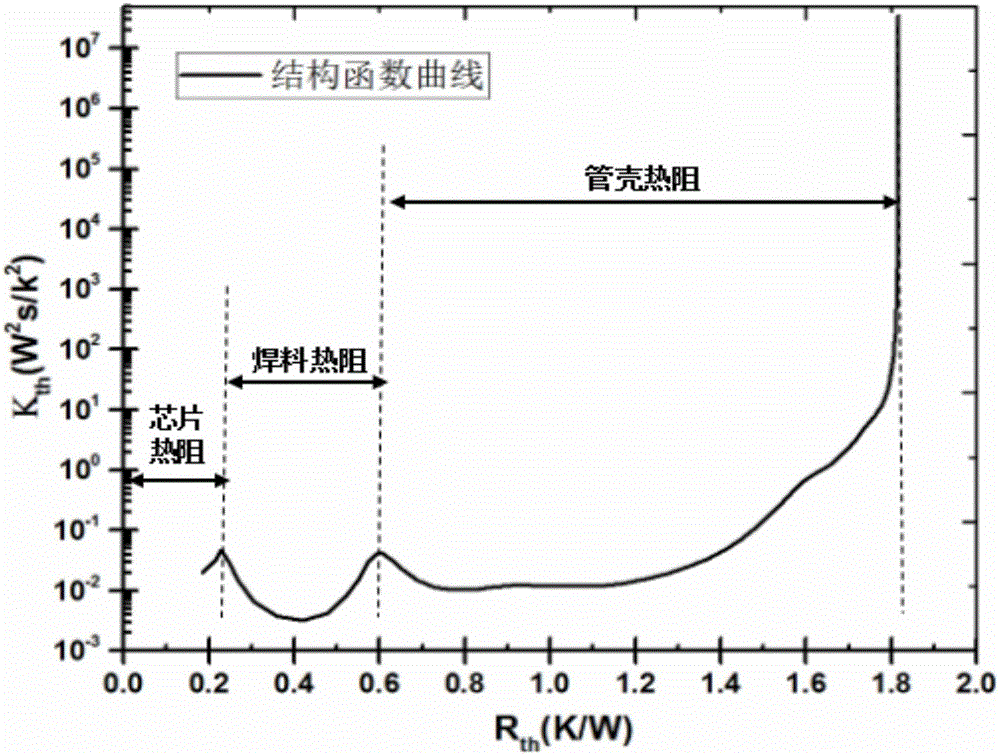
Method for measuring thermal resistance of multi-layer heat-conducting material
InactiveCN103105410ARealize thermal resistance measurementRealize analysisMaterial thermal analysisNon destructiveHeat conducting
The invention discloses a method for measuring the thermal resistance of a multi-layer heat-conducting material, which relates to the field of testing, and can be used for measuring the thermal resistance of each material layer in the multi-layer heat-conducting material. A semiconductor device in a testing system has a heat source function and a testing function. The method comprises the following steps of: fixing the semiconductor device on the upper surface of the multi-layer heat-conducting material, and fixing the lower surface of the multi-layer heat-conducting material on a constant temperature platform; and applying operating current to the semiconductor device for a period of time at any moment, removing the operating current after a steady state is achieved, and measuring a change curve of the junction temperature of the semiconductor device along with the time under the testing current. Because the thermal resistance, thermal capacity and heat transfer rate of each material layer in the multi-layer heat-conducting material are different, the thermal resistance and thermal capacity of each heat-conducting material layer are reflected through the measured change curve of the junction temperature of the semiconductor device along with the time; and according to a structure function method, the thermal resistance composition in each material layer in the multi-layer heat-conducting material is calculated. Moreover, the method belongs to non-destructive testing.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
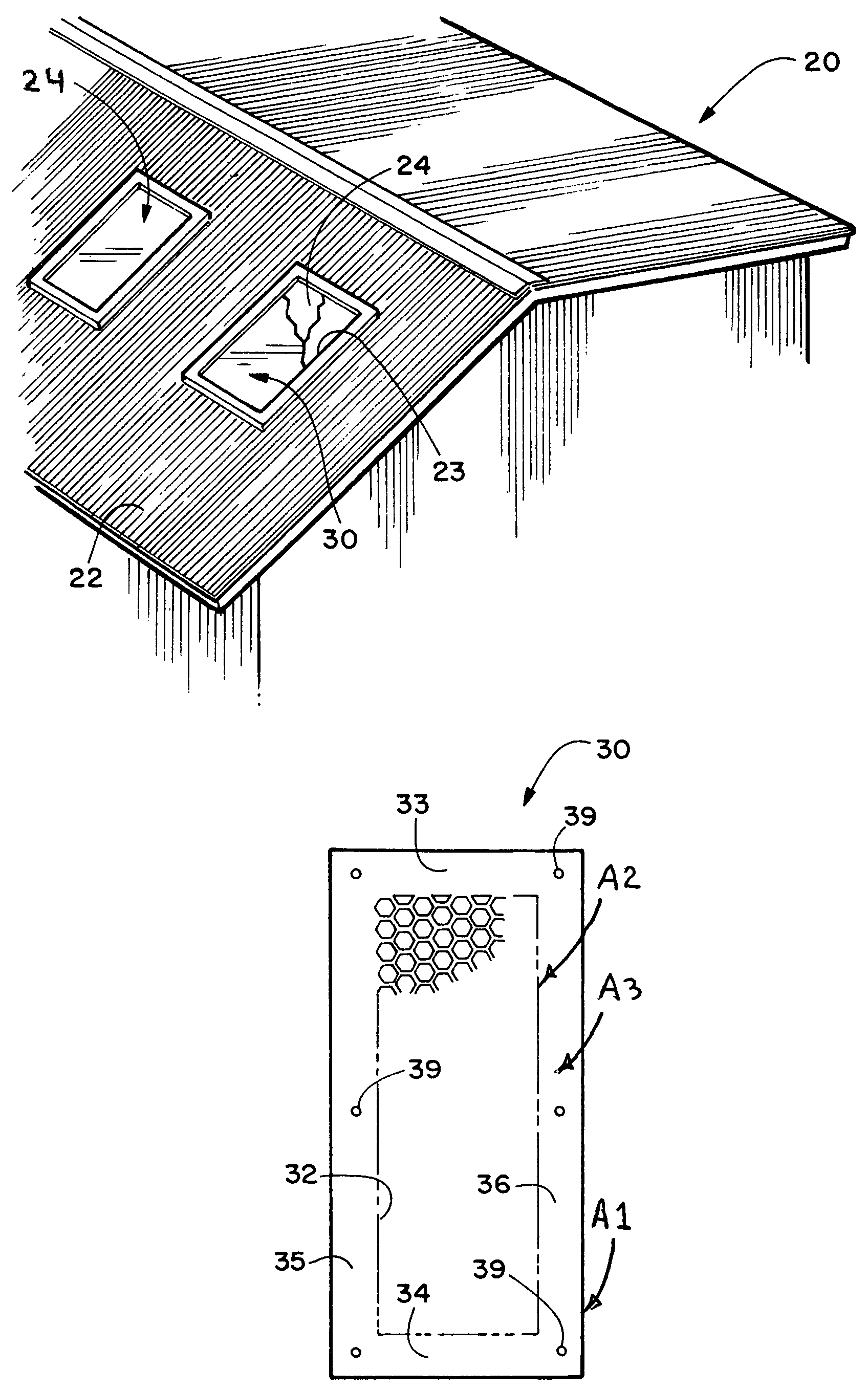
Skylight fall protection safety panel and method of making
A skylight fall protection safety panel formed from a single sheet of metal having a predetermined surface area A1 and a plurality of apertures are punched out of at least one central perimeter surface area A3. A2 is as great as or greater than 0.60A1. The shape of the apertures can take many different forms but they would have a greatest width D1 that is less than 2.0 inches. The central perforated portion has a sufficient number of apertures of a sufficient size that 50 percent of A2 is open to pass light therethrough. The sheet metal safety panel would be secured under an existing fiberglass skylight panel. The sheet panel can also be corrugated to match translucent skylight panels that are corrugated. The sheet metal panel can also be inserted into a mold or cast with a top layer of resin material and a bottom layer of resin material and also having the central perforated portion apertures filled with resin. This assembled structure functions both as a skylight panel and also as a fall protection safety panel that will prevent workers stepping on the top of the assembled structure from falling therethrough and injuring themselves.
Owner:VAN GELDER TERRY L
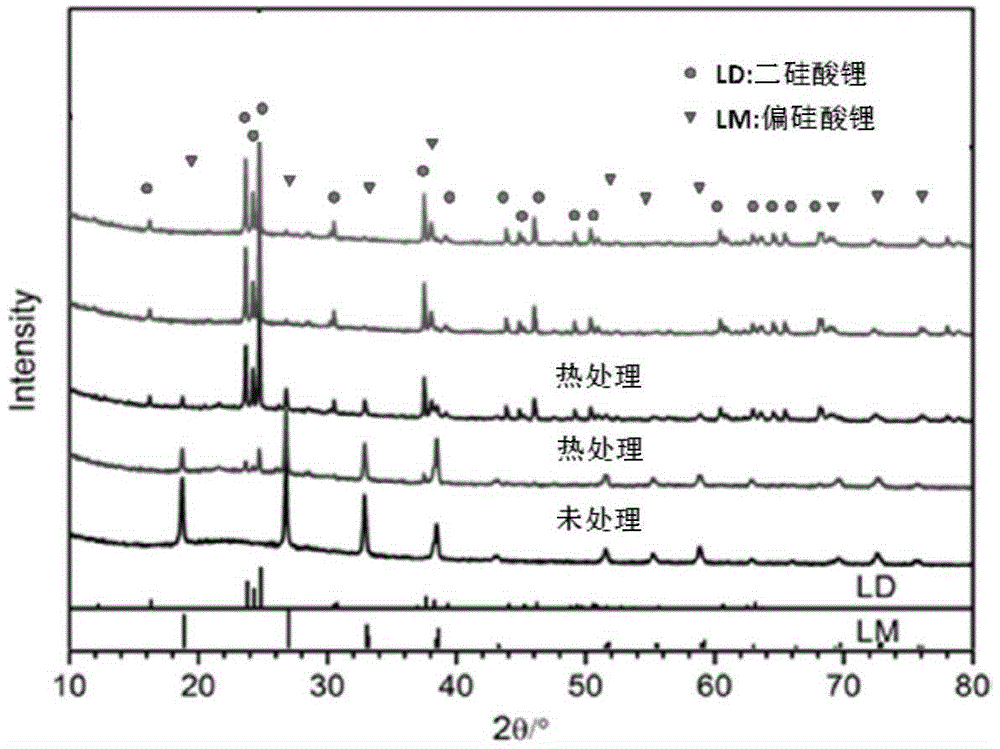
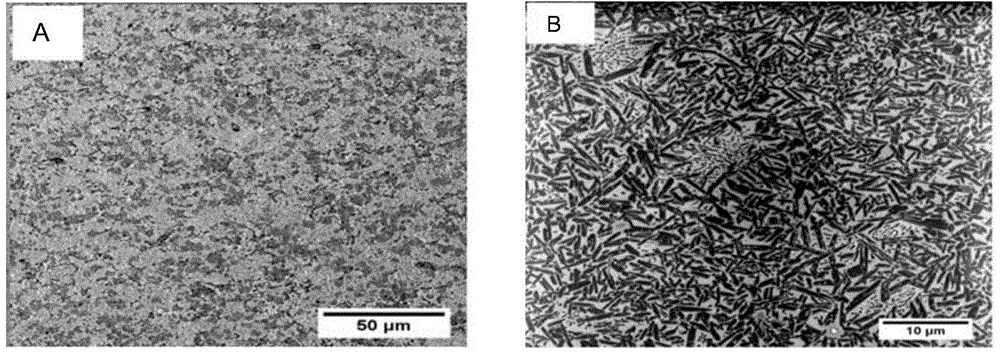
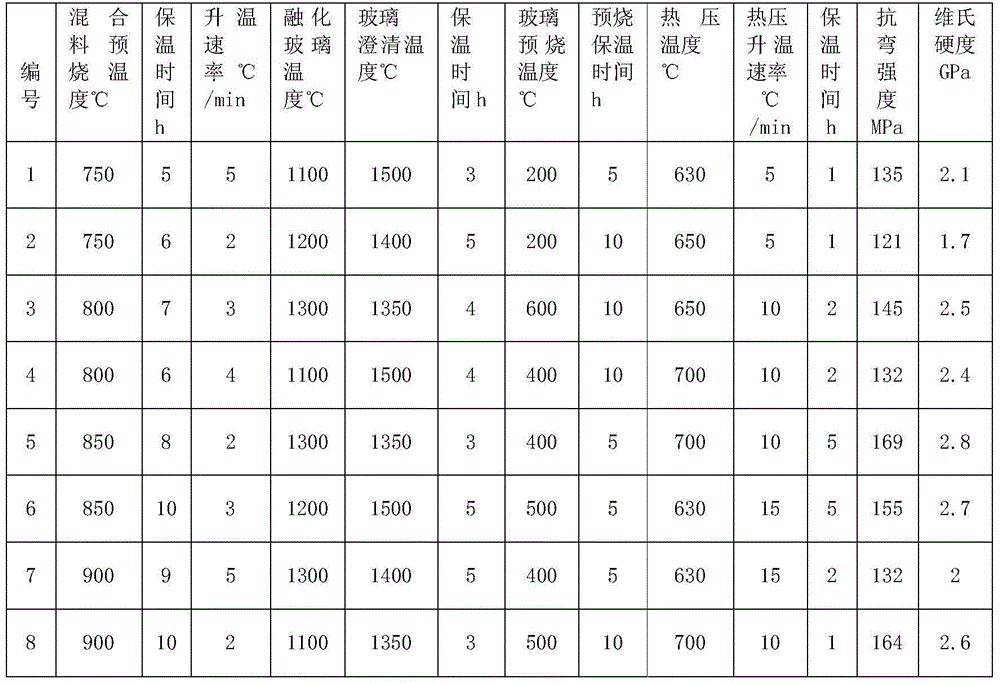
Preparation method for dental lithium silicate microcrystalline glass
ActiveCN104909571AReduce intensityHigh strengthImpression capsDentistry preparationsLithium metasilicateStructure function
The invention discloses a preparation method for dental lithium silicate microcrystalline glass. Glass powder is subjected to hot-pressing sintering, and after a compact lithium metasilicate microcrystalline glass body is formed, lithium metasilicate (Li2SiO3) crystals are converted into lithium disilicate (Li2Si2O5) crystals through heat treatment. The interior of the microcrystalline glass is uniform rod-shaped lithium disilicate (Li2Si2O5) crystals and has a rod-shaped interlock structure. Color matching agents can be intruduced in the hot-pressing sintering phase of the microcrystalline glass material, the obtained lithium metasilicate microcrystalline glass material has good processability, and unification of the manufacturability, mechanical properties and aesthetic functions of the obtained material is achieved. The technology is simple, the processability is strong, performances are stable, and the microcrystalline glass is suitable structure function integrated material.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
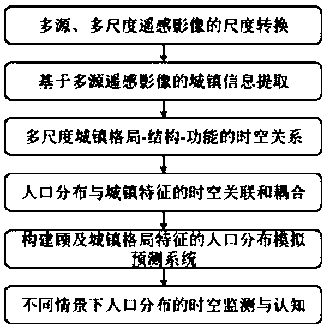
Population distribution spatial-temporal evolution and cognition considering urban pattern characteristics
InactiveCN110458048ARealize multi-scale expressionRealize dynamic simulationData processing applicationsScene recognitionResource utilizationStructure function
The invention relates to a population distribution spatial-temporal evolution and cognition method considering urban pattern characteristics. The population distribution spatial-temporal evolution andcognition method comprises the following steps: 1) carrying out scale conversion of multi-source and multi-scale remote sensing images; 2) extracting urban information based on the multi-source remote sensing image; 3) analyzing a multi-scale urban pattern-structure-function spatial-temporal relationship; 4) carrying out spatial-temporal correlation and coupling analysis on population distribution and urban characteristics; 5) constructing a population distribution simulation and prediction system considering urban pattern characteristics; and 6) carrying out spatial-temporal monitoring and cognition on population distribution in different scenes. The population distribution spatial-temporal evolution and cognition method has the advantages that population general survey and statistical data, multi-scale remote sensing data and multi-source land utilization / coverage data are used as data sources; the spatial-temporal characteristics and the evolution rule of the multi-scale urban spatial pattern are studied, and the population distribution spatial-temporal evolution model considering the town characteristic pattern is constructed, and the boundary of the population distribution density is finely described from the multi-level spatial scale, and a theoretical basis and a technical support are provided for population resource utilization and policy adjustment and social and economic resource allocation.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Natural plant freshness preserving agent for lichee and longan and its use
InactiveCN1586231ANo side effectsReduce manufacturing costFruits/vegetable preservation using chemicalsStructure functionCall structure
The present invention discloses natural plant freshness preserving agent for lichee and longan. Various effective components are extracted from several kinds of plant to constitute with the peel and pulp of lichee and longan the so-called structure-function relationship, so as to reach the effects of strengthening the activity of fruit cell, fixig the color, sterilizing, antisepticising and preventing cell void chocking for preservation. The natural plant freshness preserving agent is green, and has no environmental pollution, low cost and high preserving effect.
Owner:WUHUA COUNTY SUPPLY & MARKETING GROUP GUANGDONG PROV
Method and system for predicting junction temperature of power device
ActiveCN107315877AAccurately Predict Junction TemperatureAccurately Characterize Thermal Distribution PropertiesDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor chip
The invention discloses a method and a system for predicting a junction temperature of a power device. The method comprises the steps of obtaining an integral structure function curve of a tested device; determining a first chip layer according to a packaging form, a packaging material and a starting point of the integral structure function curve of the tested device; performing layering on the first chip layer according to a slope of a curve segment corresponding to the first chip layer in the integral structure function curve to obtain thermal equivalent layers and corresponding thermal resistance values; and building a thermal equivalent layering model of the chip layer of the tested device according to the thermal equivalent layers and the corresponding thermal resistance values, thereby predicting the junction temperature of the tested device. The thermal equivalent layering model is built for the chip layer by adopting a thermal equivalent layering structure instead of physical layering, so that the thermal equivalent layering model can accurately represent a thermal distribution characteristic of the chip layer in the power semiconductor device; the model can accurately predict the junction temperature of the power device; and the method for building the thermal equivalent layering model is used for all power semiconductor chips, and is convenient to implement and popularize.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Preparation method of thermosetting shape memory resin with two glass transition temperatures
InactiveCN103740054ALower glass transition temperatureAchieve deformationStructure functionResin matrix
The invention belongs to the technical field of shape memory functional applications of high-performance resin-based composite materials and relates to a preparation method of thermosetting shape memory resin with two glass transition temperatures. The thermosetting shape memory resin comprises a thermoplastic polymer, thermosetting resin and a curing agent, wherein the glass transition temperature after the reaction of the thermosetting resin and the curing agent is 10 DEG C-200 DEG C higher than the glass transition temperature of the thermoplastic polymer. The thermosetting shape memory resin with the two glass transition temperatures provided by the invention has not only a shape memory function, but also relatively high mechanical properties and temperature-resistant glass, and can be used as a resin matrix of the shape memory composite material for intelligent morphing aircrafts and aerospace large-scale mechanisms which can be expanded automatically and realize structure-function integration of the fiber-reinforced resin-based composite material.
Owner:AVIC COMPOSITES
Power MOS device temperature rise and thermal resistance component test device and method
ActiveCN106443401AGet goodLossless acquisitionIndividual semiconductor device testingTest powerStructure function
The invention relates to a power MOS device temperature rise and thermal resistance component test device and method and belongs to the power MOS device reliability design and test field. According to the test device and method of the invention, a fast switching switch of drain-source voltage and gate-source voltage signal control of a tested power MOS device and a fast switching switch of drain-source high-current work are designed; and an FPGA is adopted to design the acquisition and setting function of drain-source voltage, gate-source voltage and drain-source current. In a testing process, a temperature-sensitive parameter curve is obtained at first; operating current is applied to the device, so that the temperature of the device can rise; after the output power of the device achieves a steady state, the operating current is cut off, and test current is switched on; the junction voltage of the drain-source parasitic diode of the power MOS device is acquired, so that the junction temperature curve of the device can be obtained correspondingly; processing analysis is carried out through adopting a structural function method, so that the thermal resistance components of the power MOS device can be obtained. With the power MOS device temperature rise and thermal resistance component test device and method of the invention adopted, the problems of high prices of test instruments, complicated operation of measurement technologies and long measurement period can be solved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com