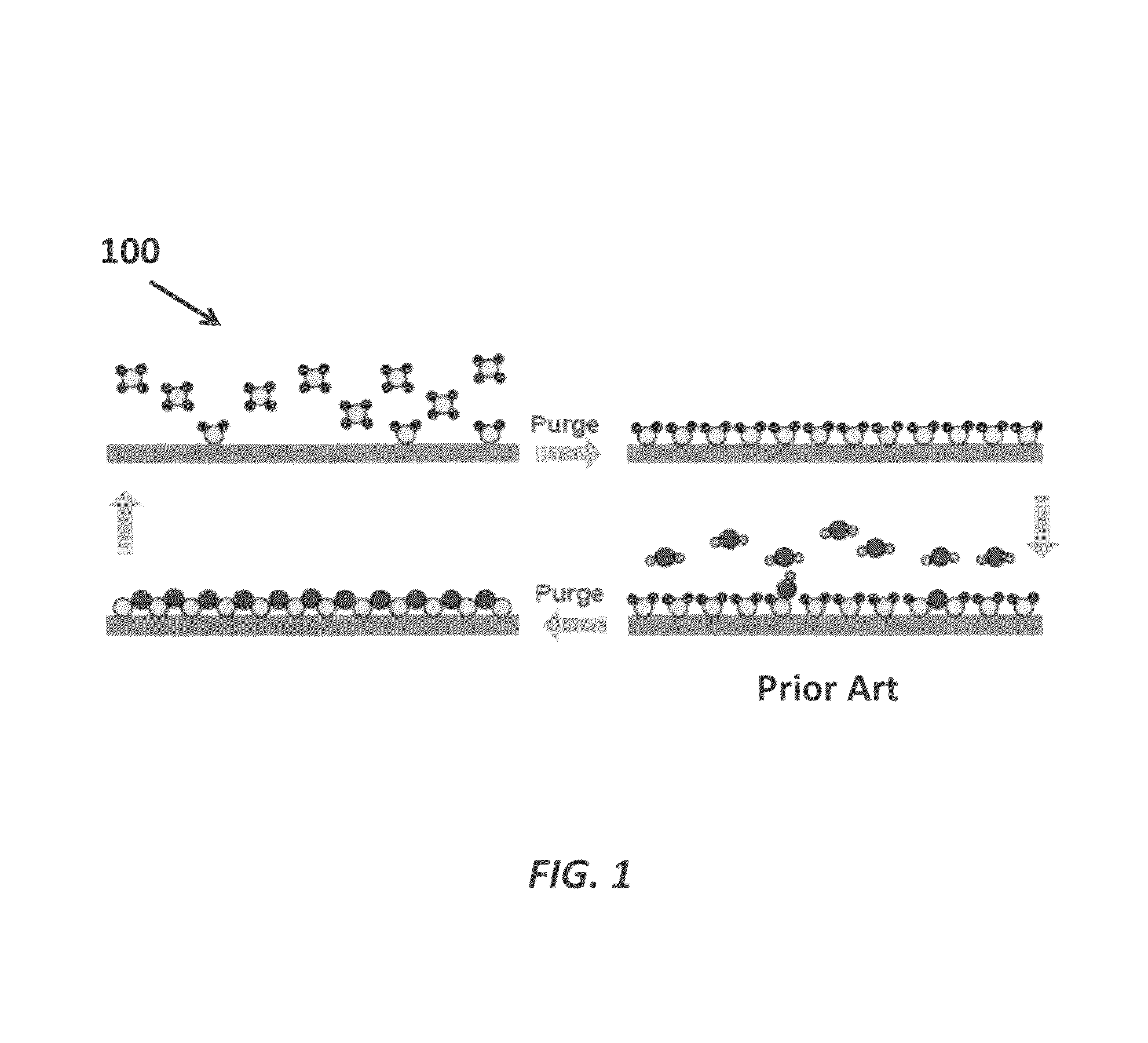
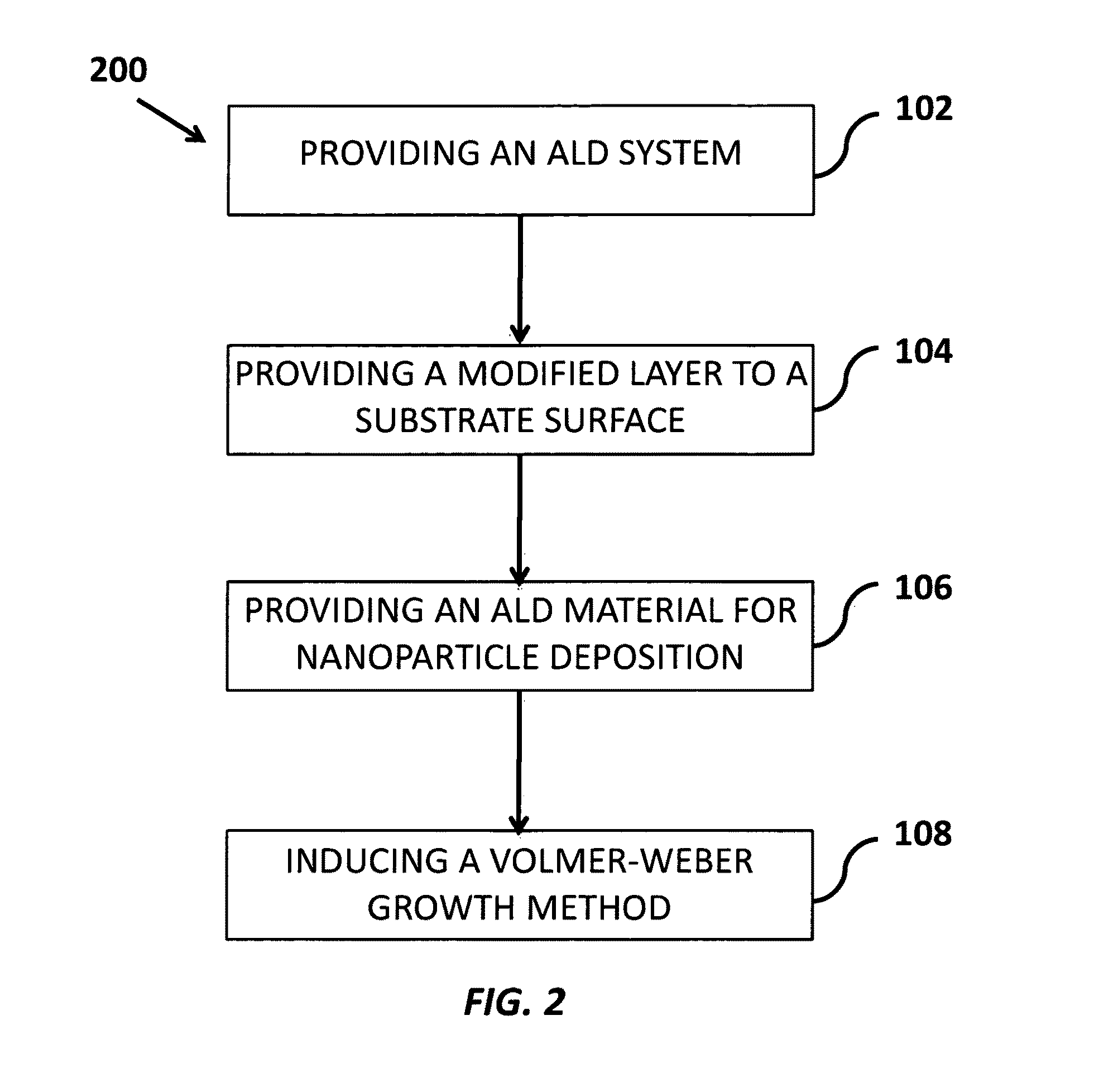
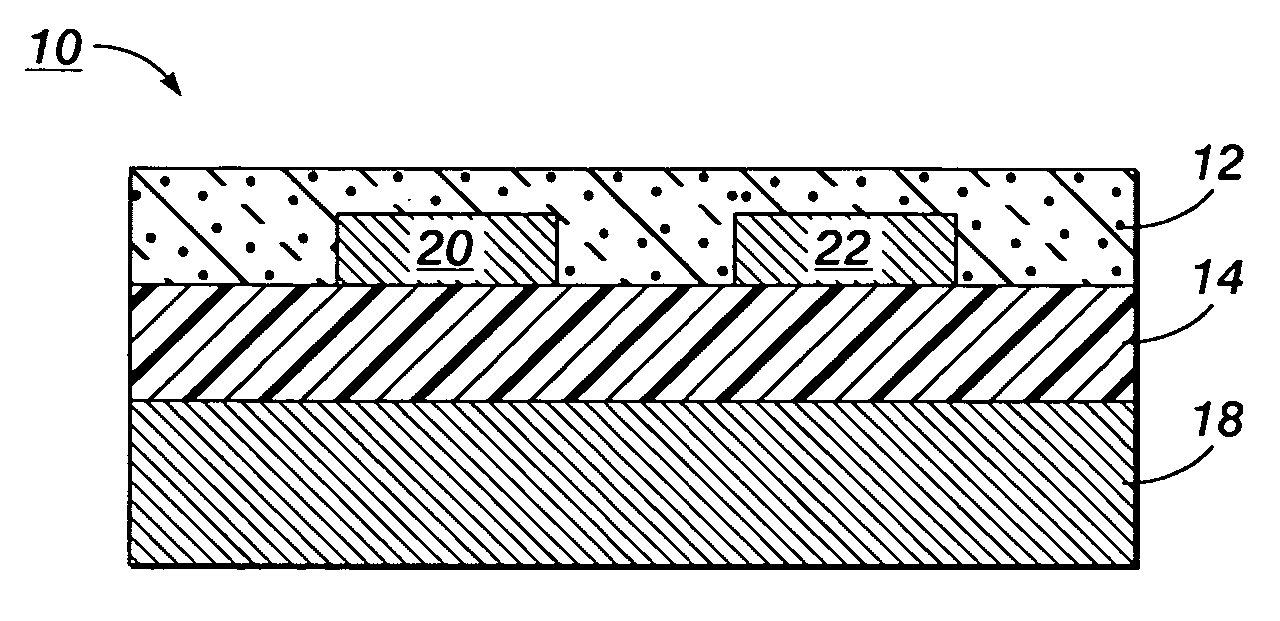
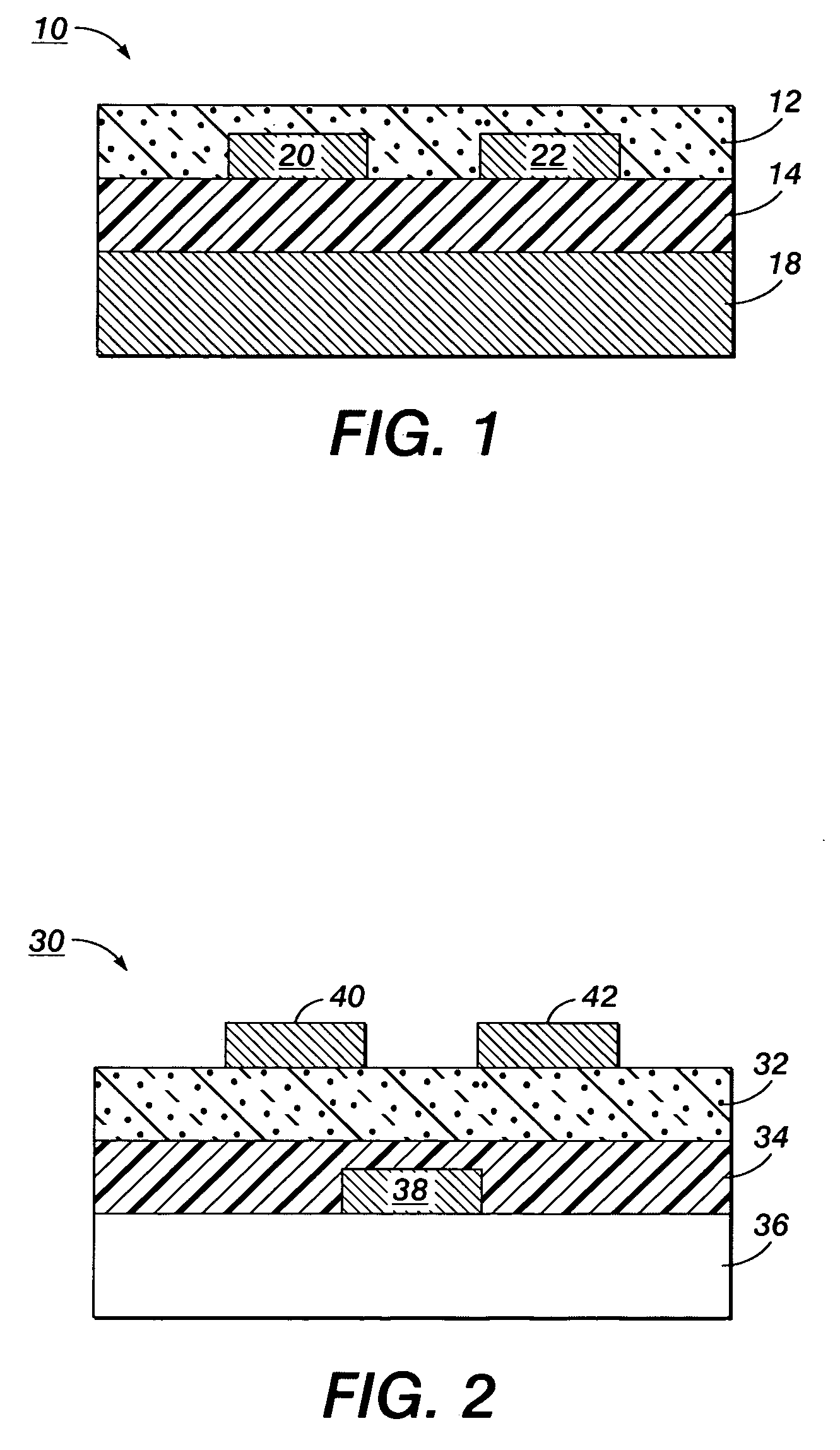
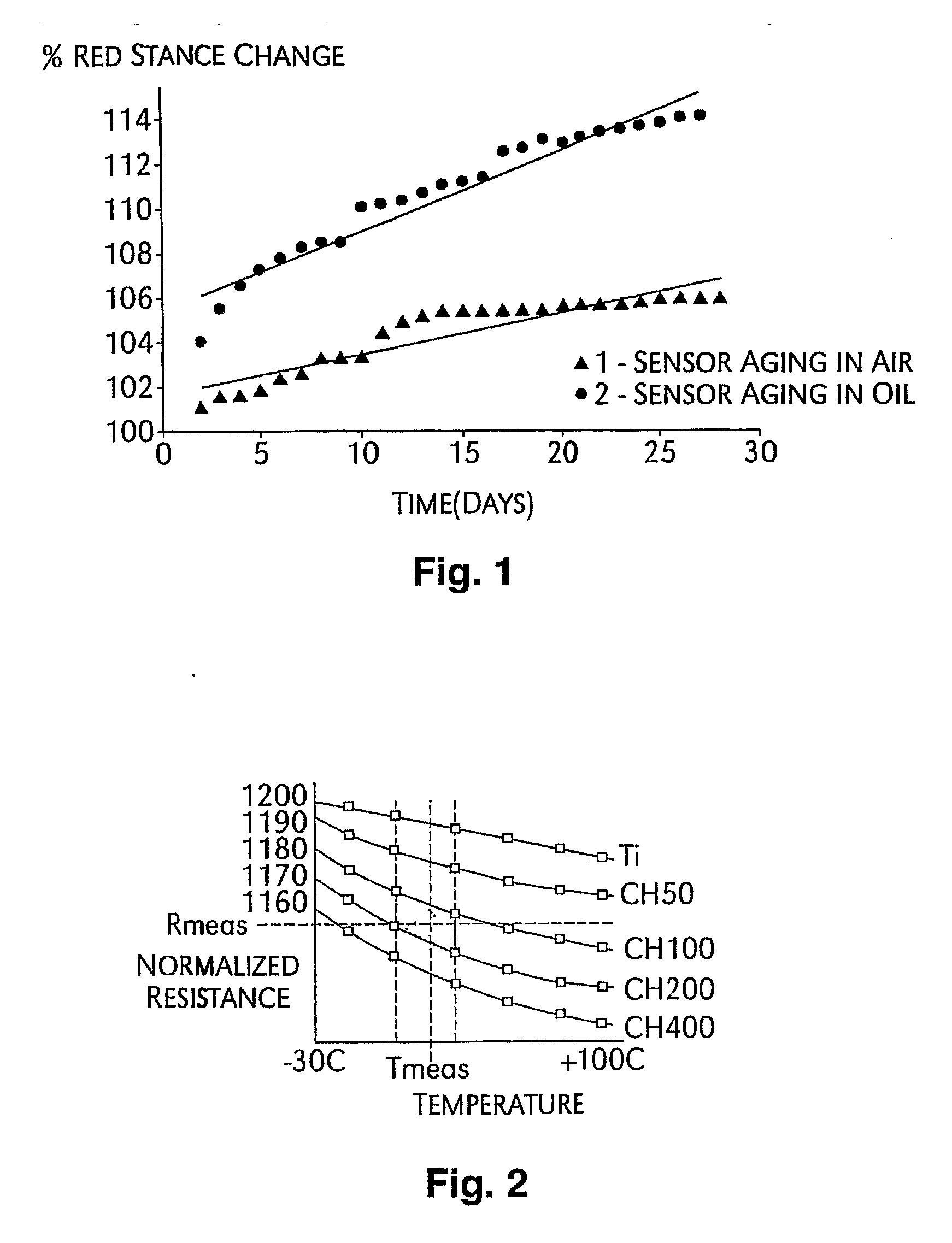
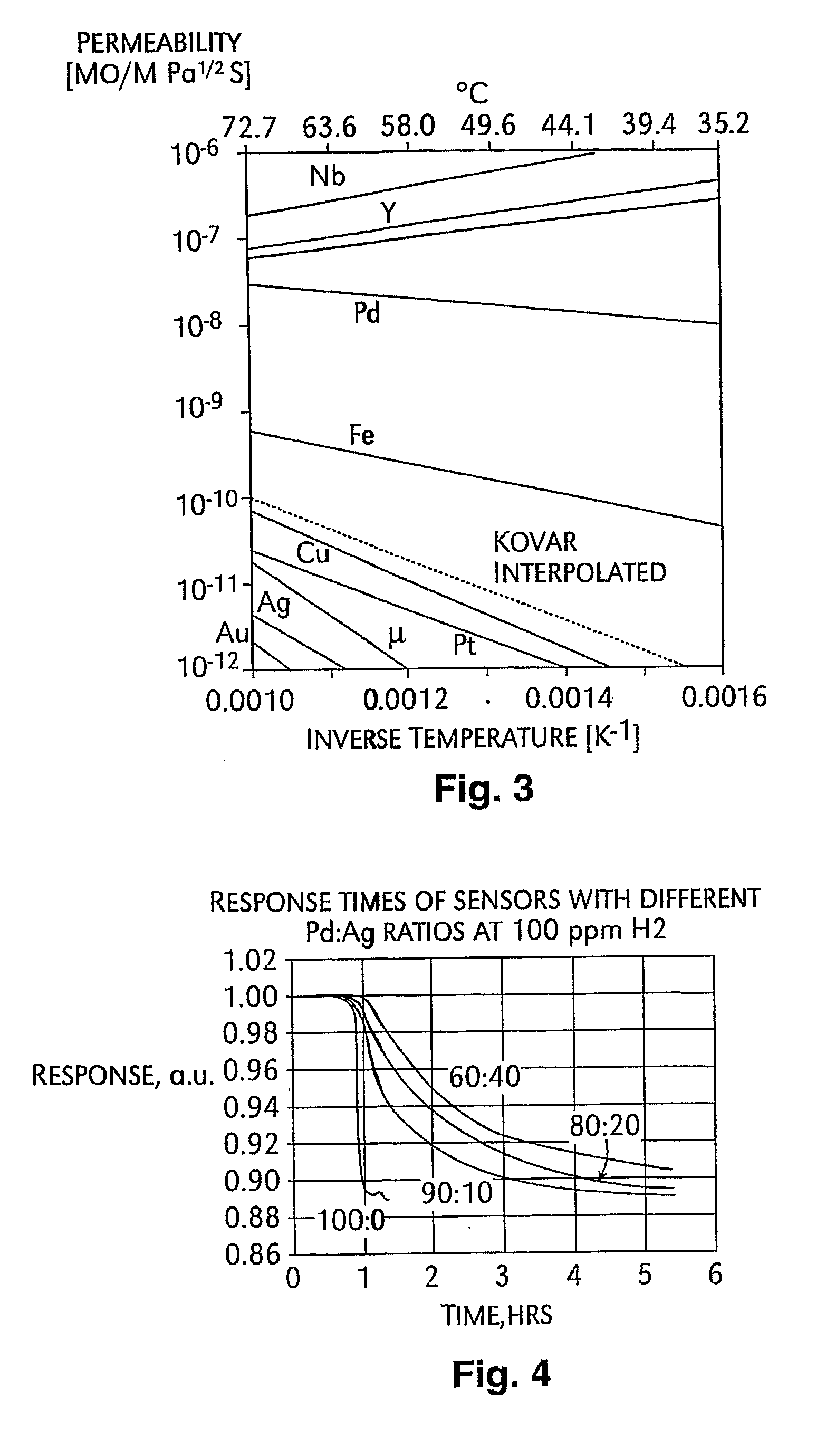
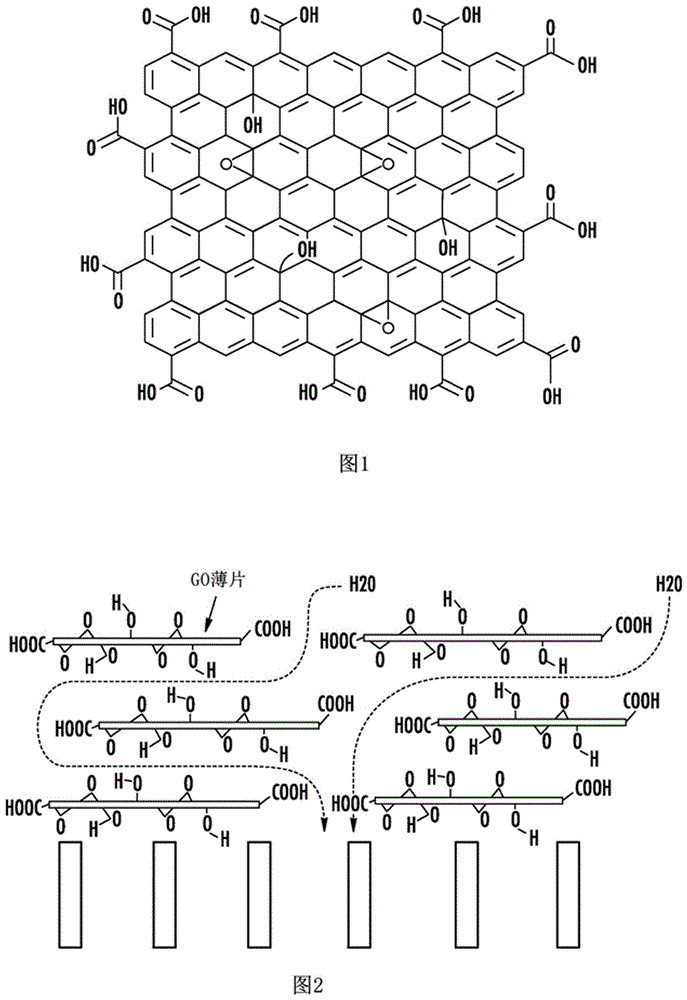
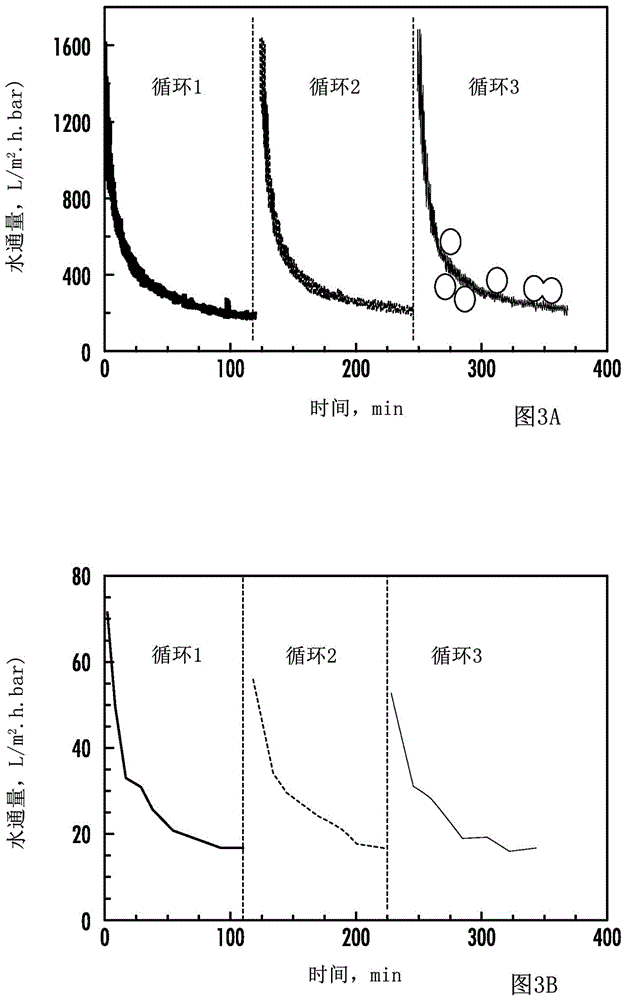
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
151 results about "Nanoparticle deposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
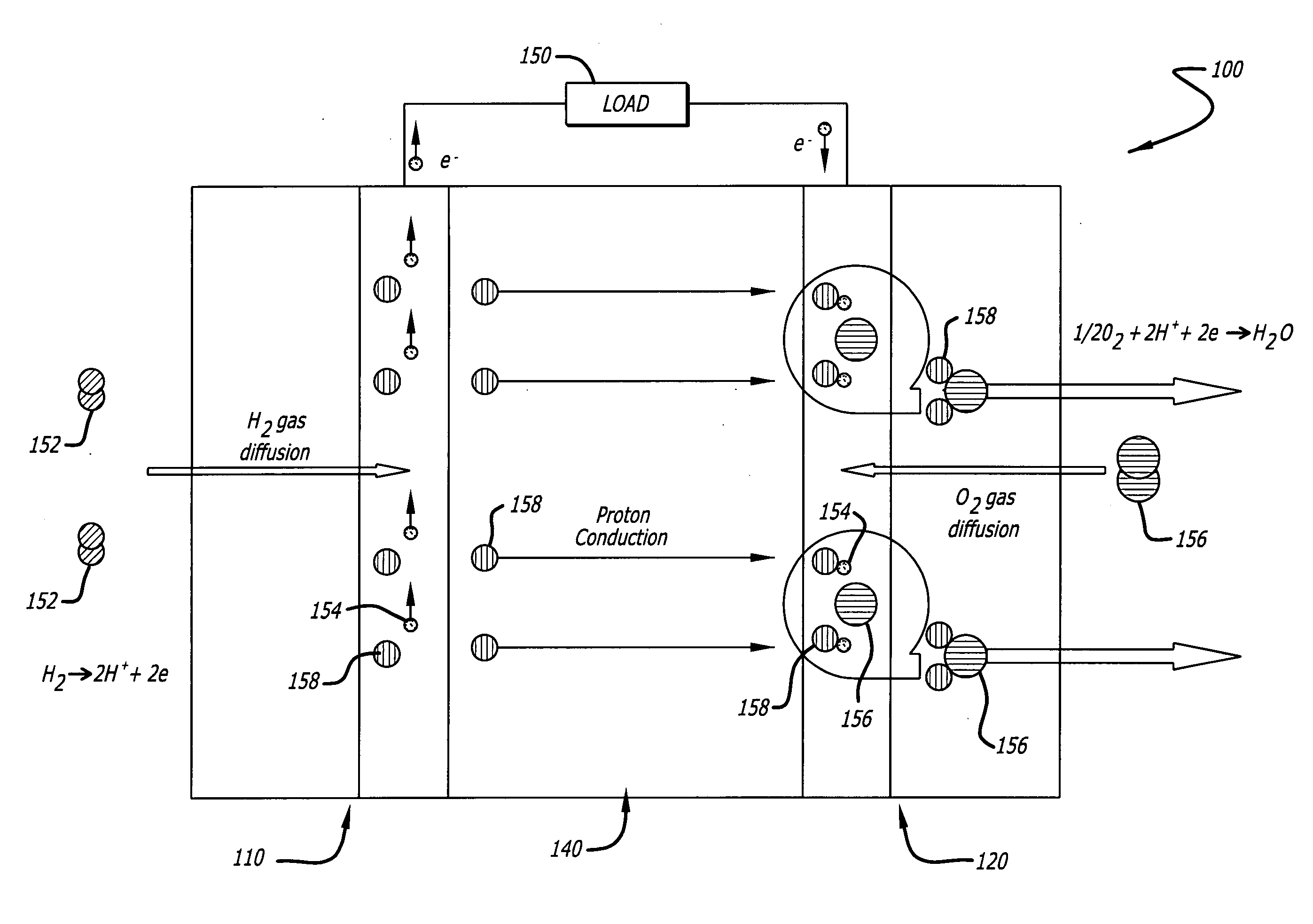
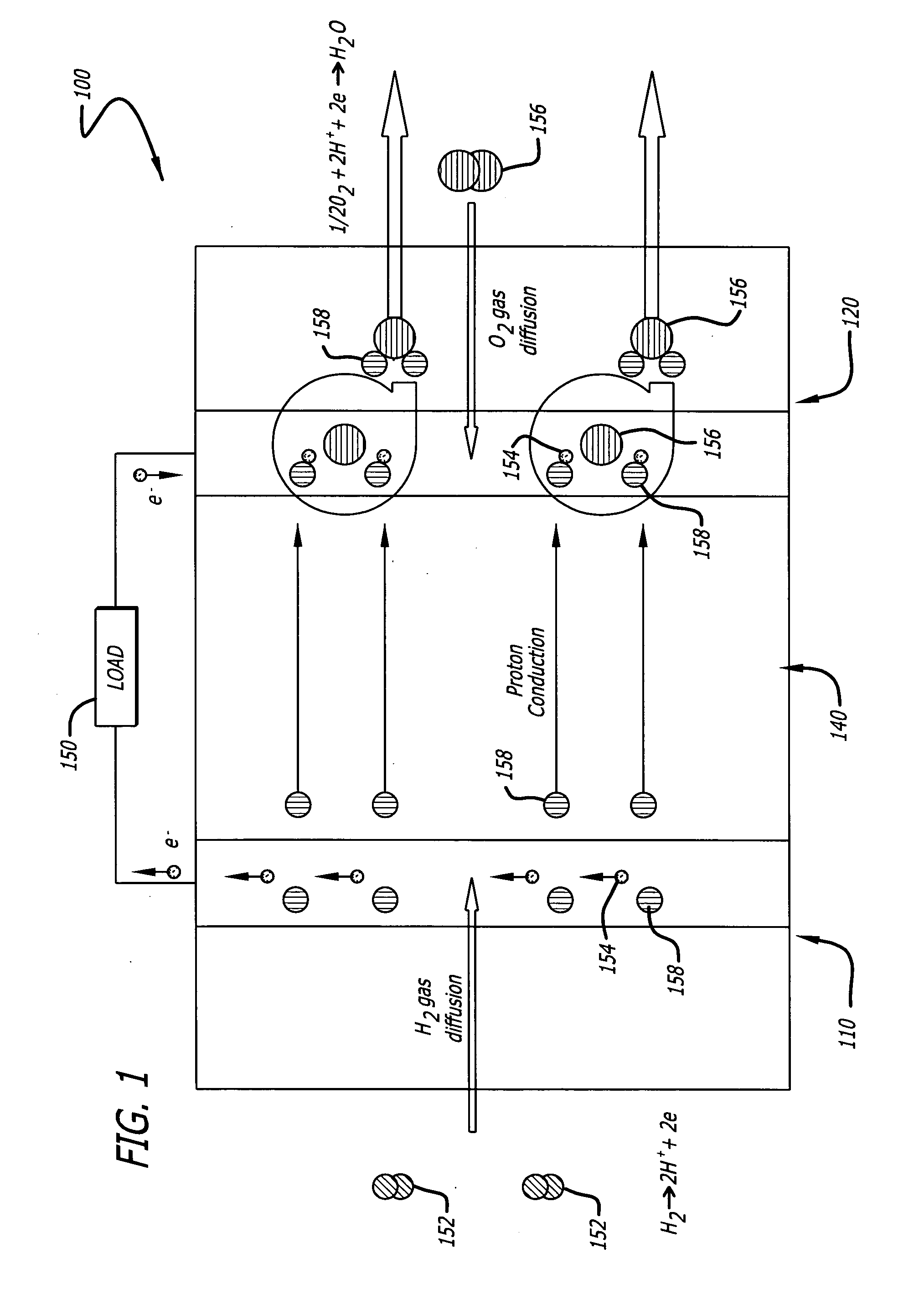
Nanoparticle deposition refers to the process of attaching nanoparticles to solid surfaces called substrates to create coatings of nanoparticles. The coatings can have a monolayer or a multilayer and organized or unorganized structure based on the coating method used. Nanoparticles are typically difficult to deposit due to their physical properties.
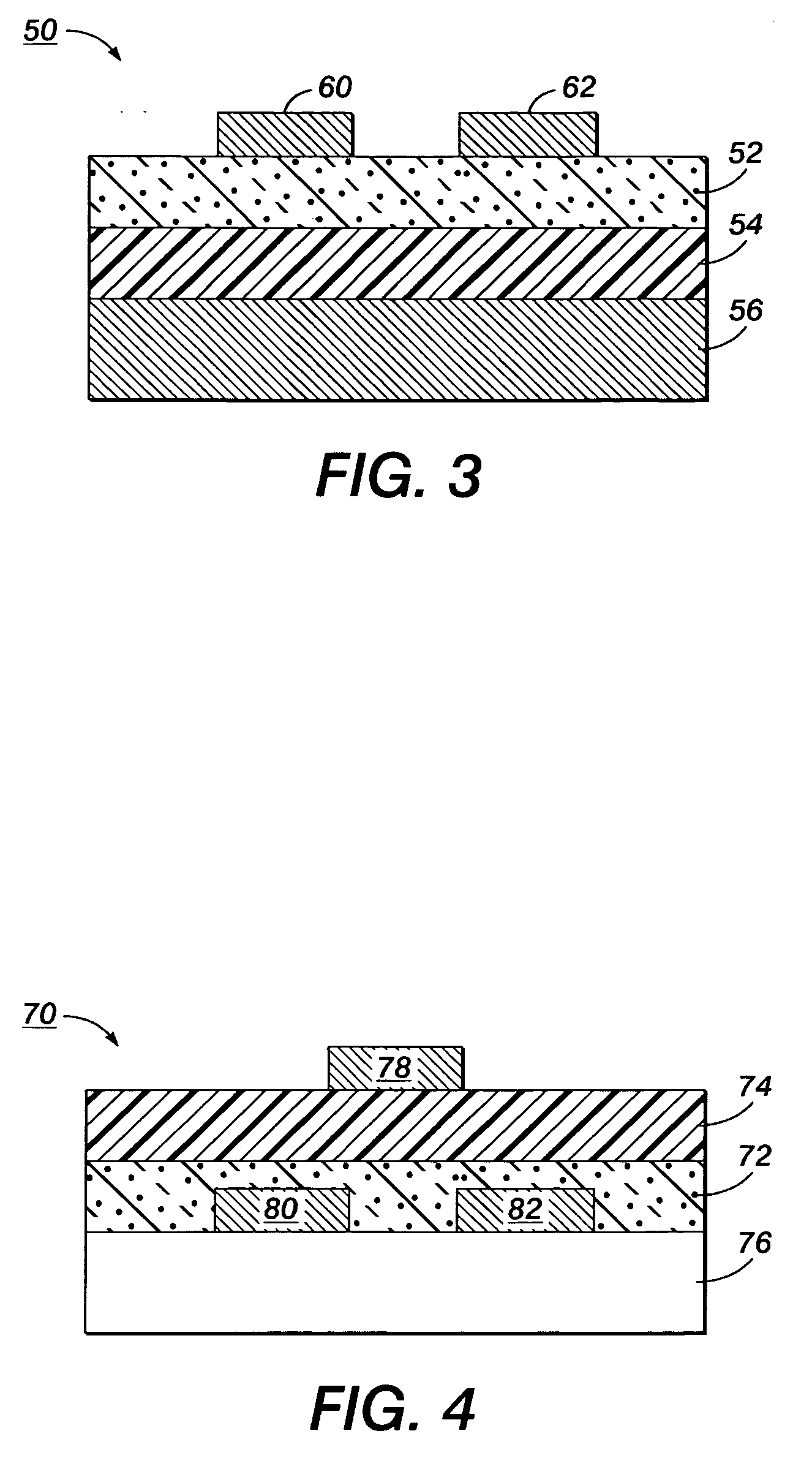
Nanoscale electronic devices & frabrication methods
InactiveUS20050064618A1Raise the possibilityConductive layers on insulating-supportsNanostructure manufactureNanowireElectric devices
The invention relates to a method of forming a conducting nanowire between two contacts on a substrate surface wherein a plurality of nanoparticles is deposited on the substrate in the region between the contacts, and the single nanowire running substantially between the two contacts is formed by either by monitoring the conduction between the contacts and ceasing deposition at the onset of conduction, and / or modifying the substrate to achieve, or taking advantage of pre-existing topographical features which will cause the nanoparticles to form the nanowire. The resultant conducting nanowires are also claimed as well as devices incorporating such nanowires.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CANTERBURY
Nanoparticle deposition process
A process including: (a) solution depositing a composition composed of a liquid and a plurality of metal nanoparticles with a stabilizer on a substrate to result in a deposited composition; and (b) heating the deposited composition to cause the metal nanoparticles to form an electrically conductive layer of an electronic device, wherein one or more of the liquid, the stabilizer, and a decomposed stabilizer is optionally part of the electrically conductive layer but if present is in a residual amount.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Direct epoxidation catalyst and process
InactiveUS20110152550A1Similar and good olefin selectivityOrganic chemistryMolecular sieve catalystsHydrogenTitanium
A catalyst, useful for the direct epoxidation of olefins, is disclosed. The catalyst comprises palladium nanoparticles, support nanoparticles, and a titanium zeolite having a particle size of 2 microns or greater. The palladium nanoparticles are deposited on the support nanoparticles to form supported palladium nanoparticles, and the supported palladium nanoparticles are deposited on the titanium zeolite; or the supported palladium nanoparticles are deposited on a carrier having a particle size of 2 microns or greater. The invention also includes a process for producing an epoxide comprising reacting an olefin, hydrogen and oxygen in the presence of the catalyst. The catalysts are more active in epoxidation reactions, while demonstrating the same or better selectivity.
Owner:LYONDELL CHEM TECH LP
Nano-graphite alkenyl composite wave-absorbing material and method of preparing the same
The present invention provides a nano-graphite alkenyl composite wave-absorbing material and method of preparing the same. The wave-absorbing material includes graphite alkenyl and nanoparticle deposition material which is metal or metallic oxide; the weight percentage of the graphite alkenyl is 15-95%, the weight percentage of the nanoparticle deposition material is 5-85%, the metal or metallic oxide nanoparticle is deposited on the graphite alkenyl surface and between the layers, prepared by the metal salt and graphite alkenyl in the electrodeposition pattern. The nano-graphite alkenyl composite wave-absorbing material is provided with stable capability, thin thickness, low density, corrosion resistant, simple manufacture, good wave-absorbing capability and favourable application foreground.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Carbon based electrocatalysts for fuel cells
InactiveUS20100159305A1High utilization rateHigh power densityActive material electrodesCoatingsHot pressPrecious metal
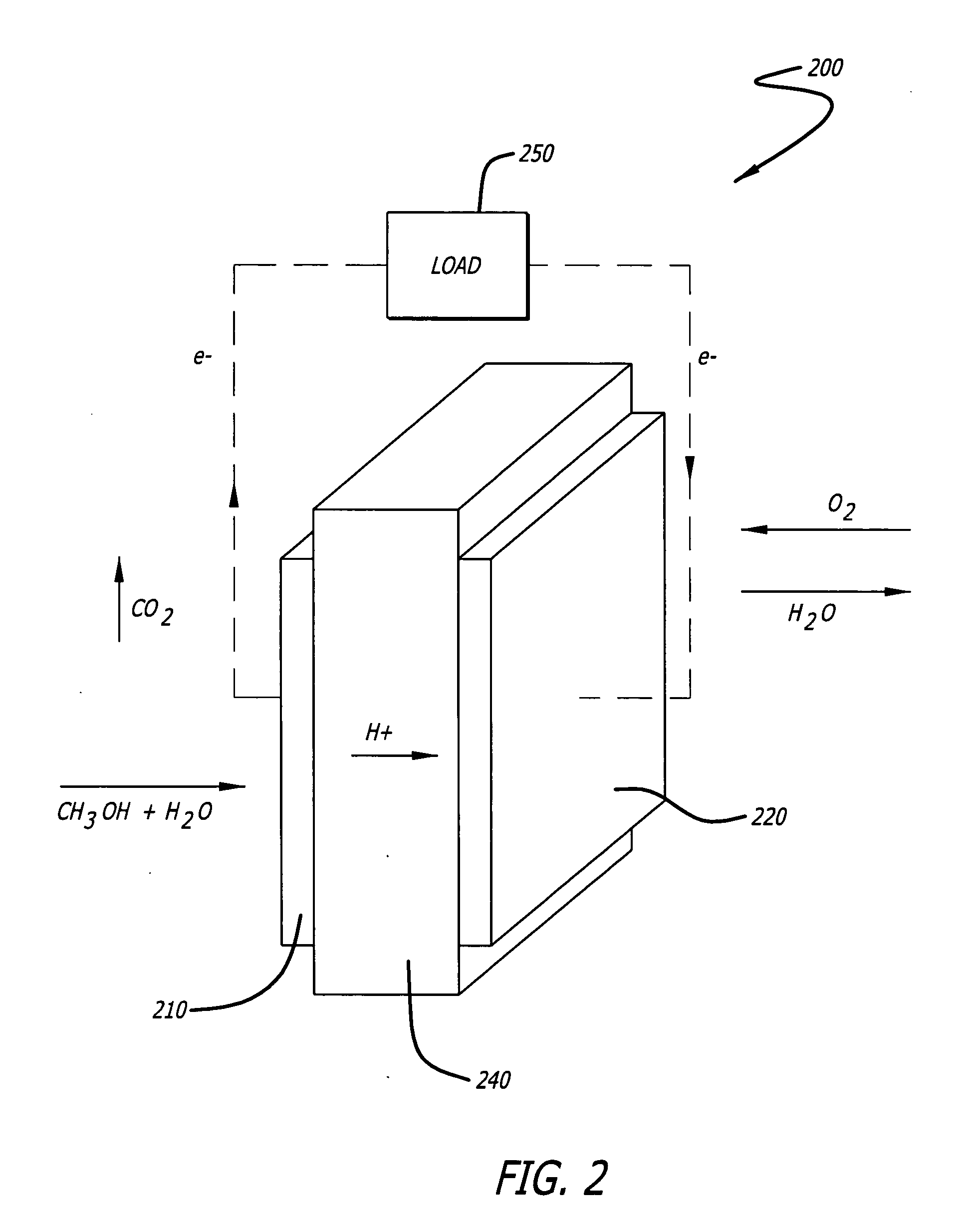
Novel proton exchange membrane fuel cells and direct methanol fuel cells with nanostructured components are configured with higher precious metal utilization rate at the electrodes, higher power density, and lower cost. To form a catalyst, platinum or platinum-ruthenium nanoparticles are deposited onto carbon-based materials, for example, single-walled, dual-walled, multi-walled and cup-stacked carbon nanotubes. The deposition process includes an ethylene glycol reduction method. Aligned arrays of these carbon nanomaterials are prepared by filtering the nanomaterials with ethanol. A membrane electrode assembly is formed by sandwiching the catalyst between a proton exchange membrane and a diffusion layer that form a first electrode. The second electrode may be formed using a conventional catalyst. The several layers of the MEA are hot pressed to form an integrated unit. Proton exchange membrane fuel cells and direct methanol fuel cells are developed by stacking the membrane electrode assemblies in a conventional manner.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for the lithographic deposition of materials containing nanoparticles
A method for depositing nanoparticles in a thin film through the dispersion of such nanoparticles in a precursor solution which is deposited on a substrate and converted into a metal or metal oxide film. The resulting metal or metal oxide film will contain embedded nanoparticles. Such films can be used in a variety of applications such as diffusion barriers, electrodes for capacitors, conductors, resistors, inductors, dielectrics, or magnetic materials. The nanoparticle material may be selected by one skilled in the art based on the particular application.
Owner:SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY
Super-hydrophobic textile prepared from modified polyester fiber based on dopamine and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a super-hydrophobic textile prepared from a modified polyester fiber based on dopamine and a preparation method thereof, the preparation method comprises the steps that a polyester fabric is soaked into different buffer solutions in sequence, nano-particles produced by dopamine polymerization are deposited on the fiber surface adhered with polydopamine, the fiber is finally treated by a low surface energy modifier to obtain the super-hydrophobic textile; the buffer solution at east comprises two kinds of different buffer solutions, namely, a phosphate buffer solution of the dopamine and a trihydroxymethyl aminomethane buffer solution of the dopamine. According to the super-hydrophobic textile prepared from the modified polyester fiber based on the dopamine and the preparation method thereof, the characteristic that the sizes of polydopamine nano particles produced by dopamine polymerization in different buffer solution systems is utilized, autoxidation polymerization of dopamine is utilized to be adhered to and deposited on the fiber surface to form a rough structure required by the super-hydrophobic surface, and the super-hydrophobic surface can be prepared after the rough structure is treated by the low surface energy; the reaction process is simple, the condition is mild; and the water drop contact angle of the super-hydrophobic surface prepared by the invention is more than 150 degree.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparation of metal chalcogenide solar cells on complexly shaped surfaces
InactiveUS20120100660A1Electrolytic coatingsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumMetal chalcogenides
Methods for fabricating a photovoltaic device on complexly shaped fabricated objects, such as car bodies are disclosed. Preferably the photovoltaic device includes absorber layers comprising Copper, Indium, Gallium, Selenide (CIGS) or Copper, Zinc, Tin, Sulfide (CZTS). The method includes the following steps: a colloidal suspension of metal surface-charged nanoparticles is formed; electrophoretic deposition is used to deposit the nanopartieles in a metal thin film onto a complexly shaped surface of the substrate; the metal thin film is heated in the presence of a chalcogen source to convert the metal thin film into a metal chalcogenide thin film layer; a buffer layer is formed on the metal chalcogenide thin film layer using a chemical bath deposition; an intrinsic zinc oxide insulating layer is formed adjacent to a side of the buffer layer, opposite the metal chalcogenide thin film layer, by chemical vapor deposition; and finally, a transparent conducting oxide is formed adjacent to a side of the intrinsic zinc oxide, opposite the buffer layer, by chemical vapor deposition.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Method for producing functional glass surfaces by changing the composition of the original surface
InactiveUS20090104369A1Change the functionality of glassSpecial surfacesCoatingsNanometreMaterials science
A method for modifying glassy surfaces including: producing nanoparticles; depositing the said nanoparticles on a surface; providing energy to the particles and / or surface so that the nanoparticles are at least partly diffused / dissolved into the glassy surface; and reducing the cohesive energy of the nanoparticles during the production of the nanoparticles or after the production of the nanoparticles.
Owner:BENEQ OY
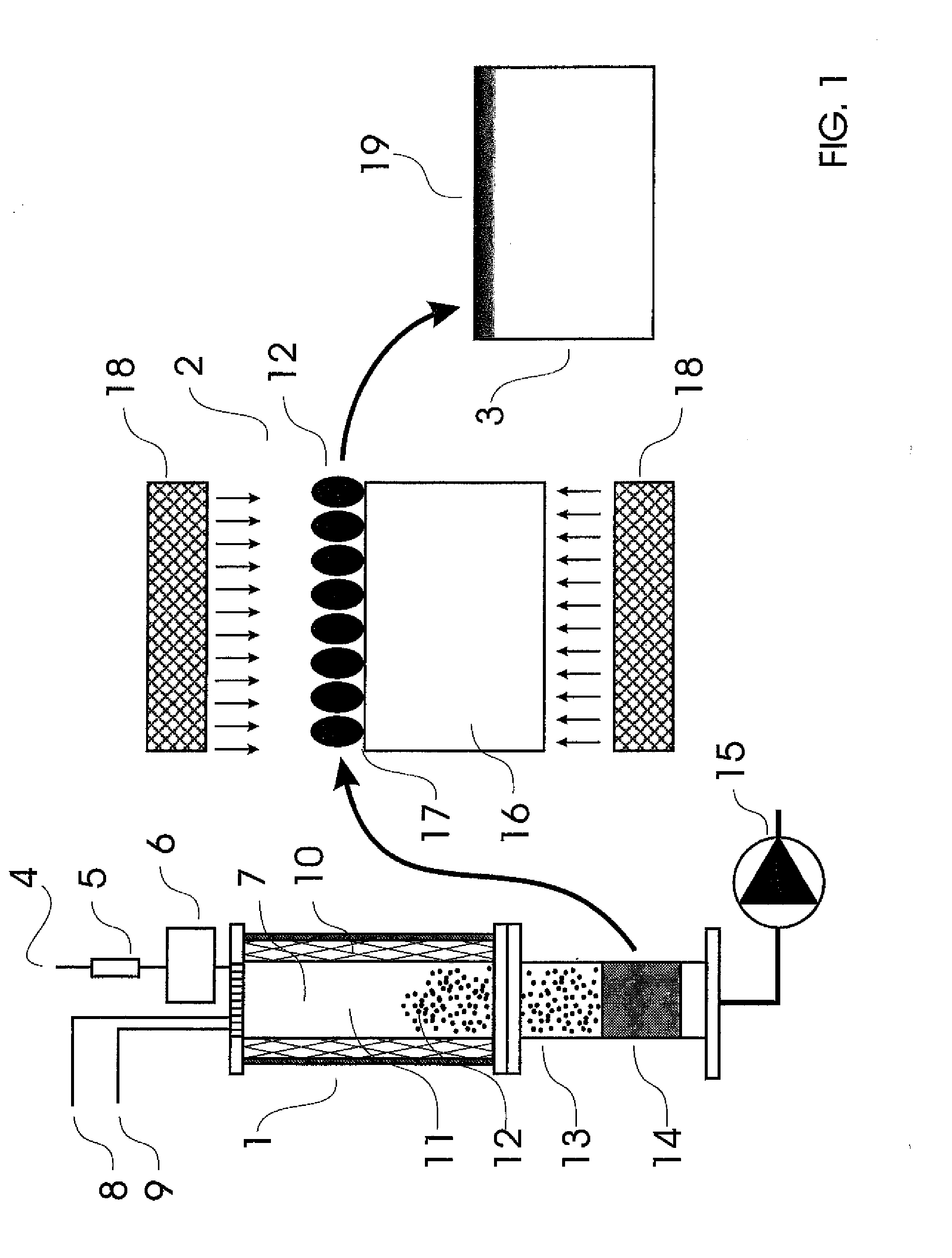
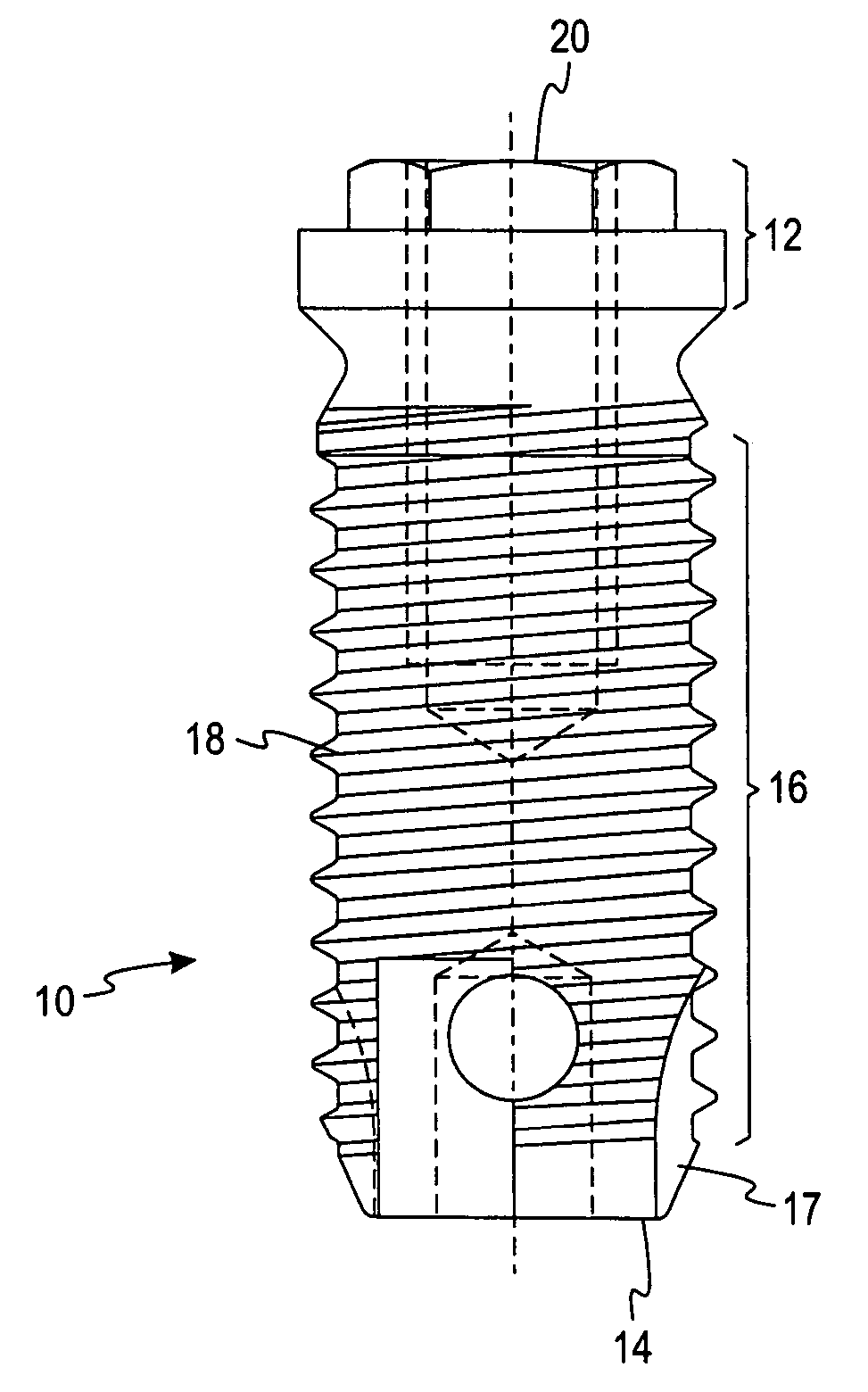
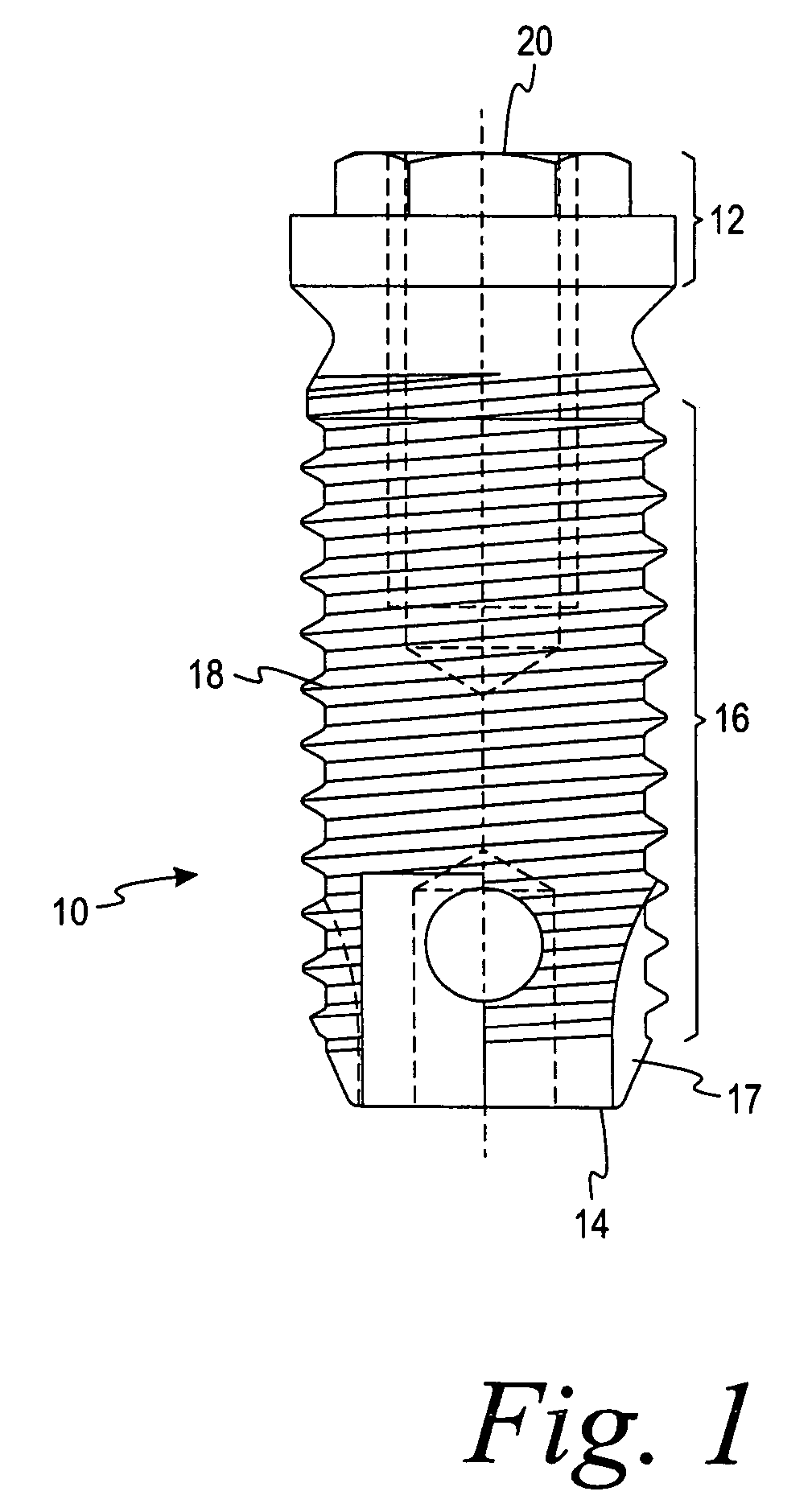
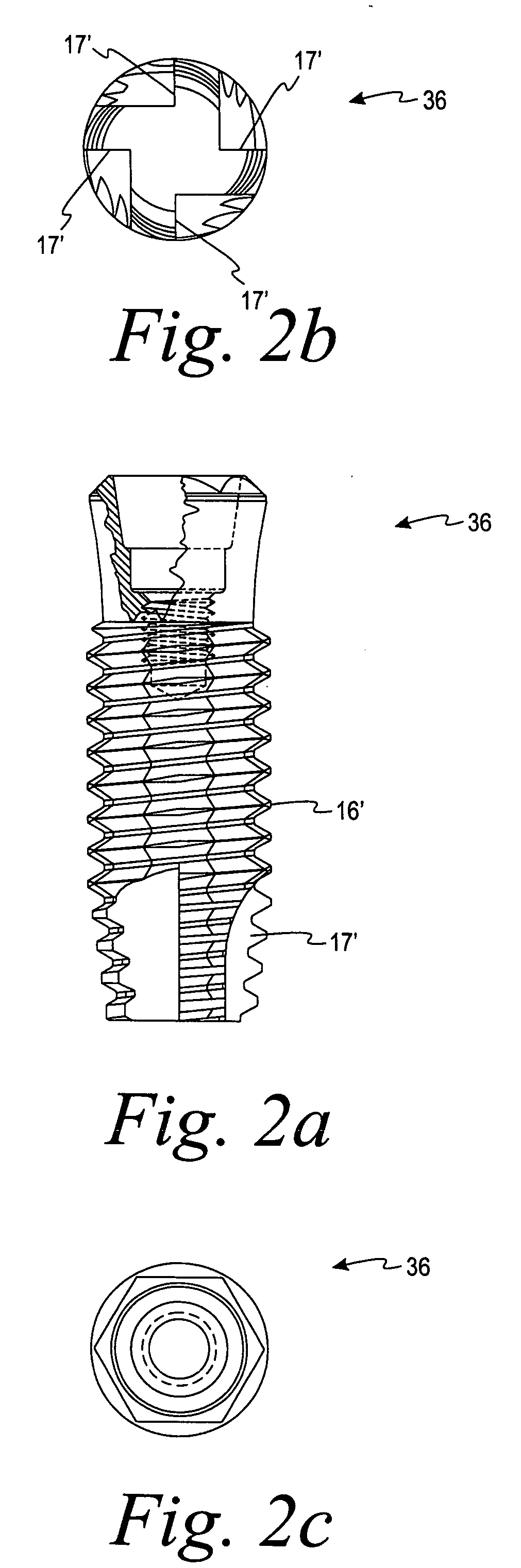
Deposition of discrete nanoparticles on an implant surface
A method of forming an implant to be implanted into living bone is disclosed. The method comprises the act of roughening at least a portion of the implant surface to produce a roughened surface. The method further comprises the act of depositing discrete nanoparticles on the roughened surface though a one-step process of exposing the roughened surface to a solution. The nanoparticles comprise a material having a property that promotes osseointegration.
Owner:BIOMET 3I LLC
Method for the prevention of nanoparticle agglomeration at high temperatures
A method includes: (a) conformally depositing a barrier coating, provided in liquid form, on at least one surface of a substrate; (b) embedding a plurality of nanoparticles in the barrier coating to a selected depth; and (c) fully curing the barrier coating after embedding the plurality of nanoparticles; the embedded plurality of nanoparticles are in continuous contact with the cured barrier coating. The order in which the barrier coating and nanoparticles are deposited on the substrate can be switched or they can be deposited simultaneously. An article includes a substrate having a cured barrier coating conformally disposed on at least one surface of the substrate and a plurality of nanoparticles embedded to a selected depth in the barrier coating creating an embedded portion of each of the plurality of nanoparticles. The embedded portion of each of the plurality of nanoparticles in continuous contact with the cured barrier coating.
Owner:APPL NANOSTRUCTURED SOLUTIONS LLC
Methods for the lithographic deposition of materials containing nanoparticles
A method for depositing nanoparticles in a thin film through the dispersion of such nanoparticles in a precursor solution which is deposited on a substrate and converted into a metal or metal oxide film. The resulting metal or metal oxide film will contain embedded nanoparticles. Such films can be used in a variety of applications such as diffusion barriers, electrodes for capacitors, conductors, resistors, inductors, dielectrics, or magnetic materials. The nanoparticle material may be selected by one skilled in the art based on the particular application.
Owner:SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY
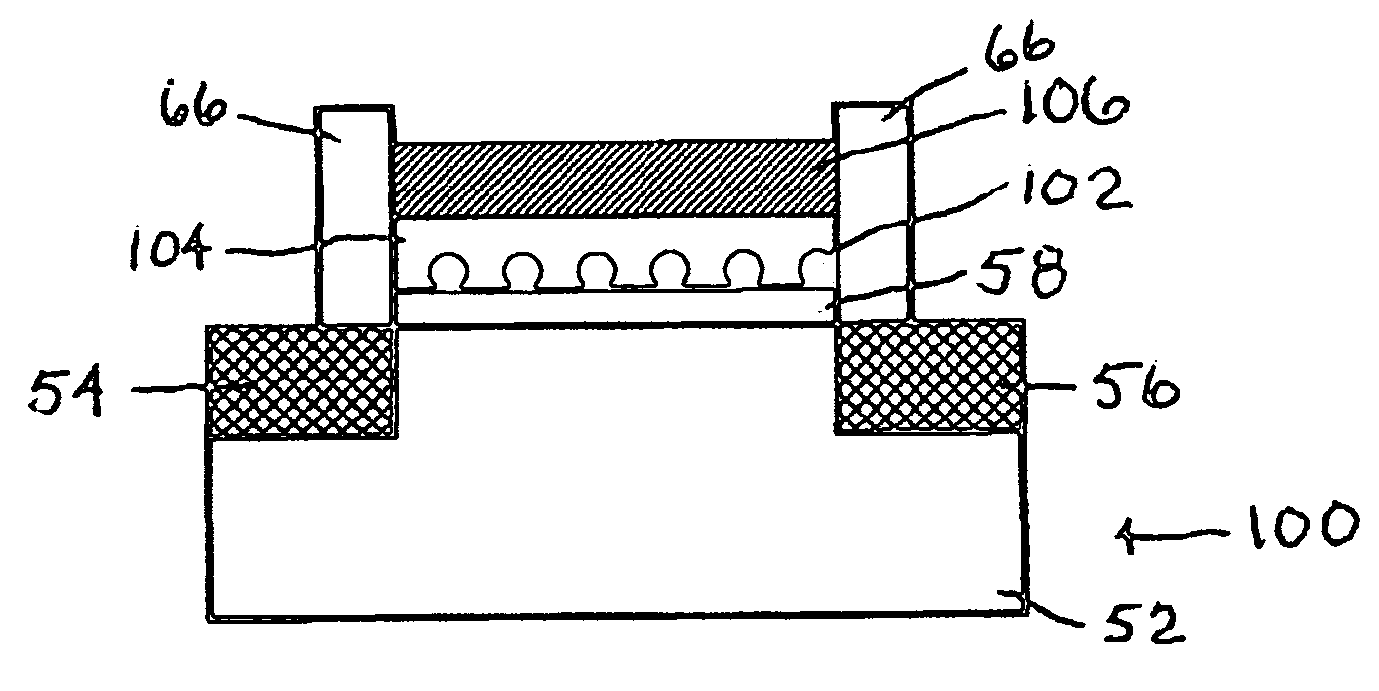
Construction of flash memory chips and circuits from ordered nanoparticles
Methods, apparatus and systems form memory structures, such as flash memory structures from nanoparticles by providing a source of nanoparticles as a conductive layer. The particles are moved by application of a field, such as an electrical field, magnetic field and even electromagnetic radiation. The nanoparticles are deposited onto an insulating surface over a transistor in a first distribution of the nanoparticles. A field is applied to the nanoparticles on the surface that applies a force to the particles, rearranging the nanoparticles on the surface by the force from the field to form a second distribution of nanoparticles on the surface. A protective and enclosing insulating layer is deposited on the nanoparticle second distribution. The addition of a top conductive layer completes a basic flash memory structure.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT NEVADA SYST OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF NEVADA RENO
Preparation of Cu2O/TNTs (TiO2 nanotubes) heterojunction nano composite material and CO2 photoreduction method
InactiveCN103225097ASimple materialEasy to operateElectrolytic inorganic material coatingDispersed particle separationElectrolytic agentHeterojunction
The invention discloses preparation of a Cu2O / TNTs (TiO2 nanotubes) heterojunction nano composite material and a CO2 photoreduction method. The preparation comprises the following specific steps: preparing TNTs through an anodic oxidation method; in electrolyte of lactic acid containing copper sulfate, controlling electrochemical deposition parameters and performing electrodeposition to deposit Cu2O nanoparticles into the TNTs; and after the reaction is finished, cleaning, drying, and performing annealing treatment to obtain the Cu2O / TNTs heterojunction nano composite material. CO2 gas is converted into methanol through photoreduction by putting the composite material in distilled water and taking high-power pulse laser having a wavelength of 355nm as a light source, the maximum conversion efficiency is about 1.66%, and the maximum photon efficiency of the methanol conversion is about 6.63%. The invention is simple in required equipment, easy to operate, suitable for industrial production and convenient to perform recovery.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
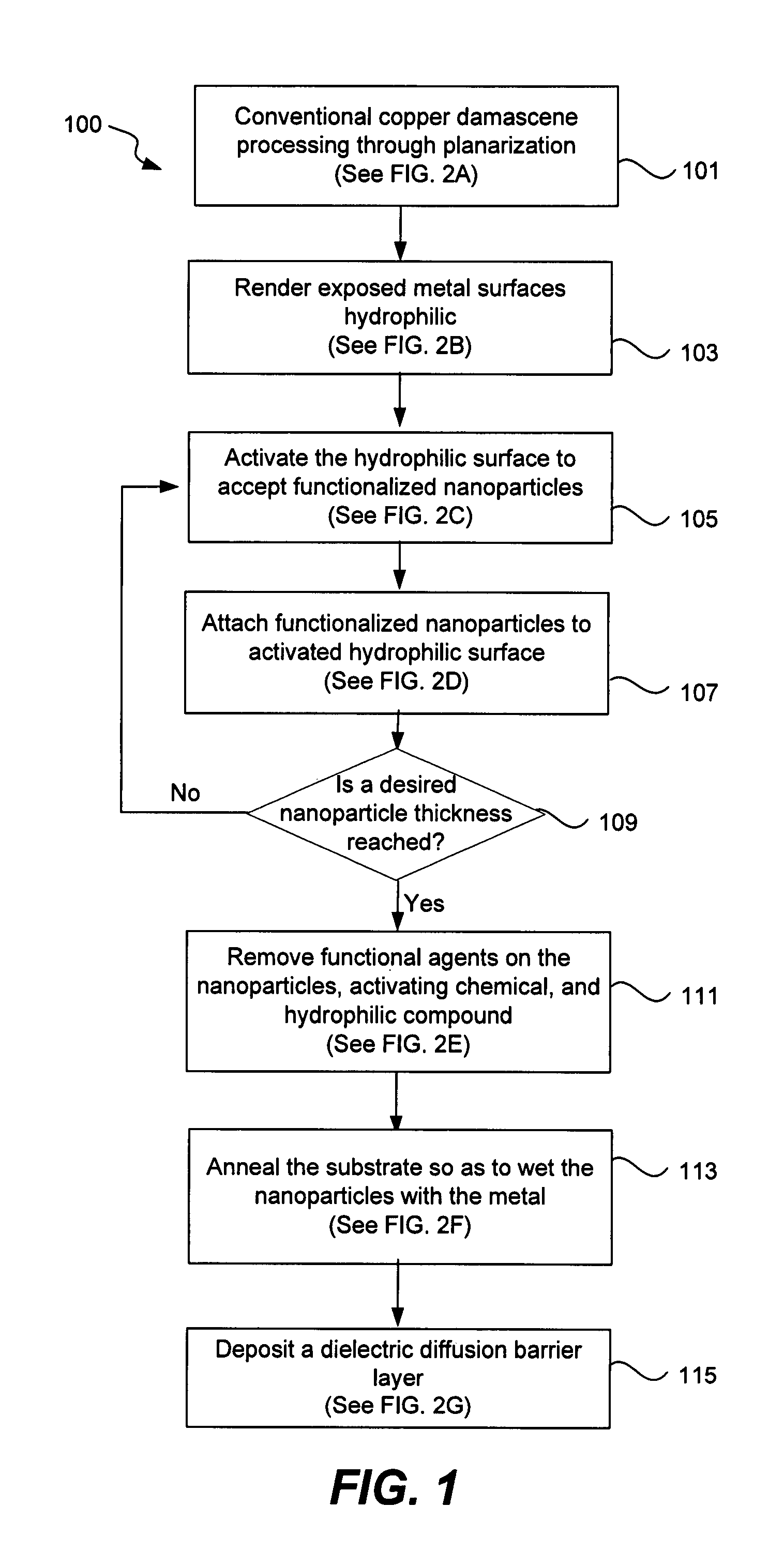
Nanoparticle cap layer
InactiveUS8039379B1Reduce electromigrationIncrease the footprintSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricFunctionalized nanoparticles
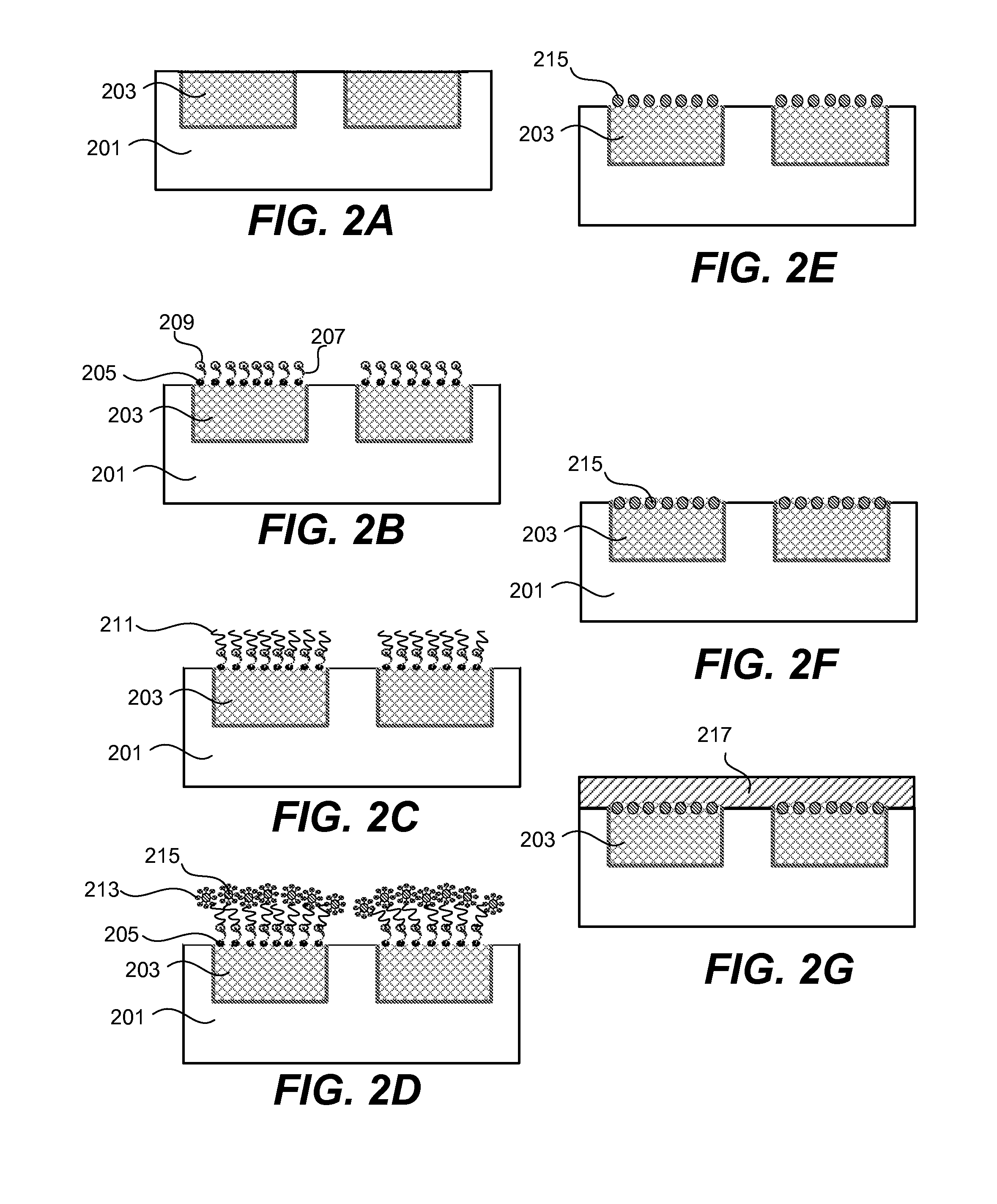
Functionalized nanoparticles are deposited on metal lines inlaid in dielectric to form a metal cap layer that reduces electromigration in the metal line. The functionalized nanoparticles are deposited onto activated metal surfaces, then sintered and annealed to remove the functional agents leaving behind a continuous capping layer. The resulting cap layer is about 1 to 10 nm thick with 30-100% atomic of the nanoparticle material. Various semiconductor processing tools may be adapted for this deposition process without adding footprint in the semiconductor fabrication plant.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
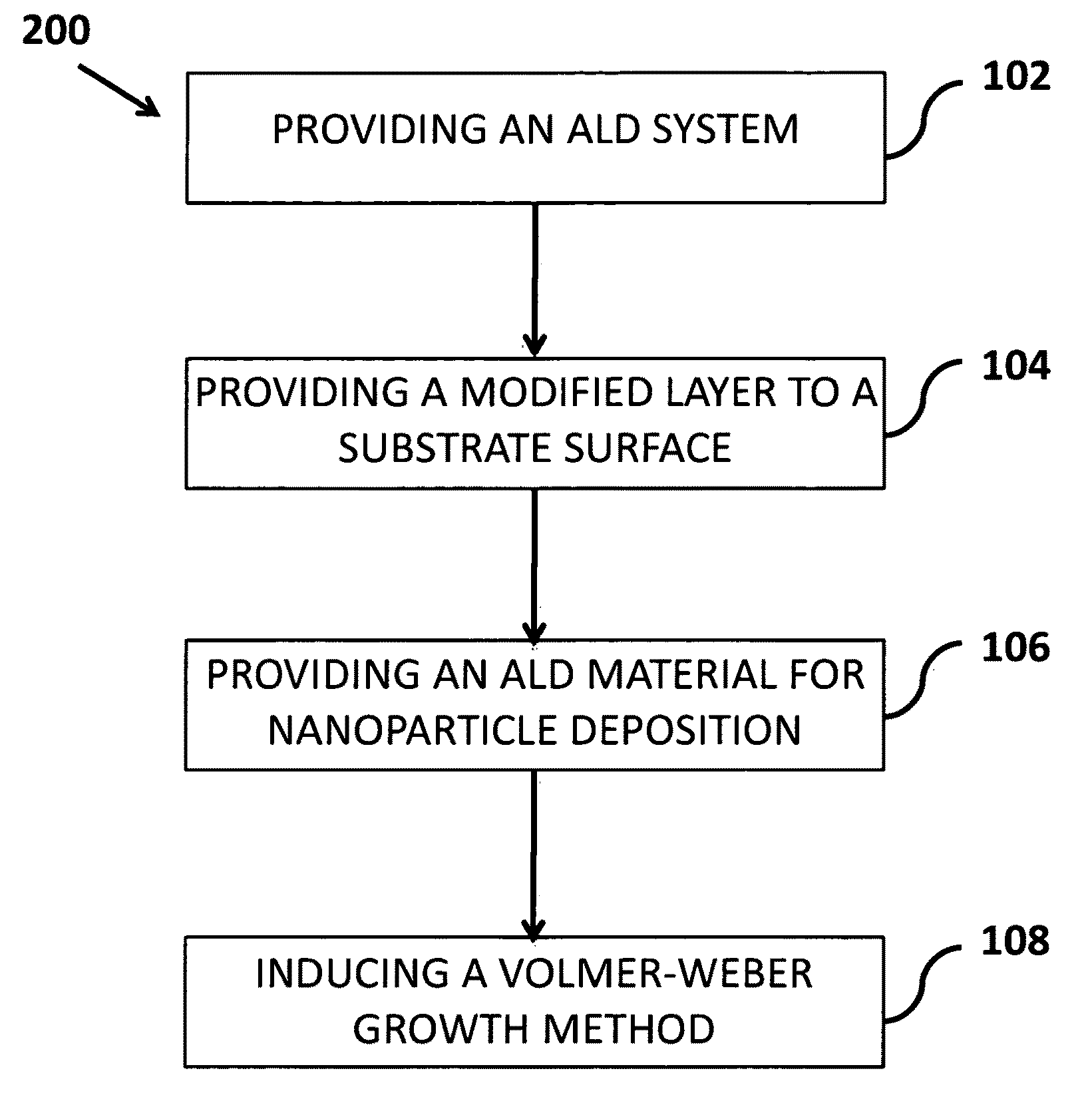
Fabrication method of size-controlled, spatially distributed nanostructures by atomic layer deposition
InactiveUS8084087B2Catalyst geometry is enhancedReduce loadChemical vapor deposition coatingSelf-assembled monolayerVolumetric Mass Density
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Nanoparticle deposition process
An apparatus composed of: (a) a substrate; and (b) a deposited composition comprising a liquid and a plurality of metal nanoparticles with a covalently bonded stabilizer.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Light irradiation preparation method and use of ultra-sensitive surface enhanced Raman scattering active base
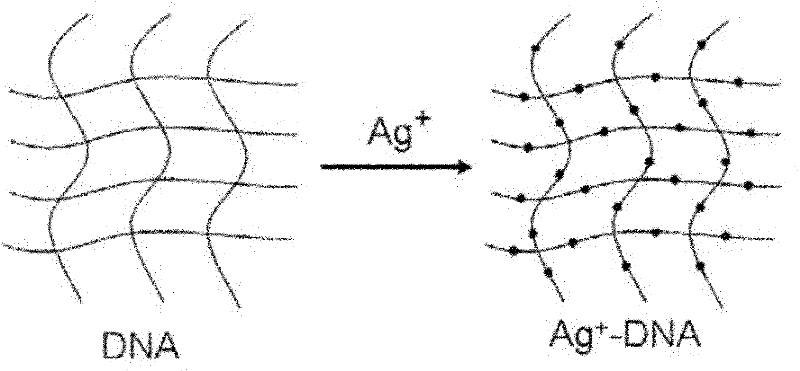
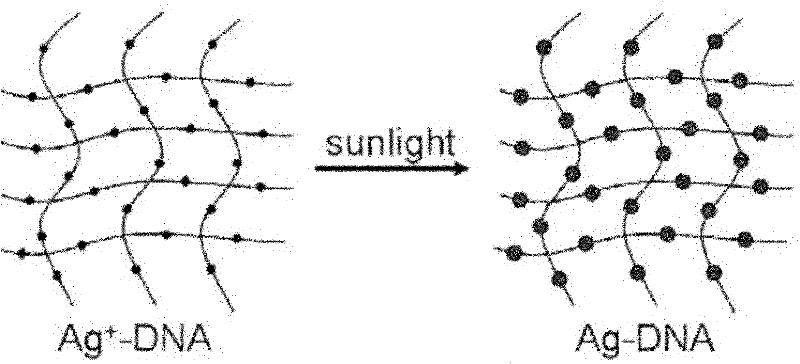
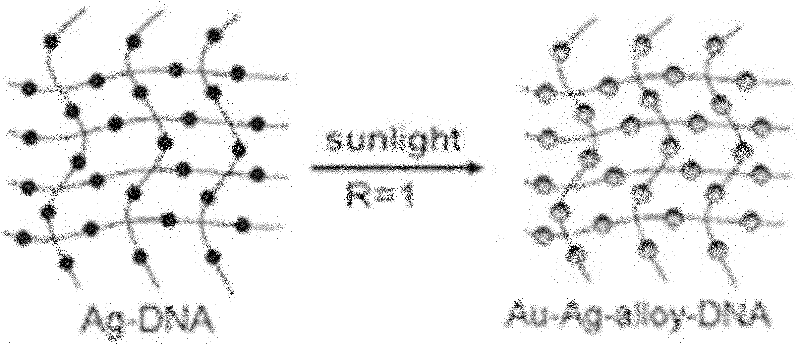
InactiveCN102183503ARaise the enhancement factorGood repeatabilityRaman scatteringNanotechnologyLight irradiationGold particles
The invention discloses a light irradiation preparation method and a use of an ultra-sensitive surface enhanced Raman scattering active base. The light irradiation preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, depositing silver nano particles on a surface of a DNA, then, taking the silver as a nucleation site to assemble the gold on the silver; and then, depositing small gold particles on a nano structure of silver-DNA by the sunlight again. The silver-nucleus gold-shell or silver-gold alloy nano DNA network structure is a good surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) active base obviously effective in TNT detection. The lowest detection limit can reach the prior lowest detection level, and enhancement factors can reach the order of magnitude of 1011-1012. The Light irradiation preparation method and the use of the ultra-sensitive surface enhanced Raman scattering active base provide a quick and accurate detection method for detecting explosives, such as TNT and the like.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
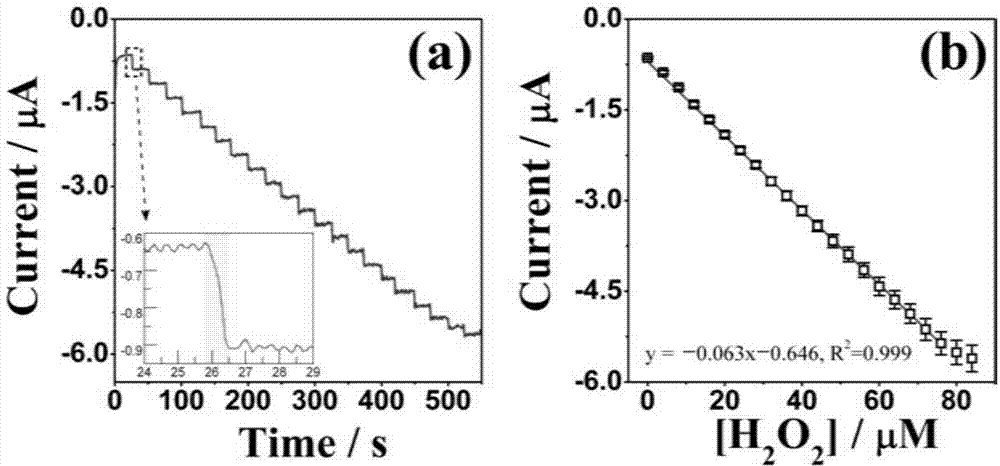
Hydrogen peroxide non-enzyme electrochemical sensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103792271AIncrease the areaImprove stabilityMaterial electrochemical variablesIridiumElectrochemical gas sensor
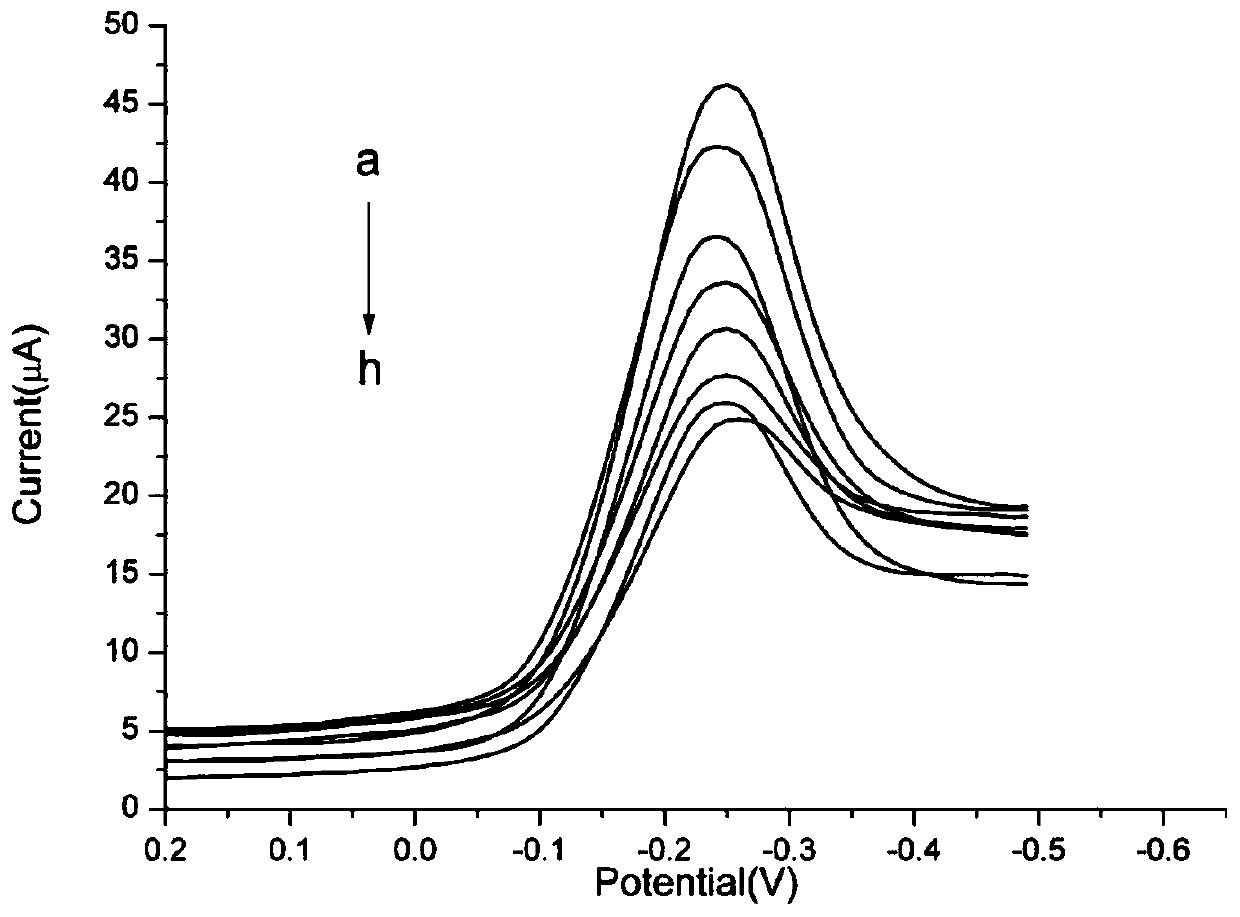
The invention discloses a hydrogen peroxide non-enzyme electrochemical sensor for detecting H2O2 by utilizing the response of a chemical electrode under H2O2. A chemical electrode is a pair of electrodes embellished by noble metal nanometer particles, and the noble metals are gold, silver, platinum, palladium or iridium; the electrodes embellished by noble metal nanometer particles are the noble metal nanometer particles which are deposited on an electrode material through a beam depositing method, the deposit rate of the nanometer particles in the deposition of the nanometer particles is controlled to be more than 0.3 layer and less than 5 layers, and a glassy carbon electrode material or nano-graphite is adopted as an electrode material. The hydrogen peroxide non-enzyme electrochemical sensor provided by the invention has the advantages that the electrode embellished by the method enables the surface of the electrode to have the good dispersibility and crystallinity as well as the clean surface, a problem that a catalyst of the traditional method is easy to gather and fall is solved, using of a conductive binding agent is avoided, the effective catalyzing area and stability of the electrode are improved, and the delivery of an electron between the electrode and the catalyst is accelerated.
Owner:SUZHOU SINORAYBO NANO SCI & TECH +1
Synthesis method of graphite phase carbonitride homotype heterojunction photocatalysis material with multilayer structure and application
InactiveCN106732712APromote absorptionThe synthesis method is simplePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationHeterojunctionSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a synthesis method of a graphite phase carbonitride homotype heterojunction photocatalysis material with a multilayer structure. The method comprises the following steps of preparing a melamine / cyanuric acid suspension and urea water solution; performing preparation by using the melamine / cyanuric acid suspension to obtain melamine / cyanuric acid suspension macromolecular crystals completing the assembly reaction; adding the melamine / cyanuric acid suspension macromolecular crystals into the urea water solution; performing calcination on the urea-(melamine / cyanuric acid) composite precursor obtained through preparation to obtain the graphite phase carbon nitride (g-C3N4) homotype heterojunction photocatalysis material with multilayer structures with g-C3N4 nanometer particles deposited on the g-C3N4 micrometer tubes. The synthesis method provided by the invention has the advantages that the conditions are mild; the preparation process is simple and convenient; the controllability is high; the obtained photocatalysis material can be applied to methyl orange degradation in visible light; the effect is obvious.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Nanoparticle cap layer
ActiveUS7994640B1Effectively “ wet ”High surface energySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricFunctionalized nanoparticles
Functionalized nanoparticles are deposited on metal lines inlaid in dielectric to form a metal cap layer that reduces electromigration in the metal line. The functionalized nanoparticles are deposited onto activated metal surfaces, then sintered and annealed to remove the functional agents leaving behind a continuous capping layer. The resulting cap layer is about 1 to 10 nm thick with 30-100% atomic of the nanoparticle material. Various semiconductor processing tools may be adapted for this deposition process without adding footprint in the semiconductor fabrication plant.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Dry type lubricant without containing grease, its mother liquor and its preparation method
ActiveCN102226123ANo pollutionNo high temperature resistanceAdditivesOil and greaseNanoparticles dispersion
The invention belongs to the field of industrial lubricant, concretely relates to a dry type lubricant without containing grease and its mother liquor. According to the invention, the mother liquor of the dry type lubricant without containing grease is prepared by 0.01 to 95 parts of nanoparticle and 5 to 99.99 parts of volatile solvent which is in a liquid state under the normal temperature. Theinvention also discloses a nanometer lubricating agent without containing grease, which consists of a nanoparticle deposition layer attached on a frictional pairs surface or a residual volatile hydrocarbon deposition layer existed in liquid state under the normal temperature. Nanoparticles are dispersed for dissolving in volatile hydrocarbon, nanoparticles can be stablely attached to the frictional secondary surface due to large surface energy when using, only nanoparticles with lubrication efficacy are left after volatilizing hydrocarbon, a dry type oil free film can be formed, thereby the lubricant has the effect of pollution resistance and high temperature resistance, and has good lubricity.
Owner:卓建材
Construction of flash memory chips and circuits from ordered nanoparticles
ActiveUS7790560B2NanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesElectromagnetic radiationCondensed matter physics
Methods, apparatus and systems form memory structures, such as flash memory structures from nanoparticles by providing a source of nanoparticles as a conductive layer. The particles are moved by application of a field, such as an electrical field, magnetic field and even electromagnetic radiation. The nanoparticles are deposited onto an insulating surface over a transistor in a first distribution of the nanoparticles. A field is applied to the nanoparticles on the surface that applies a force to the particles, rearranging the nanoparticles on the surface by the force from the field to form a second distribution of nanoparticles on the surface. A protective and enclosing insulating layer is deposited on the nanoparticle second distribution. The addition of a top conductive layer completes a basic flash memory structure.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT NEVADA SYST OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF NEVADA RENO
Preparation method of electrochemical aptamer sensor for detecting aflatoxin B1
ActiveCN109870497AHigh sensitivityImprove stabilityMaterial electrochemical variablesNanometreMesoporous carbon
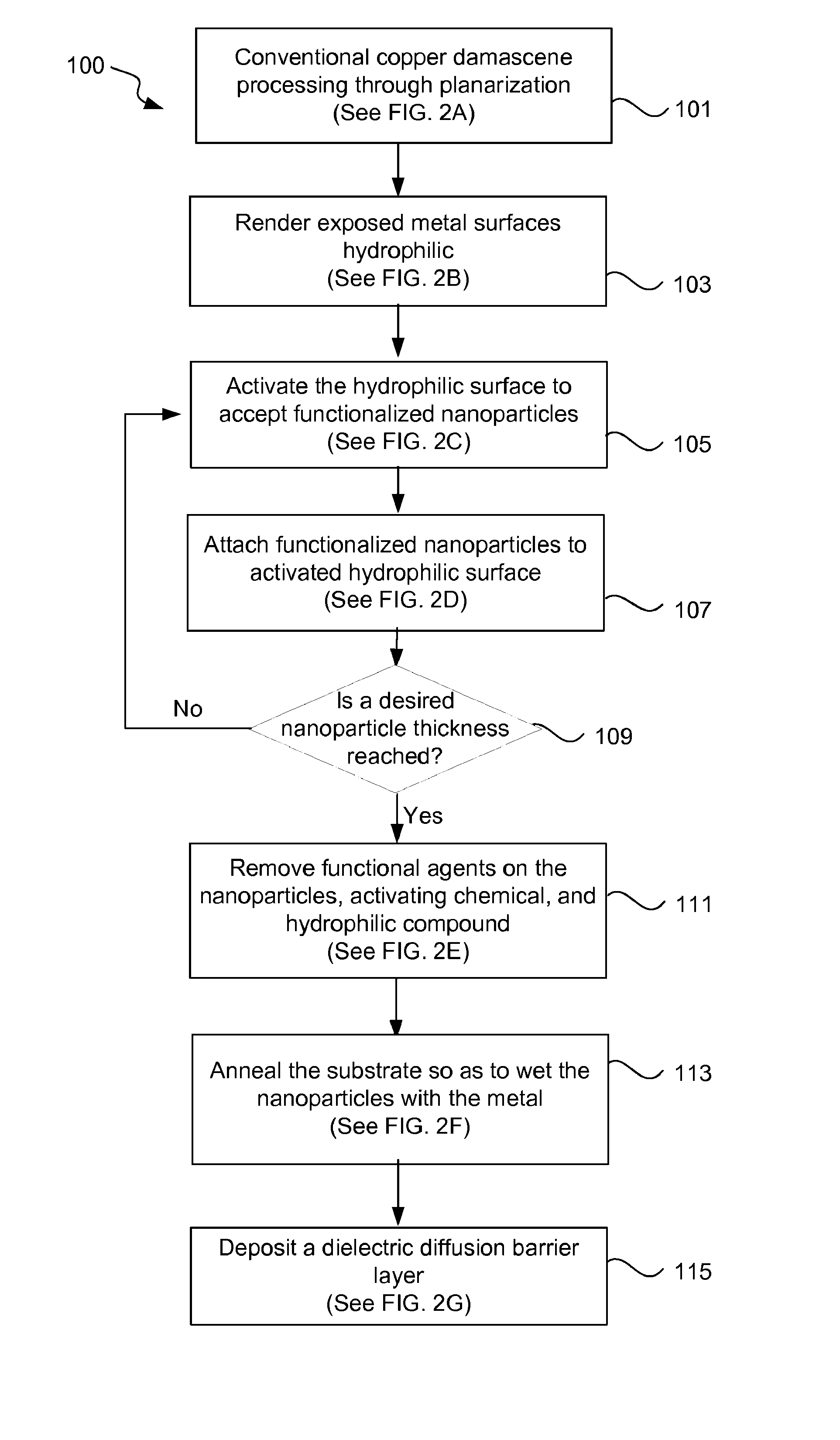
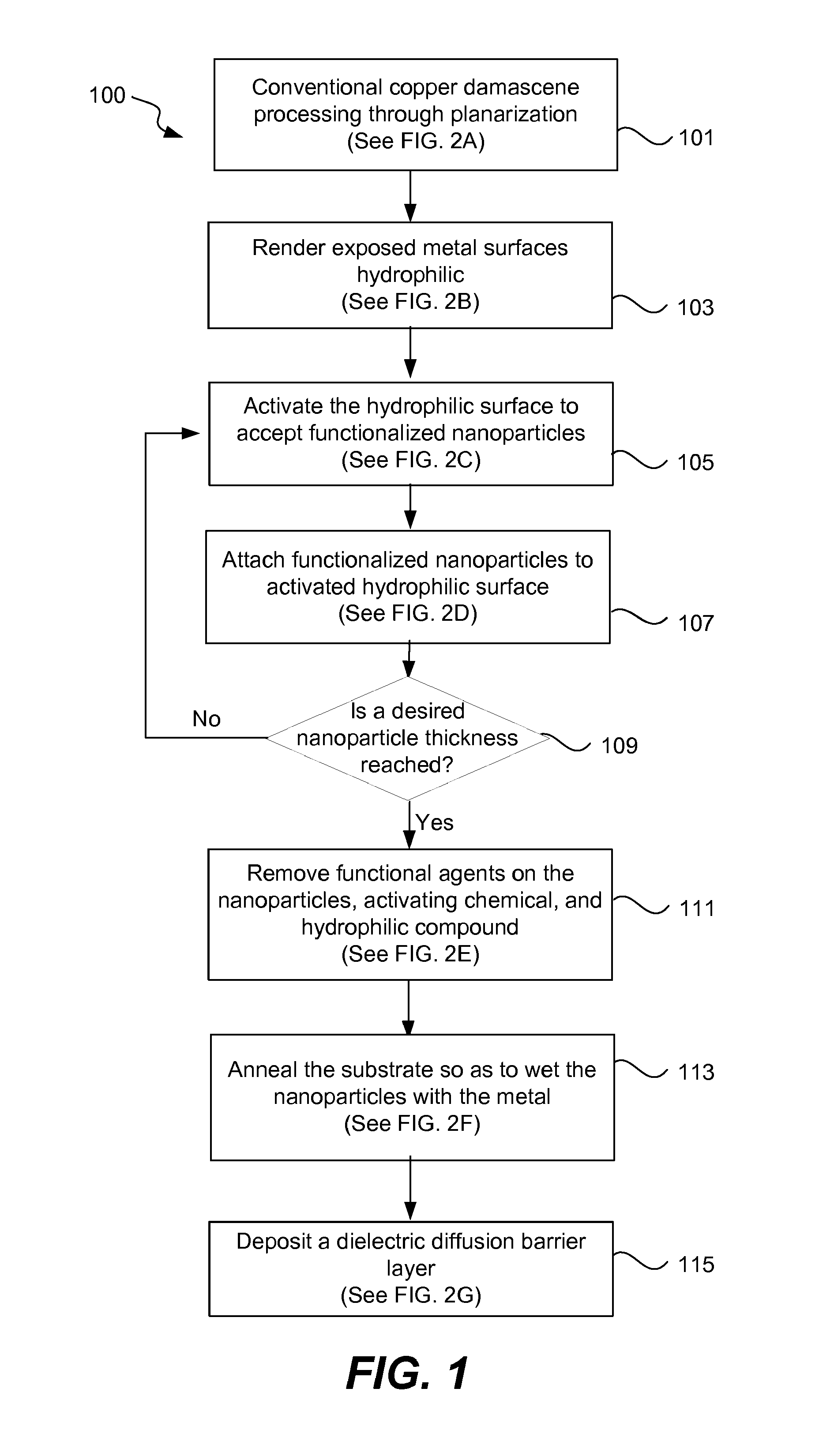
The invention provides a preparation method of an electrochemical aptamer sensor for detecting aflatoxin B1. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) dropwise adding mesoporous carbon onto a work electrode; (2) performing potentiostatic gold nanoparticle deposition for modifying CMK / GCE; (3) dropwise adding an AFB1 aptamer modified with sulfydryl at one end onto an AuNPs / CMK / GCEelectrode; (4) immersing the Apt / AuNPs / CMK / GCE into an MB (Methylene Blue) solution, so that the MB is adsorbed on an aptamer chain to obtain an MB-Apt / AuNPs / CMK / GCE electrode; and (5) detecting thereduction peak current value. The electrochemical aptamer sensor for detecting aflatoxin B1 can achieve the goal of quantitatively detecting a target object; the characteristics of high speed and operation simplicity are realized; and the defects of operation complexity and long detection period of a large-scale detecting instrument are overcome.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Instruments for measuring nanoparticle exposure
ActiveUS7812306B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationParticle separator tubesHEPAAudio power amplifier
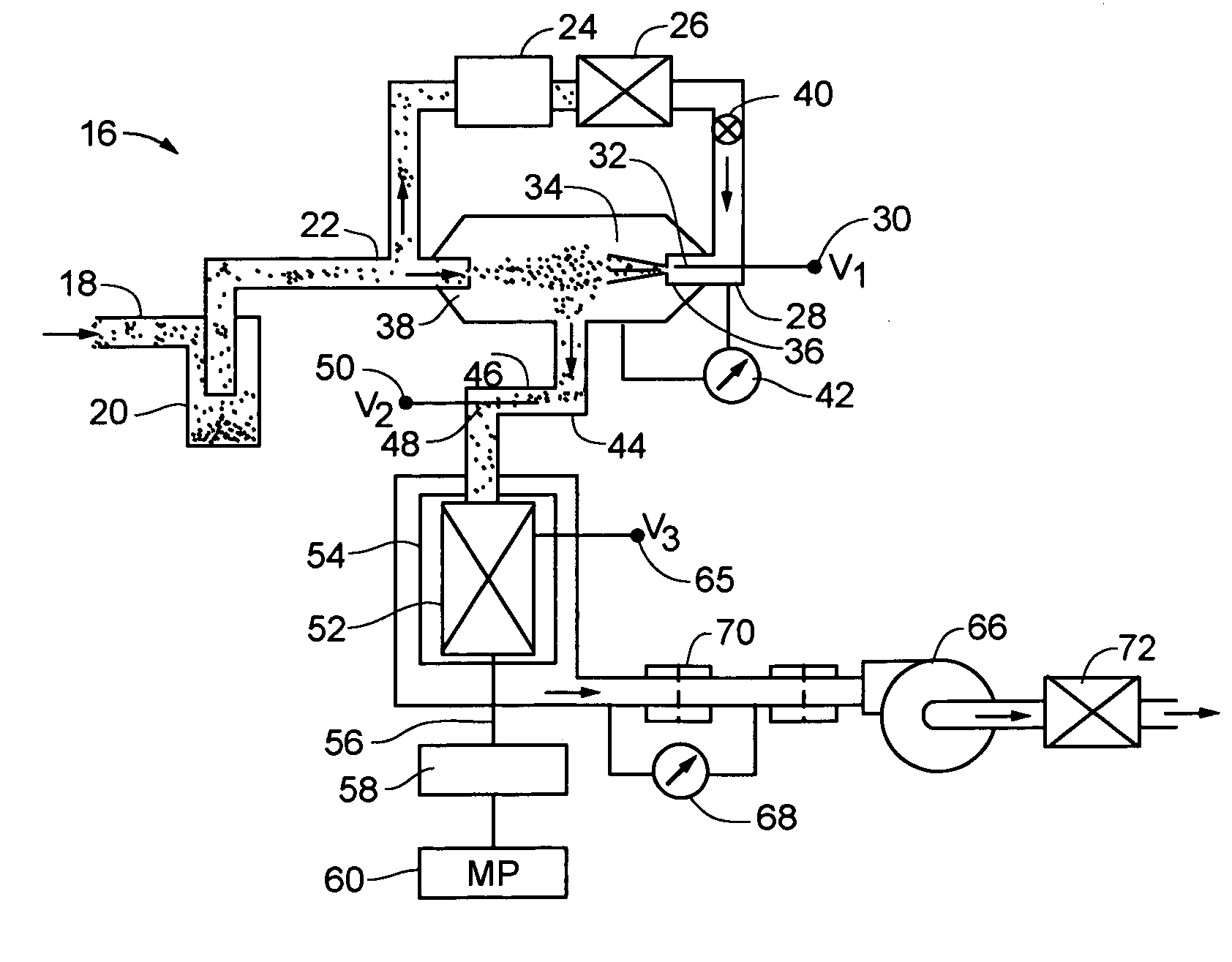
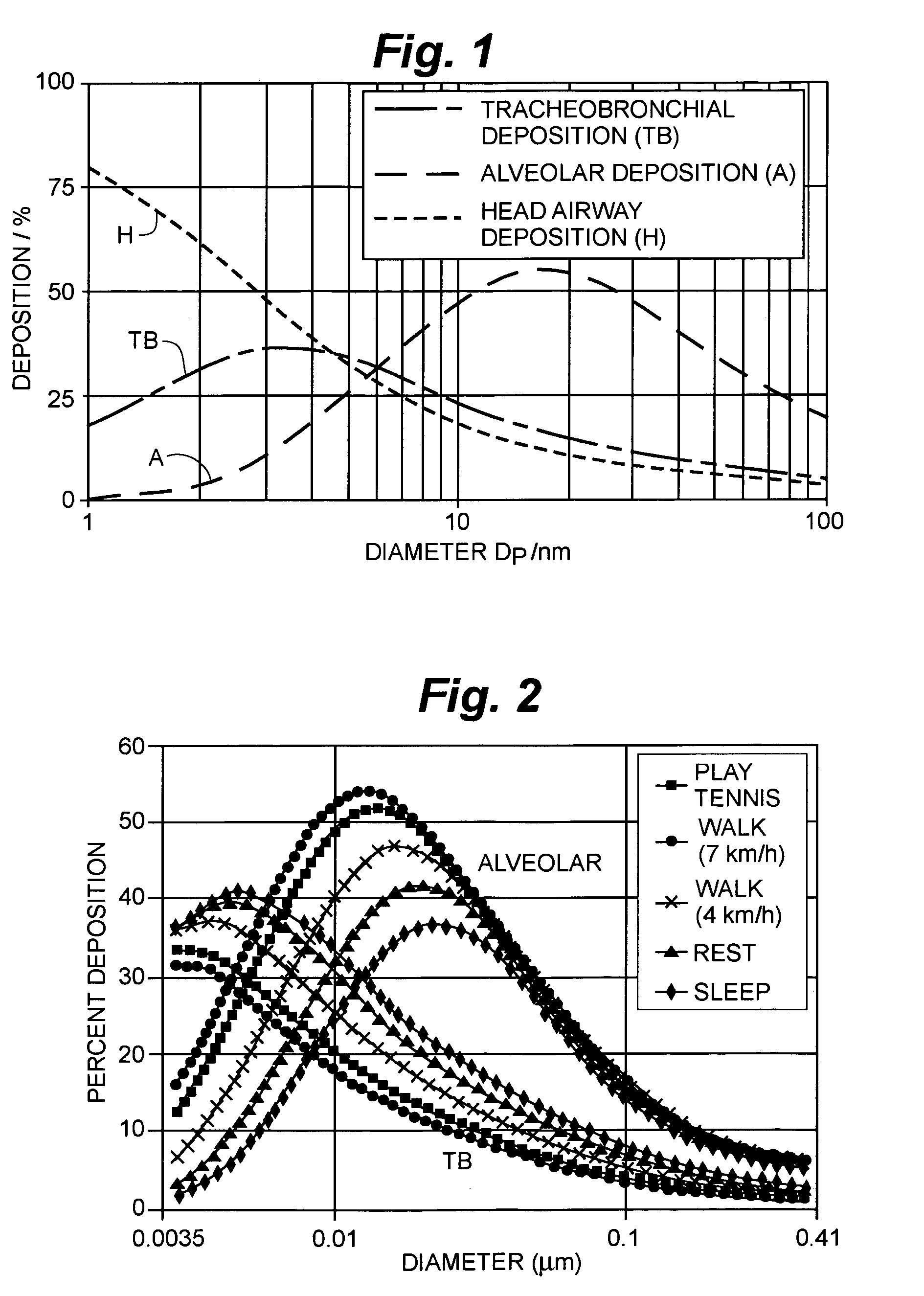
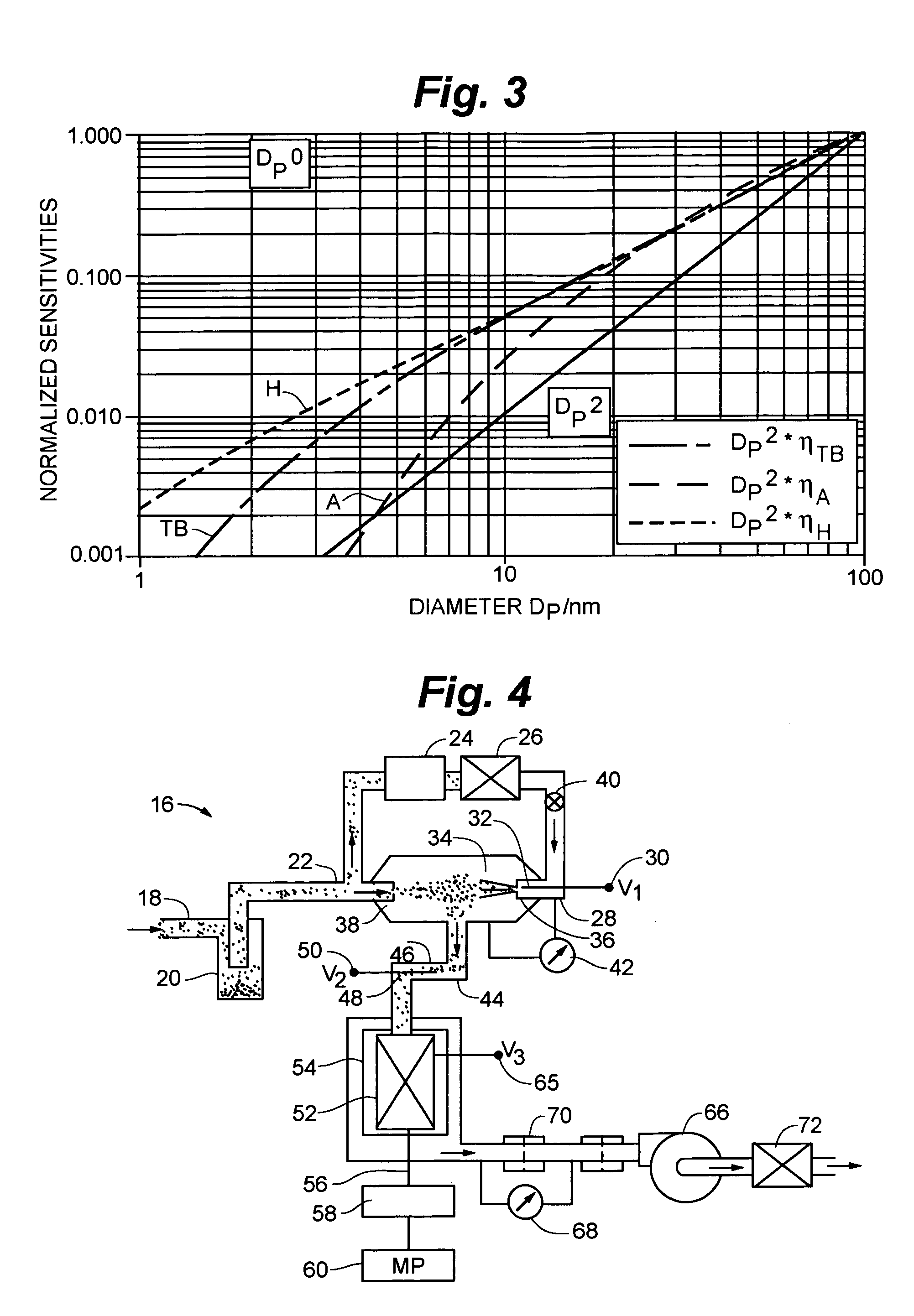
An instrument for non-invasively measuring nanoparticle exposure includes a corona discharge element generating ions to effect unipolar diffusion charging of an aerosol, followed by an ion trap for removing excess ions and a portion of the charged particles with electrical mobilities above a threshold. Downstream, an electrically conductive HEPA filter or other collecting element accumulates the charged particles and provides the resultant current to an electrometer amplifier. The instrument is tunable to alter the electrometer amplifier output toward closer correspondence with a selected function describing particle behavior, e.g. nanoparticle deposition in a selected region of the respiratory system. Tuning entails adjusting voltages applied to one or more of the ion trap, the corona discharge element and the collecting element. Alternatively, tuning involves adjusting the aerosol flow rate, either directly or in comparison to the flow rate of a gas conducting the ions toward merger with the aerosol.
Owner:TSI INC
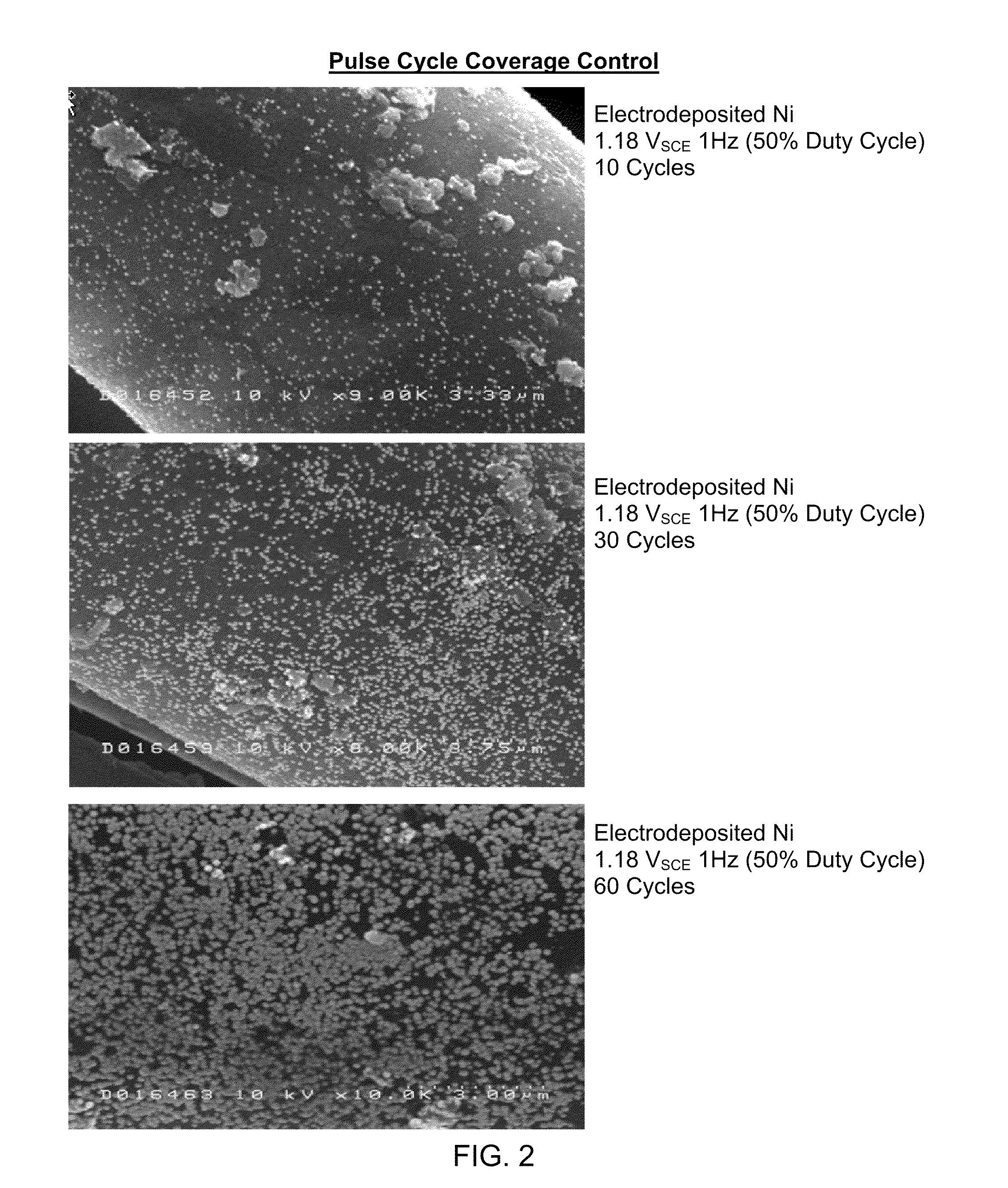
Controlled electrodeposition of nanoparticles
InactiveUS20100126870A1Increased rugosity and increaseEnhancing carbon surface rugosityElectrolysis componentsElectrophoretic coatingsActivated carbonChemical composition
Deposition of nanoparticles onto carbon surfaces is described. Metal and / or metal oxide ions are deposited on a carbon surface by electrodeposition, such as by immersing a carbon and an anode in a salt bath, and applying a number of electrical pulses having a defined pulse width. The size, coverage density, and metallic composition of the nanoparticles may be affected by the pulse width of the electrical pulses, the number of electrical pulses, and the chemical composition of the salt bath, respectively. The carbon may be anodized before electrodeposition. If the carbon is a carbon precursor, after electrodeposition, the carbon precursor is carbonized to form a carbon. After electrodeposition, the carbon may be activated to form an activated carbon. The nanoparticles may serve as catalysts for activation rugosity of mesoporous carbons. The catalytically activated carbon materials may be used in all manner of devices that contain carbon materials.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Catalysts for degradation of organic pollutants in printing and dyeing wastewater and method of preparation thereof
ActiveUS20180093260A1Improve degradation rateImprove catalytic performanceWater contaminantsCatalyst activation/preparationMetal oxide nanoparticlesPorous carbon
This invention discloses a method for preparing a catalyst for catalyzing the degradation of organic pollutants in printing and dyeing wastewater by ozone, wherein the catalyst comprises a porous carbon material as a substrate and metal oxide nanoparticles deposited on the surface of the substrate. The method comprises the steps of: allowing a mixture of resorcinol, formaldehyde, trimethylhexadecyl ammonium bromide, multi-walled carbon nanotubes and deionized water to react to form cured product, which is then calcinated and carbonized at high temperature to produce the porous carbon material; impregnating the resulting porous carbon material with nitrate solution, drying the porous carbon material, and calcinating it at high temperature, wherein the absorbed nitrate is decomposed into metal oxide and embedded into the porous carbon material. Depending on the requirement of applications, the raw material for preparation of the catalyst of the present invention can be pulverized to screen out the appropriate particle size to fit into practical engineering applications. With the optimization of catalytic oxidation process, the catalyst can be used to promote the rapid degradation of organic matter in printing and dyeing wastewater by ozonation, and the percentage of degradation can be greatly improved. As a result, indicators of wastewater, including the chromaticity and COD, can be significantly reduced.
Owner:THE HONG KONG RES INST OF TEXTILES & APPAREL
Continuous Range Hydrogen Sensor
InactiveUS20100005853A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansNanosensorsHydrogen sensorNanometre
Owner:NANO
PDMS-based bionic sharkskin replica super-hydrophobic surface and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a PDMS-based bionic sharkskin replica super-hydrophobic surface and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of hydrophobic surface preparation. According to the PDMS-based bionic sharkskin replica super-hydrophobic surface and the preparation method thereof, a sharkskin replica is obtained through twice mold changing of PDMS with a sharkskin as a template, and the surface of the sharkskin replica has a micron-scale groove structure; the PDMS sharkskin replica is put above a flame of an alcohol lamp or a lighter to be subjected to uniform combustion treatment, so that nano-particles generated during combustion are deposited on the PDMS sharkskin replica to enable the surface structure to become a micro-nano structure, and finally, the PDMS sharkskin replica is subjected to heating treatment. According to the super-hydrophobic surface preparation method provided by the invention, the contact angle of liquid drops is greater than 150 degrees, the rolling angle of the liquid drops is less than 10 degrees, and the material shows the super-hydrophobic property. The PDMS-based bionic sharkskin replica super-hydrophobic surface is simple in process, low in cost and easy to control and has good application prospects in the fields such as fog and ice prevention, self-cleaning, resistance reduction and oil-water separation.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
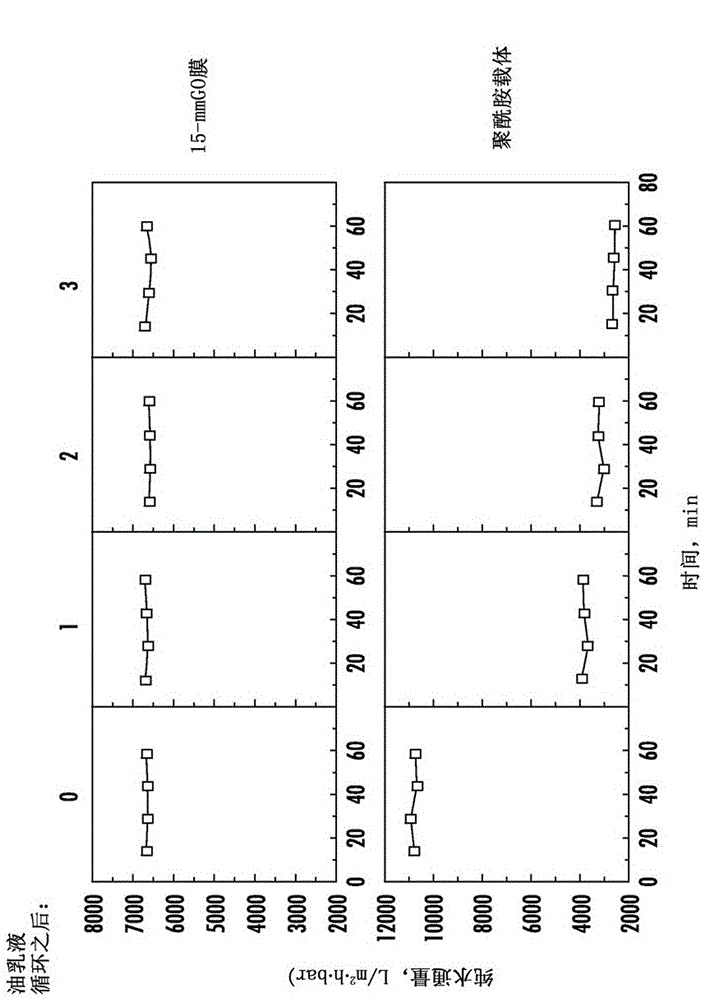
Ultrathin, graphene-based membranes for water treatment and methods of their formation and use
Methods are generally provided for forming a membrane. In one embodiment, the method includes: dispersing GO nanoparticles in a solvent; depositing the GO nanoparticles on a support to form a GO membrane; and reducing the GO membrane to form a rGO membrane. Also provided is the rGO membrane formed from such methods, along with a plurality of stacked rGO layers. Methods are also provided for separating water from a water / oil emulsion by, for example, passing water through the rGO membrane.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com